CN115927780A - Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motor - Google Patents
Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115927780A CN115927780ACN202211374026.3ACN202211374026ACN115927780ACN 115927780 ACN115927780 ACN 115927780ACN 202211374026 ACN202211374026 ACN 202211374026ACN 115927780 ACN115927780 ACN 115927780A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- slag
- tapping
- steel
- silicon steel
- molten
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 229910000976Electrical steelInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription44
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription21
- 238000009628steelmakingMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription14
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription35
- 239000002893slagSubstances0.000claimsdescription143
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-NIronChemical compound[Fe]XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription74
- 229910000831SteelInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription59
- 239000010959steelSubstances0.000claimsdescription59
- 238000010079rubber tappingMethods0.000claimsdescription51
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription44
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription44
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000claimsdescription44
- 229910052742ironInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription34
- 239000010936titaniumSubstances0.000claimsdescription28
- 229910052782aluminiumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription22
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-NArgonChemical compound[Ar]XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription18
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NIron oxideChemical compound[Fe]=OUQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription18
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription17
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-NCalciumChemical compound[Ca]OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription16
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-NaluminiumChemical compound[Al]XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription16
- 239000011575calciumSubstances0.000claimsdescription16
- 229910052791calciumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription16
- 238000007670refiningMethods0.000claimsdescription15
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 235000008733Citrus aurantifoliaNutrition0.000claimsdescription12
- 235000011941Tilia x europaeaNutrition0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000004571limeSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000005261decarburizationMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000claimsdescription10
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000claimsdescription10
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 229910052786argonInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription9
- 230000000903blocking effectEffects0.000claimsdescription9
- CYUOWZRAOZFACA-UHFFFAOYSA-Naluminum ironChemical compound[Al].[Fe]CYUOWZRAOZFACA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000claimsdescription8
- 238000006477desulfuration reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000023556desulfurizationEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilicium dioxideChemical compoundO=[Si]=OVYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- AZDRQVAHHNSJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NalumaneChemical compound[AlH3]AZDRQVAHHNSJOQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000007664blowingMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000009826distributionMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- AMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-Lhydroxy(oxo)manganese;manganeseChemical compound[Mn].O[Mn]=O.O[Mn]=OAMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000003647oxidationEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000007254oxidation reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000003723SmeltingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000001590oxidative effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052719titaniumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910000629Rh alloyInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitaniumChemical compound[Ti]RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-Naluminium oxideInorganic materials[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3]PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000003749cleanlinessEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910052681coesiteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000009749continuous castingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910052593corundumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910052906cristobaliteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000009792diffusion processMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000005189flocculationMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000016615flocculationEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000377silicon dioxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000012239silicon dioxideNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910052682stishoviteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910052905tridymiteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- 229910001845yogo sapphireInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription3
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphorusChemical compound[P]OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052698phosphorusInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011574phosphorusSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000013078crystalSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description9
- 230000006698inductionEffects0.000description4
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000description4
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 230000005381magnetic domainEffects0.000description2
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000description2
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000description2
- 229910052717sulfurInorganic materials0.000description2
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910000885Dual-phase steelInorganic materials0.000description1
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulfurChemical compound[S]NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitan oxideChemical compoundO=[Ti]=OGWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000000137annealingMethods0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000470constituentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description1
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000005415magnetizationEffects0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 239000008188pelletSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052761rare earth metalInorganic materials0.000description1
- 150000002910rare earth metalsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 239000011593sulfurSubstances0.000description1
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntitanium oxideInorganic materials[Ti]=OOGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000009489vacuum treatmentMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P10/00—Technologies related to metal processing
- Y02P10/20—Recycling
Landscapes
- Treatment Of Steel In Its Molten State (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及冶金材料领域,尤其涉及一种提高电机用无取向硅钢电磁性的炼钢生产方法。The invention relates to the field of metallurgical materials, in particular to a steelmaking production method for improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel for motors.
背景技术Background technique
无取向硅钢号称钢铁产品中的“工艺品”。由于生产工序较多,它们都能通过影响钢种的微观组织结构,从而对产品的电磁性能产生影响,但是影响机理和影响程度并不相同。冷轧无取向硅钢作为电磁转换载体,是电机铁心制造中的重要功能材料,具有低铁损、高磁感等电磁特性,广泛应用于发电机以及各类电机、E1片等设备的制造。对于无取向硅钢而言,化学成分、晶粒尺寸、晶体结构、析出物等都对硅钢铁损和磁感具有重要的影响。其中,析出物的存在,既表现在对退火过程中再结晶晶粒长大的抑制,进而降低成品晶粒尺寸、恶化铁损,又增加了磁化过程中磁畴转动的能量,从而降低磁感;同时,析出物的存在,还直接影响磁畴壁的移动,增加硅钢材料磁化的难度,降低磁感Ti、S是无取向硅钢第二相的主要组成元素,因此钛、硫元素对第二相析出物的大小、形态以及分布的影响,是无取向硅钢电磁性能的主要影响因素之一,牌号越高,影响越明显。Non-oriented silicon steel is known as the "handicraft" in steel products. Since there are many production processes, they can affect the electromagnetic properties of the product by affecting the microstructure of the steel, but the mechanism and degree of influence are not the same. As the carrier of electromagnetic conversion, cold-rolled non-oriented silicon steel is an important functional material in the manufacture of motor cores. It has low iron loss, high magnetic induction and other electromagnetic properties, and is widely used in the manufacture of generators, various motors, E1 sheets and other equipment. For non-oriented silicon steel, chemical composition, grain size, crystal structure, precipitates, etc. all have important effects on the loss and magnetic induction of silicon steel. Among them, the existence of precipitates not only suppresses the growth of recrystallized grains during the annealing process, but also reduces the grain size of the finished product, worsens the iron loss, and increases the energy of the magnetic domain rotation during the magnetization process, thereby reducing the magnetic induction. At the same time, the existence of precipitates also directly affects the movement of magnetic domain walls, increases the difficulty of magnetizing silicon steel materials, and reduces the magnetic induction. Ti and S are the main constituent elements of the second phase of non-oriented silicon steel. The influence of the size, shape and distribution of phase precipitates is one of the main factors affecting the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel. The higher the grade, the more obvious the influence.
因此,本专利提供一种提高无取向硅钢的电磁性的生产工艺,对提高电机用双相钢组织及性能具有广阔的市场前景和良好的经济效益。Therefore, this patent provides a production process for improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel, which has broad market prospects and good economic benefits for improving the structure and performance of dual-phase steel for motors.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种提高电机用无取向硅钢电磁性的炼钢生产方法,通过控制在生产无取向硅钢炼钢时Ti含量,从而提高无取向硅钢的电磁性能。The object of the present invention is to provide a steelmaking production method for improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel for motors, by controlling the Ti content in the production of non-oriented silicon steel during steelmaking, thereby improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明采用如下技术方案:In order to solve the problems of the technologies described above, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions:
本发明一种提高电机用无取向硅钢电磁性的炼钢生产方法,包括:The invention discloses a steelmaking production method for improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel for motors, comprising:
1).铁水预处理:铁水通过KR脱硫铁水预处理后,要求铁水中[S]≤0.002%、铁水温度≮1300℃、采用气动双重拔渣,减少铁水含渣量,从铁水预处理脱硫后,采取扒渣措施,扒渣后铁水裸露面积达到95%以上;铁水经KR脱硫后,采用吹气赶渣技术,同时在利用扒渣手段,将脱硫后的炉渣95%以上扒去;1).Molten iron pretreatment: After the molten iron is pretreated by KR desulfurization, it is required that the molten iron [S]≤0.002%, the temperature of the molten iron is ≮1300℃, and adopts pneumatic double slag removal to reduce the slag content of the molten iron. After desulfurization from the molten iron pretreatment , taking slag removal measures, after slag removal, the exposed area of molten iron reaches more than 95%; after the molten iron is desulfurized by KR, the technology of blowing slag is adopted, and at the same time, more than 95% of the desulfurized slag is removed by means of slag removal;
2).转炉冶炼:转炉出钢控制,转炉出钢前加挡渣帽,出钢结束采取滑板挡渣技术,减少下渣量;通过分阶段控制转炉氧枪流量、枪位,同时适当调大前期底吹气体流量,保证合理的动力学条件,降低转炉终点氧化性;采用滑板挡渣技术,有效避免了出钢下渣现象;2).Converter smelting: BOF tapping control, slag blocking cap is added before BOF tapping, and sliding plate slag blocking technology is adopted at the end of tapping to reduce the amount of slag dropping; the flow rate and lance position of the BOF oxygen lance are controlled in stages, and at the same time, the slag is appropriately adjusted. The bottom blowing gas flow in the early stage ensures reasonable dynamic conditions and reduces the oxidation at the end of the converter; the sliding plate slag blocking technology is used to effectively avoid the phenomenon of slag dropping when tapping;
于出钢1/3时加入顶渣改质渣料,2/3时加入完毕,出钢开始到出钢2/3时保证氩气量控制在1700Nl/m3,剩余1/3采用小流量控制200-300Nl/m3,直到出钢完毕始终保证氩气的搅拌,促进渣化,保证顶渣改质的完成;Add the top slag modified slag at 1/3 of the time of tapping, and complete the addition at 2/3 of the time. From the beginning of tapping to 2/3 of tapping, ensure that the amount of argon gas is controlled at 1700Nl/m3 , and the remaining 1/3 is controlled at a small flow rate 200-300Nl/m3 , until the steel is tapped, the argon gas is always stirred to promote slag formation and ensure the completion of top slag modification;
3).RH精炼:RH添加合金方式调整:根据转炉终点样,RH采取前期配加磷铁措施,避免脱氧后补加磷铁导致增Ti;RH精炼根据钢水成分情况,在脱碳前期加入磷铁,将磷铁中的Ti氧化,有效避免了钢水增钛现象;合理控制RH脱碳前期游离氧含量,尽量将游离氧控制在400-600ppm,减少脱氧产物Al2O3、SiO2进入炉渣的数量,控制稳定的Ti在钢渣的分配比;生产高牌号无取向硅钢时采用“BOF一RH一CC”工艺路线生产硅钢时,由于不能常规LF精炼那样对钢包顶渣充分改质还原,所以在RH精炼结束以后渣中的FeO和MnO含量较高,钢包顶渣仍然属于高氧化性渣,连铸过程中,渣中的氧大量向钢水传递,与钢中AIs反应产生大量的A12O3夹杂,影响钢水洁净度,严重的还会引起絮流;为了克服现有技术的缺点,提高钢水质量,在RH工序对顶渣进一步改质,具体方法为:通过向钢水表面均匀加入铝铁粉,然后采取钙处理的方式向钢水里喂入钙线,通过钙在钢水表面的剧烈反应,搅动渣层使渣中的氧被表面的铝铁粉和喂入的钙脱除,从而降低渣中的氧含量;之后通过静置一定的时间,使钢中因喂入钙线混入的渣子和氧化物夹杂上浮,从而降低顶渣中氧化铁和氧化锰含量,改善浇注的钢水质量,满足硅钢的生产要求。3). RH refining: RH alloy addition method adjustment: according to the final sample of the converter, RH takes the measure of adding ferrophosphorus in the early stage to avoid adding ferrophosphorus after deoxidation and causing Ti increase; RH refining according to the composition of molten steel, adding phosphorus in the early stage of decarburization Iron, to oxidize Ti in ferrophosphorus, effectively avoiding the phenomenon of titanium increase in molten steel; reasonably control the free oxygen content in the early stage of RH decarburization, try to control the free oxygen at 400-600ppm, reduce the amount of deoxidation products Al2O3 andSiO2 entering the slag, Control the stable distribution ratio of Ti in steel slag; when producing high-grade non-oriented silicon steel, adopt the "BOF-RH-CC" process route to produce silicon steel, because the ladle top slag cannot be fully modified and reduced like conventional LF refining, so RH refining After the end, the content of FeO and MnO in the slag is relatively high, and the ladle top slag is still a highly oxidizing slag. During the continuous casting process, a large amount of oxygen in the slag is transferred to the molten steel, and reacts with Als in the steel to produce a large amount of A12 O3 inclusions. Affect the cleanliness of molten steel, and even cause flocculation in serious cases; in order to overcome the shortcomings of the existing technology and improve the quality of molten steel, the top slag is further modified in the RH process. The specific method is: by adding aluminum and iron powder evenly to the surface of the molten steel, and then Calcium treatment is used to feed calcium wire into molten steel, and through the violent reaction of calcium on the surface of molten steel, the slag layer is stirred to remove the oxygen in the slag by the aluminum iron powder on the surface and the fed calcium, thereby reducing the oxygen in the slag. content; after standing for a certain period of time, the slag and oxide inclusions mixed in the steel due to feeding the calcium wire will float up, thereby reducing the content of iron oxide and manganese oxide in the top slag, improving the quality of poured molten steel, and meeting the production requirements of silicon steel .
进一步的,改质渣料配比:固定石灰的使用量,根据出钢氧含量,进行合成渣加入量调整;调整方法为:终点氧含量高,减少化渣料合成渣的用量,用量配比石灰、合成渣为3.3:1,反之增加合成渣的用量,石灰、合成渣配比为2.5:1,保证出钢过程中石灰全部融化,降低渣中氧化性。Further, the ratio of modified slag: fix the amount of lime used, and adjust the amount of synthetic slag added according to the oxygen content of tapping; the adjustment method is: the oxygen content at the end point is high, reduce the amount of synthetic slag used in the slag material, and the dosage ratio The ratio of lime and synthetic slag is 3.3:1. On the contrary, increase the amount of synthetic slag. The ratio of lime and synthetic slag is 2.5:1 to ensure that the lime is completely melted during the tapping process and reduce the oxidation of slag.
进一步的,顶渣改质:出钢结束后,根据出钢氧含量向钢包中投入铝粒,进行顶渣改质,将渣中氧向钢种扩散能力降低最低;Further, top slag modification: after tapping is finished, put aluminum particles into the ladle according to the tapping oxygen content, carry out top slag modification, and reduce the diffusion ability of oxygen in the slag to the steel grade to the minimum;
出钢完成后,加入低碳覆盖剂,保证顶渣流动性;After tapping is completed, low-carbon covering agent is added to ensure the fluidity of top slag;
最终,转炉供RH钢水目标为:[C]:0.02%~0.05%,[O]:(500~750)×10-6,T=1615~1630℃,炉渣FeO+MnO≤5%。Ultimately, the targets for RH molten steel supply to the converter are: [C]: 0.02%-0.05%, [O]: (500-750)×10-6, T=1615-1630°C, slag FeO+MnO≤5%.
进一步的,铝铁粉加入的重量可以按照以下方式计算:铝铁粉加入量=1.5×54×G×[O]/48/η,G为顶渣重量,[O]为RH脱碳终点时钢水中游离氧的重量百分含量,η为铝铁粉中铝的质量百分含量。Further, the added weight of aluminum and iron powder can be calculated according to the following method: the added amount of aluminum and iron powder=1.5×54×G×[O]/48/η, G is the weight of top slag, and [O] is the end point of RH decarburization The percentage by weight of free oxygen in molten steel, and η is the percentage by mass of aluminum in the aluminum-iron powder.
进一步的,出钢氧含量1000-900ppm时,铝粒加入量为350-400kg;出钢氧含量900-800ppm时,铝粒加入量为250-300kg;;出钢氧含量800-700ppm时,铝粒加入量为150-200kg;出钢氧含量小于700ppm时,铝粒加入量为50-100kg。Further, when the oxygen content of tapping is 1000-900ppm, the amount of aluminum particles added is 350-400kg; when the oxygen content of tapping is 900-800ppm, the amount of aluminum particles added is 250-300kg; The amount of aluminum particles added is 150-200kg; when the oxygen content of tapping is less than 700ppm, the amount of aluminum particles added is 50-100kg.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益技术效果:Compared with prior art, beneficial technical effect of the present invention:
通过优化磷铁添加方式,Ti含量明显降低,钢坯中粗大晶粒增加,产品性能得以提高。本发明的方法实施后硅钢Ti合格率由原来的60%,提高到98.5%,一级品率上升10%硅钢一级品率的提高,增加了产品卖价,每吨提高100元。提高了产品合格率,赢得了用户认可。By optimizing the addition method of ferrophosphorus, the Ti content is significantly reduced, the coarse grains in the billet are increased, and the product performance is improved. After the method of the present invention is implemented, the qualified rate of silicon steel Ti is increased from 60% to 98.5%, and the rate of first-grade silicon steel is increased by 10%. The qualified rate of products has been improved and user recognition has been won.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面结合附图说明对本发明作进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
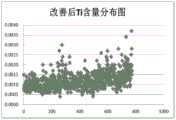
图1为调整前Ti含量分布图;Fig. 1 is the distribution diagram of Ti content before adjustment;
图2为调整后Ti含量分布图。Figure 2 is a distribution diagram of Ti content after adjustment.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
无取向硅钢在炼钢过程中主要从铁水、废钢、炉渣、加入合金中使Ti含量增加,RH真空精炼后离站的Ti含量部分达到了30ppm,RH真空处理后渣中含有一部分钛的氧化物,钙处理操作是会有一部分被还原进入钢液,由于Ti会细化晶粒所以Ti含量的增加严重影响了无取向硅钢的性能。In the steelmaking process of non-oriented silicon steel, the Ti content is mainly increased from molten iron, scrap steel, slag, and alloys. After RH vacuum refining, the Ti content of the off-site part reaches 30ppm. After RH vacuum treatment, the slag contains a part of titanium oxide. , Calcium treatment operation will be part of the reduction into molten steel, because Ti will refine the grain so the increase in Ti content seriously affects the performance of non-oriented silicon steel.
基于这些影响因素考虑,本发明提供一种一种提高电机用无取向硅钢电磁性的炼钢生产方法,其炼钢生产工艺流程为:铁水预处理——转炉冶炼——RH炉外精炼。具体实施方式包括:Based on these influencing factors, the present invention provides a steelmaking production method for improving the electromagnetic properties of non-oriented silicon steel for motors. The steelmaking production process is: molten iron pretreatment—converter smelting—RH external refining. Specific implementation methods include:
1.铁水预处理:铁水通过KR脱硫铁水预处理后,要求铁水中[S]≤0.002%、铁水温度≮1300℃、采用气动双重拔渣,减少铁水含渣量,从铁水预处理脱硫后,采取扒渣措施,扒渣后铁水裸露面积达到95%以上。铁水经KR脱硫后,采用吹气赶渣技术,同时在利用扒渣手段,将脱硫后的炉渣95%以上扒去。1. Molten iron pretreatment: After the molten iron is pretreated by KR desulfurization, it is required that the [S] in the molten iron is ≤0.002%, the temperature of the molten iron is ≮1300°C, and the pneumatic double slag removal is adopted to reduce the slag content of the molten iron. After desulfurization from the molten iron pretreatment, Take slag removal measures, after slag removal, the exposed area of molten iron reaches more than 95%. After the molten iron is desulfurized by KR, the slag removal technology is adopted by blowing air, and at the same time, more than 95% of the desulfurized slag is removed by means of slag removal.
2.转炉冶炼:转炉工序是无取向硅钢生产中非常重要的环节,其连续稳定钢水供应是RH精炼成分及温度的基础保证。由于高性能无取向硅钢要求超低碳,所以必须将转炉终点[C]和[O]含量控制在合理范围内,且[C]、[O]协调一致出钢尤为重要。由于稀土无取向硅钢要求超低硫含量,冶炼必须采用自产废钢及深脱铁水,由于铁水经KR脱硫后温降约15-25℃,铁水温降较大,铁渣少,转炉吹炼过程中出现容易低温“返干”现象,影响终点控制。经过多次试验摸索,转炉制定了硅钢操作控制模型,具体控制如下转炉出钢控制,转炉出钢前加挡渣帽,出钢结束采取滑板挡渣技术,减少下渣量。通过分阶段控制转炉氧枪流量、枪位,同时适当调大前期底吹气体流量,保证合理的动力学条件,降低了转炉终点氧化性。采用滑板挡渣技术,有效避免了出钢下渣现象,具体情况见表1、表2。2. Converter smelting: The converter process is a very important link in the production of non-oriented silicon steel, and its continuous and stable molten steel supply is the basic guarantee for the composition and temperature of RH refining. Since high-performance non-oriented silicon steel requires ultra-low carbon, it is necessary to control the content of [C] and [O] at the end of the converter within a reasonable range, and it is particularly important to coordinate [C] and [O] to tap steel. Since rare earth non-oriented silicon steel requires ultra-low sulfur content, self-produced steel scrap and deep demetalized molten iron must be used for smelting. Since the temperature drop of molten iron is about 15-25°C after KR desulfurization, the temperature drop of molten iron is relatively large, and there is less iron slag. It is easy to "return to dry" phenomenon at low temperature, which affects the control of the end point. After many experiments and explorations, the converter has formulated a silicon steel operation control model. The specific control is as follows: converter tapping control, adding a slag cap before tapping the converter, and adopting a sliding plate slag blocking technology at the end of tapping to reduce the amount of slag. By controlling the oxygen lance flow rate and lance position of the converter in stages, and at the same time appropriately increasing the bottom blowing gas flow rate in the early stage, reasonable kinetic conditions are ensured, and the oxidation at the end of the converter is reduced. The sliding plate slag blocking technology is adopted to effectively avoid the phenomenon of slag dropping after tapping. See Table 1 and Table 2 for details.
表1氧流量调整前情况Table 1 Situation before oxygen flow adjustment
表2氧流量调整好情况Table 2 Oxygen flow adjustment status
于出钢1/3时加入顶渣改质渣料,2/3时加入完毕,出钢开始到出钢2/3时保证氩气量控制在1700Nl/m3,剩余1/3采用小流量控制200-300Nl/m3,直到出钢完毕始终保证氩气的搅拌,促进渣化,保证顶渣改质的完成。Add the top slag modified slag at 1/3 of the tapping time, complete the addition at 2/3 of the tapping time, ensure that the argon gas volume is controlled at 1700Nl/m3 from the beginning of tapping to 2/3 of tapping, and use small flow control for the remaining 1/3 at 200 -300Nl/m3, argon stirring is always ensured until the completion of tapping to promote slag formation and ensure the completion of top slag modification.
(1)改质渣料配比(1) Ratio of modified slag
固定石灰的使用量,根据出钢氧含量,进行合成渣加入量调整。调整方法为:终点氧含量高,减少化渣料合成渣的用量,用量配比石灰、合成渣为3.3:1,反之增加合成渣的用量,石灰、合成渣配比为2.5:1,保证出钢过程中石灰全部融化,降低渣中氧化性。The usage amount of fixed lime is adjusted according to the oxygen content of tapping, and the addition amount of synthetic slag is adjusted. The adjustment method is: the oxygen content at the end point is high, reduce the amount of synthetic slag used as the slag material, and the ratio of lime and synthetic slag is 3.3:1; on the contrary, increase the amount of synthetic slag, and the ratio of lime and synthetic slag is 2.5:1 to ensure the output During the steel process, the lime is completely melted to reduce the oxidation in the slag.
(2)出钢氩气控制(2) Tapping argon control
由于出钢1/3时加入渣料,2/3时加入完毕,出钢开始到出钢2/3时保证氩气量控制在1700Nl/m3,剩余1/3采用小流量控制200-300Nl/m3,直到出钢完毕始终保证氩气的搅拌,促进渣化,促进顶渣改质的完成。Since the slag is added at 1/3 of the tapping, and the addition is completed at 2/3, the amount of argon gas is controlled at 1700Nl/m3 from the beginning of tapping to 2/3 of tapping, and the remaining 1/3 is controlled by a small flow rate of 200-300Nl/m3 , Stirring of argon gas is always ensured until the completion of tapping to promote slag transformation and the completion of top slag modification.
(3)顶渣改质(3) Top slag modification
出钢结束后,根据出钢氧含量向钢包中投入铝粒,进行顶渣改质,将渣中氧向钢种扩散能力降低最低,具体配比见下表3.3After tapping, aluminum particles are put into the ladle according to the oxygen content of tapping, and the top slag is modified to minimize the diffusion ability of oxygen in the slag to the steel grade. The specific ratio is shown in the following table 3.3
表3铝粒配比量Table 3 Proportion of aluminum particles
(4)顶渣的流动性(4) Fluidity of top slag
出钢完成后,加入低碳覆盖剂,保证顶渣流动性。After tapping is completed, a low-carbon covering agent is added to ensure the fluidity of the top slag.
最终,转炉供RH钢水目标为:[C]:0.02%~0.05%,[O]:(500~750)×10-6,T=1615~1630℃,炉渣FeO+MnO≤5%Ultimately, the targets for RH molten steel supply to the converter are: [C]: 0.02%~0.05%, [O]: (500~750)×10-6, T=1615~1630℃, slag FeO+MnO≤5%
3.RH精炼:RH添加合金方式调整:根据转炉终点样,RH采取前期配加磷铁措施,避免脱氧后补加磷铁导致增Ti。RH精炼根据钢水成分情况,在脱碳前期加入磷铁,将磷铁中的Ti氧化,有效避免了钢水增钛现象。合理控制RH脱碳前期游离氧含量,尽量将游离氧控制在400-600ppm,减少脱氧产物Al2O3、SiO2进入炉渣的数量,控制稳定的Ti在钢渣的分配比。生产高牌号无取向硅钢时采用“BOF一RH一CC”工艺路线生产硅钢时,由于不能常规LF精炼那样对钢包顶渣充分改质还原,所以在RH精炼结束以后渣中的FeO和MnO含量较高,钢包顶渣仍然属于高氧化性渣,连铸过程中,渣中的氧大量向钢水传递,与钢中AIs反应产生大量的A12O3夹杂,影响钢水洁净度,严重的还会引起絮流。为了克服现有技术的缺点,提高钢水质量,我们在硅钢顶渣改质方面进行攻关探索,在RH工序对顶渣进一步改质,具体方法为:通过向钢水表面均匀加入铝铁粉(加入的重量可以按照以下方式计算:铝铁粉加入量=1.5×54×G×[O]/48/η,G为顶渣重量,[O]为RH脱碳终点时钢水中游离氧的重量百分含量,η为铝铁粉中铝的质量百分含量),然后采取钙处理的方式向钢水里喂入钙线,通过钙在钢水表面的剧烈反应,搅动渣层使渣中的氧被表面的铝铁粉和喂入的钙脱除,从而降低渣中的氧含量。之后通过静置一定的时间,使钢中因喂入钙线混入的渣子和氧化物夹杂上浮,从而降低顶渣中氧化铁和氧化锰含量,改善浇注的钢水质量,满足硅钢的生产要求。3. RH refining: Adjustment of RH alloy addition method: According to the final sample of the converter, RH takes measures to add ferrophosphorus in the early stage to avoid adding ferrophosphorus after deoxidation to increase Ti. In RH refining, according to the composition of molten steel, ferrophosphorus is added in the early stage of decarburization to oxidize Ti in ferrophosphorus, effectively avoiding the phenomenon of titanium addition in molten steel. Reasonably control the free oxygen content in the early stage of RH decarburization, try to control the free oxygen at 400-600ppm, reduce the amount of deoxidation products Al2O3 and SiO2 entering the slag, and control the stable distribution ratio of Ti in steel slag. When producing high-grade non-oriented silicon steel using the "BOF-RH-CC" process route to produce silicon steel, since the ladle top slag cannot be fully modified and reduced like conventional LF refining, the content of FeO and MnO in the slag after RH refining is relatively low. High, ladle top slag is still a highly oxidizing slag. During the continuous casting process, a large amount of oxygen in the slag is transferred to the molten steel, and reacts with AIs in the steel to produce a large amount of A12O3 inclusions, which affects the cleanliness of the molten steel, and even causes flocculation in severe cases. In order to overcome the shortcomings of the existing technology and improve the quality of molten steel, we have carried out research and exploration in the modification of silicon steel top slag, and further modified the top slag in the RH process. The specific method is: by uniformly adding aluminum and iron powder to the surface of molten steel (added The weight can be calculated according to the following method: the amount of aluminum and iron powder added = 1.5 × 54 × G × [O]/48/η, G is the weight of top slag, [O] is the weight percentage of free oxygen in molten steel at the end of RH decarburization content, η is the mass percentage of aluminum in the aluminum-iron powder), and then the calcium wire is fed into the molten steel by calcium treatment, and through the violent reaction of calcium on the surface of the molten steel, the slag layer is stirred so that the oxygen in the slag is absorbed by the surface The aluminum iron powder and the calcium fed are removed, thereby reducing the oxygen content in the slag. After standing for a certain period of time, the slag and oxide inclusions mixed in the steel due to the feeding of the calcium wire will float up, thereby reducing the content of iron oxide and manganese oxide in the top slag, improving the quality of poured molten steel, and meeting the production requirements of silicon steel.
经过RH处理后的钢水,最终完全满足高性能无取向硅钢的成分要求:The molten steel after RH treatment finally fully meets the compositional requirements of high-performance non-oriented silicon steel:
如图1和2所示:优化工艺前后进行对比,优化后由于出钢挡渣成功率提高,转炉终点氧化性炉渣带入较少,即带入的Ti的氧化物较少。在RH脱碳前期,钢水氧含量在500ppm左右,加入磷铁合金后,合金中的Ti元素被氧化进入炉渣当中,采用以上措施后,顶渣改质良好,浇注过程无絮钢现象发生。钢中Ti含量较低后,无取向硅钢Ti含量明显降低,仅有个别炉次超过30ppm。通过优化磷铁添加方式,Ti含量明显降低,钢坯中粗大晶粒增加,产品性能得以提高。本发明的方法实施后硅钢Ti合格率由原来的60%,提高到98.5%,一级品率上升10%硅钢一级品率的提高,增加了产品卖价,每吨提高100元。提高了产品合格率,赢得了用户认可。As shown in Figures 1 and 2: the comparison before and after the optimization process shows that after the optimization, the success rate of slag blocking in tapping is improved, and less oxidative slag is brought into the end of the converter, that is, less Ti oxides are brought in. In the early stage of RH decarburization, the oxygen content of molten steel is about 500ppm. After adding ferrophosphorus alloy, the Ti element in the alloy is oxidized and enters the slag. After adopting the above measures, the top slag is well modified, and no flocculent steel phenomenon occurs during the pouring process. After the Ti content in the steel is low, the Ti content of non-oriented silicon steel decreases significantly, and only a few heats exceed 30ppm. By optimizing the addition method of ferrophosphorus, the Ti content is significantly reduced, the coarse grains in the billet are increased, and the product performance is improved. After the method of the present invention is implemented, the qualified rate of silicon steel Ti is increased from 60% to 98.5%, and the rate of first-grade silicon steel is increased by 10%. The qualified rate of products has been improved and user recognition has been won.
以上所述的实施例仅是对本发明的优选方式进行描述,并非对本发明的范围进行限定,在不脱离本发明设计精神的前提下,本领域普通技术人员对本发明的技术方案做出的各种变形和改进,均应落入本发明权利要求书确定的保护范围内。The above-mentioned embodiments are only to describe the preferred mode of the present invention, not to limit the scope of the present invention. Without departing from the design spirit of the present invention, those skilled in the art may make various Variations and improvements should fall within the scope of protection defined by the claims of the present invention.
Claims (5)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211374026.3ACN115927780A (en) | 2022-11-03 | 2022-11-03 | Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211374026.3ACN115927780A (en) | 2022-11-03 | 2022-11-03 | Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115927780Atrue CN115927780A (en) | 2023-04-07 |
Family
ID=86699878
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211374026.3APendingCN115927780A (en) | 2022-11-03 | 2022-11-03 | Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115927780A (en) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104805252A (en)* | 2015-05-14 | 2015-07-29 | 内蒙古包钢钢联股份有限公司 | Method for modifying silicon steel top slags |
| CN104975141A (en)* | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-14 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Method for heating molten steel in refining process of non-oriented low-grade aluminum-free silicon steel |
| CN110042200A (en)* | 2019-04-09 | 2019-07-23 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Smelting method of ultra-low sulfur steel |
| CN110129508A (en)* | 2019-05-23 | 2019-08-16 | 包头钢铁(集团)有限责任公司 | A kind of technique improving rare earth high-strength steel impact flexibility |
| CN111961802A (en)* | 2020-09-02 | 2020-11-20 | 北京科技大学 | Process for smelting molten steel by using high-phosphorus iron ore as raw material |
| CN112899552A (en)* | 2021-01-21 | 2021-06-04 | 江苏省沙钢钢铁研究院有限公司 | Method for controlling inclusions in ultra-low-aluminum non-oriented silicon steel |
| CN114317867A (en)* | 2021-11-30 | 2022-04-12 | 山东钢铁股份有限公司 | Method for controlling nitrogen content of molten steel in converter process |
- 2022
- 2022-11-03CNCN202211374026.3Apatent/CN115927780A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104975141A (en)* | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-14 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Method for heating molten steel in refining process of non-oriented low-grade aluminum-free silicon steel |
| CN104805252A (en)* | 2015-05-14 | 2015-07-29 | 内蒙古包钢钢联股份有限公司 | Method for modifying silicon steel top slags |
| CN110042200A (en)* | 2019-04-09 | 2019-07-23 | 鞍钢股份有限公司 | Smelting method of ultra-low sulfur steel |
| CN110129508A (en)* | 2019-05-23 | 2019-08-16 | 包头钢铁(集团)有限责任公司 | A kind of technique improving rare earth high-strength steel impact flexibility |
| CN111961802A (en)* | 2020-09-02 | 2020-11-20 | 北京科技大学 | Process for smelting molten steel by using high-phosphorus iron ore as raw material |
| CN112899552A (en)* | 2021-01-21 | 2021-06-04 | 江苏省沙钢钢铁研究院有限公司 | Method for controlling inclusions in ultra-low-aluminum non-oriented silicon steel |
| CN114317867A (en)* | 2021-11-30 | 2022-04-12 | 山东钢铁股份有限公司 | Method for controlling nitrogen content of molten steel in converter process |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108660294B (en) | A method for controlling inclusions in silicon-manganese killed non-oriented silicon steel | |
| CN111910045B (en) | A kind of smelting method of high-purity austenitic stainless steel | |
| CN112921237B (en) | A kind of smelting method of silicon manganese killed non-oriented silicon steel | |
| CN107299196A (en) | Method for synchronously desulfurizing molten steel and slag of non-oriented silicon steel RH vacuum furnace | |
| CN101041878A (en) | Low-manganese low- sulfur raw material ferroferrite for amorphous usage and method of production | |
| MX2014010513A (en) | Non-oriented electrical steel sheet with fine magnetic performance, and calcium treatment method therefor. | |
| CN108588541B (en) | Low-nitrogen boron-containing steel smelting method for improving boron element yield | |
| CN112899437A (en) | Oxygen content control method of aluminum-free low-alloy non-oriented silicon steel | |
| CN113249639A (en) | Production method for improving castability of silicon-manganese killed silicon steel | |
| CN110438389A (en) | A kind of high-purity rare earth steel production method | |
| CN107365949A (en) | A kind of method of smelting ultralow-carbon high-alloy stainless steel | |
| CN107058867B (en) | high-Si pure iron for energy-saving transformer iron core and production method thereof | |
| CN113430334B (en) | GOR smelting method for improving scrap steel ratio of 200 series stainless steel | |
| CN113373278B (en) | A kind of RH vacuum slag surface feeding device and slag modification method | |
| CN107012384B (en) | High-purity low-carbon ferrosilicon for silicon steel and smelting method thereof | |
| CN107619899B (en) | A kind of production method and steel material of molten steel with low residual chromium content | |
| CN112626312B (en) | Low-carbon aluminum killed steel Al for reducing RH single process 2 O 3 Method of inclusion | |
| CN115927780A (en) | Steelmaking production method for improving electromagnetic property of non-oriented silicon steel for motor | |
| CN117165743A (en) | Low-cost modification method for ladle top slag in IF steel smelting | |
| CN114790503B (en) | Smelting method with addition of iron ore | |
| CN115141904A (en) | Continuous casting billet for preparing low-carbon cold-rolled substrate and smelting process thereof | |
| CN113201686A (en) | Smelting method of low manganese steel | |
| CN113278884A (en) | Smelting process and production method of blank for refractory steel bar | |
| CN111575441A (en) | A method of using slag to modify deoxidized products in steel | |
| CN112375961A (en) | Method for producing high-purity industrial pure iron by adopting intermediate frequency furnace duplex method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |