CN201424476Y - A photobioreactor - Google Patents
A photobioreactorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN201424476Y CN201424476YCN 200920160301CN200920160301UCN201424476YCN 201424476 YCN201424476 YCN 201424476YCN 200920160301CN200920160301CN 200920160301CN 200920160301 UCN200920160301 UCN 200920160301UCN 201424476 YCN201424476 YCN 201424476Y
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- box
- reactor
- photobioreactor
- support frame
- column
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000005273aerationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 239000011521glassSubstances0.000claimsdescription17
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethyl methacrylateChemical compoundCOC(=O)C(C)=CVVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 229920005372Plexiglas®Polymers0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000004698PolyethyleneSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011152fibreglassSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000515polycarbonatePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004417polycarbonateSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- -1polyethylenePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000573polyethylenePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000915polyvinyl chloridePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004800polyvinyl chlorideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000004026adhesive bondingMethods0.000claims1
- 238000003306harvestingMethods0.000abstractdescription13
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000008569processEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000012531culture fluidSubstances0.000abstract1
- 241000195493CryptophytaSpecies0.000description22
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description11
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description10
- 229920001296polysiloxanePolymers0.000description6
- 239000003292glueSubstances0.000description5
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description5
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description5
- 235000015097nutrientsNutrition0.000description5
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description5
- CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbon dioxideChemical compoundO=C=OCURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 230000012010growthEffects0.000description4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 241000196324EmbryophytaSpecies0.000description3
- 230000008901benefitEffects0.000description3
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description3
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description3
- 244000005700microbiomeSpecies0.000description3
- 230000029553photosynthesisEffects0.000description3
- 238000010672photosynthesisMethods0.000description3
- 230000000243photosynthetic effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000004033plasticSubstances0.000description3
- 229920003023plasticPolymers0.000description3
- 238000007789sealingMethods0.000description3
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 229910002092carbon dioxideInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000001569carbon dioxideSubstances0.000description2
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description2
- 238000004140cleaningMethods0.000description2
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description2
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000description2
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethaneChemical compoundCVNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 150000002894organic compoundsChemical class0.000description2
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description2
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description2
- 238000000746purificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000002787reinforcementEffects0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 241000894007speciesSpecies0.000description2
- 238000004659sterilization and disinfectionMethods0.000description2
- 239000002351wastewaterSubstances0.000description2
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description1
- 239000002028BiomassSubstances0.000description1
- UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbon monoxideChemical compound[O+]#[C-]UGFAIRIUMAVXCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 241000195649Chlorella <Chlorellales>Species0.000description1
- 241000192700CyanobacteriaSpecies0.000description1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphorusChemical compound[P]OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 102000007056Recombinant Fusion ProteinsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010008281Recombinant Fusion ProteinsProteins0.000description1
- 239000013543active substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013019agitationMethods0.000description1
- 230000005791algae growthEffects0.000description1
- 235000019730animal feed additiveNutrition0.000description1
- 235000019728animal nutritionNutrition0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 244000052616bacterial pathogenSpecies0.000description1
- 239000003225biodieselSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002551biofuelSubstances0.000description1
- 238000009395breedingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001488breeding effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000006227byproductSubstances0.000description1
- 230000005779cell damageEffects0.000description1
- 208000037887cell injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 235000014113dietary fatty acidsNutrition0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000428dustSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 229930195729fatty acidNatural products0.000description1
- 239000000194fatty acidSubstances0.000description1
- 150000004665fatty acidsChemical class0.000description1
- 239000003337fertilizerSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001914filtrationMethods0.000description1
- 239000003546flue gasSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013305foodNutrition0.000description1
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000description1
- 239000002054inoculumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052500inorganic mineralInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000001788irregularEffects0.000description1
- 238000012269metabolic engineeringMethods0.000description1
- 239000011707mineralSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052757nitrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 235000016709nutritionNutrition0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 238000006213oxygenation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000000575pesticideSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052698phosphorusInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000011574phosphorusSubstances0.000description1
- 230000035479physiological effects, processes and functionsEffects0.000description1
- 239000000049pigmentSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description1
- 235000018102proteinsNutrition0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 230000003014reinforcing effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000565sealantSubstances0.000description1
- 229930000044secondary metaboliteNatural products0.000description1
- 239000004590silicone sealantSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000description1
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 235000000346sugarNutrition0.000description1
- 150000008163sugarsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description1
- 239000002699waste materialSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M21/00—Bioreactors or fermenters specially adapted for specific uses
- C12M21/02—Photobioreactors
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M23/00—Constructional details, e.g. recesses, hinges
- C12M23/20—Material Coatings
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M31/00—Means for providing, directing, scattering or concentrating light
- C12M31/02—Means for providing, directing, scattering or concentrating light located outside the reactor
- C12M31/04—Mirrors
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12M—APPARATUS FOR ENZYMOLOGY OR MICROBIOLOGY; APPARATUS FOR CULTURING MICROORGANISMS FOR PRODUCING BIOMASS, FOR GROWING CELLS OR FOR OBTAINING FERMENTATION OR METABOLIC PRODUCTS, i.e. BIOREACTORS OR FERMENTERS
- C12M41/00—Means for regulation, monitoring, measurement or control, e.g. flow regulation
- C12M41/12—Means for regulation, monitoring, measurement or control, e.g. flow regulation of temperature
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Clinical Laboratory Science (AREA)
- Apparatus Associated With Microorganisms And Enzymes (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本实用新型涉及一种光生物反应器,可用于培养光合微生物或植物细胞。The utility model relates to a photobioreactor, which can be used for cultivating photosynthetic microorganisms or plant cells.
背景技术Background technique
光合微生物或植物细胞,尤其是微藻和蓝细菌(简称藻类)的生长繁殖主要依靠简单的矿物质。藻类通过光合作用,利用光能(如太阳光和人工照明)将水和二氧化碳转化成色素、蛋白质、脂肪酸、糖类及次生代谢物等高价值有机化合物。藻类因具有极高的光及营养利用效率表现出比高等植物更强的生长潜力。The growth and reproduction of photosynthetic microorganisms or plant cells, especially microalgae and cyanobacteria (referred to as algae), mainly rely on simple minerals. Through photosynthesis, algae use light energy (such as sunlight and artificial lighting) to convert water and carbon dioxide into high-value organic compounds such as pigments, proteins, fatty acids, sugars, and secondary metabolites. Algae show stronger growth potential than higher plants because of their extremely high light and nutrient utilization efficiency.
在已知的40000多种物种中,藻类是一类与众不同的生物群体,因此它们(自然)可产生许多类新的、尚未开发的生物产品。2004年全球藻类产品(如药品、营养品、农药、食品及动物饲料)年销售量估计达到了2×109美元。通过利用分子生物学、代谢工程、功能基因组研究等方面的最新突破,将藻类这一极好地基因表达载体,应用于生产人及动物营养保健方面的重组蛋白和其它生物活性物质。由于藻类具有快速从周围环境中吸收CO2、氮、磷等营养物质并将其转化为有机化合物(如储存在细胞中的蛋白)的能力,它已被提出并在自然及工程系统中测试,去除或回收废水及和火电站富含CO2的烟气中的营养废弃物。藻类作为生物净化过程的副产物可作为生产生物燃料(如生物柴油,酒精和甲烷)、动物饲料添加剂和有机肥料的原料。虽然藻类在气、液态可再生生物能源、高附加值产品和环境生物净化方面的应用是科学的、符合环境要求的,但藻类应用的经济可行性是由供藻类生长、繁殖的工业规模光反应器的效率和成本效益决定的。Algae are a distinct group of organisms among the more than 40,000 known species, and as such they (naturally) produce many new and untapped classes of biological products. In 2004, the annual global sales of algae products (such as pharmaceuticals, nutritional products, pesticides, food and animal feed) was estimated to reach 2×109 US dollars. By utilizing the latest breakthroughs in molecular biology, metabolic engineering, and functional genomics research, algae, an excellent gene expression carrier, is applied to the production of recombinant proteins and other biologically active substances in human and animal nutrition and health care. Algae have been proposed and tested in natural and engineered systems due to their ability to rapidly absorb nutrients such as CO2 , nitrogen, and phosphorus from the surrounding environment and convert them into organic compounds such as proteins stored in cells, Removal or recovery of waste water and nutrient waste inCO2- rich flue gas from thermal power plants. Algae, as a by-product of the biological purification process, can be used as a feedstock for the production of biofuels (such as biodiesel, alcohol, and methane), animal feed additives, and organic fertilizers. Although the application of algae in gas, liquid renewable bioenergy, high value-added products and environmental bio-purification is scientific and environmentally sound, the economic feasibility of algae application is determined by the industrial scale photoreaction for algae growth and reproduction. determined by the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the device.
当前工业规模光反应器一般为开放式跑道池,多建成1000~5000m2环形的浅池(水深15~30cm),用浆轮使培养液循环流动。这种生产模式的优点在于其结构和维护相对简单,但它在藻类户外生长生产力因素的控制方面有许多不足。开放式跑道池总体生产率低主要是因为缺乏温度控制、光程长及混合不均匀。培养藻类的开放式跑道池直接与空气接触而易于染菌,常导致培养失败。The current industrial-scale photoreactor is generally an open racetrack pool, and acircular shallow pool of 1000-5000m2 (water depth 15-30cm) is usually built, and a paddle wheel is used to circulate the culture medium. The advantage of this production mode is that its structure and maintenance are relatively simple, but it has many shortcomings in the control of algae outdoor growth productivity factors. The overall low productivity of open raceway pools is mainly due to lack of temperature control, long light paths, and uneven mixing. The open runway pool for cultivating algae is directly in contact with the air and is easy to be infected with bacteria, which often leads to culture failure.
开放式跑道池的缺陷推动了封闭式培养系统的发展。如用透明的管或容器制成,并用泵或气泡实现培养液混合的光生物反应器。但管式反应器自身也存在着问题。首先,管式反应器的气体交换罐是一个很大的“暗区或暗体积”(通常占总培养体积的10~15%)。其次,管式反应器中易于积累光合作用过程中生成的氧,从而抑制光合作用及生物量生产潜力。再次,在长的管式光生物反应器中一般都用泵来实现藻液的混合及循环,但泵会造成严重的细胞损伤。同时,管式反应器的应用也受到其高成本及维护费用的限制,仅用于生产小批量、高价值特种产品。The deficiencies of open raceway pools have motivated the development of closed culture systems. For example, a photobioreactor made of a transparent tube or container, and a pump or air bubbles are used to realize the mixing of the culture solution. But tubular reactors also have their own problems. First, the gas exchange tank of a tubular reactor is a large "dark space or dark volume" (typically 10-15% of the total culture volume). Second, oxygen generated during photosynthesis tends to accumulate in tubular reactors, thereby inhibiting photosynthesis and biomass production potential. Thirdly, pumps are generally used in long tubular photobioreactors to achieve mixing and circulation of algae liquid, but pumps will cause serious cell damage. At the same time, the application of tubular reactors is also limited by their high cost and maintenance costs, and they are only used to produce small batches of high-value specialty products.
然而,近十年,人们将注意力集中到了板式光生物反应器上。板式反应器与管式系统相比,其设计优点在于:1)没有“暗区”,整个反应器可受光,从而提高了光合生产力;2)通气系统不但使藻液混合均匀而且由于气泡产生的液体动力最小,其对细胞的危害性也小;3)由于反应器高度低(如:3~10英尺)不会有O2抑制作用;4)板式反应器可在不同的方位或以不同的倾斜角度放置,以在全年中最大限度的利用太阳光能,来提高产量;5)与管式反应器相比,板式反应器的成本和维护费用相当低。然而,目前板式反应器只是作为实验室培养装置和小型户外箱体,用于研究藻类生长生理,还未应用于藻类的工业化规模培养。However, in the past decade, people have focused their attention on plate photobioreactors. Compared with the tubular system, the design advantages of the plate reactor are: 1) There is no "dark area", and the whole reactor can receive light, thereby improving the photosynthetic productivity; The hydrodynamic force is the smallest, and its harm to cells is also small; 3) Due to the low height of the reactor (such as: 3 to 10 feet), there will be no O2 inhibition; 4) The plate reactor can be placed in different directions or in different directions. Placed at an inclined angle to maximize the use of solar energy throughout the year to increase production; 5) Compared with tube reactors, the cost and maintenance costs of plate reactors are quite low. However, at present, the plate reactor is only used as a laboratory cultivation device and a small outdoor box for studying the growth and physiology of algae, and has not been applied to the industrial scale cultivation of algae.
胡强设计的反应器WO 2007/098150 A2就是板式反应器中的一个典型代表,它具有上述优点,但该板式反应器也存在着以下不足:1)反应器中间设有挡板、两侧面相对的支撑架间在反应器顶部有连接横梁、顶部加盖、反应器下端设有收获出口。这样该反应器不能采用贯通式整体收获,其收获过程是将反应器中的全部藻液泵出或排出,然后处理所有藻液,由于藻液中藻的浓度很低,一般低于1%,所以最终只能得到其中很少的微藻。这样整个过程中动力消耗很大,处理量大,运行成本很高。2)该反应器棱角处存在处于静止状态的死角,导致清洗、消毒不完全,反应器局部培养液搅动不充分,营养分布不均匀,细胞在死角区贴壁、沉降严重甚至死亡,从而降低了培养效率。Reactor WO 2007/098150 A2 designed by Hu Qiang is a typical representative of plate reactors. It has the above advantages, but this plate reactor also has the following disadvantages: 1) There is a baffle in the middle of the reactor, and the two sides are opposite to each other. There are connecting beams on the top of the reactor between the support frames, a cover on the top, and a harvesting outlet at the lower end of the reactor. This reactor can not adopt through-type overall harvesting like this, and its harvesting process is to pump out or discharge all the algae liquid in the reactor, and then process all the algae liquid, because the concentration of algae in the algae liquid is very low, generally lower than 1%, So you end up with very little microalgae in it. In this way, the power consumption in the whole process is very large, the processing capacity is large, and the operating cost is very high. 2) There are dead corners in a static state at the corners of the reactor, which lead to incomplete cleaning and disinfection, insufficient agitation of the local culture medium in the reactor, uneven nutrient distribution, and cells in the dead corners. Cultivate efficiency.
实用新型内容Utility model content
本实用新型的目的是提供一种光生物反应器,其是结构简单,便于整体收获,运行费用低,可连续培养的反应器,且完全消除了板式反应器普遍存在的死角。The purpose of the utility model is to provide a photobioreactor, which is simple in structure, convenient for overall harvesting, low in operating costs, and capable of continuous cultivation, and completely eliminates the common dead angle of plate reactors.
为达到上述目的,本实用新型的技术解决方案是:For achieving the above object, the technical solution of the utility model is:
一种光生物反应器,包括曝气系统,用于控制所述箱体中培养液的温度的控温系统,反应器控制系统和至少一个反应器单元;其反应器单元包括箱体及其支撑框架,箱体为适于容纳液体的盒体,其顶部是开放式开口,内腔整体贯通;A photobioreactor, including an aeration system, a temperature control system for controlling the temperature of the culture solution in the box, a reactor control system and at least one reactor unit; the reactor unit includes a box and its support The frame, the box body is a box body suitable for containing liquid, the top of which is an open opening, and the inner cavity is integrally connected;
该箱体纵向相对的两长侧面是整体结构,至少一个长侧面是透明的;The two longitudinally opposite long sides of the box are integral structures, and at least one long side is transparent;
在横向相对的短侧面上设有进料口、取样口、排液口;A feed port, a sampling port, and a liquid discharge port are provided on the laterally opposite short sides;
该箱体的两长侧面外侧以支撑框架支撑,支撑框架沿箱体纵向均匀布设,支撑框架的高不小于箱体的高;The outside of the two long sides of the box is supported by a support frame, which is evenly arranged along the longitudinal direction of the box, and the height of the support frame is not less than the height of the box;
支撑框架呈梯形,垂直地面,以箱体的横向中垂面两侧对称设置,每侧呈直角三角形,直角三角形的垂直边为支撑框架立柱,两支撑框架立柱间固夹箱体,定位,两直角三角形底边为一根支撑杆件相连接,底边位于支撑面上。The support frame is trapezoidal, vertical to the ground, symmetrically arranged on both sides of the horizontal vertical plane of the box, each side is a right triangle, the vertical side of the right triangle is the support frame column, and the box is fixed between the two support frame columns, positioning, two The bases of the right triangles are connected by a support rod, and the bases are located on the support surface.
所述的光生物反应器,其横向相对的两短侧面和底面为圆弧形面。As for the photobioreactor, its two short lateral sides and the bottom surface opposite in the transverse direction are arc-shaped surfaces.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述箱体两长侧面外侧面上,还固设有井字形箱体框架,箱体框架的竖直件为箱体框架立柱,箱体框架立柱与支撑框架立柱相适配,两者之间以连接件固接。In the photobioreactor, on the outer sides of the two long sides of the box, a well-shaped box frame is fixed, and the vertical part of the box frame is a box frame column, and the box frame column and the support frame The uprights are matched, and the two are fixed with connectors.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述支撑框架立柱固夹箱体、两长侧面外侧固设箱体框架,是通过粘合或螺栓其中之一方式连接,或两者组合的方式连接。In the photobioreactor, the supporting frame column clamps the box, and the box frame is fixed on the outside of the two long sides, and is connected by one of bonding or bolts, or a combination of both.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述连接件,为U型卡箍和螺栓,U型卡箍两自由端及中点上有螺孔,自由端的两通孔穿设一螺栓,中点通孔穿设另一螺栓;U型卡箍横向包围箱体框架立柱和支撑框架立柱后,通过一螺栓穿过箱体框架立柱固定,另一螺栓通过U型卡箍中点的螺孔与支撑框架立柱相抵固,使箱体框架立柱与支撑框架立柱的紧密结合。In the photobioreactor, the connectors are U-shaped clamps and bolts. There are screw holes on the two free ends and the midpoint of the U-shaped clamps. Two through holes at the free ends are pierced with a bolt. The hole is pierced with another bolt; after the U-shaped clamp laterally surrounds the box frame column and the support frame column, one bolt passes through the box frame column to fix it, and the other bolt passes through the screw hole at the midpoint of the U-shaped clamp and the support frame. The uprights are against each other, so that the box frame uprights are closely combined with the support frame uprights.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述圆弧形的两短侧面和底面,在纵向两侧边内侧设有贯通的沟槽,沟槽与长侧面的厚度相适配,长侧面固接于沟槽内;短侧面和底面相对端部设有过渡件,过渡件为四分之一球状片;短侧面、底面和长侧面间,短侧面、底面和球状片间粘合固接。In the photobioreactor, the arc-shaped two short sides and the bottom surface are provided with through grooves on the inner sides of the longitudinal sides, the grooves are adapted to the thickness of the long sides, and the long sides are fixed on the In the groove; there is a transition piece at the opposite end of the short side and the bottom surface, and the transition piece is a quarter spherical piece; between the short side, the bottom surface and the long side, and between the short side, the bottom surface and the spherical piece.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述两长侧面是整体结构,是依据需要以多数个侧面片的垂直侧边相互顺序固接构成的整体结构。In the photobioreactor, the two long sides are an integral structure, which is an integral structure composed of vertical sides of a plurality of side panels connected to each other sequentially as required.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述箱体长度不小于0.5米,高度在0.2~3米之间。In the photobioreactor, the length of the box is not less than 0.5 meters, and the height is between 0.2 and 3 meters.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述多个反应器单元串联后,为反应器组,反应器组内的反应器单元,摆放时,相互之间间距为0.5~3米。In the photobioreactor, the multiple reactor units connected in series form a reactor group, and the reactor units in the reactor group are arranged with a distance of 0.5 to 3 meters between them.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述反应器组,每个相邻的反应器单元,在相对各自的支撑框架立柱上端外侧,以一横梁相互固连支撑。In the photobioreactor, in the reactor group, each adjacent reactor unit is fixedly connected and supported by a crossbeam on the outer side of the upper end of the column of the supporting frame.
所述的光生物反应器,其还包括反光镜,将照射光反射到箱体上。The photobioreactor also includes a reflector to reflect the irradiated light onto the box.
所述的光生物反应器,其所述箱体,为透明或半透明,以玻璃、玻璃纤维、PVC、聚碳酸酯、聚乙烯或金属其中之一制作;支撑框架、箱体框架,为金属或有机玻璃材料制作。In the photobioreactor, the box body is transparent or translucent, made of one of glass, fiberglass, PVC, polycarbonate, polyethylene or metal; the supporting frame and box frame are made of metal Or made of plexiglass material.
本实用新型的一种光生物反应器针对现有反应器不便于整体收获,现有反应器运行成本高,以及现有反应器存在的死角问题,设计的板式反应器具有以下特点:1)反应器两长侧面内部及顶部开口处无连接结构。且支撑框架中相对的两立柱在反应器的顶部没有连接横梁,相邻两个反应器单元通过各自支撑框架立柱上的横梁相互连接、支撑,这样的结构即保证了反应器的强度,又保持了反应器内部整体连通,这样可以采取整体收获,收获的过程中藻液无需泵出,始终在反应器内,能耗少;2)反应器短侧面及底面采用弧形设计,完全消除了死角区,避免了反应器清洗、消毒不完全,及其中的培养液营养分布不均匀等问题。3)本实用新型反应器可以与一种特殊的贯通式整体收获装置配合使用,培养结束后,该收获装置在反应器内部缓慢从反应器一端运行到另一端,同时将培养物富集在反应器的一端,最后将培养物的富集液由排液口排出。整个收获过程无需将培养液全部排出,能耗少,运行费用低。从而使该反应器实现产业化连续培养应用。A kind of photobioreactor of the present utility model is inconvenient to the overall harvest of existing reactor, and existing reactor operating cost is high, and the dead angle problem that existing reactor exists, and the plate type reactor of design has the following characteristics: 1) reaction There is no connection structure inside the two long sides of the device and at the top opening. In addition, the two opposing columns in the supporting frame are not connected with beams at the top of the reactor, and two adjacent reactor units are connected and supported by the beams on the columns of the supporting frame respectively. Such a structure not only ensures the strength of the reactor, but also maintains The internal connection of the reactor is integrated, so that the overall harvest can be adopted. During the harvesting process, the algae liquid does not need to be pumped out, and it is always in the reactor, with less energy consumption; 2) The short side and bottom of the reactor are designed with arcs, which completely eliminates dead ends. area, avoiding the problems of incomplete cleaning and disinfection of the reactor, and uneven nutrient distribution of the culture solution. 3) The utility model reactor can be used in conjunction with a special through-type overall harvesting device. After the cultivation is completed, the harvesting device slowly runs from one end of the reactor to the other end inside the reactor, and at the same time enriches the culture in the reaction One end of the container, and finally the enriched solution of the culture is discharged from the discharge port. There is no need to discharge all the culture medium during the whole harvesting process, with less energy consumption and low operating costs. Therefore, the reactor realizes the application of industrialized continuous cultivation.
附图说明Description of drawings
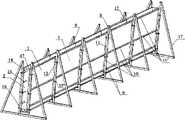
图1a本实用新型的一种光生物反应器单元结构图;Fig. 1a is a structural diagram of a photobioreactor unit of the utility model;
图1b本实用新型的光生物反应器采用圆弧侧面及圆弧底面消除死角示意图;Fig. 1b The photobioreactor of the present utility model adopts a schematic diagram of arc side and arc bottom to eliminate dead angle;
图1c本实用新型中圆弧底面或圆弧侧面结构图;Fig. 1c is the structure diagram of arc bottom or arc side in the utility model;
图1d 为图1a中反应器的底面局部结构图;Fig. 1d is the partial structural diagram of the bottom surface of reactor among Fig. 1a;
图2本实用新型中反应器组示意图;Reactor group schematic diagram in Fig. 2 utility model;
图3a本实用新型中箱体框架与支撑框架连接件结构图;Fig. 3a is a structural diagram of the box frame and the supporting frame connector in the utility model;
图3b本实用新型中箱体框架与支撑框架连接方式示意图;Figure 3b is a schematic diagram of the connection between the box frame and the support frame in the utility model;
图4本实用新型中利用反光镜增大光生物反应器对光的利用效率的侧视示意图;Fig. 4 utilizes reflective mirror to increase the side view schematic diagram of light utilization efficiency of photobioreactor in the utility model;
图5本实用新型的光生物反应器曝气系统示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the aeration system of the photobioreactor of the present utility model.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本实用新型的一种光生物反应器,为进一步说明其结构,现列举4个实施例:1.短侧面及底面为平面的反应器。2.短侧面及底面为为圆弧的反应器。3.反应器组。4.养殖实例。A kind of photobioreactor of the present utility model, for further illustrating its structure, enumerates 4 embodiments now: 1. short side and bottom surface are the reactor of plane. 2. The short side and bottom are arc-shaped reactors. 3. Reactor group. 4. Breeding examples.
实施例1:Example 1:
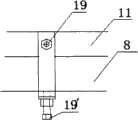
如图1a、图1d、图2、图3a、图3b、图4、图5所示,为本实用新型的光生物反应器结构示意图。其中,长侧面1、短侧面2、支撑框架立柱8、支撑框架9、箱体框架10、箱体框架立柱11、箱体框架横筋11’、U型卡箍12、进料口14、取样口15、排液口16、反应器旁边的支撑框架17、支撑框架立柱上的横梁18、螺栓19、U型卡箍顶部螺栓19’、孔20、反光镜21、入射光22、反射光23、曝气管24、导气管25、气泵26、过滤装置27、气体28、端口密封条47。As shown in Fig. 1a, Fig. 1d, Fig. 2, Fig. 3a, Fig. 3b, Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, they are schematic structural diagrams of the photobioreactor of the present invention. Among them,
光生物反应器,包括:箱体、支撑框架9、曝气系统,曝气系统见图5。The photobioreactor includes: a box body, a
箱体由长侧面1、短侧面2组成。长侧面1由8mm普通玻璃通过天马牌硅酮结构胶粘贴到箱体框架10上制成。短侧面2由3mm厚衬塑不锈钢板制成。长侧面1是可以无限延长的,可由无数块首尾相连的玻璃固定于箱体框架10上构成。The box body is composed of a
本实用新型的光生物反应器长10m、高1.2米,宽度为15cm。长侧面1中的箱体框架10高1.2m,长10m,由截面为40mm×40mm的冷弯空心型钢衬塑制成,箱体两长侧面1上相对的两箱体框架立柱11间距离111mm,三根箱体框架横筋11’间的距离由上至下分别为600mm和440mm.支撑框架由截面为40mm×40mm的冷弯空心型钢衬塑制成,同一箱体长侧面1上相邻支撑框架立柱8间的距离与该长侧面上相邻的箱体框架立柱11间的距离一致为945mm,支撑框架立柱8与箱体框架立柱11间通过U型卡箍12相连。U型卡箍12从支撑框架立柱8一侧半包围住支撑框架立柱8和箱体框架立柱11,螺栓19穿过U型卡箍12上的孔20和相应位置箱体框架立柱11上的孔,将U型卡箍12和箱体框架立柱11固定,然后将U型卡箍顶部的螺栓19’旋入,使箱体框架立柱11和支撑框架立柱8贴紧,从而实现箱体与支撑框架的紧密连接。短侧面2高1.2m,宽度与箱体两侧长侧面1的箱体框架立柱11的外侧之间的距离相等。短侧面与长侧面1端口处的玻璃通过硅酮结构胶粘和后,其外侧利用硅酮结构胶与端口封闭条47粘和,端口密封条47材料与箱体框架10材料相同,再利用U型卡箍12从支撑框架立柱8一侧半包围住支撑框架立柱8和端口封闭条47,螺栓19穿过U型卡箍12上的孔20和相应位置端口封闭条47及短侧面2上的孔,将U型卡箍12和端口封闭条47和短侧面2固定,然后将螺栓19’旋入,使端口封闭条47、短侧面2和支撑框架立柱8贴紧,从而实现箱体端口处的紧密连接。箱体两长侧面1及两短侧面2通过硅酮结构胶,实现连接及密封。The photobioreactor of the utility model is 10m long, 1.2m high, and 15cm wide. The
光生物反应器的短侧面2上还设有进料口14、取样口15和排液口16,分别为管路外直径为58mm、28mm、58mm,管壁厚为:4mm。管路上分别安装相应的塑料球阀,并通过硅酮密封胶与短侧面相连。培养液30和微藻藻种分别从进料口14注入反应器,微藻培养过程中,可从取样口15取出不同深度处的藻液,以供分析研究。分批培养完毕或清洗时,含成熟微藻的藻液或洗涤水废水由排液口16排出。The
见图1d所示,光生物反应器箱体底面玻璃46宽度大于反应器箱体宽度,为25cm。箱体底面玻璃46边缘距离与其同侧的长侧面上的玻璃5cm,在箱体长侧面1玻璃外侧及箱体底面46上部,用硅酮结构胶粘入防漏加固条45。防漏加固条45材料为4mm厚普通玻璃,宽度为4cm,长度与相邻箱体框架立柱11间的距离相等。防漏加固条45的粘入,有效的防止了箱体底面玻璃46与长侧面玻璃粘接处漏水。As shown in Fig. 1d, the width of the
本实用新型的光生物反应器还包括曝气系统(见图5),包括:气泵26、过滤装置27、和曝气管24、和导气管25。The photobioreactor of the present utility model also includes an aeration system (see FIG. 5 ), including: an air pump 26 , a filtering device 27 , an aeration pipe 24 , and an air guide pipe 25 .
二氧化碳和空气的混合物气体28,通过过滤装置27,除去其中的微生物、病菌和粉尘,成为气体无菌气体。经由输气管25达到气泵26,气体28在气泵处26获得动能,经由输气管25,从曝气管24的两端输入。曝气管为山河牌超微孔曝气增氧管,管径2cm、孔径为微米级,所生成气泡直径为20-30微米,购自江阴江达机械装备有限公司,其全部表面无规则的分布着微米级孔径,一方面,气体通过曝气管24由箱体底部相上扩散,实现了培养液30竖直方向上的循环;另一方面,气体28由曝气管24的两端通入,使得曝气管24中两端气压高于中部气压,促进了培养液30水平方向上的循环流动。The mixture gas 28 of carbon dioxide and air passes through the filter device 27 to remove microorganisms, germs and dust therein, and becomes a sterile gas. The gas 28 reaches the air pump 26 via the gas delivery pipe 25 , and the gas 28 obtains kinetic energy at the air pump 26 , and is input from both ends of the aeration pipe 24 via the gas delivery pipe 25 . The aeration tube is Shanhe brand ultra-microporous aeration and oxygenation tube with a diameter of 2cm and a micron pore size. The diameter of the generated bubbles is 20-30 microns. It was purchased from Jiangyin Jiangda Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. The entire surface is irregular On the one hand, the gas diffuses from the bottom of the box through the aeration tube 24, realizing the circulation of the culture solution 30 in the vertical direction; on the other hand, the gas 28 passes through the two ends of the aeration tube 24. Inlet, so that the air pressure at both ends of the aeration tube 24 is higher than the air pressure in the middle, which promotes the circulation of the culture solution 30 in the horizontal direction.
本实用新型还可以利用反光镜增大反应器对光的利用效率(见图4)。在箱体的背光面放置反光镜21,没有照射到箱体或透过箱体的入射光22经反光镜21反射后,其反射光23再次照射到反应器上。这样更大程度上的利用了光源,增大了光生物反应器对光的利用效率。The utility model can also utilize the mirror to increase the light utilization efficiency of the reactor (see Fig. 4). A
实施例2:Example 2:
如图1b、图1c,其中圆弧形侧面6、圆弧形底面7、圆弧底面或圆弧侧面结构6/7、圆弧底面或圆弧侧面截面图6a/7a、圆弧底面或圆弧侧面上的沟槽6b/7b、与圆弧底面或圆弧侧面相粘贴的玻璃48、玻璃内侧面49、圆弧侧面中内圆弧50。As shown in Figure 1b and Figure 1c, the arc-shaped
本实用新型反应器的短侧面2及底面采用圆弧型结构,如图1b、图1c所示。圆弧侧面6和圆弧底面7材料为有机玻璃或塑料,经模具加工而成。圆弧底面或圆弧侧面上具有沟槽6b/7b,玻璃48与圆弧侧面6和圆弧底面7在沟槽6b/7b处通过硅酮结构密封胶连接。玻璃内侧面49与圆弧底面或圆弧侧面6/7的内圆弧50相切。因此完全消除了侧壁和底面的棱角处的死角。The
其它同实施例1。Others are with
实施例3:Example 3:
本实用新型即可做成独立的光生物反应器单元,如图1a所示,也可做成光生物反应器组(见图2)。其中每个反应器单元高1.2m,长50m,厚0.15m。各反应器单元平行放置,间距为0.6m,反应器组中边缘处反应器的外长侧面支撑框架立柱8与反应器旁边的支撑框架17相连接,以保持反应器组图3的稳定性。反应器组图3内部的反应器单元各自的支撑框架立柱8通过支撑框架上的横梁18与相邻反应器单元对应的支撑框架立柱8相连,以相互支撑,实现反应器组整体的稳定性。The utility model can be made into an independent photobioreactor unit, as shown in Figure 1a, and can also be made into a photobioreactor group (see Figure 2). Each reactor unit is 1.2m high, 50m long and 0.15m thick. Each reactor unit is placed in parallel with a distance of 0.6m. The outer long side
实施例4:Example 4:
用本实用新型的光生物反应器培养小球藻,培养基为:NaNO3 0.25g、K2HPO4·3HO2 0.075g、MgSO4·7H2O 0.075g、CaCl2·2H2O 0.025g,KH2PO40.015g、NaCl 0.025g、FeCl3·6H2O 0.005g,接种量为10%,温度控制在25℃,曝气气速为1m3/h,连续培养20天,通过进行整体贯通打捞式收获(参考200910137526.3号专利),不必循环培养液,产量达到18g/(m2·d)。The photobioreactor of the utility model is used to cultivate chlorella, and the culture medium is: NaNO3 0.25g, K2 HPO4 3HO2 0.075g, MgSO4 7H2 O 0.075g, CaCl2 2H2 O 0.025g , KH2 PO4 0.015g, NaCl 0.025g, FeCl3 6H2 O 0.005g, the inoculum size was 10%, the temperature was controlled at 25°C, the aeration rate was 1m3 /h, and the continuous culture was carried out for 20 days. Whole through salvage harvesting (refer to patent No. 200910137526.3), no need to circulate the culture medium, and the yield can reach 18g/(m2 ·d).
Claims (12)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200920160301CN201424476Y (en) | 2009-06-19 | 2009-06-19 | A photobioreactor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200920160301CN201424476Y (en) | 2009-06-19 | 2009-06-19 | A photobioreactor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN201424476Ytrue CN201424476Y (en) | 2010-03-17 |
Family
ID=42023916
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200920160301Expired - LifetimeCN201424476Y (en) | 2009-06-19 | 2009-06-19 | A photobioreactor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN201424476Y (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102115776A (en)* | 2010-01-04 | 2011-07-06 | 新奥科技发展有限公司 | Microalgae screening method and system thereof |
| CN102286363A (en)* | 2011-07-22 | 2011-12-21 | 暨南大学 | External reinforced internally communicated plate photobioreactor |
| CN102443562A (en)* | 2010-10-12 | 2012-05-09 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | Culture medium and culture method for promoting rapid proliferation of microalgae |
| CN102577922A (en)* | 2011-12-30 | 2012-07-18 | 北京工业大学 | Submerged plant and algae coculture equipment |
| CN107034135A (en)* | 2015-08-06 | 2017-08-11 | 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所 | A kind of flat board airlift loop photosynthetic microorganism culture apparatus |
| CN108854865A (en)* | 2018-08-23 | 2018-11-23 | 浙江工业大学上虞研究院有限公司 | A kind of flat flow micro passage reaction |
- 2009
- 2009-06-19CNCN 200920160301patent/CN201424476Y/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102115776A (en)* | 2010-01-04 | 2011-07-06 | 新奥科技发展有限公司 | Microalgae screening method and system thereof |
| CN102443562A (en)* | 2010-10-12 | 2012-05-09 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | Culture medium and culture method for promoting rapid proliferation of microalgae |
| CN102443562B (en)* | 2010-10-12 | 2016-04-13 | 中国石油化工股份有限公司 | A kind of substratum and cultural method promoting proliferation of microalgae papidly |
| CN102286363A (en)* | 2011-07-22 | 2011-12-21 | 暨南大学 | External reinforced internally communicated plate photobioreactor |
| CN102577922A (en)* | 2011-12-30 | 2012-07-18 | 北京工业大学 | Submerged plant and algae coculture equipment |
| CN107034135A (en)* | 2015-08-06 | 2017-08-11 | 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所 | A kind of flat board airlift loop photosynthetic microorganism culture apparatus |
| CN107034135B (en)* | 2015-08-06 | 2020-04-07 | 中国科学院青岛生物能源与过程研究所 | Flat plate airlift circulating type photosynthetic microorganism culture device |
| CN108854865A (en)* | 2018-08-23 | 2018-11-23 | 浙江工业大学上虞研究院有限公司 | A kind of flat flow micro passage reaction |
| CN108854865B (en)* | 2018-08-23 | 2024-05-07 | 浙江工业大学上虞研究院有限公司 | Advection type microchannel reactor |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101709264B (en) | Optical bioreactor | |
| KR101148194B1 (en) | Photobioreactor with Transparent Film | |
| Xu et al. | Microalgal bioreactors: challenges and opportunities | |
| ES2433367T3 (en) | Algae production and harvesting apparatus | |
| CN201424476Y (en) | A photobioreactor | |
| CN102296022B (en) | Bioreactor | |
| CN1317379C (en) | Pipeline Photobioreactor for Scale Cultivation of Microalgae | |
| WO2007098150A2 (en) | Photobioreactor and uses therefor | |
| CN102329720B (en) | Photobioreactor capable of realizing high-efficiency carbon dioxide immobilization | |
| CN101942388B (en) | Optical bioreactor | |
| US20140004600A1 (en) | Methods and apparatus for cultivating photoautotrophic organisms | |
| CN104726321B (en) | A kind of racetrack bioreactor suitable for sunlight batch production | |
| CN203904335U (en) | Bionic laminated microalga photosynthesis reactor | |
| MX2008010831A (en) | Cooling device for use in an electric arc furnace. | |
| CN102296025B (en) | A Photobioreactor Realizing Internal and External Circulation of Algae Liquid | |
| CN104031822B (en) | A kind of biomimetic type lamination declines algae photosynthetic reactor | |
| Carlozzi | Closed photobioreactor assessments to grow, intensively, light dependent microorganisms: a twenty-year Italian outdoor investigation | |
| EP2459695A1 (en) | Low-cost photobioreactor for microalgae cultivation | |
| CN205035361U (en) | Photobioreactor that little algae was cultivateed | |
| CN102286363A (en) | External reinforced internally communicated plate photobioreactor | |
| CN202297574U (en) | Shower type photo-bioreactor | |
| Khor et al. | Installations of algal bioreactors: Design and operational issues in commercial plants | |
| CN207713715U (en) | A kind of array pillar Photoreactor unit and the microalgae culture system containing the unit | |
| CN102154093B (en) | A flat plate photobioreactor | |
| CN202246643U (en) | Coupling-type photo-bioreactor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right | Owner name:XINNENG (DAQI) BIOENERGY CO., LTD. Free format text:FORMER OWNER: XINAO SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT CO., LTD. Effective date:20110617 | |
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| COR | Change of bibliographic data | Free format text:CORRECT: ADDRESS; FROM: 065001 TOWER B, SOUTH AREA OF ENN INDUSTRIAL PARK, HUAXIANG ROAD, ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT ZONE, LANGFANG CITY, HEBEI PROVINCE TO: 014300 MICROALGAE PROJECT GROUP, HEADQUARTERS OF ENGINEERING CONSTRUCTION, SHULINZHAO ENN INDUSTRIAL PARK, DALAD BANNER, ORDOS CITY, INNER MONGOLIA | |
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20110617 Address after:014300, Inner Mongolia Erdos Dalate flag calling New Austrian industrial park construction project headquarters microalgae project group Patentee after:New energy (bio energy Co. Ltd. Dalateqi) Address before:065001 Hebei Province Economic Development Zone Langfang City Huaxiang new Austrian industrial park in the south of block B Patentee before:ENN SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT Co.,Ltd. | |
| PE01 | Entry into force of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Denomination of utility model:Optical bioreactor Effective date of registration:20111212 Granted publication date:20100317 Pledgee:China Development Bank Co Pledgor:New energy (bio energy Co. Ltd. Dalateqi) Registration number:2011990000488 | |
| PC01 | Cancellation of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Date of cancellation:20141219 Granted publication date:20100317 Pledgee:China Development Bank Co Pledgor:New energy (bio energy Co. Ltd. Dalateqi) Registration number:2011990000488 | |
| PLDC | Enforcement, change and cancellation of contracts on pledge of patent right or utility model | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | Granted publication date:20100317 |