CN115983255A - Emergency management method and device, computer equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Emergency management method and device, computer equipment and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115983255A CN115983255ACN202310275728.4ACN202310275728ACN115983255ACN 115983255 ACN115983255 ACN 115983255ACN 202310275728 ACN202310275728 ACN 202310275728ACN 115983255 ACN115983255 ACN 115983255A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- classification
- classification result
- emergency
- model
- result
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000007726management methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription34
- 238000003860storageMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription10
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription21
- 230000010354integrationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription27
- 238000012549trainingMethods0.000claimsdescription24
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000004140cleaningMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000011218segmentationEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000013434data augmentationMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000013135deep learningMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claims1
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description5
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000description5
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description3
- 239000000779smokeSubstances0.000description3
- 206010024453Ligament sprainDiseases0.000description2
- 208000010040Sprains and StrainsDiseases0.000description2
- 239000003990capacitorSubstances0.000description2
- 238000002485combustion reactionMethods0.000description2
- 230000001186cumulative effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000002372labellingMethods0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000description2
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000description2
- 230000002269spontaneous effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000010200validation analysisMethods0.000description2
- 101001121408Homo sapiens L-amino-acid oxidaseProteins0.000description1
- 101000827703Homo sapiens Polyphosphoinositide phosphataseProteins0.000description1
- 102100026388L-amino-acid oxidaseHuman genes0.000description1
- 102100023591Polyphosphoinositide phosphataseHuman genes0.000description1
- 101100012902Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) FIG2 geneProteins0.000description1
- 101100233916Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) KAR5 geneProteins0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000010801machine learningMethods0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000000750progressive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001737promoting effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000013179statistical modelMethods0.000description1
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A10/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE at coastal zones; at river basins
- Y02A10/40—Controlling or monitoring, e.g. of flood or hurricane; Forecasting, e.g. risk assessment or mapping
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本发明涉及计算机软件技术领域,特别涉及一种突发事件管理方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质。The present invention relates to the field of computer software technology, and in particular to an emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium.
背景技术Background Art
突发事件的类型很多,如果人工对突发事件信息进行分类分级,需要大量的人力的同时还可能会存在较多的误判,且响应效率满足不了需求。以历史数据作为标签,通过自然语言理解的方式对物业报警的突发事件文本信息进行分类,例如将突发事件分类等级划分为一级12大级,二级66小级,紧急程度3大级,可以提高分类分级的速度和响应效率,同时通过对历史数据的学习,能够不断优化模型,提高突发事件分类分级的准确率。There are many types of emergencies. If emergency information is manually classified and graded, a lot of manpower is required and there may be many misjudgments, and the response efficiency cannot meet the needs. Using historical data as labels, the text information of property alarm emergencies is classified through natural language understanding. For example, the emergency classification level is divided into 12 major levels at the first level, 66 minor levels at the second level, and 3 major levels of urgency. This can improve the speed of classification and response efficiency. At the same time, by learning from historical data, the model can be continuously optimized to improve the accuracy of emergency classification and grading.
现有技术对于突发事件的分类分级,都存在着各自的不足。例如基于正则、传统机器学习的自然语言的泛化能力不足,基于深度学习的自然语言进行标注需要的人力成本较大等,因此需要一种兼备泛化能力和标注效率的突发事件管理方法。Existing technologies for the classification and grading of emergencies all have their own shortcomings. For example, the generalization ability of natural language based on regularization and traditional machine learning is insufficient, and the human cost required for labeling natural language based on deep learning is high. Therefore, an emergency management method with both generalization ability and labeling efficiency is needed.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明实施例提供了一种突发事件管理方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质,旨在提高对突发事件的管理效率。The embodiments of the present invention provide an emergency management method, an apparatus, a computer device and a storage medium, aiming to improve the management efficiency of emergency events.
第一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种突发事件管理方法,包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides an emergency event management method, including:
获取突发事件信息,并对所述突发事件信息进行预处理,得到模型数据集;Acquire emergency event information, and pre-process the emergency event information to obtain a model data set;
基于预置分类范围对所述模型数据集进行关键词提取,并对提取的关键词进行正则匹配处理,得到第一分类结果;Extracting keywords from the model data set based on a preset classification range, and performing regular matching processing on the extracted keywords to obtain a first classification result;
将所述模型数据集输入至多任务学习模型中,并基于预置分类范围由所述多任务学习模型输出得到第二分类结果;Inputting the model data set into a multi-task learning model, and obtaining a second classification result output by the multi-task learning model based on a preset classification range;
对所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,并将投票集成结果作为最终分类结果输出。The first classification result and the second classification result are voted and integrated, and the voting integration result is output as the final classification result.
第二方面,本发明实施例提供了一种突发事件管理装置,包括:In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides an emergency event management device, including:
数据处理单元,用于获取突发事件信息,并对所述突发事件信息进行预处理,得到模型数据集;A data processing unit, used to obtain emergency event information and pre-process the emergency event information to obtain a model data set;
第一分类单元,用于基于预置分类范围对所述模型数据集进行关键词提取,并对提取的关键词进行正则匹配处理,得到第一分类结果;A first classification unit, configured to extract keywords from the model data set based on a preset classification range, and perform regular matching processing on the extracted keywords to obtain a first classification result;
第二分类单元,用于将所述模型数据集输入至多任务学习模型中,并基于预置分类范围由所述多任务学习模型输出得到第二分类结果;A second classification unit, used for inputting the model data set into the multi-task learning model, and obtaining a second classification result output by the multi-task learning model based on a preset classification range;
投票集成单元,用于对所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,并将投票集成结果作为最终分类结果输出。The voting integration unit is used to perform voting integration on the first classification result and the second classification result, and output the voting integration result as the final classification result.
第三方面,本发明实施例提供了一种计算机设备,包括存储器、处理器及存储在所述存储器上并可在所述处理器上运行的计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述计算机程序时实现如第一方面所述的一种突发事件管理方法。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer device, comprising a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and executable on the processor, wherein when the processor executes the computer program, an emergency event management method as described in the first aspect is implemented.
第四方面,本发明实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质上存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被处理器执行时实现如第一方面所述的一种突发事件管理方法。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer-readable storage medium having a computer program stored thereon, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the emergency event management method as described in the first aspect is implemented.
本发明实施例提供了一种突发事件管理方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质,该方法包括:获取突发事件信息,并对所述突发事件信息进行预处理,得到模型数据集;基于预置分类范围对所述模型数据集进行关键词提取,并对提取的关键词进行正则匹配处理,得到第一分类结果;将所述模型数据集输入至多任务学习模型中,并基于预置分类范围由所述多任务学习模型输出得到第二分类结果;对所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,并将投票集成结果作为最终分类结果输出。与现有技术相比,本发明实施例通过正则匹配和多任务学习模型分别对突发事件信息进行分类,并将分类结果进行投票集成,得到最终分类结果,不仅能够提高突发事件管理方法的泛化能力,而且还能对不同类型和等级的突发事件更准确地进行分类。The embodiment of the present invention provides an emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium, the method comprising: obtaining emergency information, and preprocessing the emergency information to obtain a model data set; extracting keywords from the model data set based on a preset classification range, and performing regular matching processing on the extracted keywords to obtain a first classification result; inputting the model data set into a multi-task learning model, and outputting a second classification result from the multi-task learning model based on a preset classification range; voting and integrating the first classification result and the second classification result, and outputting the voting integration result as the final classification result. Compared with the prior art, the embodiment of the present invention classifies emergency information respectively through regular matching and a multi-task learning model, and votes and integrates the classification results to obtain a final classification result, which can not only improve the generalization ability of the emergency management method, but also more accurately classify emergencies of different types and levels.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention, the accompanying drawings required for use in the description of the embodiments will be briefly introduced below. Obviously, the accompanying drawings described below are some embodiments of the present invention. For ordinary technicians in this field, other accompanying drawings can be obtained based on these accompanying drawings without paying any creative work.
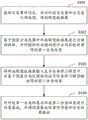
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理方法的流程示意图;FIG1 is a schematic flow chart of an emergency management method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理方法的子流程示意图;FIG2 is a schematic diagram of a sub-process of an emergency management method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理方法另一子流程示意图;FIG3 is a schematic diagram of another sub-process of an emergency management method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
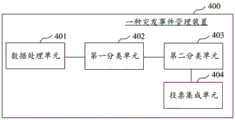
图4为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理装置的示意性框图;FIG4 is a schematic block diagram of an emergency management device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理装置的子示意性框图;FIG5 is a sub-schematic block diagram of an emergency management device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理装置的另一子示意性框图。FIG. 6 is another sub-schematic block diagram of an emergency event management device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The following will be combined with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention to clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are part of the embodiments of the present invention, not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by ordinary technicians in this field without creative work are within the scope of protection of the present invention.
应当理解,当在本说明书和所附权利要求书中使用时,术语“包括”和 “包含”指示所描述特征、整体、步骤、操作、元素和/或组件的存在,但并不排除一个或多个其它特征、整体、步骤、操作、元素、组件和/或其集合的存在或添加。It should be understood that when used in this specification and the appended claims, the terms "include" and "comprises" indicate the presence of described features, integers, steps, operations, elements and/or components, but do not exclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, integers, steps, operations, elements, components and/or combinations thereof.
还应当理解,在此本发明说明书中所使用的术语仅仅是出于描述特定实施例的目的而并不意在限制本发明。如在本发明说明书和所附权利要求书中所使用的那样,除非上下文清楚地指明其它情况,否则单数形式的“一”、“一个”及“该”意在包括复数形式。It should also be understood that the terms used in this specification of the present invention are only for the purpose of describing specific embodiments and are not intended to limit the present invention. As used in the specification of the present invention and the appended claims, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise, the singular forms "a", "an" and "the" are intended to include plural forms.
还应当进一步理解,在本发明说明书和所附权利要求书中使用的术语“和/ 或”是指相关联列出的项中的一个或多个的任何组合以及所有可能组合,并且包括这些组合。It should be further understood that the term "and/or" used in the present description and the appended claims refers to and includes any and all possible combinations of one or more of the associated listed items.
下面请参见图1,图1为本发明实施例提供的一种突发事件管理方法的流程示意图,具体包括:步骤S101~S104。Please refer to FIG. 1 below, which is a flow chart of an emergency event management method provided by an embodiment of the present invention, specifically comprising steps S101 to S104.
S101、获取突发事件信息,并对所述突发事件信息进行预处理,得到模型数据集;S101, acquiring emergency event information, and preprocessing the emergency event information to obtain a model data set;
S102、基于预置分类范围对所述模型数据集进行关键词提取,并对提取的关键词进行正则匹配处理,得到第一分类结果;S102, extracting keywords from the model data set based on a preset classification range, and performing regular matching processing on the extracted keywords to obtain a first classification result;
S103、将所述模型数据集输入至多任务学习模型中,并基于预置分类范围由所述多任务学习模型输出得到第二分类结果;S103, inputting the model data set into a multi-task learning model, and obtaining a second classification result output by the multi-task learning model based on a preset classification range;
S104、对所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,并将投票集成结果作为最终分类结果输出。S104: Voting and integrating the first classification result and the second classification result, and outputting the voting integration result as the final classification result.
本实施例中,首先根据突发事件信息得到模型数据集,其次对所述模型数据集提取关键词,对所述关键词进行正则匹配,并输出第一分类结果,然后将所述模型数据集输入所述多任务学习模型,通过所述多任务学习模型输出第二分类结果,最后将所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,得到最终分类结果,通过所述最终分类结果对突发事件进行管理。本发明实施例通过正则匹配和多任务学习模型分别对突发事件信息进行分类,并将分类结果进行投票集成,得到最终分类结果,不仅能够提高突发事件管理方法的泛化能力,而且能对不同类型和等级的突发事件更准确地进行分类,便于针对突发事件的不同分类和等级进行快速响应,从而实现对突发事件的安全管理。In this embodiment, firstly, a model data set is obtained according to the emergency information, then keywords are extracted from the model data set, regular matching is performed on the keywords, and a first classification result is output, then the model data set is input into the multi-task learning model, and a second classification result is output through the multi-task learning model, and finally the first classification result and the second classification result are voted and integrated to obtain a final classification result, and the emergency is managed through the final classification result. The embodiment of the present invention classifies the emergency information respectively through regular matching and multi-task learning models, and votes and integrates the classification results to obtain the final classification result, which can not only improve the generalization ability of the emergency management method, but also can more accurately classify emergencies of different types and levels, so as to facilitate rapid response to different classifications and levels of emergencies, thereby realizing safe management of emergencies.
在一实施例中,所述突发事件信息包括事件时间,事件主题,事件主要内容;所述步骤S101包括:In one embodiment, the emergency event information includes event time, event subject, and event main content; step S101 includes:
获取突发事件信息对应的事件主表ID,根据所述事件主表ID关联事件类型,并根据所述事件类型对所述突发事件信息进行特征工程处理;Obtaining an event master table ID corresponding to the emergency event information, associating an event type according to the event master table ID, and performing feature engineering processing on the emergency event information according to the event type;
对所述突发事件信息进行文本清洗,以及基于特征工程处理的结果对所述突发事件信息进行数据转换,以此构建模型数据集。The emergency information is subjected to text cleaning, and data conversion is performed on the emergency information based on the result of feature engineering processing, so as to construct a model data set.
在本实施例中,根据突发事件信息的事件主表ID关联事件类型,并对所述突发事件信息进行特征工程处理、文本清洗和数据转换,以此构建模型数据集。进一步的,还可将所述模型数据集划分为训练集、验证集和测试集。其中训练集用于更新输入的参数对模型进行训练;所述验证集用于评估多种不同模型或者是带着不同参数的同一模型的训练效果;测试集用于评估模型的泛化能力。In this embodiment, the event type is associated with the event master table ID of the emergency information, and the emergency information is subjected to feature engineering, text cleaning and data conversion to construct a model data set. Furthermore, the model data set can be divided into a training set, a validation set and a test set. The training set is used to update the input parameters to train the model; the validation set is used to evaluate the training effects of multiple different models or the same model with different parameters; and the test set is used to evaluate the generalization ability of the model.
在具体实施例中,所述特征工程处理以所述模型数据集中的突发事件的主题、详细信息和主要内容为特征,以突发事件的分类和风险等级作为目标值。In a specific embodiment, the feature engineering process uses the subject, detailed information and main content of the emergency in the model data set as features, and uses the classification and risk level of the emergency as target values.
结合表1,在一具体实施例中,文本清洗操作可将文本中的无用信息去除,例如去除文本中的标点符号、地点、事件等。In conjunction with Table 1, in a specific embodiment, the text cleaning operation can remove useless information in the text, such as removing punctuation marks, places, events, etc. in the text.
表1Table 1
结合表2,所述数据转换为将突发事件分类等级名称转换为类别特征。Combined with Table 2, the data is converted to convert the emergency classification level name into category features.
表2Table 2
结合图2,在一实施例中,步骤S102包括:步骤S201~S205。With reference to FIG. 2 , in one embodiment, step S102 includes steps S201 to S205 .
S201、将所述模型数据集中的所有突发事件信息合并为同一文档,并对所述文档进行切词处理;S201, merging all emergency information in the model data set into the same document, and performing word segmentation processing on the document;
S202、通过gensim工具中的doc2bow函数对切词处理后的文档进行词频统计,得到二维数组;S202, using the doc2bow function in the gensim tool to perform word frequency statistics on the document after word segmentation processing, to obtain a two-dimensional array;
S203、利用所述二维数组输入至TF-IDF模型,并由所述TF-IDF模型输出所述关键词;S203, using the two-dimensional array to input into a TF-IDF model, and having the TF-IDF model output the keyword;
S204、基于预置分类范围对所述关键词进行正则匹配,得到所述关键词的匹配结果;S204, performing regular expression matching on the keyword based on a preset classification range to obtain a matching result of the keyword;
S205、当匹配结果成功时,获取所述关键词在所述文档中的位置信息,并结合所述分类结果和位置信息生成第一分类结果;当匹配结果失败时,则设置其他类为第一分类结果。S205. When the matching result is successful, obtain the position information of the keyword in the document, and generate a first classification result in combination with the classification result and the position information; when the matching result fails, set other categories as the first classification result.
在本实施例中,首先将所述模型数据集中的所有突发事件信息合并的文档进行切词处理,其次通过gensim工具中的doc2bow函数对所述文档中的文本进行词频统计,以得到二维数组,再次将二维数组输入至TF-IDF模型并输出关键词,然后基于预置分类范围对所述关键词进行正则匹配,以得到第一分类结果。In this embodiment, firstly, the document in which all the emergency information in the model data set is merged is segmented, and then the word frequency statistics of the text in the document are performed through the doc2bow function in the gensim tool to obtain a two-dimensional array, and then the two-dimensional array is input into the TF-IDF model again and the keywords are output, and then the keywords are regularly matched based on the preset classification range to obtain the first classification result.
结合表3,在具体实施例中,所述二维数组的最小元素为[[(0, 1), (1, 1), (2,1)], [(3, 1), (4, 1)], [(5, 1), (6, 1), (7, 1), (8, 1), (9, 1)]],其中(词的ID号,词频)。举例来说,将二维数组输入TF-IDF模型后,TF-IDF模型输出的关键词如表3所示,所述模型数据集中突发事件1的文本内容是:因为起火导致电梯停运,则输出的关键词包括:“起火”和“电梯停运”,对所述关键词进行正则匹配,其中关键词“起火”的分类结果属于A1类,关键词“电梯停运”的分类结果属于B2类,但“起火”在文本中出现的顺序早于“电梯停运”,所以最后选择突发事件1的分类类别为A1。Combined with Table 3, in a specific embodiment, the minimum element of the two-dimensional array is [[(0, 1), (1, 1), (2,1)], [(3, 1), (4, 1)], [(5, 1), (6, 1), (7, 1), (8, 1), (9, 1)]], where (word ID number, word frequency). For example, after the two-dimensional array is input into the TF-IDF model, the keywords output by the TF-IDF model are shown in Table 3. The text content of the emergency event 1 in the model data set is: the elevator stopped due to fire, and the output keywords include: "fire" and "elevator stopped", and the keywords are matched regularly. The classification result of the keyword "fire" belongs to category A1, and the classification result of the keyword "elevator stopped" belongs to category B2, but the order of "fire" appearing in the text is earlier than "elevator stopped", so the classification category of the emergency event 1 is finally selected as A1.
表3Table 3
结合图3,在一实施例中,步骤S103包括步骤S301~S304:In conjunction with FIG. 3 , in one embodiment, step S103 includes steps S301 to S304:
S301、采用AT-BTM模型中的预训练模型对所述模型数据集输出对应的分类标签;S301, using the pre-trained model in the AT-BTM model to output corresponding classification labels for the model data set;
S302、判断所述分类标签是否属于基于预置分类范围;S302, determining whether the classification label belongs to a preset classification range;
S303、若所述分类标签不属于基于预置分类范围,则设置其他类为第二分类结果;S303: If the classification label does not belong to the preset classification range, set other categories as the second classification result;
S304、若所述分类标签属于基于预置分类范围,则利用CRF层解码器对所述分类标签进行解码处理,以提取所述分类标签的证据,并结合所述分类标签和证据生成第二分类结果。S304: If the classification label belongs to a preset classification range, the classification label is decoded by using a CRF layer decoder to extract evidence of the classification label, and a second classification result is generated by combining the classification label and the evidence.
在本实施例中,采用AT-BTM模型作为所述多任务学习模型的基本框架,AT-BTM模型是以非监督学习的方式对文集的隐含语义结构进行聚类的统计模型,利用AT-BTM模型中的预训练模型输出所述模型数据集对应的分类标签,当所述分类标签属于基于预置分类范围时,则利用CRF层解码器对所述分类标签进行解码处理,并将解码处理结果和结合所述分类标签生成第二分类结果。举例来说,在具体应用场景中,所述模型数据集中突发事件2为小朋友玩单杠摔倒扭伤,得到的分类标签为“摔倒扭伤”,解码处理得到的编码为[0,0......1,1],其中0代表非证据,1表示证据,通过所述证据结合分类标签生成突发事件2的第二分类结果为F8,F8即代表“摔倒扭伤”。In this embodiment, the AT-BTM model is used as the basic framework of the multi-task learning model. The AT-BTM model is a statistical model that clusters the implicit semantic structure of the corpus in an unsupervised learning manner. The pre-trained model in the AT-BTM model is used to output the classification label corresponding to the model data set. When the classification label belongs to the preset classification range, the CRF layer decoder is used to decode the classification label, and the decoding result is combined with the classification label to generate a second classification result. For example, in a specific application scenario, the emergency event 2 in the model data set is a child falling and spraining while playing on the horizontal bar. The classification label obtained is "falling and spraining". The code obtained by the decoding process is [0, 0...1, 1], where 0 represents non-evidence and 1 represents evidence. The second classification result of the emergency event 2 generated by combining the evidence with the classification label is F8, which represents "falling and spraining".
在一实施例中,步骤S103之前还包括:In one embodiment, before step S103, the method further includes:
通过对抗训练模型对所述模型数据集进行数据增强处理,并通过对抗训练迭代构建对抗嵌入;Performing data augmentation processing on the model dataset through an adversarial training model, and constructing adversarial embedding through adversarial training iterations;
采用start指针和end指针对所述多任务学习模型进行边界匹配约束。The start pointer and the end pointer are used to perform boundary matching constraints on the multi-task learning model.
在本实施例中,首先通过对抗训练模型对所述模型数据集进行扰动,以扩充所述模型数据集,其次进行多次PGD迭代来构建对抗嵌入,并在每次迭代中迭代出累积参数梯度,然后通过虚拟创建一个采样小批次,利用累积梯度有效地逐一更新所述多任务学习模型的参数,并利用在嵌入空间上操作的对抗性训练作为有效的正则化,以改善共享编码器的泛化,从而提高多任务学习模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性。例如,突发事件2为小朋友玩单杠摔倒扭伤,对所述突发事件2进行扰动,则得到具体内容为老人走路摔倒扭伤的突发事件3,突发事件2和突发事件3的分类标签都是F8(扭伤跌倒),将分类标签经过词嵌入后和所述模型数据集一起输入到CRF层解码器中对多任务学习模型进行训练,使同一类别突发事件的描述不同时多任务学习模型能正确进行结果分类,从而减少噪音文本对多任务学习模型的干扰,提高多任务学习模型的分类能力。In this embodiment, the model data set is first perturbed by the adversarial training model to expand the model data set, and then multiple PGD iterations are performed to construct adversarial embedding, and cumulative parameter gradients are iterated in each iteration, and then a small sampling batch is virtually created, and the parameters of the multi-task learning model are effectively updated one by one using the cumulative gradients, and adversarial training operated on the embedding space is used as an effective regularization to improve the generalization of the shared encoder, thereby improving the generalization ability and robustness of the multi-task learning model. For example, emergency 2 is a child falling and spraining while playing on the horizontal bar. The emergency 2 is perturbed, and the specific content is emergency 3 in which the elderly fall and sprain while walking. The classification labels of emergency 2 and emergency 3 are both F8 (sprain and fall). The classification labels are embedded in words and input into the CRF layer decoder together with the model data set to train the multi-task learning model, so that the description of the same category of emergency events is different when the multi-task learning model can correctly classify the results, thereby reducing the interference of noise text on the multi-task learning model and improving the classification ability of the multi-task learning model.
此外,本实施例还采用start指针和end指针作为所述多任务学习模型的边界限制,从而促进所述多任务学习模型更准确的定位证据边界,通过对边界位置进行边界匹配约束,使得所述多任务学习模型能够进一步关注模型边界相关的区域,以提高所述多任务学习模型分类的准确度。In addition, this embodiment also uses a start pointer and an end pointer as boundary limits of the multi-task learning model, thereby promoting the multi-task learning model to more accurately locate the evidence boundary. By performing boundary matching constraints on the boundary position, the multi-task learning model can further focus on areas related to the model boundary to improve the classification accuracy of the multi-task learning model.
在一实施例中,步骤S103还包括:In one embodiment, step S103 further includes:
按照下式,计算总的损失函数L对所述多任务学习模型进行优化更新:According to the following formula, the total loss function L is calculated to optimize and update the multi-task learning model:
, ,
式中,表示预训练模型的损失函数,表示CRF层的损失函数,表示对抗训练模型的损失函数,表示边界匹配约束的损失函数,和均表示超参数。In the formula, represents the loss function of the pre-trained model, represents the loss function of the CRF layer, represents the loss function of the adversarial training model, represents the loss function of the boundary matching constraint, and All represent hyperparameters.
在本实施例中,通过计算多任务学习模型的损失函数,得到损失函数之后,多任务学习模型通过反向传播去更新各个参数,来降低输出结果的真实值与预测值之间的损失,使得多任务学习模型生成的预测值往真实值方向靠拢,从而达到学习的目的。损失函数可以很好地反映模型与实际数据的差距,更好地对后续优化工具(梯度下降等)进行分析与理解。In this embodiment, by calculating the loss function of the multi-task learning model, after obtaining the loss function, the multi-task learning model updates each parameter through back propagation to reduce the loss between the true value and the predicted value of the output result, so that the predicted value generated by the multi-task learning model is closer to the true value, thereby achieving the purpose of learning. The loss function can well reflect the gap between the model and the actual data, and better analyze and understand the subsequent optimization tools (gradient descent, etc.).
在具体实施例中,预训练模型、CRF层、对抗训练模型、边界约束共享同一编码pretained Encode。所述模型数据集一方面用于预训练模型输出分类标签,一方面用于CRF层输出证据,按照下式,计算预训练模型的损失函数:In a specific embodiment, the pre-trained model, CRF layer, adversarial training model, and boundary constraints share the same encoding pretained Encode. On the one hand, it is used to output classification labels for pre-trained models , on the one hand, is used for CRF layer output evidence , calculate the loss function of the pre-trained model according to the following formula :
, ,
式中,i表示所述模型数据集中文字的序号,n表示所述模型数据集文字总数。In the formula, i represents the sequence number of the characters in the model data set, and n represents the total number of characters in the model data set.
将预训练模型输出的分类标签经过词嵌入生成序列,并和所述模型数据集一起输入到CRF层解码器中对多任务学习模型进行训练,得到证据,按照下式,计算对应预训练模型的损失函数:The classification labels output by the pre-trained model are embedded into a sequence and input into the CRF layer decoder together with the model dataset to train the multi-task learning model and obtain evidence , calculate the loss function of the corresponding pre-trained model according to the following formula:
, ,
式中,j表示分类类别的序号,m表示分类类别的总数。In the formula, j represents the ordinal number of the classification category, and m represents the total number of classification categories.
按照下式,计算对抗训练模型的损失函数:According to the following formula, calculate the loss function of the adversarial training model :
其中:in:
, ,
式中,是基于扰动的对抗训练PAT的损失,是正则项,θ表示先验分布中的参数,表示对抗嵌入的交叉熵损失,表示扰动,表示范数,,均表示交叉熵损失,y表示预训练模型的预测结果。In the formula, is the loss of perturbation-based adversarial training PAT, is a regular term, θ represents the parameter in the prior distribution, represents the cross entropy loss of adversarial embedding, represents disturbance, represents the norm, , Both represent cross entropy loss, and y represents the prediction result of the pre-training model.
利用在嵌入空间上操作的对抗性训练作为有效的正则化,以改善共享编码器的泛化,减少鲁棒性错误。对抗性训练通过PGD(Projected gradient descent,投影梯度下降算法)监督进行,K步PGD 需要通过网络进行K次前向-后向传播,计算成本较高,此外,K步PGD之后只有最后一步的扰动用于对抗训练模型参数更新。因此本实施例通过遵循 FreeLB算法中的自由对抗训练框架,进行多次PGD 迭代来构建对抗嵌入,并在每次迭代中迭代出累积参数梯度,然后通过虚拟创建一个采样小批次,利用累积梯度有效地逐一更新模型参数。Adversarial training operating on the embedding space is used as an effective regularization to improve the generalization of the shared encoder and reduce robustness errors. Adversarial training is supervised by PGD (Projected gradient descent). K-step PGD requires K forward-backward propagation through the network, which has a high computational cost. In addition, only the last perturbation after K-step PGD is used to update the parameters of the adversarial training model. Therefore, this embodiment constructs adversarial embedding by following the free adversarial training framework in the FreeLB algorithm, performing multiple PGD iterations, and iterating the accumulated parameter gradients in each iteration, and then effectively updating the model parameters one by one by using the accumulated gradients by virtually creating a small sampling batch.
通过下式计算边界约束的损失函数:The loss function of the boundary constraint is calculated by the following formula :
其中:in:
, ,
式中,表示在分类标签下,证据对应的预测起始索引与其对应的结束索引匹配的概率,W表示模型隐藏层的权重函数,表示模型权重系数,表示每个词作为起始词的概率分布,表示每个词作为结束词的概率分布,i=1,...,L,j=1,...,L。In the formula, represents the probability that the predicted start index corresponding to the evidence matches its corresponding end index under the classification label, W represents the weight function of the hidden layer of the model, represents the model weight coefficient, represents the probability distribution of each word as the starting word, Represents the probability distribution of each word as the end word, i=1,...,L, j=1,...,L.
本实施例中的CRF层存在生成非法标签序列的局限性,因为CRF层鼓励合理的标签序列,而对于不合理的过渡惩罚较低。因此,本实施例使用边界约束来鼓励CRF层在定位边界时更加准确。The CRF layer in this embodiment has the limitation of generating illegal label sequences, because the CRF layer encourages reasonable label sequences and has a low penalty for unreasonable transitions. Therefore, this embodiment uses boundary constraints to encourage the CRF layer to be more accurate in locating boundaries.
在一实施例中,步骤S104包括:In one embodiment, step S104 includes:
判断所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果是否为其他类;Determine whether the first classification result and the second classification result are other categories;
若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果均为其他类,则将最终分类结果输出为其他类;If the first classification result and the second classification result are both other categories, outputting the final classification result as other categories;
若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果中的任意一个为其他类,则将另一个分类结果作为最终分类结果输出;If any one of the first classification result and the second classification result is other class, the other classification result is output as the final classification result;
若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果均不为其他类,则获取第一分类结果和第二分类结果的风险等级,并选择风险等级高的分类结果作为最终分类结果输出。If both the first classification result and the second classification result are not other categories, the risk levels of the first classification result and the second classification result are obtained, and the classification result with a higher risk level is selected as the final classification result to be output.
在本实施例中,通过判断所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果是否为其他类,并将判断结果进行集成,得到最终分类结果,能够更准确地对突发事件进行分类分级,以提高突发事件安全管理的效率。在具体应用场景中,还可在突发事件报事人上报突发事件后,提供突发事件管理方法输出的分类结果作为参考,使报事人可参考分类结果,从而决定是否修改自己上报的突发事件的分类分级,通过报事人的反馈能够进一步提到突发事件分类分级的准确度,实现突发事件安全管理的进一步优化。In this embodiment, by judging whether the first classification result and the second classification result are other categories, and integrating the judgment results to obtain the final classification result, the emergency can be classified and graded more accurately to improve the efficiency of emergency safety management. In a specific application scenario, after the emergency reporter reports the emergency, the classification result output by the emergency management method can be provided as a reference, so that the reporter can refer to the classification result to decide whether to modify the classification and grading of the emergency reported by himself. The feedback from the reporter can further improve the accuracy of the classification and grading of the emergency, and further optimize the emergency safety management.
在具体应用场景中,本发明实施例还对模型的召回率和准确率进行评估。In a specific application scenario, the embodiment of the present invention also evaluates the recall rate and accuracy of the model.
按照下式计算精确率Precision,精确率为分类正确的正样本数 (TP) 占 预测为正样本的总样本数 (TP + FP) 的比例:The precision is calculated according to the following formula. The precision is the ratio of the number of correctly classified positive samples (TP) to the total number of samples predicted as positive samples (TP + FP):
按照下式计算召回率Recall ,召回率为分类正确的正样本数 (TP) 占 实际的正样本总数 (TP + FN) 的比例:The recall rate Recall is calculated according to the following formula. The recall rate is the ratio of the number of correctly classified positive samples (TP) to the total number of actual positive samples (TP + FN):
在一具体实施例中,第一分类结果的、第二分类结果和最终分类结果对于突发事件D1、D2、D3、D4的精确率如表4所示,结合表4可以得到投票集成所得最终分类结果相较于第一分类结果和第二分类结果的精确率更高的结论,可见投票集成的预测性能更优秀。In a specific embodiment, the accuracy of the first classification results, the second classification results and the final classification results for the emergencies D1, D2, D3 and D4 are shown in Table 4. Combining Table 4, it can be concluded that the final classification result obtained by the voting integration has a higher accuracy than the first classification result and the second classification result, which shows that the prediction performance of the voting integration is better.
表4Table 4
数据处理单元401,用于获取突发事件信息,并对所述突发事件信息进行预处理,得到模型数据集;The
第一分类单元402,用于基于预置分类范围对所述模型数据集进行关键词提取,并对提取的关键词进行正则匹配处理,得到第一分类结果;A
第二分类单元403,用于将所述模型数据集输入至多任务学习模型中,并基于预置分类范围由所述多任务学习模型输出得到第二分类结果;A
投票集成单元404,用于对所述第一分类结果与所述第二分类结果进行投票集成,并将投票集成结果作为最终分类结果输出。The
在一实施例中,所述突发事件信息包括事件时间,事件主题,事件主要内容,所述数据处理单元401包括:In one embodiment, the emergency event information includes event time, event subject, and event main content. The
特征工程单元,用于获取突发事件信息对应的事件主表ID,根据所述事件主表ID关联事件类型,并根据所述事件类型对所述突发事件信息进行特征工程处理;A feature engineering unit, used to obtain an event master table ID corresponding to the emergency event information, associate an event type according to the event master table ID, and perform feature engineering processing on the emergency event information according to the event type;
数据转换单元,用于对所述突发事件信息进行文本清洗,以及基于特征工程处理的结果对所述突发事件信息进行数据转换,以此构建模型数据集。The data conversion unit is used to perform text cleaning on the emergency information and perform data conversion on the emergency information based on the result of feature engineering processing, so as to construct a model data set.
结合图5,在一实施例中,所述第一分类单元402包括:In conjunction with FIG5 , in one embodiment, the
切词处理单元501,用于将所述模型数据集中的所有突发事件信息合并为同一文档,并对所述文档进行切词处理;A word
词频统计单元502,用于通过gensim工具中的doc2bow函数对切词处理后的文档进行词频统计,得到二维数组;The word
关键词输出单元503,用于利用所述二维数组输入至TF-IDF模型,并由所述TF-IDF模型输出所述关键词;A
正则匹配单元504,用于基于预置分类范围对所述关键词进行正则匹配,得到所述关键词的匹配结果;A
匹配结果单元505,用于当匹配结果成功时,获取所述关键词在所述文档中的位置信息,并结合所述分类结果和位置信息生成第一分类结果;当匹配结果失败时,则设置其他类为第一分类结果。The matching
结合图6,在一实施例中,所述第二分类单元403包括:In conjunction with FIG6 , in one embodiment, the
预训练单元601,用于采用AT-BTM模型中的预训练模型对所述模型数据集输出对应的分类标签;A
范围判断单元602,用于判断所述分类标签是否属于基于预置分类范围;A
分类标签判断单元603,用于若所述分类标签不属于基于预置分类范围,则设置其他类为第二分类结果;A classification
证据提取单元604,用于若所述分类标签属于基于预置分类范围,则利用CRF层解码器对所述分类标签进行解码处理,以提取所述分类标签的证据,并结合所述分类标签和证据生成第二分类结果。The
在一实施例中,所述第二分类单元403之前,还包括:In one embodiment, before the
数据增强单元,用于通过对抗训练模型对所述模型数据集进行数据增强处理,并通过对抗训练迭代构建对抗嵌入;A data enhancement unit, configured to perform data enhancement processing on the model dataset through an adversarial training model, and to iteratively construct an adversarial embedding through adversarial training;
边界约束单元,用于采用start指针和end指针对所述多任务学习模型进行边界匹配约束。The boundary constraint unit is used to use the start pointer and the end pointer to perform boundary matching constraints on the multi-task learning model.
在一实施例中,所述第二分类单元403还包括:In one embodiment, the
优化更新单元,用于按照下式,采用损失函数L对所述多任务学习模型进行优化更新:The optimization and updating unit is used to optimize and update the multi-task learning model using the loss function L according to the following formula:
, ,
式中,表示预训练模型的损失函数,表示CRF层的损失函数,表示对抗训练模型的损失函数,表示边界匹配约束的损失函数,和均表示超参数。In the formula, represents the loss function of the pre-trained model, represents the loss function of the CRF layer, represents the loss function of the adversarial training model, represents the loss function of the boundary matching constraint, and All represent hyperparameters.
在一实施例中,所述投票集成单元404包括:In one embodiment, the
结果判断单元,用于判断所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果是否为其他类;A result judgment unit, used to judge whether the first classification result and the second classification result are other categories;
其他类结果输出单元,用于若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果均为其他类,则将最终分类结果输出为其他类;An other-category result output unit, configured to output the final classification result as other categories if both the first classification result and the second classification result are other categories;
第一最终分类结果单元,用于若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果中的任意一个为其他类,则将另一个分类结果作为最终分类结果输出;A first final classification result unit, configured to output the other classification result as a final classification result if any one of the first classification result and the second classification result is other class;
第二最终分类结果单元,用于若所述第一分类结果和第二分类结果均不为其他类,则获取第一分类结果和第二分类结果的风险等级,并选择风险等级高的分类结果作为最终分类结果输出。The second final classification result unit is used to obtain the risk level of the first classification result and the second classification result if both the first classification result and the second classification result are not other categories, and select the classification result with a higher risk level as the final classification result to output.
由于装置部分的实施例与方法部分的实施例相互对应,因此装置部分的实施例请参见方法部分的实施例的描述,这里暂不赘述。Since the embodiments of the apparatus part correspond to the embodiments of the method part, please refer to the description of the embodiments of the method part for the embodiments of the apparatus part, which will not be repeated here.
本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存有计算机程序,该计算机程序被执行时可以实现上述实施例所提供的步骤。该存储介质可以包括:U盘、移动硬盘、只读存储器(Read-Only Memory,ROM)、随机存取存储器(Random Access Memory,RAM)、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。The embodiment of the present invention further provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed, the steps provided in the above embodiment can be implemented. The storage medium may include: a USB flash drive, a mobile hard disk, a read-only memory (ROM), a random access memory (RAM), a magnetic disk or an optical disk, and other media that can store program codes.
本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机设备,可以包括存储器和处理器,存储器中存有计算机程序,处理器调用存储器中的计算机程序时,可以实现上述实施例所提供的步骤。当然计算机设备还可以包括各种网络接口,电源等组件。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer device, which may include a memory and a processor, wherein a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the processor calls the computer program in the memory, the steps provided in the above embodiment may be implemented. Of course, the computer device may also include various network interfaces, power supplies and other components.
说明书中各个实施例采用递进的方式描述,每个实施例重点说明的都是与其他实施例的不同之处,各个实施例之间相同相似部分互相参见即可。对于实施例公开的系统而言,由于其与实施例公开的方法相对应,所以描述的比较简单,相关之处参见方法部分说明即可。应当指出,对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本申请原理的前提下,还可以对本申请进行若干改进和修饰,这些改进和修饰也落入本申请权利要求的保护范围内。The various embodiments in the specification are described in a progressive manner, and each embodiment focuses on the differences from other embodiments. The same and similar parts between the various embodiments can be referred to each other. For the system disclosed in the embodiment, since it corresponds to the method disclosed in the embodiment, the description is relatively simple, and the relevant parts can be referred to the method part description. It should be pointed out that for ordinary technicians in this technical field, without departing from the principles of this application, several improvements and modifications can be made to the present application, and these improvements and modifications also fall within the scope of protection of the claims of this application.
还需要说明的是,在本说明书中,诸如第一和第二等之类的关系术语仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的状况下,由语句“包括一个……”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备中还存在另外的相同要素。It should also be noted that, in this specification, relational terms such as first and second, etc. are only used to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, and do not necessarily require or imply any such actual relationship or order between these entities or operations. Moreover, the terms "comprises", "comprising" or any other variants thereof are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion, so that a process, method, article or device including a series of elements includes not only those elements, but also other elements not explicitly listed, or also includes elements inherent to such process, method, article or device. In the absence of further restrictions, an element defined by the statement "comprising a ..." does not exclude the presence of other identical elements in the process, method, article or device including the element.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310275728.4ACN115983255B (en) | 2023-03-21 | 2023-03-21 | Emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310275728.4ACN115983255B (en) | 2023-03-21 | 2023-03-21 | Emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115983255Atrue CN115983255A (en) | 2023-04-18 |
| CN115983255B CN115983255B (en) | 2023-06-02 |
Family
ID=85976523
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310275728.4AActiveCN115983255B (en) | 2023-03-21 | 2023-03-21 | Emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115983255B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118277836A (en)* | 2024-05-31 | 2024-07-02 | 航安云创科技(北京)有限公司 | Method, device and equipment for determining classification and treatment measures of unsafe events |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107846493B (en)* | 2017-12-21 | 2019-10-25 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Call contact control method, device, storage medium and mobile terminal |
| US10388272B1 (en)* | 2018-12-04 | 2019-08-20 | Sorenson Ip Holdings, Llc | Training speech recognition systems using word sequences |
| CN111897964B (en)* | 2020-08-12 | 2023-10-17 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Text classification model training method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN112526606A (en)* | 2021-02-08 | 2021-03-19 | 南京云创大数据科技股份有限公司 | Seismic source type prediction method and system based on heterogeneous multi-classification model |
| CN114782054B (en)* | 2022-03-14 | 2025-07-25 | 中国人寿保险股份有限公司 | Customer service quality detection method and related equipment based on deep learning algorithm |
| CN114724710A (en)* | 2022-06-10 | 2022-07-08 | 北京大学第三医院(北京大学第三临床医学院) | Recommended method, device and storage medium for emergency plan for emergencies |
| CN115269833B (en)* | 2022-06-29 | 2024-08-16 | 国家计算机网络与信息安全管理中心 | Event information extraction method and system based on deep semantics and multi-task learning |
| CN115130110B (en)* | 2022-07-08 | 2024-03-19 | 国网浙江省电力有限公司电力科学研究院 | Vulnerability discovery method, device, equipment and medium based on parallel integrated learning |
- 2023
- 2023-03-21CNCN202310275728.4Apatent/CN115983255B/enactiveActive
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118277836A (en)* | 2024-05-31 | 2024-07-02 | 航安云创科技(北京)有限公司 | Method, device and equipment for determining classification and treatment measures of unsafe events |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115983255B (en) | 2023-06-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110969024A (en) | Method and device for rewriting query statement | |
| US10678625B2 (en) | Log-based computer system failure signature generation | |
| CN110457707B (en) | Method and device for extracting real word keywords, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN111930931B (en) | Abstract evaluation method and device | |
| CN107679031B (en) | Advertisement and blog identification method based on stacking noise reduction self-coding machine | |
| Susanti et al. | Twitter’s sentiment analysis on GSM services using Multinomial Naïve Bayes | |
| CN111651585A (en) | Information verification method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN108776673A (en) | Automatic switching method, device and the storage medium of relation schema | |
| CN116128544A (en) | A method and system for active auditing of abnormal business data in electric power marketing | |
| CN115983255B (en) | Emergency management method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN107357851B (en) | An information processing method and system | |
| CN105426425A (en) | Big data marketing method based on mobile signaling | |
| Girsang | Sentiment analysis of COVID-19 public activity restriction (PPKM) impact using BERT method | |
| CN116521133B (en) | Software function safety requirement analysis method, device, equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN115658956B (en) | Hot topic mining method and system based on conference audio data | |
| CN114610576A (en) | Log generation monitoring method and device | |
| Cepeda et al. | Sentiment analysis on covid-19 vaccinations in Ireland using support vector machine | |
| CN113034057A (en) | Risk identification method, device and equipment | |
| CN119025625B (en) | A method and device for data processing based on knowledge graph | |
| CN118333637B (en) | Product recall prediction method and system based on topic model | |
| CN119441497B (en) | Event identification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115438101B (en) | Data feature construction system and method based on feature morphology and data relationship | |
| KR102853790B1 (en) | Method for domain specific named entity recognition based on zero shot learning | |
| CN111199170A (en) | Formula file identification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114021571B (en) | A security entity detection method and device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20241122 Address after:518000 second and third floors of Meilin Vanke center, 63 Meilin Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Patentee after:SHENZHEN VANKE PROPERTY SERVICE Co.,Ltd. Country or region after:China Patentee after:SHENZHEN WANWUYUN TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd. Address before:518000 Room 201, building A, 1 front Bay Road, Shenzhen Qianhai cooperation zone, Shenzhen, Guangdong Patentee before:SHENZHEN WANWUYUN TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd. Country or region before:China |