CN116269308A - Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilation - Google Patents
Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116269308A CN116269308ACN202310279963.9ACN202310279963ACN116269308ACN 116269308 ACN116269308 ACN 116269308ACN 202310279963 ACN202310279963 ACN 202310279963ACN 116269308 ACN116269308 ACN 116269308A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- electrical impedance
- activity
- dimensional electrical
- lung
- value
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/05—Detecting, measuring or recording for diagnosis by means of electric currents or magnetic fields; Measuring using microwaves or radio waves
- A61B5/053—Measuring electrical impedance or conductance of a portion of the body
- A61B5/0536—Impedance imaging, e.g. by tomography
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/08—Measuring devices for evaluating the respiratory organs
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A90/00—Technologies having an indirect contribution to adaptation to climate change
- Y02A90/10—Information and communication technologies [ICT] supporting adaptation to climate change, e.g. for weather forecasting or climate simulation
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种临床辅助诊断技术,特别涉及一种融合肺通气时空特征获取方法。The invention relates to a clinical auxiliary diagnosis technology, in particular to a method for acquiring temporal and spatial characteristics of fusion lung ventilation.
背景技术Background technique
呼吸系统疾病是影响人们生命健康和生活质量的一大难题。呼吸系统的主要器官是肺,肺通气功能是临床上关注重点。肺部疾病的常用检查手段有X射线、核磁共振、计算机断层成像等,但是这些手段只能表征肺部的结构特征,无法体现先于结构病变发生的功能病变;并且这类设备有辐射、成本高,所以可及性非常有限。Respiratory diseases are a major problem affecting people's health and quality of life. The main organ of the respiratory system is the lung, and the ventilation function of the lung is the focus of clinical attention. Common examination methods for lung diseases include X-rays, nuclear magnetic resonance, and computerized tomography, but these methods can only characterize the structural characteristics of the lungs, and cannot reflect the functional lesions that precede structural lesions; and such equipment has radiation, cost, etc. High, so accessibility is very limited.
肺功能测试更关注肺部活动的一般特点和严重程度,例如肺容量的大小、气道的通畅程度等;可以用来明确呼吸功能减退的程度和类型,是评价病情发展或治疗效果的主要手段。肺功能测试中,受试者一般通常采取站位或坐位,在医生指导下进行规定呼吸动作,借助鼻夹和吹嘴使气流完全流经肺量计,由后者给出肺部气体的进出容量与速度。这种方法只能对呼吸系统进行整体评价,难以刻画出如早期气道改变和局部肺实质破坏等局部肺功能变化,这对慢性呼吸系统疾病的防治非常不利。分侧肺功能测试可分别测定单侧肺的功能变化,但是需要进行双腔气管插管,创伤较大且操作不便,临床上极少应用。Pulmonary function tests pay more attention to the general characteristics and severity of lung activity, such as the size of the lung volume, the degree of airway patency, etc.; they can be used to clarify the degree and type of respiratory function decline, and are the main means to evaluate the development of the disease or the effect of treatment . In the pulmonary function test, the subjects generally take a standing or sitting position, perform prescribed breathing actions under the guidance of a doctor, and use a nose clip and a mouthpiece to make the airflow completely flow through the spirometer, which gives the air in and out of the lungs capacity and speed. This method can only make an overall evaluation of the respiratory system, and it is difficult to describe changes in local lung function such as early airway changes and local lung parenchymal destruction, which is very unfavorable for the prevention and treatment of chronic respiratory diseases. The lateral lung function test can measure the functional changes of one side of the lung separately, but it requires double-lumen endotracheal intubation, which is relatively traumatic and inconvenient to operate, so it is rarely used clinically.
发明内容Contents of the invention
针对肺功能精确测试问题,提出了一种融合肺通气时空特征获取方法,借助三维EIT技术,进行肺部动态通气情况可视化,融合评价肺通气的时间和空间异质性,转换为三维电阻抗活跃度曲线,反应呼吸特性,用于综合评判被试者的肺通气情况。Aiming at the problem of accurate testing of lung function, a method for obtaining the temporal and spatial characteristics of lung ventilation is proposed. With the help of three-dimensional EIT technology, the dynamic ventilation of the lungs can be visualized, and the temporal and spatial heterogeneity of lung ventilation can be evaluated by fusion, and converted into three-dimensional electrical impedance active The degree curve reflects the respiratory characteristics and is used to comprehensively evaluate the lung ventilation of the subject.
本发明的技术方案为:一种融合肺通气时空特征获取方法,具体包括如下步骤:The technical solution of the present invention is: a method for acquiring temporal and spatial characteristics of fusion lung ventilation, which specifically includes the following steps:
1)通过电阻抗成像获得三维电阻抗图像:电阻抗成像为采集成像区域内的电导率数值,将某一时刻所有像素的电导率数值加和得到该时刻的全局电导率值,获得该时刻的三维电阻抗图像,整个呼吸过程的全局电导率值按照时间顺序排列,获得呼吸过程的时间序列三维电阻抗图像;1) Obtain a three-dimensional electrical impedance image through electrical impedance imaging: electrical impedance imaging is to collect the conductivity value in the imaging area, add the conductivity values of all pixels at a certain moment to obtain the global conductivity value at that moment, and obtain the conductivity value at that moment. Three-dimensional electrical impedance image, the global conductivity values of the entire breathing process are arranged in time order, and the time-series three-dimensional electrical impedance image of the breathing process is obtained;
2)定义活跃像素:像素值在前x%的像素,x为经验值;定义活跃度:活跃像素占整体成像区域像素的比例;对步骤1)时间序列三维电阻抗图像进行活跃度计算;2) Define active pixels: pixels whose pixel values are in the first x%, x is an empirical value; define activity: the ratio of active pixels to pixels in the overall imaging area; calculate the activity of step 1) time-series three-dimensional electrical impedance images;
3)对于动态的呼吸过程,将步骤2)获得每幅三维电阻抗图像的活跃度按照时间顺序排列得到三维电阻抗活跃度曲线,从三维电阻抗活跃度曲线提取融合肺通气时空特征,包括ARmax、ARsec和Sexp;3) For the dynamic breathing process, the activity of each three-dimensional electrical impedance image obtained in step 2) is arranged in time order to obtain a three-dimensional electrical impedance activity curve, and the fusion of lung ventilation spatiotemporal features is extracted from the three-dimensional electrical impedance activity curve, including ARmax , ARsec and Sexp ;
ARmax为活跃度曲线的峰值;ARmax is the peak value of the activity curve;
峰值开始为呼气段开始Fstart,Fstart后一秒对应的活跃度值定义为呼气一秒时的活跃度值ARsec;The start of the peak value is the start of the expiratory segment Fstart , and the activity value corresponding to one second after Fstart is defined as the activity value ARsec when exhaling for one second;
Sexp为呼气段下阴影面积,从呼气段开始Fstart到呼气段结束Fend活跃度曲线所包含的面积。Sexp is the shaded area under the expiratory segment, the area covered by the activity curve from the beginning of the expiratory segment Fstart to the end of the expiratory segment Fend .
一种利于融合肺通气时空特征的三维电阻抗活跃度曲线评估肺通气的方法,所述三维电阻抗活跃度曲线用于评估肺通气阻塞程度:所述活跃度曲线的峰值ARmax用于反应用力吸气末肺扩张的程度;所述呼气一秒时的活跃度值为ARsec和呼气段下阴影面积Sexp用于反应气管通畅程度或肺阻塞程度。A method for assessing lung ventilation with a three-dimensional electrical impedance activity curve that integrates the spatiotemporal characteristics of lung ventilation, the three-dimensional electrical impedance activity curve is used to evaluate the degree of pulmonary ventilation obstruction: the peak value ARmax of the activity curve is used to respond to exertion The degree of lung expansion at the end of inspiration; the activity value when exhaling for one second is ARsec and the shadow area under the expiratory segment Sexp is used to reflect the degree of tracheal patency or pulmonary obstruction.
本发明的有益效果在于:本发明融合肺通气时空特征获取方法,电阻抗成像时间分辨率高、结构紧凑、成本低廉、安全无辐射、对环境要求低,能够实现长期的连续动态监测;首次使用三维EIT进行肺功能研究,可以对全肺通气进行动态观测,融合评价肺通气的时间和空间异质性,转换为三维电阻抗活跃度曲线,利于临床辅助诊断和局部肺功能表征。The beneficial effect of the present invention is that: the method for obtaining temporal and spatial characteristics of fusion lung ventilation of the present invention has high time resolution of electrical impedance imaging, compact structure, low cost, safety and no radiation, low environmental requirements, and can realize long-term continuous dynamic monitoring; the first use Three-dimensional EIT for lung function research can dynamically observe the whole lung ventilation, integrate and evaluate the temporal and spatial heterogeneity of lung ventilation, and convert it into a three-dimensional electrical impedance activity curve, which is beneficial to clinical auxiliary diagnosis and local pulmonary function characterization.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明三维电阻抗成像肺呼气动态过程示意图;Fig. 1 is the schematic diagram of the lung exhalation dynamic process of three-dimensional electrical impedance imaging of the present invention;
图2为本发明三维成像区域兴趣域划分示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the domain of interest division of the three-dimensional imaging region of the present invention;
图3A为本发明呼气中段平均流速MF值在正常组和异常组间对比图;Figure 3A is a comparison chart between the normal group and the abnormal group between the average flow velocity MF value in the middle part of the exhalation of the present invention;
图3B为本发明对MF进行受试者曲线分析图;Fig. 3B is a subject curve analysis diagram for MF in the present invention;
图4为本发明活跃度曲线统计参数示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of statistical parameters of the activity curve of the present invention;
图5A为本发明各组的平均活跃度曲线图;Fig. 5A is the average activity graph of each group of the present invention;
图5B为本发明各组的呼气一秒时的活跃度值ARsec图;Fig. 5B is the graph of activity value ARsec when each group of the present invention exhales for one second;
图5C为本发明各组的活跃度曲线的峰值ARmax图;Fig. 5C is the peak ARmax diagram of the activity curves of each group of the present invention;
图5D为本发明各组的呼气段下阴影面积Sexp图;Fig. 5 D is the shadow area Sexp diagram under the expiratory section of each group of the present invention;
图6为本发明支扩阳性被试支扩前后的活跃度曲线图;Fig. 6 is the activity graph before and after bronchiectasis of the positive subject of bronchiectasis in the present invention;
图7为本发明不同阻塞程度受试的活跃度曲线示意图。Fig. 7 is a schematic diagram of activity curves of subjects with different degrees of obstruction in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和具体实施例对本发明进行详细说明。本实施例以本发明技术方案为前提进行实施,给出了详细的实施方式和具体的操作过程,但本发明的保护范围不限于下述的实施例。The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is carried out on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation and specific operation process are given, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following embodiments.
电阻抗成像EIT是一种无辐射、非侵入、低成本、可功能成像的技术。电阻抗成像的基本原理可以描述为,按照不同的电极排布方案,采用多种激励方式对人体施加低于细胞兴奋阈值的安全电流,基于体表电压分布数据反演得到体内电导率分布情况或变化状态的图像。电阻抗成像能够捕捉呼吸过程中胸腔内的电阻抗改变,体现肺通气的时空异质性。Electrical impedance imaging (EIT) is a radiation-free, non-invasive, low-cost, functional imaging technique. The basic principle of electrical impedance imaging can be described as, according to different electrode arrangement schemes, a variety of excitation methods are used to apply a safe current lower than the cell excitation threshold to the human body, and the conductivity distribution in the body is obtained based on the surface voltage distribution data or Image of changing state. Electrical impedance imaging can capture the electrical impedance changes in the thoracic cavity during respiration, reflecting the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of lung ventilation.
电阻抗成像时间分辨率高、结构紧凑、成本低廉、安全无辐射、对环境要求低,能够实现长期的连续动态监测。目前,二维EIT已经广泛应用于临床研究,但是对肺通气的评估并不全面。Electrical impedance imaging has high time resolution, compact structure, low cost, safety and no radiation, low environmental requirements, and can realize long-term continuous dynamic monitoring. At present, two-dimensional EIT has been widely used in clinical research, but the evaluation of lung ventilation is not comprehensive.
使用三维EIT进行肺功能研究,可以对全肺通气进行动态观测。如图1所示三维电阻抗成像技术重建得到的肺呼气动态过程示意图。随着呼气进行,肺部电导率逐渐降低,表示肺部逐渐排空,空气含量降低。Using three-dimensional EIT for pulmonary function research, dynamic observation of whole lung ventilation can be performed. Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the dynamic process of lung exhalation reconstructed by three-dimensional electrical impedance imaging technology. As exhalation progresses, the conductivity of the lungs gradually decreases, indicating that the lungs are gradually emptying and containing less air.
可以看到,肺通气是一个兼具时空异质性的过程:时间上变化较大,空间上分布不均。EIT重建得到的是成像区域内的电导率数值,将某一时刻所有像素的电导率数值加和可以得到该时刻的全局电导率值。某个呼吸过程的全局电导率值按照时间顺序排列即得到EIT全局电导率曲线。It can be seen that pulmonary ventilation is a process with both spatiotemporal heterogeneity: large temporal changes and uneven spatial distribution. The EIT reconstruction obtains the conductivity value in the imaging area, and the global conductivity value at that moment can be obtained by adding the conductivity values of all pixels at a certain moment. The global conductivity values of a respiratory process are arranged in chronological order to obtain the EIT global conductivity curve.
为了评价肺通气的空间异质性,把成像区域按照空间分布划分为8个子区分别作为兴趣域,如图2所示三维成像区域兴趣域划分示意图,用两两互相垂直的三个面将成像区域按照空间均分为8个子区。In order to evaluate the spatial heterogeneity of lung ventilation, the imaging area is divided into 8 sub-areas according to the spatial distribution, which are respectively used as domains of interest, as shown in Figure 2. The area is divided into 8 sub-areas according to the space.
基于EIT全局电导率曲线,提出使用呼气中段平均流速(MF用力呼出肺活量25%~75%的平均流量)用以描述通气的顺畅程度,一定程度上体现了肺通气的时间异质性。将研究像素限制为某一子区的全部像素,即可同理得到该子区的局部电导率曲线。同样地,某个区域的rMF可以反映该区域的通气顺畅程度。将第i个子区的局部MF值记为rMFi。对于某一通气过程,rMF1-8的变异系数一定程度上可以融合反映通气的时空异质性。Based on the EIT global conductivity curve, it is proposed to use the average flow rate in the middle of expiration (the average flow rate of 25% to 75% of MF forced expiratory vital capacity) to describe the smoothness of ventilation, which reflects the temporal heterogeneity of lung ventilation to a certain extent. By limiting the research pixels to all the pixels in a certain sub-area, the local conductivity curve of the sub-area can be obtained similarly. Similarly, the rMF of a certain area can reflect the smoothness of ventilation in this area. The local MF value of the i-th subregion is denoted as rMFi . For a certain ventilation process, the coefficient of variation of rMF1-8 can reflect the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of ventilation to a certain extent.
根据上述获得三维EIT图像信息,研究共纳入137例被试者,按照肺功能测试结果划分为正常(Normal)及异常组(Abnormal)。针对上述划分的八个子区域,如图3A所示,MF值在正常组和异常组间观察到了显著的差异(差异统计P<0.01)。此外,如图3B所示,对MF进行受试者特征曲线ROC分析(ROC通过判断点cutoff point/cutoff value的移动,获得多对灵敏度sensitivity和误判率1-Specificity特异度,以灵敏度为纵轴,以误判率为横轴,连接各点绘制曲线,然后计算曲线下的面积,面积越大,判断价值越高),临床统计获得17.24为诊断界值,MF识别异常通气的敏感度(实际为真值的判断为真值的概率)为74%,特异度(把实际为假值的判断为假值的概率)为69%,预测效度的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.747(95%CI 0.665-0.829;P=0.001),然而对比二维EIT经典参数全局不均匀指数(globalinhomogeneity,GI),GI预测异常通气的AUC为0.535。因此,MF体现了前所未有的优越性,上述理论在实测数据上得到了较好的验证。According to the three-dimensional EIT image information obtained above, a total of 137 subjects were included in the study, and were divided into normal (Normal) and abnormal (Abnormal) groups according to the results of pulmonary function tests. For the above-mentioned eight sub-regions, as shown in Figure 3A, a significant difference was observed in the MF value between the normal group and the abnormal group (statistical difference P<0.01). In addition, as shown in Figure 3B, perform receiver characteristic curve ROC analysis on MF (ROC obtains multiple pairs of sensitivity sensitivity and misjudgment rate 1-Specificity specificity through the movement of the judgment point cutoff point/cutoff value, with sensitivity as the longitudinal Axis, take the misjudgment rate as the horizontal axis, connect the points to draw a curve, and then calculate the area under the curve, the larger the area, the higher the judgment value), the clinical statistics obtained 17.24 as the diagnostic cut-off value, the sensitivity of MF to identify abnormal ventilation ( The probability of judging the actual value as true value) is 74%, the specificity (the probability of judging the actual value as false value as false value) is 69%, and the area under the curve (AUC) of predictive validity is 0.747 (95 %CI 0.665-0.829; P=0.001), however, compared with the two-dimensional EIT classic parameter global inhomogeneity index (globalinhomogeneity, GI), the AUC of GI to predict abnormal ventilation is 0.535. Therefore, MF embodies unprecedented superiority, and the above theory has been well verified on the measured data.
结合MF特征曲线ROC分析以及三维EIT图像信息,在不同时刻,肺通气活跃部分占整体成像区域的比例是不同的,反映了气体分布的空间变化。因此,对于某一三维EIT图像,我们设计了活跃度这一指标用以融合时空异质特性。首先需要明确几个定义:Combined with ROC analysis of MF characteristic curve and 3D EIT image information, at different times, the proportion of active part of lung ventilation to the overall imaging area is different, reflecting the spatial variation of gas distribution. Therefore, for a 3D EIT image, we designed an index of activity to incorporate spatiotemporal heterogeneity. First, a few definitions need to be clarified:
活跃像素:像素值在前x%的像素,x为经验值,这里取值为80。Active pixels: pixels whose pixel values are in the top x%, where x is the experience value, and the value here is 80.
活跃度:活跃像素占整体成像区域像素的比例。Activeness: The ratio of active pixels to pixels in the overall imaging area.
对于动态的呼吸过程,将每幅图像的活跃度按照时间顺序排列得到活跃度曲线,如图4所示,其中ARmax为活跃度曲线的峰值,峰值开始为呼气段开始Fstart,Fstart后一秒对应的活跃度值定义为呼气一秒时的活跃度值为ARsec,从呼气段开始Fstart到呼气段结束Fend活跃度曲线所包含的面积为呼气段下阴影面积Sexp。For the dynamic breathing process, the activity of each image is arranged in chronological order to obtain the activity curve, as shown in Figure 4, where ARmax is the peak value of the activity curve, and the beginning of the peak value is the beginning of the expiratory segment Fstart , Fstart The activity value corresponding to the next second is defined as the activity value ARsec when exhaling for one second, and the area covered by the activity curve from the start of the exhalation segment Fstart to the end of the exhalation segment Fend is the shadow under the exhalation segment Area Sexp .
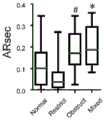
活跃度曲线可以反应呼吸的一些特点。具体来说,活跃度曲线的峰值ARmax可以一定程度上反应用力吸气末肺扩张的程度。呼气一秒时的活跃度值ARsec和呼气段下阴影面积Sexp可以反映呼气的顺畅程度。我们将137例被试按照肺功能测试结果划分为正常、阻塞、限制、混合四组(Normal,Restrict,Obstruct,and Mixed)。各组的活跃度情况如图5A-5D所示。可以看到,限制组Obstruct的ARmax较低,表示肺部扩张欠佳;阻塞组Restrict与混合组Mixed的呼气一秒时的活跃度值ARsec和呼气段下阴影面积Sexp较高,表示呼气不畅,符合理论预期及MF分析结果。综合临床实测数据,所述方法可以完成对异常通气情况的判别。The activity curve can reflect some characteristics of breathing. Specifically, the peak ARmax of the activity curve can reflect the degree of lung expansion at the end of forced inspiration to a certain extent. The activity value ARsec and the shaded area Sexp under the expiratory segment when exhaling for one second can reflect the smoothness of exhalation. We divided 137 subjects into four groups (Normal, Restrict, Obstruct, and Mixed) according to the results of pulmonary function tests. The activity of each group is shown in Figures 5A-5D. It can be seen that the ARmax of Obstruct in the restriction group is lower, indicating that the lung expansion is not good; the activity value ARsec and the shadow area Sexp under the expiratory segment are higher in the restriction group Restrict and the mixed group Mixed when exhaling for one second , indicating poor breathing, in line with theoretical expectations and MF analysis results. Based on the clinically measured data, the method can complete the discrimination of abnormal ventilation conditions.
为了减小受试间个体差异的影响,我们对比了一例支气管扩张实验阳性的被试结果。如图6所示,支气管扩张前后,ARmax值接近,表示吸气末肺部扩张的程度差异不大。支扩后,气管通畅性增加,ARsec和Sexp明显降低,与生理预期相符。In order to reduce the influence of individual differences among the subjects, we compared the results of a subject with a positive bronchiectasis test. As shown in Figure 6, before and after bronchiectasis, ARmax values were close, indicating that there was little difference in the degree of lung expansion at the end of inspiration. After bronchiectasis, tracheal patency increased, and ARsec and Sexp decreased significantly, which was consistent with physiological expectations.
进一步地,我们初步验证了活跃度曲线用以评估阻塞程度的可行性。我们选取四位被试者,分别编号1-2-3-4,对应肺功能结论分别是轻度阻塞、中重度阻塞、重度阻塞、极重度阻塞。如图7所示,对应可见其被试的活跃度曲线ARsec和Sexp递增。Furthermore, we preliminarily verified the feasibility of using the activity curve to evaluate the degree of blockage. We selected four subjects, numbered 1-2-3-4, respectively, and the corresponding lung function conclusions were mild obstruction, moderate to severe obstruction, severe obstruction, and very severe obstruction. As shown in Figure 7, correspondingly, it can be seen that the activity curve ARsec and Sexp of the subjects are increasing.
以上所述实施例仅表达了本发明的几种实施方式,其描述较为具体和详细,但并不能因此而理解为对发明专利范围的限制。应当指出的是,对于本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变形和改进,这些都属于本发明的保护范围。因此,本发明专利的保护范围应以所附权利要求为准。The above-mentioned embodiments only express several implementation modes of the present invention, and the descriptions thereof are relatively specific and detailed, but should not be construed as limiting the patent scope of the invention. It should be noted that, for those skilled in the art, several modifications and improvements can be made without departing from the concept of the present invention, and these all belong to the protection scope of the present invention. Therefore, the protection scope of the patent for the present invention should be based on the appended claims.
Claims (2)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310279963.9ACN116269308A (en) | 2023-03-20 | 2023-03-20 | Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310279963.9ACN116269308A (en) | 2023-03-20 | 2023-03-20 | Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilation |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116269308Atrue CN116269308A (en) | 2023-06-23 |
Family
ID=86777636
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310279963.9APendingCN116269308A (en) | 2023-03-20 | 2023-03-20 | Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116269308A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116956061A (en)* | 2023-07-03 | 2023-10-27 | 浙江工业大学 | Automatic synchronization method and device for pulmonary impedance imaging signals and mechanical ventilation signals |
| CN117883067A (en)* | 2023-12-19 | 2024-04-16 | 杭州永川科技有限公司 | GI and time constant-based lung ventilation function monitoring method, equipment and system thereof |
| CN118121183A (en)* | 2024-03-08 | 2024-06-04 | 广州医科大学 | Pulmonary function assessment method and system based on pulmonary impedance image time characteristics |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170079544A1 (en)* | 2014-04-24 | 2017-03-23 | Industry-Academic Cooperation Foundation Gyeongsang National Universtiy | Apparatus for diagnosing and imaging obstruction of upper airway in real time by using electrical impedance tomography |
| CN110087540A (en)* | 2016-11-18 | 2019-08-02 | 百来 | Method and apparatus for pulmonary function test (pft) |
| CN114343603A (en)* | 2022-02-15 | 2022-04-15 | 点奇生物医疗科技(苏州)有限公司 | Pulmonary blood flow monitoring system, monitoring method and analysis system based on impedance data |
| CN115153500A (en)* | 2022-07-04 | 2022-10-11 | 北京华睿博视医学影像技术有限公司 | Method and device for presenting respiratory impedance and respiratory impedance change rate relation |
| CN115590497A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2023-01-13 | 重庆大学(Cn) | Lung ventilation dysfunction disease diagnosis system based on gas-electricity synchronous measurement |
| CN115721535A (en)* | 2022-09-24 | 2023-03-03 | 首都医科大学附属北京康复医院(北京工人疗养院) | Data processing method for airway clearance and related system |
- 2023
- 2023-03-20CNCN202310279963.9Apatent/CN116269308A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170079544A1 (en)* | 2014-04-24 | 2017-03-23 | Industry-Academic Cooperation Foundation Gyeongsang National Universtiy | Apparatus for diagnosing and imaging obstruction of upper airway in real time by using electrical impedance tomography |
| CN110087540A (en)* | 2016-11-18 | 2019-08-02 | 百来 | Method and apparatus for pulmonary function test (pft) |
| CN114343603A (en)* | 2022-02-15 | 2022-04-15 | 点奇生物医疗科技(苏州)有限公司 | Pulmonary blood flow monitoring system, monitoring method and analysis system based on impedance data |
| CN115153500A (en)* | 2022-07-04 | 2022-10-11 | 北京华睿博视医学影像技术有限公司 | Method and device for presenting respiratory impedance and respiratory impedance change rate relation |
| CN115590497A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2023-01-13 | 重庆大学(Cn) | Lung ventilation dysfunction disease diagnosis system based on gas-electricity synchronous measurement |
| CN115721535A (en)* | 2022-09-24 | 2023-03-03 | 首都医科大学附属北京康复医院(北京工人疗养院) | Data processing method for airway clearance and related system |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116956061A (en)* | 2023-07-03 | 2023-10-27 | 浙江工业大学 | Automatic synchronization method and device for pulmonary impedance imaging signals and mechanical ventilation signals |
| CN116956061B (en)* | 2023-07-03 | 2025-07-25 | 浙江工业大学 | Automatic synchronization method and device for pulmonary impedance imaging signals and mechanical ventilation signals |
| CN117883067A (en)* | 2023-12-19 | 2024-04-16 | 杭州永川科技有限公司 | GI and time constant-based lung ventilation function monitoring method, equipment and system thereof |
| CN118121183A (en)* | 2024-03-08 | 2024-06-04 | 广州医科大学 | Pulmonary function assessment method and system based on pulmonary impedance image time characteristics |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN116269308A (en) | Method for acquiring temporal and spatial features of fused lung ventilation | |
| CN102973273B (en) | Sleep respiratory function monitoring system based on infrared radiation detection | |
| CN110087540B (en) | Method and apparatus for pulmonary function testing | |
| JP4755801B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for displaying information obtained from electrical impedance tomography data | |
| CN111449657B (en) | Image Monitoring System and Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis System | |
| US20030055331A1 (en) | Methods of endobronchial diagnosis using imaging | |
| US7794399B2 (en) | System and method for three-dimensional airway reconstruction, assessment and analysis | |
| CN112842321B (en) | Pulmonary ventilation function detection method, equipment and medium based on flow-volume loop diagram | |
| CN114587347B (en) | Pulmonary function detection method, system, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| Brabant et al. | Thoracic electrical impedance tomography—the 2022 veterinary consensus statement | |
| CN118121183B (en) | Pulmonary function assessment method and system based on pulmonary impedance image time characteristics | |
| Lamers et al. | Reproducibility of spirometrically controlled CT lung densitometry in a clinical setting | |
| CA3212096A1 (en) | Device and a method for determination of a measure for the homogeneity of the lung | |
| CN118121184A (en) | Pulmonary function assessment method, system and equipment based on respiratory impedance change | |
| US20170100059A1 (en) | Lung function monitoring | |
| CN115590497B (en) | Pulmonary ventilation dysfunction disease diagnosis system based on gas-electricity synchronous measurement | |
| CN110623668A (en) | A rapid magnetic resonance imaging method for quantitative assessment of lung compliance | |
| CN202942113U (en) | Sleep respiratory function monitoring system based on infrared radiation detection | |
| CN118216898B (en) | State monitoring method based on lung resistance tomography and application thereof | |
| Song et al. | A novel method for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease detection using comprehensive respiratory impedance and electrocardiogram-derived respiration | |
| Zouari et al. | Standalone electrical impedance tomography predicts spirometry indicators and enables regional lung assessment | |
| US20240074724A1 (en) | Monitoring airflow with b-mode ultrasound | |
| KR20240158489A (en) | mart spirometer capable of measuring expiratory temperature (EBT) and COPD patient screening system using the same | |
| CN210903016U (en) | Device for evaluating airflow limitation of subject | |
| RU2487662C2 (en) | METHOD OF DIAGNOSING RESPIRATORY FUNCTION BY MEANS OF IMPEDANCE SPIROGRAPHY AND COMPUTER APPLIANCE "BIA-lab Spiro" FOR ITS REALISATION |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |