CN116048377A - Solid state disk data processing method and related equipment - Google Patents
Solid state disk data processing method and related equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116048377A CN116048377ACN202111266426.8ACN202111266426ACN116048377ACN 116048377 ACN116048377 ACN 116048377ACN 202111266426 ACN202111266426 ACN 202111266426ACN 116048377 ACN116048377 ACN 116048377A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data operation
- operation instruction
- logical address
- solid
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
- G06F12/02—Addressing or allocation; Relocation
- G06F12/0223—User address space allocation, e.g. contiguous or non contiguous base addressing
- G06F12/023—Free address space management
- G06F12/0238—Memory management in non-volatile memory, e.g. resistive RAM or ferroelectric memory
- G06F12/0246—Memory management in non-volatile memory, e.g. resistive RAM or ferroelectric memory in block erasable memory, e.g. flash memory
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0655—Vertical data movement, i.e. input-output transfer; data movement between one or more hosts and one or more storage devices
- G06F3/0656—Data buffering arrangements
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/0671—In-line storage system
- G06F3/0673—Single storage device
- G06F3/0679—Non-volatile semiconductor memory device, e.g. flash memory, one time programmable memory [OTP]
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Memory System Of A Hierarchy Structure (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及硬盘技术领域,尤其涉及一种固态硬盘的数据处理方法及相关设备。The invention relates to the technical field of hard disks, in particular to a data processing method and related equipment for solid state hard disks.
背景技术Background technique
基于非易失性内存主机控制器接口规范(Non Volatile Memory HostController Interface Specification,NVMe)的固态硬盘(Solid State Disk,SSD)系统中,固态硬盘与主机端通过输入/输出(Input/Output,IO)接口通信。主机端可发起多个数据操作指令,并将多个数据操作指令均匀地分配到多个IO队列中。固态硬盘收到数据操作指令后解析指令,调用缓存(cache)管理单元完成对固态硬盘的读取或写入操作,并在闪存转换层(Flash Translation Layer,FTL)进行记录。具体的,当固态硬盘进行写入操作时,固态硬盘将数据操作指令下的数据写入闪存(Nand Flash)中,并将该数据的逻辑地址到闪存的物理地址间的映射关系记录到FTL;当主机读取该数据时,固态硬盘会根据FTL中的映射关系从闪存中读取该数据,然后返回给主机。In a Solid State Disk (SSD) system based on the Non Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMe), the SSD and the host end are connected via Input/Output (IO) interface communication. The host can initiate multiple data operation instructions and evenly distribute the multiple data operation instructions to multiple IO queues. After receiving the data operation instruction, the solid-state disk parses the instruction, calls the cache (cache) management unit to complete the read or write operation to the solid-state disk, and records it in the Flash Translation Layer (FTL). Specifically, when the solid-state hard disk performs a write operation, the solid-state hard disk writes the data under the data operation instruction into the flash memory (Nand Flash), and records the mapping relationship between the logical address of the data and the physical address of the flash memory to the FTL; When the host reads the data, the SSD will read the data from the flash memory according to the mapping relationship in the FTL, and then return it to the host.
通常主机端发起的多个数据操作指令中,各个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址之间具有连续性。但主机端将这些数据操作指令拆成多段连续的命令集,并将多段连续的命令集均匀地分配到多个队列里面。例如,在主机端支持8个队列的情况下,主机端将0B到2MB的数据(对应16KB到128KB的数据操作指令)存入队列1,2MB到4MB的数据存入队列2,4MB到6MB的数据存入队列3,6MB到8MB的数据存入队列4,8MB到10MB的数据存入队列5,10MB到12MB的数据存入队列6,12MB到14MB的数据存入队列7,14MB到16MB的数据存入队列8,16MB到18MB的数据存入到队列1。这样,队列1中的数据会是一段0B到2MB的数据,接着是一段16MB到18MB的数据,并不连续,即一个队列里面的数据操作指令由多段不连续的数据操作指令集组成的情况。Usually, in multiple data operation instructions initiated by the host, there is continuity between logical addresses corresponding to each data operation instruction. However, the host side splits these data operation instructions into multiple consecutive command sets, and evenly distributes the multiple consecutive command sets into multiple queues. For example, if the host side supports 8 queues, the host side stores data from 0B to 2MB (corresponding to data operation instructions from 16KB to 128KB) into
固态硬盘在接收到这些数据操作指令后仅按照队列顺序依次将所有队列中的数据操作指令进行写入操作,这使得原本逻辑上顺序排列的数据操作指令可能被存储在了分散的物理空间中,同时也将各个数据操作指令下的逻辑地址与物理地址的映射关系记录到了FTL中。当用户对这段连续的逻辑地址进行访问的时候,固态硬盘端会根据FTL的映射关系非顺序地读取Nand Flash中的数据,这样不仅影响了固态硬盘的读写性能,也使得固态硬盘的FTL中映射关系复杂,管理效率低下。After receiving these data operation instructions, the solid state disk only writes the data operation instructions in all the queues sequentially according to the order of the queues, which makes the data operation instructions that are originally logically arranged in sequence may be stored in scattered physical spaces. At the same time, the mapping relationship between the logical address and the physical address under each data operation instruction is also recorded in the FTL. When the user accesses this continuous logical address, the SSD side will read the data in the Nand Flash non-sequentially according to the FTL mapping relationship, which not only affects the read and write performance of the SSD, but also makes the SSD The mapping relationship in FTL is complex and the management efficiency is low.
发明内容Contents of the invention
鉴于以上内容,有必要提出一种固态硬盘的数据处理方法及相关设备,以在有限的内存空间下实现高效地排序,提高固态硬盘的读写性能和对FTL的管理效率。In view of the above, it is necessary to propose a data processing method and related equipment for solid-state hard drives, so as to achieve efficient sorting under limited memory space, improve the read-write performance of solid-state hard drives and the management efficiency of FTL.
第一方面,本发明实施例提供一种固态硬盘的数据处理方法,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口通信,IO接口包括多个IO队列,包括:确定IO队列的个数;根据IO队列的个数创建缓存区域;其中,缓存区域由多组链表构成,链表的组数与IO队列的个数相同;一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令;接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中;确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址;目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。In the first aspect, the embodiment of the present invention provides a data processing method of a solid-state hard disk. The solid-state hard disk communicates with the host through an IO interface. The IO interface includes a plurality of IO queues, including: determining the number of IO queues; The cache area is created by the number; among them, the cache area is composed of multiple groups of linked lists, and the number of linked lists is the same as the number of IO queues; a set of linked lists is used to store multiple data operation instructions under one IO queue; multiple data operation instructions sent by the host end are received. According to the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue, store multiple data operation instructions in multiple linked lists in the cache area; determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list ; If the logical address is continuous with the target logical address, execute the data operation instruction, and update the target logical address to the logical address of the currently executed data operation instruction; the target logical address is the logical address of the executed data operation instruction.
可选的,接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,包括:从中间存储器中接收主机端发送的数据操作指令;中间存储器用于接收并存放主机端发送的数据操作指令,并将数据操作指令发送至固态硬盘。Optionally, receiving multiple data operation instructions sent by the host end includes: receiving the data operation instructions sent by the host end from the intermediate storage; the intermediate storage is used to receive and store the data operation instructions sent by the host end, and store the data operation instructions Send to SSD.
可选的,确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址,包括:遍历每组链表中的第一个数据操作指令,并解析当前遍历到的数据操作指令,得到当前数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。Optionally, determining the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each group of linked lists includes: traversing the first data operation instruction in each group of linked lists, and parsing the currently traversed data operation instructions to obtain the current data operation instruction Corresponding logical address.
可选的,该固态硬盘的数据处理方法还包括:若遍历完成后,无符合执行条件的数据操作指令,则更新所有链表中的数据操作指令;执行条件为解析出的逻辑地址与目标地址连续;确定更新后每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。Optionally, the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk also includes: if after the traversal is completed, there is no data operation instruction that meets the execution conditions, then updating the data operation instructions in all linked lists; the execution condition is that the parsed logical address is continuous with the target address ; Determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list after the update.
可选的,该固态硬盘的数据处理方法还包括:若预设时间内,无数据操作指令被执行,则执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令。Optionally, the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk further includes: if no data operation instruction is executed within a preset time, executing the currently traversed data operation instruction.
可选的,接收主机端发送的数据操作指令包括:通过第一线程接收主机端发送的数据操作指令;确定每个链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址包括:通过第二线程确定每个链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;其中,第一线程先于第二线程开始执行,第一线程与第二线程的执行时间差△t满足,△t>0。Optionally, receiving the data operation instruction sent by the host end includes: receiving the data operation instruction sent by the host end through the first thread; determining the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list includes: determining each The logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in a linked list; wherein, the first thread starts executing before the second thread, and the execution time difference Δt between the first thread and the second thread satisfies, Δt>0.
第二方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种固态硬盘,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口通信,IO接口包括多个IO队列,包括:确定模块,用于确定IO队列的个数;创建模块,用于根据IO队列的个数创建缓存区域;其中,缓存区域由多组链表构成,链表的组数与IO队列的个数相同;一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令;接收模块,用于接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,并根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中;确定模块还用于确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;判断模块,用于判断确定模块确定到的逻辑地址与目标地址是否连续;执行模块,用于若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址;目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。In the second aspect, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a solid-state hard disk, the solid-state hard disk communicates with the host through an IO interface, and the IO interface includes a plurality of IO queues, including: a determination module, used to determine the number of IO queues; a creation module , used to create a cache area according to the number of IO queues; wherein, the cache area is composed of multiple sets of linked lists, and the number of linked lists is the same as the number of IO queues; a set of linked lists is used to store multiple data operations under one IO queue instruction; the receiving module is used to receive a plurality of data operation instructions sent by the host, and store the plurality of data operation instructions into multiple linked lists in the cache area according to the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue; determine The module is also used to determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each group of linked lists; the judging module is used to judge whether the logical address determined by the module is continuous with the target address; the execution module is used to determine whether the logical address is consistent with the target logic If the addresses are continuous, the data operation instruction is executed, and the target logical address is updated to the logical address of the currently executed data operation instruction; the target logical address is the logical address of the executed data operation instruction.
第三方面,本发明实施例又提供了一种存储一个或多个程序的计算机可读存储介质,一个或多个程序包括指令,指令当被计算机执行时使计算机执行第一方面的固态硬盘的数据处理方法。In the third aspect, the embodiment of the present invention further provides a computer-readable storage medium storing one or more programs, one or more programs include instructions, and when the instructions are executed by a computer, the computer executes the solid-state disk of the first aspect. data processing method.
第四方面,本发明实施例也提供了一种电子设备,包括:处理器以及存储器;其中,存储器用于存储一个或多个程序,一个或多个程序包括计算机执行指令,当电子设备运行时,处理器执行存储器存储的计算机执行指令,以使电子设备执行第一方面的固态硬盘的数据处理方法。In a fourth aspect, the embodiment of the present invention also provides an electronic device, including: a processor and a memory; wherein, the memory is used to store one or more programs, and the one or more programs include computer-executable instructions. When the electronic device is running, The processor executes the computer-executable instructions stored in the memory, so that the electronic device executes the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk according to the first aspect.
上述实施例中,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口通信,IO接口包括多个IO队列。固态硬盘首先确定IO队列的个数;然后根据IO队列的个数创建具有相同链表组数的缓存区域,一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令;这样可以保障固态硬盘中缓存区域的链表组数与IO队列的个数相对应,以便后续对IO队列中数据操作指令的存储。接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中;由于主机通常将具有连续逻辑地址的数据操作指令按顺序发送到IO队列中,可以保障各个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置与缓存到链表组中的位置相对应,尽可能保障每个链表组中各个数据操作指令在逻辑地址上的连续性。确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址;目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。这样一来,通过执行具有连续逻辑地址的数据操作指令的方式,实现了将主机端发送的多个数据操作指令按照逻辑地址排序的效果,用户对这段连续的逻辑地址进行访问的时候,固态硬盘可以顺序的读取数据,进而提高了固态硬盘的读取性能;通过上述执行操作,固态硬盘将连续逻辑地址的数据存入连续物理地址中,使得固态硬盘的FTL中映射关系清晰,提高了管理效率。In the above embodiments, the solid state disk communicates with the host through an IO interface, and the IO interface includes multiple IO queues. The solid-state disk first determines the number of IO queues; then creates a cache area with the same number of linked list groups according to the number of IO queues, and a set of linked lists is used to store multiple data operation instructions under one IO queue; The number of linked list groups in the cache area corresponds to the number of IO queues for subsequent storage of data operation instructions in the IO queues. Receive multiple data operation instructions sent by the host, and store multiple data operation instructions in multiple linked lists in the cache area according to the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue; since the host usually has consecutive logical addresses The data operation instructions are sent to the IO queue in order, which can ensure that the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue corresponds to the position cached in the linked list group, and ensure that each data operation instruction in each linked list group is on the logical address as much as possible continuity. Determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list; if the logical address is continuous with the target logical address, execute the data operation instruction, and update the target logical address to the logical address of the currently executing data operation instruction; the target logic The address is the logical address of the executed data manipulation instruction. In this way, by executing the data operation instructions with continuous logical addresses, the effect of sorting the multiple data operation instructions sent by the host side according to the logical addresses is realized. When the user accesses this continuous logical address, the solid state The hard disk can read data sequentially, thereby improving the reading performance of the solid-state hard disk; through the above-mentioned execution operations, the solid-state hard disk stores the data of continuous logical addresses into continuous physical addresses, making the mapping relationship in the FTL of the solid-state hard disk clear and improving management efficiency.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘存储系统的架构示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the architecture of a solid state disk storage system provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法第一流程示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic flow chart of a first data processing method of a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据存储第一示意图;Fig. 3 is the first schematic diagram of the data storage of the solid-state hard disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention;
图4是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据存储第二示意图;4 is a second schematic diagram of data storage in a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图5是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法第二流程示意图;Fig. 5 is a second schematic flow chart of a data processing method for a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6a是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据存储第三示意图;Fig. 6a is a third schematic diagram of data storage in a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6b是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据存储第四示意图;Fig. 6b is a fourth schematic diagram of data storage in a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图7是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法第三流程示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic flowchart of a third data processing method of a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法第四流程示意图;8 is a schematic diagram of a fourth flow chart of a data processing method for a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图9是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法第五流程示意图;9 is a schematic diagram of a fifth flow chart of a data processing method for a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图10是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法的线程第一分布图;Fig. 10 is a thread first distribution diagram of the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention;
图11是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法的线程第二分布图;Fig. 11 is a second thread distribution diagram of the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention;
图12是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法的线程执行时序图;Fig. 12 is a thread execution sequence diagram of a data processing method for a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图13是本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法的软件测试图;Fig. 13 is a software test chart of the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention;
图14是本发明实施例提供的一种固态硬盘的架构示意图;FIG. 14 is a schematic structural diagram of a solid-state hard disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图15是本发明实施例提供的一种电子设备的架构示意图。Fig. 15 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
在对本申请实施例进行详细地解释说明之前,先对本申请实施例涉及的名词进行解释。Before explaining the embodiment of the present application in detail, the nouns involved in the embodiment of the present application will be explained first.
IO队列:位于IO接口中,主机通过IO接口中的IO队列与外部设备进行数据交换;例如主机在向固态硬盘写入数据或是从固态硬盘读出数据时,IO请求要先进入IO队列,等待固态硬盘进行资源调度。IO queue: Located in the IO interface, the host performs data exchange with external devices through the IO queue in the IO interface; for example, when the host writes data to or reads data from the SSD, the IO request must first enter the IO queue. Wait for the SSD to perform resource scheduling.
链表:一种物理存储单元上的存储结构,由一系列节点(node)组成。节点为链表的存储单元,用于存储数据。Linked list: A storage structure on a physical storage unit, consisting of a series of nodes. The node is the storage unit of the linked list, which is used to store data.
逻辑地址:固态硬盘写入数据的逻辑层地址。Logical address: The logical layer address of the data written to the SSD.
物理地址:固态硬盘物理介质对应的地址。Physical address: The address corresponding to the physical medium of the SSD.
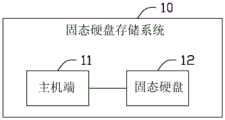
本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法可以适用于固态硬盘存储系统。图1示出了该固态硬盘存储系统的一种结构示意图。如图1所示,固态硬盘存储系统10用于提高固态硬盘的读写性能。固态硬盘存储系统10包括主机端11以及固态硬盘12。其中,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口链接,IO接口中包括多个IO队列。The data processing method for a solid-state hard disk provided in the embodiment of the present invention may be applicable to a solid-state hard disk storage system. FIG. 1 shows a schematic structural diagram of the solid state disk storage system. As shown in FIG. 1 , a solid state
固态硬盘12可以是基于闪速存储器的存储设备。例如移动硬盘、安全数字(SD)卡或通用串行总线(USB)闪存驱动器。Solid state drive 12 may be a flash memory based storage device. Examples include removable hard drives, Secure Digital (SD) cards, or Universal Serial Bus (USB) flash drives.
需要说明的,固态硬盘12可以用于确定IO队列的个数,并根据IO队列的个数创建缓存区域。It should be noted that the
固态硬盘12还可以用于与主机端11进行数据交互。例如,固态硬盘12接收主机端10发送的多个数据操作指令,根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中。The
固态硬盘12还可以用于确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。The
主机端11可以是上位机或其他前端设备。主机端11可以用于向固态硬盘发送用户输入的数据操作指令。The
在不同的应用场景中,主机端11和固态硬盘12可以为相互独立的设备,也可以集成于同一设备中,本发明实施例对此不作具体限定。In different application scenarios, the
图2是根据一些示例性实施例示出的一种固态硬盘的数据处理方法的流程示意图。在一些实施例中,上述固态硬盘的数据处理方法可以应用到如图1所示的固态硬盘或者主机端或其他类似设备。Fig. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a data processing method for a solid state disk according to some exemplary embodiments. In some embodiments, the above data processing method for a solid-state disk can be applied to a solid-state disk as shown in FIG. 1 or a host or other similar devices.
S201、确定IO队列的个数。S201. Determine the number of IO queues.
需要说明的,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口连接,IO接口中包括多个IO队列。其中,IO队列的最大个数由固态硬盘的型号决定,不同型号的固态硬盘所支持的最大IO队列个数不同。主机端在与固态硬盘进行数据交互时,可以根据固态硬盘支持的最大IO队列个数,创建小于或者等于最大IO队列个数的多条IO队列,并将多条数据操作指令均匀分配到多条IO队列中。It should be noted that the solid state disk is connected to the host through an IO interface, and the IO interface includes multiple IO queues. Wherein, the maximum number of IO queues is determined by the model of the solid state disk, and the maximum number of IO queues supported by different types of solid state disks is different. When the host end interacts with the SSD, it can create multiple IO queues that are less than or equal to the maximum number of IO queues based on the maximum number of IO queues supported by the SSD, and evenly distribute multiple data operation instructions to multiple IO queues. In the IO queue.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘确定主机端在IO接口中创建的IO队列的个数。As a possible implementation manner, the solid state disk determines the number of IO queues created in the IO interface on the host side.
S202、根据IO队列的个数创建缓存区域。S202. Create a cache area according to the number of IO queues.
其中,缓存区域由多组链表构成,链表的组数与IO队列的个数相同;一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令。Wherein, the cache area is composed of multiple sets of linked lists, and the number of linked lists is the same as the number of IO queues; a set of linked lists is used to store multiple data operation instructions under one IO queue.
需要说明的,通常一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令的逻辑地址连续。It should be noted that usually the logical addresses of multiple data operation instructions under one IO queue are consecutive.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘根据IO队列的个数,创建具有相同个数的链表组,作为缓存区域。As a possible implementation, the solid-state disk creates a linked list group with the same number as the cache area according to the number of IO queues.
需要说明的,一组链表由一系列节点组成;节点为链表的存储单元,用于存储数据。It should be noted that a set of linked lists is composed of a series of nodes; nodes are storage units of linked lists for storing data.
此外,本发明实施例创建的缓存区域仅需满足链表的组数与IO队列的个数相同即可,链表的深度与队列的深度可以不同。In addition, the cache area created in the embodiment of the present invention only needs to satisfy that the number of groups of the linked list is the same as the number of IO queues, and the depth of the linked list and the depth of the queues may be different.
示例性的,如图3所示,在IO队列个数为8个,每个队列中包括512个数据操作指令(command,以下简称cmd)的情况下,固态硬盘在缓存区域创建了8组链表,每组链表可容纳8条cmd。即固态硬盘在创建缓存区域时,仅需链表组数与IO队列数相同即可,每条链表可容纳的cmd个数并不需与IO队列相同。可以理解的,上述缓存区域的创建方法既保证了IO队列与链表组的对应性,同时也避免了创建的缓存区域过大,占用过多存储资源的问题。Exemplarily, as shown in Figure 3, when the number of IO queues is 8, and each queue includes 512 data operation instructions (command, hereinafter referred to as cmd), the solid state disk creates 8 groups of linked lists in the cache area , each linked list can hold 8 cmds. That is, when creating a cache area for a solid state drive, only the number of linked list groups needs to be the same as the number of IO queues, and the number of cmds that can be accommodated in each linked list does not need to be the same as the number of IO queues. It can be understood that the above method of creating the cache area not only ensures the correspondence between the IO queue and the linked list group, but also avoids the problem that the created cache area is too large and occupies too many storage resources.
S203、接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令。S203. Receive multiple data operation instructions sent by the host.
需要说明的,主机端将多条数据操作指令均匀分配到多条IO队列中后,会向固态硬盘发送IO请求消息,IO请求消息用于请求固态硬盘进行资源调度。It should be noted that after the host side evenly distributes multiple data operation instructions to multiple IO queues, it will send an IO request message to the solid-state disk, and the IO request message is used to request the solid-state disk to perform resource scheduling.
示例性的,如图4所示,假设一个cmd对应的数据长度为128KB,每个IO队列的深度为512个,即每个队列最多存放512条数据操作指令。当主机端需要写入1G大小连续的数据的情况下,则需要8192个cmd,但将8个IO队列同时塞满,最多也只能放下4096个cmd。按照平均分配的原则,主机端根据IO队列的个数,将8192个在逻辑地址上连续的cmd平均分成8组,每组1024个cmd;之后,再分别从每组中取出512个cmd塞入8条IO队列中。Exemplarily, as shown in FIG. 4 , it is assumed that the length of data corresponding to one cmd is 128KB, and the depth of each IO queue is 512, that is, each queue can store up to 512 data operation instructions. When the host side needs to write 1G continuous data, 8192 cmds are needed, but if 8 IO queues are filled at the same time, only 4096 cmds can be placed at most. According to the principle of equal distribution, according to the number of IO queues, the host divides 8192 consecutive cmds on the logical address into 8 groups, each group has 1024 cmds; after that, it takes 512 cmds from each group and inserts them into 8 IO queues.
通过上述主机端向多条IO队列中分配数据操作指令的过程也可以看出,原本连续的多条数据操作指令,在分配到做个IO队列中后,相邻IO队列之间的数据操作指令也不再连续。Through the process of assigning data operation instructions to multiple IO queues on the host side, it can also be seen that after the original continuous multiple data operation instructions are assigned to an IO queue, the data operation instructions between adjacent IO queues Also no longer continuous.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘在收到主机端发送的IO请求消息后,接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令。As a possible implementation manner, after receiving the IO request message sent by the host, the solid state disk receives multiple data operation instructions sent by the host.
此步骤的具体实施方式,可以参照本发明实施例的后续描述,此处不再进行赘述。For the specific implementation manner of this step, reference may be made to the subsequent description of the embodiments of the present invention, and details are not repeated here.
S204、根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中。S204. According to the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue, respectively store multiple data operation instructions in multiple sets of linked lists in the cache area.
需要说明的,主机端会为每个数据操作指令分配队列标识信息,队列标识信息用于反映一个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置。It should be noted that the host end will allocate queue identification information for each data operation instruction, and the queue identification information is used to reflect the position of a data operation instruction in the IO queue.
固态硬盘在接收到一个数据操作指令后,根据该数据操作指令的队列标识信息,确定该数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置;然后根据该数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,将该数据操作指令存储到一个对应的链表中。After receiving a data operation instruction, the solid state disk determines the position of the data operation instruction in the IO queue according to the queue identification information of the data operation instruction; then according to the position of the data operation instruction in the IO queue, the data operation Instructions are stored into a corresponding linked list.
固态硬盘按上述规则,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中。The solid state disk stores multiple data operation instructions in multiple linked lists in the cache area according to the above rules.
示例性的,如图3所示,固态硬盘将队列1的cmd1-cmd8存储在链表1中,将队列2的cmd1025-cmd1032存储在链表2中,将队列3的cmd2049-cmd2056存储在链表3中,将队列4的cmd3073-cmd3080存储在链表4中,将队列5的cmd4097-cmd4104存储在链表5中,将队列6的cmd5121-cmd5128存储在链表6中,将队列7的cmd6145-cmd6152存储在链表7中,将队列8的cmd7169-cmd7176存储在链表8中。Exemplarily, as shown in Figure 3, the solid state disk stores cmd1-cmd8 of
S205、确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。S205. Determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each set of linked lists.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘分别解析每组链表中第一个数据操作指令,得到每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。As a possible implementation method, the solid-state disk separately parses the first data operation instruction in each group of linked lists to obtain the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each group of linked lists.
此步骤的具体实施方式,可以参照本发明实施例的后续描述,此处不再进行赘述。For the specific implementation manner of this step, reference may be made to the subsequent description of the embodiments of the present invention, and details are not repeated here.
S206、每确定到一个逻辑地址,判断该逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址是否连续。S206. Whenever a logical address is determined, determine whether the logical address is continuous with the target logical address.
其中,目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。Wherein, the target logical address is the logical address of the executed data operation instruction.
需要说明的,已执行的数据操作指令可以为固态硬盘最新执行的数据操作指令,也可以为初始操作指令。其中,初始操作指令为固态硬盘执行的第一个数据操作指令,无需进行地址的判断。当初始操作指令执行完毕后,开始对后续操作指令的逻辑地址进行判断。本发明实施例对此不作具体限定。It should be noted that the executed data operation instruction may be the latest executed data operation instruction of the solid state disk, or may be an initial operation instruction. Wherein, the initial operation instruction is the first data operation instruction executed by the solid state disk, and no address judgment is required. After the initial operation instruction is executed, start to judge the logical address of the subsequent operation instruction. This embodiment of the present invention does not specifically limit it.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘每解析到一个数据操作指令的逻辑地址,将该逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址对比,判断该逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址是否连续。As a possible implementation manner, each time the solid-state disk resolves a logical address of a data operation instruction, the logical address is compared with the target logical address, and it is judged whether the logical address is continuous with the target logical address.
若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行S207:执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。If the logical address is continuous with the target logical address, perform S207: Execute the data operation instruction, and update the target logical address to the logical address of the currently executed data operation instruction.
作为一种可能实现的方式,若判断结果为连续,则固态硬盘执行该数据操作指令(例如写入数据),并将目标逻辑地址更新为该数据操作指令的逻辑地址。As a possible implementation manner, if the judgment result is continuous, the solid state disk executes the data operation instruction (for example, writes data), and updates the target logical address to the logical address of the data operation instruction.
需要说明的,当固态硬盘执行完该数据操作指令后,该数据操作指令所属的IO队列删除该条数据操作指令,本队列中的第二个数据操作指令成为队列中新的第一个数据操作指令。之后,固态硬盘会继续确定本组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址,此处不再赘述。It should be noted that after the solid state disk executes the data operation instruction, the IO queue to which the data operation instruction belongs deletes the data operation instruction, and the second data operation instruction in this queue becomes the new first data operation instruction in the queue instruction. Afterwards, the solid state disk will continue to determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in this group of linked lists, which will not be repeated here.
S208、若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址不连续,则跳过该数据操作指令。S208. If the logical address is not continuous with the target logical address, skip the data operation instruction.
需要说明的,固态硬盘跳过该数据操作指令后,继续判断下一组链表中第一个数据操作是否与目标操作指令连续,直至所有的链表中第一个数据操作指令判断完成。It should be noted that after the solid state disk skips the data operation instruction, it continues to judge whether the first data operation in the next group of linked lists is continuous with the target operation instruction until the judgment of the first data operation instruction in all the linked lists is completed.
在一种设计中,为了在对缓存区域的逻辑地址进行排序的同时,不影响新的数据操作指令的获取,如图5所示,本发明实施例提供的上述S203,具体可以包括下述S2031。In one design, in order to sort the logical addresses of the cache area without affecting the acquisition of new data operation instructions, as shown in FIG. 5, the above S203 provided by the embodiment of the present invention may specifically include the following S2031 .
S2031、从中间存储器中接收主机端发送的数据操作指令。S2031. Receive a data operation instruction sent by the host from the intermediate storage.
其中,中间存储器用于接收并存放主机端发送的数据操作指令并将数据操作指令发送至固态硬盘。Wherein, the intermediate memory is used to receive and store the data operation instruction sent by the host end and send the data operation instruction to the solid state disk.
需要说明的,中间存储器为主机端与固态硬盘之间的中间存储单元。如图6a以及图6b所示,中间存储器在接收并存放主机端发送的数据操作指令后,固态硬盘接收中间存储器中的数据操作指令,将数据操作指令存储在缓存区域中,以便固态硬盘在缓存区域对数据操作指令的逻辑地址进行排序。It should be noted that the intermediate storage is an intermediate storage unit between the host and the solid state disk. As shown in Figure 6a and Figure 6b, after the intermediate memory receives and stores the data operation instruction sent by the host, the solid state disk receives the data operation instruction in the intermediate memory and stores the data operation instruction in the cache area, so that the solid state disk Regions sequence the logical addresses of data manipulation instructions.
可以理解的,当固态硬盘将中间存储器中的数据操作指令取走后,在缓存区域对数据操作指令的逻辑地址进行排序的同时,中间存储器可以继续接收并存放主机端发送的数据操作指令,提高了固态硬盘的工作效率。It is understandable that after the solid state disk takes away the data operation instructions from the intermediate storage, the intermediate storage can continue to receive and store the data operation instructions sent by the host while sorting the logical addresses of the data operation instructions in the cache area, improving improve the efficiency of solid-state drives.
在一种设计中,为了确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址,如图7所示,本发明实施例提供的上述S205,具体可以包括下述S2051-S2052。In one design, in order to determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list, as shown in FIG. 7 , the above S205 provided by the embodiment of the present invention may specifically include the following S2051-S2052.
S2051、遍历每组链表中的第一个数据操作指令。S2051. Traverse the first data operation instruction in each set of linked lists.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘获取每组链表中的第一节点的数据操作指令,遍历获取到的数据操作指令。As a possible implementation manner, the solid state disk obtains the data operation instructions of the first node in each group of linked lists, and traverses the obtained data operation instructions.
S2052、解析当前遍历到的数据操作指令,得到当前数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。S2052. Analyze the currently traversed data operation instruction to obtain a logical address corresponding to the current data operation instruction.
作为一种可能实现的方式,在遍历过程中,固态硬盘每访问到一个数据操作指令,读取该数据操作指令的指令编码,根据指令编码确定当前数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。As a possible implementation, during the traversal process, each time the solid-state disk accesses a data operation instruction, it reads the instruction code of the data operation instruction, and determines the logical address corresponding to the current data operation instruction according to the instruction code.
在一种设计中,为了继续寻找与目标地址连续的数据操作指令,如图8所示,若遍历完成,没有解析出与目标地址连续的逻辑地址(例如,参考图3,当固态硬盘执行完链表1中的cmd8后,将cmd8对应的逻辑地址作为目标逻辑地址;此时链表1中已经无数据操作指令可判断,因此固态硬盘会判断链表2中的第一个数据操作指令,而链表中第一个数据操作指令为cmd1025,与cmd8不连续,同理后续链表中的第一个数据操作指令均与cmd8不连续,即没有解析出与目标地址连续的逻辑地址),本发明实施例提供的上述固态硬盘的数据处理方法,还包括下述S209-S210。In one design, in order to continue to search for data operation instructions continuous with the target address, as shown in Figure 8, if the traversal is completed, no logical address continuous with the target address is resolved (for example, referring to Figure 3, when the solid-state hard drive finishes executing After cmd8 in linked
S209、更新所有链表中的数据操作指令。S209. Update the data operation instructions in all linked lists.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘清除所有链表中的数据操作指令,继续从中间存储器中获取新的数据操作指令,并将新获取到的数据操作指令存储到对应的链表组中,直到将所有链表组存满或者中间存储器中没有数据操作指令为止。As a possible implementation, the solid-state disk clears all data operation instructions in the linked list, continues to obtain new data operation instructions from the intermediate storage, and stores the newly acquired data operation instructions in the corresponding linked list group until the Until all linked list groups are full or there is no data operation instruction in the intermediate memory.
S210、确定更新后每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。S210. Determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each set of linked lists after the update.
此步骤的具体实施方式可以参考上述S205,此处不再做赘述。For the specific implementation manner of this step, reference may be made to the above S205, which will not be repeated here.
在一种设计中,为了避免找不到连续的数据操作指令而造成超时问题,如图9所示,本发明实施例提供的上述固态硬盘的数据处理方法,还包括下述S211。In one design, in order to avoid the timeout problem caused by not being able to find continuous data operation instructions, as shown in FIG. 9 , the data processing method for the solid state disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention further includes the following S211.
S211、若预设时间内,无数据操作指令被执行,则执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令。S211. If no data operation instruction is executed within the preset time, execute the currently traversed data operation instruction.
需要说明的,预设时间为预先在固态硬盘中设置的,例如,预设时间为50ms。本发明实施例对此不做具体限定。It should be noted that the preset time is pre-set in the solid state disk, for example, the preset time is 50ms. This embodiment of the present invention does not specifically limit it.
作为一种可能实现的方式,固态硬盘在预设时间内,判断是否收到执行数据操作指令的指示;若在预设时间内,没有收到执行数据操作指令的指示,固态硬盘则执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令。示例性的,在50ms内,固态硬盘没有执行任何数据操作指令,那么固态硬盘则会执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令,无论该数据操作指令的逻辑地址是否与目标逻辑地址连续。As a possible implementation method, the solid-state hard disk judges whether it has received the instruction to execute the data operation instruction within the preset time; to the data manipulation instructions. Exemplarily, within 50 ms, if the solid-state disk does not execute any data operation instruction, then the solid-state disk will execute the currently traversed data operation instruction, regardless of whether the logical address of the data operation instruction is continuous with the target logical address.
可以理解的,当固态硬盘在一段时间内没有执行任何数据操作指令,则表明可能已经没有与目标逻辑地址连续的数据操作指令,这时,为了避免存储超时,固态硬盘直接执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令即可。It can be understood that when the solid-state disk does not execute any data operation instructions for a period of time, it indicates that there may be no data operation instructions continuous with the target logical address. At this time, in order to avoid storage timeout, the solid-state disk directly executes the currently traversed data Operation instructions are enough.
在一种设计中,为了提高固态硬盘的数据处理效率,本发明实施例提供的上述S203,如图10所示,具体可以包括:固态硬盘通过第一线程接收主机端发送的数据操作指令。本发明实施例提供的上述S205,如图11所示,具体可以包括:固态硬盘通过第二线程确定每个链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。In one design, in order to improve the data processing efficiency of the solid state disk, the above S203 provided by the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 10 , may specifically include: the solid state disk receives the data operation instruction sent by the host through the first thread. The above S205 provided by the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 11 , may specifically include: the solid state disk determines the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list through the second thread.
其中,第一线程先于第二线程开始执行,第一线程与第二线程的执行时间差△t满足,△t>0。Wherein, the first thread starts executing before the second thread, and the execution time difference Δt between the first thread and the second thread satisfies, Δt>0.
为了更加直观地表示第一线程与第二线程的执行情况,如图12所示,用时序图表示出了第一线程与第二线程的执行情况。In order to show the execution of the first thread and the second thread more intuitively, as shown in FIG. 12 , the execution of the first thread and the second thread is shown in a sequence diagram.
可以理解的,固态硬盘使用两个线程协调调度来平衡获取数据操作指令命令的时间和确定逻辑地址的时间,即在第一线程获取到多个数据操作指令后,启动第二线程来确定各个数据操作指令的逻辑地址,以判断是否执行确定到的数据操作指令。这样一来,可以更加高效地利用线程资源,提高固态硬盘对数据的处理性能。It can be understood that the solid-state disk uses two thread coordinated scheduling to balance the time for obtaining data operation instructions and the time for determining the logical address, that is, after the first thread obtains multiple data operation instructions, start the second thread to determine each data The logical address of the operation instruction is used to judge whether to execute the determined data operation instruction. In this way, thread resources can be used more efficiently and the data processing performance of the SSD can be improved.
本发明实施例提供的固态硬盘的数据处理方法中,固态硬盘与主机端通过IO接口通信,IO接口包括多个IO队列。固态硬盘首先确定IO队列的个数;然后根据IO队列的个数创建具有相同链表组数的缓存区域,一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令;这样可以保障固态硬盘中缓存区域的链表组数与IO队列的个数相对应,以便后续对IO队列中数据操作指令的存储。接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中;由于主机通常将具有连续逻辑地址的数据操作指令按顺序发送到IO队列中,可以保障各个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置与缓存到链表组中的位置相对应,尽可能保障每个链表组中各个数据操作指令在逻辑地址上的连续性。确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址;目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。这样一来,通过执行具有连续逻辑地址的数据操作指令的方式,实现了将主机端发送的多个数据操作指令按照逻辑地址排序的效果,用户对这段连续的逻辑地址进行访问的时候,固态硬盘可以顺序的读取数据,进而提高了固态硬盘的读取性能。另外,通过上述执行操作,固态硬盘将连续逻辑地址的数据存入连续物理地址中,使得固态硬盘的FTL中映射关系清晰,提高了管理效率。In the data processing method of the solid-state hard disk provided by the embodiment of the present invention, the solid-state hard disk communicates with the host through an IO interface, and the IO interface includes a plurality of IO queues. The solid-state disk first determines the number of IO queues; then creates a cache area with the same number of linked list groups according to the number of IO queues, and a set of linked lists is used to store multiple data operation instructions under one IO queue; The number of linked list groups in the cache area corresponds to the number of IO queues for subsequent storage of data operation instructions in the IO queues. Receive multiple data operation instructions sent by the host, and store multiple data operation instructions in multiple linked lists in the cache area according to the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue; since the host usually has consecutive logical addresses The data operation instructions are sent to the IO queue in order, which can ensure that the position of each data operation instruction in the IO queue corresponds to the position cached in the linked list group, and ensure that each data operation instruction in each linked list group is on the logical address as much as possible continuity. Determine the logical address corresponding to the first data operation instruction in each linked list; if the logical address is continuous with the target logical address, execute the data operation instruction, and update the target logical address to the logical address of the currently executed data operation instruction; the target logic The address is the logical address of the executed data manipulation instruction. In this way, by executing the data operation instructions with continuous logical addresses, the effect of sorting the multiple data operation instructions sent by the host side according to the logical addresses is realized. When the user accesses this continuous logical address, the solid state The hard disk can read data sequentially, thereby improving the reading performance of the solid-state hard disk. In addition, through the above execution operations, the solid-state hard disk stores the data of continuous logical addresses into continuous physical addresses, so that the mapping relationship in the FTL of the solid-state hard disk is clear, and the management efficiency is improved.
如图13所示,使用硬盘测试软件分别测试了使用本发明实施例之前固态硬盘的读写性能,以及使用本发明实施例之后固态硬盘的读写性能。从测试结果可以看出,在使用本发明实施例数据处理方法后,固态硬盘的性能得到了明显提升。As shown in FIG. 13 , the read-write performance of the solid-state hard disk before using the embodiment of the present invention and the read-write performance of the solid-state hard disk after using the embodiment of the present invention were respectively tested by using the hard disk test software. It can be seen from the test results that after using the data processing method of the embodiment of the present invention, the performance of the solid-state hard disk has been significantly improved.
上述主要从方法的角度对本发明实施例提供的方案进行了介绍。为了实现上述功能,其包括了执行各个功能相应的硬件结果和/或软件模块。本领域技术人员应该很容易意识到,结合本文中所公开的实施例描述的各示例的单元及算法步骤,本发明实施例能够以硬件还是计算机软件驱动硬件的方式来执行,取决于技术方案的特点应用和涉及约束条件。专业人员可以对每个特定的应用来使用不同方法来实现所描述的功能,但是这种实现不应认为超出本发明的范围。The foregoing mainly introduces the solutions provided by the embodiments of the present invention from the perspective of methods. In order to realize the above-mentioned functions, it includes hardware components and/or software modules corresponding to each function. Those skilled in the art should easily realize that, in combination with the units and algorithm steps of each example described in the embodiments disclosed herein, whether the embodiments of the present invention can be implemented in the form of hardware or computer software driving hardware depends on the technical solution. Features apply and involve constraints. Professionals may use different methods to implement the described functions for each specific application, but such implementation should not be regarded as exceeding the scope of the present invention.
本发明实施例可以根据上述方法示例对上述设备进行功能模块的划分,例如,可以对应各个功能划分各个功能模块,也可以将两个或两个以上的功能集成在一个处理模块中。上述集成的模块既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能模块的形式实现。可选的,本发明实施例中对模块的划分是示意性的,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分。In the embodiment of the present invention, the functional modules of the above-mentioned device can be divided according to the above-mentioned method examples. For example, each functional module can be divided corresponding to each function, or two or more functions can be integrated into one processing module. The above-mentioned integrated modules can be implemented in the form of hardware or in the form of software function modules. Optionally, the division of modules in the embodiment of the present invention is schematic, and is only a logical function division, and there may be other divisions in actual implementation.
图14是本发明实施例提供的一种固态硬盘的架构示意图。参图14,固态硬盘30用于提升固态硬盘的读写性能,例如用于执行图2所示的固态硬盘的数据处理方法。固态硬盘30与主机端通过IO接口通信,IO接口包括多个IO队列,固态硬盘30包括确定模块301、创建模块302、接收模块303、判断模块304以及执行模块305。FIG. 14 is a schematic structural diagram of a solid state disk provided by an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to FIG. 14 , the solid-state
确定模块301,用于确定IO队列的个数。A determining
创建模块302,用于根据IO队列的个数创建缓存区域;其中,缓存区域由多组链表构成,链表的组数与IO队列的个数相同;一组链表用于存储一个IO队列下的多个数据操作指令。
接收模块303,用于接收主机端发送的多个数据操作指令,并根据每个数据操作指令在IO队列中的位置,分别将多个数据操作指令存储到缓存区域的多组链表中。The receiving
确定模块301还用于确定每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。The determining
判断模块304,用于判断确定模块确定到的逻辑地址与目标地址是否连续。A judging
执行模块305,用于若逻辑地址与目标逻辑地址连续,则执行数据操作指令,并将目标逻辑地址更新为当前执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址,目标逻辑地址为已执行的数据操作指令的逻辑地址。The
可选的,接收模块303还用于:从中间存储器中接收主机端发送的数据操作指令;中间存储器用于接收并存放主机端发送的数据操作指令。Optionally, the receiving
可选的,确定模块301还用于:遍历每组链表中的第一个数据操作指令,并解析当前遍历到的数据操作指令,得到当前数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。Optionally, the
可选的,固态硬盘30还包括更新模块306。更新模块306用于,若遍历完成后,无符合执行条件的数据操作指令,则更新所有链表中的数据操作指令;执行条件为解析出的逻辑地址与目标地址连续;Optionally, the
确定模块301还用于确定更新后每组链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址。The determining
可选的,执行模块305还用于:若预设时间内,无数据操作指令被执行,则执行当前遍历到的数据操作指令。Optionally, the
可选的,接收模块303还用于通过第一线程接收主机端发送的数据操作指令;确定模块301还用于通过第二线程确定每个链表中第一个数据操作指令对应的逻辑地址;其中,第一线程与第二线程的执行时间差△t满足,△t>0。Optionally, the receiving
图15是本公开提供的一种电子设备的架构示意图。参图15,电子设备40用于提高固态硬盘的读写性能,例如用于执行图2所示的固态硬盘的数据处理方法。电子设备40可以包括至少一个处理器401以及用于存储处理器可执行指令的存储器403。其中,处理器401被配置为执行存储器403中的指令,以实现上述实施例中的数据处理方法。Fig. 15 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by the present disclosure. Referring to FIG. 15 , the
另外,电子设备40还可以包括通信总线402以及至少一个通信接口404。In addition, the
处理器401可以是一个处理器(central processing units,CPU),微处理单元,ASIC,或一个或多个用于控制本公开方案程序执行的集成电路。The
通信总线402可包括一通路,在上述组件之间传送信息。
通信接口404,使用任何收发器一类的装置,用于与其他设备或通信网络通信,如以太网,无线接入网(radio access network,RAN),无线局域网(wireless local areanetworks,WLAN)等。The
存储器403可以是只读存储器(read-only memory,ROM)或可存储静态信息和指令的其他类型的静态存储设备,随机存取存储器(random access memory,RAM)或者可存储信息和指令的其他类型的动态存储设备,也可以是电可擦可编程只读存储器(electricallyerasable programmable read-only memory,EEPROM)、磁盘存储介质或者其他磁存储设备、或者能够用于携带或存储具有指令或数据结构形式的期望的程序代码并能够由计算机存取的任何其他介质,但不限于此。存储器可以是独立存在,通过总线与处理单元相连接。存储器也可以和处理单元集成在一起。
其中,存储器403用于存储执行本公开方案的指令,并由处理器401来控制执行。处理器401用于执行存储器403中存储的指令,从而实现本公开方法中的功能。Wherein, the
在具体实现中,作为一种实施例,处理器401可以包括一个或多个CPU,例如图15中的CPU0和CPU1。In a specific implementation, as an embodiment, the
在具体实现中,作为一种实施例,电子设备40可以包括多个处理器,例如图15中的处理器401和处理器407。这些处理器中的每一个可以是一个单核(single-CPU)处理器,也可以是一个多核(multi-CPU)处理器。这里的处理器可以指一个或多个设备、电路、和/或用于处理数据(例如计算机程序指令)的处理核。In a specific implementation, as an embodiment, the
在具体实现中,作为一种实施例,电子设备40还可以包括输出设备405和输入设备406。输出设备405和处理器401通信,可以以多种方式来显示信息。例如,输出设备405可以是液晶显示器(liquid crystal display,LCD),发光二级管(light emitting diode,LED)显示设备,阴极射线管(cathode ray tube,CRT)显示设备,或投影仪(projector)等。输入设备406和处理器401通信,可以以多种方式接受用户的输入。例如,输入设备406可以是鼠标、键盘、触摸屏设备或传感设备等。In a specific implementation, as an embodiment, the
本领域技术人员可以理解,图15中示出的结构并不构成对电子设备40的限定,可以包括比图示更多或更少的组件,或者组合某些组件,或者采用不同的组件布置。Those skilled in the art can understand that the structure shown in FIG. 15 does not constitute a limitation to the
另外,本公开还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,包括指令,当指令由处理器执行时,使得处理器执行如上述实施例所提供的应用程序的启动方法。In addition, the present disclosure also provides a computer-readable storage medium, including instructions, which, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to execute the method for starting an application program as provided in the above-mentioned embodiments.
进一步地,本公开还提供一种计算机程序产品,包括指令,当指令由处理器执行时,使得处理器执行如上述实施例所提供的应用程序的启动方法。Further, the present disclosure also provides a computer program product, including instructions, which, when executed by a processor, cause the processor to execute the method for starting an application program as provided in the foregoing embodiments.
本领域技术人员在考虑说明书及实践这里公开的发明后,将容易想到本公开的其它实施方案。本公开旨在涵盖本公开的任何变型、用途或者适应性变化,这些变型、用途或者适应性变化遵循本公开的一般性原理并包括本公开未公开的本技术领域中的公知常识或惯用技术手段。说明书和实施例仅被视为示例性的,本公开的真正范围和精神由权利要求指出。Other embodiments of the present disclosure will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art from consideration of the specification and practice of the invention disclosed herein. The present disclosure is intended to cover any modification, use or adaptation of the present disclosure. These modifications, uses or adaptations follow the general principles of the present disclosure and include common knowledge or conventional technical means in the technical field not disclosed in the present disclosure. . The specification and examples are to be considered exemplary only, with the true scope and spirit of the disclosure indicated by the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111266426.8ACN116048377A (en) | 2021-10-28 | 2021-10-28 | Solid state disk data processing method and related equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111266426.8ACN116048377A (en) | 2021-10-28 | 2021-10-28 | Solid state disk data processing method and related equipment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116048377Atrue CN116048377A (en) | 2023-05-02 |
Family
ID=86113798
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111266426.8APendingCN116048377A (en) | 2021-10-28 | 2021-10-28 | Solid state disk data processing method and related equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116048377A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116431099A (en)* | 2023-06-13 | 2023-07-14 | 摩尔线程智能科技(北京)有限责任公司 | Data processing method, multiple input and output queue circuit and storage medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106649131A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-10 | 郑州云海信息技术有限公司 | Solid state disk, logic address range conflict monitoring method and logic address range conflict monitoring system |
| US20170371554A1 (en)* | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-28 | Seagate Technology Llc | Internal Data Transfer Management in a Hybrid Data Storage Device |
| CN111831575A (en)* | 2019-04-16 | 2020-10-27 | 武汉海康存储技术有限公司 | Storage method and device of logical address range and storage equipment |
| CN112486416A (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-03-12 | 北京泽石科技有限公司 | Data processing method, data processing device, storage medium and processor |
| US20210157753A1 (en)* | 2019-11-25 | 2021-05-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Direct memory access (dma) commands for noncontiguous source and destination memory addresses |
- 2021
- 2021-10-28CNCN202111266426.8Apatent/CN116048377A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170371554A1 (en)* | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-28 | Seagate Technology Llc | Internal Data Transfer Management in a Hybrid Data Storage Device |
| CN106649131A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-10 | 郑州云海信息技术有限公司 | Solid state disk, logic address range conflict monitoring method and logic address range conflict monitoring system |
| CN111831575A (en)* | 2019-04-16 | 2020-10-27 | 武汉海康存储技术有限公司 | Storage method and device of logical address range and storage equipment |
| US20210157753A1 (en)* | 2019-11-25 | 2021-05-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Direct memory access (dma) commands for noncontiguous source and destination memory addresses |
| CN112486416A (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-03-12 | 北京泽石科技有限公司 | Data processing method, data processing device, storage medium and processor |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116431099A (en)* | 2023-06-13 | 2023-07-14 | 摩尔线程智能科技(北京)有限责任公司 | Data processing method, multiple input and output queue circuit and storage medium |
| CN116431099B (en)* | 2023-06-13 | 2023-09-19 | 摩尔线程智能科技(北京)有限责任公司 | Data processing method, multiple input-output queue circuit and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2024078429A1 (en) | Memory management method and apparatus, computer device, and storage medium | |
| CN113835887B (en) | Video memory allocation method, device, electronic device and readable storage medium | |
| JP2018518733A (en) | File operation method and apparatus | |
| US10049035B1 (en) | Stream memory management unit (SMMU) | |
| CN114168490B (en) | Method and related device for determining memory reclamation threshold | |
| WO2020125396A1 (en) | Processing method and device for shared data and server | |
| CN109359063B (en) | Cache replacement method, storage device and storage medium for storage system software | |
| CN111722908A (en) | A method, system, device and medium for creating a virtual machine | |
| WO2025112885A1 (en) | Resource adjustment method and apparatus, electronic device, storage medium and training platform | |
| CN114327917A (en) | Memory management method, computing device and readable storage medium | |
| CN117692322B (en) | Network card configuration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN117827449A (en) | Physical memory expansion architecture of server, method, equipment and medium | |
| CN118838550A (en) | Solid state disk garbage recycling method, solid state disk controller, storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| CN116400982A (en) | Method and apparatus for configuring relay register module, computing device and readable medium | |
| CN116048377A (en) | Solid state disk data processing method and related equipment | |
| WO2015161804A1 (en) | Cache partitioning method and device | |
| CN118689786A (en) | Mapping table management method of storage chip, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN119088317A (en) | Data reading and writing method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN115729438A (en) | Data access method, device and storage medium | |
| CN112513822B (en) | Information processing method, device, equipment, and system | |
| CN117742793A (en) | Instruction merging circuit, method and chip for data cache instructions | |
| CN117806526A (en) | Data migration method, device, chip and computer-readable storage medium | |
| CN116955212A (en) | Methods, devices, equipment and storage media for defragmenting memory | |
| CN117271107A (en) | Data processing method, device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN119292764B (en) | Data processing method, device, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |