CN116342570A - Image processing method, device, equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Image processing method, device, equipment and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116342570A CN116342570ACN202310348507.5ACN202310348507ACN116342570ACN 116342570 ACN116342570 ACN 116342570ACN 202310348507 ACN202310348507 ACN 202310348507ACN 116342570 ACN116342570 ACN 116342570A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- brain
- voxel
- image
- segmented image
- sub
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0012—Biomedical image inspection
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/50—Image enhancement or restoration using two or more images, e.g. averaging or subtraction
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/10—Segmentation; Edge detection
- G06T7/11—Region-based segmentation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/77—Processing image or video features in feature spaces; using data integration or data reduction, e.g. principal component analysis [PCA] or independent component analysis [ICA] or self-organising maps [SOM]; Blind source separation
- G06V10/774—Generating sets of training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10072—Tomographic images
- G06T2207/10088—Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20021—Dividing image into blocks, subimages or windows
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30016—Brain
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Apparatus (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及图像处理领域,更具体地,涉及一种图像处理的方法、装置、设备及存储介质。The present application relates to the field of image processing, and more specifically, to an image processing method, device, device, and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
随着医学的发展,影像检查已经成为临床诊断中重要的常规手段,例如,通过核磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging,简称MRI)、计算机断层扫描(Computedtomography,简称CT)和三维超声成像(Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging)等影响确定诊断结果。With the development of medicine, image examination has become an important routine method in clinical diagnosis, for example, through magnetic resonance imaging (Magnetic Resonance Imaging, referred to as MRI), computed tomography (Computedtomography, referred to as CT) and three-dimensional ultrasound imaging (Three-dimensional Ultrasound imaging) and other influences to determine the diagnosis result.
目前,确定诊断结果依赖于专业人员的工作经验,主观性强,实时性较差,且容易误诊,导致患者病情加重,错失最佳治疗时间。由于帕金森病(PD)和帕金森综合征(P-plus)临床症状高度相似,导致PD和P-plus的误诊率超过23.5%,但是PD和P-plus发病机制、疾病进展、治疗方法等有着本质上的区别。At present, the determination of the diagnosis results depends on the work experience of professionals, which is highly subjective, poor in real-time, and easy to misdiagnose, leading to aggravation of the patient's condition and missing the best treatment time. Due to the highly similar clinical symptoms of Parkinson's disease (PD) and Parkinson syndrome (P-plus), the misdiagnosis rate of PD and P-plus exceeds 23.5%, but the pathogenesis, disease progression, and treatment methods of PD and P-plus There is an essential difference.
随着人工智能技术的发展,基于深度学习技术自动对患者的医学影像(例如,MRI影像)进行分析,从而进行疾病的辅助诊断。但是对于PD和P-plus的区别鉴别诊断的研究还较少,并且都是依据单一特异性特征对二者进行区分,准确率较低。因此,如何高效、快速的对PD和P-plus进行鉴别诊断,并且保证鉴别诊断结果的准确性,是现阶段亟待解决的技术问题。With the development of artificial intelligence technology, medical images (eg, MRI images) of patients are automatically analyzed based on deep learning technology, so as to assist in the diagnosis of diseases. However, there are few studies on the differential diagnosis of PD and P-plus, and the distinction between the two is based on a single specific feature, and the accuracy rate is low. Therefore, how to efficiently and quickly differentially diagnose PD and P-plus, and ensure the accuracy of differential diagnosis results, is an urgent technical problem to be solved at this stage.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请的一些实施方式提供了可至少部分解决现有技术中存在的上述问题的一种图像处理的方法、装置、设备及存储介质。Some implementations of the present application provide an image processing method, device, device, and storage medium that can at least partially solve the above-mentioned problems in the prior art.
根据本申请的一个方面,提供一种图像处理的方法,所述方法可包括:对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,所述第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域;将所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,所述第二分割图像包含多个体素块;以及将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块;基于每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块,获取所述脑部子区域的体积。According to one aspect of the present application, an image processing method is provided, the method may include: performing a first segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure to obtain a first segmented image, wherein the first The segmented image includes a plurality of brain subregions; performing a second segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image based on voxel blocks to obtain a second segmented image, wherein the second segmented image includes a plurality of voxel blocks; and Fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image to determine the voxel blocks included in each of the brain subregions; based on the voxel blocks included in each of the brain subregions , to obtain the volume of the brain subregion.
在本申请一个实施方式中,将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块,还可包括:将每个所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比;响应于所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于所述体素块数量阈值范围内,将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合;响应于所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出所述体素块数量阈值范围,基于所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行所述第二分割。In one embodiment of the present application, fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image, and determining the voxel blocks contained in each of the brain sub-regions may further include: The number of voxel blocks included in the brain sub-region is compared with the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks; in response to the number of voxel blocks included in the brain sub-region is within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, Fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image; in response to the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region exceeding the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, based on the brain magnetic resonance The voxels of the preprocessed image are re-performed on said second segmentation.
在本申请一个实施方式中,将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块,可包括:基于所述第一分割图像确定每个所述脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签;结合所述第二分割图像,获取所述体素块中对应的所述体素标签的数量;基于所述体素标签的数量确定所述体素块的标签;基于所述体素块的标签确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块。In one embodiment of the present application, fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image, and determining the voxel blocks contained in each of the brain sub-regions may include: based on the first Segment the image to determine the voxel label corresponding to the voxel in each of the brain sub-regions; combine the second segmented image to obtain the number of the corresponding voxel label in the voxel block; based on the volume The number of voxel labels determines the labels of the voxel blocks; and the voxel blocks contained in each of the brain sub-regions are determined based on the labels of the voxel blocks.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述方法还可包括:将所述脑部子区域的体积输入到完成训练的分类模型,并获得对应的目标分类结果。In one embodiment of the present application, the method may further include: inputting the volume of the brain subregion into the trained classification model, and obtaining a corresponding target classification result.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述方法还可包括:对获取的脑部核磁共振图像进行预处理,获得所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像。In one embodiment of the present application, the method may further include: performing preprocessing on the acquired MRI image of the brain to obtain the MRI preprocessed image of the brain.
本申请另一方面提供了一种图像处理的装置,所述装置可包括:第一分割模块,用于对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,所述第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域;第二分割模块,用于将所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,所述第二分割图像包含多个体素块;以及融合模块,用于将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块;体积获取模块,用于基于每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块,获取所述脑部子区域的体积。Another aspect of the present application provides an image processing device, the device may include: a first segmentation module, configured to perform a first segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure to obtain the first segmented image, Wherein, the first segmented image includes a plurality of brain subregions; the second segmenting module is configured to perform a second segmenting of the brain MRI preprocessing image based on voxel blocks to obtain a second segmented image, wherein, The second segmented image includes a plurality of voxel blocks; and a fusion module, configured to fuse the first segmented image with the second segmented image, and determine the voxels included in each of the brain subregions block; a volume acquisition module, configured to acquire the volume of the brain sub-region based on the voxel blocks contained in each of the brain sub-regions.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述第二分割模块可用于:将每个所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比;响应于所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于所述体素块数量阈值范围内,将所述第一分割图像与所述第二分割图像进行融合;响应于所述脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出所述体素块数量阈值范围,基于所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行所述第二分割。In one embodiment of the present application, the second segmentation module can be used to: compare the number of voxel blocks contained in each of the brain sub-regions with a threshold range of the number of voxel blocks; The number of voxel blocks contained in the sub-region is within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, and the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image; in response to the voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region If the number of voxel blocks exceeds the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, the second segmentation is re-performed based on the voxels of the brain MRI preprocessed image.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述融合模块可用于:基于所述第一分割图像确定每个所述脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签;结合所述第二分割图像,获取所述体素块中对应的所述体素标签的数量;基于所述体素标签的数量确定所述体素块的标签;基于所述体素块的标签确定每个所述脑部子区域包含的所述体素块。In one embodiment of the present application, the fusion module can be used to: determine voxel labels corresponding to voxels in each of the brain subregions based on the first segmented image; combine the second segmented image to obtain The number of corresponding voxel labels in the voxel block; determining the label of the voxel block based on the number of voxel labels; determining each of the brain subregions based on the label of the voxel block Contains the voxel block.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述装置还可包括:分类模块,用于将所述脑部子区域的体积输入到完成训练的分类模型,并获得对应的目标分类结果。In one embodiment of the present application, the device may further include: a classification module, configured to input the volume of the brain sub-region into the trained classification model, and obtain a corresponding target classification result.
在本申请一个实施方式中,所述装置还可包括:预处理模块,用于对获取的脑部核磁共振图像进行预处理,获得所述脑部核磁共振预处理图像。In one embodiment of the present application, the device may further include: a preprocessing module, configured to preprocess the acquired MRI images of the brain to obtain the MRI preprocessed images of the brain.
本申请再一方面提供了一种电子设备,所述电子设备可包括:处理器,适于执行计算机程序;以及计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质中存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被所述处理器执行时,实现上述任一项的图像处理的方法。Another aspect of the present application provides an electronic device, the electronic device may include: a processor adapted to execute a computer program; and a computer-readable storage medium, the computer-readable storage medium stores the computer program, the When the computer program is executed by the processor, any one of the above image processing methods can be realized.
本申请又一方面提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质用于存储计算机程序,所述计算机程序使得计算机执行上述任一项的图像处理的方法。Another aspect of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, which is used to store a computer program, and the computer program causes a computer to execute any one of the image processing methods described above.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过将将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,综合利用脑部子区域的灰度、密度、纹理等信息,对脑部子区域进行精准分割,确定每个脑部子区域的体积更加精准,在一定程度上可以提高PD和P-plus鉴别诊断结果的准确性。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by fusing the first segmented image and the second segmented image, the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region are determined, and the gray level, density, and texture of the brain sub-region are comprehensively utilized Accurately segment the brain sub-regions and determine the volume of each brain sub-region more accurately, which can improve the accuracy of the differential diagnosis results of PD and P-plus to a certain extent.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过阅读参照以下附图所作的对非限制性实施例的详细描述,本申请的其它特征、目的和优点将会变得更明显。其中:Other features, objects and advantages of the present application will become more apparent by reading the detailed description of non-limiting embodiments made with reference to the following drawings. in:
图1为根据本申请实施方式的图像处理的方法1000的流程图;FIG. 1 is a flowchart of an
图2为根据本申请示例性实施方式的进行第二分割中形成体素块流程示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic flow chart of forming a voxel block during the second segmentation according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application;
图3为根据本申请示例性实施方式的确定脑部子区域包含的体素块的流程示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic flowchart of determining voxel blocks contained in brain subregions according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application;
图4为根据本申请示例性实施方式的对第二分割图像进行验证流程示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of a process for verifying a second segmented image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application;
图5为根据本申请实施方式的图像处理的装置2000的示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of an
图6是根据本公开的实施例的适于用来实现本公开的实施例的电子设备700的结构示意图。Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of an
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了更好地理解本申请,将参考附图对本申请的各个方面做出更详细的说明。应理解,这些详细说明只是对本申请的示例性实施方式的描述,而非以任何方式限制本申请的范围。在说明书全文中,相同的附图标号指代相同的元件。表述“和/或”包括相关联的所列项目中的一个或多个的任何和全部组合。For a better understanding of the application, various aspects of the application will be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that these detailed descriptions are descriptions of exemplary embodiments of the application only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the application in any way. Throughout the specification, the same reference numerals refer to the same elements. The expression "and/or" includes any and all combinations of one or more of the associated listed items.
在附图中,为了便于说明,已稍微调整了元素的大小、尺寸和形状。附图仅为示例而并非严格按比例绘制。如在本文中使用的,用语“大致”、“大约”以及类似的用语用作表近似的用语,而不用作表程度的用语,并且旨在说明将由本领域普通技术人员认识到的、测量值或计算值中的固有偏差。另外,在本申请中,各步骤处理描述的先后顺序并不必然表示这些处理在实际操作中出现的顺序,除非有明确其它限定或者能够从上下文推导出的除外。In the drawings, the size, dimensions, and shapes of elements have been slightly adjusted for illustrative purposes. The drawings are examples only and are not strictly drawn to scale. As used herein, the words "approximately," "approximately," and similar words are used as words of approximation, not of degree, and are intended to describe measurements that would be recognized by those of ordinary skill in the art. Or inherent bias in calculated values. In addition, in the present application, the order of description of the processing of each step does not necessarily indicate the order in which these processes appear in actual operation, unless there is a clear other limitation or can be deduced from the context.
还应理解的是,诸如“包括”、“包括有”、“具有”、“包含”和/或“包含有”等表述在本说明书中是开放性而非封闭性的表述,其表示存在所陈述的特征、元件和/或部件,但不排除一个或多个其它特征、元件、部件和/或它们的组合的存在。此外,当诸如“...中的至少一个”的表述出现在所列特征的列表之后时,其修饰整列特征,而非仅仅修饰列表中的单独元件。此外,当描述本申请的实施方式时,使用“可”表示“本申请的一个或多个实施方式”。并且,用语“示例性的”旨在指代示例或举例说明。It should also be understood that expressions such as "comprises", "comprises", "has", "comprises" and/or "comprising" in this specification are open rather than closed expressions, which mean that there are all The stated features, elements and/or components do not exclude the presence of one or more other features, elements, components and/or combinations thereof. Furthermore, expressions such as "at least one of," when preceding a list of listed features, modify the entire list of features and do not modify just the individual elements of the list. In addition, when describing the embodiments of the present application, the use of "may" means "one or more embodiments of the present application". Also, the word "exemplary" is intended to mean an example or illustration.
除非另外限定,否则本文中使用的所有措辞(包括工程术语和科技术语)均具有与本申请所属领域普通技术人员的通常理解相同的含义。还应理解的是,除非本申请中有明确的说明,否则在常用词典中定义的词语应被解释为具有与它们在相关技术的上下文中的含义一致的含义,而不应以理想化或过于形式化的意义解释。Unless otherwise defined, all terms (including engineering terms and scientific and technical terms) used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this application belongs. It should also be understood that unless there is an explicit statement in this application, words defined in commonly used dictionaries should be interpreted as having meanings consistent with their meanings in the context of related technologies, and should not be idealized or overly Formal meaning interpretation.
需要说明的是,在不冲突的情况下,本申请中的实施方式及实施方式中的特征可以相互组合。下面将参考附图并结合实施方式来详细说明本申请。It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the implementations in the present application and the features in the implementations can be combined with each other. Hereinafter, the present application will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings and in combination with embodiments.
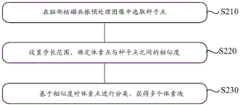
图1为根据本申请实施方式的图像处理的方法1000的流程图。如图1所示,图像处理的方法1000可包括:FIG. 1 is a flowchart of an
步骤S100:对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域;Step S100: performing a first segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure to obtain a first segmented image, wherein the first segmented image includes multiple brain sub-regions;
步骤S200:将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,第二分割图像包含多个体素块;Step S200: performing a second segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessed image based on voxel blocks to obtain a second segmented image, wherein the second segmented image includes a plurality of voxel blocks;
步骤S300:将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块;以及Step S300: Fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image to determine the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region; and
步骤S400:基于每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,获取脑部子区域的体积。Step S400: Obtain the volume of the brain sub-region based on the voxel blocks included in each brain sub-region.
下面将详细说明上述图像处理的方法1000的各个步骤的具体内容。The specific content of each step of the above
脑部核磁共振图像(MRI)对于PD和P-plus的诊断是必不可少的,帕金森病(PD)和帕金森综合征(P-plus)中在脑部核磁共振图像(MRI)存在区别特征。例如,帕金森综合征(P-plus)中多系统萎缩(Multiple system atrophy,简称MSA)和进行性核上性麻痹(Progressive superanuclear palsy,简称PSP),其脑部MRI可以显示P-plus中出现但PD中没有的各种特征。例如,PSP患者表现出明显的中脑萎缩(蜂鸟标志),脑桥和第三脑室宽度的增大;在MSA-P(帕金森症状)患者中,会出现壳核萎缩,侧缘变平(裂隙标志);MSA-C(小脑性共济失调症状)患者的小脑会出现萎缩,中脑与脑桥的比值增加;而对于尾状核、壳核和苍白球是基底神经节的主要组成部分,一般认为大多数神经退行性疾病的发生都与这些部位的组织结构改变相关。但是在获取脑部MRI图像的过程中,由于头部大小差异以及摆放位置等,导致获取的脑部图像之间具有较大的差异性,因此,需要对获取的脑部图像进行预处理。Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is essential for the diagnosis of PD and P-plus, and there is a difference in brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) between Parkinson's disease (PD) and Parkinson's syndrome (P-plus) feature. For example, multiple system atrophy (MSA for short) and progressive superanuclear palsy (PSP for short) in Parkinson's syndrome (P-plus), the MRI of the brain can show that in P-plus But various features that are not in PD. For example, patients with PSP show marked atrophy of the midbrain (hummingbird sign), and enlargement of the width of the pons and third ventricle; signs); in patients with MSA-C (cerebellar ataxia symptoms), the cerebellum will atrophy and the ratio of midbrain to pons will increase; while the caudate nucleus, putamen and pallidus are the main components of the basal ganglia, generally It is believed that the occurrence of most neurodegenerative diseases is associated with changes in the tissue structure of these sites. However, in the process of obtaining brain MRI images, due to differences in head size and placement positions, etc., there are large differences between the obtained brain images. Therefore, it is necessary to preprocess the obtained brain images.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,对获取的脑部核磁共振图像进行预处理,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像。示例性地,获取不同类型患者的脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像,并检测脑部MRI图像的数据类型是否为DICOM格式,如果脑部MRI图像不是DICOM格式,可以对脑部MRI图像的格式进行转换,有利于后期统一对图像进行处理。然后将脑部MRI图像随机划分成训练数据集和测试数据集,并将一个三维大脑MRI图像切片转化为若干个二维大脑磁共振图像。例如,在数据集中包含149例PD患者的脑部MRI图像,57例PSP患者的脑部MRI图像,86例MSA患者的脑部MRI图像,按照随机比例划分为训练集和测试集,并将所有脑部MRI图像转化为DICOM格式。将格式转化后的脑部MRI图像进行序列切片,切片的尺寸为256像素×256像素,对应的体素大小为1.172×1.172×3.5mm3。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, preprocessing is performed on the acquired MRI images of the brain to obtain preprocessed MRI images of the brain. Exemplarily, obtain brain magnetic resonance (MRI) images of different types of patients, and detect whether the data type of the brain MRI images is in DICOM format, if the brain MRI images are not in DICOM format, the format of the brain MRI images can be The conversion is beneficial to the unified image processing in the later stage. Then the brain MRI images are randomly divided into training data sets and test data sets, and a 3D brain MRI image slice is converted into several 2D brain MRI images. For example, the data set contains 149 brain MRI images of PD patients, 57 brain MRI images of PSP patients, and 86 brain MRI images of MSA patients, which are randomly divided into training set and test set, and all Brain MRI images were converted to DICOM format. The format-converted brain MRI images were serially sliced. The size of the slices was 256 pixels×256 pixels, and the corresponding voxel size was 1.172×1.172×3.5 mm3 .
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,对于脑部MRI图像的预处理过程还可以包括:将二维大脑磁共振图像进行中心裁剪,去除部分背景图像,使脑部MRI图像的大小一致,以降低脑部MRI图像背景的干扰,减小脑部MRI图像的尺寸。然后,可以对经过中心裁剪的脑部MRI图像进行偏置场矫正,主要是对脑部MRI图像中不均匀的低频部分进行矫正,去除伪影,避免影响后续图像处理的结果。最后对经过偏置场矫正的图像进行归一化处理,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the preprocessing process for the brain MRI image may also include: performing center cropping on the two-dimensional brain MRI image, removing part of the background image, and making the size of the brain MRI image consistent, so as to reduce the Interference in the background of brain MRI images reduces the size of brain MRI images. Then, the bias field correction can be performed on the center-cropped brain MRI image, mainly to correct the uneven low-frequency part in the brain MRI image, remove artifacts, and avoid affecting the results of subsequent image processing. Finally, normalize the image corrected by the bias field to obtain the brain MRI preprocessed image.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过对脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像进行预处理,预处理过程可以包括对脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像进行格式转换、序列切片、中心裁剪、偏置场矫正、归一化处理等操作,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像,在一定程度上,可以提高后续对脑部核磁共振预处理图像分割的准确度,并且也可以节约后续分割模型训练的时间。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by preprocessing the brain magnetic resonance (MRI) image, the preprocessing process may include performing format conversion, sequence slicing, center cropping, and bias field on the brain magnetic resonance (MRI) image. Operations such as correction and normalization processing to obtain brain MRI preprocessing images can, to a certain extent, improve the accuracy of subsequent segmentation of brain MRI preprocessing images, and can also save time for subsequent segmentation model training.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像之后,对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域。示例性地,可以建立第一分割模型并设置训练参数对模型进行训练。以第一分割模型为3D-VNet模型为例,在建立3D-VNet模型之后,可以将3D-VNet模型的训练参数设置如下:基础学习率设置为0.003,学习率衰减频率为每40轮衰减10倍,批处理大小为16,训练的迭代周期设置为400,损失函数为交叉熵损失函数和DICE损失函数。完成参数设置之后,可以基于训练数据集中脑部核磁共振预处理图像对3D-VNet模型进行训练,并获得完成训练的3D-VNet模型。进一步地,可以将测试数据集合中的脑部核磁共振预处理图像输入到完成训练的3D-VNet模型,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像的多个脑部子区域可以包括:小脑、中脑、脑桥、尾状核、壳核、苍白球和第三脑室。本领域技术人员可知,本申请的第一分割模型的参数设置为示例性的说明,可以根据实际的情况进行参数调整,本申请对此不做限制。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the brain MRI preprocessing image is obtained, the brain MRI preprocessing image is first segmented based on the brain structure to obtain the first segmented image, wherein the first segmented image Includes multiple brain subregions. Exemplarily, a first segmentation model may be established and training parameters may be set to train the model. Taking the 3D-VNet model as the first split model as an example, after the 3D-VNet model is established, the training parameters of the 3D-VNet model can be set as follows: the basic learning rate is set to 0.003, and the learning rate decay frequency is 10 per 40 rounds. times, the batch size is 16, the training iteration period is set to 400, and the loss function is the cross-entropy loss function and the DICE loss function. After the parameter setting is completed, the 3D-VNet model can be trained based on the brain MRI preprocessed images in the training data set, and the trained 3D-VNet model can be obtained. Further, the brain MRI preprocessed image in the test data set can be input to the 3D-VNet model that has completed the training to obtain the first segmented image, wherein the multiple brain subregions of the first segmented image can include: cerebellum , midbrain, pons, caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus and third ventricle. Those skilled in the art know that the parameter setting of the first segmentation model in the present application is an exemplary description, and the parameters can be adjusted according to the actual situation, which is not limited in the present application.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得包括多个脑部子区域第一分割图像,可以在后续过程中,更好的与第二分割结果进行融合,获得更准确的分割结果。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by first segmenting the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure, the first segmented image including multiple brain sub-regions can be obtained, which can be better compared with The second segmentation result is fused to obtain a more accurate segmentation result.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,本申请还可以将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,第二分割图像包含多个体素块。其中,第二分割可以基于3D-SLIC模型对脑部核磁共振预处理图像进行第二分割,具体地,可以将脑部核磁共振预处理图像中的体素基于像素值、纹理等形态学特征对体素进行迭代聚类,将脑部核磁共振预处理图像中相似的体素整合成体素块。图2为根据本申请示例性实施方式的进行第二分割中形成体素块流程示意图。如图2所示,第二分割的步骤可以包括:In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the present application may further perform a second segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessed image based on voxel blocks to obtain a second segmented image, wherein the second segmented image includes a plurality of voxel blocks. Wherein, the second segmentation can be based on the 3D-SLIC model to perform the second segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image, specifically, the voxels in the brain MRI preprocessing image can be divided based on morphological features such as pixel value and texture Voxels are iteratively clustered to integrate similar voxels in preprocessed brain MRI images into voxel blocks. Fig. 2 is a schematic flow chart of forming a voxel block during the second segmentation according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 2, the steps of the second segmentation may include:
步骤S210:在脑部核磁共振预处理图像中选取种子点;Step S210: selecting seed points in the brain MRI preprocessing image;
步骤S220:设置步长范围,确定体素点与种子点之间的相似度;Step S220: set the step size range, and determine the similarity between the voxel point and the seed point;
步骤S230:基于相似度对体素点进行分类,获得多个体素块。Step S230: Classify the voxel points based on the similarity to obtain multiple voxel blocks.
示例性地,若脑部核磁共振预处理图像包含了N个体素点,经过第二分割之后预计可以得到K个体素块,则每个体素块包含N/K个体素,相邻的种子点之间的距离可以设置为S=√N/K。在选取种子点时,为了减少种子点落在脑部子区域边缘位置,可以在原种子点的一定区域内选择一个梯度较小的位置作为新的种子点。然后基于设置的步长范围,确定在步长范围内,种子点与体素点之间的相似度。进一步地,基于相似度对体素点进行分类,获得多个体素块。例如,可以设置相似度阈值,若种子点与体素点之间的相似度超过相似度阈值,则将体素点与种子点划分到同一体素块。Exemplarily, if the brain MRI preprocessing image contains N voxel points, K voxel blocks are expected to be obtained after the second segmentation, each voxel block contains N/K voxels, and the adjacent seed points The distance between can be set as S=√N/K. When selecting the seed point, in order to reduce the seed point falling on the edge of the brain sub-region, a position with a small gradient can be selected as a new seed point within a certain area of the original seed point. Then, based on the set step size range, determine the similarity between the seed point and the voxel point within the step size range. Further, the voxel points are classified based on the similarity to obtain multiple voxel blocks. For example, a similarity threshold can be set, and if the similarity between the seed point and the voxel point exceeds the similarity threshold, the voxel point and the seed point are divided into the same voxel block.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在获得第一分割图像和第二分割图像之后,将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。图3为根据本申请示例性实施方式的确定脑部子区域包含的体素块的流程示意图。如图3所示,确定脑部子区域包含的体素块可以包括以下步骤:In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the first segmented image and the second segmented image are obtained, the first segmented image and the second segmented image are fused to determine the voxel blocks included in each brain subregion. Fig. 3 is a schematic flowchart of determining voxel blocks contained in brain sub-regions according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 3, determining the voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region may include the following steps:
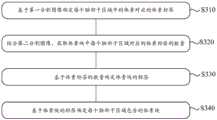
步骤S310:基于第一分割图像确定每个脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签;Step S310: Determine voxel labels corresponding to voxels in each brain subregion based on the first segmented image;
步骤S320:结合第二分割图像,获取体素块中每个脑部子区域对应的体素标签的数量;Step S320: Obtain the number of voxel labels corresponding to each brain sub-region in the voxel block in combination with the second segmented image;
步骤S330:基于体素标签的数量确定体素块的标签;Step S330: Determine the label of the voxel block based on the number of voxel labels;
步骤S340:基于体素块的标签确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。Step S340: Determine the voxel blocks included in each brain sub-region based on the labels of the voxel blocks.
示例性地,首先基于第一分割图像确定每个脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签,其中,体素标签可以表示体素所属的脑部子区域。体素标签可以使用数字代表脑部子区域,例如,将小脑中的体素标签设置为1,中脑的体素标签设置为2、脑桥的体素标签设置为3、尾状核的体素标签设置为4,壳核的体素标签设置为5、苍白球的体素标签设置为6以及第三脑室的体素标签设置为7,通过体素标签,可以确认体素所位于的脑部子区域。然后结合第二分割图像,获取体素块对应的体素标签的数量。例如,基于第二分割图像,确定体素块中对应的体素,并确定体素对应的体素标签。对每个体素块中的体素标签的数量进行统计,将体素标签最多的标签设置成体素块的标签。进一步地,可以基于体素块标签确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。Exemplarily, firstly, a voxel label corresponding to a voxel in each brain subregion is determined based on the first segmented image, wherein the voxel label may indicate the brain subregion to which the voxel belongs. Voxel labels can use numbers to represent brain subregions, for example, set the voxel label to 1 in the cerebellum, 2 in the midbrain, 3 in the pons, 3 in the caudate The label is set to 4, the voxel label of the putamen is set to 5, the voxel label of the globus pallidum is set to 6, and the voxel label of the third ventricle is set to 7. Through the voxel label, the brain where the voxel is located can be confirmed subregion. Then combined with the second segmented image, the number of voxel labels corresponding to the voxel block is obtained. For example, based on the second segmented image, a corresponding voxel in the voxel block is determined, and a voxel label corresponding to the voxel is determined. The number of voxel labels in each voxel block is counted, and the label with the most voxel labels is set as the label of the voxel block. Further, the voxel blocks included in each brain sub-region can be determined based on the voxel block labels.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过将将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,综合利用脑部子区域的灰度、密度、纹理等信息,对脑部子区域进行精准分割,使后续过程中确定每个脑部子区域的体积更加精准。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by fusing the first segmented image and the second segmented image, the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region are determined, and the gray level, density, and texture of the brain sub-region are comprehensively utilized And other information, the brain sub-regions are accurately segmented, so that the volume of each brain sub-region can be determined more accurately in the subsequent process.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合之后,还可以对第二分割图像进行验证。图4为根据本申请示例性实施方式的对第二分割图像进行验证流程示意图。如图4所示,对第二分割图像进行验证可以包括以下步骤:In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image, the second segmented image may also be verified. Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of a process of verifying a second segmented image according to an exemplary embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 4, verifying the second segmented image may include the following steps:
步骤S350:将每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比;Step S350: comparing the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region with the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks;
步骤S360:响应于脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于体素块数量阈值范围内,将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合;Step S360: Fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image in response to the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region being within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks;
步骤S370:响应于脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出体素块数量阈值范围,基于脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行第二分割。Step S370: In response to the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region exceeds the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, re-perform the second segmentation based on the voxels of the brain MRI preprocessed image.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,由于每个脑部子区域的大小不同,可以基于每个脑部子区域的大小设置体素块数量阈值范围。如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块数量较少,在基于体素块计算脑部子区域的体积时,会产生较大的误差,可能导致后续患病类型确定错误;如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块数量过多,对硬件的要求较高,并且计算脑部子区域的体积所花费的时间较多,因此,可以基于每个脑部子区域的大小设置合理的体素块数量阈值范围。在进行第二分割的过程中,可以将每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比,如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于体素块数量阈值范围内,将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合;如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出体素块数量阈值范围,基于脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行体素块划分并第二分割。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, since each brain subregion has a different size, a threshold range for the number of voxel blocks may be set based on the size of each brain subregion. If the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain subregion is small, large errors will occur when calculating the volume of the brain subregion based on voxel blocks, which may lead to errors in the determination of subsequent disease types; if the brain subregion The number of voxel blocks contained in is too large, the hardware requirements are high, and it takes more time to calculate the volume of the brain sub-region. Therefore, a reasonable voxel block can be set based on the size of each brain sub-region Quantity threshold range. In the process of performing the second segmentation, the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region can be compared with the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, if the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region is within the volume Within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image; if the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region exceeds the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, based on the brain MRI preprocessing image The voxels are re-divided into voxel blocks and secondly divided.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过对每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量进行检测,可以确定第二分割结果的合理性,在保证计算脑部子区域的体积的同时,可以在一定程度上提高第二分割的效率。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by detecting the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region, the rationality of the second segmentation result can be determined, while ensuring the calculation of the volume of the brain sub-region, The efficiency of the second split can be improved to a certain extent.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在完成第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合之后,还可以基于每个脑部子区域包含的体素块的数量及每个像素块的大小,获取脑部子区域的体积。通过将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,可以获得更准确的脑部子区域的体积。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the fusion of the first segmented image and the second segmented image is completed, based on the number of voxel blocks included in each brain subregion and the size of each pixel block, the Volumes of brain subregions. By fusing the first segmented image with the second segmented image, more accurate volumes of brain subregions can be obtained.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在获得脑部子区域的体积之后,可以将脑部子区域的体积输入到完成训练的分类模型,并获得对应的目标分类结果。示例性地,可以建立分类模型并设置训练参数对模型进行训练。例如,分类模型可以为基于集成学习算法(GBDT)模型为例,在建立分类模型之后,可以将分类模型的训练参数设置如下:决策树个数设置为50,深度为3,学习率为0.1。利用决策树作为学习器针对残差进行拟合,进而降低分类模型的偏差和方差,获得更准确的PD和P-plus分类结果。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the volume of the brain sub-region is obtained, the volume of the brain sub-region may be input into the trained classification model, and a corresponding target classification result is obtained. Exemplarily, a classification model may be established and training parameters may be set to train the model. For example, the classification model can be based on an integrated learning algorithm (GBDT) model as an example. After the classification model is established, the training parameters of the classification model can be set as follows: the number of decision trees is set to 50, the depth is 3, and the learning rate is 0.1. The decision tree is used as a learner to fit the residual, thereby reducing the bias and variance of the classification model, and obtaining more accurate PD and P-plus classification results.
本申请另一方面还提供了一种图像处理的装置2000。图5为根据本申请实施方式的图像处理的装置2000的示意图。如图5所示,图像处理的装置2000可包括:第一分割模块2100、第二分割模块2200、融合模块2300以及体积获取模块2400。Another aspect of the present application also provides an
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,图像处理的装置2000还可以包括预处理模块2500,其中,预处理模块2500可以用于对获取的脑部核磁共振图像进行预处理,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像。示例性地,获取不同类型患者的脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像,并检测脑部MRI图像的数据类型是否为DICOM格式,如果脑部MRI图像不是DICOM格式,可以对脑部MRI图像的格式进行转换,有利于后期统一对图像进行处理。然后将脑部MRI图像随机划分成训练数据集和测试数据集,并将一个三维大脑MRI图像切片转化为若干个二维大脑磁共振图像。例如,在数据集中包含149例PD患者的脑部MRI图像,57例PSP患者的脑部MRI图像,86例MSA患者的脑部MRI图像,按照随机比例划分为训练集和测试集,并将所有脑部MRI图像转化为DICOM格式。将格式转化后的脑部MRI图像进行序列切片,切片的尺寸为256像素×256像素,对应的体素大小为1.172×1.172×3.5mm3。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,对于脑部MRI图像的预处理过程还可以包括:将二维大脑磁共振图像进行中心裁剪,去除部分背景图像,使脑部MRI图像的大小一致,以降低脑部MRI图像背景的干扰,减小脑部MRI图像的尺寸。然后,可以对经过中心裁剪的脑部MRI图像进行偏置场矫正,主要是对脑部MRI图像中不均匀的低频部分进行矫正,去除伪影,避免影响后续图像处理的结果。最后对经过偏置场矫正的图像进行归一化处理,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the preprocessing process for the brain MRI image may also include: performing center cropping on the two-dimensional brain MRI image, removing part of the background image, and making the size of the brain MRI image consistent, so as to reduce the Interference in the background of brain MRI images reduces the size of brain MRI images. Then, the bias field correction can be performed on the center-cropped brain MRI image, mainly to correct the uneven low-frequency part in the brain MRI image, remove artifacts, and avoid affecting the results of subsequent image processing. Finally, normalize the image corrected by the bias field to obtain the brain MRI preprocessed image.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过对脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像进行预处理,预处理过程可以包括对脑部核磁共振(MRI)图像进行格式转换、序列切片、中心裁剪、偏置场矫正、归一化处理等操作,获得脑部核磁共振预处理图像,在一定程度上,可以提高后续对脑部核磁共振预处理图像分割的准确度,并且也可以节约后续分割模型训练的时间。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by preprocessing the brain magnetic resonance (MRI) image, the preprocessing process may include performing format conversion, sequence slicing, center cropping, and bias field on the brain magnetic resonance (MRI) image. Operations such as correction and normalization processing to obtain brain MRI preprocessing images can, to a certain extent, improve the accuracy of subsequent segmentation of brain MRI preprocessing images, and can also save time for subsequent segmentation model training.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,第一分割模块2100可以用于对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域。示例性地,可以建立第一分割模型并设置训练参数对模型进行训练。以第一分割模型为3D-VNet模型为例,在建立3D-VNet模型之后,可以将3D-VNet模型的训练参数设置如下:基础学习率设置为0.003,学习率衰减频率为每40轮衰减10倍,批处理大小为16,训练的迭代周期设置为400,损失函数为交叉熵损失函数和DICE损失函数。完成参数设置之后,可以基于训练数据集中脑部核磁共振预处理图像对3D-VNet模型进行训练,并获得完成训练的3D-VNet模型。进一步地,可以将测试数据集合中的脑部核磁共振预处理图像输入到完成训练的3D-VNet模型,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像的多个脑部子区域可以包括:小脑、中脑、脑桥、尾状核、壳核、苍白球和第三脑室。本领域技术人员可知,本申请的第一分割模型的参数设置为示例性的说明,可以根据实际的情况进行参数调整,本申请对此不做限制。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得包括多个脑部子区域第一分割图像,可以在后续过程中,更好的与第二分割结果进行融合,获得更准确的分割结果。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by first segmenting the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure, the first segmented image including multiple brain sub-regions can be obtained, which can be better compared with The second segmentation result is fused to obtain a more accurate segmentation result.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,第二分割模块2200可以用于将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,第二分割图像包含多个体素块。其中,第二分割可以基于3D-SLIC模型对脑部核磁共振预处理图像进行第二分割,具体地,可以将脑部核磁共振预处理图像中的体素基于像素值、纹理等形态学特征对体素进行迭代聚类,将脑部核磁共振预处理图像中相似的体素整合成体素块。第二分割可以包括:在脑部核磁共振预处理图像中选取种子点;设置步长范围,确定体素点与种子点之间的相似度;基于相似度对体素点进行分类,获得多个体素块。示例性地,若脑部核磁共振预处理图像包含了N个体素点,经过第二分割之后预计可以得到K个体素块,则每个体素块包含N/K个体素,相邻的种子点之间的距离可以设置为S=√N/K。在选取种子点时,为了减少种子点落在脑部子区域边缘位置,可以在原种子点的一定区域内选择一个梯度较小的位置作为新的种子点。然后基于设置的步长范围,确定在步长范围内,种子点与体素点之间的相似度。进一步地,基于相似度对体素点进行分类,获得多个体素块。例如,可以设置相似度阈值,若种子点与体素点之间的相似度超过相似度阈值,则将体素点与种子点划分到同一体素块。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,融合模块2300可以用于将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。确定脑部子区域包含的体素块可以包括:基于第一分割图像确定每个脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签;结合第二分割图像,获取体素块中每个脑部子区域对应的体素标签的数量;基于体素标签的数量确定体素块的标签;基于体素块的标签确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。示例性地,首先基于第一分割图像确定每个脑部子区域中的体素对应的体素标签,其中,体素标签可以表示体素所属的脑部子区域。体素标签可以使用数字代表脑部子区域,例如,将小脑中的体素标签设置为1,中脑的体素标签设置为2、脑桥的体素标签设置为3、尾状核的体素标签设置为4,壳核的体素标签设置为5、苍白球的体素标签设置为6以及第三脑室的体素标签设置为7,通过体素标签,可以确认体素所位于的脑部子区域。然后结合第二分割图像,获取体素块对应的体素标签的数量。例如,基于第二分割图像,确定体素块中对应的体素,并确定体素对应的体素标签。对每个体素块中的体素标签的数量进行统计,将体素标签最多的标签设置成体素块的标签。进一步地,可以基于体素块标签确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过将将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,综合利用脑部子区域的灰度、密度、纹理等信息,对脑部子区域进行精准分割,使后续过程中确定每个脑部子区域的体积更加精准。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by fusing the first segmented image and the second segmented image, the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region are determined, and the gray level, density, and texture of the brain sub-region are comprehensively utilized And other information, the brain sub-regions are accurately segmented, so that the volume of each brain sub-region can be determined more accurately in the subsequent process.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,在将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合之后,还可以对第二分割图像进行验证。对第二分割图像进行验证可以包括:将每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比;响应于脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于体素块数量阈值范围内,将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合;响应于脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出体素块数量阈值范围,基于脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行第二分割。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, after the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image, the second segmented image may also be verified. Verifying the second segmented image may include: comparing the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain subregion with a threshold range of the number of voxel blocks; in response to the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain subregion being within Within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image; in response to the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region exceeds the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, based on brain MRI preprocessing The voxels of the image are redone for a second segmentation.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,由于每个脑部子区域的大小不同,可以基于每个脑部子区域的大小设置体素块数量阈值范围。如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块数量较少,在基于体素块计算脑部子区域的体积时,会产生较大的误差,可能导致后续患病类型确定错误;如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块数量过多,对硬件的要求较高,并且计算脑部子区域的体积所花费的时间较多,因此,可以基于每个脑部子区域的大小设置合理的体素块数量阈值范围。在进行第二分割的过程中,可以将每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量与体素块数量阈值范围进行对比,如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量位于体素块数量阈值范围内,将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合;如果脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量超出体素块数量阈值范围,基于脑部核磁共振预处理图像的体素重新进行体素块划分并第二分割。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, since each brain subregion has a different size, a threshold range for the number of voxel blocks may be set based on the size of each brain subregion. If the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain subregion is small, large errors will occur when calculating the volume of the brain subregion based on voxel blocks, which may lead to errors in the determination of subsequent disease types; if the brain subregion The number of voxel blocks contained in is too large, the hardware requirements are high, and it takes more time to calculate the volume of the brain sub-region. Therefore, a reasonable voxel block can be set based on the size of each brain sub-region Quantity threshold range. In the process of performing the second segmentation, the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region can be compared with the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, if the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region is within the volume Within the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, the first segmented image is fused with the second segmented image; if the number of voxel blocks contained in the brain sub-region exceeds the threshold range of the number of voxel blocks, based on the brain MRI preprocessing image The voxels are re-divided into voxel blocks and secondly divided.
根据本申请示例性的实施方式,通过对每个脑部子区域中包含的体素块的数量进行检测,可以确定第二分割结果的合理性,在保证计算脑部子区域的体积的同时,可以在一定程度上提高第二分割的效率。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present application, by detecting the number of voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region, the rationality of the second segmentation result can be determined, while ensuring the calculation of the volume of the brain sub-region, The efficiency of the second split can be improved to a certain extent.
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,体积获取模块2400可以用于基于每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,获取脑部子区域的体积。通过将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,可以获得更准确的脑部子区域的体积。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
在本申请示例性的实施方式中,图像处理的装置2000还可以包括分类模块2600可以用于将脑部子区域的体积输入到完成训练的分类模型,并获得对应的目标分类结果。示例性地,可以建立分类模型并设置训练参数对模型进行训练。例如,分类模型可以为基于集成学习算法(GBDT)模型为例,在建立分类模型之后,可以将分类模型的训练参数设置如下:决策树个数设置为50,深度为3,学习率为0.1。利用决策树作为学习器针对残差进行拟合,进而降低分类模型的偏差和方差,获得更准确的PD和P-plus分类结果。In an exemplary embodiment of the present application, the
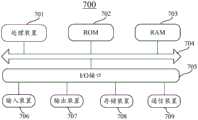
本申请还提供了一种电子设备和计算机可读存储介质。图6是根据本公开的实施例的适于用来实现本公开的实施例的电子设备700的结构示意图。The present application also provides an electronic device and a computer-readable storage medium. Fig. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of an
下面参考图6,其示出了适于用来实现本公开的实施例的电子设备700的结构示意图。本公开的实施例中的终端设备可以包括但不限于诸如移动电话、笔记本电脑、数字广播接收器、PDA(个人数字助理)、PAD(平板电脑)、PMP(便携式多媒体播放器)、车载终端(例如车载导航终端等等的移动终端以及诸如数字TV、台式计算机等等的固定终端。图6示出的终端设备/服务器仅仅是一个示例,不应对本公开的实施例的功能和使用范围带来任何限制。Referring now to FIG. 6 , it shows a schematic structural diagram of an
如图6所示,电子设备700可以包括处理装置(例如中央处理器、图形处理器等)701,其可以根据存储在只读存储器(ROM)702中的程序或者从存储装置708加载到随机访问存储器(RAM)703中的程序而执行各种适当的动作和处理。在RAM703中,还存储有电子设备700操作所需的各种程序和数据。处理装置701、ROM702以及RAM703通过总线704彼此相连。输入/输出(I/O)接口705也连接至总线704。As shown in FIG. 6, an
通常,以下装置可以连接至I/O接口705:包括例如触摸屏、触摸板、键盘、鼠标、摄像头、麦克风、加速度计、陀螺仪等的输入装置706;包括例如液晶显示器(LCD)、扬声器、振动器等的输出装置707;包括例如磁带、硬盘等的存储装置708;以及通信装置709。通信装置709可以允许电子设备700与其他设备进行无线或有线通信以交换数据。虽然图6示出了具有各种装置的电子设备700,但是应理解的是,并不要求实施或具备所有示出的装置。可以替代地实施或具备更多或更少的装置。图6中示出的每个方框可以代表一个装置,也可以根据需要代表多个装置。Typically, the following devices can be connected to the I/O interface 705:
特别地,根据本公开的实施例,上文参考流程图描述的过程可以被实现为计算机软件程序。例如,本公开的实施例包括一种计算机程序产品,其包括承载在计算机可读介质上的计算机程序,该计算机程序包含用于执行流程图所示的方法的程序代码。在这样的实施例中,该计算机程序可以通过通信装置709从网络上被下载和安装,或者从存储装置708被安装,或者从ROM702被安装。在该计算机程序被处理装置701执行时,执行本公开的实施例的方法中限定的上述功能。In particular, according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the processes described above with reference to the flowcharts can be implemented as computer software programs. For example, embodiments of the present disclosure include a computer program product, which includes a computer program carried on a computer-readable medium, where the computer program includes program codes for executing the methods shown in the flowcharts. In such an embodiment, the computer program may be downloaded and installed from a network via communication means 709 , or from storage means 708 , or from
需要说明的是,本公开的实施例所述的计算机可读介质可以是计算机可读信号介质或者计算机可读存储介质或者是上述两者的任意组合。计算机可读存储介质例如可以是电、磁、光、电磁、红外线、或半导体的系统、装置或器件,或者任意以上的组合。计算机可读存储介质的更具体的例子可以包括但不限于:具有一个或多个导线的电连接、便携式计算机磁盘、硬盘、随机访问存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、可擦式可编程只读存储器(EPROM或闪存)、光纤、便携式紧凑磁盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、光存储器件、磁存储器件、或者上述的任意合适的组合。在本公开的实施例中,计算机可读存储介质可以是任何包含或存储程序的有形介质,该程序可以被指令执行系统、装置或者器件使用或者与其结合使用。而在本公开的实施例中,计算机可读信号介质可以包括在基带中或者作为载波一部分传播的数据信号,其中承载了计算机可读的程序代码。这种传播的数据信号可以采用多种形式,包括但不限于电磁信号、光信号或上述的任意合适的组合。计算机可读信号介质还可以是计算机可读存储介质以外的任何计算机可读介质,该计算机可读信号介质可以发送、传播或者传输用于由指令执行系统、装置或者器件使用或者与其结合使用的程序。计算机可读介质上包含的程序代码可以用任何适当的介质传输,包括但不限于:电线、光缆、RF(射频)等等,或者上述的任意合适的组合。It should be noted that the computer-readable medium described in the embodiments of the present disclosure may be a computer-readable signal medium or a computer-readable storage medium, or any combination of the above two. A computer-readable storage medium may be, for example, an electrical, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor system, device, or device, or any combination thereof. More specific examples of computer-readable storage media may include, but are not limited to, electrical connections with one or more wires, portable computer diskettes, hard disks, random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), erasable Programmable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), optical fiber, portable compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), optical storage device, magnetic storage device, or any suitable combination of the above. In the embodiments of the present disclosure, a computer-readable storage medium may be any tangible medium containing or storing a program that can be used by or in conjunction with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device. In the embodiments of the present disclosure, however, a computer-readable signal medium may include a data signal propagated in baseband or as part of a carrier wave, carrying computer-readable program code therein. Such propagated data signals may take many forms, including but not limited to electromagnetic signals, optical signals, or any suitable combination of the foregoing. A computer-readable signal medium may also be any computer-readable medium other than a computer-readable storage medium, which can transmit, propagate, or transmit a program for use by or in conjunction with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device . Program code embodied on a computer readable medium may be transmitted by any appropriate medium, including but not limited to wires, optical cables, RF (radio frequency), etc., or any suitable combination of the above.
上述计算机可读介质可以是上述电子设备中所包含的,也可以是单独存在,而未装配入该电子设备中。上述计算机可读介质承载有一个或者多个程序,当上述一个或者多个程序被该电子设备执行时,使得该电子设备可以实现:对脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于脑部结构进行第一分割,获得第一分割图像,其中,第一分割图像包括多个脑部子区域;将脑部核磁共振预处理图像基于体素块进行第二分割,获得第二分割图像,其中,第二分割图像包含多个体素块;将第一分割图像与第二分割图像进行融合,确定每个脑部子区域包含的体素块;基于每个脑部子区域包含的体素块,获取脑部子区域的体积。The above-mentioned computer-readable medium may be included in the above-mentioned electronic device, or may exist independently without being incorporated into the electronic device. The above-mentioned computer-readable medium carries one or more programs, and when the above-mentioned one or more programs are executed by the electronic device, the electronic device can realize: the first segmentation of the brain MRI preprocessing image based on the brain structure , to obtain a first segmented image, wherein the first segmented image includes a plurality of brain subregions; perform a second segmentation on the brain MRI preprocessing image based on voxel blocks to obtain a second segmented image, wherein the second segmented image Contains a plurality of voxel blocks; fuses the first segmented image and the second segmented image to determine the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region; obtains the brain sub-region based on the voxel blocks contained in each brain sub-region volume of.
可以以一种或多种程序设计语言或其组合来编写用于执行本公开的实施例的操作的计算机程序代码,所述程序设计语言包括面向对象的程序设计语言—诸如Java、Smalltalk、C++,还包括常规的过程式程序设计语言—诸如“C”语言或类似的程序设计语言。程序代码可以完全地在用户计算机上执行、部分地在用户计算机上执行、作为一个独立的软件包执行、部分在用户计算机上部分在远程计算机上执行、或者完全在远程计算机或服务器上执行。在涉及远程计算机的情形中,远程计算机可以通过任意种类的网络,包括局域网(LAN)或广域网(WAN),连接到用户计算机,或者,可以连接到外部计算机(例如利用因特网服务提供商来通过因特网连接)。Computer program code for carrying out operations of embodiments of the present disclosure may be written in one or more programming languages, or combinations thereof, including object-oriented programming languages—such as Java, Smalltalk, C++, Also included are conventional procedural programming languages - such as the "C" language or similar programming languages. The program code may execute entirely on the user's computer, partly on the user's computer, as a stand-alone software package, partly on the user's computer and partly on a remote computer or entirely on the remote computer or server. In cases involving a remote computer, the remote computer can be connected to the user computer through any kind of network, including a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN), or it can be connected to an external computer (such as through the Internet using an Internet service provider). connect).
附图中的流程图和框图,图示了按照本公开各种实施例的系统、方法和计算机程序产品的可能实现的体系架构、功能和操作。在这点上,流程图或框图中的每个方框可以代表一个模块、程序段、或代码的一部分,该模块、程序段、或代码的一部分包含一个或多个用于实现规定的逻辑功能的可执行指令。也应当注意,在有些作为替换的实现中,方框中所标注的功能也可以以不同于附图中所标注的顺序发生。例如,两个接连地表示的方框实际上可以基本并行地执行,它们有时也可以按相反的顺序执行,这依所涉及的功能而定。也要注意的是,框图和/或流程图中的每个方框、以及框图和/或流程图中的方框的组合,可以用执行规定的功能或操作的专用的基于硬件的系统来实现,或者可以用专用硬件与计算机指令的组合来实现。The flowchart and block diagrams in the Figures illustrate the architecture, functionality, and operation of possible implementations of systems, methods and computer program products according to various embodiments of the present disclosure. In this regard, each block in a flowchart or block diagram may represent a module, program segment, or portion of code that contains one or more logical functions for implementing specified executable instructions. It should also be noted that, in some alternative implementations, the functions noted in the block may occur out of the order noted in the figures. For example, two blocks shown in succession may, in fact, be executed substantially concurrently, or they may sometimes be executed in the reverse order, depending upon the functionality involved. It should also be noted that each block of the block diagrams and/or flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams and/or flowchart illustrations, can be implemented by a dedicated hardware-based system that performs the specified functions or operations , or may be implemented by a combination of dedicated hardware and computer instructions.
如上所述的具体实施方式,对本发明的目的、技术方案和有益效果进行了进一步详细说明。应理解的是,以上所述仅为本发明的具体实施方式,并不用于限制本发明。凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The purpose, technical solution and beneficial effects of the present invention are further described in detail in the specific implementation manner described above. It should be understood that the above descriptions are only specific embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310348507.5ACN116342570A (en) | 2023-04-03 | 2023-04-03 | Image processing method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310348507.5ACN116342570A (en) | 2023-04-03 | 2023-04-03 | Image processing method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116342570Atrue CN116342570A (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=86882179
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310348507.5APendingCN116342570A (en) | 2023-04-03 | 2023-04-03 | Image processing method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116342570A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118628498A (en)* | 2024-08-14 | 2024-09-10 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | A method, device and apparatus for detecting brain damage area in brain magnetic resonance images |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104915924A (en)* | 2015-05-14 | 2015-09-16 | 常州迪正雅合电子科技有限公司 | Automatic three-dimensional ultrasound image scaling method |
| CN107146228A (en)* | 2017-03-22 | 2017-09-08 | 东南大学 | A method for supervoxel generation of brain magnetic resonance images based on prior knowledge |
| CN109285176A (en)* | 2018-10-08 | 2019-01-29 | 东南大学 | A brain tissue segmentation method based on regularized graph cuts |
| CN111047611A (en)* | 2020-03-13 | 2020-04-21 | 北京深睿博联科技有限责任公司 | Focal volume measuring method and device |
| CN112446417A (en)* | 2020-10-16 | 2021-03-05 | 山东大学 | Spindle-shaped fruit image segmentation method and system based on multilayer superpixel segmentation |
| CN114445400A (en)* | 2022-03-04 | 2022-05-06 | 上海长征医院 | Kidney volume measurement method, device, electronic device, and readable storage medium |
| CN115841490A (en)* | 2023-02-23 | 2023-03-24 | 山东泗水山岭石材厂 | Mining process ore particle segmentation method and system based on image processing |
- 2023
- 2023-04-03CNCN202310348507.5Apatent/CN116342570A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104915924A (en)* | 2015-05-14 | 2015-09-16 | 常州迪正雅合电子科技有限公司 | Automatic three-dimensional ultrasound image scaling method |
| CN107146228A (en)* | 2017-03-22 | 2017-09-08 | 东南大学 | A method for supervoxel generation of brain magnetic resonance images based on prior knowledge |
| CN109285176A (en)* | 2018-10-08 | 2019-01-29 | 东南大学 | A brain tissue segmentation method based on regularized graph cuts |
| CN111047611A (en)* | 2020-03-13 | 2020-04-21 | 北京深睿博联科技有限责任公司 | Focal volume measuring method and device |
| CN112446417A (en)* | 2020-10-16 | 2021-03-05 | 山东大学 | Spindle-shaped fruit image segmentation method and system based on multilayer superpixel segmentation |
| CN114445400A (en)* | 2022-03-04 | 2022-05-06 | 上海长征医院 | Kidney volume measurement method, device, electronic device, and readable storage medium |
| CN115841490A (en)* | 2023-02-23 | 2023-03-24 | 山东泗水山岭石材厂 | Mining process ore particle segmentation method and system based on image processing |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118628498A (en)* | 2024-08-14 | 2024-09-10 | 西安交通大学医学院第一附属医院 | A method, device and apparatus for detecting brain damage area in brain magnetic resonance images |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110298897B (en) | System and method for positron emission tomography image reconstruction | |
| CN112055879B (en) | Method and system for generating medical images based on text data in medical reports | |
| Vadmal et al. | MRI image analysis methods and applications: an algorithmic perspective using brain tumors as an exemplar | |
| US20190096060A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for annotating medical image | |
| US11430123B2 (en) | Sampling latent variables to generate multiple segmentations of an image | |
| CN112614144B (en) | Image segmentation method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| KR102460257B1 (en) | Method or apparatus for providing diagnostic results | |
| CN104573742B (en) | Classification method of medical image and system | |
| CN112396605B (en) | Network training method and device, image recognition method and electronic equipment | |
| CN107633522A (en) | Brain image dividing method and system based on local similarity movable contour model | |
| CN115512110A (en) | Medical image tumor segmentation method related to cross-modal attention mechanism | |
| CN112927799A (en) | Life cycle analysis system fusing multi-example learning and multi-task depth imaging group | |
| CN117152442B (en) | Automatic image target area sketching method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| WO2021139351A1 (en) | Image segmentation method, apparatus, medium, and electronic device | |
| Velichko et al. | A comprehensive review of deep learning approaches for magnetic resonance imaging liver tumor analysis | |
| CN116797554A (en) | Image processing method and device | |
| Qin et al. | Application of artificial intelligence in diagnosis of craniopharyngioma | |
| GB2625069A (en) | Method and system for training a machine learning system for image processing | |
| CN116342570A (en) | Image processing method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113850796A (en) | Lung disease identification method and device, medium and electronic equipment based on CT data | |
| CN117952930A (en) | Image processing method and device for mental diseases of brain | |
| US20230186463A1 (en) | Estimation of b-value in prostate magnetic resonance diffusion weighted images | |
| CN112749718B (en) | Multimodal feature selection and image data classification method, device and computer equipment | |
| Kim et al. | Impact of Deep Learning 3D CT Super-Resolution on AI-Based Pulmonary Nodule Characterization | |
| WO2020064664A1 (en) | Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy classifier based on volume and shape of subcortical brain regions |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |