CN116225330A - Control method and device, equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Control method and device, equipment and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116225330A CN116225330ACN202310189128.6ACN202310189128ACN116225330ACN 116225330 ACN116225330 ACN 116225330ACN 202310189128 ACN202310189128 ACN 202310189128ACN 116225330 ACN116225330 ACN 116225330A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- target
- parameter value
- storage unit
- mapping relationship
- frequency
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/3003—Monitoring arrangements specially adapted to the computing system or computing system component being monitored
- G06F11/3024—Monitoring arrangements specially adapted to the computing system or computing system component being monitored where the computing system component is a central processing unit [CPU]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/30—Monitoring
- G06F11/3055—Monitoring arrangements for monitoring the status of the computing system or of the computing system component, e.g. monitoring if the computing system is on, off, available, not available
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0629—Configuration or reconfiguration of storage systems
- G06F3/0634—Configuration or reconfiguration of storage systems by changing the state or mode of one or more devices
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P90/00—Enabling technologies with a potential contribution to greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions mitigation
- Y02P90/02—Total factory control, e.g. smart factories, flexible manufacturing systems [FMS] or integrated manufacturing systems [IMS]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- General Factory Administration (AREA)
- Numerical Control (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请实施例涉及电子技术,涉及但不限于一种控制方法及装置、设备和存储介质。The embodiments of the present application relate to electronic technology, and relate to but are not limited to a control method, device, equipment, and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
随着技术的发展,电子设备的使用率越来越频繁。其中,各类存储单元作为电子设备的重要组成部分,发挥着不可替代的作用。As technology develops, electronic devices are used more and more frequently. Among them, various storage units, as an important part of electronic equipment, play an irreplaceable role.
在电子设备的使用过程中需要对存储单元的工作参数进行调整,但是目前现有的针对存储单元的工作参数进行调整的方案已无法满足电子设备的使用性能。During the use of the electronic device, the working parameters of the storage unit need to be adjusted, but the current existing solutions for adjusting the working parameters of the storage unit cannot meet the performance of the electronic device.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本申请实施例提供一种控制方法及装置、设备和存储介质。In view of this, embodiments of the present application provide a control method, device, device, and storage medium.
本申请实施例的技术方案是这样实现的:The technical scheme of the embodiment of the application is realized in this way:
第一方面,本申请实施例提供一种控制方法,所述方法包括:In the first aspect, the embodiment of the present application provides a control method, the method comprising:
获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;obtaining first running information of a first processing unit of a processing module;
获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;obtaining second operating information of a second processing unit of the processing module;
根据所述第一运行信息和所述第二运行信息,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;determining working parameters of a storage unit according to the first operation information and the second operation information, the storage unit being able to communicate with the processing module;
控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。The storage unit is controlled to work with the working parameters.
在一些实施例中,所述根据所述第一运行信息和所述第二运行信息,确定存储单元的工作参数,包括:根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;根据所述目标运行信息,从多个预设的映射关系中确定出目标映射关系;基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数。In some embodiments, the determining the working parameters of the storage unit according to the first running information and the second running information includes: according to preset rules, combining the first running information or the second running information The information is determined as target operation information; according to the target operation information, a target mapping relationship is determined from a plurality of preset mapping relationships; based on the target mapping relationship, working parameters of the storage unit are determined.
在一些实施例中,所述根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息,包括:确定所述第一运行信息所需的存储单元的第一属性参数,以及所述第二运行信息所需的存储单元的第二属性参数;根据所述第一属性参数和所述第二属性参数的比对结果,确定将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息。In some embodiments, the determining the first operating information or the second operating information as the target operating information according to preset rules includes: determining the first storage unit required by the first operating information attribute parameter, and the second attribute parameter of the storage unit required by the second operation information; according to the comparison result of the first attribute parameter and the second attribute parameter, it is determined that the first operation information or the The second running information is determined as target running information.
在一些实施例中,所述根据所述目标运行信息,从多个预设的映射关系中确定出目标映射关系,包括:获得所述第一处理单元对应的第一映射关系,以及所述第二处理单元对应的第二映射关系;如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第一处理单元,将所述第一映射关系确定为目标映射关系;如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第二处理单元,将所述第二映射关系确定为目标映射关系;其中,所述第一映射关系包括所述工作参数的第一参数值集合,所述第二映射关系包括所述工作参数的第二参数值集合,所述第一参数值集合与所述第二参数值集合不同。In some embodiments, the determining the target mapping relationship from multiple preset mapping relationships according to the target operation information includes: obtaining the first mapping relationship corresponding to the first processing unit, and the second mapping relationship A second mapping relationship corresponding to two processing units; if the target operation information belongs to the first processing unit, determine the first mapping relationship as a target mapping relationship; if the target operation information belongs to the second processing unit , determining the second mapping relationship as a target mapping relationship; wherein, the first mapping relationship includes a first parameter value set of the working parameter, and the second mapping relationship includes a second parameter value of the working parameter set, the first set of parameter values is different from the second set of parameter values.
在一些实施例中,所述基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数,包括:从所述目标映射关系包括的参数值集合中,确定出与所述目标运行信息相匹配的目标工作参数值;对应地,所述控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作,包括:获得存储单元的当前工作参数值;控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值。In some embodiments, the determining the operating parameters of the storage unit based on the target mapping relationship includes: determining the target operating information that matches the target operating information from the set of parameter values included in the target mapping relationship. parameter value; correspondingly, the controlling the storage unit to work with the working parameter includes: obtaining the current working parameter value of the storage unit; controlling the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the target working parameter value.
在一些实施例中,所述控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值,包括:确定所述当前工作参数值与所述目标工作参数值之间的差值;如果所述差值大于预设阈值,确定中间参数值;控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述中间参数值,再从所述中间参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值;其中,所述中间参数值位于所述当前工作参数值和所述目标工作参数值之间、且所述中间参数值属于所述目标映射关系。In some embodiments, the controlling the storage unit to adjust from the current operating parameter value to the target operating parameter value includes: determining the difference between the current operating parameter value and the target operating parameter value ; If the difference is greater than a preset threshold, determine an intermediate parameter value; control the storage unit to adjust from the current operating parameter value to the intermediate parameter value, and then adjust from the intermediate parameter value to the target operating parameter value; wherein, the intermediate parameter value is located between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value, and the intermediate parameter value belongs to the target mapping relationship.
在一些实施例中,所述第一处理单元和所述第二处理单元的处理能力不同。In some embodiments, the first processing unit and the second processing unit have different processing capabilities.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供一种控制装置,所述装置包括:In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a control device, the device comprising:
第一获取单元,用于获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;a first acquiring unit, configured to acquire first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
第二获取单元,用于获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;a second acquiring unit, configured to acquire second running information of a second processing unit of the processing module;
确定单元,用于根据所述第一运行信息和所述第二运行信息,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;a determining unit, configured to determine working parameters of a storage unit capable of communicating with the processing module according to the first operating information and the second operating information;
控制单元,用于控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。a control unit, configured to control the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
第三方面,本申请实施例提供一种电子设备,包括存储器和处理器,所述存储器存储有可在处理器上运行的计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述程序时实现上述控制方法中的步骤。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an electronic device, including a memory and a processor, the memory stores a computer program that can run on the processor, and the processor implements the above control method when executing the program step.
第四方面,本申请实施例提供一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时实现上述控制方法中的步骤。In a fourth aspect, the embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps in the above control method are implemented.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本申请实施例控制方法的实现流程示意图一;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the implementation flow of the control method of the embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例控制方法的实现流程示意图二;FIG. 2 is a second schematic diagram of the implementation flow of the control method in the embodiment of the present application;
图3A为SAGV调频方案的原理示意图;FIG. 3A is a schematic diagram of the principle of the SAGV frequency modulation scheme;
图3B为本申请实施例内存智能跳频技术的原理示意图一;FIG. 3B is a first schematic diagram of the principle of memory intelligent frequency hopping technology according to the embodiment of the present application;
图3C为本申请实施例内存智能跳频技术的原理示意图二;FIG. 3C is a schematic diagram 2 of the principle of memory intelligent frequency hopping technology according to the embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例控制装置的组成结构示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the composition and structure of the control device of the embodiment of the present application;
图5为本申请实施例电子设备的一种硬件实体示意图。FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a hardware entity of an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和实施例对本申请的技术方案进一步详细阐述。显然,所描述的实施例仅是本申请一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本申请的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本申请保护的范围。The technical solution of the present application will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. Apparently, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present application, rather than all the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present application, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the scope of protection of the present application.
在以下的描述中,涉及到“一些实施例”,其描述了所有可能实施例的子集,但是可以理解,“一些实施例”可以是所有可能实施例的相同子集或不同子集,并且可以在不冲突的情况下相互结合。In the following description, references to "some embodiments" describe a subset of all possible embodiments, but it is understood that "some embodiments" may be the same subset or a different subset of all possible embodiments, and Can be combined with each other without conflict.
在后续的描述中,使用用于表示元件的诸如“模块”、“部件”或“单元”的后缀仅为了有利于本申请的说明,其本身没有特定的意义。因此,“模块”、“部件”或“单元”可以混合地使用。In the following description, the use of suffixes such as 'module', 'part' or 'unit' for denoting elements is only for facilitating the description of the present application and has no specific meaning by itself. Therefore, 'module', 'part' or 'unit' may be used in combination.
需要指出,本申请实施例所涉及的术语“第一\第二\第三”仅仅是区别类似的对象,不代表针对对象的特定排序,可以理解地,“第一\第二\第三”在允许的情况下可以互换特定的顺序或先后次序,以使这里描述的本申请实施例能够以除了在这里图示或描述的以外的顺序实施。It should be pointed out that the term "first\second\third" involved in the embodiment of this application is only to distinguish similar objects, and does not represent a specific ordering of objects. Understandably, "first\second\third" Where permitted, the specific order or sequencing may be interchanged such that the embodiments of the application described herein can be practiced in sequences other than those illustrated or described herein.
基于此,本申请实施例提供一种控制方法,该方法所实现的功能可以通过电子设备中的处理器调用程序代码来实现,当然程序代码可以保存在所述电子设备的存储介质中。图1为本申请实施例控制方法的实现流程示意图一,如图1所示,所述方法包括:Based on this, an embodiment of the present application provides a control method. The functions implemented by the method can be realized by calling a program code by a processor in the electronic device. Of course, the program code can be stored in a storage medium of the electronic device. Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the implementation flow of the control method of the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Fig. 1, the method includes:
步骤S101、获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;Step S101, obtaining the first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
这里,所述电子设备可以为各种类型的具有信息处理能力的设备,例如导航仪、智能手机、平板电脑、可穿戴设备、膝上型便携计算机、扫地机器人、智能厨卫、智能家居、汽车、服务器或者服务器集群等。Here, the electronic devices may be various types of devices with information processing capabilities, such as navigators, smart phones, tablet computers, wearable devices, laptop computers, sweeping robots, smart kitchens, smart homes, automobiles, etc. , server or server cluster, etc.
本申请实施例中,所述处理模块包括各类具有处理功能的模块,例如CPU(CentralProcessing Unit,中央处理器)、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit,图形处理器)、SCP(Service Control Point,业务控制点)、MCU(Micro Controller Unit,微控制单元)等。并且,所述处理模块能够与电子设备的存储单元通信,例如,可以将计算处理的结果放入存储单元中,或者从存储单元中读取目标数据进行处理。In the embodiment of the present application, the processing module includes various modules with processing functions, such as CPU (Central Processing Unit, central processing unit), GPU (Graphics Processing Unit, graphics processing unit), SCP (Service Control Point, business control point ), MCU (Micro Controller Unit, micro control unit), etc. In addition, the processing module can communicate with the storage unit of the electronic device, for example, it can put the result of calculation processing into the storage unit, or read the target data from the storage unit for processing.
其中,本申请实施例中的处理模块包括至少两个处理单元,所述至少两个中不同的处理单元具有不同的处理能力。例如,处理模块为CPU时,第一处理单元可以为CPU中的大核,第二处理单元可以为CPU中的小核。其中,大核主要通过高频率与超线程负责重负载任务,小核则主要负责较轻负载任务,以及多线程性能吞吐与协同能力。本申请实施例中的第一处理单元可以为所述至少两个处理单元中的一个处理单元。Wherein, the processing module in the embodiment of the present application includes at least two processing units, and different processing units among the at least two processing units have different processing capabilities. For example, when the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit may be a large core in the CPU, and the second processing unit may be a small core in the CPU. Among them, the large core is mainly responsible for heavy load tasks through high frequency and hyper-threading, while the small core is mainly responsible for light load tasks, as well as multi-thread performance throughput and collaboration capabilities. The first processing unit in this embodiment of the present application may be one of the at least two processing units.
这里,所述第一处理单元的第一运行信息指的是第一处理单元在运行过程中的各类信息。通过该第一运行信息能够确定第一处理单元的工作状态,进而判断第一处理单元对存储单元的参数需求。例如,第一处理单元为CPU中的大核,则第一运行信息包括但不限于大核的时钟频率、大核占用的功耗、大核中处理的进程数等。Here, the first running information of the first processing unit refers to various types of information during the running of the first processing unit. The working state of the first processing unit can be determined through the first running information, and then the parameter requirements of the first processing unit for the storage unit can be judged. For example, if the first processing unit is a large core in the CPU, the first running information includes but not limited to the clock frequency of the large core, the power consumption occupied by the large core, the number of processes processed in the large core, and the like.
步骤S102、获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;Step S102, obtaining second running information of a second processing unit of the processing module;
这里,第二处理单元可以为所述至少两个处理单元中的另一个处理单元。所述第二处理单元的第二运行信息指的是第二处理单元在运行过程中的各类信息。通过该第二运行信息能够确定第二处理单元的工作状态,进而判断第二处理单元对存储单元的参数需求。例如,第二处理单元为CPU中的小核,则第二运行信息包括但不限于小核的时钟频率、小核占用的功耗、小核中处理的进程数等。Here, the second processing unit may be another processing unit of the at least two processing units. The second running information of the second processing unit refers to various types of information during the running of the second processing unit. The working state of the second processing unit can be determined through the second running information, and then the parameter requirements of the second processing unit for the storage unit can be judged. For example, if the second processing unit is a small core in the CPU, the second running information includes but not limited to the clock frequency of the small core, the power consumption occupied by the small core, the number of processes processed in the small core, and the like.
步骤S103、根据所述第一运行信息和所述第二运行信息,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;Step S103, according to the first operation information and the second operation information, determine the working parameters of the storage unit, the storage unit can communicate with the processing module;
这里,存储单元指的是电子设备中具有存储功能的单元,可以包括缓存(Cache),也可以包括内存,如DDR(Double Data Rate,双倍速率同步动态随机存储器)、ROM(Read-Only Memory,只读存储器)、RAM(Random Access Memory,随机存取存储器),还可以包括外存、硬盘等。存储单元的工作参数包括但不限于:存储单元的频率、存储单元的容量、存储单元的时钟周期、存储单元的反应时间等。Here, the storage unit refers to a unit with a storage function in an electronic device, which may include a cache (Cache) or a memory, such as DDR (Double Data Rate, double-rate synchronous dynamic random access memory), ROM (Read-Only Memory , read-only memory), RAM (Random Access Memory, random access memory), and may also include external memory, hard disk, etc. The working parameters of the storage unit include but are not limited to: the frequency of the storage unit, the capacity of the storage unit, the clock cycle of the storage unit, the response time of the storage unit, and the like.
本申请实施例中,在处理模块的第一处理单元和第二处理单元均处于工作状态的情况下,能够根据第一处理单元的第一运行信息和第二处理单元的第二运行信息来确定存储单元的工作参数。例如,处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核。第一运行信息为大核的功耗,第二运行信息为小核的功耗,则可以根据大核的功耗和小核的功耗来确定内存的频率,从而在满足功能需求的同时达到性能的最优化。又如,处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核。第一运行信息为大核处理的进程数量,第二运行信息为小核处理的进程数量,则可以根据上述两个进程数量来确定硬盘的传输速率(即硬盘读写数据的速度)。In the embodiment of the present application, when both the first processing unit and the second processing unit of the processing module are in working state, it can be determined according to the first operation information of the first processing unit and the second operation information of the second processing unit Operating parameters of the storage unit. For example, the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU. The first operation information is the power consumption of the large core, and the second operation information is the power consumption of the small core. The frequency of the memory can be determined according to the power consumption of the large core and the power consumption of the small core, so as to meet the functional requirements while achieving Performance optimization. In another example, the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU. The first operation information is the number of processes processed by the large core, and the second operation information is the number of processes processed by the small core. Then the transmission rate of the hard disk (ie the speed of reading and writing data of the hard disk) can be determined according to the above two process numbers.
步骤S104、控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。Step S104, controlling the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
本申请实施例中,在确定出存储单元的工作参数后,需要控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。例如,如果通过大核的功耗和小核的功耗确定出内存的工作频率为4800MHz(兆赫),则控制内存以4800MHz的频率进行工作。In the embodiment of the present application, after the working parameters of the storage unit are determined, it is necessary to control the storage unit to work with the working parameters. For example, if the operating frequency of the memory is determined to be 4800 MHz (megahertz) through the power consumption of the large core and the power consumption of the small core, then the memory is controlled to work at a frequency of 4800 MHz.
举例来说,现有技术中内存频率调整一般是设定4个固定的频点,然后根据CPU的整体使用情况在这4个固定的频点中进行切换。本申请实施例考虑CPU的大小核模式,即SOC(System On Chip,片上系统)内部有高性能的P-CORE(即大核),也有低功耗的E-CORE(即小核),进而基于大核的运行信息和小核的运行信息来确定内存的工作频率。For example, in the prior art, memory frequency adjustment is generally to set 4 fixed frequency points, and then switch between these 4 fixed frequency points according to the overall usage of the CPU. The embodiment of the present application considers the size and core mode of the CPU, that is, there is a high-performance P-CORE (ie, a large core) inside the SOC (System On Chip, a large core), and there is also a low-power E-CORE (ie, a small core), and then The operating frequency of the memory is determined based on the operating information of the large core and the operating information of the small core.
这里,通过上述步骤S101至步骤S104中的控制方法,能够根据处理模块的不同处理单元的运行信息综合确定存储单元的工作参数,从而在满足处理模块功能的同时达到处理模块和存储模块的性能最优化。Here, through the control method in the above step S101 to step S104, the working parameters of the storage unit can be comprehensively determined according to the operation information of different processing units of the processing module, so as to achieve the maximum performance of the processing module and the storage module while satisfying the functions of the processing module. optimization.
在一些实施例中,所述第一处理单元和所述第二处理单元的处理能力不同;或,所述第一处理单元和所述第二处理单元的处理能力相同。例如,第一处理单元和第二处理单元为CPU中大核和小核,具有不同的处理能力。又如,第一处理单元和第二处理单元为CPU中两个相同规格的核心,具有相同的处理能力。In some embodiments, the processing capabilities of the first processing unit and the second processing unit are different; or, the processing capabilities of the first processing unit and the second processing unit are the same. For example, the first processing unit and the second processing unit are large cores and small cores in the CPU, and have different processing capabilities. In another example, the first processing unit and the second processing unit are two cores of the same specification in the CPU and have the same processing capability.
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例再提供一种控制方法,所述方法应用于电子设备,图2为本申请实施例控制方法的实现流程示意图二,如图2所示,所述方法包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, the embodiment of the present application further provides a control method, the method is applied to electronic equipment, and FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the second implementation flow of the control method of the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 2, the method includes :
步骤S201、获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;Step S201, obtaining the first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S202、获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;Step S202, obtaining second running information of a second processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S203、根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;Step S203, determining the first operation information or the second operation information as target operation information according to preset rules;
举例来说,如果处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核,通常情况下大核和小核均处于工作状态,CPU会动态均衡的分配大核和小核的使用情况。在运行信息为功耗的情况下,如果大核的功耗大于小核的功耗,则目标运行信息为第一运行信息;反之,如果小核的功耗大于大核的功耗,则目标运行信息为第二运行信息。For example, if the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is the large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is the small core of the CPU, usually both the large core and the small core are in working state, and the CPU will dynamically and evenly allocate large The usage of cores and small cores. In the case where the running information is power consumption, if the power consumption of the large core is greater than that of the small core, the target running information is the first running information; otherwise, if the power consumption of the small core is greater than the power consumption of the large core, the target The running information is the second running information.
需要说明的是,运行信息包括但不限于运行频率、使用率、功耗、处理的进程数等信息,不同属性的运行信息可以对应不同的预设规则,例如当运行信息为频率时可以对应第一预设规则,当运行信息为功耗时可以对应第二预设规则,所述第一预设规则与所述第二预设规则不同。It should be noted that the running information includes but is not limited to running frequency, usage rate, power consumption, number of processed processes, etc., and different attributes of running information can correspond to different preset rules. For example, when the running information is frequency, it can correspond to the first A preset rule may correspond to a second preset rule when the running information is power consumption, and the first preset rule is different from the second preset rule.
步骤S204、根据所述目标运行信息,从多个预设的映射关系中确定出目标映射关系;Step S204, according to the target operation information, determine the target mapping relationship from a plurality of preset mapping relationships;
本申请实施例中,需要预先设置多个映射关系,进而根据目标运行信息从该多个映射关系中确定出目标映射关系,从而确定存储单元的工作参数。需要说明的是,所述映射关系的表现形式包括但不限于:映射表、映射函数等。本申请实施例对所述映射关系的表现形式并不做限制,任一表现形式(即任一类型)的映射关系均在本申请的保护范围内。In the embodiment of the present application, multiple mapping relationships need to be set in advance, and then the target mapping relationship is determined from the multiple mapping relationships according to the target running information, so as to determine the working parameters of the storage unit. It should be noted that, the expression form of the mapping relationship includes but is not limited to: a mapping table, a mapping function, and the like. The embodiment of the present application does not limit the expression form of the mapping relationship, and the mapping relationship of any expression form (that is, any type) falls within the protection scope of the present application.
举例来说,如果处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核、且大核和小核均处于工作状态。并且,大核对应第一频率表,小核对应第二频率表,所述第一频率表和所述第二频率表中包括不同的内存频率。如果目标运行信息为第一运行信息,则目标映射关系为第一频率表;反之,如果目标运行信息为第二运行信息,则目标映射关系为第二频率表。For example, if the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU, and both the large core and the small core are in a working state. In addition, the large core corresponds to the first frequency table, and the small core corresponds to the second frequency table, and the first frequency table and the second frequency table include different memory frequencies. If the target operating information is the first operating information, the target mapping relationship is the first frequency table; otherwise, if the target operating information is the second operating information, the target mapping relationship is the second frequency table.
在一些实施例中,每一处理单元均对应一预设的映射关系。即,所述多个预设的映射关系的数量和处理模块包括的处理单元的数量相关。In some embodiments, each processing unit corresponds to a preset mapping relationship. That is, the number of the plurality of preset mapping relationships is related to the number of processing units included in the processing module.
步骤S205、基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;Step S205, based on the target mapping relationship, determine the working parameters of the storage unit, the storage unit can communicate with the processing module;
举例来说,如果目标映射关系为第一频率表,存储单元的工作参数为内存频率,则确定内存的频率为所述第一频率表中的一目标频率值,并基于所述第一频率表进行跳频和/或调频,使得内存的频率切换为所述目标频率值。For example, if the target mapping relationship is the first frequency table, and the working parameter of the storage unit is the memory frequency, then determine that the frequency of the memory is a target frequency value in the first frequency table, and based on the first frequency table Perform frequency hopping and/or frequency modulation, so that the frequency of the memory is switched to the target frequency value.
步骤S206、控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。Step S206, controlling the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
这里,通过上述步骤S201至步骤S206中的控制方法,能够根据处理模块的不同处理单元的运行信息从多个映射关系中确定出目标映射关系,进而确定存储单元的工作参数,从而实现最佳的处理模块的性能和存储单元的性能的搭配。Here, through the control method in the above step S201 to step S206, the target mapping relationship can be determined from multiple mapping relationships according to the operation information of different processing units of the processing module, and then the working parameters of the storage unit can be determined, so as to achieve the best The collocation of the performance of the processing module and the performance of the storage unit.
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例再提供一种控制方法,所述方法应用于电子设备,所述方法包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment of the present application further provides a control method, the method is applied to electronic equipment, and the method includes:
步骤S211、获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;Step S211, obtaining the first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S212、获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;Step S212, obtaining second running information of the second processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S213、确定所述第一运行信息所需的存储单元的第一属性参数,以及所述第二运行信息所需的存储单元的第二属性参数;Step S213, determining the first attribute parameter of the storage unit required by the first operation information, and the second attribute parameter of the storage unit required by the second operation information;
这里,第一处理单元和第二处理单元能够与存储单元通信,进而可以通过第一处理单元的运行信息确定第一处理单元所需的存储单元的第一属性参数,也可以通过第二处理单元的运行信息确定第二处理单元所需的存储单元的第二属性参数。其中,所述第一属性参数和所述第二属性参数包括但不限于:存储单元的带宽、存储单元的容量等。Here, the first processing unit and the second processing unit can communicate with the storage unit, and then the first attribute parameter of the storage unit required by the first processing unit can be determined through the operation information of the first processing unit, or the second processing unit can The running information of the second processing unit determines the second attribute parameter of the storage unit required by the second processing unit. Wherein, the first attribute parameter and the second attribute parameter include, but are not limited to: the bandwidth of the storage unit, the capacity of the storage unit, and the like.
例如,如果处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核、且大核和小核均处于工作状态。则第一运行信息所需的存储单元的第一属性参数,以及所述第二运行信息所需的存储单元的第二属性参数可以为大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求,以及小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求。For example, if the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU, and both the large core and the small core are in a working state. Then the first attribute parameter of the storage unit required for the first operation information and the second attribute parameter of the storage unit required for the second operation information may be the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core, and the memory bandwidth requirement of the small core Memory bandwidth requirements corresponding to power consumption.
步骤S214、根据所述第一属性参数和所述第二属性参数的比对结果,确定将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;Step S214, according to the comparison result of the first attribute parameter and the second attribute parameter, determine that the first operation information or the second operation information is determined as the target operation information;
举例来说,第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核,可以将大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求和小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求进行比对,如果大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求高于小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求,则确定第一运行信息为目标运行信息。反之,如果大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求小于小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求,则确定第二运行信息为目标运行信息。For example, the first processing unit is the large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is the small core of the CPU. The memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core can be compared with the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the small core. , if the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core is higher than the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the small core, then determine the first running information as the target running information. On the contrary, if the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core is smaller than the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the small core, then the second running information is determined as the target running information.
步骤S215、根据所述目标运行信息,从多个预设的映射关系中确定出目标映射关系;Step S215, according to the target operation information, determine the target mapping relationship from a plurality of preset mapping relationships;
举例来说,如果大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求高于小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求,则确定第一运行信息为目标运行信息,进而目标映射关系为大核对应的映射关系。反之,如果大核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求小于小核的功耗对应的内存带宽需求,则确定第二运行信息为目标运行信息,进而目标映射关系为小核对应的映射关系。For example, if the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core is higher than the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the small core, then determine the first running information as the target running information, and then the target mapping relationship is the mapping relationship corresponding to the large core . Conversely, if the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the large core is smaller than the memory bandwidth requirement corresponding to the power consumption of the small core, then determine the second running information as the target running information, and then the target mapping relationship is the mapping relationship corresponding to the small core.
这里,可以通过不同处理单元所需的存储单元的属性参数信息,来确定目标映射关系,进而根据该目标映射关系确定存储单元的工作参数。如此,本申请实施例能够考虑各处理单元的运行状态,从而根据当前实际运行的应用来确定内存单元的工作参数,在满足功能的同时实现处理模块的各处理单元的性能最优化,以及存储单元的性能最优化。Here, the target mapping relationship may be determined through attribute parameter information of storage units required by different processing units, and then the working parameters of the storage unit may be determined according to the target mapping relationship. In this way, the embodiment of the present application can consider the running state of each processing unit, so as to determine the working parameters of the memory unit according to the currently running application, and realize the performance optimization of each processing unit of the processing module while satisfying the function, and the storage unit performance optimization.
步骤S216、基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;Step S216, based on the target mapping relationship, determine the working parameters of the storage unit, the storage unit can communicate with the processing module;
步骤S217、控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。Step S217, controlling the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例再提供一种控制方法,所述方法应用于电子设备,所述方法包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment of the present application further provides a control method, the method is applied to electronic equipment, and the method includes:
步骤S221、获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;Step S221, obtaining the first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S222、获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;Step S222, obtaining second running information of the second processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S223、根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;Step S223. Determine the first operation information or the second operation information as target operation information according to preset rules;
步骤S224、获得所述第一处理单元对应的第一映射关系,以及所述第二处理单元对应的第二映射关系;Step S224, obtaining a first mapping relationship corresponding to the first processing unit, and a second mapping relationship corresponding to the second processing unit;
这里,第一处理单元对应第一映射关系,第二处理单元对应第二映射关系。例如,如果处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核。大核对应第一内存频率表,小核对应第二内存频率表。第一内存频率表中包括4个频率:8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz、3600MHz。第二内存频率表中包括3个频率:6000MHz、4800MHz、2400MHz。Here, the first processing unit corresponds to the first mapping relationship, and the second processing unit corresponds to the second mapping relationship. For example, if the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU. The large core corresponds to the first memory frequency table, and the small core corresponds to the second memory frequency table. The first memory frequency table includes four frequencies: 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, and 3600MHz. The second memory frequency table includes three frequencies: 6000MHz, 4800MHz, and 2400MHz.
步骤S225、如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第一处理单元,将所述第一映射关系确定为目标映射关系;Step S225, if the target operation information belongs to the first processing unit, determine the first mapping relationship as the target mapping relationship;
步骤S226、如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第二处理单元,将所述第二映射关系确定为目标映射关系;Step S226, if the target operation information belongs to the second processing unit, determine the second mapping relationship as the target mapping relationship;
其中,所述第一映射关系包括所述工作参数的第一参数值集合,所述第二映射关系包括所述工作参数的第二参数值集合,所述第一参数值集合与所述第二参数值集合不同;Wherein, the first mapping relationship includes a first parameter value set of the working parameter, the second mapping relationship includes a second parameter value set of the working parameter, and the first parameter value set and the second The set of parameter values is different;
步骤S227、基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;Step S227, based on the target mapping relationship, determine the working parameters of the storage unit, the storage unit can communicate with the processing module;
举例来说,如果处理模块为CPU、第一处理单元为CPU的大核,第二处理单元为CPU的小核。大核对应第一内存频率表,小核对应第二内存频率表。第一内存频率表中包括4个频率:8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz、3600MHz。第二内存频率表中包括3个频率:6000MHz、4800MHz、2400MHz。大核的功耗所需的内存带宽大于小核的功耗所需的内存带宽,则根据第一内存频率表确定内存的目标频率,并跳频、调频至所述目标频率。反之,小核的功耗所需的内存带宽大于大核的功耗所需的内存带宽,则根据第二内存频率表确定内存的目标频率,并跳频、调频至所述目标频率。For example, if the processing module is a CPU, the first processing unit is a large core of the CPU, and the second processing unit is a small core of the CPU. The large core corresponds to the first memory frequency table, and the small core corresponds to the second memory frequency table. The first memory frequency table includes four frequencies: 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, and 3600MHz. The second memory frequency table includes three frequencies: 6000MHz, 4800MHz, and 2400MHz. If the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the large core is greater than the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the small core, the target frequency of the memory is determined according to the first memory frequency table, and the frequency is hopped and tuned to the target frequency. On the contrary, if the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the small core is greater than the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the large core, the target frequency of the memory is determined according to the second memory frequency table, and the frequency is hopped and tuned to the target frequency.
步骤S228、控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。Step S228, controlling the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例再提供一种控制方法,所述方法应用于电子设备,所述方法包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, this embodiment of the present application further provides a control method, the method is applied to electronic equipment, and the method includes:
步骤S231、获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;Step S231, obtaining the first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S232、获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;Step S232, obtaining second running information of the second processing unit of the processing module;
步骤S233、根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;Step S233. Determine the first operation information or the second operation information as target operation information according to preset rules;
步骤S234、获得所述第一处理单元对应的第一映射关系,以及所述第二处理单元对应的第二映射关系;Step S234, obtaining a first mapping relationship corresponding to the first processing unit, and a second mapping relationship corresponding to the second processing unit;
步骤S235、如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第一处理单元,将所述第一映射关系确定为目标映射关系;Step S235, if the target operation information belongs to the first processing unit, determine the first mapping relationship as the target mapping relationship;
步骤S236、如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第二处理单元,将所述第二映射关系确定为目标映射关系;Step S236, if the target operation information belongs to the second processing unit, determine the second mapping relationship as the target mapping relationship;
其中,所述第一映射关系包括所述工作参数的第一参数值集合,所述第二映射关系包括所述工作参数的第二参数值集合,所述第一参数值集合与所述第二参数值集合不同;Wherein, the first mapping relationship includes a first parameter value set of the working parameter, the second mapping relationship includes a second parameter value set of the working parameter, and the first parameter value set and the second The set of parameter values is different;
步骤S237、从所述目标映射关系包括的参数值集合中,确定出与所述目标运行信息相匹配的目标工作参数值,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;Step S237, from the parameter value set included in the target mapping relationship, determine the target operating parameter value that matches the target operation information, and the storage unit can communicate with the processing module;
举例来说,大核的功耗所需的内存带宽大于小核的功耗所需的内存带宽,则目标映射关系为大核对应的第一内存频率表。第一内存频率表包括的内存频率值为:8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz、3600MHz,且假设大核的功耗为第一数值,则从第一内存频率表所包括的内存频率值集合中,确定出与所述第一数值的功耗相匹配的目标内存频率为5200MHz。进而,需要控制内存以所述目标内存频率进行工作。For example, if the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the large core is greater than the memory bandwidth required by the power consumption of the small core, the target mapping relationship is the first memory frequency table corresponding to the large core. The memory frequency values included in the first memory frequency table are: 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, 3600MHz, and assuming that the power consumption of the large core is the first value, then from the memory frequency value set included in the first memory frequency table, determine The target memory frequency matching the power consumption of the first numerical value is 5200MHz. Furthermore, it is necessary to control the memory to work at the target memory frequency.
步骤S238、获得存储单元的当前工作参数值;Step S238, obtaining the current working parameter value of the storage unit;
例如,在从第一内存频率表所包括的内存频率值集合中,确定出与所述第一数值的功耗相匹配的目标内存频率后,需要获取内存的当前频率值,使得所述内存能够从当前频率值调整到目标内存频率。For example, after determining the target memory frequency that matches the power consumption of the first value from the set of memory frequency values included in the first memory frequency table, it is necessary to obtain the current frequency value of the memory so that the memory can Adjust from current frequency value to target memory frequency.
步骤S239、控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值。Step S239, controlling the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the target working parameter value.
这里,通过上述步骤S231至步骤S239所述的控制方法,能够根据不同处理单元的运行信息从各处理单元对应的映射关系中选择出一目标映射关系,进而确定存储单元的工作参数,从而实现最佳的处理模块的性能和存储单元的性能的搭配。Here, through the control method described in the above step S231 to step S239, a target mapping relationship can be selected from the mapping relationships corresponding to each processing unit according to the operation information of different processing units, and then the working parameters of the storage unit can be determined, so as to realize the optimal The best combination of processing module performance and storage unit performance.
在一些实施例中,所述步骤S239、控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值,包括:In some embodiments, the step S239, controlling the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the target working parameter value, includes:
步骤S2391、确定所述当前工作参数值与所述目标工作参数值之间的差值;Step S2391. Determine the difference between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value;
步骤S2392、如果所述差值大于预设阈值,确定中间参数值;Step S2392, if the difference is greater than a preset threshold, determine an intermediate parameter value;
举例来说,第一内存频率表中包括4个频率:8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz、3600MHz。第二内存频率表中包括3个频率:6000MHz、4800MHz、2400MHz。如果当前内存频率为5200MHz、目标内存频率为2400MHz、预设阈值为2000MHz,则当前内存频率与目标内存频率之间的差值大于预设阈值,需要确定中间参数值,确定出的中间参数值为4800MHz。又如,如果当前内存频率为8500MHz、目标内存频率为2400MHz、预设阈值为2000MHz,则当前内存频率与目标内存频率之间的差值大于预设阈值,需要确定中间参数值,确定出的中间参数值可以包括6000MHz和4800MHz。For example, the first memory frequency table includes four frequencies: 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, and 3600MHz. The second memory frequency table includes three frequencies: 6000MHz, 4800MHz, and 2400MHz. If the current memory frequency is 5200MHz, the target memory frequency is 2400MHz, and the preset threshold is 2000MHz, then the difference between the current memory frequency and the target memory frequency is greater than the preset threshold, and the intermediate parameter value needs to be determined. The determined intermediate parameter value is 4800MHz. As another example, if the current memory frequency is 8500MHz, the target memory frequency is 2400MHz, and the preset threshold is 2000MHz, then the difference between the current memory frequency and the target memory frequency is greater than the preset threshold, and the intermediate parameter value needs to be determined. Parameter values may include 6000MHz and 4800MHz.
需要说明的是,如果当前工作参数值与目标工作参数值之间的差值大于预设阈值,确定出的中间参数值可以包括一个参数值,也可以包括多个参数值。It should be noted that, if the difference between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value is greater than a preset threshold, the determined intermediate parameter value may include one parameter value, or may include multiple parameter values.
步骤S2393、控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述中间参数值,再从所述中间参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值;Step S2393, controlling the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the intermediate parameter value, and then adjust from the intermediate parameter value to the target working parameter value;
其中,所述中间参数值位于所述当前工作参数值和所述目标工作参数值之间、且所述中间参数值属于所述目标映射关系。Wherein, the intermediate parameter value is located between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value, and the intermediate parameter value belongs to the target mapping relationship.
本申请实施例中,如果当前工作参数值与目标工作参数值之间切换的跨度较大,则可以将所述中间参数值作为桥梁,先将存储单元从当前工作参数值切换至中间参数值,然后再将存储单元从中间参数值切换至目标工作参数值。并且,所述中间参数值属于目标映射关系,从而在工作参数为内存频率的情况下实现了不同映射关系间先跳频,同一映射关系内再切频的频率调整方案。In the embodiment of the present application, if the switching span between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value is large, the intermediate parameter value can be used as a bridge, and the storage unit is first switched from the current working parameter value to the intermediate parameter value, Then switch the storage unit from the intermediate parameter value to the target working parameter value. In addition, the intermediate parameter value belongs to the target mapping relationship, so that when the working parameter is the memory frequency, the frequency adjustment scheme of frequency hopping between different mapping relationships and frequency switching within the same mapping relationship is realized.
例如,第一内存频率表中包括4个频率:8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz、3600MHz。第二内存频率表中包括3个频率:6000MHz、4800MHz、2400MHz。当前内存频率为8500MHz属于第一内存频率表,目标内存频率为2400MHz属于第二内存频率表,则可以控制内存的内存频率先从第一内存频率表中的8500MHz切换至第二内存频率表中的6000MHz(即不同映射关系间先跳频),间隔1秒后,再控制内存的内存频率从第二内存频率表中的6000MHz切换至第二内存频率表中的4800MHz(即同一映射关系内再切频),间隔1秒后,再控制内存的内存频率从第二内存频率表中的4800MHz切换至第二内存频率表中的2400(即同一映射关系内再继续切频),从而实现智能动态的频率切换。即,本申请实施例中可以先确定当前工作参数值与目标工作参数值之间的参数值跨度(即包括的中间参数值数量),每间隔预设时间完成相邻两参数值之间的切换,直至切换至目标参数值。For example, the first memory frequency table includes four frequencies: 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, and 3600MHz. The second memory frequency table includes three frequencies: 6000MHz, 4800MHz, and 2400MHz. The current memory frequency is 8500MHz and belongs to the first memory frequency table, and the target memory frequency is 2400MHz and belongs to the second memory frequency table, then the memory frequency of the memory can be controlled from 8500MHz in the first memory frequency table to the second memory frequency table. 6000MHz (that is, frequency hopping between different mapping relationships first), and after an interval of 1 second, the memory frequency of the control memory is switched from 6000MHz in the second memory frequency table to 4800MHz in the second memory frequency table (that is, switching within the same mapping relationship Frequency), after an interval of 1 second, control the memory frequency of the memory to switch from 4800MHz in the second memory frequency table to 2400 in the second memory frequency table (that is, continue to switch frequency within the same mapping relationship), so as to realize intelligent and dynamic frequency switching. That is, in the embodiment of the present application, the parameter value span (that is, the number of intermediate parameter values included) between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value can be determined first, and the switching between two adjacent parameter values can be completed every preset time interval until switching to the target parameter value.
这里,通过上述步骤S2391至步骤S2393所述的方法,能够做到不同映射关系间先跳频,然后同一映射关系内切频。从而在频率跨度太大的情况下,减少体验不流畅的问题。Here, through the method described in the above step S2391 to step S2393, frequency hopping between different mapping relationships can be achieved first, and then frequency switching within the same mapping relationship can be achieved. In this way, when the frequency span is too large, the problem of unsmooth experience can be reduced.
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例再提供一种控制方法,该控制方法为一种内存智能跳频技术,能够实时地实现最佳的CPU性能与内存性能的搭配。下面,对该控制方法进行详细地说明:Based on the above-mentioned embodiments, the embodiments of the present application further provide a control method, which is a memory intelligent frequency hopping technology, which can realize the optimal combination of CPU performance and memory performance in real time. Below, this control method is described in detail:
内存的最大频率越来越高,内存频率从最小频率到最大频率跨度太大,而目前的SAGV调频方案中的频点只有4个,会导致每个频点间的跨度也很大,实际工作中不利于根据即时运行的应用实现极致性能的需求。The maximum frequency of the memory is getting higher and higher, and the span of the memory frequency from the minimum frequency to the maximum frequency is too large, while the current SAGV frequency modulation scheme only has 4 frequency points, which will lead to a large span between each frequency point. This is not conducive to the need for extreme performance based on instant-running applications.
并且,现在的CPU已经是异构计算(即支持大、小核计算),将来的CPU可能还会支持大、中、小核计算。由于大、中、小核设计的目的不一样,大核注重于性能方向,中核采用平衡模式,小核注重于电池续航方向,因此,目前的SAGV调频方案主要是针对大核的性能方向的优化,根本没有做到针对异构计算的优化,进行无法满足多种核心下的性能最优化。Moreover, the current CPU is already heterogeneous computing (that is, supporting large and small core computing), and future CPUs may also support large, medium, and small core computing. Due to the different design purposes of large, medium and small cores, the large core focuses on performance, the medium core adopts a balanced mode, and the small core focuses on battery life. Therefore, the current SAGV frequency modulation scheme is mainly aimed at optimizing the performance of large cores. , There is no optimization for heterogeneous computing at all, and performance optimization that cannot satisfy multiple cores.
图3A为SAGV调频方案的原理示意图,如图3A所示,即使电子设备的CPU支持大小核心,但是SAGV调频方式依然采用原本单一种类CPU核心对应的内存调频方式。也就是说,无论是大核心还是小核心,都采用一样的频率,即4个频点,8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz和3600MHz。这种情况下,大小核心相应带宽需求与内存提供的带宽需求不匹配,进而无法满足多种核心下的性能最优化。Figure 3A is a schematic diagram of the principle of the SAGV frequency modulation scheme. As shown in Figure 3A, even if the CPU of the electronic device supports large and small cores, the SAGV frequency modulation method still adopts the original memory frequency modulation method corresponding to a single type of CPU core. That is to say, whether it is a large core or a small core, the same frequency is used, that is, 4 frequency points, 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz and 3600MHz. In this case, the corresponding bandwidth requirements of the large and small cores do not match the bandwidth requirements provided by the memory, and thus cannot meet the performance optimization under multiple cores.
对于异构计算CPU的同频不代表同性能,应该按照CPU实时性能对应的内存带宽需求选择内存的频率。For heterogeneous computing, the same CPU frequency does not mean the same performance, and the frequency of the memory should be selected according to the memory bandwidth requirements corresponding to the real-time performance of the CPU.
即,针对异构计算的不同特性,本申请实施例增加对应的频率表(如大核对应一个频率表,小核也对应一个频率表,两个频率表不相同),实现多种核心的性能对内存带宽的需求,使内存在满足不同CPU核心功能的同时,能把性能做到最优。That is, in view of the different characteristics of heterogeneous computing, the embodiment of the present application adds corresponding frequency tables (for example, a large core corresponds to a frequency table, and a small core also corresponds to a frequency table, and the two frequency tables are different), so as to realize the performance of various cores The demand for memory bandwidth enables the memory to achieve optimal performance while meeting the core functions of different CPUs.
同时,增加不同频率表间的跳频技术,做到不同频率表间先跳频,然后同一频率表内再切频。如此,能够解有某些情况下频率需要的跨度太大,导致体验不流畅的问题。At the same time, increase the frequency hopping technology between different frequency tables, so that frequency hopping between different frequency tables is achieved first, and then frequency switching within the same frequency table. In this way, it is possible to solve the problem that in some cases the span required by the frequency is too large, resulting in an unsmooth experience.
在一些实施例中,可以根据程序在CPU中的占用率,即根据系统实际运行状态来进行内存频率的切换,例如据程序在CPU中的占用率较大的话则需要的内存频率高。跟CPU频率也有关系,如果切到小核后小核频率过高的话,是高频运行,需要的内存频率也要高些。并且,如果是集成显卡的话,可以根据CPU的不同核心的运行信息以及GPU的运行信息来共同决定内存的频率值。In some embodiments, the memory frequency can be switched according to the CPU occupancy rate of the program, that is, according to the actual operating state of the system. For example, if the CPU occupancy rate of the program is large, the memory frequency needs to be high. It is also related to the CPU frequency. If the frequency of the small core is too high after switching to the small core, it will run at high frequency, and the required memory frequency should be higher. Moreover, if it is an integrated graphics card, the frequency value of the memory can be jointly determined according to the operating information of different cores of the CPU and the operating information of the GPU.
下面针对本申请实施例的方案进行举例说明:The following is an example for the scheme of the embodiment of the present application:
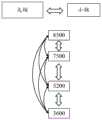
(1)大核和小核的调频、跳频方式;(1) Frequency modulation and frequency hopping of large core and small core;
图3B为本申请实施例内存智能跳频技术的原理示意图一,如图3B所示,CPU为异构计算,支持大核和小核两种核心。大核对应的频率表包括8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz和3600MHz四个频率,小核对应的频率表包括6000MHz、4800MHz、2400MHz三个频率。本申请实施例采取了更多种类频率调频,并且对应大小核采用不同等级的频率表调频方式。大小核心切换时,支持内存与CPU对应的跳频方式,如此,能够满足多种核心下的性能最优化。如图3B所示,当大核对应的内存频率切换为小核对应的内存频率时,频率先向下跳频,再调频。当小核对应的内存频率切换为大核对应的内存频率时,频率先向上跳频,再调频。当然,同一频率表中的不同频率值之间可以相互切换,例如小核对应的频率表中的三个频率值之间可以互相切换没有任何限制。对于不同频率表的频率值之间的切换可以设置允许的切换路径,例如,大核对应的频率表中的8500MHz如果切换至小核对应的频率表中的频率值,仅允许切换至小核对应的频率表中的6000MHz和4800MHz。又如,小核对应的频率表中的4800MHz如果切换至大核对应的频率表中的频率值,仅允许切换至大核对应的频率表中的5200MHz、7500MHz和8500MHz。FIG. 3B is a first schematic diagram of the principle of memory intelligent frequency hopping technology according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 3B , the CPU is heterogeneous computing and supports two types of cores: large core and small core. The frequency table corresponding to the large core includes four frequencies of 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz, and 3600MHz, and the frequency table corresponding to the small core includes three frequencies of 6000MHz, 4800MHz, and 2400MHz. The embodiment of the present application adopts more types of frequency modulation, and adopts frequency table frequency modulation methods of different levels corresponding to large and small cores. When the size of the core is switched, it supports the frequency hopping mode corresponding to the memory and the CPU. In this way, it can meet the performance optimization under multiple cores. As shown in FIG. 3B , when the memory frequency corresponding to the large core is switched to the memory frequency corresponding to the small core, the frequency is first hopped downwards and then adjusted. When the memory frequency corresponding to the small core is switched to the memory frequency corresponding to the large core, the frequency jumps up first, and then adjusts the frequency. Certainly, different frequency values in the same frequency table can be switched between each other, for example, there is no restriction on switching among the three frequency values in the frequency table corresponding to the small core. For the switching between the frequency values of different frequency tables, the allowed switching path can be set. For example, if 8500MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the large core is switched to the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to the small core, it is only allowed to switch to the frequency value corresponding to the small core. 6000MHz and 4800MHz in the frequency table. For another example, if the 4800MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the small core is switched to the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to the large core, it is only allowed to switch to 5200MHz, 7500MHz and 8500MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the large core.
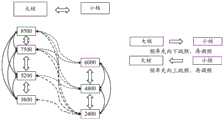
(2)大中小核调频、跳频方式;(2) Frequency modulation and frequency hopping of large, medium and small cores;
图3C为本申请实施例内存智能跳频技术的原理示意图二,如图3C所示,CPU为异构计算,支持大核、中核和小核三种核心。大核对应的频率表包括8500MHz、7500MHz、5200MHz和3600MHz四个频率,中核对应的频率表包括6000MHz、4800MHz和2400MHz三个频率,小核对应的频率表包括3600MHz、2400MHz和1333MHz三个频率。本申请实施例采取了更多种类频率调频,并且对应大中小核采用不同等级的频率表调频方式。大中小核心切换时,支持内存与CPU对应的跳频方式,如此,能够满足多种核心下的性能最优化。如图3C所示,当大核对应的内存频率、中核对应的内存频率和小核对应的内存频率存下切换时,频率先跳频,再调频。FIG. 3C is the second schematic diagram of the principle of memory intelligent frequency hopping technology according to the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 3C , the CPU is heterogeneous computing and supports three types of cores: large core, medium core and small core. The frequency table corresponding to the large core includes four frequencies of 8500MHz, 7500MHz, 5200MHz and 3600MHz, the frequency table corresponding to the medium core includes three frequencies of 6000MHz, 4800MHz and 2400MHz, and the frequency table corresponding to the small core includes three frequencies of 3600MHz, 2400MHz and 1333MHz. The embodiment of the present application adopts more types of frequency modulation, and adopts frequency table frequency modulation methods of different levels corresponding to large, medium and small cores. When switching between large, medium and small cores, it supports the frequency hopping mode corresponding to memory and CPU, so that it can meet the performance optimization under multiple cores. As shown in FIG. 3C , when the memory frequency corresponding to the large core, the memory frequency corresponding to the medium core, and the memory frequency corresponding to the small core are switched, the frequency is first hopped and then tuned.
在一些实施例中,还可以设置不同频率表的频率值之间的切换路径。如图3C所示,大核对应的频率表中的8500MHz如果切换至中核对应的频率表中的频率值,可以切换至中核对应的频率表中的6000MHz和4800MHz。中核对应的频率表中的4800MHz如果切换至小核对应的频率表中的频率值,可以切换至小核对应的频率表中的3600MHz、2400MHz和1333MHz。小核对应的频率表中的2400MHz如果切换至大核对应的频率表中的频率值,可以切换至大核对应的频率表中的3600MHz、5200MHz和7500MHz。In some embodiments, switching paths between frequency values of different frequency tables may also be set. As shown in FIG. 3C , if the 8500MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the large core is switched to the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to the medium core, it can be switched to 6000MHz and 4800MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the medium core. If the 4800MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the medium core is switched to the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to the small core, it can be switched to 3600MHz, 2400MHz and 1333MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the small core. If the 2400MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the small core is switched to the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to the large core, it can be switched to 3600MHz, 5200MHz and 7500MHz in the frequency table corresponding to the large core.
当然,图3B和图3C中每一核心对应的频率表,以及不同频率表的频率值之间的切换路径仅为示例。即,本领域技术人员可以根据实际使用需求设定每一核心对应的频率表中的频率值,以及不同频率表的频率值之间的切换路径,本申请实施例对此并不做限制。Of course, the frequency tables corresponding to each core in FIG. 3B and FIG. 3C , and the switching paths between frequency values in different frequency tables are just examples. That is, those skilled in the art can set the frequency value in the frequency table corresponding to each core and the switching path between frequency values in different frequency tables according to actual usage requirements, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
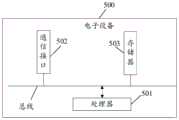
基于前述的实施例,本申请实施例提供一种控制装置,该装置包括所包括的各单元、以及各单元所包括的各模块、以及各模块所包括的各部件,可以通过电子设备中的处理器来实现;当然也可通过具体的逻辑电路实现;在实施的过程中,处理器可以为CPU(Central Processing Unit,中央处理器)、MPU(Microprocessor Unit,微处理器)、DSP(Digital Signal Processing,数字信号处理器)或FPGA(Field Programmable GateArray,现场可编程门阵列)等。Based on the aforementioned embodiments, this embodiment of the present application provides a control device, which includes each unit included, each module included in each unit, and each component included in each module, which can be processed by electronic equipment It can also be realized by a specific logic circuit; in the process of implementation, the processor can be CPU (Central Processing Unit, central processing unit), MPU (Microprocessor Unit, microprocessor), DSP (Digital Signal Processing , digital signal processor) or FPGA (Field Programmable GateArray, Field Programmable Gate Array), etc.
图4为本申请实施例控制装置的组成结构示意图,如图4所示,所述装置400包括:Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of the composition and structure of the control device of the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Fig. 4, the device 400 includes:
第一获取单元401,用于获得处理模块的第一处理单元的第一运行信息;The first obtaining unit 401 is configured to obtain first running information of the first processing unit of the processing module;
第二获取单元402,用于获得所述处理模块的第二处理单元的第二运行信息;A second acquiring unit 402, configured to acquire second running information of a second processing unit of the processing module;
确定单元403,用于根据所述第一运行信息和所述第二运行信息,确定存储单元的工作参数,所述存储单元能够与所述处理模块通信;A determining unit 403, configured to determine working parameters of a storage unit capable of communicating with the processing module according to the first operating information and the second operating information;
控制单元404,用于控制所述存储单元以所述工作参数工作。The control unit 404 is configured to control the storage unit to work with the working parameters.
在一些实施例中,所述确定单元403,包括:In some embodiments, the determining unit 403 includes:
第一确定模块,用于根据预设规则,将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息;A first determining module, configured to determine the first operating information or the second operating information as target operating information according to preset rules;
第二确定模块,用于根据所述目标运行信息,从多个预设的映射关系中确定出目标映射关系;The second determination module is configured to determine the target mapping relationship from a plurality of preset mapping relationships according to the target operation information;
第三确定模块,用于基于所述目标映射关系,确定存储单元的工作参数。The third determination module is configured to determine the working parameters of the storage unit based on the target mapping relationship.
在一些实施例中,所述第一确定模块,包括:In some embodiments, the first determination module includes:
第一确定子模块,用于确定所述第一运行信息所需的存储单元的第一属性参数,以及所述第二运行信息所需的存储单元的第二属性参数;A first determining submodule, configured to determine a first attribute parameter of a storage unit required by the first operating information, and a second attribute parameter of a storage unit required by the second operating information;
所述第一确定子模块,还用于根据所述第一属性参数和所述第二属性参数的比对结果,确定将所述第一运行信息或所述第二运行信息确定为目标运行信息。The first determination submodule is further configured to determine whether the first operation information or the second operation information is determined as the target operation information according to the comparison result of the first attribute parameter and the second attribute parameter .
在一些实施例中,所述第二确定模块,包括:In some embodiments, the second determination module includes:
获取部件,用于获得所述第一处理单元对应的第一映射关系,以及所述第二处理单元对应的第二映射关系;an acquiring component, configured to acquire a first mapping relationship corresponding to the first processing unit, and a second mapping relationship corresponding to the second processing unit;
确定部件,用于如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第一处理单元,将所述第一映射关系确定为目标映射关系;A determining component, configured to determine the first mapping relationship as a target mapping relationship if the target operation information belongs to the first processing unit;
所述确定部件,还用于如果所述目标运行信息属于所述第二处理单元,将所述第二映射关系确定为目标映射关系;The determining component is further configured to determine the second mapping relationship as a target mapping relationship if the target operation information belongs to the second processing unit;
其中,所述第一映射关系包括所述工作参数的第一参数值集合,所述第二映射关系包括所述工作参数的第二参数值集合,所述第一参数值集合与所述第二参数值集合不同。Wherein, the first mapping relationship includes a first parameter value set of the working parameter, the second mapping relationship includes a second parameter value set of the working parameter, and the first parameter value set and the second The set of parameter values is different.
在一些实施例中,所述第三确定模块,包括:In some embodiments, the third determination module includes:
第三确定子模块,用于从所述目标映射关系包括的参数值集合中,确定出与所述目标运行信息相匹配的目标工作参数值;The third determination submodule is used to determine the target operating parameter value matching the target operation information from the parameter value set included in the target mapping relationship;
对应地,所述控制单元404,包括:Correspondingly, the control unit 404 includes:
控制子单元,用于获得存储单元的当前工作参数值;The control subunit is used to obtain the current working parameter value of the storage unit;
所述控制子单元,还用于控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值。The control subunit is further configured to control the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the target working parameter value.
在一些实施例中,所述控制子单元,包括:In some embodiments, the control subunit includes:
差值确定模块,用于确定所述当前工作参数值与所述目标工作参数值之间的差值;a difference determination module, configured to determine the difference between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value;
中间值确定模块,用于如果所述差值大于预设阈值,确定中间参数值;An intermediate value determination module, configured to determine an intermediate parameter value if the difference is greater than a preset threshold;
控制模块,用于控制所述存储单元从所述当前工作参数值调整为所述中间参数值,再从所述中间参数值调整为所述目标工作参数值;A control module, configured to control the storage unit to adjust from the current working parameter value to the intermediate parameter value, and then adjust from the intermediate parameter value to the target working parameter value;
其中,所述中间参数值位于所述当前工作参数值和所述目标工作参数值之间、且所述中间参数值属于所述目标映射关系。Wherein, the intermediate parameter value is located between the current working parameter value and the target working parameter value, and the intermediate parameter value belongs to the target mapping relationship.
在一些实施例中,所述第一处理单元和所述第二处理单元的处理能力不同。In some embodiments, the first processing unit and the second processing unit have different processing capabilities.
以上装置实施例的描述,与上述方法实施例的描述是类似的,具有同方法实施例相似的有益效果。对于本申请装置实施例中未披露的技术细节,请参照本申请方法实施例的描述而理解。The description of the above device embodiment is similar to the description of the above method embodiment, and has similar beneficial effects as the method embodiment. For technical details not disclosed in the device embodiments of the present application, please refer to the description of the method embodiments of the present application for understanding.
需要说明的是,本申请实施例中,如果以软件功能模块的形式实现上述的控制方法,并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,也可以存储在一个计算机可读取存储介质中。基于这样的理解,本申请实施例的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一台电子设备(可以是个人计算机、服务器等)执行本申请各个实施例所述方法的全部或部分。而前述的存储介质包括:U盘、移动硬盘、ROM(Read Only Memory,只读存储器)、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。这样,本申请实施例不限制于任何特定的硬件和软件结合。It should be noted that, in the embodiment of the present application, if the above control method is implemented in the form of software function modules and sold or used as an independent product, it can also be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. Based on this understanding, the technical solution of the embodiment of the present application is essentially or the part that contributes to the prior art can be embodied in the form of a software product. The computer software product is stored in a storage medium and includes several instructions for Make an electronic device (which may be a personal computer, a server, etc.) execute all or part of the methods described in the various embodiments of the present application. The aforementioned storage medium includes: various media capable of storing program codes such as U disk, mobile hard disk, ROM (Read Only Memory, read only memory), magnetic disk or optical disk. Thus, embodiments of the present application are not limited to any specific combination of hardware and software.
对应地,本申请实施例提供一种电子设备,包括存储器和处理器,所述存储器存储有可在处理器上运行的计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述程序时实现上述实施例中提供的控制方法中的步骤。Correspondingly, an embodiment of the present application provides an electronic device, including a memory and a processor, the memory stores a computer program that can run on the processor, and the processor implements the computer programs provided in the above-mentioned embodiments when executing the program. The steps in the control method.
对应地,本申请实施例提供一种可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时实现上述控制方法中的步骤。Correspondingly, an embodiment of the present application provides a readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps in the above control method are implemented.
这里需要指出的是:以上存储介质和设备实施例的描述,与上述方法实施例的描述是类似的,具有同方法实施例相似的有益效果。对于本申请存储介质和设备实施例中未披露的技术细节,请参照本申请方法实施例的描述而理解。It should be pointed out here that: the descriptions of the above storage medium and device embodiments are similar to the descriptions of the above method embodiments, and have similar beneficial effects to those of the method embodiments. For technical details not disclosed in the storage medium and device embodiments of the present application, please refer to the description of the method embodiments of the present application for understanding.
需要说明的是,图5为本申请实施例电子设备的一种硬件实体示意图,如图5所示,该电子设备500的硬件实体包括:处理器501、通信接口502和存储器503,其中It should be noted that FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of a hardware entity of an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 5 , the hardware entity of the
处理器501通常控制电子设备500的总体操作。The
通信接口502可以使电子设备500通过网络与其他电子设备或服务器或平台通信。The
存储器503配置为存储由处理器501可执行的指令和应用,还可以缓存待处理器501以及电子设备500中各模块待处理或已经处理的数据(例如,图像数据、音频数据、语音通信数据和视频通信数据),可以通过FLASH(闪存)或RAM(Random Access Memory,随机访问存储器)实现。The memory 503 is configured to store instructions and applications executable by the
在本申请所提供的几个实施例中,应该理解到,所揭露的设备和方法,可以通过其它的方式实现。以上所描述的设备实施例仅仅是示意性的,例如,所述单元的划分,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式,如:多个单元或组件可以结合,或可以集成到另一个系统,或一些特征可以忽略,或不执行。另外,所显示或讨论的各组成部分相互之间的耦合、或直接耦合、或通信连接可以是通过一些接口,设备或单元的间接耦合或通信连接,可以是电性的、机械的或其它形式的。In the several embodiments provided in this application, it should be understood that the disclosed devices and methods may be implemented in other ways. The device embodiments described above are only illustrative. For example, the division of the units is only a logical function division. In actual implementation, there may be other division methods, such as: multiple units or components can be combined, or May be integrated into another system, or some features may be ignored, or not implemented. In addition, the coupling, or direct coupling, or communication connection between the components shown or discussed may be through some interfaces, and the indirect coupling or communication connection of devices or units may be electrical, mechanical or other forms of.
上述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是、或也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是、或也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,也可以分布到多个网络单元上;可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或全部单元来实现本实施例方案的目的。The units described above as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components displayed as units may or may not be physical units, that is, they may be located in one place or distributed to multiple network units; Part or all of the units can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment.
另外,在本申请各实施例中的各功能单元可以全部集成在一个处理模块中,也可以是各单元分别单独作为一个单元,也可以两个或两个以上单元集成在一个单元中;上述集成的单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用硬件加软件功能单元的形式实现。本领域普通技术人员可以理解:实现上述方法实施例的全部或部分步骤可以通过程序指令相关的硬件来完成,前述的程序可以存储于一计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,执行包括上述方法实施例的步骤;而前述的存储介质包括:移动存储设备、ROM、RAM、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application can be integrated into one processing module, or each unit can be used as a single unit, or two or more units can be integrated into one unit; the above-mentioned integration The unit can be realized in the form of hardware or in the form of hardware plus software functional unit. Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps to realize the above method embodiments can be completed by hardware related to program instructions, and the aforementioned program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the program is executed, the It includes the steps of the above method embodiments; and the aforementioned storage medium includes: various media that can store program codes such as removable storage devices, ROM, RAM, magnetic disks or optical disks.
本申请所提供的几个方法实施例中所揭露的方法,在不冲突的情况下可以任意组合,得到新的方法实施例。The methods disclosed in several method embodiments provided in this application can be combined arbitrarily to obtain new method embodiments under the condition of no conflict.
本申请所提供的几个产品实施例中所揭露的特征,在不冲突的情况下可以任意组合,得到新的产品实施例。The features disclosed in several product embodiments provided in this application can be combined arbitrarily without conflict to obtain new product embodiments.
本申请所提供的几个方法或设备实施例中所揭露的特征,在不冲突的情况下可以任意组合,得到新的方法实施例或设备实施例。The features disclosed in several method or device embodiments provided in this application can be combined arbitrarily without conflict to obtain new method embodiments or device embodiments.
以上所述,仅为本申请的具体实施方式,但本申请的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本申请揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到变化或替换,都应涵盖在本申请的保护范围之内。因此,本申请的保护范围应以所述权利要求的保护范围为准。The above is only a specific implementation of the application, but the scope of protection of the application is not limited thereto. Anyone familiar with the technical field can easily think of changes or substitutions within the technical scope disclosed in the application. Should be covered within the protection scope of this application. Therefore, the protection scope of the present application should be determined by the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310189128.6ACN116225330A (en) | 2023-02-22 | 2023-02-22 | Control method and device, equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310189128.6ACN116225330A (en) | 2023-02-22 | 2023-02-22 | Control method and device, equipment and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116225330Atrue CN116225330A (en) | 2023-06-06 |
Family
ID=86569217
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310189128.6APendingCN116225330A (en) | 2023-02-22 | 2023-02-22 | Control method and device, equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116225330A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170192480A1 (en)* | 2015-12-31 | 2017-07-06 | Le Holdings (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | Method for adjusting frequency modulation parameters and electronic device |
| US20180167878A1 (en)* | 2016-12-09 | 2018-06-14 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Core frequency/count decision-based thermal mitigation optimization for a multi-core integrated circuit |
| WO2022141735A1 (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2022-07-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | Processing apparatus, processing method, and related device |
| CN115237204A (en)* | 2022-07-25 | 2022-10-25 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Electronic device control method and electronic device |
| CN115269466A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-11-01 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | An electronic device and control method |
- 2023
- 2023-02-22CNCN202310189128.6Apatent/CN116225330A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170192480A1 (en)* | 2015-12-31 | 2017-07-06 | Le Holdings (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | Method for adjusting frequency modulation parameters and electronic device |
| US20180167878A1 (en)* | 2016-12-09 | 2018-06-14 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Core frequency/count decision-based thermal mitigation optimization for a multi-core integrated circuit |
| WO2022141735A1 (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2022-07-07 | 华为技术有限公司 | Processing apparatus, processing method, and related device |
| CN115237204A (en)* | 2022-07-25 | 2022-10-25 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | Electronic device control method and electronic device |
| CN115269466A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-11-01 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | An electronic device and control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9772967B2 (en) | I/O co-processor coupled hybrid computing device | |
| US12282378B2 (en) | Techniques for memory access in a reduced power state | |
| US10296069B2 (en) | Bandwidth-monitored frequency hopping within a selected DRAM operating point | |
| US8433931B2 (en) | Integrating energy budgets for power management | |
| US9612648B2 (en) | System and method for memory channel interleaving with selective power or performance optimization | |
| CN107924225B (en) | System and method for dynamically adjusting memory state transition timers | |
| US10503238B2 (en) | Thread importance based processor core parking and frequency selection | |
| EP3384395A1 (en) | System and method for memory management using dynamic partial channel interleaving | |
| CN109906421A (en) | Processor core based on thread importance divides | |
| JP2018505476A (en) | System and method for providing dynamic cache expansion in a multi-cluster heterogeneous processor architecture | |
| CN116028205A (en) | Resource scheduling method and electronic device | |
| CN116027880B (en) | Resource scheduling method and electronic device | |
| CN113127194A (en) | Management chip resource self-adaptive distribution method, device and medium | |
| WO2020102929A1 (en) | Unified power management | |
| CN117421129A (en) | Service execution method and device based on heterogeneous storage cluster and electronic equipment | |
| CN116028209B (en) | Resource scheduling method, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112667478A (en) | Control method and control device | |
| US20050039067A1 (en) | Method and related system for dynamically adjusting operational frequency | |
| US20160343416A1 (en) | Method of Dynamic Random Access Memory Resource Control | |
| CN116225330A (en) | Control method and device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115712337A (en) | Scheduling method and device of processor, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116721007B (en) | Mission control methods, systems and devices, electronic equipment and storage media | |
| CN106557365A (en) | Self-adaptive same-page memory merging method and electronic device thereof | |
| CN110809754B (en) | System and method for dynamic buffer size setting in a computing device | |
| CN118981282A (en) | Storage resource management method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |