CN1817325A - Mouse hearing and vision memory model and intelligent action inspecting system - Google Patents
Mouse hearing and vision memory model and intelligent action inspecting systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1817325A CN1817325ACNA2006100458689ACN200610045868ACN1817325ACN 1817325 ACN1817325 ACN 1817325ACN A2006100458689 ACNA2006100458689 ACN A2006100458689ACN 200610045868 ACN200610045868 ACN 200610045868ACN 1817325 ACN1817325 ACN 1817325A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- area
- box
- training
- auditory
- experimental
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 230000015654memoryEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription30
- 230000009471actionEffects0.000titledescription2
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription58
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000claimsabstractdescription51
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription43
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription34
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 241000699666Mus <mouse, genus>Species0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- 230000006399behaviorEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription25
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription20
- 230000003542behavioural effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 238000013480data collectionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 238000005192partitionMethods0.000claimsdescription27
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000claimsdescription11
- 239000004020conductorSubstances0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000003446memory effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000abstractdescription35
- 230000001766physiological effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000013461designMethods0.000abstract1
- 230000013016learningEffects0.000description16
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description5
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description4
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 230000006978adaptationEffects0.000description3
- 230000001149cognitive effectEffects0.000description3
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000description3
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description3
- 230000009977dual effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description3
- 238000002955isolationMethods0.000description3
- 210000000653nervous systemAnatomy0.000description3
- 208000024827Alzheimer diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 102000001068Neural Cell Adhesion MoleculesHuman genes0.000description2
- 108010069196Neural Cell Adhesion MoleculesProteins0.000description2
- 208000018737Parkinson diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description2
- 230000001143conditioned effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description2
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description2
- 230000005611electricityEffects0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 230000003203everyday effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000037406food intakeEffects0.000description2
- 235000012631food intakeNutrition0.000description2
- 238000003209gene knockoutMethods0.000description2
- 230000036403neuro physiologyEffects0.000description2
- 235000020925non fastingNutrition0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description2
- 230000004936stimulating effectEffects0.000description2
- 208000031648Body Weight ChangesDiseases0.000description1
- 241000282326Felis catusSpecies0.000description1
- 208000026350Inborn Genetic diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000012902Nervous system diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 206010036631Presenile dementiaDiseases0.000description1
- 230000004888barrier functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000037396body weightEffects0.000description1
- 230000004579body weight changeEffects0.000description1
- 230000003925brain functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000019771cognitionEffects0.000description1
- 230000003930cognitive abilityEffects0.000description1
- 239000002131composite materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007405data analysisMethods0.000description1
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description1
- 238000007877drug screeningMethods0.000description1
- 206010015037epilepsyDiseases0.000description1
- 208000016361genetic diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 230000002068genetic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000005286illuminationMethods0.000description1
- 238000010921in-depth analysisMethods0.000description1
- 230000007787long-term memoryEffects0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 230000006386memory functionEffects0.000description1
- 206010027175memory impairmentDiseases0.000description1
- 238000010172mouse modelMethods0.000description1
- 230000035772mutationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000926neurological effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002664nootropic agentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000description1
- 238000004886process controlMethods0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 230000011514reflexEffects0.000description1
- 230000002787reinforcementEffects0.000description1
- 238000012216screeningMethods0.000description1
- 238000007493shaping processMethods0.000description1
- 230000035939shockEffects0.000description1
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002269spontaneous effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007619statistical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000009182swimmingEffects0.000description1
- 230000031836visual learningEffects0.000description1
Images
Landscapes
- Catching Or Destruction (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种有关研究建立动物学习和记忆行为训练方法的模型及其检测系统,特别是一种鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型及智能化行为检测系统。它可应用于神经生理学、神经药理学和心理学等领域。The invention relates to a model and a detection system related to research and establishment of animal learning and memory behavior training methods, in particular to a mouse auditory and visual memory model and an intelligent behavior detection system. It can be applied in the fields of neurophysiology, neuropharmacology and psychology.
背景技术Background technique
目前,动物行为实验是研究脑高级功能及其他神经科学的不可缺少的重要手段,尤其在神经生理学、神经药理学等行为医学研究方面具有更重要地位。其中迷宫实验是行为实验的经典项目,是研究大鼠(或小鼠)学习记忆功能最常用的实验之一,也是认知药物筛选常用的动物模型。迷宫装置的种类较多,但都包含三个基本组成部分:训练区——放置动物;目的区——系安全区或食物放置区;通道——有长有短,有一个以上通道交叉口,供动物选择到达目的区的正确行动方向。At present, animal behavior experiments are indispensable and important means for studying advanced brain functions and other neurosciences, especially in behavioral medical research such as neurophysiology and neuropharmacology. Among them, the maze test is a classic project of behavioral experiments, and it is one of the most commonly used experiments to study the learning and memory function of rats (or mice), and it is also a commonly used animal model for cognitive drug screening. There are many types of labyrinth devices, but they all include three basic components: training area - place animals; target area - safety zone or food placement area; channel - long or short, with more than one channel intersection, For animals to choose the correct direction of action to reach the destination area.
现有Y型迷宫,即为三等分辐射式迷宫,由三个支臂和一个连接区组成,三臂相互夹角为120°,每臂底部铺以细铜棒。铜棒可与刺激电源相通。各臂未端装有信号灯,信号灯开启指示该臂为安全区,即该臂底部不通电。安全区的方位可随机变换,当某臂为安全区时,另两臂和连接区均带电,可训练动物学会主动逃避反应,逃向安全区。在实验中,如动物在信号灯亮后或遭受到电击后直接逃避至安全区者为正确反应,反之为错误反应。一般将动物经训练而达到学会的标准定为连续10次测试中有9次正确者。记录每一动物迷路分辨学习达到学会标准所需的训练数,以此作为评价动物学习能力好坏的客观指标。The existing Y-shaped labyrinth is a trisection radial labyrinth, which consists of three arms and a connection area. The angle between the three arms is 120°, and the bottom of each arm is covered with thin copper rods. The copper rod can communicate with the stimulating power supply. Each arm end is equipped with a signal light, and the signal light is turned on to indicate that the arm is a safe area, that is, the bottom of the arm is not powered. The orientation of the safety zone can be changed randomly. When a certain arm is the safety zone, the other two arms and the connection zone are charged, which can train animals to learn to actively escape and flee to the safety zone. In the experiment, if the animal escapes directly to the safe area after the signal light is on or receives an electric shock, it is a correct response, otherwise it is an incorrect response. Generally, the animal is trained to meet the learning standard as 9 out of 10 consecutive tests are correct. Record the number of trainings required for each animal's maze discrimination learning to meet the learning standards, and use this as an objective indicator to evaluate the animal's learning ability.
现有水迷宫,则是一个在其通道中注入一定深度水的迷宫。内部通道形状多为T形、F形或II形,其中有一个或多个盲端而出口端只有一个。将动物放在训练区内,训练它学习选择出口、顺利游至目的区的能力。实验过程中逐渐增加盲端个数,观察、记录动物进入盲端次数(即错误次数)及游泳所用的时间,以评价其学习成绩、记忆获得和长时间记忆功能。The existing water labyrinth is a labyrinth in which water of a certain depth is injected in its channel. The shape of the internal channel is mostly T-shaped, F-shaped or II-shaped, with one or more blind ends and only one outlet end. Put the animal in the training area and train it to learn to choose the exit and swim to the destination area smoothly. During the experiment, the number of blind ends was gradually increased, and the number of times the animals entered the blind end (ie, the number of errors) and the time spent in swimming were observed and recorded, so as to evaluate their academic performance, memory acquisition and long-term memory function.
实际应用表明,目前的迷宫实验,特别是Y型迷宫受其结构限制无法形成封闭的循环回路,水迷宫只能强迫动物游泳,不能自主运动。因此,训练时无论是过程控制,还是数据采集、处理,都是由实验者手动操作,人工操作比较烦琐,人工记录相应数据主观因素较多,既费人力,同时主观误差也大,影响其准确性。Practical applications show that the current maze experiments, especially the Y-shaped maze, cannot form a closed circulation loop due to its structural limitations, and the water maze can only force animals to swim, but cannot move autonomously. Therefore, whether it is process control or data collection and processing during training, it is manually operated by the experimenter. The manual operation is cumbersome, and the manual recording of the corresponding data has many subjective factors, which is labor-intensive and has large subjective errors, which affects its accuracy. sex.
在专利号为97245361.X的“电驱动、电刺激自动计数鼠迷宫”中,本发明人曾公开了一种设置三个刺激区(即训练区)、一个安全区和一个隔离区(设有将鼠返回训练区的电动输送带)的长条形多通道迷宫。它是针对实验鼠对多通道迷宫学习、条件反射等生理指标记忆情况设计的,根据自动实验记录的实验鼠用药后通过迷宫失败的次数,可判定药效及性能指标。实验结果表明,该装置的迷宫形状存在必须通过输送带将鼠由隔离区送回训练区、通道门的结构单一、不能按照实验要求调整等缺陷,还是无法适应鼠的自然生活习性的需要。In the patent No. 97245361.X "electrically driven, electrically stimulated automatic counting mouse maze", the inventor once disclosed a kind of setting three stimulation areas (i.e. training areas), a safety area and an isolation area (with A long strip multi-channel maze that returns the rat to the training area (motorized conveyor belt). It is designed for the memory of experimental rats on physiological indicators such as multi-channel maze learning and conditioned reflex. According to the number of times that experimental rats fail to pass the maze after taking medicine, the drug efficacy and performance indicators can be determined according to the automatic experiment records. The experimental results show that the labyrinth shape of the device has defects such as the need to send the mice from the isolation area back to the training area through the conveyor belt, the structure of the passage door is single, and cannot be adjusted according to the experimental requirements, and it still cannot adapt to the needs of the natural life habits of the mice.
依据建立动物学习和记忆行为训练方法的模型的实际需要,现有的模型存在明显的局限性:即人为因素较多,技术操作烦琐,准确性较差;作为行为数据采集装置的迷宫,形状、分区及洞(通道)的空间结构不能适应鼠的自然生活习性,应用较局限(如只适合大鼠);现有数据处理控制单元较单一,检测结果处理时,需将实验数据转换成Foxpro数据库文件才可以利用;以及缺少电、声音(噪音)和光等条件刺激的综合影响因素。由此可见,进一步发展与鼠的生活习性贴近,建立较复杂的动物学习和记忆行为训练方法的模型、但易于对其进行检测的系统,仍是当务之急。According to the actual needs of establishing a model of animal learning and memory behavior training methods, the existing models have obvious limitations: that is, there are many human factors, technical operations are cumbersome, and the accuracy is poor; The spatial structure of partitions and holes (channels) cannot adapt to the natural life habits of rats, and the application is limited (for example, only suitable for rats); the existing data processing control unit is relatively simple, and the experimental data needs to be converted into Foxpro database when processing the test results files are available; and the combined influence of the lack of conditioned stimuli such as electricity, sound (noise), and light. It can be seen that it is still a top priority to further develop a system that is close to the living habits of mice and establishes a more complex model of animal learning and memory behavior training methods, but is easy to detect.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型及智能化行为检测系统,模型设计合理,调整方便,行为刺激作用温和,模拟环境更符合动物正常生理行为学活动的实际,可检测动物的听觉及视觉辨别能力,实验数据采集和处理准确,容易实现检测系统的自动化、科学化管理,适应范围广,更适用于建立复杂的认知记忆模型,以满足更深入的学习记忆行为分析的需要。The object of the present invention is to provide a mouse auditory and visual memory model and an intelligent behavior detection system. Excellent auditory and visual discrimination ability, accurate experimental data collection and processing, easy to realize automation and scientific management of the detection system, wide range of adaptation, more suitable for establishing complex cognitive memory models to meet the needs of more in-depth learning and memory behavior analysis need.
本发明的目的是这样实现的:该鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型包括带有训练区、目的区及其连接通道的迷宫,其技术要点是:所述迷宫采用多通道闭合回路的圆形暗箱式迷宫,在其带有上盖和栅栏底的箱体内,通过箱体内壁与中间立柱的滑槽按径向设置插装式分区隔板,将箱体内腔分隔成至少三个测试区,其中一个为目的区,其余为数据采集区,每个隔板底部等间距分布外观相同的带有可调式单向门的洞形通道,每个洞形通道门侧置有两组红外发射、接收光电元件,被隔离的各区内分别设置可控灯光照明,各区的栅栏底分别设置随机控制的产生不同梯度电压带的电击导体,在箱体中间立柱上部控制箱内设置强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头。The object of the present invention is achieved like this: the auditory and visual memory model of this mouse comprises the labyrinth with training area, target area and connecting passage thereof, and its technical gist is: described labyrinth adopts the circular obscura formula of multi-channel closed circuit In the labyrinth, in the box with the upper cover and the bottom of the fence, plug-in partition partitions are arranged radially through the inner wall of the box and the chute of the middle column to divide the inner cavity of the box into at least three test areas, one of which is It is the target area, and the rest is the data collection area. At the bottom of each partition, there are holes with the same appearance and adjustable one-way doors at equal intervals. There are two sets of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements on the side of each hole-shaped door. , Controllable lighting is set in each isolated area, electric shock conductors that generate different gradient voltage bands are randomly controlled at the bottom of the fence in each area, and strong light generators, noise generators and Video tracking head.
所述插装式分区隔板的上端面内低外高,低端插装在中间立柱外周的竖向滑槽内,高端插装在箱体内壁的与中间立柱滑槽相对应的滑槽内。The upper end surface of the plug-in partition partition is low inside and high outside, the low end is inserted in the vertical chute on the outer periphery of the middle column, and the high end is inserted in the chute corresponding to the middle column chute on the inner wall of the box .
所述鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型的智能化行为检测系统,包括行为数据采集装置、数据处理控制单元、PCI数据总线和微机控制系统,其技术要点是:所述行为数据采集装置采用上述圆形暗箱式迷宫作为鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型,让实验鼠在所述迷宫的箱体内,进行指定路径通过训练、多路径选择训练、食物控制和听觉、视觉刺激训练,通过所述径向设置的插装式分区隔板底部的带有可调式单向门的洞形通道,沿指定的逆时针或顺时针路径通过训练区、目的区所形成的闭合回路,依次完成循环训练,其间利用所述分别设置在被隔离的各区内的可控灯光照明来适应鼠的趋暗习性,使其在箱体内进行自主运动,利用所述分别设置在各区栅栏底分别设置的电击导体产生的不同梯度电压带,以电击刺激进行驱动来随机控制鼠的被动运动,再结合检测系统中集成在数据采集卡上的设置在所述每个洞形通道门侧置的两组红外发射、接收光电元件、各区内的可控灯光照明和设置在所述立柱上部控制箱内的强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头的控制元件所组成的各数据处理控制单元,根据实验要求,将分别采集到的实验鼠适应活动时的路径、成功所需的次数、各次的时间、成功前出现错误的位置、次数诸数据,所形成的通道门的电压信号、控制电击刺激信号、声刺激信号及光刺激信号,经过由CMOS集成元件组成的逻辑电路取得所需的信号,连同显示器观察到的视频跟踪头采集的图像,通过PCI数据总线传输到微机控制系统中的Access数据库,并利用SAS统计软件包进行处理,随时控制和全程监测鼠的听觉、视觉记忆活动行为。The intelligent behavior detection system of the auditory and visual memory model of the mouse comprises a behavior data acquisition device, a data processing control unit, a PCI data bus and a microcomputer control system, and its technical points are: the behavior data acquisition device adopts the above-mentioned circular The camera obscura maze is used as the auditory and visual memory model of rats, allowing the experimental rats to carry out specified path passing training, multi-path selection training, food control and auditory and visual stimulation training in the box of the maze. The hole-shaped channel with an adjustable one-way door at the bottom of the plug-in partition partition passes through the closed loop formed by the training area and the target area along the designated counterclockwise or clockwise path, and completes the cycle training in sequence. The controllable lights installed in the isolated areas are used to adapt to the dark habit of the rats, so that they can move autonomously in the box, and use the different gradient voltage bands generated by the electric shock conductors respectively arranged at the bottom of the fences in each area , driven by electric shock stimulation to randomly control the passive movement of the mouse, combined with the two groups of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements on the side of each hole-shaped channel door, which are integrated on the data acquisition card in the detection system, and in each area Each data processing control unit composed of the controllable lighting and the strong light generating device, the noise generating device and the control elements of the video tracking head arranged in the control box on the upper part of the column, according to the experimental requirements, will collect the experimental data respectively The path of the mouse to adapt to the activity, the number of times required for success, the time of each time, the position of the error before success, the number of times, the voltage signal of the channel gate formed, the control electric shock stimulation signal, the sound stimulation signal and the light stimulation signal , the required signal is obtained through the logic circuit composed of CMOS integrated components, together with the image collected by the video tracking head observed by the monitor, it is transmitted to the Access database in the microcomputer control system through the PCI data bus, and processed by the SAS statistical software package , to control and monitor the auditory and visual memory activities of mice at any time.
由于本发明鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型采用圆形暗箱式迷宫作为行为数据采集装置,以指定的顺时针或逆时针路径的闭合回路,利用可控灯光照明适应鼠的趋暗习性,使其在箱体内进行自主运动,结合各区栅栏底分别设置的电击导体产生的不同梯度电压带,以电击刺激进行驱动来随机控制鼠的被动运动,所以实验鼠的训练模拟环境更符合动物正常生理行为学活动的实际,对禁食及非禁食鼠都适用,也将极大地克服现有长条形多通道迷宫存在必须通过输送带将鼠由隔离区送回训练区、通道空间结构单一等缺陷。其次,与现有水迷宫的强迫动物游泳的训练不同,本发明采用鼠自然活动模式的自主运动和梯度电压被动驱动相结合,作用温和,防止受试鼠接受单一电刺激后远离指定通道,避免模型动物在数据采集装置各区停留时间不一致,使时间类数据更为准确。再有,选用可靠的两组红外发射、接收光电元件安置在迷宫的各通道门侧,能实时、准确地检测动物在迷宫中的行踪。在圆形迷宫每个训练区内,设计有多个外观相同的通道供动物选择,每个通道各有两对红外光电元件,利用延迟消除原“训练系统”在鼠尝试进洞而又快速退出所造成的数据不准确。另外,带有可调式单向门的洞形通道根据实验鼠的大小调节,解决了应用局限的问题,尤其是可消除由于实验鼠月龄不同而体积大小不一致,对实验结果准确性的干扰。考虑到实验要求和难易度不同,迷宫箱体内按径向设置插装式分区隔板,将箱体内腔分隔成多个训练区,因此,可根据需要来增减训练区数目。Because the auditory and visual memory model of the mouse of the present invention adopts a circular black box-type maze as a behavioral data acquisition device, with a closed loop of a designated clockwise or counterclockwise path, the controllable light illumination is used to adapt to the dark habit of the mouse, so that it can Autonomous movement in the box, combined with the different gradient voltage bands generated by the electric shock conductors set at the bottom of the fences in each area, is driven by electric shock stimulation to randomly control the passive movement of the rats, so the training simulation environment of the experimental rats is more in line with the normal physiological and behavioral activities of animals In reality, it is applicable to both fasting and non-fasting rats, and will greatly overcome the defects that the existing elongated multi-channel maze must return the rats from the isolation area to the training area through the conveyor belt, and the channel space structure is single. Secondly, different from the existing training of forcing animals to swim in the water maze, the present invention adopts the combination of the spontaneous movement of the rat's natural activity mode and the passive drive of the gradient voltage, which has a mild effect and prevents the rat from being away from the designated channel after receiving a single electrical stimulation, avoiding The dwell time of the model animals in each area of the data acquisition device is inconsistent, which makes the time data more accurate. Furthermore, two groups of reliable infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements are selected to be arranged on the side of each passage door of the maze, which can detect the whereabouts of animals in the maze in real time and accurately. In each training area of the circular maze, there are multiple passages with the same appearance for animals to choose from. Each passage has two pairs of infrared photoelectric elements, and the original "training system" is used to eliminate the delay when the mouse tries to enter the hole and exit quickly. The resulting data is inaccurate. In addition, the hole-shaped channel with an adjustable one-way door is adjusted according to the size of the experimental mice, which solves the problem of application limitations, especially eliminates the interference of the accuracy of the experimental results due to the inconsistent volume and size of the experimental mice due to different ages of the experimental mice. Considering the different experimental requirements and degrees of difficulty, plug-in partition partitions are arranged radially in the maze box to divide the inner cavity of the box into multiple training areas. Therefore, the number of training areas can be increased or decreased according to needs.
本发明鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型的智能化行为检测系统中,除建立上述独特的训练模型及与之相适应的训练策略外,还采用流行的Visual Studio程序设计组件和Access数据库链接取代现有技术中的采用的C语言和Foxpro数据库文件,组成智能化行为检测系统。使设置在每个洞形通道门侧置的两组红外发射、接收光电元件、各区内的可控灯光照明和设置在立柱上部控制箱内的强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头的控制元件所组成的各数据处理控制单元,都集中在数据采集卡上,根据实验要求,分别采集和处理相应的信号,可以直接通过PCI数据总线插入到微机控制系统,利用视频跟踪头观察检测范围内的实验鼠动态,将多项任务同时操作,记录、分析同步进行,操作更简便,界面会更友好,获得的实验数据会更准确。而且检测系统可实现多路径自动设置及声、光、电多种条件刺激,因此,可适用于复杂的认知记忆模型的建立。本发明尽量减少人工痕迹和人为干扰,提供给鼠足够的活动空间,建立一套新的鼠智能化行为检测系统。In the intelligent behavior detection system of the auditory and visual memory models of rats of the present invention, in addition to setting up the above-mentioned unique training model and the training strategy adapted thereto, popular Visual Studio programming components and Access database links are also used to replace the existing The C language and Foxpro database files used in the technology form an intelligent behavior detection system. The two groups of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements arranged on the side of each hole-shaped passage door, the controllable lighting in each area, and the strong light generating device, noise generating device and video tracking head installed in the control box on the upper part of the column Each data processing control unit composed of control components is concentrated on the data acquisition card. According to the experimental requirements, the corresponding signals are respectively collected and processed, which can be directly inserted into the microcomputer control system through the PCI data bus, and the detection range can be observed by the video tracking head. The dynamics of the experimental mice in the computer can operate multiple tasks at the same time, record and analyze simultaneously, the operation is easier, the interface will be more friendly, and the experimental data obtained will be more accurate. Moreover, the detection system can realize multi-path automatic setting and multiple conditional stimulations of sound, light and electricity, so it can be applied to the establishment of complex cognitive memory models. The invention minimizes artificial traces and human interference, provides enough space for the mice to move, and establishes a new intelligent behavior detection system for the mice.
该系统的建立可用于(1)用于研究动物空间定向及认知能力,如中枢神经系统神经元退行性改变的阿尔采默氏疾病(AD or presenile dementia)、帕金森病(parkinson’s disease)、癫痫(epilepsy)等鼠动物模型的建立。(2)检测神经药物或其它因素对动物学习、记忆和空间认知能力的影响,筛选促智药物。(3)可用于听觉、视觉特殊学习记忆模型的建立。(4)本系统路径复杂、可变,可提供筛选神经系统基因功能的行为学检测平台,如α-CaMKII(α-Calcium-CalmodulinKinase II)、Fyn和N-CAM(neural-cell adhesion molecules)等基因突变的空间学习记忆障碍小鼠、基因敲出(gene knock-out)、各种基因病的病因学及治疗学建立鼠的模型所需要。旨在从一个侧面研究神经系统的最复杂的高级功能,如学习、记忆等,从而为诊断和防治神经系统疾病,乃至改善神经系统遗传素质,发展计算和智能技术提供新构思和新概念。The establishment of this system can be used to (1) study the spatial orientation and cognitive ability of animals, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD or presenile dementia), Parkinson's disease (parkinson's disease), Establishment of mouse animal models such as epilepsy. (2) Detect the effects of neurological drugs or other factors on animal learning, memory and spatial cognition, and screen nootropic drugs. (3) It can be used in the establishment of auditory and visual special learning and memory models. (4) The path of this system is complex and variable, and can provide a behavioral detection platform for screening nervous system gene functions, such as α-CaMKII (α-Calcium-CalmodulinKinase II), Fyn and N-CAM (neural-cell adhesion molecules), etc. Spatial learning and memory impairment mice with genetic mutations, gene knock-out (gene knock-out), etiology and therapeutics of various genetic diseases are needed to establish mouse models. It aims to study the most complex advanced functions of the nervous system from one side, such as learning and memory, so as to provide new ideas and concepts for the diagnosis and prevention of nervous system diseases, and even improve the genetic quality of the nervous system, and the development of computing and intelligent technology.
附图说明Description of drawings
以下结合附图对本发明作进一步描述。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
图1是本发明的一种行为数据采集装置迷宫的具体结构示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the concrete structure of a labyrinth, a behavioral data collection device of the present invention.
图2是图1沿A-A线的剖视图。Fig. 2 is a sectional view along line A-A of Fig. 1 .
图3是本发明行为检测系统的一种采集门控电压信号的原理示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the principle of collecting a gating voltage signal of the behavior detection system of the present invention.
图4是本发明行为检测系统的一种采集控制电击刺激信号的原理示意图。Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the principle of collecting and controlling electric shock stimulation signals of the behavior detection system of the present invention.
图5是本发明行为检测系统的一种采集声刺激信号的原理示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the principle of collecting acoustic stimulation signals of the behavior detection system of the present invention.
图6是本发明行为检测系统的一种采集光刺激信号的原理示意图。Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram of the principle of collecting light stimulation signals of the behavior detection system of the present invention.
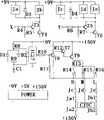
图中各序号说明:Explanation of each serial number in the figure:
1箱体、2铰链、3单向门、4立柱、5洞形通道、6栅栏、7光电元件、1 box, 2 hinges, 3 one-way doors, 4 columns, 5 hole-shaped passages, 6 fences, 7 photoelectric components,
8滑槽、9隔板、10控制箱、11滑槽、12上盖。8 chute, 9 partition, 10 control box, 11 chute, 12 upper cover.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
根据图1-6详细说明本发明的具体结构。实验鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型采用带有训练区、目的区及其连接通道的迷宫。该迷宫采用多通道闭合回路的圆形暗箱式迷宫(如图1-2所示),在其带有上盖12和栅栏底6的箱体1内,根据实验要求,通过箱体1内壁与中间立柱4的滑槽8、11按径向设置插装式分区隔板9,将箱体1内腔分隔成至少三个测试区,其中一个为目的区,其余为数据采集区。本实施例采用五个测试区,即一个目的区,四个数据采集区。在所设的五个测试区中,I区、II区、III区为实验鼠通行路径信号采集区,IV区为返回信号采集区,V区为诱饵区和进入I区数据采集区的信号区。每个隔板9底部等间距分布外观相同的带有可调式单向门3的洞形通道5,根据实验鼠规格大、小在不同规格的插装式分区隔板9底部设置相应的大、小洞形通道5,以消除由于实验鼠月龄不同而体积大小不一致,对实验结果准确性的干扰,扩大训练模型的应用范围。每个洞形通道5门侧置有两组红外发射、接收光电元件7。其中单向门3采用铰链2连接的活动门结构,也可采用其它连接结构形式,单向门3的形状、大小应根据洞形通道5的规格要求确定。本实施例根据实验需要在每个控制区设置四个洞形通道5,每个控制区的绿色通道(实验鼠通过路径所选择的指定通道)有4种变化,实验鼠由I区到IV区的绿色通道可有多种变化,以实现到达不同区域通道灵活多变的需要。本实施例返回区的洞形通道5根据实际需要选择,只开通两个通道。被隔离的各区内分别设置可控灯光照明,针对鼠的自然活动模式趋暗习性控制光照,仅实验鼠所在区有光照(25W),各区的栅栏底6分别设置随机控制的产生不同梯度电压带的电击导体(图中未示出)。为便于梯度电压带的控制,I~IV区都分别设置为45V、40V、35V三个梯度电压带。每区的绿色通道随机变换,非绿色通道则可给予声(90dB),光(100W),电(50~60V)等条件刺激,以动物产生逃避行为为准。在箱体1中间立柱4上部控制箱10内设置强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头(图中未示出)。为更好地发挥强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头的作用,将插装式分区隔板9的上端面设计成内低外高的形式,低端插装在中间立柱4外周的竖向滑槽11内,高端插装在箱体1内壁的与中间立柱滑槽11相对应的滑槽8内。The specific structure of the present invention will be described in detail according to Figs. 1-6. The auditory and visual memory model of experimental rats adopts a maze with a training area, a target area and its connecting passages. The labyrinth adopts a multi-channel closed-loop circular obscura labyrinth (as shown in Figure 1-2). In the box body 1 with the
将上述设计独特的听觉、视觉记忆模型作为鼠的行为学检测平台,建立一套新的动物智能化行为检测系统。该系统包括行为数据采集装置、数据处理控制单元、PCI数据总线和微机控制系统。其中行为数据采集装置采用上述圆形暗箱式迷宫作为鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型。进行训练时,让实验鼠在该迷宫的箱体1内,通过按径向设置的插装式分区隔板9底部的带有可调式单向门3的洞形通道5,沿指定的顺时针路径通过训练区、目的区所形成的闭合回路,完成依次循环训练,变换单向门3的通行方向也可指定逆时针路径。在指定路径通过训练的基础上,重复该训练方法还可以进行多路径选择训练。在此期间,利用所述分别设置在被隔离的各区内的可控灯光照明来适应鼠的趋暗习性,使其在箱体1内进行自主运动,利用所述分别设置在各区栅栏6底的电击导体产生的不同梯度电压带,以电击刺激进行驱动来随机控制鼠的被动运动,再结合该系统中集成在数据采集卡上的设置在每个洞形通道5门侧置的两组红外发射、接收光电元件7、各区内的可控灯光照明的数据处理控制单元,设置在立柱4上部控制箱10内的强光发生装置、噪音发生装置和视频跟踪头的数据处理控制单元,根据实验要求,将分别采集到的实验鼠适应活动时的路径、成功所需的次数、各次的时间、成功前出现错误的位置、次数诸数据,所形成的通道门的电压信号、控制电击刺激信号、声刺激信号及光刺激信号,经过由CMOS集成元件组成的逻辑电路取得所需的信号,连同显示器观察到的视频跟踪头采集的图像,通过PCI数据总线传输到微机控制系统中的Access数据库,并利用SAS统计软件包进行处理,随时控制和全程监测鼠的听觉、视觉记忆活动行为。Using the above-mentioned uniquely designed auditory and visual memory models as the behavioral detection platform of mice, a new set of animal intelligent behavior detection system is established. The system includes a behavioral data acquisition device, a data processing control unit, a PCI data bus and a microcomputer control system. Wherein the behavioral data acquisition device adopts the above-mentioned circular box-in-the-dark maze as the auditory and visual memory models of the rats. When training, let the experimental rats pass through the hole-shaped channel 5 with the adjustable one-
本发明的检测系统把圆形暗箱式迷宫作为行为数据采集装置,并结合鼠的生活习性,充分利用鼠趋暗习性的自主运动和梯度电压被动驱动,借助阻隔和电击、声、光刺激等单一或组合的惩罚方式,让动物识别较复杂的通行路径,从整体上力图主要反映动物的听觉及视觉辨别能力,开发较为复杂的训练模型,以满足更深入的分析动物学习记忆行为的需要。使研制的动物行为训练方法及检测系统既简单,又能反应智力水平,既有模型的一般特点,又要接近生活原样,模拟正常生活环境,有效消除检测时对数据采集、分析处理过程中的干扰,使该检测系统实现自动化、准确化、科学化,确保不同模型的建立都有相应的动物训练方法和数据选取策略。The detection system of the present invention uses a circular black box labyrinth as a behavioral data acquisition device, and combines the living habits of the mouse, fully utilizes the autonomous movement of the dark habit of the mouse and the passive drive of the gradient voltage, with the help of barriers and electric shocks, sound, and light stimulation. Or a combination of punishment methods, allowing animals to recognize more complex passages, trying to reflect the auditory and visual discrimination abilities of animals as a whole, and developing more complex training models to meet the needs of more in-depth analysis of animal learning and memory behavior. The developed animal behavior training method and detection system are both simple and able to reflect the level of intelligence, not only have the general characteristics of the model, but also be close to the original life, simulating the normal living environment, and effectively eliminate the need for data collection, analysis and processing during detection. Interference makes the detection system automatic, accurate, and scientific, and ensures that the establishment of different models has corresponding animal training methods and data selection strategies.
系统的软件编辑,采用通用的WindowsXP作为开发平台,选用流行的Visual Studio程序设计组件和Access数据库链接取代现有技术中的C语言和Foxpro数据库文件作为开发工具,通过集中在数据采集卡上的各数据处理控制单元,根据实验要求(条件刺激,定时,路径,数据采集),来完成对实验仪器的设置,以其能直接对硬件端口操作的特点,完成信号的采集,处理和对实验仪器的控制。数据采集时首先检测参数设置的正确性,采集过程中系统的软件根据采集的数据反馈控制仪器,动态显示鼠的位置,保留实验参数,记录实验结果,并对实验结果进行统计分析。因此,本发明不仅能实时、准确地检测动物对变化情况的应变能力,而且还可以随时控制和全程监测鼠的听觉、视觉记忆活动行为。The software editing of the system adopts the common WindowsXP as the development platform, selects the popular Visual Studio programming components and the Access database link to replace the C language and Foxpro database files in the prior art as the development tools, and uses various components concentrated on the data acquisition card The data processing control unit completes the setting of the experimental instrument according to the experimental requirements (conditional stimulus, timing, path, data acquisition), and completes the signal acquisition, processing and control of the experimental instrument due to its ability to directly operate on the hardware port. control. During the data collection, the correctness of the parameter settings is first checked. During the collection process, the system software controls the instrument according to the collected data feedback, dynamically displays the mouse's position, saves the experimental parameters, records the experimental results, and performs statistical analysis on the experimental results. Therefore, the present invention can not only detect the adaptability of animals to changing situations in real time and accurately, but also can control and monitor the auditory and visual memory activities of mice at any time.
以下结合具体的听觉、视觉记忆方法,进一步说明实验鼠的听觉、视觉记忆模型的智能化行为检测系统对数据的采集和处理的策略。Combined with specific auditory and visual memory methods, the strategies for collecting and processing data by the intelligent behavior detection system of the auditory and visual memory models of experimental mice will be further described below.
1、指定路径通过训练1. Specify the path to pass the training
采用实验鼠自主运动和梯度电压被动驱动相结合的训练方法,使其按指定的路径通过,以避免受单一电击后,远离绿色通道,达到反映动物对固定的复杂空间的听觉及视觉辨别能力的目的。The training method of combining autonomous movement of experimental mice and passive drive of gradient voltage is used to make them pass through the designated path, so as to avoid a single electric shock and stay away from the green channel, so as to reflect the auditory and visual discrimination ability of animals in a fixed complex space. Purpose.
训练前,实验鼠禁食、供水24小时或正常进食。训练时,先让其在圆形暗箱式迷宫中适应30-60s,此时迷宫中所有的通道开放,自由活动。据前期实验观察,实验鼠会在迷宫中不停的跑动,一般会访问所有的区域,随后停于某处。实验开始时,将实验鼠放入V区(作为适应区),使其适应环境1min,对于禁食24h的实验鼠,可任意选择指定路径,受食物诱惑,一般会访问I区所有的区域,随后选择一个通道通过。如果是非绿色通道,实验鼠则会受到电击等刺激。对于未禁食的实验鼠和个别禁食的实验鼠需采用其所在区有光照,而下一个区黑暗,使实验鼠自主运动,必要时结合梯度电压电击,以促使其尽快通过绿色或非绿色通道。如访问无关路段,停留超过2s,则通电惩罚。动物依次通过各区,至V区的诱饵处进食3s后,由定时器控制的食物槽将自动移开。各区之间为顺时针或逆时针单向通道,实验鼠自动进入I区开始下一循环训练。如此循环5~6次后,动物会迅速离开I区进入V区。此即视为训练初步成功。达到学会的标准拟定为连续10次测试中有9次完成全程耗时<5.5min。Before training, the experimental rats were fasted and supplied with water for 24 hours or ate normally. During training, first let it adapt to the circular obscura maze for 30-60 seconds, at this time all the passages in the maze are open, and they can move freely. According to previous experimental observations, the experimental rats will keep running in the maze, usually visit all the areas, and then stop somewhere. At the beginning of the experiment, put the experimental mice into the V area (as an adaptation area) to adapt to the environment for 1 minute. For the experimental mice that have fasted for 24 hours, they can choose the designated path arbitrarily. Tempted by food, they will generally visit all the areas in the I area. Then select a channel to pass through. If it is a non-green channel, the experimental mice will receive electric shocks and other stimuli. For non-fasting experimental mice and individual fasting experimental mice, it is necessary to use light in the area where they are located, while the next area is dark, so that the experimental mice can move autonomously, and if necessary, combine gradient voltage electric shocks to encourage them to pass through green or non-green as soon as possible. aisle. If you visit an irrelevant road section and stay for more than 2 seconds, you will be punished by powering on. Animals pass through each area in turn, and after eating at the bait in area V for 3 seconds, the food trough controlled by the timer will automatically move away. There is a clockwise or counterclockwise one-way passage between each area, and the experimental rats automatically enter the I area to start the next cycle training. After 5-6 cycles like this, the animals will quickly leave the I area and enter the V area. This is regarded as the initial success of the training. To reach the standard of the society, it is proposed that 9 out of 10 consecutive tests take less than 5.5 minutes to complete the whole process.
数据采集:①适应活动时的路径;②初步成功所需的次数、各次的时间;③初步成功前出现错误的位置、次数和电击的次数。Data collection: ①The path when adapting to the activity; ②The number of times required for initial success and the time of each time; ③The location, number of errors and the number of electric shocks before initial success.
2、多路径选择训练2. Multi-path selection training
在指定通过训练的基础上,再进入V区之前,在多条可选择的路径中随机提供一条可通行的路径,重复上述训练方法,每只鼠每天训练一条路径,连续5天,每天训练10次。特点:可达到反映实验鼠对变化情况的应变能力的目的。On the basis of passing the training, before entering the V area, a passable path is randomly provided among multiple optional paths, and the above training method is repeated. Each mouse trains a path every day for 5 consecutive days, and trains 10 times a day. Second-rate. Features: It can achieve the purpose of reflecting the adaptability of experimental mice to changing situations.
数据采集:①适应每条可通行路径所需的次数、时间。②每次训练通过可通行路径的通道正确选择次数,错误次数。Data collection: ① Adapt to the number of times and time required for each passable path. ② The number of correct selections and the number of wrong times through the passage of the passable path for each training.
3、食物控制和听觉、视觉刺激训练3. Food control and auditory and visual stimulation training
利用迷宫,通过听觉、视觉刺激和食物强化,训练实验鼠的听觉、视觉辨别学习。所有经过指定路径通过、多路径路选择训练的实验鼠在清洁级动物实验室内饲养,并控制照明条件(每天24小时照明或暗室内避光)。适应期为5天,期间所有实验鼠自由饮食、水,并监测体重变化。第6天开始控制实验鼠进食量,使其体重降为正常的85%,进食控制持续至实验结束。第9天开始进入2天的训练前期,即实验鼠被置于迷宫内自由行走,通道左右两侧的灯光均亮,当它进入下一侧,无论错误与否都给予一粒食物奖励,目的是使实验鼠熟悉迷宫并能主动觅食。第11天开始正式的训练,首先是所有实验鼠的正常视觉辨别学习,实验鼠被任意置于V区中,此为起始区,待实验鼠正确进入某一区后,该区的灯亮(25W),而下一区则为暗区。如果实验鼠进入绿色通道,则记为正确,给予一粒食物奖励;如果进入非绿色通道,则记为错误,无食物奖励,根据实验要求,而给予强光(100W,1s)或噪音(90dB,1s)刺激。当实验鼠进入迷宫V区,即作为下一次训练的起始。实验鼠每天进行6次训练,当动物连续2天的正确次数达到90%以上时,则达到了正常学习的标准。检测系统对数据采集和处理的具体工作原理如下:Using a maze, through auditory, visual stimulation and food reinforcement, the experimental rats are trained to learn auditory and visual discrimination. All the experimental rats who have passed through the specified path and multi-path path selection training were raised in a clean animal laboratory, and the lighting conditions were controlled (24 hours of lighting every day or dark room to avoid light). The adaptation period was 5 days, during which all experimental mice had free access to food and water, and body weight changes were monitored. On the 6th day, the food intake of the experimental mice was controlled to reduce their body weight to 85% of normal, and the food intake control continued until the end of the experiment. On the 9th day, it entered the pre-training period of 2 days, that is, the experimental rat was placed in the maze to walk freely, the lights on the left and right sides of the passage were bright, and when it entered the next side, it was rewarded with a grain of food regardless of whether it was wrong or not. It is to make the experimental mice familiar with the maze and actively seek food. Formal training began on the 11th day. At first, it was the normal visual discrimination learning of all experimental mice. The experimental mice were randomly placed in the V area, which was the starting area. After the experimental mice entered a certain area correctly, the lights in this area were on ( 25W), and the next area is a dark area. If the experimental rat enters the green channel, it is recorded as correct and a food reward is given; if it enters the non-green channel, it is recorded as an error and there is no food reward. According to the experimental requirements, strong light (100W, 1s) or noise (90dB) is given. , 1s) stimulus. When the experimental rat enters the V area of the maze, it is the start of the next training session. The experimental rats were trained 6 times a day, and when the correct number of times reached more than 90% for 2 consecutive days, the standard of normal learning was reached. The specific working principle of the detection system for data collection and processing is as follows:
1、数据采集部分-取得准确的实验鼠通过通道的电压信号1. Data acquisition part - to obtain accurate voltage signals of experimental mice passing through the channel
由图1~3可知,在圆形暗箱式迷宫中所设的五个测试区中,每个控制区绿色通道有4种变化,实验鼠由I区到IV区绿色通道可有64种变化。实现了到达不同区域通道灵活多变的需要。由IC1-1C4(与非门CD4011)组成的振荡信号(振荡频率可调)经过T1、T2功率放大后提供给发射电路,接收电路经过电阻R分压与红外发射接收管FJ(每个通道门上安装的两组红外发射、接收光电元件)连接,这样就能采集到开关电压信号,经过整型电路整型从而获得标准的电压控制信号。为了避免由于实验鼠尾巴的“隔时”触发带来的信号采集错误,所以在每个通道门上安装了两组红外发射、接收光电元件,将每组红外发射、接收光电元件分别获得的电压信号经门电路IC5-IC26逻辑处理,从而消除上述误差。It can be seen from Figures 1 to 3 that among the five test areas set up in the circular obscura maze, there are 4 changes in the green channel in each control area, and there are 64 changes in the green channel of the experimental mice from area I to area IV. It realizes the flexible and changeable access to different areas. The oscillating signal (adjustable oscillating frequency) composed of IC1-1C4 (NAND gate CD4011) is supplied to the transmitting circuit after being amplified by T1 and T2, and the receiving circuit is divided by resistor R and infrared transmitting and receiving tube FJ (each channel gate The two sets of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements installed on it are connected, so that the switch voltage signal can be collected, and the standard voltage control signal can be obtained through the shaping circuit. In order to avoid the signal acquisition error caused by the "time-lapse" trigger of the tail of the experimental rat, two sets of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements are installed on each channel door, and the voltage obtained by each group of infrared emitting and receiving photoelectric elements is respectively The signal is processed logically by the gate circuit IC5-IC26, thereby eliminating the above-mentioned errors.
2、编码电路部分2. Encoding circuit part
将采集到的通道门的电压信号经过由CMOS集成元件组成的逻辑电路取得所需的信号。每个区所获得的门控电压信号经过“或非门IC5-IC18(CD4001)”求出所需信号。I、II两区取得的过门信号为1y1、1y2、1y3、1y4。然后,将1y1、1y2、1y3、1y4经过门电路IC19(4输入或门CD4072)求或后得到信号1F,即1F=1y1+1y2+1y3+1y4。同理,用IC20(CD4072)取得II、III区的过门信号求得2F,即2F=2y1+2y2+2y3+2y4。用IC21(CD4072)取得III、IV区及返回区的过门信号求得3F,即3F=3y1+3y2+3y3+3y4+G1+G2,其中G1、G2为返回区获得的信号。然后,将1F、2F、3F经过IC22(3输入或非门CD4075)求或得信号F,F=1F+2F+3F。将所取得的信号输入双4选1数据选择器IC23(SL253),上述过门信号按组3Y1,2Y1,1Y1;3Y2,2Y2,1Y2;3Y3,2Y3,1Y3;3Y4,2Y4,1Y4分别输入IC24~IC26(双4选1选择器LS253)。选择控制输出信号由计算机的PCI口获得,由软件控制,从双4选1选择器的数据输出端取得数据信号,经PCI数据总线输入计算机,经软件处理后判定区号、通道号及是否绿色通道等分析处理后,将每区尝试失败次数存到文档中,同时发出定时信号(PCI口)、非绿色门刺激信号(PCI口)等控制信号。The collected voltage signal of the channel gate is passed through a logic circuit composed of CMOS integrated components to obtain the required signal. The gate control voltage signal obtained by each area passes through "NOR gate IC5-IC18 (CD4001)" to obtain the required signal. The pass signals obtained in the I and II areas are 1y1, 1y2, 1y3, and 1y4. Then, 1y1, 1y2, 1y3, and 1y4 are ORed through gate circuit IC19 (4-input OR gate CD4072) to obtain
3、控制、刺激电路部分3. Control and stimulation circuit part
在圆形暗箱式迷宫底部安装的刺激电极(正、负电极相间),负极安装在通道门反面挡板的附铜板上,正极安装在门的底部,刺激输出大小由电脑元件连续控制。为防止实验鼠长时间不动,该迷宫底部可由电机带动旋转机构驱动或进行电刺激来驱赶实验鼠进入下一区。由软件控制实现对刺激电路实行定时控制(定时时间由人、机界面设定),计算机打印端口发出的定时信号(高电平有效)经推动电路控制继电器的常开触点,推动电路为复合管推动电路。实验鼠欲通过非绿色通道时将受到较强的电刺激,为了使实验鼠在通过设定的绿色通道时不受电刺激,计算机实时发出控制刺激信号。同时为了奖励实验鼠进入下一区,每当实验鼠进入返回区时,放诱饵的装置(直流电机带动)给出定时时间对实验鼠进行奖励,奖励结束后,撤走诱饵开始电刺激。即每当实验鼠进入第IV区时,让实验鼠吃到食物奖励,定时结束后诱饵自动收回。之后实验鼠在梯度电压的驱赶下,通过返回区回到第I区,重复上述实验。当取得此种指定路径通过的实验数据后,由人、机界面设定下一次的指定路径通过,以此类推。实验数据只需查阅文档即可。Stimulating electrodes (positive and negative electrodes alternate) are installed at the bottom of the circular obscura maze. The negative electrode is installed on the copper plate attached to the back baffle of the channel door, and the positive electrode is installed at the bottom of the door. The size of the stimulation output is continuously controlled by computer components. In order to prevent the experimental mice from moving for a long time, the bottom of the maze can be driven by a motor to drive the rotating mechanism or electrically stimulated to drive the experimental mice into the next area. The timing control of the stimulation circuit is realized by software control (the timing time is set by the man-machine interface), and the timing signal (high level active) sent by the computer print port is controlled by the push circuit to control the normally open contact of the relay, and the push circuit is a composite Tube drive circuit. The experimental mice will receive strong electrical stimulation when they want to pass through the non-green channel. In order to prevent the experimental mice from being electrically stimulated when they pass through the set green channel, the computer sends out control stimulation signals in real time. At the same time, in order to reward the experimental mice to enter the next area, whenever the experimental mice enter the return area, the device (driven by DC motor) that puts the bait gives a regular time to reward the experimental mice. After the reward is over, the bait is removed to start electrical stimulation. That is, whenever the experimental mice enter the IV area, let the experimental mice eat food rewards, and the bait will be automatically withdrawn after the timer ends. Afterwards, under the drive of the gradient voltage, the experimental mice returned to the first zone through the return zone, and the above experiment was repeated. After obtaining the experimental data of passing through the specified path, the next time passing through the specified path is set by the man-machine interface, and so on. Experimental data only needs to be consulted in the documentation.
电刺激电路如图4:定时信号X由PCI总线发出,使T3、T4导通,Ja、Jb导通,继电器常开触点Ja1、Jb1导通。非绿色通道刺激信号Y由PCI总线发出,使继电器常开触点Jc、Jd、Te导通从而获得梯度电压刺激。The electrical stimulation circuit is shown in Figure 4: the timing signal X is sent out by the PCI bus, which makes T3 and T4 conduction, Ja and Jb conduction, and the relay normally open contacts Ja1 and Jb1 conduction. The non-green channel stimulation signal Y is sent by the PCI bus, which makes the normally open contacts Jc, Jd, and Te of the relay conduct to obtain gradient voltage stimulation.
光刺激电路如图5:非绿色通道刺激信号Y由PCI总线发出使继电器工作,Jg常开触点Jg1导通白炽,灯(100W)L1发光,从而获得光刺激。The light stimulation circuit is shown in Figure 5: the non-green channel stimulation signal Y is sent by the PCI bus to make the relay work, the Jg normally open contact Jg1 turns on the incandescent light, and the lamp (100W) L1 emits light, thereby obtaining light stimulation.
声刺激电路如图6:非绿色通道刺激信号Z由PCI总线发出使继电器Jf工作,常开触点Jf1导通,集成音乐电路MU工作,使扬声器P发出模拟猫声响,从而获得声刺激。The sound stimulation circuit is shown in Figure 6: the non-green channel stimulation signal Z is sent by the PCI bus to make the relay Jf work, the normally open contact Jf1 is turned on, and the integrated music circuit MU works to make the speaker P emit a simulated cat sound, thereby obtaining sound stimulation.
4、电源电路部分:4. Power circuit part:
电源电路提供各电路所需的工作电压值。市电经过降压变压器提供五组独立交流电压输出,分别经整流、滤波后经三端集成稳压块(7805、7809)稳压,输出+5V提供给集成组件控制元件,+9V电压提供给红外发射、接收电路(7809采用F-2封装)其余三组由三端可调稳压器LM317提供给刺激电路。The power supply circuit provides the operating voltage value required by each circuit. The utility power provides five sets of independent AC voltage outputs through step-down transformers, which are respectively rectified and filtered and stabilized by three-terminal integrated voltage regulator blocks (7805, 7809). Infrared transmitting and receiving circuits (7809 adopts F-2 package) and the remaining three groups are provided to the stimulation circuit by the three-terminal adjustable voltage regulator LM317.
图中的其它元件:IC27采用HA17555,T1~T13采用三极管3DG6,D1~D6采用普通二极管,R1~R22采用匹配电阻,R采用等值电阻,红外发射接收管FJ采用TCRT5000。Other components in the figure: IC27 uses HA17555, T1~T13 uses triode 3DG6, D1~D6 uses ordinary diodes, R1~R22 uses matching resistors, R uses equivalent resistance, and infrared transmitting and receiving tube FJ uses TCRT5000.
Claims (3)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2006100458689ACN100471465C (en) | 2006-02-21 | 2006-02-21 | Auditory and Visual Memory Models and Intelligent Behavior Detection System of Rats |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2006100458689ACN100471465C (en) | 2006-02-21 | 2006-02-21 | Auditory and Visual Memory Models and Intelligent Behavior Detection System of Rats |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1817325Atrue CN1817325A (en) | 2006-08-16 |
| CN100471465C CN100471465C (en) | 2009-03-25 |
Family
ID=36917656
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB2006100458689AExpired - Fee RelatedCN100471465C (en) | 2006-02-21 | 2006-02-21 | Auditory and Visual Memory Models and Intelligent Behavior Detection System of Rats |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN100471465C (en) |
Cited By (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100588367C (en)* | 2008-04-23 | 2010-02-10 | 中国科学技术大学 | Ring platform for testing the learning and memory ability of mice and its control method |
| CN101779601A (en)* | 2010-03-11 | 2010-07-21 | 复旦大学 | Rat/mouse labyrinth automatic training device |
| CN101214168B (en)* | 2007-12-28 | 2010-08-11 | 上海移数信息科技有限公司 | Animal behavior monitoring and analyzing system |
| CN102057873A (en)* | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-18 | 陈同 | White mouse tester |
| CN101828529B (en)* | 2010-01-29 | 2011-12-28 | 中国科学院武汉物理与数学研究所 | Rat dual-visual cue-training and detecting experimental system |
| CN102314779A (en)* | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-11 | 上海科技馆 | Poultry embryo growth-to-hatching process demonstration device and demonstration method thereof |
| CN102577996A (en)* | 2012-03-14 | 2012-07-18 | 浙江大学城市学院 | Noise Y labyrinth device |
| WO2012119322A1 (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | 沈阳医学院 | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system |
| WO2012119321A1 (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | 沈阳医学院 | Animal memory training system with closed rotary maze |
| CN102687676A (en)* | 2012-01-14 | 2012-09-26 | 河南科技大学 | Labyrinth based on color identifying information and animal experiment method |
| CN102972309A (en)* | 2012-08-15 | 2013-03-20 | 昆明医科大学 | Improved Y-arm electronic maze experimental device |
| CN103445788A (en)* | 2013-09-06 | 2013-12-18 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Behavioristics monitoring device and behavioristics monitoring system |
| CN103828733A (en)* | 2014-01-27 | 2014-06-04 | 中国科学院生物物理研究所 | Animal stimulation system and method |
| CN104381141A (en)* | 2014-11-12 | 2015-03-04 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal behavior test system and method |
| CN105393926A (en)* | 2015-12-16 | 2016-03-16 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院毒物药物研究所 | Non-human primate animal self-drug delivery system operation box |
| CN105467107A (en)* | 2015-12-15 | 2016-04-06 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Analysis system |
| CN106135054A (en)* | 2016-07-13 | 2016-11-23 | 陕西师范大学 | A kind of chicken environment Preference choice experiment case |
| CN106508714A (en)* | 2016-10-25 | 2017-03-22 | 郑州大学 | Animal object target recognizing learning training system |
| CN106665401A (en)* | 2016-12-14 | 2017-05-17 | 陆振中 | Physical training device for police dogs |
| CN107372309A (en)* | 2017-07-28 | 2017-11-24 | 安庆师范大学 | Amphibian animal behavioural characteristic test device and its application method |
| CN107423821A (en)* | 2017-07-11 | 2017-12-01 | 李家宝 | The intelligence system of human and animal's interaction |
| CN108029581A (en)* | 2017-11-23 | 2018-05-15 | 浙江大学 | A kind of auto-teaching system that behavior is differentiated for the rat sense of hearing |
| CN108289434A (en)* | 2015-07-24 | 2018-07-17 | 蒙彼利埃大学 | Instrumentation for Characterizing the Ability of a Mouse to Orient Itself |
| CN108665768A (en)* | 2018-04-27 | 2018-10-16 | 江苏苏威尔科技有限公司 | A kind of tester of influence of the research abiotic factor to pillworm |
| CN110833047A (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2020-02-25 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal visual space cognitive memory behavioristics experimental device and experimental method |
| CN110839558A (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2020-02-28 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal auditory association matching behavioristics experimental device and experimental method |
| CN111657172A (en)* | 2020-07-14 | 2020-09-15 | 中国人民解放军空军军医大学 | A kind of constant temperature flow pool for swimming exercise training of rodents and using method thereof |
| CN111568429B (en)* | 2020-04-14 | 2021-05-11 | 清华大学 | Virtual reality system and method for animal experiment |
| CN112790114A (en)* | 2021-04-04 | 2021-05-14 | 中国人民解放军第二军医大学 | Experimental device system for giving stress stimulation to rodents |
| CN113796335A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2021-12-17 | 五邑大学 | Control method, device and equipment of mouse behavior training system and storage medium |
| CN115500280A (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2022-12-23 | 中国科学技术大学 | Infrared visual resolution behavioristics detection method and device |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102119670B (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-10-03 | 沈阳医学院 | Automated mechanical arm stimulating device for animal memory training system |
| CN102160527B (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-11-28 | 沈阳医学院 | Intelligent wireless remote control simulation device used for animal memory training system |
- 2006
- 2006-02-21CNCNB2006100458689Apatent/CN100471465C/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Cited By (45)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101214168B (en)* | 2007-12-28 | 2010-08-11 | 上海移数信息科技有限公司 | Animal behavior monitoring and analyzing system |
| CN100588367C (en)* | 2008-04-23 | 2010-02-10 | 中国科学技术大学 | Ring platform for testing the learning and memory ability of mice and its control method |
| CN102057873A (en)* | 2009-11-17 | 2011-05-18 | 陈同 | White mouse tester |
| CN101828529B (en)* | 2010-01-29 | 2011-12-28 | 中国科学院武汉物理与数学研究所 | Rat dual-visual cue-training and detecting experimental system |
| CN101779601A (en)* | 2010-03-11 | 2010-07-21 | 复旦大学 | Rat/mouse labyrinth automatic training device |
| CN102314779A (en)* | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-11 | 上海科技馆 | Poultry embryo growth-to-hatching process demonstration device and demonstration method thereof |
| US8726842B2 (en) | 2011-03-07 | 2014-05-20 | Shenyang Medical College | Animal memory training system with closed rotary maze |
| WO2012119322A1 (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | 沈阳医学院 | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system |
| WO2012119321A1 (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2012-09-13 | 沈阳医学院 | Animal memory training system with closed rotary maze |
| GB2498685B (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2015-06-10 | Shenyang Medical College | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system |
| GB2498685A (en)* | 2011-03-07 | 2013-07-24 | Shenyang Medical College | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system |
| CN102687676A (en)* | 2012-01-14 | 2012-09-26 | 河南科技大学 | Labyrinth based on color identifying information and animal experiment method |
| CN102577996B (en)* | 2012-03-14 | 2013-08-14 | 浙江大学城市学院 | Noise Y labyrinth device |
| CN102577996A (en)* | 2012-03-14 | 2012-07-18 | 浙江大学城市学院 | Noise Y labyrinth device |
| CN102972309A (en)* | 2012-08-15 | 2013-03-20 | 昆明医科大学 | Improved Y-arm electronic maze experimental device |
| CN103445788A (en)* | 2013-09-06 | 2013-12-18 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Behavioristics monitoring device and behavioristics monitoring system |
| CN103445788B (en)* | 2013-09-06 | 2015-07-08 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Behavioral monitoring device and behavioral monitoring system |
| CN103828733A (en)* | 2014-01-27 | 2014-06-04 | 中国科学院生物物理研究所 | Animal stimulation system and method |
| CN103828733B (en)* | 2014-01-27 | 2016-04-20 | 中国科学院生物物理研究所 | Animal stimulation system |
| CN104381141A (en)* | 2014-11-12 | 2015-03-04 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal behavior test system and method |
| CN108289434B (en)* | 2015-07-24 | 2021-03-09 | 蒙彼利埃大学 | Instrumented device for characterizing the ability of a mouse to orient itself |
| CN108289434A (en)* | 2015-07-24 | 2018-07-17 | 蒙彼利埃大学 | Instrumentation for Characterizing the Ability of a Mouse to Orient Itself |
| CN105467107A (en)* | 2015-12-15 | 2016-04-06 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Analysis system |
| CN105393926B (en)* | 2015-12-16 | 2018-02-06 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院毒物药物研究所 | Non-human primate self administration system operatio case |
| CN105393926A (en)* | 2015-12-16 | 2016-03-16 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院毒物药物研究所 | Non-human primate animal self-drug delivery system operation box |
| CN106135054A (en)* | 2016-07-13 | 2016-11-23 | 陕西师范大学 | A kind of chicken environment Preference choice experiment case |
| CN106508714A (en)* | 2016-10-25 | 2017-03-22 | 郑州大学 | Animal object target recognizing learning training system |
| CN106508714B (en)* | 2016-10-25 | 2019-04-05 | 郑州大学 | Animal material object target identification learning training system |
| CN106665401A (en)* | 2016-12-14 | 2017-05-17 | 陆振中 | Physical training device for police dogs |
| CN107423821A (en)* | 2017-07-11 | 2017-12-01 | 李家宝 | The intelligence system of human and animal's interaction |
| CN107372309A (en)* | 2017-07-28 | 2017-11-24 | 安庆师范大学 | Amphibian animal behavioural characteristic test device and its application method |
| CN107372309B (en)* | 2017-07-28 | 2023-07-18 | 湖南人文科技学院 | Amphibian Behavioral Characteristics Testing Device and Using Method |
| CN108029581A (en)* | 2017-11-23 | 2018-05-15 | 浙江大学 | A kind of auto-teaching system that behavior is differentiated for the rat sense of hearing |
| CN108029581B (en)* | 2017-11-23 | 2020-02-21 | 浙江大学 | An automatic training system for auditory discrimination of rats |
| CN108665768A (en)* | 2018-04-27 | 2018-10-16 | 江苏苏威尔科技有限公司 | A kind of tester of influence of the research abiotic factor to pillworm |
| CN110839558A (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2020-02-28 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal auditory association matching behavioristics experimental device and experimental method |
| WO2021098655A1 (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2021-05-27 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Ethological experimentation device for animal auditory association and matching, and experimentation method |
| CN110839558B (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2021-07-06 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | A behavioral experimental device and experimental method for animal auditory association matching |
| CN110833047A (en)* | 2019-11-19 | 2020-02-25 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Animal visual space cognitive memory behavioristics experimental device and experimental method |
| CN111568429B (en)* | 2020-04-14 | 2021-05-11 | 清华大学 | Virtual reality system and method for animal experiment |
| CN111657172A (en)* | 2020-07-14 | 2020-09-15 | 中国人民解放军空军军医大学 | A kind of constant temperature flow pool for swimming exercise training of rodents and using method thereof |
| CN112790114A (en)* | 2021-04-04 | 2021-05-14 | 中国人民解放军第二军医大学 | Experimental device system for giving stress stimulation to rodents |
| CN112790114B (en)* | 2021-04-04 | 2022-11-01 | 中国人民解放军第二军医大学 | Experimental device system for giving stress stimulation to rodents |
| CN113796335A (en)* | 2021-08-26 | 2021-12-17 | 五邑大学 | Control method, device and equipment of mouse behavior training system and storage medium |
| CN115500280A (en)* | 2022-10-11 | 2022-12-23 | 中国科学技术大学 | Infrared visual resolution behavioristics detection method and device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN100471465C (en) | 2009-03-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1817325A (en) | Mouse hearing and vision memory model and intelligent action inspecting system | |
| CN100471466C (en) | An Intelligent Behavioral Detection System of the Spatial Memory Retention Model in Rats | |
| CN100477970C (en) | Mouse path exercising model and intelligent action inspecting system | |
| CN108633771B (en) | EEG synchronous learning and training system for animal groups | |
| WO2012119321A1 (en) | Animal memory training system with closed rotary maze | |
| WO2012119322A1 (en) | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system | |
| CN103026973B (en) | Award property operant conditioning reflex tests and analyzes processing unit in real time | |
| Myers | Methods in Psychobiology: Specialized laboratory techniques in neuropsychology and neurobiology | |
| Fenrich et al. | Improved single pellet grasping using automated ad libitum full-time training robot | |
| US20170332602A1 (en) | Systems and methods for behavioral and task training of laboratory animals | |
| CN105165661A (en) | Double-layer semi-closed automatic cross-shaped labyrinth for pigeons | |
| CN112535115B (en) | Behavior training device and method for researching rat risk choice | |
| CN201967488U (en) | Closed rotary maze device for animal memory training system | |
| CN102499105A (en) | Method for building a water maze spatial learning and memory model for tree shrews | |
| CN213343917U (en) | Sleep deprivation device suitable for rodent | |
| Cook et al. | Touchscreen-enhanced visual learning in rats | |
| WO2012119323A1 (en) | Automatic mechanical arm stimulating device for animal memory training system | |
| Bozis et al. | Neural network simulations of the primate oculomotor system III. An one-dimensional, one-directional model of the superior colliculus | |
| CN106889022A (en) | Rat risk chooses the training method of behavior | |
| Matell et al. | Temporal memory averaging and post-encoding alterations in temporal expectation | |
| CN206895531U (en) | Rodent cognitive ability towards drug law enforcement anti-terrorism examines detection ecological experiment cabin | |
| Graham et al. | Neurobehavioral testing for developmental toxicity | |
| CN115191363A (en) | A joint motion testing system and testing method for experimental animals | |
| CN214758571U (en) | Cognitive movement dual task training device | |
| Bian et al. | Automated sleep deprivation setup using a shaking platform in mice |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20090325 Termination date:20120221 |