CN116109871A - Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116109871A CN116109871ACN202310146110.8ACN202310146110ACN116109871ACN 116109871 ACN116109871 ACN 116109871ACN 202310146110 ACN202310146110 ACN 202310146110ACN 116109871 ACN116109871 ACN 116109871A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- image
- serum
- region
- valley
- whole blood
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/10—Segmentation; Edge detection
- G06T7/11—Region-based segmentation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/77—Processing image or video features in feature spaces; using data integration or data reduction, e.g. principal component analysis [PCA] or independent component analysis [ICA] or self-organising maps [SOM]; Blind source separation
- G06V10/774—Generating sets of training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医学检测领域,特别涉及一种血清状态识别方法、装置、设备及存储介质。The invention relates to the field of medical detection, in particular to a serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
医学全自动生化免疫检测流水线运行的过程中,经离心后的每一个血液样本都需要通过取样针吸取一定量的血清进行各项生化免疫检测。当对血液样本处理不得当时,会导致血清(血液凝固析出的淡黄色透明液体)中存在纤维蛋白丝或血凝块等,在流水线取样针吸取血清时导致堵针问题或者部分堵塞问题。发生堵针时,需要专业人员进行处理,增加了整体的检测周期和成本;若发生部分堵塞,使生化检测项目需要的血清量不足,导致检测结果不准确。所以取样针在吸取血清之前需要准确识别血清状态,过滤血清异常状态样本,避免取样针发生堵针问题。During the operation of the medical automatic biochemical immunoassay assembly line, each centrifuged blood sample needs to draw a certain amount of serum through the sampling needle for various biochemical immunoassays. When the blood sample is not handled properly, it will lead to the presence of fibrin filaments or blood clots in the serum (light yellow transparent liquid that is coagulated and precipitated), which will cause needle blocking or partial blockage when the pipeline sampling needle draws serum. When needle blockage occurs, professionals are required to deal with it, which increases the overall detection cycle and cost; if partial blockage occurs, the amount of serum required for biochemical test items will be insufficient, resulting in inaccurate test results. Therefore, before the sampling needle draws serum, it is necessary to accurately identify the serum state, filter the abnormal serum samples, and avoid the needle blocking problem of the sampling needle.
一般常用手段为采用人工的方式检测血清状态,需要专业人员对每一个离心后的待检测样本通过经验进行判别,此方法主观性强,经验要求高,工作量大。通常还可以进行MTS(Mahalanobis-Taguchi System,马氏田口系统)检堵检测,但该方法发出报警时已发生堵针,需要专业人员处理,无法避免堵针的发生。The commonly used method is to detect the serum status manually, which requires professionals to judge each sample to be tested after centrifugation through experience. This method is highly subjective, requires high experience, and requires a lot of work. Usually, MTS (Mahalanobis-Taguchi System) blockage detection can also be carried out. However, when the method sends out an alarm, the needle blockage has occurred, which requires professional handling, and the occurrence of needle blockage cannot be avoided.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明的目的在于提供一种血清状态识别方法、装置、设备及存储介质,解决了现有技术中血清状态检测效率低的问题。In view of this, the object of the present invention is to provide a serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium, which solves the problem of low serum state detection efficiency in the prior art.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明提供了一种血清状态识别方法,包括:In order to solve the above technical problems, the present invention provides a serum status recognition method, comprising:
获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;Obtain the image of the blood collection tube containing the serum and use it as a sample image;
利用目标检测算法对所述样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;Using a target detection algorithm to detect the sample image to obtain a whole blood region image;
利用分割算法对所述全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;Segmenting the whole blood region image by using a segmentation algorithm to obtain a serum region image;
对所述血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,所述预处理包括压缩处理;Preprocessing the serum area image to obtain a preprocessed serum area image, the preprocessing includes compression processing;
利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。The improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model is used to identify the pretreated serum area image to determine the serum status.
可选的,所述利用分割算法对所述全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像,包括:Optionally, using a segmentation algorithm to segment the whole blood region image to obtain a serum region image includes:
对所述全血区域图像进行灰度化处理,得到灰度化图像;performing grayscale processing on the image of the whole blood region to obtain a grayscale image;
利用高斯滤波对所述灰度化图像进行平滑处理,得到平滑图像;smoothing the grayscale image by using Gaussian filtering to obtain a smooth image;
计算所述平滑图像的图像直方图,根据所述图像直方图的波谷确定阈值;Calculating the image histogram of the smooth image, determining the threshold according to the valley of the image histogram;
利用所述阈值对所述平滑图像进行二值化处理和形态学开运算,得到二值化图像;performing binarization processing and morphological opening operation on the smoothed image by using the threshold value to obtain a binarized image;
计算所述二值化图像中最大面积对应的外接矩形,得到血凝块区域上边界值;Calculate the circumscribed rectangle corresponding to the largest area in the binarized image to obtain the upper boundary value of the blood clot area;
根据所述血凝块区域上边界值确定截取区间,根据所述截取区间对所述全血区域图像进行截取,得到所述血清区域图像。A clipping interval is determined according to the upper boundary value of the blood clot region, and the image of the whole blood region is clipped according to the clipping interval to obtain the image of the serum region.
可选的,所述计算所述平滑图像的图像直方图,根据所述图像直方图的波谷确定阈值,包括:Optionally, the calculating the image histogram of the smoothed image, and determining the threshold according to the valley of the image histogram includes:
统计所述图像直方图中每个灰度值对应像素的个数,得到统计值数组;Counting the number of pixels corresponding to each gray value in the image histogram to obtain an array of statistical values;
计算所述统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值,并根据所述差值确定波动点;calculating the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array, and determining fluctuation points according to the difference;
对所述波动点进行过滤,得到第一数组;Filtering the fluctuation points to obtain a first array;
根据所述第一数组计算得到第一波峰信息、第一波谷信息、第二波峰信息和第二波谷信息,所述第一波峰信息包括所述第一波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第一波谷信息包括所述第一波谷对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第二波峰信息包括所述第二波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第二波谷信息包括所述第二波谷对应的灰度值和统计值;The first peak information, the first valley information, the second peak information and the second valley information are calculated according to the first array, and the first peak information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the first peak, so The first valley information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the first valley, the second peak information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the second peak, and the second valley information includes the The gray value and statistical value corresponding to the second valley;
当所述第二波峰对应的统计值与所述第一波峰对应的统计值的比值大于第一预设值或所述第一波谷对应的灰度值与所述第一波峰对应的灰度值的差值小于第二预设值时,则所述第二波谷对应的灰度值为所述阈值;否则,所述第一波谷对应的灰度值为所述阈值。When the ratio of the statistical value corresponding to the second peak to the statistical value corresponding to the first peak is greater than the first preset value or the gray value corresponding to the first valley and the gray value corresponding to the first peak When the difference is smaller than the second preset value, the gray value corresponding to the second valley is the threshold; otherwise, the gray value corresponding to the first valley is the threshold.
可选的,所述对所述血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,所述预处理包括压缩处理,包括:Optionally, the preprocessing is performed on the serum area image to obtain a preprocessed serum area image, and the preprocessing includes compression processing, including:
利用自动对比度算法对所述血清区域图像进行细节处理,得到第一图像;performing detailed processing on the image of the serum region by using an automatic contrast algorithm to obtain a first image;
将所述第一图像进行无形变尺寸压缩得到所述预处理血清区域图像。performing non-deformable size compression on the first image to obtain the preprocessed serum region image.
可选的,所述利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态,包括:Optionally, the use of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the preprocessed serum area image and determine the serum status includes:
所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型中第一阶段、第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段各包括两个残差模块,所述残差模块包括注意力机制模块;The first stage, the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage each include two residual modules in the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model, and the residual module includes an attention mechanism module;
利用所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述血清区域图像进行识别,确定识别结果。Using the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the serum region image, and determine the identification result.
可选的,所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型,还包括:Optionally, the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model also includes:
所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型的所述第二阶段、所述第三阶段和所述第四阶段的输出分别经自适应平均池化层后进行级联,所述级联后的输出与全连接层连接。The output of the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model is cascaded after the adaptive average pooling layer respectively, and the output after the cascade is Connect with the fully connected layer.
可选的,所述利用目标检测算法对所述样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像,包括:Optionally, the detection of the sample image by using a target detection algorithm to obtain an image of a whole blood region includes:
利用YOLOv5s目标检测模型对所述样本图像进行检测,得到所述全血区域图像。The sample image is detected by using the YOLOv5s target detection model to obtain the whole blood region image.
本发明还提供了一种血清状态识别装置,包括:The present invention also provides a serum status identification device, comprising:
获取模块,用于获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;The obtaining module is used to obtain the image of the blood collection tube containing the serum as a sample image;
目标检测模块,用于利用目标检测算法对所述样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;A target detection module, configured to detect the sample image using a target detection algorithm to obtain an image of a whole blood region;
区域分割模块,用于利用分割算法对所述全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;A region segmentation module, configured to segment the whole blood region image using a segmentation algorithm to obtain a serum region image;
预处理模块,用于对所述血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,所述预处理包括压缩处理;A preprocessing module, configured to preprocess the serum area image to obtain a preprocessed serum area image, the preprocessing includes compression processing;
图像识别模块,用于利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。The image recognition module is used to use the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to recognize the preprocessed serum area image and determine the serum state.
本发明还提供了一种血清状态识别设备,包括:The present invention also provides a serum status identification device, comprising:
存储器,用于存储计算机程序;memory for storing computer programs;
处理器,用于执行所述计算机程序时实现上述的血清状态识别方法的步骤。A processor, configured to implement the steps of the above-mentioned serum status identification method when executing the computer program.
本发明还提供了一种存储介质,所述存储介质上存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被处理器执行时实现上述的血清状态识别方法的步骤。The present invention also provides a storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the above serum status identification method are realized.
可见,本发明通过获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理;利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。本发明采用机器视觉和深度学习相结合的技术准确识别采血管中血清状态,可以实现取样针在吸取血清之前准确识别血清状态,过滤血清异常状态样本,避免取样针发生堵针问题,还可以兼容多种规格采血管和含分离胶的采血管,对采血管血清中含有纤维蛋白丝和血凝块等异常状态能够准确识别。It can be seen that the present invention obtains the image of the blood collection tube containing serum as a sample image; uses the target detection algorithm to detect the sample image to obtain the whole blood area image; uses the segmentation algorithm to segment the whole blood area image to obtain the serum area image ; Preprocess the serum area image to obtain the preprocessed serum area image, and the preprocessing includes compression processing; use the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the preprocessed serum area image to determine the serum status. The present invention uses the combination of machine vision and deep learning technology to accurately identify the serum state in the blood collection tube, can realize the accurate identification of the serum state by the sampling needle before absorbing the serum, filters the abnormal state samples of the serum, avoids the needle blocking problem of the sampling needle, and is also compatible Blood collection tubes of various specifications and blood collection tubes containing separating gel can accurately identify abnormal states such as fibrin filaments and blood clots in serum of blood collection tubes.
此外,本发明还提供了一种血清状态识别装置、设备及存储介质,同样具有上述有益效果。In addition, the present invention also provides a serum state identification device, equipment and storage medium, which also have the above beneficial effects.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据提供的附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are only It is an embodiment of the present invention, and those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings according to the provided drawings without creative work.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别方法的流程图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a method for identifying serum status provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态分类模型的示例图;Figure 2 is an example diagram of a serum status classification model provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明实施例提供的一种残差模块和注意力机制模块的示例图;FIG. 3 is an example diagram of a residual module and an attention mechanism module provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图4为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别装置的结构示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a serum status identification device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别设备的结构示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a serum status identification device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is only some embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
请参考图1,图1为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别方法的流程图。该方法可以包括:Please refer to FIG. 1 , which is a flowchart of a serum status identification method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The method can include:
S101:获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像。S101: Obtain an image of a blood collection tube filled with serum and use it as a sample image.
本实施例的执行主体为终端。本实施例并不限定终端的种类,只要是能够完成血清状态识别的操作即可。例如,终端可以是专用型终端;或者终端还可以是通用性终端。本实施例并不限定装有血清的采血管图像的获取方式。例如,可以使用工业相机拍摄装有血清的采血管以此得到视频流,从视频流中截取拍摄效果明显的图像;或者还可以采用相机拍摄装有血清的采血管以此得到图像。本实施例可以利用工业相机拍摄获取离心后的血液样本图像,得到装有血清的采血管图像,通过该图像识别血清中含有纤维蛋白丝、血凝块等异常状态。The execution subject of this embodiment is a terminal. This embodiment does not limit the type of terminal, as long as it can complete the operation of serum state identification. For example, the terminal may be a dedicated terminal; or the terminal may also be a general purpose terminal. This embodiment does not limit the manner of acquiring the image of the blood collection tube containing serum. For example, an industrial camera can be used to capture a blood collection tube containing serum to obtain a video stream, and an image with an obvious shooting effect can be intercepted from the video stream; or a camera can be used to capture a blood collection tube containing serum to obtain an image. In this embodiment, an industrial camera can be used to capture images of centrifuged blood samples to obtain images of blood collection tubes containing serum, and to identify abnormal states such as fibrin filaments and blood clots in serum through the images.
S102:利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像。S102: Using a target detection algorithm to detect the sample image to obtain a whole blood region image.
本实施例并不限定具体的目标检测算法,只要是能够实现目标检测即可。例如,目标检测算法可以是YOLOv5s目标检测算法;或者目标检测算法还可以是YOLOv4目标检测算法。This embodiment does not limit a specific target detection algorithm, as long as it can realize target detection. For example, the target detection algorithm may be the YOLOv5s target detection algorithm; or the target detection algorithm may also be the YOLOv4 target detection algorithm.
进一步的,为了保证目标检测效果,上述利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像,可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to ensure the target detection effect, the above-mentioned detection of the sample image by using the target detection algorithm to obtain the image of the whole blood region may include the following steps:
利用YOLOv5s目标检测模型对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像。The sample image is detected by using the YOLOv5s target detection model to obtain the image of the whole blood area.
本实施例可以采用YOLOv5s(一种目标检测算法模型)目标检测模型实现对采血管中全血区域的检测。本实施例并不限定YOLOv5s目标检测算法中的具体设置,例如可以采用Adam优化器(自适应矩估计优化器),将初始学习率设置为0.001,模型训练次数设定为100轮,在测试集上0.996map@0.5(map@0.5:Iou=0.5时(Iou:Intersection over Union(一种测量在特定数据集中检测相应物体准确度的一个标准)),计算每个类别下所有图片的平均ap(ap:average precision,模型评价指标))。可以理解的是,在训练目标检测模型之前,需要对样本数据集的收集,本技术利用LabelImg(图形图像注释工具)标注工具对收集的血清样本图像进行目标标注,并可以按照7:2:1的比例随机划分为训练集、验证集和测试集并进行模型的训练以获得最佳的模型参数。目标检测模型训练完成后,就可以利用目标检测模型对样本图像进行目标检测,得到全血区域图像。In this embodiment, the YOLOv5s (a target detection algorithm model) target detection model can be used to detect the whole blood area in the blood collection tube. This embodiment does not limit the specific settings in the YOLOv5s target detection algorithm. For example, an Adam optimizer (adaptive moment estimation optimizer) can be used, the initial learning rate is set to 0.001, and the number of model training times is set to 100 rounds. In the test set On 0.996map@0.5 (map@0.5: Iou=0.5 (Iou: Intersection over Union (a standard for measuring the accuracy of detecting corresponding objects in a specific data set)), calculate the average ap of all pictures under each category ( ap: average precision, model evaluation index)). It can be understood that before training the target detection model, the collection of sample data sets is required. This technology uses the LabelImg (graphic image annotation tool) labeling tool to carry out target labeling on the collected serum sample images, and can follow the 7:2:1 The ratio of is randomly divided into training set, verification set and test set and the model is trained to obtain the best model parameters. After the target detection model is trained, the target detection model can be used to perform target detection on the sample image to obtain an image of the whole blood region.
S103:利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像。S103: Using a segmentation algorithm to segment the whole blood region image to obtain a serum region image.
本实施例中的全血区域包括上层血清区域、下层血凝块区域、采血管为分离胶采血管时,会存在中间层的分离胶区域。本实施例并不限定具体的分割算法,只要是能够实现图像分割即可。本实施例并不限定具体的分割处理流程。例如,可以直接采用分割算法直接对全血区域图像进行分割;或者还可以将全血区域图像进行灰度化平滑处理后,再采用分割算法进行分割。The whole blood area in this embodiment includes the upper serum area, the lower blood clot area, and when the blood collection tube is a separation gel blood collection tube, there will be a separation gel area in the middle layer. This embodiment does not limit the specific segmentation algorithm, as long as the image segmentation can be realized. This embodiment does not limit the specific segmentation processing flow. For example, the image of the whole blood region can be directly segmented by using a segmentation algorithm; or the image of the whole blood region can be grayscaled and smoothed, and then segmented by a segmentation algorithm.
进一步的,为了更有效地对全血区域图像进行分割,提取得到血清区域图像,上述利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像,可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to more effectively segment the whole blood region image and extract the serum region image, the above-mentioned segmenting the whole blood region image by using the segmentation algorithm to obtain the serum region image may include the following steps:
步骤21:对全血区域图像进行灰度化处理,得到灰度化图像;Step 21: Perform grayscale processing on the image of the whole blood region to obtain a grayscale image;
步骤22:利用高斯滤波对灰度化图像进行平滑处理,得到平滑图像;Step 22: smoothing the grayscale image by using Gaussian filtering to obtain a smooth image;
步骤23:计算平滑图像的图像直方图,根据图像直方图的波谷确定阈值;Step 23: Calculate the image histogram of the smooth image, and determine the threshold according to the valley of the image histogram;
步骤24:利用阈值对平滑图像进行二值化处理和形态学开运算,得到二值化图像;Step 24: Perform binarization processing and morphological opening operation on the smoothed image by thresholding to obtain a binarized image;
步骤25:计算二值化图像中最大面积对应的外接矩形,得到血凝块区域上边界值;Step 25: Calculate the circumscribed rectangle corresponding to the largest area in the binarized image to obtain the upper boundary value of the blood clot area;
步骤26:根据血凝块区域上边界值确定截取区间,根据截取区间对所述全血区域图像进行截取,得到血清区域图像。Step 26: Determine a clipping interval according to the upper boundary value of the blood clot region, and clip the image of the whole blood region according to the clipping interval to obtain a serum region image.
本实施例对全血区域图像进行灰度化处理,并进一步利用高斯滤波进行平滑处理,计算经灰度化、平滑处理后图像的图像直方图,根据图像直方图的波谷对应的灰度值确定阈值,利用该阈值对平滑图像进行二值化处理和形态学开运算,得到二值化图像,计算该二值化图像中最大面积对应的外接矩形,以此确定血凝块区域的上边界值,在该上边界值的基础上,设定截取区间,得到截取区域,得到血清区域图像。本实施例并不限定截取区间。例如,截取区域可以是根据上边界值向下浮动100像素值得到的截取区域;或者截取区间还可以是根据上边界值向下浮动50像素值得到的截取区域。本实施例并不限定阈值的具体确定方式。例如,可以是将图像直方图的第一个波谷值对应的灰度值确定为阈值;或者还可以是将图像直方图的波动点进行过滤,通过第一波谷、第一波峰、第二波峰和第二波谷,确定得到第一有效波谷,并将第一有效波谷对应的灰度值作为该阈值。In this embodiment, grayscale processing is performed on the image of the whole blood region, and Gaussian filtering is further used for smoothing processing, and the image histogram of the grayscaled and smoothed image is calculated, and determined according to the gray value corresponding to the trough of the image histogram Threshold, using the threshold to perform binarization and morphological opening operations on the smooth image to obtain a binarized image, and calculate the circumscribed rectangle corresponding to the largest area in the binarized image to determine the upper boundary value of the blood clot area , on the basis of the upper boundary value, the clipping interval is set to obtain the clipped area and the image of the serum area. This embodiment does not limit the clipping interval. For example, the clipping area may be a clipping area obtained by floating 100 pixels downward according to the upper boundary value; or the clipping interval may be a clipping area obtained by floating 50 pixels downward according to the upper boundary value. This embodiment does not limit the specific manner of determining the threshold. For example, the gray value corresponding to the first valley value of the image histogram may be determined as the threshold; or the fluctuation point of the image histogram may be filtered, and the The second valley is determined to obtain the first effective valley, and the gray value corresponding to the first effective valley is used as the threshold.
进一步的,为了提高分割阈值的精确性,提高图像分割的准确性,上述计算平滑图像的图像直方图,根据图像直方图的波谷确定阈值,可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to improve the accuracy of the segmentation threshold and improve the accuracy of image segmentation, the above-mentioned calculation of the image histogram of the smooth image, and determining the threshold according to the valley of the image histogram may include the following steps:
步骤31:统计图像直方图中每个灰度值对应像素的个数,得到统计值数组;Step 31: Count the number of pixels corresponding to each gray value in the image histogram to obtain an array of statistical values;
步骤32:计算统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值,并根据差值确定波动点;Step 32: Calculate the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array, and determine the fluctuation point according to the difference;
步骤33:对波动点进行过滤,得到第一数组;Step 33: Filter the fluctuation points to obtain the first array;
步骤34:根据第一数组计算得到第一波峰信息、第一波谷信息、第二波峰信息和第二波谷信息,第一波峰信息包括第一波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,第一波谷信息包括第一波谷对应的灰度值和统计值,第二波峰信息包括第二波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,第二波谷信息包括第二波谷对应的灰度值和统计值;Step 34: Calculate the first peak information, the first valley information, the second peak information and the second valley information according to the first array, the first peak information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the first peak, the first valley information Including the grayscale value and statistical value corresponding to the first trough, the second peak information includes the grayscale value and statistical value corresponding to the second peak, and the second trough information includes the grayscale value and statistical value corresponding to the second trough;
步骤35:当第二波峰对应的统计值与第一波峰对应的统计值的比值大于第一预设值或第一波谷对应的灰度值与第一波峰对应的灰度值的差值小于第二预设值时,则第二波谷对应的灰度值为阈值;否则,第一波谷对应的灰度值为阈值。Step 35: When the ratio of the statistical value corresponding to the second peak to the statistical value corresponding to the first peak is greater than the first preset value or the difference between the gray value corresponding to the first valley and the gray value corresponding to the first peak is smaller than the first preset value When two preset values are used, the gray value corresponding to the second valley is the threshold; otherwise, the gray value corresponding to the first valley is the threshold.
本实施例中通过统计图像直方图中每个灰度值对应像素的个数,得到统计值数组,并计算统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值,即与相邻前一位的差值,根据差值确定波动点,将波动点进行过滤,得到第一数组,根据第一数组计算得到两个波谷和两个波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,当第二波峰对应的统计值与第一波峰对应的统计值的比值大于第一预设值或第一波谷对应的灰度值与第一波峰对应的灰度值的差值小于第二预设值时,则第二波谷对应的灰度值为阈值;否则,第一波谷对应的灰度值为阈值。本实施例中并不限定统计值数组中相邻值之间差值的计算个数。例如,可以只计算前128位灰度值对应的统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值;或者还可以计算全部即256位灰度值对应的统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值。本实施例并不限定第一预设值和第二预设值,用户可以根据实际情况进行设定。In this embodiment, by counting the number of pixels corresponding to each gray value in the image histogram, the statistical value array is obtained, and the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array is calculated, that is, the difference with the previous adjacent one Value, determine the fluctuation point according to the difference, filter the fluctuation point to obtain the first array, calculate the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the two troughs and two peaks according to the first array, when the statistical value corresponding to the second peak When the ratio of the statistical value corresponding to the first peak is greater than the first preset value or the difference between the gray value corresponding to the first valley and the gray value corresponding to the first peak is smaller than the second preset value, the second valley corresponds to The gray value of is the threshold; otherwise, the gray value corresponding to the first valley is the threshold. In this embodiment, the number of calculated differences between adjacent values in the statistical value array is not limited. For example, you can only calculate the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array corresponding to the first 128-bit grayscale value; or you can also calculate the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array corresponding to all 256-bit grayscale values value. This embodiment does not limit the first preset value and the second preset value, and the user can set them according to actual conditions.
为了更好的理解分割阈值的确定过程,举例如下:第一阶段为图像直方图的统计值数组;第二阶段为前128位统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值;第三阶段为过滤波动点后的差值,过滤过程为当在一段区间内突然存在一个异号数值,则将该异号数值设为与该区间内符号相同的数值,例如:{-2177、-615、-465、31、-1015、-598}过滤为{-2177、-615、-465、-1、-1015、-598};{4、4、-8、28、23、142}过滤为{4、4、1、28、23、142};第四阶段为根据过滤波动点后的数据得到的第一波峰、第一波谷、第二波峰和第二波谷对应的灰度值。In order to better understand the determination process of the segmentation threshold, an example is as follows: the first stage is the statistical value array of the image histogram; the second stage is the difference between adjacent values in the first 128-bit statistical value array; the third stage is The difference after filtering the fluctuation points. The filtering process is that when there is a value with a different sign in a range suddenly, the value with the different sign is set to the same value as the sign in the range, for example: {-2177, -615, - 465, 31, -1015, -598} are filtered as {-2177, -615, -465, -1, -1015, -598}; {4, 4, -8, 28, 23, 142} are filtered as {4 , 4, 1, 28, 23, 142}; the fourth stage is the gray value corresponding to the first peak, the first trough, the second peak and the second trough obtained according to the data after filtering the fluctuation points.
S104:对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理。S104: Perform preprocessing on the serum area image to obtain a preprocessed serum area image, where the preprocessing includes compression processing.
本实施例对血清区域图像进行包括压缩处理的预处理操作,以此得到可以进行后续分类模型的图像。本实施例并不限定预处理操作的具体内容。例如预处理可以只包括压缩处理;或者预处理还可以包括细节处理和无形变尺寸压缩处理。In this embodiment, a preprocessing operation including compression processing is performed on the image of the serum region, so as to obtain an image that can be used for subsequent classification models. This embodiment does not limit the specific content of the preprocessing operation. For example, the preprocessing may only include compression processing; or the preprocessing may also include detail processing and non-deformable size compression processing.
进一步的,为了提高识别准确性,上述对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理,可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to improve the recognition accuracy, the above-mentioned serum region image is preprocessed to obtain the preprocessed serum region image, and the preprocessing includes compression processing, which may include the following steps:
步骤41:利用自动对比度算法对血清区域图像进行细节处理,得到第一图像;Step 41: using an automatic contrast algorithm to perform detailed processing on the image of the serum area to obtain the first image;
步骤42:将第一图像进行无形变尺寸压缩得到预处理血清区域图像。Step 42: Perform non-deformable size compression on the first image to obtain a preprocessed serum region image.
本实施例采用自动对比度算法提升血清区域的细节,然后将图像进行无形变尺寸压缩处理,得到尺寸为240x464的图像。In this embodiment, an automatic contrast algorithm is used to enhance the details of the serum area, and then the image is subjected to deformation-free size compression processing to obtain an image with a size of 240x464.
S105:利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。S105: Using the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the pre-processed serum region image to determine the serum status.
Resnet50网络结构是经典的图像分类模型,本实施例采用改进的Resnet50网络结构(Residual Neural Network,残差神经网络)图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别。本实施例中图像分类模型的训练时采用迁移学习,使用ImageNet(一个公开数据集)数据集上预训练的改进的Resnet50网络结构模型初始化新模型的参数,以此得到训练好的图像分类模型,利用该模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。The Resnet50 network structure is a classic image classification model. In this embodiment, an improved Resnet50 network structure (Residual Neural Network, residual neural network) image classification model is used to identify the preprocessed serum region image. In the present embodiment, the training of the image classification model adopts migration learning, and uses the improved Resnet50 network structure model pre-trained on the ImageNet (a public data set) data set to initialize the parameters of the new model, so as to obtain the trained image classification model. The model is used to identify pre-treated serum region images to determine serum status.
进一步的,为了保证识别精度同时加速模型推理的速度,上述利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态,可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to ensure the recognition accuracy and accelerate the speed of model reasoning, the above-mentioned use of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the pre-processed serum area image and determine the serum status may include the following steps:
步骤51:改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型中第一阶段、第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段各包括两个残差模块,残差模块包括注意力机制模块;Step 51: In the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model, the first stage, the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage each include two residual modules, and the residual module includes an attention mechanism module;
步骤52:利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对血清区域图像进行识别,确定识别结果。Step 52: Use the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the image of the serum region, and determine the identification result.
进一步的,为了增加低维度特征信息,提高分类准确性,上述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型,还可以包括以下步骤:Further, in order to increase the low-dimensional feature information and improve the classification accuracy, the above-mentioned improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model may also include the following steps:
改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型的第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段的输出分别经自适应平均池化层进行级联,级联后的输出与全连接层连接。The output of the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model are respectively cascaded through the adaptive average pooling layer, and the cascaded output is connected with the fully connected layer.
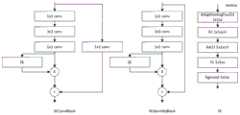
为了更好的理解血清状态分类过程,可以参考图2和图3,图2为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态分类模型的示例图、图3为本发明实施例提供的一种残差模块和注意力机制模块的示例图。In order to better understand the serum status classification process, you can refer to Figure 2 and Figure 3, Figure 2 is an example diagram of a serum status classification model provided by the embodiment of the present invention, and Figure 3 is a residual provided by the embodiment of the present invention Example diagram of modules and attention mechanism modules.
应用本发明实施例提供的血清状态识别方法,通过获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理;利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。本发明采用机器视觉和深度学习相结合的技术准确识别采血管中血清状态,可以实现取样针在吸取血清之前准确识别血清状态,过滤血清异常状态样本,避免取样针发生堵针问题,还可以兼容多种规格采血管和含分离胶的采血管,对采血管血清中含有纤维蛋白丝和血凝块等异常状态能够准确识别。并且,采用YOLOv5s目标检测模型保证了目标检测效果;并且,对全血区域图像进行一系列的处理,能够更有效地对全血区域图像进行分割;并且,采用对波动点进行过滤计算得到阈值,提高分割阈值和图像分割的精确性;并且,对血清区域图像进行细节处理和无形变尺寸压缩处理,提高了识别准确性;并且,分类模型中各个阶段包括两个残差模块,且残差模块中包括注意力机制模块,保证了识别精度同时加速模型推理的速度;并且,改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型的第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段的输出分别经自适应平均池化层进行级联,级联输出与全连接层连接,增加了低维度特征信息。Applying the serum state recognition method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, by acquiring the image of the blood collection tube containing the serum as a sample image; using the target detection algorithm to detect the sample image, and obtaining the whole blood area image; using the segmentation algorithm to analyze the whole blood area The image is segmented to obtain the serum area image; the serum area image is preprocessed to obtain the preprocessed serum area image, and the preprocessing includes compression processing; the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model is used to identify the preprocessed serum area image to determine the serum area state. The present invention uses the combination of machine vision and deep learning technology to accurately identify the serum state in the blood collection tube, can realize the accurate identification of the serum state by the sampling needle before absorbing the serum, filters the abnormal state samples of the serum, avoids the needle blocking problem of the sampling needle, and is also compatible Blood collection tubes of various specifications and blood collection tubes containing separating gel can accurately identify abnormal states such as fibrin filaments and blood clots in serum of blood collection tubes. Moreover, the YOLOv5s target detection model is used to ensure the target detection effect; and a series of processing is performed on the whole blood area image, which can more effectively segment the whole blood area image; and, the threshold value is obtained by filtering the fluctuation points, Improve the accuracy of the segmentation threshold and image segmentation; and, perform detail processing and non-deformable size compression processing on the serum area image, which improves the recognition accuracy; and, each stage in the classification model includes two residual modules, and the residual module Including the attention mechanism module, which ensures the recognition accuracy and accelerates the speed of model reasoning; and, the output of the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model are respectively passed through the adaptive average pooling layer Carry out cascading, the cascading output is connected with the fully connected layer, and the low-dimensional feature information is added.
下面对本发明实施例提供的血清状态识别装置进行介绍,下文描述的血清状态识别装置与上文描述的血清状态识别方法可相互对应参照。The following is an introduction to the serum state identification device provided by the embodiment of the present invention. The serum state identification device described below and the serum state identification method described above can be referred to in correspondence.
具体请参考图4,图4为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别装置的结构示意图,可以包括:Please refer to Figure 4 for details. Figure 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a serum status identification device provided by an embodiment of the present invention, which may include:
获取模块100,用于获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;An
目标检测模块200,用于利用目标检测算法对所述样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;A
区域分割模块300,用于利用分割算法对所述全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;A
预处理模块400,用于对所述血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,所述预处理包括压缩处理;A
图像识别模块500,用于利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。The
基于上述实施例,所述区域分割模块300,可以包括:Based on the above embodiments, the
灰度化处理单元,用于对所述全血区域图像进行灰度化处理,得到灰度化图像;a grayscale processing unit, configured to perform grayscale processing on the whole blood region image to obtain a grayscale image;
平滑处理单元,用于利用高斯滤波对所述灰度化图像进行平滑处理,得到平滑图像;a smoothing processing unit, configured to perform smoothing processing on the grayscaled image by using Gaussian filtering to obtain a smoothed image;
阈值确定单元,用于计算所述平滑图像的图像直方图,根据所述图像直方图的波谷确定阈值;a threshold determination unit, configured to calculate an image histogram of the smooth image, and determine a threshold according to a valley of the image histogram;
二值化处理单元,用于利用所述阈值对所述平滑图像进行二值化处理和形态学开运算,得到二值化图像;a binarization processing unit, configured to use the threshold to perform binarization processing and morphological opening operation on the smoothed image to obtain a binarized image;
上边界值确定单元,用于计算所述二值化图像中最大面积对应的外接矩形,得到血凝块区域上边界值;The upper boundary value determination unit is used to calculate the circumscribed rectangle corresponding to the largest area in the binarized image to obtain the upper boundary value of the blood clot area;
截取单元,用于根据所述血凝块区域上边界值确定截取区间,根据所述截取区间对所述全血区域图像进行截取,得到所述血清区域图像。The clipping unit is configured to determine a clipping interval according to the upper boundary value of the blood clot region, and clip the whole blood region image according to the clipping interval to obtain the serum region image.
基于上述实施例,所述阈值确定单元,可以包括:Based on the above embodiments, the threshold determining unit may include:
统计子单元,用于统计所述图像直方图中每个灰度值对应像素的个数,得到统计值数组;A statistical subunit is used to count the number of pixels corresponding to each gray value in the image histogram to obtain an array of statistical values;
第一计算子单元,用于计算所述统计值数组中相邻值之间的差值,并根据所述差值确定波动点;The first calculation subunit is used to calculate the difference between adjacent values in the statistical value array, and determine the fluctuation point according to the difference;
过滤子单元,用于对所述波动点进行过滤,得到第一数组;a filtering subunit, configured to filter the fluctuation points to obtain a first array;
第二计算子单元,用于根据所述第一数组计算得到第一波峰信息、第一波谷信息、第二波峰信息和第二波谷信息,所述第一波峰信息包括所述第一波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第一波谷信息包括所述第一波谷对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第二波峰信息包括所述第二波峰对应的灰度值和统计值,所述第二波谷信息包括所述第二波谷对应的灰度值和统计值;The second calculation subunit is used to calculate and obtain the first peak information, the first valley information, the second peak information and the second valley information according to the first array, and the first peak information includes the corresponding Gray value and statistical value, the first valley information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the first valley, the second peak information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the second peak, so The second trough information includes the gray value and statistical value corresponding to the second trough;
判断子单元,用于当所述第二波峰对应的统计值与所述第一波峰对应的统计值的比值大于第一预设值或所述第一波谷对应的灰度值与所述第一波峰对应的灰度值的差值小于第二预设值时,则所述第二波谷对应的灰度值为所述阈值;否则,所述第一波谷对应的灰度值为所述阈值。A judging subunit, configured to be used when the ratio of the statistical value corresponding to the second peak to the statistical value corresponding to the first peak is greater than a first preset value or the gray value corresponding to the first valley is equal to the first When the difference of the grayscale values corresponding to the peaks is smaller than the second preset value, the grayscale value corresponding to the second valley is the threshold; otherwise, the grayscale value corresponding to the first valley is the threshold.
基于上述实施例,所述预处理模块400,可以包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, the
细节处理单元,用于利用自动对比度算法对所述血清区域图像进行细节处理,得到第一图像;a detail processing unit, configured to use an automatic contrast algorithm to perform detail processing on the serum region image to obtain a first image;
压缩单元,用于将所述第一图像进行无形变尺寸压缩得到所述预处理血清区域图像。A compression unit, configured to perform non-deformable size compression on the first image to obtain the preprocessed serum region image.
基于上述任意实施例,所述图像识别模块500,可以包括:Based on any of the above embodiments, the
识别单元,用于利用所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对所述血清区域图像进行识别,确定识别结果,所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型中第一阶段、第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段各包括两个残差模块,所述残差模块包括注意力机制模块。The recognition unit is used to use the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to identify the serum area image and determine the recognition result. In the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model, the first stage, the second stage, the third stage The first stage and the fourth stage each include two residual modules, which include an attention mechanism module.
基于上述实施例,所述图像识别模块500中的述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型还包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model in the
连接单元,用于所述改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型的所述第二阶段、所述第三阶段和所述第四阶段的输出分别经自适应平均池化层后进行级联,所述级联后的输出与全连接层连接。The connection unit is used for the output of the second stage, the third stage and the fourth stage of the improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model to be cascaded after the adaptive average pooling layer respectively, and the The cascaded output is connected with a fully connected layer.
基于上述实施例,所述目标检测模块200,可以包括:Based on the foregoing embodiments, the
目标检测单元,用于利用YOLOv5s目标检测模型对所述样本图像进行检测,得到所述全血区域图像。The target detection unit is configured to use the YOLOv5s target detection model to detect the sample image to obtain the whole blood region image.
需要说明的是,上述血清状态识别装置中的模块以及单元在不影响逻辑的情况下,其顺序可以前后进行更改。It should be noted that the order of the modules and units in the above serum status recognition device can be changed back and forth without affecting the logic.
应用本发明实施例提供的血清状态识别装置,该装置通过获取模块100,用于获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;目标检测模块200,用于利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;区域分割模块300,用于利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;预处理模块400,用于对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理;图像识别模块500,用于利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。本装置采用机器视觉和深度学习相结合的技术准确识别采血管中血清状态,可以实现取样针在吸取血清之前准确识别血清状态,过滤血清异常状态样本,避免取样针发生堵针问题,还可以兼容多种规格采血管和含分离胶的采血管,对采血管血清中含有纤维蛋白丝和血凝块等异常状态能够准确识别。并且,采用YOLOv5s目标检测模型保证了目标检测效果;并且,对全血区域图像进行一系列的处理,能够更有效地对全血区域图像进行分割;并且,采用对波动点进行过滤计算得到阈值,提高分割阈值和图像分割的精确性;并且,对血清区域图像进行细节处理和无形变尺寸压缩处理,提高了识别准确性;并且,分类模型中各个阶段包括两个残差模块,且残差模块中包括注意力机制模块,保证了识别精度同时加速模型推理的速度;并且,改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型的第二阶段、第三阶段和第四阶段的输出分别经自适应平均池化层后进行级联,级联后的输出与全连接层连接,增加了低维度特征信息。The serum state recognition device provided by the embodiment of the present invention is applied, and the device is used to obtain the image of a blood collection tube containing serum through the
下面对本发明实施例提供的血清状态识别设备进行介绍,下文描述的血清状态识别设备与上文描述的血清状态识别方法可相互对应参照。The serum status identification device provided by the embodiment of the present invention is introduced below, and the serum status identification device described below and the serum status identification method described above can be referred to in correspondence.
请参考图5,图5为本发明实施例提供的一种血清状态识别设备的结构示意图,可以包括:Please refer to FIG. 5. FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of a serum status identification device provided by an embodiment of the present invention, which may include:
存储器10,用于存储计算机程序;
处理器20,用于执行计算机程序,以实现上述的血清状态识别方法。The
存储器10、处理器20、通信接口31和通信总线32。存储器10、处理器20、通信接口31均通过通信总线32完成相互间的通信。
在本发明实施例中,存储器10中用于存放一个或者一个以上程序,程序可以包括程序代码,程序代码包括计算机操作指令,在本申请实施例中,存储器10中可以存储有用于实现以下功能的程序:In the embodiment of the present invention, the
获取装有血清的采血管图像,并作为样本图像;Obtain the image of the blood collection tube containing the serum and use it as a sample image;
利用目标检测算法对样本图像进行检测,得到全血区域图像;Use the target detection algorithm to detect the sample image to obtain the image of the whole blood area;
利用分割算法对全血区域图像进行分割,得到血清区域图像;Using a segmentation algorithm to segment the image of the whole blood area to obtain the image of the serum area;
对血清区域图像进行预处理,得到预处理血清区域图像,预处理包括压缩处理;Preprocessing the serum area image to obtain a preprocessed serum area image, the preprocessing includes compression processing;
利用改进的Resnet50网络结构图像分类模型对预处理血清区域图像进行识别,确定血清状态。The improved Resnet50 network structure image classification model was used to identify the pre-processed serum region images to determine the serum status.
在一种可能的实现方式中,存储器10可包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统,以及至少一个功能所需的应用程序等;存储数据区可存储使用过程中所创建的数据。In a possible implementation, the
此外,存储器10可以包括只读存储器和随机存取存储器,并向处理器提供指令和数据。存储器的一部分还可以包括NVRAM。存储器存储有操作系统和操作指令、可执行模块或者数据结构,或者它们的子集,或者它们的扩展集,其中,操作指令可包括各种操作指令,用于实现各种操作。操作系统可以包括各种系统程序,用于实现各种基础任务以及处理基于硬件的任务。Additionally,
处理器20可以为中央处理器(Central Processing Unit,CPU)、特定应用集成电路、数字信号处理器、现场可编程门阵列或者其他可编程逻辑器件,处理器20可以是微处理器或者也可以是任何常规的处理器等。处理器20可以调用存储器10中存储的程序。The
通信接口31可以为通信模块的接口,用于与其他设备或者系统连接。The
当然,需要说明的是,图5所示的结构并不构成对本申请实施例中血清状态识别设备的限定,在实际应用中血清状态识别设备可以包括比图5所示的更多或更少的部件,或者组合某些部件。Of course, it should be noted that the structure shown in FIG. 5 does not constitute a limitation on the serum state identification device in the embodiment of the present application. In practical applications, the serum state identification device may include more or less components, or combinations of certain components.
下面对本发明实施例提供的存储介质进行介绍,下文描述的存储介质与上文描述的血清状态识别方法可相互对应参照。The storage medium provided by the embodiment of the present invention is introduced below, and the storage medium described below and the serum status identification method described above can be referred to in correspondence.
本发明还提供一种存储介质,该存储介质上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现上述的血清状态识别方法的步骤。The present invention also provides a storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the above serum status identification method are realized.
该存储介质可以包括:U盘、移动硬盘、只读存储器(Read-Only Memory,ROM)、随机存取存储器(Random Access Memory,RAM)、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。The storage medium may include: U disk, mobile hard disk, read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM), random access memory (Random Access Memory, RAM), magnetic disk or optical disk and other media that can store program codes.
本说明书中各个实施例采用递进的方式描述,每个实施例重点说明的都是与其它实施例的不同之处,各个实施例之间相同或相似部分互相参见即可。对于实施例公开的装置而言,由于其与实施例公开的方法相对应,所以描述的比较简单,相关之处参见方法部分说明即可。Each embodiment in this specification is described in a progressive manner, each embodiment focuses on the difference from other embodiments, and the same or similar parts of each embodiment can be referred to each other. As for the device disclosed in the embodiment, since it corresponds to the method disclosed in the embodiment, the description is relatively simple, and for relevant details, please refer to the description of the method part.
专业人员还可以进一步意识到,结合本文中所公开的实施例描述的各示例的单元及算法步骤,能够以电子硬件、计算机软件或者二者的结合来实现,为了清楚地说明硬件和软件的可互换性,在上述说明中已经按照功能一般性地描述了各示例的组成及步骤。这些功能究竟以硬件还是软件的方式来执行,取决于技术方案的特定应用和设计约束条件。专业技术人员可以对每个特定的应用来使用不同方法来实现所描述的功能,但是这种实现不应该认为超出本发明的范围。Professionals can further realize that the units and algorithm steps of the examples described in conjunction with the embodiments disclosed herein can be implemented by electronic hardware, computer software or a combination of the two. In order to clearly illustrate the possible For interchangeability, in the above description, the composition and steps of each example have been generally described according to their functions. Whether these functions are executed by means of hardware or software depends on the specific application and design constraints of the technical solution. Those skilled in the art may use different methods to implement the described functions for each specific application, but such implementation should not be regarded as exceeding the scope of the present invention.
最后,还需要说明的是,在本文中,诸如第一和第二等之类的关系属于仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或者操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其他任何变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。Finally, it should also be noted that in this article, relationships such as first and second etc. are only used to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, and do not necessarily require or imply that these entities or operations, any such actual relationship or order exists. Furthermore, the term "comprises", "comprising", or any other variation is intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion such that a process, method, article, or apparatus comprising a set of elements includes not only those elements, but also items not expressly listed. other elements, or also include elements inherent in such a process, method, article, or apparatus.
以上对本发明所提供的一种血清状态识别方法、装置、设备及存储介质进行了详细介绍,本文中应用了具体个例对本发明的原理及实施方式进行了阐述,以上实施例的说明只是用于帮助理解本发明的方法及其核心思想;同时,对于本领域的一般技术人员,依据本发明的思想,在具体实施方式及应用范围上均会有改变之处,综上所述,本说明书内容不应理解为对本发明的限制。The method, device, equipment and storage medium for identifying serum status provided by the present invention have been described above in detail. In this paper, specific examples are used to illustrate the principle and implementation of the present invention. The description of the above embodiments is only for To help understand the method of the present invention and its core idea; at the same time, for those of ordinary skill in the art, according to the idea of the present invention, there will be changes in the specific implementation and scope of application. In summary, the content of this specification It should not be construed as a limitation of the invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310146110.8ACN116109871A (en) | 2023-02-21 | 2023-02-21 | Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310146110.8ACN116109871A (en) | 2023-02-21 | 2023-02-21 | Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116109871Atrue CN116109871A (en) | 2023-05-12 |
Family
ID=86257934
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310146110.8APendingCN116109871A (en) | 2023-02-21 | 2023-02-21 | Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116109871A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116993629A (en)* | 2023-09-27 | 2023-11-03 | 福建晟哲自动化科技有限公司 | Smoothing method and device based on image decomposition, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN118446971A (en)* | 2024-04-28 | 2024-08-06 | 康那生物技术(山东)有限公司 | Method, system and storage medium for identifying abnormal serum status based on image analysis |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108961208A (en)* | 2018-05-21 | 2018-12-07 | 江苏康尚生物医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of aggregation leucocyte segmentation number system and method |
| CN111812012A (en)* | 2020-06-29 | 2020-10-23 | 迈克医疗电子有限公司 | Method and device for identifying nucleated red blood cell region and blood analyzer |
| CN114037699A (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2022-02-11 | 中国医学科学院北京协和医院 | Pathological image classification method, equipment, system and storage medium |
| CN114638850A (en)* | 2020-12-15 | 2022-06-17 | 上海微创卜算子医疗科技有限公司 | Image segmentation method, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN115527198A (en)* | 2022-10-09 | 2022-12-27 | 山东倍科信息技术有限公司 | Artificial intelligence technology for machine learning modeling image recognition |
- 2023
- 2023-02-21CNCN202310146110.8Apatent/CN116109871A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108961208A (en)* | 2018-05-21 | 2018-12-07 | 江苏康尚生物医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of aggregation leucocyte segmentation number system and method |
| CN111812012A (en)* | 2020-06-29 | 2020-10-23 | 迈克医疗电子有限公司 | Method and device for identifying nucleated red blood cell region and blood analyzer |
| CN114638850A (en)* | 2020-12-15 | 2022-06-17 | 上海微创卜算子医疗科技有限公司 | Image segmentation method, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN114037699A (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2022-02-11 | 中国医学科学院北京协和医院 | Pathological image classification method, equipment, system and storage medium |
| CN115527198A (en)* | 2022-10-09 | 2022-12-27 | 山东倍科信息技术有限公司 | Artificial intelligence technology for machine learning modeling image recognition |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 刘 聪等: "基于图像识别的采血管血清液位检测", 传感器与微系统, 30 November 2021 (2021-11-30), pages 0 - 3* |
| 王济民等: "基于LeNet-5卷积神经网络和颜色特征的限速标志识别", 计算机科学, 30 November 2021 (2021-11-30), pages 1 - 4* |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116993629A (en)* | 2023-09-27 | 2023-11-03 | 福建晟哲自动化科技有限公司 | Smoothing method and device based on image decomposition, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN116993629B (en)* | 2023-09-27 | 2023-12-19 | 福建晟哲自动化科技有限公司 | Smoothing method and device based on image decomposition, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN118446971A (en)* | 2024-04-28 | 2024-08-06 | 康那生物技术(山东)有限公司 | Method, system and storage medium for identifying abnormal serum status based on image analysis |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN116109871A (en) | Serum state identification method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111445459A (en) | A method and system for image defect detection based on deep twin network | |
| CN112801987B (en) | Mobile phone part abnormity detection method and equipment | |
| CN108154105A (en) | Aquatic organism detects and recognition methods, device, server and terminal device | |
| CN109035273A (en) | A kind of picture signal fast partition method of immune chromatography test card | |
| CN113763348A (en) | Image quality determination method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111986183A (en) | Chromosome scattergram image automatic segmentation and identification system and device | |
| CN114627113B (en) | A printed circuit board defect detection method, system, device and medium | |
| CN113610773B (en) | Gasket hole quality detection method, system, device and storage medium | |
| CN115187530A (en) | Ultrasound automatic breast full volume image identification method, device, terminal and medium | |
| CN114332058A (en) | Serum quality identification method, device, equipment and medium based on neural network | |
| CN115205541A (en) | Leak detection method, leak detection apparatus, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| CN116152191A (en) | Display screen crack defect detection method, device and equipment based on deep learning | |
| CN115564707A (en) | Intelligent product quality defect detection method and system based on AI image recognition | |
| CN118657736A (en) | A drip detection method, product and device based on differential background modeling | |
| CN116229508A (en) | Human body attribute recognition method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN119323567B (en) | Module lens dirt detection and glue line detection method | |
| CN108550142A (en) | A kind of tooth hole inspection method and hole inspection and device | |
| CN119599976A (en) | Intelligent quality inspection method and system for intelligent production of security equipment | |
| CN110111311B (en) | Image quality evaluation method and device | |
| CN118657346B (en) | Method and system for optimizing the manufacturing process of communication module housing | |
| CN110751004A (en) | Two-dimensional code detection method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112329572B (en) | Rapid static living body detection method and device based on frame and flash point | |
| CN111163332A (en) | Video pornography detection method, terminal and medium | |
| CN117433966A (en) | Non-contact measurement method and system for particle size of grinding particles |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |