CN115856985B - Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution - Google Patents
Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollutionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115856985B CN115856985BCN202310167084.7ACN202310167084ACN115856985BCN 115856985 BCN115856985 BCN 115856985BCN 202310167084 ACN202310167084 ACN 202310167084ACN 115856985 BCN115856985 BCN 115856985B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- uav
- dose rate
- formation
- radiation dose
- pollution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/20—Air quality improvement or preservation, e.g. vehicle emission control or emission reduction by using catalytic converters
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于环境监测技术领域,应用于大气放射性污染的监测过程中,具体为一种大气放射性污染的无人机协同监测方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental monitoring, is applied in the monitoring process of atmospheric radioactive pollution, and specifically relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative monitoring method of atmospheric radioactive pollution.
背景技术Background technique
大气放射性污染具有扩散范围广、转移变化快和持续性强等特点,而陆地放射性污染通常是围绕固定的放射源,呈点状辐射污染,因此,陆地环境中的放射性污染监测技术并不适合大气环境中的放射性污染监测工作。现有技术中,大气放射性污染监测主要围绕气溶胶采样、测量和数据分析等过程进行调查,通过测量大气中的核素迁移扩散浓度,判断分析污染强度和污染范围;现有的这种监测方法存在如下缺点:1、采样和测量都具有繁琐的工序;2、在面对突发的放射性污染时,不能及时和高效地完成污染区域内的放射性监测,监测结果迟滞,参考价值不高。Atmospheric radioactive pollution has the characteristics of wide diffusion, rapid transfer and change, and strong persistence, while terrestrial radioactive pollution usually surrounds fixed radioactive sources and presents point-like radiation pollution. Therefore, radioactive pollution monitoring technology in the terrestrial environment is not suitable for atmospheric pollution. Monitoring of radioactive contamination in the environment. In the prior art, the monitoring of atmospheric radioactive pollution mainly revolves around the process of aerosol sampling, measurement and data analysis. By measuring the concentration of nuclide migration and diffusion in the atmosphere, the pollution intensity and scope are judged and analyzed; the existing monitoring method There are the following disadvantages: 1. Both sampling and measurement have cumbersome procedures; 2. In the face of sudden radioactive pollution, the radioactive monitoring in the contaminated area cannot be completed in a timely and efficient manner, and the monitoring results are sluggish, and the reference value is not high.
随着无人机技术的快速发展,通过无人机搭载核辐射探测器的方式,应用于辐射环境本底调查、核事故/核泄漏污染情况监测、辐射事故中放射源搜寻等工作的场景越来越多;此类方式可有效降低工作人员的受照剂量、提高监测效率和获取空间辐射场数据,因此越来越受到研发人员的关注;无人机是远距离、多功能天空探测作业装置的重要内容和组成部分,其携带的辐射传感器能够以移动平台为载体,在其周围数百公里的范围内完成全方位的放射性污染监测任务。通过无人机的智能控制模块、目标探测与环境数据采集模块、导航模块、通讯模块、安全检测、自救单元和能源单元等组成结构,能够保证无人机的各项性能指标及工作的顺利完成,同时便于使用和维护。如何发挥无人机的优势,特别是多无人机编队及协同的方式,结合大气环境,得到一种及时、高效和范围广的大气放射性污染监测方法,以取代现有技术中传统的大气放射性污染监测过程,是目前的研究中亟待解决的问题。With the rapid development of UAV technology, the use of UAVs equipped with nuclear radiation detectors is becoming more and more widely used in background investigations of radiation environments, monitoring of nuclear accidents/nuclear leakage pollution, and search for radioactive sources in radiation accidents. More and more; such methods can effectively reduce the exposure dose of workers, improve monitoring efficiency and obtain space radiation field data, so they are getting more and more attention from R&D personnel; UAV is a long-distance, multi-functional sky detection operation device The radiation sensor carried by it can use the mobile platform as a carrier to complete a full range of radioactive pollution monitoring tasks within hundreds of kilometers around it. Through the intelligent control module, target detection and environmental data acquisition module, navigation module, communication module, safety detection, self-rescue unit and energy unit of the UAV, it can ensure the smooth completion of various performance indicators and work of the UAV. , and easy to use and maintain. How to give full play to the advantages of UAVs, especially the way of multi-UAV formation and coordination, combined with the atmospheric environment, to obtain a timely, efficient and wide-ranging atmospheric radioactive pollution monitoring method to replace the traditional atmospheric radioactive pollution in the existing technology The pollution monitoring process is an urgent problem to be solved in the current research.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种能解决现有技术问题的无人机协同监测方法,该方法可高效监测大气环境中的放射性污染;利用目标空域中携带辐射传感器的无人机编队,进行放射性污染的协同监测,通过对无人机编队中各个辐射传感器采集得到的信息进行融合决策,实时获取空间的污染强度,得出辐射剂量率分布等值面图,从而使无人机编队能对大气放射性污染进行高效监测,具有监测及时、范围广和效率高的优点。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a cooperative monitoring method for unmanned aerial vehicles that can solve the problems of the prior art, which can efficiently monitor radioactive pollution in the atmospheric environment; use the formation of unmanned aerial vehicles carrying radiation sensors in the target airspace to carry out radioactive pollution The coordinated monitoring of the UAV formation, through the fusion of the information collected by each radiation sensor in the UAV formation, obtains the pollution intensity of the space in real time, and obtains the isosurface map of the radiation dose rate distribution, so that the UAV formation can control the atmospheric radioactivity. Efficient monitoring of pollution has the advantages of timely monitoring, wide range and high efficiency.
本发明采用了以下技术方案来实现目的:The present invention adopts the following technical solutions to achieve the purpose:
一种大气放射性污染的无人机协同监测方法,包括如下步骤:An unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution, comprising the following steps:
S1、携带有核辐射传感器的无人机编队到达核污染目标空域,起飞并准备在目标区域中开始探测;S1. The UAV formation carrying the nuclear radiation sensor arrives at the airspace of the nuclear pollution target, takes off and prepares to start detection in the target area;
S2、无人机编队初始化,在核污染目标空域内进行多点随机探测,获取放射源在多个探测点处的辐射剂量率;S2. The UAV formation is initialized, and multi-point random detection is performed in the airspace of the nuclear pollution target to obtain the radiation dose rate of the radioactive source at multiple detection points;
S3、无人机编队中,中心无人机通过自身搭载的数据处理单元,对多个探测点处的辐射剂量率信息进行收集,并计算放射性污染强度,绘制出放射源的辐射剂量率分布等值面图,并共享给编队中的其他无人机;S3. In the drone formation, the central drone collects the radiation dose rate information at multiple detection points through its own data processing unit, calculates the intensity of radioactive pollution, and draws the radiation dose rate distribution of radioactive sources, etc. Surface map and share it with other UAVs in the formation;
S4、无人机编队中的所有无人机,依据步骤S3中绘制的辐射剂量率分布等值面图,沿着辐射剂量率强度上升最快的方向前进并进行探测,接近并确定放射源的所在位置;S4. All UAVs in the UAV formation, according to the isosurface map of radiation dose rate distribution drawn in step S3, advance and detect along the direction where the radiation dose rate intensity rises fastest, approach and determine the location of the radioactive source location;
S5、重复步骤S2至S4,直至完成整个核污染目标空域的大气放射性污染监测工作,得到目标空域的大气放射性污染监测结果数据。S5. Steps S2 to S4 are repeated until the air radioactive pollution monitoring work of the entire nuclear pollution target airspace is completed, and the air radioactive pollution monitoring result data of the target airspace is obtained.
具体的,步骤S1中,无人机编队通过移动平台被运送至核污染目标空域所在地点,随后起飞至空中开始探测;所述移动平台包括地面载具、空中载具和水面载具。Specifically, in step S1, the UAV formation is transported to the location of the nuclear pollution target airspace through a mobile platform, and then takes off into the air to start detection; the mobile platform includes ground vehicles, air vehicles and water surface vehicles.
进一步的,步骤S2中,无人机编队在位于空中后,各个无人机之间以一定距离保持通信和信息共享。Further, in step S2, after the UAV formation is in the air, each UAV maintains communication and information sharing at a certain distance.
具体的,无人机编队中,无人机的通信包括内部通信和外部通信;所述内部通信为单个无人机的自身通信系统,进行无人机内部的数据处理单元中各个软件模块的通信,所述软件模块包括污染数据采集模块、导航模块、剂量率测量数据实时接收模块和剂量率等值线制图模块;所述外部通信为不同无人机之间的通信,进行无人机编队的信息共享和数据传输。Specifically, in the drone formation, the communication of the drone includes internal communication and external communication; the internal communication is the self-communication system of a single drone, which communicates with each software module in the data processing unit inside the drone , the software module includes a pollution data acquisition module, a navigation module, a dose rate measurement data real-time receiving module and a dose rate contour mapping module; the external communication is communication between different drones, and the drone formation is carried out Information Sharing and Data Transfer.
进一步的,步骤S2中,无人机编队中的每个无人机均携带有核辐射传感器,当无人机编队随机抵达空域中的某一位置时,各个无人机分别获取当前自身所在位置的辐射剂量率,从而完成多点随机探测过程。Further, in step S2, each UAV in the UAV formation carries a nuclear radiation sensor. When the UAV formation randomly arrives at a certain position in the airspace, each UAV obtains its current location The radiation dose rate, thus completing the multi-point random detection process.
进一步的,步骤S3中,所述辐射剂量率分布等值面图,是通过获得多个辐射剂量率等值面后,经过拟合的方式得到的。Further, in step S3, the isosurface map of radiation dose rate distribution is obtained by fitting after obtaining multiple isosurfaces of radiation dose rate.
进一步的,所述多个辐射剂量率等值面的获得方法为:Further, the method for obtaining the plurality of radiation dose rate isosurfaces is:
S31、无人机编队进行多点随机探测时,获取当前每个无人机所在点的辐射剂量率,随后仍保持原有或设定的移动方向前进一定距离,到达目标空域中的另一处位置并获取新位置中每个无人机所在点的辐射剂量率;S31. When the UAV formation conducts multi-point random detection, obtain the current radiation dose rate of each UAV point, and then maintain the original or set movement direction to advance a certain distance to reach another place in the target airspace position and obtain the radiation dose rate of each UAV point in the new position;
S32、每个无人机计算自身探测的当前点剂量率与前一点剂量率的差值,若差值的绝对值不超过预设阈值,则认为当前点与前一点的剂量率相同;S32. Each UAV calculates the difference between the dose rate at the current point detected by itself and the dose rate at the previous point. If the absolute value of the difference does not exceed the preset threshold, it is considered that the dose rate at the current point is the same as that at the previous point;
S33、重复S31至S32的步骤,在核污染目标空域中的不同位置,不断进行不同点的剂量率差值判断,并实时调整无人机编队的飞行方向,从而依据剂量率差值数据,拟合得出当前的辐射剂量率等值面;S33. Repeat the steps from S31 to S32. In different positions in the nuclear pollution target airspace, continuously judge the dose rate difference at different points, and adjust the flight direction of the UAV formation in real time, so that according to the dose rate difference data, the planned Combined to obtain the current radiation dose rate isosurface;
S34、无人机编队沿当前的辐射剂量率等值面的法线方向移动前进,并重复S31至S33的步骤,最终得到多个辐射剂量率等值面。S34. The UAV formation moves forward along the normal direction of the current radiation dose rate isosurface, and repeats the steps from S31 to S33, finally obtaining multiple radiation dose rate isosurfaces.
进一步的,无人机编队的移动前进过程中,整个编队保持菱形梯队形状;在步骤S3及步骤S4中,中心无人机不固定,无人机编队中的所有无人机均搭载有数据处理单元;中心无人机为位于整个无人机编队几何中心处的无人机,在无人机编队移动及方向变换的过程中,中心无人机自适应的进行切换,始终满足整个无人机编队几何中心处的无人机作为中心无人机的条件。Further, during the moving process of the UAV formation, the entire formation maintains a rhombus echelon shape; in steps S3 and S4, the central UAV is not fixed, and all UAVs in the UAV formation are equipped with data processing unit; the central UAV is the UAV located at the geometric center of the entire UAV formation. During the process of UAV formation movement and direction change, the central UAV switches adaptively to always meet the requirements of the entire UAV formation. The UAV at the geometric center of the formation acts as the condition for the central UAV.
具体的,中心无人机自适应的切换过程为:无人机编队中,每个无人机将自身的最新位置信息进行实时共享,整个编队通过计算中心位置,将位于中心位置处或最靠近中心位置处的无人机切换为中心无人机。Specifically, the self-adaptive switching process of the central UAV is: in the UAV formation, each UAV will share its latest position information in real time, and the entire formation will be located at the central position or the closest The drone at the center position switches to the center drone.
具体的,所述放射源为碘131,所述辐射剂量率分布等值面图为碘131剂量率分布等值面图。Specifically, the radioactive source is iodine-131, and the isosurface diagram of radiation dose rate distribution is an isosurface diagram of iodine-131 dose rate distribution.
综上所述,由于采用了本技术方案,本发明的有益效果如下:In summary, due to the adoption of the technical solution, the beneficial effects of the present invention are as follows:
1、针对目标空域的大气放射性污染,无人机编队可以形成覆盖面积大的实时监测区域,通过本发明方法中的编队信息和数据共享特点,无人机编队能够快速完成大范围的监测任务,节省任务作业时间,这是单个无人机进行大气污染监测所无法达到的效果。1. For the atmospheric radioactive pollution in the target airspace, the UAV formation can form a real-time monitoring area with a large coverage area. Through the characteristics of formation information and data sharing in the method of the present invention, the UAV formation can quickly complete a wide range of monitoring tasks. Save mission operation time, which is an effect that cannot be achieved by a single drone for air pollution monitoring.
2、本发明方法通过无人机编队随机获取多点位置的放射性污染数据,构建了辐射剂量率分布等值面图,并计算出辐射强度梯度上升最大的方向,从而引领无人机编队快速向放射性污染严重的区域移动并进行监测;通过无人机编队中的信息共享和编队控制,无人机编队在辐射强度上升慢的区域可实行快速探测,在辐射强度上升快的区域可实行慢速探测,从而平衡了监测效率和辐射探测精度的关系,能实现更精准、更高效的大气放射性污染监测过程。2. The method of the present invention randomly obtains radioactive pollution data at multiple points through the UAV formation, constructs the isosurface map of the radiation dose rate distribution, and calculates the direction in which the radiation intensity gradient rises the most, thereby leading the UAV formation to quickly move towards Move and monitor areas with severe radioactive pollution; through information sharing and formation control in UAV formations, UAV formations can implement fast detection in areas where radiation intensity rises slowly, and slow detection in areas where radiation intensity rises rapidly. Detection, thus balancing the relationship between monitoring efficiency and radiation detection accuracy, can achieve a more accurate and efficient monitoring process of atmospheric radioactive pollution.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明的方法的流程示意图;Fig. 1 is a schematic flow sheet of the method of the present invention;
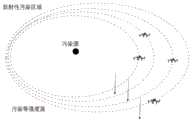
图2为本发明中无人机编队绘制辐射剂量率分布等值面图的过程示意图。Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the process of drawing the radiation dose rate distribution isosurface map by the UAV formation in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。通常在此处附图中描述和示出的本发明实施例的组件可以按各种不同的配置来布置和设计。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. The components of the embodiments of the invention generally described and illustrated in the figures herein may be arranged and designed in a variety of different configurations.
因此,以下对在附图中提供的本发明的实施例的详细描述并非旨在限制要求保护的本发明的范围,而是仅仅表示本发明的选定实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。Accordingly, the following detailed description of the embodiments of the invention provided in the accompanying drawings is not intended to limit the scope of the claimed invention, but merely represents selected embodiments of the invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
如图1所示,一种大气放射性污染的无人机协同监测方法,包括如下步骤:As shown in Figure 1, a UAV collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution includes the following steps:
S1、携带有核辐射传感器的无人机编队到达核污染目标空域,起飞并准备在目标区域中开始探测;S1. The UAV formation carrying the nuclear radiation sensor arrives at the airspace of the nuclear pollution target, takes off and prepares to start detection in the target area;
S2、无人机编队初始化,在核污染目标空域内进行多点随机探测,获取放射源在多个探测点处的辐射剂量率;S2. The UAV formation is initialized, and multi-point random detection is performed in the airspace of the nuclear pollution target to obtain the radiation dose rate of the radioactive source at multiple detection points;
S3、无人机编队中,中心无人机通过自身搭载的数据处理单元,对多个探测点处的辐射剂量率信息进行收集,并计算放射性污染强度,绘制出放射源的辐射剂量率分布等值面图,并共享给编队中的其他无人机;S3. In the drone formation, the central drone collects the radiation dose rate information at multiple detection points through its own data processing unit, calculates the intensity of radioactive pollution, and draws the radiation dose rate distribution of radioactive sources, etc. Surface map and share it with other UAVs in the formation;
S4、无人机编队中的所有无人机,依据步骤S3中绘制的辐射剂量率分布等值面图,沿着辐射剂量率强度上升最快的方向前进并进行探测,接近并确定放射源的所在位置;S4. All UAVs in the UAV formation, according to the isosurface map of radiation dose rate distribution drawn in step S3, advance and detect along the direction where the radiation dose rate intensity rises fastest, approach and determine the location of the radioactive source location;
S5、重复步骤S2至S4,直至完成整个核污染目标空域的大气放射性污染监测工作,得到目标空域的大气放射性污染监测结果数据。S5. Steps S2 to S4 are repeated until the air radioactive pollution monitoring work of the entire nuclear pollution target airspace is completed, and the air radioactive pollution monitoring result data of the target airspace is obtained.
以下介绍本实施例中方法的具体过程,以无人机协同监测大气环境中碘131污染物的放射性泄露为例。The following describes the specific process of the method in this embodiment, taking the cooperative monitoring of radioactive leakage of iodine-131 pollutants in the atmospheric environment by drones as an example.
在步骤S1中,将携带核辐射传感器的无人机通过移动平台运送至核污染空域,无人机编队起飞上升到高空,在一个较大的区域进行大范围的探测;移动平台依据具体实施单位的情况,可包括地面载具、空中载具和水面载具。In step S1, the UAV carrying the nuclear radiation sensor is transported to the nuclear-contaminated airspace through the mobile platform, the UAV formation takes off and rises to high altitude, and conducts a large-scale detection in a larger area; the mobile platform depends on the specific implementation unit In the case of , it may include ground vehicles, air vehicles and water surface vehicles.
在步骤S2中,无人机编队初始化,编队内无人机在编队所在的区域内进行随机的探测,获取得到多点位置碘131的辐射剂量率;在飞行移动过程中,各个无人机之间以一定的距离保持通信和信息共享。In step S2, the UAV formation is initialized, and the UAVs in the formation conduct random detection in the area where the formation is located, and obtain the radiation dose rate of iodine-131 at multiple positions; Maintain communication and information sharing at a certain distance.
在步骤S3中,利用编队几何中心无人机搭载的数据处理单元对编队无人机多点位置获取的探测信息进行收集,计算各点的放射性污染强度,绘制出碘131剂量率分布等值面图,如图2所示,从而获得剂量率的分布规律,并且共享给其他无人机。In step S3, use the data processing unit carried by the UAVs in the geometric center of the formation to collect the detection information obtained from the multi-point positions of the UAVs in the formation, calculate the radioactive pollution intensity at each point, and draw the isosurface of the iodine-131 dose rate distribution As shown in Figure 2, the distribution of the dose rate can be obtained and shared with other UAVs.
本实施例中,编队中的无人机搭载的数据处理单元,获取多点位置的包括位置信息、角度信息和剂量率强度信息;通过这些信息,编队几何中心无人机的数据处理单元通过构建剂量率分布图,来计算各个无人机位置之间的剂量率差值,获取当前位置剂量率强度梯度上升的最快方向,并共享给其他无人机。In this embodiment, the data processing unit carried by the drones in the formation acquires position information, angle information and dose rate intensity information of multi-point positions; through these information, the data processing unit of the drones in the formation geometric center is constructed The dose rate distribution map is used to calculate the dose rate difference between the positions of each drone, obtain the fastest direction of the dose rate intensity gradient at the current position, and share it with other drones.
而碘131剂量率分布等值面图,是通过获得多个碘131剂量率等值面后,经过拟合的方式得到的,多个碘131剂量率等值面的获得方法为:The isosurface diagram of the iodine 131 dose rate distribution is obtained by fitting after obtaining multiple iodine 131 dose rate isosurfaces. The method for obtaining multiple iodine 131 dose rate isosurfaces is as follows:
S31、无人机编队进行多点随机探测时,获取当前每个无人机所在点的碘131剂量率,随后仍保持原有或设定的移动方向前进一定距离,到达目标空域中的另一处位置并获取新位置中每个无人机所在点的碘131剂量率;S31. When the UAV formation conducts multi-point random detection, obtain the iodine-131 dose rate at the current point where each UAV is located, and then still maintain the original or set moving direction to advance a certain distance to reach another point in the target airspace. position and obtain the iodine-131 dose rate of each UAV point in the new position;
S32、每个无人机计算自身探测的当前点剂量率与前一点剂量率的差值,若差值的绝对值不超过预设阈值,则认为当前点与前一点的剂量率相同;S32. Each UAV calculates the difference between the dose rate at the current point detected by itself and the dose rate at the previous point. If the absolute value of the difference does not exceed the preset threshold, it is considered that the dose rate at the current point is the same as that at the previous point;
S33、重复S31至S32的步骤,在碘131污染目标空域中的不同位置,不断进行不同点的剂量率差值判断,并实时调整无人机编队的飞行方向,从而依据剂量率差值数据,拟合得出当前的碘131剂量率等值面;S33. Repeat the steps from S31 to S32. In different positions in the iodine-131 polluted target airspace, continuously judge the dose rate difference at different points, and adjust the flight direction of the UAV formation in real time, so that according to the dose rate difference data, Fitting results in the current iodine-131 dose rate isosurface;
S34、无人机编队沿当前的辐射剂量率等值面的法线方向移动前进,并重复S31至S33的步骤,最终得到多个辐射剂量率等值面。S34. The UAV formation moves forward along the normal direction of the current radiation dose rate isosurface, and repeats the steps from S31 to S33, finally obtaining multiple radiation dose rate isosurfaces.
上述过程总体而言为:首先由无人机携带的核辐射传感器测量并记录当前点的核素剂量率值,然后以当前方向前进一定的距离到另一点,测量并且记录另一点的核素剂量率值,比较当前点与另一点剂量率的差值,若差值绝对值不超过一个阈值,则认为这两点的剂量率相同;接着重复上述步骤找到第三个点,拟合出剂量率等值面,然后无人机开始以最新当前点的等值面的法线方向前进,重复之前的步骤,找到第二个剂量率等值面;根据上述的步骤记录的数据模拟绘制出多个剂量率分布等值面,然后计算出剂量率强度上升最快的方向。The above process is generally as follows: first, the nuclear radiation sensor carried by the UAV measures and records the nuclide dose rate value at the current point, and then advances a certain distance to another point in the current direction, and measures and records the nuclide dose at another point Rate value, compare the difference between the current point and the dose rate of another point, if the absolute value of the difference does not exceed a threshold, it is considered that the dose rate of the two points is the same; then repeat the above steps to find the third point, and fit the dose rate isosurface, and then the UAV starts to advance in the normal direction of the isosurface at the latest current point, repeat the previous steps to find the second dose rate isosurface; draw multiple simulations based on the data recorded in the above steps The dose rate distribution isosurface, and then calculate the direction of the fastest rising dose rate intensity.
在步骤S4中,无人机根据共享的信息,沿着剂量率强度上升最快的方向前进,各个无人机之间以一定的距离保持通信和信息共享。具体的来说就是编队内各无人机接受来自中心无人机共享的剂量率强度上升最快方向信息,控制自身按照剂量率强度上升最快的方向前进。其中,中心无人机不是固定的,按照无人机将自身最新的位置信息进行编队内共享,重新计算中心位置,将位于该位置或离该位置最近的无人机设定为中心。In step S4, according to the shared information, the UAVs advance along the direction of the fastest increase in dose rate intensity, and communication and information sharing are maintained between each UAV at a certain distance. Specifically, each UAV in the formation receives the information of the fastest rising direction of dose rate intensity shared by the central UAV, and controls itself to move forward in the direction of the fastest rising dose rate intensity. Among them, the central UAV is not fixed, and the UAV shares its latest position information in the formation according to the UAV, recalculates the central position, and sets the UAV at or near this position as the center.
最后,重复上述步骤S2至S4,直至完成目标空域放射性污染探测。Finally, the above steps S2 to S4 are repeated until the detection of radioactive contamination in the target airspace is completed.
本实施例中,无人机在初始位置周边进行随机多点快速探测,获取一定范围内的多点辐射强度信息,通过中心无人机搭载的计算单元,得出区域放射性剂量率分布等值面图,多点之间的梯度上升值通过计算绘制出来,通过比较,得出初始点位置强度梯度上升最大方向,并通过编队内协同导航,将相关信息传输给编队内其他无人机,实现信息共享。当编队开始进行探测时,编队无人机快速沿着强度梯度上升最大的方向前进探测,重复上述步骤2-4,周期性的获取多位置的辐射强度,最终快速实现目标区域的放射性污染监测。In this embodiment, the UAV conducts random multi-point rapid detection around the initial position, obtains multi-point radiation intensity information within a certain range, and obtains the isosurface of the regional radioactive dose rate distribution through the computing unit carried by the central UAV In the figure, the gradient rise value between multiple points is calculated and drawn, and by comparison, the maximum direction of the strength gradient rise of the initial point position is obtained, and the relevant information is transmitted to other UAVs in the formation through collaborative navigation in the formation to realize information shared. When the formation starts to detect, the formation UAVs quickly move forward in the direction where the intensity gradient rises the most, repeat the above steps 2-4, periodically obtain the radiation intensity of multiple locations, and finally quickly realize the monitoring of radioactive contamination in the target area.
同时,无人机编队中,无人机的通信包括内部通信和外部通信;内部通信为单个无人机的自身通信系统,进行无人机内部的数据处理单元中各个软件模块的通信,软件模块包括污染数据采集模块、导航模块、剂量率测量数据实时接收模块和剂量率等值线制图模块;外部通信为不同无人机之间的通信,进行无人机编队的信息共享和数据传输。At the same time, in the UAV formation, the communication of the UAV includes internal communication and external communication; the internal communication is the self-communication system of a single UAV, which communicates with each software module in the data processing unit inside the UAV. Including pollution data acquisition module, navigation module, dose rate measurement data real-time receiving module and dose rate contour mapping module; external communication is communication between different UAVs, for information sharing and data transmission of UAV formation.
本实施例中的大气放射性污染的无人机协同监测方法,无人机编队保持菱形梯队。所述的菱形梯队利用中心无人机来控制整个编队的运动趋势,该队形适用于大面积空域内的放射性污染监测;同时在编队投放和探测过程中,对于编队所获取的污染强度信息、污染强度上升最快方向的信息实时更新记录,并且注明绝对位置信息。In the UAV cooperative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution in this embodiment, the UAV formation maintains a diamond-shaped echelon. The diamond-shaped echelon uses the central UAV to control the movement trend of the entire formation. This formation is suitable for radioactive pollution monitoring in a large area of airspace; at the same time, during the formation launch and detection process, the pollution intensity information obtained by the formation, The information of the fastest rising direction of pollution intensity is updated and recorded in real time, and the absolute position information is indicated.
而至于中心无人机的切换设计,无人机编队协同导航很大程度上依赖于彼此之间的通信,通过共享探测信息来提高整个编队的探测效率和精度。编队内无人机把自身最新的位置、速度信息以及所需要发送的放射性污染处理数据通过数据传输给相邻的无人机;内部传输的信息主要是编队协同完成任务所需的信息,受到空间环境和外部干扰信号等的影响,编队本身运动和通信范围限制容易影响无人机之间的通信质量。在信息共享的同时,需要自适应的切换中心无人机,以保证通信质量达到一个最佳的状态。As for the switching design of the central drone, the cooperative navigation of the drone formation largely depends on the communication between each other, and the detection efficiency and accuracy of the entire formation can be improved by sharing detection information. The UAVs in the formation transmit their latest position and speed information and the radioactive pollution treatment data they need to send to adjacent UAVs through data; The influence of the environment and external interference signals, etc., the movement of the formation itself and the limitation of the communication range are likely to affect the communication quality between UAVs. At the same time of information sharing, an adaptive switching center UAV is required to ensure that the communication quality reaches an optimal state.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310167084.7ACN115856985B (en) | 2023-02-27 | 2023-02-27 | Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310167084.7ACN115856985B (en) | 2023-02-27 | 2023-02-27 | Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115856985A CN115856985A (en) | 2023-03-28 |
| CN115856985Btrue CN115856985B (en) | 2023-05-12 |
Family
ID=85658959
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310167084.7AActiveCN115856985B (en) | 2023-02-27 | 2023-02-27 | Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115856985B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118981040B (en)* | 2024-08-13 | 2025-05-09 | 中国人民解放军92609部队 | A nuclear radioactive contamination assessment method based on fan array tracing strategy |
| CN120315454B (en)* | 2025-06-12 | 2025-08-15 | 西南科技大学 | Nuclear security inspection method and system based on unmanned aerial vehicle |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105277927A (en)* | 2014-06-19 | 2016-01-27 | 南京理工大学 | Time-domain order step-by-step analysis method for transient electromagnetic characteristics of aircraft formation |
| WO2017209316A1 (en)* | 2016-05-30 | 2017-12-07 | 전자부품연구원 | Method and system for detecting remote radiation dose rate by using laser altimeter-based unmanned aerial vehicle |
| CN108549403A (en)* | 2018-03-30 | 2018-09-18 | 北京润科通用技术有限公司 | A kind of collaborative obstacle avoidance method and device |
| CN109407694A (en)* | 2017-08-18 | 2019-03-01 | 清华大学 | Unmanned plane formation control method, readable storage medium storing program for executing, equipment and unmanned plane |
| JP2019091326A (en)* | 2017-11-16 | 2019-06-13 | みこらった株式会社 | Cleaning system, robot cleaning device comprising cleaning system, and flying object device |
| WO2019238596A1 (en)* | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Determining control parameters for formation of multiple uavs |
| US10866226B1 (en)* | 2017-02-07 | 2020-12-15 | Air Stations Llc/Elevated Analytics Llc Joint Venture | Multi-point ground emission source sensor system |
| CN112130581A (en)* | 2020-08-19 | 2020-12-25 | 昆明理工大学 | A coordinated mission planning method for UAV swarms for air maneuver operations |
| CN113467507A (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2021-10-01 | 中交遥感载荷(江苏)科技有限公司 | Atmospheric environment sampling method based on unmanned aerial vehicle system and unmanned aerial vehicle system thereof |
| CN115469666A (en)* | 2022-09-21 | 2022-12-13 | 浙江大学 | A Cooperative Isosurface Tracking Method for Multi-robots with Limited Communication |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001153952A (en)* | 1999-11-26 | 2001-06-08 | Nippon Anzen Hosho Keibi Kk | System for grasping radioactive proliferation state |
| CN203941294U (en)* | 2014-05-20 | 2014-11-12 | 西南科技大学 | A kind of nuclear radiation monitoring system based on air-robot |
| US9878257B2 (en)* | 2014-06-10 | 2018-01-30 | University Of Kansas | Aerial vehicles and methods of use |
| US10114384B2 (en)* | 2016-09-13 | 2018-10-30 | Arrowonics Technologies Ltd. | Formation flight path coordination of unmanned aerial vehicles |
| CN107117312A (en)* | 2017-05-22 | 2017-09-01 | 中国原子能科学研究院 | A kind of unmanned vehicle low latitude radiation monitoring system |
| CN107807665B (en)* | 2017-11-29 | 2020-11-17 | 合肥工业大学 | Unmanned aerial vehicle formation detection task cooperative allocation method and device |
| CN109061707A (en)* | 2018-07-23 | 2018-12-21 | 河南省核工业放射性核素检测中心 | Nuclear pollution region nuclear radiation monitoring system and method based on unmanned plane |
| CN109856668B (en)* | 2019-03-21 | 2020-09-01 | 西南科技大学 | A multi-machine collaborative monitoring method for marine radioactive pollution |
| RU2755604C1 (en)* | 2021-01-11 | 2021-09-17 | Федеральное государственное казённое учреждение "12 Центральный научно-исследовательский институт" Министерства обороны Российской Федерации | Method for determining parameters of emergency radiation source according to data of aerial radiation reconnaissance of area |
| CN117859074A (en)* | 2021-06-11 | 2024-04-09 | 网络无人机公司 | System and method for unmanned aerial vehicle group wireless communication |
- 2023
- 2023-02-27CNCN202310167084.7Apatent/CN115856985B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105277927A (en)* | 2014-06-19 | 2016-01-27 | 南京理工大学 | Time-domain order step-by-step analysis method for transient electromagnetic characteristics of aircraft formation |
| WO2017209316A1 (en)* | 2016-05-30 | 2017-12-07 | 전자부품연구원 | Method and system for detecting remote radiation dose rate by using laser altimeter-based unmanned aerial vehicle |
| US10866226B1 (en)* | 2017-02-07 | 2020-12-15 | Air Stations Llc/Elevated Analytics Llc Joint Venture | Multi-point ground emission source sensor system |
| CN109407694A (en)* | 2017-08-18 | 2019-03-01 | 清华大学 | Unmanned plane formation control method, readable storage medium storing program for executing, equipment and unmanned plane |
| JP2019091326A (en)* | 2017-11-16 | 2019-06-13 | みこらった株式会社 | Cleaning system, robot cleaning device comprising cleaning system, and flying object device |
| CN108549403A (en)* | 2018-03-30 | 2018-09-18 | 北京润科通用技术有限公司 | A kind of collaborative obstacle avoidance method and device |
| WO2019238596A1 (en)* | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Determining control parameters for formation of multiple uavs |
| CN112130581A (en)* | 2020-08-19 | 2020-12-25 | 昆明理工大学 | A coordinated mission planning method for UAV swarms for air maneuver operations |
| CN113467507A (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2021-10-01 | 中交遥感载荷(江苏)科技有限公司 | Atmospheric environment sampling method based on unmanned aerial vehicle system and unmanned aerial vehicle system thereof |
| CN115469666A (en)* | 2022-09-21 | 2022-12-13 | 浙江大学 | A Cooperative Isosurface Tracking Method for Multi-robots with Limited Communication |
Non-Patent Citations (6)
| Title |
|---|
| APPLICATIONS OF NETWORKED UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES TO COOPERATIVE FIRE DETECTION USING GRID-BASED DATA FUSION TECHNIQUES;Luis Merino et al;《IFAC Proceedings Volumes 》;全文* |
| Cooperative communication framework design for the unmanned aerial vehicles-unmanned surface vehicles formation;Ma,Y et al.;《Advances In Mechanical Engineering》;全文* |
| 一种应用于机器人行为控制的算法研究;张江梅 等;《黑龙江科技信息》;全文* |
| 军用装备重大核事故应急处置模拟训练系统实践研究;袁伟 等;《中国应急救援》;全文* |
| 无人旋翼机机载放射性气溶胶在线监测系统的研制;王泽宇;《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 工程科技Ⅰ辑 》;全文* |
| 空中抛撒的微小型多机器人抗冲击设计与协同控制;李月;《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技》;全文* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115856985A (en) | 2023-03-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115856985B (en) | Unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative monitoring method for atmospheric radioactive pollution | |
| CN103078673B (en) | A kind of dedicated unmanned Helicopter System being applicable to mountain area electrical network and patrolling and examining | |
| CN106405040A (en) | Unmanned-device-based water quality patrolling, contaminant originating system and method thereof | |
| CN206388203U (en) | A kind of environmental monitoring system | |
| CN108303995B (en) | A substation inspection UAV flight safety system and its use method | |
| CN103135550B (en) | Multiple obstacle-avoidance control method of unmanned plane used for electric wire inspection | |
| CN103606852B (en) | The electric power line inspection method of depopulated helicopter | |
| CN113848226B (en) | An autonomous traceability system and traceability method for intelligent space mobile pollutants | |
| CN110579768B (en) | Method for designing power line-patrol route of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicle laser radar | |
| CN112527010B (en) | Indoor substation unmanned aerial vehicle multi-machine cooperative inspection method based on artificial potential field and particle optimization | |
| CN113534844B (en) | Method and device for inspecting transmission line of rotorcraft in unknown environment | |
| CN113075686B (en) | Cable trench intelligent inspection robot graph building method based on multi-sensor fusion | |
| CN116679011A (en) | An unmanned aerial vehicle device and monitoring method for monitoring carbon emission sources | |
| CN109002057A (en) | A kind of intelligent patrol detection UAV system of cable tunnel | |
| CN109856668B (en) | A multi-machine collaborative monitoring method for marine radioactive pollution | |
| CN106125092A (en) | A kind of unmanned plane automatic obstacle-avoiding system and method based on two-dimensional laser radar | |
| CN105915275B (en) | A kind of wide area cooperates with accurate remote sensing platform and its remote sensing technique | |
| CN108168506A (en) | A kind of air pollution emission monitoring samples Cross Location Method with unmanned plane | |
| CN113009100A (en) | Base station type unmanned aerial vehicle watershed water environment monitoring system | |
| CN114813493A (en) | Raise dust on-line monitoring system based on unmanned aerial vehicle unites ground fixed point and deploys | |
| CN206021087U (en) | A kind of quadrotor condition of a fire inspection device with automatic obstacle avoiding function | |
| CN108263606A (en) | One kind is based on VTOL fixed-wing unmanned plane and its natural gas line cruising inspection system, method | |
| CN107402579A (en) | A kind of haze detection method based on unmanned plane | |
| CN116743525A (en) | Transformer substation unmanned aerial vehicle situation awareness method based on hong-Mongolian distributed soft bus | |
| CN108105593A (en) | A kind of infrared camera and the unmanned plane that natural gas line inspection is carried out based on infrared camera |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |