CN202204518U - A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D Switching - Google Patents
A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D SwitchingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN202204518U CN202204518UCN2011201704102UCN201120170410UCN202204518UCN 202204518 UCN202204518 UCN 202204518UCN 2011201704102 UCN2011201704102 UCN 2011201704102UCN 201120170410 UCN201120170410 UCN 201120170410UCN 202204518 UCN202204518 UCN 202204518U
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- image display
- navigation system
- display screen
- navigation
- signal converter
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本实用新型涉及导航系统,更具体地,涉及一种能自由进行2D图像显示和3D图像显示切换的导航系统。 The utility model relates to a navigation system, in particular to a navigation system capable of freely switching between 2D image display and 3D image display. the
背景技术Background technique
GPS导航系统作为车辆等交通工具的多媒体导航系统,已经被广泛使用。目前,GPS导航系统均为2D平面显示技术。随着,汽车市场和以及导航技术的迅猛发展,越来越需要提供一种比2D图像显示更为直观和立体的3D导航系统。 The GPS navigation system has been widely used as a multimedia navigation system for vehicles and other vehicles. At present, GPS navigation systems are all 2D plane display technology. With the rapid development of the automobile market and navigation technology, it is increasingly necessary to provide a 3D navigation system that is more intuitive and three-dimensional than 2D image display. the
这里,先对3D图像显示技术进行简单介绍。现有的3D图像显示装置一般可分为两大类:眼镜型立体图像显示装置和无眼镜型立体图像显示装置(即裸眼3D图像显示装置)。 Here, the 3D image display technology is briefly introduced first. Existing 3D image display devices can generally be divided into two categories: glasses-type stereoscopic image display devices and glasses-free stereoscopic image display devices (ie naked-
无眼镜型立体图像显示装置(即裸眼3D图像显示装置)由于其不需要适配3D眼镜就观看到3D图像,因此被更广泛地应用。 Glasses-free stereoscopic image display devices (ie naked-
无眼镜型立体图像显示装置的立体图像显示方法主要包括有透镜方法、全息方法以及视差栅栏方法。由于透镜方法和全息方法具有复杂的结构以及需要高额的费用,因此,它们仅用于特定的应用。 The stereoscopic image display method of the glasses-free stereoscopic image display device mainly includes a lens method, a holographic method, and a parallax barrier method. Since the lens method and the holographic method have complicated structures and require high costs, they are used only for specific applications. the
其中,视差栅栏(Barrier)方法被积极研究、开发并开始商业利用。这种方法中,使用了被称为栅栏条纹的细条纹状的遮光缝隙。例如,在距离遮光缝隙后方一定间隔的位置上交替显示条纹状的右眼用图像以及左眼用图像,通过经过遮光缝隙观看,从而设定成仅右眼用图像进入观察者的右眼,仅左眼用图像进入观察者的左眼。由此不用眼镜也可以观看立体图像。 Among them, a parallax barrier (Barrier) method has been actively researched, developed, and commercially utilized. In this method, thin stripe-shaped light-shielding slits called fence stripes are used. For example, stripe-shaped right-eye images and left-eye images are alternately displayed at a certain distance behind the light-shielding slit, and by viewing through the light-shielding slit, it is set so that only the right-eye image enters the observer's right eye. The left eye uses the image to enter the observer's left eye. Thus, stereoscopic images can be viewed without glasses. the
其中,视差栅栏方法是基于多通道自动立体显示技术,视差栅栏即视差障壁被安置在显示器的背光模块和LCD面板之间。它利用特定的掩模算法,将展示影像交互排列,然后通过特定的视差屏障由两眼捕捉观察。通过摩尔干涉条纹判别法精确安装在显示器液晶板平面上的光栅阵列,可以准确控制每一个像素透过的光线,将左眼及右眼 可视的画面分开。由于左眼或右眼观看屏幕的角度不同,利用这一角度差遮住光线就可将图像分配给左眼或右眼,经过用户大脑将这两幅有差别的图像合成为一幅具有空间深度信息的立体图像。 Among them, the parallax barrier method is based on the multi-channel autostereoscopic display technology, and the parallax barrier, that is, the parallax barrier, is arranged between the backlight module of the display and the LCD panel. It uses a specific mask algorithm to alternately arrange the displayed images, and then captures and observes them with two eyes through a specific parallax barrier. The grating array that is precisely installed on the plane of the liquid crystal panel of the display through the moiré interference fringe discrimination method can accurately control the light transmitted by each pixel and separate the images visible to the left eye and the right eye. Since the left or right eye watches the screen at different angles, the image can be assigned to the left or right eye by covering the light with this angle difference, and the two different images are synthesized into one with spatial depth through the user's brain. Stereoscopic image of information. the
图1所示为现有的视差栅栏的结构示意图。如图1所示视差栅栏10包括依次由上向下堆叠设置的偏光片11、第一透明电极基板121、液晶层122以及第二透明电极基板123,其中,第一透明电极基板121、液晶层122以及第二透明电极基板123共同基本组成视差栅栏液晶盒12,具体地,第一透明电极基板121和第二透明电极基板123均为ITO(Indium Tin Oxide,铟锡金属氧化物)导电玻璃层,ITO导电玻璃层相向于液晶层122的一面上设置有ITO电极。第一透明电极基板121和第二透明电极基板123上的ITO电极的具体形状不是限制性的。当给液晶盒加电时,直线偏振光垂直射入液晶层后,其偏光方向会被不上电的液晶扭转90度(以TN液晶为例,不通电时,通过液晶光线的偏振角度旋转90度,通电时,ITO电极作用部分通过的光线偏振角度不旋转,ITO电极不作用部分通过的光线的偏振角度旋转90度),从而使得视差栅栏液晶盒12可以在平行偏振片间遮光,从而可以显示栅栏。 FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of an existing parallax barrier. As shown in Figure 1, the
图2所示为现有的TFT-LCD(Thin Film Transistor-Liquid CrystalDisplay,薄膜晶体管液晶显示器)的结构示意图。如图2所示,TFT-LCD 20一般地包括依次由上向下堆叠设置的偏光片21、彩色滤光片221、液晶层222、透明电极基板223、以及偏光片23,其中彩色滤光片221、液晶层222、第二透明电极基板223共同基本组成TFT液晶盒22。由于彩色滤光片221的存在,TFT液晶盒22是彩色液晶盒。具体地,透明电极基板223可以为ITO导电玻璃层,ITO导电玻璃层相向于液晶层222的一面上设置有薄膜晶体管(TFT)电路层。该TFT-LCD 20可以实现2D图像显示。 Figure 2 is a schematic structural view of an existing TFT-LCD (Thin Film Transistor-Liquid Crystal Display, Thin Film Transistor-Liquid Crystal Display). As shown in FIG. 2, TFT-LCD 20 generally includes a polarizer 21, a color filter 221, a liquid crystal layer 222, a transparent electrode substrate 223, and a polarizer 23 that are stacked sequentially from top to bottom, wherein the color filter 221 , the liquid crystal layer 222 , and the second transparent electrode substrate 223 together basically constitute the TFT liquid crystal cell 22 . Due to the existence of the color filter 221, the TFT liquid crystal cell 22 is a color liquid crystal cell. Specifically, the transparent electrode substrate 223 may be an ITO conductive glass layer, and a thin film transistor (TFT) circuit layer is disposed on the side of the ITO conductive glass layer facing the liquid crystal layer 222 . The TFT-LCD 20 can realize 2D image display. the
图3所示为现有的采用视差栅栏方法的3D图像显示装置。为方便地实现3D图像显示,如图3所示,可以将图1中所示的视差栅栏10贴合于或者设置于图2所示的TFT-LCD 20上,从而就可以实现3D图像显示。 FIG. 3 shows a conventional 3D image display device using a parallax barrier method. In order to realize 3D image display conveniently, as shown in FIG. 3, the
然而,虽然3D图像显示技术虽然已经较为成熟,但还未并应用于车辆导航系统中。 However, although the 3D image display technology is relatively mature, it has not yet been applied to the vehicle navigation system. the
实用新型内容Utility model content
本实用新型旨在提供一种能够实现2D/3D图像显示的自由转换的导航系统。 The utility model aims to provide a navigation system capable of realizing free conversion of 2D/3D image display. the
进一步地,本实用新型还能够提供一种屏幕能够卷曲的2D/3D导航系统。 Furthermore, the present invention can also provide a 2D/3D navigation system whose screen can be rolled. the
本实用新型的导航系统其特征在于,包括:能转换显示2D画面和3D画面的2D/3D图像显示屏;对导航系统供给电源的工作电源;用于提供导航服务的GPS模块;控制所述2D/3D图像显示屏以在2D图像显示和3D图像显示之间进行切换的2D/3D信号转换器;以及控制2D/3D信号转换器的开闭的2D/3D信号转换器,所述2D/3D图像显示屏为柔性显示屏。 The navigation system of the present utility model is characterized in that it includes: a 2D/3D image display screen capable of switching and displaying 2D images and 3D images; a working power supply for supplying power to the navigation system; a GPS module for providing navigation services; controlling the
利用本实用新型,通过将3D成像技术应用在导航系统,同时利用上述2D/3D图像显示屏,可以使导航系统显示更加立体、直观,实现真正的“实时”、“实感”导航显示。而且,利用本实用新型,能够自由地在3D图像显示和2D图像显示之间进行切换,这样能够方便使用者根据自身的需求选择相应的显示方式,提高导航的实用性以及乐趣性。进一步,在本实用新型中,实现了导航系统由2D平面向3D空间的转化,提高了导航功能的准确度和驾驶乐趣。 Utilizing the utility model, by applying 3D imaging technology to the navigation system and using the above-mentioned 2D/3D image display screen, the display of the navigation system can be more three-dimensional and intuitive, and real "real-time" and "real sense" navigation display can be realized. Moreover, the utility model can freely switch between 3D image display and 2D image display, which can facilitate users to select corresponding display modes according to their own needs, and improve the practicability and fun of navigation. Further, in the utility model, the transformation of the navigation system from the 2D plane to the 3D space is realized, and the accuracy of the navigation function and the driving pleasure are improved. the
其中,优选地,所述2D/3D图像显示屏能够拉伸和卷曲。 Wherein, preferably, the 2D/3D image display screen can be stretched and rolled. the
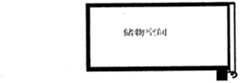
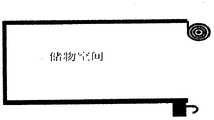
这样,通过将2D/3D图像显示屏设计成能够拉伸和卷曲的卷曲屏幕,在本实用新型中,能够充分利用车辆内部空间,可以将原有的显示器空间变为储物空间。 In this way, by designing the 2D/3D image display screen as a curly screen that can be stretched and curled, in the utility model, the interior space of the vehicle can be fully utilized, and the original display space can be changed into a storage space. the
其中,优选地,还具备用于控制导航系统开闭的手动开关。 Among them, preferably, a manual switch for controlling the opening and closing of the navigation system is also provided. the
这样,能够手动地控制导航系统的开闭,使用者可以根据自身的需求选择是否开启导航系统,由此哪个提高导航的实用性。 In this way, the opening and closing of the navigation system can be manually controlled, and the user can choose whether to turn on the navigation system according to his own needs, thereby improving the practicability of the navigation. the
优选地,2D/3D图像显示屏在显示3D图像时为裸眼型3D图像显示装置。 Preferably, the 2D/3D image display screen is a naked-
这样,通过应用裸眼3D技术,使用者不需任何的辅助眼镜等设备的协助下就能够观看3D显示,使用上非常方便。 In this way, by applying the naked-
优选地,所述裸眼型3D图像显示装置采用视差栅栏的结构。 Preferably, the naked-
由于视差栅栏的结构较为常用,因此其成本会比较低廉。 Since the structure of the parallax barrier is relatively common, its cost will be relatively low. the
综上所述,利用本实用新型的导航系统,通过利用2D/3D图像显 示屏,可以使导航系统进行2D或者3D显示,能够按照使用者的自身需求选择所需要的显示方式,能够实现更加立体、直观的显示,提高了导航功能的便捷性和准确性。 In summary, using the navigation system of the present invention, by using the 2D/3D image display screen, the navigation system can be displayed in 2D or 3D, and the required display mode can be selected according to the user's own needs, and more The three-dimensional and intuitive display improves the convenience and accuracy of the navigation function. the
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是现有技术的视差栅栏的结构示意图。 FIG. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a parallax barrier in the prior art. the
图2是现有技术的TFT-LCD的结构示意图。 FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a TFT-LCD in the prior art. the
图3是现有技术的采用视差栅栏方法的立体图像显示装置。 FIG. 3 is a stereoscopic image display device using a parallax barrier method in the prior art. the
图4是本实用新型的导航系统的结构方框图。 Fig. 4 is a structural block diagram of the navigation system of the present invention. the
图5A是表示本实用新型的导航系统在柔性显示屏拉伸模式下的使用状态示意图。图5B是表示本实用新型的导航系统在柔性显示屏收起模式下的使用状态示意图。 FIG. 5A is a schematic view showing the use state of the navigation system of the present invention in the stretching mode of the flexible display screen. FIG. 5B is a schematic view showing the use state of the navigation system of the present invention in the flexible display screen retracted mode. the
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面介绍的是本实用新型的多个可能实施例中的一些,旨在提供对本实用新型的基本了解。并不旨在确认本实用新型的关键或决定性的要素或限定所要保护的范围。 Introduced below are some of the many possible embodiments of the present invention, intended to provide a basic understanding of the present invention. It is not intended to identify key or decisive elements of the present invention or to limit the scope of protection. the
图4是本实用新型的导航系统的结构方框图。 Fig. 4 is a structural block diagram of the navigation system of the present invention. the
如图4所示,本实用新型的导航系统包括:能够切换显示2D画面和3D画面的2D/3D图像显示屏1、工作电源2、手动开关3、GPS模块4、2D/3D信号转换开关5以及2D/3D信号转换器6。 As shown in Figure 4, the navigation system of the present invention includes: a 2D/3D
2D/3D图像显示屏1能切换显示2D画面和3D画面,由2D/3D转换器6进行控制,能够在2D图像显示和3D图像显示之间进行切换。 The 2D/3D
这里,通过2D/3D信号转换开关5来控制2D/3D转换器6的转换,以实现对2D/3D图像显示屏1进行2D图像显示或者3D图像显示的切换。 Here, the conversion of the 2D/
工作电源2用于给本实用新型的导航系统供给电源。手动开关3用于控制导航系统的开闭。GPS模块4为实现导航功能的模块,其为现有技术。 The working
这里,2D/3D图像显示屏1可以采用例如背景技术中的3D技术, 作为一个示例,例如,2D/3D显示屏是裸眼型3D图像显示装置,具体地,可以将图1所示的视差栅栏10贴合于或者设置于图2所示的TFT-LCD 20上,来实现3D图像显示。 Here, the 2D/3D
其次,由2D/3D转换开关5、2D/3D信号转换器6来实现2D/3D图像显示的切换控制。例如,可以将2D/3D转换开关5、2D/3D信号转换器6设置成在导通时,使得视差栅栏10与TFT-LCD 20一起工作来实现3D图像显示,在关闭时,使得视差栅栏10与TFT-LCD 20不一起工作而仅TFT-LCD 20工作,来实现2D图像显示,反之亦可。 Secondly, the switching control of 2D/3D image display is realized by the 2D/
这样,利用人眼的视觉差和2D/3D图像显示屏1的视差栅栏10的特殊效果,在切换成3D图像显示的情况下,显示三维立体的视图,能够提供立体、精准的导航图像。 In this way, by using the visual difference of human eyes and the special effect of the
这样,对于不适应三维立体的使用者,也可以通过切换2D/3D转换开关5切换到2D图像显示模式。这样,在切换成2D图像显示的情况下,显示二维的平面视图,由此,能够提供较为便捷、简化的导航图像,对于不适应观看三维立体的使用者,能够通过切换显示成2D图像显示来进行导航。 In this way, for users who are not used to three-dimensional stereo, they can also switch to the 2D image display mode by switching the 2D/
另一方面,对于2D/3D图像显示屏1最好采用柔性材料构成。 On the other hand, the 2D/3D
由此,2D/3D图像显示屏1能够拉伸和卷曲,在需要使用导航系统时,可以将2D/3D图像显示屏1拉伸开,以进行正常显示,在不使用导航系统时,可以将2D/3D图像显示屏1卷曲起来。 Thus, the 2D/3D
图5A是表示本实用新型的导航系统在柔性显示屏拉伸模式下的使用状态示意图。图5B是表示本实用新型的导航系统在柔性显示屏收起模式下的使用状态示意图。 FIG. 5A is a schematic view showing the use state of the navigation system of the present invention in the stretching mode of the flexible display screen. FIG. 5B is a schematic view showing the use state of the navigation system of the present invention in the flexible display screen retracted mode. the
图5A表示需要观看导航系统时拉伸2D/3D图像显示屏1的模式,图5B表示需要不使用导航系统时卷曲2D/3D图像显示屏1的模式。 FIG. 5A shows the mode of stretching the 2D/3D
这样,在不使用导航系统时,可以将2D/3D图像显示屏1卷曲收纳,减少了占用空间。尤其是将实用新型的导航系统应用于车辆的情况下,能够有效地提高车辆内部的利用效率。 In this way, when the navigation system is not in use, the 2D/3D
另外,在本实用新型中虽然列举了采用视差栅栏10(即视差栅栏方法)的实现3D图像显示的实施方案,但不限定于此,也可以采用透镜方法和全息方法来实现3D。 In addition, although the embodiment of realizing 3D image display using the parallax barrier 10 (that is, the parallax barrier method) is listed in the present invention, it is not limited to this, and the lens method and the holographic method can also be used to realize 3D. the
以上例子主要说明了本实用新型的可实现2D/3D切换的导航系 统。尽管只对其中一些本实用新型的实施方式进行了描述,但是本领域普通技术人员应当了解,本实用新型可以在不偏离其主旨与范围内以许多其他的形式实施。因此,所展示的例子与实施方式被视为示意性的而非限制性的,在不脱离如所附各权利要求所定义的本实用新型精神及范围的情况下,本实用新型可能涵盖各种的修改与替换。 Above example mainly has illustrated the navigation system that can realize 2D/3D switching of the present utility model. Although only some embodiments of the utility model have been described, those skilled in the art should understand that the utility model can be implemented in many other forms without departing from the gist and scope thereof. The examples and implementations shown are therefore to be regarded as illustrative and not restrictive, and the present invention may cover various modification and replacement. the
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011201704102UCN202204518U (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2011-05-25 | A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D Switching |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011201704102UCN202204518U (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2011-05-25 | A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D Switching |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN202204518Utrue CN202204518U (en) | 2012-04-25 |
Family
ID=45968638
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2011201704102UExpired - Fee RelatedCN202204518U (en) | 2011-05-25 | 2011-05-25 | A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D Switching |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN202204518U (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104335008A (en)* | 2012-06-05 | 2015-02-04 | 苹果公司 | Navigation application |
| CN104536522A (en)* | 2014-12-23 | 2015-04-22 | 深圳市华富泽科技有限公司 | Manufacturing method for naked eye 3D tablet computer |
| CN104034342B (en)* | 2014-06-27 | 2017-03-01 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Instruction device, guider and indicating means |
| US9880019B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-01-30 | Apple Inc. | Generation of intersection information by a mapping service |
| US9886794B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-02-06 | Apple Inc. | Problem reporting in maps |
| US9903732B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-02-27 | Apple Inc. | Providing navigation instructions while device is in locked mode |
| US9997069B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-06-12 | Apple Inc. | Context-aware voice guidance |
| US10006505B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-06-26 | Apple Inc. | Rendering road signs during navigation |
| US10018478B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-07-10 | Apple Inc. | Voice instructions during navigation |
| US10176633B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-01-08 | Apple Inc. | Integrated mapping and navigation application |
| US10318104B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-06-11 | Apple Inc. | Navigation application with adaptive instruction text |
| US10366523B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-07-30 | Apple Inc. | Method, system and apparatus for providing visual feedback of a map view change |
- 2011
- 2011-05-25CNCN2011201704102Upatent/CN202204518U/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10156455B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-12-18 | Apple Inc. | Context-aware voice guidance |
| US10176633B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-01-08 | Apple Inc. | Integrated mapping and navigation application |
| CN104335008B (en)* | 2012-06-05 | 2016-12-21 | 苹果公司 | navigation application |
| US11956609B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2024-04-09 | Apple Inc. | Context-aware voice guidance |
| US9880019B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-01-30 | Apple Inc. | Generation of intersection information by a mapping service |
| US9886794B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-02-06 | Apple Inc. | Problem reporting in maps |
| US9903732B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-02-27 | Apple Inc. | Providing navigation instructions while device is in locked mode |
| US9997069B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-06-12 | Apple Inc. | Context-aware voice guidance |
| US10006505B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-06-26 | Apple Inc. | Rendering road signs during navigation |
| US10318104B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-06-11 | Apple Inc. | Navigation application with adaptive instruction text |
| US11727641B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2023-08-15 | Apple Inc. | Problem reporting in maps |
| CN104335008A (en)* | 2012-06-05 | 2015-02-04 | 苹果公司 | Navigation application |
| US10018478B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2018-07-10 | Apple Inc. | Voice instructions during navigation |
| US10323701B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-06-18 | Apple Inc. | Rendering road signs during navigation |
| US10366523B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-07-30 | Apple Inc. | Method, system and apparatus for providing visual feedback of a map view change |
| US10508926B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2019-12-17 | Apple Inc. | Providing navigation instructions while device is in locked mode |
| US10718625B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2020-07-21 | Apple Inc. | Voice instructions during navigation |
| US10732003B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2020-08-04 | Apple Inc. | Voice instructions during navigation |
| US11055912B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2021-07-06 | Apple Inc. | Problem reporting in maps |
| US11290820B2 (en) | 2012-06-05 | 2022-03-29 | Apple Inc. | Voice instructions during navigation |
| CN104034342B (en)* | 2014-06-27 | 2017-03-01 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Instruction device, guider and indicating means |
| CN104536522A (en)* | 2014-12-23 | 2015-04-22 | 深圳市华富泽科技有限公司 | Manufacturing method for naked eye 3D tablet computer |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN202204518U (en) | A Navigation System Capable of 2D/3D Switching | |
| CN101971237B (en) | monitor | |
| CN102073142B (en) | Stereoscopic display unit | |
| KR100824539B1 (en) | Touch panel stereoscopic image display device | |
| CN102436101B (en) | Liquid crystal lens grating and three-dimensional display device | |
| KR102171611B1 (en) | Stereopsis image display device | |
| US20060268196A1 (en) | Liquid crystal panel, display device having liquid crystal panel, and driving method thereof | |
| US8928823B2 (en) | 3D display device adopting half-source driving structure | |
| CN102768437B (en) | Three-dimensional (3D) image display device | |
| US20150241710A1 (en) | Naked-eye 3d display device and liquid crystal lens thereof | |
| CN102654701B (en) | Array substrate, display panel and display device | |
| CN103048836B (en) | Thin film transistor (TFT) array substrate, liquid crystal display, driving method thereof and three-dimensional (3D) display system | |
| CN102778777B (en) | Display panel of stereoscopic image display | |
| US9671659B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| TW200530675A (en) | Display panel and display device | |
| CN102778757B (en) | Three-dimensional (3D) display device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US20150070476A1 (en) | Three-dimensional display device | |
| CN102436100A (en) | Liquid crystal slit grating and stereo display device | |
| CN101017251A (en) | Three-dimensional auto-stereoscopic display device based on light polarizing parallax strip and grid screen | |
| CN102636909A (en) | Liquid crystal slit grating and three-dimensional display device | |
| CN102354071A (en) | Liquid crystal grating type free stereo display device | |
| CN202149995U (en) | Naked-eye 3D screen device | |
| KR101881163B1 (en) | Integral image system and driving method of the same | |
| WO2015035713A1 (en) | Stereo display apparatus | |
| US20130100375A1 (en) | Display device, spacer, and electronic apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20120425 Termination date:20200525 |