CN115946846A - Low-speed longitudinal stability augmentation control surface of plane without horizontal tail and plane with control surface - Google Patents
Low-speed longitudinal stability augmentation control surface of plane without horizontal tail and plane with control surfaceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115946846A CN115946846ACN202211659169.9ACN202211659169ACN115946846ACN 115946846 ACN115946846 ACN 115946846ACN 202211659169 ACN202211659169 ACN 202211659169ACN 115946846 ACN115946846 ACN 115946846A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- flaperon
- wing
- aircraft
- lower cover
- cover plate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T50/00—Aeronautics or air transport
- Y02T50/40—Weight reduction
Landscapes
- Toys (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请属于飞机操纵舵面设计领域,特别涉及一种无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面及具有其的飞机。The application belongs to the field of aircraft control rudder design, in particular to a low-speed longitudinal stability-increasing control rudder for an aircraft without a horizontal tail and an aircraft with the same.
背景技术Background technique
无平尾飞机,特别是对于飞翼布局式的飞机,具有较为普遍的低速纵向力矩特性特点,即在飞机达到最大升力系数对应的失速迎角(即升力系数“拐点”)前,纵向力矩系数对迎角的导数逐渐变大,由负值转为正值,也即是纵向力矩系数先出现“拐点”,之后继续上仰值升力系数出现拐点,这期间飞机的纵向稳定性逐渐变小,由静稳定变为中立稳定、静不稳定,如果不采用主动飞控系统,飞机在纵向力矩系数“拐点”之后、升力系数“拐点”之前无法正常安全飞行,而且飞机的相当大的一部分升力系数和迎角将无法使用,飞机的飞行性能难以达到预期。Airplanes without a horizontal tail, especially those with flying wings, have relatively common low-speed longitudinal moment characteristics, that is, before the aircraft reaches the stall angle of attack corresponding to the maximum lift coefficient (that is, the "inflection point" of the lift coefficient), the longitudinal moment coefficient The derivative of the angle of attack becomes larger gradually, and turns from a negative value to a positive value, that is, the longitudinal moment coefficient first appears an "inflection point", and then continues to raise the lift coefficient to an inflection point. During this period, the longitudinal stability of the aircraft gradually decreases, from Static stability becomes neutral stability and static instability. If the active flight control system is not used, the aircraft cannot fly normally and safely after the "inflection point" of the longitudinal moment coefficient and before the "inflection point" of the lift coefficient, and a considerable part of the aircraft's lift coefficient and The angle of attack will be unusable and the flight performance of the aircraft will be difficult to meet expectations.
目前无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳主要采用主动飞控系统的“软”增稳,主动控制系统的“软”增稳利用闭环状态反馈,改变飞机本体的动力学特性,实现对飞机模态特性的调整。主动控制系统的“软”增稳设计,在一定程度上改善了无平尾飞机的稳定性特性,使得无平尾飞机的相对安全、可靠飞行成为可能,但主动控制增稳设计,往往依赖传感器、飞控软件、作动系统、操纵舵面等分系统,整体而言很大程度增加了系统的复杂度,降低了可靠性。同时主动控制增稳设计往往受舵面偏转速率、舵效、偏转权限等条件的约束,一般而言,只是对飞机整体气动特性的“修补”,并不允许较大范围地改变飞机的稳定性特性,防止操纵特性过度降低。At present, the low-speed longitudinal stabilization of aircraft without a horizontal tail mainly adopts the "soft" stabilization of the active flight control system. The "soft" stabilization of the active control system uses closed-loop state feedback to change the dynamic characteristics of the aircraft body and realize the control of the modal characteristics of the aircraft. Adjustment. The "soft" stability enhancement design of the active control system improves the stability characteristics of the aircraft without a horizontal tail to a certain extent, making it possible for the aircraft without a horizontal tail to fly relatively safely and reliably. However, the active control stability enhancement design often relies on sensors, flight The control software, actuation system, control rudder surface and other sub-systems greatly increase the complexity of the system as a whole and reduce the reliability. At the same time, the design of active control stability enhancement is often constrained by conditions such as rudder surface deflection rate, rudder effect, and deflection authority. Generally speaking, it is only a "repair" of the overall aerodynamic characteristics of the aircraft, and does not allow large-scale changes in the stability of the aircraft. characteristics to prevent excessive degradation of handling characteristics.
相对于采用主动飞控系统的“软”增稳,只依靠飞机本体操纵舵面的“硬”增稳的可靠性和安全性更高,在“硬”增稳无法实现所需的稳定性的时候,才不得不采用“硬”增稳和“软”增稳结合的方法或完全“软”增稳的方法。自从有了无平尾飞机以来,人们一直在研究如何能解决其稳定性问题。无平尾飞机“硬”增稳的相关的探索研究一直在开展,但尚未找到“硬”增稳的实现途径和方法,主要的原因是“硬”增稳的约束多、难度大。Compared with the "soft" stabilization of the active flight control system, the reliability and safety of the "hard" stabilization only relying on the control surface of the aircraft body is higher, and the "hard" stabilization cannot achieve the required stability. Sometimes, it is necessary to adopt the method of combining "hard" stabilization and "soft" stabilization or completely "soft" stabilization. Since there has been no horizontal tail plane, people have been studying how to solve its stability problem always. Exploratory research on "hard" stabilization of aircraft without a horizontal tail has been carried out, but no way and method to achieve "hard" stabilization has been found. The main reason is that "hard" stabilization has many constraints and is difficult.
无平尾飞机由于没有平尾,纵向配平主要依靠机翼后缘的简单襟翼、副翼、简单襟副翼等操纵舵面,相对于常规布局飞机,这些操纵舵面离飞机的重心很近,导致纵向配平能力较小、配平导致的升力损失较大,为了实现无平尾飞机的隐身、重量控制、机构简单等综合性能,这就要求采取的“硬”增稳措施需要具备低头力矩增量小、纵向静稳定性增量合适、升力损失小、机构数量尽量不增加或少增加、机构控制简单、隐身影响小、重量增量小等等。Since the aircraft without a horizontal tail has no horizontal tail, the longitudinal trim mainly depends on the control surfaces such as simple flaps, ailerons, and simple flaperons on the trailing edge of the wing. Compared with the aircraft with a conventional layout, these control surfaces are very close to the center of gravity of the aircraft, resulting in The longitudinal trim capability is small, and the lift loss caused by trim is relatively large. In order to achieve the comprehensive performance of the aircraft without a horizontal tail, such as stealth, weight control, and simple mechanism, this requires the "hard" stability enhancement measures to be adopted. Appropriate increase in longitudinal static stability, small lift loss, minimal or no increase in the number of mechanisms, simple mechanism control, small influence of stealth, small weight increase, etc.
发明内容Contents of the invention
为了解决上述技术问题至少之一,本申请设计了一种无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面,通过“硬”增稳措施改善飞机的低速纵向静稳定性。In order to solve at least one of the above-mentioned technical problems, the present application designs a low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface for an aircraft without a horizontal tail, and improves the low-speed longitudinal static stability of the aircraft through "hard" stabilization measures.
本申请第一方面提供了一种无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面,主要包括:The first aspect of the present application provides a low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface for an aircraft without a horizontal tail, which mainly includes:
主翼,所述主翼具有通过主翼后翼梁支撑的上下翼面,主翼后端设置有连接上下翼面的弧形槽;Main wing, the main wing has upper and lower airfoils supported by the rear spar of the main wing, and the rear end of the main wing is provided with an arc-shaped groove connecting the upper and lower airfoils;
襟副翼,其前端设置为弧形面,在所述襟副翼受控相对于主翼偏转时,该弧形面在所述弧形槽内转动;The front end of the flaperon is set as an arc surface, and when the flaperon is controlled to deflect relative to the main wing, the arc surface rotates in the arc groove;
上盖板,后端搭接在襟副翼的前端弧形面的上侧,前端铰接在主翼的上翼面;The upper cover plate, the rear end is lapped on the upper side of the front arc surface of the flaperon, and the front end is hinged on the upper surface of the main wing;
下盖板,包括主翼的下翼面铰接的前下盖板,以及与襟副翼的前端弧形面的下侧固定的后下盖板,前下盖板与后下盖板的另一端相互搭接;The lower cover, including the front lower cover hinged on the lower wing surface of the main wing, and the rear lower cover fixed to the underside of the front end arc surface of the flaperon, the other end of the front lower cover and the rear lower cover are connected to each other overlap;
作动装置,用于驱动上盖板绕其与主翼的铰接点向上转动,以使上盖板与襟副翼之间形成第一通道,同时用于驱动前下盖板绕其与主翼的铰接点向上转动,以使前下盖板与所述襟副翼之间形成第二通道,所述第一通道与所述第二通道形成引导主翼下表面的气流流动至襟副翼的上表面。The actuating device is used to drive the upper cover to rotate upward around its hinge point with the main wing, so that the first channel is formed between the upper cover and the flaperon, and is used to drive the front lower cover around its hinge with the main wing The point is turned upwards so that a second passage is formed between the front lower cover plate and the flaperon, and the first passage and the second passage guide the airflow on the lower surface of the main wing to flow to the upper surface of the flaperon.
优选的是,所述襟副翼能够绕襟副翼铰链点转动,所述襟副翼的襟副翼铰链点位于所述主翼后翼梁后方的第一设定距离处,所述第一设定距离为机翼当地弦长的9%~11%。Preferably, the flaperon can rotate around a flaperon hinge point, the flaperon hinge point of the flaperon is located at a first set distance behind the rear spar of the main wing, and the first set The fixed distance is 9% to 11% of the local chord length of the wing.
优选的是,所述第一设定距离为机翼当地弦长的10%。Preferably, the first set distance is 10% of the local chord length of the wing.
优选的是,所述上盖板通过上盖板铰链点铰接在距离所述主翼后翼梁后方的第二设定距离处,所述第二设定距离为机翼当地弦长的3.5%~4.5%,所述前下盖板通过前下盖板铰链点铰接在主翼的靠近所述主翼后翼梁的位置处,前下盖板与后下盖板的长度比为8:2。Preferably, the upper cover plate is hinged at a second set distance behind the rear spar of the main wing through the hinge point of the upper cover plate, and the second set distance is 3.5% to 3.5% of the local chord length of the wing. 4.5%, the front lower cover is hinged at the position of the main wing near the rear spar of the main wing through the hinge point of the front lower cover, and the length ratio of the front lower cover to the rear lower cover is 8:2.
优选的是,所述上盖板绕其与主翼的铰接点向上转动到最大角度处时,上盖板的后端距襟副翼的上端面的距离为机翼当地弦长的0.5%~1.5%,所述前下盖板绕其与主翼的铰接点向上转动到前下盖板的后端触碰到上盖板。Preferably, when the upper cover plate rotates up to the maximum angle around its hinge point with the main wing, the distance between the rear end of the upper cover plate and the upper end surface of the flaperon is 0.5% to 1.5% of the local chord length of the wing. %, the front lower cover rotates upward around its hinge point with the main wing until the rear end of the front lower cover touches the upper cover.
本申请第二方面提供了一种具有无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面的飞机,所述飞机包括左侧机翼主体及右侧机翼主体,左侧机翼主体后端设置有左侧外襟副翼及左侧内襟副翼,右侧机翼主体后端设置有右侧外襟副翼及右侧内襟副翼,其中,左侧外襟副翼、左侧内襟副翼、右侧外襟副翼及右侧内襟副翼中的至少一个配备有如上所述的无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面。The second aspect of the present application provides an aircraft with a low-speed longitudinal stabilizing steering surface for an aircraft without a horizontal tail. The aircraft includes a left wing main body and a right wing main body. The outer flaperon and the left inner flaperon, and the right outer flaperon and the right inner flaperon are arranged at the rear end of the right wing main body, wherein, the left outer flaperon, the left inner flaperon At least one of the right side outer flaperon and the right side inner flaperon is equipped with the low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface of the non-horizontal aircraft as described above.
优选的是,当飞机处于起飞或着陆状态时,上盖板与前下盖板受控向上偏转,打开第一通道与第二通道,当飞机处于巡航状态时,上盖板与前下盖板不偏转。Preferably, when the aircraft is in the take-off or landing state, the upper cover and the front lower cover are controlled to deflect upwards to open the first passage and the second passage; when the aircraft is in the cruising state, the upper cover and the front lower cover Not deflected.
本申请能够改变飞机的静稳定性,实现纵向静稳定特性的改善,有效降低了飞控系统设计的复杂度,降低飞机舵效要求,增加无尾飞机失速后改出的能力,整体上提高了飞机飞行的可靠性和安全性。This application can change the static stability of the aircraft, realize the improvement of the longitudinal static stability characteristics, effectively reduce the complexity of the design of the flight control system, reduce the requirements for the rudder effect of the aircraft, increase the ability to recover after the tailless aircraft stalls, and improve the overall Reliability and safety of aircraft flight.
附图说明Description of drawings
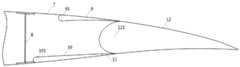
图1是本申请无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面的一优选实施方式的上下盖板收起状态示意图。Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the retracted state of the upper and lower cover plates of a preferred embodiment of the low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface of an aircraft without a horizontal tail according to the present application.
图2是本申请无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面的一优选实施方式的上下盖板打开状态示意图。Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of an open state of the upper and lower cover plates of a preferred embodiment of the low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface of an aircraft without a horizontal tail according to the present application.
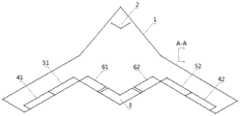
图3是本申请一优选实施例的无平尾飞机结构示意图。Fig. 3 is a schematic structural view of an aircraft without a horizontal tail in a preferred embodiment of the present application.
其中,1-无平尾飞机,2-进气口,3-排气口,41-左侧阻力舵,42-右侧阻力舵,51-左侧外襟副翼,52-右侧外襟副翼,61-左侧内襟副翼,62右侧内襟副翼;Among them, 1-aircraft without flat tail, 2-air intake, 3-exhaust port, 41-left resistance rudder, 42-right resistance rudder, 51-left outer flap aileron, 52-right outer flap aeron Wing, 61-left inner flaperon, 62 right inner flaperon;
7-主翼,8-主翼后翼梁,9-上盖板,91-上盖板铰链点,10-前下盖板,101-前下盖板铰链点,11-后下盖板,12-襟副翼,121-襟副翼铰链点。7-main wing, 8-main wing rear spar, 9-upper cover, 91-hinge point of upper cover, 10-front lower cover, 101-hinge point of front lower cover, 11-rear lower cover, 12- Flaperon, 121 - Flaperon hinge point.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本申请实施的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本申请实施方式中的附图,对本申请实施方式中的技术方案进行更加详细的描述。在附图中,自始至终相同或类似的标号表示相同或类似的元件或具有相同或类似功能的元件。所描述的实施方式是本申请一部分实施方式,而不是全部的实施方式。下面通过参考附图描述的实施方式是示例性的,旨在用于解释本申请,而不能理解为对本申请的限制。基于本申请中的实施方式,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施方式,都属于本申请保护的范围。下面结合附图对本申请的实施方式进行详细说明。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the implementation of the application clearer, the technical solutions in the implementation modes of the application will be described in more detail below with reference to the drawings in the implementation modes of the application. In the drawings, the same or similar reference numerals denote the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The described embodiments are some, but not all, embodiments of the present application. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary and are intended to explain the present application, and should not be construed as limiting the present application. Based on the implementation manners in this application, all other implementation manners obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the scope of protection of this application. Embodiments of the present application will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
本申请第一方面提供了一种无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面,如图1及图2所示,主要包括:The first aspect of the present application provides a low-speed longitudinal stabilization control rudder surface for an aircraft without a horizontal tail, as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, mainly including:
主翼7,所述主翼7具有通过主翼后翼梁8支撑的上下翼面,主翼7后端设置有连接上下翼面的弧形槽;The main wing 7, the main wing 7 has the upper and lower airfoils supported by the main wing
襟副翼12,其前端设置为弧形面,在所述襟副翼12受控相对于主翼7偏转时,该弧形面在所述弧形槽内转动;The front end of the
上盖板9,后端搭接在襟副翼12的前端弧形面的上侧,前端铰接在主翼7的上翼面;The
下盖板,包括主翼7的下翼面铰接的前下盖板10,以及与襟副翼12的前端弧形面的下侧固定的后下盖板11,前下盖板10与后下盖板11的另一端相互搭接;Lower cover plate, comprises the front
作动装置,用于驱动上盖板9绕其与主翼7的铰接点向上转动,以使上盖板9与襟副翼12之间形成第一通道,同时用于驱动前下盖板10绕其与主翼7的铰接点向上转动,以使前下盖板10与所述襟副翼12之间形成第二通道,所述第一通道与所述第二通道形成引导主翼7下表面的气流流动至襟副翼12的上表面。The actuating device is used to drive the
本申请的技术方案采用无平尾飞机简单襟副翼及其前部上下盖板组合设计、上下盖板组合向上不同角度偏转,在简单襟副翼不偏转的情况下,在简单襟副翼和上盖板之间形成气流通道,如图2所示,增加机翼后缘上表面流动能量,在失速迎角之前,消除或减缓机翼后缘上表面流动分离,改善飞机的低速纵向静稳定性。The technical scheme of the present application adopts the simple flaperon of an aircraft without a horizontal tail and the combined design of the upper and lower cover plates at the front, and the combination of the upper and lower cover plates deflects upwards at different angles. Airflow channels are formed between the cover plates, as shown in Figure 2, which increases the flow energy on the upper surface of the trailing edge of the wing, eliminates or slows down the flow separation on the upper surface of the trailing edge of the wing before the stall angle of attack, and improves the low-speed longitudinal static stability of the aircraft .
在一些可选实施方式中,所述襟副翼12能够绕襟副翼铰链点121转动,所述襟副翼12的襟副翼铰链点121位于所述主翼后翼梁8后方的第一设定距离处,所述第一设定距离为机翼当地弦长的9%~11%。In some optional embodiments, the
在一些可选实施方式中,所述第一设定距离为机翼当地弦长的10%。In some optional implementation manners, the first set distance is 10% of the local chord length of the wing.
在一些可选实施方式中,所述上盖板9通过上盖板铰链点91铰接在距离所述主翼后翼梁8后方的第二设定距离处,所述第二设定距离为机翼当地弦长的3.5%~4.5%,所述前下盖板10通过前下盖板铰链点101铰接在主翼7的靠近所述主翼后翼梁8的位置处,前下盖板10与后下盖板11的长度比为8:2。In some optional embodiments, the
该实施例中,可以认为在机翼后翼梁8后方10%左右弦长处设计襟副翼12,在机翼后翼梁8和襟副翼12之间,靠近襟副翼12一侧设计6%弦长左右长度的上盖板和8%弦长左右的前下盖板、2%弦长左右的后下盖板。In this embodiment, it can be considered that the
在一些可选实施方式中,所述上盖板9绕其与主翼7的铰接点向上转动到最大角度处时,上盖板9的后端距襟副翼12的上端面的距离为机翼当地弦长的0.5%~1.5%,所述前下盖板10绕其与主翼7的铰接点向上转动到前下盖板10的后端触碰到上盖板9。In some optional embodiments, when the
本申请利用作动装置,上盖板可绕其前端铰链点向上偏转,前下盖板可绕圈前端铰链点向上偏转,直到与上盖板接触,前下盖板、上盖板偏转后可与襟副翼形成气流通道,后下盖板通过支撑结构固定在机翼后梁上。一般情况下,襟副翼不偏转,如有操纵和配平需要,襟副翼可根据需要进行上偏或下偏。This application utilizes an actuating device. The upper cover can deflect upward around its front hinge point, and the front lower cover can deflect upward around the front hinge point until it contacts the upper cover. After deflecting, the front lower cover and the upper cover can It forms an airflow channel with the flaperon, and the rear lower cover is fixed on the rear spar of the wing through the supporting structure. Under normal circumstances, the flaperon does not deflect. If there is a need for control and trimming, the flaperon can be deflected up or down as required.
本申请提供的简单襟副翼及其前部上下盖板组合设计能够充分利用飞机原有的简单襟副翼及其前部上下盖板机构实现了纵向力矩“拐点”与升力系数“拐点”的同步和纵向静稳定性的改善,而且机构控制简单方便,不影响简单襟副翼原有功能,对飞机的升力系数、重量及隐身性能影响很小,低头力矩增量小,纵向静稳定性增量合适,充分利用了飞机的升力系数和迎角,扩展或提升了飞机的低速飞行性能。The combined design of the simple flaperon and its front upper and lower cover plates provided by this application can make full use of the original simple flaperon of the aircraft and its front upper and lower cover plate mechanism to realize the "inflection point" of the longitudinal moment and the "inflection point" of the lift coefficient. Synchronization and longitudinal static stability are improved, and the mechanism control is simple and convenient, does not affect the original function of the simple flaperon, has little effect on the lift coefficient, weight and stealth performance of the aircraft, the nose-down moment increment is small, and the longitudinal static stability increases The amount is appropriate, making full use of the lift coefficient and angle of attack of the aircraft, and expanding or improving the low-speed flight performance of the aircraft.
相对于采用主动飞控系统的“软”增稳,本发明通过操纵舵面设计,不需要特定权限和舵效占用的操纵舵面主动控制,只需要进行操纵舵面预置偏转,就可改变飞机的静稳定性,实现纵向静稳定特性的改善,有效降低飞控系统设计的复杂度,降低飞机舵效要求,增加无尾飞机失速后改出的能力,整体上提高了飞机飞行的可靠性和安全性。Compared with the "soft" stabilization of the active flight control system, the present invention, through the control surface design, does not require the active control of the control surface occupied by specific authority and rudder effect, and only needs to carry out the preset deflection of the control surface to change The static stability of the aircraft realizes the improvement of the longitudinal static stability characteristics, effectively reduces the complexity of the design of the flight control system, reduces the requirements for the rudder effect of the aircraft, increases the ability of the tailless aircraft to recover after a stall, and improves the reliability of the aircraft flight as a whole and security.
本申请第二方面提供了一种具有无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面的飞机,如图3所示,该飞机为无平尾飞机1,其前部具有进气口2,后部具有排气口3,所述飞机还包括左侧机翼主体及右侧机翼主体,左侧机翼主体后端设置有左侧阻力舵41、左侧外襟副翼51及左侧内襟副翼61,右侧机翼主体后端设置有右侧阻力舵42、右侧外襟副翼52及右侧内襟副翼62,其特征在于,左侧外襟副翼51、左侧内襟副翼61、右侧外襟副翼52及右侧内襟副翼62中的至少一个配备有如上所述的无平尾飞机低速纵向增稳操纵舵面。The second aspect of the present application provides an aircraft with a low-speed longitudinal stability-increasing control rudder for an aircraft without a horizontal tail. As shown in Figure 3, the aircraft is an aircraft 1 without a horizontal tail.
在一些可选实施方式中,当飞机处于起飞或着陆状态时,上盖板9与前下盖板10受控向上偏转,按照图2的方式打开第一通道与第二通道,当飞机处于巡航状态时,上盖板9与前下盖板10不偏转,按照图1的方式收起。In some optional embodiments, when the aircraft is in the take-off or landing state, the
以上所述,仅为本申请的具体实施方式,但本申请的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本申请揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到的变化或替换,都应涵盖在本申请的保护范围之内。因此,本申请的保护范围应以所述权利要求的保护范围为准。The above is only a specific embodiment of the application, but the scope of protection of the application is not limited thereto. Any person familiar with the technical field can easily think of changes or substitutions within the technical scope disclosed in the application. All should be covered within the scope of protection of this application. Therefore, the protection scope of the present application should be determined by the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (7)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211659169.9ACN115946846B (en) | 2022-12-22 | 2022-12-22 | Low-speed longitudinal stability-increasing control surface of plane-tail-free aircraft and aircraft with same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211659169.9ACN115946846B (en) | 2022-12-22 | 2022-12-22 | Low-speed longitudinal stability-increasing control surface of plane-tail-free aircraft and aircraft with same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115946846Atrue CN115946846A (en) | 2023-04-11 |
| CN115946846B CN115946846B (en) | 2025-05-30 |
Family
ID=87287171
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211659169.9AActiveCN115946846B (en) | 2022-12-22 | 2022-12-22 | Low-speed longitudinal stability-increasing control surface of plane-tail-free aircraft and aircraft with same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115946846B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118928753A (en)* | 2024-09-10 | 2024-11-12 | 中国航空工业集团公司沈阳飞机设计研究所 | High lift device and aircraft |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102826215A (en)* | 2012-09-11 | 2012-12-19 | 北京航空航天大学 | Light and small flying-wing manned aircraft with short takeoff and landing capacity |
| US20140061385A1 (en)* | 2012-08-28 | 2014-03-06 | The Boeing Company | Bonded Composite Aircraft Wing |
| US20190291860A1 (en)* | 2016-10-27 | 2019-09-26 | Mono Aerospace Ip Ltd | Vertical take-off and landing aircraft and control method |
| CN110466755A (en)* | 2019-09-20 | 2019-11-19 | 西北工业大学 | It is applicable in the chord length self-adapting stretching formula flapping wing and flapping-wing aircraft of active twist flapping mechanism |
| CN113562162A (en)* | 2021-08-07 | 2021-10-29 | 中国航空工业集团公司沈阳飞机设计研究所 | Method for using wing trailing edge flaperon for improving large attack angle pitching characteristic of airplane |
- 2022
- 2022-12-22CNCN202211659169.9Apatent/CN115946846B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140061385A1 (en)* | 2012-08-28 | 2014-03-06 | The Boeing Company | Bonded Composite Aircraft Wing |
| CN102826215A (en)* | 2012-09-11 | 2012-12-19 | 北京航空航天大学 | Light and small flying-wing manned aircraft with short takeoff and landing capacity |
| US20190291860A1 (en)* | 2016-10-27 | 2019-09-26 | Mono Aerospace Ip Ltd | Vertical take-off and landing aircraft and control method |
| CN110466755A (en)* | 2019-09-20 | 2019-11-19 | 西北工业大学 | It is applicable in the chord length self-adapting stretching formula flapping wing and flapping-wing aircraft of active twist flapping mechanism |
| CN113562162A (en)* | 2021-08-07 | 2021-10-29 | 中国航空工业集团公司沈阳飞机设计研究所 | Method for using wing trailing edge flaperon for improving large attack angle pitching characteristic of airplane |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118928753A (en)* | 2024-09-10 | 2024-11-12 | 中国航空工业集团公司沈阳飞机设计研究所 | High lift device and aircraft |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115946846B (en) | 2025-05-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110316370A (en) | A kind of layout and control method of distributed-power tilting wing aircraft | |
| US20070278354A1 (en) | Slotted high lift aerofoils | |
| CN108128448A (en) | The coaxial tilting rotor wing unmanned aerial vehicle of double shoe formulas and its control method | |
| US12397910B2 (en) | Flight efficiency improving system for compound helicopter | |
| CN110431076B (en) | Tailless airplane | |
| CN103057695A (en) | Combined control surface of tailless airplane | |
| US11655021B2 (en) | Rotary wing aircraft with an asymmetrical rear section | |
| CN115946846A (en) | Low-speed longitudinal stability augmentation control surface of plane without horizontal tail and plane with control surface | |
| US20080230656A1 (en) | Aircraft wings having hinged vanes and aircraft having said wings | |
| CN204507270U (en) | Novel high lift joined wing configuration aircraft | |
| US12049299B2 (en) | Airfoil system | |
| CN103171758A (en) | Lift-rising method of flying wing type airplane | |
| CN113226921B (en) | Aircraft wing | |
| CN204264454U (en) | Novel high lift canard configuration connects rotor aircraft | |
| US12084183B2 (en) | Rotary wing aircraft with an asymmetrical front section | |
| US12103672B2 (en) | Rotary wing aircraft with a stabilizer arrangement | |
| CN110667824A (en) | A variable area rotatable bionic horizontal stabilizer | |
| CN204750567U (en) | High -speed fan wing aircraft | |
| CN218317283U (en) | Trailing edge cracking type wing | |
| CN217945496U (en) | Trailing edge flap structure for improving wing surface flow characteristics of electric vertical take-off and landing aircraft | |
| CN113086170B (en) | Distributed coaxial ducted power system and aircraft comprising same | |
| JP7510279B2 (en) | Composite helicopter | |
| EP4400415A1 (en) | Systems and methods for controlling a variable camber flight control system of an aircraft in a cruise flight phase | |
| JP7752692B2 (en) | Wing assembly for an aircraft | |
| CN212501015U (en) | Small unmanned tilt rotor aircraft overall pneumatic layout |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |