CN116071343A - Improved refinishedet pipeline defect detection method - Google Patents
Improved refinishedet pipeline defect detection methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116071343A CN116071343ACN202310158656.5ACN202310158656ACN116071343ACN 116071343 ACN116071343 ACN 116071343ACN 202310158656 ACN202310158656 ACN 202310158656ACN 116071343 ACN116071343 ACN 116071343A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- module
- branch
- anchor
- loss function
- convolution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0004—Industrial image inspection
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/70—Determining position or orientation of objects or cameras
- G06T7/73—Determining position or orientation of objects or cameras using feature-based methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P90/00—Enabling technologies with a potential contribution to greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions mitigation
- Y02P90/30—Computing systems specially adapted for manufacturing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本发明属于计算机视觉目标检测领域。尤其涉及一种基于改进的RefineDet的管道缺陷检测方法。The present invention belongs to the field of computer vision target detection, and in particular relates to a pipeline defect detection method based on improved RefineDet.
背景技术Background Art
管道为工业领域常用的液体和气体传输介质,由于工作环境和传输材料的复杂性,其在使用过程中极容易发生腐蚀、堵塞甚至破裂等问题,因此定期对管道进行检测,以确保其使用寿命和安全性是必须的。传统的管道缺陷人工检测方法存在耗费时间多、容易误检漏检等情况,因此,智能的缺陷检测方法是更佳的选择。管道缺陷检测是指对管道表面缺陷的检测,表面缺陷检测一般采用先进的人工智能视觉检测技术,对工件表面的斑点、凹坑、划痕、色差、缺损等缺陷进行检测。Pipelines are commonly used in the industrial field to transmit liquids and gases. Due to the complexity of the working environment and transmission materials, they are prone to corrosion, blockage, and even rupture during use. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly inspect pipelines to ensure their service life and safety. Traditional manual pipeline defect detection methods are time-consuming and prone to false detections and missed detections. Therefore, intelligent defect detection methods are a better choice. Pipeline defect detection refers to the detection of surface defects on pipelines. Surface defect detection generally uses advanced artificial intelligence visual inspection technology to detect defects such as spots, pits, scratches, color differences, and defects on the surface of the workpiece.
本发明利用基于改进的RefineDet目标检测模型对管道进行缺陷检测,其中RefineDet模型可以看成是SSD、RPN和FPN算法的结合,其主要思想是:Faster-RCNN等two-stage算法,对box进行两次回归,因此精度高,但是速度慢;YOLO等one-stage算法,对box只进行一次回归,速度快,但是精度低;RefineDet将两者结合起来,对box进行两次回归,但是还是one-stage算法,既提高了精度,同时速度也比较快;RefineDet的使用的框架是SSD,同时引入了FPN的特征融合操作,提高对小目标的检测效果。The present invention uses an improved RefineDet target detection model to perform defect detection on pipelines, wherein the RefineDet model can be regarded as a combination of SSD, RPN and FPN algorithms, and its main idea is: two-stage algorithms such as Faster-RCNN regress the box twice, so the accuracy is high but the speed is slow; one-stage algorithms such as YOLO only regress the box once, the speed is fast, but the accuracy is low; RefineDet combines the two and regresses the box twice, but it is still a one-stage algorithm, which not only improves the accuracy, but also has a faster speed; the framework used by RefineDet is SSD, and the feature fusion operation of FPN is introduced to improve the detection effect of small targets.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明要解决的技术问题是,提供一种基于RefineDet的改进方法,克服目标缺陷检测中平均准确率低的问题。本发明通过修改RefineDet的网络架构以及训练策略的方式来提高管道缺陷数据集平均准确率,使训练好的深度卷积神经网络模型准确率更高,从而提高网络模型对管道缺陷的分类和定位能力。为实现上述目的,本发明采用如下的技术方案:The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide an improved method based on RefineDet to overcome the problem of low average accuracy in target defect detection. The present invention improves the average accuracy of the pipeline defect data set by modifying the network architecture and training strategy of RefineDet, so that the trained deep convolutional neural network model has a higher accuracy, thereby improving the network model's ability to classify and locate pipeline defects. To achieve the above purpose, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions:
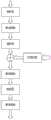
一种改进的RefineDet的管道缺陷检测方法,其特征在于,包括以下步骤:An improved pipeline defect detection method of RefineDet, characterized by comprising the following steps:
步骤1:获取管道缺陷数据集Xs(包含Ns个样本)以及对应的标签YS;将Xs按7:3的比例划分为训练集Xtrain(包含Ntrain个样本)和测试集Xtest(包含Ntest个样本);Step 1: Obtain the pipeline defect datasetXs (includingNs samples) and the corresponding labelYs ; divideXs into a training setXtrain (includingNtrain samples) and a test setXtest (includingNtest samples) in a ratio of 7:3;
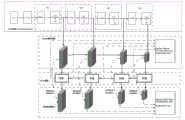
步骤2:构建改进的RefineDet模型,该模型由4个分支组成,分别为主干网络、Neck模块、anchor细化模块和目标检测模块:Step 2: Build an improved RefineDet model, which consists of four branches: backbone network, Neck module, anchor refinement module, and target detection module:
步骤2.1:构建主干网络;主干网络为Swin Transformer网络,该网络以层次化的方式构建了4个特征提取阶段,分别记为S1、S2、S3和S4,每个阶段的输出特征图分别记为Os1、Os2、Os3和Os4;每个阶段包括两个部分,分别是补丁合并(Patch Merging)层和SwinTransformer块;4个特征提取阶段中补丁合并层的数量都为1,Swin Transformer块的数量分别为2、2、6和2,两个Swin Transformer块为一组;补丁合并的操作是将高度、宽度和通道数为H×W×C大小的特征图划分为4个大小的特征图,然后将这4个特征图在通道维度拼接后得到大小的特征图,最后将拼接后的特征图经过归一化和线性变换变成大小的特征图,其中第一阶段的补丁合并操作是线性变换,特征图大小不变,故每阶段补丁合并层输入的H×W×C分别为80×80×48、80×80×96、40×40×192和20×20×384;在一组Swin Transformer块中,第一个Swin Transformer块的结构为一个归一化层、一个窗口多头注意力模块、一个归一化层和一个多层感知器模块,第二个SwinTransformer块结构为一个归一化层、一个偏移窗口多头注意力模块、一个归一化层和一个多层感知器模块;Step 2.1: Construct the backbone network; the backbone network is a Swin Transformer network, which constructs four feature extraction stages in a hierarchical manner, denoted asS1 ,S2 ,S3 andS4 , and the output feature maps of each stage are denoted asOs1 ,Os2 ,Os3 andOs4 respectively; each stage consists of two parts, namely the patch merging layer and the Swin Transformer block; the number of patch merging layers in the four feature extraction stages is 1, the number of Swin Transformer blocks is 2, 2, 6 and 2 respectively, and two Swin Transformer blocks are a group; the patch merging operation is to divide the feature map with a height, width and number of channels of H×W×C into 4 The feature maps of size are then concatenated in the channel dimension to obtain The size of the feature map is finally normalized and linearly transformed into The patch merging operation in the first stage is a linear transformation, and the size of the feature map remains unchanged. Therefore, the H×W×C of the patch merging layer input in each stage is 80×80×48, 80×80×96, 40×40×192, and 20×20×384 respectively; in a group of Swin Transformer blocks, the structure of the first Swin Transformer block is a normalization layer, a window multi-head attention module, a normalization layer, and a multi-layer perceptron module, and the structure of the second Swin Transformer block is a normalization layer, an offset window multi-head attention module, a normalization layer, and a multi-layer perceptron module;
步骤2.2:构建Neck模块,Neck模块的功能与特征金字塔模块功能类似,通过对低级特征添加高级特征来丰富语义信息,以提高检测准确性;Neck模块包含了4个传输连接块,分别记为T1、T2、T3和T4,其对应了主干网络的S1、S2、S3和S4;其中T4只包含一个分支,Os4做为该分支的输入,经过3次卷积操作,输出的特征图大小不变,剩余的传输连接块Ti(i=1,2,3)包含了两个分支,第一个分支以Osi做为该分支的输入,第二个分支以Ti+1的输出特征图做为该分支的输入,由于第一个分支与第二个分支的输入特征图大小不匹配,为了匹配它们之间的维度,第一个分支使用反卷积操作来放大输入特征图,使之与第二个分支的输入特征图大小相同,然后第二个分支对输入特征图进行两次卷积操作,此时该分支输出的特征图大小不变,之后以逐元素相加方式对两个分支的输出求和;最后,在求和后增加一个卷积层,以保证检测特征的可分辨性;Neck模块的4个传输连接块T1、T2、T3和T4的输出分别记为Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4;Step 2.2: Construct the Neck module. The function of the Neck module is similar to that of the feature pyramid module. It enriches semantic information by adding high-level features to low-level features to improve detection accuracy. The Neck module contains four transmission connection blocks, which are denoted as T1 , T2 , T3 and T4 , which correspond to S1 , S2 , S3 and S4 of the backbone network. Among them, T4 contains only one branch, Os4 is used as the input of the branch. After three convolution operations, the size of the output feature map remains unchanged. The remaining transmission connection block Ti (i=1,2,3) contains two branches. The first branch uses Osi as the input of the branch, and the second branch uses T The output feature map ofi+1 is used as the input of this branch. Since the sizes of the input feature maps of the first branch and the second branch do not match, in order to match their dimensions, the first branch uses a deconvolution operation to enlarge the input feature map to make it the same size as the input feature map of the second branch. Then the second branch performs two convolution operations on the input feature map. At this time, the size of the feature map output by this branch remains unchanged. Then, the outputs of the two branches are summed in an element-by-element addition manner. Finally, a convolution layer is added after the summation to ensure the distinguishability of the detection features. The outputs of the four transmission connection blocksT1 ,T2 ,T3 andT4 of the Neck module are recorded asOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 respectively.
步骤2.3:构建anchor细化模块;anchor细化模块通过调整anchors的位置和大小,为目标检测模块中的边框回归提供更好的初始化;anchor细化模块包含4个卷积块,每个卷积块又分别由两个卷积层构成;4个卷积块分别用于对输入的4个不同尺度的特征图Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4进行anchors微调的位置预测以及对anchors是正样本的置信度进行预测;Step 2.3: Construct an anchor refinement module; the anchor refinement module provides better initialization for the bounding box regression in the object detection module by adjusting the position and size of the anchors; the anchor refinement module contains 4 convolution blocks, each of which is composed of two convolution layers; the 4 convolution blocks are used to predict the position of the anchors fine-tuning for the input feature maps of 4 different scalesOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 , and predict the confidence that the anchors are positive samples;
步骤2.4:构建目标检测模块;目标检测模块与anchor细化模块结构类似,也包含4个卷积块,每个卷积块分别由两个卷积层构成;4个卷积块分别对输入的4个不同尺度的特征图Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4进行目标边框的偏移量预测以及目标的缺陷类别预测;Step 2.4: Construct a target detection module. The target detection module has a similar structure to the anchor refinement module and also contains four convolution blocks. Each convolution block consists of two convolution layers. The four convolution blocks predict the offset of the target border and the defect category of the target for the input feature mapsOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 of four different scales.
步骤3:损失函数包括anchor细化模块的损失函数和目标检测模块的损失函数,具体为:Step 3: The loss function includes the loss function of the anchor refinement module and the loss function of the target detection module, specifically:
步骤3.1:anchor细化模块根据每个anchor是否存在目标分为两类,进行anchors的二分类和回归损失计算;使用的损失函数分别为交叉熵损失函数和平滑L1损失函数;Step 3.1: The anchor refinement module divides each anchor into two categories according to whether there is a target, and performs binary classification and regression loss calculation of anchors; the loss functions used are cross entropy loss function and smooth L1 loss function respectively;
交叉熵损失函数为:The cross entropy loss function is:
其中,yi是标签值,y'i是预测值,n为训练集Xtrain样本的数量Ntrain;Whereyi is the label value,y'i is the predicted value, and n is the number of samples in the training setXtrain,Ntrain ;
平滑L1损失函数的公式为:The formula for the smoothed L1 loss function is:
其中v=(vx,vy,vw,vh)表示真实边框的中心点坐标(vx,vy)和框的宽度vw以及高度vh,表示预测框的中心点坐标和框的宽度以及高度k∈{x,y,h,w},x、y、w和h表示框的中心点坐标(x,y)以及框的宽度w和高度h;in v = (vx ,vy ,vw ,vh ) represents the coordinates of the center point of the real bounding box (vx ,vy ) and the widthvw and heightvh of the box. Represents the center point coordinates of the prediction box and the width of the box and height k∈{x,y,h,w}, where x, y, w and h represent the coordinates of the center point of the box (x, y) and the width w and height h of the box;
步骤3.2:目标检测模块的损失函数分别为交叉熵损失函数和平滑L1损失函数;Step 3.2: The loss functions of the target detection module are the cross entropy loss function and the smooth L1 loss function;
交叉熵损失函数为:The cross entropy loss function is:
其中,yi是标签值,y'i是预测值,n为训练集Xtrain样本的数量Ntrain;Whereyi is the label value,y'i is the predicted value, and n is the number of samples in the training setXtrain,Ntrain ;
平滑L1损失函数的公式为:The formula for the smoothed L1 loss function is:
其中v=(vx,vy,vw,vh)表示真实边框的中心点坐标(vx,vy)和框的宽度vw以及高度vh,表示预测框的中心点坐标和框的宽度以及高度k∈{x,y,h,w},x、y、w和h表示框的中心点坐标(x,y)以及框的宽度w和高度h;in v = (vx ,vy ,vw ,vh ) represents the coordinates of the center point of the real bounding box (vx ,vy ) and the widthvw and heightvh of the box. Represents the center point coordinates of the prediction box and the width of the box and height k∈{x,y,h,w}, where x, y, w and h represent the coordinates of the center point of the box (x, y) and the width w and height h of the box;
步骤4:使用warmup和cosine的学习率调整策略,使用Adamw优化器训练改进的RefineDet网络;Step 4: Use the learning rate adjustment strategy of warmup and cosine and train the improved RefineDet network using the Adamw optimizer;
步骤5:在测试集上测试训练好的改进的RefineDet网络,计算平均准确率。Step 5: Test the trained improved RefineDet network on the test set and calculate the average accuracy.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
图1为本发明的基本方法流程示意图;FIG1 is a schematic diagram of a basic method flow chart of the present invention;
图2为本文整体网络架构设计;Figure 2 shows the overall network architecture design of this article;
图3为主干网络结构图;Figure 3 is a diagram of the backbone network structure;
图4为Neck模块包含的传输连接块结构图;FIG4 is a structural diagram of a transmission connection block included in the Neck module;
图5为anchor细化模块结构图;Figure 5 is a structural diagram of the anchor refinement module;
图6为目标检测模块结构图;Figure 6 is a structural diagram of the target detection module;
表1为改进前和改进后RefineDet模型在测试集上的平均准确率结果;Table 1 shows the average accuracy results of the RefineDet model on the test set before and after improvement;
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
本发明提供一种基于RefineDet的改进方法,下面结合相关附图对本发明进行解释和阐述:The present invention provides an improved method based on RefineDet, which is explained and illustrated below in conjunction with the relevant drawings:
本发明使用的管道缺陷数据集,数据集包含了20种类别,共有6010个样本以及对应的标签,其中训练集样本为4258,测试集样本为1752。The pipeline defect dataset used in the present invention includes 20 categories, a total of 6010 samples and corresponding labels, of which the training set samples are 4258 and the test set samples are 1752.
本发明的实施方案流程如下:The implementation scheme of the present invention is as follows:
步骤1:获取管道缺陷数据集Xs(包含6010个样本)以及对应的标签YS(包含6010个样本);将Xs按7:3的比例划分为训练集Xtrain(包含4258个样本以及对应标签)和测试集Xtest(包含1752个样本以及对应标签);Step 1: Obtain the pipeline defect datasetXs (containing 6010 samples) and the corresponding labelsYs (containing 6010 samples); divideXs into a training setXtrain (containing 4258 samples and corresponding labels) and a test setXtest (containing 1752 samples and corresponding labels) in a ratio of 7:3;
步骤2:构建改进的RefineDet模型,该模型由4个分支组成,分别为主干网络、Neck模块、anchor细化模块和目标检测模块:Step 2: Build an improved RefineDet model, which consists of four branches: backbone network, Neck module, anchor refinement module, and target detection module:
步骤2.1:构建主干网络;主干网络为Swin Transformer网络,该网络以层次化的方式构建了4个特征提取阶段,分别记为S1、S2、S3和S4,每个阶段的输出特征图分别记为Os1、Os2、Os3和Os4;每个阶段包括两个部分,分别是补丁合并(Patch Merging)层和SwinTransformer块;4个特征提取阶段中补丁合并层的数量都为1,Swin Transformer块的数量分别为2、2、6和2,两个Swin Transformer块为一组;补丁合并的操作是将样本数、高度、宽度和通道数为H×W×C大小的特征图划分为4个大小的特征图,然后将这4个特征图在通道维度拼接后得到大小的特征图,最后将拼接后的特征图经过归一化和线性变换变成大小的特征图,其中第一阶段的补丁合并操作是线性变换,特征图大小不变,故每阶段补丁合并层输入的H×W×C分别为80×80×48、80×80×96、40×40×192和20×20×384;在一组Swin Transformer块中,第一个Swin Transformer块的结构为一个归一化层、一个窗口多头注意力模块、一个归一化层和一个多层感知器模块,第二个Swin Transformer块结构为一个归一化层、一个偏移窗口多头注意力模块、一个归一化层和一个多层感知器模块;Step 2.1: Construct the backbone network; the backbone network is a Swin Transformer network, which constructs four feature extraction stages in a hierarchical manner, denoted asS1 ,S2 ,S3 andS4 , and the output feature maps of each stage are denoted asOs1 ,Os2 ,Os3 andOs4 respectively; each stage consists of two parts, namely the patch merging layer and the Swin Transformer block; the number of patch merging layers in the four feature extraction stages is 1, the number of Swin Transformer blocks is 2, 2, 6 and 2 respectively, and two Swin Transformer blocks are a group; the patch merging operation is to divide the feature map with the number of samples, height, width and number of channels of H×W×C into 4 The feature maps of size are then concatenated in the channel dimension to obtain The size of the feature map is finally normalized and linearly transformed into The patch merging operation in the first stage is a linear transformation, and the size of the feature map remains unchanged. Therefore, the H×W×C of the patch merging layer input in each stage is 80×80×48, 80×80×96, 40×40×192, and 20×20×384 respectively; in a group of Swin Transformer blocks, the structure of the first Swin Transformer block is a normalization layer, a window multi-head attention module, a normalization layer, and a multi-layer perceptron module, and the structure of the second Swin Transformer block is a normalization layer, an offset window multi-head attention module, a normalization layer, and a multi-layer perceptron module;
步骤2.2:构建Neck模块,Neck模块的功能与特征金字塔模块功能类似,通过对低级特征添加高级特征来丰富语义信息,以提高检测准确性;Neck模块包含了4个传输连接块,分别记为T1、T2、T3和T4,其对应了主干网络的S1、S2、S3和S4;其中T4只包含一个分支,Os4做为该分支的输入,经过3次卷积操作,输出的特征图大小不变,剩余的传输连接块Ti(i=1,2,3)包含了两个分支,第一个分支以Osi做为该分支的输入,第二个分支以Ti+1的输出特征图做为该分支的输入,由于第一个分支与第二个分支的输入特征图大小不匹配,为了匹配它们之间的维度,第一个分支使用反卷积操作来放大输入特征图,使之与第二个分支的输入特征图大小相同,然后第二个分支对输入特征图进行两次卷积操作,此时该分支输出的特征图大小不变,之后以逐元素相加方式对两个分支的输出求和;最后,在求和后增加一个卷积层,以保证检测特征的可分辨性;Neck模块的4个传输连接块T1、T2、T3和T4的输出分别记为Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4;Step 2.2: Construct the Neck module. The function of the Neck module is similar to that of the feature pyramid module. It enriches semantic information by adding high-level features to low-level features to improve detection accuracy. The Neck module contains four transmission connection blocks, which are denoted as T1 , T2 , T3 and T4 , which correspond to S1 , S2 , S3 and S4 of the backbone network. Among them, T4 contains only one branch, Os4 is used as the input of the branch. After three convolution operations, the size of the output feature map remains unchanged. The remaining transmission connection block Ti (i=1,2,3) contains two branches. The first branch uses Osi as the input of the branch, and the second branch uses T The output feature map ofi+1 is used as the input of this branch. Since the sizes of the input feature maps of the first branch and the second branch do not match, in order to match their dimensions, the first branch uses a deconvolution operation to enlarge the input feature map to make it the same size as the input feature map of the second branch. Then the second branch performs two convolution operations on the input feature map. At this time, the size of the feature map output by this branch remains unchanged. Then, the outputs of the two branches are summed in an element-by-element addition manner. Finally, a convolution layer is added after the summation to ensure the distinguishability of the detection features. The outputs of the four transmission connection blocksT1 ,T2 ,T3 andT4 of the Neck module are recorded asOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 respectively.
步骤2.3:构建anchor细化模块;anchor细化模块通过调整anchors的位置和大小,为目标检测模块中的边框回归提供更好的初始化;anchor细化模块包含4个卷积块,每个卷积块又分别由两个卷积层构成;4个卷积块分别用于对输入的4个不同尺度的特征图Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4进行anchors微调的位置预测以及对anchors是正样本的置信度进行预测;Step 2.3: Construct an anchor refinement module; the anchor refinement module provides better initialization for the bounding box regression in the object detection module by adjusting the position and size of the anchors; the anchor refinement module contains 4 convolution blocks, each of which is composed of two convolution layers; the 4 convolution blocks are used to predict the position of the anchors fine-tuning for the input feature maps of 4 different scalesOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 , and predict the confidence that the anchors are positive samples;
步骤2.4:构建目标检测模块;目标检测模块与anchor细化模块结构类似,也包含4个卷积块,每个卷积块又分别由两个卷积层构成;4个卷积块分别对输入的4个不同尺度的特征图Ot1、Ot2、Ot3和Ot4进行目标边框的偏移量预测以及目标的缺陷类别预测;Step 2.4: Construct the target detection module; the target detection module has a similar structure to the anchor refinement module and also contains four convolution blocks, each of which is composed of two convolution layers; the four convolution blocks respectively predict the offset of the target border and the defect category of the target for the input feature maps of four different scalesOt1 ,Ot2 ,Ot3 andOt4 ;
步骤3:损失函数包括anchor细化模块的损失函数和目标检测模块的损失函数,具体为:Step 3: The loss function includes the loss function of the anchor refinement module and the loss function of the target detection module, specifically:
步骤3.1:anchor细化模块根据每个anchor是否存在目标分为两类,进行anchors的二分类和回归损失计算;使用的损失函数分别为交叉熵损失函数和平滑L1损失函数;Step 3.1: The anchor refinement module divides each anchor into two categories according to whether there is a target, and performs binary classification and regression loss calculation of anchors; the loss functions used are cross entropy loss function and smooth L1 loss function respectively;
交叉熵损失函数为:The cross entropy loss function is:
其中,yi是标签值,y′i是预测值,n为训练集Xtrain样本数量,共4258个样本;Among them,yi is the label value,y′i is the predicted value, and n is the number of samples in the training setXtrain , a total of 4258 samples;
平滑L1损失函数的公式为:The formula for the smoothed L1 loss function is:
其中v=(vx,vy,vw,vh)表示真实边框的中心点坐标(vx,vy)和框的宽度vw以及高度vh,表示预测框的中心点坐标和框的宽度以及高度k∈{x,y,h,w},x、y、w和h表示框的中心点坐标(x,y)以及框的宽度w和高度h;in v = (vx ,vy ,vw ,vh ) represents the coordinates of the center point of the real bounding box (vx ,vy ) and the widthvw and heightvh of the box. Represents the center point coordinates of the prediction box and the width of the box and height k∈{x,y,h,w}, where x, y, w and h represent the coordinates of the center point of the box (x, y) and the width w and height h of the box;
步骤3.2:目标检测模块的损失函数分别为交叉熵损失函数和平滑L1损失函数;Step 3.2: The loss functions of the target detection module are the cross entropy loss function and the smooth L1 loss function;
交叉熵损失函数为:The cross entropy loss function is:
其中,yi是标签值,y′i是预测值,n为训练集Xtrain样本数量,共4258个样本;Among them,yi is the label value,y′i is the predicted value, and n is the number of samples in the training setXtrain , a total of 4258 samples;
平滑L1损失函数的公式为:The formula for the smoothed L1 loss function is:
其中v=(vx,vy,vw,vh)表示真实边框的中心点坐标(vx,vy)和框的宽度vw以及高度vh,表示预测框的中心点坐标和框的宽度以及高度k∈{x,y,h,w},x、y、w和h表示框的中心点坐标(x,y)以及框的宽度w和高度h;in v = (vx ,vy ,vw ,vh ) represents the coordinates of the center point of the real bounding box (vx ,vy ) and the widthvw and heightvh of the box. Represents the center point coordinates of the prediction box and the width of the box and height k∈{x,y,h,w}, where x, y, w and h represent the coordinates of the center point of the box (x, y) and the width w and height h of the box;
步骤4:使用warmup和cosine的学习率调整策略,使用Adamw优化器训练改进的RefineDet网络;Step 4: Use the learning rate adjustment strategy of warmup and cosine and train the improved RefineDet network using the Adamw optimizer;
步骤5:在测试集上测试训练好的改进的RefineDet网络,计算出的平均准确率为91.8%。Step 5: Test the trained improved RefineDet network on the test set, and the calculated average accuracy is 91.8%.
表1不同模型的测试结果Table 1 Test results of different models
以上实例仅用于描述本发明,而非限制本发明所描述的技术方案。因此,一切不脱离本发明精神和范围的技术方案及其改进,均应涵盖在本发明的权利要求范围中。The above examples are only used to describe the present invention, rather than to limit the technical solutions described in the present invention. Therefore, all technical solutions and improvements that do not depart from the spirit and scope of the present invention should be included in the scope of the claims of the present invention.
Claims (2)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310158656.5ACN116071343B (en) | 2023-02-13 | 2023-02-13 | An improved pipeline defect detection method based on RefineDet |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310158656.5ACN116071343B (en) | 2023-02-13 | 2023-02-13 | An improved pipeline defect detection method based on RefineDet |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116071343Atrue CN116071343A (en) | 2023-05-05 |
| CN116071343B CN116071343B (en) | 2025-09-26 |
Family
ID=86175430
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310158656.5AActiveCN116071343B (en) | 2023-02-13 | 2023-02-13 | An improved pipeline defect detection method based on RefineDet |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116071343B (en) |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110619356A (en)* | 2019-08-28 | 2019-12-27 | 电子科技大学 | Target detection method based on regional suggestion attention |
| WO2020233414A1 (en)* | 2019-05-20 | 2020-11-26 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | Object recognition method and apparatus, and vehicle |
| CN112381165A (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2021-02-19 | 河南爱比特科技有限公司 | Intelligent pipeline defect detection method based on RSP model |
| WO2021129691A1 (en)* | 2019-12-23 | 2021-07-01 | 长沙智能驾驶研究院有限公司 | Target detection method and corresponding device |
| WO2021139069A1 (en)* | 2020-01-09 | 2021-07-15 | 南京信息工程大学 | General target detection method for adaptive attention guidance mechanism |
| CN114065847A (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2022-02-18 | 武汉纺织大学 | A Fabric Defect Detection Method Based on Improved RefineDet |
| CN114202672A (en)* | 2021-12-09 | 2022-03-18 | 南京理工大学 | A small object detection method based on attention mechanism |
| CN115147380A (en)* | 2022-07-08 | 2022-10-04 | 中国计量大学 | Small transparent plastic product defect detection method based on YOLOv5 |
- 2023
- 2023-02-13CNCN202310158656.5Apatent/CN116071343B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020233414A1 (en)* | 2019-05-20 | 2020-11-26 | 阿里巴巴集团控股有限公司 | Object recognition method and apparatus, and vehicle |
| CN110619356A (en)* | 2019-08-28 | 2019-12-27 | 电子科技大学 | Target detection method based on regional suggestion attention |
| WO2021129691A1 (en)* | 2019-12-23 | 2021-07-01 | 长沙智能驾驶研究院有限公司 | Target detection method and corresponding device |
| WO2021139069A1 (en)* | 2020-01-09 | 2021-07-15 | 南京信息工程大学 | General target detection method for adaptive attention guidance mechanism |
| CN112381165A (en)* | 2020-11-20 | 2021-02-19 | 河南爱比特科技有限公司 | Intelligent pipeline defect detection method based on RSP model |
| CN114065847A (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2022-02-18 | 武汉纺织大学 | A Fabric Defect Detection Method Based on Improved RefineDet |
| CN114202672A (en)* | 2021-12-09 | 2022-03-18 | 南京理工大学 | A small object detection method based on attention mechanism |
| CN115147380A (en)* | 2022-07-08 | 2022-10-04 | 中国计量大学 | Small transparent plastic product defect detection method based on YOLOv5 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 王若霄;徐智勇;张建林;: "跨深度的卷积特征增强目标检测算法", 计算机工程与设计, no. 07, 16 July 2020 (2020-07-16)* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN116071343B (en) | 2025-09-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Xue et al. | An optimization strategy to improve the deep learning‐based recognition model of leakage in shield tunnels | |
| CN113643268B (en) | Industrial product defect quality inspection method and device based on deep learning and storage medium | |
| CN110348384B (en) | A method for attribute recognition of small target vehicles based on feature fusion | |
| Yao et al. | A feature memory rearrangement network for visual inspection of textured surface defects toward edge intelligent manufacturing | |
| Dong et al. | Innovative method for pavement multiple damages segmentation and measurement by the Road-Seg-CapsNet of feature fusion | |
| CN113393438B (en) | A resin lens defect detection method based on convolutional neural network | |
| Lin et al. | DeepCrackAT: An effective crack segmentation framework based on learning multi-scale crack features | |
| CN114240886B (en) | Steel picture defect detection method in industrial production based on self-supervision contrast characterization learning technology | |
| Yang et al. | A scratch detection method based on deep learning and image segmentation | |
| CN117078651A (en) | Defect detection methods, devices, equipment and storage media | |
| CN115829995A (en) | Cloth flaw detection method and system based on pixel-level multi-scale feature fusion | |
| Fang et al. | Automatic zipper tape defect detection using two-stage multi-scale convolutional networks | |
| CN118154993B (en) | Dual-modal underwater dam crack detection method based on acoustic-optical image fusion | |
| CN116597270A (en) | Road damage target detection method based on integrated learning network of attention mechanism | |
| CN114399665A (en) | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for identifying defect types of external thermal insulation layer of external wall | |
| CN117036333A (en) | Wafer defect detection method with high precision and adaptability to different density changes | |
| CN114429461A (en) | A cross-scenario strip surface defect detection method based on domain adaptation | |
| Chen et al. | TFT‐LCD mura defect visual inspection method in multiple backgrounds | |
| CN117636044A (en) | Urban solid waste extraction method, system, equipment and medium | |
| CN118736270A (en) | A method and system for identifying internal defects of sewer pipes | |
| Zhang et al. | Research on high-precision recognition model for multi-scene asphalt pavement distresses based on deep learning | |
| Pan et al. | High-precision segmentation and quantification of tunnel lining crack using an improved DeepLabV3+ | |
| Liu et al. | An improved YOLOv8 model and mask convolutional autoencoder for multi-scale defect detection of ceramic tiles | |
| CN115082650A (en) | Implementation method of automatic pipeline defect labeling tool based on convolutional neural network | |
| CN115170793A (en) | Small sample image segmentation self-calibration method for industrial product quality inspection |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |