CN115987739A - A communication-aware integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales - Google Patents
A communication-aware integrated signal processing method based on dual time scalesDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115987739A CN115987739ACN202310045640.3ACN202310045640ACN115987739ACN 115987739 ACN115987739 ACN 115987739ACN 202310045640 ACN202310045640 ACN 202310045640ACN 115987739 ACN115987739 ACN 115987739A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- time
- channel
- communication
- path
- delay
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于6G无线接入网演进以及通信感知一体化信号设计、信号处理和波束赋形领域,尤其涉及一种基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化信号处理方法。The invention belongs to the fields of 6G wireless access network evolution and communication-aware integrated signal design, signal processing and beamforming, and in particular relates to a communication-aware integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales.
背景技术Background technique
通信感知一体化(integrated sensing and communication,ISAC)作为6G的一个新兴研究领域,引起了各界广泛的研究兴趣。一般来说,ISAC可以基于单站或者双站两种架构实现。对于单站ISAC,通信基站或者用户同时作为通信/感知信号的发送端,以及雷达感知的接收端。在这种情况下,通信和感知往往具有不同的信道,因此需要各自独立分析,难以实现通信和感知互惠。另一方面,对于双站ISAC架构,在传统通信的过程中,接收端可基于收到的多径信号进行环境感知,因此通信和感知共享同一信道。特别地,当信号频段逐步向毫米波、太赫兹波段迈进,信道具有稀疏性,并呈现出一定的几何特性,环境感知和通信信道估计可以相互结合,实现互惠。As an emerging research field of 6G, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has aroused extensive research interest from all walks of life. In general, ISAC can be implemented based on single-site or dual-site architectures. For single-station ISAC, the communication base station or user is simultaneously the transmitter of communication/sensing signals and the receiver of radar perception. In this case, communication and perception often have different channels, so they need to be analyzed independently, and it is difficult to realize the mutual benefit of communication and perception. On the other hand, for the dual-station ISAC architecture, in the process of traditional communication, the receiving end can perform environment perception based on the received multipath signal, so communication and perception share the same channel. In particular, when the signal frequency band is gradually moving towards the millimeter wave and terahertz bands, the channel is sparse and presents certain geometric characteristics. Environmental perception and communication channel estimation can be combined to achieve mutual benefit.
另一方面,对于双站ISAC而言,尽管可以认为通信和感知共享同一信道,但通信和感知各自感兴趣的信道参数却有着不同的时间变化尺度。对于通信而言,需要估计由所有路径叠加而成的时频信道增益或信道脉冲响应(channel impulse response,CIR),其往往在毫秒(millisecond,ms)级变动。然而,对于感知而言,最感兴趣的是各路径对应散射体的状态信息(如角度、时延、多普勒频率)。相对于CIR,其往往变化得较慢,通常可以认为在几十甚至几百个毫秒内保持不变。因此,可以在不同时间尺度上进行通信和感知信号处理。On the other hand, for dual-station ISAC, although it can be considered that communication and sensing share the same channel, the channel parameters of interest for communication and sensing have different time scales. For communication, it is necessary to estimate the time-frequency channel gain or channel impulse response (channel impulse response, CIR) formed by the superposition of all paths, which often changes at the millisecond (ms) level. However, for perception, the state information (such as angle, time delay, Doppler frequency) of each path corresponding to the scatterer is of most interest. Compared with CIR, it tends to change slowly, and it can generally be considered to remain unchanged within tens or even hundreds of milliseconds. Thus, communication and perceptual signal processing can be performed on different time scales.
传统通信波形,如正交频分复用(orthogonal frequency divisionmultiplexing,OFDM)在低频低速场景中具有很好的性能。然而,对于毫米波等高频段,以及高速场景,信道的多普勒频偏愈发严重,严重降低了OFDM的通信和感知性能。另一方面,OFDM受限于高峰均功率比(peak-to-average-power ratio,PAPR)和低发送能量,严重制约了其在通信感知一体化系统中的性能。Traditional communication waveforms, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), have good performance in low-frequency and low-speed scenarios. However, for high-frequency bands such as millimeter waves and high-speed scenarios, the Doppler frequency deviation of the channel becomes more and more serious, which seriously reduces the communication and perception performance of OFDM. On the other hand, OFDM is limited by the peak-to-average-power ratio (PAPR) and low transmission energy, which seriously restricts its performance in the communication-aware integrated system.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明目的在于利用通信和感知的双时间尺度,,提供一种基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化信号处理方法,以解决基于环境感知,解决高速移动场景下通信感知一体化系统中信道估计复杂度高、开销大的问题,以及传统OFDM信号峰均比过高的技术问题。The purpose of the present invention is to use the dual time scales of communication and perception to provide a communication-sensing integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales to solve the complex channel estimation in the communication-sensing integrated system based on environment perception and high-speed mobile scenarios. The problem of high accuracy and high overhead, as well as the technical problem of high peak-to-average ratio of traditional OFDM signals.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明的具体技术方案如下:In order to solve the problems of the technologies described above, the specific technical solutions of the present invention are as follows:
一种基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化信号处理方法,包括以下步骤:A dual-time-scale-based integrated signal processing method for communication perception, comprising the following steps:
步骤1、根据先验的信道和环境信息,划分通信感知一体化系统中信道的双时间尺度,其中一个环境状态不变时间内包含多个信道相干时间;对于通信,信道相干时间是指信道脉冲响应在该时间内保持不变;对于感知,环境状态不变时间是指各路径对应散射体的状态信息包括角度、时延和多普勒频率在该时间内保持不变。
步骤2、根据步骤1中的双时间尺度划分,利用信道中散射体的状态信息在多个连续信道相干时间内保持不变的特性,联合多个信道相干时间内接收到的导频信号,利用信道的稀疏性,基于分布式压缩感知算法,进行信道估计和环境感知,估计各路径时延、到达角度和信道复增益;Step 2. According to the dual time scale division in
步骤3、根据估计到的各路径时延和信道复增益,在各个信道相干时间内,对接收到的多径信号进行逐路径时延补偿和接收波束赋形,解调通信信号;Step 3. According to the estimated time delay of each path and channel complex gain, within the coherence time of each channel, perform path-by-path time delay compensation and receive beamforming on the received multipath signal, and demodulate the communication signal;
步骤4、联合多个信道相干时间内解调出的通信信号和已知导频信号,根据步骤2中估计到的各路径角度和时延信息,对每个路径生成角度时延域的二维匹配滤波器,利用匹配滤波分解各个路径,并对每条路径进行多普勒频率估计;Step 4. Combining the communication signals demodulated within the coherence time of multiple channels and known pilot signals, according to the angle and delay information of each path estimated in step 2, generate a two-dimensional angle delay domain for each path A matched filter, using matched filtering to decompose each path, and perform Doppler frequency estimation on each path;
步骤5、根据步骤2中估计到的各路径时延和信道复增益和步骤4中估计到多普勒频率,对一个环境状态不变时间内剩余的多个信道相干时间内接收到的通信信号联合处理,逐路径进行时延和多普勒补偿,以及接收波束赋形,解调通信信号。Step 5. According to the estimated path delay and channel complex gain in step 2 and the Doppler frequency estimated in step 4, the communication signals received in the coherent time of multiple channels remaining in an environment state constant time Joint processing, path-by-path delay and Doppler compensation, and receive beamforming, demodulates communication signals.
进一步地,根据通信信道响应和感知散射体状态信息在不同时间尺度上变化的特性,面向通信和感知信号处理进行双时间尺度划分;对于通信,信道脉冲响应在一个信道相干时间内保持不变;对于感知,环境中散射体的状态信息在一个环境状态不变时间内保持不变。Furthermore, according to the characteristics of communication channel response and perception scatterer state information changing on different time scales, a dual time scale division is carried out for communication and perception signal processing; for communication, the channel impulse response remains unchanged within a channel coherence time; For perception, the state information of scatterers in the environment remains unchanged for an environment state constant time.
进一步地,步骤2中,通过利用信道中散射体状态在多个连续信道相干时间内保持不变的特性,以及毫米波信道的稀疏性,运用分布式压缩感知算法,挖掘不同信道相干时间内接收到导频信号具有相同的稀疏结构,将多个信道相干时间内接收到的导频信号进行联合处理,估计导频信号经过不同散射体到达接收端的角度、时延,以及各路径信道复增益。Furthermore, in step 2, by using the characteristic that the scatterer state in the channel remains unchanged in the coherence time of multiple consecutive channels, and the sparsity of the millimeter-wave channel, the distributed compressed sensing algorithm is used to mine the received The pilot signals have the same sparse structure, and the pilot signals received during the coherence time of multiple channels are jointly processed to estimate the angle, time delay, and channel complex gain of each path for the pilot signals to reach the receiving end after passing through different scatterers.
进一步地,步骤3中,时延补偿和接收波束赋形均在接收端进行处理,在复杂多径环境中,发射端仅需单载波传输,降低了发射端复杂度,实现了低峰均比无码间串扰通信。Furthermore, in step 3, both delay compensation and receive beamforming are processed at the receiving end. In a complex multipath environment, the transmitting end only needs single-carrier transmission, which reduces the complexity of the transmitting end and achieves a low peak-to-average ratio. Intersymbol-free communication.
进一步地,步骤4中,根据步骤2中估计的各路径到达角度和时延,利用毫米波信道的稀疏性和大规模天线阵列的丰富的空间自由度,在角度时延域,设计二维匹配滤波器可分离多径信号,对每一路信号进行多普勒估计,降低算法复杂度。此外,步骤4中,联合多个信道相干时间中已解调的通信信号和已知的导频信号进行多普勒估计,可提高输出信噪比,提升多普勒频率估计精度。Further, in step 4, according to the angle of arrival and time delay of each path estimated in step 2, using the sparsity of the millimeter wave channel and the rich spatial degrees of freedom of the large-scale antenna array, in the angle delay domain, design a two-dimensional matching The filter can separate multipath signals, and perform Doppler estimation on each signal, reducing algorithm complexity. In addition, in step 4, the Doppler estimation is performed by combining the demodulated communication signals and the known pilot signals in multiple channel coherence times, which can improve the output signal-to-noise ratio and improve the accuracy of Doppler frequency estimation.
进一步地,步骤5中,对于同一个信道状态不变时间内,散射体的状态信息保持不变,对于剩余信道相干时间,不必进行信道估计,无需导频开销。根据步骤2和步骤4中估计的各路径时延、多普勒和信道复增益,进行逐路径时延多普勒补偿和波束赋形,可实现高频谱效率无码间串扰通信。Furthermore, in step 5, for the same channel state constant time, the state information of the scatterer remains unchanged, and for the remaining channel coherence time, no channel estimation is required, and no pilot overhead is required. According to each path delay, Doppler and channel complex gain estimated in step 2 and step 4, perform path-by-path delay Doppler compensation and beamforming, which can realize communication with high spectral efficiency and no intersymbol interference.
本发明的一种基于双时间尺度的通感一体化系统及信号处理方法具有以下优点:A synesthesia integration system and signal processing method based on dual time scales of the present invention has the following advantages:
1、本方法利用通信和感知的双时间尺度,联合多个信道相干处理时间,挖掘在毫米波大规模MIMO信道下,不同信道相干时间内接收到的信号在角度时延域上具有相同的稀疏性,基于分布式压缩感知算法,可在较低导频开销下,联合多个信道相干时间内的导频实现高分辨率环境感知和信道估计。1. This method uses the dual time scale of communication and perception, and combines the coherent processing time of multiple channels to discover that under the millimeter-wave massive MIMO channel, the signals received in different channel coherence times have the same sparseness in the angular delay domain. Based on the distributed compressed sensing algorithm, it can achieve high-resolution environment perception and channel estimation by combining pilots in the coherence time of multiple channels with low pilot overhead.
2、本方法基于时延多普勒对齐调制,可将复杂的时频双选衰落信道转化为简单的复高斯信道,利用简单的单载波传输,就可实现低峰均比无码间串扰通信。2. This method is based on delay-Doppler aligned modulation, which can convert complex time-frequency double-selective fading channels into simple complex Gaussian channels, and use simple single-carrier transmission to achieve low peak-to-average ratio and no intersymbol interference communication.
3、本方法基于通感一体化系统的双时间尺度,利用散射体状态信息在多个信道相干时间内保持不变的特性,利用已估计到的信道各路径时延、多普勒和信道复增益信息,接收端利用简单的时延多普勒对齐和波束赋形设计,就可实现高速率通信,无需重复进行信道估计,降低了系统的导频开销。另外,对于每个信道相干时间内只需要插入一个保护间隔以避免不同相干时间块之间的干扰,与传统OFDM相比,本方法降低了通信的开销,提高了通信的频谱效率。此外,与传统OFDM相比,本方法还具有较低的峰均比。3. This method is based on the dual time scale of the synaesthesia integrated system, using the property that the scatterer state information remains unchanged in multiple channel coherence times, and using the estimated channel delay, Doppler and channel complex For gain information, the receiving end can realize high-speed communication by using simple delay-Doppler alignment and beamforming design, without repeated channel estimation, which reduces the pilot overhead of the system. In addition, only one guard interval needs to be inserted in the coherence time of each channel to avoid interference between different coherence time blocks. Compared with traditional OFDM, this method reduces communication overhead and improves communication spectrum efficiency. In addition, compared with traditional OFDM, this method also has a lower peak-to-average ratio.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例提供的多径环境下双站通信感知一体化系统示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a dual-station communication perception integrated system in a multipath environment provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例提供的通信和感知信道双时间尺度示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of dual time scales of communication and perception channels provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是本发明实施例提供的基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化信号发送方案图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of a dual-time-scale-based communication-aware integrated signal transmission scheme provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
图4是本发明实施例提供的基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化接收信号处理流程图。Fig. 4 is a flow chart of receiving signal processing based on dual-time-scale integrated communication perception provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了更好地了解本发明的目的、结构及功能,下面结合附图,对本发明一种基于双时间尺度的通感一体化系统及信号处理方法做进一步详细的描述。In order to better understand the purpose, structure and function of the present invention, a dual-time-scale-based synaesthesia integration system and signal processing method of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
本技术领域技术人员可以理解的是,除非另外定义,这里使用的所有术语(包括技术术语和科学术语)具有与本发明所属领域中的普通技术人员的一般理解相同的意义。还应该理解的是,诸如通用字典中定义的那些术语应该被理解为具有与现有技术的上下文中的意义一致的意义,并且除非像这里一样定义,不会用理想化或过于正式的含义来解释。Those skilled in the art can understand that, unless otherwise defined, all terms (including technical terms and scientific terms) used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the art to which this invention belongs. It should also be understood that terms such as those defined in commonly used dictionaries should be understood to have a meaning consistent with the meaning in the context of the prior art, and will not be interpreted in an idealized or overly formal sense unless defined as herein explain.
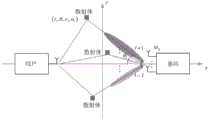
图1是根据实施例示出的多径环境下双站通信感知一体化的场景,其中通信基站和通信用户分别作为通信感知一体化的接收机和发送机。通信用户发送信号进行上行通信。通信基站服务用户上行通信的同时,利用接收到多径信号进行环境感知和信道估计。Fig. 1 shows a scenario of dual-station communication perception integration in a multipath environment according to an embodiment, in which a communication base station and a communication user serve as a receiver and a transmitter of communication perception integration respectively. Communication users send signals for uplink communication. While the communication base station serves the uplink communication of the user, it uses the received multipath signal to perform environment perception and channel estimation.
图2是根据实施例示出的通信和感知信道双时间尺度示意图。通信信道响应和感知中散射体的状态包括,角度、时延、多普勒频率,在不同的时间尺度上变化。对于通信,认为其信道冲激响应h(t,τ)在一个信道相干时间Tc内保持不变;对于感知,认为多径信号经环境中散射体到达基站的多径数目L以及每路信号的时延τl、到达角度θl、多普勒频率νl和信道复增益αl在一个信道状态不变时间内保持不变,即散射体状态信息η(t)在第q个信道状态不变时间内有其中,一个环境状态不变时间包含K个信道相干时间Tc,即Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram showing dual time scales of communication and perception channels according to an embodiment. The state of scatterers in communication channel response and perception, including angle, delay, and Doppler frequency, vary on different time scales. For communication, it is considered that its channel impulse response h(t,τ) remains unchanged within a channel coherence time Tc ; for perception, it is considered that the multipath number L of multipath signals reaching the base station through scatterers in the environment and each signal Delay τl , angle of arrival θl , Doppler frequency νl and channel complex gain αl in a channel state constant time remains unchanged, that is, the scatterer state information η(t) is constant in the qth channel state have Among them, an environment state constant time Contains K channel coherence times Tc , namely
图3是根据实施例示出的基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化信号发送方案。对于一个环境状态不变时间将前J个信道相干时间Tc划为第一阶段,后K-J个信道相干时间Tc划为第二阶段,其中J<K。对于第一阶段,以信道相干时间Tc为周期,发送导频信号和通信数据。接收端利用导频和解调出的通信信号进行信道估计和环境感知。利用已估计到的信道,第二阶段无需发送导频和进行信道估计,全部发送通信信号。Fig. 3 is a dual-time-scale based communication-aware integrated signal transmission scheme shown according to an embodiment. For an environment state invariant time The first J channel coherence times Tc are classified as the first stage, and the last KJ channel coherence times Tc are classified as the second stage, where J<K. For the first stage, the pilot signal and communication data are sent with the channel coherence timeTc as the period. The receiving end uses the pilot frequency and the demodulated communication signal to perform channel estimation and environment perception. Using the estimated channel, the second stage does not need to send pilots and conduct channel estimation, and all communication signals are sent.
图4是根据实施例示出的基于双时间尺度的通信感知一体化接收信号处理流程。基站预先设置第一阶段和第二阶段的时间长度,接收到信号进行如下处理:首先累计时间长度为JTc的接收信号,利用信道在角度时延域的稀疏性,对接收信号进行离散,构建压缩感知信号恢复问题。接着,利用信道状态信息在T内不变的特点,联合第一阶段内J个信道相干时间内收到的导频信号,基于分布式压缩感知算法,估计接收多径信号的数目,时延、到达角度以及信道复增益。接着,利用已估计到的信道,对每个信道相干时间内收到的通信信号进行解调,并将解调后的数据保存,用于后续多普勒估计。联合第一阶段收到的导频和通信信号进行多普勒估计。最后,第二阶段利用第一阶段估计到的信道参数进行基于时延多普勒对齐调制的通信数据解调。Fig. 4 is a flow chart showing a dual-time-scale-based communication-aware integrated reception signal processing flow according to an embodiment. The base station presets the time lengths of the first phase and the second phase, and the received signals are processed as follows: firstly, the received signals with a time length of JTc are accumulated, and the received signals are discretized by using the sparsity of the channel in the angular delay domain to construct Compressed Sensing Signal Restoration Problem. Then, using the characteristic that the channel state information is invariable within T, combined with the pilot signals received in the J channel coherence time in the first stage, based on the distributed compressed sensing algorithm, the number of received multipath signals, time delay, Angle of arrival and channel complex gain. Then, using the estimated channel, the communication signal received within the coherence time of each channel is demodulated, and the demodulated data is saved for subsequent Doppler estimation. Doppler estimation is performed jointly with pilot and communication signals received in the first stage. Finally, in the second stage, the channel parameters estimated in the first stage are used to demodulate communication data based on delay-Doppler aligned modulation.
基于以上定义,实施例的具体实现步骤可概括为如下:Based on the above definition, the specific implementation steps of the embodiment can be summarized as follows:
步骤1、参数初始化。基站和用户根据先验信息预先设置第一阶段和第二阶段信号的时间长度,即
步骤2、基站接收用户第一阶段发送的信号。对接收信号在角度时延域进行离散,构建压缩感知信号恢复问题。利用信道状态信息在多个信道相干时间内保持不变的特性,联合第一阶段J个信道相干时间内收到的导频信号,利用其共有的稀疏性,基于分布式压缩感知算法估计接收信号的多径数目以及各路径信号的到达角度时延信道复增益Step 2. The base station receives the signal sent by the user in the first stage. The received signal is discretized in the angular delay domain, and the compressed sensing signal recovery problem is constructed. Using the characteristic that the channel state information remains unchanged in multiple channel coherence times, combined with the pilot signals received in the J channel coherence time in the first stage, and using their common sparsity, the received signal is estimated based on the distributed compressed sensing algorithm number of multipath and the angle of arrival of each path signal time delay channel complex gain
步骤3、基站根据已估计到的信道参数设置各路径的时延补偿参数其中设置各路径的多普勒补偿参数为逐路径波束赋形迫零消除接收信号的码间串扰,并解调通信信号。Step 3, the base station according to the estimated channel parameters Set delay compensation parameters for each path in Set the Doppler compensation parameters of each path as Path-by-path beamforming zero-forcing eliminates the intersymbol interference of the received signal and demodulates the communication signal.
步骤4、基站根据步骤2估计得到的各路径到达角度和时延、已知的导频信号以及步骤3中解调恢复得到的通信信号,逐路径设计角度时延域的二维匹配滤波器。基站逐路径进行二维匹配滤波,联合第一阶段J个信道相干时间匹配滤波器的输出结果,基于快速傅里叶变换估计各个路径的多普勒频率为Step 4. The base station designs a two-dimensional matched filter in the angular delay domain path by path according to the angle of arrival and time delay of each path estimated in step 2, the known pilot signal, and the communication signal demodulated and recovered in step 3. The base station performs two-dimensional matched filtering path by path, combined with the output results of J channel coherent time matched filters in the first stage, and estimates the Doppler frequency of each path based on fast Fourier transform as
步骤5、基站接收用户第二阶段发送的信号,并根据步骤2和步骤3中估计得到的信道参数设置各路径的时延补偿为和多普勒补偿为基站进行逐路径迫零接收波束赋形消除接收信号的码间串扰,并解调通信信号。Step 5, the base station receives the signal sent by the user in the second stage, and according to the channel parameters estimated in steps 2 and 3 Set the delay compensation of each path as and Doppler compensation as The base station performs path-by-path zero-forcing receiving beamforming to eliminate the intersymbol interference of the received signal, and demodulates the communication signal.
上述方法利用通信和感知信道的双时间尺度,通过联合多个信道相干时间内的导频信号进行信道估计和感知(步骤2),相对于传统方法只在一个相干时间内进行信道估计,具有更高的估计精度,且不需要重复估计。同时,在基站接收端进行时延多普勒对齐调制的通信信号解调(步骤3),对用户端的要求较低,用户通过简单的单载波信号传输就可实现复杂多径环境的无码间串扰高速通信,相比于该环境下传统的OFDM传输,降低了PAPR和循环前缀的开销,提高了通信的频谱效率。此外,基站端通过联合第一阶段多个信道相干时间内的导频和通信信号(步骤4),进行多普勒估计,相对传统仅基于导频估计多普勒的方法,可获得更高的信噪比和估计精度。最后,基站端利用第一阶段已估计的信道参数,在第二阶段,基于时延多普勒对齐调制,可无需进行信道估计就可实现无码间串扰高速率通信(步骤5)。The above method utilizes the dual time scale of the communication and sensing channels, and performs channel estimation and sensing by combining pilot signals in multiple channel coherence times (step 2). High estimation accuracy and no need for repeated estimation. At the same time, the demodulation of the communication signal modulated by delay-Doppler alignment is performed at the receiving end of the base station (step 3), which has lower requirements on the user end, and the user can realize no intersymbol interference in a complex multipath environment through simple single-carrier signal transmission Compared with traditional OFDM transmission in this environment, high-speed communication reduces the overhead of PAPR and cyclic prefix, and improves the spectral efficiency of communication. In addition, the base station performs Doppler estimation by combining pilots and communication signals within the coherence time of multiple channels in the first stage (step 4). Compared with the traditional method of estimating Doppler based only on pilots, a higher Signal-to-noise ratio and estimation accuracy. Finally, the base station uses the estimated channel parameters in the first stage. In the second stage, based on the delay-Doppler alignment modulation, high-speed communication without intersymbol interference can be realized without channel estimation (step 5).
可以理解,本发明是通过一些实施例进行描述的,本领域技术人员知悉的,在不脱离本发明的精神和范围的情况下,可以对这些特征和实施例进行各种改变或等效替换。另外,在本发明的教导下,可以对这些特征和实施例进行修改以适应具体的情况及材料而不会脱离本发明的精神和范围。因此,本发明不受此处所公开的具体实施例的限制,所有落入本申请的权利要求范围内的实施例都属于本发明所保护的范围内。It can be understood that the present invention is described through some embodiments, and those skilled in the art know that various changes or equivalent substitutions can be made to these features and embodiments without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. In addition, the features and examples may be modified to adapt a particular situation and material to the teachings of the invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Therefore, the present invention is not limited by the specific embodiments disclosed here, and all embodiments falling within the scope of the claims of the present application belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (6)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310045640.3ACN115987739B (en) | 2023-01-30 | 2023-01-30 | A communication-perception integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310045640.3ACN115987739B (en) | 2023-01-30 | 2023-01-30 | A communication-perception integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115987739Atrue CN115987739A (en) | 2023-04-18 |
| CN115987739B CN115987739B (en) | 2025-02-11 |
Family
ID=85962415
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310045640.3AActiveCN115987739B (en) | 2023-01-30 | 2023-01-30 | A communication-perception integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115987739B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116938363A (en)* | 2023-06-21 | 2023-10-24 | 江苏科技大学 | Unmanned aerial vehicle-to-ship communication channel switching method based on jitter detection and coherence time |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110519189A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-11-29 | 东南大学 | Compressed sensing based millimeter wave channel estimation methods under highly mobile scene |
| CN113765581A (en)* | 2021-09-27 | 2021-12-07 | 北京理工大学 | Fast Time-varying Channel Estimation Method for RIS Based on Compressed Sensing and Beam Alignment |
| CN114325679A (en)* | 2021-10-21 | 2022-04-12 | 南方科技大学 | Perception communication integration method based on time delay Doppler domain signal processing |
| CN114866124A (en)* | 2022-04-28 | 2022-08-05 | 东南大学 | Synaesthesia integrated signal design and beamforming method based on delay-aligned modulation |
| WO2022165872A1 (en)* | 2021-02-03 | 2022-08-11 | 重庆邮电大学 | Path parameter extraction method for millimeter wave 3d mimo channel |
| CN115550358A (en)* | 2022-08-31 | 2022-12-30 | 北京邮电大学 | A wireless communication transmission method that realizes the deep integration of communication perception computing |
| CN115604843A (en)* | 2021-07-09 | 2023-01-13 | 维沃移动通信有限公司(Cn) | Transmission method, device, communication device and storage medium |
- 2023
- 2023-01-30CNCN202310045640.3Apatent/CN115987739B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110519189A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-11-29 | 东南大学 | Compressed sensing based millimeter wave channel estimation methods under highly mobile scene |
| WO2022165872A1 (en)* | 2021-02-03 | 2022-08-11 | 重庆邮电大学 | Path parameter extraction method for millimeter wave 3d mimo channel |
| CN115604843A (en)* | 2021-07-09 | 2023-01-13 | 维沃移动通信有限公司(Cn) | Transmission method, device, communication device and storage medium |
| CN113765581A (en)* | 2021-09-27 | 2021-12-07 | 北京理工大学 | Fast Time-varying Channel Estimation Method for RIS Based on Compressed Sensing and Beam Alignment |
| CN114325679A (en)* | 2021-10-21 | 2022-04-12 | 南方科技大学 | Perception communication integration method based on time delay Doppler domain signal processing |
| CN114866124A (en)* | 2022-04-28 | 2022-08-05 | 东南大学 | Synaesthesia integrated signal design and beamforming method based on delay-aligned modulation |
| CN115550358A (en)* | 2022-08-31 | 2022-12-30 | 北京邮电大学 | A wireless communication transmission method that realizes the deep integration of communication perception computing |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| JIAWEI LIU等: "Transceiver Co-design for Full-Duplex Integrated Sensing and Communications", 《2022 IEEE GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS CONFERENCE: SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS: FULL-DUPLEX COMMUNICATIONS 3821》, 11 January 2023 (2023-01-11)* |
| ZHIQIANG XIAO等: "Exploiting Double Timescales for Integrated Sensing and Communication with Delay-Doppler Alignment Modulation", 《2023 IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMMUNICATIONS (ICC): SIGNAL PROCESSING FOR COMMUNICATIONS SYMPOSIUM》, 23 October 2023 (2023-10-23)* |
| 王志勤等: "6G联邦边缘学习新范式:基于任务导向的资源管理策略", 《通信学报》, vol. 43, no. 6, 30 June 2022 (2022-06-30)* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116938363A (en)* | 2023-06-21 | 2023-10-24 | 江苏科技大学 | Unmanned aerial vehicle-to-ship communication channel switching method based on jitter detection and coherence time |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115987739B (en) | 2025-02-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1756248B (en) | MIMO OFDM mobile communication system and channel estimating method | |
| EP2432183B1 (en) | Demodulation method and demodulator for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing - multiple input multiple output system | |
| CN104243370B (en) | A kind of time-domain channel estimating method applied in multiaerial system | |
| CN110213185B (en) | Three-dimensional channel parameter estimation method based on atomic norm minimization | |
| CN114866124B (en) | Synaesthesia integrated signal design and beamforming method based on time-delay alignment modulation | |
| WO2017219389A1 (en) | Methods for sending and receiving synchronization signals and signals subjected to perfect omnidirectional pre-coding in large-scale mimo system | |
| US10785060B2 (en) | Efficient channel estimation and symbol detection for massive MIMO-OFDM | |
| CN107465636B (en) | A channel estimation method for a millimeter-wave large-scale array space-frequency dual-broadband system | |
| CN115021843A (en) | A cooperative sensing method for millimeter-wave communication multi-user system | |
| CN103685096A (en) | Optimal pilot frequency based MIMO-OFDM (Multiple Input Multiple Output-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) system channel estimation method | |
| CN103825850A (en) | Upstream channel estimation method and upstream channel estimation system suitable for LTE (Long Term Evolution)-Advanced system | |
| CN103560991B (en) | The method being applicable to OFDM receiver suppression rangefinder impulse disturbances | |
| CN118444273A (en) | Angle-range-Doppler three-dimensional joint super-resolution method based on OFDM waveform | |
| CN108650005B (en) | Pilot structure and channel estimation method for MIMO-FBMC/OQAM system | |
| Li et al. | On the potential of spatially-spread orthogonal time frequency space modulation for ISAC transmissions | |
| CN101291311B (en) | Synchronization implementing method and device for multi-input multi-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system | |
| CN106341362B (en) | Pilot frequency transmission method, pilot frequency reception method and device thereof | |
| Guo et al. | Low-complexity joint activity detection and channel estimation with partially orthogonal pilot for asynchronous massive access | |
| CN104378319A (en) | Channel estimation method based on short wave channel MIMO-OFDM communication system | |
| CN115987739A (en) | A communication-aware integrated signal processing method based on dual time scales | |
| CN107147597B (en) | Hardware Implementation Method of Fractional Spaced Frequency Domain Equalization in Millimeter-Wave Communication System | |
| CN118214445A (en) | Full duplex sense integrated device and system | |
| CN116471147B (en) | Low pilot overhead channel estimation method for OTFS system | |
| CN104218984B (en) | Using the both-end frequency domain beam search method of compressed sensing | |
| CN115913865B (en) | Signal receiving and transmitting method of OFDM symbiotic wireless communication system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |