CN115969592A - Vascular implant - Google Patents
Vascular implantDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115969592A CN115969592ACN202211284816.2ACN202211284816ACN115969592ACN 115969592 ACN115969592 ACN 115969592ACN 202211284816 ACN202211284816 ACN 202211284816ACN 115969592 ACN115969592 ACN 115969592A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- implant
- developing
- mark
- braided
- thickness
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/04—Hollow or tubular parts of organs, e.g. bladders, tracheae, bronchi or bile ducts
- A61F2/06—Blood vessels
- A61F2/07—Stent-grafts
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2/00—Filters implantable into blood vessels; Prostheses, i.e. artificial substitutes or replacements for parts of the body; Appliances for connecting them with the body; Devices providing patency to, or preventing collapsing of, tubular structures of the body, e.g. stents
- A61F2/02—Prostheses implantable into the body
- A61F2/04—Hollow or tubular parts of organs, e.g. bladders, tracheae, bronchi or bile ducts
- A61F2/06—Blood vessels
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F2250/00—Special features of prostheses classified in groups A61F2/00 - A61F2/26 or A61F2/82 or A61F9/00 or A61F11/00 or subgroups thereof
- A61F2250/0058—Additional features; Implant or prostheses properties not otherwise provided for
- A61F2250/0096—Markers and sensors for detecting a position or changes of a position of an implant, e.g. RF sensors, ultrasound markers
- A61F2250/0098—Markers and sensors for detecting a position or changes of a position of an implant, e.g. RF sensors, ultrasound markers radio-opaque, e.g. radio-opaque markers
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Transplantation (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Media Introduction/Drainage Providing Device (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医疗器械技术领域,特别涉及一种血管植入物。The invention relates to the technical field of medical devices, in particular to a blood vessel implant.
背景技术Background technique
微创伤介入是血管动脉瘤的一种治疗手段,通常涉及将血管植入物,例如但不仅限于支架、弹簧圈、动脉瘤封堵装置等,通过输送装置输送至血管中的病变位置,随后,输送杆在实现血管植入物的释放的同时保持植入物设计结构,以起到扩张血管,封堵动脉瘤等治疗作用。Minimally invasive intervention is a treatment for vascular aneurysms, which usually involves delivering vascular implants, such as but not limited to stents, coils, aneurysm occlusion devices, etc., to the lesion in the blood vessel through a delivery device, and then , the delivery rod maintains the design structure of the implant while realizing the release of the vascular implant, so as to expand the blood vessel, seal the aneurysm and other therapeutic effects.
自膨编织支架是血管植入物的一种形式,由于其良好的输送性能被广泛使用。在现有技术中,自膨编织支架仅靠支架两端的显影结构和/或穿插在支架中的显影丝显影,不利于判断支架在弯曲血管内的打开和贴壁状态,同时两端显影结构辨识度一般,也不易判断支架两端打开和贴壁状态,因而降低了手术操作的安全性和准确性,也会增加手术时间。Self-expanding braided stents are a form of vascular implants that are widely used due to their good delivery properties. In the prior art, self-expandable braided stents are visualized only by the developing structures at both ends of the stent and/or the developing wire interspersed in the stent, which is not conducive to judging the opening and adhering state of the stent in the curved blood vessel. In general, it is not easy to judge the opening and adhering state of both ends of the stent, thus reducing the safety and accuracy of the operation and increasing the operation time.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的在于提供一种血管植入物,该血管植入物的两端以及中段在X光下均具有显影性,且血管植入物的两端在X光下的显影性能优于中段的显影性能,以便于操作者判断血管植入物两端的位置和姿态,从而提高手术操作安全性和准确性。The object of the present invention is to provide a kind of vascular implant, the two ends and the middle section of the vascular implant all have developing properties under X-ray, and the developing performance of the two ends of the vascular implant under X-ray is better than that of the middle section. Excellent imaging performance, so that the operator can judge the position and posture of the two ends of the vascular implant, thereby improving the safety and accuracy of the operation.
为实现上述目的,本发明提供的一种血管植入物,包括管状的植入物主体以及位于所述植入物主体轴向两端的第一端和第二端;In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a vascular implant, comprising a tubular implant body and a first end and a second end located at both axial ends of the implant body;
所述植入物主体由至少两根编织丝交错编织而成,至少两根所述编织丝中的至少一根编织丝具有显影性,具有显影性的所述编织丝包括可显影芯丝和包覆在所述可显影芯丝外的套管,所述可显影芯丝的截面积占所述编织丝的总截面积的20%~35%;The implant body is braided by at least two braided filaments interlaced, at least one braided filament in the at least two braided filaments has developability, and the braided filaments with developability include a developable core filament and a sheath A sleeve covering the developable core wire, the cross-sectional area of the developable core wire accounts for 20%-35% of the total cross-sectional area of the braided wire;
所述植入物主体轴向的所述第一端上至少设置有一个第一端显影标记,所述第一端显影标记距所述第一端的最远端部0.1mm~0.9mm,所述植入物主体轴向的所述第二端上至少设置有一个第二端显影标记,所述第二端显影标记距所述第二端的端部端面0.5mm~4.0mm;At least one first-end developing mark is provided on the axial first end of the implant body, and the first-end developing mark is 0.1 mm to 0.9 mm away from the farthest end of the first end. At least one second-end developing mark is provided on the second end in the axial direction of the implant body, and the distance between the second-end developing mark and the end surface of the second end is 0.5 mm to 4.0 mm;
所述第一端显影标记、所述植入物主体和所述第二端显影标记在X光下的辨识度的比值为0.99:(0.32~0.66):1.0,所述血管植入物的材料相对密度为15~25,所述血管植入物在X光方向上的厚度为0.015mm~0.2mm。The ratio of the visibility of the first-end imaging mark, the implant body and the second-end imaging marking under X-ray is 0.99:(0.32-0.66):1.0, the material of the vascular implant The relative density is 15-25, and the thickness of the blood vessel implant in the X-ray direction is 0.015mm-0.2mm.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记和所述植入物主体在以下方面中的至少一种设置为不相同:所选用的不透射线材料以及在X光方向上的厚度;Optionally, at least one of the following aspects of the first-end visible marker and the implant body is set to be different: the selected radiopaque material and the thickness in the X-ray direction;
所述第二端显影标记和所述植入物主体在以下方面中的至少一种设置为不相同:所选用的不透射线材料以及在X光方向上的厚度。The second end-visible marker and the implant body are configured to be different in at least one of the following aspects: the selected radiopaque material and the thickness in the X-ray direction.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记中的不透射线材料与所述编织丝中的不透射线材料相同,所述第一端显影标记在X光方向上的厚度大于所述植入物主体在X光方向上的厚度,或者,Optionally, the radiopaque material in the first-end imaging mark is the same as the radio-opaque material in the braided wire, and the thickness of the first-end imaging marking in the X-ray direction is greater than that of the implant the thickness of the subject in the x-ray direction, or,
所述第一端显影标记中的不透射线材料与所述编织丝中的不透射线材料不相同,所述第一端显影标记在X光方向上的厚度大于、等于或小于所述植入物主体在X光方向上的厚度。The radiopaque material in the first end-visible marker is different than the radiopaque material in the braided filament, and the thickness of the first end-visible marker in the x-ray direction is greater than, equal to, or less than that of the implanted The thickness of the object body in the X-ray direction.
可选的,所述第二端显影标记中的不透射线材料与所述编织丝中的不透射线材料相同,所述第二端显影标记在X光方向上的厚度大于所述植入物主体在X光方向上的厚度,或者,Optionally, the radiopaque material in the second end imaging mark is the same as the radiopaque material in the braided wire, and the thickness of the second end imaging marking in the X-ray direction is greater than that of the implant the thickness of the subject in the x-ray direction, or,
所述第二端显影标记中的不透射线材料与所述编织丝中的不透射线材料不相同,所述第二端显影标记在X光方向上的厚度大于、等于或小于所述植入物主体在X光方向上的厚度。The radiopaque material in the second end visualized marker is different from the radiopaque material in the braided filament, and the thickness of the second end visualized marker in the X-ray direction is greater than, equal to, or less than that of the implanted The thickness of the object body in the X-ray direction.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记和所述第二端显影标记在以下方面中的至少一种设置为不相同:所选用的不透射线材料以及在X光方向上的厚度。Optionally, at least one of the following aspects: the radiopaque material selected and the thickness in the X-ray direction, of the first-end developing mark and the second-end developing mark are set to be different.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记在X光下的辨识度与所述植入物主体在X光下的辨识度的比值为1.80~2.30;和/或,所述第二端显影标记在X光下的辨识度与所述植入物主体在X光下的辨识度的比值为1.82~2.33。Optionally, the ratio of the visibility of the first-end visible mark under X-ray to the visibility of the implant body under X-ray is 1.80-2.30; and/or, the second-end visible mark The ratio of the visibility under X-ray to the visibility of the implant body under X-ray is 1.82-2.33.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记和/或所述第二端显影标记为显影弹簧或显影套管,所述显影弹簧或显影套管的外径为0.003英寸~0.007英寸。Optionally, the developing mark at the first end and/or the developing mark at the second end is a developing spring or a developing sleeve, and the outer diameter of the developing spring or developing sleeve is 0.003 inches to 0.007 inches.
可选的,所述显影弹簧的簧丝包括芯丝和包覆在所述芯丝外的套管,所述显影弹簧的套管具有非显影性,所述显影弹簧的芯丝具有显影性,其中,所述簧丝中的所述芯丝的截面积占所述簧丝的总截面积的20%~35%。Optionally, the spring wire of the developing spring includes a core wire and a sleeve covering the core wire, the sleeve of the developing spring has non-developability, and the core wire of the development spring has developability, Wherein, the cross-sectional area of the core wire in the spring wire accounts for 20%-35% of the total cross-sectional area of the spring wire.
可选的,所述第一端为血管植入物的远端,所述第二端为血管植入物的近端,所述第一端显影标记的数量为至少两个,至少两个所述第一端显影标记在所述血管植入物的圆周方向上均匀排布,所述第二端显影标记的数量为至少两个,至少两个所述第二端显影标记在所述血管植入物的同一圆周方向上均匀排布。Optionally, the first end is the distal end of the vascular implant, the second end is the proximal end of the vascular implant, the number of the first end imaging marks is at least two, at least two of the The first-end developing marks are uniformly arranged in the circumferential direction of the vascular implant, the number of the second-end developing marks is at least two, and at least two of the second-end developing marks are on the vascular implant. Evenly arranged in the same circumferential direction of the incoming objects.
可选的,至少两个所述第一端显影标记在所述血管植入物的不同圆周上排布。Optionally, at least two of the first-end imaging marks are arranged on different circumferences of the vascular implant.
可选的,所述第一端显影标记的数量与所述第二端显影标记的数量不相同。Optionally, the number of developing marks at the first end is different from the number of developing marks at the second end.
在本发明提供的血管植入物中,所述血管植入物包括管状的植入物主体以及位于所述植入物主体轴向两端的第一端和第二端,所述植入物主体由至少两根编织丝交错编织而成,至少两根所述编织丝中的至少一根编织丝具有显影性,即,血管植入物采用具有可显影芯丝的编织丝编织而成,使得血管植入物整体达到良好显影,方便操作者准确判断血管植入物在弯曲血管内的打开和贴壁状态,同时限定了编织丝中的可显影芯丝在该编织丝中的所占比例(截面积)以兼顾编织支架的径向支撑力;此外,血管植入物轴向的第一端上的第一端显影标记和第二端上的第二端显影标记在X光下的辨识度均要大于植入物主体在X光下的辨识度,从而使得血管植入物的两端的显影性能优于植入物中段的显影性能,以方便操作者准确判断血管植入物两端的位置和姿态,及时调整植入物以达到良好的定位、打开、锚定、贴壁等效果,提高手术操作的安全性和准确性;另外,在确保植入物主体、第一端显影标记与第二端显影标记的显影性能的前提下,还兼顾了血管植入物的输送性能和贴壁性,为此,限定了第一端显影标记与第二端显影标记分别在植入物主体轴向第一端与第二端的位置,将第一端显影标记距所述第一端的最远端部控制在0.1mm~0.9mm,并将第二端显影标记距所述第二端的端部端面控制在0.5mm~4.0mm,这样设置,一方面防止第一端显影标记和第二端显影标记与植入物主体在输送过程中发生干涉,减小了血管植入物的推送阻力,另一方面避免植入物主体轴向两端过长,降低了血管植入物释放后在弯曲血管中不贴壁的风险。如此一来,使得本发明的血管植入物具备良好的整体显影性,两端显影标记可准确辨识,同时还兼顾了径向支撑性,也减小了血管植入物的推送阻力,又确保了血管植入物的打开贴壁性能。In the vascular implant provided by the present invention, the vascular implant includes a tubular implant body and a first end and a second end located at two axial ends of the implant body, the implant body It is braided by at least two braided filaments interlaced, and at least one braided filament in the at least two braided filaments has developing property, that is, the vascular implant is braided by braided filaments with a developable core filament, so that the blood vessel The whole implant achieves good development, which is convenient for the operator to accurately judge the open and adherent state of the vascular implant in the curved blood vessel, and at the same time, the proportion of the visualized core filament in the braided filament is limited (cutoff area) to take into account the radial support force of the braided stent; in addition, the visibility of the first-end imaging mark on the axial first end of the vascular implant and the second-end imaging marking on the second end under X-rays is uniform. It should be greater than the visibility of the main body of the implant under X-ray, so that the imaging performance of the two ends of the vascular implant is better than that of the middle section of the implant, so that the operator can accurately judge the position and posture of the two ends of the vascular implant , adjust the implant in time to achieve good positioning, opening, anchoring, and wall-attachment effects, and improve the safety and accuracy of surgical operations; On the premise of the development performance of the development mark, the delivery performance and wall adhesion of the vascular implant are also taken into account. The position of the first end and the second end is controlled within 0.1 mm to 0.9 mm from the farthest end of the first end development mark to the first end, and the end surface of the second end development mark is controlled at the end surface of the second end. 0.5mm to 4.0mm, this setting, on the one hand, prevents the first-end development mark and the second-end development mark from interfering with the main body of the implant during delivery, reduces the push resistance of the vascular implant, and on the other hand avoids The axial ends of the implant body are too long to reduce the risk of non-adherence in curved vessels after release of the vascular implant. In this way, the vascular implant of the present invention has good overall visualization, and the development marks at both ends can be accurately identified, and at the same time, it also takes into account the radial support, reduces the pushing resistance of the vascular implant, and ensures Open and adherent properties of vascular implants.
在本发明提供的血管植入物中,优选血管植入物的第一端上的第一端显影标记在X光下的辨识度与第二端上的第二端显影标记在X光下的辨识度不相同,如所述第一端显影标记在X光下的辨识度与所述植入物主体在X光下的辨识度的比值为1.80~2.30,所述第二端显影标记在X光下的辨识度与所述植入物主体在X光下的辨识度的比值为1.82~2.33,即血管植入物轴向两端的显影性能存在差异,便于医生准确快速地判别血管植入物的远近端,使手术操作更为灵活和方便。In the vascular implant provided by the present invention, it is preferred that the visibility of the first end developing mark on the first end of the vascular implant under X-ray is the same as that of the second end developing mark on the second end under X-ray. The recognizability is not the same, for example, the ratio of the recognizability of the first end-developed mark under X-ray to the recognizability of the implant body under X-ray is 1.80-2.30, and the second-end developed mark is X-ray The ratio of the recognition degree under light to the recognition degree of the implant body under X-ray is 1.82-2.33, that is, there is a difference in the imaging performance at both ends of the axial direction of the vascular implant, which is convenient for doctors to accurately and quickly identify the vascular implant The distal and proximal ends make the operation more flexible and convenient.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明优选实施例的血管植入物的主视图;Fig. 1 is the front view of the vascular implant of the preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图2是对比实施例的血管植入物主体轴向第一端上的第一端显影标记距第一端的最远端部0.95mm时,第一端显影标记与植入物主体输送状态图;Fig. 2 is a diagram of the conveying state of the first end development mark and the implant body when the first end development mark on the first axial end of the vascular implant body of the comparative embodiment is 0.95mm away from the farthest end of the first end ;
图3是对比实施例的血管植入物主体轴向第二端上的第二端显影标记距第二端的端部的所述编织丝的第一个交点形成的端面0.4mm时,第二端显影标记与植入物主体输送状态图;Fig. 3 is when the second end development mark on the second end of the vascular implant main body of the comparative example is 0.4 mm away from the end face formed by the first intersection point of the braided wire at the end of the second end, the second end Visualization mark and implant main body conveying state map;
图4是对比实施例的血管植入物主体轴向第二端上的第二端显影标记距第二端的端部端面4.5mm时,血管植入物在弯曲血管内的释放图,该释放图为体外血管模拟释放后支架贴壁的情况;Fig. 4 is a release view of the vascular implant in a curved blood vessel when the second end development mark on the second axial end of the vascular implant body of the comparative example is 4.5 mm from the end face of the second end. To simulate the situation of the stent sticking to the wall after the release of the blood vessel in vitro;
图5是本发明优选实施例的第一端显影标记与植入物主体在X光下的成像图;Fig. 5 is an imaging diagram of the first end developing mark and the main body of the implant under X-ray according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention;
图6是本发明优选实施例的第二端显影标记与植入物主体在X光下的成像图。Fig. 6 is an imaging diagram of the second end developing mark and the main body of the implant under X-ray according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、优点和特征更加清楚,以下结合附图对本发明作进一步详细说明。需说明的是,附图均采用非常简化的形式且均使用非精准的比例,仅用以方便、明晰地辅助说明本发明实施例的目的。In order to make the purpose, advantages and features of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that all the drawings are in a very simplified form and use imprecise scales, and are only used to facilitate and clearly assist the purpose of illustrating the embodiments of the present invention.
如在本说明书中所使用的,单数形式“一”、“一个”以及“该”包括复数对象,除非内容另外明确指出外。如在本说明书中所使用的,术语“或”通常是以包括“和/或”的含义而进行使用的,除非内容另外明确指出外。术语“多个”通常是以包括两个或两个以上的含义而进行使用的,除非内容另外明确指出外。术语“若干”以包括一个或多个的含义而进行使用的,除非内容另外明确指出外。As used in this specification, the singular forms "a", "an" and "the" include plural referents unless the content clearly dictates otherwise. As used in this specification, the term "or" is generally employed in its sense including "and/or" unless the content clearly dictates otherwise. The term "plurality" is usually used to include two or more meanings, unless the content clearly states otherwise. The term "several" is used in its sense including one or more, unless the content clearly dictates otherwise.
此外,在以下说明中,为了便于描述,使用了“远端”和“近端”;离心脏近的一端称为“近端”,即近心端;离心脏远的一端称为“远端”,即“远心端”。另外,在下文的描述中,给出了大量具体的细节以便提供对本发明更为彻底的理解。然而,对于本领域技术人员而言显而易见的是,本发明可以无需一个或多个这些细节而得以实施。在其他的例子中,为了避免与本发明发生混淆,对于本领域公知的一些技术特征未进行描述。In addition, in the following description, for the convenience of description, "distal end" and "proximal end" are used; the end near the heart is called "proximal end", that is, the proximal end; ", that is, "far-center end". Additionally, in the following description, numerous specific details are given in order to provide a more thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be apparent, however, to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without one or more of these details. In other examples, some technical features known in the art are not described in order to avoid confusion with the present invention.
本发明的核心思想在于提供一种血管植入物,尤其是一种应用于颅内血管疾病治疗的编织支架,该血管植入物通过输送装置递送至目标位置,可用于治疗颅内动脉瘤等血管疾病。可以理解的是,该血管植入物也可以应用于颅内或非颅内的血管动脉瘤、血管扩张、血管栓塞捕获或其他管腔病变的治疗。The core idea of the present invention is to provide a vascular implant, especially a braided stent applied to the treatment of intracranial vascular diseases. The vascular implant is delivered to the target position through a delivery device and can be used to treat intracranial aneurysms, etc. Vascular disease. It can be understood that the vascular implant can also be applied to the treatment of intracranial or non-intracranial vascular aneurysm, vascular dilation, vascular embolism capture or other lumen lesions.
本发明提供的血管植入物,包括管状的植入物主体,所述植入物主体由至少两根编织丝交错编织而成,所述植入物主体具有位于所述植入物主体轴向两端的第一端和第二端。其中至少两根所述编织丝中的至少一根编织丝具有显影性,即至少一根编织丝包含不透射线材料。进一步的,至少两根所述编织丝中的至少一根编织丝包括可显影芯丝和包覆在所述可显影芯丝外面的套管,所述编织丝中的可显影芯丝的材料包括但不限于为铂、铱、金、银、钽和钨中的一种或其合金,所述编织丝中的套管的材料包括但不限于为镍钛合金、镍钛诺、不锈钢、钴铬合金、镍钴合金的一种或多种组合。进一步的,所述编织丝中的可显影芯丝的截面积占所述编织丝的总截面积的20%~35%,且所述套管的外径优选为0.0010英寸~0.0030英寸(0.0254mm~0.0762mm)。The vascular implant provided by the present invention includes a tubular implant body, the implant body is braided by at least two braided wires interlaced, and the implant body has a The first end and the second end at both ends. Wherein at least one of the at least two braided filaments is visualized, ie at least one of the braided filaments comprises a radiopaque material. Further, at least one of the at least two braided filaments includes a developable core filament and a sleeve covering the developable core filament, and the material of the developable core filament in the braided filaments includes But not limited to platinum, iridium, gold, silver, tantalum and tungsten or their alloys, the material of the sleeve in the braided wire includes but not limited to nickel titanium alloy, nitinol, stainless steel, cobalt chromium One or more combinations of alloys and nickel-cobalt alloys. Further, the cross-sectional area of the developable core wire in the braided wire accounts for 20% to 35% of the total cross-sectional area of the braided wire, and the outer diameter of the sleeve is preferably 0.0010 inch to 0.0030 inch (0.0254mm ~0.0762mm).
其中所述血管植入物被配置为两端的X光显影性能优于中段的X光显影性能,也就是说,所述血管植入物被配置为第一端和第二端在X光下的辨识度大于植入物主体在X光下的辨识度。本文中,“辨识度”可以理解为在X光下有人体软组织遮挡下的成像清晰度,辨识度越大,成像清晰度越好,也即显影性能越好。Wherein the vascular implant is configured so that the X-ray imaging performance of both ends is better than that of the middle section, that is to say, the vascular implant is configured such that the first end and the second end are X-ray imaging The visibility is greater than that of the main body of the implant under X-ray. In this article, "recognition" can be understood as the imaging clarity under the occlusion of human soft tissue under X-ray. The greater the recognition, the better the imaging clarity, that is, the better the imaging performance.
对于显影性能,可以理解为,两种物质在X光下的辨识度(即对比度),在X光下的辨识度的计算公式为:As for developing performance, it can be understood as the recognition degree (i.e. contrast) of two substances under X-ray, and the calculation formula of the recognition degree under X-ray is:
SC=1-ecΔμ (1)SC=1-ecΔμ (1)
其中:SC为在X光下,物质A在物质B中的对比度,如编织支架在人体组织中的对比度即为编织支架在X光下的辨识度;c为物质A在X光方向上的厚度;Δμ为物质A和物质B的衰减系数的差值。Wherein: SC is the contrast of material A in material B under X-ray, such as the contrast of woven stent in human tissue is the recognition degree of woven stent under X-ray; c is the thickness of material A in the X-ray direction ; Δμ is the difference between the attenuation coefficients of substance A and substance B.
由上式(1)可以得到,血管植入物在血管中的辨识度的计算公式为:From the above formula (1), it can be obtained that the calculation formula of the recognition degree of the vascular implant in the blood vessel is:
其中:e为自然常数;μ0为人体软组织如肌肉、血液的X光衰减系数;c为血管植入物在X光方向上的厚度;ρk为血管植入物的材料相对密度,等于血管植入物的材料密度与人体组织密度的比值;k为与血管植入物的材料原子序数有关的经验系数,可通过实验获取,具体为:Among them: e is a natural constant; μ0 is the X-ray attenuation coefficient of human soft tissue such as muscle and blood; c is the thickness of the vascular implant in the X-ray direction; ρk is the relative density of the material of the vascular implant, which is equal to the The ratio of the material density of the implant to the density of human tissue; k is an empirical coefficient related to the atomic number of the material of the vascular implant, which can be obtained through experiments, specifically:
其中:Z为血管植入物的材料原子序数。Where: Z is the atomic number of the material of the vascular implant.
根据式(2)和式(3)可知,当血管植入物的材料相对密度ρk越大或血管植入物的材料在X光方向上的厚度c越大时,血管植入物在X光下的辨识度越好,显影性能越好。According to formula (2) and formula (3), when the relative density ρk of the material of the vascular implant is larger or the thickness c of the material of the vascular implant in the X-ray direction is larger, the vascular implant in X The better the visibility under light, the better the developing performance.
因此,已知60kev的光强下,人体软组织如肌肉、血液的X光衰减系数约0.22,人体骨骼的X光衰减系数约0.63,则衰减系数的差值为0.41,而人体颅骨的厚度通常约为10mm,此时,根据公式(1)可知10mm厚的颅骨在人体软组织中的辨识度约为0.33。故,为了使血管植入物在X光下具有良好的辨识度,其在血管中的辨识度也应不小于0.33。为此,血管植入物中各部分的材料相对密度约为15≤ρk≤25,血管植入物的各部分在X光方向上的厚度约为0.015mm≤c≤0.2mm。以此方式,使血管植入物在X光下具有良好的辨识度。Therefore, it is known that under the light intensity of 60kev, the X-ray attenuation coefficient of human soft tissue such as muscle and blood is about 0.22, and the X-ray attenuation coefficient of human bone is about 0.63, so the difference in attenuation coefficient is 0.41, and the thickness of the human skull is usually about At this time, according to the formula (1), it can be seen that the recognition degree of a 10mm thick skull in human soft tissue is about 0.33. Therefore, in order to make the vascular implant have good visibility under X-ray, its visibility in blood vessels should not be less than 0.33. Therefore, the material relative density of each part of the vascular implant is about15≤ρk≤25 , and the thickness of each part of the vascular implant in the X-ray direction is about 0.015mm≤c≤0.2mm. In this way, the vascular implant has good visibility under X-ray.
以下结合附图和若干实施例对本发明提出的血管植入物作进一步的说明。The vascular implant proposed by the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and several embodiments.
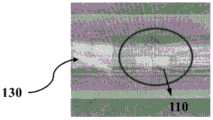
如图1所示,本发明一优选实施例提供一种血管植入物,该血管植入物可为编织支架,该编织支架包括管状的植入物主体110,植入物主体110为由至少两根编织丝140交错编织而成。其中,至少两根所述编织丝140中的至少一根编织丝包括可显影芯丝和包覆在可显影芯丝外面的套管。其中,所述可显影芯丝在X光下具有显影性,所述可显影芯丝的材料包括但不限于为铂、铱、金、银、钽和钨等不透射线材料中的一种或其合金,套管不具有显影性,套管的材料包括但不限于为镍钛合金、镍钛诺、不锈钢、钴铬合金、镍钴合金的一种或多种组合。该编织支架采用显影材料作为编织丝,可以使得编织支架整体的X光显影性更好,方便操作者准确判断血管植入物在弯曲血管内的打开和贴壁状态,提高手术操作安全性和准确性。As shown in Figure 1, a preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a vascular implant, which can be a braided stent, and the braided stent includes a
在一些实施方式中,植入物主体110中所有的编织丝140都采用可显影芯丝和包覆在可显影芯丝外面的套管的双层编织丝(即DFT材料),该编织丝的丝径为0.001英寸~0.003英寸。所述可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的20%~35%。在其他一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的部分编织丝140采用可显影芯丝和包覆在可显影芯丝外面的套管的双层编织丝,其他部分可采用不同的材料和/或不同尺寸的编织丝,例如采用其他丝径范围的双层编织丝,或采用材料为镍钛合金、镍钛诺、不锈钢、钴铬合金、镍钴合金的一种或多种制成的编织丝。采用不同材料和/或不同尺寸的编织丝可以降低成本、增加支架的使用场合和使用范围。In some embodiments, all braided
在一些实施方式中,植入物主体110由12~32根编织丝140交错编织成菱形网状结构,这些编织丝在轴向形成的交点个数为每英寸10~75个。可以理解的是,编织支架在自然状态(即非压缩状态),这些编织丝在轴向形成的交点个数根据支架设计尺寸的不同可以为每英寸10~75个;编织支架在压缩状态,根据处于血管尺寸/位置不同(即压缩度不同),这些编织丝在轴向形成的交点个数可以低至每英寸10个。在较优的实施方式中,植入物主体110为由16~24根编织丝140交错编织成菱形网状结构,例如,16根,20根,24根。这些编织丝在轴向形成的交点个数为每英寸30~55个。In some embodiments, the
为使植入物主体110的边缘具有理想的显影效果,植入物主体110优选具有较高的编织丝数和编织密度,更优选的,编织丝140形成在植入物主体110的金属覆盖率(即编织密度)为8%~25%,使编织支架中段的显影效果好。应理解,本文中所述“中段”指的是位于血管植入物的第一端和第二端之间的编织部分。In order to make the edge of the
需说明的是,对于植入物主体110,其材料应首先满足血管植入物的各项性能如推送力、径向支撑力、兼容性、生物相容性等。在满足血管植入物性能的前提下,可尽量选用密度较大的材料以加强显影性。为了最大化优化血管植入物的性能和显影性,可使用DFT材料,采用可显影芯丝加套管的构造,套管的材料主要满足血管植入物的径向支撑力等各项性能,可显影芯丝的材料满足显影性。在一种较优的实施例中,DFT的外层套管材料选择镍钛合金(Ni-Ti),可显影芯丝的材料选择铂金。除了材料外,编织丝的套管外径和芯丝外径也会影响血管植入物的径向支撑力等各项性能以及显影性。例如:为了使血管植入物有较好的推送性和兼容性,应选择较小的套管外径和较大的芯丝外径;为了使血管植入物有较好的径向支撑力,应选择较大的套管外径和较小的芯丝外径;为了使血管植入物有较好的显影性,应选择较大的套管外径和较大的芯丝外径。It should be noted that, for the
在一些实施方式中,植入物主体110采用钽材料的编织丝140编织而成,其中编织丝140的丝径为0.027mm,ρk=15.9,c=0.027mm,SC=0.34。In some embodiments, the
在另一些实施方式中,植入物主体110采用铂金材料的编织丝140编织而成,其中编织丝140的丝径为0.16mm,其ρk=20.4,c=0.16mm,SC=1.00。In some other embodiments, the
在另一些实施方式中,植入物主体110中的编织丝140均采用双层编织丝(即DFT材料),即包括可显影芯丝和包覆在可显影芯丝外面的套管,在这种情况下,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的20%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.0238mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.0238mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.46。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.052N,实验证明了整个血管植入物的径向支撑性较好。应理解,当编织丝包括可显影芯丝时,在X光方向的厚度即为可显影芯丝的外径。而当编织丝不包括可显影芯丝时,在X光方向的厚度即为编织丝的丝径。In some other embodiments, the
在另一些实施方式中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.0292mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.0292mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.52。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.059N,同样证明了整个血管植入物的径向支撑性较好。In other embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的63%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.042mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.042mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.66。采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.045N,此时,由于可显影芯丝的占比提高,导致血管植入物的径向支撑力有所降低。In a comparative example, the material of the braided wire in the
在另一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的9%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.016mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.34。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.043N,那么,可显影芯丝的占比降低也会对径向支撑性造成影响,导致径向支撑力减小,而且也难以兼顾良好的显影性。In another comparative example, the braided wire in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的34%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.031mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.031mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.55。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.056N,确保了整个血管植入物的径向支撑力,还兼顾了显影性。In some embodiments, the material of the braided wire in the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的17%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.022mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.022mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.43。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.049N,径向支撑力能有所下降。In a comparative example, the material of the braided wire in the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的8%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.015mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.015mm,相对密度=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.32。此时,采用局部抗挤压方式测得的支架径向力为0.041N,显然可显影芯丝的占比较低,显影性不足,而且径向支撑也不足。In a comparative example, the material of the braided wire in the
由以上可见,植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度与支架材料、编织丝的丝径以及可显影芯丝的外径相关。通常,编织丝的丝径或可显影芯丝的外径越大,在X光下的辨识度越好,或者所选用的显影材料的材料相对密度越大,辨识度也越好。而植入物的径向支撑性能则随着可显影芯丝的外径的变化而变化,因此,基于上述实验验证,为了获得良好的显影性的同时兼顾足够的径向支撑力,血管植入物编织丝中的可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的20%~35%。此外,为方便分辨血管植入物的远端和近端位置,两端在X光下的可辨识度应越高越好,选择密度较大的不透射线材料制备显影标记,以及较大尺寸的显影标记,如较大外径的显影环或显影弹簧。It can be seen from the above that the visibility of the
继续参阅图1,血管植入物还包括位于植入物主体110轴向两端的第一端111和第二端112。在一些实施方式中,第一端111为血管植入物的远端,第二端112为血管植入物的近端。其中,第一端111上至少设置一个第一端显影标记120,第二端112上至少设置一个第二端显影标记130。第一端显影标记120和第二端显影标记130的设置可以使得编织支架在手术过程中的显影性能更好,方便操作者准确判断血管植入物两端的位置和姿态,及时调整血管植入物以达到良好的定位、打开、锚定、贴壁等效果,提高手术操作的安全性和准确性。Continuing to refer to FIG. 1 , the vascular implant further includes a
在一些实施方式中,第一端111包括多个回绕编织环1111,多个回绕编织环111周向间隔排布。多个回绕编织环111中的至少一个的圆周上设置至少一个第一端显影标记120。为避免增大编织支架的轴向尺寸或挫伤血管以及增大血管植入物输送过程的推送阻力,该第一端显影标记120设置在回绕编织环111非顶点的其他位置,且第一端显影标记120距第一端111的最远端部0.1mm~0.9mm,即D=0.1mm~0.9mm。第一端111的最远端部由各回绕编织环111的顶点限定,D为第一端显影标记120远离植入物主体110的一端到编织环的顶点的距离。In some embodiments, the
需特别说明的是,以上0.1mm~0.9mm是申请人根据血管植入物在颅内血管内的尺寸以及大量的实验数据进行设定的,以使得本发明的血管植入物在确保显影性和径向支撑力的同时,还能兼顾第一端显影标记120对血管植入物的推送性能和打开贴壁性能的影响。需特别说明的是,如果D小于0.1mm,则血管植入物无法压缩到匹配0.017英寸微导管进行推送,且申请人在研究过程中意外地发现如果D大于0.9mm,则推送阻力很大,此时,第一端显影标记120会与编织支架主体相互干涉,增大编织支架的压缩状态。因此,将D设置在0.1mm~0.9mm的范围内,可减小第一端显影标记120对推送性能的影响,而且尽可能地防止了第一端显影标记120与编织支架(即植入物主体110)的干涉,防止增大编织支架的压缩状态。It should be noted that the above 0.1mm-0.9mm is set by the applicant based on the size of the vascular implant in the intracranial blood vessel and a large number of experimental data, so that the vascular implant of the present invention can ensure the visualization At the same time as the radial support force, the influence of the first-
优选的,第一端显影标记120为3个或4个,分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上。同时,使用3个或4个第一端显影标记120是在保证X光显影性能的同时,尽可能减小压缩后的支架径向尺寸,使得支架可以在小尺寸的输送系统中进行输送。优选的,对于适配0.017英寸的导管管腔,第一端显影标记120(远端)的数量为4个,且可容纳的单个第一端显影标记120的最大外径约为0.0055英寸,此时考虑到第一端显影标记120的周围存在编织丝,故第一端显影标记120的外径比第二端显影标记130的尺寸更小,如果第一端显影标记120的外径大,将使血管植入物难以通过0.017英寸的导管管腔进行输送,或增大输送阻力。Preferably, there are 3 or 4 first-
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.1mm,即D=0.1mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为125gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.15mm,即D=0.15mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为121gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.3mm,即D=0.3mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为115gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.5mm,即D=0.5mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为109gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.8mm,即D=0.8mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为111gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.9mm,即D=0.9mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为118gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,设置为4个,4个第一端显影标记120分别设置在不同的回绕编织环111上,距第一端111的最远端部0.95mm,即D=0.95mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明该推送阻力为238gf,远大于125gf、121gf、115gf、109gf、111gf、118gf。故而,D超过0.9mm后,第一端显影标记120与植入物主体110在输送过程中发生干涉,会增大血管植入物压缩状态的尺寸,增大推送阻力,如图2所示。图2中黑色线框所圈示的部位发生干涉。In a comparative example, the braided wires in the
由以上可见,为避免增大编织支架的轴向尺寸或挫伤血管,第一端显影标记120设置在回绕编织环111非顶点的其他位置,为防止显影标记与植入物主体在输送过程中发生干涉,降低植入物输送过程的推送阻力,优选该第一端显影标记120距第一端最远端部0.1~0.9mm,即D=0.1~0.9mm。It can be seen from the above that in order to avoid increasing the axial size of the braided stent or contusing blood vessels, the first
回绕编织环1111为一根编织丝回编而成的圆弧,圆弧为半圆形、半椭圆形或类半圆形,或者,回绕编织环111为一根编织丝回编后与另一根编织丝粘接或焊接在一起,其中,编织丝回编后的端部绕制成弹簧状的第一端显影标记120后通过粘接或焊接的形式与另一根编织丝连接在一起,又或者,回绕编织环111为一根编织丝回编后与另一根编织丝粘接或焊接在一起,其中编织丝回编后通过第一端显影标记120与另一根编织丝粘接或焊接在一起,其中第一端显影标记120可以为显影弹簧或显影套管。在一优选的实施例中,第一端显影标记120的外径为0.0055英寸,便于适配0.017英寸的导管管腔,第一端显影标记120的材料包括铂金(Pt),铂金的材料密度大,可辨识度好。为了进一步降低加工难度,第一端显影标记120的材料可选铂钨合金(Pt-W)或铂铱合金(Pt-Ir),血管植入物的推送阻力小,而且第一端显影标记120的可辨识度好,同时连接强度高。The revolving
继续参阅图1,第二端112包括多个第一连接部1121,第一连接部1121是由至少两根编织丝140连接在一起形成的无创连接部,编织丝140的连接方式可采用但不限于拧结、胶结、焊接等方式。第一连接部1121为两根编织丝相互缠绕连接在一起后,通过第二端显影标记130粘接或焊接在一起,同时第二端显影标记130的端部使用端面球化焊接的方式进行激光焊接,形成圆滑的封闭端,即形成无创连接部。其中第二端显影标记130可以为显影弹簧或显影套管。在其他实施方式中,第一连接部1121为两根编织丝相互并丝焊接在一起,并丝焊接后,使用第二端显影标记130套在外侧,并在第二端显影标记130的端部使用端面球化焊接的方式进行激光焊接,形成圆滑的封闭端,即形成无创连接部,此时第二端显影标记130亦可为显影弹簧或显影套管。Continuing to refer to FIG. 1, the
特别地,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部的编织丝的第一个交点形成的端面0.5mm~4.0mm,即d=0.5mm~4.0mm。该0.5mm~4.0mm是申请人根据血管植入物在颅内血管内的尺寸以及大量的实验数据进行设定的,以使得本发明的血管植入物在确保整体显影性和径向支撑力的同时,还能兼顾第二端显影标记130对血管植入物的推送性能和打开贴壁性能的影响。In particular, the second
申请人在研究过程中发现,编织支架(血管植入物)释放到曲率半径例如为4.5mm的弯曲血管中,第二端显影标记130会产生不贴壁现象。为了解决该问题,申请人曾尝试多种方案来改善打开贴壁性能,如将镍钛编织丝与DFT复合编织丝混合编织,或降低编织密度,或将图1或图4中的两个相邻第二端显影标记130之间的短波A剪开等,这些方式虽然理论上可行,但是实验结果证明,血管植入物还是打开后不贴壁。进一步地,申请人在研究过程中意外地发现,将第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面设定在上述范围内时,能够防止血管植入物的打开不贴壁。因此,当d为0.5mm~4.0mm时,编织支架释放到曲率半径如为4.5mm的弯曲血管中,第二端显影标记130可以贴壁,确保了血管植入物的打开贴壁性能,由此取得了预料不到的技术效果。申请人在研究过程中还发现,如果d大于4.0mm,编织支架释放到曲率半径为4.5mm的弯曲血管中,第二端显影标记130还是会不贴壁,进而分析造成该问题的原因后发现,由于第二端112采用喇叭口设计,在弯曲段无法顺应血管的曲率,第二端显影标记130就会翘起不贴壁。此外,如果d小于0.5mm,则推送阻力会很大,第二端显影标记130会与编织支架相互干涉,增大编织支架的压缩状态。During the research process, the applicant found that when the braided stent (vascular implant) is released into a curved blood vessel with a radius of curvature such as 4.5 mm, the second-end developed
最终经过大量的实验证明,将d设置在0.5mm~4.0mm时,会改善血管植入物的顺应性,确保血管植入物的打开贴壁性能。本申请文件中,第二端112的端部为第二端编织丝的第一个交点形成的端面,也即,短波A的顶点为第二端端部,d为第二端显影标记130靠近植入物主体110的远端到第二端112的端部的距离。Finally, a large number of experiments have proved that when d is set at 0.5 mm to 4.0 mm, the compliance of the vascular implant will be improved, and the opening and adherence performance of the vascular implant will be ensured. In this application document, the end of the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面0.4mm,即d=0.4mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为246gf,并且观察发现第二端显影标记130在输送过程中与植入物主体110发生干涉,增大了血管植入物压缩状态的尺寸,如图3所示。可以理解,图3中黑色线框所圈示的部位发生干涉。In a comparative example, the braided wires in the
在一对比实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面4.5mm,即d=4.5mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,实验证明,该血管植入物的推送阻力为104gf,且观察发现释放在弯曲血管中部分第二端显影标记130存在贴壁不良,如图4所示。需理解,图4中两个黑色线框所圈出的部位存在贴壁不良的情形。In a comparative example, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面0.5mm,即d=0.5mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,经由实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为112gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面1.5mm,即d=1.5mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,经由实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为109gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面3.0mm,即d=3.0mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,经由实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为113gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
在一些实施例中,植入物主体110中的编织丝均选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm(0.0021英寸),可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的30%,第二端显影标记120的外径为0.0063英寸,设置为4个,4个第二端显影标记130沿第二端112的周向间隔设置,第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面4.0mm,即d=4.0mm,采用0.017英寸微导管推送,经由实验证明,血管植入物的推送阻力为119gf。In some embodiments, the braided wires in the
由以上可见,第二端112上的第二端显影标记130距第二端112的端部端面的距离d与血管植入物在输送过程中的推送阻力以及释放后的贴壁性密切相关。d越大,推送阻力较小且达到最低值,而第二端显影标记130的贴壁性越差;d越小,第二端显影标记130的贴壁性改善,而推送阻力逐渐升高。因此,为了平衡推送阻力和贴壁性,优选第二端112上的第二端显影标记130距第二端112的最远端部0.5mm~4.0mm,即dmm=0.5mm~4.0mm。It can be seen from the above that the distance d between the second
优选的,对于适配0.017英寸的导管管腔,第二端显影标记130(近端)的数量为4个,且可容纳的单个第二端显影标记130的最大外径约为0.0063英寸,此时如果第二端显影标记130的外径大,将使血管植入物难以通过0.017英寸的导管管腔进行输送,或增大输送阻力。在一优选的实施例中,第二端显影标记130的外径为0.0063英寸,便于适配0.017英寸的导管管腔,第二端显影标记130的材料包括铂金(Pt),铂金的材料密度大,可辨识度好。为了进一步降低加工难度,第二端显影标记130的材料可选铂钨合金(Pt-W)或铂铱合金(Pt-Ir),血管植入物的推送阻力小,而且第二端显影标记130的可辨识度好,同时连接强度高。Preferably, for a catheter lumen of 0.017 inches, the number of second-end visible markers 130 (near end) is four, and the maximum outer diameter of a single second-end
本实施例中,所述血管植入物的各部分的在X光下的辨识度不同,尤其是编织支架一端或两端的显影性能优于与支架中段的显影性能,更优选编织支架两端的显影性能也不同。具体地,可通过调整第一端显影标记120、植入物主体110以及第二端显影标记130,该三者的材料、在X光方向上的厚度(或外径),来调整三者在X光下的辨识度。如显影标记采用显影弹簧或显影套管时,可调整显影弹簧或显影套管的材料及比例、外径及壁厚,调整显影标记的辨识度。而对于编织支架,可调整编织支架的材料及比例、编织丝丝径、芯丝的直径,调整植入物主体和两端的辨识度。In this embodiment, the visibility of each part of the vascular implant under X-rays is different, especially the imaging performance of one end or both ends of the braided stent is better than that of the middle section of the stent, more preferably the visualization of both ends of the braided stent Performance is also different. Specifically, by adjusting the first-
在一些实施方式中,第一端显影标记120在X光下的辨识度大于植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度,以便判别编织支架的第一端111在血管中的打开和贴壁状态,从而增强第一端111在X光下的显影性能,使第一端111的辨识度相对于人体组织和植入物主体110较高,在血管中显影清晰且能有效的区别于编织支架的其他部位,方便判断支架的第一端111的位置和形态。第一端显影标记120在X光下的辨识度与植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度的比值优选为1.5~3.1,更优选的,第一端显影标记120在X光下的辨识度与植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度的比值为1.8~2.3,如辨识度比值为1.5、1.8、1.91、2.11、2.3、2.91或3.09。辨识度值越大,显影性能越好。In some embodiments, the visibility of the first end
在一些实施方式中,第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度大于植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度,以便判断编织支架的第二端112在血管中的打开和贴壁状态,从而增强第二端112在X光下的显影性能,使第二端112的辨识度相对于人体组织和编织植入物主体110较高,在血管中显影清晰且能有效的区别于编织支架的其他部位,方便判断支架的第二端112的位置和形态。第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度与植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度的比值优选为1.5~3.2,更优选的,第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度与植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度的比值优选为1.82~2.33,如辨识度比值为1.52、1.82、2.13、2.33、2.94或3.13。In some embodiments, the visibility of the second end
在一优选实施方式中,第一端显影标记120在X光下的辨识度和第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度均大于植入物主体110在X光下的辨识度,使得编织支架的两端显影标记的辨识度相对于人体组织和编织植入物主体110均较高,在血管中显影清晰且能有效的区别于编织支架的其他部位,方便判断支架的两端位置和形态。因此,编织支架两端显影标记的辨识度较高,方便判断编织支架两端形态,达到良好的定位、打开、锚定和贴壁效果,提高手术操作安全性。In a preferred embodiment, the visibility of the first end
进一步的,为了便于判别支架的头尾,优选第一端显影标记120在X光下的辨识度与第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度不相同,使编织支架的两端的显影性能存在显著差异,以达到便于医生操作的显影效果。第一端显影标记120的辨识度和第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值优选为0.8~1.2,更优选的,第一端显影标记120的辨识度和第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.9或0.99。Further, in order to facilitate the identification of the head and tail of the stent, it is preferable that the visibility of the first
在一些实施方式中,植入物主体110所选用的编织丝140的丝径为0.0533mm,且编织丝选用DFT材料,DFT材料中套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝为铂金材料,可显影芯丝的截面积占比为20%,则ρk=20.4,c=0.024mm,辨识度SC=0.46,同时第一端显影标记120的材料为钽,材料相对密度ρk=15.9,其在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm(0.0055英寸),辨识度SC=0.88;同时第二端显影标记130的材料为铂金,材料相对密度ρk=20.4,其在X光方向上的厚度c=0.16mm,辨识度SC=0.98。因此,第一端显影标记120与植入物主体110的辨识度比值0.88/0.46≈1.91ρk,第二端显影标记130与植入物主体110的辨识度之比0.98/0.46≈2.13,且第一端显影标记120、植入物主体110和第二端显影标记130的辨识度比值约为1.91:1:2.13,以及第一端显影标记120和第二端显影标记130的辨识度比值为0.88/0.98≈0.9。In some embodiments, the diameter of the
在另一些实施方式中,植入物主体110所选用的编织丝140的丝径为0.0533mm,且编织丝选用DFT材料,DFT材料中套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝为铂金材料,可显影芯丝的截面积占比为20%,则ρk=20.4,c=0.024mm,SC=0.46,同时第一端显影标记120的材料为铂金,材料相对密度ρk=20.4,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,辨识度SC=0.97,同时第二端显影标记130的材料为铂金,相对密度ρk=20.4,其在X光方向上的厚度c=0.16mm,辨识度SC=0.98。因此,第一端显影标记120与植入物主体110的辨识度比值0.97/0.46≈2.11,第二端显影标记130与植入物主体110的辨识度0.98/0.46≈2.13,且第一端显影标记120、植入物主体110和第二端显影标记130的辨识度比值约为2.11:1:2.13,以及第一端显影标记120与第二端显影标记130的辨识度比值0.97/0.98≈0.99。In other embodiments, the diameter of the
在一对比实施例中,第一端显影标记120的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0055英寸,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.99;第二端显影标记130的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0063英寸,第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=1.0;同时植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的63%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.042mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.042mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.66。该方案中,第一端显影标记120的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为1.5,第二端显影标记130的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为1.52,第一端显影标记120的辨识度、植入物主体110的辨识度以及第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.99:0.66:1.0。In a comparative embodiment, the material of the first
在一对比实施例中,第一端显影标记120的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0055英寸,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.99;第二端显影标记130的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0063英寸,第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=1.0;同时植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的9%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.016mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.34。该方案中,第一端显影标记120的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为2.91,第二端显影标记130的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为2.94,第一端显影标记120的辨识度、植入物主体110的辨识度以及第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.99:0.34:1.0。In a comparative embodiment, the material of the first
在一些实施方式中,第一端显影标记120的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0055英寸,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.99;第二端显影标记130的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0063英寸,第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=1.0;同时植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的34%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.031mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.031mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.55。该方案中,第一端显影标记120的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为1.8,第二端显影标记130的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为1.82,第一端显影标记120的辨识度、植入物主体110的辨识度以及第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.99:0.55:1.0。In some embodiments, the material of the first-
在一对比实施例中,第一端显影标记120的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0055英寸,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.99;第二端显影标记130的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0063英寸,第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=1.0;同时植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的17%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.022mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.022mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.43。该方案中,第一端显影标记120的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为2.3,第二端显影标记130的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为2.33,第一端显影标记120的辨识度、植入物主体110的辨识度以及第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.99:0.43:1.0。In a comparative embodiment, the material of the first
在一对比实施方式中,第一端显影标记120的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0055英寸,第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,相对密度=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.99;第二端显影标记130的材料为铂钨合金或铂铱合金,外径为0.0063英寸,第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度c=0.016mm,相对密度=20.4,可辨识度SC=1.0;同时植入物主体110中的编织丝的材料选用DFT材料,套管为镍钛合金,可显影芯丝的材料为铂金,套管外径为0.0533mm,可显影芯丝的截面积占编织丝的总截面积的8%,即可显影芯丝的外径约为0.015mm,此时,可显影芯丝在X光方向上的厚度c=0.015mm,相对密度ρk=20.4,可辨识度SC=0.32。该方案中,第一端显影标记120的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为3.09,第二端显影标记130的辨识度与植入物主体110的辨识度的比值为3.13,第一端显影标记120的辨识度、植入物主体110的辨识度以及第二端显影标记130的辨识度的比值为0.99:0.32:1.0。In a comparative embodiment, the material of the first
本实施例中,第一端显影标记120、植入物主体110和第二端显影标记130在X光下的辨识度的比值优选为0.99:(0.32~0.66):1.0。In this embodiment, the ratio of the visibility of the first-end imaged
在一实施方式中,第一端显影标记120的材料为钽,相对密度ρk=15.9,其在X光方向上的厚度c=0.14mm,辨识度SC=0.88,同时第二端显影标记130的材料为铂金,相对密度ρk=20.4,其在X光方向上的厚度c=0.16mm,辨识度SC=0.98,第一端显影标记120和第二端显影标记130的辨识度之比0.88/0.98≈0.90,此时,第二端显影标记130的显影性能优于第一端显影标记120的显影性能。In one embodiment, the material of the first-
请参考图5,当第一端显影标记120的辨识度高于植入物主体110的辨识度时,通过成像设备所显示的图像中,第一端显影标记120在X光下的成像清晰度显然高于植入物主体110在X光下的成像清晰度,因此,第一端111的辨识度高,使得医生可以方便的判别支架的第一端111的位置和形态。Please refer to FIG. 5 , when the visibility of the first-end developed
请参考图6,当第二端显影标记130的辨识度高于植入物主体110的辨识度时,通过成像设备所显示的图像中,第二端显影标记130在X光下的成像清晰度显然高于植入物主体110在X光下的成像清晰度,因此,第二端112的辨识度高,使得医生可以方便的判别支架的第二端112的位置和形态。Please refer to FIG. 6, when the visibility of the second-end developed
本实施例中,可通过显影弹簧或显影套管制作显影标记。显影弹簧或显影套管的材料包括镍钛合金、镍钛诺、不锈钢、钴铬合金、镍钴合金的一种或多种组合,当然还包括不透射线的显影材料,显影材料包括但不限于为铂、铱、金、银、钽和钨中的一种或其合金。In this embodiment, a developing mark can be made by a developing spring or a developing sleeve. Materials for developing springs or developing sleeves include one or more combinations of nitinol, nitinol, stainless steel, cobalt chromium, nickel cobalt and of course radiopaque developing materials including but not limited to It is one of platinum, iridium, gold, silver, tantalum and tungsten or an alloy thereof.
在一些实施例中,显影弹簧的簧丝丝径为0.0010英寸~0.0020英寸(0.0254mm~0.0508mm),显影弹簧的外径为0.0030英寸~0.0070英寸((0.0762mm~0.1778mm),显影弹簧的轴向长度为0.4mm~1.5mm。在一些实施例中,显影套管的壁厚为0.0010英寸~0.0020英寸,显影套管的外径为0.0030英寸~0.0070英寸,显影套管的轴向长度为0.4mm~0.8mm。In some embodiments, the spring wire diameter of the developing spring is 0.0010 inch-0.0020 inch (0.0254mm-0.0508mm), the outer diameter of the developing spring is 0.0030 inch-0.0070 inch ((0.0762mm-0.1778mm), the developing spring Axial length is 0.4mm~1.5mm.In some embodiments, the wall thickness of developing sleeve is 0.0010 inch~0.0020 inch, and the outer diameter of developing sleeve is 0.0030 inch~0.0070 inch, and the axial length of developing sleeve is 0.4mm~0.8mm.
显影标记不能过长和过短,过长会影响支架的性能,过短则显影效果不好。其中显影弹簧的簧丝可以包括芯丝和包覆在芯丝外面的套管,其中所述簧丝中的芯丝材料包括但不限于为铂、铱、金、银、钽和钨中的一种或其合金,所述簧丝中套管的材料包括但不限于为镍钛合金、镍钛诺、不锈钢、钴铬合金、镍钴合金的一种或多种组合。优选的,所述显影弹簧中的芯丝的截面积占簧丝的总截面积的20%~35%,显影弹簧中套管的外径为0.0010英寸~0.0020英寸。应理解,就显影标记来说,显影弹簧或显影套管的外径就是显影标记在X光方向上的厚度c。The developing mark should not be too long or too short, too long will affect the performance of the stent, and too short will result in poor developing effect. The reed wire of the developing spring may include a core wire and a sleeve covering the core wire, wherein the core wire material in the reed wire includes but is not limited to one of platinum, iridium, gold, silver, tantalum and tungsten The material of the sleeve in the spring wire includes but is not limited to one or more combinations of nickel-titanium alloy, nitinol, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium alloy, and nickel-cobalt alloy. Preferably, the cross-sectional area of the core wire in the developing spring accounts for 20%-35% of the total cross-sectional area of the spring wire, and the outer diameter of the sleeve in the developing spring is 0.0010-0.0020 inch. It should be understood that, as far as the developing mark is concerned, the outer diameter of the developing spring or the developing sleeve is the thickness c of the developing mark in the X-ray direction.
本申请对第一端显影标记120的数量没有特别的要求。在一实施例中,所述第一端显影标记120的数量为1~6个,为了方便判断支架端部的形态,第一端显影标记120的数量优选为3个或4个,并在圆周方向上均匀排布。进一步的,第一端显影标记120在血管植入物的不同圆周上分布,即在轴上错落分层排布,以减小支架压缩尺寸,降低推送阻力。In this application, there is no special requirement on the number of the first
本申请对第二端显影标记130的数量也没有特别的要求。在一实施例中,所述第二端显影标记130的数量为1~6个。为了方便判断支架端部的形态,第二端显影标记130的数量优选为4个或6个,并在同一圆周方向上均匀排布。In this application, there is no special requirement on the number of the second-end developing marks 130 . In one embodiment, the number of the second-
优选的,第一端显影标记120和第二端显影标记130的数量不同,以便区分支架头尾,使手术操作更为方便。在一些实施方式中,第一端显影标记120为3个,第二端显影标记130为4个,在另一些实施方式中,第一端显影标记120为3个,第二端显影标记130为6个。Preferably, the number of the first-
根据本发明实施例提供的技术方案,为了使血管植入物的一端或两端的显影性能优于支架中段的显影性能,在实际加工时,主要调整显影材料(即不透射线材料)和血管植入物在X光方向上的厚度,以此调整相应部分在X光下的辨识度。According to the technical solution provided by the embodiments of the present invention, in order to make the imaging performance of one end or both ends of the vascular implant better than that of the middle section of the stent, during actual processing, the imaging material (that is, the radiopaque material) and the vascular implant should be mainly adjusted. The thickness of the object in the X-ray direction is used to adjust the recognition of the corresponding part under X-ray.
如,当所述第一端显影标记120的辨识度大于植入物主体110的辨识度时,第一端显影标记120和植入物主体110所选用的不透射线材料不相同,或者两者在X光方向上的厚度不相同,又或者不透射线材料和在X光方向上的厚度都不相同;如当所述第二端显影标记130的辨识度大于植入物主体110的辨识度时,第二端显影标记130和植入物主体110所选用的不透射线材料不相同,或者两者在X光方向上的厚度不相同,又或者不透射线材料和在X光方向上的厚度都不相同。For example, when the visibility of the first-end
当所述第一端显影标记120的辨识度大于植入物主体110的辨识度时,所述第一端显影标记120中的不透射线材料与植入物主体110的编织丝中的不透射线材料可以相同,此时,所述第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度大于植入物主体110在X光方向上的厚度,或者,所述第一端显影标记120中的不透射线材料与植入物主体110的编织丝中的不透射线材料不相同,此时,所述第一端显影标记120在X光方向上的厚度大于、等于或小于植入物主体110在X光方向上的厚度都可。When the visibility of the first
同样的,当所述第二端显影标记130的辨识度大于植入物主体110的辨识度时,所述第二端显影标记130中的不透射线材料与植入物主体110的编织丝中的不透射线材料可以相同,所述第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度大于植入物主体110在X光方向上的厚度,或者,所述第二端显影标记130中的不透射线材料与植入物主体110的编织丝中的不透射线材料不相同,所述第二端显影标记130在X光方向上的厚度大于、等于或小于植入物主体110在X光方向上的厚度。Similarly, when the visibility of the second
应理解,显影标记在X光方向上的厚度主要由显影弹簧的外径、壁厚或显影套管的外径及壁厚确定,而植入物主体在X光方向上的厚度主要由编织丝的丝径或芯丝的直径确定。此外,所应理解,不同的显影材料具有不同的材料密度,因此,通过选择相应的显影材料可调整材料相对密度,另外,编织密度(即金属覆盖率)在一定程度上也会影响显影性能,因此,还可进一步调整编织密度来调整植入物主体的显影性能。It should be understood that the thickness of the development mark in the X-ray direction is mainly determined by the outer diameter and wall thickness of the development spring or the outer diameter and wall thickness of the development sleeve, while the thickness of the implant body in the X-ray direction is mainly determined by the braided wire. The wire diameter or the diameter of the core wire is determined. In addition, it should be understood that different developing materials have different material densities, therefore, the relative density of the materials can be adjusted by selecting the corresponding developing materials, and in addition, the weaving density (i.e. metal coverage) will also affect the developing performance to a certain extent, Therefore, the weaving density can be further adjusted to adjust the imaging performance of the implant body.
需特别强调的是,本发明提供的技术方案具有突出的实质性特点,为了达到准确判断血管植入物两端位置的目的,有众多方法提高两端的辨识度,例如提高两端的显影密度或者增加材料显影厚度,但这又会带来推送阻力、打开难以贴壁等问题,另外从技术上来讲,也是较难实现的,尽管可以想到将两端的显影强度设置为高于植入物中段,也需要多角度的考量,同时做到与植入物匹配,需要进行显影标记的尺寸、显影性、个数、推送阻力的验证,这需要大量的临床实验数据才能实现。It should be emphasized that the technical solution provided by the present invention has outstanding substantive features. In order to achieve the purpose of accurately judging the positions of both ends of the vascular implant, there are many methods to improve the recognition of both ends, such as increasing the development density of both ends or increasing the The thickness of the material is developed, but this will bring problems such as push resistance, difficulty in opening and sticking to the wall, and technically speaking, it is also difficult to achieve, although it is conceivable to set the development intensity at both ends higher than that in the middle of the implant. Considering the angle and matching with the implant at the same time, it is necessary to verify the size, developing property, number, and push resistance of the developing marks, which requires a large amount of clinical experiment data to realize.
与现有技术相比,本发明提供的血管植入物的不同部分在X光下的显影性能不同,便于满足不同医生操作条件的需求,便于判断支架在弯曲血管内的打开和贴壁状态,同时一端或两端的显影标记的辨识度高,易于医生判断支架一端或两端的打开和贴壁状态,提高手术操作安全性和手术操作的准确性,并缩短手术时间,提高手术效率和治疗效果。Compared with the prior art, different parts of the vascular implant provided by the present invention have different imaging performances under X-rays, which is convenient to meet the needs of different doctors' operating conditions, and to judge the opening and adhering state of the stent in the curved blood vessel. At the same time, the recognition degree of the developed marks at one end or both ends is high, which is easy for doctors to judge the opening and adhering status of one end or both ends of the stent, improves the safety and accuracy of surgical operation, shortens the operation time, and improves the operation efficiency and treatment effect.
虽然本发明披露如上,但并不局限于此。本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。Although the present invention is disclosed above, it is not limited thereto. Those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications to the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Thus, if these modifications and variations of the present invention belong to the scope of the present invention and its equivalent technology, the present invention also intends to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (11)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2023/124676WO2024083064A1 (en) | 2021-10-15 | 2023-10-16 | Blood vessel implant |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2021112006668 | 2021-10-15 | ||
| CN202111200666.8ACN113633433A (en) | 2021-10-15 | 2021-10-15 | Vascular implant |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115969592Atrue CN115969592A (en) | 2023-04-18 |
Family
ID=78426974
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111200666.8APendingCN113633433A (en) | 2021-10-15 | 2021-10-15 | Vascular implant |
| CN202211284816.2APendingCN115969592A (en) | 2021-10-15 | 2022-10-17 | Vascular implant |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111200666.8APendingCN113633433A (en) | 2021-10-15 | 2021-10-15 | Vascular implant |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (2) | CN113633433A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2024083064A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024083064A1 (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2024-04-25 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Blood vessel implant |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112754584A (en)* | 2021-01-06 | 2021-05-07 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Vascular implant and medical equipment |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101502693A (en)* | 2009-03-27 | 2009-08-12 | 北京天地和协科技有限公司 | Guiding wire |
| CN104487024A (en)* | 2012-03-16 | 2015-04-01 | 麦克柔文绅有限公司 | Stent and stent delivery device |
| CN212234823U (en)* | 2020-06-30 | 2020-12-29 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Blood vessel support |
| CN112754584A (en)* | 2021-01-06 | 2021-05-07 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Vascular implant and medical equipment |
| CN113384383A (en)* | 2021-07-20 | 2021-09-14 | 复旦大学附属中山医院 | Bifurcation guide wire for positioning coronary artery opening position during stent release |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6669722B2 (en)* | 2000-09-22 | 2003-12-30 | Cordis Corporation | Stent with optimal strength and radiopacity characteristics |
| US7810223B2 (en)* | 2007-05-16 | 2010-10-12 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Method of attaching radiopaque markers to intraluminal medical devices, and devices formed using the same |
| WO2009085757A2 (en)* | 2007-12-21 | 2009-07-09 | Cook Incorporated | Radiopaque alloy and medical device made of this alloy |
| EP2803339B1 (en)* | 2010-03-26 | 2016-12-28 | Olympus Corporation | Medical stent |
| EP2651347B1 (en)* | 2010-12-13 | 2021-06-30 | Microvention, Inc. | Stent |
| CN202724037U (en)* | 2012-08-01 | 2013-02-13 | 吕文峰 | Support and conveying system thereof for treating arterial aneurysm |
| US20140277397A1 (en)* | 2013-03-12 | 2014-09-18 | DePuy Synthes Products, LLC | Variable porosity intravascular implant and manufacturing method |
| EP3099274A4 (en)* | 2014-01-29 | 2017-08-09 | Concentric Medical, Inc. | Vascular and bodily duct treatment devices and methods |
| CN203885667U (en)* | 2014-06-06 | 2014-10-22 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Stent |
| CN107427377B (en)* | 2015-01-12 | 2019-09-03 | 微仙美国有限公司 | bracket |
| CN105486703A (en)* | 2015-12-17 | 2016-04-13 | 南车戚墅堰机车车辆工艺研究所有限公司 | Double X-ray negative film radiographing method |
| CN107029306B (en)* | 2016-02-04 | 2020-05-15 | 中国科学院金属研究所 | A marker capable of developing degraded stent under X-ray and preparation method thereof |
| EP3573575A1 (en)* | 2017-05-22 | 2019-12-04 | Boston Scientific Scimed, Inc. | Devices and methods of use with devices having a radiopaque filament |
| CN209548046U (en)* | 2018-02-11 | 2019-10-29 | 南京普微森医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of braided support system |
| CN109498210B (en)* | 2018-11-08 | 2021-01-26 | 深圳市先健畅通医疗有限公司 | Lumen stent |
| CN113329716A (en)* | 2018-11-16 | 2021-08-31 | 微仙美国有限公司 | Radiopaque vascular prosthesis |
| CN113633433A (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2021-11-12 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Vascular implant |
| CN113967116A (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2022-01-25 | 北京泰杰伟业科技有限公司 | Intracranial stent and intracranial stent conveying system |
| CN114287989B (en)* | 2021-12-24 | 2023-12-08 | 珠海通桥医疗科技有限公司 | Blood flow guiding device bracket |
- 2021
- 2021-10-15CNCN202111200666.8Apatent/CN113633433A/enactivePending
- 2022
- 2022-10-17CNCN202211284816.2Apatent/CN115969592A/enactivePending
- 2023
- 2023-10-16WOPCT/CN2023/124676patent/WO2024083064A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101502693A (en)* | 2009-03-27 | 2009-08-12 | 北京天地和协科技有限公司 | Guiding wire |
| CN104487024A (en)* | 2012-03-16 | 2015-04-01 | 麦克柔文绅有限公司 | Stent and stent delivery device |
| CN212234823U (en)* | 2020-06-30 | 2020-12-29 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Blood vessel support |
| CN112754584A (en)* | 2021-01-06 | 2021-05-07 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Vascular implant and medical equipment |
| CN113384383A (en)* | 2021-07-20 | 2021-09-14 | 复旦大学附属中山医院 | Bifurcation guide wire for positioning coronary artery opening position during stent release |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024083064A1 (en)* | 2021-10-15 | 2024-04-25 | 微创神通医疗科技(上海)有限公司 | Blood vessel implant |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2024083064A1 (en) | 2024-04-25 |
| CN113633433A (en) | 2021-11-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2543345B1 (en) | Surgical apparatus for aneurysms | |
| JP6295318B2 (en) | Torque-releasing airway lung volume reduced compression implant structure | |
| EP2836165B1 (en) | Intracorporeal imaging aid (ima) | |
| KR20230127282A (en) | Vascular implants and medical equipment | |
| CN115969592A (en) | Vascular implant | |
| CN113423347B (en) | Vascular Occlusive Devices | |
| JP2017501840A (en) | Biological structure independent deflection device | |
| KR20100015521A (en) | An implant, a mandrel, and a method of forming an implant | |
| JPH06505660A (en) | Improved pulmonary embolism prevention filter and attached positioning attachment kit | |
| CN113413186B (en) | Embolic coil system | |
| CN114287989B (en) | Blood flow guiding device bracket | |
| WO2022042347A1 (en) | Hemangioma occlusion apparatus, hemangioma occlusion and treatment apparatus, and hemangioma occlusion system | |
| CN215874793U (en) | Vascular implant and medical equipment | |
| CN219814416U (en) | Distal embolic protection device | |
| EP4319653B1 (en) | Vaso-occlusive devices | |
| CN110403739A (en) | A guiding device that does not block blood flow | |
| CN218356482U (en) | Blood flow guiding device | |
| CN209032756U (en) | A kind of guiding device of not blocking blood flow | |
| CN114404785A (en) | Percutaneous aortic valve implantation guide wire | |
| WO2022042346A1 (en) | Hemangioma occlusion apparatus, hemangioma occlusion treatment apparatus, and hemangioma occlusion system | |
| CN115887879A (en) | Guide catheter | |
| CN114652494A (en) | Support frame | |
| CN116250885A (en) | Occluder and Closure System | |
| CN114432578A (en) | Adjustable sacculus pipe | |
| CN111084664A (en) | Radiopacity system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |