CN1753344A - The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) - Google Patents
The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA)Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1753344A CN1753344ACNA2004100780315ACN200410078031ACN1753344ACN 1753344 ACN1753344 ACN 1753344ACN A2004100780315 ACNA2004100780315 ACN A2004100780315ACN 200410078031 ACN200410078031 ACN 200410078031ACN 1753344 ACN1753344 ACN 1753344A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- node
- transmission
- confirmation
- modulation mode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及WCDMA,特别是涉及WCDMA中的设定确认信息调制方式的设备和方法。The present invention relates to WCDMA, in particular to a device and a method for setting modulation mode of confirmation information in WCDMA.
背景技术Background technique
服务质量(以下简称QoS)是指用户所能觉察和测量的服务性能。QoS的参数用来定量地表示QoS。宽带码分多址(以下简称WCDMA)系统中定义的QoS参数主要包括:最大比特率、SDU错误率和传输时延等。其中,最大比特率定义了在单位时间内网络所能传输的最大比特数,SDU错误率定义了出错或者丢失的SDU的比率,而传输时延则定义了数据到达目的地所需要的时间。WCDMA的业务分成了四种流量类型:会话型、流型、交互型和后台型。其中,会话型主要用于传输对时延要求非常严格的实时业务,如语音业务;流型主要用于传输对时延要求不是非常严格的实时业务,如流式媒体业务;交互型主要用于传输请求-响应型的非实时业务,如网页浏览业务;而后台型主要用于传输对时延不敏感的非实时业务,如后台下载电子邮件业务。Quality of Service (hereinafter referred to as QoS) refers to the service performance that users can perceive and measure. The parameters of QoS are used to express QoS quantitatively. The QoS parameters defined in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (hereinafter referred to as WCDMA) system mainly include: maximum bit rate, SDU error rate, and transmission delay. Among them, the maximum bit rate defines the maximum number of bits that can be transmitted by the network per unit time, the SDU error rate defines the ratio of SDUs that are erroneous or lost, and the transmission delay defines the time required for data to reach the destination. WCDMA business is divided into four traffic types: conversational, streaming, interactive and background. Among them, the conversational type is mainly used to transmit real-time services that have very strict requirements on delay, such as voice services; the stream type is mainly used to transmit real-time services that do not have very strict requirements on delay, such as streaming media services; the interactive type is mainly used for Transmission request-response non-real-time services, such as web page browsing services; while the background type is mainly used to transmit non-real-time services that are not sensitive to delay, such as downloading email services in the background.
为了对下行的高速数据业务进行优化,WCDMA在Rel-5中引入了高速下行数据接入(以下简称HSDPA)技术。HSDPA中采用了HARQ技术。HARQ是一种将前项纠错(以下简称FEC)和自动选择重传(以下简称ARQ)结合起来的技术。ARQ是指对传输的数据添加校验保护。当接收方检测到校验保护错误时,会通知发送方将错误的数据重新发送。FEC是指依靠插入的冗余来纠正数据传输可能出现的错误的机制。HARQ则是指数据本身同时添加了校验保护和编码保护。编码保护提供的编码增益降低了传输数据所需的信噪比。一旦校验保护发现数据传输出现了错误,该数据会被重新发送。通常,数据的第一次发送被称为首次传输,数据的重新发送被称为重传。在HARQ的实现中,接收机需要分配一定的缓冲区存储空间。对于首次传输出现错误的数据,接收机将接收到的数据储存在缓冲区中。当接收到重传的数据时,接收机将其与缓冲区中的数据进行合并。HARQ的优虑在于错误传输的数据的能量在以后的解码过程中也会被利用,同时由于重传所引入的时间分集使所需的总能量相比无HARQ时少,从而提高了链路效率。HSDPA中每个终端(以下简称UE)有多个下行的进程来传输数据,每个进程都有相应的信令指示。当首次传输在一个进程中出现错误时,重传数据将在同一个进程内被传输。UE为每个进程保留一个单独的缓冲区用来做软合并。采用多进程的好处是,一个进程多次出现错误不会阻塞其他进程传输数据。在HSDPA中,传输信令的物理信道是HS-SCCH。HS-SCCH中主要传输新数据指示(以下简称NDI)、冗余版本和进程信息等。NDI为一个比特,用来指示进程的数据是否是新数据。对于重传,NDI保持不变;对于首次传输,NDI会加1(模2),即当NDI为1时变为0(为0时则变为1)。In order to optimize the downlink high-speed data service, WCDMA introduces a high-speed downlink data access (hereinafter referred to as HSDPA) technology in Rel-5. The HARQ technology is adopted in HSDPA. HARQ is a technology that combines forward error correction (hereinafter referred to as FEC) and automatic selective retransmission (hereinafter referred to as ARQ). ARQ refers to adding parity protection to transmitted data. When the receiver detects a verification protection error, it will notify the sender to resend the wrong data. FEC refers to a mechanism that relies on inserted redundancy to correct possible errors in data transmission. HARQ means that the data itself is added with verification protection and coding protection at the same time. The coding gain provided by code protection reduces the signal-to-noise ratio required to transmit data. Once the check protection finds that there is an error in data transmission, the data will be resent. Usually, the first sending of data is called first transmission, and the resending of data is called retransmission. In the implementation of HARQ, the receiver needs to allocate a certain buffer storage space. For the first transmission error data, the receiver will store the received data in the buffer. When the retransmitted data is received, the receiver combines it with the data in the buffer. The advantage of HARQ is that the energy of erroneously transmitted data will also be utilized in the subsequent decoding process, and at the same time, due to the time diversity introduced by retransmission, the total energy required is less than that without HARQ, thereby improving link efficiency. . In HSDPA, each terminal (hereinafter referred to as UE) has multiple downlink processes to transmit data, and each process has a corresponding signaling indication. When an error occurs in a process for the first transmission, the retransmitted data will be transmitted in the same process. UE reserves a separate buffer for each process for soft merging. The advantage of using multiple processes is that multiple errors in one process will not block other processes from transmitting data. In HSDPA, the physical channel for transmitting signaling is HS-SCCH. The HS-SCCH mainly transmits New Data Indicator (hereinafter referred to as NDI), redundancy version and process information, etc. NDI is a bit used to indicate whether the data of the process is new data. For retransmission, NDI remains unchanged; for the first transmission, NDI will be increased by 1 (modulo 2), that is, when NDI is 1, it becomes 0 (when it is 0, it becomes 1).
HSDPA中由于采用了HARQ技术,需要在上行链路中传输对下行发送数据的确认信息(ACK/NACK):即当UE对接收到的数据译码并且译码后的数据经过CRC校验正确时,UE发送ACK(确认);反之,当译码后的数据CRC校验失败时,UE发送NACK(否定确认)。基站(以下简称Node B)在收到UE发送的ACK后,将会在同一个进程内发送新数据;当Node B收到UE发送的NACK后,将会在同一个进程内重传数据。Due to the use of HARQ technology in HSDPA, it is necessary to transmit the acknowledgment information (ACK/NACK) for the downlink transmission data in the uplink: that is, when the UE decodes the received data and the decoded data is correct after the CRC check , the UE sends an ACK (acknowledgment); otherwise, when the decoded data CRC check fails, the UE sends a NACK (negative acknowledgment). The base station (hereinafter referred to as Node B) will send new data in the same process after receiving the ACK sent by the UE; when the Node B receives the NACK sent by the UE, it will retransmit the data in the same process.
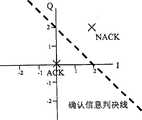
HSDPA中,确认信息采用了正反极性调制。正反极性调制是将ACK和NACK分别调制为两个极性相反的信号。图1显示了正反极性调制的星座图。在图1中,ACK位于星座图中的第一象限,其相位角为45度,而NACK位于星座图中的第三象限,其相位角与ACK相反,为225度。图1中的确认信息判决线是接收方用来判断发送的确认信息是ACK还是NACK。当接收到的数据点的位置处于判决线的上方时,接收方认为发送的是ACK,反之则认为是NACK。欧式距离是指ACK和NACK调制后的点间距。图1中的欧式距离是对于不同的调制方式而言,为了使解调的性能相同,ACK和NACK间的欧式距离必须相同。图1中的星座图只是为了说明正反极性调制的特征而用。HSDPA中的确认信息的调制方式与此不尽相同。在HSDPA系统中,由于对ACK和NACK的性能要求不同,两者的发射功率可能不同。另外,由于确认信息的加扰、扩频等操作,实际发送的ACK和NACK的相位也不完全如图1所示。In HSDPA, the confirmation information adopts forward and reverse polarity modulation. Forward and reverse polarity modulation is to modulate ACK and NACK into two opposite polarity signals respectively. Figure 1 shows the constellation diagram for forward and reverse polarity modulation. In Figure 1, ACK is located in the first quadrant of the constellation diagram with a phase angle of 45 degrees, while NACK is located in the third quadrant of the constellation diagram with a phase angle of 225 degrees opposite to ACK. The acknowledgment information judgment line in Figure 1 is used by the receiver to judge whether the sent acknowledgment information is ACK or NACK. When the position of the received data point is above the decision line, the receiver considers that what was sent is an ACK, otherwise it considers it to be a NACK. The Euclidean distance refers to the point spacing between ACK and NACK modulation. The Euclidean distance in Figure 1 is For different modulation methods, in order to achieve the same demodulation performance, the Euclidean distance between ACK and NACK must be the same. The constellation diagram in Figure 1 is only used to illustrate the characteristics of forward and reverse polarity modulation. The modulation method of the acknowledgment information in HSDPA is not the same as this. In the HSDPA system, due to different performance requirements for ACK and NACK, the transmission power of the two may be different. In addition, due to operations such as scrambling and spectrum spreading of the acknowledgment information, the phases of the actually sent ACK and NACK are not exactly as shown in FIG. 1 .
下文讨论其它几种确认信息的调制方式。需要明确的是,HSDPA的调制方式是正反极性调制。开关键控(以下简称OOK)是指当信息比特取特定的值时不予发送。例如,当确认信息是ACK时予以发送;而当确认信息是NACK时则不发送。这种方式被称为ACK导向OOK,如图2所示。另外一种方式是NACK导向OOK,即当确认信息是NACK时予以发送;而当确认信息是ACK时则不发送。这种调制方式如图3所示。对于OOK而言,为了达到与正反极性调制相同的解调性能,ACK与NACK的欧式距离必须相同。如图2所示,欧式距离与正反极性调制相同是这就意味着在ACK导向OOK中,ACK的发射功率比在正反极性调制中要高。对于这三种确认信息的调制方式而言,在保证解调性能的前提下,需要考虑平均发射功率的问题。在这里,平均发射功率需要综合考虑发送ACK和NACK的功率,以及ACK和NACK的发送概率。当ACK的发送概率非常高时,采用NACK导向OOK会使平均发射功率较小,这是因为ACK没有被发送。类似的,当NACK的发送概率非常高时,采用ACK导向OOK会使平均发射功率较小。而当ACK和NACK的发送概率接近时,采用正反极性调制会使平均发射功率较小。此外,如果数据的最大传输次数被限制,例如流型业务的最大传输次数被限制到两次,则当达到最大传输次数时(对于流型业务是第二次传输),相应的确认信息可以不用发送,即无论是ACK还是NACK,Node B都不发送确认信息。这是由于UE在发送数据到达最大传输次数时,无论Node B的接收是否正确都会发送新数据。这就意味着对最大传输次数的确认信息对于UE没有意义。这种极端的调制方式可以称为停止传输。Several other modulation modes of confirmation information are discussed below. What needs to be clear is that the modulation method of HSDPA is forward and reverse polarity modulation. On-off keying (hereinafter referred to as OOK) refers to not sending when the information bit takes a specific value. For example, it is sent when the acknowledgment is ACK; it is not sent when the acknowledgment is NACK. This approach is called ACK-oriented OOK, as shown in Figure 2. Another way is that NACK leads to OOK, that is, when the confirmation information is NACK, it is sent; when the confirmation information is ACK, it is not sent. This modulation method is shown in Figure 3. For OOK, in order to achieve the same demodulation performance as forward and reverse polarity modulation, the Euclidean distances of ACK and NACK must be the same. As shown in Figure 2, the Euclidean distance is the same as the forward and reverse polarity modulation This means that in ACK-directed OOK, the transmit power of ACK is higher than in forward and reverse polarity modulation. For these three modulation modes of confirmation information, under the premise of ensuring demodulation performance, the issue of average transmission power needs to be considered. Here, the average transmit power needs to comprehensively consider the power of sending ACK and NACK, and the sending probability of ACK and NACK. When the probability of ACK transmission is very high, using NACK-directed OOK results in lower average transmit power because ACKs are not sent. Similarly, when the transmission probability of NACK is very high, using ACK-oriented OOK will make the average transmission power smaller. However, when the transmission probabilities of ACK and NACK are close, the average transmission power will be smaller by using forward and reverse polarity modulation. In addition, if the maximum number of data transmissions is limited, for example, the maximum number of transmissions for streaming services is limited to two times, when the maximum number of transmissions is reached (the second transmission for streaming services), the corresponding confirmation information may not be used. Send, that is, whether it is ACK or NACK, Node B does not send confirmation information. This is because the UE will send new data no matter whether the Node B receives it correctly or not when sending data reaches the maximum number of transmissions. This means that the acknowledgment information for the maximum number of transmissions is meaningless to the UE. This extreme modulation can be called stop transmission.
上行专用信道增强(以下简称E-DCH)是WCDMA系统中正在为之制定相关标准以对现有的上行专用信道进行增强的研究项目。其研究目的是通过研究自适应调制编码、HARQ和Node B控制的调度等技术来增强WCDMA系统的上行系统性能。E-DCH是对现有的上行专用信道的增强,其所支持的服务类型非常的广泛,包括流型、交互型和后台型业务等。Uplink Dedicated Channel Enhancement (hereinafter referred to as E-DCH) is a research project for which relevant standards are being formulated in WCDMA systems to enhance existing uplink dedicated channels. Its research purpose is to enhance the uplink system performance of WCDMA system by studying technologies such as adaptive modulation and coding, HARQ and Node B-controlled scheduling. E-DCH is an enhancement to the existing uplink dedicated channel, and it supports a wide range of service types, including streaming, interactive, and background services.
在E-DCH中,物理信道E-DPCCH用于传输物理层的控制信息。在E-DPCCH中可以传输冗余版本、重传编号(以下简称RSN)和QoS指示等。其中RSN用来指示本次传输是第几次传输同一份数据,例如,对于首次传输,RSN为0,对于第一次重传,RSN=1,依此类推。QoS指示用来表明当前数据所对应的服务类型。此外,NDI等信息也可以被传送(需要注意的是,在某些配置条件下,RSN和NDI二者中只有一个被传送;在另外一些配置条件下,二者都可以被传送)。In E-DCH, the physical channel E-DPCCH is used to transmit the control information of the physical layer. A redundancy version, a retransmission number (hereinafter referred to as RSN), and a QoS indication can be transmitted in the E-DPCCH. The RSN is used to indicate how many times the same data is transmitted in this transmission, for example, for the first transmission, RSN is 0, for the first retransmission, RSN=1, and so on. The QoS indication is used to indicate the service type corresponding to the current data. In addition, information such as NDI can also be transmitted (it should be noted that under certain configuration conditions, only one of RSN and NDI is transmitted; under other configuration conditions, both can be transmitted).
与HSDPA类似,由于采用了HARQ技术,E-DCH需要在下行链路中传输对上行发送数据的确认信息。确认信息在下行的专用信道或者共享信道中发送。由于确认信息占用了下行的功率资源,因此下行的确认信息的发送需要在保证确认信息接收质量的前提下选用适当的调制方式来尽可能减少对下行功率的需求。Similar to HSDPA, due to the adoption of HARQ technology, E-DCH needs to transmit confirmation information for uplink transmission data in the downlink. The acknowledgment information is sent on the downlink dedicated channel or shared channel. Since the acknowledgment information occupies downlink power resources, the transmission of the downlink acknowledgment information needs to select an appropriate modulation method under the premise of ensuring the quality of the acknowledgment information to reduce the demand for downlink power as much as possible.
在E-DCH中采用与HSDPA相同的调制方式来发送确认信息的缺点在于需要占用较多的下行功率资源。为了保证HARQ协议的可靠实施,对确认信息的性能要求通常会非常严格。这样采用通常的正反极性调制需要用很大的功率来发射确认信息。这个问题在软切换时尤为严重。在软切换时,有多个Node B与UE间保持无线连接。其中一些Node B由于无线信道较差,需要极高的功率来发射确认信息。确认信息占用过多的下行发射功率会减小下行的系统容量。The disadvantage of using the same modulation method as HSDPA to send confirmation information in E-DCH is that it needs to occupy more downlink power resources. In order to ensure the reliable implementation of the HARQ protocol, the performance requirements for the acknowledgment information are usually very strict. It is necessary to use a lot of power to transmit the confirmation information by adopting the usual forward and reverse polarity modulation in this way. This problem is especially serious during soft handover. During soft handover, multiple Node Bs maintain wireless connections with the UE. Some of these Node Bs require extremely high power to transmit acknowledgments due to poor wireless channels. The acknowledgment information occupies too much downlink transmission power, which will reduce the downlink system capacity.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种宽带码分多址中的设定确认信息调制方式的设备和方法。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a device and method for setting the modulation mode of confirmation information in wideband code division multiple access.
按照本发明的一方面,一种宽带码分多址中设定确认信息调制方式的方法,包括步骤:According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for setting the modulation mode of confirmation information in wideband code division multiple access includes the steps of:
对应于特定服务质量数据的每次传输所对应的确认信息,RNC设定其调制方式并通知Node B和UE;Corresponding to the confirmation information corresponding to each transmission of specific quality of service data, RNC sets its modulation mode and notifies Node B and UE;
Node B根据接收到的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来设定确认信息的调制方式;The Node B sets the modulation mode of the confirmation information according to the quality of service corresponding to the received data and the number of transmissions;
UE根据所发送的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来确定Node B发送确认信息的调制方式并进行相应的解调。The UE determines the modulation mode of the acknowledgment message sent by the Node B according to the quality of service and the number of transmissions corresponding to the sent data and performs corresponding demodulation.
按照本发明的另一方面,一种宽带码分多址中设定确认信息调制方式的设备,包括发射部分和接收部分,其特征在于还包括:According to another aspect of the present invention, a device for setting the modulation mode of confirmation information in wideband code division multiple access, including a transmitting part and a receiving part, is characterized in that it also includes:
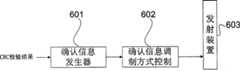
确认信息发生器,根据接收部分的CRC检验结果,产生确认信息;A confirmation information generator generates confirmation information according to the CRC inspection result of the receiving part;
确认信息调制方式控制模块,根据接收部分的E-DPCCH中的RSN和QoS指示来设定确认信息的调制方式,确认信息通过发射部分的调制器进行调制。The acknowledgment information modulation mode control module sets the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information according to the RSN and QoS indication in the E-DPCCH of the receiving part, and the acknowledgment information is modulated by the modulator of the transmitting part.
本发明通过根据服务质量来灵活配置每次传输的确认信息的调制方式,有效地降低了确认信息对下行功率资源的占用,提高了下行的系统容量。The present invention flexibly configures the modulation mode of the confirmation information for each transmission according to the service quality, effectively reduces the occupation of the downlink power resources by the confirmation information, and improves the downlink system capacity.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是正反极性调制的星座图;Figure 1 is a constellation diagram of forward and reverse polarity modulation;
图2是ACK导向OOK的星座图;Figure 2 is a constellation diagram of ACK-oriented OOK;
图3是NACK导向OOK的星座图;Figure 3 is a constellation diagram of NACK-oriented OOK;
图4显示了Node B产生和发送确认信息的操作;Figure 4 shows the operation of Node B to generate and send confirmation information;
图5显示了UE处理确认信息的操作;Figure 5 shows the operation of UE processing confirmation information;
图6显示了Node B设定确认信息调制方式的设备;Figure 6 shows the equipment for Node B to set the modulation mode of confirmation information;
图7显示了在配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程;Fig. 7 shows the process that RNC notifies Node B and UE of the modulation mode of confirmation information when configuring the parameters of the wireless link;
图8显示了在重新配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程;Fig. 8 shows the process that RNC notifies Node B and UE of the modulation mode of confirmation information when reconfiguring the parameters of the wireless link;
图9显示了UE的硬件框图的一个示例;Figure 9 shows an example of a hardware block diagram of a UE;
图10显示了Node B的硬件框图的一个示例。Figure 10 shows an example of a Node B hardware block diagram.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
对应于特定服务质量数据的每次传输所对应的确认信息,RNC设定Corresponding to the confirmation information corresponding to each transmission of the specific quality of service data, the RNC sets其调制方式并通知Node B和UE。Its modulation method and notify Node B and UE.
每种服务质量的数据在物理层中的传输对于时延和剩余误块率(即在最后一次传输后的误块率)的要求不完全相同。例如,流型的业务对传输时延的要求可能是数据最多允许传输两次,而后台型的业务可能允许数据传输四次。这样每种业务在每次传输时的错误概率不同。例如,流型业务的第一次和第二次传输的误块率可能分别是0.3和0.01,这就意味着对应于第一次和第二次传输,Node B发送NACK的概率分别是0.3和0.01。后台型业务的第一次、第二次、第三次和第四次传输的误块率可能分别是0.9,0.8,0.3和0.03,这就意味着对应于第一次、第二次、第三次和第四次传输,Node B发送NACK的概率分别是0.9,0.8,0.3和0.03。这样,对于流型业务而言,对应于第一次和第二次传输,Node B发送确认信息使用的调制方式分别为正反极性调制和NACK导向OOK时所需的平均发射功率最小。对于后台型业务而言,对应于第一次、第二次、第三次和第四次传输,Node B发送确认信息使用的调制方式分别为ACK导向OOK,ACK导向OOK,正反极性调制和NACK导向OOK时所需的平均发射功率最小。根据使确认信息平均发射功率最小的原则,RNC设定每次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式。例如,对于流型业务,当最大传输次数没有限制时,设定第一次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式为正反极性调制,对于以后的传输,调制方式均为NACK导向OOK。如果流型业务的最大传输次数限制为两次,则设定第一次传输和第二次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式分别为正反极性调制和停止传输。又例如,对于后台型业务,当最大传输次数没有限制时,设定第一次、第二次和第三次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式分别为ACK导向OOK,ACK导向OOK,和正反极性调制,对于以后的传输,调制方式均为NACK导向OOK。如果后台型业务的最大传输次数限制为四次,则设定第一次、第二次、第三次和第四次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式分别为ACK导向OOK,ACK导向OOK,正反极性调制和停止传输。注意,在以上的讨论中,所有的数字以及相对应的调制方式只是为了说明本发明所用的示例。The transmission of data of each quality of service in the physical layer has different requirements on delay and residual block error rate (that is, the block error rate after the last transmission). For example, the transmission delay requirement of stream-type services may be that data is allowed to be transmitted up to two times, while background-type services may allow data to be transmitted four times. In this way, the error probability of each service is different in each transmission. For example, the block error rates of the first and second transmissions of streaming services may be 0.3 and 0.01 respectively, which means that corresponding to the first and second transmissions, the probability of Node B sending NACK is 0.3 and 0.01 respectively. 0.01. The block error rates of the first, second, third, and fourth transmissions of background services may be 0.9, 0.8, 0.3, and 0.03, respectively, which means that corresponding to the first, second, and fourth For the third and fourth transmissions, the probability of Node B sending a NACK is 0.9, 0.8, 0.3 and 0.03, respectively. In this way, for streaming services, corresponding to the first and second transmissions, the modulation methods used by Node B to send confirmation information are forward and reverse polarity modulation and NACK-oriented OOK, and the average transmission power required is the smallest. For background services, corresponding to the first, second, third, and fourth transmissions, the modulation methods used by Node B to send confirmation information are ACK-oriented OOK, ACK-oriented OOK, positive and negative polarity modulation The average transmit power required when leading to OOK and NACK is the smallest. According to the principle of minimizing the average transmission power of the acknowledgment information, the RNC sets the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information corresponding to each transmission. For example, for streaming services, when the maximum number of transmissions is not limited, the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information corresponding to the first transmission is set as forward and reverse polarity modulation, and for subsequent transmissions, the modulation mode is NACK-oriented OOK. If the maximum number of transmissions of the streaming service is limited to two, the modulation modes of the confirmation information corresponding to the first transmission and the second transmission are set to be forward and reverse polarity modulation and stop transmission respectively. As another example, for background services, when the maximum number of transmissions is not limited, the modulation modes of the confirmation information corresponding to the first, second and third transmissions are respectively set as ACK-oriented OOK, ACK-oriented OOK, and positive Reverse polarity modulation, for future transmission, the modulation mode is NACK-oriented OOK. If the maximum number of transmissions of the background service is limited to four times, the modulation modes of the confirmation information corresponding to the first, second, third and fourth transmissions are respectively set as ACK-oriented OOK, ACK-oriented OOK, Forward and reverse polarity modulation and stop transmission. Note that in the above discussion, all numbers and corresponding modulation modes are just examples used to illustrate the present invention.
在配置和重新配置无线链路的参数时,RNC将确认信息的调制方式通过信令通知Node B和UE。When configuring and reconfiguring the parameters of the wireless link, the RNC notifies the Node B and the UE of the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information through signaling.
Node B根据接收到的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来设定确认Node B sets the confirmation according to the service quality corresponding to the received data and the number of transmissions信息的调制方式。How the information is modulated.
Node B根据UE在E-DPCCH中发送的信令判断数据所对应的服务质量以及数据的传输次数。然后Node B根据RNC的配置来设定确认信息的调制方式。例如,按上文设定的流型业务的确认信息的调制方式,假定正反极性调制和NACK导向OOK的星座图分别如图1和图3所示,对于数据的第一次传输,确认信息的调制方式为正反极性调制,即当确认信息为ACK时,按照图1星座图中ACK点的位置来发送确认信息,而当确认信息为NACK时,按照图1星座图中NACK点的位置来发送确认信息。对于数据的第二次传输,当最大传输次数没有限制时,确认信息的调制方式为NACK导向OOK,即当确认信息为NACK时,按照图3星座图中NACK点的位置来发送确认信息,而当确认信息为ACK时,不发送确认信息;当最大传输次数限制为两次时,无论确认信息是ACK还是NACK都不发送确认信息。The Node B judges the service quality corresponding to the data and the number of data transmissions according to the signaling sent by the UE in the E-DPCCH. Then the Node B sets the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information according to the configuration of the RNC. For example, according to the modulation method of the acknowledgment information of the streaming service set above, assuming the constellation diagrams of forward and reverse polarity modulation and NACK-oriented OOK are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 3 respectively, for the first transmission of data, the acknowledgment The modulation method of the information is forward and reverse polarity modulation, that is, when the confirmation information is ACK, the confirmation information is sent according to the position of the ACK point in the constellation diagram in Figure 1, and when the confirmation information is NACK, according to the NACK point in the constellation diagram in Figure 1 location to send a confirmation message. For the second transmission of data, when the maximum number of transmissions is not limited, the modulation method of the acknowledgment information is NACK-oriented OOK, that is, when the acknowledgment information is NACK, the acknowledgment information is sent according to the position of the NACK point in the constellation diagram in Figure 3, and When the confirmation information is ACK, no confirmation information is sent; when the maximum number of transmissions is limited to two, no confirmation information is sent regardless of whether the confirmation information is ACK or NACK.
UE根据所发送的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来确定Node BThe UE determines the Node B according to the quality of service corresponding to the sent data and the number of transmissions发送确认信息的调制方式并进行相应的解调。Send the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information and perform corresponding demodulation.
UE根据接收到的Node B在下行发送的确认信息判断其所对应的数据的服务质量以及数据的传输次数,再根据RNC的配置来明确该确认信息的调制方式。通常确认信息与其所对应的数据有确定的时序关序,UE可根据这个时序关系确定确认信息所对应的数据。例如,按上文设定的流型业务的确认信息的调制方式,对于数据的第一次传输,确认信息的调制方式为正反极性调制;对于数据的第二次传输,确认信息的调制方式为NACK导向OOK。The UE judges the service quality of the corresponding data and the number of data transmissions according to the received acknowledgment information sent by the Node B in the downlink, and then specifies the modulation method of the acknowledgment information according to the configuration of the RNC. Usually, the acknowledgment information and its corresponding data have a definite time sequence relationship, and the UE can determine the data corresponding to the acknowledgment information according to this time sequence relationship. For example, according to the modulation method of the confirmation information of the streaming service set above, for the first transmission of data, the modulation method of the confirmation information is forward and reverse polarity modulation; for the second transmission of data, the modulation method of the confirmation information is The method is NACK leading to OOK.
UE按照确定的调制方式对确认信息进行解调。例如,按上文设定的流型业务的确认信息的调制方式,假定正反极性调制和NACK导向OOK的星座图分别如图1和图3所示。对于数据的第一次传输,参照图1,当接收到的确认信息的数据点的位置处于判决线的上方时,UE认为确认信息是ACK,反之则认为是NACK。对于数据的第二次传输,参照图3,当接收到的确认信息的数据点的位置处于判决线的上方时,UE认为确认信息是NACK,反之则认为是ACK。The UE demodulates the acknowledgment information according to the determined modulation mode. For example, according to the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information of the streaming service set above, assuming the constellation diagrams of forward and reverse polarity modulation and NACK-oriented OOK are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 3 respectively. For the first transmission of data, referring to FIG. 1 , when the position of the data point of the received acknowledgment information is above the decision line, the UE considers the acknowledgment information to be ACK, otherwise, it considers it to be NACK. For the second transmission of data, referring to FIG. 3 , when the position of the data point of the received acknowledgment information is above the decision line, the UE considers the acknowledgment information to be NACK, otherwise, it considers it to be ACK.
如图6所示的Node B设定确认信息调制方式的设备中,Node B的确认信息调制方式控制模块602是本发明的体现。Node B根据对E-DCH数据CRC检验的结果由确认信息发生器601来产生确认信息。当译码的数据通过CRC检验为正确时,确认信息为ACK;否则为NACK。Node B的确认信息调制方式控制模块602则根据接收到的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来设定确认信息的调制方式。确认信息通过编码,复用等步骤按照设定的调制方式由Node B的发射装置603发送。具体的Node B硬件框图在实施例中给出。In the device for setting the modulation mode of the confirmation information by the Node B as shown in FIG. 6 , the modulation
实施例Example
参照所附图纸,下面给出了本发明的两个实施例。为了避免使本专利的描述过于冗长,在下面的说明中,略去了对公众熟知的功能或者装置等的详细描述。Referring to the accompanying drawings, two embodiments of the present invention are given below. In order to avoid making the description of this patent too lengthy, in the following description, detailed descriptions of functions or devices that are well known to the public are omitted.
第一实施例first embodiment
在本实施例中,UE在不同的传输时间间隔中可以传输不同的服务质量的数据。In this embodiment, the UE may transmit data with different service qualities in different transmission time intervals.
图7显示了在配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程。701是RNC通过NBAP信令将E-DCHCONFIGURATION信令通知Node B的过程。702是RNC通过RRC信令将E-DCH CONFIGURATION信令通知UE的过程。出于简化考虑,图7中没有画出Node B和UE向RNC返回的信令。同时图7中的信令的时序关系并不重要:既可以先发送给UE的RRC信令,也可以先发送给Node B的NBAP信令。701信令既可以是一条新的NBAP信令,也可以是对现有的NBAP信令加以扩展。类似,702信令既可以是一条新的RRC信令,也可以是对现有的RRC信令加以扩展。701信令和702信令是在UE与网络建立专用的无线链路的开始由RNC发给Node B和UE用来配置无线链路的参数。在701信令和702信令中,对于UE可能传输的每一种服务质量业务的数据,配置其所对应的每次传输的确认信息的调制方式。例如,如果UE可能传输两种服务质量的业务:流型业务和后台型业务。则在701信令和702信令中,可以指定:对于流型业务,当最大传输次数没有限制时,设定第一次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式为正反极性调制,对于以后的传输,调制方式均为NACK导向OOK。如果流型业务的最大传输次数限制为两次,则设定第一次传输和第二次传输所对应的确认信息的调制方式分别为正反极性调制和停止传输。对于后台型业务,可以根据服务质量的需求作相应的设定。Figure 7 shows the process in which the RNC notifies the Node B and the UE of the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information when configuring the parameters of the wireless link. 701 is a process in which the RNC notifies the Node B of the E-DCH CONFIGURATION signaling through the NBAP signaling. 702 is a process in which the RNC notifies the UE of the E-DCH CONFIGURATION signaling through the RRC signaling. For the sake of simplification, the signaling returned by Node B and UE to RNC is not shown in Fig. 7 . At the same time, the timing relationship of the signaling in Figure 7 is not important: either the RRC signaling to the UE or the NBAP signaling to the Node B can be sent first. The 701 signaling can be a new NBAP signaling, or an extension of the existing NBAP signaling. Similarly, the 702 signaling can be a new RRC signaling, or it can be an extension of the existing RRC signaling. The 701 signaling and 702 signaling are parameters sent by the RNC to the Node B and the UE to configure the wireless link at the beginning of establishing a dedicated wireless link between the UE and the network. In signaling 701 and signaling 702, for data of each quality of service service that may be transmitted by the UE, the corresponding modulation mode of the acknowledgment information for each transmission is configured. For example, if the UE may transmit services with two qualities of service: streaming services and background services. Then in 701 signaling and 702 signaling, it can be specified: for streaming services, when there is no limit to the maximum number of transmissions, set the modulation mode of the confirmation information corresponding to the first transmission as forward and reverse polarity modulation. The transmission and modulation methods are all NACK-oriented OOK. If the maximum number of transmissions of the streaming service is limited to two, the modulation modes of the confirmation information corresponding to the first transmission and the second transmission are set to be forward and reverse polarity modulation and stop transmission respectively. For back-office services, corresponding settings can be made according to service quality requirements.
图8显示了在重新配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程。801是RNC通过NBAP信令将E-DCHRECONFIGURATION信令通知Node B的过程。802是RNC通过RRC信令将E-DCH RECONFIGURATION信令通知UE的过程。出于简化考虑,图8中没有画出Node B和UE向RNC返回的信令。同时图8中的信令的时序关系并不重要:既可以先发送给UE的RRC信令,也可以先发送给Node B的NBAP信令。801信令既可以是一条新的NBAP信令,也可以是对现有的NBAP信令加以扩展。类似,802信令既可以是一条新的RRC信令,也可以是对现有的RRC信令加以扩展。801信令和802信令是RNC发给Node B和UE用来重新配置无线链路的参数。在801信令和802信令中,对于新增加的每一种服务质量业务的数据,配置其所对应的每次传输的确认信息的调制方式;或者是当某些服务质量业务的需求发生改变时,修改这些服务质量业务的数据所对应的每次传输的确认信息的调制方式。Figure 8 shows the process of RNC notifying Node B and UE of the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information when reconfiguring the parameters of the wireless link. 801 is a process in which the RNC notifies the Node B of the E-DCH RECONFIGURATION signaling through the NBAP signaling. 802 is a process in which the RNC notifies the UE of the E-DCH RECONFIGURATION signaling through the RRC signaling. For the sake of simplification, the signaling returned by Node B and UE to RNC is not shown in Fig. 8 . At the same time, the timing relationship of the signaling in Figure 8 is not important: either the RRC signaling to the UE can be sent first, or the NBAP signaling to the Node B can be sent first. The 801 signaling can be a new NBAP signaling or an extension of the existing NBAP signaling. Similarly, the 802 signaling can be a new RRC signaling, or it can be an extension of the existing RRC signaling. 801 signaling and 802 signaling are parameters sent by RNC to Node B and UE to reconfigure the radio link. In 801 signaling and 802 signaling, for the data of each newly added quality of service service, configure the modulation mode of the confirmation information corresponding to each transmission; or when the requirements of some quality of service services change , modify the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information for each transmission corresponding to the data of these QoS services.
Node B根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的QoS指示来确定收到的数据的服务质量。UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的QoS指示。The Node B determines the service quality of the received data according to the QoS indication transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH. For each data transmission, the UE transmits the corresponding QoS indication in the uplink E-DPCCH.
Node B判断收到的数据是第几次传输有两种方法:一种方法是根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的RSN:当RSN=0时,确定数据是第一次传输,当RSN=1时,则确定数据是第二次传输,依此类推。另一种方法是根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的NDI:当NDI第一次发生变化时,确定数据是第一次传输,对于第一次重传,则确定数据是第二次传输,依此类推。对于第一种方法,UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的RSN;对于第二种方法,UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的NDI。There are two methods for Node B to determine the number of times the received data is transmitted: one method is based on the RSN transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH: when RSN=0, it is determined that the data is the first transmission; when RSN=1 , the data is determined to be the second transfer, and so on. Another method is based on the NDI transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH: when the NDI changes for the first time, it is determined that the data is the first transmission, and for the first retransmission, it is determined that the data is the second transmission, and so on analogy. For the first method, the UE transmits the corresponding RSN in the uplink E-DPCCH for each data transmission; for the second method, the UE transmits the corresponding RSN in the uplink E-DPCCH for each data transmission NDI.
Node B根据接收到的数据所对应的服务质量,传输的次数和701信令或801信令中的配置来设定确认信息的调制方式。The Node B sets the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information according to the service quality corresponding to the received data, the number of transmissions and the configuration in the 701 signaling or 801 signaling.
图4显示了Node B产生和发送确认信息的操作。Figure 4 shows the operation of Node B to generate and send confirmation information.
上述图4中的401 Node B接收到UE发送的上行数据。The 401 Node B in Figure 4 above receives the uplink data sent by the UE.
上述图4中的402 Node B对接收到的数据进行译码,并根据CRC检验结果产生确认信息。当译码的数据通过CRC检验为正确时,确认信息为ACK;否则为NACK。The 402 Node B in Figure 4 above decodes the received data, and generates confirmation information according to the CRC check result. When the decoded data is correct through the CRC check, the confirmation information is ACK; otherwise, it is NACK.
上述图4中的403 Node B判断数据所对应的服务质量以及数据的传输次数再根据RNC的配置来设定确认信息的调制方式。The 403 Node B in the above Figure 4 judges the service quality corresponding to the data and the number of data transmissions, and then sets the modulation mode of the confirmation information according to the configuration of the RNC.
上述图4中的404 Node B通过编码,复用等步骤按照设定的调制方式发送确认信息(这一步骤也包括上文所说的不发送确认信息的情况)。The 404 Node B in the above Figure 4 sends the confirmation information according to the set modulation mode through steps such as encoding and multiplexing (this step also includes the above-mentioned situation of not sending the confirmation information).
图5显示了UE处理确认信息的操作。Figure 5 shows the operation of the UE to process the acknowledgment information.
上述图5中的501 UE判断是否有最大传输次数的限制并且数据发送达到最大传输次数。如果是,执行过程507;否则,执行过程502。The 501 UE in the above Figure 5 judges whether there is a limit on the maximum number of transmissions and the data transmission reaches the maximum number of transmissions. If yes, go to process 507; otherwise, go to process 502.
上述图5中的502 UE接收确认信息,这一过程中UE可能要执行解复用等操作。The 502 UE in FIG. 5 above receives the confirmation information. During this process, the UE may perform demultiplexing and other operations.
上述图5中的503 UE根据该确认信息判断其所对应的数据的服务质量以及数据的传输次数,再根据RNC的配置来明确该确认信息的调制方式。The 503 UE in FIG. 5 above judges the service quality of the corresponding data and the number of data transmissions according to the acknowledgment information, and then specifies the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information according to the configuration of the RNC.
上述图5中的504 UE解调确认信息。The 504 UE demodulation confirmation information in Fig. 5 above.
上述图5中的505 UE判断确认信息是否是ACK。如果是,执行过程507;否则,执行过程506。505 UE in the above-mentioned Fig. 5 judges whether the acknowledgment information is ACK. If yes, go to process 507; otherwise, go to process 506.
上述图5中的506 UE在与确认信息对应的进程内重传数据。506 UE in the above Figure 5 retransmits data in the process corresponding to the acknowledgment information.
上述图5中的507 UE在与确认信息对应的进程内发送新数据。The 507 UE in the above-mentioned Figure 5 sends new data in the process corresponding to the confirmation information.
图9显示了应用本实施例的UE的硬件框图的一个示例。在本示例中,UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的RSN来指示是第几次传输。FIG. 9 shows an example of a hardware block diagram of a UE to which this embodiment is applied. In this example, for each data transmission, the UE transmits the corresponding RSN in the uplink E-DPCCH to indicate the number of transmissions.
先说明UE发送端的硬件构成。RSN 904和QoS指示905在模块906中与其他信息复用为E-DPCCH,这些信息可能包括NDI等。E-DCH数据经过Turbo编码模块901进行信道编码。编码后的数据进入HARQ处理模块902。在HARQ处理模块902中,UE根据冗余版本来选择编码后的部分或全部数据进行发送。被HARQ处理模块902处理后的数据接着在交织器903内进行交织以减小衰落信道带来的性能损失。被交织器903处理后的E-DCH数据与E-DPCCH以及其他物理信道在模块907中复用。基带信号在模块908中加扰。加扰的目的是使UE的信号与其它UE的信号可以区分。加扰后的信号然后经过脉冲成形滤波器909。脉冲成形滤波器的目的是将UE发射的信号限制在特定的频带内。然后信号经过数/模转换器910由数字信号转变为模拟信号。之后信号进入射频发射机911进行射频相关的操作。从射频发射机出来的信号进入双工器912,最后通过天线913发射到无线信道中。Firstly, the hardware configuration of the sending end of the UE is described.
接着说明UE接收端的硬件构成。Node B下行发射的信号由UE的天线913接收,通过双工器912进入UE的射频接收机914。射频接收机的主要任务是调整振荡器,并作自动增益控制。接收信号然后在模/数转换器915内从模拟信号抽样为数字信号。数字信号在RAKE接收机917内解扰、解扩并进行多径合并,最后进行解调。解调后的数据通过解复用器918分解出确认信息。在确认信息解调器919中,UE根据所发送的数据所对应的服务质量和传输的次数来确定Node B发送确认信息的调制方式并进行相应的解调。UE然后判断确认信息是否是ACK。如果是,UE在与确认信息对应的进程内发送新的E-DCH数据;否则,UE在与确认信息对应的进程内重传E-DCH数据。Next, the hardware configuration of the receiving end of the UE will be described. The signal transmitted by the Node B downlink is received by the
图10显示了应用本实施例的Node B的硬件框图的一个示例。在本示例中,Node B根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的RSN来判断收到的数据是第几次传输。FIG. 10 shows an example of a hardware block diagram of a Node B to which this embodiment is applied. In this example, the Node B judges the number of transmissions of the received data according to the RSN transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH.
先说明Node B发送端的硬件构成。Node B根据E-DCH数据CRC检验1025的结果由确认信息发生器601来产生确认信息。当CRC检验为正确时,确认信息为ACK;否则为NACK。Node B的确认信息调制方式控制模块602则根据接收到的E-DPCCH中的RSN 1020和QoS指示1021来设定确认信息的调制方式。确认信息通过调制器1001进行调制,由1002和1003分别在I支路和Q支路扩频。Q支路的信号由模块1004乘以j因子。I支路和Q支路的信号在模块1005形成基带信号并在模块1006中加扰。加扰后的信号然后在模块1007乘以增益因子后与下行的其他物理信道以CDM的方式由加法器1008复用起来。下行信号经过脉冲成形滤波器1009后经过数/模转换器1010由数字信号转变为模拟信号。之后信号进入射频发射机1011进行射频相关的操作。从射频发射机出来的信号进入双工器1012,最后通过天线1013发射到无线信道中。Firstly, the hardware composition of the Node B sending end is explained. The Node B generates confirmation information by the
接着说明Node B接收端的硬件构成。UE上行发射的信号由Node B的天线1013接收,通过双工器1012进入Node B的射频接收机1014。接收信号然后在模/数转换器1015内从模拟信号抽样为数字信号。数字信号通过射频滤波器1016然后在RAKE接收机1017内解扰、解扩并进行多径合并,最后进行解调。解调后的数据通过解复用器1018分解出E-DCH数据和E-DPCCH等信道。E-DPCCH经过解复用器1019分解出RSN 1020,QoS指示1021和其他信息,如NDI等。RSN 1020和QoS指示1021被确认信息调制方式控制模块602用来设定确认信息的调制方式。E-DCH数据通过解交织器1022,HARQ处理模块1023和译码器1024后在模块1025内进行CRC检验。该检验结果被确认信息发生器601用来产生确认信息。Next, the hardware configuration of the Node B receiving end will be described. The signal transmitted by the UE uplink is received by the
第二实施例second embodiment
在本实施例中,UE传输的所有数据的服务质量相同。In this embodiment, all data transmitted by the UE have the same quality of service.
在配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程仍然如图7所示。在重新配置无限链路的参数时RNC将确认信息的调制方式通知Node B和UE的过程仍然如图8所示。区别在于801信令和802信令中RNC只对一种服务质量业务的数据所对应的每次传输的确认信息的调制方式进行配置。When configuring the parameters of the wireless link, the process of the RNC notifying the Node B and the UE of the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information is still as shown in Figure 7. When reconfiguring the parameters of the wireless link, the process of the RNC notifying the Node B and the UE of the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information is still as shown in Figure 8. The difference is that in the 801 signaling and the 802 signaling, the RNC only configures the modulation mode of the confirmation information for each transmission corresponding to the data of one quality of service service.
Node B判断收到的数据是第几次传输有两种方法:一种方法是根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的RSN:当RSN=0时,确定数据是第一次传输,当RSN=1时,则确定数据是第二次传输,依此类推。另一种方法是根据上行E-DPCCH中传输的NDI:当NDI第一次发生变化时,确定数据是第一次传输,对于第一次重传,则确定数据是第二次传输,依此类推。对于第一种方法,UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的RSN;对于第二种方法,UE对于每一次数据传输,都在上行的E-DPCCH中传输相应的NDI。There are two methods for Node B to determine the number of times the received data is transmitted: one method is based on the RSN transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH: when RSN=0, it is determined that the data is the first transmission; when RSN=1 , the data is determined to be the second transfer, and so on. Another method is based on the NDI transmitted in the uplink E-DPCCH: when the NDI changes for the first time, it is determined that the data is the first transmission, and for the first retransmission, it is determined that the data is the second transmission, and so on analogy. For the first method, the UE transmits the corresponding RSN in the uplink E-DPCCH for each data transmission; for the second method, the UE transmits the corresponding RSN in the uplink E-DPCCH for each data transmission NDI.
Node B根据接收到的数据所对应的传输的次数和701信令或801信令中的配置来设定确认信息的调制方式。The Node B sets the modulation mode of the acknowledgment information according to the number of transmissions corresponding to the received data and the configuration in the 701 signaling or 801 signaling.
Node B产生和发送确认信息的操作,以及UE处理确认信息的操作与第一实施例相同。The operation of the Node B to generate and send the acknowledgment information, and the operation of the UE to process the acknowledgment information are the same as those in the first embodiment.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2004100780315ACN1753344A (en) | 2004-09-20 | 2004-09-20 | The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2004100780315ACN1753344A (en) | 2004-09-20 | 2004-09-20 | The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1753344Atrue CN1753344A (en) | 2006-03-29 |
Family
ID=36680042
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2004100780315APendingCN1753344A (en) | 2004-09-20 | 2004-09-20 | The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN1753344A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101145889B (en)* | 2007-10-24 | 2011-07-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A self-adapted control method for time-division synchronization code division multi-address system |
| CN101123600B (en)* | 2006-08-11 | 2012-01-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | Orthogonal frequency division multi-address access system and its device, transmission method and terminal |
- 2004
- 2004-09-20CNCNA2004100780315Apatent/CN1753344A/enactivePending
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101123600B (en)* | 2006-08-11 | 2012-01-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | Orthogonal frequency division multi-address access system and its device, transmission method and terminal |
| CN101145889B (en)* | 2007-10-24 | 2011-07-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | A self-adapted control method for time-division synchronization code division multi-address system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1173515C (en) | Method and device for effectively retransmitting data in data superimposed voice communication system | |
| CN1131617C (en) | Method for transmitting data in wireless system and wireless system | |
| KR101023330B1 (en) | Method of requesting complex automatic retransmission to guarantee quality of service in wireless communication system | |
| JP4970462B2 (en) | Configurable response mode corresponding to retransmission protocol for hybrid automatic retransmission request | |
| US8780812B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for asynchronous and adaptive hybrid ARQ scheme in a wireless network | |
| CN101075859B (en) | Method and device for packet transmission mixing automatic repeat request and transmission system | |
| US8667357B2 (en) | Method for conducting HARQ with a wireless communications system | |
| US7813379B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving wireless packet data | |
| KR100971159B1 (en) | Multi-carrier wireless communication access terminal and data transmission method | |
| CN1645786A (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting/receiving a control signal on a high speed shared control channel | |
| CN1739257A (en) | Operation of forward link acknowledgment channel on reverse link data | |
| WO2007136002A1 (en) | Radio transmission device and radio transmission method | |
| CN1471254A (en) | Device and method for encoding and decoding channel quality identification information | |
| KR20090118988A (en) | Method and apparatus for multicasting with feedback information | |
| JP2008219925A (en) | Transport block set segmentation | |
| JPWO2008114510A1 (en) | Radio communication base station apparatus and radio communication method | |
| JP2011525088A (en) | Method and apparatus in a communication network | |
| CN1843002A (en) | point-to-multipoint transmission | |
| CN1808958A (en) | Adaptive modulation scheme and coding rate control method | |
| US8284777B2 (en) | Uplink cell changes in a mobile communication network | |
| US20090046713A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting non-decodable packets | |
| WO2010048747A1 (en) | A method for receiving feedback in multi-channel harq, and an apparatus and equipment thereof | |
| CN101060387A (en) | HARQ-based data transmission method | |
| CN1753344A (en) | The equipment of setting confirming information modulation mode and method in the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) | |
| US9008016B2 (en) | Data transmission method and system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Open date:20060329 |