CN115884485A - Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection Systems - Google Patents
Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection SystemsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115884485A CN115884485ACN202211742642.XACN202211742642ACN115884485ACN 115884485 ACN115884485 ACN 115884485ACN 202211742642 ACN202211742642 ACN 202211742642ACN 115884485 ACN115884485 ACN 115884485A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- target
- radiation source
- energy
- accelerator
- ray beam
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Analysing Materials By The Use Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本公开的实施例涉及电子加速器与安全检查领域,特别是涉及一种基于反射式加速器的辐射源,进行安全检查的辐射检查系统。Embodiments of the present disclosure relate to the field of electron accelerators and safety inspections, and in particular to a radiation inspection system for safety inspections based on radiation sources of reflective accelerators.
背景技术Background technique
各种运输工具(例如厢式货车或集装箱卡车等)具有机动性高、货物隐蔽性强等特点,成为安全检查排爆工作的重点对象之一。随着对安全检查系统穿透能力和重金属识别能力成像指标要求的提升,加速器逐渐成为检查系统的主流辐射源核心器件。辐射源和辐射检查系统等安全检查装置作为对待检查对象进行安全检查的关键技术性产品,能清楚、准确、有效的辨别车厢或集装箱内部物品,从而能够提高安全检查效率并保障公共安全,已经开始应用于大型物流运输场所、重要卡口、机场、活动场馆、车站和码头等公共场所。Various means of transportation (such as vans or container trucks, etc.) have the characteristics of high mobility and strong cargo concealment, and have become one of the key objects of safety inspection and detonation work. With the improvement of the imaging index requirements for the penetration capability and heavy metal identification capability of the security inspection system, the accelerator has gradually become the core device of the mainstream radiation source of the inspection system. Safety inspection devices such as radiation sources and radiation inspection systems, as key technical products for safety inspection of objects to be inspected, can clearly, accurately and effectively identify items inside carriages or containers, thereby improving safety inspection efficiency and ensuring public safety, and have already begun to be used It is widely used in public places such as large-scale logistics and transportation places, important checkpoints, airports, event venues, stations and docks.
然而目前的辐射源和辐射检查系统难以同时满足高标准的穿透力、丝分辨力、以及物质类别识别能力等技术指标。However, the current radiation sources and radiation inspection systems are difficult to simultaneously meet high standards of technical indicators such as penetrating power, silk resolution, and material category identification capabilities.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本公开的实施例可以解决现有技术中存在的上述问题和缺陷的至少一个方面。Embodiments of the present disclosure can solve at least one aspect of the above-mentioned problems and defects existing in the prior art.
根据本公开的一个方面的实施例,提供一种辐射源,其特征在于,辐射源包括反射式加速器,反射式加速器包括靶,反射式加速器被构造为:响应于电子束轰击靶,发出X射线束,在反射式加速器中,电子束沿第一方向入射到靶上,X射线束沿第二方向自靶发出,第一方向和第二方向均位于靶的同一侧,第一方向和第二方向之间存在第一设定夹角,第一设定夹角在20°~160°之间。According to an embodiment of an aspect of the present disclosure, a radiation source is provided, wherein the radiation source includes a reflective accelerator, the reflective accelerator includes a target, and the reflective accelerator is configured to emit X-rays in response to an electron beam bombarding the target. In a reflective accelerator, the electron beam is incident on the target along the first direction, and the X-ray beam is emitted from the target along the second direction. Both the first direction and the second direction are located on the same side of the target, and the first direction and the second There is a first set angle between the directions, and the first set angle is between 20° and 160°.
根据本公开的一种实施例,反射式加速器还包括电子枪,加速装置。电子枪用于发出具有第一设定电子能量的电子束;加速装置用于加速具有第一设定电子能量的电子束,其中,电子枪发出的电子束经加速装置加速后沿第一方向入射到靶上,第一方向与靶平面的法线方向之间存在第二设定夹角,第二设定夹角在10°~80°之间。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the reflective accelerator further includes an electron gun and an accelerating device. The electron gun is used to emit the electron beam with the first set electron energy; the accelerating device is used to accelerate the electron beam with the first set electron energy, wherein, the electron beam emitted by the electron gun is accelerated by the accelerating device and then incident on the target along the first direction Above, there is a second set included angle between the first direction and the normal direction of the target plane, and the second set included angle is between 10° and 80°.
根据本公开的一种实施例,第二方向与靶平面的法线方向之间存在第三设定夹角,第三设定夹角与第二设定夹角之和为第一设定夹角。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, there is a third set angle between the second direction and the normal direction of the target plane, and the sum of the third set angle and the second set angle is the first set angle horn.
根据本公开的一种实施例,反射式加速器发出的X射线束具有连续能谱,X射线束包括具有第一能量的第一X射线束和具有第二能量的第二X射线束,第一能量的能量范围为0~200keV,第二能量的能量范围为大于200keV,在反射式加速器发出的X射线束中,第一X射线束所占的比例大于第二X射线束所占的比例。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the X-ray beam emitted by the reflective accelerator has a continuous energy spectrum, the X-ray beam includes a first X-ray beam with a first energy and a second X-ray beam with a second energy, the first The energy range is 0-200keV, and the energy range of the second energy is greater than 200keV. Among the X-ray beams emitted by the reflective accelerator, the proportion of the first X-ray beam is greater than that of the second X-ray beam.
根据本公开的一种实施例,加速装置包括加速管和与加速管连接的微波装置,加速管用于在微波装置发出的微波的作用下将具有第一设定电子能量的电子束加速到具有第二设定电子能量的电子束。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the accelerating device includes an accelerating tube and a microwave device connected to the accelerating tube, and the accelerating tube is used to accelerate an electron beam with a first set electron energy to a first set electron beam under the action of microwaves emitted by the microwave device. Two electron beams with set electron energies.
根据本公开的一种实施例,第一设定电子能量的能量范围为10keV至100keV;和/或,第二设定电子能量的能量范围为500keV至9MeV。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the energy range of the first set electron energy is 10keV to 100keV; and/or, the energy range of the second set electron energy is 500keV to 9MeV.
根据本公开的一种实施例,靶的材料包括原子序数位于47与92之间的高原子序数材料,靶沿靶平面的法线方向的厚度为0.3~100毫米。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target includes a material with a high atomic number between 47 and 92, and the thickness of the target along the normal direction of the target plane is 0.3-100 mm.
根据本公开的一种实施例,靶的材料选自钨、钽、铼、金或银中的至少一种。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target is selected from at least one of tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, gold or silver.
根据本公开的一种实施例,靶的材料包括原子序数位于10与46之间的中等原子序数材料,靶沿靶平面的法线方向的厚度为1~200毫米。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target includes a medium atomic number material between 10 and 46, and the thickness of the target along the normal direction of the target plane is 1-200 mm.
根据本公开的一种实施例,靶的材料选自铜、不锈钢或铝中的至少一种。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target is selected from at least one of copper, stainless steel or aluminum.
根据本公开的一种实施例,反射式加速器还包括靶腔和真空密封窗,真空密封窗设置于X射线束的射出路径上,用于保持靶腔真空环境并引出X射线束。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the reflective accelerator further includes a target cavity and a vacuum-sealed window, and the vacuum-sealed window is arranged on the emission path of the X-ray beam for maintaining a vacuum environment in the target cavity and extracting the X-ray beam.
根据本公开的一种实施例,真空密封窗的制备材料选自铍、石墨或铝中的至少一种,真空密封窗的厚度为0.5~6毫米;或者,真空密封窗的制备材料选自不锈钢或铜中的至少一种,真空密封窗的厚度为0.3~2毫米。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the preparation material of the vacuum sealing window is selected from at least one of beryllium, graphite or aluminum, and the thickness of the vacuum sealing window is 0.5-6 mm; or, the preparation material of the vacuum sealing window is selected from stainless steel or at least one of copper, and the thickness of the vacuum-tight window is 0.3-2 mm.
根据本公开的一种实施例,辐射源还包括屏蔽结构,屏蔽结构包围反射式加速器;屏蔽结构在对应真空密封窗的位置处开设有出射口,出射口被构造成用于引出X射线束作用于待检查对象,其中,X射线束的束流面为扇形或者圆锥形。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the radiation source further includes a shielding structure, and the shielding structure surrounds the reflective accelerator; the shielding structure has an exit opening at a position corresponding to the vacuum-sealed window, and the exit opening is configured to extract the X-ray beam. For the object to be inspected, the beam flow surface of the X-ray beam is fan-shaped or conical.
根据本公开的一种实施例,靶为材料选自钨、钽、铼、金、银、不锈钢或铝中至少一种而形成的多层靶;或者,靶为材料选自钨、钽、铼、金、银、不锈钢或铝中至少两种而形成的合金靶。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the target is a multilayer target formed of at least one material selected from tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, gold, silver, stainless steel or aluminum; or, the target is a material selected from tungsten, tantalum, rhenium , gold, silver, stainless steel or aluminum at least two alloy targets formed.
根据本公开的一种实施例,真空密封窗为材料选自铍、石墨、铝、铁或铜中至少两种而形成的多层密封窗。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the vacuum sealing window is a multilayer sealing window formed of at least two materials selected from beryllium, graphite, aluminum, iron or copper.
根据本公开的另一个方面的实施例,提供一种辐射检查系统,其特征在于,包括:检查通道,如以上所述的辐射源,以及探测器。待检查对象适于设置于检查通道中;探测器用于探测从辐射源发出且与待检查对象相互作用后的X射线束的至少一部分,其中,待检查对象为车辆,在辐射检查过程中,车辆沿行进方向在检查通道中移动;辐射源设置于检查通道的顶侧,探测器设置于检查通道的底侧、第一侧或第二侧中的至少一侧,第一侧和第二侧为检查通道的相对侧。According to an embodiment of another aspect of the present disclosure, a radiation inspection system is provided, which is characterized by comprising: an inspection channel, the radiation source as described above, and a detector. The object to be inspected is suitable for being arranged in the inspection channel; the detector is used to detect at least a part of the X-ray beam emitted from the radiation source and interacted with the object to be inspected, wherein the object to be inspected is a vehicle, and during the radiation inspection process, the vehicle Moving in the inspection channel along the traveling direction; the radiation source is arranged on the top side of the inspection channel, and the detector is arranged on at least one of the bottom side, the first side or the second side of the inspection channel, and the first side and the second side are inspection channels. opposite side of the channel.
根据本公开的一种实施例,辐射检查系统还包括准直器,准直器设置于辐射源与待检查对象之间,用于将X射线束约束为扇形束流。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the radiation inspection system further includes a collimator, which is arranged between the radiation source and the object to be inspected, and is used for confining the X-ray beam into a fan-shaped beam.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射源的结构框图;Fig. 1 schematically shows a structural block diagram of a radiation source according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图2示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的靶的工作原理图;Fig. 2 schematically shows a working principle diagram of a target according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图3a示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的第一设定夹角为90°时1.5MeV透射式加速器和反射式加速器的能谱对比图;Fig. 3a schematically shows a comparison diagram of the energy spectra of a 1.5 MeV transmission accelerator and a reflection accelerator when the first set angle is 90° according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图3b示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的反射式加速器不同的第一设定夹角情况下1.5MeV反射式加速器的能谱对比图;Fig. 3b schematically shows a comparison diagram of the energy spectrum of a 1.5MeV reflective accelerator in the case of different first set angles of the reflective accelerator according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图4示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的立体图;Fig. 4 schematically shows a perspective view of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图5示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的俯视图;Fig. 5 schematically shows a top view of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图6示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的正面视图;Fig. 6 schematically shows a front view of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图7示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的组成框图;FIG. 7 schematically shows a block diagram of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图8示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统空气丝分辨指标和穿透力指标图;Fig. 8 schematically shows an air filament resolution index and a penetration index diagram of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图9示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的质量厚度区间2~30g/cm2四种物质类别(有机物、无机物、混合物、重金属)的识别图;FIG. 9 schematically shows an identification diagram of four substance categories (organic substances, inorganic substances, mixtures, and heavy metals) in the mass thickness range of 2 to 30 g/cm2 according to an embodiment of the present disclosure;
图10示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查方法的流程图;以及FIG. 10 schematically shows a flowchart of a radiation inspection method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure; and
图11示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的电子设备的方框图。Fig. 11 schematically shows a block diagram of an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本公开实施例中的附图,对本公开实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本公开一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。以下对至少一个示例性实施例的描述实际上仅仅是说明性的,决不作为对本公开及其应用或使用的任何限制。基于本公开中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有开展创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本公开保护的范围。The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present disclosure with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present disclosure. Apparently, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present disclosure, not all of them. The following description of at least one exemplary embodiment is merely illustrative in nature and in no way intended as any limitation of the disclosure, its application or uses. Based on the embodiments in the present disclosure, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present disclosure.
在下面的详细描述中,为便于解释,阐述了许多具体的细节以提供对本披露实施例的全面理解。然而明显地,一个或多个实施例在没有这些具体细节的情况下也可以被实施。在其他情况下,公知的结构和装置以图示的方式体现以简化附图。对于相关领域普通技术人员已知的技术、方法和设备可能不作详细讨论,但在适当情况下,所述技术、方法和设备应当被视为授权说明书的一部分。In the following detailed description, for purposes of explanation, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the disclosed embodiments. It may be evident, however, that one or more embodiments may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-known structures and devices are shown in diagrammatic form to simplify the drawings. Techniques, methods and devices known to those of ordinary skill in the relevant art may not be discussed in detail, but where appropriate, such techniques, methods and devices should be considered part of the Authorized Specification.
在本公开的描述中,需要理解的是,方位词如“前、后、上、下、左、右”、“横向、竖向、垂直、水平”和“顶、底”等所指示的方位或位置关系通常是基于附图所示的方位或位置关系,并且以车辆的行进方向为基础,仅是为了便于描述本公开和简化描述,在未作相反说明的情况下,这些方位词并不指示和暗示所指的装置或元件必须具有特定的方位或者以特定的方位构造和操作,因此不能理解为对本公开保护范围的限制;方位词“内、外”是指相对于各部件本身的轮廓的内外。In the description of the present disclosure, it should be understood that orientation words such as "front, back, up, down, left, right", "horizontal, vertical, vertical, horizontal" and "top, bottom" etc. indicate the orientation Or positional relationship is usually based on the orientation or positional relationship shown in the drawings, and is based on the direction of travel of the vehicle, and is only for the convenience of describing the present disclosure and simplifying the description. Indicates and implies that the device or element referred to must have a specific orientation or be constructed and operated in a specific orientation, and therefore should not be construed as limiting the scope of the present disclosure; the orientation words "inner and outer" refer to the outline of each part inside and outside.
