CN116271265A - A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116271265A CN116271265ACN202111569575.1ACN202111569575ACN116271265ACN 116271265 ACN116271265 ACN 116271265ACN 202111569575 ACN202111569575 ACN 202111569575ACN 116271265 ACN116271265 ACN 116271265A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- hydrogel
- tissue adhesion
- solution
- preventing postoperative
- add
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/14—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- A61L31/145—Hydrogels or hydrocolloids
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/02—Inorganic materials
- A61L31/028—Other inorganic materials not covered by A61L31/022 - A61L31/026
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/04—Macromolecular materials
- A61L31/042—Polysaccharides
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/04—Macromolecular materials
- A61L31/06—Macromolecular materials obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61L—METHODS OR APPARATUS FOR STERILISING MATERIALS OR OBJECTS IN GENERAL; DISINFECTION, STERILISATION OR DEODORISATION OF AIR; CHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES; MATERIALS FOR BANDAGES, DRESSINGS, ABSORBENT PADS OR SURGICAL ARTICLES
- A61L31/00—Materials for other surgical articles, e.g. stents, stent-grafts, shunts, surgical drapes, guide wires, materials for adhesion prevention, occluding devices, surgical gloves, tissue fixation devices
- A61L31/14—Materials characterised by their function or physical properties, e.g. injectable or lubricating compositions, shape-memory materials, surface modified materials
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/30—Against vector-borne diseases, e.g. mosquito-borne, fly-borne, tick-borne or waterborne diseases whose impact is exacerbated by climate change
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于高分子医用生物材料技术领域,具体涉及一种具有预防术后组织粘连的温敏型复合水凝胶及其制备方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer medical biomaterials, and in particular relates to a temperature-sensitive composite hydrogel capable of preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and a preparation method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
外科手术是一种使用频率较高的治疗疾病的方式之一。但是手术也会造成手术部位血管组织受损。在术后恢复过程中,手术部位的血管内皮细胞、成纤维细胞和肌成纤维细胞在血液中的细胞生长因的促进下,在进行组织胶原修复的同时,生长出纤维带。纤维带会将手术部位与其接触的腹部器官与组织连在一起,而形成腹部组织粘连。据统计,术后腹部组织粘连发生率超过90%。腹部组织粘连会引发如腹痛、盆腔疼痛、不孕和肠梗阻等严重的术后并发症。Surgery is one of the most frequently used methods of treating diseases. However, surgery can also cause damage to the vascular tissue at the surgical site. During postoperative recovery, vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts at the surgical site grow fibrous bands while undergoing tissue collagen repair under the promotion of cell growth factors in the blood. Abdominal tissue adhesions are formed by fibrous bands that bind the surgical site to the abdominal organs and tissues in contact with it. According to statistics, the incidence of postoperative abdominal tissue adhesions exceeds 90%. Abdominal tissue adhesions can lead to serious postoperative complications such as abdominal pain, pelvic pain, infertility, and ileus.
目前,已经开发出了多种可用于预防术后组织粘连的医疗产品。主要包括药物治疗、物理屏障和药物与物理屏障相结合的方式。常用的药物有布洛芬、阿司匹林等消炎药和肝素、二甲基亚砜等抗凝血药物。常用的物理屏障有壳聚糖、聚乳酸等水凝胶和聚己内酯、聚乙二醇等薄膜材料。然而,已开发的预防术后组织粘连的材料,治疗效果较为有限,且存在一些副作用。所以缺乏具有广泛认可度的产品。Currently, a variety of medical products that can be used to prevent postoperative tissue adhesions have been developed. It mainly includes drug treatment, physical barrier and the combination of drug and physical barrier. Commonly used drugs include anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and aspirin, and anticoagulant drugs such as heparin and dimethyl sulfoxide. Commonly used physical barriers include hydrogels such as chitosan and polylactic acid, and film materials such as polycaprolactone and polyethylene glycol. However, the materials that have been developed to prevent postoperative tissue adhesions have limited therapeutic effects and some side effects. So there is a lack of products with wide acceptance.
从术后组织粘连的机理可知,预防粘连的屏障材料要满足以下要求:1)预防粘连的材料用能够在一段时间内稳定的固定在手术部位;2)预防粘连的材料具有较好的生物降解性能。因此,通过控制防粘连屏障的降解行为和生物特性是预防术后组织粘连的有效策略。From the mechanism of postoperative tissue adhesion, the barrier material for preventing adhesion should meet the following requirements: 1) The material for preventing adhesion can be stably fixed on the surgical site for a period of time; 2) The material for preventing adhesion has better biodegradability performance. Therefore, controlling the degradation behavior and biological properties of the anti-adhesion barrier is an effective strategy to prevent postoperative tissue adhesions.
发明内容Contents of the invention
针对上述问题,本发明的目的在于提供一种无毒可降解的温敏型水凝胶及其制备方法,该方法制备的水凝胶在术后喷涂于伤口部位,可有效预防术后组织粘连。同时,该水凝胶细胞相容性好,制备工艺简单,成本低廉。In view of the above problems, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a non-toxic and degradable temperature-sensitive hydrogel and its preparation method. The hydrogel prepared by this method is sprayed on the wound site after operation, which can effectively prevent postoperative tissue adhesion . At the same time, the hydrogel has good cytocompatibility, simple preparation process and low cost.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明采用如下技术方案。In order to solve the above technical problems, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions.
具有预防术后组织粘连效果的水凝胶,其特征在于,所述水凝胶包含肝素钠、泊洛沙姆、羧甲基壳聚糖和氯化钙 。其制备方法,包含以下步骤:The hydrogel having the effect of preventing postoperative tissue adhesion is characterized in that the hydrogel contains heparin sodium, poloxamer, carboxymethyl chitosan and calcium chloride. Its preparation method comprises the following steps:
1)将肝素钠溶解于纯水中,制成肝素钠水溶液; 1) Dissolve heparin sodium in pure water to make heparin sodium aqueous solution;
2)向步骤1)制得的溶液中加入羧甲基壳聚糖,制备成溶液; 2) adding carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in step 1) to prepare a solution;
3)向步骤2)制得的溶液中加入泊洛沙姆; 3) Adding poloxamer to the solution prepared in step 2);
4)向步骤3)制得的溶液中加入氯化钙,制得水凝胶。 4) Add calcium chloride to the solution prepared in step 3) to prepare a hydrogel.
所述步骤1)中肝素钠溶液的浓度为30000-200000 IU/L;The concentration of heparin sodium solution in step 1) is 30000-200000 IU/L;
所述步骤2)中羧甲基壳聚糖的浓度为2.5%~3.5%;The concentration of carboxymethyl chitosan in the step 2) is 2.5% to 3.5%;
所述步骤2)中羧甲基壳聚糖的溶解温度为2-8℃;The dissolving temperature of carboxymethyl chitosan in the step 2) is 2-8°C;
所述步骤2)中羧甲基壳聚糖的溶解时间为15-48h;The dissolving time of carboxymethyl chitosan in the step 2) is 15-48h;
所述步骤2)中羧甲基壳聚糖的脱乙酰度≥90%,取代度≥80%;The degree of deacetylation of carboxymethyl chitosan in the step 2) is ≥ 90%, and the degree of substitution is ≥ 80%;
所述步骤3)中泊洛沙姆的浓度为22%~25%;The concentration of poloxamer in step 3) is 22% to 25%;
所述步骤3)中泊洛沙姆平均分子量为8000~18000;The average molecular weight of the poloxamer in the step 3) is 8000-18000;
所述步骤3)中泊洛沙姆的溶解温度为2~8℃;The dissolution temperature of the poloxamer in the step 3) is 2-8°C;
所述步骤3)中泊洛沙姆的溶解时间为70~90h;The dissolution time of the poloxamer in the step 3) is 70 to 90 hours;
所述步骤4)中氯化钙的添加量为0.09~0.12%。The amount of calcium chloride added in the step 4) is 0.09-0.12%.
本发明制备的预防术后组织粘连的温敏型水凝胶及其制备方法与其它相比,优点是:Compared with others, the temperature-sensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion prepared by the present invention and its preparation method have the following advantages:
1)在水凝胶成胶机理方面,选用了热致变固化机理的基础上,引入离子交联机理,使制备的水凝胶在拥有优异的温敏特性的同时拥有较好的机械强度,能满足在伤口部位维持一定时间的要求,有效隔绝腹部组织;1) In terms of hydrogel gelation mechanism, based on the thermotropic curing mechanism, the ionic cross-linking mechanism is introduced, so that the prepared hydrogel has good mechanical strength while having excellent temperature-sensitive properties. It can meet the requirements of maintaining a certain period of time at the wound site and effectively isolate the abdominal tissue;
2)使用过程中,不仅隔绝组织或器官与手术部位接触,同时能吸收伤口部位的多余的组织渗出液;2) During use, it not only isolates tissues or organs from contact with the surgical site, but also absorbs excess tissue exudate from the wound site;
3)所述水凝胶制备方法简单,制备工艺稳定可控,易于规模化生产。3) The preparation method of the hydrogel is simple, the preparation process is stable and controllable, and it is easy for large-scale production.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是预防术后组织粘连温敏型水凝胶在温度变化下的溶胶—凝胶相转变图。Figure 1 is a sol-gel phase transition diagram of the temperature-sensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion under temperature changes.
图2是预防术后组织粘连温敏型水凝胶材料的体外水解性能图。Fig. 2 is a diagram of the in vitro hydrolysis performance of the temperature-sensitive hydrogel material for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion.
图3 是预防术后组织粘连温敏型水凝胶大鼠腹部粘连实验组织粘连评价结果图。Fig. 3 is a graph showing the tissue adhesion evaluation results of the abdominal adhesion experiment of the temperature-sensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion in rats.
图4是预防术后组织粘连温敏型水凝胶大鼠腹部粘连实验术后14天内老鼠体重变化图。Fig. 4 is a graph showing the changes in body weight of rats within 14 days after the abdominal adhesion experiment of the temperature-sensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion in rats.
图5是预防术后组织粘连温敏型水凝胶大鼠腹部粘连细胞毒性实验图。Fig. 5 is a graph showing the cytotoxicity experiment of the temperature-sensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesions in rat abdominal adhesions.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
一种预防术后组织粘连的水凝胶的制备方法包括以下步骤:A preparation method of hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion comprises the following steps:
1)将肝素钠溶解于纯水中,制成肝素钠水溶液;1) Dissolve heparin sodium in pure water to make heparin sodium aqueous solution;
2)向步骤1)制得的溶液中加入羧甲基壳聚糖,制备成溶液;2) adding carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in step 1) to prepare a solution;
3)向步骤2)制得的溶液中加入泊洛沙姆;3) Adding poloxamer to the solution prepared in step 2);
4)向步骤3)制得的溶液中加入氯化钙,制得水凝胶。4) Add calcium chloride to the solution prepared in step 3) to prepare a hydrogel.
下面通过结合具体实施方式,对本发明内容作进一步的详细描述。但本发明的范围并不因此局限于下述实施例。实例中采用的试剂和仪器及实验条件可以根据实际情况做进一步调整,未注明实施条件为常规实验条件,未注明生产厂商的试剂和仪器,均为可以通过市售购买的常规产品。The content of the present invention will be described in further detail below in combination with specific embodiments. However, the scope of the present invention is not therefore limited to the following examples. The reagents, instruments and experimental conditions used in the examples can be further adjusted according to the actual situation. The implementation conditions not indicated are conventional experimental conditions, and the reagents and instruments not indicated by the manufacturer are all conventional products that can be purchased commercially.
实施例中主要试剂、仪器及实验动物Main reagent, instrument and experimental animal in the embodiment
泊洛沙姆(Mn~14600,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司);羧甲基壳聚糖(CAS:83512-85-0,成都麦克林生物科技有限公司);肝素钠;氯化钙;SD大鼠(成都达硕实验动物有限公司)。Poloxamer (Mn~14600, Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.); carboxymethyl chitosan (CAS: 83512-85-0, Chengdu McLean Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); heparin sodium; calcium chloride; SD rats (Chengdu Dashuo Experimental Animal Co., Ltd.).
实施例1Example 1
1)将0.067g肝素钠溶解到79.96g纯水中,得到肝素钠溶液; 1) Dissolve 0.067g of heparin sodium into 79.96g of pure water to obtain heparin sodium solution;
2)将8.219g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到(1)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀60h; 2) Add 8.219g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in (1), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 60 hours;
3)将65.76g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀96h;3) Add 65.76g of poloxamer to (2), and place in a refrigerator at 4°C to swell for 96 hours;
4)将0.20g 氯化钙加入到9.80g纯水中,制备得到浓度为2%的氯化钙溶液;4) Add 0.20g of calcium chloride to 9.80g of pure water to prepare a 2% calcium chloride solution;
5)将步骤(3)和步骤(4)的溶液进行混合,制得水凝胶。5) Mix the solutions in step (3) and step (4) to prepare a hydrogel.
实施例2Example 2
1)将0.067g肝素钠溶解到89.96g纯水中,得到肝素钠溶液;1) Dissolve 0.067g of heparin sodium into 89.96g of pure water to obtain heparin sodium solution;
2)将8.219g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到(1)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀60h;2) Add 8.219g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in (1), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 60 hours;
3)将65.76g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀96h,即制得水凝胶。3) 65.76g of poloxamer was added to (2), and placed in a refrigerator at 4°C for swelling for 96 hours to obtain a hydrogel.
实施例3Example 3
1)将0.016g肝素钠溶解到28g纯水中,制得肝素钠溶液; 1) Dissolve 0.016g of heparin sodium into 28g of pure water to prepare heparin sodium solution;
2)将1.217g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到(1)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀48h; 2) Add 1.217g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in (1), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 48 hours;
3)将8.825g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀80h; 3) Add 8.825g of poloxamer to (2), and place in a refrigerator at 4°C to swell for 80 hours;
4)将0.2g 氯化钙加入到9.8g纯水中,制备得到浓度为2%的氯化钙溶液; 4) Add 0.2g of calcium chloride to 9.8g of pure water to prepare a 2% calcium chloride solution;
5)将步骤(3)和步骤(4)的2ml溶液进行混合,制得水凝胶。5) Mix 2ml of the solution from step (3) and step (4) to prepare a hydrogel.
实施例4Example 4
1)将0.016g肝素钠溶解到28g纯水中,制得肝素钠溶液;1) Dissolve 0.016g of heparin sodium into 28g of pure water to prepare heparin sodium solution;
2)将0.2g氯化钙加入到9.8g纯水中,制备得到浓度为2%的氯化钙溶液;2) Add 0.2g of calcium chloride to 9.8g of pure water to prepare a calcium chloride solution with a concentration of 2%;
3)将步骤(1)和2ml步骤(2)的溶液进行混合;3) Mix the solution of step (1) and 2ml of step (2);
4)将1.217g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到3)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀48h;4) Add 1.217g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in 3), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 48 hours;
5)将8.825g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀80h,制得水凝胶。5) Add 8.825g of poloxamer to (2), place in a refrigerator at 4°C to swell for 80 hours, and obtain a hydrogel.
实施例5Example 5
1)将0.019g肝素钠溶解到27.65g纯水中,制得肝素钠溶液;1) Dissolve 0.019g of heparin sodium into 27.65g of pure water to prepare heparin sodium solution;
2)将0.825g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到1)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀48h;2) Add 0.825g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in 1), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 48 hours;
3)将9.626g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀80h;3) Add 9.626g of poloxamer to (2), and place in a refrigerator at 4°C to swell for 80 hours;
4)将0.2g氯化钙加入到9.8g纯水中,制备得到浓度为2%的氯化钙溶液;4) Add 0.2g of calcium chloride to 9.8g of pure water to prepare a 2% calcium chloride solution;
5)将步骤(3)和2ml步骤(4)的溶液进行混合,制得水凝胶。5) Mix step (3) and 2ml of the solution in step (4) to prepare a hydrogel.
实施例6Example 6
1)将0.027g肝素钠溶解到29.2g纯水中,得到肝素钠溶液;1) Dissolve 0.027g of heparin sodium into 29.2g of pure water to obtain heparin sodium solution;
2)将0.844g羧甲基壳聚糖加入到(1)中制备的溶液中,置于4℃冰箱中,溶胀60h;2) Add 0.844g carboxymethyl chitosan to the solution prepared in (1), place in a refrigerator at 4°C, and swell for 60 hours;
3)将8.345g泊洛沙姆加入到(2)中,置于4℃的冰箱中溶胀96h;3) Add 8.345g of poloxamer to (2), and place in a refrigerator at 4°C to swell for 96 hours;
4)将0.20g 氯化钙加入到9.80g纯水中,制备得到浓度为2%的氯化钙溶液;4) Add 0.20g of calcium chloride to 9.80g of pure water to prepare a 2% calcium chloride solution;
将步骤(3)和2ml步骤(4)的溶液进行混合,制得水凝胶。Mix the solution of step (3) and 2ml of step (4) to prepare a hydrogel.
实施例7Example 7
体外降解实验In vitro degradation test
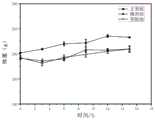
两个分别于50ml锥形瓶中装入15g实施例1与实施例2制备的水凝胶,将其置于37℃环境中20min,水凝胶完成溶胶-凝胶转变,加入20ml PBS溶液(pH7.4),温度(37±0.5)℃,震荡转速100r/min,于2,4,7,24,36,48,72,96,120,144,168,192,216,240,264,288,312,36,360h依次倒出培养基,称量水凝胶重量,补充等温度等体积的同批PBS。根据降解公式Wt=1-(Mt/M0)(%),绘制体外降解曲线。结果见图2。Two 50ml Erlenmeyer flasks were loaded with 15g of the hydrogels prepared in Example 1 and Example 2 respectively, and placed in a 37°C environment for 20min, the hydrogel completed the sol-gel transition, and 20ml of PBS solution was added ( pH 7.4), temperature (37±0.5) ℃, shaking speed 100r/min, pour out the medium at 2, 4, 7, 24, 36, 48, 72, 96, 120, 144, 168, 192, 216, 240, 264, 288, 312, 36, 360h, and weigh the weight of the hydrogel , supplemented with the same batch of PBS at the same temperature and volume. According to the degradation formula Wt =1-(Mt /M0 )(%), the in vitro degradation curve was drawn. The results are shown in Figure 2.
根据图2可知实施例1制备的水凝胶体外降解效果明显优于实例2制备的水凝胶。Cacl2的加入能有效的增强水凝胶的强度。实施例1制备的水凝胶在水凝胶体外降解时间能满足对该产品的要求。According to Figure 2, it can be seen that the in vitro degradation effect of the hydrogel prepared in Example 1 is significantly better than that of the hydrogel prepared in Example 2. The addition of Cacl2 can effectively enhance the strength of the hydrogel. The degradation time of the hydrogel prepared in Example 1 in vitro can meet the requirements of the product.
实施例8Example 8
细胞毒性实验Cytotoxicity test
将NIH/3T3细胞按3*105的密度接种于96孔板,37℃,5%CO2环境培养24h后,去除原有培养基,分别添加含有0mg/ml、0.1mg/ml、1mg/ml、10mg/ml和100mg/ml的实施例1的水凝胶的培养基培养24h。采用cck-8试剂,表征水凝胶的细胞毒性。其结果见图5。NIH/3T3 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 3*105 , cultured at 37°C in a 5% CO2 environment for 24 hours, the original medium was removed, and 0 mg/ml, 0.1 mg/ml, 1 mg/ml ml, 10 mg/ml and 100 mg/ml of the hydrogel of Example 1 were cultured for 24 hours. The cytotoxicity of the hydrogel was characterized using cck-8 reagent. The results are shown in Figure 5.
1)实验动物分组1) Grouping of experimental animals
大鼠腹部组织粘连模型:将12只雌性大鼠随机分为三组:对照组(n=2)、模型组(n=5)及实验组(n=5)。Rat abdominal tissue adhesion model: 12 female rats were randomly divided into three groups: control group (n=2), model group (n=5) and experimental group (n=5).
2)大鼠腹部组织粘连2) Abdominal tissue adhesion in rats
6-8周的SD大鼠术前培养三天,对照组不做任何处理,模型组与实验组,术前腹部注射0.7ml的10%多聚甲醛溶液麻醉,麻醉好的大鼠皮下注射0.5ml的17mg/ml的氨苄青霉素,用于预防术后感染。之后将老鼠固定于手术板上,剔除腹部毛发,用碘伏消毒皮肤表面,沿腹白线做3cm切口,取出盲肠,用无菌纱布擦拭盲肠表面,直直出现3cm2的面积脱色,并出现点状出血,用手术刀反复轻刮腹壁组织,实验组将适量实施例1制备水凝胶涂覆在创面(模型组涂覆等量生理盐水),然后将盲肠放回腹腔,采用2-0与3-0的可吸收缝合线缝合腹腔组织和皮肤组织。术后间隔两天称量老鼠体重,用于评价水凝胶生物相容性。手术后第14天,对所有老鼠进行安乐死,开腹评价腹部组织粘连情况。The SD rats of 6-8 weeks were cultured for three days before operation. The control group did not receive any treatment. The model group and the experimental group were anesthetized by injecting 0.7ml of 10% paraformaldehyde solution into the abdomen before operation. The anesthetized rats were subcutaneously injected with 0.5 17mg/ml of ampicillin in ml is used to prevent postoperative infection. Then the mouse was fixed on the operating board, the abdominal hair was removed, the skin surface was disinfectedwith iodophor, a 3 cm incision was made along the alba linea, the cecum was taken out, and the surface of the cecum was wiped with sterile gauze. For spotting bleeding, use a scalpel to gently scrape the abdominal wall tissue repeatedly. In the experimental group, apply an appropriate amount of hydrogel prepared in Example 1 on the wound surface (the model group is coated with the same amount of normal saline), and then put the cecum back into the abdominal cavity, and use 2-0 Suture the abdominal tissue and skin tissue with 3-0 absorbable sutures. The body weight of the mice was weighed two days after the operation to evaluate the biocompatibility of the hydrogel. On the 14th day after the operation, all mice were euthanized, and the abdominal tissue adhesion was evaluated by laparotomy.
3)动物实验结果3) Results of animal experiments
腹部组织粘连评价标准如下:The evaluation criteria for abdominal tissue adhesion are as follows:
1) 组织未发生粘连记为0;1) No tissue adhesion was recorded as 0;
2)组织粘连面积在0-100mm2 记为1;2) Tissue adhesion area is recorded as1 in the range of 0-100mm2;
3)组织粘连面积在100-300mm2记为2;3) The tissue adhesion area is 100-300mm2 recorded as 2;
4)组织粘连在300-500mm2 记为3。4) Tissue adhesion at 300-500mm2 is recorded as 3.
从图3可知实验组的老鼠腹部组织粘连程度,明显优于模型组,且60%的实验组老鼠未发生粘连。模型组中40%的老鼠产生严重的粘连。说明该温敏型水凝胶可以有效预防术后组织粘连。It can be seen from Figure 3 that the degree of adhesion in the abdominal tissue of the rats in the experimental group was significantly better than that in the model group, and 60% of the rats in the experimental group had no adhesion. 40% of the mice in the model group developed severe adhesions. It shows that the temperature-sensitive hydrogel can effectively prevent postoperative tissue adhesion.
从图4可知,进行手术后的老鼠体重明显低于正常组的老鼠,且实验组的重在中后期优于模型组。从图5可知在0.1-100mg/ml的浓度范围内,细胞活性均高于90%,所以说明该水凝胶,的细胞毒性较低。因此该水凝胶具有较高的生物相容性。It can be seen from Figure 4 that the weight of the mice after surgery was significantly lower than that of the normal group, and the weight of the experimental group was better than that of the model group in the middle and late stages. It can be seen from Figure 5 that within the concentration range of 0.1-100mg/ml, the cell viability is higher than 90%, so it shows that the cytotoxicity of the hydrogel is low. Therefore, the hydrogel has high biocompatibility.
上述实例只为说明本发明的技术构造及特点,其目的在于让熟悉此项技术的人员能够了解本发明的内容并据以实施,并不能以此限制本发明的保护范围。凡根据本发明精神实质所做的等效变换或修饰,都应涵盖在本发明的保护范围之内。The above examples are only to illustrate the technical structure and characteristics of the present invention, and its purpose is to allow those familiar with this technology to understand the content of the present invention and implement it accordingly, and cannot limit the protection scope of the present invention. All equivalent changes or modifications made according to the spirit of the present invention shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111569575.1ACN116271265A (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2021-12-21 | A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111569575.1ACN116271265A (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2021-12-21 | A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116271265Atrue CN116271265A (en) | 2023-06-23 |
Family
ID=86776603
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111569575.1APendingCN116271265A (en) | 2021-12-21 | 2021-12-21 | A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116271265A (en) |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101297973A (en)* | 2008-05-22 | 2008-11-05 | 武汉华纳生物工程有限公司 | Highly bioadhesive and thermosensitive hydrogel, and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN101327344A (en)* | 2008-07-17 | 2008-12-24 | 杭州协合医疗用品有限公司 | Carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel material and preparation method thereof |
| CN102068719A (en)* | 2011-01-18 | 2011-05-25 | 复旦大学 | Adhesion prevention material formed by physical crosslinking hydrogel composition and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN102459351A (en)* | 2009-04-17 | 2012-05-16 | 帝人株式会社 | Polysaccharide derivative and hydrogel thereof |
| CN102949754A (en)* | 2012-05-25 | 2013-03-06 | 江西圣济药业有限公司 | Uterine cavity hemostasis anti-adhersion temperature-sensitive gel and preparation method thereof |
| CN105854090A (en)* | 2016-04-11 | 2016-08-17 | 大连诺伊生物技术有限责任公司 | Quick release-slow release drug membrane and preparation method thereof |
| US20180110897A1 (en)* | 2015-04-10 | 2018-04-26 | Tricol Biomedical, Inc. | Bioadhesive chitosan gel for controlling bleeding and for promoting healing with scar reduction without obscuring or interfering with access to a surgical field |
| CN108047467A (en)* | 2017-12-12 | 2018-05-18 | 广州昊江新材料有限公司 | Medical cross-linked sponge of chitosan carboxymethyl chitosan and preparation method thereof |
| CN109957115A (en)* | 2017-12-25 | 2019-07-02 | 成都昕才医药科技有限公司 | A kind of temperature-sensitive hydrogel |
| CN110755695A (en)* | 2019-11-18 | 2020-02-07 | 西安交通大学 | A physiologically responsive chitosan gel and its application in intrauterine anti-adhesion |
| CN111298188A (en)* | 2019-12-04 | 2020-06-19 | 戴建英 | Self-curing double-component ion and temperature double-sensitive digestive tract mucosa protective adhesive and application thereof |
- 2021
- 2021-12-21CNCN202111569575.1Apatent/CN116271265A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101297973A (en)* | 2008-05-22 | 2008-11-05 | 武汉华纳生物工程有限公司 | Highly bioadhesive and thermosensitive hydrogel, and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN101327344A (en)* | 2008-07-17 | 2008-12-24 | 杭州协合医疗用品有限公司 | Carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel material and preparation method thereof |
| CN102459351A (en)* | 2009-04-17 | 2012-05-16 | 帝人株式会社 | Polysaccharide derivative and hydrogel thereof |
| CN102068719A (en)* | 2011-01-18 | 2011-05-25 | 复旦大学 | Adhesion prevention material formed by physical crosslinking hydrogel composition and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN102949754A (en)* | 2012-05-25 | 2013-03-06 | 江西圣济药业有限公司 | Uterine cavity hemostasis anti-adhersion temperature-sensitive gel and preparation method thereof |
| US20180110897A1 (en)* | 2015-04-10 | 2018-04-26 | Tricol Biomedical, Inc. | Bioadhesive chitosan gel for controlling bleeding and for promoting healing with scar reduction without obscuring or interfering with access to a surgical field |
| CN105854090A (en)* | 2016-04-11 | 2016-08-17 | 大连诺伊生物技术有限责任公司 | Quick release-slow release drug membrane and preparation method thereof |
| CN108047467A (en)* | 2017-12-12 | 2018-05-18 | 广州昊江新材料有限公司 | Medical cross-linked sponge of chitosan carboxymethyl chitosan and preparation method thereof |
| CN109957115A (en)* | 2017-12-25 | 2019-07-02 | 成都昕才医药科技有限公司 | A kind of temperature-sensitive hydrogel |
| CN110755695A (en)* | 2019-11-18 | 2020-02-07 | 西安交通大学 | A physiologically responsive chitosan gel and its application in intrauterine anti-adhesion |
| CN111298188A (en)* | 2019-12-04 | 2020-06-19 | 戴建英 | Self-curing double-component ion and temperature double-sensitive digestive tract mucosa protective adhesive and application thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| LANG PUXIN: "Degradable temperature-sensitive hydrogel loaded with heparin effectively prevents post-operative tissue adhesions", ACS BIOMATERIALS SCIENCE & ENGINEERING, vol. 9, no. 6, 14 May 2023 (2023-05-14), pages 3618 - 3631* |
| XU HELIN: "Temperature-sensitive heparin-modified poloxamer hydrogel with affinity to KGF facilitate the morphologic and functional recovery of the injured rat uterus", DRUG DELIVERY, vol. 24, no. 1, 2 June 2017 (2017-06-02), pages 867 - 881* |
| 胡亦清: "多糖及多糖衍生物/泊洛沙姆温敏水凝胶的制备及其性能研究", 中山大学学报, vol. 54, no. 6, 30 November 2015 (2015-11-30), pages 104 - 110* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Chandel et al. | Advancement of biomaterial‐based postoperative adhesion barriers | |
| JP5479739B2 (en) | Anti-adhesion composition | |
| US6610078B1 (en) | Suture material for wounds based on methylidene malonate | |
| Chu et al. | Recent advances in injectable dual crosslinking hydrogels for biomedical applications | |
| CN104981259B (en) | Kit containing an anti-adhesion hydrogel membrane | |
| US20030073663A1 (en) | Bioabsorbable medical devices from oxidized polysaccharides | |
| CN100379462C (en) | A tissue-coated medical material comprising a poorly water-soluble soluble cellulose derivative and its manufacturing method | |
| WO2000049084A1 (en) | Hyaluronic acid gel composition, process for producing the same, and medical material containing the same | |
| EP2549899B1 (en) | Functionalized adhesive for medical devices | |
| CN101848739A (en) | Surgical hydrogel | |
| US20120156176A1 (en) | Thermoresponsive, biodegradable, elastomeric material and uses therefor | |
| JP2002514235A (en) | Polymerizable biodegradable polymers containing carbonate or dioxanone linkages | |
| EP0815879A2 (en) | Bioabsorbable medical devices from oxidized polysaccharides | |
| CN107519541B (en) | Hydrogel for preventing postoperative adhesion of abdominal cavity and preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP6916353B1 (en) | Polymer composition for preventing adhesions | |
| CN113663116A (en) | Ion-based hydrogel with hemostasis and adhesion resistance and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN110384831A (en) | Preparation method for the amphoteric ion hydrogel and crosslinking agent of post-operation adhesion preventing, polymer | |
| CN101618045B (en) | Anti-adhesion gel containing polyhydroxyalkanoate | |
| CN116271265A (en) | A thermosensitive hydrogel for preventing postoperative tissue adhesion and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114748677B (en) | Anti-adhesion hydrogel adhesive, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| KR101799534B1 (en) | Composition for preventing tissue adhesion and method for preparing the same | |
| CN115300665A (en) | Antibacterial and absorbable nasal cavity hemostatic sponge and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN114432494A (en) | Hydrogel loaded with notoginseng and preparation method | |
| CN103951950B (en) | Flexible biological degradable composite material | |
| JP2003019194A (en) | Co-crosslinked gel composition comprising hyaluronic acid and carboxymethyl cellulose |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20230623 |