CN115980149A - Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment device - Google Patents
Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115980149A CN115980149ACN202211528698.5ACN202211528698ACN115980149ACN 115980149 ACN115980149 ACN 115980149ACN 202211528698 ACN202211528698 ACN 202211528698ACN 115980149 ACN115980149 ACN 115980149A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- electrolyte
- test probe
- chemical test
- probe
- liquid storage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Testing Resistance To Weather, Investigating Materials By Mechanical Methods (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本申请属于化学检测技术领域,具体涉及一种化学测试探头电解液、制备方法及自动补加电解液装置。The present application belongs to the field of chemical detection technology, and specifically relates to a chemical test probe electrolyte, a preparation method and an automatic electrolyte replenishing device.
背景技术Background Art
在对一些液体的化学成分的检测分析过程中,需要用到各种化学分析设备,一些化学分析设备采用检测探头伸入待检测液体,以对液体成分进行检测分析。为了避免探头长时间暴露在空气中,导致探头表面附着其他物质,进而影响检测精准性,通常在不使用探头时,将探头放置于氯化钾电解液中,对探头进行保护。然而,探头放入氯化钾电解液中后,氯化钾电解液会析出白色晶体附着于探头上,影响探头对待检测液体的检测准确性,也加快了探头的损耗程度。为此,需要提出一种电解液,在能够保护探头的同时,不易结晶。化学测试探头在使用过程中,需要不断地从电解液中取出,因此盛放探头的机构中电解液的常需要补加和更换,如果补加和更换不及时,则会影响探头的使用,也不能为探头起到足够的保护作用,因此,也需要提出一种可以自动补加电解液的装置。In the process of detecting and analyzing the chemical composition of some liquids, various chemical analysis equipment is needed. Some chemical analysis equipment uses a detection probe to extend into the liquid to be detected to detect and analyze the liquid components. In order to avoid the probe being exposed to the air for a long time, causing other substances to adhere to the surface of the probe, thereby affecting the detection accuracy, the probe is usually placed in a potassium chloride electrolyte when not in use to protect the probe. However, after the probe is placed in the potassium chloride electrolyte, the potassium chloride electrolyte will precipitate white crystals attached to the probe, affecting the detection accuracy of the probe to the liquid to be detected, and also accelerating the loss of the probe. For this reason, it is necessary to propose an electrolyte that is not easy to crystallize while being able to protect the probe. During use, the chemical test probe needs to be continuously taken out of the electrolyte, so the electrolyte in the mechanism containing the probe often needs to be replenished and replaced. If the replenishment and replacement are not timely, it will affect the use of the probe and cannot provide sufficient protection for the probe. Therefore, it is also necessary to propose a device that can automatically replenish the electrolyte.
发明内容Summary of the invention
鉴于以上内容,有必要提出一种化学测试探头电解液能够保护探头且不易结晶。In view of the above, it is necessary to propose a chemical test probe electrolyte that can protect the probe and is not easy to crystallize.
另外,本申请还提供一种所述化学测试探头电解液的制备方法。In addition, the present application also provides a method for preparing the chemical test probe electrolyte.
还有必要提供一种自动补加电解液装置。It is also necessary to provide an automatic electrolyte replenishment device.
为了实现上述目的,本申请提供一种化学测试探头电解液,按重量百分比包括:0.3%~0.6%的无机盐,25%~30%的硫酸镁,0.1%~0.6%的硼酸,2%~5%的防腐剂,其余为水。In order to achieve the above-mentioned purpose, the present application provides a chemical test probe electrolyte, which includes, by weight percentage: 0.3% to 0.6% of inorganic salt, 25% to 30% of magnesium sulfate, 0.1% to 0.6% of boric acid, 2% to 5% of preservative, and the rest is water.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述硫酸镁的含量为26%~28%。In some possible implementations, the content of magnesium sulfate is 26% to 28%.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述硼酸的含量为0.1%~0.3%。In some possible implementations, the content of the boric acid is 0.1% to 0.3%.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述防腐剂的含量为3%~4%。In some possible implementations, the content of the preservative is 3% to 4%.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述无机盐是氯化钠。In some possible implementations, the inorganic salt is sodium chloride.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述防腐剂选自是环十二烷基丙醇、苯甲酸、苯甲酸钠、山梨酸钾或丙酸钙。In some possible implementations, the preservative is selected from cyclododecyl propanol, benzoic acid, sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate or calcium propionate.
在一些可能的实现方式中,所述防腐剂是环十二烷基丙醇。In some possible implementations, the preservative is cyclododecyl propanol.
本申请中提供的化学测试探头电解液中,通过电解液中的无机盐成分可以维持溶液的离子平衡,有效地对探头起到保护作用;通过电解液中的硼酸,可以抑制电解液中细菌的生成,有效提高电解液的使用寿命;通过电解液中的硫酸镁,可以抑制电解液结晶;通过电解液中的防腐剂,可以延长电解液的使用周期,有利于节省成本。In the chemical test probe electrolyte provided in the present application, the inorganic salt components in the electrolyte can maintain the ion balance of the solution, effectively protecting the probe; the boric acid in the electrolyte can inhibit the formation of bacteria in the electrolyte, effectively improving the service life of the electrolyte; the magnesium sulfate in the electrolyte can inhibit the crystallization of the electrolyte; the preservative in the electrolyte can extend the service life of the electrolyte, which is conducive to cost saving.
本申请还提供了一种制备方法,用于制备上述的化学测试探头电解液,该方法由以下步骤组成:(a)将无机盐和硼酸溶于水中,搅拌溶解;(b)将硫酸镁溶于水中,并缓缓煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤;(c)将步骤(a)的溶液和步骤(b)的溶液混合在一起后,加入防腐剂,搅拌均匀。The present application also provides a preparation method for preparing the above-mentioned chemical test probe electrolyte, which comprises the following steps: (a) dissolving an inorganic salt and boric acid in water and stirring to dissolve; (b) dissolving magnesium sulfate in water and slowly boiling for 10 minutes, cooling and filtering; (c) mixing the solution of step (a) and the solution of step (b) together, adding a preservative and stirring evenly.
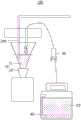
本申请还提供一种自动补加电解液装置,包括:容纳组件,包括容纳件和排空阀,所述容纳件用于容纳化学测试探头以及电解液,所述排空阀安装于所述容纳件,用于排出所述容纳组件内的所述电解液;储液桶,用于储存所述电解液;供液泵,分别与所述容纳件和所述储液桶连通,用于将所述储液桶中的所述电解液传输至所述容纳件中;控制器,与所述供液泵和排空阀均电性连接,用于控制所述供液泵间隔性地向所述容纳件内供液,并控制所述排空阀的打开与闭合;及监测组件,设置于所述储液桶内,用于监测所述储液桶中的所述电解液的量。The present application also provides an automatic electrolyte replenishing device, comprising: a containing component, comprising a containing part and a drain valve, the containing part is used to contain a chemical test probe and an electrolyte, the drain valve is installed in the containing part, and is used to discharge the electrolyte in the containing component; a liquid storage barrel, used to store the electrolyte; a liquid supply pump, which is connected to the containing part and the liquid storage barrel, respectively, and is used to transfer the electrolyte in the liquid storage barrel to the containing part; a controller, which is electrically connected to the liquid supply pump and the drain valve, and is used to control the liquid supply pump to intermittently supply liquid to the containing part, and control the opening and closing of the drain valve; and a monitoring component, which is arranged in the liquid storage barrel, and is used to monitor the amount of the electrolyte in the liquid storage barrel.
在一些可能的实现方式中,还包括远程监测系统,所述远程监测系统与控制器和监测组件均电性连接,用于接收所述控制器和所述监测组件的数据。In some possible implementations, a remote monitoring system is further included. The remote monitoring system is electrically connected to the controller and the monitoring component and is used to receive data from the controller and the monitoring component.
本申请提供的自动补加电解液装置,通过容纳件容纳电解液和化学测试探头,通过排空阀可以将容纳件中的电解液排出,通过供液泵可以将储液桶中的电解液传输至容纳件内,通过控制器可控制排空阀和供液泵工作,以排空容纳件中的电解液或向容纳件中加入电解液,通过检测组件可以实时检测容纳件中的电解液的量。如此,可以实现监控容纳件中的电解液的量以及自动补充或更换容纳件中的电解液。The automatic electrolyte replenishing device provided by the present application contains electrolyte and chemical test probes through a container, the electrolyte in the container can be discharged through a drain valve, the electrolyte in the liquid storage barrel can be transferred to the container through a liquid supply pump, the drain valve and the liquid supply pump can be controlled by a controller to empty the electrolyte in the container or add electrolyte to the container, and the amount of electrolyte in the container can be detected in real time through a detection component. In this way, the amount of electrolyte in the container can be monitored and the electrolyte in the container can be automatically replenished or replaced.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
图1为本申请一些实施例提供的电解液的制备方法的流程示意图。FIG. 1 is a schematic flow chart of a method for preparing an electrolyte provided in some embodiments of the present application.
图2为本申请一些实施例提供的自动补加电解液装置的立体示意图。FIG. 2 is a three-dimensional schematic diagram of an automatic electrolyte replenishing device provided in some embodiments of the present application.
主要元件符号说明Main component symbols
自动补加电解液装置 100Automatic
容纳组件 10Accommodating
容纳件 11
排空阀 12
储液桶 20
供液泵 30
监测组件 40
探头 200
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
下面将结合具体实施例对本发明的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述。显然,所描述的实施方式仅是本发明一部分实施方式,而不是全部的实施方式。基于本发明中的实施方式,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施方式,都属于本发明保护的范围。The technical solution of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with specific embodiments. Obviously, the described implementation is only a part of the implementation of the present invention, not all of the implementations. Based on the implementation of the present invention, all other implementations obtained by ordinary technicians in the field without creative work are within the scope of protection of the present invention.
除非另有定义,本文所使用的所有的技术和科学术语与属于本发明的技术领域的技术人员通常理解的含义相同。在本发明的说明书中所使用的技术手段的名称只是为了描述具体的实施例的目的,不是旨在于限制本发明。Unless otherwise defined, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as those commonly understood by those skilled in the art of the present invention. The names of the technical means used in the specification of the present invention are only for the purpose of describing specific embodiments and are not intended to limit the present invention.
以下描述将参考附图以更全面地描述本申请内容。附图中所示为本申请的示例性实施例。然而,本申请可以以许多不同的形式来实施,并且不应该被解释为限于在此阐述的示例性实施例。提供这些示例性实施例是为了使本申请透彻和完整,并且将本申请的范围充分地传达给本领域技术人员。类似的附图标记表示相同或类似的组件。The following description will refer to the accompanying drawings to more fully describe the content of the present application. Shown in the accompanying drawings are exemplary embodiments of the present application. However, the present application can be implemented in many different forms and should not be interpreted as being limited to the exemplary embodiments set forth herein. These exemplary embodiments are provided to make the present application thorough and complete, and to fully convey the scope of the present application to those skilled in the art. Similar reference numerals represent identical or similar components.
本文使用的术语仅用于描述特定示例性实施例的目的,而不意图限制本申请。如本文所使用的,除非上下文另外清楚地指出,否则单数形式“一”,“一个”和“该”旨在也包括复数形式。此外,当在本文中使用时,“包括”和/或“包含”和/或“具有”,整数,步骤,操作,但不排除存在或添加一个或多个其它特征,区域,整数,步骤,操作,组件和/或其群组。The terms used herein are only used for the purpose of describing specific exemplary embodiments and are not intended to limit the present application. As used herein, the singular forms "a", "an" and "the" are intended to include plural forms as well, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. In addition, when used herein, "includes" and/or "comprises" and/or "has", integers, steps, operations, but do not exclude the existence or addition of one or more other features, regions, integers, steps, operations, components and/or groups thereof.
除非另外定义,否则本文使用的所有术语(包括技术和科学术语)具有与本申请所属领域的普通技术人员通常理解的相同的含义。此外,除非文中明确定义,诸如在通用字典中定义的那些术语应该被解释为具有与其在相关技术和本申请内容中的含义一致的含义,并且将不被解释为理想化或过于正式的含义。Unless otherwise defined, all terms (including technical and scientific terms) used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by those of ordinary skill in the art to which this application belongs. In addition, unless explicitly defined herein, terms such as those defined in general dictionaries should be interpreted as having a meaning consistent with their meaning in the relevant technology and the content of this application, and will not be interpreted as an idealized or overly formal meaning.
以下内容将结合附图对示例性实施例进行描述。须注意的是,参考附图中所描绘的组件不一定按比例显示;而相同或类似的组件将被赋予相同或相似的附图标记表示或类似的技术用语。The following will describe exemplary embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that the components depicted in the reference drawings are not necessarily shown to scale; and the same or similar components will be given the same or similar reference numerals or similar technical terms.
在本说明书的描述中,参考术语“一个实施例”、“一些实施例”、“示例”、“具体示例”、或“一些示例”等的描述意指结合该实施例或示例描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点包含于本发明的至少一个实施例或示例中。在本说明书中,对上述术语的示意性表述不一定指的是相同的实施例或示例。而且,描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点可以在任何的一个或多个实施例或示例中以合适的方式结合。In the description of this specification, the description with reference to the terms "one embodiment", "some embodiments", "examples", "specific examples", or "some examples" means that the specific features, structures, materials or characteristics described in conjunction with the embodiment or example are included in at least one embodiment or example of the present invention. In this specification, the schematic representation of the above terms does not necessarily refer to the same embodiment or example. Moreover, the specific features, structures, materials or characteristics described may be combined in any one or more embodiments or examples in a suitable manner.
目前常用的化学检测探头保护电解液为氯化钾溶液,优点是保护作用好,配制方便。为了起到保护作用,通常采用饱和的氯化钾溶液,浓度为3mol/L。但是化学检测探头放入氯化钾溶液中,氯化钾易析出,而在化学检测探头上形成白色晶体,若不及时处理甚至会包裹化学检测探头。化学检测探头上若形成白色晶体,会影响检测结果的准确性,甚至会损坏化学检测探头。At present, the commonly used chemical detection probe protection electrolyte is potassium chloride solution, which has the advantages of good protection and easy preparation. In order to play a protective role, a saturated potassium chloride solution with a concentration of 3 mol/L is usually used. However, when the chemical detection probe is placed in the potassium chloride solution, potassium chloride is easy to precipitate, and white crystals are formed on the chemical detection probe. If not handled in time, they may even wrap the chemical detection probe. If white crystals are formed on the chemical detection probe, it will affect the accuracy of the test results and even damage the chemical detection probe.
本申请提供一种化学测试探头电解液,按重量百分比包括:0.3%~0.6%的无机盐,25%~30%的硫酸镁,0.1%~0.6%的硼酸,2%~5%的防腐剂,其余为水。The present application provides a chemical test probe electrolyte, which comprises, by weight percentage: 0.3% to 0.6% of inorganic salt, 25% to 30% of magnesium sulfate, 0.1% to 0.6% of boric acid, 2% to 5% of preservative, and the rest is water.
在一些实施例中,硫酸镁的含量为26%~28%。In some embodiments, the content of magnesium sulfate is 26% to 28%.
在一些实施例中,硼酸的含量为0.1%~0.3%。In some embodiments, the content of boric acid is 0.1% to 0.3%.
在一些实施例中,防腐剂的含量为3%~4%。In some embodiments, the content of preservatives is 3% to 4%.
在一些实施例中,无机盐是氯化钠。In some embodiments, the inorganic salt is sodium chloride.
在一些实施例中,防腐剂选自是环十二烷基丙醇、苯甲酸、苯甲酸钠、山梨酸钾或丙酸钙。In some embodiments, the preservative is selected from cyclododecyl propanol, benzoic acid, sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, or calcium propionate.
在一些实施例中,防腐剂是环十二烷基丙醇。In some embodiments, the preservative is cyclododecylpropanol.
本申请的化学测试探头例如是pH计测试探头,在不使用时放入电解液中进行保护。本申请提供的化学测试探头电解液,包含0.3%~0.6%的无机盐,可以维持溶液的离子平衡。为放入化学测试探头电解液中的化学测试探头提供保护作用,避免化学测试探头长时间干放或者浸泡在蒸馏水中而导致使用寿命缩短。化学测试探头电解液中还包含25%~30%的硫酸镁,可以有效地抑制无机盐结晶,避免探头上附着晶体而影响检测的准确性。化学测试探头电解液中的0.1%~0.6%的硼酸,可以起到润滑和灭菌的作用,可以有效地避免化学测试探头电解液中产生细菌,提高电解液的使用时间。化学测试探头电解液中的2%~5%防腐剂,可以起到防腐作用,进一步提高化学测试探头电解液的使用寿命。The chemical test probe of the present application is, for example, a pH meter test probe, which is placed in an electrolyte for protection when not in use. The chemical test probe electrolyte provided by the present application contains 0.3% to 0.6% of inorganic salts, which can maintain the ion balance of the solution. It provides protection for the chemical test probe placed in the chemical test probe electrolyte to prevent the chemical test probe from being placed dry or immersed in distilled water for a long time, which will shorten its service life. The chemical test probe electrolyte also contains 25% to 30% of magnesium sulfate, which can effectively inhibit the crystallization of inorganic salts and prevent crystals from adhering to the probe and affecting the accuracy of the detection. The 0.1% to 0.6% boric acid in the chemical test probe electrolyte can play a role in lubrication and sterilization, which can effectively prevent the generation of bacteria in the chemical test probe electrolyte and increase the service life of the electrolyte. The 2% to 5% preservative in the chemical test probe electrolyte can play a role in corrosion protection and further increase the service life of the chemical test probe electrolyte.
请参阅图1,本申请还提供一种化学测试探头电解液的制备方法,该方法由以下步骤组成:Please refer to FIG1 . The present application also provides a method for preparing a chemical test probe electrolyte, which comprises the following steps:
S1:将无机盐和硼酸溶于水中,搅拌溶解;S1: Dissolve the inorganic salt and boric acid in water and stir to dissolve;
S2:将硫酸镁溶于水中,并缓缓煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤;S2: Dissolve magnesium sulfate in water and slowly boil for 10 minutes, then filter after cooling;
S3:将步骤S1配制的溶液和步骤S2配制的溶液混合在一起后,加入防腐剂,搅拌均匀。S3: After mixing the solution prepared in step S1 and the solution prepared in step S2, add a preservative and stir evenly.
该化学测试探头电解液的制备方法简单,便于操作,容易在工业生产中使用,是一种极具商业价值的化学测试探头电解液。The preparation method of the chemical test probe electrolyte is simple, the operation is convenient, and the electrolyte is easy to use in industrial production. The chemical test probe electrolyte is highly commercially valuable.
请参阅图2,本申请还提供一种自动补加电解液装置100,包括容纳组件10、储液桶20、供液泵30、控制器(图未示)和监测组件40。Please refer to FIG. 2 , the present application further provides an automatic
具体地,请继续参阅图2,容纳组件10包括容纳件11和排空阀12,容纳件11用于容纳化学测试探头200以及电解液,排空阀12安装于容纳件11,用于排出容纳组件10内的电解液;储液桶20用于储存电解液;供液泵30分别与容纳件11和储液桶20连通,用于将储液桶20中的电解液传输至容纳件11中;控制器与供液泵30和排空阀12均电性连接,用于控制供液泵30间隔性地向容纳件11内供液,并控制排空阀12的打开与闭合;监测组件40设置于储液桶20内,用于监测储液桶20中的电解液的量。Specifically, please continue to refer to Figure 2. The containing
容纳件11例如是具有一开口的容置液体的瓶子,可以为圆柱体性、漏洞形等。容纳件11用于容纳电解液,该电解液例如是上述的化学测试探头200电解液。容纳件11还用于容纳化学测试探头200,可以理解,在不使用探头200检测时,将探头200通过容纳件11上部的开口放置于容纳件11中,进而使探头200浸泡在容纳件11内的电解液中。容纳件11下端安装有排空阀12,排空阀12例如是蠕动泵等物件,可以将容纳件11中的电解液抽出进而排空容纳件11中的电解液,以便于更换新的电解液。The
储液桶20用于储存未经使用的电解液,在使用过程中,可以先配置大量的电解液,并注入储液桶20中,以备使用。如此,储液桶20不仅可以为容纳件11提供电解液,还起到储存电解液的作用,以减少配置电解液的次数,提高工作效率。The
供液泵30分别与容纳件11和储液桶20连接,用于在容纳件11中的电解液排空后,将储液桶20中的电解液注入容纳件11中,以配合排空阀12工作,来不断更新容纳件11中的电解液。The
控制器与供液泵30和排空阀12均电性连接,用于控制排空阀12打开以将容纳件11中的使用过的电解液排出,然后关闭排空阀12,并控制供液泵30向容纳件11中注入新的电解液。The controller is electrically connected to the
监测组件40设于储液桶20中,用于检测储液桶20中的电解液的量,监测组件40例如是水位检测器等装置。可以理解,监测组件40还可以配置有警报装置,例如警示灯、喇叭等。监测组件40可以监测储液桶20中的上液位和下液位,当向储液桶20中加入电解液到达上液位时,监测组件40可以发出提醒信息,例如闪灯提醒或者鸣笛提醒等;当储液桶20中的电解液使用至下液位时,检测组件也发出提醒,例如闪灯提醒或者鸣笛提醒等。The
在一些实施例中,自动补加电解液装置100还包括远程监测系统(图未示),远程监测系统与控制器和监测组件40均电性连接,用于接收控制器和监测组件40的数据。如此,可以通过远程检测系统实时检测电解液的使用情况。In some embodiments, the automatic
一些实施例提供的自动补加电解液的工作过程大致为:首先,将电解液加入储液桶20中,储液桶20中的电解液最大的量至监测组件40所监测的上液位。然后控制器控制供液泵30从储液桶20中将电解液注入容纳件11内,可以理解,控制器控制供液泵30向容纳件11内注入电解液时,单次注入的量可以依据容纳件11的容积大小进行设定,使供液泵30向容纳件11内单次注入的电解液的量,在容纳件11内放入探头200后可以不会溢出,且可以使探头200浸泡在电解液中。当探头200从容纳件11中移出进行检测时,控制器控制排空阀12打开,将容纳件11中剩余的电解液排出,然后控制器控制排空阀12关闭,容纳件11中剩余的电解液排出后,控制器控制供液泵30工作,从储液桶20中抽出电解液并注入容纳件11中,如此,即可实现自动补加电解液。当储液桶20中的电解液使用到最低液位时,监测组件40发出信号,提醒向储液桶20中补充电解液。The working process of automatic electrolyte replenishment provided in some embodiments is roughly as follows: first, electrolyte is added to the
控制器和监测组件40均与远程检测系统电性连接,远程监测系统可以设置于例如电脑等装置中,控制器和监测组件40会将实时数据上传至远程检测系统,作业人员可以通过远程检测系统查看控制器和监测组件40的工作状态,以及历史记录等,便于作业人员及时了解自动补加电解液装置100的工作状态。The controller and the
本申请实施例提供的自动补加电解液装置100,自通过容纳件11容纳电解液和化学测试探头200,通过排空阀12可以将容纳件11中的电解液排出,通过供液泵30可以将储液桶20中的电解液传输至容纳件11内,通过控制器可控制排空阀12和供液泵30工作,以排空容纳件11中的电解液或向容纳件11中加入电解液,通过检测组件可以实时检测容纳件11中的电解液的量。如此,可以实现监控容纳件11中的电解液的量以及自动补充或更换容纳件11中的电解液。The automatic
下面将结合实施例对本发明的方案进行解释。本领域技术人员将会理解,下面示例仅用于解释本发明,而不能理解为对本发明的限制。除另有交待,以下实施例中涉及的未特别交待的试剂、软件及仪器,都是常规市售产品或者开源的。The scheme of the present invention will be explained below in conjunction with the embodiments. It will be understood by those skilled in the art that the following examples are only used to explain the present invention and cannot be construed as limiting the present invention. Unless otherwise stated, the reagents, software and instruments not specifically stated in the following embodiments are all conventional commercial products or open source.
实施例1Example 1
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例2Example 2
称量氯化钠7.5g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 7.5 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例3Example 3
称量氯化钠15g,硼5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 15 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boron, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例4Example 4
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸2.5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 2.5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例5Example 5
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸7.5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 7.5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例6Example 6
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁700g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 700 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water, then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例7Example 7
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁800g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 800 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water, then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入75mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 75mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例8Example 8
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入50mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 50mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
实施例9Example 9
称量氯化钠10g,硼酸5g,并溶于500mL蒸馏水中,搅拌溶解。Weigh 10 g of sodium chloride and 5 g of boric acid, dissolve them in 500 mL of distilled water, and stir to dissolve.
称量硫酸镁750g,并溶于1000mL蒸馏水中,然后加热煮沸10分钟,冷却后过滤。Weigh 750 g of magnesium sulfate and dissolve it in 1000 mL of distilled water. Then heat and boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter.
将上述配制好的氯化钠和硼酸溶液与硫酸镁溶液转入一2.5L标液桶中,再加入100mL环十二烷基丙醇充分混合,然后加入蒸馏水至标液桶液位线,静置10分钟。Transfer the prepared sodium chloride and boric acid solutions and magnesium sulfate solution into a 2.5L standard solution barrel, add 100mL of cyclododecyl propanol and mix thoroughly, then add distilled water to the liquid level line of the standard solution barrel and let it stand for 10 minutes.
对比例1Comparative Example 1
3%的氯化钾溶液。3% potassium chloride solution.
对比例2Comparative Example 2
2%的氯化钾溶液。2% potassium chloride solution.
对比例3Comparative Example 3
1%的氯化钾溶液。1% potassium chloride solution.
对比例4Comparative Example 4
2%的氯化钾与柠檬酸混合溶液。2% potassium chloride mixed with citric acid solution.
对比例5Comparative Example 5
2%的氯化钾与抗氧剂混合溶液,抗氧剂例如采用碳酸钙、乙二胺四乙酸二钠等。A 2% potassium chloride mixed solution with an antioxidant, wherein the antioxidant is, for example, calcium carbonate, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate, or the like.
对比例6Comparative Example 6
2%的氯化钾与苯甲酸钠混合溶液。2% potassium chloride and sodium benzoate mixed solution.
对比例7Comparative Example 7
2%的氯化钾与5%的氢氟酸混合溶液。A solution of 2% potassium chloride and 5% hydrofluoric acid.
对比例8Comparative Example 8
双氧水溶液。Hydrogen peroxide solution.
对比例9Comparative Example 9
蒸馏水。Distilled water.
对比例10Comparative Example 10
0.5%的氯化钠溶液。0.5% sodium chloride solution.
对比例11Comparative Example 11
0.5%的氯化钠和0.1%的高锰酸钾混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride and 0.1% potassium permanganate.
对比例12Comparative Example 12
0.5%的氯化钠和0.2%的硼酸混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride and 0.2% boric acid.
对比例13Comparative Example 13
0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及5%硫酸钠混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 5% sodium sulfate.
对比例14Comparative Example 14
0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及15%硫酸镁混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 15% magnesium sulfate.
对比例15Comparative Example 15
0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及30%硫酸镁混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 30% magnesium sulfate.
对比例16Comparative Example 16
0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸、30%硫酸镁以及2%脱氢乙酸钠混合溶液。A mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid, 30% magnesium sulfate and 2% sodium dehydroacetate.
本申请将化学测试探头放入实施例1-5制备的溶液中进行测试,同时还将化学测试探头放入对比例1-16的溶液中进行对比实验,结果如表1和表2所示。The present application puts the chemical test probe into the solution prepared in Examples 1-5 for testing, and also puts the chemical test probe into the solution prepared in Comparative Examples 1-16 for comparative experiments. The results are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
表1.实施例1-9制备的电解液对探头的保护效果Table 1. Protection effect of the electrolytes prepared in Examples 1-9 on the probe
表2.对比例1-16溶液对探头的保护效果Table 2. Protection effect of solutions of comparative examples 1-16 on the probe
由表1中的实验结果可知,无机盐即氯化钠为7.5g~15g、硼酸为2.5g~7.5g、硫酸镁为700g~800g以及环十二烷基丙醇50mL~100mL,与1500mL毫升水所配制电解液,不易结晶,保存时间长,有效期为90天,且探头无腐蚀现象。转换为重量百分比,则电解液的成分由0.3%~0.6%的无机盐、25%~30%的硫酸镁、0.1%~0.6%的硼酸、2%~5%的防腐剂以及蒸馏水组成时,不易结晶,且能够有效保护探头,保存时间长。From the experimental results in Table 1, it can be seen that the electrolyte prepared by inorganic salt, i.e., sodium chloride, is 7.5g-15g, boric acid is 2.5g-7.5g, magnesium sulfate is 700g-800g, and cyclododecyl propanol is 50mL-100mL, and 1500mL of water is not easy to crystallize, has a long shelf life, is valid for 90 days, and the probe has no corrosion. Converted to weight percentage, the electrolyte is composed of 0.3%-0.6% inorganic salt, 25%-30% magnesium sulfate, 0.1%-0.6% boric acid, 2%-5% preservative and distilled water, is not easy to crystallize, can effectively protect the probe, and has a long shelf life.
同时,根据表2中的实验结果,其中,对比例1-3为氯化钾溶液,当单纯使用氯化钾溶液时,易产生结晶,且探头有轻微氧化现象。对比例2和对比例3为降低氯化钾的浓度后进行实验,其结果仍有结晶现象和探头氧化现象发生,与对比例1的区别仅在于发生结晶的时间有所延长。因此,由对比例1-3可知,仅降低氯化钾的浓度,不能达到电解液不结晶的目的。At the same time, according to the experimental results in Table 2, among them, Comparative Examples 1-3 are potassium chloride solutions. When potassium chloride solutions are used alone, crystallization is easy to occur, and the probe has a slight oxidation phenomenon. Comparative Examples 2 and Comparative Examples 3 are experiments conducted after reducing the concentration of potassium chloride. The results still show crystallization and probe oxidation. The only difference from Comparative Example 1 is that the time for crystallization to occur is extended. Therefore, it can be seen from Comparative Examples 1-3 that only reducing the concentration of potassium chloride cannot achieve the purpose of preventing the electrolyte from crystallizing.
对比例4-7为在氯化钾溶液中添加抑制剂的实验,其中,抑制剂采用了柠檬酸、抗氧剂、苯甲酸钠以及氢氟酸。当在氯化钾溶液中加入柠檬酸时,电解液无结晶出现,但是探头仍存在氧化现象,不能有效保护探头。当在氯化钾溶液中加入抗氧剂时,抗氧剂例如采用碳酸钙、乙二胺四乙酸二钠等,电解液易结晶有絮状物产生,无法满足需求。当在氯化钾溶液中加入苯甲酸钠时,苯甲酸钠会发生化学反应,析出碳酸钠固体,不能满足本申请的需求。在氯化钾溶液中加入氢氟酸时,由于氢氟酸是一种强酸,会腐蚀探头,导致探头腐蚀严重。因此,由对比例4-7可知,仅在氯化钾溶液中添加抑制剂不能得到既无结晶、又能保护探头的电解液。Comparative Examples 4-7 are experiments in which inhibitors are added to potassium chloride solution, wherein the inhibitors are citric acid, antioxidants, sodium benzoate and hydrofluoric acid. When citric acid is added to potassium chloride solution, no crystallization occurs in the electrolyte, but oxidation still occurs in the probe, and the probe cannot be effectively protected. When an antioxidant is added to potassium chloride solution, the antioxidant is, for example, calcium carbonate, disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, etc., and the electrolyte is easy to crystallize and floccules are produced, which cannot meet the demand. When sodium benzoate is added to potassium chloride solution, sodium benzoate will react chemically and precipitate sodium carbonate solid, which cannot meet the needs of this application. When hydrofluoric acid is added to potassium chloride solution, since hydrofluoric acid is a strong acid, it will corrode the probe, causing serious corrosion of the probe. Therefore, it can be seen from Comparative Examples 4-7 that only adding an inhibitor to potassium chloride solution cannot obtain an electrolyte that is both crystal-free and can protect the probe.
对比例8-16为对电解液成分的验证试验。对比例8采用双氧水作为电解液,虽无结晶,但腐蚀性强,存在安全隐患,探头损坏严重。对比例9采用蒸馏水对探头进行实验,蒸馏水不含电解离子,无法满足探头工作需求。对比例10采用0.5%的氯化钠溶液,在实验过程中,虽无结晶产生,但是溶液内容易产生了细菌,经过多次实验,其保存时间为3天,因此,氯化钠溶液保存时间短,不能满足需求。对比例11采用0.5%的氯化钠和0.1%的高锰酸钾混合溶液,当溶液中加入高锰酸钾后,液体呈紫色,导致探头损坏,且影响探头检测时的准确性,因此不满足需求。对比例12采用0.5%的氯化钠和0.2%的硼酸混合溶液,硼酸可以起到灭菌的作用,避免电解液内产生细菌,但是氯化钠和硼酸的混合溶液会有少量结晶出现,因此也不符合需求。对比例13采用0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及5%硫酸钠混合溶液,溶液内产生了絮状物,导致该混合溶液不能作用保护探头的电解液。对比例14采用0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及15%硫酸镁混合溶液,该混合溶液在十五天后才出现结晶,结晶时间大大延长,但是探头出现被轻微腐蚀的现象,因此也不符合需求。对比例15采用了0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸以及30%硫酸镁混合溶液,与对比例14相比,增加了硫酸镁的浓度,该混合溶液在三十五后才出现结晶,相对于对比例14抑制结晶的效果大大提高,但是探头仍有被轻微腐蚀的现象。对比例16采用0.5%的氯化钠、0.2%的硼酸、30%硫酸镁以及2%脱氢乙酸钠混合溶液,与对比例15相比,增加了脱氢乙酸钠进行防腐蚀,该混合溶液在第九十天后才出现结晶,进一步地提高了抑制结晶的效果,但是探头仍有被腐蚀的现象出现。实施例1-5在对比例16的基础上,将脱氢乙酸钠替换为环十二烷基丙醇,可以起到抑制结晶并保护探头的作用。可以理解,环十二烷基丙醇作为防腐剂使用,也可以替换为例如苯甲酸、苯甲酸钠、山梨酸钾或丙酸钙等。Comparative Examples 8-16 are verification tests for the composition of the electrolyte. Comparative Example 8 uses hydrogen peroxide as the electrolyte. Although there is no crystallization, it is highly corrosive, has safety hazards, and the probe is seriously damaged. Comparative Example 9 uses distilled water to experiment on the probe. Distilled water does not contain electrolytic ions and cannot meet the working requirements of the probe. Comparative Example 10 uses a 0.5% sodium chloride solution. During the experiment, although no crystallization occurs, bacteria are easily produced in the solution. After multiple experiments, its storage time is 3 days. Therefore, the storage time of the sodium chloride solution is short and cannot meet the requirements. Comparative Example 11 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride and 0.1% potassium permanganate. When potassium permanganate is added to the solution, the liquid is purple, causing damage to the probe and affecting the accuracy of the probe detection, so it does not meet the requirements. Comparative Example 12 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride and 0.2% boric acid. Boric acid can play a sterilizing role and avoid bacteria in the electrolyte, but a small amount of crystals will appear in the mixed solution of sodium chloride and boric acid, so it does not meet the requirements. Comparative Example 13 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 5% sodium sulfate. Floccules are produced in the solution, which makes the mixed solution unable to act as an electrolyte to protect the probe. Comparative Example 14 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 15% magnesium sulfate. The mixed solution does not crystallize until fifteen days later, and the crystallization time is greatly extended. However, the probe is slightly corroded, so it does not meet the requirements. Comparative Example 15 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid and 30% magnesium sulfate. Compared with Comparative Example 14, the concentration of magnesium sulfate is increased. The mixed solution does not crystallize until thirty-five days later. The effect of inhibiting crystallization is greatly improved compared with Comparative Example 14, but the probe is still slightly corroded. Comparative Example 16 uses a mixed solution of 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.2% boric acid, 30% magnesium sulfate and 2% sodium dehydroacetate. Compared with Comparative Example 15, sodium dehydroacetate is added for corrosion protection. The mixed solution does not crystallize until the 90th day, further improving the effect of inhibiting crystallization, but the probe still corrodes. Based on Comparative Example 16, Examples 1-5 replace sodium dehydroacetate with cyclododecyl propanol, which can inhibit crystallization and protect the probe. It can be understood that cyclododecyl propanol is used as a preservative and can also be replaced by, for example, benzoic acid, sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate or calcium propionate.
对于本领域技术人员而言,显然本申请不限于上述示范性实施例的细节,而且在不背离本申请的精神或基本特征的情况下,能够以其他的具体形式实现本申请。因此,无论从哪一点来看,均应将实施例看作是示范性的,而且是非限制性的,本申请的范围由所附权利要求而不是上述说明限定,因此旨在将落在权利要求的等同要件的含义和范围内的所有变化涵括在本申请内。It is obvious to those skilled in the art that the present application is not limited to the details of the exemplary embodiments described above, and that the present application can be implemented in other specific forms without departing from the spirit or essential features of the present application. Therefore, no matter from which point of view, the embodiments should be regarded as exemplary and non-restrictive, and the scope of the present application is defined by the appended claims rather than the above description, and it is intended that all changes falling within the meaning and scope of the equivalent elements of the claims are included in the present application.
最后应说明的是,以上实施例仅用以说明本申请的技术方案而非限制,尽管参照较佳实施例对本申请进行了详细说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解,可以对本申请的技术方案进行修改或等同替换,而不脱离本申请技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solution of the present application and are not intended to limit it. Although the present application has been described in detail with reference to the preferred embodiments, a person of ordinary skill in the art should understand that the technical solution of the present application may be modified or replaced by equivalents without departing from the spirit and scope of the technical solution of the present application.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211528698.5ACN115980149A (en) | 2022-11-30 | 2022-11-30 | Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211528698.5ACN115980149A (en) | 2022-11-30 | 2022-11-30 | Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115980149Atrue CN115980149A (en) | 2023-04-18 |
Family
ID=85957007
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211528698.5APendingCN115980149A (en) | 2022-11-30 | 2022-11-30 | Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115980149A (en) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4617244A (en)* | 1985-06-24 | 1986-10-14 | Greene Roland M | Additive for electrolyte of lead-acid batteries |
| US4705668A (en)* | 1985-03-27 | 1987-11-10 | Medica Corporation | Electrolyte analyzer |
| US5133856A (en)* | 1984-12-28 | 1992-07-28 | Terumo Kabushiki Kaisha | Ion sensor |
| US5945236A (en)* | 1998-08-10 | 1999-08-31 | Willis; John | Lead-acid battery electrolyte fluid solution additive |
| CN103779621A (en)* | 2014-01-09 | 2014-05-07 | 广州北峻工业材料有限公司 | Service life prolonging liquid of lead-acid storage battery and preparation method thereof |
| CN206832740U (en)* | 2017-06-26 | 2018-01-02 | 湖北华图环境检测技术有限公司 | Water quality testing meter |
| CN114335756A (en)* | 2021-01-11 | 2022-04-12 | 骆驼集团襄阳蓄电池有限公司 | Electrolyte, manufacturing method thereof and lead-acid storage battery prepared from electrolyte |
- 2022
- 2022-11-30CNCN202211528698.5Apatent/CN115980149A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5133856A (en)* | 1984-12-28 | 1992-07-28 | Terumo Kabushiki Kaisha | Ion sensor |
| US4705668A (en)* | 1985-03-27 | 1987-11-10 | Medica Corporation | Electrolyte analyzer |
| US4617244A (en)* | 1985-06-24 | 1986-10-14 | Greene Roland M | Additive for electrolyte of lead-acid batteries |
| US5945236A (en)* | 1998-08-10 | 1999-08-31 | Willis; John | Lead-acid battery electrolyte fluid solution additive |
| CN103779621A (en)* | 2014-01-09 | 2014-05-07 | 广州北峻工业材料有限公司 | Service life prolonging liquid of lead-acid storage battery and preparation method thereof |
| CN206832740U (en)* | 2017-06-26 | 2018-01-02 | 湖北华图环境检测技术有限公司 | Water quality testing meter |
| CN114335756A (en)* | 2021-01-11 | 2022-04-12 | 骆驼集团襄阳蓄电池有限公司 | Electrolyte, manufacturing method thereof and lead-acid storage battery prepared from electrolyte |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 文爱东等: "2020年版《中国药典》配套用书 最新实用药物手册", vol. 1, 31 October 2021, 中国医药科技出版社, pages: 728 - 729* |
| 辽宁省农机局: "拖拉机", 28 February 1982, 辽宁人民出版社, pages: 138* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20120028308A (en) | Disposable catridge for an electrolytic cell | |
| CN209631032U (en) | A kind of integrated device of urea for vehicle solution | |
| CN115980149A (en) | Chemical test probe electrolyte, preparation method and automatic electrolyte replenishment device | |
| JPH11300359A (en) | Ice having bactericidal effect and its production | |
| US11781233B2 (en) | Copper oxide solid for use in plating of a substrate, method of producing the copper oxide solid, and apparatus for supplying a plating solution into a plating tank | |
| CN103390771A (en) | Battery electrolyte blending system | |
| CN102730635B (en) | Method, device and composition for preparing hydrogen suitable for civil use | |
| CN206832740U (en) | Water quality testing meter | |
| CN218115607U (en) | Recycling system of caustic soda evaporation condensate water | |
| CN211718070U (en) | A small-size salt fog testing machine for high strength spring production | |
| CN215894335U (en) | Hydrogen sulfide gas supply device and test system | |
| US20070240782A1 (en) | System and method for preparing a flowable mixture for a battery | |
| CN205353109U (en) | Fluid monitoring station | |
| CN116121787A (en) | Disinfectant fluid preparation device and control method | |
| CN209169339U (en) | A kind of aluminum air battery system | |
| CN212024876U (en) | Circulating water concentrated sulfuric acid dosing system | |
| CN222212381U (en) | Online liquid medicine sampling device and electroplating equipment | |
| CN223023560U (en) | Automatic fluid infusion device and energy storage liquid cooling system | |
| CN219161929U (en) | Salt dissolving device for salt fog test of battery pack | |
| CN223422783U (en) | Electrolyte automatic configuration and supplementing device suitable for water electrolysis hydrogen production equipment | |
| CN119320183A (en) | Source water deoxidization system and deoxidization method | |
| CN221945316U (en) | An online monitoring device for water level of fire water pool in tunnel | |
| CN222636038U (en) | Local corrosion monitoring device for air conditioner water cooling system of nuclear power plant | |
| US12224462B2 (en) | Electrolyte supply system and secondary battery using same | |
| CN217846226U (en) | Device for analyzing and controlling concentration of alcoholic acid in water washing tower |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |