CN1780591A - Method and device for treating patent foramen ovale - Google Patents
Method and device for treating patent foramen ovaleDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1780591A CN1780591ACN 200480011741CN200480011741ACN1780591ACN 1780591 ACN1780591 ACN 1780591ACN 200480011741CN200480011741CN 200480011741CN 200480011741 ACN200480011741 ACN 200480011741ACN 1780591 ACN1780591 ACN 1780591A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- patent foramen
- catheter
- tissue
- needle
- ellipsoid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese相关申请related application
本申请要求对以下美国临时专利申请的优先权:2003年3月27日提交的Nos.60/458,854(代理人文档号No.022128-000100US);2003年6月11日提交的Nos.60/478,035(代理人文档号No.022128-000110US);2003年7月24日提交的Nos.60/490082(代理人文档号No.022128-000120US);本文援引它们的全部内容以供参考。本申请涉及到以下美国专利申请:2003年9月16日提交的Nos.10/665974(代理人文档号No.022128-000300US);2003年10月2日提交的Nos.10/679245(代理人文档号No.022128-000200US);以及2004年2月25日提交的Nos.10/787532(代理人文档号No.022128-000130US);本文援引它们的全部内容以供参考。This application claims priority to the following U.S. Provisional Patent Applications: Nos. 60/458,854 filed March 27, 2003 (Attorney Docket No. 022128-000100US); Nos. 60/ 478,035 (Attorney Docket No. 022128-000110US); Nos. 60/490082 filed July 24, 2003 (Attorney Docket No. 022128-000120US); incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. This application is related to the following U.S. patent applications: Nos. 10/665974 filed September 16, 2003 (Attorney Docket No. 022128-000300US); Nos. 10/679245 filed October 2, 2003 (Attorney No. 022128-000200US); and Nos. 10/787532, filed February 25, 2004 (Attorney Docket No. 022128-000130US); the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
技术领域technical field
本发明一般地涉及医疗装置和方法。具体来说,本发明涉及用于治疗未闭椭圆孔(PFO)的装置和方法。The present invention generally relates to medical devices and methods. In particular, the present invention relates to devices and methods for treating patent foramen ovale (PFO).
背景技术Background technique
胎儿的血液循环与成人血液循环有很大不同。因为胎儿血液依靠胎盘供氧,而不是由胎儿的肺供氧,所以,血液一般地远离肺通过多个血管和在胎儿生命过程中保持开口(即,打开)的诸孔分流到周围的组织,通常未闭的孔在出生后不久就可关闭。例如,胎儿血液从右心房通过椭圆孔直接流入左心房,循环通过肺动脉大血管的一部分血液通过动脉导管流到大动脉。胎儿的这种循环示于附图1中。The blood circulation of a fetus is very different from that of an adult. Because fetal blood is oxygenated by the placenta and not by the fetal lungs, blood is generally shunted away from the lungs to surrounding tissues through multiple blood vessels and pores that remain open (ie, open) during fetal life, Usually the patent foramen closes soon after birth. For example, fetal blood flows from the right atrium through the foramen oval directly into the left atrium, and part of the blood that circulates through the great vessels of the pulmonary artery flows through the ductus arteriosus to the aorta. This cycle of the fetus is shown in Figure 1 of the accompanying drawings.
胎儿出生时一新生命开始呼吸,左心房内的血压高于右心房内的血压。在大多数婴儿中,组织皮片关闭椭圆孔并痊愈在一起。在美国每年大约有20,000个出生的婴儿缺乏这种组织皮片,因此,孔仍保持打开,称其为房间隔缺损(ASD)。在更高的百分比人口中(估计范围在全人口的5%至20%),存在有皮片但没有痊愈在一起。这种病例称之为椭圆孔未闭(PFO)。每次右心房内的血压高于左心房内的血压,血压会推开该未闭的椭圆孔,从而允许血从右心房流到左心房。When the fetus is born, a new life begins to breathe, and the blood pressure in the left atrium is higher than the blood pressure in the right atrium. In most babies, a flap of tissue closes the foramen oval and heals together. About 20,000 babies are born each year in the United States without this tissue flap, so the hole remains open, known as an atrial septal defect (ASD). In a higher percentage of the population (estimates range from 5% to 20% of the population), skin flaps are present but do not heal together. This case is called a patent foramen ellipsoid (PFO). Every time the blood pressure in the right atrium is higher than the blood pressure in the left atrium, the blood pressure pushes open the patent oval foramen, allowing blood to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium.
由于椭圆孔未闭对于全身的血液循环通常影响很小,所以一直被认为是一种相对良性的病例。然而,最近以来,发现至少部分地起因于PFO而可导致相当多人大脑功能突然丧失。在某些病例中,因为PFO允许含有小血栓的血液从静脉循环直接流到动脉循环并流入脑中,而不是流入血栓可在其中被截留和逐渐溶解的肺内,所以,可造成大脑功能突然丧失。在另外一些病例中,血栓可形成在PFO本身的敞开通道内,并当血压造成血从右心房流到左心房时,形成的血栓可被逐走。据估计,已经发生过病因不明的大脑功能突然丧失的PFO病人每年有4%发生另外大脑功能突然丧失的风险。Because the patent foramen ellipsoid usually has little effect on the blood circulation of the whole body, it has been considered a relatively benign case. More recently, however, it has been discovered that a significant number of people experience a sudden loss of brain function, at least in part, due to PFO. In some cases, sudden brain function can be caused because the PFO allows blood containing small clots to flow directly from the venous circulation to the arterial circulation and into the brain, rather than into the lungs, where the clots can become trapped and gradually dissolve lost. In other cases, a thrombus can form in the open channel of the PFO itself and be dislodged when blood pressure causes blood to flow from the right atrium to the left atrium. It is estimated that PFO patients who have experienced a sudden loss of brain function of unknown etiology are at an annual risk of 4% for another sudden loss of brain function.
目前进一步的研究正将PFO和大脑功能突然丧失联系起来。目前,如果某一患有PFO的人发生两次或多次大脑功能突然丧失,则美国的保健系统会可偿付外科的或其它干预的手术费用以确定地关闭PFO。然而,很可能获得更加预防性的方法来关闭PFO以防止将来发生大脑功能突然丧失。然而,由于因PFO引起的发病率相对较低,所以,这样一手术的费用和可能的副作用和复杂性必须低。例如,在年轻的病人中,PFO经过一段时间有时会自行关闭而对健康没有任何不利影响。Further research is now linking PFO to sudden loss of brain function. Currently, if a person with a PFO experiences two or more sudden loss of brain function, the US health care system reimburses for surgical or other interventions to definitively close the PFO. However, it may well be possible to obtain a more preventive approach to closing the PFO to prevent sudden loss of brain function in the future. However, since the morbidity due to PFO is relatively low, the cost and possible side effects and complications of such a procedure must be low. For example, in young patients, the PFO sometimes closes itself over time without any adverse health effects.
其它普遍流行和虚弱的病例-慢性偏头疼-也与PFO有关。尽管准确的原因还未作出解释,但PFO的关闭已经显示出在许多病人中已经消除或显著地减小了偏头疼。再者,如果可提供相对非侵入性的手术,则可准许预防性的PFO关闭来治疗慢性偏头疼。Another prevalent and debilitating condition - chronic migraine - is also associated with PFO. Although the exact reason has not been explained, closure of the PFO has been shown to eliminate or significantly reduce migraine in many patients. Furthermore, prophylactic PFO closure may be warranted for the treatment of chronic migraine if a relatively non-invasive procedure is available.
目前,对于PFO可提供的干预性治疗通常是相对侵入性的治疗和/或具有潜在的缺点。一种策略是在为其它目的(诸如心瓣膜外科手术)实施的打开心脏手术过程中简单地关闭PFO。这通常通过一简单的手术就可实现,例如,用脉管缝合线在PFO上缝合一针或两针。然而,纯粹为了关闭一无症状的PFO或甚至一非常小的ASD而实施心脏打开手术,很难判断其合理性。Currently available interventional treatments for PFO are often relatively invasive treatments and/or have potential disadvantages. One strategy is to simply close the PFO during open heart surgery performed for other purposes, such as heart valve surgery. This is usually accomplished with a simple procedure, eg, one or two stitches on the PFO with vascular sutures. However, it is difficult to justify performing open-heart surgery purely to close an asymptomatic PFO or even a very small ASD.
人们已经提出和研究出许多用于关闭PFO的经由皮肤的干预性装置。大部分这些装置与心房间隔缺损(ASD)关闭装置相同或相似。它们通常呈“蛤壳”或“双伞”形状的装置,它们在房间隔的各侧上展开一生物相容的金属网或织物(例如,ePTFE或Dacron)的面积,连同一中心轴向元件固定住,以此关闭PFO。然后,该伞愈合到房间隔内,利用痊愈的响应,在该装置上形成一均匀的组织层或“血管翳”。例如,这样的装置已经由诸如Nitinol Medical Technologies,Inc.(Boston,马萨诸塞州)和AGA Medical,Inc.(White Bear Lake,明尼苏达州)两家公司研制出品。美国专利No.6,401,720描述了一用于胸腔镜心脏内手术的方法和装置,其可用于PFO的治疗。A number of percutaneous interventional devices for closing the PFO have been proposed and developed. Most of these devices are the same as or similar to atrial septal defect (ASD) closure devices. They are usually "clamshell" or "double umbrella" shaped devices that deploy an area of biocompatible metal mesh or fabric (e.g., ePTFE or Dacron) on each side of the interatrial septum, along with a central axial element Hold in place to close the PFO. The umbrella then heals into the interatrial septum, with the healing response forming a uniform layer of tissue or "pannus" over the device. For example, such devices have been developed by companies such as Nitinol Medical Technologies, Inc. (Boston, MA) and AGA Medical, Inc. (White Bear Lake, MN). US Patent No. 6,401,720 describes a method and apparatus for thoracoscopic endocardiac surgery, which may be used in the treatment of PFO.
特别有意义的是,人们已提出使用一具有一带有研磨元件的气囊的导管来研磨一PFO的内表面以造成一血栓形成区域。见美国专利No.5,919,200。经过一段时间希望该区域形成一结痂和关闭PFO。其它有关的专利包括美国专利Nos.6,056,760、6,482,224和6,702,835,以及PCT出版物No.WO98/07375。有关的已出版的专利申请包括美国出版物Nos.2003/0045893和2003/0225421,以及PCT出版物Nos.WO 03/053493和WO 03/082076。Of particular interest, it has been proposed to use a catheter having a balloon with abrasive elements to abrade the inner surface of a PFO to create a thrombosed area. See US Patent No. 5,919,200. Over time it is hoped that the area will form a scab and close the PFO. Other related patents include US Patent Nos. 6,056,760, 6,482,224 and 6,702,835, and PCT Publication No. WO98/07375. Related published patent applications include US Publication Nos. 2003/0045893 and 2003/0225421, and PCT Publication Nos. WO 03/053493 and WO 03/082076.
尽管所提供的装置在某些病例中可很好地得到使用,但它们也面临许多挑战。例如,复杂性相当频繁地造成的结果包括:不合适地展开、装置栓塞到循环中,以及装置断裂等。在某些情形中,一部署的装置没有完全地愈合到隔膜壁内,留下一本身可成为血栓形成的病灶的暴露组织。此外,目前可供的装置通常复杂且制造昂贵,这使得它们用于PFO的预防性治疗不可行。另外,使用目前可提供的经由皮肤插入的导管,有时难于将一导管或导向丝插入直接地通过PFO的内腔。While the provided devices work well in some cases, they also present a number of challenges. For example, complications have fairly frequently resulted in improper deployment, embolization of the device into the circulation, and fracture of the device, among others. In some instances, a deployed device does not fully heal into the septal wall, leaving exposed tissue that itself can become a foci for thrombosis. Furthermore, currently available devices are often complex and expensive to manufacture, making their use in the prophylactic treatment of PFO impractical. Additionally, with currently available percutaneously inserted catheters, it is sometimes difficult to insert a catheter or guide wire directly through the lumen of the PFO.
因此,有利地是需有改进的方法和装置用来治疗PFO。理想的是,这样的方法和装置将帮助密封PF0,同时,在体内很少或没有留下外部的材料。还为理想的是,这样的方法和装置制造和使用相对简单,因此,给予预防性治疗PFO,例如,防止大脑突然丧失功能,一种可行的选择。还为有利地是,需有这样一装置,其可实现PFO关闭而不要求插入导管通过PFO。本发明将满足至少上述某些目的。Accordingly, it would be advantageous to have improved methods and devices for treating PFO. Ideally, such methods and devices would help seal PFO while leaving little or no external material in vivo. It would also be desirable that such methods and devices be relatively simple to manufacture and use, thus rendering prophylactic treatment of PFO, eg, preventing sudden loss of brain function, a viable option. It would also be advantageous to have a device that would achieve PFO closure without requiring catheterization through the PFO. The present invention will satisfy at least some of the above objects.
发明内容Contents of the invention
用来治疗未闭椭圆孔(PFO)的方法和装置通常包括使用一具有位于其远端处的治疗装置的导管。在某些实施例中,治疗装置包括一个或多个可缩回的研磨针,其用来研磨邻近PFO的组织而导致关闭PFO。在某些实施例中,治疗装置可变化地或附加地包括一能量传输部件,例如射频、超声波、微波、激光或低温能量传输部件。在其它的实施例中,治疗装置可包括一个或多个孔以便分配一流体而接触和关闭PFO。Methods and devices for treating a patent foramen ovale (PFO) generally involve the use of a catheter having a treatment device at its distal end. In certain embodiments, the treatment device includes one or more retractable abrasive needles that are used to abrade tissue adjacent the PFO to cause closure of the PFO. In certain embodiments, the treatment device may alternatively or additionally include an energy delivery component, such as a radiofrequency, ultrasonic, microwave, laser or cryogenic energy delivery component. In other embodiments, the treatment device may include one or more holes for dispensing a fluid to contact and close the PFO.
在某些实施例中,治疗装置包括一个或多个关闭装置,例如,一个或多个夹子、U形钉、补缀、自关闭附连部件、螺旋针等。某些关闭装置具有至少一部分,其驻留在PFO内并对PFO相对侧的组织施加侧向力,因此,将组织集合在相对侧之间。关闭装置可以选择地使用能量和/或能量中介的焊接料或组织胶进行灌输。可供选择的是,关闭装置可以是生物可降解的或可以是由非降解的材料形成。在示范的装置中,一供应导管可包括一回挡,用来定位在左心房内以便提供一工作表面而便于关闭装置的展开。该回挡可以在PFO关闭之后移去。In certain embodiments, the therapeutic device includes one or more closure devices, eg, one or more clips, staples, patches, self-closing attachment members, helical needles, and the like. Certain closure devices have at least a portion that resides within the PFO and applies a lateral force to tissue on opposite sides of the PFO, thereby bringing tissue together between the opposite sides. The closure device can optionally be infused with energy and/or energy-mediated solder or tissue glue. Alternatively, the closure device may be biodegradable or may be formed from a non-degradable material. In an exemplary device, a supply catheter may include a backstop for positioning within the left atrium to provide a working surface to facilitate deployment of the closure device. This backstop can be removed after the PFO is closed.
方法一般地包括前进导管将其远端定位在PFO附近,并可以多种方式中的任何一种使用治疗装置来关闭PFO。在一第一实施例中,使用一个或多个研磨针或其它研磨元件来研磨或其它方式使邻近PFO的组织损伤而导致PFO的关闭。在其它实施例中,PFO用一关闭装置进行关闭,该装置可供选择地采用能量和/或焊接料或组织胶固定到组织。关闭装置可以是一实体地覆盖PFO的塞子。或者,该装置可以是自关闭的,以便捕获和关闭PFO。The method generally involves advancing the catheter to position its distal end adjacent the PFO, and closing the PFO using a therapeutic device in any of a variety of ways. In a first embodiment, one or more abrasive needles or other abrasive elements are used to abrade or otherwise injure tissue adjacent to the PFO resulting in closure of the PFO. In other embodiments, the PFO is closed with a closure device that is optionally secured to tissue using energy and/or solder or tissue glue. The closure device may be a plug that physically covers the PFO. Alternatively, the device can be self-closing to capture and close the PFO.
在一个方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端和靠近远端的至少一个研磨针的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近;从导管中暴露出多个研磨针;前进暴露的研磨针通过未闭椭圆孔;以及相对于未闭椭圆孔缩回研磨针而研磨邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织的至少一部分。在某些实施例中,前进导管包括前进通过病人的以下中的至少一个:一股静脉、一髋静脉、一内部腔静脉、一臂静脉、一轴向静脉、一锁骨下静脉,以及一上腔静脉。在某些实施例中,前进导管包括在一导向丝上前进。In one aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale comprises: advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one abrasive needle proximate the distal end, through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end in the unclosed proximate to the patent foramen ellipsoid; exposing a plurality of abrasive needles from the catheter; advancing the exposed abrasive needles through the patent foramen ellipsoid; and retracting the abrasive needles relative to the patent foramen ellipsoid to abrade at least a portion of tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid. In certain embodiments, the advancing catheter includes advancing through at least one of the patient's: a femoral vein, a hip vein, an internal vena cava, a brachial vein, an axial vein, a subclavian vein, and a superior vena cava. In some embodiments, advancing the catheter includes advancing over a guide wire.
在某些实施例中,暴露研磨针包括:缩回导管的导管体而将针暴露出导管的远端处或其附近的导管体内的开口。或者,暴露研磨针可包括:相对于导管体前进针。在某些实施例中,前进研磨针包括:传递至少一个针通过直接邻近PFO的组织。前进研磨针可包括:相对于导管前进针,前进导管本身从而前进针,或在各种实施例中两者都前进。在一实施例中,缩回研磨针包括:用针的锯齿形边缘研磨未闭椭圆孔的至少一部分。在任何的实施例中,研磨针可以按要求缩回和前进许多次。可供选择的是,任何实施例可以包括使用一个或多个可视装置来观察PFO和/或包围PFO的组织。In certain embodiments, exposing the abrasive needle includes retracting the catheter body of the catheter to expose the needle through an opening in the catheter body at or near the distal end of the catheter. Alternatively, exposing the abrasive needle may include advancing the needle relative to the catheter body. In certain embodiments, advancing the abraded needle includes passing at least one needle through tissue immediately adjacent the PFO. Advancing the abrasive needle may include advancing the needle relative to the catheter, advancing the catheter itself thereby advancing the needle, or both in various embodiments. In one embodiment, retracting the abrading needle includes abrading at least a portion of the patent foramen ovale with the serrated edge of the needle. In either embodiment, the grinding needle can be retracted and advanced as many times as desired. Optionally, any of the embodiments may include viewing the PFO and/or tissue surrounding the PFO using one or more visualization devices.
在另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端和靠近远端的至少一个研磨针的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近;从导管中暴露出至少一个研磨针;前进至少一个暴露的研磨针通过邻近PFO的心脏壁组织;例如,通过第一房间隔和/或第二房间隔的组织;以及相对于组织缩回至少一个研磨针而研磨组织的至少一部分。该方法可包括上述的任何可供选择的步骤或元件。In another aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale includes advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one abrasive needle proximate the distal end through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end at Proximity to the patent foramen ovale; exposure of at least one abrasive needle from the catheter; advancement of the at least one exposed abrasive needle through heart wall tissue adjacent to the PFO; for example, through tissue of the first interatrial septum and/or second interatrial septum; At least a portion of the tissue is abraded by retracting the at least one abrading needle from the tissue. The method may include any optional steps or elements described above.
在还有的另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端和靠近远端的至少一个研磨针的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近;从导管中暴露出一第一研磨针,以使暴露的第一研磨针延伸通过PFO的至少一部分;从导管暴露至少一个第二研磨针,以使暴露的第二研磨针延伸通过PFO;以及相对于PFO缩回第一和第二研磨针而研磨邻近PFO的组织的至少一部分。可供选择的是,该方法还可包括从导管中暴露出一第三研磨针,以使暴露的第三研磨针延伸通过PFO,并相对于PFO缩回第三研磨针而研磨邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织的至少一部分。该方法还可进一步包括从导管中暴露出一第四研磨针,以使暴露的第四研磨针延伸通过PFO,并相对于PFO缩回第四研磨针而研磨邻近PFO的组织的至少一部分。再者,上述的任何特征、步骤或元件可应用于该方法。In yet another aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale includes: advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one abrasive needle proximate the distal end through a patient's vasculature to place the distal The end is positioned near the patent foramen ovale; a first abrasive needle is exposed from the catheter such that the exposed first abrasive needle extends through at least a portion of the PFO; at least one second abrasive needle is exposed from the catheter such that the exposed first abrasive needle Two abrasive needles extend through the PFO; and retracting the first and second abrasive needles relative to the PFO abrades at least a portion of tissue adjacent the PFO. Optionally, the method may further include exposing a third abrasive needle from the catheter such that the exposed third abrasive needle extends through the PFO, and retracting the third abrasive needle relative to the PFO abrades the adjacent patent ellipse At least a portion of the tissue of the pores. The method may further include exposing a fourth abrasive needle from the catheter, such that the exposed fourth abrasive needle extends through the PFO, and retracting the fourth abrasive needle relative to the PFO to abrade at least a portion of tissue adjacent the PFO. Furthermore, any feature, step or element described above may be applied to the method.
在另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端和靠近远端的一个能量传输部件的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近,并从能量传输部件传输能量而接触邻近PFO的组织以便导致关闭PFO。例如,传递的能量可以包括激光能、射频能、超声波能、微波能、低温能,通过冷却或类似方法移去能量。通过施加能量可直接地实现关闭,其次,或在施加能量之后由于痊愈而实现关闭。在某些实施例中,能量传输部件可包括前进到邻近PFO的组织内的针。在某些这样的实施例中,针可以这样一方式供应,在施加能量之前其将组织拉在一起。In another aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale includes advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and an energy delivery member proximate the distal end through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end at The vicinity of the patent foramen ellipse, and energy delivered from the energy delivery component contacts tissue adjacent to the PFO to cause closure of the PFO. For example, the delivered energy may include laser energy, radio frequency energy, ultrasonic energy, microwave energy, cryogenic energy, removal of energy by cooling or the like. Closure can be achieved directly by application of energy, secondarily, or by healing after application of energy. In certain embodiments, the energy delivery component may include a needle advanced into tissue adjacent the PFO. In some of these embodiments, the needles may be delivered in such a way that they draw the tissue together prior to application of energy.
在另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端和靠近远端的至少一个孔的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近;从至少一个孔中分配至少一种流体而接触邻近PFO的组织以便导致关闭PFO。例如,流体可包括诸如一酸或一粘结剂之类的生物相容的流体。在某些实施例中,该方法可包括对邻近远端的气囊或其它部件充气,以便将心房间隔的区域与血流隔绝,因此,增加流体位于PFO附近的时间。In another aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ellipsoid comprises: advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one hole proximate the distal end, through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end in an unclosed position. Proximate to the closed foramen ellipsoid; dispensing at least one fluid from at least one of the holes to contact tissue adjacent the PFO to cause closure of the PFO. For example, the fluid may include a biocompatible fluid such as an acid or a binder. In certain embodiments, the method may include inflating a balloon or other component proximal to the distal end to isolate a region of the atrial septum from blood flow, thereby increasing the time that fluid is in the vicinity of the PFO.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗心脏内的未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近,并供应一关闭装置而至少局部地通过未闭椭圆孔以便导致关闭未闭椭圆孔。在此方法中,设置在未闭椭圆孔内的关闭装置的一部分对未闭椭圆孔的相对侧处的组织施加侧向力,从而将组织集合在两侧之间。可供选择的是,该方法还可包括传递以下的能量(但不限于):激光能、射频能、超声波能、微波能、低温能,或通过冷却从导管移去能量从而将关闭装置固定在未闭椭圆孔内。In another aspect of the present invention, a method of treating a patent foramen ellipsoid in the heart comprises: advancing a catheter device having a proximal end and a distal end through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end in the patent ellipsoid near the orifice, and supply a closing device at least partially through the patent foramen ovale to cause closure of the patent foramen ovale. In this method, a portion of the closure device disposed within the patent foramen ovale applies a lateral force to tissue at opposite sides of the patent foramen ovale, thereby bringing the tissue together between the sides. Optionally, the method may also include delivering energy such as, but not limited to, laser energy, radiofrequency energy, ultrasonic energy, microwave energy, cryogenic energy, or cooling to remove energy from the catheter to secure the closure device in place. Inside the patent oval foramen.
还有可供选择的是,该方法可包括允许关闭装置坍瘪和抽拉关闭的未闭椭圆孔。在某些实施例中,该方法包括:当关闭装置展开时将一回挡装置定位在左心房内。某些实施例包括供应一组织焊接材料,其通过能量而固化,从而将关闭装置粘结到组织。其它的实施例可包括:对与远端附近的导管装置偶联的可充气的气囊进行充气,以便将关闭装置展开在未闭椭圆孔内。Still alternatively, the method may include allowing the closure device to collapse and draw closed the patent oval. In some embodiments, the method includes positioning a backstop within the left atrium when the closure device is deployed. Certain embodiments include supplying a tissue welding material that is cured by energy to bond the closure device to the tissue. Other embodiments may include inflating an inflatable balloon coupled to the catheter device near the distal end to deploy the closure device within the patent foramen ovale.
在某些实施例中,供应关闭装置包括:从导管装置释放关闭装置的左心房部分,以使它从心脏的左心房内接触邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织,以及从导管装置释放关闭装置的右心房部分,以使它从心脏的右心房内接触邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织。在如此的实施例中,关闭装置的一搭桥部分延伸通过左心房部分和右心房部分之间的未闭椭圆孔,并对未闭椭圆孔的相对侧处的组织施加侧向力。在某些实施例中,左心房部分在右心房部分前释放,而在其它的实施例中,右心房部分在左心房部分前释放。某些实施例还可包括:使用导管装置从未闭椭圆孔移去关闭装置,以及通过未闭椭圆孔至少局部地重新定位关闭装置以便接触邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织。在某些实施例中,移去关闭装置包括:在关闭装置上前进导管装置而伸直关闭装置和释放导管装置,以便从未闭椭圆孔移去关闭装置。在某些实施例中,左心房部分在右心房部分前伸直,而在其它的实施例中,右心房部分在左心房部分前伸直。In some embodiments, supplying the closure device includes releasing the left atrial portion of the closure device from the catheter device such that it contacts tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid from within the left atrium of the heart, and releasing the right atrial portion of the closure device from the catheter device. The portion of the atrium so that it contacts the tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid from within the right atrium of the heart. In such an embodiment, a bridging portion of the closure device extends through the patent foramen ellipsoid between the left and right atrial portions and applies a lateral force to tissue at opposite sides of the patent foramen ellipsoid. In some embodiments, the left atrial portion is released before the right atrial portion, while in other embodiments, the right atrial portion is released before the left atrial portion. Certain embodiments may also include removing the closure device from the patent foramen ovale using a catheter device, and at least partially repositioning the closure device through the patent foramen ovale to contact tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ovale. In some embodiments, removing the closure device includes advancing a catheter device over the closure device to straighten the closure device and releasing the catheter device to remove the closure device from the foramen ovale. In some embodiments, the left atrium portion straightens before the right atrium portion, while in other embodiments, the right atrium portion straightens ahead of the left atrium portion.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:将关闭装置的至少一部分设置在未闭椭圆孔内,并使用设置在未闭椭圆孔内的关闭装置的部分对未闭椭圆孔的相对侧处的组织施加侧向、朝向相对方向的力,以使第一房间隔和第二房间隔集合在相对侧之间以便发生接触。可供选择的是,该方法也可包括:放置至少一个装置以保持第一房间隔和第二房间隔之间的接触。这样一方法可选择地还包括施加能量而保持第一房间隔和第二房间隔之间的接触。在某些实施例中,可以引入组织焊接料来保持第一房间隔和第二房间隔之间的接触。In another aspect of the present invention, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale includes disposing at least a portion of a closure device within the patent foramen ovale, and closing the patent foramen ovale with the portion of the closure device disposed within the patent foramen ovale. Tissue at opposite sides of the atrial septum exerts a lateral, toward opposite direction force to bring the first atrial septum and the second atrial septum together between the opposite sides for contact. Optionally, the method may also include placing at least one device to maintain contact between the first interatrial septum and the second interatrial septum. Such a method optionally further includes applying energy to maintain contact between the first interatrial septum and the second interatrial septum. In some embodiments, tissue solder may be introduced to maintain contact between the first interatrial septum and the second interatrial septum.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗心脏内的未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一具有一近端、一远端的导管装置,通过一病人的脉管系统而将远端定位在未闭椭圆孔附近,并供应一从导管起自关闭的关闭装置而接触邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织。在此方法中,供应自关闭的关闭装置而将未闭椭圆孔的组织集合在一起。在某些实施例中,例如,供应自关闭的关闭装置包括:驱动多个组织附连部件,其与一自关闭的展幅机偶联而进入到组织内。In another aspect of the present invention, a method of treating a patent foramen ellipsoid in the heart comprises: advancing a catheter device having a proximal end and a distal end through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end in the patent ellipsoid adjacent to the foramen ellipsoid, and supply a closure device that self-closes from the catheter to contact tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid. In this method, the tissue of the patent foramen ovale is brought together by supplying a self-closing closure device. In some embodiments, for example, providing a self-closing closure device includes actuating a plurality of tissue-attachment members coupled with a self-closing stenter into tissue.
在另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:将关闭装置附连到心脏的卵圆窝的一边缘,并允许关闭装置的一部分从边缘悬下而覆盖未闭椭圆孔的开口。这样一方法可供选择地还包括施加能量而固定关闭装置。In another aspect, a method of treating a patent foramen ovale includes attaching a closure device to a rim of a fossa ovale of the heart and allowing a portion of the closure device to hang from the rim to cover the opening of the patent foramen ovale. Such a method optionally further includes applying energy to immobilize the closure device.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗心脏内的未闭椭圆孔的方法包括:前进一细长的导管装置,通过邻近未闭椭圆孔的第一房间隔;调整一离导管装置的可缩回的供应臂,该供应臂通过一万能接头与导管装置的远端偶联;以及操纵导管装置从供应臂到邻近未闭椭圆孔内展开一螺旋形针以便将组织集合在一起。在某些实施例中,螺旋形针通过第一房间隔和第二房间隔展开。例如,操纵导管装置可包括围绕其纵向轴线转动或扭转装置。In another aspect of the present invention, a method of treating a patent foramen ellipsoid in the heart comprises: advancing an elongated catheter device through a first interatrial septum adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid; a supply arm coupled to the distal end of the catheter device by a universal joint; and manipulating the catheter device from the supply arm into the adjacent patent foramen ellipsoid to deploy a helical needle to bring tissue together. In certain embodiments, the helical needle is deployed through the first interatrial septum and the second interatrial septum. For example, manipulating the catheter device may include turning or twisting the device about its longitudinal axis.
在另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一细长的导管体,其具有一近端和一远端,以及至少一个可在一缩回位置和一展开位置之间移动的可缩回的研磨针,在缩回位置中,针全部地驻留在导管体内,而在展开位置中,针的至少一部分延伸通过邻近远端的导管体内的一开口。在某些实施例中,导管体可在一导向丝上通过。还在某些实施例中,至少一个可缩回的研磨针包括至少一个锯齿形边缘以便研磨邻近PFO的组织。可供选择的是,至少一个可缩回的研磨针包括多个针。在某些实施例中,多个针各个别地可缩回到导管体内。在还有的某些实施例中,至少一个可缩回的研磨针相对于导管体可移动,从而延伸至少一个针通过PFO并缩回针而通过椭圆孔。在某些实施例中,装置可包括一用来便于观看PFO的可视装置。In another aspect, an apparatus for treating PFO includes an elongated catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end, and at least one retractable abrasive needle movable between a retracted position and a deployed position , in the retracted position, the needle resides entirely within the catheter body, and in the deployed position, at least a portion of the needle extends through an opening in the catheter body adjacent the distal end. In some embodiments, the catheter body can be passed over a guide wire. In still some embodiments, at least one retractable abrasive needle includes at least one serrated edge to abrade tissue adjacent the PFO. Optionally, the at least one retractable abrasive needle comprises a plurality of needles. In certain embodiments, the plurality of needles are each individually retractable within the catheter body. In still other embodiments, the at least one retractable abrasive needle is movable relative to the catheter body to extend the at least one needle through the PFO and retract the needle through the oval foramen. In some embodiments, the device may include a visual device to facilitate viewing of the PFO.
在另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一细长的导管体,其具有一近端和一远端,以及与邻近远端的导管体偶联的至少一个能量传输部件,以便传输能量而接触邻近PFO的组织从而导致关闭PFO。如上所述,能量传输部件可传输任何合适形式的能量,例如(但不限于),激光能、射频能、超声波能、微波能,或低温能。在某些实施例中,将能量供应到或邻近于PFO的装置可包括一个或多个针,它们可以相对于导管体移动,且它们可以是锯齿形也可不是锯齿形。在某些这样的实施例中,针可以设计成将PFO的组织拉在一起以及供应能量。In another aspect, a device for treating PFO includes an elongated catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end, and at least one energy delivery member coupled to the catheter body adjacent the distal end for transmitting energy into contact with adjacent The organization of the PFO thus leads to the closure of the PFO. As noted above, the energy delivery component may deliver any suitable form of energy, such as, but not limited to, laser energy, radio frequency energy, ultrasonic energy, microwave energy, or cryogenic energy. In certain embodiments, the means for supplying energy to or adjacent to the PFO may include one or more needles that are movable relative to the catheter body, and which may or may not be serrated. In some of these embodiments, the needles may be designed to draw together the tissue of the PFO as well as supply energy.
在另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一细长的导管体,其具有一近端和一远端,以及邻近远端的导管体内的至少一个孔,其用来分配至少一种流体而接触邻近PFO的组织,从而导致PFO的关闭。如上所述,可以使用任何合适的流体,例如(但不限于),诸如酸或粘结剂之类的生物相容的流体。在某些实施例中,该装置可包括一充气的气囊或邻近导管远端的其它装置,以便将心房间隔的区域与血流隔绝,因此,增加流体在PFO区域内逗留的时间。In another aspect, a device for treating PFO includes an elongated catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end, and at least one hole in the catheter body adjacent the distal end for dispensing at least one fluid into contact with the adjacent The organization of the PFO, which leads to the closure of the PFO. As noted above, any suitable fluid may be used, for example, but not limited to, a biocompatible fluid such as an acid or a binder. In certain embodiments, the device may include an inflatable balloon or other device adjacent the distal end of the catheter to isolate the region of the atrial septum from blood flow, thereby increasing the residence time of fluid in the region of the PFO.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一细长的导管体,其具有一近端和一远端,以及从导管体伸展的至少一个关闭装置。具体来说,该关闭装置附连到邻近PFO的组织并可自关闭而将组织集合在一起。在某些实施例中,关闭装置是生物可降解的。在某些实施例中,关闭装置包括一可膨胀的、自关闭的展幅器,其与多个组织附连部件偶联,例如(但不限于),组织传刺针。在某些实施例中,关闭装置包括一个部分,其在PFO内延伸且对PFO相对侧处的组织施加侧向力,因此,将组织集合在两个相对侧之间。导管体可在一导向丝上通过。实施例可供选择地包括至少一个与远端附近的导管体偶联的可视装置,以便观察PFO和PFO周围的组织。某些实施例可包括至少一个与邻近远端的导管体偶联的传输能量部件,以便接触邻近PFO组织。可以使用任何合适的能量。In another aspect of the invention, a device for treating PFO includes an elongated catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end, and at least one closure device extending from the catheter body. Specifically, the closing device is attached to tissue adjacent the PFO and self-closing to bring the tissue together. In certain embodiments, the closure device is biodegradable. In certain embodiments, the closure device includes an expandable, self-closing stent coupled to a plurality of tissue-attachment members, such as, but not limited to, tissue-lancing needles. In certain embodiments, the closure device includes a portion that extends within the PFO and applies a lateral force to tissue at opposite sides of the PFO, thereby bringing the tissue together between the two opposing sides. The catheter body can be passed over a guide wire. Embodiments optionally include at least one visualization device coupled to the catheter body near the distal end for viewing the PFO and tissue surrounding the PFO. Certain embodiments may include at least one energy delivery component coupled to the catheter body adjacent the distal end for contacting tissue adjacent the PFO. Any suitable energy can be used.
在另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一夹子,其可从第一尺寸扩展到一较大的第二尺寸以便接合PFO的组织。处于较大尺寸的夹子对PFO的相对侧处的组织施加侧向力,以将组织集合在两个相对侧之间。再者,夹子可回复到其第一尺寸或迫使其回复到第一尺寸。In another aspect, a device for treating a PFO includes a clip expandable from a first size to a second, larger size to engage tissue of the PFO. The clips at the larger size exert a lateral force on the tissue at opposite sides of the PFO to bring the tissue together between the two opposite sides. Also, the clip can return to its first size or be forced to return to its first size.
在另一方面,用于治疗PFO的装置包括一细长的导管体,其具有一近端和一远端,以及与远端偶联的至少一个施加力的部件以便对PFO的相对侧施加侧向力,因此,将组织集合在相对侧之间而发生接触。在某些实施例中,远端包括至少两个臂,它们侧向地挠曲而接合PFO的边缘。变化地或添加地是,该远端可包括一可拆卸的关闭装置。该远端还可选择地包括能量供应装置。这样的实施例还可包括供应组织焊料或粘结剂的装置。该装置还可包括供应一关闭装置的装置。例如,关闭装置可包括至少一个U形钉、夹子、组织焊料、粘结剂等。In another aspect, a device for treating a PFO includes an elongated catheter body having a proximal end and a distal end, and at least one force-applying member coupled to the distal end for applying lateral force to opposite sides of the PFO. Axial forces, therefore, bring tissue together between opposing sides to make contact. In certain embodiments, the distal end includes at least two arms that flex laterally to engage the edges of the PFO. Alternatively or additionally, the distal end may include a removable closure. The distal end may also optionally include an energy supply. Such embodiments may also include means for supplying tissue solder or adhesive. The device may also include means for supplying a closing means. For example, the closure device may comprise at least one staple, clip, tissue solder, adhesive, or the like.
在另一方面,治疗PFO的装置包括一附连部件,其用来附连到PFO的卵圆窝的边缘,以及一覆盖部件,其与附连部件偶联,用来从边缘延伸而覆盖PFO的开口。在某些实施例中,覆盖部件包括一支承结构和一覆盖该支承结构的网。例如,支承结构可包括一丝线框架,诸如多个镍钛诺的环。在某些实施例中,施加能量以将装置固定到邻近PFO的边缘和/或其它组织。可供选择的是,该装置还可包括引入组织焊料或粘结剂的装置。在某些实施例中,附连部件构造成穿透边缘的组织。在一实施例中,覆盖部件包括相对的钳夹。In another aspect, an apparatus for treating a PFO includes an attachment member for attaching to a rim of the fossa ovale of the PFO, and a covering member coupled to the attachment member for extending from the rim to cover the PFO opening. In some embodiments, the covering member includes a support structure and a mesh covering the support structure. For example, the support structure may comprise a wire frame, such as a plurality of rings of Nitinol. In certain embodiments, energy is applied to secure the device to the rim and/or other tissue adjacent to the PFO. Optionally, the device may also include means for introducing tissue solder or adhesive. In some embodiments, the attachment member is configured to penetrate tissue of the margin. In one embodiment, the cover member includes opposing jaws.
在本发明的另一方面,治疗未闭椭圆孔的装置包括:一细长的导管,其构造成穿过邻近未闭椭圆孔的第一房间隔组织;一可缩回的供应臂,其在一万能接头处与细长导管的一远端偶联;以及一螺旋针,其与可缩回的供应臂偶联并从中伸展开来。转动导管可伸展该螺旋针进入邻近未闭椭圆孔的组织内。例如,在某些实施例中,螺旋针构造成穿透第一房间隔组织和第二房间隔组织,而将第一房间隔和第二房间隔集合在一起。In another aspect of the present invention, an apparatus for treating a patent foramen ovale includes: an elongated catheter configured to pass through a first interatrial septal tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ovale; a universal joint coupled to a distal end of the elongated catheter; and a helical needle coupled to and extending from the retractable delivery arm. Turning the catheter extends the helical needle into the tissue adjacent to the patent foramen ovale. For example, in some embodiments, the helical needle is configured to penetrate the first and second interatrial septum to bring the first and second atrial septum together.
在下文中将参照附图,详细地描述上述的和其它的方面以及诸实施例。Hereinafter, the above-mentioned and other aspects and embodiments will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
附图的简要说明Brief description of the drawings
图1是胎儿血液循环的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of fetal blood circulation;
图2是根据本发明的一实施例的具有一针的导管装置的示意图,导管通过内部腔静脉和右心房,并通过未闭椭圆孔;2 is a schematic diagram of a catheter device having a needle through the internal vena cava and right atrium and through the patent foramen ellipsoid according to one embodiment of the present invention;
图3是根据本发明的一实施例的具有多个针的导管装置的示意图,导管通过内部腔静脉和右心房,并通过未闭椭圆孔;Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a catheter device with multiple needles through the internal vena cava and right atrium, and through the patent foramen ellipsoid, according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4是根据本发明的一实施例的具有一能量传输部件的导管装置的示意图,导管通过内部腔静脉和右心房,以邻近未闭椭圆孔定位端部受动器;Figure 4 is a schematic illustration of a catheter device having an energy delivery component through the internal vena cava and right atrium to position the end effector adjacent to the patent foramen ellipsoid according to one embodiment of the present invention;
图5是根据本发明的一实施例的用来分配流体的导管装置的示意图,导管通过内部腔静脉和右心房,以邻近未闭椭圆孔定位端部受动器;5 is a schematic illustration of a catheter device for dispensing fluid through the internal vena cava and right atrium to position an end effector adjacent to a patent foramen ellipsoid, according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图6A和6B示出根据本发明的一实施例的包括一用来治疗一PFO的回挡和可充气的部件的导管装置;6A and 6B illustrate a catheter device including a backstop and inflatable components for treating a PFO, according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图7A-7C示出根据本发明的一实施例的包括一“宽边帽形”的PFO的关闭部件的导管装置;7A-7C illustrate a catheter device including a "sombrero" PFO closure member according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图7D和7E示出一用于图7A-7C中的宽边帽形部件的锁定机构;Figures 7D and 7E illustrate a locking mechanism for the sombrero in Figures 7A-7C;
图8示出根据本发明的一实施例的一PFO关闭装置;Figure 8 shows a PFO closing device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图9A-9C示出根据本发明的一实施例的另一PFO关闭装置;9A-9C illustrate another PFO closing device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图10A-10C示出根据本发明的一实施例的用于一PFO关闭装置的供应导管;10A-10C illustrate supply conduits for a PFO closure device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图11A-11F示出根据本发明的一实施例的一自关闭的展幅PFO关闭装置;11A-11F illustrate a self-closing stented PFO closing device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图12A和12B示出根据本发明的一实施例的另一自关闭的展幅PFO关闭装置;12A and 12B illustrate another self-closing stented PFO closing device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图13A和13B示出根据本发明的一实施例的补缀PFO关闭装置;13A and 13B illustrate a patch PFO closure device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图14A和14B示出根据本发明的一实施例的一“鱼嘴”PFO关闭装置;14A and 14B illustrate a "fish mouth" PFO closure device according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图15A和15B示出根据本发明的两个实施例的一鱼嘴PFO关闭装置的变化的实施例;Figures 15A and 15B illustrate a variant embodiment of a fish mouth PFO closing device according to two embodiments of the present invention;
图16A-16C示出根据本发明的一实施例的带有夹子的鱼嘴PFO关闭装置;16A-16C illustrate a fish mouth PFO closing device with clips according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图17A和17B示出根据本发明的两个实施例的带有夹子的鱼嘴PFO关闭装置的变化的实施例;Figures 17A and 17B show variant embodiments of fish mouth PFO closing devices with clips according to two embodiments of the present invention;
图18示出根据本发明的一实施例的PFO夹子;Figure 18 shows a PFO clip according to an embodiment of the invention;
图19示出根据本发明的另一实施例的PFO夹子;Figure 19 shows a PFO clip according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图20示出根据本发明的另一实施例的PFO夹子;Figure 20 shows a PFO clip according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图21示出根据本发明的另一实施例的PFO夹子;Figure 21 shows a PFO clip according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图22A和22B示出根据本发明的一实施例的用于附连卵圆窝的边缘的PFO关闭补缀;22A and 22B show a PFO closure patch for attaching the edge of the fossa ovale according to an embodiment of the invention;
图23A和23B示出根据本发明的一实施例的螺旋针PFO关闭装置。23A and 23B illustrate a helical needle PFO closure device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明的方法和装置通常用来医治邻近未闭椭圆孔(PFO)的组织而致使椭圆孔关闭。该方法和装置通常包括一导管装置,其可前进通过一病人的脉管系统将导管的远端定位在PFO附近而予以治疗。然后,设置在导管的远端或其附近处的治疗装置可用来治疗围绕PFO的心壁组织的至少一部分,致使PFO关闭。在许多实施例中,治疗装置用来致使PFO周围的组织造成创伤,然后,创伤在组织内导致一种致使PFO关闭的响应。在一实施例中,治疗装置包括一个或多个研磨针,其具有至少一个诸如锯齿刃的研磨表面。这样的针可以缩回到(和伸展出)导管体内。在其它的实施例中,治疗装置可包括能量传输装置,诸如激光、超声波、RF或微波发射器。在还有一些其它的实施例中,治疗装置可包括一个或多个位于导管远端处或其附近的用来分配流体之用的孔,以便导致PFO的关闭。The methods and devices of the present invention are generally used to treat tissue adjacent to a patent foramen ovale (PFO) resulting in closure of the foramen ovale. The methods and devices generally include a catheter device that is advanced through the vasculature of a patient to position the distal end of the catheter near the PFO for treatment. A treatment device disposed at or near the distal end of the catheter may then be used to treat at least a portion of the heart wall tissue surrounding the PFO, causing the PFO to close. In many embodiments, the treatment device is used to cause trauma to the tissue surrounding the PFO, which then causes a response within the tissue that causes the PFO to close. In one embodiment, the treatment device includes one or more abrasive needles having at least one abrasive surface, such as a serrated edge. Such a needle can be retracted (and extended) into the catheter body. In other embodiments, the treatment device may include an energy delivery device, such as a laser, ultrasound, RF or microwave transmitter. In still other embodiments, the treatment device may include one or more holes at or near the distal end of the catheter for dispensing fluid to cause closure of the PFO.
现参照图2,一具有一可缩回的研磨针12的导管10的实施例显示为处于一治疗PFO的位置。在一实施例中,导管10经由皮肤引入,例如,使用一护套和/或其它引入器装置,通过股静脉和内部腔静脉引入。一般来说,导管10的各种实施例可以通过任何合适的脉管系统或任何其它合适的路线引入,例如,通过一臂静脉、锁骨下静脉、髂骨静脉、上腔静脉和/或诸如此类的静脉。在某些实施例中,导管10可在一可移动的导向丝上前进,例如,直径在约0.038”至0.014”范围内的标准导向丝。通常地来说(但不是必要的),针12可缩回,这样,导管10可以前进,而使针12处于导管10体内的一缩回位置。一旦导管10的远端处于使用中的位置,针12则可延伸通过导管体远端处或其附近的一孔。Referring now to FIG. 2, an embodiment of a
一旦针12延伸,它可用来研磨邻近PFO组织。在一实施例中,针12可类似于预成形的Brockenbrough针,它通常用来做通过隔膜的穿刺。针12可包括任何用来研磨组织的合适的装置。例如,在某些实施例中,针12可具有一个或多个表面或边缘,它们可以呈锯齿形、齿轮形,并覆盖有诸如砂纸状材料或诸如此类材料的研磨材料。在其它实施例中,针12的表面可以涂敷药物或化学品,这样,当它接触PFO周围的心房间隔的组织时,可造成导致PFO关闭的组织反应。一般地来说,针12移动通过PFO和/或通过邻近PFO的组织,然后,后拉通过PFO和/或组织而造成研磨。在某些情形中,可以延伸针12通过PFO本身,而在另一些情形中,它难于定位PFO和/或延伸针12通过椭圆孔。在后者的情形中,针12可以延伸通过邻近PFO的心房间隔的组织,然后,缩回而造成所要求的研磨。因此,放置针12通过PFO本身不总是需要的。显然,针12可以按照要求多次地前进和缩回通过PFO和/或邻近PFO的组织,以达到所要求的组织研磨量。在某些情形中,外科医生可使用一个或多个可视技术来评估研磨过程的进展,从而确定何时达到所要求的水平。Once the
尽管导管10的近端在图2中未予示出,但这可以具有任何合适的构造,并可包括任何类型或任何数量的致动器。例如,在具有一个或多个针12的实施例中,通常在导管10的近端处或其附近有至少一个致动器,以便前进和/或缩回针12。在具有多个针12的实施例中,诸针可以通过单独的致动器个别地前进和缩回,或在各种实施例中可通过一共同的致动器一起前进和缩回。导管10近端的其它特征可包括(但不限于)一导向丝端口、一用来引入一个或多种流体的端口、将导管与能源偶联的装置,和/或诸如此类的装置。Although the proximal end of
针12通常可用任何合适的装置移动通过/横贯PFO和/或邻近PFO的组织。在某些实施例中,如上所述,针12可以相对于导管10的导管体移动,例如,使用一近端致动器相对于导管10缩回和前进针12。在其它实施例中,简单地通过前进和缩回导管10,针12可以横贯/通过PFO移动。当然,在某些实施例中,可以使用这些运动的组合,这样,可相对于导管10操纵针12,并还可通过整体操纵导管10来前进和缩回通过PFO。
现参照图3,导管10的另一实施例显示为具有多个针12(在此实例中为三个)。这样一实施例可以与上述具有一个针12的实施例非常相象的方式使用。这里,三个针12通过导管10远端附近的导管体内的三个单独的孔14延伸出导管10之外。一般来说,在任何给定的实施例中,针12可以从导管10通过导管10的极端远端、靠近远端等的一个或多个孔延伸。可以考虑采用任何合适的构造。在图3的实施例中,显示两个针12延伸通过邻近PFO的心房间隔组织,而一个针12延伸通过椭圆孔本身。再者,可以考虑对以下方式的组合:穿刺通过心房间隔组织,通过延伸通过PFO来研磨隔膜组织等。Referring now to FIG. 3, another embodiment of a
图3中所示的实施例示出针12可具有任何合适的结构。在此实施例中,与图2中的至少在两个表面上呈锯齿形的针12相比较,针12具有一个锯齿形边缘。再者,在本发明的范围内,可以考虑用于研磨针12的任何合适的结构。在某些实施例中,针可具有弧形的或波浪形的构造。在某些实施例中,针基本上可以是刚性的,而在其它的实施例中,它们可以是柔性的。针的各种实施例可以是锯齿形的边缘、齿轮形的边缘、研磨的砂纸状的表面,和/或用于研磨组织的任何其它合适的装置。The embodiment shown in Figure 3 shows that the
使用上述装置的方法已经稍作描述。一般来说,方法包括:前进一导管装置,其具有一近端、一远端,以及至少一个邻近远端的研磨针,其通过一病人脉管系统将远端定位在PFO附近,从导管中暴露出研磨针,前进针通过PFO和/或邻近PFO的组织,以及相对于PFO和/或组织缩回针,以便研磨邻近PFO的组织的至少一部分。在某些实施例中,在PFO治疗手术之前和/或之后,就可对一病人进行治疗,使用合适的抗凝固剂,例如,阿斯匹林(aspirin)、下丙酮香豆素钠(coumadin)、2B-3A抑制剂等,以防止在痊愈时间过程中在痊愈组织上形成凝块和发生栓塞。如上所讨论的,通过任何合适的装置可获得进入病人的心脏和PFO,但经常涉及通过股静脉和内部腔静脉或其它静脉经由皮肤的进入。The method of using the device described above has been briefly described. In general, methods include advancing a catheter device having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one abrasive needle adjacent the distal end through a patient's vasculature to position the distal end near the PFO, The grinding needle is exposed, advanced through the PFO and/or tissue adjacent the PFO, and retracted relative to the PFO and/or tissue to abrade at least a portion of the tissue adjacent the PFO. In certain embodiments, a patient may be treated with an appropriate anticoagulant, e.g., aspirin, coumadin, prior to and/or after PFO treatment surgery. ), 2B-3A inhibitors, etc., to prevent clot formation and embolism on the healing tissue during the healing time. As discussed above, access to the patient's heart and PFO may be obtained by any suitable means, but often involves percutaneous access through the femoral vein and the internal vena cava or other veins.
在前进导管而将远端定位在PFO附近之后和/或在治疗PFO的方法中的任何其它阶段中,一外科医生可使用一个或多个可视装置来成像PFO。例如,外科医生可将造影剂注入右心房内,而病人同时咳嗽,实施佛萨瓦氏压力均衡法(Valsalvamaneuver)或其它动作以使血液流过PFO,可以获得一个或多个图像。在某些实施例中,在摄取一个或多个PFO的图像之后,可放置一导向丝通过PFO,而导管10可在导向丝上前进。在某些情形中,可以前进导向丝和导管10通过PFO,而在其它情形中,这将是困难的事情。在后者的情形中,外科医生可将导管10的远端定位在PFO附近,并前进一个或多个针12通过包围或邻近PFO的心房间隔的组织。在包括多个针12的实施例中,诸针12可以一下子前进或一次前进一个。如上所述,某些针12在一个或多个边缘或表面上具有锯齿形,它们允许针12相当容易地前进,同时,在针12缩回时提供足够的研磨。如图2和3中的双头箭头所示,针12可以前进和缩回任何多次,以达到所要求的研磨量。在某些实施例中,通过观察PFO和周围的组织,可以确定研磨量。当研磨完成时,针12可以缩回到导管10内,而导管10可以从病人中移去。After advancing the catheter to position the distal end near the PFO and/or at any other stage in the method of treating the PFO, a surgeon may use one or more visualization devices to image the PFO. For example, the surgeon may inject contrast material into the right atrium while the patient coughs, performs a Valsalvamaneuver or other maneuver to move blood through the PFO, and one or more images may be obtained. In certain embodiments, after images of one or more PFOs are taken, a guide wire may be placed through the PFO and
现参照图4,导管10的另一实施例在其远端处或其附近包括至少一个能量传输部件16,用来将能量18传输到组织。例如,该传输的能量可包括激光、超声波、射频、微波能、低温能、通过冷却移去能量,或任何其它合适的能量形式。一般来说,能量18用来分裂、收缩、焊接或创伤组织,以引起导致PFO关闭的组织响应。例如,可产生结痂的组织来关闭PFO。在某些实施例中,能量传输部件可包括一个或多个针,其具有研磨表面或没有研磨表面。诸针可以横贯或通过PFO或邻近组织插入以便将能量供应给组织。在某些实施例中,诸针和其展开系统可以布置成将PFO的组织集合在一起,例如,沿轴向或径向方向,并在能量施加到组织之前、之中和/或之后。Referring now to FIG. 4, another embodiment of a
在还有的另一实施例中,现参照图5,导管10可包括一个或多个孔20,以允许一种或多种生物相容的流体22从导管10中被部署。在某些实施例中,气囊24可在导管远端处或其附近充气,以便减缓或阻挡PFO区域内的血液流动,而增加注入到PFO内的流体驻留时间。各种生物相容的和/或生物吸收的流体22可使用在各种实施例中,以引起PFO的关闭。在某些实施例中,例如,可使用酸或粘结剂,它们将致使PFO组织局部地灼烧或结痂。然而,当流体离开PFO区域时,它将通过与血液的混合而快速地稀释成为一安全的稀释液,并通过进入病人的血液流将对病人不造成伤害。例如,可使用生物相容的异丁烯酸盐来有效地“胶合”关闭的PFO,同时激发愈合的响应。In yet another embodiment, referring now to FIG. 5 ,
根据本发明的装置和方法可依赖于呈各种形式的能量来密封PFO,可以用一相关的移植物或不使用移植物。诸如补缀、自关闭的元件等的移植物可以使用呈各种方式的能量焊接到位置上。在各种实施例中,可以使用任何合适类型或构造的焊接物质、基体、补缀等,以提高能量的施加而提供PFO的关闭。使用各种类型的能量和组织焊接物质来关闭PFO的装置和方法完整地描述在美国专利申请No.10/665974(代理人案卷号No.22128-000300US)中,上文中已援引该专利以供参考。Devices and methods according to the present invention may rely on energy in various forms to seal the PFO, with or without an associated graft. Implants such as patches, self-closing elements, etc. can be welded into place using energy in various ways. In various embodiments, any suitable type or configuration of welding substances, substrates, patches, etc. may be used to enhance the application of energy to provide closure of the PFO. Apparatus and methods for closing a PFO using various types of energy and tissue welding substances are fully described in U.S. Patent Application No. 10/665974 (Attorney Docket No. 22128-000300US), which was incorporated above for reference. refer to.
作为对基于移植物的装置的变体,根据本发明的系统可用来焊接PFO关闭而其后不留下移植物。如图6A和6B所示,在某些实施例中,可放置一回挡和能量供应导管以与PFO接触,供应能量来分裂第一和第二胶原质基体,以致使PFO的两部分融合。所使用的能量可以是单极的或双极的RF(在此情形中,回挡用作能量返回,或接地电极)、超声波、激光、微波,或电阻加热。可引入蛋白质结合物以便于焊接。As a variant to graft-based devices, the system according to the invention can be used to weld the PFO closed without leaving a graft thereafter. As shown in Figures 6A and 6B, in some embodiments, a backstop and energy supply catheter can be placed in contact with the PFO to supply energy to disrupt the first and second collagen matrices so that the two parts of the PFO fuse. The energy used can be monopolar or bipolar RF (in which case the backstop acts as an energy return, or ground electrode), ultrasound, laser, microwave, or resistive heating. Protein conjugates can be introduced to facilitate welding.
参照图6A,治疗PFO(第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS之间的开口)的一导管装置30的实施例可包括一外导管轴34、一可滑动地设置在外轴34内的内导管轴36、一与回挡致动器38偶联且延伸通过内轴36的回挡32,以及能量供应部件33。能量供应部件33可以供应任何合适形式的能量以使PFO关闭,例如(但不限于),RF、超声波、激光或微波能。在某些实施例中,回挡32可用作一能量返回部件,例如,当使用双极RF能量时。Referring to FIG. 6A, an embodiment of a
如图6B所示,一导管装置40的另一变化的实施例可包括一导管轴42、一可膨胀的部件46、一设置在可膨胀部件46内的能量供应部件48,以及一近端与一致动器44偶联的回挡43。可膨胀部件46和回挡43用来将导管装置40定位在一要求的部位内以便治疗PFO,而通过能量供应部件48施加能量。在一实施例中,例如,能量供应部件可包括一超声波压电箔,但在其它变化的实施例中,可使用任何其它合适的供应装置。As shown in Figure 6B, another alternative embodiment of a
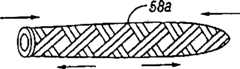
使用一回挡部件的另一实施例示于图7A-7E中。如图7A所示,用于治疗PFO的导管装置50的一实施例可包括一导管轴52、一近端与一致动器54偶联的回挡56,以及一“宽边帽形”的补缀58。回挡56用来帮助定位导管50和将邻近PFO的组织(诸如第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS)集合在一起。然后,补缀58抵靠第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS固定就位而覆盖PFO的开口。在某些实施例中,导管装置可包括一个或多个能量传输部件,以便施加任何合适形式的能量来将补缀58焊接或粘结到邻近PFO的组织。在其它的实施例中,可使用一组织粘结剂。其它的实施例可使用一锁定组织附连机构,以便将补缀58固定到PFO组织,这将在下面作进一步讨论。一般来说,如图7B和7C所示,宽边帽形部件58可从一第一细长形状58a(图7B)起进行操作,以便于通过导管轴52供应到宽边帽形58b(图7C),该形状将允许补缀58覆盖PFO开口。在一实施例中,补缀58由一编结材料制成,以允许从细长形状58a转换到宽边帽形状58b。Another embodiment using a backstop is shown in Figures 7A-7E. As shown in FIG. 7A, one embodiment of a
如图7D和7E所示,导管装置50的一实施例包括一锁定的远端59,其将补缀58锁定到其宽边帽形状的构造,并且还将补缀58固定到PFO。一内轴59a相对于一外轴59b朝向远端地移动,和/或外轴59b朝向近端地移动(见实心末端的箭头),这样,位于内轴59a上的突出53锁定到位于外轴59b上的孔51内。图7E示出处于其锁定位置的锁定远端59。如果远端59定位在一PFO内并然后放置在其锁定位置内,则某些突出53将穿入邻近PFO的组织内而将远端59固定在PFO内,因此,将补缀58的部位固定在PFO的开口处。As shown in Figures 7D and 7E, one embodiment of
在其它实施例中,根据本发明的PFO关闭系统可利用一个或多个夹子来关闭PFO。这样的系统可以分成多个设计,它们涉及一右和左心房部件,以及仅是右侧的那些设计。尽管它们通常不是通电的,但它们可要求对任何这些设计添加能量以便于粘结和密封。In other embodiments, a PFO closure system according to the present invention may utilize one or more clips to close a PFO. Such systems can be divided into designs involving a right and left atrial component, and those that are only on the right side. Although they are not usually energized, they may require energy to be added to any of these designs to facilitate bonding and sealing.
一右和左侧PFO夹子60的实施例示于图8中。在该实施例中,夹子60通常具有一Z或S形状,使一右心房腿62设置在心脏的右心房内,而一左心房腿64设置在左心房内,且一搭桥腿63延伸通过PFO而连接其它两个腿。夹子60可以由金属丝制成,例如,使用任何合适的丝材,诸如但不限于镍钛诺、不锈钢、铂、金、钽,或任何这些金属的组合或合金。在所示的实施例中,夹子60是一连续的丝材,但也可根据变化的实施例构思出许多其它的构造。也可使用诸如PLLA、PLGA、铁、镁合金之类的可再吸收的材料。可再吸收的材料可以设计而形成一旺盛的发炎响应,以便在装置腐蚀和再吸收之前导致PFO的密封。通常地,一供应导管前进通过PFO,左心房腿64展开,供应装置拉回到右心房内,且右心房腿62展开。倒刺、钩或其它固定辅助物可包括在内。An embodiment of a right and left
在某些实施例中,搭桥腿63可以包括两个或多个部分,例如,线丝等,当在PFO内展开时,它们彼此分散开。这种分散的动作对PFO相对侧处的组织施加相对的侧向力,因此,侧向地扩展PFO并将组织集合在两个分散部件之间。下文中将描述的任何合适的夹子或其它PFO关闭装置可包括一个或多个元件以施加这样的侧向力,而某些具体的实施例将在下文中作描述。In some embodiments, bridging
现参照图9A-9C,一Z形夹子70的另一实施例还包括一右心房腿72、左心房腿74和搭桥部件73。如图9B所示,右心房部件72可包括与一网材料76偶联的多个丝线环75。环75和网76一起用作一位于PFO右侧上的补缀状的结构。如图9C所示,左心房部件74可包括一成形的丝线。在某些实施例中,左心房部件74可包括两个臂74a、74b。当从一供应导管中释放时,臂74a、74b可在朝向第一房间隔SP移动和与其接触之前侧向地移出。在各种实施例中,左心房部件74可给定为任何合适的形状,当从供应导管中释放而更好地接触和保持第一房间隔SP时,以使臂74a、74b沿一个或多个理想的方向移动。如同上述的实施例那样,搭桥部件73可以构造成在PFO内施加侧向力而将组织集合在一起。Referring now to FIGS. 9A-9C , another embodiment of a Z-shaped clip 70 also includes a right
现参照图10A,一用来供应如图9A-9C所示的夹子的供应导管装置80显示在纵向的截面图中。在一实施例中,供应装置80可包括一导管轴82,其具有一近端部分82a和一远端部分82b,以及一设置在轴82内的推力部件84。一夹子86朝向轴82内的推力部件84的远端加载,而导管装置80可以在一导向丝85上送进。在所示的实施例中,近端部分82a具有一比远端部分82b大的截面直径,并在其远端处包括一孔83。由于供应装置80的构造,当推力部件84相对于导管体82侧向地前进时,在夹子86的一左心房腿86b释放之前,夹子86的右心房腿86a从孔83中释放出。相对于左心房腿在右心房腿之前释放的技术来说,这样一供应技术有时很有利。在某些实施例中,供应装置80也可用来从PFO中移去夹子86,然后,在一更加理想的位置内再定位夹子86。在这样的情形中,在夹子86上前进供应导管80可以起到伸直和脱开夹子86。由于轴82的远端部分82b延伸,导管80在夹子86上的前进可以首先伸直和脱开左心房腿86b,然后,此后可以伸直并与右心房腿86a脱开。导管80然后可撤回而从PFO中移去夹子86,并可用来再次在PFO内展开夹子86。Referring now to FIG. 10A, a
图10B和10C示出轴向截面图中的供应导管装置80。图10B示出导管体82可包括一夹子供应内腔87,夹子86可设置在该内腔中,以及一导向丝内腔88,其中可设置导向丝85。夹子供应内腔87可具有任何合适的形状和尺寸以便于供应夹子。在所示的实施例中,夹子供应内腔87是一具有隔间的连续的内腔,隔间用于夹子的右心房腿86a和左心房腿86b。图10C示出推力部件84设置在夹子86近端处的夹子供应内腔87内。Figures 10B and 10C show the
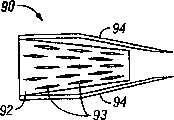
右侧夹子装置的一实例示于图11A-11F中。一般地说,右侧夹子装置展开一通常关闭的可膨胀的装置,其引入到PFO,膨胀并驱动到第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS的组织内,并允许返回到其通常关闭的位置,从而关闭PFO。可以采用气囊或机械的装置来实现膨胀,并可使用任何上述的夹子材料。An example of a right clip device is shown in Figures 11A-11F. In general, the right clip device deploys a normally closed expandable device that is introduced into the PFO, expanded and driven into the tissue of the first SP and second SS, and allowed to return to its normally closed position. position, thereby closing the PFO. Expansion can be achieved using balloon or mechanical means and any of the clip materials described above can be used.
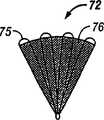
如图11A所示,夹子装置90可合适地包括一可膨胀的、自关闭的展幅机92,其具有多个狭槽93,以及与展幅机92偶联的多个组织附连部件94。展幅机92可通过导管装置供应到一部位以便在其未展开的状态下(如图11A所示)治疗一PFO。展幅机92然后可膨胀(如图11B所示)而膨胀开组织附连部件94。组织附连部件94然后前进而刺入第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS的组织内,展幅机92从膨胀力中释放而允许其关闭到其未膨胀的形式,因此,将组织附连部件94拉在一起,因此,将第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS集合在一起。As shown in FIG. 11A , the
刚才所描述的技术示于图11C-11F中。图11C示出设置在其未膨胀开的构造下的夹子装置90,该构造位于一具有一可充气的气囊96的供应导管95上。在图11D中,气囊96已经充气而膨胀开夹子装置90。如图11E所示,夹子装置90然后被驱动到PFO内,以使组织附连部件94刺穿和将其本身附连到第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS。如图11F所示,然后,气囊96放气并撤回,以允许夹子装置90返回到其未膨胀的构造,因此,将第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS拉在一起而关闭PFO。The technique just described is shown in Figures 11C-11F. FIG. 11C shows
刚才所述夹子装置的一变化的实施例示于图12A和12B中。在此实施例中,一PFO关闭系统100包括一供应导管102和一夹子装置104。供应导管102包括一外轴106和一可滑动地设置在外轴106内的内轴108。在某些实施例中,供应导管102可在一导向丝上前进入/通过一PF0。夹子装置104包括一与多个组织附连部件105偶联的可膨胀的展幅机103。如图12A中的实心末端的箭头所示,内轴108可相对于外轴106朝向远端前进。如图12B所示,内轴106还可前进延伸通过展幅机103并推开组织附连部件105,因此,膨胀开展幅机103。组织附连部件105然后可驱动到邻近PFO的组织内,可撤回内轴而允许展幅机103向下关闭到其未展开的状态,因此,通过组织附连部件105将PF0组织拉在一起。An alternate embodiment of the clip device just described is shown in Figures 12A and 12B. In this embodiment, a
现参照图13A和13B,在一实施例中,一PFO关闭装置110构造为用作一补缀。关闭装置110包括诸如上述丝线那样的多个丝线112、一网114或与丝线112偶联的基体、近端的钩118以及远端的钩116。一导管装置113可用来供应关闭装置110,其通过诸如内部腔静脉IVC的合适的血管。(其它标示的解剖上的参照物是上腔静脉SVC和冠状窦CS。)如图13B所示,关闭装置110可使用一推力杆115(或在其它变化的实施例中,任何其它合适的机构)前进跑出导管装置113,以使远端钩116接触和附连到第二房间隔SS,而近端钩118将其自身固定到第一房间隔SP。然后,丝线112的网络和网114用作为一补缀而密封PFO。Referring now to Figures 13A and 13B, in one embodiment, a
通常要求使用超声波来观察展开之后的装置。可以用一生物相容的涂层对上述所有的装置进行涂敷,在涂层中,空气或惰性气体的微小气泡被捕获在涂层内,以使它们在超声波下更加容易看见。在降解聚合物的情形中,在挤压加工过程中可以引入微小气泡到材料中。Ultrasound is often required to view the device after deployment. All of the above devices can be coated with a biocompatible coating in which tiny bubbles of air or an inert gas are trapped within the coating to make them more visible under ultrasound. In the case of degraded polymers, microscopic air bubbles can be introduced into the material during the extrusion process.
现参照图14A和14B,一PFO关闭装置120的实施例包括一导管122和一对附连到导管122的柔性弹簧臂124。侧向力用作两个用途:它相对于PFO转动地定向一供应导管,以及将第一房间隔和第二房间隔集合在一起,并将PFO定位在其自然的关闭位置。一旦它保持在其自然的关闭位置(如图14B所示),可以应用一穿透的U形钉、非穿透的夹子或其它合适的装置永久地将PFO保持在一起和密封PFO。或者,可使用侧向弹簧臂将第一房间隔和第二房间隔集合在一起,并用上述任何的能量供应机构焊接在一起,可以使用蛋白质焊料也可不使用,以便关闭PFO。Referring now to FIGS. 14A and 14B , an embodiment of a
现参照图15A和15B,在PFO内施加侧向力的装置的某些实施例包括侧向力的夹子。在图15A中,夹子130是一连续的丝材、金属或任何其它合适的材料,并构造成不仅施加侧向力(实心末端的箭头)而且对第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS施加力(中空末端箭头)。如图15B所示,在一变化的实施例中,一开口的夹子132施加侧向力(实心末端的箭头)和对第一房间隔SP施加力(中空末端箭头)。Referring now to Figures 15A and 15B, some embodiments of the means for applying lateral force within the PFO include lateral force clips. In FIG. 15A, clip 130 is a continuous wire, metal, or any other suitable material, and is configured to apply not only a lateral force (solid-ended arrows) but also Force (hollow-ended arrow). As shown in Figure 15B, in an alternate embodiment, an
现参照图16A-16C,一PFO关闭装置140的实施例包括一导管142和一对与导管142偶联的柔性弹簧臂144。设置在导管体内且从中展开的是一用来附连到邻近PFO的组织的钉装置146(或夹子装置)。图16B示出带有臂144的装置140,诸臂144设置在PFO内,并因此在PFO内施加侧向力而将邻近的组织集合在一起。钉装置146然后通过相同的或一第二导管予以供应。钉装置146穿过(图16B中虚线)并将形成PFO的第一房间隔和第二房间隔的表面拉在一起。钉装置146还可具有机械的特征,例如,倒刺或针,或由某种材料制成,其引起一痊愈的响应而促进第一房间隔和第二房间隔痊愈在一起。代替一对柔性的弹簧臂144,导管142可变化地包括一对臂,它们之间的距离可通过一位于导管142手柄内的机构进行控制。在某些实施例中,诸臂144可与一个或多个钉装置146(或其它关闭装置)偶联,这样,当诸臂彼此移开时,它们也将钉装置分散开。钉装置的散开可帮助对各种钉突出提供相等的间距,这样,PFO组织以规则的间距横贯PFO的宽度固定。在钉装置展开到组织内之后,导管142和臂144从PFO中移去,如图16C所示,将钉装置146留在位置上。在一变化的实施例中,不是将穿入组织的钉装置146展开,而是展开一非穿入的夹子装置。Referring now to FIGS. 16A-16C , an embodiment of a
侧向力施加钉系统的变化的实施例示于图17A和17B中。在图17A中,一PFO关闭装置150包括一导管152、柔性弹簧臂154以及一钉装置156。在此实施例中,弹簧臂154包括一成形的部分158,其锁定到PFO的隧道内,以在展开钉装置156之前便于定位装置150。如图17B所示,在另一实施例中,一关闭装置160也包括一导管、柔性弹簧臂164以及一钉装置166。在此实施例中,弹簧臂164包括钩形的部分168以从左心房内钩住在第一房间隔上而用作为一回挡。在本发明的范围之内,可以构思出用于这样柔性弹簧臂的任何其它合适的构造。An example of a variation of the lateral force applying tack system is shown in Figures 17A and 17B. In FIG. 17A , a
一具有弹簧力并至少局部地位于PFO内的移植物,是施加集合和固定PFO的第一房间隔和第二房间隔表面所需要的力的另一种方法。该移植物可包括任何材料、金属或塑料,其可提供一预设的弹簧力。移植物通过一导管供应。该移植物也可具有造成痊愈响应的诸特征。这样的弹簧力移植物(一般地称之为“夹子”)的实例示于图18-21中。这样的夹子通常通过导管供应,成为附连到第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS的组织。A spring-loaded graft positioned at least partially within the PFO is another means of applying the force required to bring together and immobilize the first and second interseptal surfaces of the PFO. The implant can comprise any material, metal or plastic, that provides a predetermined spring force. The graft is supplied through a catheter. The graft may also have characteristics that lead to a healing response. An example of such a spring force implant (commonly referred to as a "clip") is shown in Figures 18-21. Such clips are usually supplied through a catheter as tissue attached to the first SP and second SS septum.
参照图18,一简化的弹簧夹子170附连到第二房间隔SS和第一房间隔SP,并将组织拉在一起。如图19所示,弹簧夹子172的另一实施例可包括一上部173a和一下部173b,并可包括诸如倒刺174的附连特征。如图20所示,在另一实施例中,一弹簧夹子178可具有一带有保持倒刺180的砂漏形状。在还有的另一实施例中,如图21所示,一弹簧夹子182可包括释放的部分185,以便于从供应导管183中释放夹子182。当夹子182拉回到供应导管183内(实心末端的箭头)时,由于释放的部分185,夹子182的叉张开。当夹子182前进到组织内时,诸叉从其扩张的构造集合在一起,不仅刺入组织而且抓住或捏住组织将组织集合在叉之间。在其它的实施例中,导管本身可包括一个或多个零件以便于夹子的放置。在一实施例中,例如,位于导管内表面上的一可充气的气囊可膨胀而挤压一夹子,使它伸展出导管的端部。在各种实施例中,可构思出许多其它的供应系统。Referring to Figure 18, a
在另一实施例中,一钉装置或具有一补缀198和一带有齿196的钳夹的夹子装置190固定到卵圆窝的边缘。在由同样丝线材料制成的某些实施例中,夹子装置190可包括一右心房丝线框架192,以及一相对的钳夹部件194。齿196、倒刺、钩、钉等附连到丝线框架192和钳夹部件194,以将装置190附连到边缘。丝线框架192和补缀198然后向下悬挂在PFO上而将其关闭。在某些实施例中,夹子装置190的一部分还可锚固在第一房间隔上,例如,通过附加的齿197,或诸如倒刺、钩之类的其它的特征。诸如齿196、197、钉腿或倒刺之类的夹子装置190的诸零件可穿入卵圆窝的边缘而将合成材料的补缀198固定在PFO上。此外,夹子装置190的几何形有助于其相对于PFO准确地定位。In another embodiment, a staple device or
现参照图23A和23B,在另一实施例中,一PFO螺旋针200可从左心房内的一位置施加到邻近PFO的组织而关闭PFO。如图23A所示,在一实施例中,用螺旋针200和缩回在导管202内的可缩回的供应臂204,导管202通过心房间隔AS予以供应。一旦导管202的远端部分定位在左心房内,供应臂可围绕一万用接头203从导管202延伸。然后,导管202可转动、扭转或施加扭矩而驱动螺旋形针200离开供应臂204并进入邻近PFO的组织内。在一实施例中,如图所示,螺旋形针200被驱动入和通过第一房间隔SP组织并进入第二房间SS组织内,以将两个组织集合在一起。一位于螺旋针200上的钩或倒刺201帮助将针200保持在组织内的位置上。如图23B所示,当螺旋针200就位时,它将第一房间隔SP和第二房间隔SS拉在一起。然后,可缩回的供应臂204缩回到导管202内,且撤回导管202。Referring now to Figures 23A and 23B, in another embodiment, a PFO
尽管以上的描述是完整和精确的,但它只描述了本发明的几个实施例。在不脱离本发明范围的前提下,可以对本发明的一个或多个实施例作出各种变化、添加、省略等。此外,本发明的不同元件可以组合来达到任何上述的效果。因此,提供以上的描述只是为了示范的目的,不应解释为其限制由附后的权利要求书所阐述的本While the foregoing description is complete and precise, it describes only a few embodiments of the invention. Various changes, additions, omissions, etc. may be made to one or more embodiments of the present invention without departing from the scope of the present invention. Furthermore, different elements of the present invention may be combined to achieve any of the above-mentioned effects. Accordingly, the foregoing description is provided for exemplary purposes only and should not be construed as limiting the present invention as set forth in the appended claims.
发明的范围。the scope of the invention.
Claims (109)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US45885403P | 2003-03-27 | 2003-03-27 | |
| US60/458,854 | 2003-03-27 | ||
| US60/478,035 | 2003-06-11 | ||
| US60/490,082 | 2003-07-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1780591Atrue CN1780591A (en) | 2006-05-31 |
Family
ID=36770594
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN 200480011741PendingCN1780591A (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Method and device for treating patent foramen ovale |
| CN200480011731AExpired - LifetimeCN100584286C (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Energy-based device for the treatment of patent foramen ovale |
| CN200480011740.XAExpired - LifetimeCN1780590B (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Energy-based device for treating patent foramen ovale |
| CNB2004800117363AExpired - LifetimeCN100413476C (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Method and device for treating patent foramen ovale |
Family Applications After (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200480011731AExpired - LifetimeCN100584286C (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Energy-based device for the treatment of patent foramen ovale |
| CN200480011740.XAExpired - LifetimeCN1780590B (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Energy-based device for treating patent foramen ovale |
| CNB2004800117363AExpired - LifetimeCN100413476C (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2004-03-26 | Method and device for treating patent foramen ovale |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (4) | CN1780591A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107920812A (en)* | 2015-05-20 | 2018-04-17 | 爱德华兹生命科学公司 | Atrial septal closure device for re-entry |
| CN109044481A (en)* | 2018-07-10 | 2018-12-21 | 杭州电子科技大学 | The biological spur method for grinding of imitative anteater tongue |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10413284B2 (en) | 2006-11-07 | 2019-09-17 | Corvia Medical, Inc. | Atrial pressure regulation with control, sensing, monitoring and therapy delivery |
| US9232997B2 (en) | 2006-11-07 | 2016-01-12 | Corvia Medical, Inc. | Devices and methods for retrievable intra-atrial implants |
| EP2097012A4 (en) | 2006-11-07 | 2012-08-15 | David Stephen Celermajer | Devices and methods for the treatment of heart failure |
| US20110257723A1 (en) | 2006-11-07 | 2011-10-20 | Dc Devices, Inc. | Devices and methods for coronary sinus pressure relief |
| US9757107B2 (en) | 2009-09-04 | 2017-09-12 | Corvia Medical, Inc. | Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having adjustable sizes |
| EP2528646A4 (en) | 2010-01-29 | 2017-06-28 | DC Devices, Inc. | Devices and systems for treating heart failure |
| WO2011094521A2 (en) | 2010-01-29 | 2011-08-04 | Dc Devices, Inc. | Devices and methods for reducing venous pressure |
| US8911434B2 (en)* | 2010-10-22 | 2014-12-16 | Medtronic Cryocath Lp | Balloon catheter with deformable fluid delivery conduit |
| US12303119B2 (en) | 2011-02-10 | 2025-05-20 | Corvia Medical, Inc. | Apparatus and methods to create and maintain an intra-atrial pressure relief opening |
| WO2012109557A2 (en)* | 2011-02-10 | 2012-08-16 | Dc Devices, Inc. | Apparatus and methods to create and maintain an intra-atrial pressure relief opening |
| US8951223B2 (en) | 2011-12-22 | 2015-02-10 | Dc Devices, Inc. | Methods and devices for intra-atrial shunts having adjustable sizes |
| CN103393467B (en)* | 2013-08-06 | 2015-04-15 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Laser cutting stitching instrument |
| GB201321710D0 (en)* | 2013-12-09 | 2014-01-22 | Creo Medical Ltd | Electrosurgical apparatus |
| US10675450B2 (en) | 2014-03-12 | 2020-06-09 | Corvia Medical, Inc. | Devices and methods for treating heart failure |
| JP6799526B2 (en) | 2014-07-23 | 2020-12-16 | コルヴィア メディカル インコーポレイテッド | Equipment and methods for the treatment of heart failure |
| CN111803209A (en)* | 2020-07-24 | 2020-10-23 | 珠海富伊特科技有限公司 | Disposable laser metal thermotherapy target head |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2134071C (en)* | 1992-04-23 | 1999-04-27 | Sew Wah Tay | Apparatus and method for sealing vascular punctures |
| AU1077799A (en)* | 1997-10-10 | 1999-05-03 | Hearten Medical, Inc. | A catheter for causing thermal trauma to a patent foramen ovale and method of using the catheter |
| US6325798B1 (en)* | 1998-02-19 | 2001-12-04 | Curon Medical, Inc. | Vacuum-assisted systems and methods for treating sphincters and adjoining tissue regions |
| US5919200A (en)* | 1998-10-09 | 1999-07-06 | Hearten Medical, Inc. | Balloon catheter for abrading a patent foramen ovale and method of using the balloon catheter |
- 2004
- 2004-03-26CNCN 200480011741patent/CN1780591A/enactivePending
- 2004-03-26CNCN200480011731Apatent/CN100584286C/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-26CNCN200480011740.XApatent/CN1780590B/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
- 2004-03-26CNCNB2004800117363Apatent/CN100413476C/ennot_activeExpired - Lifetime
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107920812A (en)* | 2015-05-20 | 2018-04-17 | 爱德华兹生命科学公司 | Atrial septal closure device for re-entry |
| CN109044481A (en)* | 2018-07-10 | 2018-12-21 | 杭州电子科技大学 | The biological spur method for grinding of imitative anteater tongue |
| CN109044481B (en)* | 2018-07-10 | 2020-09-15 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Using method of bone grinding device imitating tongue of ant feeding animal |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN1780590B (en) | 2010-06-09 |
| CN100413476C (en) | 2008-08-27 |
| CN1780589A (en) | 2006-05-31 |
| CN1787789A (en) | 2006-06-14 |
| CN1780590A (en) | 2006-05-31 |
| CN100584286C (en) | 2010-01-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7637924B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for treatment of patent foramen ovale | |
| US11331190B2 (en) | Steerable lesion excluding heart implants for congestive heart failure | |
| US7914527B2 (en) | Energy based devices and methods for treatment of patent foramen ovale | |
| CN1780591A (en) | Method and device for treating patent foramen ovale | |
| US8021362B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for closing a layered tissue defect | |
| JP6356665B2 (en) | Vascular closure device and method | |
| US11723639B2 (en) | Vascular closure device | |
| US20170095257A1 (en) | Devices and methods for occluding an atrial appendage |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right | Owner name:TERUMO CORP. Free format text:FORMER OWNER: CIERRA INC Effective date:20080627 | |
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TA01 | Transfer of patent application right | Effective date of registration:20080627 Address after:Tokyo, Japan Applicant after:Terumo Corporation Address before:American California Applicant before:Cierra Inc. | |
| C12 | Rejection of a patent application after its publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |