CN116012506A - A processing method, generating method and related device for three-dimensional model data - Google Patents
A processing method, generating method and related device for three-dimensional model dataDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN116012506A CN116012506ACN202111236216.4ACN202111236216ACN116012506ACN 116012506 ACN116012506 ACN 116012506ACN 202111236216 ACN202111236216 ACN 202111236216ACN 116012506 ACN116012506 ACN 116012506A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- rendering
- patch
- electronic device
- rendering data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T15/00—3D [Three Dimensional] image rendering
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T17/00—Three dimensional [3D] modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/70—Determining position or orientation of objects or cameras
- G06T7/73—Determining position or orientation of objects or cameras using feature-based methods
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Image Generation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及媒体技术领域,尤其涉及一种三维模型数据的处理方法、生成方法及相关装置。The present application relates to the field of media technology, and in particular to a processing method, a generating method and a related device for 3D model data.
背景技术Background technique
随着渲染技术及游戏产业的发展,三维(3-dimension,3D)应用所渲染的三维场景越来越大且越来越精细,从而使得渲染所需的三维数据越来越大。由于终端设备上的算力和存储空间受限,目前大部分三维场景的数据量已经达到终端设备的数据渲染极限。因此,目前需要一种能够在算力和存储空间受限的设备上渲染大型三维场景的方式。With the development of rendering technology and game industry, 3-dimensional (3-dimension, 3D) applications render more and more 3-dimensional scenes and become more and more detailed, so that the 3-dimensional data required for rendering becomes larger and larger. Due to the limited computing power and storage space on the terminal device, the data volume of most 3D scenes has reached the data rendering limit of the terminal device. Therefore, there is currently a need for a way to render large 3D scenes on devices with limited computing power and storage space.
相关技术中,在服务器上将大型的三维场景划分为多个较小的三维场景,并生成各个较小的三维场景对应的三维资源文件。在终端设备运行三维应用的过程中,终端设备从服务器上下载相应的三维资源文件并执行当前场景的渲染。在场景发生切换时,终端设备再从服务器上下载新的场景所对应的三维资源文件,并删除原先所下载的三维资源文件。In related technologies, a large 3D scene is divided into multiple smaller 3D scenes on a server, and 3D resource files corresponding to each smaller 3D scene are generated. During the process of running the 3D application on the terminal device, the terminal device downloads the corresponding 3D resource file from the server and executes the rendering of the current scene. When the scene is switched, the terminal device downloads the 3D resource file corresponding to the new scene from the server, and deletes the previously downloaded 3D resource file.
然而,在终端设备所运行的三维应用中的场景发生切换时,终端设备重新从服务器下载三维资源文件往往需要花费一定的时间,从而导致三维应用出现卡顿的现象。However, when the scene in the 3D application running on the terminal device is switched, it often takes a certain amount of time for the terminal device to re-download the 3D resource file from the server, thus causing the 3D application to freeze.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请提供了一种三维模型数据的处理方法,能够保证设备在渲染大规模的场景时的效率,而不会出现设备上的三维应用卡顿的现象。The present application provides a method for processing 3D model data, which can ensure the efficiency of a device when rendering a large-scale scene without causing the 3D application on the device to freeze.
本申请第一方面提供一种三维模型数据的处理方法,应用于第一电子设备上。该方法包括:第一电子设备接收来自于第二电子设备的第一数据请求,该第一数据请求包括第一观察点位置,该第一数据请求用于向第一电子设备请求相应的三维模型数据,以实现在第二电子设备执行三维模型数据的渲染。The first aspect of the present application provides a method for processing three-dimensional model data, which is applied to a first electronic device. The method includes: the first electronic device receives a first data request from the second electronic device, the first data request includes the position of a first observation point, and the first data request is used to request a corresponding three-dimensional model from the first electronic device data, so as to implement the rendering of the 3D model data on the second electronic device.
所述第一电子设备根据所述第一数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据,所述第一目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第一观察点位置相关。也就是说,所述第一电子设备确定了三维模型中的第一观察点位置之后,即可确定三维模型中需要渲染的物体,即基于第一观察点位置能够观察到的物体,从而能够确定用于渲染的第一目标数据。其中,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离。The first electronic device determines first target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the first data request, and the first target data is consistent with the first observation in the three-dimensional model running in the second electronic device point location. That is to say, after the first electronic device determines the position of the first observation point in the three-dimensional model, it can determine the object that needs to be rendered in the three-dimensional model, that is, the object that can be observed based on the position of the first observation point, so that it can determine The first target data used for rendering. Wherein, the first target data includes rendering data for performing 3D model rendering, the rendering data includes rendering data of the first object and rendering data of the second object, and the rendering data of the first object has high fineness Due to the fineness of the rendering data of the second object, the distance between the first object and the first viewpoint location is smaller than the distance between the second object and the first viewpoint location.
其中,所述第一对象和所述第二对象均为从所述第一观察点位置能够观察到的物体。并且,第一对象和第二对象均可以为一个完整的物体,第一对象和第二对象也可以是一个物体中的不同部位。第一对象和第二对象均是由多个面片构成的,因此第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据可以是顶点、面片、位置、形状、表面纹理、颜色等用于渲染场景的参数。Wherein, both the first object and the second object are objects that can be observed from the position of the first observation point. Moreover, both the first object and the second object may be a complete object, and the first object and the second object may also be different parts of an object. Both the first object and the second object are composed of multiple patches, so the rendering data of the first object and the rendering data of the second object can be vertices, patches, positions, shapes, surface textures, colors, etc. for rendering The parameters of the scene.
所述第一电子设备向所述第二电子设备发送所述第一目标数据。The first electronic device sends the first target data to the second electronic device.
本方案中,第一电子设备可以实时获取第二电子设备发送的数据请求,并根据该数据请求从大量的三维模型数据中确定与第二电子设备中三维模型的观察点位置相关的部分数据,进而向第二电子设备返回所确定的部分数据,保证第二电子设备能够实现实时渲染三维模型。并且,由于每次向第二电子设备发送的数据都是与观察点位置相关的一小部分数据,因此并不需要耗费太长的时间来实现三维数据的传输,保证了三维应用的流畅运行。In this solution, the first electronic device can obtain the data request sent by the second electronic device in real time, and determine part of the data related to the position of the observation point of the 3D model in the second electronic device from a large amount of 3D model data according to the data request, Further, the determined part of the data is returned to the second electronic device to ensure that the second electronic device can render the three-dimensional model in real time. Moreover, since the data sent to the second electronic device each time is a small part of data related to the position of the observation point, it does not need to take too long to realize the transmission of the 3D data, which ensures the smooth operation of the 3D application.
此外,由于在三维模型执行渲染而得到二维图像的过程中,对于相同大小的两个物体,离观察点位置越远的物体在二维图像上所显示的图像面积越小,而离观察点位置越近的物体在二维图像上所显示的图像面积越大。因此,对于距离第一观察点位置较远的第二对象,即便降低第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,也不会影响第二对象在最终渲染得到的二维图像上的显示效果。In addition, due to the process of obtaining a 2D image by rendering the 3D model, for two objects of the same size, the farther the object is from the observation point, the smaller the image area displayed on the 2D image is, while the object farther away from the observation point is smaller. The closer the object is, the larger the image area will be displayed on the two-dimensional image. Therefore, for the second object that is far away from the first viewing point, even if the fineness of the rendering data of the second object is reduced, the display effect of the second object on the final rendered two-dimensional image will not be affected.
本方案中,通过降低距离观察点较远位置的对象的渲染数据的精细度,能够减少所需传输的数据量,减轻带宽压力的同时,提高三维模型数据的传输速度,保证三维应用的渲染效率,避免出现三维应用卡顿的现象。In this solution, by reducing the fineness of the rendering data of objects far from the observation point, the amount of data to be transmitted can be reduced, the pressure on bandwidth can be reduced, and the transmission speed of 3D model data can be improved to ensure the rendering efficiency of 3D applications. , to avoid the phenomenon of 3D application freezing.
一般来说,对于三维模型中的同一个对象,三维模型数据中用于构成该对象的面片数量越多,则代表三维模型数据的精细度越高;三维模型数据中用于构成该对象的面片数量越少,则代表三维模型数据的精细度越低。Generally speaking, for the same object in the 3D model, the more patches used to form the object in the 3D model data, the higher the fineness of the 3D model data; The smaller the number of patches, the lower the fineness of the 3D model data.
对于三维模型中的不同对象,可以通过对比不同对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前后的最大误差来判断不同对象的渲染数据之间的精细度大小。例如,对于上述的第一对象和第二对象,先分别确定第一对象和第二对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前后所渲染得到的模型的最大误差;然后再通过对比第一对象对应的最大误差和第二对象对应的最大误差来确定第一对象的渲染数据与第二对象的渲染数据之间的精细度高低。如果第一对象对应的最大误差小于第二对象对应的最大误差,则代表第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于第二对象的渲染数据的精细度;相反,如果第一对象对应的最大误差大于第二对象对应的最大误差,则代表第一对象的渲染数据的精细度低于第二对象的渲染数据的精细度。For different objects in the 3D model, the fineness of the rendering data of different objects can be judged by comparing the maximum error of the rendering data of different objects before and after lightweight processing. For example, for the above-mentioned first object and the second object, first determine the maximum error of the model rendered by the rendering data of the first object and the second object before and after lightweight processing; and then compare the corresponding The maximum error and the maximum error corresponding to the second object determine the fineness level between the rendering data of the first object and the rendering data of the second object. If the maximum error corresponding to the first object is smaller than the maximum error corresponding to the second object, it means that the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is higher than that of the rendering data of the second object; on the contrary, if the maximum error corresponding to the first object Greater than the maximum error corresponding to the second object, it means that the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is lower than the fineness of the rendering data of the second object.
其中,轻量化处理是指对三维模型进行简化,以降低渲染得到的三维模型的精度为代价来减少三维模型的数据量。对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前后的最大误差则是指基于轻量化处理后的渲染数据所渲染得到的三维模型与基于轻量化处理前的渲染数据所渲染得到的三维模型之间的顶点位置误差。三维模型的轻量化处理级别越高,则轻量化处理后的三维模型与轻量化处理前的三维模型之间的误差越大。Wherein, the lightweight processing refers to simplifying the 3D model, and reducing the amount of data of the 3D model at the cost of reducing the accuracy of the rendered 3D model. The maximum error of the object's rendering data before and after lightweight processing refers to the vertex position between the 3D model rendered based on the rendered data after lightweight processing and the 3D model rendered based on the rendering data before lightweight processing error. The higher the weight reduction processing level of the 3D model, the larger the error between the 3D model after the weight reduction processing and the 3D model before the weight reduction processing.
此外,对于三维模型中的不同对象,也可以通过对比不同对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前后的数据量占比来判断不同对象的渲染数据之间的精细度高低。比如,对于任意一个对象,该对象在轻量化处理后的数据量与轻量化处理前数据量的比值越高,说明该对象轻量化的程度越低,该对象经过轻量化处理后的精细度越高。对于两个不同的对象,例如上述的第一对象和第二对象,如果第一对象轻量化后的数据量占第一对象轻量化前数据量的80%,而第二对象轻量化后的数据量占第二对象轻量化前数据量的50%,则说明第二对象的轻量化程度高于第一对象的轻量化程度,即,第二对象的精细度低于第一对象的精细度。In addition, for different objects in the 3D model, the fineness of the rendering data of different objects can also be judged by comparing the data volume ratio of the rendering data of different objects before and after lightweight processing. For example, for any object, the higher the ratio of the object's data volume after lightweight processing to the data volume before lightweight processing, the lower the object's lightweight, and the finer the object's fineness after lightweight processing. high. For two different objects, such as the above-mentioned first object and second object, if the data volume of the first object after weight reduction accounts for 80% of the data volume of the first object before weight reduction, and the data volume of the second object after weight reduction If the amount accounts for 50% of the data volume before the weight reduction of the second object, it means that the weight reduction degree of the second object is higher than that of the first object, that is, the fineness of the second object is lower than that of the first object.
或者,对于三维模型中的不同对象,也可以通过对比不同对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前后的面片数量比值来判断不同对象的渲染数据之间的精细度高低。对于任意一个对象,其在轻量化处理后包括的面片数量和在轻量化处理前包括的面片数量的比值越大表示该对象的轻量化程度越低,那么该对象经过轻量化处理后的精细度就越高。可以确定该对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前所包括的面片数量,以及该对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理后所包括的面片数量,从而求取该对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理后的面片数量与该对象的渲染数据在执行轻量化处理前的面片数量的比值。例如,对于上述的第一对象和第二对象,如果第一对象对应的面片数量比值大于第二对象对应的面片数量比值,则可以确定第一对象的渲染数据的轻量化程度低于第二对象的渲染数据的轻量化程度,经过轻量化处理之后,第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于第二对象的渲染数据的精细度。Or, for different objects in the 3D model, it is also possible to judge the fineness of the rendered data of different objects by comparing the ratio of the number of patches of the rendered data of different objects before and after lightweight processing. For any object, the larger the ratio of the number of patches included after lightweight processing to the number of patches included before lightweight processing, the lower the lightweight of the object, then the weight of the object after lightweight processing The higher the precision. You can determine the number of patches included in the rendering data of the object before performing lightweight processing, and the number of patches included in the rendering data of the object after performing lightweight processing, so as to obtain the rendering data of the object after performing lightweight processing. The ratio of the number of patches after quantization processing to the number of patches of the object's rendering data before performing lightweight processing. For example, for the above-mentioned first object and second object, if the ratio of the number of patches corresponding to the first object is greater than the ratio of the number of patches corresponding to the second object, it can be determined that the rendering data of the first object is less lightweight than the second object. The lightness degree of the rendering data of the second object, after light weight processing, the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is higher than the fineness of the rendering data of the second object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括第一对象对应的多份渲染数据,所述多份渲染数据的精细度不同。所述第一电子设备可以根据所述第一数据请求中的第一观察点位置,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;然后,所述第一电子设备根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度与所述距离具有负相关关系,即所述距离越大,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度则越低;所述距离越小,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度则越高。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the multiple pieces of rendering data have different finenesses. The first electronic device may determine the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the first viewpoint position according to the first viewpoint position in the first data request; then, the first An electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data. Wherein, the fineness of the rendering data of the first object has a negative correlation with the distance, that is, the greater the distance, the lower the fineness of the rendering data of the first object; the smaller the distance, The higher the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is.
简单来说,所述第一电子设备根据第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离,从多份精细度不同的渲染数据选择其中一份渲染数据作为第一对象的渲染数据,以使得所选择的渲染数据的精细度并不会影响第一对象最终的成像质量,同时还能够尽可能地降低第一对象的渲染数据的数据量。In simple terms, the first electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from multiple pieces of rendering data with different finenesses as the rendering data of the first object according to the distance between the first object and the position of the first observation point, so that The fineness of the selected rendering data will not affect the final imaging quality of the first object, and at the same time, the data volume of the rendering data of the first object can be reduced as much as possible.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据中的第一份渲染数据均包括多组渲染数据,所述多组渲染数据中的每组渲染数据用于渲染所述第一对象,且所述多组渲染数据的精细度不同,所述第一份渲染数据是所述多份渲染数据中的任意一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the first piece of rendering data among the multiple pieces of rendering data each includes multiple sets of rendering data, and each set of rendering data in the multiple sets of rendering data is used to render the first object, In addition, the multiple sets of rendering data have different finenesses, and the first set of rendering data is any one of the multiple sets of rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行多次面片缩减处理后得到的,其中,每执行一次面片缩减处理均得到一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple copies of rendering data are obtained after multiple mesh reduction processes are performed on the original rendering data of the first object, and one copy is obtained each time the mesh reduction processing is performed. Render data.
所述第一份渲染数据包括的所述多组渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行相同次数和不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。The multiple sets of rendering data included in the first rendering data are obtained by performing the same number of times of mesh reduction processing and different multiples on the original rendering data of the first object.
简单来说,第一对象对应的多份渲染数据分别是经过不同次数的面片缩减处理后得到的,而每份渲染数据中的多组渲染数据则是基于不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。这样一来,多份渲染数据中的每份渲染数据的精细度均不相同,且相同的一份渲染数据中的多组渲染数据的精细度也不相同。To put it simply, the multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object are obtained after different times of mesh reduction processing, and the multiple sets of rendering data in each piece of rendering data are obtained based on different times of mesh reduction processing . In this way, the fineness of each piece of rendering data in the multiple pieces of rendering data is different, and the fineness of multiple sets of rendering data in the same piece of rendering data are also different.
在一种可能的实现方式中,在第一对象的多份渲染数据中的每份渲染数据均包括多组渲染数据的情况下,第一电子设备可以根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据;然后,第一电子设备根据所述第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,从所选择的一份渲染数据的多组渲染数据中选择一组渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, when each of the multiple pieces of rendering data of the first object includes multiple sets of rendering data, the first electronic device may select one piece of rendering data from the plurality of pieces of rendering data; then, the first electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data according to the performance index and/or network status of the second electronic device A group of rendering data is selected from the group of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object.
也就是说,第一电子设备可以根据第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离,从多个层次的渲染数据中确定其中一个层次,然后基于第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,进一步从该层次中的多个轻量化级别中确定其中一个轻量化级别的渲染数据,以得到最终需要向第二电子设备发送的渲染数据。That is to say, the first electronic device can determine one of the layers from the rendering data of multiple layers according to the distance between the first object and the first observation point, and then based on the performance index and/or network of the second electronic device state, and further determine the rendering data of one of the lightweight levels from the multiple lightweight levels in the hierarchy, so as to obtain the rendering data that needs to be sent to the second electronic device finally.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述性能指标包括所述第二电子设备的帧率、渲染延迟和温度参数中的一个或多个;所述网络状态包括所述第二电子设备的带宽和网络时延中的一个或多个。In a possible implementation manner, the performance index includes one or more of the frame rate, rendering delay, and temperature parameters of the second electronic device; the network status includes bandwidth and One or more of network delays.
例如,在第二电子设备的帧率较高的情况下,代表第二电子设备的性能较高,可以选择轻量化级别较低的渲染数据,即从多组渲染数据中选择精细度较高的渲染数据;又例如,在第二电子设备的温度较高的情况下,代表第二电子设备的功耗较高,可以选择轻量化级别较高的渲染数据,即从多组渲染数据中选择精细度较低的渲染数据,以降低第二电子设备的渲染消耗。For example, when the frame rate of the second electronic device is high, it means that the performance of the second electronic device is high, and the rendering data with a lower lightweight level can be selected, that is, the rendering data with higher fineness can be selected from multiple sets of rendering data. Rendering data; for another example, when the temperature of the second electronic device is high, it means that the power consumption of the second electronic device is high, and you can select rendering data with a higher lightweight level, that is, select finer rendering data from multiple sets of rendering data low-density rendering data, so as to reduce the rendering consumption of the second electronic device.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据还包括缓冲数据,所述缓冲数据包括所述第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,所述N为大于1的整数,所述N份渲染数据均用于执行所述第一对象的渲染,且所述N份渲染数据的精细度不同。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data further includes buffer data, and the buffer data includes N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the N pieces of rendering data The rendering data are all used to execute the rendering of the first object, and the N pieces of rendering data have different finenesses.
本方案中,通过由第一电子设备向第二电子设备发送缓冲数据,所述第二电子设备能够在三维模型中的观察点位置发生变化或者设备状态发生变化时,采用接收到的缓冲数据来执行渲染,以避免重新从第一电子设备处获取新的数据,从而提高渲染的速度。In this solution, by sending buffer data from the first electronic device to the second electronic device, the second electronic device can use the received buffer data when the position of the observation point in the three-dimensional model changes or the device state changes Perform rendering to avoid re-obtaining new data from the first electronic device, thereby improving rendering speed.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括所述第一对象对应的M份渲染数据,所述M份渲染数据的精细度不同,所述M为大于所述N的整数。所述第一电子设备根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离,所述第一数据请求包括所述第一观察点位置;根据所述距离,从所述多份渲染数据中确定一份渲染数据为所述第一对象的目标渲染数据,所述目标渲染数据的精细度满足所述第一对象的精细度要求,所述第一对象的精细度要求与所述距离相关;从所述M份渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为所述缓冲数据,所述N份渲染数据的精细度均小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes M pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the fineness of the M pieces of rendering data is different, and the M is an integer greater than the N . The first electronic device determines the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the position of the first observation point according to the first data request, and the first data request includes the first observation point position; according to the distance, determine one piece of rendering data from the plurality of pieces of rendering data as the target rendering data of the first object, the fineness of the target rendering data meets the fineness requirement of the first object, The fineness requirement of the first object is related to the distance; N pieces of rendering data are selected from the M pieces of rendering data as the buffer data, and the fineness of the N pieces of rendering data are all less than or equal to the target The granularity of the rendered data.
本方案中,通过在多份精细度不同的渲染数据中选择多份精细度较低的渲染数据作为缓冲数据发送给第二电子设备,可以使得第二电子设备能够在三维模型的观察点位置发生变化时(例如观察点位置离对象越来越远),快速地从缓冲数据中选择相应精细度的数据作为实时渲染的数据,避免了重新从第一电子设备处获取新的数据,从而提高渲染的速度。此外,第二电子设备在自身的设备状态发生变化时,例如温度升高时,从缓冲数据中选择精细度较低的数据作为实时渲染的数据,从而降低第二电子设备的渲染功耗,保证第二电子设备的温度在合理范围内。In this solution, by selecting a plurality of rendering data with lower fineness among multiple rendering data with different fineness and sending them as buffer data to the second electronic device, it is possible to enable the second electronic device to generate When changing (for example, the position of the observation point is getting farther and farther away from the object), quickly select the data of corresponding fineness from the buffer data as the data for real-time rendering, avoiding re-obtaining new data from the first electronic device, thereby improving rendering speed. In addition, when the second electronic device's own device status changes, for example, when the temperature rises, it selects data with lower fineness from the buffered data as data for real-time rendering, thereby reducing the rendering power consumption of the second electronic device and ensuring The temperature of the second electronic device is within a reasonable range.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述方法还包括:所述第一电子设备接收来自于所述第二电子设备的第二数据请求;所述第一电子设备根据所述第二数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据,所述第二目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第二观察点位置相关;所述第一电子设备根据所述第一目标数据和所述第二目标数据确定第三目标数据,并生成第一信息,其中所述第一目标数据不包括所述第三目标数据,且所述第二目标数据包括所述第三目标数据,所述第一信息用于指示待删除的第四目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括所述第四目标数据,且所述第二目标数据不包括所述第四目标数据;所述第一电子设备向所述第二电子设备发送所述第三目标数据和所述第一信息。In a possible implementation manner, the method further includes: the first electronic device receiving a second data request from the second electronic device; and the first electronic device according to the second data request, Determining second target data from the data of the three-dimensional model, the second target data is related to the position of the second observation point in the three-dimensional model running in the second electronic device; the first electronic device according to the first electronic device A target data and the second target data determine third target data, and generate first information, wherein the first target data does not include the third target data, and the second target data includes the third target data Target data, the first information is used to indicate fourth target data to be deleted, the first target data includes the fourth target data, and the second target data does not include the fourth target data; The first electronic device sends the third target data and the first information to the second electronic device.
简单来说,第一电子设备在接收到新的数据请求之后,第一电子设备基于该新的数据请求确定第二电子设备所需的数据,并将所确定的数据与之前已向第二电子设备发送的数据进行对比,挑选出新增的数据以及不再需要的数据,从而向第二电子设备发送新增的数据以及指示第二电子设备删除不再需要的数据,从而实现第二电子设备中的数据的复用,避免向第二电子设备发送大量重复的数据。In simple terms, after the first electronic device receives a new data request, the first electronic device determines the data required by the second electronic device based on the new data request, and compares the determined data with the data previously sent to the second electronic device. Compare the data sent by the device, select the newly added data and the data that is no longer needed, so as to send the new data to the second electronic device and instruct the second electronic device to delete the data that is no longer needed, so that the second electronic device The multiplexing of the data in the device avoids sending a large amount of repeated data to the second electronic device.
本申请第二方面提供一种三维模型数据的生成方法,包括:获取三维模型文件,所述三维模型文件包括用于构成三维模型的多个面片。其中,该三维模型文件可以包括多个mesh的数据,通过多个mesh的数据来定义三维模型中各个物体的形状。一般来说,每个mesh由一组顶点、边和面片组成,通过顶点信息可以定义出边的信息,接着通过边的信息构成面片的信息,最终由一个个面片组合得到mesh。三维模型中的物体则可以是通过由多个面片组合得到的mesh定义得到。A second aspect of the present application provides a method for generating 3D model data, including: acquiring a 3D model file, where the 3D model file includes a plurality of meshes for constituting a 3D model. Wherein, the 3D model file may include data of multiple meshes, and the shape of each object in the 3D model is defined by the data of multiple meshes. Generally speaking, each mesh is composed of a set of vertices, edges, and patches. The edge information can be defined through the vertex information, and then the edge information is used to form the patch information, and finally the mesh is obtained by combining each patch. The objects in the 3D model can be obtained by mesh definition obtained by combining multiple faces.
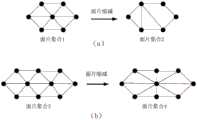
将所述多个面片分成多个第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合中的每个第一面片集合包括多个连接的面片,且所述每个第一面片集合中的面片数量相同。例如,将10000个面片分成100个面片集合,每个面片集合中包括100个连接的面片。dividing the plurality of patches into a plurality of first patch sets, each first patch set in the plurality of first patch sets includes a plurality of connected patches, and each first surface The number of patches in the patchset is the same. For example, 10000 patches are divided into 100 patch sets, and each patch set includes 100 connected patches.
将所述多个面片集合分成多个第一面片集合组,所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组包括多个所述第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成第一三维模型。例如,将100个面片集合分为25个面片集合组,每个面片集合组中包括4个面片集合,且每个面片集合中包括100个面片。dividing the plurality of patch sets into a plurality of first patch set groups, each first patch set group in the plurality of first patch set groups includes a plurality of the first patch sets, so The plurality of first mesh sets are used to form the first three-dimensional model. For example, 100 mesh sets are divided into 25 mesh set groups, each mesh set group includes 4 mesh sets, and each mesh set includes 100 mesh sets.
对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第二面片集合组,通过执行面片缩减处理,可以将由多个面片构成的网格A转换为另一个网格B。相比于网络A,网格B具有更少的顶点、边和面片。其中,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成第一三维模型(即原始的三维模型),所述多个第二面片集合组用于构成第二三维模型,由于第二三维模型是由面片缩减后的第二面片集合组构成的,因此第二三维模型的精细度要低于原始的第一三维模型,但是第二三维模型的数据量要小于原始的第一三维模型的数据量。Perform patch reduction processing on each of the plurality of first patch collection groups to obtain a plurality of second patch collection groups with reduced number of patches, by performing patch reduction processing , you can convert a mesh A composed of multiple patches into another mesh B. Compared to network A, mesh B has fewer vertices, edges and patches. Wherein, the plurality of first mesh collection groups are used to form the first three-dimensional model (ie, the original three-dimensional model), and the plurality of second mesh collection groups are used to form the second three-dimensional model, because the second three-dimensional model It is composed of the second set of meshes reduced by meshes, so the fineness of the second 3D model is lower than that of the original first 3D model, but the data volume of the second 3D model is smaller than that of the original first 3D model amount of data.
对所述多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,得到多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二面片集合中每个第二面片集合的面片数量与所述多个第一面片集合中每个第一面片集合的面片数量相同。Splitting the multiple second patch sets to obtain multiple second patch sets, the number of patches in each second patch set in the multiple second patch sets is the same as the number of patches in the multiple second patch sets Each first patch set in the first patch set has the same number of patches.
也就是说,以面片集合组为单位执行面片缩减处理后,面片集合组中的面片数量发生了变化,因此可以对面片缩减处理后得到的多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,重新组成多个第二面片集合,从而保证每个面片集合中的面片数量是固定的。That is to say, after the patch reduction process is performed in the unit of the patch set group, the number of patches in the patch set group has changed, so the multiple second patch set groups obtained after the patch reduction process can be disassembled. points, and recompose multiple second patch sets, so as to ensure that the number of patches in each patch set is fixed.
这样一来,在得到重新组合的多个第二面片集合之后,可以循环执行上述的多个步骤,即将面片集合分成面片集合组、对面片集合组执行面片缩减处理以及拆分面片缩减处理后的面片集合组,以得到执行不同次数的面片缩减处理后的面片集合。其中,执行不同次数的面片缩减处理后的面片集合所构成的三维模型的精度各不相同,从而能够得到不同精度下的三维模型数据。In this way, after obtaining the reassembled multiple second patch sets, the above-mentioned multiple steps can be executed cyclically, that is, dividing the patch set into patch set groups, performing patch reduction processing on the patch set groups, and splitting faces. The patch set group after patch reduction processing is obtained to obtain the patch set after performing different times of patch reduction processing. Wherein, the accuracy of the three-dimensional model formed by the mesh set after performing different times of mesh reduction processing is different, so that the three-dimensional model data with different accuracy can be obtained.
本方案中,通过执行上述的三维模型数据的生成方法,能够得到精细度以及数据量均不相同的三维模型数据,以便于满足不同场景下的模型渲染需求。在三维模型数据的实际使用阶段,电子设备则可以是根据终端设备中的观察点位置或者终端设备的性能选择相应精细度的三维模型数据,从而能够在满足不同终端设备的要求的情况下尽可能地降低所需传输的模型数据量,保证三维模型的实时渲染。In this solution, by executing the above method for generating 3D model data, 3D model data with different fineness and data volume can be obtained, so as to meet model rendering requirements in different scenarios. In the actual use stage of the 3D model data, the electronic device can select the 3D model data of the corresponding fineness according to the position of the observation point in the terminal device or the performance of the terminal device, so that it can meet the requirements of different terminal devices as much as possible. Minimize the amount of model data that needs to be transmitted and ensure real-time rendering of the 3D model.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述方法还包括:对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第三面片集合组,所述多个第三面片集合组用于构成第三三维模型,所述多个第三面片集合组中每个第三面片集合组的面片数量与所述多个第二面片集合组中每个第二面片集合组的面片数量不同。In a possible implementation manner, the method further includes: performing patch reduction processing on each first patch set group in the plurality of first patch set groups, so as to obtain the reduced number of patches A plurality of third mesh collection groups, the plurality of third mesh collection groups are used to form a third three-dimensional model, the number of meshes of each third mesh collection group in the plurality of third mesh collection groups The number of patches is different from that of each second patch set in the plurality of second patch sets.
例如,假设多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组包括400个面片,对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理后,得到的多个第二面片集合组中的每个第二面片集合组包括200个面片,即面片缩减了200个;对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理后,得到的多个第三面片集合组中的每个第三面片集合组包括100个面片,即面片缩减了300个。For example, assuming that each of the plurality of first patch set groups includes 400 patches, performing faceting on each of the plurality of first patch set groups After the sheet reduction process, each second patch set group in the plurality of second patch set groups obtained includes 200 patches, that is, the number of patches has been reduced by 200; for the plurality of first patch set groups After performing the patch reduction process on each of the first patch set groups in , each of the obtained multiple third patch set groups includes 100 patches, that is, 300 patches are reduced .
也就是说,通过执行多次面片缩减处理,能够得到多个层次的三维模型数据,每个层次的三维模型数据的精细度不同;通过在生成多个层次的三维模型数据的过程中,以不同的面片缩减倍数执行面片缩减处理,则能够在三维模型数据的各个层次中进一步生成级别不一样的三维模型数据,同一层次但级别不同的三维模型数据的精细度不同。That is to say, by performing multiple mesh reduction processes, multiple levels of 3D model data can be obtained, and the fineness of each level of 3D model data is different; during the process of generating multiple levels of 3D model data, the Different mesh reduction multiples perform mesh reduction processing, so that 3D model data of different levels can be further generated in each level of 3D model data, and the fineness of 3D model data of the same level but different levels is different.
在一种可能的实现方式中,每个所述第二面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/N,N为大于1的整数;每个所述第三面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/M,其中,M为大于N的整数。In a possible implementation, the number of patches in each of the second patch sets is 1/N of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where N is an integer greater than 1; The number of patches in each of the third patch sets is 1/M of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where M is an integer greater than N.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述方法还包括:根据所述多个第一面片集合和所述多个第二面片集合生成树结构;其中,所述树结构包括多个第一节点和多个第二节点,所述多个第一节点分别对应于所述多个第一面片集合,所述多个第二节点分别对应于所述多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二节点中的每个节点均连接有所述多个第一节点中的多个节点。In a possible implementation manner, the method further includes: generating a tree structure according to the multiple first patch sets and the multiple second patch sets; wherein the tree structure includes multiple first patch sets node and a plurality of second nodes, the plurality of first nodes respectively correspond to the plurality of first patch sets, the plurality of second nodes respectively correspond to the plurality of second patch sets, the Each node of the plurality of second nodes is connected to a plurality of nodes of the plurality of first nodes.
由于所述多个第二面片集合中的面片集合实际上是对多个第一面片集合进行面片缩减处理以及合并操作后得到的,因此所述多个第二面片集合中的一个面片集合对应于所述多个第一面片集合中的多个面片集合。也就是说,在所述树结构中,所述多个第二节点中的每个节点均连接有所述多个第一节点中的多个节点。Since the patch sets in the multiple second patch sets are actually obtained after performing patch reduction and merging operations on multiple first patch sets, the multiple second patch sets One patch set corresponds to multiple patch sets in the plurality of first patch sets. That is, in the tree structure, each node in the plurality of second nodes is connected to a plurality of nodes in the plurality of first nodes.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多个面片中的每个面片由多个顶点构成;所述对所述多个第一面片集合中的每个面片集合执行面片缩减处理,包括:确定第一面片集合中位于边缘位置的多个目标顶点,所述第一面片集合为所述多个第一面片集合中的任意一个面片集合;锁定所述多个目标顶点,重新生成多个面片,以得到第二面片集合,所述第二面片集合的面片数量小于所述第一面片集合的面片数量,所述第二面片集合为所述多个第二面片集合中的一个面片集合。In a possible implementation manner, each patch in the plurality of patches is composed of a plurality of vertices; performing patch reduction on each patch set in the plurality of first patch sets The processing includes: determining a plurality of target vertices at edge positions in a first patch set, where the first patch set is any patch set in the plurality of first patch sets; locking the multiple target vertex, regenerate multiple patches to obtain a second patch set, the number of patches in the second set of patches is smaller than the number of patches in the first set of patches, and the second set of patches is A patch set in the plurality of second patch sets.
本方案,在对面片集合执行面片缩减处理的过程中,保持面片集合边缘位置的顶点不变,只缩减面片集合内部的顶点,从而实现面片的缩减处理,能够保证执行面片缩减处理后,面片集合的边缘不会出现破碎或者断裂的问题。In this solution, in the process of performing patch reduction processing on the patch set, the vertices at the edge positions of the patch set are kept unchanged, and only the vertices inside the patch set are reduced, so as to realize the reduction process of the patch and ensure the execution of the patch reduction After processing, the edges of the mesh collection will not appear broken or broken.
本申请第三方面提供一种三维模型数据的处理方法,应用于第二电子设备上。该方法包括:第二电子设备获取三维模型中的第一观察点位置;所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据,所述第一目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第一观察点位置相关;所述第二电子设备向第一电子设备发送所述第一目标数据的索引,所述第一目标数据的索引用于指示所述第一目标数据。The third aspect of the present application provides a method for processing three-dimensional model data, which is applied to a second electronic device. The method includes: the second electronic device acquires the position of the first observation point in the three-dimensional model; the second electronic device determines the first target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the position of the first observation point, and the first target The data is related to the position of the first observation point in the three-dimensional model running in the second electronic device; the second electronic device sends the index of the first target data to the first electronic device, and the first target data The index of is used to indicate the first target data.
本方案中,通过由第二电子设备根据观察点位置确定渲染所需的目标数据,并向存储三维模型数据的第一电子设备发送目标数据的索引,以指示第一电子设备向第二电子设备返回目标数据,从而实现三维模型的实时渲染。In this solution, the second electronic device determines the target data required for rendering according to the position of the observation point, and sends the index of the target data to the first electronic device storing the 3D model data, so as to instruct the first electronic device to send the target data to the second electronic device Return target data, enabling real-time rendering of 3D models.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据,其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data includes rendering data for performing 3D model rendering, and the rendering data includes rendering data of a first object and rendering data of a second object, wherein the first The fineness of the rendering data of an object is higher than the fineness of the rendering data of the second object, and the distance between the first object and the position of the first observation point is smaller than the distance between the second object and the first The distance between watch point locations.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括第一对象对应的多份渲染数据,所述多份渲染数据的精细度不同;所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据中的所述第一对象的渲染数据,包括:所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;所述第二电子设备根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据,其中所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度与所述距离具有负相关关系。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the multiple pieces of rendering data have different fineness; the second electronic device according to the first observation Determining the rendering data of the first object in the first target data from the data of the three-dimensional model includes: the second electronic device determining the first object in the three-dimensional model according to the position of the first viewing point The distance between the object and the position of the first observation point; the second electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data as the set according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data The rendering data of the first object, wherein the fineness of the rendering data of the first object has a negative correlation with the distance.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据中的第一份渲染数据包括多组渲染数据,所述多组渲染数据中的每组渲染数据用于渲染以得到所述第一对象,且所述多组渲染数据的精细度不同,所述第一份渲染数据是所述多份渲染数据中的任意一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the first piece of rendering data in the multiple pieces of rendering data includes multiple sets of rendering data, and each set of rendering data in the multiple sets of rendering data is used for rendering to obtain the first object , and the fineness of the multiple sets of rendering data is different, and the first set of rendering data is any one of the multiple sets of rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行多次面片缩减处理后得到的,其中,每执行一次面片缩减处理均得到一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple copies of rendering data are obtained after multiple mesh reduction processes are performed on the original rendering data of the first object, and one copy is obtained each time the mesh reduction processing is performed. Render data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一份渲染数据包括的所述多组渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行相同次数和不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple sets of rendering data included in the first rendering data are obtained by performing the same number of times of mesh reduction processing and different multiples of the original rendering data of the first object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据,包括:根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据;根据所述第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,从所选择的一份渲染数据的多组渲染数据中选择一组渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the selecting one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data includes : according to the distance and the fineness of the plurality of rendering data, select a rendering data from the multiple rendering data; according to the performance index and/or network status of the second electronic device, select from the selected A set of rendering data is selected from multiple sets of rendering data in one piece of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述性能指标包括所述第二电子设备的帧率、渲染延迟和温度参数中的一个或多个;所述网络状态包括所述第二电子设备的带宽和网络时延中的一个或多个。In a possible implementation manner, the performance index includes one or more of the frame rate, rendering delay, and temperature parameters of the second electronic device; the network status includes bandwidth and One or more of network delays.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据还包括缓冲数据,所述缓冲数据包括所述第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,所述N为大于1的整数,所述N份渲染数据均用于执行所述第一对象的渲染,且所述N份渲染数据的精细度不同。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data further includes buffer data, and the buffer data includes N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the N pieces of rendering data The rendering data are all used to execute the rendering of the first object, and the N pieces of rendering data have different finenesses.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括所述第一对象对应的M份渲染数据,所述M份渲染数据的精细度不同,所述M为大于所述N的整数;所述根据所述第一观察点位置,从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据中的所述缓冲数据,包括:根据所述第一观察点位置,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;根据所述距离,从所述多份渲染数据中确定一份渲染数据为所述第一对象的目标渲染数据,所述目标渲染数据的精细度满足所述第一对象的精细度要求,所述第一对象的精细度要求与所述距离相关;从所述M份渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为所述缓冲数据,所述N份渲染数据的精细度均小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes M pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the fineness of the M pieces of rendering data is different, and the M is an integer greater than the N ; Determining the buffer data in the first target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the position of the first observation point includes: determining the first object in the three-dimensional model according to the position of the first observation point The distance between the object and the position of the first viewing point; according to the distance, one piece of rendering data is determined from the plurality of pieces of rendering data as the target rendering data of the first object, and the fineness of the target rendering data The fineness requirement of the first object is satisfied, and the fineness requirement of the first object is related to the distance; N pieces of rendering data are selected from the M pieces of rendering data as the buffer data, and the N pieces of rendering data are selected as the buffer data. The fineness of the rendering data is less than or equal to the fineness of the target rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述方法还包括:所述第二电子设备根据第二观察点位置,从三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据,所述第二目标数据与所述第二观察点位置相关;所述第二电子设备根据所述第一目标数据和所述第二目标数据确定第三目标数据,并生成第一信息,其中所述第一目标数据不包括所述第三目标数据,且所述第二目标数据包括所述第三目标数据,所述第一信息用于指示待删除的第四目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括所述第四目标数据,且所述第二目标数据不包括所述第四目标数据;所述第二电子设备向所述第一电子设备发送所述第三目标数据的索引和所述第一信息。In a possible implementation manner, the method further includes: the second electronic device determines second target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the position of the second observation point, and the second target data is consistent with the first The positions of the two observation points are related; the second electronic device determines third target data according to the first target data and the second target data, and generates first information, wherein the first target data does not include the first target data three target data, and the second target data includes the third target data, the first information is used to indicate fourth target data to be deleted, the first target data includes the fourth target data, and The second target data does not include the fourth target data; the second electronic device sends an index of the third target data and the first information to the first electronic device.
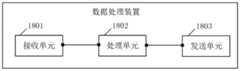
本申请第四方面提供一种数据处理装置,包括:接收单元、处理单元和发送单元;所述接收单元,用于接收来自于第二电子设备的第一数据请求,所述第一数据请求包括第一观察点位置;所述处理单元,用于根据所述第一数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据,其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;所述发送单元,用于向所述第二电子设备发送所述第一目标数据。The fourth aspect of the present application provides a data processing device, including: a receiving unit, a processing unit, and a sending unit; the receiving unit is configured to receive a first data request from a second electronic device, and the first data request includes The position of the first observation point; the processing unit is configured to determine first target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the first data request, the first target data includes rendering data for performing rendering of the three-dimensional model, The rendering data includes rendering data of a first object and rendering data of a second object, wherein the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is higher than that of the rendering data of the second object, and the first The distance between the object and the position of the first observation point is smaller than the distance between the second object and the position of the first observation point; the sending unit is configured to send the first observation point to the second electronic device a target data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括第一对象对应的多份渲染数据,所述多份渲染数据的精细度不同;所述处理单元,还用于:根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据,其中所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度与所述距离具有负相关关系。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the multiple pieces of rendering data have different finenesses; the processing unit is further configured to: according to the The first data request is to determine the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the position of the first observation point; according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple rendering data, from the multiple rendering data A piece of rendering data is selected as the rendering data of the first object, wherein the fineness of the rendering data of the first object has a negative correlation with the distance.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据中的第一份渲染数据包括多组渲染数据,所述多组渲染数据中的每组渲染数据用于渲染以得到所述第一对象,且所述多组渲染数据的精细度不同,所述第一份渲染数据是所述多份渲染数据中的任意一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the first piece of rendering data in the multiple pieces of rendering data includes multiple sets of rendering data, and each set of rendering data in the multiple sets of rendering data is used for rendering to obtain the first object , and the fineness of the multiple sets of rendering data is different, and the first set of rendering data is any one of the multiple sets of rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行多次面片缩减处理后得到的,其中,每执行一次面片缩减处理均得到一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple copies of rendering data are obtained after multiple mesh reduction processes are performed on the original rendering data of the first object, and one copy is obtained each time the mesh reduction processing is performed. Render data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一份渲染数据包括的所述多组渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行相同次数和不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple sets of rendering data included in the first rendering data are obtained by performing the same number of times of mesh reduction processing and different multiples of the original rendering data of the first object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元,还用于:根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据;根据所述第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,从所选择的一份渲染数据的多组渲染数据中选择一组渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the processing unit is further configured to: select one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data; The performance index and/or network status of the second electronic device, selecting a set of rendering data from multiple sets of rendering data in the selected piece of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述性能指标包括所述第二电子设备的帧率、渲染延迟和温度参数中的一个或多个;所述网络状态包括所述第二电子设备的带宽和网络时延中的一个或多个。In a possible implementation manner, the performance index includes one or more of the frame rate, rendering delay, and temperature parameters of the second electronic device; the network status includes bandwidth and One or more of network delays.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据还包括缓冲数据,所述缓冲数据包括所述第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,所述N为大于1的整数,所述N份渲染数据均用于执行所述第一对象的渲染,且所述N份渲染数据的精细度不同。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data further includes buffer data, and the buffer data includes N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the N pieces of rendering data The rendering data are all used to execute the rendering of the first object, and the N pieces of rendering data have different finenesses.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括所述第一对象对应的M份渲染数据,所述M份渲染数据的精细度不同,所述M为大于所述N的整数;所述处理单元,还用于:根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;根据所述距离,从所述多份渲染数据中确定一份渲染数据为所述第一对象的目标渲染数据,所述目标渲染数据的精细度满足所述第一对象的精细度要求,所述第一对象的精细度要求与所述距离相关;从所述M份渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为所述缓冲数据,所述N份渲染数据的精细度均小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes M pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the fineness of the M pieces of rendering data is different, and the M is an integer greater than the N The processing unit is further configured to: according to the first data request, determine the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the position of the first observation point; according to the distance, from the multiple One piece of rendering data is determined as the target rendering data of the first object, the fineness of the target rendering data meets the fineness requirement of the first object, and the fineness requirement of the first object is consistent with the specified The distance correlation; select N pieces of rendering data from the M pieces of rendering data as the buffer data, and the fineness of the N pieces of rendering data is less than or equal to the fineness of the target rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一数据请求中包括数据索引,所述数据索引用于指示所述第一目标数据,所述数据索引是所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置确定的。In a possible implementation manner, the first data request includes a data index, the data index is used to indicate the first target data, and the data index is the second electronic device according to the first The position of the observation point is fixed.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述接收单元,还用于接收来自于所述第二电子设备的第二数据请求;所述处理单元,还用于根据所述第二数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据,所述第二目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第二观察点位置相关;所述处理单元,还用于根据所述第一目标数据和所述第二目标数据确定第三目标数据,并生成第一信息,其中所述第一目标数据不包括所述第三目标数据,且所述第二目标数据包括所述第三目标数据,所述第一信息用于指示待删除的第四目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括所述第四目标数据,且所述第二目标数据不包括所述第四目标数据;所述发送单元,还用于向所述第二电子设备发送所述第三目标数据和所述第一信息。In a possible implementation manner, the receiving unit is further configured to receive a second data request from the second electronic device; The second target data is determined in the data of the model, and the second target data is related to the position of the second observation point in the three-dimensional model running in the second electronic device; the processing unit is also used to determine according to the first A target data and the second target data determine third target data, and generate first information, wherein the first target data does not include the third target data, and the second target data includes the third target data Target data, the first information is used to indicate fourth target data to be deleted, the first target data includes the fourth target data, and the second target data does not include the fourth target data; The sending unit is further configured to send the third target data and the first information to the second electronic device.
本申请第五方面提供一种数据生成装置,包括:获取单元和处理单元;所述获取单元,用于获取三维模型文件,所述三维模型文件包括用于构成三维模型的多个面片;所述处理单元,用于:将所述多个面片分成多个第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合中的每个第一面片集合包括多个连接的面片,且所述每个第一面片集合中的面片数量相同;将所述多个第一面片集合分成多个第一面片集合组,所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组包括多个所述第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成第一三维模型;对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第二面片集合组,所述多个第二面片集合组用于构成第二三维模型,所述第一三维模型的精细度高于所述第二三维模型的精细度;对所述多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,得到多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二面片集合中每个第二面片集合的面片数量与所述多个第一面片集合中每个第一面片集合的面片数量相同。The fifth aspect of the present application provides a data generation device, including: an acquisition unit and a processing unit; the acquisition unit is used to acquire a 3D model file, and the 3D model file includes a plurality of patches used to form a 3D model; The processing unit is configured to: divide the plurality of patches into a plurality of first patch sets, each of the plurality of first patch sets includes a plurality of connected patches, and The number of patches in each of the first patch sets is the same; the multiple first patch sets are divided into multiple first patch sets, and each of the multiple first patch sets The first mesh collection group includes a plurality of the first mesh collection groups, and the plurality of first mesh collection groups are used to form the first three-dimensional model; for each of the plurality of first mesh collection groups The first mesh set group performs mesh reduction processing to obtain a plurality of second mesh set groups after the number of meshes has been reduced, and the plurality of second mesh set groups are used to form a second three-dimensional model. The fineness of a three-dimensional model is higher than that of the second three-dimensional model; the plurality of second mesh sets are split to obtain a plurality of second mesh sets, and the plurality of second mesh sets are The number of patches in each second patch set in the set is the same as the number of patches in each first patch set in the plurality of first patch sets.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元,还用于:对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第三面片集合组,所述多个第三面片集合组用于构成第三三维模型,所述多个第三面片集合组中每个第三面片集合组的面片数量与所述多个第二面片集合组中每个第二面片集合组的面片数量不同。In a possible implementation manner, the processing unit is further configured to: perform patch reduction processing on each first patch set group in the plurality of first patch set groups, so as to obtain the number of patches A plurality of reduced third mesh set groups, the plurality of third mesh set groups are used to form a third three-dimensional model, and each of the third mesh set groups in the plurality of third mesh set groups The number of patches is different from that of each second patch set in the plurality of second patch sets.
在一种可能的实现方式中,每个所述第二面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/N,N为大于1的整数;每个所述第三面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/M,其中,M为大于N的整数。In a possible implementation, the number of patches in each of the second patch sets is 1/N of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where N is an integer greater than 1; The number of patches in each of the third patch sets is 1/M of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where M is an integer greater than N.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元,还用于:根据所述多个第一面片集合和所述多个第二面片集合生成树结构;其中,所述树结构包括多个第一节点和多个第二节点,所述多个第一节点分别对应于所述多个第一面片集合,所述多个第二节点分别对应于所述多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二节点中的每个节点均连接有所述多个第一节点中的多个节点。In a possible implementation manner, the processing unit is further configured to: generate a tree structure according to the multiple first patch sets and the multiple second patch sets; wherein the tree structure includes multiple a first node and a plurality of second nodes, the plurality of first nodes are respectively corresponding to the plurality of first patch sets, and the plurality of second nodes are respectively corresponding to the plurality of second patch sets , each node in the plurality of second nodes is connected to a plurality of nodes in the plurality of first nodes.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多个面片中的每个面片由多个顶点构成;所述处理单元,具体用于:确定第一面片集合组中位于边缘位置的多个目标顶点,所述第一面片集合为所述多个第一面片集合组中的任意一个面片集合组;锁定所述多个目标顶点,重新生成多个面片,以得到第二面片集合组,所述第二面片集合组的面片数量小于所述第一面片集合组的面片数量,所述第二面片集合组为所述多个第二面片集合组中的一个面片集合组。In a possible implementation manner, each of the plurality of patches is composed of a plurality of vertices; the processing unit is specifically configured to: determine a plurality of vertices in the first patch set group The target vertex, the first patch set is any one of the multiple first patch set groups; lock the multiple target vertices, and regenerate multiple patches to obtain the second surface A patch set group, the number of patches in the second patch set group is smaller than the number of patches in the first patch set group, and the second patch set group is one of the plurality of second patch set groups A collection of patches for .
本申请第六方面提供了一种电子设备,可以包括处理器,处理器和存储器耦合,存储器存储有程序指令,当存储器存储的程序指令被处理器执行时实现上述第一方面至第三方面所述的方法。对于处理器执行第一方面至第三方面的各个可能实现方式中的步骤,具体均可以参阅第一方面至第三方面,此处不再赘述。The sixth aspect of the present application provides an electronic device, which may include a processor, the processor is coupled to a memory, the memory stores program instructions, and when the program instructions stored in the memory are executed by the processor, the above-mentioned first to third aspects are implemented. described method. For the steps in each possible implementation manner of the processor executing the first aspect to the third aspect, reference may be made to the first aspect to the third aspect for details, and details are not repeated here.
本申请第七方面提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质中存储有计算机程序,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行上述第一方面至第三方面中任一实现方式所述的方法。The seventh aspect of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, where a computer program is stored in the computer-readable storage medium, and when it runs on a computer, the computer executes any one of the above-mentioned first to third aspects. Implement the method described in the manner.
本申请第八方面提供了一种电路系统,所述电路系统包括处理电路,所述处理电路配置为执行上述第一方面至第三方面中任一实现方式所述的方法。An eighth aspect of the present application provides a circuit system, where the circuit system includes a processing circuit configured to execute the method described in any one of the above first to third aspects.
本申请第九方面提供了一种计算机程序产品,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行上述第一方面至第三方面中任一实现方式所述的方法。A ninth aspect of the present application provides a computer program product, which, when run on a computer, causes the computer to execute the method described in any one of the above-mentioned first to third aspects.
附图说明Description of drawings
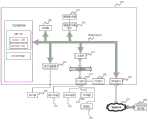
图1为相关技术的一种三维模型的资源文件的下载示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of downloading a resource file of a three-dimensional model in the related art;
图2为本申请实施例提供的一种电子设备101的结构示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of an
图3为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成和处理的流程示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic flowchart of the generation and processing of a 3D model data provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成方法400的流程示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic flowchart of a
图5为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型文件的数据结构示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the data structure of a three-dimensional model file provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图6为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型中的物体的示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of an object in a three-dimensional model provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图7为本申请实施例提供的一种面片缩减处理的示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of a patch reduction process provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图8为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成过程示意图;Fig. 8 is a schematic diagram of a generation process of three-dimensional model data provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图9为本申请实施例提供的一种基于三维模型中的面片生成无向图的示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of generating an undirected graph based on patches in a three-dimensional model provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图10为本申请实施例提供的一种生成多层次的三维模型数据的示意图;FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of generating multi-level three-dimensional model data provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图11为本申请实施例提供的一种树结构的示意图;FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram of a tree structure provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图12A为本申请实施例提供的链表结构示意图;FIG. 12A is a schematic diagram of the linked list structure provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图12B为本申请实施例提供的基于不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据渲染得到的三维模型示意图;FIG. 12B is a schematic diagram of a three-dimensional model rendered based on three-dimensional model data of different lightweight levels provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图13为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的处理方法1300的流程示意图;FIG. 13 is a schematic flowchart of a
图14为本申请实施例提供的一种确定三维模型数据的流程示意图;FIG. 14 is a schematic flow chart of determining three-dimensional model data provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图15为本申请实施例提供的一种渲染球和缓冲球的示意图;Fig. 15 is a schematic diagram of a rendering ball and a buffer ball provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图16为本申请实施例提供的多层渲染球和多层缓冲球的示意图;Fig. 16 is a schematic diagram of a multi-layer rendering ball and a multi-layer buffer ball provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图17为本申请实施例提供的一种观察点位置变化时的渲染示意图;Fig. 17 is a rendering schematic diagram when the position of the observation point changes according to the embodiment of the present application;
图18为本申请实施例提供的一种数据处理装置的结构示意图;FIG. 18 is a schematic structural diagram of a data processing device provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图19为本申请实施例提供的一种数据生成装置的结构示意图;FIG. 19 is a schematic structural diagram of a data generation device provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图20为本申请实施例提供的电子设备的一种结构示意图。FIG. 20 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图,对本申请的实施例进行描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本申请一部分的实施例,而不是全部的实施例。本领域普通技术人员可知,随着技术的发展和新场景的出现,本申请实施例提供的技术方案对于类似的技术问题,同样适用。Embodiments of the present application are described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Apparently, the described embodiments are only part of the embodiments of the present application, not all of the embodiments. Those of ordinary skill in the art know that, with the development of technology and the emergence of new scenarios, the technical solutions provided in the embodiments of the present application are also applicable to similar technical problems.
本申请的说明书和权利要求书及上述附图中的术语“第一”、“第二”等是用于区别类似的对象,而不必用于描述特定的顺序或先后次序。应该理解这样使用的数据在适当情况下可以互换,以便这里描述的实施例能够以除了在这里图示或描述的内容以外的顺序实施。The terms "first", "second" and the like in the specification and claims of the present application and the above drawings are used to distinguish similar objects, and are not necessarily used to describe a specific sequence or sequence. It is to be understood that the terms so used are interchangeable under appropriate circumstances such that the embodiments described herein can be practiced in sequences other than those illustrated or described herein.
此外,术语“包括”和“具有”以及他们的任何变形,意图在于覆盖不排他的包含,例如,包含了一系列步骤或模块的过程、方法、系统、产品或设备不必限于清楚地列出的那些步骤或模块,而是可包括没有清楚地列出的或对于这些过程、方法、产品或设备固有的其它步骤或模块。在本申请中出现的对步骤进行的命名或者编号,并不意味着必须按照命名或者编号所指示的时间/逻辑先后顺序执行方法流程中的步骤,已经命名或者编号的流程步骤可以根据要实现的技术目的变更执行次序,只要能达到相同或者相类似的技术效果即可。Furthermore, the terms "comprising" and "having", as well as any variations thereof, are intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion, for example, a process, method, system, product or device comprising a series of steps or modules is not necessarily limited to the expressly listed Instead, other steps or modules not explicitly listed or inherent to the process, method, product or apparatus may be included. The naming or numbering of the steps in this application does not mean that the steps in the method flow must be executed in the time/logic sequence indicated by the naming or numbering. The execution order of the technical purpose is changed, as long as the same or similar technical effect can be achieved.
为便于理解,以下先对本实施例所提出的技术术语进行介绍。For ease of understanding, the technical terms proposed in this embodiment are firstly introduced below.
三维模型是物体的多边形表示,通常用计算机或者其它视频设备进行显示。显示的物体可以是现实世界的实体,也可以是虚构的物体。任何物理自然界存在的东西都可以用三维模型表示。一般来说,三维模型是由顶点和三角面片组合而成的,通过顶点信息定义出边的信息,接着通过边的信息构成三角面片的信息,最终三维模型由这一个个三角面片组合而成。A 3D model is a polygonal representation of an object, usually displayed on a computer or other video device. Objects shown may be real-world entities or fictional objects. Anything that exists in physical nature can be represented by a three-dimensional model. Generally speaking, a 3D model is composed of vertices and triangular patches. The edge information is defined through the vertex information, and then the information of the triangular patches is formed through the edge information. The final 3D model is composed of each triangular patch. made.
多边形网格(Mesh):Mesh是三维计算机图形学和实体建模领域的一个专有名词。Mesh由一组顶点、边和面片组成,用于定义三维物体的形状。简单的形状如立方体、球、椭圆等,复杂的形状如岩石、树、水体湖泊等都可以由一组组Mesh拼接成。Mesh分组即将一个大的复杂的mesh拆分成一块块小的简单的mesh,如将山脉拆除一块块岩石、将大楼拆成一块块砖等。Polygonal mesh (Mesh): Mesh is a proper term in the field of 3D computer graphics and solid modeling. A Mesh consists of a set of vertices, edges, and patches that define the shape of a three-dimensional object. Simple shapes such as cubes, spheres, ellipses, etc., and complex shapes such as rocks, trees, water lakes, etc. can be spliced into groups of Mesh. Mesh grouping is about splitting a large complex mesh into small simple meshes, such as removing rocks from mountains and bricks from buildings.
三维数据格式:三维应用程序在运行时所使用的渲染数据的组织方式及数据标准称为数据格式,通用的数据格式如glb、fbx、obj等。3D data format: The organization method and data standard of the rendering data used by 3D applications at runtime is called data format, and common data formats are glb, fbx, obj, etc.
三维流媒体数据:是指将用于渲染的三维数据进行特殊处理以后,通过网络传输的方式分段按需传送,而不需要一次性完整下载所有数据。通过此技术可以解决终端设备存储空间不足的问题。3D streaming media data: After the 3D data used for rendering is specially processed, it is transmitted in segments and on demand through network transmission, without the need to download all the data at once. This technology can solve the problem of insufficient storage space of the terminal device.
多细节层次(Levels of Detail,LOD):是指根据物体模型的节点在显示环境中所处的位置和重要度,决定物体渲染的资源分配,降低非重要物体的面数和细节度,从而获得高效率的渲染运算。如摄像机离物体较远,则使用低精度模型。若摄像机离物体逐渐拉近,则将物体模型从低精度替换为中精度再替换为高精度。Levels of Detail (LOD): According to the position and importance of the nodes of the object model in the display environment, the allocation of resources for object rendering is determined, and the number of faces and details of non-important objects are reduced to obtain Efficient rendering operations. If the camera is far from the object, a low-resolution model is used. If the camera is getting closer to the object, the object model is replaced from low precision to medium precision and then to high precision.
N级轻量化:在三维模型领域,轻量化技术是指将一个复杂的模型进行简化,以降低渲染效果为代价提升渲染性能。N级轻量化即是指将原始模型轻量化处理为N个不同精细度的模型副本。如1级轻量化将三维模型的面片数削减为1/2、2级轻量化将三维模型的面片数削减为1/4等。N-level lightweight: In the field of 3D models, lightweight technology refers to simplifying a complex model to improve rendering performance at the cost of reducing rendering effects. N-level lightweight refers to the lightweight processing of the original model into N model copies of different fineness. For example,
锁边:是指在模型轻量化的过程中,忽略模型的边缘。简单来说,如果当前顶点位于模型的边缘,那么就不对当前顶点进行轻量化。该操作主要是为了解决模型轻量化以后,边缘破碎、断裂的问题。Overlock: It refers to ignoring the edge of the model during the process of model lightweighting. Simply put, if the current vertex is on the edge of the model, then the current vertex is not lightweighted. This operation is mainly to solve the problem of broken and broken edges after the model is lightweight.
渲染球:直接用于渲染的三维流媒体数据构成的数据缓冲区,该缓冲区的大小受终端设备性能、网络性能影响,能够通过一定的算法动态管理数据的增减。Rendering Sphere: A data buffer composed of 3D streaming media data directly used for rendering. The size of the buffer is affected by the performance of the terminal device and the network. It can dynamically manage the increase or decrease of data through a certain algorithm.
缓冲球:用于备选渲染的三维流媒体数据构成的数据缓冲区,该缓冲区用于提高渲染目标命中率,其大小同样受用户设备性能、网络性能影响,其原始数据来源于服务端下载,同样能够通过一定的算法动态管理数据的增减。Buffer ball: a data buffer composed of 3D streaming media data for alternative rendering. This buffer is used to improve the hit rate of the rendering target. Its size is also affected by the performance of the user device and network performance. The original data comes from the server download , and can also dynamically manage the increase or decrease of data through a certain algorithm.
渲染剔除:渲染剔除是指通过一定的算法和策略,剔除掉某些模型,从而通过减少需要渲染的目标来提高渲染效率和性能。如位于视野背面的物体、被遮挡的物体、距离过远的物体等,可以从渲染缓冲中剔除掉。Rendering culling: Rendering culling refers to the elimination of certain models through certain algorithms and strategies, thereby improving rendering efficiency and performance by reducing the number of objects that need to be rendered. For example, objects located at the back of the field of view, occluded objects, objects that are too far away, etc., can be removed from the rendering buffer.
级联坐标系:是指多个级别的坐标系通过级联的方式组织到一起,上层节点的坐标只记录基于下层坐标系的相对值,而无需记录完整的绝对值。例如,对于下层坐标系中的一个节点,该节点的坐标为(6666.6666,6666.6666,6666.6666);如果上层节点的坐标仅仅是相对该节点分别在x轴、y轴和z轴上偏移了1.1111,则上层节点的坐标可以记录为(1.1111,1.1111,1.1111),而不需要继续记录为(6667.7777,6667.7777,6667.7777)。通过级联坐标系可以极大减小数据存储占用空间,并解决超大规模场景下,数据表示位数不足造成的误差问题。Cascade coordinate system: refers to the cascading of multiple levels of coordinate systems organized together, the coordinates of the upper node only record the relative value based on the lower coordinate system, without recording the complete absolute value. For example, for a node in the lower coordinate system, the coordinates of the node are (6666.6666, 6666.6666, 6666.6666); if the coordinates of the upper node are only offset by 1.1111 on the x-axis, y-axis and z-axis relative to the node, Then the coordinates of the upper layer node can be recorded as (1.1111, 1.1111, 1.1111) instead of (6667.7777, 6667.7777, 6667.7777). The cascaded coordinate system can greatly reduce the space occupied by data storage, and solve the error problem caused by insufficient data representation digits in ultra-large-scale scenarios.
在传统方法中,在终端设备上运行三维应用时,通常需要先在终端设备上下载好三维应用需要渲染的三维模型的相关资源文件,以便于三维应用基于终端设备中的资源文件执行三维模型的渲染。由于终端设备的算力和存储空间受限,目前大部分三维场景的数据量已经达到终端设备的数据渲染极限。例如,目前大部分游戏应用中所需要渲染的三维场景的数据量已经达到数百兆字节(MB)甚至数千兆字节(GB),超出了部分终端设备的数据渲染极限。In traditional methods, when running a 3D application on a terminal device, it is usually necessary to first download the relevant resource files of the 3D model that the 3D application needs to render on the terminal device, so that the 3D application can execute the rendering of the 3D model based on the resource file in the terminal device. rendering. Due to the limited computing power and storage space of terminal devices, the data volume of most 3D scenes has reached the data rendering limit of terminal devices. For example, the data volume of the 3D scenes that need to be rendered in most game applications has reached hundreds of megabytes (MB) or even gigabytes (GB), which exceeds the data rendering limit of some terminal devices.
相关技术中,在服务器上将大型的三维场景划分为多个较小的三维场景,并生成各个较小的三维场景对应的三维资源文件。在终端设备运行三维应用的过程中,终端设备从服务器上下载相应的三维资源文件并执行当前场景的渲染。在场景发生切换时,终端设备再从服务器上下载新的场景所对应的三维资源文件,并删除原先所下载的三维资源文件。例如,可以参阅图1,图1为相关技术的一种三维模型的资源文件的下载示意图。对于部分关卡式的游戏,可以将游戏中的每个关卡切分为一个独立的资源文件;当玩家进入相应的关卡时,再从服务器上下载当前关卡对应的资源文件,并删除之前关卡对应的资源文件。In related technologies, a large 3D scene is divided into multiple smaller 3D scenes on a server, and 3D resource files corresponding to each smaller 3D scene are generated. During the process of running the 3D application on the terminal device, the terminal device downloads the corresponding 3D resource file from the server and executes the rendering of the current scene. When the scene is switched, the terminal device downloads the 3D resource file corresponding to the new scene from the server, and deletes the previously downloaded 3D resource file. For example, please refer to FIG. 1 , which is a schematic diagram of downloading a resource file of a 3D model in the related art. For some level-based games, you can divide each level in the game into an independent resource file; when the player enters the corresponding level, download the resource file corresponding to the current level from the server, and delete the resource file corresponding to the previous level. resource.
然而,在终端设备所运行的三维应用中的场景发生切换时,终端设备重新从服务器下载三维资源文件往往需要花费一定的时间,从而导致三维应用出现卡顿的现象。However, when the scene in the 3D application running on the terminal device is switched, it often takes a certain amount of time for the terminal device to re-download the 3D resource file from the server, thus causing the 3D application to freeze.
有鉴于此,本申请实施例提供了一种三维模型数据的生成方法及处理方法,通过将用户所上传的大型三维数据文件进行数据处理,从而将大型三维数据文件拆分为大量的小型三维数据,并存储在数据库中。然后,第一电子设备可以实时获取第二电子设备发送的数据请求,并根据该数据请求从大量的三维模型数据中确定与第二电子设备中三维模型的观察点位置相关的部分数据,进而向第二电子设备返回所确定的部分数据,保证第二电子设备能够实现实时渲染三维模型。并且,由于第一电子设备是以三维流媒体数据的形式向第二电子设备发送三维模型数据,即每次向第二电子设备发送的数据都是与观察点位置相关的一小部分数据,因此并不需要耗费太长的时间来实现三维数据的传输,保证了三维应用的流畅运行。In view of this, the embodiment of the present application provides a method for generating and processing 3D model data. By processing the large 3D data files uploaded by users, the large 3D data files are split into a large number of small 3D data files. , and stored in the database. Then, the first electronic device can obtain the data request sent by the second electronic device in real time, and determine part of the data related to the position of the observation point of the three-dimensional model in the second electronic device from a large amount of three-dimensional model data according to the data request, and then send the The second electronic device returns the determined part of the data, ensuring that the second electronic device can render the 3D model in real time. Moreover, since the first electronic device sends 3D model data to the second electronic device in the form of 3D streaming media data, that is, each time the data sent to the second electronic device is a small part of data related to the position of the observation point, therefore It does not need to take too long to realize the transmission of 3D data, which ensures the smooth running of 3D applications.
示例性地,本申请实施例中的第一电子设备和第二电子设备可以是服务器、智能手机(mobile phone)、个人电脑(personal computer,PC)、笔记本电脑、平板电脑、智慧电视、移动互联网设备(mobile internet device,MID)、可穿戴设备(如智能手表、智能眼镜或者智能头盔等),虚拟现实(virtual reality,VR)设备、增强现实(augmented reality,AR)设备、工业控制(industrial control)中的无线电子设备、无人驾驶(self driving)中的无线电子设备、远程手术(remote medical surgery)中的无线电子设备、智能电网(smart grid)中的无线电子设备、运输安全(transportation safety)中的无线电子设备、智慧城市(smart city)中的无线电子设备、智慧家庭(smart home)中的无线电子设备等。以下实施例对该电子设备的具体形式不做特殊限制。Exemplarily, the first electronic device and the second electronic device in the embodiment of the present application may be a server, a smart phone (mobile phone), a personal computer (personal computer, PC), a notebook computer, a tablet computer, a smart TV, a mobile Internet Devices (mobile internet device, MID), wearable devices (such as smart watches, smart glasses or smart helmets, etc.), virtual reality (virtual reality, VR) devices, augmented reality (augmented reality, AR) devices, industrial control (industrial control) ), wireless electronic devices in self driving, wireless electronic devices in remote medical surgery, wireless electronic devices in smart grid, transportation safety ), wireless electronic devices in smart cities, wireless electronic devices in smart homes, etc. The following embodiments do not specifically limit the specific form of the electronic device.
在一种可能的示例中,第一电子设备例如可以为服务器,第二电子设备例如可以为智能手机、笔记本电脑或平板电脑等移动设备。In a possible example, the first electronic device may be, for example, a server, and the second electronic device may be, for example, a mobile device such as a smart phone, a notebook computer, or a tablet computer.
可以参阅图2,图2为本申请实施例提供的一种电子设备101的结构示意图。如图2所示,电子设备101包括处理器103,处理器103和系统总线105耦合。处理器103可以是一个或者多个处理器,其中每个处理器都可以包括一个或多个处理器核。显示适配器(videoadapter)107,显示适配器可以驱动显示器109,显示器109和系统总线105耦合。系统总线105通过总线桥111和输入输出(I/O)总线耦合。I/O接口115和I/O总线耦合。I/O接口115和多种I/O设备进行通信,比如输入设备117(如:触摸屏等),外存储器121,(例如,硬盘、软盘、光盘或优盘),多媒体接口等)。收发器123(可以发送和/或接收无线电通信信号),摄像头155(可以捕捉静态和动态数字视频图像)和外部USB端口125。其中,可选地,和I/O接口115相连接的接口可以是USB接口。Refer to FIG. 2 , which is a schematic structural diagram of an
其中,处理器103可以是任何传统处理器,包括精简指令集计算(reducedinstruction set Computing,RISC)处理器、复杂指令集计算(complex instruction setcomputing,CISC)处理器或上述的组合。可选地,处理器可以是诸如ASIC的专用装置。Wherein, the
电子设备101可以通过网络接口129和软件部署服务器149通信。示例性的,网络接口129是硬件网络接口,比如,网卡。网络127可以是外部网络,比如因特网,也可以是内部网络,比如以太网或者虚拟私人网络(virtual private network,VPN)。可选地,网络127还可以是无线网络,比如WiFi网络,蜂窝网络等。The
硬盘驱动器接口131和系统总线105耦合。硬件驱动接口和硬盘驱动器133相连接。内存储器135和系统总线105耦合。运行在内存储器135的数据可以包括电子设备101的操作系统(OS)137、应用程序143和调度表。Hard
处理器103可以通过系统总线105与内存储器135通信,从内存储器135中取出应用程序143中的指令和数据,从而实现程序的执行。The
操作系统包括Shell 139和内核(kernel)141。Shell 139是介于使用者和操作系统的内核间的一个接口。Shell 139是操作系统最外面的一层。Shell 139管理使用者与操作系统之间的交互:等待使用者的输入,向操作系统解释使用者的输入,并且处理各种各样的操作系统的输出结果。The operating system includes a
内核141由操作系统中用于管理存储器、文件、外设和系统资源的那些部分组成。内核141直接与硬件交互,操作系统内核通常运行进程,并提供进程间的通信,提供CPU时间片管理、中断、内存管理和IO管理等等。
示例性地,在电子设备101为智能手机的情况下,应用程序143包括即时通讯相关的程序。在一个实施例中,在需要执行应用程序143时,电子设备101可以从软件部署服务器149下载应用程序143。Exemplarily, when the
为了便于理解,以下将结合附图介绍本申请实施例所提供的三维模型数据的生成和处理的总体流程。可以参阅图3,图3为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成和处理的流程示意图。For ease of understanding, the general process of generating and processing 3D model data provided by the embodiments of the present application will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Please refer to FIG. 3 , which is a schematic flow chart of generating and processing 3D model data provided by an embodiment of the present application.
如图3所示,用户可以预先向云端上传三维模型的原文件,由云端的服务器对三维模型的原文件进行处理,以生成后续能够使用的三维模型数据。As shown in FIG. 3 , the user can upload the original file of the 3D model to the cloud in advance, and the server in the cloud processes the original file of the 3D model to generate 3D model data that can be used later.
在三维模型数据生成阶段,服务器可以对三维模型的原文件中的mesh进行拆分,重新组合得到多个面片集合。然后,服务器对重组得到的多个面片集合进行面片缩减处理,即轻量化处理,从而得到精细度降低的模型副本。进一步地,服务器可以通过对执行面片缩减处理后的面片集合进行合并,并对合并后的面片集合执行面片缩减处理,以得到精细度进一步降低的模型副本。通过循环执行合并面片集合以及面片缩减处理操作,能够得到多层次数据,每一层次的数据均能够用于渲染模型中相同的对象,但不同层次的数据的精细度不同。进一步地,在生成多层次数据的同时,服务器可以是对三维模型执行N级轻量化,即在生成多层次数据时采用不同的轻量化级别对面片集合进行面片缩减处理,从而生成多级别、多层次的模型数据。不同级别以及不同层次的模型数据对应的精细度不同。最后,服务器为所生成的三维模型数据生成相关的索引数据,以便于能够快速定位所需的数据。其中,服务器所生成的三维模型数据可以是存储于三维云数据库中,以便于服务器查找和获取。In the stage of 3D model data generation, the server can split the mesh in the original file of the 3D model, and recombine to obtain multiple mesh sets. Then, the server performs mesh reduction processing, that is, lightweight processing, on the reorganized multiple mesh sets, so as to obtain a model copy with reduced fineness. Further, the server may merge the mesh sets after the mesh reduction processing is performed, and perform mesh reduction processing on the merged mesh set, so as to obtain a model copy with a further reduced fineness. Multi-level data can be obtained by cyclically performing the combined patch collection and patch reduction processing operations, and the data at each level can be used to render the same object in the model, but the fineness of the data at different levels is different. Further, while generating multi-level data, the server can perform N-level lightweighting on the 3D model, that is, when generating multi-level data, use different lightweight levels to perform mesh reduction processing on the mesh set, thereby generating multi-level, Multi-level model data. Different levels and different levels of model data correspond to different degrees of precision. Finally, the server generates relevant index data for the generated 3D model data, so that the required data can be quickly located. Wherein, the 3D model data generated by the server may be stored in a 3D cloud database, so as to facilitate the server to search and acquire.
在三维模型数据处理阶段,服务器可以根据终端设备所反馈的三维模型中的观察点位置,确定并从三维云数据库中获取渲染所需的数据。然后,服务器可以根据所获取的数据装配得到三维流媒体数据,并且剔除其中被遮挡物相关的数据,以减少所传输的数据。最后,服务器生成缓冲球、渲染球相关的帧数据,并将生成的帧数据发送给终端设备。其中,缓冲球对应的帧数据是用于缓冲的三维模型数据,渲染球对应的帧数据则是用于直接渲染三维模型的数据。这样一来,终端设备在接收到服务器发送的帧数据后,则可以根据接收到的帧数据执行三维模型的渲染。In the 3D model data processing stage, the server can determine and obtain data required for rendering from the 3D cloud database according to the observation point position in the 3D model fed back by the terminal device. Then, the server can assemble the three-dimensional streaming media data according to the acquired data, and remove the data related to the occluded object, so as to reduce the transmitted data. Finally, the server generates buffer balls, renders frame data related to the ball, and sends the generated frame data to the terminal device. The frame data corresponding to the buffer ball is 3D model data for buffering, and the frame data corresponding to the rendering ball is data for directly rendering the 3D model. In this way, after receiving the frame data sent by the server, the terminal device can perform rendering of the 3D model according to the received frame data.
以上介绍了生成和处理三维模型数据的总体流程,以下将分别详细介绍三维模型数据的生成方法和三维模型数据的处理方法。The overall process of generating and processing 3D model data is introduced above, and the following will introduce in detail the generation method of 3D model data and the processing method of 3D model data respectively.
可以参阅图4,图4为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成方法400的流程示意图。如图4所示,该方法400包括以下的步骤401-405。Please refer to FIG. 4 , which is a schematic flowchart of a
步骤401,获取三维模型文件,所述三维模型文件包括用于构成三维模型的多个面片。In
本实施例中,用于生成三维模型数据的电子设备可以获取到需要处理的三维模型文件,该三维模型文件可以是用户(例如三维模型的设计者)上传至电子设备的。其中,该三维模型文件可以包括多个mesh的数据,通过多个mesh的数据来定义三维模型中各个物体的形状。In this embodiment, the electronic device for generating 3D model data may obtain a 3D model file to be processed, and the 3D model file may be uploaded to the electronic device by a user (such as a designer of the 3D model). Wherein, the 3D model file may include data of multiple meshes, and the shape of each object in the 3D model is defined by the data of multiple meshes.
示例性地,可以参阅图5,图5为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型文件的数据结构示意图。如图5所示,在三维模型文件的数据结构中,包括多个层级结构,分别为:场景(scene)、节点(node)、网格点(mesh)和材质(material)。其中,scene层级为三维模型中整个场景的入口点,scene层级下包括三维模型中整个场景的渲染相关参数;node层级为scene层级中的一个节点,node层级为三维模型中的场景的组织者,用于描述场景的构成;mesh层级位于node层级之下,用于描述在场景中出现的几何物体;material层级位于mesh层级之下,material层级下包括了用于定义几何物体的模型外观的参数。比如,material层级下包括了材质属性参数,该材质属性参数可以包括基础色、法线、高光、粗糙度以及金属度等参数。For example, refer to FIG. 5 , which is a schematic diagram of a data structure of a 3D model file provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 5 , the data structure of the 3D model file includes multiple hierarchical structures, namely: scene (scene), node (node), grid point (mesh) and material (material). Among them, the scene level is the entry point of the entire scene in the 3D model, and the scene level includes the rendering related parameters of the entire scene in the 3D model; the node level is a node in the scene level, and the node level is the organizer of the scene in the 3D model. It is used to describe the composition of the scene; the mesh level is located under the node level, and is used to describe the geometric objects appearing in the scene; the material level is located under the mesh level, and the material level includes parameters used to define the appearance of the model of the geometric object. For example, the material level includes material attribute parameters, which may include parameters such as base color, normal line, highlight, roughness, and metalness.
一般来说,每个mesh由一组顶点、边和面片组成,通过顶点信息可以定义出边的信息,接着通过边的信息构成面片的信息,最终由一个个面片组合得到mesh。三维模型中的物体则可以是通过由多个面片组合得到的mesh定义得到。示例性地,可以参阅图6,图6为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型中的物体的示意图。如图6所示,对于三维模型中的一个人头模型,该人头模型可以是由多个位于不同位置的顶点连接得到多个边,并且由相互连接的边构成多个面片,该多个面片即可用于描述整个人头模型的形状。Generally speaking, each mesh is composed of a set of vertices, edges, and patches. The edge information can be defined through the vertex information, and then the edge information is used to form the patch information, and finally the mesh is obtained by combining each patch. The objects in the 3D model can be obtained by mesh definition obtained by combining multiple faces. For example, refer to FIG. 6 , which is a schematic diagram of an object in a three-dimensional model provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 6, for a human head model in a three-dimensional model, the human head model can be connected by a plurality of vertices located in different positions to obtain multiple edges, and a plurality of facets are formed by the interconnected edges, and the plurality of faces A slice can then be used to describe the shape of the entire human head model.
步骤402,将所述多个面片分成多个第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合中的第一每个面片集合包括多个连接的面片,且所述每个第一面片集合中的面片数量相同。
其中,所述多个第一面片集合中的每个第一面片集合中所包括的面片都是相互连接的,并没有在空间上分离的面片。例如,将10000个面片分成100个面片集合,每个面片集合中包括100个连接的面片。一般来说,在本实施例中,由多个面片所构成的面片集合中的面片数量均是固定的。Wherein, the patches included in each of the plurality of first patch sets are connected to each other, and there is no spatially separated patch. For example, 10000 patches are divided into 100 patch sets, and each patch set includes 100 connected patches. Generally speaking, in this embodiment, the number of patches in the patch set composed of multiple patches is fixed.
步骤403,将所述多个第一面片集合分成多个第一面片集合组,所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组包括多个第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成第一三维模型。Step 403: Divide the multiple first patch sets into multiple first patch set groups, each first patch set group in the multiple first patch set groups includes multiple first patch sets set, the plurality of first mesh set groups are used to form the first three-dimensional model.
通常,三维模型文件中的面片是以mesh的形式进行组织的,即每个mesh中包括多个用于定义物体形状的面片,且每个mesh中的面片大小和数量可以是不相同的。Usually, the patches in the 3D model file are organized in the form of mesh, that is, each mesh includes multiple patches used to define the shape of the object, and the size and number of patches in each mesh can be different of.
本实施例中,为了便于后续对面片执行缩减处理,电子设备将三维模型文件中的多个第一面片集合分成多个第一面片集合组,并且该多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组中均包括多个第一面片集合。In this embodiment, in order to facilitate subsequent reduction processing on patches, the electronic device divides the multiple first patch sets in the 3D model file into multiple first patch set groups, and among the multiple first patch set groups Each first patch set group of includes multiple first patch sets.
示例性地,对于三维模型文件中的一个mesh,该mesh中共包括A个面片,则电子设备可以将该mesh中的A个面片分为B个面片集合,每个面片集合中包括C个面片,其中C=A/B;然后B个面片集合可以组成D个面片集合组,每个面片集合组包括的面片集合数量为B/D。Exemplarily, for a mesh in a 3D model file, the mesh includes a total of A faces, then the electronic device can divide the A faces in the mesh into B face sets, and each face set includes C patches, where C=A/B; then B patch sets can form D patch set groups, and the number of patch sets included in each patch set group is B/D.
步骤404,对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第二面片集合组,所述多个第二面片集合组用于构成第二三维模型,所述第一三维模型的精细度高于所述第二三维模型的精细度。Step 404: Perform patch reduction processing on each of the plurality of first patch set groups to obtain a plurality of second patch set groups with reduced number of patches. A second mesh set group is used to form a second three-dimensional model, and the fineness of the first three-dimensional model is higher than that of the second three-dimensional model.
本实施例中,通过执行面片缩减处理,可以将由多个面片构成的网格A转换为另一个网格B。相比于网络A,网格B具有更少的顶点、边和面片。因此,对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,可以缩减每个面片集合组中的面片,从而得到面片数量缩减后的多个第二面片集合组。其中,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成原始的第一三维模型,所述多个第二面片集合组则用于构成第二三维模型。由于第二三维模型是由面片缩减后的面片集合组构成的,因此第二三维模型的精细度要低于原始的第一三维模型,但是第二三维模型的数据量要小于原始的第一三维模型的数据量。例如,在第二面片集合组中,面片缩减处理后的各个面片集合组的面片数量均是面片缩减处理前的1/2,即多个第一面片集合组中的每个面片集合组都被缩减了1/2的面片。In this embodiment, mesh A composed of a plurality of patches can be converted into another mesh B by performing patch reduction processing. Compared to network A, mesh B has fewer vertices, edges and patches. Therefore, performing patch reduction processing on each of the plurality of first patch set groups can reduce the patches in each patch set group, thereby obtaining a plurality of reduced numbers of patches. The second patch collection group. Wherein, the plurality of first mesh collection groups are used to form the original first three-dimensional model, and the plurality of second mesh collection groups are used to form the second three-dimensional model. Since the second 3D model is composed of mesh sets after face reduction, the fineness of the second 3D model is lower than that of the original first 3D model, but the amount of data in the second 3D model is smaller than that of the original first 3D model. A data volume of a three-dimensional model. For example, in the second patch set group, the number of patches in each patch set group after the patch reduction process is 1/2 of that before the patch reduction process, that is, each of the multiple first patch set groups Each patch collection group is reduced by 1/2 of the patches.
可选的,为了保证执行面片缩减处理后,面片集合的边缘不会出现破碎或者断裂的问题,本实施例可以是对面片集合进行锁边后,再执行面片缩减处理。简单来说,在对面片集合执行面片缩减处理的过程中,保持面片集合边缘位置的顶点不变,只缩减面片集合内部的顶点缩减,从而实现面片的缩减处理。Optionally, in order to ensure that the edge of the mesh set will not be broken or broken after the mesh reduction process is performed, in this embodiment, the mesh reduction process may be performed after the edge locking is performed on the mesh set. To put it simply, in the process of performing patch reduction processing on the patch set, the vertices at the edge positions of the patch set are kept unchanged, and only the vertex reduction inside the patch set is reduced, so as to realize the patch reduction process.
示例性地,在多个第一面片集合组中的每个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理的过程中,电子设备可以确定第一面片集合组中位于边缘位置的多个目标顶点,所述第一面片集合组为所述多个第一面片集合组中的任意一个面片集合组。由于第一面片集合组中的多个面片是相互连接的,因此第一面片集合组中位于边缘位置的多个目标顶点实际上则是第一面片集合组中的多个面片最外围的顶点。然后,电子设备锁定所述多个目标顶点,重新生成多个面片,以得到第二面片集合组,所述第二面片集合组的面片数量小于所述第一面片集合组的面片数量,所述第二面片集合组为所述多个第二面片集合组中的一个面片集合组。具体地,电子设备可以是保持所述多个目标顶点的位置不变,并移除一部分除目标顶点之外的其他顶点,并且重新连接剩余的顶点,进而重新生成更少的面片,以得到同样包括多个连接的面片的第二面片集合组。Exemplarily, during the process of performing patch reduction processing on each of the plurality of first patch set groups, the electronic device may determine a plurality of target vertices at edge positions in the first patch set group, The first patch collection group is any one patch collection group in the plurality of first patch collection groups. Since the multiple patches in the first patch collection group are connected to each other, the multiple target vertices at the edge positions in the first patch collection group are actually multiple patches in the first patch collection group The outermost vertices. Then, the electronic device locks the plurality of target vertices, and regenerates a plurality of facets to obtain a second set of facets, the number of faces of the second set of facets is smaller than that of the first set of facets The number of patches, the second patch collection group is one patch collection group in the plurality of second patch collection groups. Specifically, the electronic device may keep the positions of the plurality of target vertices unchanged, remove a part of vertices other than the target vertices, and reconnect the remaining vertices, thereby regenerating fewer facets, to obtain A second patch collection group that also includes a plurality of connected patches.
可以参阅图7,图7为本申请实施例提供的一种面片缩减处理的示意图。如图7中的(a)所示,左侧的面片集合1共包括7个顶点和6个面片,其中位于边缘位置的顶点共有6个。在对左侧的面片集合1执行面片缩减处理的过程中,移除面片集合1中间的顶点,并且重新连接剩余的6个顶点,以得到右侧的面片集合2,面片集合2中位于边缘位置的顶点保持不变。此外,面片集合2中共包括6个顶点以及4个面片,面片数量从6缩减到了4。Refer to FIG. 7 , which is a schematic diagram of a mesh reduction process provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in (a) of FIG. 7 , the patch set 1 on the left includes 7 vertices and 6 patches, among which there are 6 vertices at edge positions. In the process of performing patch reduction on the patch set 1 on the left, the vertices in the middle of the patch set 1 are removed, and the remaining 6 vertices are reconnected to obtain the patch set 2 on the right, the patch set Vertices at edge positions in 2 remain unchanged. In addition, the patch set 2 includes 6 vertices and 4 patches, and the number of patches is reduced from 6 to 4.
如图7中的(b)所示,面片集合3共包括10个顶点和10个面片,其中位于边缘位置的顶点共有8个。在对的面片集合3执行面片缩减处理的过程中,移除面片集合3中间的两个顶点,并且在中间重新生成一个新的顶点,然后连接剩余的9个顶点,以得到右侧的面片集合4,面片集合4中位于边缘位置的顶点保持不变。此外,面片集合4中共包括9个顶点以及8个面片,面片数量从10缩减到了8。As shown in (b) of FIG. 7 , the patch set 3 includes 10 vertices and 10 patches in total, among which there are 8 vertices at edge positions. In the process of performing the patch reduction process on the patch set 3, remove the two vertices in the middle of the patch set 3, and regenerate a new vertex in the middle, and then connect the remaining 9 vertices to get the right side The patch set 4 of the patch set 4, the vertices at the edge positions in the patch set 4 remain unchanged. In addition, the patch set 4 includes 9 vertices and 8 patches, and the number of patches is reduced from 10 to 8.
步骤405,对所述多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,得到多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二面片集合中每个第二面片集合的面片数量与所述多个第一面片集合中每个第一面片集合的面片数量相同。
也就是说,以面片集合组为单位执行面片缩减处理后,面片集合组中的面片数量发生了变化,因此可以对面片缩减处理后得到的多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,重新组成多个第二面片集合,从而保证每个面片集合中的面片数量是固定的。That is to say, after the patch reduction process is performed in the unit of the patch set group, the number of patches in the patch set group has changed, so the multiple second patch set groups obtained after the patch reduction process can be disassembled. points, and recompose multiple second patch sets, so as to ensure that the number of patches in each patch set is fixed.
这样一来,在得到重新组合的多个第二面片集合之后,可以循环执行上述的步骤402-405,即将面片集合分成面片集合组、对面片集合组执行面片缩减处理以及拆分面片缩减处理后的面片集合组,以得到执行不同次数的面片缩减处理后的面片集合。其中,执行不同次数的面片缩减处理后的面片集合所构成的三维模型的精度各不相同,从而能够得到不同精度下的三维模型数据。这样一来,电子设备每次重新划分得到的多个面片集合组进行面片缩减处理后,都能够得到一份新的三维模型数据。最终,电子设备得到的多份精细度不同的三维模型数据可以构成多个层次的三维模型数据,不同层次的三维模型数据的精细度不同,三维模型数据的层次越低,三维模型数据的精细度则越高。In this way, after obtaining the recombined multiple second patch sets, the above-mentioned steps 402-405 can be executed cyclically, that is, the patch set is divided into patch set groups, and the patch reduction processing and splitting are performed on the patch set groups. The mesh set group after the patch reduction process is used to obtain the mesh set after performing the patch reduction process for different times. Wherein, the accuracy of the three-dimensional model formed by the mesh set after performing different times of mesh reduction processing is different, so that the three-dimensional model data with different accuracy can be obtained. In this way, a new piece of three-dimensional model data can be obtained after each re-division of multiple facet set groups obtained by the electronic device undergoes facet reduction processing. In the end, multiple 3D model data with different degrees of fineness obtained by electronic equipment can form multiple layers of 3D model data. The fineness of 3D model data at different levels is different. is higher.
示例性地,在多个第二面片集合组中的每个面片集合组都被缩减了1/2的面片的情况下,则总的面片数量变成原来的面片数量的1/2。然后,将执行面片缩减处理后得到的所有面片重新拆分为多个新的面片集合(即多个第二面片集合),每个面片集合中的面片数量固定,这样多个第二面片集合的面片集合数量是多个第一面片集合数量的1/2。然后,再将多个第二面片集合分为多个面片集合组,该多个面片集合组的数量为多个第一面片集合组的1/2,且该多个面片集合组能够再次用于执行面片缩减处理。Exemplarily, in the case that each of the plurality of second patch collection groups is reduced by 1/2 of the patches, the total number of patches becomes 1 of the original number of patches /2. Then, all the patches obtained after performing the patch reduction process are re-split into multiple new patch sets (that is, multiple second patch sets), and the number of patches in each patch set is fixed, so many The number of patch sets of the second patch set is 1/2 of the number of multiple first patch sets. Then, divide the plurality of second patch sets into multiple patch set groups, the number of the plurality of patch set groups is 1/2 of the plurality of first patch set groups, and the plurality of patch sets Groups can be used again to perform patch reduction processing.
这样一来,通过执行上述的三维模型数据的生成方法,能够得到精细度以及数据量均不相同的三维模型数据,以便于满足不同场景下的模型渲染需求。在三维模型数据的实际使用阶段,电子设备则可以是根据终端设备中的观察点位置或者终端设备的性能选择相应精细度的三维模型数据,从而能够在满足不同终端设备的要求的情况下尽可能地降低所需传输的模型数据量,保证三维模型的实时渲染。In this way, by executing the above method for generating 3D model data, 3D model data with different fineness and data volume can be obtained, so as to meet model rendering requirements in different scenarios. In the actual use stage of the 3D model data, the electronic device can select the 3D model data of the corresponding fineness according to the position of the observation point in the terminal device or the performance of the terminal device, so that it can meet the requirements of different terminal devices as much as possible. Minimize the amount of model data that needs to be transmitted and ensure real-time rendering of the 3D model.
可选的,除了通过对面片集合组执行多次面片缩减处理,以得到精细度不同的三维模型数据之外,本实施例还可以是通过在面片缩减处理阶段采用不同的面片缩减倍数,进一步获得精细度不同的三维模型数据。简单来说,对于同一份三维模型数据,通过对该份三维模型数据中的面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,能够得到另一份精细度不同的三维模型数据;但是,如果通过不同的面片缩减倍数对该份三维模型数据执行面片缩减处理,则能够进一步得到多组精细度互不相同的三维模型数据。Optionally, in addition to performing multiple mesh reduction processes on the mesh set group to obtain 3D model data with different fineness, this embodiment can also use different mesh reduction factors in the mesh reduction processing stage , and further obtain 3D model data with different fineness. To put it simply, for the same 3D model data, another 3D model data with different fineness can be obtained by performing mesh reduction processing on the mesh set group in the 3D model data; however, if different facets If the patch reduction process is performed on the 3D model data according to the patch reduction factor, multiple sets of 3D model data with different degrees of fineness can be further obtained.
示例性地,上述的方法400还可以包括:对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第三面片集合组,所述多个第三面片集合组用于构成第三三维模型,所述多个第三面片集合组中每个第三面片集合组的面片数量与所述多个第二面片集合组中每个第二面片集合组的面片数量不同。Exemplarily, the above-mentioned
本步骤与上述的步骤404类似,都是对多个第一面片集合组中的每个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理。不同之处在于:本步骤中所执行的面片缩减处理的面片缩减量大于步骤404中所执行的面片缩减处理的面片缩减量。因此,本步骤中所得到的多个第三面片集合组中面片集合组的面片缩减数量大于步骤404所得到的多个第二面片集合组中面片集合组的面片缩减数量。This step is similar to the above-mentioned
例如,假设多个第一面片集合组中各个面片集合组的面片数量为400,步骤404基于面片缩减倍数为2执行面片缩减处理后得到的多个第二面片集合组中各个面片集合组的面片数量为200,本步骤基于面片缩减倍数为4执行面片缩减处理后得到的多个第三面片集合组中各个面片集合组的面片数量为100。显然,第三面片集合中各个面片集合组的面片缩减量为300,大于第二面片集合组中各个面片集合组的面片缩减量(200)。For example, assuming that the number of patches in each of the multiple first patch set groups is 400,
也就是说,第三三维模型和第二三维模型都是经过一次面片缩减处理后得到的,即第三三维模型和第一三维模型对应的模型数据是属于同一个层次的模型数据;但是,第三三维模型和第二三维模型是采用不同的面片缩减倍数执行面片缩减处理后得到的,因此第三三维模型和第二三维模型对应的模型数据是属于不同级别的模型数据。其中,第三三维模型对应的面片缩减倍数更高,即第三三维模型的轻量化级别更高,因此第三三维模型对应的模型数据的级别高于第二三维模型对应的模型数据的级别。That is to say, both the third 3D model and the second 3D model are obtained after a mesh reduction process, that is, the model data corresponding to the third 3D model and the first 3D model belong to the same level of model data; however, The third 3D model and the second 3D model are obtained after performing mesh reduction processing with different mesh reduction factors, so the model data corresponding to the third 3D model and the second 3D model belong to different levels of model data. Among them, the patch reduction factor corresponding to the third 3D model is higher, that is, the lightweight level of the third 3D model is higher, so the level of the model data corresponding to the third 3D model is higher than that of the model data corresponding to the second 3D model .
可选的,所述第一面片集合组中的每个面片集合组可以包括相同数量的面片。本步骤和上述的步骤404中可以是基于不同的面片缩减倍数来对面片集合执行面片缩减处理,从而使得面片缩减后的面片集合的面片数量与面片缩减前具有倍数关系。Optionally, each patch set in the first patch set may include the same number of patches. In this step and the above-mentioned
示例性地,每个所述第二面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/N,N为大于1的整数;每个所述第三面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/M,其中,M为大于N的整数。例如,N可以为2,M可以为3。Exemplarily, the number of patches in each of the second patch sets is 1/N of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where N is an integer greater than 1; The number of patches in the three patch sets is 1/M of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where M is an integer greater than N. For example, N can be 2, and M can be 3.
也就是说,通过执行多次面片集合的合并操作和面片缩减处理,能够得到多个层次的三维模型数据,每个层次的三维模型数据的精细度不同;通过在生成多个层次的三维模型数据的过程中,以不同的面片缩减倍数执行面片缩减处理,则能够在三维模型数据的各个层次中进一步生成级别不一样的三维模型数据,同一层次但级别不同的三维模型数据的精细度不同。That is to say, by performing the merging operation and mesh reduction processing of multiple mesh sets, multiple levels of 3D model data can be obtained, and the fineness of each level of 3D model data is different; by generating multiple levels of 3D model data In the process of model data, if the mesh reduction process is performed with different mesh reduction factors, 3D model data of different levels can be further generated in each level of 3D model data, and the fineness of 3D model data of the same level but different levels can be generated. degrees vary.
可选的,在生成多个层次以及多个级别的三维模型数据的情况下,为了便于索引到特定精细度下的三维模型数据,本实施例中可以生成相应的树结构,以便于基于树结构的层次结构和级别结构索引到相应的三维模型数据。Optionally, in the case of generating multiple levels and multiple levels of 3D model data, in order to facilitate indexing to 3D model data at a specific level of fineness, a corresponding tree structure can be generated in this embodiment, so that based on the tree structure The hierarchical and level structure indexes to the corresponding 3D model data.
具体地,上述的方法400还可以包括:根据所述多个第一面片集合和所述多个第二面片集合生成树结构;其中,所述树结构包括多个第一节点和多个第二节点,所述多个第一节点分别对应于所述多个第一面片集合,即所述多个第一面片集合中的各个面片集合以第一节点来表示;所述多个第二节点分别对应于所述多个第二面片集合,即所述多个第二面片集合中的各个面片集合以第二节点来表示。Specifically, the
由于所述多个第二面片集合中的面片集合实际上是对多个第一面片集合进行面片缩减处理以及合并操作后得到的,因此所述多个第二面片集合中的一个面片集合对应于所述多个第一面片集合中的多个面片集合。也就是说,在所述树结构中,所述多个第二节点中的每个节点均连接有所述多个第一节点中的多个节点。Since the patch sets in the multiple second patch sets are actually obtained after performing patch reduction and merging operations on multiple first patch sets, the multiple second patch sets One patch set corresponds to multiple patch sets in the plurality of first patch sets. That is, in the tree structure, each node in the plurality of second nodes is connected to a plurality of nodes in the plurality of first nodes.
可选的,在电子设备通过不同的面片缩减倍数对面片集合进行面片缩减处理的情况下,上述的多个第一节点和多个第二节点中的每个节点均可以表示多个不同级别下的面片集合。例如,对于所述多个第一节点中的任意一个节点而言,该节点可以表示所述多个第二面片集合中的一个面片集合以及所述多个第五面片集合中的一个面片集合;并且,该节点所表示的不同面片集合可以通过不同的级别来区分。Optionally, in the case where the electronic device performs mesh reduction processing on the mesh set by different mesh reduction factors, each of the above-mentioned multiple first nodes and multiple second nodes may represent multiple different A collection of patches under the level. For example, for any node in the plurality of first nodes, the node may represent one of the plurality of second patch sets and one of the plurality of fifth patch sets patch set; and, different patch sets represented by this node can be distinguished by different levels.
为了便于理解,以下将结合具体例子详细介绍上述的三维模型数据的生成过程。可以参阅图8,图8为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成过程示意图。如图8所示,三维模型数据的生成过程包括以下的步骤801-808。For ease of understanding, the above-mentioned 3D model data generation process will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific examples. Refer to FIG. 8 , which is a schematic diagram of a process of generating 3D model data provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 8, the process of generating three-dimensional model data includes the following steps 801-808.
步骤801,以原始三维模型数据中的面片为顶点,面片之间的连接关系为边,构造无向图。Step 801: Construct an undirected graph by using the patches in the original 3D model data as vertices and the connections between the patches as edges.
首先,在读取得到原始三维模型文件之后,获取原始三维模型文件中的所有面片。由于三维模型中的面片都是相互连接的,因此可以是以面片为顶点,面片之间的连接关系为边,构造无向图。其中,无向图是指边没有方向的图。假设,本实施例中用于构造无向图的面片数量为s。First, after the original 3D model file is read, all facets in the original 3D model file are obtained. Since the patches in the 3D model are all connected to each other, an undirected graph can be constructed with the patches as vertices and the connections between the patches as edges. Among them, an undirected graph refers to a graph whose edges have no direction. Assume that the number of patches used to construct the undirected graph in this embodiment is s.
示例性地,可以参阅图9,图9为本申请实施例提供的一种基于三维模型中的面片生成无向图的示意图。如图9所示,通过将面片作为顶点,以面片之间的连接关系作为顶点之间所连接的边,能够清楚地展示各个面片之间的连接关系。For example, refer to FIG. 9 , which is a schematic diagram of generating an undirected graph based on patches in a 3D model according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 9 , by using the patches as vertices and the connection relationship between the patches as the edges connected between the vertices, the connection relationship between the various patches can be clearly displayed.
步骤802,基于图分割算法,对无向图进行分割,划分得到b个面片集合组。Step 802: Based on the graph segmentation algorithm, segment the undirected graph to obtain b patch set groups.
其中,图分割算法是指将网络顶点分割为指定规模,指定数量的非重叠群组,并使得群组之间的边数最小。由于在无向图中,面片是以顶点的形式来表示的,因此通过图分割算法对无向图中的顶点进行分割,则能够得到b组顶点群组,每个顶点群组实际上对应多个面片集合,即得到b个面片集合组。其中,b个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组包括c个面片集合,且每个面片集合中包括相同数量的面片。因此,每个面片集合组中的面片数量d=s/b,每个面片集合中的面片数量e=s/(bc)。Among them, the graph segmentation algorithm refers to dividing the vertices of the network into non-overlapping groups of a specified size and a specified number, and minimizing the number of edges between the groups. Since in an undirected graph, a patch is represented in the form of vertices, the vertices in the undirected graph can be segmented through the graph segmentation algorithm, and the b group of vertex groups can be obtained, and each vertex group actually corresponds to Multiple facet collections, that is, b facet collection groups are obtained. Wherein, each patch set group in b patch set groups includes c patch sets, and each patch set includes the same number of patches. Therefore, the number of patches in each patch set d=s/b, and the number of patches in each patch set e=s/(bc).
步骤803,将b个面片集合组锁边,分别采用G个轻量化级别对b个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到G份三维模型数据。Step 803 : Lock the edges of the b mesh set groups, and perform mesh reduction processing on the b mesh set groups using G lightweight levels respectively, so as to obtain G pieces of 3D model data.
在得到b个面片集合组之后,可以分别对b个面片集合组进行锁边,并且分别采用G个轻量化级别(即面片缩减倍数)对b个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到G份三维模型数据。其中,每份三维模型数据中包括b个面片缩减后的面片集合组,且不同份的三维模型数据之间的面片缩减数量不一样。After obtaining the b patch set groups, you can lock the edges of the b patch set groups respectively, and use G lightweight levels (that is, the patch reduction factor) to repair each face in the b patch set groups. The patch set group performs patch reduction processing to obtain G pieces of 3D model data. Wherein, each piece of 3D model data includes b mesh set sets after mesh reduction, and the number of mesh reductions is different among different pieces of 3D model data.
例如,假设G为3,3个轻量化级别对应的面片缩减倍数分别为2、3和5,基于面片缩减倍数为2的轻量化级别对b个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理后,以得到b个面片数量为d/2的面片集合组;基于面片缩减倍数为3的轻量化级别对b个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理后,以得到b个面片数量为c/3的面片集合组;基于面片缩减倍数为5的轻量化级别对b个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理后,以得到b个面片数量为c/5的面片集合组。For example, assuming that G is 3, the mesh reduction factors corresponding to the three lightweight levels are 2, 3, and 5 respectively. Based on the lightweight level of the mesh reduction factor of 2, the b mesh set groups are subjected to the mesh reduction process. , to obtain b mesh set groups with the number of d/2 patches; based on the lightweight level of the patch reduction factor of 3, perform the mesh reduction process on the b mesh set groups to obtain the number of b mesh sets The patch set group is c/3; based on the lightweight level of the patch reduction factor of 5, perform the patch reduction process on the b patch set groups to obtain b patch sets with the number of c/5 patches Group.
一般来说,原始三维模型数据中的各个面片均有对应的法线数据、表面纹理数据以及贴图数据等用于渲染模型的相关数据。在得到G份三维模型数据之后,由于三维模型数据中的面片集合执行了面片缩减处理,因此可以重新生成每份三维模型数据中的面片集合对应的法线数据、表面纹理数据以及贴图数据等用于渲染模型的数据。Generally speaking, each patch in the original 3D model data has corresponding normal data, surface texture data, texture data and other relevant data for rendering the model. After G pieces of 3D model data are obtained, since the mesh set in the 3D model data has been subjected to mesh reduction processing, the normal data, surface texture data, and maps corresponding to the mesh set in each piece of 3D model data can be regenerated Data, etc. are used to render the data of the model.
步骤804,当前层M=1。
将基于原始三维模型文件划分得到的b个面片集合组对应的层次M确定为0,并将执行一次面片缩减后得到的G份三维模型数据对应的层次M确定为1。Determine the level M corresponding to the b mesh set groups obtained based on the division of the original 3D model file as 0, and determine the level M corresponding to the G pieces of 3D model data obtained after performing one mesh reduction as 1.
步骤805,对于执行面片缩减处理后的多个面片集合组,每N个面片集合组合并为新的一个面片集合组,以使得新的面片集合组与执行面片缩减处理前的面片集合组的面片数量相同,即保持面片集合组中的面片数量不变。
其中,N可以理解为面片集合的合并速率,可以根据实际情况来确定。例如,对于面片缩减倍数为2的一份三维模型数据,该份三维模型数据对应的N值可以为2,即每两个面片集合组合并为新的一个面片集合组。这样一来,对于合并前的b个面片集合组,合并后则变为b/2个面片集合组。此外,对于面片缩减倍数不同的三维模型数据,其N值也可以是不同的。Among them, N can be understood as the merging rate of the patch set, which can be determined according to the actual situation. For example, for a piece of 3D model data whose mesh reduction factor is 2, the N value corresponding to the piece of 3D model data can be 2, that is, every two mesh sets are merged into a new mesh set. In this way, for the b patch set groups before merging, it becomes b/2 patch set sets after merging. In addition, for 3D model data with different mesh reduction factors, their N values may also be different.
步骤806,分别采用G个轻量化级别分别对合并后的面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到G份三维模型数据。In
在对面片集合组进行合并后,继续采用G个轻量化级别分别对各个级别所对应的合并后的面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到G份面片再次缩减后的三维模型数据。After merging the mesh set groups, continue to use G lightweight levels to perform mesh reduction processing on the merged mesh set groups corresponding to each level, so as to obtain the 3D model data after G mesh pieces have been reduced again.
步骤807,M=M+1。
将再次执行面片缩减处理后得到的G份三维模型数据对应的层次M在原来的M值的基础上加1,即每次执行面片缩减处理后的三维模型数据对应的层次都会提高1。Add 1 to the level M corresponding to the G pieces of 3D model data obtained after the mesh reduction process is performed again, that is, the level corresponding to the 3D model data after the mesh reduction process is increased by 1 each time.
步骤808,判断剩余的面片集合组数量是否大于1。
如果剩余的面片集合组数量大于1,则转至继续执行上述的步骤805;如果剩余的面片集合组数量不大于1,则可以停止对面片集合组的处理。If the number of remaining patch sets is greater than 1, go to step 805 above; if the remaining number of patch sets is not greater than 1, then stop processing the patch sets.
通过上述的多个步骤,可以对多个面片集合组执行多次面片缩减处理,每次面片缩减处理得到的三维模型数据均作为一个层次的三维模型数据。此外,对于相同层次内的三维模型数据,通过采用G个轻量化级别对面片集合执行面片缩减处理,从而能够得到G份轻量化级别不同的三维模型数据。Through the above multiple steps, multiple mesh reduction processes can be performed on multiple mesh sets, and the three-dimensional model data obtained by each mesh reduction process is regarded as one level of three-dimensional model data. In addition, for the 3D model data in the same level, by using G lightweight levels to perform mesh reduction processing on the mesh set, G pieces of 3D model data with different lightweight levels can be obtained.
为便于理解,以下将以一个轻量化级别为例,对生成多层次的三维模型数据的过程进行介绍。For ease of understanding, the following will take a lightweight level as an example to introduce the process of generating multi-level 3D model data.
可以参阅图10,图10为本申请实施例提供的一种生成多层次的三维模型数据的示意图。如图10所示,在原始的三维模型数据中,共包括256个面片,该256个面片可以划分为64个面片集合组,每个面片集合组包括4个面片。其中,该64个面片集合组即为第0层的三维模型数据。Refer to FIG. 10 , which is a schematic diagram of generating multi-level 3D model data provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 10 , in the original 3D model data, there are 256 meshes in total, and the 256 meshes can be divided into 64 mesh sets, and each mesh set includes 4 meshes. Wherein, the set of 64 facets is the 3D model data of the 0th layer.
在轻量化级别为2的情况下,该轻量化级别对应的面片缩减倍数为4,因此对上述的64个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理之后,64个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组的面片被缩减为1个。通过对该64个缩减面片后的面片集合组执行合并操作,每4个面片集合组重新合并为一个新的面片集合组,以得到新的16个面片集合组,该16个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组均包括4个面片。其中,该16个面片集合组即为第1层的三维模型数据。In the case where the lightweight level is 2, the patch reduction factor corresponding to this lightweight level is 4, so after performing the patch reduction process on the above 64 patch set groups, each of the 64 patch set groups The patches of the patch collection group are reduced to 1. By performing the merging operation on the 64 reduced patch sets, every 4 patch sets are re-merged into a new patch set to obtain 16 new patch sets, the 16 Each patch set in the patch set includes 4 patches. Wherein, the 16 mesh set groups are the 3D model data of the first layer.
类似地,对上述的16个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理之后,16个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组的面片被缩减为1个。通过对该16个缩减面片后的面片集合组执行合并操作,每4个面片集合组重新合并为一个新的面片集合组,以得到新的4个面片集合组,该4个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组均包括4个面片。其中,该4个面片集合组即为第2层的三维模型数据。Similarly, after the patch reduction processing is performed on the above-mentioned 16 patch set groups, the number of patches in each of the 16 patch set groups is reduced to one. By performing the merging operation on the 16 reduced patch sets, every 4 patch sets are re-merged into a new patch set to obtain 4 new patch sets, the 4 Each patch set in the patch set includes 4 patches. Wherein, the 4 mesh set groups are the 3D model data of the second layer.
类似地,对上述的4个面片集合组执行面片缩减处理之后,4个面片集合组中的每个面片集合组的面片被缩减为1个。通过对该4个缩减面片后的面片集合组执行合并操作,每4个面片集合组重新合并为一个新的面片集合组,以得到新的1个面片集合组,该面片集合组包括4个面片。其中,该1个面片集合组即为第3层的三维模型数据。Similarly, after the patch reduction processing is performed on the above four patch set groups, the number of patches in each of the four patch set groups is reduced to one. By performing the merging operation on the 4 reduced patch sets, each 4 patch sets are re-merged into a new patch set to obtain a new patch set, the patch The collection set consists of 4 patches. Wherein, the one mesh set group is the 3D model data of the third layer.
可以理解的是,以上是以轻量化级别为2为例对三维模型数据的生成过程进行介绍,实际上电子设备可以分别基于不同的轻量化级别来生成多层次的三维模型数据,从而使得每一个层次都具有不同的轻量化级别的三维模型数据,最终得到多层次、多级别的三维模型数据。It can be understood that the above is an introduction to the generation process of 3D model data with a lightweight level of 2 as an example. In fact, electronic devices can generate multi-level 3D model data based on different lightweight levels, so that each All layers have different lightweight levels of 3D model data, and finally obtain multi-level and multi-level 3D model data.
进一步地,为了便于索引所生成的多层次的三维模型数据,电子设备可以生成树状的树结构,并通过树结构中的各个节点来表示各个层次的面片集合,从而实现三维模型数据的索引。Furthermore, in order to facilitate the indexing of the generated multi-level 3D model data, the electronic device can generate a tree-like tree structure, and each node in the tree structure represents a set of patches at each level, thereby realizing the indexing of the 3D model data .
示例性地,可以参阅图11,图11为本申请实施例提供的一种树结构的示意图。如图11所示,在树结构的第0层,共包括8个节点,该8个节点分别用于表示第0层的8个面片集合。For example, refer to FIG. 11 , which is a schematic diagram of a tree structure provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 11 , the 0th layer of the tree structure includes a total of 8 nodes, and the 8 nodes are respectively used to represent the 8 patch sets of the 0th layer.
在树结构的第1层,共包括4个节点,该4个节点分别用于表示第1层的4个面片集合。其中,在三维模型数据的生成过程中,通过对第0层的8个面片集合执行面片缩减处理,并将缩减面片后的面片集合合并,即每两个面片集合合并为一个新的面片集合,从而得到第1层的4个面片集合。The first layer of the tree structure includes 4 nodes in total, and the 4 nodes are respectively used to represent the 4 patch sets of the first layer. Among them, in the process of generating the 3D model data, the patch reduction process is performed on the 8 patch sets of the 0th layer, and the reduced patch sets are merged, that is, every two patch sets are merged into one A new patch set, thus obtaining the 4 patch sets of the first layer.
在树结构的第2层,共包括2个节点,该2个节点分别用于表示第2层的2个面片集合。其中,在三维模型数据的生成过程中,通过对第1层的4个面片集合执行面片缩减处理,并将缩减面片后的面片集合合并,即每两个面片集合合并为一个新的面片集合,从而得到第2层的2个面片集合。The second layer of the tree structure includes 2 nodes in total, and the 2 nodes are respectively used to represent the 2 patch sets of the second layer. Among them, in the process of generating the 3D model data, the mesh reduction process is performed on the four mesh sets of the first layer, and the mesh sets after the reduced mesh are merged, that is, every two mesh sets are merged into one A new set of patches, thus obtaining 2 sets of patches on the second layer.
在树结构的第3层,共包括1个节点,该1个节点用于表示第3层的1个面片集合。其中,在三维模型数据的生成过程中,通过对第2层的2个面片集合执行面片缩减处理,并将缩减面片后的面片集合合并,即每两个面片集合合并为一个新的面片集合,从而得到第3层的1个面片集合。In the third layer of the tree structure, there is a total of one node, and the one node is used to represent a collection of patches in the third layer. Among them, in the process of generating the 3D model data, the mesh reduction process is performed on the two mesh sets of the second layer, and the mesh sets after the reduced mesh are merged, that is, every two mesh sets are merged into one A new set of patches, thus obtaining a set of patches on the third layer.
这样一来,通过树状的树结构中的各个节点即可实现索引多层次的三维模型数据。并且,由于上层节点所表示的面片集合是由上层节点所连接的多个下层节点表示的面片集合合并得到的,因此上层节点所指示的三维模型数据与多个下层节点所指示的三维模型数据是用于表示三维模型中相同的物体的。In this way, multi-level three-dimensional model data can be indexed through each node in the tree structure. Moreover, since the patch set represented by the upper node is obtained by merging the patch sets represented by multiple lower nodes connected to the upper node, the 3D model data indicated by the upper node and the 3D model indicated by the multiple lower nodes The data is used to represent the same objects in the 3D model.
此外,在每次执行面片缩减处理的过程中,如果电子设备是采用不同的轻量化级别(即采用多个不同的面片缩减倍数)来执行面片缩减处理,则电子设备能够生成多层次、多级别的三维模型数据。因此,在树状的树结构中,每个层次的各个节点还可以是表示多个轻量化级别下的三维模型数据。In addition, in the process of performing mesh reduction processing each time, if the electronic device uses different lightweight levels (that is, uses multiple different mesh reduction factors) to perform mesh reduction processing, the electronic device can generate multi-level , Multi-level 3D model data. Therefore, in the tree structure, each node of each level may also represent 3D model data at multiple lightweight levels.
示例性地,可以参阅图12A,图12A为本申请实施例提供的链表结构示意图。如图12A所示,对于图11中各个层次的节点,每一个节点均能够表示为如图12A所示的链表结构,该链表结构中包括多个项目,每一个项目均表示某一个轻量化级别下的三维模型数据。For example, refer to FIG. 12A , which is a schematic diagram of a linked list structure provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 12A, for each level of nodes in Figure 11, each node can be represented as a linked list structure as shown in Figure 12A, the linked list structure includes multiple items, and each item represents a certain lightweight level The 3D model data below.
示例性地,可以参阅图12B,图12B为本申请实施例提供的基于不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据渲染得到的三维模型示意图。如图12B所示,随着轻量化级别的提高,三维模型的精细度逐渐降低,但是三维模型对应的三维模型数据的数据量也逐渐降低。For example, refer to FIG. 12B , which is a schematic diagram of a three-dimensional model rendered based on three-dimensional model data of different lightweight levels provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 12B , as the lightweight level increases, the fineness of the 3D model decreases gradually, but the data volume of the 3D model data corresponding to the 3D model also decreases gradually.
以上介绍了本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的生成方法,以下将详细介绍本申请实施例所提供的三维模型数据的处理方法,即如何将所生成的三维模型数据发送至需要渲染三维模型的电子设备上。The above describes a method for generating 3D model data provided by the embodiment of the present application. The following will introduce in detail the processing method of the 3D model data provided by the embodiment of the present application, that is, how to send the generated 3D model data to the Model electronics.
可以参阅图13,图13为本申请实施例提供的一种三维模型数据的处理方法1300的流程示意图。如图13所示,该方法1300包括以下的步骤1301-1303。Please refer to FIG. 13 , which is a schematic flowchart of a
步骤1301,第一电子设备接收来自于第二电子设备的第一数据请求,所述第一数据请求包括第一观察点位置。
可以理解的是,本实施例中用于执行三维模型数据的处理方法的第一电子设备与上述用于执行三维模型数据的生成方法的电子设备可以是同一个设备,也可以是不同的设备,本实施例对此不做具体限定。It can be understood that the first electronic device used to execute the method for processing 3D model data in this embodiment and the above-mentioned electronic device used to execute the method for generating 3D model data may be the same device or different devices, This embodiment does not specifically limit it.
例如,本实施例中的第一电子设备和上述实施例中执行三维模型数据的生成方法的电子设备为同一个服务器,该服务器在生成相应的三维模型数据之后,能够接收第二电子设备的数据请求,从而向第二电子设备发送相应的三维模型数据。For example, the first electronic device in this embodiment and the electronic device executing the method for generating 3D model data in the above embodiments are the same server, and the server can receive the data of the second electronic device after generating the corresponding 3D model data request, so as to send the corresponding three-dimensional model data to the second electronic device.
又例如,本实施例中的第一电子设备和上述实施例中执行三维模型数据的生成方法的电子设备可以为不同的服务器,用于生成三维模型数据的服务器根据用户所上传的三维模型文件生成相应的三维模型数据,将生成的三维模型数据存储至云数据库中或者发送给本实施例中执行三维模型数据处理的另一个服务器,由另一个服务器基于第二电子设备的数据请求执行三维模型数据的处理。For another example, the first electronic device in this embodiment and the electronic device executing the method for generating 3D model data in the above embodiments may be different servers, and the server for generating 3D model data generates 3D model data based on the 3D model file uploaded by the user For the corresponding 3D model data, store the generated 3D model data in the cloud database or send it to another server that performs 3D model data processing in this embodiment, and the other server executes the 3D model data based on the data request of the second electronic device. processing.
其中,第二电子设备的第一数据请求用于向第一电子设备请求相应的三维模型数据,以实现在第二电子设备执行三维模型数据的渲染。Wherein, the first data request of the second electronic device is used to request corresponding 3D model data from the first electronic device, so as to implement rendering of the 3D model data on the second electronic device.
所述第一数据请求中可以包括第一观察点位置,所述第一观察点位置为第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的一个位置。一般来说,三维模型的渲染实际上基于某一个位置观察立体的三维模型,并将观察到的景物以二维图像的形式在显示设备上展示。简单来说,三维模型的渲染可以理解为通过一个相机在某一个位置上拍摄得到的二维图像。因此,在确定了三维模型中的观察点位置之后,即可确定三维模型中需要渲染的物体,从而能够确定用于渲染的三维模型数据。The first data request may include a first viewpoint position, and the first viewpoint position is a position in a three-dimensional model running on the second electronic device. Generally speaking, the rendering of a 3D model is actually based on observing a three-dimensional 3D model at a certain position, and displaying the observed scene on a display device in the form of a 2D image. In simple terms, the rendering of a 3D model can be understood as a 2D image captured by a camera at a certain position. Therefore, after the position of the observation point in the 3D model is determined, the object to be rendered in the 3D model can be determined, so that the 3D model data used for rendering can be determined.
步骤1302,所述第一电子设备根据所述第一数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据,所述第一目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第一观察点位置相关。
本实施例中,第一电子设备在根据第一数据请求确定了三维模型中的第一观察点位置之后,即可确定三维模型中需要渲染的物体(即基于第一观察点位置能够观察到的物体),从而能够确定用于渲染的第一目标数据。In this embodiment, after the first electronic device determines the position of the first observation point in the 3D model according to the first data request, it can determine the object to be rendered in the 3D model (that is, the object that can be observed based on the position of the first observation point object), so that the first target data for rendering can be determined.
可选的,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据。其中,所述第一对象和所述第二对象均为从所述第一观察点位置能够观察到的物体。并且,第一对象和第二对象均可以为一个完完整的物体,例如第一对象为一块岩石,第二对象为一颗小草;第一对象和第二对象也可以是一个物体中的一部分,例如第一对象为一块岩石的某一面,第二对象为一颗树木中的一片叶子。第一对象和第二对象均是由多个面片构成的,因此第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据可以是顶点、面片、位置、形状、表面纹理、颜色等用于渲染场景的参数。Optionally, the first target data includes rendering data for performing three-dimensional model rendering, and the rendering data includes rendering data of the first object and rendering data of the second object. Wherein, both the first object and the second object are objects that can be observed from the position of the first observation point. Moreover, both the first object and the second object can be a complete object, for example, the first object is a rock, and the second object is a grass; the first object and the second object can also be a part of an object , for example, the first object is a certain side of a rock, and the second object is a leaf in a tree. Both the first object and the second object are composed of multiple patches, so the rendering data of the first object and the rendering data of the second object can be vertices, patches, positions, shapes, surface textures, colors, etc. for rendering The parameters of the scene.
此外,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离。In addition, the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is higher than the fineness of the rendering data of the second object, and the distance between the first object and the position of the first observation point is smaller than that of the second object The distance from the first observer position.
可以理解的是,在三维模型执行渲染而得到二维图像的过程中,在相机渲染参数相同的情况下,对于相同大小的两个物体,离观察点位置越远的物体在二维图像上所显示的图像面积越小,而离观察点位置越近的物体在二维图像上所显示的图像面积越大。因此,对于距离第一观察点位置较远的第二对象,即便降低第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,也不会影响第二对象在最终渲染得到的二维图像上的显示效果。并且,通过降低距离观察点较远位置的对象的渲染数据的精细度,能够减少所需传输的数据量,减轻带宽压力的同时,提高三维模型数据的传输速度,保证三维应用的渲染效率,避免出现三维应用卡顿的现象。It can be understood that, in the process of rendering a 3D model to obtain a 2D image, in the case of the same camera rendering parameters, for two objects of the same size, the distance of the object farther from the observation point is greater than that of the 2D image. The displayed image area is smaller, and the closer the object is to the observation point, the larger the image area displayed on the two-dimensional image is. Therefore, for the second object that is far away from the first viewing point, even if the fineness of the rendering data of the second object is reduced, the display effect of the second object on the final rendered two-dimensional image will not be affected. In addition, by reducing the fineness of the rendering data of objects far from the observation point, the amount of data to be transmitted can be reduced, the pressure on bandwidth can be reduced, and the transmission speed of 3D model data can be improved to ensure the rendering efficiency of 3D applications and avoid There is a phenomenon that the 3D application freezes.
示例性地,在基于上述实施例的三维模型数据的生成方法生成多层次的三维模型数据的情况下,所述第一对象的渲染数据可以为较低层次的三维模型数据,而第二对象的渲染数据可以为较高层次的三维模型数据。例如,第一对象的渲染数据为第1层的三维模型数据,而第二对象的渲染数据为第2层的三维模型数据,因此第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度。Exemplarily, in the case of generating multi-level 3D model data based on the method for generating 3D model data in the above embodiment, the rendering data of the first object may be lower-level 3D model data, while the rendering data of the second object The rendering data may be higher-level 3D model data. For example, the rendering data of the first object is the 3D model data of the first layer, and the rendering data of the second object is the 3D model data of the second layer, so the rendering data of the first object has higher fineness than the second object The granularity of the rendered data.
可选的,所述三维模型的数据中包括第一对象对应的多份渲染数据,所述多份渲染数据的精细度不同。所述第一电子设备根据所述第一数据请求中的第一观察点位置,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;然后,所述第一电子设备根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度与所述距离具有负相关关系,即所述距离越大,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度则越低;所述距离越小,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度则越高。Optionally, the data of the three-dimensional model includes multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the multiple pieces of rendering data have different finenesses. The first electronic device determines the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the first viewpoint position according to the first viewpoint position in the first data request; then, the first The electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data as the rendering data of the first object according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data. Wherein, the fineness of the rendering data of the first object has a negative correlation with the distance, that is, the greater the distance, the lower the fineness of the rendering data of the first object; the smaller the distance, The higher the fineness of the rendering data of the first object is.
简单来说,所述第一电子设备根据第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离,从多份精细度不同的渲染数据选择其中一份渲染数据作为第一对象的渲染数据,以使得所选择的渲染数据的精细度并不会影响第一对象最终的成像质量,同时还能够尽可能地降低第一对象的渲染数据的数据量。In simple terms, the first electronic device selects one piece of rendering data from multiple pieces of rendering data with different finenesses as the rendering data of the first object according to the distance between the first object and the position of the first observation point, so that The fineness of the selected rendering data will not affect the final imaging quality of the first object, and at the same time, the data volume of the rendering data of the first object can be reduced as much as possible.
例如,第一电子设备可以计算每一份渲染数据的粗糙值,并且通过比较每一份渲染数据的粗糙值与预置阈值之间的大小来决定所选择的渲染数据。其中,渲染数据的粗糙值能够用于表示基于该份渲染数据渲染得到的二维图像的粗糙度。具体地,每份渲染数据的粗糙值可以表示为f=E/R,其中,f表示每份渲染数据的粗糙值,f越大,表示渲染得到的二维图像的粗糙度越高,即二维图像的清晰度越差;E表示渲染数据的渲染误差,E与每份渲染数据本身的精细度相关,渲染数据的精细度越高,则E越小;R与渲染数据所表示的对象与观察点位置之间的距离相关,距离越远,则R越大。这样一来,可以计算每一份渲染数据的粗糙值f,并且判断粗糙值f是否小于或等于预置阈值,最终选择一份精细度最低且粗糙值f小于或等于预置阈值的渲染数据作为第一对象的渲染数据。For example, the first electronic device may calculate the roughness value of each piece of rendering data, and determine the selected rendering data by comparing the roughness value of each piece of rendering data with a preset threshold. Wherein, the roughness value of the rendering data can be used to represent the roughness of the two-dimensional image rendered based on the rendering data. Specifically, the roughness value of each piece of rendering data can be expressed as f=E/R, where f represents the roughness value of each piece of rendering data, and the larger f is, the higher the roughness of the rendered two-dimensional image is, that is, two The worse the clarity of the three-dimensional image; E represents the rendering error of the rendering data, E is related to the fineness of each rendering data itself, the higher the fineness of the rendering data, the smaller the E; R and the object represented by the rendering data The distance between the positions of the observation points is related, and the farther the distance is, the larger R is. In this way, the rough value f of each piece of rendering data can be calculated, and whether the rough value f is less than or equal to the preset threshold can be judged, and finally a piece of rendering data with the lowest fineness and roughness f less than or equal to the preset threshold can be selected as the Render data for the first object.
示例性地,在基于上述实施例的三维模型数据的生成方法生成多层次的三维模型数据的情况下,第一对象对应的多份渲染数据可以为多个层次下的三维模型数据,不同层次下的三维模型数据的精细度并不相同。Exemplarily, in the case of generating multi-level 3D model data based on the method for generating 3D model data in the above-mentioned embodiments, the multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object may be 3D model data at multiple levels. The fineness of the 3D model data is not the same.
可选的,所述第一对象对应的多份渲染数据中的第一份渲染数据包括多组渲染数据,每组渲染数据用于渲染以得到所述第一对象,且所述多组渲染数据的精细度不同,所述第一份渲染数据是所述多份渲染数据中的任意一份渲染数据。示例性地,在基于上述实施例的三维模型数据的生成方法生成多层次的三维模型数据的情况下,第一对象对应的多份渲染数据可以为多个层次下的三维模型数据,每份渲染数据中所包括的多组渲染数据则可以是同一个层次下不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据。Optionally, the first piece of rendering data among the pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object includes multiple sets of rendering data, each set of rendering data is used for rendering to obtain the first object, and the multiple sets of rendering data The fineness of the rendering data is different, and the first rendering data is any rendering data in the plurality of rendering data. Exemplarily, in the case of generating multi-level 3D model data based on the method for generating 3D model data in the above-mentioned embodiments, the multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object may be 3D model data at multiple levels, and each piece of rendering data The multiple sets of rendering data included in the data may be 3D model data of different lightweight levels under the same layer.
所述多份渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行多次面片缩减处理后得到的,其中,每执行一次面片缩减处理均得到一份渲染数据;所述第一份渲染数据包括的所述多组渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行相同次数和不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。简单来说,第一对象对应的多份渲染数据分别是经过不同次数的面片缩减处理后得到的,而每份渲染数据中的多组渲染数据则是基于不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。这样一来,多份渲染数据中的每份渲染数据的精细度均不相同,且相同的一份渲染数据中的多组渲染数据的精细度也不相同。The multiple pieces of rendering data are obtained after multiple mesh reduction processes are performed on the original rendering data of the first object, wherein one piece of rendering data is obtained each time the mesh reduction process is performed; the first rendering The multiple sets of rendering data included in the data are obtained by performing the same number of times of mesh reduction processing with different multiples on the original rendering data of the first object. To put it simply, the multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object are obtained after different times of mesh reduction processing, and the multiple sets of rendering data in each piece of rendering data are obtained based on different times of mesh reduction processing . In this way, the fineness of each piece of rendering data in the multiple pieces of rendering data is different, and the fineness of multiple sets of rendering data in the same piece of rendering data are also different.
在第一对象的多份渲染数据中的每份渲染数据均包括多组渲染数据的情况下,第一电子设备可以根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据;然后,第一电子设备根据所述第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,从所选择的一份渲染数据的多组渲染数据中选择一组渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。In the case that each of the multiple pieces of rendering data of the first object includes multiple sets of rendering data, the first electronic device may select from the multiple pieces of rendering data according to the distance and the fineness of the multiple pieces of rendering data Select a piece of rendering data from the rendering data; then, the first electronic device selects a set of rendering data from multiple sets of rendering data in the selected piece of rendering data according to the performance index and/or network status of the second electronic device as the rendering data of the first object.
也就是说,第一电子设备可以根据第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离,从多个层次的渲染数据中确定其中一个层次,然后基于第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,进一步从该层次中的多个轻量化级别中确定其中一个轻量化级别的渲染数据,以得到最终需要向第二电子设备发送的渲染数据。That is to say, the first electronic device can determine one of the layers from the rendering data of multiple layers according to the distance between the first object and the first observation point, and then based on the performance index and/or network of the second electronic device state, and further determine the rendering data of one of the lightweight levels from the multiple lightweight levels in the hierarchy, so as to obtain the rendering data that needs to be sent to the second electronic device finally.
其中,所述第二电子设备的性能指标可以包括所述第二电子设备的帧率、渲染延迟和温度参数中的一个或多个。例如,在第二电子设备的帧率较高的情况下,代表第二电子设备的性能较高,可以选择轻量化级别较低的渲染数据,即从多组渲染数据中选择精细度较高的渲染数据;又例如,在第二电子设备的温度较高的情况下,代表第二电子设备的功耗较高,可以选择轻量化级别较高的渲染数据,即从多组渲染数据中选择精细度较低的渲染数据,以降低第二电子设备的渲染消耗。Wherein, the performance index of the second electronic device may include one or more of frame rate, rendering delay and temperature parameters of the second electronic device. For example, when the frame rate of the second electronic device is high, it means that the performance of the second electronic device is high, and the rendering data with a lower lightweight level can be selected, that is, the rendering data with higher fineness can be selected from multiple sets of rendering data. Rendering data; for another example, when the temperature of the second electronic device is high, it means that the power consumption of the second electronic device is high, and you can select rendering data with a higher lightweight level, that is, select finer rendering data from multiple sets of rendering data low-density rendering data, so as to reduce the rendering consumption of the second electronic device.
所述第二电子设备的网络状态可以包括所述第二电子设备的带宽和网络时延中的一个或多个。例如,在所述第二电子设备的带宽较高的情况下,代表所述第二电子设备在单位时间内能够接收较多的数据,因此可以选择轻量化级别较低的渲染数据,即从多组渲染数据中选择精细度较高的渲染数据。The network state of the second electronic device may include one or more of bandwidth and network delay of the second electronic device. For example, when the bandwidth of the second electronic device is high, it means that the second electronic device can receive more data per unit time, so it can select rendering data with a lower lightweight level, that is, from multiple Select the rendering data with higher fineness in the group rendering data.
步骤1303,所述第一电子设备向所述第二电子设备发送所述第一目标数据。
本实施例中,在所述第一电子设备根据第一数据请求确定第一目标数据后,则向第二电子设备发送所述第一目标数据,以使得第二电子设备基于所述第一目标数据执行三维模型的渲染。In this embodiment, after the first electronic device determines the first target data according to the first data request, it sends the first target data to the second electronic device, so that the second electronic device The data performs the rendering of the 3D model.
以上介绍了第一电子设备所确定的第一目标数据包括第二电子设备用于实时渲染的数据,在一些实施例中,第一电子设备所确定的第一目标数据中还可以包括缓冲数据。所述第二电子设备能够在三维模型中的观察点位置发生变化或者设备状态发生变化时,采用接收到的缓冲数据来执行渲染,以避免重新从第一电子设备处获取新的数据,从而提高渲染的速度。It is introduced above that the first target data determined by the first electronic device includes data used by the second electronic device for real-time rendering. In some embodiments, the first target data determined by the first electronic device may also include buffer data. The second electronic device can use the received buffer data to perform rendering when the position of the observation point in the three-dimensional model changes or the state of the device changes, so as to avoid re-obtaining new data from the first electronic device, thereby improving Rendering speed.
示例性地,所述第一目标数据还包括缓冲数据,所述缓冲数据包括所述第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,所述N为大于1的整数,所述N份渲染数据均用于执行所述第一对象的渲染,且所述N份渲染数据的精细度不同。也就是说,所述第一目标数据中同时包括渲染数据和缓冲数据,渲染数据为第一对象对应的一份渲染数据,缓冲数据则为第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,渲染数据和缓冲数据均能够用于渲染同一个对象。Exemplarily, the first target data further includes buffer data, and the buffer data includes N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the N pieces of rendering data are all used for The rendering of the first object is performed, and the fineness of the N rendering data is different. That is to say, the first target data includes rendering data and buffer data at the same time, the rendering data is one piece of rendering data corresponding to the first object, the buffer data is N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the rendering data and buffer The data can all be used to render the same object.
其中,第二电子设备在接收到第一目标数据之后,基于第一目标数据中的渲染数据实时渲染三维模型,而第一目标数据中的缓冲数据则用于在三维模型中的观察点位置发生变化或者第二电子设备的状态发生变化时执行三维模型的渲染。Wherein, after receiving the first target data, the second electronic device renders the 3D model in real time based on the rendering data in the first target data, and the buffer data in the first target data is used to generate The rendering of the three-dimensional model is performed when the state of the second electronic device changes or the state of the second electronic device changes.
具体地,在第一对象具有多份精细度不同的渲染数据的情况下,第二电子设备可以从多份精细度不同的渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为向第二电子设备发送的缓冲数据。Specifically, in the case that the first object has multiple pieces of rendering data with different fineness, the second electronic device may select N pieces of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data with different fineness as the buffer data sent to the second electronic device .
示例性地,所述三维模型的数据中包括所述第一对象对应的M份渲染数据,所述M份渲染数据的精细度不同,所述M为大于所述N的整数。Exemplarily, the data of the three-dimensional model includes M pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, the M pieces of rendering data have different finenesses, and the M is an integer greater than the N.
首先,所述第一电子设备可以根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离,所述第一数据请求包括所述第一观察点位置。First, the first electronic device may determine the distance between the first object in the three-dimensional model and the position of the first observation point according to the first data request, and the first data request includes the first A point of view.
然后,所述第一电子设备根据所述距离,从所述多份渲染数据中确定一份渲染数据为目标渲染数据,所述目标渲染数据的精细度满足所述第一对象的精细度要求,所述第一对象的精细度要求与所述距离相关。具体来说,所述第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离越远,则所述第一对象的精细度要求越低,则所确定的目标渲染数据的精细度也越低;所述第一对象与第一观察点位置之间的距离越近,则所述第一对象的精细度要求越高,则所确定的目标渲染数据的精细度也越高。Then, according to the distance, the first electronic device determines one piece of rendering data from the multiple pieces of rendering data as the target rendering data, the fineness of the target rendering data meets the fineness requirement of the first object, The fineness requirement of the first object is related to the distance. Specifically, the farther the distance between the first object and the first observation point is, the lower the fineness requirement of the first object is, and the lower the fineness of the determined target rendering data is; The closer the distance between the first object and the first observation point is, the higher the fineness requirement of the first object is, and the higher the fineness of the determined target rendering data is.
其次,所述第一电子设备从所述M份渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为所述缓冲数据,所述N份渲染数据的精细度均小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度。也就是说,在确定目标渲染数据之后,则可以从M份渲染数据中选择精细度小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度的渲染数据作为缓冲数据。Secondly, the first electronic device selects N pieces of rendering data from the M pieces of rendering data as the buffer data, and the fineness of the N pieces of rendering data is less than or equal to the fineness of the target rendering data. That is to say, after the target rendering data is determined, rendering data whose fineness is smaller than or equal to the fineness of the target rendering data may be selected from the M pieces of rendering data as buffer data.
本实施例中,通过在多份精细度不同的渲染数据中选择多份精细度较低的渲染数据作为缓冲数据发送给第二电子设备,可以使得第二电子设备能够在三维模型的观察点位置发生变化时(例如观察点位置离对象越来越远),快速地从缓冲数据中选择相应精细度的数据作为实时渲染的数据,避免了重新从第一电子设备处获取新的数据,从而提高渲染的速度。此外,第二电子设备在自身的设备状态发生变化时,例如温度升高时,从缓冲数据中选择精细度较低的数据作为实时渲染的数据,从而降低第二电子设备的渲染功耗,保证第二电子设备的温度在合理范围内。In this embodiment, by selecting a plurality of rendering data with a lower fineness among multiple rendering data with different fineness and sending them as buffered data to the second electronic device, the second electronic device can When a change occurs (for example, the position of the observation point is getting farther and farther away from the object), the data of the corresponding fineness is quickly selected from the buffer data as the data for real-time rendering, which avoids re-obtaining new data from the first electronic device, thereby improving Rendering speed. In addition, when the second electronic device's own device status changes, for example, when the temperature rises, it selects data with lower fineness from the buffered data as data for real-time rendering, thereby reducing the rendering power consumption of the second electronic device and ensuring The temperature of the second electronic device is within a reasonable range.
以上介绍了第一电子设备基于数据请求向第二电子设备发送渲染数据以及缓冲数据的过程。可以理解的是,由于第二电子设备所运行的三维模型中的观察点位置可能是实时变化的,因此第二电子设备往往需要实时向第一电子设备发送新的数据请求,以请求新的用于渲染三维模型的数据。然而,在大多数情况下,第二电子设备所运行的三维模型中的观察点位置是缓慢变化的,因此第二电子设备之前所接收到的部分数据仍可继续用于三维模型的渲染,第一电子设备实际上只需要向第二电子设备发送部分第二电子设备没有接收过的数据。The above describes the process of the first electronic device sending rendering data and buffering data to the second electronic device based on the data request. It can be understood that since the position of the observation point in the 3D model run by the second electronic device may change in real time, the second electronic device often needs to send a new data request to the first electronic device in real time to request a new user Data for rendering 3D models. However, in most cases, the position of the observation point in the 3D model run by the second electronic device changes slowly, so part of the data previously received by the second electronic device can still continue to be used for the rendering of the 3D model. In fact, an electronic device only needs to send part of the data that the second electronic device has not received to the second electronic device.
示例性地,上述的方法1300还可以包括以下的多个步骤。Exemplarily, the above-mentioned
在向第二电子设备发送了第一目标数据之后,所述第一电子设备接收来自于所述第二电子设备的第二数据请求,所述第二数据请求中可以包括第二观察点位置,所述第二观察点位置为所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的位置。其中,第二观察点位置与上述的第一观察点位置不同,即第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型的观察点位置发生了变化。After sending the first target data to the second electronic device, the first electronic device receives a second data request from the second electronic device, the second data request may include a second observation point position, The position of the second viewing point is a position in the 3D model running in the second electronic device. Wherein, the position of the second observation point is different from the position of the first observation point above, that is, the position of the observation point of the three-dimensional model running in the second electronic device has changed.
然后,所述第一电子设备根据所述第二数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据,所述第二目标数据与所述第二观察点位置相关。类似地,所述第一电子设备可以基于第二观察点位置在三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据。其中,所述第一电子设备确定第二目标数据的过程与确定第一目标数据的过程类似,具体可以参考上述的步骤1302,在此不再赘述。Then, the first electronic device determines second target data from the data of the three-dimensional model according to the second data request, and the second target data is related to the position of the second observation point. Similarly, the first electronic device may determine the second target data in the data of the three-dimensional model based on the second viewpoint position. Wherein, the process of determining the second target data by the first electronic device is similar to the process of determining the first target data, for details, reference may be made to the above-mentioned
所述第一电子设备根据所述第一目标数据和所述第二目标数据确定第三目标数据,并生成第一信息。其中,所述第一目标数据不包括所述第三目标数据,且所述第二目标数据包括所述第三目标数据,即第三目标数据是基于第二观察点位置新确定的数据。所述第一信息用于指示待删除的第四目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括所述第四目标数据,且所述第二目标数据不包括所述第四目标数据,即第四目标数据为不再需要的数据。The first electronic device determines third target data according to the first target data and the second target data, and generates first information. Wherein, the first target data does not include the third target data, and the second target data includes the third target data, that is, the third target data is newly determined data based on the position of the second observation point. The first information is used to indicate the fourth target data to be deleted, the first target data includes the fourth target data, and the second target data does not include the fourth target data, that is, the fourth target Data is data that is no longer needed.
所述第一电子设备向所述第二电子设备发送所述第三目标数据和所述第一信息。这样一来,第二电子设备可以接收到基于第二观察点位置新确定的数据(即第三目标数据);并且,第二电子设备可以根据所述第一信息删除第二电子设备之前所接收到的第四目标数据。The first electronic device sends the third target data and the first information to the second electronic device. In this way, the second electronic device can receive the newly determined data based on the position of the second observation point (that is, the third target data); and, the second electronic device can delete the previously received data according to the first information. to the fourth target data.
简单来说,第一电子设备在接收到新的数据请求之后,第一电子设备基于该新的数据请求确定第二电子设备所需的数据,并将所确定的数据与之前已向第二电子设备发送的数据进行对比,挑选出新增的数据以及不再需要的数据,从而向第二电子设备发送新增的数据以及指示第二电子设备删除不再需要的数据,从而实现第二电子设备中的数据的复用,避免向第二电子设备发送大量重复的数据。In simple terms, after the first electronic device receives a new data request, the first electronic device determines the data required by the second electronic device based on the new data request, and compares the determined data with the data previously sent to the second electronic device. Compare the data sent by the device, select the newly added data and the data that is no longer needed, so as to send the new data to the second electronic device and instruct the second electronic device to delete the data that is no longer needed, so that the second electronic device The multiplexing of the data in the device avoids sending a large amount of repeated data to the second electronic device.
可以理解的是,以上介绍的是第二电子设备在向第一电子设备发送的数据请求中携带观察点位置,以使得第一电子设备基于观察点位置确定需要向第二电子设备发送的数据。在一些实施例中,第二电子设备也可以是基于三维模型中的观察点位置确定需要使用的数据,并向第一电子设备发送数据索引,以请求所需使用的数据。也就是说,基于观察点位置确定目标数据的过程在第二电子设备中执行。It can be understood that, as described above, the second electronic device carries the position of the observation point in the data request sent to the first electronic device, so that the first electronic device determines the data to be sent to the second electronic device based on the position of the observation point. In some embodiments, the second electronic device may also determine the data to be used based on the position of the observation point in the three-dimensional model, and send a data index to the first electronic device to request the data to be used. That is, the process of determining the target data based on the position of the observation point is performed in the second electronic device.
示例性地,所述第一数据请求中可以包括数据索引,所述数据索引用于指示所述第一目标数据,所述数据索引是所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置确定的。具体来说,第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置确定所述第一目标数据之后,则可以获取所述第一目标数据的数据索引,并通过在向第一电子设备发送的所述第一数据请求中携带所述数据索引,来请求第一电子设备发送所述第一目标数据。Exemplarily, the first data request may include a data index, the data index is used to indicate the first target data, and the data index is determined by the second electronic device according to the position of the first observation point. of. Specifically, after the second electronic device determines the first target data according to the position of the first observation point, it can obtain the data index of the first target data, and use the The first data request carries the data index to request the first electronic device to send the first target data.
为了便于理解,以下将结合具体例子详细介绍上述的三维模型数据的处理方法。For ease of understanding, the above-mentioned three-dimensional model data processing method will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific examples.
在第一电子设备获取到基于上述的三维模型数据的生成方法所生成的多层次、多级别的三维模型数据以及树状的树结构的情况下,第一电子设备获取到数据请求之后,可以通过遍历树状的树结构中各个节点的方式来确定该数据请求对应的目标数据。具体地,第一电子设备可以计算数据请求中所携带的观察点位置与各个节点所表示的对象之间的距离,并结合各个节点对应的三维模型数据的精细度,确定各个节点对应的数据是否能够作为目标数据。When the first electronic device obtains the multi-level and multi-level three-dimensional model data and the tree structure generated based on the above-mentioned method for generating three-dimensional model data, after the first electronic device obtains the data request, it can pass The target data corresponding to the data request is determined by traversing each node in the tree structure. Specifically, the first electronic device may calculate the distance between the position of the observation point carried in the data request and the object represented by each node, and combine the fineness of the 3D model data corresponding to each node to determine whether the data corresponding to each node can be used as target data.
此外,本实施例中,可以在第二电子设备中引入渲染球和缓冲球,其中渲染球为第二电子设备中用来存储直接用于渲染的三维模型数据的数据缓冲区;缓冲球则为第二电子设备中用来存储备选渲染的三维模型数据的数据缓冲区。简单来说,渲染球用于存储上述实施例所述的渲染数据,缓冲球则用于存储上述实施例所述的缓冲数据。In addition, in this embodiment, a rendering ball and a buffering ball can be introduced into the second electronic device, wherein the rendering ball is a data buffer for storing 3D model data directly used for rendering in the second electronic device; the buffering ball is A data buffer for storing 3D model data for optional rendering in the second electronic device. In short, the rendering ball is used to store the rendering data described in the above embodiments, and the buffer ball is used to store the buffer data described in the above embodiments.
示例性地,可以参阅图14,图14为本申请实施例提供的一种确定三维模型数据的流程示意图。如图14所示,确定三维模型数据的流程包括以下的步骤1401-1413。For example, refer to FIG. 14 , which is a schematic flowchart of determining three-dimensional model data provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 14 , the process of determining three-dimensional model data includes the following steps 1401-1413.
步骤1401,基于设备参数/用户自定义参数,确定渲染球/缓冲球层级,以及轻量化级别。
在执行三维模型的渲染之前,第一电子设备可以获取到第二电子设备所反馈的设备参数或者是用户自定义参数。其中,设备参数可以包括帧率、渲染延迟和温度等性能参数以及带宽和网络时延等网络参数。基于设备参数,第一电子设备可以确定第二电子设备中的渲染球的层级以及缓冲球的层级,以及待发送数据的轻量化级别。Before performing the rendering of the three-dimensional model, the first electronic device may obtain device parameters fed back by the second electronic device or user-defined parameters. The device parameters may include performance parameters such as frame rate, rendering delay, and temperature, and network parameters such as bandwidth and network delay. Based on the device parameters, the first electronic device may determine the level of the rendering ball and the buffering ball in the second electronic device, as well as the lightweight level of the data to be sent.
例如,第一电子设备可以根据设备参数确定第二电子设备中渲染球和缓冲球的层级均为3层,即第二电子设备中包括3层渲染球和3层缓冲球,其中,渲染球和缓冲球的不同层级可以用于存储不同轻量化级别的数据。由于第一电子设备所获取到的三维模型数据是多层次以及多级别的,因此第一电子设备可以在三维模型数据所具有的多个轻量化级别中确定其中的3个轻量化级别为待发送数据的轻量化级别。For example, the first electronic device may determine that the levels of the rendering ball and the buffering ball in the second electronic device are both three layers according to the device parameters, that is, the second electronic device includes three layers of rendering balls and three layers of buffering balls, wherein the rendering ball and the buffering ball Different layers of buffer balls can be used to store data at different lightweight levels. Since the 3D model data acquired by the first electronic device is multi-level and multi-level, the first electronic device can determine three lightweight levels among the multiple lightweight levels of the 3D model data as the Data lightweight level.
又例如,第一电子设备可以根据设备参数确定第二电子设备中渲染球和缓冲球的层级均为1层,即第二电子设备中只包括1层渲染球和1层缓冲球。因此,第一电子设备可以在三维模型数据所具有的多个轻量化级别中确定其中的1个轻量化级别为待发送数据的轻量化级别。For another example, the first electronic device may determine according to the device parameters that the levels of the rendering ball and the buffering ball in the second electronic device are both 1 layer, that is, the second electronic device only includes 1 layer of rendering ball and 1 layer of buffering ball. Therefore, the first electronic device may determine one of the multiple lightweight levels of the three-dimensional model data as the lightweight level of the data to be sent.
此外,在用户自定义参数中也可以是直接指定渲染球和缓冲球的层级,以及轻量化级别,第一电子设备通过解析用户自定义参数即可确定渲染球和缓冲球的层级,以及轻量化级别。In addition, the user-defined parameters can also directly specify the level of the rendering ball and the buffering ball, and the lightweight level. The first electronic device can determine the level of the rendering ball and the buffering ball, and the lightweight level by analyzing the user-defined parameters. level.
步骤1402,获取三维模型中的观察点位置。
其中,第一电子设备可以基于第二电子设备发送的数据请求,获取三维模型中的观察点位置。Wherein, the first electronic device may acquire the position of the observation point in the three-dimensional model based on the data request sent by the second electronic device.
步骤1403,找到树状树结构中的下一个节点i。
其中,树状树结构用于索引所生成的多层次、多级别的三维模型数据,树状树结构中的各个节点能够表示三维模型数据中各个层次的面片集合。具体地,关于树状树结构的介绍可以参考上述的图11和图12A对应的实施例的介绍,在此不再赘述。Wherein, the tree structure is used for indexing the generated multi-level and multi-level 3D model data, and each node in the tree structure can represent a set of patches of each level in the 3D model data. Specifically, for the introduction of the tree structure, reference may be made to the introduction of the above-mentioned embodiments corresponding to FIG. 11 and FIG. 12A , and details are not repeated here.
步骤1404,判断节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)是否小于或等于阈值1。
其中,节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)可以是指节点i所指示的三维模型数据的粗糙值,f(i,p)越大,表示基于节点i对应的三维模型数据渲染得到的二维图像的粗糙度越高,即二维图像的清晰度越差。Wherein, the rough value f(i, p) corresponding to node i may refer to the rough value of the 3D model data indicated by node i, and the larger f(i, p) is, the result obtained based on the rendering of the 3D model data corresponding to node i The higher the roughness of the two-dimensional image, the poorer the definition of the two-dimensional image.
具体地,f(i,p)=E/R,E表示节点i对应的三维模型数据的渲染误差,节点i对应的三维模型数据的精细度越高,则E越小,即节点i所在的层次越低,则E越小;R与节点i对应的三维模型数据所表示的对象与观察点位置之间的距离相关,距离越远,则R越大。也就是说,节点i所在的层次越低,且节点i对应的三维模型数据所表示的对象与观察点位置之间的距离越远时,则f(i,p)越小。Specifically, f(i, p)=E/R, E represents the rendering error of the 3D model data corresponding to node i, the higher the fineness of the 3D model data corresponding to node i, the smaller E is, that is, the location where node i is located The lower the level, the smaller E is; R is related to the distance between the object represented by the 3D model data corresponding to node i and the position of the observation point, and the farther the distance is, the larger R is. That is to say, the lower the level of the node i is, and the farther the distance between the object represented by the 3D model data corresponding to the node i and the position of the observation point is, the smaller f(i, p) is.
具体地,阈值1可以表示为λ1,即判断f(i,p)是否满足f(i,p)≤λ1。其中,λ1可以理解为缓冲球的半径,λ1可以是根据第二电子设备的性能来决定。示例性地,第二电子设备的性能较高时,λ1的取值可以较大;第二电子设备的性能较差时,λ1的取值可以较小。Specifically, the
可选的,R还可以是与观察点位置的视线范围相关,对象位于视线范围内越靠近中间的位置,则R越大。一般来说,在相机对三维景色进行拍摄得到二维图像的过程中,对于相同大小的物体,物体越靠近相机取景框的视线范围内中间的位置,则物体最终在二维图像中的成像面积越小,物体越远离相机取景框的视线范围内中间的位置,则物体最终在二维图像中的成像面积越大。因此,本实施例中可以基于对象与观察点位置的距离以及与观察点位置的视线范围之间的关系,确定上述的R。Optionally, R may also be related to the line-of-sight range of the observation point position, and the closer the object is located in the line-of-sight range, the greater R is. Generally speaking, in the process of obtaining a two-dimensional image from a three-dimensional scene, for an object of the same size, the closer the object is to the middle position within the line of sight of the camera viewfinder, the final imaging area of the object in the two-dimensional image will be The smaller the value is, the farther the object is from the middle position within the line of sight of the camera frame, and the final imaging area of the object in the two-dimensional image is larger. Therefore, in this embodiment, the above R can be determined based on the distance between the object and the observation point and the relationship between the object and the sight range of the observation point.
步骤1405,如果节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)小于或等于λ1,则将节点i对应的三维模型数据加入缓冲球对应的缓冲数据中。
也就是说,如果节点i对应粗糙值小于或等于缓冲球的半径时,则可以将节点i对应的三维模型数据视为需要向第二电子设备发送的缓冲数据。That is to say, if the roughness value corresponding to node i is less than or equal to the radius of the buffer sphere, the 3D model data corresponding to node i may be regarded as buffer data that needs to be sent to the second electronic device.
步骤1406,如果节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)大于λ1,则将节点i对应的三维模型数据从缓冲球对应的缓冲数据中移除。
也就是说,如果节点i对应粗糙值小于或等于缓冲球的半径时,则可以将节点i对应的三维模型数据视为第二电子设备的缓冲球中不需要再存储的数据。That is to say, if the roughness value corresponding to node i is less than or equal to the radius of the buffer ball, the 3D model data corresponding to node i can be regarded as data that does not need to be stored in the buffer ball of the second electronic device.
步骤1407,判断树状树结构是否遍历完成。
如果树状树结构没有遍历完成,则转至继续执行上述的步骤1403,即重新找到树状树结构中的下一个节点;如果树状树结构遍历完成,则转至执行步骤1413,即返回渲染球的变化量和缓冲球的变化量。If the tree structure has not been traversed, go to
步骤1408,找到树状树结构中的下一个节点i。
步骤1409,判断节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)是否小于或等于阈值2。
具体地,阈值2可以表示为λ2,即判断f(i,p)是否满足f(i,p)≤λ2。其中,λ2可以理解为渲染球的半径,λ2小于λ1,即渲染球的半径要小于缓冲球的半径,即渲染数据的精细度要高于缓冲数据的精细度。λ2可以是根据第二电子设备的性能来决定。示例性地,第二电子设备的性能较高时,λ2的取值可以较大;第二电子设备的性能较差时,λ2的取值可以较小。Specifically, the
步骤1410,如果节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)小于或等于λ2,将节点i对应的三维模型数据加入渲染球对应的渲染数据中。
也就是说,如果节点i对应粗糙值小于或等于渲染球的半径时,则可以将节点i对应的三维模型数据视为需要向第二电子设备发送的渲染数据。That is to say, if the roughness value corresponding to node i is less than or equal to the radius of the rendering sphere, the 3D model data corresponding to node i can be regarded as rendering data that needs to be sent to the second electronic device.
可选的,第一电子设备可以进一步判断节点i对应的三维模型数据是否已经加入缓冲球对应的缓冲数据中;以及第一电子设备判断节点i的父节点对应的粗糙值是否大于阈值2,如果节点i满足上述的三个条件,则可以将节点i对应的三维模型数据加入渲染球对应的渲染数据中。Optionally, the first electronic device may further determine whether the 3D model data corresponding to node i has been added to the buffer data corresponding to the buffer ball; and the first electronic device may determine whether the roughness value corresponding to the parent node of node i is greater than
步骤1411,如果节点i对应的粗糙值f(i,p)大于λ2,则将节点i对应的三维模型数据从渲染球对应的渲染数据中移除。
也就是说,如果节点i对应粗糙值小于或等于渲染球的半径时,则可以将节点i对应的三维模型数据视为第二电子设备的渲染球中不需要再存储的数据。That is to say, if the roughness value corresponding to node i is less than or equal to the radius of the rendering sphere, the 3D model data corresponding to node i can be regarded as data that does not need to be stored in the rendering sphere of the second electronic device.
步骤1412,判断树状树结构是否遍历完成。
如果树状树结构没有遍历完成,则转至继续执行上述的步骤1408,即重新找到树状树结构中的下一个节点;如果树状树结构遍历完成,则转至执行步骤1413,即返回渲染球的变化量和缓冲球的变化量。If the tree structure has not been traversed, proceed to step 1408, that is, to find the next node in the tree structure; if the tree structure is traversed, proceed to step 1413, that is, return to rendering The change amount of the ball and the change amount of the buffer ball.
其中,步骤1408-1412可以是与上述的步骤1403-1407同步执行,即同步确定渲染球对应的渲染数据以及缓冲球对应的缓冲数据。Wherein, steps 1408-1412 may be executed synchronously with the above-mentioned steps 1403-1407, that is, the rendering data corresponding to the rendering ball and the buffering data corresponding to the buffering ball are determined synchronously.
步骤1413,返回渲染球的变化量和缓冲球的变化量。
经过上述的多个步骤,第一电子设备可以确定需要加入渲染数据中的三维模型数据以及需要从渲染球中移除的渲染数据,因此第一电子设备可以向第二电子设备返回渲染球新增的渲染数据以及旧的待删除的渲染数据。After the above steps, the first electronic device can determine the 3D model data that needs to be added to the rendering data and the rendering data that needs to be removed from the rendering sphere, so the first electronic device can return the rendering sphere to the second electronic device. and the old rendering data to be deleted.
类似地,第一电子设备可以确定需要加入缓冲数据中的三维模型数据以及需要从缓冲球中移除的渲染数据,因此第一电子设备可以向第二电子设备返回缓冲球新增的缓冲数据以及旧的待删除的缓冲数据。Similarly, the first electronic device can determine the 3D model data that needs to be added to the buffer data and the rendering data that needs to be removed from the buffer ball, so the first electronic device can return the newly added buffer data and the buffer ball to the second electronic device. Old cached data to be deleted.
在第二电子设备接收上述的缓冲数据和渲染数据之后,第二电子设备遍历渲染数据,并使用级联坐标转换算法将渲染数据中的节点的三维坐标转换至对应的维度空间,以执行相应的渲染操作。After the second electronic device receives the above-mentioned buffer data and rendering data, the second electronic device traverses the rendering data, and uses the cascade coordinate transformation algorithm to convert the three-dimensional coordinates of the nodes in the rendering data to the corresponding dimensional space, so as to perform corresponding Rendering operation.
示例性地,可以参阅图15,图15为本申请实施例提供的一种渲染球和缓冲球的示意图。如图15所示,观察点位置位于渲染球和缓冲球的中心位置,缓冲球的半径为λ1,渲染球的半径为λ2,且λ1大于λ2。在三维模型数据的处理过程中,电子设备先基于三维模型数据的精细度以及三维模型数据所表示的对象与观察点位置之间的距离求得粗糙值,再通过判断粗糙值与λ1、λ2之间的大小关系,来决定是否将三维模型数据加入缓冲球或渲染球中。可以看出,由于λ1大于λ2,因此缓冲球中包括的三维模型数据多于渲染球中的三维模型数据,在观察点位置发生偏移时,第二电子设备可以优先从缓冲球选择部分满足要求的数据填充至渲染球中,从而避免重新从第一电子设备处获取新的数据,提高渲染的速度。For example, refer to FIG. 15 , which is a schematic diagram of a rendering ball and a buffering ball provided in an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 15, the position of the observer is located at the center of the rendering sphere and the buffer sphere, the radius of the buffer sphere is λ1 , the radius of the rendering sphere is λ2 , and λ1 is greater than λ2 . During the processing of the 3D model data, the electronic device first calculates the rough value based on the fineness of the 3D model data and the distance between the object represented by the 3D model data and the position of the observation point, and then judges the relationship between the rough value and λ1 , λ2 to determine whether to add the 3D model data to the buffer ball or the rendering ball. It can be seen that since λ1 is greater than λ2 , the 3D model data included in the buffer sphere is more than the 3D model data in the rendering sphere, and when the position of the observation point shifts, the second electronic device can preferentially select a part from the buffer sphere The data meeting the requirements is filled into the rendering sphere, thereby avoiding re-obtaining new data from the first electronic device, and improving the rendering speed.
可以参阅图16,图16为本申请实施例提供的多层渲染球和多层缓冲球的示意图。如图16所示,第二电子设备中可以包括多层级的渲染球以及多层级的缓冲球,不同层级的渲染球和缓冲球可以用于存储不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据。在树状树结构中,对于某一个层次的节点,该节点还可以用于表示不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据。因此,在通过上述的图14对应的实施例确定待加入缓冲球以及渲染球的节点之后,可以将这些节点对应的多个轻量化级别的三维模型数据发送给第二电子设备,第二电子设备通过不同层级的缓冲球以及渲染球来存储不同轻量化级别的三维模型数据。Refer to FIG. 16 , which is a schematic diagram of a multi-layer rendering ball and a multi-layer buffer ball provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 16 , the second electronic device may include multi-level rendering balls and multi-level buffering balls, and different levels of rendering balls and buffering balls may be used to store 3D model data of different lightweight levels. In the tree structure, for a node of a certain level, the node can also be used to represent 3D model data of different lightweight levels. Therefore, after the nodes to be added to the buffer ball and the rendering ball are determined through the above-mentioned embodiment corresponding to FIG. 3D model data of different lightweight levels are stored through different levels of buffer balls and rendering balls.
可以理解的是,通过在第二电子设备上配置图15和图16所示的渲染球和缓冲球,可以使得第二电子设备上能够同时存储同一对象所对应的不同层次、不同级别的三维模型数据,即同一对象所对应的不同精细度下的三维模型数据。这样一来,第二电子设备能够根据三维模型中观察点位置的变化或者设备自身的状态变化,从多种精细度下的三维模型数据中挑选合适精细度的三维模型数据,从而实现三维模型的快速渲染。It can be understood that by configuring the rendering ball and buffer ball shown in Figure 15 and Figure 16 on the second electronic device, it is possible to simultaneously store three-dimensional models of different levels and levels corresponding to the same object on the second electronic device Data, that is, 3D model data corresponding to the same object at different degrees of fineness. In this way, the second electronic device can select 3D model data with appropriate fineness from 3D model data with various finenesses according to the change of the position of the observation point in the 3D model or the state change of the device itself, so as to realize the realization of the 3D model. Fast rendering.
示例性地,可以参阅图17,图17为本申请实施例提供的一种观察点位置变化时的渲染示意图。如图17所示,在第二电子设备上渲染一个完整的地球的过程中,当观察点位置位于地球中的某一个点时,能够基于渲染球中的数据渲染得到地球上某座山峰上的一块岩石;当观察点位置逐渐发生变化时,将缓冲球中的数据逐渐填充至渲染球中,从而能够看到更多的景物,直至看到整个地球表面的全貌。在观察点位置发生变化的整个过程中,能够保持帧率的稳定,而不会出现卡顿的现象。For example, you can refer to FIG. 17 , which is a schematic rendering diagram when the position of the observation point changes according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 17, in the process of rendering a complete earth on the second electronic device, when the observation point is located at a certain point on the earth, the data on a certain mountain on the earth can be rendered based on the data in the rendering sphere. A piece of rock; when the position of the observation point gradually changes, the data in the buffer ball is gradually filled into the rendering ball, so that more scenery can be seen, until the whole picture of the entire earth's surface can be seen. During the entire process of changing the position of the observation point, the frame rate can be kept stable without stuttering.
也就是说,基于本实施例所提供的三维模型数据的生成方法和处理方法,可以不再依赖渲染模型的硬件的配置,即可以使用普通的智能手机或者个人电脑,渲染大规模的三维模型,并且能够实现顺畅地拉近观看细节,拉远观看全局。此外,本实施例中通过网络流媒体的方式传输渲染数据,无需占用渲染设备的本地存储空间。That is to say, based on the method for generating and processing 3D model data provided in this embodiment, it is no longer dependent on the configuration of the hardware for rendering the model, that is, an ordinary smart phone or personal computer can be used to render a large-scale 3D model, And it is possible to smoothly zoom in on the details and zoom out to see the overall situation. In addition, in this embodiment, the rendering data is transmitted through network streaming, without occupying the local storage space of the rendering device.
在图1至图17所对应的实施例的基础上,为了更好的实施本申请实施例的上述方案,下面还提供用于实施上述方案的相关设备。On the basis of the embodiments corresponding to FIG. 1 to FIG. 17 , in order to better implement the above-mentioned solution of the embodiment of the present application, related equipment for implementing the above-mentioned solution is also provided below.
可以参阅图18,图18为本申请实施例提供的一种数据处理装置的结构示意图。如图18所示,该数据处理装置包括:接收单元1801、处理单元1802和发送单元1803;所述接收单元1801,用于接收来自于第二电子设备的第一数据请求,所述第一数据请求包括第一观察点位置;所述处理单元1802,用于根据所述第一数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第一目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据,其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;所述发送单元1803,用于向所述第二电子设备发送所述第一目标数据。Refer to FIG. 18 , which is a schematic structural diagram of a data processing device provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 18, the data processing apparatus includes: a receiving
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据包括用于执行三维模型渲染的渲染数据,所述渲染数据包括第一对象的渲染数据和第二对象的渲染数据,其中,所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度高于所述第二对象的渲染数据的精细度,所述第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离小于所述第二对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data includes rendering data for performing 3D model rendering, and the rendering data includes rendering data of a first object and rendering data of a second object, wherein the first The fineness of the rendering data of an object is higher than the fineness of the rendering data of the second object, and the distance between the first object and the position of the first observation point is smaller than the distance between the second object and the first The distance between watch point locations.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括第一对象对应的多份渲染数据,所述多份渲染数据的精细度不同;所述处理单元1802,还用于:根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据,其中所述第一对象的渲染数据的精细度与所述距离具有负相关关系。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the 3D model includes multiple pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the multiple pieces of rendering data have different fineness; the
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据中的第一份渲染数据包括多组渲染数据,所述多组渲染数据中的每组渲染数据用于渲染以得到所述第一对象,且所述多组渲染数据的精细度不同,所述第一份渲染数据是所述多份渲染数据中的任意一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the first piece of rendering data in the multiple pieces of rendering data includes multiple sets of rendering data, and each set of rendering data in the multiple sets of rendering data is used for rendering to obtain the first object , and the fineness of the multiple sets of rendering data is different, and the first set of rendering data is any one of the multiple sets of rendering data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多份渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行多次面片缩减处理后得到的,其中,每执行一次面片缩减处理均得到一份渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple copies of rendering data are obtained after multiple mesh reduction processes are performed on the original rendering data of the first object, and one copy is obtained each time the mesh reduction processing is performed. Render data.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一份渲染数据包括的所述多组渲染数据是对所述第一对象的原始渲染数据执行相同次数和不同倍数的面片缩减处理得到的。In a possible implementation manner, the multiple sets of rendering data included in the first rendering data are obtained by performing the same number of times of mesh reduction processing and different multiples of the original rendering data of the first object.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元1802,还用于:根据所述距离以及所述多份渲染数据的精细度,从所述多份渲染数据中选择一份渲染数据;根据所述第二电子设备的性能指标和/或网络状态,从所选择的一份渲染数据的多组渲染数据中选择一组渲染数据作为所述第一对象的渲染数据。In a possible implementation manner, the
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述性能指标包括所述第二电子设备的帧率、渲染延迟和温度参数中的一个或多个;所述网络状态包括所述第二电子设备的带宽和网络时延中的一个或多个。In a possible implementation manner, the performance index includes one or more of the frame rate, rendering delay, and temperature parameters of the second electronic device; the network status includes bandwidth and One or more of network delays.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一目标数据还包括缓冲数据,所述缓冲数据包括所述第一对象对应的N份渲染数据,所述N为大于1的整数,所述N份渲染数据均用于执行所述第一对象的渲染,且所述N份渲染数据的精细度不同。In a possible implementation manner, the first target data further includes buffer data, and the buffer data includes N pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, where N is an integer greater than 1, and the N pieces of rendering data The rendering data are all used to execute the rendering of the first object, and the N pieces of rendering data have different finenesses.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述三维模型的数据中包括所述第一对象对应的M份渲染数据,所述M份渲染数据的精细度不同,所述M为大于所述N的整数;所述处理单元1802,还用于:根据所述第一数据请求,确定所述三维模型中的第一对象与所述第一观察点位置之间的距离;根据所述距离,从所述多份渲染数据中确定一份渲染数据为所述第一对象的目标渲染数据,所述目标渲染数据的精细度满足所述第一对象的精细度要求,所述第一对象的精细度要求与所述距离相关;从所述M份渲染数据中选择N份渲染数据作为所述缓冲数据,所述N份渲染数据的精细度均小于或等于所述目标渲染数据的精细度。In a possible implementation manner, the data of the three-dimensional model includes M pieces of rendering data corresponding to the first object, and the fineness of the M pieces of rendering data is different, and the M is an integer greater than the N The
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述第一数据请求中包括数据索引,所述数据索引用于指示所述第一目标数据,所述数据索引是所述第二电子设备根据所述第一观察点位置确定的。In a possible implementation manner, the first data request includes a data index, the data index is used to indicate the first target data, and the data index is the second electronic device according to the first The position of the observation point is determined.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述接收单元1801,还用于接收来自于所述第二电子设备的第二数据请求;所述处理单元1802,还用于根据所述第二数据请求,从三维模型的数据中确定第二目标数据,所述第二目标数据与所述第二电子设备中所运行的三维模型中的第二观察点位置相关;所述处理单元1802,还用于根据所述第一目标数据和所述第二目标数据确定第三目标数据,并生成第一信息,其中所述第一目标数据不包括所述第三目标数据,且所述第二目标数据包括所述第三目标数据,所述第一信息用于指示待删除的第四目标数据,所述第一目标数据包括所述第四目标数据,且所述第二目标数据不包括所述第四目标数据;所述发送单元1803,还用于向所述第二电子设备发送所述第三目标数据和所述第一信息。In a possible implementation manner, the receiving
可以参阅图19,图19为本申请实施例提供的一种数据生成装置的结构示意图。如图19所示,该数据生成装置包括:获取单元1901和处理单元1902;所述获取单元1901,用于获取三维模型文件,所述三维模型文件包括用于构成三维模型的多个面片;所述处理单元1902,用于:将所述多个面片分成多个第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合中的每个第一面片集合包括多个连接的面片,且所述每个第一面片集合中的面片数量相同;将所述多个第一面片集合分成多个第一面片集合组,所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组包括多个所述第一面片集合,所述多个第一面片集合组用于构成第一三维模型;对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第二面片集合组,所述多个第二面片集合组用于构成第二三维模型,所述第一三维模型的精细度高于所述第二三维模型的精细度;对所述多个第二面片集合组进行拆分,得到多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二面片集合中每个第二面片集合的面片数量与所述多个第一面片集合中每个第一面片集合的面片数量相同。You can refer to FIG. 19 , which is a schematic structural diagram of a data generating device provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 19, the data generation device includes: an acquisition unit 1901 and a processing unit 1902; the acquisition unit 1901 is configured to acquire a 3D model file, and the 3D model file includes a plurality of meshes for constituting a 3D model; The processing unit 1902 is configured to: divide the plurality of patches into a plurality of first patch sets, each of the plurality of first patch sets includes a plurality of connected patches , and the number of patches in each first patch set is the same; the multiple first patch sets are divided into multiple first patch set groups, and the multiple first patch set groups are Each first mesh set group includes a plurality of first mesh sets, and the plurality of first mesh set groups are used to form a first three-dimensional model; for the plurality of first mesh set groups Each first mesh set group performs mesh reduction processing to obtain a plurality of second mesh set groups after the number of meshes is reduced, and the plurality of second mesh set groups are used to form a second three-dimensional model, so The fineness of the first three-dimensional model is higher than the fineness of the second three-dimensional model; the plurality of second mesh set groups are split to obtain a plurality of second mesh sets, and the plurality of second mesh sets are obtained. The number of patches in each second patch set in the patch sets is the same as the number of patches in each first patch set in the plurality of first patch sets.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元1902,还用于:对所述多个第一面片集合组中的每个第一面片集合组执行面片缩减处理,以得到面片数量缩减后的多个第三面片集合组,所述多个第三面片集合组用于构成第三三维模型,所述多个第三面片集合组中每个第三面片集合组的面片数量与所述多个第二面片集合组中每个第二面片集合组的面片数量不同。In a possible implementation manner, the
在一种可能的实现方式中,每个所述第二面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/N,N为大于1的整数;每个所述第三面片集合组的面片数量为每个所述第一面片集合组的面片数量的1/M,其中,M为大于N的整数。In a possible implementation, the number of patches in each of the second patch sets is 1/N of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where N is an integer greater than 1; The number of patches in each of the third patch sets is 1/M of the number of patches in each of the first patch sets, where M is an integer greater than N.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述处理单元1902,还用于:根据所述多个第一面片集合和所述多个第二面片集合生成树结构;其中,所述树结构包括多个第一节点和多个第二节点,所述多个第一节点分别对应于所述多个第一面片集合,所述多个第二节点分别对应于所述多个第二面片集合,所述多个第二节点中的每个节点均连接有所述多个第一节点中的多个节点。In a possible implementation manner, the
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述多个面片中的每个面片由多个顶点构成;所述处理单元1902,具体用于:确定第一面片集合组中位于边缘位置的多个目标顶点,所述第一面片集合为所述多个第一面片集合组中的任意一个面片集合组;锁定所述多个目标顶点,重新生成多个面片,以得到第二面片集合组,所述第二面片集合组的面片数量小于所述第一面片集合组的面片数量,所述第二面片集合组为所述多个第二面片集合组中的一个面片集合组。In a possible implementation manner, each of the plurality of patches is composed of a plurality of vertices; the
接下来介绍本申请实施例提供的一种电子设备,请参阅图20,图20为本申请实施例提供的电子设备的一种结构示意图,电子设备2000具体可以表现为手机、平板、笔记本电脑、智能穿戴设备、服务器等,此处不做限定。其中,电子设备2000上可以部署有图11对应实施例中所描述的声音处理装置,用于实现图11对应实施例中声音处理的功能。具体的,电子设备2000包括:接收器2001、发射器2002、处理器2003和存储器2004(其中电子设备2000中的处理器2003的数量可以一个或多个,图20中以一个处理器为例),其中,处理器2003可以包括应用处理器20031和通信处理器20032。在本申请的一些实施例中,接收器2001、发射器2002、处理器2003和存储器2004可通过总线或其它方式连接。Next, an electronic device provided by the embodiment of the present application is introduced. Please refer to FIG. 20. FIG. 20 is a schematic structural diagram of the electronic device provided by the embodiment of the present application. Smart wearable devices, servers, etc. are not limited here. Wherein, the sound processing apparatus described in the embodiment corresponding to FIG. 11 may be deployed on the
存储器2004可以包括只读存储器和随机存取存储器,并向处理器2003提供指令和数据。存储器2004的一部分还可以包括非易失性随机存取存储器(non-volatile randomaccess memory,NVRAM)。存储器2004存储有处理器和操作指令、可执行模块或者数据结构,或者它们的子集,或者它们的扩展集,其中,操作指令可包括各种操作指令,用于实现各种操作。The memory 2004 may include read-only memory and random-access memory, and provides instructions and data to the processor 2003 . A part of the memory 2004 may also include a non-volatile random access memory (non-volatile random access memory, NVRAM). The memory 2004 stores processors and operating instructions, executable modules or data structures, or their subsets, or their extended sets, wherein the operating instructions may include various operating instructions for implementing various operations.
处理器2003控制电子设备的操作。具体的应用中,电子设备的各个组件通过总线系统耦合在一起,其中总线系统除包括数据总线之外,还可以包括电源总线、控制总线和状态信号总线等。但是为了清楚说明起见,在图中将各种总线都称为总线系统。The processor 2003 controls the operation of the electronic device. In a specific application, various components of an electronic device are coupled together through a bus system, where the bus system may include a power bus, a control bus, and a status signal bus in addition to a data bus. However, for the sake of clarity, the various buses are referred to as bus systems in the figures.
上述本申请实施例揭示的方法可以应用于处理器2003中,或者由处理器2003实现。处理器2003可以是一种集成电路芯片,具有信号的处理能力。在实现过程中,上述方法的各步骤可以通过处理器2003中的硬件的集成逻辑电路或者软件形式的指令完成。上述的处理器2003可以是通用处理器、数字信号处理器(digital signal processing,DSP)、微处理器或微控制器,还可进一步包括专用集成电路(application specific integratedcircuit,ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(field-programmable gate array,FPGA)或者其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件。该处理器2003可以实现或者执行本申请实施例中的公开的各方法、步骤及逻辑框图。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者该处理器也可以是任何常规的处理器等。结合本申请实施例所公开的方法的步骤可以直接体现为硬件译码处理器执行完成,或者用译码处理器中的硬件及软件模块组合执行完成。软件模块可以位于随机存储器,闪存、只读存储器,可编程只读存储器或者电可擦写可编程存储器、寄存器等本领域成熟的存储介质中。该存储介质位于存储器2004,处理器2003读取存储器2004中的信息,结合其硬件完成上述方法的步骤。The methods disclosed in the foregoing embodiments of the present application may be applied to the processor 2003 or implemented by the processor 2003 . The processor 2003 may be an integrated circuit chip, which has a signal processing capability. In the implementation process, each step of the above method can be completed by an integrated logic circuit of hardware in the processor 2003 or instructions in the form of software. The above-mentioned processor 2003 may be a general-purpose processor, a digital signal processor (digital signal processing, DSP), a microprocessor or a microcontroller, and may further include an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), a field programmable gate Array (field-programmable gate array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components. The processor 2003 may realize or execute various methods, steps and logic block diagrams disclosed in the embodiments of the present application. A general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor, or the processor may be any conventional processor, or the like. The steps of the method disclosed in connection with the embodiments of the present application may be directly implemented by a hardware decoding processor, or implemented by a combination of hardware and software modules in the decoding processor. The software module can be located in a mature storage medium in the field such as random access memory, flash memory, read-only memory, programmable read-only memory or electrically erasable programmable memory, register. The storage medium is located in the memory 2004, and the processor 2003 reads the information in the memory 2004, and completes the steps of the above method in combination with its hardware.
接收器2001可用于接收输入的数字或字符信息,以及产生与电子设备的相关设置以及功能控制有关的信号输入。发射器2002可用于通过第一接口输出数字或字符信息;发射器2002还可用于通过第一接口向磁盘组发送指令,以修改磁盘组中的数据;发射器2002还可以包括显示屏等显示设备。The receiver 2001 can be used to receive input digital or character information, and generate signal input related to related settings and function control of electronic equipment. The transmitter 2002 can be used to output digital or character information through the first interface; the transmitter 2002 can also be used to send instructions to the disk group through the first interface to modify the data in the disk group; the transmitter 2002 can also include display devices such as a display screen .
本申请实施例中还提供一种包括计算机程序产品,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行如前述执行设备所执行的步骤,或者,使得计算机执行如前述训练设备所执行的步骤。The embodiment of the present application also provides a computer program product, which, when running on a computer, causes the computer to perform the steps performed by the aforementioned execution device, or enables the computer to perform the steps performed by the aforementioned training device.
本申请实施例中还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质中存储有用于进行信号处理的程序,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行如前述执行设备所执行的步骤,或者,使得计算机执行如前述训练设备所执行的步骤。An embodiment of the present application also provides a computer-readable storage medium, the computer-readable storage medium stores a program for signal processing, and when it is run on a computer, the computer executes the steps performed by the aforementioned executing device , or, causing the computer to perform the steps performed by the aforementioned training device.
本申请实施例提供的执行设备或终端设备具体可以为芯片,芯片包括:处理单元和通信单元,所述处理单元例如可以是处理器,所述通信单元例如可以是输入/输出接口、管脚或电路等。该处理单元可执行存储单元存储的计算机执行指令,以使执行设备内的芯片执行上述实施例描述的编译方法。可选地,所述存储单元为所述芯片内的存储单元,如寄存器、缓存等,所述存储单元还可以是所述无线接入设备端内的位于所述芯片外部的存储单元,如只读存储器(read-only memory,ROM)或可存储静态信息和指令的其他类型的静态存储设备,随机存取存储器(random access memory,RAM)等。The execution device or terminal device provided in the embodiment of the present application may specifically be a chip. The chip includes: a processing unit and a communication unit. The processing unit may be, for example, a processor, and the communication unit may be, for example, an input/output interface, a pin or circuit etc. The processing unit may execute the computer-executable instructions stored in the storage unit, so that the chip in the execution device executes the compiling method described in the above-mentioned embodiments. Optionally, the storage unit is a storage unit in the chip, such as a register, a cache, etc., and the storage unit may also be a storage unit located outside the chip in the wireless access device, such as only Read-only memory (ROM) or other types of static storage devices that can store static information and instructions, random access memory (random access memory, RAM), etc.
另外需说明的是,以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部模块来实现本实施例方案的目的。另外,本申请提供的装置实施例附图中,模块之间的连接关系表示它们之间具有通信连接,具体可以实现为一条或多条通信总线或信号线。In addition, it should be noted that the device embodiments described above are only illustrative, and the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components shown as units may or may not be A physical unit can be located in one place, or it can be distributed to multiple network units. Part or all of the modules can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment. In addition, in the drawings of the device embodiments provided in the present application, the connection relationship between the modules indicates that they have communication connections, which can be specifically implemented as one or more communication buses or signal lines.
通过以上的实施方式的描述,所属领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到本申请可借助软件加必需的通用硬件的方式来实现,当然也可以通过专用硬件包括专用集成电路、专用CPU、专用存储器、专用元器件等来实现。一般情况下,凡由计算机程序完成的功能都可以很容易地用相应的硬件来实现,而且,用来实现同一功能的具体硬件结构也可以是多种多样的,例如模拟电路、数字电路或专用电路等。但是,对本申请而言更多情况下软件程序实现是更佳的实施方式。基于这样的理解,本申请的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在可读取的存储介质中,如计算机的软盘、U盘、移动硬盘、ROM、RAM、磁碟或者光盘等,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,训练设备,或者网络设备等)执行本申请各个实施例所述的方法。Through the description of the above embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that the present application can be implemented by means of software plus necessary general-purpose hardware, and of course it can also be realized by special hardware including application-specific integrated circuits, dedicated CPUs, dedicated memories, Special components, etc. to achieve. In general, all functions completed by computer programs can be easily realized by corresponding hardware, and the specific hardware structure used to realize the same function can also be varied, such as analog circuits, digital circuits or special-purpose circuit etc. However, for this application, software program implementation is a better implementation mode in most cases. Based on this understanding, the essence of the technical solution of this application or the part that contributes to the prior art can be embodied in the form of software products, and the computer software products are stored in readable storage media, such as computer floppy disks, U disk, mobile hard disk, ROM, RAM, magnetic disk or optical disk, etc., including several instructions to make a computer device (which can be a personal computer, training device, or network device, etc.) execute the method described in each embodiment of the application .
在上述实施例中,可以全部或部分地通过软件、硬件、固件或者其任意组合来实现。当使用软件实现时,可以全部或部分地以计算机程序产品的形式实现。In the above embodiments, all or part of them may be implemented by software, hardware, firmware or any combination thereof. When implemented using software, it may be implemented in whole or in part in the form of a computer program product.
所述计算机程序产品包括一个或多个计算机指令。在计算机上加载和执行所述计算机程序指令时,全部或部分地产生按照本申请实施例所述的流程或功能。所述计算机可以是通用计算机、专用计算机、计算机网络、或者其他可编程装置。所述计算机指令可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,或者从一个计算机可读存储介质向另一计算机可读存储介质传输,例如,所述计算机指令可以从一个网站站点、计算机、训练设备或数据中心通过有线(例如同轴电缆、光纤、数字用户线(DSL))或无线(例如红外、无线、微波等)方式向另一个网站站点、计算机、训练设备或数据中心进行传输。所述计算机可读存储介质可以是计算机能够存储的任何可用介质或者是包含一个或多个可用介质集成的训练设备、数据中心等数据存储设备。所述可用介质可以是磁性介质,(例如,软盘、硬盘、磁带)、光介质(例如,DVD)、或者半导体介质(例如固态硬盘(Solid State Disk,SSD))等。The computer program product includes one or more computer instructions. When the computer program instructions are loaded and executed on the computer, the processes or functions according to the embodiments of the present application will be generated in whole or in part. The computer can be a general purpose computer, a special purpose computer, a computer network, or other programmable devices. The computer instructions may be stored in or transmitted from one computer-readable storage medium to another computer-readable storage medium, for example, the computer instructions may be transferred from a website, computer, training device, or data The center transmits to another website site, computer, training device or data center via wired (eg, coaxial cable, fiber optic, digital subscriber line (DSL)) or wireless (eg, infrared, wireless, microwave, etc.). The computer-readable storage medium may be any available medium that can be stored by a computer, or a data storage device such as a training device or a data center integrated with one or more available media. The available medium may be a magnetic medium (such as a floppy disk, a hard disk, or a magnetic tape), an optical medium (such as a DVD), or a semiconductor medium (such as a solid state disk (Solid State Disk, SSD)), etc.
Claims (18)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111236216.4ACN116012506A (en) | 2021-10-22 | 2021-10-22 | A processing method, generating method and related device for three-dimensional model data |
| PCT/CN2022/125053WO2023066122A1 (en) | 2021-10-22 | 2022-10-13 | Three-dimensional model data processing method, three-dimensional model data generation method, and related apparatuses |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111236216.4ACN116012506A (en) | 2021-10-22 | 2021-10-22 | A processing method, generating method and related device for three-dimensional model data |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN116012506Atrue CN116012506A (en) | 2023-04-25 |
Family
ID=86021726
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111236216.4APendingCN116012506A (en) | 2021-10-22 | 2021-10-22 | A processing method, generating method and related device for three-dimensional model data |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116012506A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023066122A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118152345B (en)* | 2024-01-22 | 2025-05-13 | 深圳艾迪普信息技术有限公司 | Method and system for manufacturing and generating multi-level three-dimensional grid file |
| CN119739904B (en)* | 2025-03-04 | 2025-05-06 | 西北工业大学 | A method for constructing 3D model index structure based on object distance measurement |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103299347B (en)* | 2011-12-31 | 2016-11-02 | 华为技术有限公司 | Online rendering method, offline rendering method and related device based on cloud application |
| CN107590858A (en)* | 2017-08-21 | 2018-01-16 | 上海妙影医疗科技有限公司 | Medical sample methods of exhibiting and computer equipment, storage medium based on AR technologies |
| CN108109191A (en)* | 2017-12-26 | 2018-06-01 | 深圳创维新世界科技有限公司 | Rendering intent and system |
| CN110443893B (en)* | 2019-08-02 | 2023-04-25 | 广联达科技股份有限公司 | Large-scale building scene rendering acceleration method, system, device and storage medium |
| CN110738721B (en)* | 2019-10-12 | 2023-09-01 | 四川航天神坤科技有限公司 | Three-dimensional scene rendering acceleration method and system based on video geometric analysis |
- 2021
- 2021-10-22CNCN202111236216.4Apatent/CN116012506A/enactivePending
- 2022
- 2022-10-13WOPCT/CN2022/125053patent/WO2023066122A1/ennot_activeCeased
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2023066122A1 (en) | 2023-04-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11288857B2 (en) | Neural rerendering from 3D models | |
| KR101692193B1 (en) | Crowd-sourced video rendering system | |
| CN110706341B (en) | A high-performance rendering method, device and storage medium for urban information model | |
| US11887241B2 (en) | Learning 2D texture mapping in volumetric neural rendering | |
| EP2807587B1 (en) | Determining 3d model information from stored images | |
| US11948338B1 (en) | 3D volumetric content encoding using 2D videos and simplified 3D meshes | |
| CN104658033B (en) | Global illumination method for drafting and device under multiple light courcess | |
| CN111727462A (en) | Density coordinate hashing for volumetric data | |
| WO2023066122A1 (en) | Three-dimensional model data processing method, three-dimensional model data generation method, and related apparatuses | |
| CN109979000B (en) | Multi-view primitive block | |
| WO2019140295A1 (en) | Cross-device supervisory computer vision system | |
| CN114429513B (en) | Visible element determination method and device, storage medium and electronic device | |
| WO2025092176A1 (en) | Reconstruction method and apparatus for three-dimensional entity model, device, medium and program product | |
| CN114596423A (en) | Model rendering method, device and computer equipment based on virtual scene meshing | |
| US11418769B1 (en) | Viewport adaptive volumetric content streaming and/or rendering | |
| EP4028791A1 (en) | Point cloud geometry upsampling | |
| JP2017199354A (en) | Rendering global illumination of 3d scene | |
| JP7419522B2 (en) | Volume data reduction while preserving visual fidelity | |
| CN111325821B (en) | Grid model processing method and device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN119251436A (en) | 3D model processing system and method and storage circuit | |
| WO2024159555A1 (en) | Video processing method and apparatus, and computer readable storage medium | |
| CN115222869A (en) | Distributed rendering method and device | |
| RU2810701C2 (en) | Hybrid rendering | |
| Hjelmervik et al. | Interactive exploration of big scientific data: new representations and techniques | |
| CN120318369A (en) | Rendering method, device, computer equipment, and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |