CN1870757B - Multistandard video decoder - Google Patents
Multistandard video decoderDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1870757B CN1870757BCN 200510074637CN200510074637ACN1870757BCN 1870757 BCN1870757 BCN 1870757BCN 200510074637CN200510074637CN 200510074637CN 200510074637 ACN200510074637 ACN 200510074637ACN 1870757 BCN1870757 BCN 1870757B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- information
- decoding
- module
- packing data
- coding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/20—Servers specifically adapted for the distribution of content, e.g. VOD servers; Operations thereof
- H04N21/23—Processing of content or additional data; Elementary server operations; Server middleware
- H04N21/236—Assembling of a multiplex stream, e.g. transport stream, by combining a video stream with other content or additional data, e.g. inserting a URL [Uniform Resource Locator] into a video stream, multiplexing software data into a video stream; Remultiplexing of multiplex streams; Insertion of stuffing bits into the multiplex stream, e.g. to obtain a constant bit-rate; Assembling of a packetised elementary stream
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N21/00—Selective content distribution, e.g. interactive television or video on demand [VOD]
- H04N21/40—Client devices specifically adapted for the reception of or interaction with content, e.g. set-top-box [STB]; Operations thereof
- H04N21/43—Processing of content or additional data, e.g. demultiplexing additional data from a digital video stream; Elementary client operations, e.g. monitoring of home network or synchronising decoder's clock; Client middleware
- H04N21/434—Disassembling of a multiplex stream, e.g. demultiplexing audio and video streams, extraction of additional data from a video stream; Remultiplexing of multiplex streams; Extraction or processing of SI; Disassembling of packetised elementary stream
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Compression Or Coding Systems Of Tv Signals (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及处理编码视频流的方法和系统。The present invention relates to methods and systems for processing encoded video streams.
背景技术Background technique
在视频信号编码过程中,一种或多种编码技术,如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、SMPTE VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4,可被用于基于宏块挨着宏块进行编码该视频信号。在视频信号编码过程中,例如,同解码过程需要其他旁信息一样,预测错误信息可与预测模式信息一起编码。为编码预测错误信息,在量化或熵编码之前,可应用离散余弦变换将预测错误信息变换为频域信息。在该过程中,例如,有关预测错误的信息可能被丢失。该遗漏信息导致的结果是解码视频信号的质量下降。更特殊的是,例如,变换块效应可能以方格网人为因素的形式出现在解码视频中。其他也可能由于遗漏视频信息出现在解码视频中。In the video signal encoding process, one or more encoding technologies, such as H.261, H.263, H.263+ (Annex J), H.264, SMPTE VC-1, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and and/or MPEG-4, may be used to encode the video signal on a macroblock-by-macroblock basis. During encoding of a video signal, for example, prediction error information may be encoded together with prediction mode information, as other side information is required for decoding. To encode prediction error information, the discrete cosine transform can be applied to transform the prediction error information into frequency domain information before quantization or entropy coding. In the process, for example, information about prediction errors may be lost. The result of this missing information is a reduction in the quality of the decoded video signal. More specifically, for example, transform blocking artifacts may appear in the decoded video as grid artifacts. Others may also appear in the decoded video due to missing video information.
传统视频解码器适于解码根据单一编码标准如H.261、E VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4等编码标准编码的基本视频流。基本视频流可用单一编码技术编码。然而,应用空间可支持正使用多种标准中的任一标准编码的码流。例如,高清晰度DVD播放装置的蓝光只读存储器规范允许视频流使用MPEG-2、H.264或VC-1编码。Legacy video decoders are adapted to decode elementary video streams encoded according to a single encoding standard such as H.261, EVC-1, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and/or MPEG-4. Elementary video streams can be encoded with a single encoding technique. However, an application space may support codestreams that are being encoded using any of a variety of standards. For example, the Blu-ray ROM specification for high-definition DVD players allows video streams to be encoded using MPEG-2, H.264, or VC-1.
然而,因两个或更多解码器需要用于已依照不同编码标准编码的基本视频流的处理或解码,传统视频处理系统的解码效率大大降低。However, since two or more decoders are required for processing or decoding elementary video streams that have been encoded according to different encoding standards, the decoding efficiency of conventional video processing systems is greatly reduced.
通过以下结合附图对本发明的描述,将常规和传统方法与本发明进行比较,本技术领域的普通技术人员会更明了常规和传统方法的更多局限性和缺点。By comparing the conventional and traditional methods with the present invention through the following description of the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, those skilled in the art will understand more limitations and disadvantages of the conventional and traditional methods.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明提供了一种处理编码视频流的方法和系统的几个实施例。该方法一方面包括在芯片上接收编码视频流内的打包数据。所接收打包数据内的标识符可在该芯片上确定,在该芯片上该标识符可定义与该编码视频流中的信息包相关联的多个编码类型之一。解码方法可基于所确定的标识符,在该芯片上从多个解码方法中选择。编码视频流中该所接收打包数据的一部分可使用所选解码方法在该芯片上解码。分隔符可在所接收打包数据内确定,分隔编码视频流内的信息包。将所接收打包数据内的多个字节与确定字节序列相匹配。如果该多个字节与该确定字节序列相匹配,则从该所接收打包数据移除该多个字节。The present invention provides several embodiments of a method and system for processing encoded video streams. An aspect of the method includes receiving, on a chip, packetized data within an encoded video stream. An identifier within the received packetized data may be determined on the chip where the identifier may define one of a plurality of encoding types associated with packets in the encoded video stream. The decoding method can be selected on the chip from a plurality of decoding methods based on the determined identifier. A portion of the received packetized data in an encoded video stream can be decoded on the chip using a selected decoding method. A delimiter may be determined within the received packetized data, separating packets within the encoded video stream. Matches a number of bytes within the received packed data to a defined sequence of bytes. If the bytes match the determined sequence of bytes, the bytes are removed from the received packetized data.
如果所确定的标识符符合H.264视频编码,则所接收打包数据可用固定长度编码(fixed length coding,简称FLC)方法、可变长度编码(varible length coding,简称VLC)方法和/或上下文自适应二进制算法编码(context adaptive binary arithmetic coding,简称CABAC)方法解码。如果所确定的标识符符合VC-1、H.261、H.263、H.263+、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4视频编码,则所接收打包数据可用FLC方法和/或VLC方法解码。该解码的打包数据包括解码方法控制信息和/或预测错误信息。解码视频流可使用该解码的打包数据生成。该生成的解码视频流可使用重叠变换方法和/或解块方法滤波。对于每一该多个解码方法,所接收打包数据的一部分可用逆变换、逆量化和/或运动补偿在该芯片上解码。If the determined identifier conforms to H.264 video coding, the received packetized data can be encoded with a fixed length coding (FLC) method, a variable length coding (VLC) method and/or a context self Adaptive binary algorithm coding (context adaptive binary arithmetic coding, CABAC for short) method decoding. If the determined identifier conforms to VC-1, H.261, H.263, H.263+, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and/or MPEG-4 video coding, the received packetized data can be used with the FLC method and/or Or VLC method to decode. The decoded packetized data includes decoding method control information and/or prediction error information. A decoded video stream may be generated using the decoded packetized data. The resulting decoded video stream may be filtered using lapped transform methods and/or deblocking methods. For each of the plurality of decoding methods, a portion of the received packetized data may be decoded on-chip with inverse transform, inverse quantization, and/or motion compensation.
本发明的另一个实施例提供了一种机器可读存储器,其上存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序具有至少机器可执行的代码部分,以使该机器可执行上述处理编码视频流的步骤。Another embodiment of the present invention provides a machine-readable memory on which is stored a computer program, the computer program having at least a machine-executable code portion to enable the machine to perform the above-mentioned steps of processing an encoded video stream.
本发明的一方面还包括至少一个处理器,在芯片上接收芯片上的编码视频流内的打包数据。该处理器可在该芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的标识符,该标识符定义与该编码视频流中的信息包相关联的多个编码类型之一。解码方法可基于所确定的标识符,由该处理器从多个解码方法中选择。编码视频流中该所接收打包数据的一部分可由该处理器使用所选解码方法进行解码。所接收打包数据内的分隔符,该分隔符由该处理器确定,分隔编码视频流内的信息包。该处理器可将所接收打包数据内的多个字节与确定字节序列相匹配,如果该多个字节与该确定字节序列相匹配,则该处理器从该所接收打包数据中移除该多个字节。An aspect of the invention also includes at least one processor receiving on-chip packetized data within the on-chip encoded video stream. The processor can determine, on the chip, an identifier within the received packetized data that defines one of a plurality of encoding types associated with packets in the encoded video stream. The decoding method may be selected by the processor from a plurality of decoding methods based on the determined identifier. A portion of the received packetized data in an encoded video stream may be decoded by the processor using a selected decoding method. A delimiter within the received packetized data, determined by the processor, that separates packets within the encoded video stream. The processor may match a plurality of bytes within the received packed data to a determined sequence of bytes, and if the plurality of bytes match the determined sequence of bytes, the processor removes the bytes from the received packed data Divide that many bytes.
如果所确定的标识符符合H.264视频编码,则所接收打包数据可由该处理器用固定长度编码方法、可变长度编码方法和/或上下文自适应二进制算法编码方法解码。如果所确定的标识符符合VC-1、H.261、H.263、H.263+、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4视频编码,则所接收打包数据可由该处理器用FLC方法和/或VLC方法解码。该解码的打包数据包括解码方法控制信息和/或预测错误信息。解码视频流可由处理器使用该解码的打包数据生成。该处理器可使用重叠变换方法和/或解块方法将该生成的解码视频流滤波。If the determined identifier conforms to H.264 video coding, the received packetized data may be decoded by the processor using a fixed-length coding method, a variable-length coding method and/or a context-adaptive binary algorithm coding method. If the determined identifier conforms to VC-1, H.261, H.263, H.263+, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and/or MPEG-4 video coding, the received packetized data can be used by the processor with FLC method and/or VLC method decoding. The decoded packetized data includes decoding method control information and/or prediction error information. A decoded video stream may be generated by a processor using the decoded packetized data. The processor may filter the generated decoded video stream using a lapped transform method and/or a deblocking method.
本发明的一个方面提供了一种处理编码视频流的方法,该方法包括:One aspect of the invention provides a method of processing an encoded video stream, the method comprising:
在芯片上接收编码视频流内的打包数据;Receiving packetized data within an encoded video stream on-chip;
在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的标识符,该标识符定义与该编码视频流中的信息包相关联的多个编码类型之一;determining on said chip an identifier within the received packetized data, the identifier defining one of a plurality of encoding types associated with packets in the encoded video stream;
在所述芯片上,基于所确定的标识符,从多个解码方法中选择一个解码方法;及selecting, on said chip, a decoding method from a plurality of decoding methods based on the determined identifier; and
在所述芯片上使用所选解码方法解码编码视频流中所接收打包数据的至少一部分。At least a portion of the received packetized data in the encoded video stream is decoded on the chip using a selected decoding method.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的起始码,该起始码分隔编码视频流内的信息包。Advantageously, the method further comprises determining on said chip a start code within the received packetized data, the start code delimiting packets within the encoded video stream.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括将所接收打包数据内的多个字节与一个确定字节序列相匹配。Advantageously, the method further comprises matching bytes within the received packetized data to a determined sequence of bytes.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括如果该多个字节与该确定字节序列相匹配,则从该所接收打包数据中移除该多个字节。Advantageously, the method further comprises removing the plurality of bytes from the received packetized data if the plurality of bytes match the determined sequence of bytes.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合H.264视频编码,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法、可变长度编码(VLC)方法和上下文自适应二进制算法编码(CABAC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, the method further comprises using a Fixed Length Coding (FLC) method, a Variable Length Coding (VLC) method and a Context Adaptive Binary Algorithm Coding (CABAC) method if the determined identifier conforms to H.264 video coding At least one of the decodes the at least a portion of the received packetized data.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合VC-1视频编码,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, the method further comprises decoding said received packetized data using at least one of a fixed length coding (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method if the determined identifier complies with VC-1 video coding. at least part of it.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合H.261、H.263、H.263+、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和MPEG-4视频编码至少之一,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, the method further comprises using fixed length encoding if the determined identifier conforms to at least one of H.261, H.263, H.263+, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 video encoding At least one of a (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method decodes the at least a portion of the received packetized data.
优选地,所述解码打包数据包括预测像素信息和预测错误信息的至少其一。Preferably, the decoded packet data includes at least one of predicted pixel information and predicted error information.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括使用所述解码打包数据的至少一部分生成解码视频流。Advantageously, the method further comprises generating a decoded video stream using at least a portion of said decoded packetized data.
优选地,所述方法进一步包括,对每一所述多个解码过程,在所述芯片上使用逆变换、逆量化和运动补偿的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, the method further comprises, for each of said plurality of decoding processes, decoding said at least a portion of received packed data on said chip using at least one of inverse transform, inverse quantization and motion compensation.
根据本发明的一个方面,提供了一种机读存储器,存储具有至少一代码部分的计算机程序,以处理编码视频流,该至少一个代码部分由机器执行,执行的步骤包括:According to one aspect of the present invention, there is provided a machine-readable memory storing a computer program having at least one code portion for processing an encoded video stream, the at least one code portion is executed by a machine, and the executed steps include:
在芯片上接收编码视频流内的打包数据;Receiving packetized data within an encoded video stream on-chip;
在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的标识符,该标识符定义与该编码视频流中的信息包相关联的多个编码类型之一;determining on said chip an identifier within the received packetized data, the identifier defining one of a plurality of encoding types associated with packets in the encoded video stream;
在所述芯片上,基于所确定的标识符,从多个解码方法中选择一个解码方法;及selecting, on said chip, a decoding method from a plurality of decoding methods based on the determined identifier; and
在所述芯片上使用所选解码方法解码编码视频流中所接收打包数据的至少一部分。At least a portion of the received packetized data in the encoded video stream is decoded on the chip using a selected decoding method.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的起始码的代码,所述起始码分隔编码视频流内的信息包。Advantageously, said memory further comprises code on said chip to determine a start code within received packetized data, said start code delimiting packets within an encoded video stream.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括将所接收打包数据内的多个字节与一个确定字节序列相匹配的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises code for matching a plurality of bytes within received packed data to a defined sequence of bytes.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括如果该多个字节与该确定字节序列相匹配,则从该所接收打包数据中移除该多个字节的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises code for removing said plurality of bytes from said received packed data if said plurality of bytes match said determined sequence of bytes.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合H.264视频编码,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法、可变长度编码(VLC)方法和上下文自适应二进制算法编码(CABAC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises using a Fixed Length Coding (FLC) method, a Variable Length Coding (VLC) method and a Context Adaptive Binary Algorithm Coding (CABAC) method if the determined identifier conforms to H.264 video coding At least one of the codes that decodes the at least a portion of the received packetized data.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合VC-1视频编码,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises means for decoding received packetized data using at least one of a fixed length coding (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method if the determined identifier complies with VC-1 video coding. At least a portion of the code described above.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括如果所确定的标识符符合H.261、H.263、H.263+、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和MPEG-4视频编码至少之一,则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法的至少其一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises if the determined identifier complies with at least one of H.261, H.263, H.263+, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 video coding, using fixed length coding At least one of a (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method decodes the at least a portion of the code of the received packetized data.
优选地,所述解码打包数据包括预测像素信息和预测错误信息的至少之一。Preferably, the decoded packet data includes at least one of predicted pixel information and predicted error information.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括使用所述解码打包数据的至少一部分生成解码视频流的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises code for generating a decoded video stream using at least a portion of said decoded packetized data.
优选地,所述存储器进一步包括使用重叠变换方法和/或解块方法的至少之一滤波所生成的解码视频流的代码。Advantageously, said memory further comprises code for filtering the generated decoded video stream using at least one of a lapped transform method and/or a deblocking method.
本发明的一方面提供了一种处理编码视频流的系统,该系统包括:An aspect of the present invention provides a system for processing encoded video streams, the system comprising:
至少一个处理器,其在芯片上接收编码视频流内的打包数据;at least one processor receiving on-chip packetized data within the encoded video stream;
所述至少一个处理器在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的标识符,该标识符定义与该编码视频流中的信息包相关联的多个编码类型之一;said at least one processor determines on said chip an identifier within the received packetized data that defines one of a plurality of encoding types associated with packets in the encoded video stream;
所述至少一个处理器在所述芯片上基于该确定的标识符从多个解码方法中选择一个解码方法;及said at least one processor selects a decoding method from a plurality of decoding methods on said chip based on the determined identifier; and
所述至少一个处理器在所述芯片上使用所选解码方法解码编码视频流中所接收打包数据的至少一部分。The at least one processor decodes on the chip at least a portion of the received packetized data in the encoded video stream using the selected decoding method.
优选地,所述至少一个处理器在所述芯片上确定所接收打包数据内的起始码,该起始码分隔编码视频流内的信息包。Advantageously, said at least one processor determines on said chip a start code within received packetized data, the start code delimiting packets within the encoded video stream.
优选地,所述至少一个处理器将所接收打包数据内的多个字节与一确定字节序列相匹配。Advantageously, said at least one processor matches a plurality of bytes within received packed data to a determined sequence of bytes.
优选地,如果该多个字节与该确定字节序列相匹配,所述至少一个处理器则从该所接收打包数据中移除该多个字节。Advantageously, said at least one processor removes said plurality of bytes from said received packetized data if said plurality of bytes match said determined sequence of bytes.
优选地,如果所确定的标识符符合H.264视频编码,所述至少一处理器则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法、可变长度编码(VLC)方法和上下文自适应二进制算法编码(CABAC)方法至少之一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, said at least one processor uses a Fixed Length Coding (FLC) method, a Variable Length Coding (VLC) method and Context Adaptive Binary Algorithm Coding (CABAC) if the determined identifier is compliant with H.264 video coding At least one of the methods decodes the at least a portion of the received packetized data.
优选地,如果所确定的标识符符合VC-1视频编码,所述至少一个处理器则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法的至少之一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Advantageously, said at least one processor decodes the received packetized data using at least one of a fixed length coding (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method if the determined identifier is compliant with VC-1 video coding. said at least a portion.
优选地,如果所确定的标识符符合H.261、H.263、H.263+、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和MPEG-4视频编码至少之一,所述的至少一个处理器则使用固定长度编码(FLC)方法和可变长度编码(VLC)方法至少之一解码所接收打包数据的所述至少一部分。Preferably, said at least one processor uses fixed At least one of a length coding (FLC) method and a variable length coding (VLC) method decodes the at least a portion of the received packetized data.
优选地,所述解码打包数据包括预测像素信息和预测错误信息至少之一。Preferably, the decoded packet data includes at least one of predicted pixel information and predicted error information.
优选地,所述至少一处理器使用所述解码打包数据的至少一部分生成解码视频流。Advantageously, said at least one processor generates a decoded video stream using at least a portion of said decoded packetized data.
优选地,所述至少一处理器使用重叠变换方法和解块方法至少之一滤波所生成的解码视频流。Advantageously, said at least one processor filters the generated decoded video stream using at least one of a lapped transform method and a deblocking method.
根据本发明的一方面,其提供了一种处理编码视频流的方法,该方法包括:According to an aspect of the present invention, it provides a method of processing a coded video stream, the method comprising:
使用第一CPU解码来自编码视频流的报头信息;及decoding header information from the encoded video stream using the first CPU; and
当所述第一CPU解码所述报头信息时,使用第二CPU解码来自编码视频流的宏块信息。When the first CPU decodes the header information, a second CPU is used to decode macroblock information from the encoded video stream.
本发明的这些或其他特征和优点,将从以下结合附图对本发明的详细描述获得更全面地理解。These and other features and advantages of the present invention will be more fully understood from the following detailed description of the invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
附图说明Description of drawings
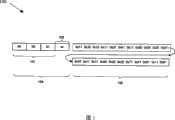
图1是根据本发明的实施例的具有分隔符的封装视频有效载荷的结构图。FIG. 1 is a structural diagram of an encapsulated video payload with delimiters according to an embodiment of the present invention.
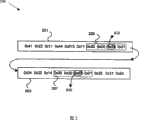
图2是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的基本视频流数据内的字节解除的结构图。FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of byte unpacking in exemplary elementary video stream data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图3A是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的多标准视频解码器的高水平结构图。FIG. 3A is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图3B是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的使用单一CPU的多标准视频解码器的高水平结构图。3B is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder using a single CPU according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图3C是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的使用CPU对的多标准视频解码器的高水平结构图。3C is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder using a CPU pair according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图4A是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的具有硬件辅助块和单一CPU的多标准视频解码器的结构图。FIG. 4A is a block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder with hardware assistance blocks and a single CPU, according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图4B是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的具有硬件辅助块和CPU对的多标准视频解码器的结构示意图。FIG. 4B is a block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder with a hardware-assisted block and a CPU pair according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图5是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码H.264视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器的运行的结构图。FIG. 5 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the multi-standard video decoder shown in FIG. 4 when decoding H.264 video data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图6是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码VC-1视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器的运行的结构图。FIG. 6 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the multi-standard video decoder shown in FIG. 4 when decoding VC-1 video data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图7是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码MPEG-1或PMEG-2视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器的运行的结构图。FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the multi-standard video decoder shown in FIG. 4 when decoding MPEG-1 or PMEG-2 video data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图8是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码MPEG-4视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器的运行的结构图。FIG. 8 is a block diagram illustrating the operation of the multi-standard video decoder shown in FIG. 4 when decoding MPEG-4 video data according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图9是根据本发明的实施例的处理视频数据流的示范性方法的流程图。9 is a flowchart of an exemplary method of processing a video data stream according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明提供了一种处理编码视频流的方法和系统的几个实施例。在视频流编码过程中,不同编码标准可被用于基本视频流内进行编码数据。在本发明的一个方面中,多标准视频解码器可适于获得根据编码标准如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4编码的基本视频流。该多标准解码器可在该基本视频流内设置一个或多个分隔符,在该基本视频流内该分隔符可分隔封装视频有效载荷内的信息包。每一分隔符包括表明视频有效载荷的开始的起始码信息和编码类型信息。The present invention provides several embodiments of a method and system for processing encoded video streams. During encoding of the video stream, different encoding standards may be used to encode data within the elementary video stream. In one aspect of the present invention, the multi-standard video decoder can be adapted to obtain data according to encoding standards such as H.261, H.263, H.263+(Annex J), H.264, VC-1, MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and/or MPEG-4 encoded elementary video stream. The multi-standard decoder can set one or more delimiters within the elementary video stream, where the delimiters can separate packets within an encapsulated video payload. Each delimiter includes start code information indicating the start of video payload and encoding type information.
该编码类型信息可与被编码器用于编码相应视频有效载荷的编码方法相关联。该多标准解码器也可从封装视频有效载荷中解除或移除一个或多个字节,在封装视频有效载荷中这样的字节被编码器插入以避免错误的起始码出现在视频有效载荷中。根据该编码类型信息,封装视频有效载荷可在芯片上使用相应解码模块解码。例如,时间或空间预测像素可在封装视频有效载荷中从解码方法控制信息生成。此外,预测错误可在封装视频有效载荷内从量化频率系数生成。然后,可使用时间和/或空间预测像素和预测错误信息重建解码视频流。根据本发明的一个方面,该多标准解码器可使用单中央处理器(central processing unit,简称CPU)处理编码比特流中的信息包内的报头信息和宏块信息。在本发明的另一个方面中,可使用CPU对,其中第一CPU可处理未来报头信息,而第二CPU可处理当前宏块信息。The encoding type information may be associated with the encoding method used by the encoder to encode the corresponding video payload. The multi-standard decoder may also strip or remove one or more bytes from the encapsulated video payload where such bytes are inserted by the encoder to avoid false start codes in the video payload middle. Based on this encoding type information, the encapsulated video payload can be decoded on-chip using the corresponding decoding module. For example, temporally or spatially predicted pixels can be generated from decoding method control information in the encapsulated video payload. Furthermore, prediction errors can be generated from quantized frequency coefficients within the encapsulated video payload. The decoded video stream can then be reconstructed using temporally and/or spatially predicted pixels and prediction error information. According to an aspect of the present invention, the multi-standard decoder may use a single central processing unit (CPU for short) to process header information and macroblock information in packets in the coded bitstream. In another aspect of the invention, a pair of CPUs can be used, where a first CPU can process future header information and a second CPU can process current macroblock information.
图1是根据本发明的实施例的具有分隔符的封装视频有效载荷100的结构图。如图1所示,该封装视频有效载荷100包括分隔符104和基本视频流数据105。该分隔符104包括起始码101和起始码后缀103,且可被解码器用于如为封装视频有效载荷100设起始位及为基本视频流数据105设起始位。此外,分隔符104包括与用于编码基本视频流数据105的编码方法相关的信息。该基本视频流数据包括多个字节,每一字节包括两个半位元组。FIG. 1 is a structural diagram of an encapsulated
起始码101包括多个字节,可被安排以唯一组合表示编码视频流内封装视频有效载荷100的开始。例如,起始码101包括示范性字节序列“00 00 01”。起始码后缀103包括一个或多个字节,设于封装视频有效载荷100内的起始码101后。在本发明的一个方面中,该起始码后缀103与用于封装视频有效载荷100内的编码基本视频流数据105的编码方法相对应。例如,当这些编码方法被用于编码基本视频流数据105时,该起始码后缀103可相应于H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPE-4。在将该编码视频流数据传送至视频解码器前,起始码101和起始码后缀103可由编码器生成。The
图2是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的基本视频流数据内的字节解除的结构图。如图2所示,基本视频流数据200包括基本视频数据序列201和203。该基本视频流数据200可被分隔符加上前言,包括起始码序列和起始码后缀,如图1所示。在视频信号编码过程中以及编码器为该基本视频流数据200生成分隔符后,该编码器可在基本视频流数据200中插入一个或多个字节,以使编码期间相应起始码序列在基本视频流数据200内可能不被编码器识别。FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of byte unpacking in exemplary elementary video stream data according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 2 , elementary
例如,在基本视频流数据200编码期间,编码器可使用包括字节序列“00 00 01”的起始码。在基本视频流数据200解码期间,解码器可能错误识别基本视频流数据200内的起始码序列“00 00 01”。为避免起始码序列的任何这种误识别,编码器可插入一个或多个额外字符或符号,或填充字节,以使得解码期间起始码序列在基本视频流数据200内不被误识别。例如,额外字符串或填充字节“03”可被插入基本视频数据序列201内的字节序列205内。同样的,填充字节“03”也可被插入基本视频数据序列203内的字节序列207内。以这种方式,可阻止解码器在基本视频流200解码期间识别起始码“00 00 01”For example, during encoding of the elementary
在基本视频流200解码过程中,视频解码器可解除或移除编码过程中被插入基本视频流200中的任何额外字符。因此,额外字符串“03”可被从基本视频数据序列201内的字节序列205移除,额外字符“2”可被从基本视频数据序列203内的字节序列207移除。以这种方式,基本视频流200内移除任何额外字符后,生成未处理的视频有效载荷。而后,该得到的未处理的视频有效载荷可由例如符号翻译器解码。During the decoding of the
图3A是根据本发明的实施例的示例性多标准视频解码器的高水平结构图。如图3所示,该多标准视频解码器200可包括存储块301、端口编码器(code-in-port,CIP)305、码流解析器307和处理模块303。该端口编码器305包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,适于获得基本视频流309。端口编码器305还可适于在基本视频流309内设起始码和起始码后缀,及从基本视频流309解除额外字节,由此生成未处理的基本视频流。Figure 3A is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 3 , the
该多标准视频解码器300可使用码流解析器307处理起始码信息和可从端口编码器305获得的新码流信息。例如,码流解析器307可适于处理来自端口编码器305生成的未处理的基本比特流的报头信息和/或宏块信息。来自未处理的基本视频流的报头信息包括如片段信息、画面信息、GOP/切入点信息和/或序列信息。端口编码器305生成的该未处理的基本视频流内的片段信息包包括相应于特定片段的片段报头信息和宏块信息。此外,码流解析器307可适于处理从端口编码器305获得的未处理的基本码流中的报头和/或宏块信息,并生成例如该未处理的基本视频流中的宏块信息解码所需的量化的频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息。The
码流解析器307包括针对每种编码模式的一个或多个解码辅助块,可用于解码该未处理的基本视频流。来自码流解析器307的输出信号可通过总线311被传送到处理模块303。该总线311可在该多标准视频解码器内实现,作为一路总线将信息传送至处理模块303,以增加处理效率和简化执行过程。该未处理的基本视频流解码过程生成的时间信息可被存储模块301中的码流解析器307和/或端口编码器305存储。该存储模块301包括DRAM。The
在本发明示范性的一个方面中,该码流解析器307可使用单一CPU和单一相应符号翻译器(SI)实现。该单一CPU或SI配置可用于处理包括起始码/后缀、报头信息和/或宏块信息的完整基本视频流。在本发明的另一个方面中,码流解析器307可使用两个单独的CPU和符号翻译器(SI)实现,以提高处理效率。例如,在示范性双CPU/SI结构中,第一CPU和第一SI可用于处理基本视频流中的报头信息,具有相应第二SI的第二CPU可用于处理来自基本比特流的宏块信息。在这一点上,后续报头信息可被第一CPU和第一SI处理,而第二CPU和第二SI可同时处理当前宏块信息。In an exemplary aspect of the present invention, the
处理模块303可使用由码流解析器307生成的处理信息生成解码视频流313。该处理模块303包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并可适于执行一个或多个以下处理任务:空间预测、运动补偿、逆量化和变换、宏块重建、回路内宏块滤波和/或宏块后处理。处理模块303中的每一处理任务可使用一个或多个辅助块,该辅助块符合被用于编码基本视频流33 1的特定编码方法。在这一点上,处理模块303可适于解码使用多个编码方法如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的基本视频流。The
图3B是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的使用单一CPU的多标准视频解码器320的高水平结构图。如图3B所示,该多标准视频解码器320包括存储模块321、端口编码器329、内部回路中央处理器(ILCPU)325、内部回路符号翻译器(ILSI)327和处理模块323。该端口编码器329包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并适于获得基本视频流331。该端口编码器329也可适于在该基本视频流331内设起始码和/或起始码后缀,并从该基本视频流331解除额外字节,从而生成未处理的基本视频流。FIG. 3B is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary
在本发明的一个示范性实施例中,该多标准视频解码器320可使用内部回路中央处理器325和内部回路符号翻译器327处理来自端口编码器329生成的未处理的基本比特流的报头信息和/或宏块信息。来自未处理的基本比特流的报头信息包括如片段信息、画面信息、GOP/切入点信息和/或序列信息。端口编码器329生成的未处理的基本视频流内的片段信息包包括相应于特定片段的片段报头信息和宏块信息。In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the
内部回路符号翻译器327包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并可适于处理从端口编码器329获得的未处理的基本视频流中的报头和/或宏块信息,并生成如该未处理的基本视频流中的宏块信息解码所需的量化的频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息。该内部回路符号翻译器327包括一个或多个特定于使用的每一编码模式的解码辅助模块,以解码该未处理的基本视频流。
内部回路中央处理器325可适于通过如通过总线333提供向内部回路符号翻译器327提供解码指令将内部回路符号翻译器327程序化。该总线333可在该多标准视频解码器内实现,作为一路总线将信息传送至处理模块303,以增加处理效率和简化执行过程。该未处理的基本视频流解码过程生成的时间信息可被存储模块321中的内部回路中央处理器325、端口编码器329和/或内部回路符号翻译器327存储。该存储模块301包括DRAM。Inner-
在操作过程中,输入的基本视频流331包括根据多个编码标准如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的视频数据。端口编码器329可适于检测一个或多个符合该基本视频流331编码模式的起始码和起始码后缀。该端口编码器329还适于生成包括报头和/或宏块信息的未处理的基本视频流。该起始码和未处理的基本视频流可通过存储器321传送至内部回路中央处理器325和内部回路符号翻译器327,以进行进一步处理。该内部回路符号翻译器327,使用来自内部回路中央处理器325的指令,可适于处理端口编码器329传送的报头和/或宏块信息。然后,该内部回路符号翻译器327可生成输出信号,该输出信号包括如获得的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息、运动矢量信息和/或量化频率系数。该输出信号可通过总线333传送至处理模块323,在宏块解码期间使用。During operation, the input
处理模块323可使用内部回路符号翻译器327生成的处理信息生成解码视频流335。该处理模块323包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,适于执行一个或多个以下处理任务:空间预测、运动补偿、逆量化和变换、宏块重建、回路内宏块滤波和/或宏块后处理。处理模块323内的每一处理任务可使用一个或多个辅助块,该辅助块符合被用于编码基本视频流331的特定编码方法。在这一点上,处理模块323可适于解码使用多个编码方法如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的基本视频流。
图3C是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的使用CPU对的多标准视频解码器340的高水平结构图。如图3C所示,该多标准视频解码器340可包括存储模块341、外部回路中央处理器(OLCPU)349、端口编码器(CPI)351、外部回路符号翻译器(OLSI)353、内部回路中央处理器(ILCPU)345、内部回路符号翻译器(OLSI)347和处理模块343。该端口编码器351包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并适于获得基本视频流355。该端口编码器329也可适于在该基本视频流355内设起始码和/或起始码后缀,并从该基本视频流355解除额外字节,从而生成未处理的基本视频流。FIG. 3C is a high-level block diagram of an exemplary
在本发明的一个示范性实施例中,该多标准视频解码器320可使用CPU对,如内部回路中央处理器345和外部回路中央处理器349,具有相应的内部回路符号翻译器347、外部回路符号翻译器353,以分别处理来自端口编码器351生成的未处理的基本比特流的报头信息和/或宏块信息。来自未处理的基本比特流的报头信息可包括如片段信息、画面信息、GOP/切入点信息和/或序列信息。端口编码器351生成的新基本视频流内的片段信息包包括相应于特定片段的片段报头信息和宏块信息。例如,外部回路中央处理器349和外部回路符号翻译器353可适于处理来自端口编码器351生成的新基本比特流的报头信息。此外,内部回路中央处理器345和内部回路符号翻译器347可适于处理来自端口编码器351生成的未处理的基本比特流的宏块信息。以这种方式,可在多标准视频解码器340中实现平行处理,当外部回路中央处理器349和外部回路符号翻译器353处理未来报头信息时,内部回路中央处理器345和内部回路符号翻译器347可处理当前宏块信息。In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the
内部回路符号翻译器347包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并可适于处理从端口编码器351获得的未处理的基本视频流中的宏块信息,并生成如该未处理的基本视频流中的宏块信息解码所需的量化的频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息。该内部回路符号翻译器347包括一个或多个特定于使用的每一编码模式的解码辅助模块,以解码该未处理的基本视频流。外部回路符号翻译器353包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,并可适于处理从端口编码器351获得的未处理的基本视频流中的报头信息。
内部回路中央处理器345可适于通过如通过总线357向内部回路符号翻译器347提供解码指令将内部回路符号翻译器347程序化。该总线357可在该多标准视频解码器内实现,作为一路总线将信息传送至处理模块343,以增加处理效率和简化执行过程。该未处理的基本视频流解码过程生成的时间信息可被存储模块341中的内部回路中央处理器345、外部回路中央处理器349、外部回路符号翻译器353、端口编码器351和/或内部回路符号翻译器347存储。该存储模块301包括如DRAM。The inner loop
操作过程中,输入的基本视频流355包括根据多个编码标准如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的视频数据。端口编码器351可适于检测一个或多个符合该基本视频流355编码模式的起始码和起始码后缀。该端口编码器351还适于生成包括报头和/或宏块信息的未处理的基本视频流。该端口编码器351生成的未处理的基本视频流内的报头信息可传送至外部回路中央处理器349和外部回路符号翻译器353以进一步处理。未处理的基本视频流内的起始码和宏块信息可通过存储器341传送至内部回路中央处理器345和内部回路符号翻译器347,以进行进一步处理。在本发明示范性的一个方面中,该外部回路中央处理器349和外部回路符号翻译器353可适于处理随后的或未来的报头信息,而内部回路中央处理器345和内部回路符号翻译器347可处理当前宏块信息。During operation, the input
该内部回路符号翻译器347可适于处理端口编码器329传送未处理的基本视频流中的宏块信息。然后,该内部回路符号翻译器347可生成输出信号,该输出信号包括如获得的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息、运动矢量信息和/或量化频率系数。该输出信号可通过总线3 57传送至处理模块343,在宏块解码期间使用。The
处理模块343可使用内部回路符号翻译器347生成的处理信息生成解码视频流361。该处理模块343包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,适于执行一个或多个以下处理任务:空间预测、运动补偿、逆量化和变换、宏块重建、回路内宏块滤波和/或宏块后处理。处理模块343内的每一处理任务可使用一个或多个辅助块,该辅助块符合被用于编码基本视频流331的特定编码方法。在这一点上,处理模块323可适于解码使用多个编码方法如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的基本视频流。
图4A是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的具有硬件辅助块和单一CPU的多标准视频解码器的结构图。如图4A所示,该多标准视频解码器400包括端口编码器(CIP)403、符号翻译器405、中央处理器(CPU)407、空间预测模块409、逆量化和变换(IQT)模块411、运动补偿模块413、重建器415、内部回路滤波器417、帧缓冲器419和后处理模块421。FIG. 4A is a block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder with hardware assistance blocks and a single CPU, according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Figure 4A, the
该端口编码器403包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于接收视频基本码流401并生成起始码、起始码后缀和未处理的基本流。端口编码器403包括起始码寻找模块423和字节解除模块425。该起始码寻找模块423可适于确定起始码和起始码后缀,如图1所示。字节解除模块425可适于从视频基本码流401解除额外字节,并生成未处理的基本流数据,如图2所示。起始码、起始码后缀和未处理的基本流在端口编码器403内生成后,该起始码后缀426可被传送至中央处理器407,未处理的基本流可被传送至符号翻译器405,以进一步处理。The
在在本发明的一个示范性实施例中,该多标准视频解码器400可使用中央处理器407和符号翻译器405处理来自端口编码器403生成的未处理的基本比特流的报头信息和/或宏块信息。来自未处理的基本比特流的报头信息可包括片段信息、画面信息、GOP/切入点信息和/或序列信息。端口编码器403生成的未处理的基本视频流内片段信息包包括相应于特定片段的片段报头信息和宏块信息。In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the
符号翻译器405包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于翻译从端口编码器403获得的未处理的基本流424,获得未处理的基本视频流424解码所需的量化的频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息。该符号翻译器405也可将随后的宏块和/或未处理的基本视频流内的帧上的视频信息通过连接406传送至中央处理器407。该中央处理器407从端口编码器403获得起始码后缀426后,可根据与获得的起始码后缀426相关的编码方法,生成符号翻译器的一个或多个解码指令。该中央处理器407可适于通过连接408将这些解码指令提供给符号翻译器405来将该符号翻译器405程序化。该中央处理器407也可根据在后续宏块或帧上的接收视频信息,通过连接406传送解码指令给符号翻译器45。The
根据本发明的一个方面,输入的基本视频流401包括根据多个编码标准如H.261、H.263、H.263+(Annex J)、H.264、VC-1、MPEG-1、MPEG-2和/或MPEG-4之一编码的视频数据。符号翻译器405,使用来自中央处理器407的指令,可适于解码一个或多个符号和/或附加处理信息,如报头和/或宏块信息,用于完成从端口编码器403接收的未处理的基本流424的解码。该符号翻译器可包括特定于每一被使用的编码模式的多个解码辅助模块,以解码未处理的基本流424。According to one aspect of the present invention, the input
在本发明的一个示例性的实施例中,该符号翻译器405包括固定长度编码(fixed length coding,简称FLC)模块427、可变长度编码(variblelength coding,简称VLC)模块429和/或上下文自适应二进制算法编码(context adaptive binary arithmetic coding,简称CABAC)模块433、系数构造模块435和矢量构造模块437。符号翻译器405内的解码辅助模块可用于根据从端口编码器403生成的起始码后缀426获得并传送至中央处理器407的解码方法信息解码过程中。FLC模块427、VLC模块429和CABAC模块433可被符号翻译器405用于解码/翻译单一语法元,该单一语法元来自分别使用固定长度编码、可变长度编码或CABAC编码技术编码的未处理的基本流424。In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the
系数构造模块435可适于从未处理的基本流424生成一个或多个量化频率系数。该系数构造模块435生成的量化的频率系数随后用于多标准视频解码器400内,以生成一个或多个宏块重建过程中使用的预测错误信息。该生成的量化频率系数可被符号翻译器405传送至IQT模块411,以进一步处理。The
相似地,矢量构造模块437可适于从未处理的基本流424生成一个或多个运动矢量。该矢量构造模块437生成的运动矢量可用于多标准视频解码器400内,以生成一个或多个宏块重建过程中使用的预测像素。该生成的运动矢量信息可被符号翻译器传送至运动补偿模块413,以进一步处理。Similarly, the vector construction module 437 may be adapted to generate one or more motion vectors from the unprocessed
空间预测模块409包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于生成被重建器415用来生成解码宏块的预测像素。该空间预测模块409可适于如从符号翻译器获得宏块类型信息、片段类型信息和/或预测模式信息。而后,该空间预测模块409可使用所获的的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息和/或预测模式信息为空间上被预测的宏块生成预测像素。
运动补偿模块413包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于使用从符号翻译器405接收的运动矢量信息,生成预测像素。例如,该运动补偿模块413可为时间上被预测的宏块生成预测像素,可与当前帧/域相邻的帧/域中的运动补偿矢量相关联。该运动补偿模块413可从帧缓冲器419获得在先和/或随后的帧/域,并使用获得的先和/或随后的帧/域预测当前宏块内的时间上的编码像素。
该运动补偿模块413包括多个运动补偿辅助模块,可用于根据用于编码未处理的基本流数据424的方法生成预测像素。例如,该运动补偿模块413包括范围重设模块447、强度补偿模块449、插入模块451、可变块尺寸模块453和双向预测模块455。该插入模块451可适于使用从符号翻译器45接收的运动矢量信息插入当前帧内一个或多个预测像素以及插入一个或多个时间上与当前帧相邻的参考帧。The
如果仅使用一个参考帧插入预测像素,该插入模块451可用于生成预测象素。然而,如果多于一个预测参考帧被用于当前像素的时间预测过程中,运动补偿模块413可使用双向预测模块455生成预测像素。例如,如果几个参考帧被用于当前像素的预测,双向预测模块455可确定当前预测像素作为参考帧中的预测像素的平均值。If only one reference frame is used to interpolate predicted pixels, the interpolation module 451 can be used to generate predicted pixels. However, if more than one prediction reference frame is used in the temporal prediction process of the current pixel, the
范围重设模块447可被运动补偿模块413用于VC-1标准编码的未处理的基本流的编码过程中。更特殊的是,该范围重设模块447可用于在插入模块451插入之前,重设参考帧的动态范围。强度补偿模块449可被运动补偿模块413用于在插入模块451插入之前,将参考帧的强度水平调整至当前帧的强度水平。The rerange module 447 can be used by the
可变块尺寸模块453可被运动补偿模块413用于控制从帧缓冲器419获得的参考帧的应用。例如,该可变块尺寸模块453可从帧缓冲器419取一个16×16、16×8和/或4×4像素尺寸宏块以用于当前宏块内像素的时间预测期间。当运动补偿模块413内运动补偿预测期间需要时,其他宏块和/或帧尺寸也可被帧缓冲器419支持。The variable block size module 453 may be used by the
IQT模块411包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于将从符号翻译器接收的量化频率系数转换为一个或多个预测错误。更特殊地是,该IQT模块411可适于使用逆量化模块443和逆变换模块445将量化频率系数变换回空间域,由此生成预测错误信息。而后,该IQT模块411生成的预测错误信息被传送至重建器415,以在宏块重建期间进一步处理。The
逆锯齿模块439可被IQT模块411用于在被逆变换模块445逆变换之前,重新排列从符号翻译器405接收的量化频率系数。符号翻译器405生成的量化频率系数可被安排锯齿(Z形)扫描顺序,以便于编码。因此逆锯齿模块439可使用一个或多个查找表将量化频率系数以如连续的顺序进行安排。The inverse aliasing module 439 may be used by the
根据未处理的基本流424地编码方法,IQT模块41在预测错误信息解码期间可使用AC/DC预测模块441。例如,量化频率系数可使用来自相邻像素的预测剩余和预测错误,在未处理的基本流424内被编码。更进一步,AC/DC预测模块441内的DC预测可相应于生成预测错误信息所使用的零频率系数。AC/DC预测模块441内的AC预测可相应于生成预测错误信息所使用的低频率系数。符号翻译器、运动补偿模块、空间预测模块和逆量化和变换模块操作上的其他信息更充分地揭露于序列号为10/963,677(机构代码案件编号为15748US02)、申请日为2004年10月13日的美国专利申请中,该申请在此作为全面参考。Depending on the encoding method of the raw
重建器415可适于分别从空间预测模块409或运动补偿模块获得空间预测像素或时间预测像素。此外,该重建器415可适于获得IQT模块411生成的预测错误信息。而后,该重建器可使用预测像素和预测错误信息重建当前宏块。该重建宏块可传送至内部回路滤波器417以作进一步处理。The reconstructor 415 may be adapted to obtain spatially predicted pixels or temporally predicted pixels from the
该内部回路滤波器417包括适合的电路、逻辑和/或代码,可适于进一步滤波从重建器415获得的解码/重建宏块。根据未处理的基本流424地编码方法,该内部回路滤波器417可包括重叠变换模块457和解块模块459。该重叠变换模块457可用于从以VC-1标准编码的未处理的基本流424生成的宏块的滤波的过程中。更特殊地是,重叠变换模块457可将重叠变换应用于重建的宏块以减小沿该重建的宏块一个或多个边缘的边缘人为因素。同样地,解块模块459也可被内部回路滤波器417用于减小沿该重建的宏块一个或多个边缘地边缘人为因素并变换块效应。解码器中解块和解块存储应用上有关的其他信息更充分地揭露于序列号为10/965,172(机构代码案件编号为15756US02)、申请日为2004年10月13日和序列号为10/972,931(机构代码案件编号为15757US02)、申请日为2004年10月25日的美国专利申请中,该两申请在此作为全面参考。The in-
重建宏块被内部回路滤波器417滤波后,附加后处理可由后处理模块421执行。根据新基本流424的编码方法,后处理模块可使用一个或多个以下后处理辅助模块:范围重设模块461、尺寸调整模块463、解块模块465和/或解环模块467。如果以VC-1标准编码的过程中,一个宏块或一组宏块的动态范围被改变,则该范围重设模块46可被后处理模块421使用。以这种方式,所有传送至显示后处理器的解码宏块469被同一个动态范围描述。After the reconstructed macroblocks are filtered by the in-
尺寸调整模块463可被后处理模块421用来缩放/调整尺寸一个编码期间被尺寸升级或降级的宏块。通过使用尺寸调整模块463,后处理模块421可生成具有相同清晰度的解码的宏块469。解环模块467可用于消弱过度量化的AC系数生成的重构宏块内的“飞蚊噪声”。解块模块465类似于内部回路滤波器417内的解块模块459,可用于进一步减小边缘人为因素,并优先于将宏块传送至如显示后处理器,变换沿该重建的宏块一个或多个边缘的块效应。The
图4B是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的具有硬件辅助块和CPU对的多标准视频解码器的结构示意图。如图4B所示,该多标准视频解码器470包括端口编码器(CIP)471、外部回路中央处理器(OLCPU)473、外部回路符号翻译器(OLSI)475、内部回路中央处理器(ILCPU)477和内部回路符号翻译器(ILSI)479。该多标准视频解码器470还可包括空间预测模块、逆量化和变换模块、运动补偿模块、重建模块、内部回路滤波模块、帧缓冲器模块和后处理模块(图4B中未示),如图4A中多标准视频编码器的细节说明和描述。FIG. 4B is a block diagram of an exemplary multi-standard video decoder with a hardware-assisted block and a CPU pair according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Figure 4B, this
在本发明的一个示范性实施例中,多标准解码器470可使用外部回路中央处理器473和外部回路符号翻译器475处理来自视频基本比特流480的报头信息。内部回路中央处理器477和内部回路符号翻译器479可用于处理来自视频基本比特流480的宏块信息。以这种方式,可在多标准视频解码器470中实现平行处理,当外部回路中央处理器473和外部回路符号翻译器475可处理未来报头信息时,内部回路中央处理器477和内部回路符号翻译器479可处理当前宏块信息。来自基本比特流480的报头信息可包括如片段信息、画面信息、GOP/切入点信息和/或序列信息。In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention,
在操作过程中,端口编码器471可接收视频基本码流480并生成起始码和起始码后缀481以及未处理的基本流482。该起始码和起始码后缀481被传送至外部回路中央处理器473处理,未处理的基本流482被传送至外部回路符号翻译器475处理。外部回路中央处理器473和外部回路符号翻译器475可适于仅处理来自起始码和起始码后缀481以及未处理的基本流482的报头信息。外部回路中央处理器473通过如系统传送端口483与离线视频处理系统相连接。During operation,
外部回路符号翻译器475包括可变长度编码(varible length coding,简称VLC)模块484和固定长度编码(fixed length coding,简称FLC)模块472。该VLC模块484和FLC模块472可用于解码来自端口解码器471接收的未处理的基本流482的报头信息。例如,报头信息485可从未处理的基本流482取出,由此生成输出比特流486。该输出比特流486包括宏块相关信息,并可传送至内部回路符号翻译器479进一步处理。外部回路中央处理器473处理来自起始码和起始码后缀481的报头信息后,结果处理控制信息476可被传送至内部回路中央处理器477进一步处理。该过程控制信息476包括控制信息,该控制信息相应于包含宏块信息的信息包,如输出比特流486中的信息包。The external loop symbol translator 475 includes a variable length coding (variable length coding, VLC for short)
当外部回路中央处理器473和外部回路符号翻译器475可处理后续报头信息时,内部回路中央处理器477和内部回路符号翻译器479可适于同时为当前宏块处理与宏块相关的信息。内部回路符号翻译器479,与图4A的符号翻译器405相似,可适于生成输出信号487。该输出信号包括如获得的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息、运动矢量信息和/或量化频率系数。该获得的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息和/或预测模式信息可传送至空间预测模块(图未示),如图4A所示空间预测模块409,以进一步处理及为空间上预测的宏块生成预测像素。While the
运动矢量信息490可传送至运动补偿模块(图未示),如图4A所示的运动补偿模块413,以进一步处理及为时间上预测的宏块生成预测像素。量化频率系数489可传送至逆量化和变换模块(图未示),如图4A所示的逆量化和变换模块411,以进一步处理及生成宏块解码期间使用的预测错误。The
图5是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码H.264视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器500的运行的结构图。如图5所示,该多标准视频解码器500可适于处理使用H.264编码技术编码的视频基本码流401。端口编码器403可使用起始码寻找模块423确定起始码和起始码后缀,使用字节解除模块425从H.264编码视频基本码流401移除额外字节。FIG. 5 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the
符号翻译器405可适于翻译从端口编码器403获得的H.264未处理的基本流424,以获得量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息,如H.264未处理的基本视频流424解码需要的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息和/或运动矢量信息。量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息生成过程中,符号翻译器405可接收中央处理器407的指令,并向中央处理器407提供后续符号信息。此外,符号翻译器可使用下列辅助模块的一个或多个:FLC模块427、VLC模块429、CABAC模块433、系数构造模块435和/或矢量构造模块437。The
逆量化频率系数可从符号翻译器405传送至IQT模块411,可生成预测错误信息。IQT模块411可使用逆锯齿模块439、逆量化模块443和/或逆变换模块445生成预测错误信息。来自符号翻译器405的旁信息可被传送至空间预测模块409或运动补偿模块413,生成预测像素。运动补偿模块413可使用帧缓冲器419以及强度补偿模块449、插入模块451、可变块尺寸模块453和/或双向预测模块455生成时间上的预测像素。The inverse quantized frequency coefficients may be passed from the
而后,重建器415可被多标准解码器500用于使用分别从空间预测模块409或运动补偿模块413获得的预测像素信息,以及从IQT模块411获得的预测错误信息,重建当前宏块。重建的宏块可被内部回路滤波器417使用解块模块459滤波。滤波后的宏块可进一步被后处理模块421处理。后处理模块421可使用解环模块467生成解码的宏块469。而后,该解码的宏块469可被传送至如显示后处理器。The reconstructor 415 can then be used by the
图6是根据本发明和实施例的示例性的当解码VC-1视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器600的运行的结构图。如图6所示,该多标准视频解码器600可适于处理使用VC-1编码技术编码的视频基本码流401。端口编码器403可使用起始码寻找模块423确定起始码和起始码后缀,使用字节解除模块425从VC-1编码视频基本码流401移除额外字节。FIG. 6 is an exemplary block diagram of the operation of the
符号翻译器405可适于翻译从端口编码器403获得的VC-1未处理的基本流424,以获得量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息,如VC-1未处理的基本视频流424解码需要的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息和/或运动矢量信息。量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息生成过程中,符号翻译器405可接收中央处理器407的指令,并向中央处理器407提供后续符号信息。此外,符号翻译器可使用下列辅助模块的一个或多个:FLC模块427、VLC模块429、系数构造模块43 5和/或矢量构造模块437。The
逆量化频率系数可从符号翻译器405传送至IQT模块411,可生成预测错误信息。IQT模块411可使用逆锯齿模块439、AC/DC预测模块441、逆量化模块443和/或逆变换模块445生成预测错误信息。来自符号翻译器405的旁信息可被传送至运动补偿模块413,生成预测像素。运动补偿模块413可使用帧缓冲器419以及强度补偿模块449、范围重设模块447、插入模块451、可变块尺寸模块453和/或双向预测模块455生成时间上的预测像素。帧缓冲器419可适于存储和提供至少两个参考帧/画面给运动补偿模块413。The inverse quantized frequency coefficients may be passed from the
而后,重建器415可被多标准解码器600用于使用从运动补偿模块413获得的预测像素信息,以及从IQT模块411获得的预测错误信息,重建当前宏块。重建的宏块可被内部回路滤波器417使用解块模块459和/或重叠变换模块457滤波。滤波后的宏块可进一步被后处理模块421处理。后处理模块421可使用解环模块467、范围重设模块461、尺寸调整模块463和/或解块模块465生成解码的宏块469。而后,该解码的宏块469可被传送至如显示后处理器。The reconstructor 415 can then be used by the
图7是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码MPEG-1或PMEG-2视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器700的运行的结构图。如图7所示,该多标准视频解码器700可适于处理使用MPEG-1或MPEG-2编码技术编码的视频基本码流401。端口编码器403可使用起始码寻找模块423确定MPEG-1或MPEG-2编码视频基本码流401内的起始码和起始码后缀。FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the
符号翻译器405可适于翻译从端口编码器403获得的MPEG-1或MPEG-2未处理的基本流424,以获得量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息,如MPEG-1或MPEG-2未处理的基本视频流424解码需要的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息和/或运动矢量信息。量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息生成过程中,符号翻译器405可接收中央处理器407的指令,并向中央处理器407提供后续符号信息。此外,符号翻译器可使用下列辅助模块的一个或多个:FLC模块427、VLC模块429、系数构造模块435和/或矢量构造模块437。The
逆量化频率系数可从符号翻译器405传送至IQT模块411,可生成预测错误信息。IQT模块411可使用逆锯齿模块439、逆量化模块443和/或逆变换模块445生成预测错误信息。来自符号翻译器405的旁信息可被传送至运动补偿模块413,生成预测像素。运动补偿模块413可使用帧缓冲器419以及插入模块451、可变块尺寸模块453和/或双向预测模块455生成时间上的预测像素。帧缓冲器419可适于存储和提供至少两个参考帧/画面给运动补偿模块413。The inverse quantized frequency coefficients may be passed from the
而后,重建器415可被多标准解码器700用于使用从运动补偿模块413获得的预测像素信息,以及从IQT模块411获得的预测错误信息,重建当前宏块。重建的宏块可进一步被后处理模块421处理。后处理模块421可使用解环模块467和/或解块模块465生成解码的宏块469。而后,该解码的宏块469可被传送至如显示后处理器。The reconstructor 415 can then be used by the
图8是根据本发明的实施例的示例性的当解码MPEG-4视频数据时,图4所示多标准视频解码器800的运行的结构图。如图8所示,该多标准视频解码器800可适于处理使用MPEG-4编码技术编码的视频基本码流401。端口编码器403可使用起始码寻找模块423确定MPEG-4编码视频基本码流401内的起始码和起始码后缀。FIG. 8 is a block diagram illustrating an exemplary operation of the multi-standard video decoder 800 shown in FIG. 4 when decoding MPEG-4 video data according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 8, the multi-standard video decoder 800 may be adapted to process a video
符号翻译器405可适于翻译从端口编码器403获得的MPEG-4未处理的基本流424,以获得量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息,如MPEG-4未处理的基本视频流424解码需要的宏块类型信息、片段类型信息、预测模式信息和/或运动矢量信息。量化频率系数信息和/或附加旁信息生成过程中,符号翻译器405可接收中央处理器407的指令,并向中央处理器407提供后续符号信息。此外,符号翻译器可使用下列辅助模块的一个或多个:FLC模块427、VLC模块429、系数构造模块43 5和/或矢量构造模块437。The
逆量化频率系数可从符号翻译器405传送至IQT模块411,可生成预测错误信息。IQT模块411可使用逆锯齿模块439、AC/DC预测模块441、逆量化模块443和/或逆变换模块445生成预测错误信息。来自符号翻译器405的旁信息可被传送至运动补偿模块413,生成预测像素。运动补偿模块413可使用帧缓冲器419以及插入模块451、可变块尺寸模块453和/或双向预测模块455生成时间上的预测像素。帧缓冲器419可适于存储和提供至少两个参考帧/画面给运动补偿模块413。The inverse quantized frequency coefficients may be passed from the
而后,重建器415可被多标准解码器800用于使用从运动补偿模块413获得的预测像素信息,以及从IQT模块411获得的预测错误信息,重建当前宏块。重建的宏块可进一步被后处理模块421处理。后处理模块421可使用解环模块467和/或解块模块465生成解码的宏块469。而后,该解码的宏块469可被传送至如显示后处理器。The reconstructor 415 can then be used by the multi-standard decoder 800 to reconstruct the current macroblock using the predicted pixel information obtained from the
图9是根据本发明的实施例的处理视频数据流的示范性方法900的流程图。如图9所示,在步骤901,接收视频基本码流内的打包数据,其中视频基本码流可根据多个编码方法之一编码。在步骤903,确定该打包数据内的起始码,其中该起始码可定义封装视频有效载荷。在步骤905,确定打包数据中的标识符,该标识符定义一种或多种与该视频基本码流中的信息包关联的编码类型。在步骤907,基于所确定的标识符,从多个解码方法中选择一个解码方法。在步骤909,基于所选解码方法,所定义的封装视频有效载荷可被解码。FIG. 9 is a flowchart of an exemplary method 900 of processing a video data stream, according to an embodiment of the invention. As shown in FIG. 9, at step 901, packetized data in a video elementary stream is received, wherein the video elementary stream can be encoded according to one of a plurality of encoding methods. In step 903, a start code within the packetized data is determined, wherein the start code may define a packed video payload. In step 905, an identifier in the packetized data is determined, and the identifier defines one or more encoding types associated with the information packets in the video elementary stream. At step 907, based on the determined identifier, a decoding method is selected from a plurality of decoding methods. At step 909, based on the selected decoding method, the defined encapsulated video payload may be decoded.
因此,本发明可以在硬件、软件、固件或硬件和软件组合中实现。本发明可以在至少一个计算机系统中以集中方式实现或以分布方式实现,该分布方式是指不同元件分布于几个相互连接的计算机系统。任一种计算机或其他适于执行这里所描述的方法的设备都是适合的。一种典型的硬件、软件和固件的结合可以是具有计算机程序的多用途计算机系统,其中计算机程序可以被下载和执行,并控制计算机系统以使计算机系统执行这里所描述的方法。Therefore, the present invention can be implemented in hardware, software, firmware, or a combination of hardware and software. The invention can be implemented in a centralized fashion in at least one computer system or in a distributed fashion, meaning that the different elements are distributed over several interconnected computer systems. Any computer or other apparatus adapted for carrying out the methods described herein is suitable. A typical combination of hardware, software and firmware can be a multipurpose computer system with a computer program that can be downloaded and executed, and which controls the computer system such that the computer system performs the methods described herein.
本发明的一个实施例也可作为组件级产品、作为单一芯片、特殊用途集成电路(ASIC)实现,或者具有集成于单一芯片、与系统的其他部分不同级,作为分开元件实现。该系统的集成度由速度或成本考量初步确定。由于现代处理器种类繁杂,使用商业上可行的处理器是可能的,该处理器可以超出现有系统的ASIC实现方式的方法实现。作为选择,如果处理器作为ASIC核或逻辑块是有效的,那么商业上有效的处理器可作为具有各种功能、作为固件实现的ASIC设备的一部分被实现。An embodiment of the invention may also be implemented as a component level product, as a single chip, application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), or with integration on a single chip, at a different level from the rest of the system, as separate components. The level of integration of the system is initially determined by speed or cost considerations. Due to the wide variety of modern processors, it is possible to use commercially viable processors that can be implemented in ways that go beyond ASIC implementations of existing systems. Alternatively, if the processor is available as an ASIC core or logic block, a commercially available processor may be implemented as part of an ASIC device having various functions implemented as firmware.
本发明也可以被嵌入计算机程序产品中,该计算机程序产品包括所有能够执行这里所描述的方法的特征,且当被下载到计算机系统中时,能够执行这些方法。这里所说的计算机程序可以采用一组指令的任何表达形式,如用任何语言、代码或符号表达,该组指令能够使一具有信息处理能力的系统执行直接或在将该指令以下列方式之一或全部处理后:a)转换成另一种语言、代码或符号,b)用不同材料形式复制,执行特定功能。然而,本领域的普通技术人员来说可以理解的计算机程序的其他方法可被本发明预期。The invention can also be embedded in a computer program product which comprises all the features enabling the implementation of the methods described herein and which, when downloaded into a computer system, is able to perform these methods. The computer program mentioned here may take any form of expression, such as any language, code or symbol, which can cause a system with information processing capabilities to execute the instructions directly or in one of the following ways: or fully processed: a) converted into another language, code or symbol, b) reproduced in a different material form to perform a specific function. However, other means of computer programs as would be understood by one of ordinary skill in the art are contemplated by the present invention.
虽然本发明已参考某些实施例进行了描述,对本领域的普通技术人员来说可以理解,各种改变及等同将不脱离本发明的范围。另外,很多对本发明所述内容的适合特别情况和材料的修改也不脱离本发明的范围。因此,本发明不限于所揭示的特定实施例,本发明将包括所有落入权利要求范围中的实施例。While the invention has been described with reference to certain embodiments, it will be understood by those skilled in the art that various changes and equivalents will be made without departing from the scope of the invention. In addition, many modifications may be made to suit a particular situation and material that are described herein without departing from the scope of the invention. Therefore, it is intended that the invention not be limited to the particular embodiments disclosed, but that the invention will include all embodiments falling within the scope of the appended claims.
本申请主张申请日为2004年5月21日的美国临时专利申请60/568926(代理机构编号15747US01)的优先权。该申请在此作为本申请的全面参考。This application claims priority to US Provisional Patent Application 60/568926 (Attorney No. 15747US01), filed May 21, 2004. This application is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety into this application.
本申请与以下申请有关,其中每件申请都可在此作为本申请的全面参考:This application is related to the following applications, each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety:
美国专利申请序列号为10/963,677(代理机构案件编号15748US02),申请日为2004年10月13日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/963,677 (Agency Case No. 15748US02), filed on October 13, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/985,501(代理机构案件编号15749US02),申请日为2004年11月10日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/985,501 (Agency Case No. 15749US02), filed on November 10, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为 (代理机构案件编号15750US02),申请日为2004年 ;The U.S. patent application serial number is (Agency Case No. 15750US02), filed in 2004 ;
美国专利申请序列号为10/985,110(代理机构案件编号15751US02),申请日为2004年11月10日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/985,110 (Agency Case No. 15751US02), filed on November 10, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/981,218(代理机构案件编号15754US02),申请日为2004年11月04日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/981,218 (Agency Case No. 15754US02), filed on November 04, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/965,172(代理机构案件编号15756US02),申请日为2004年10月13日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/965,172 (Agency Case No. 15756US02), filed on October 13, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/971,931(代理机构案件编号15757US02),申请日为2004年10月25日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/971,931 (Agency Case No. 15757US02), filed on October 25, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/974,179(代理机构案件编号15759US02),申请日为2004年10月27日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/974,179 (Agency Case No. 15759US02), filed on October 27, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/974,872(代理机构案件编号15760US02),申请日为2004年10月27日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/974,872 (Agency Case No. 15760US02), filed on October 27, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/970,923(代理机构案件编号15761US02),申请日为2004年10月21日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/970,923 (Agency Case No. 15761US02), filed on October 21, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为10/963,680(代理机构案件编号15762US02),申请日为2004年10月13日;U.S. Patent Application Serial No. 10/963,680 (Agency Case No. 15762US02), filed on October 13, 2004;
美国专利申请序列号为 (代理机构案件编号15763US02),申请日为2004年 ;The U.S. patent application serial number is (Agency Case No. 15763US02), filed in 2004 ;
美国专利申请序列号为 (代理机构案件编号15792US01),申请日为2004年 ;The U.S. patent application serial number is (Agency Case No. 15792US01), filed in 2004 ;
美国专利申请序列号为 (代理机构案件编号15810US02),申请日为2004年 ;及The U.S. patent application serial number is (Agency Case No. 15810US02), filed in 2004 ;and
美国专利申请序列号为 (代理机构案件编号15811US02),申请日为2004年 。The U.S. patent application serial number is (Agency Case No. 15811US02), filed in 2004 .
Claims (13)
Applications Claiming Priority (23)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US60/573,357 | 2004-05-21 | ||
| US10/963,680 | 2004-10-13 | ||
| US10/963,680US7688337B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-13 | System and method for reducing image scaling complexity with flexible scaling factors |
| US10/965,172 | 2004-10-13 | ||
| US10/963,677 | 2004-10-13 | ||
| US10/965,172US7680351B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-13 | Video deblocking method and apparatus |
| US10/963,677US7613351B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-13 | Video decoder with deblocker within decoding loop |
| US10/970,923US20050259735A1 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-21 | System and method for video error masking using standard prediction |
| US10/970,923 | 2004-10-21 | ||
| US10/972,931 | 2004-10-25 | ||
| US10/972,931US8090028B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-25 | Video deblocking memory utilization |
| US10/974,179US7515637B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-27 | Video decoding for motion compensation with weighted prediction |
| US10/974,872 | 2004-10-27 | ||
| US10/974,872US7570270B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-10-27 | Buffer for driving display with asynchronous display engine |
| US10/974,179 | 2004-10-27 | ||
| US10/981,218 | 2004-11-04 | ||
| US10/981,218US7742544B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-11-04 | System and method for efficient CABAC clock |
| US10/985,110US20050259742A1 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-11-10 | System and method for choosing tables in CAVLC |
| US10/985,110 | 2004-11-10 | ||
| US10/985,501US7573406B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-11-10 | System and method for decoding context adaptive variable length coding |
| US10/985,501 | 2004-11-10 | ||
| US11/000,731US7590059B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-12-01 | Multistandard video decoder |
| US11/000,731 | 2004-12-01 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1870757A CN1870757A (en) | 2006-11-29 |
| CN1870757Btrue CN1870757B (en) | 2010-11-10 |
Family
ID=43066710
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200510074637Expired - LifetimeCN1870757B (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2005-05-23 | Multistandard video decoder |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN1870757B (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8599920B2 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2013-12-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Intensity compensation techniques in video processing |
| MY167341A (en)* | 2011-09-09 | 2018-08-16 | Sun Patent Trust | Low complex deblocking filter decisions |
| CN103369311A (en)* | 2012-04-04 | 2013-10-23 | 朱洪波 | Method for preventing conflict of initial code |
| CN107979783B (en)* | 2016-10-25 | 2020-03-24 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | Streaming data analysis method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN107977551B (en)* | 2016-10-25 | 2020-07-03 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | A method, device and electronic device for protecting files |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0847204A3 (en)* | 1996-12-03 | 2000-03-01 | STMicroelectronics, Inc. | A multi-standard video decompression device |
| US6185339B1 (en)* | 1997-09-24 | 2001-02-06 | Sony Corporation | Bit stream analyzing method and apparatus |
| US6539059B1 (en)* | 2000-03-02 | 2003-03-25 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Apparatus and method for efficiently scalable digital video decoding |
- 2005
- 2005-05-23CNCN 200510074637patent/CN1870757B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0847204A3 (en)* | 1996-12-03 | 2000-03-01 | STMicroelectronics, Inc. | A multi-standard video decompression device |
| US6185339B1 (en)* | 1997-09-24 | 2001-02-06 | Sony Corporation | Bit stream analyzing method and apparatus |
| US6539059B1 (en)* | 2000-03-02 | 2003-03-25 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Apparatus and method for efficiently scalable digital video decoding |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1870757A (en) | 2006-11-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7590059B2 (en) | Multistandard video decoder | |
| KR101345015B1 (en) | Device for coding, method for coding, system for coding, method for decoding video data | |
| CN1934866B (en) | video decoding device | |
| US10382768B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for transform coefficient coding of non-square blocks | |
| JP6254294B2 (en) | HEVC range expansion remainder differential pulse code modulation method | |
| KR101919394B1 (en) | Parameter determination for exp-golomb residuals binarization for lossless intra hevc coding | |
| WO2015101173A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for scaling parameter coding for inter-component residual prediction | |
| CN108028931A (en) | Method and apparatus for adaptive inter-frame prediction for video coding and decoding | |
| JP2014506061A (en) | Method and apparatus for improved loop-type filtering process | |
| US8009740B2 (en) | Method and system for a parametrized multi-standard deblocking filter for video compression systems | |
| KR20060064008A (en) | Decoding device or encoding device in which an intermediate buffer is inserted between an arithmetic code decoder or encoder and an inverse binary converter or a binary converter | |
| US20100150242A1 (en) | Image data decoding device and image data decoding method | |
| TW202139697A (en) | Signaling quantization related parameters | |
| JP4680608B2 (en) | Image decoding apparatus and method | |
| CN114788284B (en) | Method and apparatus for encoding video data in palette mode | |
| KR102267792B1 (en) | Image block coding based on pixel-domain pre-processing operations on image block | |
| JP7696048B2 (en) | Decoding device, program, and decoding method | |
| KR20240089011A (en) | Video coding using optional neural network-based coding tools | |
| CN1870757B (en) | Multistandard video decoder | |
| EP1599049A2 (en) | Multistandard video decoder | |
| EP3910952B1 (en) | Image decoding method, decoder and storage medium | |
| TWI514851B (en) | Image encoding/decing system and method applicable thereto | |
| JP2009017472A (en) | Image decoding unit and image decoding method | |
| CN115996298A (en) | Video decoding method and related device | |
| HK1222493B (en) | Flexible band offset mode in sample adaptive offset in hevc |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term | Granted publication date:20101110 |