在本公开的描述中,需要理解的是,使用“第一”、“第二”等词语来限定零部件,仅仅是为了便于对相应零部件进行区别,如没有另行声明,上述词语并没有特殊含义,因此不能理解为对本公开保护范围的限制。In the description of the present disclosure, it should be understood that the use of words such as "first" and "second" to define components is only for the convenience of distinguishing corresponding components. meaning, and therefore cannot be construed as limiting the scope of protection of the present disclosure.
根据本公开的一种总体上的发明构思,提供一种辐射源,辐射源包括反射式加速器,反射式加速器包括靶,反射式加速器被构造为:响应于电子束轰击靶,发出X射线束,在反射式加速器中,电子束沿第一方向入射到靶上,X射线束沿第二方向自靶发出,第一方向和第二方向均位于靶的同一侧,第一方向和第二方向之间存在第一设定夹角,第一设定夹角在20°~160°之间。According to a general inventive concept of the present disclosure, a radiation source is provided, the radiation source includes a reflective accelerator, the reflective accelerator includes a target, and the reflective accelerator is configured to emit an X-ray beam in response to an electron beam bombarding the target, In a reflective accelerator, the electron beam is incident on the target along the first direction, and the X-ray beam is emitted from the target along the second direction. Both the first direction and the second direction are located on the same side of the target. There is a first set angle between them, and the first set angle is between 20° and 160°.
根据本公开的另一种总体上的发明构思,提供一种辐射检查系统,包括:检查通道,辐射源,以及探测器。待检查对象适于设置于检查通道中;探测器用于探测从辐射源发出且与待检查对象相互作用后的X射线束的至少一部分,其中,待检查对象为车辆,在辐射检查过程中,车辆沿行进方向在检查通道中移动;辐射源设置于检查通道的顶侧,探测器设置于检查通道的底侧、第一侧或第二侧中的至少一侧,第一侧和第二侧为检查通道的相对侧。According to another general inventive concept of the present disclosure, a radiation inspection system is provided, including: an inspection channel, a radiation source, and a detector. The object to be inspected is suitable for being arranged in the inspection channel; the detector is used to detect at least a part of the X-ray beam emitted from the radiation source and interacted with the object to be inspected, wherein the object to be inspected is a vehicle, and during the radiation inspection process, the vehicle Moving in the inspection channel along the traveling direction; the radiation source is arranged on the top side of the inspection channel, and the detector is arranged on at least one of the bottom side, the first side or the second side of the inspection channel, and the first side and the second side are inspection channels. opposite side of the channel.
图1示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射源的结构框图;图2示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的靶的工作原理图;图3a示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的第一设定夹角为90°时1.5MeV透射式加速器和反射式加速器的能谱对比图。图3b示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的反射式加速器不同的第一设定夹角情况下1.5MeV反射式加速器的能谱对比图。Fig. 1 schematically shows a structural block diagram of a radiation source according to an embodiment of the present disclosure; Fig. 2 schematically shows a working principle diagram of a target according to an embodiment of the present disclosure; Fig. 3a schematically shows a diagram according to an embodiment of the present disclosure Comparison diagram of the energy spectrum of the 1.5MeV transmission accelerator and reflection accelerator when the first set angle is 90°. Fig. 3b schematically shows a comparison diagram of energy spectra of a 1.5 MeV reflective accelerator under different first set angles of the reflective accelerator according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
加速器可以分为透射式和反射式,采用透射式加速器的辐射源中,通过加速器产生的电子束撞击高原子序数靶产生轫致辐射X射线,并在平行于电子束的方向上引出X射线束,采用透射式加速器作为辐射源的检查系统通常具备较好的穿透力指标(≥厚度150mm钢板),如图3a所示,其主要由于X射线能谱中高能X射线(X射线能量大于500千电子伏,下同)的平均能量较高,但同时发现检查系统的丝分辨指标通常较弱,并且无法有效识别两种或以上的物质种类(主要包括有机物、混合物、无机物、重金属四种物质种类),这主要由于X射线能谱中低能X射线(X射线能量小于200千电子伏,下同)所占比例较低,例如低能X射线数目所占比例仅为20.7%,所以为了有效提升丝分辨力与物质种类识别成像指标质量,需要显著提升低能X射线的比例。提升X射线能谱中低能X射线的比例,最简单的方式就是降低加速器的电子束能量,例如专利CN107613627与CN109195301均公开了一种能量可调的加速器,可以实现电子束在0.5~2.0兆电子伏范围内调整电子束能量,当电子束能量从1.5兆电子伏降为1.0兆电子伏时,低能X射线数目所占比例仅从20.7%上升为24.8%,无法快速提升丝分辨力与物质种类识别成像指标质量,并且这种能量可调的加速器需要设计额外的电控系统,显著增加了加速器的设计与制造成本。而反射式加速器X射线能谱明显不同于透射式加速器,如图3a所示,反射式加速器的能谱中低能X射线数目所占比例更高,反射式加速器低能X射线的数目比例约为透射式的3倍,而高能X射线平均能量较于透射式仅降低约9.6%,仅下降约72千电子伏,如表1所示:Accelerators can be divided into transmission type and reflection type. In the radiation source of the transmission type accelerator, the electron beam generated by the accelerator hits the high atomic number target to generate bremsstrahlung X-rays, and the X-ray beam is drawn in a direction parallel to the electron beam. , the inspection system using a transmission accelerator as a radiation source usually has a good penetration index (≥ 150mm thick steel plate), as shown in Figure 3a, which is mainly due to the high-energy X-rays in the X-ray energy spectrum (X-ray energy greater than 500 KeV, the same below) has a higher average energy, but at the same time, it is found that the silk resolution index of the inspection system is usually weak, and it cannot effectively identify two or more types of substances (mainly including organic substances, mixtures, inorganic substances, and heavy metals) Substance type), this is mainly due to the low proportion of low-energy X-rays (X-ray energy less than 200 keV, the same below) in the X-ray energy spectrum, for example, the proportion of low-energy X-rays is only 20.7%, so in order to effectively To improve the silk resolution and the quality of imaging indicators for material type identification, it is necessary to significantly increase the proportion of low-energy X-rays. The easiest way to increase the proportion of low-energy X-rays in the X-ray energy spectrum is to reduce the electron beam energy of the accelerator. For example, patents CN107613627 and CN109195301 both disclose an energy-adjustable accelerator, which can realize the electron beam in the range of 0.5 to 2.0 million electrons. Adjust the electron beam energy within the volt range. When the electron beam energy drops from 1.5 MeV to 1.0 MeV, the proportion of the number of low-energy X-rays only increases from 20.7% to 24.8%, which cannot quickly improve the silk resolution and material types. To identify the quality of the imaging index, and this kind of energy-adjustable accelerator needs to design an additional electronic control system, which significantly increases the design and manufacturing costs of the accelerator. The X-ray energy spectrum of reflective accelerators is obviously different from that of transmission accelerators. As shown in Figure 3a, the proportion of low-energy X-rays in the energy spectrum of reflective accelerators is higher, and the proportion of low-energy X-rays in reflective accelerators is about Compared with the transmission type, the average energy of high-energy X-rays is only reduced by about 9.6%, which is only about 72 kiloelectron volts, as shown in Table 1:
由此,本公开提出一种基于反射式加速器的辐射源,相较于透射式加速器的辐射源能够显著提升X射线能谱中低能X射线的比例,同时不会明显降低高能X射线的平均能量,并且不增加制造成本且容易实现。Therefore, the present disclosure proposes a radiation source based on a reflective accelerator, which can significantly increase the proportion of low-energy X-rays in the X-ray energy spectrum, while not significantly reducing the average energy of high-energy X-rays, compared with the radiation source of a transmission accelerator. , and does not increase the manufacturing cost and is easy to implement.
在本文中,表述“加速器”是一种利用高频电磁波将电子等带电粒子通过加速管加速到高能能量的装置。本领域技术人员应理解,“加速器”不同于X光机、X射线球管(又简称为X射线管、球管、管球等),加速器的加速原理不同于X射线球管,加速器的电子束能量普遍要高于X射线球管,相应地,二者的应用领域也不同。In this article, the expression "accelerator" is a device that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves to accelerate charged particles such as electrons to high-energy energies through an accelerating tube. Those skilled in the art should understand that "accelerator" is different from X-ray machines and X-ray tubes (also referred to as X-ray tubes, tubes, tubes, etc.), the acceleration principle of accelerators is different from that of X-ray tubes, and the electrons of accelerators are different from X-ray tubes. The beam energy is generally higher than that of the X-ray tube, and correspondingly, the application fields of the two are also different.
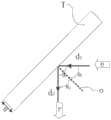
在本公开的实施例中,提供一种辐射源,结合图1和图2所示,所述辐射源120包括反射式加速器121,所述反射式加速器121包括靶T,所述反射式加速器121被构造为:响应于电子束e轰击所述靶T,发出X射线束r,在所述反射式加速器121中,所述电子束e沿第一方向d1入射到所述靶T上,所述X射线束r沿第二方向d2自所述靶T发出,所述第一方向d1和所述第二方向d2均位于所述靶T同一侧,所述第一方向d1和所述第二方向d2之间存在第一设定夹角θ1,所述第一设定夹角θ1在20°~160°之间。In an embodiment of the present disclosure, a radiation source is provided. As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. is configured to: emit an X-ray beam r in response to an electron beam e bombarding the target T, in the
在本公开的实施例中,结合图1和图2所示,所述反射式加速器121还包括电子枪1211,加速装置1212。所述电子枪1211用于发出具有第一设定电子能量的电子束e1;加速装置1212用于加速所述具有第一设定电子能量的电子束,得到电子束e。其中,所述电子枪发出的电子束经所述加速装置加速后沿第一方向d1入射到所述靶T上,所述第一方向d1与靶平面的法线O(虚线所示)的方向之间存在第二设定夹角θ2,所述第二设定夹角θ2在10°~80°之间。响应于电子束e轰击所述靶T,发出X射线束r,所述X射线束r沿第二方向d2自所述靶T发出,所述第一方向d1和所述第二方向d2之间存在第一设定夹角θ1,所述第一设定夹角θ1在20°~160°之间,例如60°、90°、120°,结合图3a和图3b所示,在第一设定夹角θ1分别为20°、90°、160°时,反射式加速器的X射线能谱中低能X射线所占比例呈由高到低的规律,且均远高于透射式加速器的X射线能谱中低能X射线所占比例,反射式加速器的X射线能谱中高能X射线分布差异较小。In an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 , the
根据本公开的实施例,如图2所示,第二方向d2与靶平面的法线O的方向之间存在第三设定夹角θ3,所述第三设定夹角θ3与所述第二设定夹角θ2之和为所述第一设定夹角θ1,例如当所述第一设定夹角θ1为90°,所述第二设定夹角θ2为45°,所述第三设定夹角θ3为45°;或者当所述第一设定夹角θ1为90°,所述第二设定夹角θ2为75°,所述第三设定夹角θ3为15°。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 2 , there is a third setangle θ 3 between the second direction d2 and the direction of the normal O of the target plane, and the third set angle θ3 and The sum of the second set angles θ2 is the first set angle θ1 , for example, when the first set angle θ1 is 90°, the second set angle θ2 is 45°, the third set angle θ3 is 45°; or when the first set angle θ1 is 90°, the second set angle θ2 is 75°, the The third set angle θ3 is 15°.
根据本公开的实施例,结合图3a和图3b所示,所述反射式加速器121发出的所述X射线束r具有连续能谱,所述X射线束r包括具有第一能量E1的第一X射线束和具有第二能量E2的第二X射线束,所述第一能量的能量E1范围为0~200keV,所述第二能量E2的能量范围为大于200keV。更优地,所述第二X射线束的平均能量高于700keV。在所述反射式加速器发出的所述X射线束中,所述第一X射线束所占的比例大于所述第二X射线束所占的比例,例如所述第一X射线束所占的比例大于60%,例如靶材料为钨,出射的X射线束的电子能量为1.5MeV,X射线能谱如如图3a所示。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 3a and FIG. 3b, the X-ray beam r emitted by the
根据本公开的实施例,如图1所示,所述加速装置1212包括加速管1212a和与所述加速管1212a连接的微波装置1212b;所述加速管1212a用于在微波装置1212b发出的微波的作用下将具有第一设定电子能量的电子束e1加速到具有第二设定电子能量的电子束e。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 1 , the
根据本公开的实施例,所述第一设定电子能量的能量范围为35keV至45keV;所述第二设定电子能量的能量范围为500keV至9MeV。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the energy range of the first set electron energy is 35keV to 45keV; the energy range of the second set electron energy is 500keV to 9MeV.
根据本公开的实施例,如图1所示,所述反射式加速器121还包括靶腔1212c和真空密封窗1212d,所述真空密封窗1212d设置于所述X射线束的射出路径上,用于保持靶腔1212c真空环境并引出X射线束r。所述真空密封窗1212d的制备材料选自铍、石墨或铝中的至少一种,所述真空密封窗1212d的厚度为0.5~6毫米;或者,所述真空密封窗1212d的制备材料选自不锈钢或铜中的至少一种,所述真空密封窗的厚度为0.3~2毫米。或者,所述真空密封窗为材料选自铍、石墨、铝、铁或铜中至少两种而形成的多层密封窗。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 1 , the
根据本公开的实施例,如图1所示,辐射源120还包括:屏蔽结构122,所述屏蔽结构包围所述反射式加速器121;所述屏蔽结构122在对应所述真空密封窗1212d的位置处开设有出射口122a,所述出射口被构造成用于使得所述X射线束作用于待检查对象,其中,所述X射线束r的束流面为扇形或者圆锥形。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 1 , the
根据本公开的实施例,所述辐射检查系统还包括准直器,所述准直器设置于所述辐射源与所述待检查对象之间,例如设置于所述出射口122a处,用于将所述X射线束约束为扇形束流。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the radiation inspection system further includes a collimator, the collimator is arranged between the radiation source and the object to be inspected, for example, at the
需要说明的是,在加速器121的电子枪中,电子是由加热后的阴极的热发射产生的;阴极杯产生的静电场将电子聚焦到阳极的一小部分。与千伏安机器中的阳极不同的是,加速器121的阳极上有一个空穴,电子在这里被聚焦,所以电子没有击中阳极,而是通过空穴进入加速结构。例如,电子枪可以有两种基本类型:二极管电子枪和三极管电子枪。在二极管电子枪中,施加到阴极的电压是脉冲式的,因此产生电子束,而不是连续的电子流。在三极管电子枪中,通过栅极来获得离散的电子束。三极管阴极具有恒定的电势,栅极的电压是脉冲式的。当施加到栅极的电压为负时,电子将停止到达阳极。当移除栅极电压时,电子将朝着阳极加速。因此,栅极可以控制进入加速结构的电子脉冲的频率。阴极或栅极的脉冲由连接到射频功率发生器的调制器控制。It should be noted that, in the electron gun of the
例如,所述加速管可以为行波加速管或驻波加速管。例如,所述微波装置可以包括微波功率源和微波传输系统。所述微波功率源提供加速管建立加速场所需的射频功率,作为微波功率源使用的有磁控管和速调管。For example, the accelerating tube may be a traveling wave accelerating tube or a standing wave accelerating tube. For example, the microwave device may include a microwave power source and a microwave transmission system. The microwave power source provides the radio frequency power required by the accelerating tube to establish the accelerating field, and magnetron and klystron are used as the microwave power source.
根据本公开的实施例,靶T的材料包括高原子序数材料,所述靶T沿靶平面的法线方向的厚度H为0.3~100毫米。所述高原子序数材料可以为原子序数位于47-92的材料,例如选自钨、钽、铼、金或银中的至少一种。根据本公开的实施例,所述靶的材料也可以包括中等原子序数材料,所述靶沿靶平面的法线方向的厚度为1~200毫米。所述中原子序数材料可以为原子序数介于10-46之间的材料,例如所述靶的材料选自铜、不锈钢或铝中的至少一种。或者,所述靶为材料选自钨、钽、铼、金、银、不锈钢或铝中至少一种而形成的多层靶;或者,所述靶为材料选自钨、钽、铼、金、银、不锈钢或铝中至少两种而形成的合金靶。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target T includes a high atomic number material, and the thickness H of the target T along the normal direction of the target plane is 0.3-100 mm. The high atomic number material may be a material with an atomic number ranging from 47 to 92, such as at least one selected from tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, gold or silver. According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the material of the target may also include a medium atomic number material, and the thickness of the target along the normal direction of the target plane is 1-200 mm. The middle atomic number material may be a material with an atomic number between 10-46, for example, the material of the target is at least one selected from copper, stainless steel or aluminum. Or, the target is a multilayer target formed by at least one material selected from tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, gold, silver, stainless steel or aluminum; or, the target is a material selected from tungsten, tantalum, rhenium, gold, An alloy target formed of at least two of silver, stainless steel or aluminum.
基于上述辐射源,本公开还提供一种辐射检查系统,辐射源和辐射检查系统这类安全检查系统的工作原理可以概括如下:通过发射特定的射线作用于待检查对象后,再探测作用于待检查对象后的射线并进行处理,进一步对待检查对象中的感兴趣部分进行识别。根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统,适用于对例如厢式货车、集装箱运输车、罐式运输车、自卸卡车、皮卡车、越野车、小轿车之类的车辆所装载的物品进行快速、高效、高质量的识别,从而实现安全检查的目的,或者不仅限于对上述车辆装载的物品进行安全检查,也可以是对其他载具或容器内的物品进行辐射检查,例如行李箱、物流包裹、罐装或桶装物品等。通过安全检查,可以确认物品中是否存在例如枪支、弹药、爆炸物、毒品、管制器具、易燃易爆物品、毒害品、腐蚀性物品、放射性物品、感染性物质、贵金属之类的违禁物品或高危物品。Based on the above-mentioned radiation source, the present disclosure also provides a radiation inspection system. The working principle of the safety inspection system such as the radiation source and the radiation inspection system can be summarized as follows: After emitting a specific ray to act on the object to be inspected, the detection acts on the object to be inspected. The ray after the object is inspected and processed, and the part of interest in the object to be inspected is further identified. The radiation inspection system according to the embodiment of the present disclosure is suitable for fast, Efficient and high-quality identification, so as to achieve the purpose of security inspection, or not limited to security inspection of the items loaded on the above vehicles, but also radiation inspection of items in other vehicles or containers, such as luggage, logistics packages, Canned or barreled items, etc. Through the security inspection, it can be confirmed whether there are prohibited items such as guns, ammunition, explosives, drugs, controlled appliances, flammable and explosive items, poisonous items, corrosive items, radioactive items, infectious substances, precious metals, etc. high-risk items.
以上相关的公共安全行业标准GAT 1731-2020《乘用车辆X射线安全检查系统技术要求》(简称:行业标准)在2020年正式发布,此行业标准中的性能指标主要包含丝分辨力、穿透力、基本物质识别能力,其中,丝分辨力为X射线安全检查系统分辨单根实芯铜线的能力,一般用线的标称直径(mm)表示。穿透力指的是X射线安全检查系统穿透被检对象的能力,一般用钢板的厚度(mm)表示。基本物质识别为X射线安全检查系统分辨有机物、混合物、无机物和重金属的能力,一般用质量厚度(g/cm2)表示,上述行业标准主要性能指标的最高级别要求如下表2所示:The above related public safety industry standard GAT 1731-2020 "Technical Requirements for Passenger Vehicle X-ray Safety Inspection System" (referred to as: industry standard) will be officially released in 2020. The performance indicators in this industry standard mainly include silk resolution, penetration Force, basic material identification ability, among them, the wire resolution is the ability of the X-ray security inspection system to distinguish a single solid copper wire, generally expressed by the nominal diameter (mm) of the wire. Penetration refers to the ability of the X-ray security inspection system to penetrate the object to be inspected, generally expressed by the thickness of the steel plate (mm). The identification of basic substances refers to the ability of the X-ray security inspection system to distinguish organic substances, mixtures, inorganic substances and heavy metals, generally expressed in mass thickness (g/cm2 ). The highest level requirements for the main performance indicators of the above industry standards are shown in Table 2 below:
表2.行业标准主要性能指标最高级表Table 2. The highest level table of main performance indicators of industry standards
在本公开的实施例中,辐射检查系统可以包括辐射源、辐射探测系统、图像处理系统及控制系统等组成部件,被扫描车辆经过辐射源产生的X射线照射,并通过辐射探测系统与图像处理成像系统获得被扫描车辆的扫描图像。In an embodiment of the present disclosure, the radiation inspection system may include components such as a radiation source, a radiation detection system, an image processing system, and a control system. The imaging system obtains a scanned image of the scanned vehicle.
具体地,当X射线穿过待检查对象后,由于不同能量X射线与待检查对象相互作用的特性不同,穿过待检查对象后的射线特性也不同,穿过待检查对象后的X射线,经过辐射探测系统后,被分离成多种特征信号,通过图像处理系统对特征信号进行优化、甄别、校正、匹配及分析,并在特征信号处理方式、匹配模式、分析算法方面均采用独特的处理,能够对扫描物进行精确有效的物质识别和准确细致的图像重建,最终构成一种更大范围物质识别、更高分辨力、更精细的扫描图像的辐射检查系统。在实现本发明的过程中,发明人发现,要满足行业标准最高级对检查系统提出的成像指标要求,需要显著提升辐射源产生的X射线能谱中低能X射线(X射线能量小于200keV,下同)的比例,同时辐射探测系统能够有效探测X射线能谱中的不同能段,充分发挥出不同能量段X射线的最佳特性,最后图像处理成像系统计算给出透射灰度图像,并对被扫描物体完成四种物质类别的识别。Specifically, after the X-ray passes through the object to be inspected, due to the different characteristics of the interaction between the X-rays with different energies and the object to be inspected, the characteristics of the rays after passing through the object to be inspected are also different. The X-rays after passing through the object to be inspected, After passing through the radiation detection system, it is separated into various characteristic signals, and the characteristic signals are optimized, screened, corrected, matched and analyzed by the image processing system, and unique processing methods, matching modes and analysis algorithms are adopted in the characteristic signal processing methods , can perform accurate and effective material identification and accurate and detailed image reconstruction on scanned objects, and finally constitute a radiation inspection system with a wider range of material identification, higher resolution, and finer scanning images. In the process of realizing the present invention, the inventors found that in order to meet the imaging index requirements proposed by the highest industry standard for the inspection system, it is necessary to significantly increase the low-energy X-rays in the X-ray energy spectrum generated by the radiation source (X-ray energy is less than 200keV, the lower At the same time, the radiation detection system can effectively detect different energy segments in the X-ray energy spectrum, and give full play to the best characteristics of X-rays in different energy segments. Finally, the image processing imaging system calculates and gives the transmission grayscale image, and The scanned object completes the identification of four substance categories.
图4示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的立体图;图5示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的俯视图;图6示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的正面视图;图7示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统的组成框图。4 schematically shows a perspective view of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure; FIG. 5 schematically shows a top view of a radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure; FIG. A front view of the radiation inspection system; FIG. 7 schematically shows a block diagram of the radiation inspection system according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
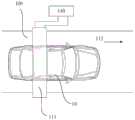
参见图4、图5和图7,以对乘用车10进行辐射检查为例进行说明,将乘用车10作为待检查对象。需要说明的是,本公开的实施例中的待检查对象不局限于乘用车,还可以包括其它任何合适类型的对象,包括但不限于厢式货车、集装箱运输车、罐式运输车、自卸卡车、皮卡车等车辆。Referring to FIG. 4 , FIG. 5 and FIG. 7 , the radiation inspection of the
根据本公开的一种示例性实施例,结合图4至图7所示,提供一种辐射检查系统100,包括:检查通道110,辐射源120,探测器130。作为待检查对象的乘用车10设置于所述检查通道110中;辐射源120设置在所述检查通道110的至少一侧,所述辐射源120发出射线,所述射线的至少一部分用于检查所述待检查对象;探测器130设置在所述检查通道110的至少一侧,所述探测器130用于探测从所述辐射源120发出且与所述待检查对象相互作用后的X射线束的至少一部分。例如探测器130可以是基于信号分离技术的、采用双层探测器的基础结构,对输入探测器130的X射线束r的特征信号进行分离,分别探测X射线能谱中的不同能段。According to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 4 to FIG. 7 , a
根据本公开的实施例,结合图4、图5和图6所示,检查通道110可以包括龙门架111和穿过龙门架111的贯穿道112,所述龙门架111和/或所述贯穿道112可移动;辐射源120例如可以设置于检查通道110的上侧和/或下侧和/或左侧和/或下侧;与辐射源120相应的,探测器130例如也可以设置于检查通道100的上侧和/或下侧和/或左侧和/或下侧。在本公开实施例中,结合图4、图5和图6所示,以辐射源120设置于检查通道100的上侧的龙门架111的横梁上,探测器设置于检查通道100的左侧(龙门架111的左侧立柱)、右侧(龙门架111的右侧立柱)、和下侧(贯穿道112上)为例进行说明。辐射源120发出的射线种类例如可以为α射线、β射线、X射线、γ射线,在本公开实施例中,以辐射源120发出X射线为例进行说明。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 4, FIG. 5 and FIG. 112 is movable; the
图8示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查系统空气丝分辨指标和穿透力指标图;图9示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的质量厚度区间2~30g/cm2四种物质类别(有机物、无机物、混合物、重金属)的识别图。Fig. 8 schematically shows the air filament resolution index and penetration index map of the radiation inspection system according to the embodiment of the present disclosure; Fig. 9 schematically shows the mass thickness interval 2-30g/cm2 according to the embodiment of the present disclosure. Identification diagram for each substance class (organic, inorganic, mixture, heavy metal).
辐射检查系统输出的探测器130的数字信号,在经过必要的校正、降噪等处理后计算得到出灰度图像,如图8所示,其中空气丝分辨指标达到0.4mm,穿透力指标达到160mm。最终给出一幅待检查对象中感兴趣部分的物质类别识别结果图像,并在图像上予以不同颜色标示物质识别结果。可以参照如图9所示的物质识别着色标准,根据第一与第二透视度均值与探测器透视度对数比R值,通过与四种典型物质材料的物质识别曲线的比对,根据线性或常见插值算法计算得到该区域的等效平均原子序数,由平均原子序数信息按照有机物、混合物、无机物和重金属4大类材料进行划分并确定色彩色调,例如其中有机物为橙色、混合物为绿色、无机物为蓝色、重金属为紫色,由透视度确定色彩饱和度和亮度,最终输出被检物四种物质类别识别结果图像。如下表3所示,本公开的辐射检查系统主要性能指标中的丝分辨力、穿透力、物质类别识别能力均可同时达到行业标准最高级,从而能够提供分辨率更高、更精细的扫描图像,并能够提供更准确的待检查对象中感兴趣部分的物质类别信息。The digital signal of the
表3.本公开的辐射检查系统与行业标准主要性能指标最高级对比表Table 3. The highest level comparison table of the main performance indicators of the disclosed radiation inspection system and industry standards
根据本公开实施例,如图4至图6所示,所述待检查对象为乘用车辆10,在辐射检查过程中,所述车辆沿行进方向在所述检查通道110中移动;所述辐射源120设置于所述检查通道110的顶侧,所述探测器130设置于所述检查通道110的底侧、第一侧或第二侧中的至少一侧,所述第一侧和所述第二侧为所述检查通道的相对侧。进一步地,检查通道外还设置有屏蔽墙160,所述屏蔽墙160用于减少X射线的外溢。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIGS. 4 to 6 , the object to be inspected is a
根据本公开的实施例,结合图4至图6,以及图7所示,所述辐射检查系统100还包括适用于控制检查通道110、辐射源120、探测器130、以及图像处理装置140完成扫描检查的扫描控制装置150;以对乘用车10作为待检查对象为例,可以采用停车检查或行车检查的方式,停车检查方式,可以控制龙门架111移动以扫描整个乘用车10,或控制贯穿道112带动所述乘用车10在所述龙门架111下移动,以使得辐射检查系统扫描整个乘用车10;行车检查方式,限定待检查对象以适当的速度匀速行驶过检查通道,使得辐射检查系统扫描整个乘用车10或乘用车10的感兴趣的某一部分,在扫描过程中,控制图像处理装置140同步生成待检查对象中感兴趣部分的物质类别识别结果图像,完成辐射检查。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 4 to FIG. 6 and FIG. 7 , the
图10示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的辐射检查方法的流程图。Fig. 10 schematically shows a flowchart of a radiation inspection method according to an embodiment of the present disclosure.
根据本公开另一方面的实施例,如图10所示,提供一种利用上述任一实施例所述的辐射检查系统检查待检查对象的辐射检查方法,包括如下步骤:步骤S1,检测待检查对象在所述检查通道中的位置;步骤S2,响应于所述待检查对象到达所述检查通道中的预定位置,控制所述辐射源发出X射线束,以利用所述X射线束照射所述待检查对象;以及步骤S3,控制所述探测器探测从所述辐射源发出且与所述待检查对象相互作用后的X射线束的至少一部分。According to another embodiment of the present disclosure, as shown in FIG. 10 , there is provided a radiation inspection method for inspecting an object to be inspected using the radiation inspection system described in any of the above embodiments, including the following steps: Step S1, detecting The position of the object in the inspection channel; Step S2, in response to the object to be inspected reaching a predetermined position in the inspection channel, controlling the radiation source to emit an X-ray beam, so as to irradiate the X-ray beam with the X-ray beam an object to be inspected; and step S3, controlling the detector to detect at least a part of the X-ray beam emitted from the radiation source and interacting with the object to be inspected.
根据本公开实施例,基于反射式加速器的辐射源的辐射检查系统,其具备高空气丝分辨力(≤0.404mm)、高穿透力(≥150mm)与四种物质类别能力(有机物、无机物、混合物、重金属),主要性能指标能够同时达到行业标准最高级,以此达到增强检查系统的安全检查能力的目的。可以对即将进入机场、码头、港口、重要物流枢纽、重要会议场馆、海关、边检等处所的车辆进行安全检查,可以在车辆不停止行驶并且驾驶员并下车的情况下,对车辆装载的物品进行快速、准确、高效地检查。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the radiation inspection system based on the radiation source of the reflective accelerator has high air filament resolution (≤0.404mm), high penetrating power (≥150mm) and four types of substances (organic, inorganic , mixtures, heavy metals), the main performance indicators can reach the highest level of industry standards at the same time, so as to achieve the purpose of enhancing the safety inspection capability of the inspection system. It can conduct security checks on vehicles that are about to enter airports, wharves, ports, important logistics hubs, important conference venues, customs, border inspections, etc., and can check the vehicles loaded on the condition that the vehicles do not stop driving and the driver gets off the vehicle. Items are inspected quickly, accurately and efficiently.
例如,图像处理装置140和扫描控制装置150可以为独立的2个装置,但是,本公开的实施例并不局限于此,在一些示例性的实施例中,图像处理装置140和扫描控制装置150可以集成于1个装置中。For example, the
图11示意性示出了根据本公开实施例的电子设备的方框图,例如,所述电子设备可以包括图像处理装置140和扫描控制装置150中的至少一个,即,所述电子设备可以为适于实现图像处理装置140和扫描控制装置150中指示一个的功能的装置。Fig. 11 schematically shows a block diagram of an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, for example, the electronic device may include at least one of an
如图11所示,根据本公开实施例的电子设备900包括处理器901,其可以根据存储在只读存储器(ROM)902中的程序或者从存储部分908加载到随机访问存储器(RAM)903中的程序而执行各种适当的动作和处理。处理器901例如可以包括通用微处理器(例如CPU)、指令集处理器和/或相关芯片组和/或专用微处理器(例如,专用集成电路(ASIC))等等。处理器901还可以包括用于缓存用途的板载存储器。处理器901可以包括用于执行根据本公开实施例的方法流程的不同动作的单一处理单元或者是多个处理单元。As shown in FIG. 11 , an
在RAM 903中,存储有电子设备900操作所需的各种程序和数据。处理器901、ROM902以及RAM 903通过总线904彼此相连。处理器901通过执行ROM 902和/或RAM 903中的程序来执行根据本公开实施例的方法流程的各种操作。需要注意,所述程序也可以存储在除ROM 902和RAM903以外的一个或多个存储器中。处理器901也可以通过执行存储在所述一个或多个存储器中的程序来执行根据本公开实施例的方法流程的各种操作。In the
根据本公开的实施例,电子设备900还可以包括输入/输出(I/O)接口905,输入/输出(I/O)接口905也连接至总线904。电子设备900还可以包括连接至I/O接口905的以下部件中的一项或多项:包括键盘、鼠标等的输入部分906;包括诸如阴极射线管(CRT)、液晶显示器(LCD)等以及扬声器等的输出部分907;包括硬盘等的存储部分908;以及包括诸如LAN卡、调制解调器等的网络接口卡的通信部分909。通信部分909经由诸如因特网的网络执行通信处理。驱动器910也根据需要连接至I/O接口905。可拆卸介质911,诸如磁盘、光盘、磁光盘、半导体存储器等等,根据需要安装在驱动器910上,以便于从其上读出的计算机程序根据需要被安装入存储部分908。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the
本公开还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质可以是上述实施例中描述的设备/装置/系统中所包含的;也可以是单独存在,而未装配入该设备/装置/系统中。上述计算机可读存储介质承载有一个或者多个程序,当上述一个或者多个程序被执行时,实现根据本公开实施例的方法。The present disclosure also provides a computer-readable storage medium. The computer-readable storage medium may be included in the device/apparatus/system described in the above embodiments; it may also exist independently without being assembled into the device/system device/system. The above-mentioned computer-readable storage medium carries one or more programs, and when the above-mentioned one or more programs are executed, the method according to the embodiment of the present disclosure is realized.
根据本公开的实施例,计算机可读存储介质可以是非易失性的计算机可读存储介质,例如可以包括但不限于:便携式计算机磁盘、硬盘、随机访问存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、可擦式可编程只读存储器(EPROM或闪存)、便携式紧凑磁盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、光存储器件、磁存储器件、或者上述的任意合适的组合。在本公开中,计算机可读存储介质可以是任何包含或存储程序的有形介质,该程序可以被指令执行系统、装置或者器件使用或者与其结合使用。例如,根据本公开的实施例,计算机可读存储介质可以包括上文描述的ROM 902和/或RAM 903和/或ROM 902和RAM 903以外的一个或多个存储器。According to an embodiment of the present disclosure, the computer-readable storage medium may be a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, such as may include but not limited to: portable computer disk, hard disk, random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM) , erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), portable compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), optical storage device, magnetic storage device, or any suitable combination of the above. In the present disclosure, a computer-readable storage medium may be any tangible medium that contains or stores a program that can be used by or in conjunction with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device. For example, according to an embodiment of the present disclosure, a computer-readable storage medium may include one or more memories other than the above-described
本公开的实施例还包括一种计算机程序产品,其包括计算机程序,该计算机程序包含用于执行流程图所示的方法的程序代码。当计算机程序产品在计算机系统中运行时,该程序代码用于使计算机系统实现本公开实施例所提供的物品推荐方法。Embodiments of the present disclosure also include a computer program product, which includes a computer program including program codes for executing the methods shown in the flowcharts. When the computer program product runs in the computer system, the program code is used to make the computer system implement the item recommendation method provided by the embodiments of the present disclosure.
在该计算机程序被处理器901执行时执行本公开实施例的系统/装置中限定的上述功能。根据本公开的实施例,上文描述的系统、装置、模块、单元等可以通过计算机程序模块来实现。When the computer program is executed by the
在一种实施例中,该计算机程序可以依托于光存储器件、磁存储器件等有形存储介质。在另一种实施例中,该计算机程序也可以在网络介质上以信号的形式进行传输、分发,并通过通信部分909被下载和安装,和/或从可拆卸介质911被安装。该计算机程序包含的程序代码可以用任何适当的网络介质传输,包括但不限于:无线、有线等等,或者上述的任意合适的组合。In one embodiment, the computer program may rely on tangible storage media such as optical storage devices and magnetic storage devices. In another embodiment, the computer program can also be transmitted and distributed in the form of a signal on a network medium, downloaded and installed through the
在这样的实施例中,该计算机程序可以通过通信部分909从网络上被下载和安装,和/或从可拆卸介质911被安装。在该计算机程序被处理器901执行时,执行本公开实施例的系统中限定的上述功能。根据本公开的实施例,上文描述的系统、设备、装置、模块、单元等可以通过计算机程序模块来实现。In such an embodiment, the computer program may be downloaded and installed from a network via
根据本公开的实施例,可以以一种或多种程序设计语言的任意组合来编写用于执行本公开实施例提供的计算机程序的程序代码,具体地,可以利用高级过程和/或面向对象的编程语言、和/或汇编/机器语言来实施这些计算程序。程序设计语言包括但不限于诸如Java,C++,python,“C”语言或类似的程序设计语言。程序代码可以完全地在用户计算设备上执行、部分地在用户设备上执行、部分在远程计算设备上执行、或者完全在远程计算设备或服务器上执行。在涉及远程计算设备的情形中,远程计算设备可以通过任意种类的网络,包括局域网(LAN)或广域网(WAN),连接到用户计算设备,或者,可以连接到外部计算设备(例如利用因特网服务提供商来通过因特网连接)。According to the embodiments of the present disclosure, the program codes for executing the computer programs provided by the embodiments of the present disclosure can be written in any combination of one or more programming languages, specifically, high-level procedural and/or object-oriented programming language, and/or assembly/machine language to implement these computing programs. Programming languages include, but are not limited to, programming languages such as Java, C++, python, "C" or similar programming languages. The program code can execute entirely on the user computing device, partly on the user device, partly on the remote computing device, or entirely on the remote computing device or server. In cases involving a remote computing device, the remote computing device may be connected to the user computing device through any kind of network, including a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN), or may be connected to an external computing device (e.g., using an Internet service provider). business to connect via the Internet).
附图中的流程图和框图,图示了按照本公开各种实施例的系统、方法和计算机程序产品的可能实现的体系架构、功能和操作。在这点上,流程图或框图中的每个方框可以代表一个模块、程序段、或代码的一部分,上述模块、程序段、或代码的一部分包含一个或多个用于实现规定的逻辑功能的可执行指令。也应当注意,在有些作为替换的实现中,方框中所标注的功能也可以以不同于附图中所标注的顺序发生。例如,两个接连地表示的方框实际上可以基本并行地执行,它们有时也可以按相反的顺序执行,这依所涉及的功能而定。也要注意的是,框图或流程图中的每个方框、以及框图或流程图中的方框的组合,可以用执行规定的功能或操作的专用的基于硬件的系统来实现,或者可以用专用硬件与计算机指令的组合来实现。The flowchart and block diagrams in the Figures illustrate the architecture, functionality, and operation of possible implementations of systems, methods and computer program products according to various embodiments of the present disclosure. In this regard, each block in a flowchart or block diagram may represent a module, program segment, or portion of code that includes one or more logical functions for implementing specified executable instructions. It should also be noted that, in some alternative implementations, the functions noted in the block may occur out of the order noted in the figures. For example, two blocks shown in succession may, in fact, be executed substantially concurrently, or they may sometimes be executed in the reverse order, depending upon the functionality involved. It should also be noted that each block in the block diagrams or flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams or flowchart illustrations, can be implemented by a dedicated hardware-based system that performs the specified function or operation, or can be implemented by a A combination of dedicated hardware and computer instructions.
本领域的技术人员可以理解,上面所描述的实施例都是示例性的,并且本领域的技术人员可以对其进行改进,各种实施例中所描述的结构在不发生结构或者原理方面的冲突的情况下可以进行自由组合。Those skilled in the art can understand that the above-described embodiments are exemplary, and those skilled in the art can improve them, and the structures described in various embodiments do not conflict with each other in terms of structure or principle Can be combined freely.
虽然结合附图对本公开进行了说明,但是附图中公开的实施例旨在对本公开优选实施方式进行示例性说明,而不能理解为对本公开的一种限制。虽然本公开发明构思的一些实施例已被显示和说明,本领域普通技术人员将理解,在不背离本总体发明构思的原则和精神的情况下,可对这些实施例做出改变,本公开的范围以权利要求和它们的等同物限定。Although the present disclosure has been described with reference to the accompanying drawings, the embodiments disclosed in the accompanying drawings are intended to illustrate preferred embodiments of the present disclosure, and should not be construed as a limitation of the present disclosure. While certain embodiments of the presently disclosed inventive concept have been shown and described, it will be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that changes may be made to these embodiments without departing from the principles and spirit of the present general inventive concept. The scope is defined by the claims and their equivalents.
Claims (17)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211742642.XACN115884485A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection Systems |
| CN202311713756.6ACN117705838A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-13 | Cargo vehicle inspection system employing electronic linac |
| CN202311714608.6ACN117816570A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-13 | Ore sorting system using electron accelerator |
| CN202311713546.7ACN118102570A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-13 | Electron linac and radiation inspection system |
| PCT/CN2023/142886WO2024140946A1 (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-28 | Ore sorting system using electron accelerator |
| PCT/CN2023/142887WO2024140947A1 (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-28 | Electron linear accelerator and radiation inspection system |
| PCT/CN2023/142811WO2024140924A1 (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2023-12-28 | Cargo/vehicle inspection system using electron linear accelerator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211742642.XACN115884485A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection Systems |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115884485Atrue CN115884485A (en) | 2023-03-31 |
Family
ID=85757860
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211742642.XAWithdrawnCN115884485A (en) | 2022-12-30 | 2022-12-30 | Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection Systems |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115884485A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024140947A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 同方威视技术股份有限公司 | Electron linear accelerator and radiation inspection system |
- 2022
- 2022-12-30CNCN202211742642.XApatent/CN115884485A/ennot_activeWithdrawn
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024140947A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 同方威视技术股份有限公司 | Electron linear accelerator and radiation inspection system |
| WO2024140946A1 (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2024-07-04 | 同方威视技术股份有限公司 | Ore sorting system using electron accelerator |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8779398B2 (en) | Compact, interleaved radiation sources | |
| US6954515B2 (en) | Radiation sources and radiation scanning systems with improved uniformity of radiation intensity | |
| US7162005B2 (en) | Radiation sources and compact radiation scanning systems | |
| US9123519B2 (en) | Methods and systems for time-of-flight neutron interrogation for material discrimination | |
| EP0466920B1 (en) | Contraband detection system using direct imaging pulsed fast neutrons | |
| US7428297B2 (en) | Methods and apparatus for e-beam scanning | |
| US9442213B2 (en) | Method of electron beam transport in an X-ray scanner | |
| US20100072405A1 (en) | Compact, short-pulse X-ray and T-ray fused source | |
| Kutsaev et al. | Electron accelerators for novel cargo inspection methods | |
| US11921252B2 (en) | Security screening device capable of detecting and locating dangerous objects by using radiation | |
| CN115884485A (en) | Radiation Sources and Radiation Inspection Systems | |
| US20060140326A1 (en) | Portable low energy neutron source for high sensitivity material characterization | |
| Dinca et al. | X-ray backscatter imaging | |
| WO2024140947A1 (en) | Electron linear accelerator and radiation inspection system | |
| CN211123312U (en) | Special nuclear material detection device | |
| KR102110211B1 (en) | A non-destructive inspection system for acquiring image information of inspection object using synchronization signal | |
| RU2238545C2 (en) | Method for detection, indentification and localization of organic substances, including explosive and narcotic substnaces, with use of impulse flow of fast neutrons | |
| CN117849077A (en) | Detection method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| WW01 | Invention patent application withdrawn after publication | ||
| WW01 | Invention patent application withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20230331 |