CN116423494A - A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method - Google Patents
A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116423494A CN116423494ACN202310095165.0ACN202310095165ACN116423494ACN 116423494 ACN116423494 ACN 116423494ACN 202310095165 ACN202310095165 ACN 202310095165ACN 116423494 ACN116423494 ACN 116423494A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- magnetic
- soft
- degree
- freedom
- magnetic field
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J9/00—Programme-controlled manipulators
- B25J9/16—Programme controls
- B25J9/1679—Programme controls characterised by the tasks executed
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J18/00—Arms
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J9/00—Programme-controlled manipulators
- B25J9/16—Programme controls
- B25J9/1656—Programme controls characterised by programming, planning systems for manipulators
- B25J9/1664—Programme controls characterised by programming, planning systems for manipulators characterised by motion, path, trajectory planning
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及磁驱动领域,尤其涉及一种六自由度软磁驱动系统及方法。The invention relates to the field of magnetic drives, in particular to a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method.
背景技术Background technique
微创医疗设备(如腹腔镜机器人和经自然腔道柔性机器人)辅助的医疗操作可以减少病人创伤并提高手术的安全性。微创器械可以更加灵活地到达体内的某些狭小复杂空间,执行更多复杂的医疗任务。微创器械可以借助人体器官的自然运动(如肠道蠕动)和体液流动来实现在体内的被动运动,但是被动驱动的微创器械缺乏灵活性和可控性,限制了它们在医疗任务中的功能。现有的微创器械主动驱动系统可以分为内部驱动系统和外部驱动系统。内部驱动系统往往通过器械内部的驱动机构(如胶囊机器人的电动腿足和尾鳍,柔性机器人的绳驱动机构等)实现运动,但在狭小的器械内部集成复杂的供电系统和运动机构十分困难;外部驱动主要通过外部磁场对器械所载磁铁的磁力来操控器械,避免了设计复杂的微小驱动机构和供电系统。但现有的磁驱动系统主要使用永磁体作为医疗器械的受力部件,无法对其施加绕磁矩主轴方向的力矩,仅可实现五自由度驱动(三自由度力驱动和两自由度力矩驱动),降低了微创医疗器械操控的灵巧性和可控性。Medical operations assisted by minimally invasive medical devices (such as laparoscopic robots and flexible robots through natural orifices) can reduce patient trauma and improve surgical safety. Minimally invasive devices can reach certain narrow and complex spaces in the body more flexibly and perform more complex medical tasks. Minimally invasive devices can achieve passive movement in the body with the help of natural movements of human organs (such as intestinal peristalsis) and body fluid flow, but passively driven minimally invasive devices lack flexibility and controllability, which limits their application in medical tasks. Function. The existing active driving systems of minimally invasive instruments can be divided into internal driving systems and external driving systems. The internal drive system often achieves movement through the drive mechanism inside the device (such as the electric legs and tail fins of the capsule robot, the rope drive mechanism of the flexible robot, etc.), but it is very difficult to integrate the complex power supply system and motion mechanism inside the narrow device; the external The drive mainly controls the device through the magnetic force of the external magnetic field on the magnet contained in the device, which avoids the design of a complicated micro-drive mechanism and power supply system. However, the existing magnetic drive system mainly uses permanent magnets as the force-bearing parts of medical devices, which cannot apply torque around the main axis of the magnetic moment, and can only realize five-degree-of-freedom drive (three-degree-of-freedom force drive and two-degree-of-freedom torque drive). ), reducing the dexterity and controllability of minimally invasive medical device manipulation.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为至少一定程度上解决现有技术中存在的技术问题之一,本发明的目的在于提供一种六自由度软磁驱动系统及方法。In order to solve one of the technical problems in the prior art at least to a certain extent, the object of the present invention is to provide a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method.
本发明所采用的技术方案是:The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种六自由度软磁驱动系统,包括以下步骤:A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system, comprising the following steps:
磁源模块,用于产生磁源磁场;A magnetic source module, used to generate a magnetic source magnetic field;
软磁体,安装在机械装置上,用于驱动所述机械装置运动;A soft magnet, installed on the mechanical device, is used to drive the movement of the mechanical device;
微控制器,用于控制磁源模块的工作参数;A microcontroller for controlling the working parameters of the magnetic source module;
其中,软磁体在磁源磁场作用下磁化形成二次磁源,其磁矩取决于软磁体所在位置的外部磁场,被磁化的软磁体在外部磁场作用下受到力和力矩,进而带动机械装置发生平移和转动。Among them, the soft magnet is magnetized under the action of the magnetic source magnetic field to form a secondary magnetic source, and its magnetic moment depends on the external magnetic field at the position of the soft magnet. The magnetized soft magnet is subjected to force and torque under the action of the external magnetic field, and then drives the mechanical device to generate Translation and rotation.
进一步地,所述磁源模块包括三轴正交的亥姆霍兹线圈或者麦克斯韦线圈,所述软磁体的工作空间在三组正交线圈的内部。Further, the magnetic source module includes three orthogonal Helmholtz coils or Maxwell coils, and the working space of the soft magnetic body is inside the three sets of orthogonal coils.
进一步地,所述磁源模块包括三组正交线圈构成的万向偶极子磁源,所述软磁体的工作空间在三组线圈外、以磁源为中心的三维空间内。Further, the magnetic source module includes a universal dipole magnetic source composed of three sets of orthogonal coils, and the working space of the soft magnetic body is outside the three sets of coils and in a three-dimensional space centered on the magnetic source.
进一步地,所述磁源模块包括由六轴机械臂控制的单轴线圈磁源,所述单轴线圈固定在机械臂末端,通过机械臂运动控制单组线圈位姿,所述软磁体的工作空间在线圈周围的空间内。Further, the magnetic source module includes a single-axis coil magnetic source controlled by a six-axis manipulator. The single-axis coil is fixed at the end of the manipulator, and the pose of a single set of coils is controlled by the movement of the manipulator. The working of the soft magnet The space is within the space around the coil.
进一步地,所述机械装置为微创医疗器械,所述微创医疗器械包括胶囊机器人或柔性导管。Further, the mechanical device is a minimally invasive medical device, and the minimally invasive medical device includes a capsule robot or a flexible catheter.
进一步地,所述软磁体的材料为镍铁磁性合金或镍铁非晶合金。Further, the material of the soft magnet is nickel-iron magnetic alloy or nickel-iron amorphous alloy.
进一步地,所述软磁体安装在所述机械装置的末端,且所述软磁体与机械装置的末端采用刚性连接,以使软磁体所受力和力矩传递到机械装置上。Further, the soft magnet is installed at the end of the mechanical device, and the soft magnet is rigidly connected to the end of the mechanical device, so that the force and torque on the soft magnet can be transmitted to the mechanical device.
进一步地,所述软磁体的形状为椭球体或椭圆柱或长方体,且三轴非对称,即其赤道半径a与b及极半径(高)c各不相等,且a>b>c。Further, the shape of the soft magnetic body is an ellipsoid, an elliptical cylinder or a cuboid, and the three axes are asymmetrical, that is, the equatorial radii a and b and the polar radius (height) c are different, and a>b>c.
本发明所采用的另一技术方案是:Another technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种六自由度软磁驱动方法,包括以下步骤:A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic driving method, comprising the following steps:
建立磁场与软磁体所受力和力矩的耦合关系模型;Establish a coupling relationship model between the magnetic field and the force and moment of the soft magnet;
根据机械装置的目标位置与姿态和当前位置与姿态,获取机械装置的运动轨迹;Obtain the movement track of the mechanical device according to the target position and attitude and the current position and attitude of the mechanical device;
根据运动轨迹计算所需的驱动力和力矩;Calculate the required driving force and torque according to the motion trajectory;
根据计算获得的力和力矩,以及耦合关系模型,计算出软磁体所需的驱动磁场;Calculate the driving magnetic field required by the soft magnet according to the calculated force and moment, as well as the coupling relationship model;
根据计算出的磁场调控磁源参数;其中磁源参数包括电磁线圈的电流值和/或电磁线圈的位姿。Regulate the parameters of the magnetic source according to the calculated magnetic field; wherein the parameters of the magnetic source include the current value of the electromagnetic coil and/or the pose of the electromagnetic coil.
进一步地,所述耦合关系模型具体为:Further, the coupling relationship model is specifically:
假设被磁化后的软磁体为磁偶极子模型,软磁体所受力矩与磁场关系为:Assuming that the magnetized soft magnet is a magnetic dipole model, the relationship between the torque on the soft magnet and the magnetic field is:
τ=m×Bτ=m×B
其中,m=vRTχaRB/μ0,m是软磁体被外界磁场磁化后的磁矩;R是从全局坐标系到软磁体坐标系的旋转矩阵,χa是软磁体磁化率,B是软磁体处磁感应强度,μ0是真空磁导率;na表示软磁体最长轴a的退磁系数,nb表示软磁体次长轴b的退磁系数,nc表示软磁体最短轴c的退磁系数;Among them, m=vRT χa RB/μ0 , m is the magnetic moment of the soft magnet magnetized by the external magnetic field; R is the rotation matrix from the global coordinate system to the soft magnet coordinate system, χa is the magnetic susceptibility of the soft magnet, B is the magnetic induction intensity at the soft magnet, μ0 is the vacuum permeability; na is the demagnetization coefficient of the longest axis a of the soft magnet, nb is the demagnetization coefficient of the second major axis b of the soft magnet, and nc is the shortest axis c of the soft magnet The demagnetization coefficient;
软磁体所受力与磁场关系为:The relationship between the force on a soft magnet and the magnetic field is:
其中,x、y、z表示三轴坐标。in, x, y, and z represent three-axis coordinates.
本发明的有益效果是:本发明通过控制磁源参数,调控软磁体受到的三自由度力和三自由度力矩,从而实现机械装置的六自由度驱动和主动操控。其次,本发明通过磁场来传递力和力矩作用,可以安全穿透人体,实现无接触驱动。另外,该磁驱动方案将在微创诊断和治疗过程更加精准、灵活、可控地完成微创医疗器械的操控和导航,可有效提升微创医疗操作的自动化和智能化水平。The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the present invention regulates the three-degree-of-freedom force and three-degree-of-freedom torque received by the soft magnet by controlling the parameters of the magnetic source, thereby realizing six-degree-of-freedom drive and active control of the mechanical device. Secondly, the present invention transmits force and torque through a magnetic field, which can safely penetrate the human body and realize non-contact driving. In addition, the magnetic drive solution will complete the manipulation and navigation of minimally invasive medical devices more accurately, flexibly and controllably during the minimally invasive diagnosis and treatment process, which can effectively improve the automation and intelligence level of minimally invasive medical operations.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或者现有技术中的技术方案,下面对本发明实施例或者现有技术中的相关技术方案附图作以下介绍,应当理解的是,下面介绍中的附图仅仅为了方便清晰表述本发明的技术方案中的部分实施例,对于本领域的技术人员而言,在无需付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获取到其他附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the following describes the accompanying drawings of the embodiments of the present invention or the related technical solutions in the prior art. It should be understood that the accompanying drawings in the following introduction are only In order to clearly describe some embodiments of the technical solutions of the present invention, those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings without creative work.
图1是本发明实施例中基于三轴亥姆霍兹线圈的六自由度软磁驱动系统的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system based on a three-axis Helmholtz coil in an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是本发明实施例中采用三轴正交线圈的驱动磁源设计示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of the design of a driving magnetic source using three-axis orthogonal coils in an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例中基于由六轴机械臂控制的单轴电磁线圈的六自由度软磁驱动系统的示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system based on a single-axis electromagnetic coil controlled by a six-axis manipulator in an embodiment of the present invention;
图4是本发明实施例中一种六自由度软磁驱动方法的步骤流程图;Fig. 4 is a flow chart of the steps of a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic driving method in an embodiment of the present invention;
图5是本发明实施例中基于软磁体的微创医疗器械六自由度磁驱动控制系统流程图;Fig. 5 is a flowchart of a six-degree-of-freedom magnetic drive control system for a minimally invasive medical device based on a soft magnet in an embodiment of the present invention;
图6是本发明实施例中软磁体在水箱中磁化前后受力(矩)对比第一示意图;Fig. 6 is the first schematic diagram of the force (moment) comparison before and after the soft magnet is magnetized in the water tank in the embodiment of the present invention;
图7是本发明实施例中软磁体在水箱中磁化前后受力(矩)对比第二示意图;Fig. 7 is the second schematic diagram of the force (moment) comparison before and after the soft magnet is magnetized in the water tank in the embodiment of the present invention;
图8是本发明实施例中软磁体在水箱中磁化前后受力(矩)对比第三示意图。Fig. 8 is a third schematic diagram of the force (moment) comparison before and after the soft magnet is magnetized in the water tank in the embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面详细描述本发明的实施例,所述实施例的示例在附图中示出,其中自始至终相同或类似的标号表示相同或类似的元件或具有相同或类似功能的元件。下面通过参考附图描述的实施例是示例性的,仅用于解释本发明,而不能理解为对本发明的限制。对于以下实施例中的步骤编号,其仅为了便于阐述说明而设置,对步骤之间的顺序不做任何限定,实施例中的各步骤的执行顺序均可根据本领域技术人员的理解来进行适应性调整。Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals designate the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary only for explaining the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention. For the step numbers in the following embodiments, it is only set for the convenience of illustration and description, and the order between the steps is not limited in any way. The execution order of each step in the embodiments can be adapted according to the understanding of those skilled in the art sexual adjustment.
在本发明的描述中,需要理解的是,涉及到方位描述,例如上、下、前、后、左、右等指示的方位或位置关系为基于附图所示的方位或位置关系,仅是为了便于描述本发明和简化描述,而不是指示或暗示所指的装置或元件必须具有特定的方位、以特定的方位构造和操作,因此不能理解为对本发明的限制。In the description of the present invention, it should be understood that the orientation descriptions, such as up, down, front, back, left, right, etc. indicated orientations or positional relationships are based on the orientations or positional relationships shown in the drawings, and are only In order to facilitate the description of the present invention and simplify the description, it does not indicate or imply that the device or element referred to must have a specific orientation, be constructed and operated in a specific orientation, and thus should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
在本发明的描述中,若干的含义是一个或者多个,多个的含义是两个以上,大于、小于、超过等理解为不包括本数,以上、以下、以内等理解为包括本数。如果有描述到第一、第二只是用于区分技术特征为目的,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的数量或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的先后关系。In the description of the present invention, several means one or more, and multiple means more than two. Greater than, less than, exceeding, etc. are understood as not including the original number, and above, below, within, etc. are understood as including the original number. If the description of the first and second is only for the purpose of distinguishing the technical features, it cannot be understood as indicating or implying the relative importance or implicitly indicating the number of the indicated technical features or implicitly indicating the order of the indicated technical features relation.
本发明的描述中,除非另有明确的限定,设置、安装、连接等词语应做广义理解,所属技术领域技术人员可以结合技术方案的具体内容合理确定上述词语在本发明中的具体含义。In the description of the present invention, unless otherwise clearly defined, words such as setting, installation, and connection should be understood in a broad sense, and those skilled in the art can reasonably determine the specific meanings of the above words in the present invention in combination with the specific content of the technical solution.
软磁体是一种具有高磁导率和低矫顽力的铁磁体,其容易被外部磁场磁化而变为磁源,可在外部磁场中受到力和力矩的作用,因此,将软磁体固定在医疗器械上作为受力元件,实现对医疗器械的驱动。作为驱动磁源的电磁线圈置于体外,软磁体会被驱动磁源发出的磁场磁化而形成一个二次磁源,其磁矩(反映磁性强度和取向)取决于驱动磁源在软磁体位置磁化它的磁场。被磁化后的软磁体可以看作一个偶极子磁源,软磁体在驱动磁场中会受到取决于当地磁场和磁场梯度的力矩和力作用,因此在了解软磁体在驱动磁场中受力的磁-力耦合关系后,结合驱动控制系统,就可以精准操控微型医疗器械或其他工业微机器人。The soft magnet is a ferromagnet with high permeability and low coercive force, which is easily magnetized by an external magnetic field and becomes a magnetic source, and can be subjected to force and torque in the external magnetic field. Therefore, the soft magnet is fixed in the As a force-bearing element on the medical device, it realizes the drive of the medical device. The electromagnetic coil as the driving magnetic source is placed outside the body, and the soft magnet will be magnetized by the magnetic field emitted by the driving magnetic source to form a secondary magnetic source. Its magnetic moment (reflecting the magnetic strength and orientation) depends on the magnetization of the driving magnetic source at the position of the soft magnet. its magnetic field. The magnetized soft magnet can be regarded as a dipole magnetic source. The soft magnet will be subjected to torque and force depending on the local magnetic field and magnetic field gradient in the driving magnetic field. Therefore, in understanding the magnetic force of the soft magnet in the driving magnetic field -After the force coupling relationship, combined with the drive control system, it is possible to precisely control micro-medical devices or other industrial micro-robots.
参见图1,本实施例提供一种六自由度软磁驱动系统,包括:Referring to Figure 1, this embodiment provides a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system, including:
磁源模块,用于产生磁源磁场;A magnetic source module, used to generate a magnetic source magnetic field;
软磁体,安装在机械装置上,用于驱动所述机械装置运动;A soft magnet, installed on the mechanical device, is used to drive the movement of the mechanical device;
微控制器,用于控制磁源模块的工作参数;A microcontroller for controlling the working parameters of the magnetic source module;
其中,软磁体在磁源磁场作用下磁化形成二次磁源,其磁矩取决于软磁体所在位置的外部磁场,被磁化的软磁体在外部磁场作用下受到力和力矩,进而带动机械装置发生平移和转动。Among them, the soft magnet is magnetized under the action of the magnetic source magnetic field to form a secondary magnetic source, and its magnetic moment depends on the external magnetic field at the position of the soft magnet. The magnetized soft magnet is subjected to force and torque under the action of the external magnetic field, and then drives the mechanical device to generate Translation and rotation.
作为一种可选的实施方式,软磁体的材料为镍铁磁性合金(1J85)或镍铁非晶合金(1K501),相对磁导率μr=104-105;形状为椭球体或椭圆柱或长方体,三轴非对称,即其赤道半径a与b及极半径(高)c各不相等,且a>b>c。As an optional embodiment, the material of the soft magnet is nickel-iron magnetic alloy (1J85) or nickel-iron amorphous alloy (1K501), relative permeability μr =104 -105 ; shape is ellipsoid or ellipse A column or a cuboid is asymmetrical in three axes, that is, its equatorial radius a and b and polar radius (height) c are not equal, and a>b>c.
作为一种可选的实施方式,软磁体安装在机械装置的末端,软磁体与机械装置末端采用刚性连接,软磁体所受力和力矩可有效传递到机械装置上。As an optional embodiment, the soft magnet is installed at the end of the mechanical device, and the soft magnet is rigidly connected to the end of the mechanical device, so that the force and torque on the soft magnet can be effectively transmitted to the mechanical device.
作为一种可选的实施方式,磁源模块包括三轴正交的亥姆霍兹线圈或者麦克斯韦线圈,软磁体的工作空间在三组正交线圈的内部。As an optional implementation manner, the magnetic source module includes three orthogonal Helmholtz coils or Maxwell coils, and the working space of the soft magnet is inside the three sets of orthogonal coils.
作为一种可选的实施方式,磁源模块包括三组正交线圈构成的万向偶极子磁源,软磁体的工作空间在三组线圈外、以磁源为中心的三维空间内。As an optional implementation, the magnetic source module includes a universal dipole magnetic source composed of three sets of orthogonal coils, and the working space of the soft magnet is outside the three sets of coils and in a three-dimensional space centered on the magnetic source.
作为一种可选的实施方式,磁源模块包括由六轴机械臂控制的单轴线圈磁源,单轴线圈固定在机械臂末端,通过机械臂运动控制单组线圈位姿,软磁体的工作空间在线圈周围的空间内。As an optional implementation, the magnetic source module includes a single-axis coil magnetic source controlled by a six-axis manipulator. The single-axis coil is fixed at the end of the manipulator, and the pose of a single set of coils is controlled by the movement of the manipulator. The working of the soft magnet The space is within the space around the coil.
以下结合附图及具体实施例对上述系统进行详细解释说明。The above system will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
在本实施例中,软磁体采用镍铁磁性合金(1J85)为材料加工椭圆柱形软磁体,相对磁导率μr=1.246×105。三轴长分别为:a=30mm,b=12mm,c=6mm。机械装置为微创医疗器械。In this embodiment, the soft magnet is made of nickel-iron magnetic alloy (1J85) to process an elliptical cylindrical soft magnet, and the relative magnetic permeability μr =1.246×105 . The three axis lengths are: a=30mm, b=12mm, c=6mm. The mechanical device is a minimally invasive medical device.
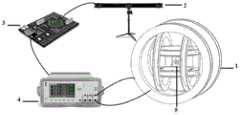
参见图1,图1为本实施例采用的亥姆霍兹线圈驱动方案。针对纯力矩驱动模式,需要采用均匀的外部驱动磁场,以避免因磁场梯度引起的对软磁体力的作用,同时采用非对称软磁体,以实现三自由度力矩驱动。图1中的系统包括三轴亥姆霍兹线圈(以下简称三组线圈1)、软磁体六自由度定位系统(以下简称定位系统2)、微控制器3、电源4和软磁体5,软磁体5设置在微创医疗器械上。具体地微创医疗器械为胶囊内窥镜机器人,软磁体5设置在胶囊内窥镜机器人内部。作为另一种可选实施方式,图1中的三轴亥姆霍兹线圈可采用三轴麦克斯韦线圈来代替。Referring to FIG. 1 , FIG. 1 shows the driving scheme of the Helmholtz coil adopted in this embodiment. For the pure torque drive mode, a uniform external drive magnetic field is required to avoid the force on the soft magnetic body caused by the gradient of the magnetic field, and an asymmetric soft magnet is used to achieve three-degree-of-freedom torque drive. The system in Fig. 1 includes a three-axis Helmholtz coil (hereinafter referred to as the three groups of coils 1), a soft magnetic six-degree-of-freedom positioning system (hereinafter referred to as the positioning system 2), a
参见图5,通过调控三组线圈1的电流大小,即可在线圈内部产生任意方向、不同大小的匀强磁场。线圈内部的软磁体5在磁场作用下磁化后,受到力矩的作用,可转向目标姿态。通过外部的定位系统2,可以确定软磁体5当前的姿态。定位系统2连接到微处理器3,微处理器3将当前姿态与目标位姿比较误差,通过磁-力矩耦合模型,计算所需磁场。微处理器3连接电源4,由微控制器3发出指令,通过电源4调节三组线圈1电流大小,产生所需磁场。软磁体5在磁场作用下运动,直到达到目标位姿为止。本实施例对亥姆霍兹线圈驱动的原理进行说明,但是其他磁源的操控原理相同,在此不进行赘述。Referring to FIG. 5 , by adjusting the magnitude of the current of the three groups of
图2为三轴正交的万向磁源线圈,针对纯力驱动或者全六自由度力和力矩驱动模式,均需要使用存在梯度的非均匀驱动磁场。由三组正交线圈构成的万向偶极子磁源,通过调控三组线圈的电流可以实现对驱动磁场大小和方向的调控,从而实现对软磁体力和力矩的调控。Figure 2 shows a three-axis orthogonal universal magnetic source coil. For pure force drive or full six degrees of freedom force and torque drive mode, a non-uniform drive magnetic field with a gradient is required. The universal dipole magnetic source composed of three sets of orthogonal coils can control the magnitude and direction of the driving magnetic field by adjusting the current of the three sets of coils, thereby realizing the control of the force and torque of the soft magnetic body.
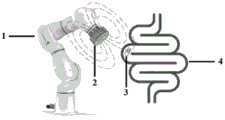
图3为六轴机械臂控制的单轴线圈磁源,通过调控单轴线圈的位姿和线圈电流可以实现对驱动磁场大小和方向的调控,进而驱动软磁体不断运动至期望位姿。图3所示的系统包括六轴协作机械臂1、单轴电磁线圈磁源2和微创医疗器械3。其中,单轴电磁线圈磁源2设置在六轴协作机械臂1的末端,通过六轴协作机械臂1改变单轴电磁线圈磁源2的位姿。本实施例中,微创医疗器械3为胶囊内窥镜机器人,内含有软磁体,当患者吞入胶囊内窥镜机器人后,胶囊内窥镜机器人沿着人体内部腔道4进行移动,具体地,通过单轴电磁线圈磁源2控制胶囊内窥镜机器人的位置和姿态。Figure 3 shows a single-axis coil magnetic source controlled by a six-axis manipulator. By adjusting the position and orientation of the single-axis coil and the coil current, the size and direction of the driving magnetic field can be adjusted, and then the soft magnet is driven to move continuously to the desired position. The system shown in FIG. 3 includes a six-axis
基于上述系统,如图4所示,本实施例提供一种六自由度软磁驱动方法,包括以下步骤:Based on the above system, as shown in Figure 4, this embodiment provides a six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic driving method, including the following steps:
S1、建立磁场与软磁体所受力和力矩的耦合关系模型。S1. Establish a coupling relationship model between the magnetic field and the force and moment on the soft magnetic body.
S2、根据机械装置的目标位置与姿态和当前位置与姿态,获取机械装置的运动轨迹。S2. According to the target position and attitude and the current position and attitude of the mechanical device, the motion trajectory of the mechanical device is obtained.
根据微创器械的目标姿态、微创器械当前的姿态以及磁场工作空间,规划出微创器械的运动轨迹,进而设计控制器。According to the target posture of the minimally invasive device, the current posture of the minimally invasive device, and the magnetic field workspace, the motion trajectory of the minimally invasive device is planned, and then the controller is designed.
S3、根据运动轨迹计算所需的驱动力和力矩。S3. Calculating the required driving force and torque according to the motion trajectory.
S4、根据计算获得的力和力矩,以及耦合关系模型,计算出软磁体所需的驱动磁场。S4. Calculate the driving magnetic field required by the soft magnet according to the calculated force and torque and the coupling relationship model.
S5、根据计算出的磁场调控磁源参数;其中磁源参数包括电磁线圈的电流值和/或电磁线圈的位姿。S5. Regulate the magnetic source parameters according to the calculated magnetic field; wherein the magnetic source parameters include the current value of the electromagnetic coil and/or the pose of the electromagnetic coil.
基于被控软磁体的轨迹误差,计算所需的驱动力矩,进而通过磁-力矩耦合关系模型,计算出软磁体所需的驱动磁场,然后分别调控三对电磁线圈电流大小以产生所需的磁场。软磁体在磁源磁场作用下磁化形成二次磁源,其磁矩取决于软磁体所在位置的外部磁场,被磁化的软磁体在外部磁场作用下受到力矩,进而带动微创器械发生转动。将当前新位姿与目标位姿比较,不断更新磁源参数,促使微创器械运动,直至微创器械达到目标位姿。Based on the trajectory error of the controlled soft magnetic body, calculate the required driving torque, and then calculate the driving magnetic field required by the soft magnetic body through the magnetic-torque coupling relationship model, and then adjust the current of the three pairs of electromagnetic coils to generate the required magnetic field . The soft magnet is magnetized under the action of the magnetic source magnetic field to form a secondary magnetic source, and its magnetic moment depends on the external magnetic field at the position of the soft magnet. The magnetized soft magnet receives torque under the action of the external magnetic field, and then drives the minimally invasive device to rotate. The current new pose is compared with the target pose, and the magnetic source parameters are continuously updated to promote the movement of the minimally invasive device until the minimally invasive device reaches the target pose.
作为一种可选的实施方式,耦合关系模型为:As an optional implementation, the coupling relationship model is:
假设被磁化后的软磁体为磁偶极子模型,软磁体所受力矩与磁场关系为:Assuming that the magnetized soft magnet is a magnetic dipole model, the relationship between the torque on the soft magnet and the magnetic field is:
τ=m×Bτ=m×B
其中,m=vRTχaRB/μ0,m是软磁体被外界磁场磁化后的磁矩。R是从全局坐标系到软磁体坐标系的旋转矩阵,χa是软磁体磁化率,B是软磁体处磁感应强度,μ0是真空磁导率。Among them, m=vRT χa RB/μ0 , m is the magnetic moment of the soft magnetic body after being magnetized by the external magnetic field. R is the rotation matrix from the global coordinate system to the soft magnet coordinate system, χa is the magnetic susceptibility of the soft magnet, B is the magnetic induction intensity at the soft magnetic body, μ0 is the vacuum permeability.
软磁体所受力与磁场关系为:The relationship between the force on a soft magnet and the magnetic field is:
其中,in,
以下结合附图和实验进行说明。The following will be described in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and experiments.
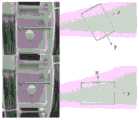
图6为安装有软磁体的胶囊外壳放置于水箱内,重力与浮力平衡的静止悬浮状态。当给一对线圈通大小为1A的同向电流,建立垂直于该对线圈的磁场时,软磁体立即绕最长轴x旋转,使得软磁体次长轴y与磁场方向对齐。其中,图6的上部分为未受磁场时的状态。图6的下部分是受到某一方向磁场时,软磁体绕最长轴x转动,最终次长轴y方向与磁场方向同向。Fig. 6 is a static suspension state in which the capsule shell equipped with soft magnets is placed in the water tank, and the gravity and buoyancy are balanced. When a current of 1A is applied to a pair of coils in the same direction to establish a magnetic field perpendicular to the pair of coils, the soft magnet immediately rotates around the longest axis x, so that the second major axis y of the soft magnet is aligned with the direction of the magnetic field. Wherein, the upper part of Fig. 6 is the state when no magnetic field is applied. The lower part of Fig. 6 shows that when receiving a magnetic field in a certain direction, the soft magnetic body rotates around the longest axis x, and finally the direction of the second longest axis y is the same as the direction of the magnetic field.
图7为安装有软磁体的胶囊外壳放置于水箱内,重力与浮力平衡的静止悬浮状态。当给一对线圈通大小为1A的同向电流,建立垂直于该对线圈的磁场时,软磁体立即绕次长轴y旋转,使得软磁体最长轴x与磁场方向对齐。其中,图7的上部分为未受磁场时的状态。图7的下部分是受到某一方向磁场时,软磁体绕次长轴y转动,最终最长轴x方向与磁场方向同向。Fig. 7 is a static suspension state in which the capsule shell installed with soft magnets is placed in the water tank and the gravity and buoyancy are balanced. When a current of 1A is passed to a pair of coils in the same direction to establish a magnetic field perpendicular to the pair of coils, the soft magnet immediately rotates around the secondary major axis y, so that the longest axis x of the soft magnet is aligned with the direction of the magnetic field. Wherein, the upper part of Fig. 7 is the state when no magnetic field is applied. The lower part of Fig. 7 is that when receiving a magnetic field in a certain direction, the soft magnetic body rotates around the secondary major axis y, and finally the longest axis x direction is in the same direction as the magnetic field direction.
图8为安装有软磁体的胶囊外壳放置于水箱内,重力与浮力平衡的静止悬浮状态。当给一对线圈通大小为1A的同向电流,建立垂直于该对线圈的磁场时,软磁体立即绕最短轴z旋转,使得软磁体最长轴x与磁场方向对齐。其中,图8的上部分为未受磁场时的状态。图8的下部分是受到某一方向磁场时,软磁体绕最短轴z转动,最终最长轴x方向与磁场方向同向。Fig. 8 is a static suspension state in which the capsule shell with the soft magnet installed is placed in the water tank and the gravity and buoyancy are balanced. When a current of 1A is passed to a pair of coils in the same direction to establish a magnetic field perpendicular to the pair of coils, the soft magnet immediately rotates around the shortest axis z, so that the longest axis x of the soft magnet is aligned with the direction of the magnetic field. Wherein, the upper part of Fig. 8 is the state when no magnetic field is applied. The lower part of Figure 8 shows that when receiving a magnetic field in a certain direction, the soft magnetic body rotates around the shortest axis z, and finally the longest axis x direction is in the same direction as the magnetic field direction.
综上所述,本实施例相对于现有技术,至少具有如下优点及有益效果:To sum up, compared with the prior art, this embodiment has at least the following advantages and beneficial effects:
(1)本发明实施例的磁驱动技术通过磁场来传递力和力矩作用,可以安全穿透人体,实现无接触驱动,适用于微创医疗中对体内运动的微型医疗器械的操控。(1) The magnetic drive technology of the embodiment of the present invention transmits force and torque through a magnetic field, can safely penetrate the human body, realizes non-contact drive, and is suitable for the control of micro medical devices moving in the body in minimally invasive medical care.
(2)本发明实施例的磁驱动技术通过调控外部驱动磁场和设计软磁体几何形状,对微创器械末端施加三自由度力和三自由度力矩,从而实现全六自由度灵巧驱动。(2) The magnetic drive technology of the embodiment of the present invention applies three-degree-of-freedom force and three-degree-of-freedom torque to the end of the minimally invasive instrument by adjusting the external driving magnetic field and designing the geometry of the soft magnet, thereby realizing smart driving with all six degrees of freedom.
在本说明书的上述描述中,参考术语“一个实施方式/实施例”、“另一实施方式/实施例”或“某些实施方式/实施例”等的描述意指结合实施方式或示例描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点包含于本发明的至少一个实施方式或示例中。在本说明书中,对上述术语的示意性表述不一定指的是相同的实施方式或示例。而且,描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点可以在任何的一个或多个实施方式或示例中以合适的方式结合。In the above description of this specification, the description with reference to the terms "one embodiment/example", "another embodiment/example" or "some embodiments/example" means that the description is described in conjunction with the embodiment or example. A particular feature, structure, material, or characteristic is included in at least one embodiment or example of the invention. In this specification, schematic representations of the above terms do not necessarily refer to the same embodiment or example. Furthermore, the described specific features, structures, materials or characteristics may be combined in any suitable manner in any one or more embodiments or examples.
尽管已经示出和描述了本发明的实施方式,本领域的普通技术人员可以理解:在不脱离本发明的原理和宗旨的情况下可以对这些实施方式进行多种变化、修改、替换和变型,本发明的范围由权利要求及其等同物限定。Although the embodiments of the present invention have been shown and described, those skilled in the art can understand that various changes, modifications, substitutions and variations can be made to these embodiments without departing from the principle and spirit of the present invention. The scope of the invention is defined by the claims and their equivalents.
以上是对本发明的较佳实施进行了具体说明,但本发明并不限于上述实施例,熟悉本领域的技术人员在不违背本发明精神的前提下还可做作出种种的等同变形或替换,这些等同的变形或替换均包含在本申请权利要求所限定的范围内。The above is a specific description of the preferred implementation of the present invention, but the present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments, and those skilled in the art can also make various equivalent deformations or replacements without violating the spirit of the present invention. Equivalent modifications or replacements are all within the scope defined by the claims of the present application.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310095165.0ACN116423494A (en) | 2023-02-06 | 2023-02-06 | A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310095165.0ACN116423494A (en) | 2023-02-06 | 2023-02-06 | A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116423494Atrue CN116423494A (en) | 2023-07-14 |
Family
ID=87086165
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310095165.0APendingCN116423494A (en) | 2023-02-06 | 2023-02-06 | A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116423494A (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110215888A1 (en)* | 2009-11-12 | 2011-09-08 | University Of Utah | Wireless control of microrobots |
| US20140187862A1 (en)* | 2011-09-05 | 2014-07-03 | Mu Ltd. | Medical device |
| CN106618640A (en)* | 2017-02-24 | 2017-05-10 | 北京汇影互联科技有限公司 | Tracer and system for assisting to obtain intestinal ultrasound image and transmission speed |
| CN109617276A (en)* | 2018-12-17 | 2019-04-12 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of stator and rotor structure and modeling method for laparoscopic robot |
| CN111839431A (en)* | 2020-07-24 | 2020-10-30 | 福建世新机器人科技有限公司 | Wireless capsule robot system and control method |
| CN114668362A (en)* | 2022-03-18 | 2022-06-28 | 元化智能科技(深圳)有限公司 | Positioning system and device of wireless capsule endoscope and computer equipment |
- 2023
- 2023-02-06CNCN202310095165.0Apatent/CN116423494A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110215888A1 (en)* | 2009-11-12 | 2011-09-08 | University Of Utah | Wireless control of microrobots |
| US20140187862A1 (en)* | 2011-09-05 | 2014-07-03 | Mu Ltd. | Medical device |
| CN106618640A (en)* | 2017-02-24 | 2017-05-10 | 北京汇影互联科技有限公司 | Tracer and system for assisting to obtain intestinal ultrasound image and transmission speed |
| CN109617276A (en)* | 2018-12-17 | 2019-04-12 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of stator and rotor structure and modeling method for laparoscopic robot |
| CN111839431A (en)* | 2020-07-24 | 2020-10-30 | 福建世新机器人科技有限公司 | Wireless capsule robot system and control method |
| CN114668362A (en)* | 2022-03-18 | 2022-06-28 | 元化智能科技(深圳)有限公司 | Positioning system and device of wireless capsule endoscope and computer equipment |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Hoang et al. | Independent electromagnetic field control for practical approach to actively locomotive wireless capsule endoscope | |
| Yang et al. | Deltamag: An electromagnetic manipulation system with parallel mobile coils | |
| Du et al. | Design and real-time optimization for a magnetic actuation system with enhanced flexibility | |
| US20210369373A1 (en) | Mobile-electromagnetic coil-based magnetic actuation systems | |
| Yang et al. | 3-D visual servoing of magnetic miniature swimmers using parallel mobile coils | |
| Wang et al. | Kinematic modeling of magnetically-actuated robotic catheter in nonlinearly-coupled multi-field | |
| Wang et al. | Development of a novel 4-DOF flexible endoscopic robot using cable-driven multisegment continuum mechanisms | |
| Yang et al. | Multimode control of a parallel-mobile-coil system for adaptable large-workspace microrobotic actuation | |
| CN113100940A (en) | A kind of multi-point magnetron catheter navigation system and using method thereof | |
| CN209103896U (en) | A magnetic field generating device | |
| Lee et al. | Enhanced motion control of magnetically actuated capsule robot using MEMA—a mobile electromagnetic actuation system | |
| Li et al. | Orientation control of an electromagnetically actuated soft-tethered colonoscope based on 2OR pseudo-rigid-body model | |
| CN116423494A (en) | A six-degree-of-freedom soft magnetic drive system and method | |
| Chen et al. | Performance metrics for a robotic actuation system using static and mobile electromagnets | |
| Song et al. | The design of 3-D space electromagnetic control system for high-precision and fast-response control of capsule robot with 5-DOF | |
| Ko et al. | Model-based real-time simulator for robotic electromagnetic actuation | |
| CN117481577A (en) | A spin-advancing magnetically controlled medical robot and its driving device and driving method | |
| Li et al. | Design, Analysis, and Kinematic Framework of a Long-Range Magnetic Anchored and Guided Endoscope | |
| Fu et al. | Performance evaluation of a magnetic microrobot driven by rotational magnetic field | |
| CN111243824A (en) | A magnetic field generating device | |
| Zhu et al. | Pentamag: A parallel moving coil system with enhanced degrees of freedom and workspace | |
| Wang et al. | Levitation control of capsule robot with 5-DOF based on arrayed Hall elements | |
| Chen et al. | Study of robotized electromagnetic actuation system for magnetic microrobots devoted to minimally invasive ophthalmic surgery | |
| Fang et al. | A magnetic actuation system based on electromagnetic coils and permanent magnets for controlling capsule robot | |
| Huang et al. | Magnetic-Actuated Flexible Instruments with Enhanced Bending Capability through Magnetic Distribution Optimization |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |