CN1529182A - Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag card - Google Patents
Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag cardDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1529182A CN1529182ACNA2003101078185ACN200310107818ACN1529182ACN 1529182 ACN1529182 ACN 1529182ACN A2003101078185 ACNA2003101078185 ACN A2003101078185ACN 200310107818 ACN200310107818 ACN 200310107818ACN 1529182 ACN1529182 ACN 1529182A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- battery
- card
- tag
- card reader
- label
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及对有源射频识别标签卡的电池电量的信息采集,以及对电池进行充电的方法。The invention relates to information collection of battery power of an active radio frequency identification tag card and a method for charging the battery.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,自动识别方法在许多服务领域、在货物销售与后勤分配方面、在商业部门、在生产企业和材料流通领域得到了快速的普及和推广。In recent years, automatic identification methods have been rapidly popularized and promoted in many service fields, in the sales of goods and logistics distribution, in the commercial sector, in the fields of production enterprises and material circulation.
自动识别技术传统上包括条形码、光学符号识别、语音识别、指纹识别等生物信息测量法、IC卡等,各自具有各自的优缺点,而得到不同的发展和应用。Automatic identification technology traditionally includes barcode, optical symbol recognition, voice recognition, fingerprint recognition and other biological information measurement methods, IC cards, etc., each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and has been developed and applied in different ways.
近年来,自动识别的一种技术上最佳的解决方案是将数据存储在一块硅芯片里。在日常生活中,具有触点排的IC卡(电话IC卡、银行卡等)是电子数据载体的最普遍的结构。然而,对IC卡来说,在许多情况下,机械触点的接通是不可靠的。数据载体与一个所属的读卡机之间的数据进行非接触传输将灵活得多。根据使用的能量和数据传输方法,我们把非接触的识别系统称作射频识别系统(RFID-Radio Frequency Identification)。因此,RFID是一种利用无线电波对纪录媒体进行读写,将射频技术与IC卡技术相结合并可用于远距离、动目标、无线识别的技术,具有无接触、工作距离大、精度高、信息收集处理快捷、全天候工作及较好的应用环境适应性等一系列优点。In recent years, one of the technically best solutions for automatic identification has been to store the data on a silicon chip. In daily life, an IC card (telephone IC card, bank card, etc.) with a contact row is the most common structure of an electronic data carrier. However, for the IC card, in many cases, the connection of the mechanical contacts is unreliable. The contactless transmission of data between the data carrier and an associated card reader is much more flexible. According to the energy and data transmission method used, we call the non-contact identification system RFID-Radio Frequency Identification (RFID-Radio Frequency Identification). Therefore, RFID is a technology that uses radio waves to read and write recording media. It combines radio frequency technology with IC card technology and can be used for long-distance, moving targets, and wireless identification. It has non-contact, large working distance, high precision, It has a series of advantages such as fast information collection and processing, all-weather work and good application environment adaptability.
RFID系统在具体的应用过程中,根据不同的应用目的和应用环境,系统的组成会有所不同,但就其工作原理来看,系统一般都由应答器、读卡机和PC机组成。应答器应放置在要识别的物体上,可以发送和接收信息,可根据收到的操作命令作读/写等处理;读卡机是采集应答器信息并对应答器发出操作命令的装置,发出的命令包括读/写,选择,取消选择等命令。In the specific application process of the RFID system, the composition of the system will be different according to different application purposes and application environments, but in terms of its working principle, the system is generally composed of transponders, card readers and PCs. The transponder should be placed on the object to be identified, it can send and receive information, and can perform read/write processing according to the received operation command; the card reader is a device that collects transponder information and issues an operation command to the transponder. The commands include read/write, select, deselect and other commands.
射频识别系统的工作频率可划归三个范围:低频LF(30kHz-300kHz)、高频或射频HF(3MHz-30MHz)和超高频UHF(300MHz-3GHz)或微波MW(>3GHz)。应答器中的耦合方式分为:电感耦合、电磁反向散射耦合和密耦合。其回送到读卡机的数据传输方法也可分为三类:应用反射或反向散射或负载调制,分谐波以及应答器中产生的高次谐波。The working frequency of the RFID system can be divided into three ranges: low frequency LF (30kHz-300kHz), high frequency or radio frequency HF (3MHz-30MHz) and ultra-high frequency UHF (300MHz-3GHz) or microwave MW (> 3GHz). The coupling methods in the transponder are divided into: inductive coupling, electromagnetic backscatter coupling and close coupling. The method of data transmission back to the reader can also be divided into three categories: application of reflection or backscatter or load modulation, subharmonics, and higher harmonics generated in the transponder.
通常情况,低频、高频或射频RFID系统采用电感耦合或密耦合的方式,负载调制或分谐波,工作距离一般在一米以内;超高频或微波RFID系统采用电磁反向散射耦合,作用距离在一米以上。Usually, low-frequency, high-frequency or radio-frequency RFID systems use inductive coupling or close coupling, load modulation or subharmonic, and the working distance is generally within one meter; ultra-high-frequency or microwave RFID systems use electromagnetic backscatter coupling. The distance is more than one meter.
电磁波反向散射耦合的基本原理是读卡机将询问和时钟信息加载到高频信号上,通过天线发送电磁波,传递给标签卡的天线,标签卡解调接收到的信息,并且将自身携带的信息通过自身的天线传递给读卡机,实现双向的通信。标签卡的天线和它的负载阻抗匹配(阻抗的实部相等,虚部复共扼)的时候认为电磁波的能量全部被天线吸收,在两者的阻抗不匹配的时候,入射的电磁波就被标签的天线反射回去,反射的电磁波能量与入射的电磁波能量取决于标签芯片的输入阻抗与天线的阻抗的失配程度。这样标签的芯片通过调节自身的输入阻抗(对于标签的天线而言是负载阻抗),反射入射的电磁波,就可以将自身的信息传递给读卡机,而不是象读卡机的天线是将电能转换成电磁能发射出去的。The basic principle of electromagnetic wave backscatter coupling is that the card reader loads the query and clock information on the high-frequency signal, sends electromagnetic waves through the antenna, and transmits them to the antenna of the tag card. The tag card demodulates the received information and transmits the information it carries The information is transmitted to the card reader through its own antenna to realize two-way communication. When the antenna of the tag card matches its load impedance (the real part of the impedance is equal and the imaginary part is complex conjugated), it is considered that all the energy of the electromagnetic wave is absorbed by the antenna. When the impedance of the two does not match, the incident electromagnetic wave is absorbed by the tag. The antenna is reflected back, and the reflected electromagnetic wave energy and the incident electromagnetic wave energy depend on the mismatch between the input impedance of the tag chip and the impedance of the antenna. In this way, the chip of the tag can transmit its own information to the card reader by adjusting its own input impedance (for the tag antenna, it is the load impedance) and reflecting the incident electromagnetic wave, instead of transferring electric energy like the antenna of the card reader. Converted into electromagnetic energy emitted.
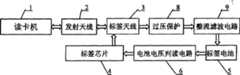
根据标签卡是否具有供电电池分为有源和无源两类。对于无源的标签卡,结构框图见图1,读卡机1通过它的天线2收发电磁波携带的信息数据,标签卡天线3接收读卡机的信息给标签芯片4,标签的芯片通过调制其天线3对读卡机1发送的电磁波的反射,将自身的信息传递给读卡机。两副天线只是起着信息交换的作用。电池5为标签的芯片供电。According to whether the tag card has a power supply battery, it is divided into two types: active and passive. For the passive tag card, the structural block diagram is shown in Figure 1. The
无源的标签卡,自身不带有电源,芯片工作需要的能量来自于标签卡的天线。天线本身具有双向工作的本性,就是说天线可以将电能转换成电磁能,以电磁波的形式发送出去,也能将接收到的电磁波转换成电能。其工作原理框图见图2。读卡机1通过它的天线2收发电磁波携带的信息数据,标签卡天线3接收读卡机的信息传递给标签芯片4,同时将接收到的电磁波转换成交流电,通过整流滤波电路,交流电变成电压稳定的直流电,提供给标签的芯片4使用。标签的芯片通过调制其天线3对读卡机发送的电磁波的反射,将自身的信息传递给读卡机。标签卡的天线起着传递信息和接收电磁波的能量的作用。和有源的标签卡相比,在性能参数和应用条件相同的前提下,由于电磁波的携带的能量在远场的时候与距离的平方成反比,而不是与距离无关,而无源的标签卡的能量来自于自身的天线转换的读卡机发射的电磁能,使得有源的标签卡的工作距离一般远大于无源的标签卡的工作距离。Passive tag cards do not have their own power supply, and the energy required for the chip to work comes from the antenna of the tag card. The antenna itself has the nature of two-way work, which means that the antenna can convert electrical energy into electromagnetic energy, send it out in the form of electromagnetic waves, and convert received electromagnetic waves into electrical energy. The block diagram of its working principle is shown in Figure 2. The
由于天线发射的能量有限,以及标签天线和读卡机的天线的增益有限,相互的阻抗匹配、极化匹配不是最佳等原因,使得射频识别的距离降低,所以远距离(一般大于2米)的射频识别一般采用有源的标签卡,天线主要起着对信息的交换作用,标签卡的能量由电池供给。Due to the limited energy emitted by the antenna, the limited gain of the tag antenna and the antenna of the card reader, mutual impedance matching, polarization matching and other reasons, the distance of radio frequency identification is reduced, so long distance (generally greater than 2 meters) RFID generally uses active tags, the antenna mainly plays the role of exchanging information, and the energy of the tags is supplied by batteries.
当载有标签的被识别目标进入读卡机的读取范围时,标签上的天线接收射频波束,解调电磁波携带的信息,同时调制标签卡天线的反射,与读卡机进行通信。读卡机将接收到的反射信号进行接收处理后,经接口传给计算机,计算机装有相应的物流软件,记录这些信息,这些信息可以通过网络进行传播。这样就可以实现对贴有标签卡的目标进行识别、归类、跟踪和处理。When the identified target carrying the tag enters the reading range of the card reader, the antenna on the tag receives the radio frequency beam, demodulates the information carried by the electromagnetic wave, and at the same time modulates the reflection of the tag antenna to communicate with the card reader. After the card reader receives and processes the received reflected signal, it transmits it to the computer through the interface, and the computer is equipped with corresponding logistics software to record the information, which can be transmitted through the network. This enables the identification, classification, tracking and processing of tagged objects.
有源的射频识别系统中,一般标签卡的用电量比较小,电池的使用时间比较长,标签装置不提供电池的电量信息。随着使用时间的延长,电池的电量下降,使得自动识别系统的作用距离下降,在使用者不清楚电池的用电量,读卡机系统可能得不到标签卡的信息而造成对标签系统的识别和记录的遗漏。In an active radio frequency identification system, the power consumption of the general tag card is relatively small, and the battery life is relatively long, and the tag device does not provide battery power information. With the prolongation of the use time, the power of the battery decreases, which makes the working distance of the automatic identification system decrease. If the user does not know the power consumption of the battery, the card reader system may not be able to obtain the information of the label card, which will cause damage to the label system. Identify and document omissions.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于提出一种对有源射频识别系统中标签卡的电池电量进行识别,并进行充电的方法。The purpose of the present invention is to propose a method for identifying and charging the battery power of a tag card in an active radio frequency identification system.
本发明提出的对有源射频识别系统中标签卡的电池电量进行识别和充电的方法,主要是对电池的电压进行测量,当电压降低到某一设定值(这值由与标签卡芯片的供电电压的波动允许要求,以及其正常工作的用电量来确定)的时候,标签卡的芯片即将不能正常工作。这时通过设置一个电压判读电路,得到电池电量信息,并传递给标签的芯片,标签的芯片在与读卡机通信的时候,将自身的电量信息反馈给读卡机;当读卡机收集到的标签卡电量信息,表明标签卡电量严重不足的时候,提示更换电池或对电池进行充电处理。在电量不足的时候,可以在标签上给予警示提示,比如点亮某种颜色的提示灯或响起蜂鸣器。这样不至于在标签卡没有经过读卡机采集其电池的电量信息的时候就不能工作了,而又得不到提示,以至于标签不能正常工作,在贴标签的物品在读卡机的工作区域的时候,读卡机不能识别标签,而遗漏贴标签的物品。The method for identifying and charging the battery power of the tag card in the active radio frequency identification system proposed by the present invention is mainly to measure the voltage of the battery. When the fluctuation of the power supply voltage allows the requirements and the power consumption of its normal work is determined), the chip of the tag card will not work normally. At this time, by setting up a voltage reading circuit, the battery power information is obtained and passed to the chip of the tag. When the chip of the tag communicates with the card reader, it will feed back its own power information to the card reader; when the card reader collects The power information of the tag card indicates that when the power of the tag card is seriously low, it prompts to replace the battery or charge the battery. When the power is low, a warning prompt can be given on the label, such as lighting a warning light of a certain color or sounding a buzzer. In this way, the tag card will not be unable to work when it does not pass through the card reader to collect its battery power information, and it will not be prompted, so that the label cannot work normally. When the labeled item is in the working area of the card reader , The card reader cannot recognize the tag, and misses the tagged item.
有源电池在供电不足的时候,需要更换,有时候由于标签卡粘贴的位置等原因,不方便更换。本发明在读卡机读到标签卡的电池电量不足的时候,或在标签卡有前面讲的电量不足警示的时候,采用电磁场对标签电池进行射频或微波充电。为了防止过高的感生电压损坏标签电路元件,标签卡设有充电保护电路,对有源的标签卡充电的工作原理和方法与前面讲的无源标签卡的供电相同。不过这需要读卡机增大发射电磁波的能量(最大能量符合国家相关标准要求)或缩短对标签卡的充电的距离。因为读卡机发射的电磁波能量在远场的时候,随着距离的平方成反比,读卡机和标签卡的距离近的时候,一般足够对标签卡的电池进行充电。这时候的读卡机相当于无线充电器。标签卡的天线将接收到的读卡机发射的电磁波转换成交流电,再经过整流滤波电路变成直流电,从而对标签卡的电池进行充电。通过标签芯片上的电压判读电路,判断电池的电压,当电压达到某设定值(与电池电量充足的时候提供的正常工多电压有关)的时候,说明已经充足了电,将该信息传递给标签卡芯片,芯片通过调制其天线的反射,将该信息反馈给读卡机,使读卡机停止充电。The active battery needs to be replaced when the power supply is insufficient, and sometimes it is inconvenient to replace due to the location of the label card and other reasons. In the present invention, when the card reader reads that the battery power of the tag card is insufficient, or when the tag card has the above-mentioned low power warning, the electromagnetic field is used to charge the tag battery with radio frequency or microwave. In order to prevent excessive induced voltage from damaging the tag circuit components, the tag card is equipped with a charging protection circuit. The working principle and method of charging the active tag card are the same as the power supply of the passive tag card mentioned above. However, this requires the card reader to increase the energy of the emitted electromagnetic waves (the maximum energy meets the requirements of relevant national standards) or shorten the charging distance of the tag card. Because the electromagnetic wave energy emitted by the card reader is in the far field, it is inversely proportional to the square of the distance. When the distance between the card reader and the tag card is short, it is generally enough to charge the battery of the tag card. At this time, the card reader is equivalent to a wireless charger. The antenna of the tag card converts the received electromagnetic wave emitted by the card reader into alternating current, which is then converted into direct current through a rectification and filtering circuit, thereby charging the battery of the tag card. The voltage of the battery is judged by the voltage reading circuit on the tag chip. When the voltage reaches a certain set value (related to the normal working voltage provided when the battery is fully charged), it means that the battery is fully charged, and the information is transmitted to the The chip of the tag card, the chip feeds back the information to the card reader by modulating the reflection of its antenna, so that the card reader stops charging.
正常情况标签处于读卡机的电磁场辐射区域的时间都大于读卡机与标签的通信的时间,使得使用电磁波对标签无线充电成为可能。天线接收读卡机发射的电磁波,转换成交流电,经过整流滤波电路,交流电变成直流电,当该电压大于标签电池的电压的时候,而电池本身又处在电量不是最充足的时候,就可以对电池进行充电。这时标签实际使用或部分使用(有可能天线转换的电能不够标签芯片使用)的是来自天线转换的电磁能;在来自天线的直流电小于电池电压的时候,不能对电池进行充电,标签芯片完全使用的是电池进行供电。很可能这种非专门的电磁波充电方式充的电量往往不能提供标签芯片的正常工作,但是它能够在只要满足:标签处于读卡机的电磁场辐射区域,电池电量不是最充足,天线转换的能量,经过整流滤波后的直流电电压大于电池的电压就可以对标签的电池进行充电,从而延长标签电池不经过专门的充电过程的使用时间。与前面的专用电磁波充电方式相比,不添加专门电路。而不象一般的有源标签无论天线转换的电能大小,该电不提供给标签卡使用。Under normal circumstances, the tag is in the electromagnetic field radiation area of the card reader for a longer time than the communication time between the card reader and the tag, making it possible to use electromagnetic waves to charge the tag wirelessly. The antenna receives the electromagnetic wave emitted by the card reader and converts it into alternating current. After the rectification and filtering circuit, the alternating current becomes direct current. When the voltage is greater than the voltage of the label battery, and the battery itself is not fully charged, it can The battery is charged. At this time, the actual use or partial use of the tag (it is possible that the electric energy converted by the antenna is not enough for the tag chip) is the electromagnetic energy converted by the antenna; when the direct current from the antenna is lower than the battery voltage, the battery cannot be charged, and the tag chip is fully used. The battery is used for power supply. It is very likely that the power charged by this non-specialized electromagnetic wave charging method often cannot provide the normal work of the tag chip, but it can be used as long as the tag is in the electromagnetic field radiation area of the card reader, the battery power is not the most sufficient, and the energy converted by the antenna, The rectified and filtered direct current voltage is greater than the voltage of the battery to charge the battery of the tag, thereby prolonging the use time of the tag battery without going through a special charging process. Compared with the previous dedicated electromagnetic wave charging method, no special circuit is added. Unlike general active tags, no matter how much power is converted by the antenna, the power is not provided to the tag card.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1有源标签卡的工作框图。Figure 1 is a working block diagram of an active label card.
图2无源标签卡的工作框图。Figure 2 is a working block diagram of a passive tag card.
图3为标签卡自身判读电池供电量电路以及电量不足提示和信息反馈给读卡机的电路。Fig. 3 is the circuit for judging the battery power supply of the tag card itself and the circuit for prompting and information feedback to the card reader when the battery is insufficient.
图4读卡机对标签进行充电示意图Figure 4 Schematic diagram of charging the tag by the card reader
图中标号:1为读卡机,2为发射天线,3为接收天线,4为标签芯片,5为标签电池,6为电池电压判读电路,7为电池电压不足警示器,8为过压保护电路。Numbers in the figure: 1 is the card reader, 2 is the transmitting antenna, 3 is the receiving antenna, 4 is the label chip, 5 is the label battery, 6 is the battery voltage reading circuit, 7 is the low battery voltage warning device, 8 is the overvoltage protection circuit.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图进一步具体描述本发明。The present invention is further specifically described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
在标签电池5用电量严重不足,将要不能是标签的芯片正常工作的时候,电池电压判读电路6会自动启动标签卡的电压不足警示装置7,如灯或声音示警,如图3。在与读卡机1通信的时候,通过标签的芯片4和标签天线3将标签卡电池电量不足的信息发给读卡机1,读卡机的操作人员酌情处理,或提示更换电池或对可充电的标签卡电池进行电磁波充电,如图3所示。When the power consumption of the tag battery 5 is seriously insufficient, and the chip of the tag will not work normally, the battery
在读卡机接收到标签的电池电量不足,需要进行充电的信息后,读卡机1(这里充当电磁波充电器)的发射天线2发送强电磁电磁波,或近距离对标签电池进行充电。标签的接收天线3接收该电磁波并转换成电能。标签的接收天线3后接过压保护电路8,防止充电电压过高对后面的电路产生破坏。过压保护电路8后紧跟整流滤波电路9,对天线3转换的交流电整流滤波成直流电,对标签电池5进行充电。在标签卡的充电电池的电压达到要求的时候,电池的电压判读电路6会发信息给标签卡的芯片4,通过标签的天线3将充电结束的信息反馈给电磁波充电器1,结束充电。After the card reader receives the message that the battery of the tag is insufficient and needs to be charged, the transmitting
为了使有源标签在读卡机天线的辐射工作区域内的时候,标签天线转换的电磁波能量不白白浪费掉,使标签卡天线转换的电磁波能量尽量的为标签芯片使用,控制充电的条件不是标签卡的电池电压严重不足,而是:标签处于读卡机的电磁场辐射区域,电池电量不是最充足,天线转换的能量,经过整流滤波后的直流电电压大于电池的电压就可以对标签的电池进行充电。具体的电路与实施过程与前面所述的使用读卡机专门对标签卡进行充电的相同,这里就不另外说明。In order to ensure that the electromagnetic wave energy converted by the tag antenna is not wasted when the active tag is in the radiation working area of the card reader antenna, so that the electromagnetic wave energy converted by the tag card antenna can be used by the tag chip as much as possible, the condition for controlling charging is not the tag card The battery voltage is seriously insufficient, but: the tag is in the electromagnetic field radiation area of the card reader, the battery power is not the most sufficient, the energy converted by the antenna, the DC voltage after rectification and filtering is greater than the voltage of the battery, and the battery of the tag can be charged. The specific circuit and implementation process are the same as that of using the card reader to charge the tag card mentioned above, and will not be further explained here.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2003101078185ACN1529182A (en) | 2003-10-01 | 2003-10-01 | Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag card |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2003101078185ACN1529182A (en) | 2003-10-01 | 2003-10-01 | Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag card |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1529182Atrue CN1529182A (en) | 2004-09-15 |
Family
ID=34304491
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNA2003101078185APendingCN1529182A (en) | 2003-10-01 | 2003-10-01 | Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag card |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN1529182A (en) |
Cited By (42)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100424723C (en)* | 2006-05-09 | 2008-10-08 | 株洲南车时代电气股份有限公司 | Wireless IC card for data read-write and storage of engine monitoring apparatus |
| CN100458841C (en)* | 2006-12-28 | 2009-02-04 | 复旦大学 | Semi-active RFID tag supporting wireless charging |
| CN101459981A (en)* | 2007-12-12 | 2009-06-17 | Lg电子株式会社 | Mobile terminal having menu providing function for wireless recharging and recharging method thereof |
| CN101955096A (en)* | 2009-07-20 | 2011-01-26 | 杭州优迈科技有限公司 | Passive type wireless remote elevator call control system and control method |
| CN102103682A (en)* | 2009-12-18 | 2011-06-22 | 上海科斗电子科技有限公司 | Electronic scanning article search system and assorted electronic tag thereof |
| CN101142491B (en)* | 2005-03-14 | 2011-08-03 | 艾利丹尼森公司 | Rfid application test systems and methods |
| CN102298717A (en)* | 2010-06-23 | 2011-12-28 | 福建新大陆电脑股份有限公司 | Active electronic tag with wireless charging device |
| CN102412856A (en)* | 2010-09-21 | 2012-04-11 | 上海科斗电子科技有限公司 | Wireless sensor system |
| CN102467102A (en)* | 2010-11-04 | 2012-05-23 | 北京天一众合科技股份有限公司 | Boundary control method and system, low-frequency locator and identification card |
| CN101395617B (en)* | 2006-03-10 | 2012-05-30 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Semiconductor device and method of operating the same |
| CN101527372B (en)* | 2008-03-06 | 2012-07-04 | 财团法人工业技术研究院 | Programmable energy storage control module and system |
| CN102842050A (en)* | 2006-12-07 | 2012-12-26 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Rfid system and semiconductor device |
| US8400278B2 (en) | 2006-05-31 | 2013-03-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and IC label, IC tag, and IC card having the same |
| CN103051360A (en)* | 2012-04-19 | 2013-04-17 | 深圳中科讯联科技有限公司 | System and method based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Devices) wireless connection |
| CN103218653A (en)* | 2013-04-23 | 2013-07-24 | 复旦大学 | Label harmonic wave obtaining method for harmonic wave radio frequency identification and harmonic wave radio frequency identification label |
| CN103226726A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-07-31 | 重庆邮电大学 | Novel semi-passive RFID label chip |
| CN103500351A (en)* | 2013-10-16 | 2014-01-08 | 章玺 | Active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag using alternating current |
| CN104077619A (en)* | 2013-09-25 | 2014-10-01 | 苏州天趣信息科技有限公司 | A device and its combination for increasing the transmission distance of radio frequency identification signals |
| CN104464068A (en)* | 2013-09-12 | 2015-03-25 | 富港电子(东莞)有限公司 | Number calling device and method of use thereof |
| CN104463307A (en)* | 2013-09-23 | 2015-03-25 | 富港电子(东莞)有限公司 | Easy card with escaping function and using method thereof |
| CN104678315A (en)* | 2004-11-08 | 2015-06-03 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Wireless Battery Status Management For Medical Devices |
| CN104700129A (en)* | 2015-03-04 | 2015-06-10 | 包建伟 | RFID reader with identity recognition and electromagnetic wave emission |
| CN104700143A (en)* | 2015-03-04 | 2015-06-10 | 包建伟 | Wireless charging active RFID (radio frequency identification) |
| CN105471023A (en)* | 2015-11-30 | 2016-04-06 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | Wireless charging method, device and system of implantable chips |
| CN106650879A (en)* | 2016-12-22 | 2017-05-10 | Tcl集团股份有限公司 | Intelligent RFID tag and working method thereof |
| CN107102272A (en)* | 2012-12-27 | 2017-08-29 | 杜拉塞尔美国经营公司 | Utilize circuit remote sense remaining battery capacity on battery |
| CN108120939A (en)* | 2017-12-23 | 2018-06-05 | 武汉瑞纳捷电子技术有限公司 | A kind of active card battery power amount calculation method |
| CN108763980A (en)* | 2011-12-27 | 2018-11-06 | 杜拉塞尔美国经营公司 | Intelligent power |
| US10684374B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2020-06-16 | Duravell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for remotely determining a battery characteristic |
| CN111289704A (en)* | 2020-03-03 | 2020-06-16 | 中国农业大学 | Multi-parameter passive flexible sensing device and method for aquatic product quality monitoring |
| US10818979B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2020-10-27 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Single sided reusable battery indicator |
| CN112528688A (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-19 | 浙江悦和科技有限公司 | Radio frequency tag control method, response method and device, storage medium, reader and radio frequency tag |
| US10964980B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2021-03-30 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Indicator circuit decoupled from a ground plane |
| US10971769B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-04-06 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Reusable battery indicator with electrical lock and key |
| US11024891B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-01 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Reusable battery indicator with lock and key mechanism |
| US11024892B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-01 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Dual sided reusable battery indicator |
| US11031686B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-08 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Positive battery terminal antenna ground plane |
| CN112968509A (en)* | 2021-04-23 | 2021-06-15 | 歌尔股份有限公司 | Control method for wireless charging device, and storage medium |
| WO2021134556A1 (en)* | 2019-12-31 | 2021-07-08 | 李庆远 | Ring with electronic tag. |
| CN116560485A (en)* | 2023-03-16 | 2023-08-08 | 深圳多为智联科技有限公司 | Power management method and system of intelligent terminal equipment |
| WO2023185904A1 (en)* | 2022-03-31 | 2023-10-05 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Energy supply method and apparatus for backscatter communication, terminal, and network side device |
| US11837754B2 (en) | 2020-12-30 | 2023-12-05 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Magnetic battery cell connection mechanism |
- 2003
- 2003-10-01CNCNA2003101078185Apatent/CN1529182A/enactivePending
Cited By (67)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104678315A (en)* | 2004-11-08 | 2015-06-03 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Wireless Battery Status Management For Medical Devices |
| CN104678315B (en)* | 2004-11-08 | 2018-03-30 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Wireless battery condition managing for portable medical equipment |
| CN101142491B (en)* | 2005-03-14 | 2011-08-03 | 艾利丹尼森公司 | Rfid application test systems and methods |
| CN101395617B (en)* | 2006-03-10 | 2012-05-30 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Semiconductor device and method of operating the same |
| CN100424723C (en)* | 2006-05-09 | 2008-10-08 | 株洲南车时代电气股份有限公司 | Wireless IC card for data read-write and storage of engine monitoring apparatus |
| US8400278B2 (en) | 2006-05-31 | 2013-03-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and IC label, IC tag, and IC card having the same |
| US8810375B2 (en) | 2006-05-31 | 2014-08-19 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and IC label, IC tag, and IC card having the same |
| CN102842050B (en)* | 2006-12-07 | 2015-12-16 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Rfid system and semiconductor device |
| CN102842050A (en)* | 2006-12-07 | 2012-12-26 | 株式会社半导体能源研究所 | Rfid system and semiconductor device |
| CN100458841C (en)* | 2006-12-28 | 2009-02-04 | 复旦大学 | Semi-active RFID tag supporting wireless charging |
| CN101459981A (en)* | 2007-12-12 | 2009-06-17 | Lg电子株式会社 | Mobile terminal having menu providing function for wireless recharging and recharging method thereof |
| CN101459981B (en)* | 2007-12-12 | 2013-07-24 | Lg电子株式会社 | Mobile terminal having menu providing function for wireless recharging and recharging method thereof |
| CN101527372B (en)* | 2008-03-06 | 2012-07-04 | 财团法人工业技术研究院 | Programmable energy storage control module and system |
| CN101955096A (en)* | 2009-07-20 | 2011-01-26 | 杭州优迈科技有限公司 | Passive type wireless remote elevator call control system and control method |
| CN102103682A (en)* | 2009-12-18 | 2011-06-22 | 上海科斗电子科技有限公司 | Electronic scanning article search system and assorted electronic tag thereof |
| CN102103682B (en)* | 2009-12-18 | 2015-03-18 | 上海本星电子科技有限公司 | Electronic scanning article search system and assorted electronic tag thereof |
| CN102298717A (en)* | 2010-06-23 | 2011-12-28 | 福建新大陆电脑股份有限公司 | Active electronic tag with wireless charging device |
| CN102412856A (en)* | 2010-09-21 | 2012-04-11 | 上海科斗电子科技有限公司 | Wireless sensor system |
| CN105959028A (en)* | 2010-09-21 | 2016-09-21 | 上海聚然智能科技有限公司 | Wireless sensor system with Zigbee as communication module |
| CN105933027A (en)* | 2010-09-21 | 2016-09-07 | 上海聚然智能科技有限公司 | Wireless sensor system with chip capacitor |
| CN105933027B (en)* | 2010-09-21 | 2019-01-08 | 上海聚然智能科技有限公司 | Using the wireless sensor system of flaky electric capacity |
| CN102467102A (en)* | 2010-11-04 | 2012-05-23 | 北京天一众合科技股份有限公司 | Boundary control method and system, low-frequency locator and identification card |
| CN102467102B (en)* | 2010-11-04 | 2014-10-29 | 北京天一众合科技股份有限公司 | Boundary control method, system thereof, low frequency positioner and identification card |
| CN108763980A (en)* | 2011-12-27 | 2018-11-06 | 杜拉塞尔美国经营公司 | Intelligent power |
| CN108763980B (en)* | 2011-12-27 | 2021-10-22 | 杜拉塞尔美国经营公司 | Intelligent power supply |
| CN103051360B (en)* | 2012-04-19 | 2015-08-12 | 深圳中科讯联科技有限公司 | Based on the system and method for RFID wireless connections |
| CN103051360A (en)* | 2012-04-19 | 2013-04-17 | 深圳中科讯联科技有限公司 | System and method based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Devices) wireless connection |
| CN107102272A (en)* | 2012-12-27 | 2017-08-29 | 杜拉塞尔美国经营公司 | Utilize circuit remote sense remaining battery capacity on battery |
| US10698032B2 (en) | 2012-12-27 | 2020-06-30 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Remote sensing of remaining battery capacity using on-battery circuitry |
| CN103218653A (en)* | 2013-04-23 | 2013-07-24 | 复旦大学 | Label harmonic wave obtaining method for harmonic wave radio frequency identification and harmonic wave radio frequency identification label |
| CN103218653B (en)* | 2013-04-23 | 2016-03-30 | 复旦大学 | For label harmonic wave acquisition methods and the harmonic RF identification label of harmonic RF identification |
| CN103226726A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-07-31 | 重庆邮电大学 | Novel semi-passive RFID label chip |
| US11307259B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2022-04-19 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for remotely determining a battery characteristic |
| US10684374B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2020-06-16 | Duravell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for remotely determining a battery characteristic |
| US10859705B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2020-12-08 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for remotely determining a battery characteristic |
| US11740291B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2023-08-29 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Systems and methods for remotely determining a battery characteristic |
| CN104464068A (en)* | 2013-09-12 | 2015-03-25 | 富港电子(东莞)有限公司 | Number calling device and method of use thereof |
| CN104463307A (en)* | 2013-09-23 | 2015-03-25 | 富港电子(东莞)有限公司 | Easy card with escaping function and using method thereof |
| CN104077619A (en)* | 2013-09-25 | 2014-10-01 | 苏州天趣信息科技有限公司 | A device and its combination for increasing the transmission distance of radio frequency identification signals |
| CN108052847A (en)* | 2013-09-25 | 2018-05-18 | 湖南湘讯企业管理有限公司 | A kind of device combination for promoting radio frequency identification signal transmission range |
| CN108052848A (en)* | 2013-09-25 | 2018-05-18 | 湖南湘讯企业管理有限公司 | A kind of device combination for promoting radio frequency identification signal transmission range |
| CN104077619B (en)* | 2013-09-25 | 2018-02-27 | 中北大学 | A combination of devices for increasing the transmission distance of radio frequency identification signals |
| CN103500351A (en)* | 2013-10-16 | 2014-01-08 | 章玺 | Active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tag using alternating current |
| US10964980B2 (en) | 2014-05-30 | 2021-03-30 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Indicator circuit decoupled from a ground plane |
| CN104700143A (en)* | 2015-03-04 | 2015-06-10 | 包建伟 | Wireless charging active RFID (radio frequency identification) |
| CN104700129A (en)* | 2015-03-04 | 2015-06-10 | 包建伟 | RFID reader with identity recognition and electromagnetic wave emission |
| CN105471023B (en)* | 2015-11-30 | 2017-11-03 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | A kind of wireless charging method, the apparatus and system of implantable chip |
| CN105471023A (en)* | 2015-11-30 | 2016-04-06 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | Wireless charging method, device and system of implantable chips |
| US10818979B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2020-10-27 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Single sided reusable battery indicator |
| US11696942B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2023-07-11 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Reusable battery indicator with electrical lock and key |
| US11664539B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2023-05-30 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Dual sided reusable battery indicator |
| US10971769B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-04-06 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Reusable battery indicator with electrical lock and key |
| US11024891B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-01 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Reusable battery indicator with lock and key mechanism |
| US11024892B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-01 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Dual sided reusable battery indicator |
| US11031686B2 (en) | 2016-11-01 | 2021-06-08 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Positive battery terminal antenna ground plane |
| CN106650879A (en)* | 2016-12-22 | 2017-05-10 | Tcl集团股份有限公司 | Intelligent RFID tag and working method thereof |
| CN108120939A (en)* | 2017-12-23 | 2018-06-05 | 武汉瑞纳捷电子技术有限公司 | A kind of active card battery power amount calculation method |
| CN108120939B (en)* | 2017-12-23 | 2020-04-10 | 武汉瑞纳捷电子技术有限公司 | Method for calculating electric quantity of battery of active card |
| CN112528688A (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-19 | 浙江悦和科技有限公司 | Radio frequency tag control method, response method and device, storage medium, reader and radio frequency tag |
| CN112528688B (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2023-08-15 | 浙江悦和科技有限公司 | Radio frequency tag control method, response method and device, storage medium, reader and radio frequency tag |
| WO2021134556A1 (en)* | 2019-12-31 | 2021-07-08 | 李庆远 | Ring with electronic tag. |
| CN111289704B (en)* | 2020-03-03 | 2021-02-09 | 中国农业大学 | Multi-parameter passive flexible sensing device and method for monitoring aquatic product quality |
| CN111289704A (en)* | 2020-03-03 | 2020-06-16 | 中国农业大学 | Multi-parameter passive flexible sensing device and method for aquatic product quality monitoring |
| US11837754B2 (en) | 2020-12-30 | 2023-12-05 | Duracell U.S. Operations, Inc. | Magnetic battery cell connection mechanism |
| CN112968509A (en)* | 2021-04-23 | 2021-06-15 | 歌尔股份有限公司 | Control method for wireless charging device, and storage medium |
| WO2023185904A1 (en)* | 2022-03-31 | 2023-10-05 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Energy supply method and apparatus for backscatter communication, terminal, and network side device |
| CN116560485A (en)* | 2023-03-16 | 2023-08-08 | 深圳多为智联科技有限公司 | Power management method and system of intelligent terminal equipment |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1529182A (en) | Battery capacity identification and charging method of active radio frequency identification tag card | |
| US6243013B1 (en) | Cascaded DC voltages of multiple antenna RF tag front-end circuits | |
| AU2003236523B2 (en) | Radio frequency identification tag with thin-film battery for antenna | |
| CN100458841C (en) | Semi-active RFID tag supporting wireless charging | |
| CN101937519A (en) | RFID electronic tags that can be charged wirelessly | |
| CN101576964B (en) | Radio frequency identification reader, radio frequency identification system and method of frequency conversion working | |
| JP2008505418A (en) | Power assisted backscatter RFID transponder | |
| MXPA04010053A (en) | Integrated circuit with enhanced coupling. | |
| TWI830310B (en) | Bluetooth electronic tag | |
| CN101140614A (en) | Protocol frequency and system thereof | |
| KR20200052745A (en) | Smart tag and object recognition system using the same | |
| Jankowski-Mihułowicz et al. | Definition, Characteristics and Determining Parameters of Antennas in Terms of Synthesizing the Interrogation | |
| CN103679082A (en) | Radio frequency tag, tag reader and radio frequency tag charging method | |
| CN104050561A (en) | Financial payment system based on RFID | |
| CN201359732Y (en) | Code reader for identity card based on RFID technology | |
| CN201741174U (en) | RFID electronic tag capable of being charged wirelessly | |
| KR20070108759A (en) | Logistics management system for battery production using wireless communication recognition chip and secondary battery with wireless communication recognition chip | |
| JP5164496B2 (en) | Goods management system | |
| CN202025341U (en) | Portable operation law-enforcement terminal | |
| CN206975655U (en) | The NFC brushing card devices of electric-field intensity change can be shown | |
| CN205486179U (en) | Terminal is handed to hyperfrequency fingerprint | |
| CN115329914A (en) | Remote identification method based on nfc tag | |
| KR100746242B1 (en) | Active RDF Tag and RDF System Using Solar Cell | |
| CN100412881C (en) | Radio Frequency Identification System | |
| US8319641B2 (en) | Article management method including shared memory and reader/writers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |