CN116269808A - System and device for a surgical robot - Google Patents
System and device for a surgical robotDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116269808A CN116269808ACN202211729696.2ACN202211729696ACN116269808ACN 116269808 ACN116269808 ACN 116269808ACN 202211729696 ACN202211729696 ACN 202211729696ACN 116269808 ACN116269808 ACN 116269808A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- operation node
- initial
- node
- pose
- path
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B34/37—Leader-follower robots
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/00234—Surgical instruments, devices or methods for minimally invasive surgery
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B2017/00743—Type of operation; Specification of treatment sites
- A61B2017/00778—Operations on blood vessels
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/10—Computer-aided planning, simulation or modelling of surgical operations
- A61B2034/107—Visualisation of planned trajectories or target regions
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B2034/301—Surgical robots for introducing or steering flexible instruments inserted into the body, e.g. catheters or endoscopes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B2034/303—Surgical robots specifically adapted for manipulations within body lumens, e.g. within lumen of gut, spine, or blood vessels
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P90/00—Enabling technologies with a potential contribution to greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions mitigation
- Y02P90/02—Total factory control, e.g. smart factories, flexible manufacturing systems [FMS] or integrated manufacturing systems [IMS]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及一种机器人的系统和装置,尤其涉及一种手术机器人的系统和装置。The present application relates to a robot system and device, in particular to a surgical robot system and device.
背景技术Background technique
在进行血管介入手术的过程中,需要依据不同的手术目的,在手术操作过程中可能需要使用多种器械、多次进入和退出人体血管。现有技术一般采用医生较强的感知能力、操作能力、判断能力和反应力。In the process of vascular interventional surgery, according to different surgical purposes, it may be necessary to use multiple instruments and enter and exit human blood vessels multiple times during the surgical operation. The prior art generally adopts a doctor's strong perception ability, operation ability, judgment ability and responsiveness.
现有技术存在如下技术问题:The prior art has the following technical problems:
1、由于此类手术对医生的要求高,所以限制了相应手术治疗方法的普及、并且不同的术者进行手术可能引入人为失误的风险因素。1. Due to the high requirements for doctors of this type of operation, the popularization of corresponding surgical treatment methods is limited, and different operators may introduce risk factors of human error when performing operations.
2、由于一台手术的时间较长,医生操作会直接影响介入器械在体内的状态,故医生需全程注意力高度集中进行术中操作,在这种负荷下人工难以长期持续,导致手术失败的可能性高。2. Due to the long operation time of one operation, the doctor's operation will directly affect the state of the interventional device in the body, so the doctor needs to concentrate on the operation during the operation. It is difficult to continue the operation for a long time under such a load, resulting in the failure of the operation. High probability.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请实施例提供一种手术机器人的系统和装置,以解决相关技术存在的问题,技术方案如下:The embodiment of the present application provides a system and device of a surgical robot to solve the problems existing in related technologies, and the technical solution is as follows:
第一方面,本申请实施例提供了一种机器人的系统,包括:主端设备、从端设备、介入器械;In the first aspect, the embodiment of the present application provides a robot system, including: a master device, a slave device, and an interventional instrument;
所述主端设备,包括:影像处理主机、主端控制器;The main-end device includes: an image processing host and a main-end controller;
所述影像处理主机,用于获取根据初始规划路径确定的初始操作节点;基于所述初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据;The image processing host is configured to acquire an initial operation node determined according to an initial planning path; generate first motion data based on the initial planning path and real-time data of an associated path node where the initial operation node is located;
所述主端控制器,用于判断是否存在预设时间段内获取的第二运动数据,若存在,则所述主端控制器配置所述第一运动数据和所述第二运动数据的权重,生成执行指令;将所述执行指令发送至所述从端控制器;The main-end controller is used to judge whether there is second exercise data acquired within a preset time period, and if so, the main-end controller configures the weights of the first exercise data and the second exercise data , generating an execution instruction; sending the execution instruction to the slave controller;
所述从端控制器,用于接受执行指令,并控制所述介入器械完成执行指令;The slave controller is used to accept execution instructions and control the interventional instrument to complete the execution instructions;
所述影像处理主机,还用于接受完成执行指令并到达下一操作节点的信息,将所述下一操作节点的指令作为新的初始操作节点,主端控制器循环执行生成执行指令的步骤,直至所述介入器械完成目标操作节点的执行指令;其中,所述初始规划路径的起点为初始操作节点,所述初始规划路径的终点为目标操作节点;The image processing host is also used to accept the information that the execution instruction has been completed and arrive at the next operation node, and use the instruction of the next operation node as a new initial operation node, and the master-side controller loops through the steps of generating the execution instruction, Until the interventional instrument completes the execution instruction of the target operation node; wherein, the starting point of the initial planning path is the initial operation node, and the end point of the initial planning path is the target operation node;
所述从端设备,用于获取所在路径的实时数据,并利用所述介入器械执行所述主端控制器发出的执行指令。The slave device is used to obtain real-time data of the path it is in, and use the interventional instrument to execute execution instructions issued by the master controller.
可选地,所述影像处理主机,用于基于所述初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据的步骤,包括:Optionally, the image processing host is configured to generate first motion data based on the initial planned path and the real-time data of the associated path node where the initial operation node is located, including:
获取所述初始操作节点的实际位姿和速度;Obtain the actual pose and velocity of the initial operation node;
参考所述初始规划路径,利用所述实际位姿和速度,生成下一操作节点的第一运动数据;Referring to the initial planned path, using the actual pose and velocity, to generate the first motion data of the next operation node;
其中,所述第一运动数据至少包括:下一操作节点的位姿变化量和加速度变化量。Wherein, the first motion data includes at least: a change in pose and an acceleration of the next operating node.
可选地,所述影像处理主机,用于生成下一操作节点的位姿变化量的步骤,包括:Optionally, the image processing host, the step of generating the pose variation of the next operation node includes:
根据所述初始操作节点的实际位姿和所述初始规划路径,确定所述初始操作节点的位姿偏差;determining a pose deviation of the initial operating node according to the actual pose of the initial operating node and the initial planned path;
根据所述初始操作节点的速度和所述初始规划路径,确定下一操作节点的位姿;determining the pose of the next operating node according to the speed of the initial operating node and the initial planned path;
根据所述初始操作节点的位姿偏差和下一操作节点的位姿,生成下一操作节点的位姿变化量。According to the pose deviation of the initial operation node and the pose of the next operation node, a pose change amount of the next operation node is generated.
可选地,所述影像处理主机,用于生成下一操作节点加速度变化量的步骤,包括:Optionally, the image processing host, the step of generating the acceleration variation of the next operation node includes:
根据所述初始规划路径以及各路段的路径情况,计算各路段的预计通行速度;Calculate the estimated traffic speed of each road section according to the initial planning path and the path conditions of each road section;
根据所述初始操作节点的速度,下一操作节点所在路段的预计通行速度,生成加速度变量。An acceleration variable is generated according to the speed of the initial operating node and the predicted passing speed of the road section where the next operating node is located.
可选地,基于初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据,包括:Optionally, the first motion data is generated based on the initial planned path and the real-time data of the associated path node where the initial operation node is located, including:
获取所述初始操作节点的实际位姿、速度、组织边界;Obtain the actual pose, velocity, and organizational boundaries of the initial operation node;
将所述初始规划路径与所述初始操作节点的实际位姿、速度、组织边界,输入至预先训练的轨迹决策神经网络,生成第一运动数据;Inputting the initial planning path and the actual pose, velocity, and organizational boundary of the initial operating node into a pre-trained trajectory decision neural network to generate first motion data;
所述第一运动数据包括:下一操作节点的位姿变化量和加速度变化量。The first motion data includes: a pose change amount and an acceleration change amount of a next operation node.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供了一种与所述机器人的系统对应的装置。该装置,包括:主端设备、从端设备、介入器械;In a second aspect, the embodiment of the present application provides a device corresponding to the robot system. The device includes: master equipment, slave equipment, and interventional equipment;
所述主端设备包括:输入控制组件,所述影像处理主机通过所述输入控制组件获取第二运动数据;The master device includes: an input control component, and the image processing host acquires second motion data through the input control component;
所述从端设备包括:轨道基板,和功能模块;所述功能模块可拆卸地安装于所述轨道基板上;所述功能模块用于实现至少一个介入器械实现直线、旋捻、控弯的独立或复合动作;The slave end device includes: a track substrate, and a functional module; the functional module is detachably installed on the track substrate; the functional module is used to realize the independent function of straight line, twisting and bending control for at least one interventional instrument. or compound action;
所述介入器械,包括:对接手柄和导管;所述对接手柄位于导管的远端,用于根据所述功能模块的控制,向导管的头端传递能量,以控制导管头端的运动方向和运动速度。The interventional instrument includes: a docking handle and a catheter; the docking handle is located at the distal end of the catheter, and is used to transmit energy to the head end of the catheter according to the control of the functional module, so as to control the movement direction and speed of the catheter head end .
上述技术方案中的优点或有益效果至少包括:The advantages or beneficial effects of the above technical solutions at least include:
通过本发明的手术机器人可以对介入器械实现全自动或半自动的控制,避免了现有技术存在的对手术医生要求高、容易存在失误、手术失败可能性高的技术问题,进而达到精准控制介入器械、降低手术对患者的伤害、提高手术成功率的技术效果。The surgical robot of the present invention can realize fully automatic or semi-automatic control of interventional instruments, avoiding the technical problems in the prior art that have high requirements for surgeons, are prone to errors, and have a high possibility of surgical failure, thereby achieving precise control of interventional instruments , The technical effect of reducing the injury of the operation to the patient and improving the success rate of the operation.
上述概述仅仅是为了说明书的目的,并不意图以任何方式进行限制。除上述描述的示意性的方面、实施方式和特征之外,通过参考附图和以下的详细描述,本申请进一步的方面、实施方式和特征将会是容易明白的。The above summary is for illustrative purposes only and is not intended to be limiting in any way. In addition to the illustrative aspects, embodiments and features described above, further aspects, embodiments and features of the present application will be readily apparent by reference to the drawings and the following detailed description.
附图说明Description of drawings
在附图中,除非另外规定,否则贯穿多个附图相同的附图标记表示相同或相似的部件或元素。这些附图不一定是按照比例绘制的。应该理解,这些附图仅描绘了根据本申请公开的一些实施方式,而不应将其视为是对本申请范围的限制。In the drawings, unless otherwise specified, the same reference numerals designate the same or similar parts or elements throughout the several drawings. The drawings are not necessarily drawn to scale. It should be understood that these drawings only depict some embodiments disclosed according to the application, and should not be regarded as limiting the scope of the application.
图1示出根据本专利一实施例的手术机器人的系统的结构图;Fig. 1 shows a structural diagram of a system of a surgical robot according to an embodiment of the present patent;
图2示出根据本申请一实施例的位姿变化量和加速度变化量的逻辑框图;Fig. 2 shows a logic block diagram of the pose variation and the acceleration variation according to an embodiment of the present application;
图3示出根据本申请另一实施例的位姿变化量和加速度变化量的逻辑框图;Fig. 3 shows a logic block diagram of pose variation and acceleration variation according to another embodiment of the present application;
图4示出根据本发明一实施例的手术机器人服务器的结构框图。Fig. 4 shows a structural block diagram of a surgical robot server according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
在下文中,仅简单地描述了某些示例性实施例。正如本领域技术人员可认识到的那样,在不脱离本申请的精神或范围的情况下,可通过各种不同方式修改所描述的实施例。因此,附图和描述被认为本质上是示例性的而非限制性的。In the following, only some exemplary embodiments are briefly described. As those skilled in the art would realize, the described embodiments may be modified in various different ways, all without departing from the spirit or scope of the present application. Accordingly, the drawings and descriptions are to be regarded as illustrative in nature and not restrictive.
术语“第一”、“第二”、“第三”等仅用于区分描述,并不表示排列序号,也不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性。The terms "first", "second", "third" and so on are only used for distinguishing descriptions, and do not represent sequence numbers, nor can they be understood as indicating or implying relative importance.
此外,术语“水平”、“竖直”、“悬垂”等术语并不表示要求部件绝对水平或悬垂,而是可以稍微倾斜。如“水平”仅仅是指其方向相对“竖直”而言更加水平,并不是表示该结构一定要完全水平,而是可以稍微倾斜。In addition, the terms "horizontal", "vertical", "overhanging" and the like do not mean that the components are absolutely horizontal or overhanging, but may be slightly inclined. For example, "horizontal" only means that its direction is more horizontal than "vertical", and it does not mean that the structure must be completely horizontal, but can be slightly inclined.
在本申请的描述中,需要说明的是,术语“内”、“外”、“左”、“右”、“上”、“下”等指示的方位或位置关系为基于附图所示的方位或位置关系,或者是该申请产品使用时惯常摆放的方位或位置关系,仅是为了便于描述本申请和简化描述,而不是指示或暗示所指的装置或元件必须具有特定的方位、以特定的方位构造和操作,因此不能理解为对本申请的限制。In the description of the present application, it should be noted that the orientation or positional relationship indicated by the terms "inner", "outer", "left", "right", "upper", "lower" etc. are based on the Orientation or positional relationship, or the orientation or positional relationship that the application product is usually placed in use, is only for the convenience of describing the application and simplifying the description, rather than indicating or implying that the referred device or element must have a specific orientation, in order to Specific orientation configurations and operations, therefore, are not to be construed as limitations on the application.
在本申请的描述中,除非另有明确的规定和限定,术语“设置”、“安装”、“相连”、“连接”应做广义理解,例如,可以是固定连接,也可以是可拆卸连接,或一体地连接;可以是机械连接,也可以是电连接;可以是直接相连,也可以通过中间媒介间接相连,可以是两个元件内部的连通。In the description of this application, unless otherwise clearly stipulated and limited, the terms "installation", "installation", "connection" and "connection" should be understood in a broad sense, for example, it can be a fixed connection or a detachable connection , or integrally connected; it may be mechanically connected or electrically connected; it may be directly connected or indirectly connected through an intermediary, and it may be the internal communication of two components.
下面将结合附图对本申请的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述。The technical solutions of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
图1示出根据本专利一实施例的手术机器人的系统的结构图。如图1所示,该一种手术机器人的系统,包括:主端设备100、从端设备200、介入器械(未在图1中示出)。Fig. 1 shows a structural diagram of a surgical robot system according to an embodiment of the present patent. As shown in FIG. 1 , the surgical robot system includes: a
具体地,所述主端设备100,包括:影像处理主机、主端控制器。影像处理主机、主端控制器均位于主端设备100中,未在图1中示出。Specifically, the
所述影像处理主机获取根据初始规划路径确定的初始操作节点。此处的初始操作节点是指介入器械进入人体的第一个节点,在实际应用中需要根据患者患病的位置确定介入器械的初始操作节点,例如,通过大腿的静脉(或动脉)进入血管最终达到人体的心脏实现治疗。The image processing host obtains the initial operation node determined according to the initial planned path. The initial operation node here refers to the first node where the interventional device enters the human body. In practical applications, the initial operation node of the interventional device needs to be determined according to the position of the patient's disease, for example, the vein (or artery) of the thigh enters the blood vessel and finally Reach the heart of the human body to achieve treatment.
基于所述初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据;判断是否存在预设时间段内获取的第二运动数据,若存在,则所述主端控制器配置所述第一运动数据和所述第二运动数据的权重,生成执行指令。此处的第一运动数据是系统根据已有的数据规划出的数据,第二运动数据是指医生控制输入控制组件获取的数据。也就是说本专利所保护的系统既可以自主实现全自动控制介入器械的运动,也可以实现半自动控制介入器械的运动。Generate first motion data based on the initial planned path and the real-time data of the associated path node where the initial operation node is located; determine whether there is second motion data acquired within a preset time period, and if so, the master terminal controls The device configures the weights of the first motion data and the second motion data, and generates an execution instruction. The first exercise data here is the data planned by the system based on the existing data, and the second exercise data refers to the data obtained by the doctor controlling the input control component. That is to say, the system protected by this patent can realize the automatic control of the movement of the interventional device, and can also realize the semi-automatic control of the movement of the interventional device.
当主端设备生成了执行指令后,就将该执行指令传输给从端设备,由从端设备控制介入器械执行相应的操作。因此,主端设备需要将所述执行指令发送至所述从端控制器;所述从端控制器接受执行指令,并由从端控制器控制所述介入器械完成执行指令。After the master device generates an execution command, it transmits the execution command to the slave device, and the slave device controls the interventional device to perform corresponding operations. Therefore, the master device needs to send the execution instruction to the slave controller; the slave controller accepts the execution instruction, and the slave controller controls the interventional instrument to complete the execution instruction.
在实际应用中可以通过介入器械上安装的传感器(如超声波传感器)或实时影像数据(如DSA影像数据)获取介入器械的实际情况。当影像处理主机接受到介入器械完成执行指令并到达下一操作节点的信息后,将所述下一操作节点的指令作为新的初始操作节点,主端控制器循环执行生成执行指令的步骤,直至所述介入器械完成目标操作节点的执行指令。也就是每到一个新的操作节点就规划执行到下一操作节点的需要的运动数据。In practical applications, the actual situation of the interventional device can be acquired through sensors installed on the interventional device (such as ultrasonic sensors) or real-time image data (such as DSA image data). When the image processing host computer receives the information that the interventional device completes the execution instruction and arrives at the next operation node, it takes the instruction of the next operation node as the new initial operation node, and the master-end controller loops through the steps of generating the execution instruction until The interventional instrument completes the execution instruction of the target operation node. That is, every time a new operation node is reached, the motion data required for execution to the next operation node is planned.
其中,所述初始规划路径的起点为初始操作节点,也就是介入人体的初始位置;所述初始规划路径的终点为目标操作节点,也就是患者的患病位置。Wherein, the starting point of the initial planning path is the initial operation node, that is, the initial position of the intervening human body; the end point of the initial planning path is the target operation node, that is, the diseased position of the patient.
所述从端设备,用于获取所在路径的实时数据,并利用所述介入器械执行所述主端控制器发出的执行指令。The slave device is used to obtain real-time data of the path it is in, and use the interventional instrument to execute execution instructions issued by the master controller.
当主端设备生成了介入器械整体的控制指令,则需要将主端的控制指令传输到从端,由从端设备将整体的控制指令进行拆解,由从端的一个或多个组件执行相应的拆解后的指令。When the master-end device generates the overall control command of the interventional device, it needs to transmit the master-end control command to the slave-end, the slave-end device disassembles the overall control command, and one or more components of the slave-end perform the corresponding disassembly following instructions.
具体地,所述从端设备还包括:从端控制器、从端驱动装置;Specifically, the slave device further includes: a slave controller, a slave drive device;
所述从端控制器用于拆解主端设备发出执行指令,生成拆解指令;The slave-side controller is used to dismantle the master-end device to issue an execution command and generate a dismantling command;
所述从端驱动装置用于根据所述从端控制器的所述拆解指令,驱动从端的各个组件执行不同的动作,共同实现带动介入器械运动的目的。The slave end driving device is used to drive each component of the slave end to perform different actions according to the disassembly instruction of the slave end controller, so as to jointly realize the purpose of driving the interventional instrument to move.
术中控制介入器械在人体内运动的过程主要包括:根据预制地图数据/实时影像数据结合形变场以及初始规划路径对介入器械进行控制。其中,预制地图数据/实时影像数据提供坐标系,形变场提供坐标系之间的对应关系,介入器械需沿初始规划路径在人体内运动,当介入器械偏离初始路径规划时,则需要校正介入器械的执行路线。The process of controlling the movement of the interventional device in the human body during the operation mainly includes: controlling the interventional device according to the prefabricated map data/real-time image data combined with the deformation field and the initial planning path. Among them, the prefabricated map data/real-time image data provide the coordinate system, and the deformation field provides the corresponding relationship between the coordinate systems. The interventional device needs to move in the human body along the initial planned path. When the interventional device deviates from the initial path planning, the interventional device needs to be corrected. execution route.
具体地,基于所述初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据,包括:Specifically, based on the initial planned path and the real-time data of the associated path node where the initial operation node is located, the first motion data is generated, including:
获取所述初始操作节点的实际位姿和速度;Obtain the actual pose and velocity of the initial operation node;
参考所述初始规划路径,利用所述实际位姿和速度,生成下一操作节点的第一运动数据;Referring to the initial planned path, using the actual pose and velocity, to generate the first motion data of the next operation node;
所述第一运动数据包括:下一操作节点的位姿变化量和加速度变化量。The first motion data includes: a pose change amount and an acceleration change amount of a next operation node.
也就是在每个位置时计算下一位置需要达到的速度、加速度,进而控制介入器械执行相应的操作。That is, at each position, the speed and acceleration to be achieved at the next position are calculated, and then the interventional instrument is controlled to perform corresponding operations.
所述位姿是指介入器械所在的位置和姿态。根据介入器械的需要达到的位姿可以用于控制介入器械在运动过程中的位置变化过程。即通过当前时刻的实际位姿和下一位置的位姿,确定运动过程中的介入器械的状态变化过程。The pose refers to the position and posture of the interventional instrument. The required pose of the interventional device can be used to control the position change process of the interventional device during movement. That is, the state change process of the interventional device during the movement is determined through the actual pose at the current moment and the pose at the next position.
实际上,生成运动数据的过程是一个循环的过程,每执行到下一操作节点时,则需要根据当前操作节点的情况执行下一操作节点的运动数据。In fact, the process of generating motion data is a cyclic process. When the next operation node is executed, the motion data of the next operation node needs to be executed according to the situation of the current operation node.
运动数据主要包括两个部分:基于位置的运动指令和基于速度的运动指令。其中,运动指令可以包括前进/后退、旋转、控弯等操作等;基于速度的运动指令相当于运动指令的参数可以包括距离、速度、加速度等。通过将运动数据拆分到各个机械模组,进而实现驱动器带动介入器械进行运动的目的。Motion data mainly includes two parts: position-based motion commands and speed-based motion commands. Among them, the motion command may include operations such as forward/backward, rotation, and bending control; the parameters of the speed-based motion command may include distance, speed, acceleration, etc. equivalent to the motion command. By splitting the motion data into each mechanical module, the purpose of the driver driving the interventional device to move is realized.
图2示出根据本申请一实施例的位姿变化量和加速度变化量的逻辑框图。Fig. 2 shows a logic block diagram of pose variation and acceleration variation according to an embodiment of the present application.
如图2所示,由于每一操作节点对应的目标位姿和速度会影响后续操作节点的运动方向。因此,需要根据初始规划路径对各个操作节点的路径进行校正。具体地,具备校正功能的生成下一操作节点的位姿变化量的步骤,包括:As shown in Figure 2, since the target pose and velocity corresponding to each operation node will affect the movement direction of subsequent operation nodes. Therefore, it is necessary to correct the path of each operating node according to the initial planned path. Specifically, the step of generating the pose variation of the next operation node with a correction function includes:
根据所述初始操作节点的实际位姿和所述初始规划路径,确定所述初始操作节点的位姿偏差;determining a pose deviation of the initial operating node according to the actual pose of the initial operating node and the initial planned path;
根据所述初始操作节点的速度和所述初始规划路径,确定下一操作节点的位姿;determining the pose of the next operating node according to the speed of the initial operating node and the initial planned path;
根据所述初始操作节点的位姿偏差和下一操作节点的位姿,生成下一操作节点的位姿变化量。According to the pose deviation of the initial operation node and the pose of the next operation node, a pose change amount of the next operation node is generated.
由于介入器械在实际执行中可能存在与初始规划路径不同的情况,因此需要根据初始规划路径对实际的执行校正,通过校正使得介入设备的执行过程不偏离规划的方向,避免因为介入器械进入错误的路径需要退回,给患者带来不必要的风险。Since the actual execution of the interventional device may be different from the initial planned path, it is necessary to correct the actual execution according to the initial planned path. Through correction, the execution process of the interventional device will not deviate from the planned direction, and avoid the error caused by the interventional device. The path needs to be backtracked, creating unnecessary risk for the patient.
参考图2,具体地,所述影像处理主机,用于生成下一操作节点加速度变化量的步骤生成下一操作节点加速度变化量的步骤,包括:Referring to FIG. 2, specifically, the image processing host, for generating the step of generating the acceleration variation of the next operation node, the step of generating the acceleration variation of the next operation node includes:
根据所述初始规划路径以及各路段的路径情况,计算各路段的预计通行速度;Calculate the estimated traffic speed of each road section according to the initial planning path and the path conditions of each road section;
根据所述初始操作节点的速度,下一操作节点所在路段的预计通行速度,生成加速度变量。An acceleration variable is generated according to the speed of the initial operating node and the predicted passing speed of the road section where the next operating node is located.
本申请的加速度变化量包括加速和减速变化量。The variation of acceleration in this application includes the variation of acceleration and deceleration.
图3示出根据本申请另一实施例的位姿变化量和加速度变化量的逻辑框图。Fig. 3 shows a logic block diagram of pose variation and acceleration variation according to another embodiment of the present application.
如图3所示,在本申请的另一可选实施例中还可以根据轨迹决策神经网络确定下一操作节点的运动状态。As shown in FIG. 3 , in another optional embodiment of the present application, the motion state of the next operating node may also be determined according to the trajectory decision neural network.
具体地,基于初始规划路径和所述初始操作节点所在关联路径节点的实时数据,生成第一运动数据,包括:Specifically, based on the initial planned path and the real-time data of the associated path node where the initial operation node is located, the first motion data is generated, including:
获取所述初始操作节点的实际位姿、速度、组织边界(例如血管壁、心脏的腔室等);Obtain the actual pose, velocity, and tissue boundaries (such as vessel walls, heart chambers, etc.) of the initial operation node;
将所述初始规划路径与所述初始操作节点的实际位姿、速度、组织边界,输入至预先训练的轨迹决策神经网络,生成第一运动数据;Inputting the initial planning path and the actual pose, velocity, and organizational boundary of the initial operating node into a pre-trained trajectory decision neural network to generate first motion data;
所述第一运动数据包括:下一操作节点的位姿变化量和加速度变化量。The first motion data includes: a pose change amount and an acceleration change amount of a next operation node.
由于介入器械的运动是在三维空间内执行,因此介入器械的位姿(例如在人体内的朝向、所在位置)是确定下一操作节点的运动数据的因素之一。组织边界是指腔体的内表面,例如血管的内壁、心脏的腔室。Since the movement of the interventional instrument is performed in three-dimensional space, the pose of the interventional instrument (such as the orientation and position in the human body) is one of the factors for determining the motion data of the next operation node. A tissue boundary refers to the inner surface of a cavity, eg, the inner wall of a blood vessel, a chamber of the heart.
通过控制介入器械的位姿变化量和加速度变化量,避免介入器械刮伤/刺破组织边界,造成对组织的伤害。By controlling the amount of change in posture and acceleration of the interventional instrument, the interventional instrument is prevented from scratching/puncturing the tissue boundary and causing damage to the tissue.
手术机器人的装置,主端设备100、从端设备200、介入器械(未在图4中示出)。该设备包括:主端设备、从端设备、介入器械。主端设备是指医生操作设备的一端,通过医生对主端设备的控制,避免了现有技术需要医生长时间控制介入设备存在的对手术医生要求高、容易存在失误、手术失败可能性高的技术问题,进而达到精准控制介入器械、降低手术对患者的伤害、提高手术成功率的技术效果。Devices of a surgical robot,
所述主端设备100还包括:输入控制组件110,所述影像处理主机通过所述输入控制组件110获取第二运动数据;其中,输入控制组件110包括如下至少之一:操作手柄111、触摸屏113、脚踏112、按钮114;The
所述从端设备200还包括:轨道基板210,和功能模块220;所述功能模块220可拆卸地安装于所述轨道基板210上;所述功能模块220用于实现至少一个介入器械实现直线、旋捻、控弯的独立或复合动作;The
所述介入器械,包括:对接手柄和导管;所述对接手柄位于导管的远端,用于根据所述功能模块的控制,向导管的头端传递能量,以控制导管头端的运动方向和运动速度。The interventional instrument includes: a docking handle and a catheter; the docking handle is located at the distal end of the catheter, and is used to transmit energy to the head end of the catheter according to the control of the functional module, so as to control the movement direction and speed of the catheter head end .
本发明实施例各装置中的各模块的功能可以参见上述方法中的对应描述,在此不再赘述。For functions of each module in each device in the embodiment of the present invention, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the foregoing method, and details are not repeated here.
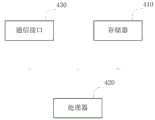
图4示出根据本发明一实施例的手术机器人服务器的结构框图。如图4所示,该手术机器人服务器包括:存储器410和处理器420,存储器410内存储有可在处理器420上运行的计算机程序。处理器4420执行该计算机程序时实现上述实施例中的控制操作。存储器410和处理器420的数量可以为一个或多个。Fig. 4 shows a structural block diagram of a surgical robot server according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 4 , the surgical robot server includes: a
该手术机器人服务器还包括:The Surgical Robot Server also includes:
通信接口430,用于与外界设备进行通信,进行数据交互传输。The
如果存储器410、处理器420和通信接口430独立实现,则存储器410、处理器420和通信接口430可以通过总线相互连接并完成相互间的通信。该总线可以是工业标准体系结构(IndustryStandardArchitecture,ISA)总线、外部设备互连(PeripheralComponentInterconnect,PCI)总线或扩展工业标准体系结构(ExtendedIndustryStandardArchitecture,EISA)总线等。该总线可以分为地址总线、数据总线、控制总线等。为便于表示,图4中仅用一条粗线表示,但并不表示仅有一根总线或一种类型的总线。If the
可选的,在具体实现上,如果存储器410、处理器420及通信接口430集成在一块芯片上,则存储器410、处理器420及通信接口430可以通过内部接口完成相互间的通信。Optionally, in a specific implementation, if the
本发明实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其存储有计算机程序,该程序被处理器执行时实现本申请实施例中提供的方法。An embodiment of the present invention provides a computer-readable storage medium, which stores a computer program, and implements the method provided in the embodiment of the present application when the program is executed by a processor.
本申请实施例还提供了一种芯片,该芯片包括,包括处理器,用于从存储器中调用并运行存储器中存储的指令,使得安装有芯片的通信设备执行本申请实施例提供的方法。The embodiment of the present application also provides a chip, the chip includes, including a processor, configured to call from the memory and execute instructions stored in the memory, so that the communication device installed with the chip executes the method provided in the embodiment of the present application.
本申请实施例还提供了一种芯片,包括:输入接口、输出接口、处理器和存储器,输入接口、输出接口、处理器以及存储器之间通过内部连接通路相连,处理器用于执行存储器中的代码,当代码被执行时,处理器用于执行申请实施例提供的方法。The embodiment of the present application also provides a chip, including: an input interface, an output interface, a processor, and a memory, the input interface, the output interface, the processor, and the memory are connected through an internal connection path, and the processor is used to execute the code in the memory , when the code is executed, the processor is used to execute the method provided by the embodiment of the application.
应理解的是,上述处理器可以是中央处理器(CentralProcessingUnit,CPU),还可以是其他通用处理器、数字信号处理器(digitalsignalprocessing,DSP)、专用集成电路(applicationspecificintegratedcircuit,ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(fieldprogrammablegatearray,FPGA)或者其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件等。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者是任何常规的处理器等。值得说明的是,处理器可以是支持进阶精简指令集机器(advancedRISCmachines,ARM)架构的处理器。It should be understood that the above-mentioned processor may be a central processing unit (Central Processing Unit, CPU), and may also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processing (digital signal processing, DSP), application specific integrated circuit (application specific integrated circuit, ASIC), field programmable gate Array (field programmable gate array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc. A general purpose processor may be a microprocessor or any conventional processor or the like. It should be noted that the processor may be a processor supporting advanced RISC machines (ARM) architecture.
进一步地,可选的,上述存储器可以包括只读存储器和随机存取存储器,还可以包括非易失性随机存取存储器。该存储器可以是易失性存储器或非易失性存储器,或可包括易失性和非易失性存储器两者。其中,非易失性存储器可以包括只读存储器(read-onlymemory,ROM)、可编程只读存储器(programmableROM,PROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(erasablePROM,EPROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(electricallyEPROM,EEPROM)或闪存。易失性存储器可以包括随机存取存储器(randomaccessmemory,RAM),其用作外部高速缓存。通过示例性但不是限制性说明,许多形式的RAM可用。例如,静态随机存取存储器(staticRAM,SRAM)、动态随机存取存储器(dynamic randomaccessmemory,DRAM)、同步动态随机存取存储器(synchronous DRAM,SDRAM)、双倍数据速率同步动态随机存取存储器(doubledatadate SDRAM,DDRSDRAM)、增强型同步动态随机存取存储器(enhancedSDRAM,ESDRAM)、同步连接动态随机存取存储器(synchlinkDRAM,SLDRAM)和直接内存总线随机存取存储器(directrambusRAM,DRRAM)。Further, optionally, the above-mentioned memory may include a read-only memory and a random access memory, and may also include a non-volatile random access memory. The memory can be either volatile memory or nonvolatile memory, or can include both volatile and nonvolatile memory. Among them, the non-volatile memory may include read-only memory (read-only memory, ROM), programmable read-only memory (programmable ROM, PROM), erasable programmable read-only memory (erasable PROM, EPROM), electrically erasable Programs read-only memory (electricallyEPROM, EEPROM) or flash memory. Volatile memory can include random access memory (RAM), which acts as external cache memory. By way of illustration and not limitation, many forms of RAM are available. For example, static random access memory (static RAM, SRAM), dynamic random access memory (dynamic random access memory, DRAM), synchronous dynamic random access memory (synchronous DRAM, SDRAM), double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (double data date) SDRAM, DDR SDRAM), enhanced synchronous dynamic random access memory (enhancedSDRAM, ESDRAM), synchronous connection dynamic random access memory (synchlinkDRAM, SLDRAM) and direct memory bus random access memory (directrambusRAM, DRRAM).
在上述实施例中,可以全部或部分地通过软件、硬件、固件或者其任意组合来实现。当使用软件实现时,可以全部或部分地以计算机程序产品的形式实现。计算机程序产品包括一个或多个计算机指令。在计算机上加载和执行计算机程序指令时,全部或部分地产生按照本申请的流程或功能。计算机可以是通用计算机、专用计算机、计算机网络、或者其他可编程装置。计算机指令可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,或者从一个计算机可读存储介质向另一个计算机可读存储介质传输。In the above embodiments, all or part of them may be implemented by software, hardware, firmware or any combination thereof. When implemented using software, it may be implemented in whole or in part in the form of a computer program product. A computer program product includes one or more computer instructions. When the computer program instructions are loaded and executed on the computer, the processes or functions according to the present application are generated in whole or in part. A computer can be a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, computer network, or other programmable device. Computer instructions may be stored in, or transmitted from, one computer-readable storage medium to another computer-readable storage medium.
在本说明书的描述中,参考术语“一个实施例”、“一些实施例”、“示例”、“具体示例”、或“一些示例”等的描述意指结合该实施例或示例描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点包括于本申请的至少一个实施例或示例中。而且,描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点可以在任一个或多个实施例或示例中以合适的方式结合。此外,在不相互矛盾的情况下,本领域的技术人员可以将本说明书中描述的不同实施例或示例以及不同实施例或示例的特征进行结合和组合。In the description of this specification, descriptions referring to the terms "one embodiment", "some embodiments", "example", "specific examples", or "some examples" mean that specific features described in connection with the embodiment or example , structure, material or characteristic is included in at least one embodiment or example of the present application. Furthermore, the described specific features, structures, materials or characteristics may be combined in any suitable manner in any one or more embodiments or examples. In addition, those skilled in the art can combine and combine different embodiments or examples and features of different embodiments or examples described in this specification without conflicting with each other.
此外,术语“第一”、“第二”仅用于描述目的,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的数量。由此,限定有“第一”、“第二”的特征可以明示或隐含地包括至少一个该特征。在本申请的描述中,“多个”的含义是两个或两个以上,除非另有明确具体的限定。In addition, the terms "first" and "second" are used for descriptive purposes only, and cannot be interpreted as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly specifying the quantity of indicated technical features. Thus, the features defined as "first" and "second" may explicitly or implicitly include at least one of these features. In the description of the present application, "plurality" means two or more, unless otherwise specifically defined.
流程图中或在此以其他方式描述的任何过程或方法描述可以被理解为,表示包括一个或更多个用于实现特定逻辑功能或过程的步骤的可执行指令的代码的模块、片段或部分。并且本申请的优选实施方式的范围包括另外的实现,其中可以不按所示出或讨论的顺序,包括根据所涉及的功能按基本同时的方式或按相反的顺序,来执行功能。Any process or method descriptions in flowcharts or otherwise described herein may be understood to represent modules, segments or portions of code comprising one or more executable instructions for implementing specific logical functions or steps of the process . Also, the scope of preferred embodiments of the present application includes additional implementations in which functions may be performed out of the order shown or discussed, including substantially concurrently or in reverse order as the functions involved are involved.
在流程图中表示或在此以其他方式描述的逻辑和/或步骤,例如,可以被认为是用于实现逻辑功能的可执行指令的定序列表,可以具体实现在任何计算机可读介质中,以供指令执行系统、装置或设备(如基于计算机的系统、包括处理器的系统或其他可以从指令执行系统、装置或设备取指令并执行指令的系统)使用,或结合这些指令执行系统、装置或设备而使用。The logic and/or steps represented in the flowcharts or otherwise described herein, for example, can be considered as a sequenced listing of executable instructions for implementing logical functions, can be embodied in any computer-readable medium, For use with instruction execution systems, devices, or devices (such as computer-based systems, systems including processors, or other systems that can fetch instructions from instruction execution systems, devices, or devices and execute instructions), or in conjunction with these instruction execution systems, devices or equipment for use.
应理解的是,本申请的各部分可以用硬件、软件、固件或它们的组合来实现。在上述实施方式中,多个步骤或方法可以用存储在存储器中且由合适的指令执行系统执行的软件或固件来实现。上述实施例方法的全部或部分步骤是可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件完成,该程序可以存储于一种计算机可读存储介质中,该程序在执行时,包括方法实施例的步骤之一或其组合。It should be understood that each part of the present application may be realized by hardware, software, firmware or a combination thereof. In the embodiments described above, various steps or methods may be implemented by software or firmware stored in memory and executed by a suitable instruction execution system. All or part of the steps of the method in the above embodiments can be completed by instructing related hardware through a program. The program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed, it includes one of the steps of the method embodiment or its combination.
此外,在本申请各个实施例中的各功能单元可以集成在一个处理模块中,也可以是各个单元单独物理存在,也可以两个或两个以上单元集成在一个模块中。上述集成的模块既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能模块的形式实现。上述集成的模块如果以软件功能模块的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,也可以存储在一个计算机可读存储介质中。该存储介质可以是只读存储器,磁盘或光盘等。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application may be integrated into one processing module, each unit may exist separately physically, or two or more units may be integrated into one module. The above-mentioned integrated modules can be implemented in the form of hardware or in the form of software function modules. If the above-mentioned integrated modules are implemented in the form of software function modules and sold or used as independent products, they can also be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The storage medium may be a read-only memory, a magnetic disk or an optical disk, and the like.
以上所述,仅为本申请的具体实施方式,但本申请的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本申请揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到其各种变化或替换,这些都应涵盖在本申请的保护范围之内。因此,本申请的保护范围应以权利要求的保护范围为准。The above is only a specific embodiment of the application, but the scope of protection of the application is not limited thereto. Any person familiar with the technical field can easily think of its various changes or modifications within the technical scope disclosed in the application. Replacement, these should be covered within the protection scope of this application. Therefore, the protection scope of the present application should be based on the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211729696.2ACN116269808A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | System and device for a surgical robot |
| PCT/CN2023/140843WO2024140437A1 (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-22 | System and apparatus for surgical robot |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211729696.2ACN116269808A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | System and device for a surgical robot |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116269808Atrue CN116269808A (en) | 2023-06-23 |
Family
ID=86776895
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211729696.2APendingCN116269808A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | System and device for a surgical robot |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116269808A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2024140437A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024140437A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | System and apparatus for surgical robot |
| WO2024140436A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | Motion planning method and system for interventional instrument, program unit, and storage medium |
| WO2024140439A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | Surgical robot system and apparatus |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107848114A (en)* | 2015-08-25 | 2018-03-27 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Industrial robot and its method of operation |
| CN114022587A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-02-08 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Marker sharing method, device, system, apparatus and medium for surgical robot |
| CN114917029A (en)* | 2022-07-22 | 2022-08-19 | 北京唯迈医疗设备有限公司 | Interventional surgical robot system, control method and medium |
| WO2022199649A1 (en)* | 2021-03-24 | 2022-09-29 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Computer-readable storage medium, electronic device, and surgical robot system |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102007045075B4 (en)* | 2007-09-21 | 2010-05-12 | Siemens Ag | Interventional medical diagnosis and / or therapy system |
| EP4167892A4 (en)* | 2020-06-19 | 2024-10-30 | Remedy Robotics, Inc. | SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR GUIDING INTRALUMINAL DEVICES WITHIN THE VASCULAR SYSTEM |
| CN115444572B (en)* | 2022-08-10 | 2025-06-24 | 上海优医基医学科技有限公司 | Flexible device control method, system, electronic device, storage medium and robot |
| CN116269808A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-06-23 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | System and device for a surgical robot |
| CN115998448A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-04-25 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | System and device for a surgical robot |
- 2022
- 2022-12-30CNCN202211729696.2Apatent/CN116269808A/enactivePending
- 2023
- 2023-12-22WOPCT/CN2023/140843patent/WO2024140437A1/enactivePending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107848114A (en)* | 2015-08-25 | 2018-03-27 | 川崎重工业株式会社 | Industrial robot and its method of operation |
| WO2022199649A1 (en)* | 2021-03-24 | 2022-09-29 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Computer-readable storage medium, electronic device, and surgical robot system |
| CN114022587A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-02-08 | 上海微创医疗机器人(集团)股份有限公司 | Marker sharing method, device, system, apparatus and medium for surgical robot |
| CN114917029A (en)* | 2022-07-22 | 2022-08-19 | 北京唯迈医疗设备有限公司 | Interventional surgical robot system, control method and medium |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024140437A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | System and apparatus for surgical robot |
| WO2024140436A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | Motion planning method and system for interventional instrument, program unit, and storage medium |
| WO2024140439A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 上海术之道机器人有限公司 | Surgical robot system and apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2024140437A1 (en) | 2024-07-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN116269808A (en) | System and device for a surgical robot | |
| WO2024140439A1 (en) | Surgical robot system and apparatus | |
| CN111568558B (en) | Electronic device, surgical robot system, and control method thereof | |
| US11690681B2 (en) | Method for bone registration and surgical robot | |
| CN113712674B (en) | Catheter robot, catheter robot system, catheter control method, computer readable storage medium, and electronic device | |
| CN111050686B (en) | Camera control for surgical robotic system | |
| JP3668865B2 (en) | Surgical device | |
| CN115252132B (en) | Navigation system based on interventional operation robot, main-end remote control navigation system and program product | |
| JP2017023339A (en) | Medical activity support device | |
| CN116919590B (en) | Surgical robot control method, device and medium for hallux valgus minimally invasive surgery | |
| JP4390146B2 (en) | Puncture control device, puncture robot, and puncture control program | |
| WO2016208140A1 (en) | Medical procedure assist device | |
| CN115363762A (en) | Positioning method, device and computer equipment of surgical robot | |
| CN115998433A (en) | Motion planning method, system, program element and storage medium for an interventional instrument | |
| CN115016493A (en) | Constant speed cruise method, device, equipment and medium for interventional robot | |
| WO2024140435A1 (en) | Tissue structure model data fusion method and apparatus for interventional surgery | |
| JP2024045418A (en) | Robot system and control method | |
| US20160184038A1 (en) | Robotic system | |
| CN113509296A (en) | Method and system for automatically adjusting position and posture of acetabular cup and surgical robot | |
| WO2024256395A1 (en) | System for autonomously carrying out a medical procedure | |
| CN117752424A (en) | Master-slave control method and device of flexible surgical robot, robot and medium | |
| CN115005979B (en) | Computer-readable storage medium, electronic device, and surgical robot system | |
| CN113040922B (en) | Method, medium, system and apparatus for motion control of focused ultrasound surgical actuators | |
| CN114681055B (en) | Surgical navigation positioning system, device and storage medium | |
| RU2806087C1 (en) | Interventional surgical robotic system, control method and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |