CN116337797A - Gas detection device and gas detection method - Google Patents
Gas detection device and gas detection methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116337797A CN116337797ACN202111578276.4ACN202111578276ACN116337797ACN 116337797 ACN116337797 ACN 116337797ACN 202111578276 ACN202111578276 ACN 202111578276ACN 116337797 ACN116337797 ACN 116337797A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- sensor
- gas
- nmhc
- ndir
- fid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription61
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethaneChemical compoundCVNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription36
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 229930195733hydrocarbonNatural products0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 150000002430hydrocarbonsChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription7
- 239000004215Carbon black (E152)Substances0.000claimsdescription4
- 125000004432carbon atomChemical groupC*0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000000769gas chromatography-flame ionisation detectionMethods0.000abstract1
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description95
- 239000003570airSubstances0.000description11
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description7
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description6
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description6
- 230000035945sensitivityEffects0.000description5
- 238000000041tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopyMethods0.000description5
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-NBenzeneChemical compoundC1=CC=CC=C1UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-NTolueneChemical compoundCC1=CC=CC=C1YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 238000000862absorption spectrumMethods0.000description3
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description3
- 150000004945aromatic hydrocarbonsChemical class0.000description3
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description3
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description3
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description3
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-NIronChemical compound[Fe]XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- URLKBWYHVLBVBO-UHFFFAOYSA-NPara-XyleneChemical groupCC1=CC=C(C)C=C1URLKBWYHVLBVBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 150000001555benzenesChemical class0.000description2
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description2
- -1methane hydrocarbonsChemical class0.000description2
- 229910052757nitrogenInorganic materials0.000description2
- 150000002894organic compoundsChemical class0.000description2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description2
- NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcrylonitrileChemical compoundC=CC#NNLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrogenChemical compound[H][H]UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- VQTUBCCKSQIDNK-UHFFFAOYSA-NIsobuteneChemical groupCC(C)=CVQTUBCCKSQIDNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910000831SteelInorganic materials0.000description1
- 150000001335aliphatic alkanesChemical class0.000description1
- 150000001336alkenesChemical class0.000description1
- 239000012080ambient airSubstances0.000description1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012159carrier gasSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007084catalytic combustion reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000013375chromatographic separationMethods0.000description1
- 239000003245coalSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002485combustion reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 239000003344environmental pollutantSubstances0.000description1
- 238000004817gas chromatographyMethods0.000description1
- 239000011521glassSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000002329infrared spectrumMethods0.000description1
- 229910052742ironInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000001285laser absorption spectroscopyMethods0.000description1
- 230000031700light absorptionEffects0.000description1
- 238000005065miningMethods0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 231100000719pollutantToxicity0.000description1
- 239000010959steelSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/17—Systems in which incident light is modified in accordance with the properties of the material investigated
- G01N21/25—Colour; Spectral properties, i.e. comparison of effect of material on the light at two or more different wavelengths or wavelength bands
- G01N21/31—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry
- G01N21/35—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light
- G01N21/3504—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light for analysing gases, e.g. multi-gas analysis
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/17—Systems in which incident light is modified in accordance with the properties of the material investigated
- G01N21/25—Colour; Spectral properties, i.e. comparison of effect of material on the light at two or more different wavelengths or wavelength bands
- G01N21/31—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry
- G01N21/35—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light
- G01N21/359—Investigating relative effect of material at wavelengths characteristic of specific elements or molecules, e.g. atomic absorption spectrometry using infrared light using near infrared light
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N27/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means
- G01N27/62—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means by investigating the ionisation of gases, e.g. aerosols; by investigating electric discharges, e.g. emission of cathode
- G01N27/626—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of electric, electrochemical, or magnetic means by investigating the ionisation of gases, e.g. aerosols; by investigating electric discharges, e.g. emission of cathode using heat to ionise a gas
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/20—Air quality improvement or preservation, e.g. vehicle emission control or emission reduction by using catalytic converters
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Materials By Optical Means (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及气体检测领域,尤其涉及气体检测装置及气体检测方法。The invention relates to the field of gas detection, in particular to a gas detection device and a gas detection method.
背景技术Background technique
在化工、钢铁、煤矿等行业,为了提高环境空气质量达到环保指标,必须控制大气中的非甲烷总烃(Nonmethane Hydrocarbon,NMHC),根据《大气污染物排放标准》(GB16297-1996)以及《大气污染物排放标准详解》,非甲烷总烃主要包括烷烃、烯烃、芳香烃和含氧烃等组分,实际上是指具有C2-C12的烃类物质。In chemical industry, iron and steel, coal mining and other industries, in order to improve the ambient air quality and meet the environmental protection targets, it is necessary to control the total non-methane hydrocarbons (Nonmethane Hydrocarbon, NMHC) in the atmosphere. Detailed Explanation of Pollutant Emission Standards", non-methane total hydrocarbons mainly include alkanes, olefins, aromatic hydrocarbons and oxygen-containing hydrocarbons, which actually refer to hydrocarbons with C2 -C12 .
目前检测NMHC最常用的方法是气相色谱火焰离子化检测器法(GC-FID)。然而,气相色谱分离(GC)装置零件多、重量大,不便于做便携产品;分析时间长,每次分析至少需要十分钟以上,无法得到连续的实时NMHC浓度值;而且GC的载气高纯氮在使用过程中是不断消耗的,需要经常更换氮气瓶,色谱柱也需要经常更换,使用和维护成本较高。At present, the most commonly used method for detecting NMHC is gas chromatography with flame ionization detector (GC-FID). However, the gas chromatographic separation (GC) device has many parts and heavy weight, which is not convenient for portable products; the analysis time is long, and each analysis takes at least ten minutes, and continuous real-time NMHC concentration values cannot be obtained; and the carrier gas of GC is high-purity Nitrogen is constantly consumed during use, and the nitrogen cylinder needs to be replaced frequently, and the chromatographic column also needs to be replaced frequently, and the use and maintenance costs are high.
因此,有必要提供一种新的NMHC气体检测装置及检测方法以解决上述问题。Therefore, it is necessary to provide a new NMHC gas detection device and detection method to solve the above problems.
发明内容Contents of the invention
鉴于以上现有技术的缺点,本发明的目的在于提供一种体积小、重量轻、结构简单的用于检测NMHC含量的气体检测装置,可形成便携式仪器且实现NMHC的实时监测。In view of the above shortcomings of the prior art, the object of the present invention is to provide a gas detection device with small volume, light weight and simple structure for detecting NMHC content, which can form a portable instrument and realize real-time monitoring of NMHC.
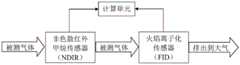
为实现上述发明目的,本发明采用如下技术方案:一种气体检测装置,用于检测气体中的非甲烷总烃(NMHC)含量,包括计算单元、与所述计算单元电性连接的火焰离子化传感器(FID)以及与所述计算单元电性连接的至少一个非色散红外甲烷传感器(NDIR)。In order to achieve the above invention, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions: a gas detection device, used to detect the non-methane total hydrocarbon (NMHC) content in the gas, including a calculation unit, a flame ionization device electrically connected to the calculation unit A sensor (FID) and at least one non-dispersive infrared methane sensor (NDIR) electrically connected to the computing unit.
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述NDIR传感器的出气口连接所述FID传感器的进气口,所述被测气体能够通过所述NDIR传感器进入所述FID传感器内。As a further improvement of the present invention, the gas outlet of the NDIR sensor is connected to the gas inlet of the FID sensor, and the measured gas can enter the FID sensor through the NDIR sensor.
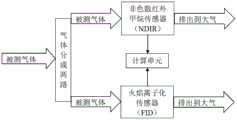
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述气体检测装置还包括三通管道,所述三通管道设有第一管道、第二管道以及第三管道,所述NDIR传感器的进气口连通所述第一管道,所述FID传感器的进气口连通所述第二管道。As a further improvement of the present invention, the gas detection device further includes a three-way pipeline, the three-way pipeline is provided with a first pipeline, a second pipeline and a third pipeline, and the air inlet of the NDIR sensor communicates with the first pipeline, the air inlet of the FID sensor communicates with the second pipeline.
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述被测气体能够通过所述第三管道进入所述第一管道后再进入所述NDIR传感器内,且所述被测气体能够通过所述第三管道进入所述第二管道后再进入所述FID传感器内。As a further improvement of the present invention, the measured gas can enter the first pipeline through the third pipeline and then enter the NDIR sensor, and the measured gas can enter the The second pipe then enters the FID sensor.
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述被测气体进入所述第一管道的流量与进入所述第二管道的流量相同。As a further improvement of the present invention, the flow rate of the measured gas entering the first pipeline is the same as the flow rate entering the second pipeline.
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述NDIR传感器包括气体腔室、位于所述气体腔室一端的光源端以及相对地位于所述气体腔室另一端的探测端。As a further improvement of the present invention, the NDIR sensor includes a gas chamber, a light source end located at one end of the gas chamber, and a detection end relatively located at the other end of the gas chamber.
作为本发明的进一步改进,所述光源端包括红外光源,所述探测端包括红外探测器和滤光片。As a further improvement of the present invention, the light source end includes an infrared light source, and the detection end includes an infrared detector and a filter.
为实现上述发明目的,本发明还采用如下技术方案:一种气体检测方法,包括上述气体检测装置,还包括以下步骤:In order to achieve the purpose of the above invention, the present invention also adopts the following technical solution: a gas detection method, including the above gas detection device, and also includes the following steps:
S1:被测气体先后进入NDIR传感器和FID传感器,然后排出到大气中;和/或,被测气体分成两路,分别进入NDIR传感器和FID传感器,然后分别排出到大气中;S1: The measured gas enters the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor successively, and then is discharged into the atmosphere; and/or, the measured gas is divided into two paths, enters the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor respectively, and is then discharged into the atmosphere;
S2:NDIR传感器测出被测气体中CH4和NMHC的浓度CNDIR,FID传感器测出被测气体中的含碳浓度CFID,NDIR传感器和FID传感器分别将测出的CNDIR和CFID传输到计算单元;S2: The NDIR sensor measures the concentration CNDIR of CH4 and NMHC in the measured gas, the FID sensor measures the carbon concentration CFID in the measured gas, and the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor respectively transmit the measured CNDIR and CFID to the computing unit;
S3:计算单元根据已知的CNDIR和CFID计算出目标值,即被测气体中NMHC的浓度CNMHC。S3: The calculation unit calculates the target value, that is, the concentration CNMHC of the NMHC in the measured gas according to the known CNDIR and CFID .
作为本发明的进一步改进,步骤S2中,所述NDIR传感器的测量波长为7.66μm±0.15μm。As a further improvement of the present invention, in step S2, the measurement wavelength of the NDIR sensor is 7.66 μm±0.15 μm.
作为本发明的进一步改进,步骤S3中,所述CNMHC使用下列等式计算:As a further improvement of the present invention, in step S3, the CNMHC is calculated using the following equation:
……...
CNMHC=C1+C2+C3+……+Cx (式6)CNMHC = C1 +C2 +C3 +...+Cx (Formula 6)
其中,为被测气体中CH4的浓度,CNMHC为被测气体中NMHC的浓度,C1,C2,C3,……,Cx分别为被测气体中NMHC各成分的浓度;in, is the concentration of CH4 in the measured gas, CNMHC is the concentration of NMHC in the measured gas, C1 , C2 , C3 ,..., Cx are the concentrations of NMHC components in the measured gas;
其中,a1,a2,a3,……,ax分别为被测气体中NMHC各成分的碳原子数,b1,b2,b3,……,bx分别为NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下对被测气体中NMHC各成分的交叉灵敏度;Among them, a1 , a2 , a3 ,..., ax are the number of carbon atoms of each component of NMHC in the measured gas, b1 , b2 , b3 ,..., bx are the NDIR sensor in 7.66 Cross-sensitivity to NMHC components in the measured gas at μm wavelength;
其中,x为被测气体中NMHC的成分的数量。Wherein, x is the number of NMHC components in the measured gas.
相较于现有技术,本发明的气体检测装置及气体检测方法的有益效果在于:Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the gas detection device and gas detection method of the present invention are:
(1)采用NDIR传感器和FID传感器的组合使用,相对于现有的GC-FID检测器,具有体积小、重量轻、结构简单、维护便捷、后期使用成本低,实现了仪器的轻量化,可便携检测NMHC含量;(1) The combination of NDIR sensor and FID sensor is used. Compared with the existing GC-FID detector, it has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple structure, convenient maintenance, and low post-use cost, which realizes the light weight of the instrument and can Portable detection of NMHC content;
(2)NDIR传感器和FID传感器均可每秒钟输出被测气体的NMHC含量值,具有较强的实时性,可进行环保在线监测或在生产过程中控制工艺数据等,而GC装置无法实现实时性;(2) Both the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor can output the NMHC content value of the measured gas every second, which has strong real-time performance, and can carry out environmental protection online monitoring or control process data during the production process, while the GC device cannot realize real-time sex;
(3)NDIR传感器对苯系物、芳香烃的交叉灵敏度相对稳定,且遇到未知气体不会造成很大误差,在实际应用中适用于绝大部分环保检测场合;(3) The cross-sensitivity of NDIR sensors to benzene series and aromatic hydrocarbons is relatively stable, and encountering unknown gases will not cause a large error, which is suitable for most environmental protection detection occasions in practical applications;
(4)利用了甲烷在红外7.66μm波长吸收强,NMHC在此波长吸收弱的特点,从而达到准确测量甲烷浓度的同时,对NMHC响应灵敏度小的目的;(4) Utilize the characteristic that methane absorbs strongly at the wavelength of infrared 7.66 μm, and NMHC absorbs weakly at this wavelength, so as to achieve the purpose of accurately measuring the concentration of methane and at the same time, the response sensitivity to NMHC is small;
(5)克服了多种NMHC的交叉干扰,可在气体检测装置中串联多个测量波长不同的NDIR传感器,测出除甲烷之外NMHC的浓度,且交叉干扰可相互扣除。(5) Overcoming the cross-interference of various NMHCs, multiple NDIR sensors with different measurement wavelengths can be connected in series in the gas detection device to measure the concentration of NMHCs other than methane, and the cross-interferences can be deducted from each other.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明一实施例提供的气体检测装置的结构示意图和被测气体流向示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic structural diagram of a gas detection device provided by an embodiment of the present invention and a schematic diagram of the flow direction of a gas to be measured;
图2为本发明另一实施例提供的气体检测装置的结构示意图和被测气体流向示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a gas detection device provided by another embodiment of the present invention and a schematic diagram of the flow direction of the gas to be measured;
图3为本发明NDIR传感器的基本结构示意图;Fig. 3 is the basic structure schematic diagram of NDIR sensor of the present invention;
图4为CH4在3.30~22μm波段的红外吸收光谱图;Figure 4 is the infrared absorption spectrum ofCH4 in the 3.30-22 μm band;
图5为C7H8在3.30~22μm波段的红外吸收光谱图。Fig. 5 is an infrared absorption spectrum diagram of C7 H8 in the 3.30-22 μm band.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合附图详细地对本发明示例性具体实施方式进行说明。如果存在若干具体实施方式,在不冲突的情况下,这些实施方式中的特征可以相互组合。当描述涉及附图时,除非另有说明,不同附图中相同的数字表示相同或相似的要素。以下示例性具体实施方式中所描述的内容并不代表与本发明相一致的所有实施方式;相反,它们仅是与本发明的权利要求书中所记载的、与本发明的一些方面相一致的装置、产品和/或方法的例子。Exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. If there are several specific embodiments, the features of these embodiments can be combined with each other under the condition of no conflict. When the description refers to the drawings, unless otherwise stated, the same numerals in different drawings identify the same or similar elements. What is described in the following exemplary embodiments does not represent all implementations consistent with the invention; rather, they are only consistent with some aspects of the invention as recited in the claims of the invention Examples of devices, products and/or methods.
在本发明中使用的术语是仅仅出于描述具体实施方式的目的,而非旨在限制本发明的保护范围。在本发明的说明书和权利要求书中所使用的单数形式的“一种”、“所述”或“该”也旨在包括多数形式,除非上下文清楚地表示其他含义。The terminology used in the present invention is only for the purpose of describing specific embodiments, and is not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention. As used in the description and claims of the present invention, the singular forms "a", "said" or "the" are also intended to include the plural forms unless the context clearly dictates otherwise.
应当理解,本发明的说明书以及权利要求书中所使用的,例如“第一”、“第二”以及类似的词语,并不表示任何顺序、数量或者重要性,而只是用来区分特征的命名。同样,“一个”或者“一”等类似词语也不表示数量限制,而是表示存在至少一个。除非另行指出,本发明中出现的“前”、“后”、“上”、“下”等类似词语只是为了便于说明,而并非限于某一特定位置或者一种空间定向。“包括”或者“包含”等类似词语是一种开放式的表述方式,意指出现在“包括”或者“包含”前面的元件涵盖出现在“包括”或者“包含”后面的元件及其等同物,这并不排除出现在“包括”或者“包含”前面的元件还可以包含其他元件。本发明中如果出现“若干”,其含义是指两个以及两个以上。It should be understood that words such as "first", "second" and similar words used in the description and claims of the present invention do not indicate any order, quantity or importance, but are only used to distinguish the nomenclature of features . Likewise, words like "a" or "one" do not denote a limitation in quantity, but indicate that there is at least one. Unless otherwise indicated, words such as "front", "rear", "upper" and "lower" appearing in the present invention are for convenience of description only, and are not limited to a specific position or a spatial orientation. "Includes" or "comprising" and other similar words are an open-ended expression, meaning that the elements appearing before "comprising" or "comprising" cover the elements appearing after "comprising" or "comprising" and their equivalents, This does not exclude that elements appearing before "comprising" or "comprising" may also contain other elements. If "several" appears in the present invention, it means two or more.
请参阅图1至图3所示,本发明揭示了一种气体检测装置,用于检测气体中的非甲烷总烃(NMHC)含量,包括计算单元、与计算单元电性连接的火焰离子化传感器(FID)以及与计算单元电性连接的至少一个非色散红外甲烷传感器(NDIR)。计算单元主要进行各种信息数据的处理,本发明中的计算单元为数控技术领域常见的计算单元,本发明中不再赘述。Please refer to Figs. 1 to 3, the present invention discloses a gas detection device for detecting non-methane total hydrocarbon (NMHC) content in gas, including a calculation unit, a flame ionization sensor electrically connected to the calculation unit (FID) and at least one non-dispersive infrared methane sensor (NDIR) electrically connected to the computing unit. The calculation unit mainly processes various information data. The calculation unit in the present invention is a common calculation unit in the field of numerical control technology, and will not be described in detail in the present invention.
进一步地,如图3所示,NDIR传感器包括气体腔室2、位于气体腔室2一端的光源端1以及相对地位于气体腔室2另一端的探测端3。光源端1包括红外光源8,探测端3包括红外探测器4、5和滤光片6、7。滤光片6、7位于红外光源8与红外探测器4、5中间。气体腔室2具有供被测气体流通的进气口和出气口,光源端1位于设有进气口的一端,探测端3位于设有出气口的一端,且进气口和出气口位于光源端1和探测端3中间。Further, as shown in FIG. 3 , the NDIR sensor includes a
本领域技术人员可以理解的是,上述“光源端1和探测端3相对地位于气体腔室2的两端”并非特指光源端1和探测端3分别位于气体腔室2的空间位置的两端,而是光源端1和探测端3分别位于红外光入射光程的两端。Those skilled in the art can understand that the above-mentioned "the
可选地,本发明中的NDIR传感器也可用分析级的可调谐激光吸收光谱仪(TunableDiode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy,TDLAS)和量子级联激光吸收光谱仪(QuantumCascade Laser Absorption Spectroscopy,QCLAS)来代替,TDLAS和QCLAS的优势在于其测量的下限可以低至ppb级。TDLAS所采用的波长是1.652μm,QCLAS所采用的波长为3.33μm和7.66μm,因为TDLAS和QCLAS可以对CH4的红外吸收谱线在几个nm的范围内扫频,所以对其他气体几乎没有交叉响应。但这两种光谱仪目前的价格是NDIR传感器的15倍以上,TDLAS在10万元以上,QCLAS在20万元以上,如此高的价格,很难大面积推广。Optionally, the NDIR sensor in the present invention can also be replaced by an analytical-grade tunable laser absorption spectrometer (TunableDiode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy, TDLAS) and a quantum cascade laser absorption spectrometer (QuantumCascade Laser Absorption Spectroscopy, QCLAS). The advantage is that the lower limit of its measurement can be as low as ppb level. The wavelength used by TDLAS is 1.652 μm, and the wavelengths used by QCLAS are 3.33 μm and 7.66 μm, because TDLAS and QCLAS can sweep the infrared absorption line of CH4 in the range of several nm, so they have almost no effect on other gases cross response. However, the current prices of these two spectrometers are more than 15 times that of NDIR sensors, TDLAS is more than 100,000 yuan, and QCLAS is more than 200,000 yuan. Such high prices are difficult to promote on a large scale.
在一实施例中,如图1所示,NDIR传感器的出气口连接FID传感器的进气口,被测气体能够通过NDIR传感器进入FID传感器内。若有多个NDIR传感器,则被测气体首先依次通过串联的多个NDIR传感器,最后通过FID传感器。In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1 , the gas outlet of the NDIR sensor is connected to the gas inlet of the FID sensor, and the gas to be measured can enter the FID sensor through the NDIR sensor. If there are multiple NDIR sensors, the gas to be measured first passes through multiple NDIR sensors connected in series, and finally passes through the FID sensor.
在另一实施例中,如图2所示,气体检测装置还包括三通管道,三通管道设有第一管道、第二管道以及第三管道,NDIR传感器的进气口连通第一管道,FID传感器的进气口连通第二管道,被测气体能够通过第三管道进入第一管道后再进入NDIR传感器内,且被测气体能够通过第三管道进入第二管道后再进入FID传感器内,被测气体进入第一管道的流量与进入第二管道的流量相同。若有多个NDIR传感器,则多个NDIR传感器串联连接在同一管道。In another embodiment, as shown in Figure 2, the gas detection device further includes a three-way pipeline, the three-way pipeline is provided with a first pipeline, a second pipeline and a third pipeline, and the air inlet of the NDIR sensor communicates with the first pipeline, The air inlet of the FID sensor is connected to the second pipeline, the measured gas can enter the first pipeline through the third pipeline and then enter the NDIR sensor, and the measured gas can enter the second pipeline through the third pipeline and then enter the FID sensor. The flow rate of the measured gas entering the first pipeline is the same as that entering the second pipeline. If there are multiple NDIR sensors, multiple NDIR sensors are connected in series in the same pipe.
本领域技术人员可以理解的是,FID传感器广泛用于挥发性碳氢化合物和许多含碳化合物的检测,其原理是:氢气燃烧形成火焰,待检测气体导入火焰中,助燃空气在火焰外侧流动,导入火焰中的气体分子到达外围时即热分解,C-H结合的一部分C原子离子化,C+、C-能以电流的形式检测出来,电流起因于C原子,其值与原子数成比例,从而测出被测气体中有多少含碳的浓度,即包括甲烷的浓度和NMHC的含碳浓度。Those skilled in the art can understand that FID sensors are widely used in the detection of volatile hydrocarbons and many carbon-containing compounds. The principle is: hydrogen combustion forms a flame, the gas to be detected is introduced into the flame, and the combustion-supporting air flows outside the flame. The gas molecules introduced into the flame will be thermally decomposed when they reach the periphery, and part of the C atoms combined with C-H will be ionized, and C+ and C- can be detected in the form of electric current. How much carbon concentration is in the measured gas, that is, including the concentration of methane and the carbon concentration of NMHC.
市场上常见的传感器有催化燃烧传感器(CAT)、电化学传感器(EC)、紫外光离子化传感器(PID)等,但这些传感器并不是什么气体都能检测,例如CO2就无法检测,而NDIR传感器可以,NDIR传感器主要用于检测化合物,例如:CH4、CO2、C2H2、C2H4、CO、CO2、NH3、VCM、CF4、SF6、CH2F2、CHCl3、NF3、甲醇、乙醇、COS、丙烯腈等,并包含绝大多数有机物(HC)和有机挥发性混合物(VOC)等。而且,NDIR传感器不需要进行燃烧,不会积碳,其光源和探测器都被玻璃或滤波片保护起来,和气体不接触,具有较高的灵敏度。Common sensors on the market include catalytic combustion sensors (CAT), electrochemical sensors (EC), ultraviolet photoionization sensors (PID), etc., but these sensors are not capable of detecting any gas, such as CO2 cannot detect, while NDIR Sensors can, NDIR sensors are mainly used to detect compounds, such as: CH4 , CO2 , C2 H2 , C2 H4 , CO, CO2 , NH3 , VCM, CF4 , SF6 , CH2 F2 , CHCl3 , NF3 , methanol, ethanol, COS, acrylonitrile, etc., and contain most organic compounds (HC) and organic volatile compounds (VOC), etc. Moreover, the NDIR sensor does not need to burn, and will not deposit carbon. Its light source and detector are protected by glass or filters, and they are not in contact with gas, so they have high sensitivity.
NDIR传感器的原理是:光线穿过光路中的被测气体,透过窄带滤波片,到达红外探测器,通过测量进入红外传感器的红外光的强度,来判断被测气体的组分和浓度,当环境中没有被测气体时,其强度是最强的,当有被测气体进入到气室之中,被测气体吸收掉一部分红外光,这样,到达探测器的光强就减弱了,通过标定零点和测量点红外光吸收的程度和刻度化,基于不同气体分子的近红外光谱选择吸收特性,利用气体浓度与吸收强度关系(朗伯-比尔Lambert-Beer定律)鉴别被测气体的组分并确定其浓度。The principle of the NDIR sensor is: the light passes through the measured gas in the optical path, passes through the narrow-band filter, and reaches the infrared detector. By measuring the intensity of the infrared light entering the infrared sensor, the composition and concentration of the measured gas are judged. When When there is no measured gas in the environment, its intensity is the strongest. When the measured gas enters the gas chamber, the measured gas absorbs part of the infrared light, so that the light intensity reaching the detector is weakened. The degree and scale of infrared light absorption at zero point and measurement point, based on the near-infrared spectrum of different gas molecules, select the absorption characteristics, use the relationship between gas concentration and absorption intensity (Lambert-Beer law) to identify the components of the measured gas and Determine its concentration.
气体检测装置中的NDIR传感器和FID传感器均分别与计算单元电性连接,将采集到的电流信号或电压信号传输至计算单元,计算单元将电流信号或电压信号转化为数据信息,再根据设定好的计算程序进行计算,并最终输出检测结果。The NDIR sensor and the FID sensor in the gas detection device are respectively electrically connected to the computing unit, and the collected current signal or voltage signal is transmitted to the computing unit, and the computing unit converts the current signal or voltage signal into data information, and then according to the set A good calculation program performs calculations and finally outputs detection results.
本发明还提供了基于上述气体检测装置的气体检测方法,包括以下步骤:The present invention also provides a gas detection method based on the above gas detection device, comprising the following steps:
S1:被测气体先后进入NDIR传感器和FID传感器,然后排出到大气中;和/或,被测气体分成两路,分别进入NDIR传感器和FID传感器,然后分别排出到大气中;S1: The measured gas enters the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor successively, and then is discharged into the atmosphere; and/or, the measured gas is divided into two paths, enters the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor respectively, and is then discharged into the atmosphere;
S2:NDIR传感器在7.66μm±0.15μm波长下测出被测气体中CH4和NMHC的浓度CNDIR,FID传感器测出被测气体中的含碳浓度CFID,NDIR传感器和FID传感器分别将测出的CNDIR和CFID传输到计算单元;S2: The NDIR sensor measures the concentration CNDIR of CH4 and NMHC in the measured gas at a wavelength of 7.66μm±0.15μm, and the FID sensor measures the carbon content CFID in the measured gas. The NDIR sensor and the FID sensor respectively measure The output CNDIR and CFID are transmitted to the calculation unit;
S3:计算单元根据已知的CNDIR和CFID计算出目标值,即被测气体中NMHC的浓度CNMHC,CNMHC使用下列等式组计算:S3: The calculation unit calculates the target value based on the known CNDIR and CFID , that is, the concentration CNMHC of NMHC in the measured gas, and CNMHC is calculated using the following equation group:
……...
CNMHC=C1+C2+C3+……+Cx (式6)CNMHC = C1 +C2 +C3 +...+Cx (Formula 6)
其中,为被测气体中CH4的浓度,CNMHC为被测气体中NMHC的浓度,C1,C2,C3,……,Cx分别为被测气体中NMHC各成分的浓度;in, is the concentration of CH4 in the measured gas, CNMHC is the concentration of NMHC in the measured gas, C1 , C2 , C3 ,..., Cx are the concentrations of NMHC components in the measured gas;
其中,a1,a2,a3,……,ax分别为被测气体中NMHC各成分的碳原子数,b1,b2,b3,……,bx分别为NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下对被测气体中NMHC各成分的交叉灵敏度;Among them, a1 , a2 , a3 ,..., ax are the number of carbon atoms of each component of NMHC in the measured gas, b1 , b2 , b3 ,..., bx are the NDIR sensor in 7.66 Cross-sensitivity to NMHC components in the measured gas at μm wavelength;
其中,x为被测气体中NMHC的成分的数量。Wherein, x is the number of NMHC components in the measured gas.
使用NDIR传感器最常见的被测气体是CH4和CO2,如图4所示,在红外吸收光谱中,CH4中C-H键的振动频率是333KHz,中心波长是3.30μm,因此现有技术中使用NDIR传感器测CH4最常用的测量波长是3.30μm。The most common measured gases using NDIR sensors are CH4 and CO2 , as shown in Figure 4, in the infrared absorption spectrum, the vibration frequency of the CH bond in CH4 is 333KHz, and the center wavelength is 3.30μm, so in the prior art The most commonly used measurement wavelength for CH4 using NDIR sensors is 3.30 μm.
而本发明中NDIR传感器采用7.66μm的测量波长,一方面是利用CH4在红外7.66μm波长吸收强,NMHC在此波长吸收弱的特点,从而达到在准确测量CH4浓度的同时,对NMHC响应灵敏度小的目的。如图5所示,C7H8在红外3.30μm波长吸收强,而在红外7.66μm波长吸收弱。NDIR传感器在3.30μm波段和7.66μm波段CH4对各种NMHC的交叉灵敏度分别见表1和表2,可以看出,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波段CH4对各种NMHC的交叉灵敏度明显小于在3.30μm波段CH4对各种NMHC的交叉灵敏度。In the present invention, the NDIR sensor adopts a measurement wavelength of 7.66 μm. On the one hand, it utilizes the characteristics thatCH absorbs strongly at the infrared wavelength of 7.66 μm, and NMHC absorbs weakly at this wavelength, so as to accurately measure the concentrationof CH and respond to NMHC. The purpose of low sensitivity. As shown in Figure 5, C7 H8 absorbs strongly at the infrared wavelength of 3.30 μm, but weakly absorbs at the infrared wavelength of 7.66 μm. The cross-sensitivity of CH4 to various NMHCs in the 3.30 μm band and 7.66 μm band of the NDIR sensor are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. It can be seen that the cross-sensitivity of the NDIR sensor to various NMHCs in the 7.66 μm band CH4 is significantly smaller than that at 3.30 Cross-sensitivity ofCH4 to various NMHCs in the μm band.
表1.NDIR传感器在3.30μm波段CH4对各种NMHC的交叉灵敏度Table 1. Cross-sensitivity of NDIR sensorCH4 to various NMHCs in the 3.30 μm band
表2.NDIR传感器在7.66μm波段CH4对各种NMHC的交叉灵敏度Table 2. Cross-sensitivity of NDIR sensor CH4 to various NMHCs in the 7.66 μm band
另一方面,NDIR传感器的测量波长为7.66μm时,相较于测量波长为3.30μm时,对检测NMHC的误差更小,分析如下:On the other hand, when the measurement wavelength of the NDIR sensor is 7.66 μm, compared with the measurement wavelength of 3.30 μm, the error in detecting NMHC is smaller. The analysis is as follows:
假设被测气体由50ppmCH4和50ppmC7H8组成,已知FID传感器的检测误差是±1%rel,NDIR传感器的检测误差是±2.5%rel,计算用3.30μm波长和7.66μm波长的NDIR传感器所测得的NMHC浓度误差分别是多少:Assuming that the measured gas is composed of 50ppm CH4 and 50ppm C7 H8 , it is known that the detection error of the FID sensor is ±1% rel, the detection error of the NDIR sensor is ± 2.5% rel, and the calculation uses the NDIR sensor with a wavelength of 3.30μm and a wavelength of 7.66μm What are the errors of the measured NMHC concentration:
FID传感器测得:The FID sensor measures:
CFID(实际)=50+7×50=400ppmCFID (actual) =50+7×50=400ppm
CFID(min)=(50+7×50)×99%=396ppmCFID(min) =(50+7×50)×99%=396ppm
CFID(max)=(50+7×50)×101%=404ppmCFID(max) =(50+7×50)×101%=404ppm
由表1可知,NDIR传感器在3.30μm波段C7H8对CH4的交叉干扰为1.7,NDIR传感器在3.30μm波长下测得:It can be seen from Table 1 that the cross-interference between C7 H8 and CH4 in the 3.30 μm band of the NDIR sensor is 1.7, and the NDIR sensor measures at a wavelength of 3.30 μm:
CNDIR3.30(实际)=50+1.7×50=135ppmCNDIR3.30 (actual) =50+1.7×50=135ppm
CNDIR3.30(min)=(50+1.7×50)×97.5%=131.625ppmCNDIR3.30(min) =(50+1.7×50)×97.5%=131.625ppm
CNDIR3.30(max)=(50+1.7×50)×102.5%=138.375ppmCNDIR3.30(max) =(50+1.7×50)×102.5%=138.375ppm
由表2可知,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波段C7H8对CH4的交叉干扰为0.16,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测得:It can be seen from Table 2 that the cross-interference between C7 H8 and CH4 in the 7.66 μm band of the NDIR sensor is 0.16, and the NDIR sensor is measured at the wavelength of 7.66 μm:
CNDIR7.66(实际)=50+0.16×50=58ppmCNDIR7.66 (actual) =50+0.16×50=58ppm
CNDIR7.66(min)=(50+0.16×50)×97.5%=56.55ppmCNDIR7.66(min) =(50+0.16×50)×97.5%=56.55ppm
CNDIR7.66(max)=(50+0.16×50)×102.5%=59.45ppmCNDIR7.66(max) =(50+0.16×50)×102.5%=59.45ppm
①假设第一种极端情况,CFID(min)与CNDIR3.30(max)、CNDIR7.66(max)同时获得,那么NDIR传感器在3.30μm波长下测得NMHC的读出误差为:① Assuming the first extreme case, CFID (min) and CNDIR3.30 (max) and CNDIR7.66 (max) are obtained at the same time, then the readout error of NMHC measured by the NDIR sensor at a wavelength of 3.30 μm is:
分别将CFID(实际)、CNDIR3.30(实际)和CFID(min)、CNDIR3.30(max)代入步骤S3的计算公式得:Substituting CFID (actual) , CNDIR3.30 (actual) and CFID (min) , CNDIR3.30 (max) into the calculation formula of step S3 respectively:
解上述方程组得测得的/>由于被测气体中只含有一种NMHC成分即C7H8,所以CNMHC(实际)=50ppm,CNMHC=48.608ppm,读出误差=(48.608-50)/50=-2.8%rel;Solving the above equations we get Measured /> Since the measured gas contains only one NMHC component, that is, C7 H8 , CNMHC (actual) = 50ppm, CNMHC = 48.608ppm, readout error = (48.608-50)/50 = -2.8% rel;
NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测得NMHC的读出误差为:The readout error of the NMHC measured by the NDIR sensor at a wavelength of 7.66 μm is:
分别将CFID(实际)、CNDIR7.66(实际)和CFID(min)、CNDIR7.66(max)代入步骤S3的计算公式得:Substituting CFID (actual) , CNDIR7.66 (actual) and CFID (min) , CNDIR7.66 (max) into the calculation formula of step S3 respectively:
解上述方程组得测得的/>CNMHC(实际)=50ppm,CNMHC=49.203ppm,读出误差=(49.203-50)/50=-1.6%rel。Solving the above equations we get Measured /> CNMHC (actual) = 50 ppm, CNMHC = 49.203 ppm, readout error = (49.203-50)/50 = -1.6% rel.
计算得出,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测NMHC的误差更小。It is calculated that the NDIR sensor has a smaller error in measuring NMHC at a wavelength of 7.66 μm.
②假设第二种极端情况,CFID(max)与CNDIR3.30(min)、CNDIR7.66(min)同时获得,那么NDIR传感器在3.30μm波长下测得NMHC的读出误差为:② Assuming the second extreme case, CFID(max) and CNDIR3.30(min) and CNDIR7.66(min) are obtained at the same time, then the readout error of NMHC measured by the NDIR sensor at a wavelength of 3.30μm is:
分别将CFID(实际)、CNDIR3.30(实际)和CFID(max)、CNDIR3.30(min)代入步骤S3的计算公式得:Substituting CFID (actual) , CNDIR3.30 (actual) and CFID (max) , CNDIR3.30 (min) into the calculation formula of step S3 respectively:
解上述方程组得测得的/>CNMHC(实际)=50ppm,CNMHC=51.392ppm,读出误差=(51.392-50)/50=2.8%rel;Solving the above equations we get Measured /> CNMHC (actual) = 50 ppm, CNMHC = 51.392 ppm, readout error = (51.392-50)/50 = 2.8% rel;
NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测得NMHC的读出误差为:The readout error of the NMHC measured by the NDIR sensor at a wavelength of 7.66 μm is:
分别将CFID(实际)、CNDIR7.66(实际)和CFID(max)、CNDIR7.66(min)代入步骤S3的计算公式得:Substituting CFID (actual) , CNDIR7.66 (actual) and CFID (max) , CNDIR7.66 (min) into the calculation formula of step S3 respectively:
解上述方程组得测得的/>CNMHC(实际)=50ppm,CNMHC=50.797ppm,读出误差=(50.797-50)/50=1.6%rel。Solving the above equations we get Measured /> CNMHC (actual) = 50 ppm, CNMHC = 50.797 ppm, readout error = (50.797-50)/50 = 1.6% rel.
计算得出,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测NMHC的误差更小。It is calculated that the NDIR sensor has a smaller error in measuring NMHC at a wavelength of 7.66 μm.
因此,NDIR传感器在7.66μm波长下测NMHC的效果更好。Therefore, the NDIR sensor is better at measuring NMHC at a wavelength of 7.66 μm.
本发明的实质在于,采用了新的NDIR传感器和FID传感器的组合,实现了便携式检测NMHC和实时监测NMHC的目的,使用7.66μm CH4的红外吸收波长替代3.30μm CH4的红外吸收波长,可以大量减少HC类物质的交叉干扰,对绝大部分NMHC的交叉响应下降了一个数量级。The essence of the present invention is that a combination of a new NDIR sensor and an FID sensor is adopted to realize the purpose of portable detection of NMHC and real-time monitoring of NMHC, and the infrared absorption wavelength of 7.66 μm CH4 is used to replace the infrared absorption wavelength of 3.30 μm CH4 , which can The cross-interference of HC substances is greatly reduced, and the cross-response to most NMHCs is reduced by an order of magnitude.
综上,相较于现有技术,本发明的气体检测装置及气体检测方法具有以下优势:In summary, compared with the prior art, the gas detection device and gas detection method of the present invention have the following advantages:
(1)采用NDIR传感器和FID传感器的组合使用,相对于现有的GC-FID检测器,具有体积小、重量轻、结构简单、维护便捷、后期使用成本低,实现了仪器的轻量化,可便携检测NMHC含量;(1) The combination of NDIR sensor and FID sensor is used. Compared with the existing GC-FID detector, it has the advantages of small size, light weight, simple structure, convenient maintenance, and low post-use cost, which realizes the light weight of the instrument and can Portable detection of NMHC content;
(2)NDIR传感器和FID传感器均可每秒钟输出被测气体的NMHC含量值,具有较强的实时性,可进行环保在线监测或在生产过程中控制工艺数据等,而GC装置无法实现实时性;(2) Both the NDIR sensor and the FID sensor can output the NMHC content value of the measured gas every second, which has strong real-time performance, and can carry out environmental protection online monitoring or control process data during the production process, while the GC device cannot realize real-time sex;
(3)NDIR传感器对苯系物、芳香烃的交叉灵敏度相对稳定,且遇到未知气体不会造成很大误差,在实际应用中适用于绝大部分环保检测场合;(3) The cross-sensitivity of NDIR sensors to benzene series and aromatic hydrocarbons is relatively stable, and encountering unknown gases will not cause a large error, which is suitable for most environmental protection detection occasions in practical applications;
(4)利用了甲烷在红外7.66μm波长吸收强,NMHC在此波长吸收弱的特点,从而达到准确测量甲烷浓度的同时,对NMHC响应灵敏度小的目的;(4) Utilize the characteristic that methane absorbs strongly at the wavelength of infrared 7.66 μm, and NMHC absorbs weakly at this wavelength, so as to achieve the purpose of accurately measuring the concentration of methane and at the same time, the response sensitivity to NMHC is small;
(5)克服了多种NMHC的交叉干扰,可在气体检测装置中串联多个测量波长不同的NDIR传感器,测出除甲烷之外NMHC的浓度,且交叉干扰可相互扣除。(5) Overcoming the cross-interference of various NMHCs, multiple NDIR sensors with different measurement wavelengths can be connected in series in the gas detection device to measure the concentration of NMHCs other than methane, and the cross-interferences can be deducted from each other.
以上实施方式仅用于说明本发明而并非限制本发明所描述的技术方案,对本说明书的理解应该以所属技术领域的技术人员为基础,尽管本说明书参照上述的实施例对本发明已进行了详细的说明,但是,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解,所属技术领域的技术人员仍然可以对本发明进行修改或者等同替换,而一切不脱离本发明的精神和范围的技术方案及其改进,均应涵盖在本发明的权利要求范围内。The above embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention rather than limit the technical solutions described in the present invention. The understanding of this description should be based on those skilled in the art, although this description has described the present invention in detail with reference to the above-mentioned embodiments. However, those skilled in the art should understand that those skilled in the art can still modify the present invention or replace it equivalently, and all technical solutions and improvements that do not depart from the spirit and scope of the present invention should be included in the within the scope of the claims of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111578276.4ACN116337797A (en) | 2021-12-22 | 2021-12-22 | Gas detection device and gas detection method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111578276.4ACN116337797A (en) | 2021-12-22 | 2021-12-22 | Gas detection device and gas detection method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116337797Atrue CN116337797A (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=86879212
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111578276.4APendingCN116337797A (en) | 2021-12-22 | 2021-12-22 | Gas detection device and gas detection method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116337797A (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060236752A1 (en)* | 2005-03-29 | 2006-10-26 | Horiba, Ltd. | Exhaust gas component analyzer |
| CN200947084Y (en)* | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-12 | 武汉四方光电科技有限公司 | Electromodulation non-dispersed infrared gaseous sensor |
| CN102768168A (en)* | 2007-09-26 | 2012-11-07 | 气体产品与化学公司 | Method for determining carbon content of a hydrocarbon-containing mixture |
| CN103743694A (en)* | 2013-12-31 | 2014-04-23 | 杭州泰林生物技术设备有限公司 | Non-dispersed infrared gas detector |
| CN108254469A (en)* | 2018-03-28 | 2018-07-06 | 昆山金宏二氧化碳有限公司 | Detect non-methane total hydrocarbons and the device and method of subitem hydrocarbon content in carbon dioxide |
| CN111879844A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-11-03 | 聚光科技(杭州)股份有限公司 | Method for detecting multiple components in gaseous pollutants |
| CN111929269A (en)* | 2020-09-23 | 2020-11-13 | 上海翼捷工业安全设备股份有限公司 | Three-channel infrared methane detector resistant to water vapor interference |
| CN112834562A (en)* | 2021-01-04 | 2021-05-25 | 吉林大学 | Device and method for detecting helium concentration in thermally conductive mixed gas |
| CN113063771A (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2021-07-02 | 广东省环境科学研究院 | Method for calculating concentration of volatile organic compounds by using concentration of non-methane total hydrocarbons in waste gas |
- 2021
- 2021-12-22CNCN202111578276.4Apatent/CN116337797A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060236752A1 (en)* | 2005-03-29 | 2006-10-26 | Horiba, Ltd. | Exhaust gas component analyzer |
| CN200947084Y (en)* | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-12 | 武汉四方光电科技有限公司 | Electromodulation non-dispersed infrared gaseous sensor |
| CN102768168A (en)* | 2007-09-26 | 2012-11-07 | 气体产品与化学公司 | Method for determining carbon content of a hydrocarbon-containing mixture |
| CN103743694A (en)* | 2013-12-31 | 2014-04-23 | 杭州泰林生物技术设备有限公司 | Non-dispersed infrared gas detector |
| CN108254469A (en)* | 2018-03-28 | 2018-07-06 | 昆山金宏二氧化碳有限公司 | Detect non-methane total hydrocarbons and the device and method of subitem hydrocarbon content in carbon dioxide |
| CN111879844A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-11-03 | 聚光科技(杭州)股份有限公司 | Method for detecting multiple components in gaseous pollutants |
| CN111929269A (en)* | 2020-09-23 | 2020-11-13 | 上海翼捷工业安全设备股份有限公司 | Three-channel infrared methane detector resistant to water vapor interference |
| CN112834562A (en)* | 2021-01-04 | 2021-05-25 | 吉林大学 | Device and method for detecting helium concentration in thermally conductive mixed gas |
| CN113063771A (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2021-07-02 | 广东省环境科学研究院 | Method for calculating concentration of volatile organic compounds by using concentration of non-methane total hydrocarbons in waste gas |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10241096B2 (en) | Non-methane total hydrocarbons analysis apparatus and method for the same | |
| US10295517B2 (en) | Heated graphite scrubber to reduce interferences in ozone monitors | |
| CN103336070B (en) | The pick-up unit of sulfur-bearing failure gas component and method in a kind of quantitative detection sulfur hexafluoride electrical equipment | |
| WO2014055947A1 (en) | Interference compensated photoionization detector | |
| CN102788764A (en) | Ultraviolet analyzer and detection method for low concentration smoke | |
| CN108489924A (en) | A kind of sensing probe and non-dispersive infrared gas sensor detecting system | |
| CN106990065B (en) | Non-spectroscopic infrared gas sensor for multi-region and multi-gas measurement | |
| CN102435581A (en) | A Calculation Method of Calorific Value of Natural Gas Based on Spectral Analysis of Natural Gas Components | |
| CN109752344B (en) | Portable non-methane total hydrocarbon concentration detector and detection method | |
| CN101806727A (en) | Method and device for measuring sulfur content in coal by ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy | |
| CN115406839A (en) | Online monitoring device for dissolved gas in transformer oil | |
| CN205067439U (en) | VOCs concentration on -line monitoring device | |
| US20090302230A1 (en) | Use of a Broad Band UV Light Source for Reducing The Mercury Interference in Ozone Measurements | |
| CN201607402U (en) | Coal Sulfur Content Ultraviolet Absorption Spectrum Measuring Device | |
| Xu et al. | Design of nitrogen oxide detection system based on non-dispersive infrared technology | |
| Wang et al. | Current status of detection technologies for indoor hazardous air pollutants and particulate matter | |
| CN115901660A (en) | A Quantitative Analysis Method, System and Application of Semi-volatile Components in Mixed Gas Based on Infrared Spectroscopy | |
| John et al. | A broadband cavity-enhanced spectrometer for atmospheric aerosol light extinction measurements | |
| CN207937352U (en) | A sensitive probe and non-spectral infrared gas sensor detection system | |
| CN101308088A (en) | A system and method for measuring volatile gases of chemical fertilizers | |
| CN204177731U (en) | A kind of portable infrared flue gas analyzer of anti-moisture interference | |
| CN101393121B (en) | Gas cell of methane gas concentration sensor based on infrared absorption principle | |
| CN116337797A (en) | Gas detection device and gas detection method | |
| CN205538815U (en) | A full-flow motorcycle exhaust gas measurement system | |
| CN203405450U (en) | Detection device for quantitatively detecting sulfur-containing fault gas components in sulphur hexafluoride electrical equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |