CN115841495A - Polyp segmentation method and system based on double-boundary guiding attention exploration - Google Patents
Polyp segmentation method and system based on double-boundary guiding attention explorationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115841495A CN115841495ACN202211632343.0ACN202211632343ACN115841495ACN 115841495 ACN115841495 ACN 115841495ACN 202211632343 ACN202211632343 ACN 202211632343ACN 115841495 ACN115841495 ACN 115841495A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- boundary
- feature
- polyp
- attention
- exploration
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及息肉分割技术领域,更具体的说是涉及一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割方法及系统。The present invention relates to the technical field of polyp segmentation, and more specifically relates to a polyp segmentation method and system based on dual boundary guided attention exploration.
背景技术Background technique
结直肠癌是一种常见的消化道恶性肿瘤,严重危害人类健康,其发病率在所有癌症中排名第三。息肉作为结直肠癌最重要的前体之一,如果不及时治疗,容易转化为恶性肿瘤。结肠镜检查是检测结肠病变的有效方法,可以为医生提供精确的定位信息,以便医生在其癌变前及时切除。然而,结直肠镜检查有时会漏诊息肉。因此,结肠镜图像中息肉的自动准确分割对临床预防结直肠癌具有重要意义。Colorectal cancer is a common malignant tumor of the digestive tract, which seriously endangers human health, and its incidence rate ranks third among all cancers. As one of the most important precursors of colorectal cancer, polyps can easily transform into malignant tumors if not treated in time. Colonoscopy is an effective method to detect colonic lesions, and can provide doctors with precise location information so that doctors can remove them in time before they become cancerous. However, colonoscopy sometimes misses polyps. Therefore, the automatic and accurate segmentation of polyps in colonoscopy images is of great significance for the clinical prevention of colorectal cancer.
传统的息肉分割方法通常依赖于手工提取的特征来识别息肉,例如纹理分析、颜色分布、几何特征和强度分布。虽然传统方法取得了相当大的进步,但基于手工特征的这些方法的息肉分割精度仍然较低,泛化能力较差,不能满足临床实践的要求。近年来,随着深度学习的不断发展,基于深度学习的息肉分割方法被证明优于传统手工提取特征的方法。随着U形网络的提出,这种编码解码网络已成为医学图像分割中的主流网络架构。最近,注意力机制越来越多被应用于医学分割,尤其是息肉分割,经常被用于增强息肉的模糊边界,或提取全局和局部特征。PraNet通过并行解码器将高级特征信息聚集在一起以预测粗糙区域,并通过反向注意机制建立息肉边界和内部结构之间的依赖关系。Traditional polyp segmentation methods usually rely on manually extracted features to identify polyps, such as texture analysis, color distribution, geometric features, and intensity distribution. Although traditional methods have made considerable progress, these methods based on manual features still have low polyp segmentation accuracy and poor generalization ability, which cannot meet the requirements of clinical practice. In recent years, with the continuous development of deep learning, polyp segmentation methods based on deep learning have been proved to be superior to traditional manual feature extraction methods. With the proposal of U-shaped network, this codec network has become the mainstream network architecture in medical image segmentation. Recently, attention mechanisms have been increasingly applied to medical segmentation, especially polyp segmentation, where they are often used to enhance the blurred boundaries of polyps, or to extract global and local features. PraNet aggregates high-level feature information through a parallel decoder to predict rough regions, and establishes dependencies between polyp boundaries and internal structures through a reverse attention mechanism.
虽然这些基于深度学习方法的分割精度和泛化能力相较于传统方法有了较大提升,但是这些方法在面对息肉分割的挑战时仍然有不足。首先是边界模糊情况,结肠镜在肠道中移动时,会导致运动模糊和反射等问题,这造成了息肉图像的边界模糊,增大息肉分割难度。其次是息肉多尺度适应性问题。由于息肉组织的大小和形状多变,目前的息肉分割方法对于多尺度特征的提取能力仍存在一定的局限性。最后是息肉与周围正常组织的相性问题。息肉与背景对比度低,其纹理和颜色与周围组织之间高度相似,导致难以识别。Although the segmentation accuracy and generalization ability of these deep learning-based methods have been greatly improved compared with traditional methods, these methods still have shortcomings in the face of the challenge of polyp segmentation. The first is the blurring of the boundary. When the colonoscope moves in the intestine, it will cause problems such as motion blur and reflection, which will cause the boundary of the polyp image to be blurred and increase the difficulty of polyp segmentation. Second is the problem of polyp multiscale adaptability. Due to the variable size and shape of polyp tissue, the current polyp segmentation methods still have certain limitations in the ability to extract multi-scale features. Finally, there is the question of the compatibility of the polyps with the surrounding normal tissues. Polyps have low contrast to the background and high similarity in texture and color to surrounding tissue, making identification difficult.
因此,如何克服现有技术中息肉边界模糊、息肉多尺度适应性问题和息肉与周围正常组织相似性问题是本领域技术人员亟需解决的问题。Therefore, how to overcome the blurred boundaries of polyps, the multi-scale adaptability of polyps, and the similarity between polyps and surrounding normal tissues in the prior art is an urgent problem to be solved by those skilled in the art.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明提供了一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割方法及系统,克服上述缺陷。In view of this, the present invention provides a method and system for polyp segmentation based on dual boundary-guided attention exploration to overcome the above-mentioned defects.
为了实现上述目的,本发明提供如下技术方案:In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides the following technical solutions:
一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割系统,包括:PVTv2主干提取网络、多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA、底层细节增强模块LDE和双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE;A polyp segmentation system based on dual boundary-guided attention exploration, including: PVTv2 backbone extraction network, multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA, underlying detail enhancement module LDE and dual boundary-guided attention exploration module DBE;
所述PVTv2主干提取网络,用于提取主干特征形成特征图;The PVTv2 backbone extraction network is used to extract backbone features to form feature maps;
所述多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA,用于融合特征图的相邻两层上下文特征信息,再对融合后的特征信息利用不同扩张速率的扩张卷积获取广泛特征,将多个广泛特征进行聚合获得初步预测分割结果;The multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA is used to fuse the adjacent two layers of context feature information of the feature map, and then use the dilated convolution with different expansion rates to obtain extensive features for the fused feature information, and aggregate multiple extensive features Obtain preliminary prediction segmentation results;
所述底层细节增强模块LDE,用于根据初步预测分割结果抑制背景干扰以及捕捉细节信息;The underlying detail enhancement module LDE is used to suppress background interference and capture detail information according to the preliminary prediction segmentation result;
所述双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE,用于通过采用既定策略获得真实息肉边界。The dual boundary-guided attention exploration module DBE is used to obtain real polyp boundaries by adopting established strategies.
可选的,所述PVTv2主干提取网络提取的特征包括第一多尺度金字塔特征X1、第二多尺度金字塔特征X2、第三多尺度金字塔特征X3和第四多尺度金字塔特征X4,其中,第一多尺度金字塔特征X1为细节特征;第二多尺度金字塔特征X2、第三多尺度金字塔特征X3和第四多尺度金字塔特征X4为语义特征。Optionally, the features extracted by the PVTv2 backbone extraction network include the first multi-scale pyramid feature X1, the second multi-scale pyramid feature X2, the third multi-scale pyramid feature X3 and the fourth multi-scale pyramid feature X4, wherein the first The multi-scale pyramid feature X1 is a detail feature; the second multi-scale pyramid feature X2, the third multi-scale pyramid feature X3 and the fourth multi-scale pyramid feature X4 are semantic features.
可选的,所述多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA中扩张卷积的数量为四个。Optionally, the number of dilated convolutions in the multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA is four.
可选的,所述底层细节增包括强模块LDE包括细节融合子模块和细节提取子模块;Optionally, the underlying detail enhancement module LDE includes a detail fusion submodule and a detail extraction submodule;
所述细节提取子模块,用于采用通道注意力和空间注意力串联的方式从不同维度捕获息肉的细节信息;The detail extraction submodule is used to capture the detail information of the polyp from different dimensions in a series manner of channel attention and spatial attention;
所述细节融合子模块,用于基于初步预测分割结果降低底层特征中的背景信息的干扰,再通过降采样的方式将细节信息与高级特征进行融合。The detail fusion sub-module is used to reduce the interference of the background information in the bottom-level features based on the preliminary prediction and segmentation results, and then fuse the detail information with the high-level features through down-sampling.
可选的,所述双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE包括三元掩码子模块和边界掩码子模块;Optionally, the dual-boundary guided attention exploration module DBE includes a triple mask submodule and a boundary mask submodule;
所述三元掩码子模块,用于将特征图进行区域划分,并对划分区域进行权重赋值,获取权重特征图;The ternary mask submodule is used to divide the feature map into regions, and assign weights to the divided regions to obtain the weighted feature map;
所述边界掩码子模块,用于将权重特征图转化成二进制掩码,再通过二进制掩码生成最终的边界掩码图。The boundary mask submodule is used to convert the weight feature map into a binary mask, and then generate a final boundary mask map through the binary mask.
可选的,所述双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE中既定策略为从粗到细的逐层逼近的策略。Optionally, the established strategy in the dual boundary-guided attention exploration module DBE is a layer-by-layer approximation strategy from coarse to fine.
可选的,三元掩码子模块输出的权重特征图Ti的表达式为:Optionally, the expression of the weight feature map Ti output by the triple mask submodule is:
其中,代表按元素相乘,fi代表3×3卷积,三元掩码Dt被描述为:in, stands for element-wise multiplication, fi stands for 3×3 convolution, and the ternary mask Dt is described as:
其中,αl和αh代表划分三元掩码的两个阈值,i代表特征图中第i个像素点。Among them, αl and αh represent the two thresholds for dividing the triplet mask, and i represents the i-th pixel in the feature map.
可选的,边界掩码子模块输出的边界掩码图Di的表达式为:Optionally, the expression of the boundary mask graph Di output by the boundary mask submodule is:
其中,边界掩码Dm被描述为:where the boundary mask Dm is described as:
Dm=Dilate(Ds)-Erode(Ds);Dm =Dilate(Ds )-Erode(Ds );
其中,Dilate和Erode分别代表形态学膨胀和腐蚀操作。Among them, Dilate and Erode represent morphological expansion and erosion operations, respectively.
可选的,每个双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE的两个子模块的输出和初步预测图采用深度监督的方法作为优化目标,总督损失函数定义如下:Optionally, the output of the two sub-modules and the preliminary prediction map of each dual-boundary guided attention exploration module DBE adopts the method of deep supervision as the optimization target, and the governor loss function is defined as follows:
L=Lmain+Laux;L=Lmain +Laux ;
其中,Lmain和Laux分别代表主要损失和辅助损失,主要损失Lmain和辅助损失Laux分别被描述为:Among them, Lmain and Laux represent the main loss and auxiliary loss respectively, and the main loss Lmain and auxiliary loss Laux are described as:
其中,Lwbce和Lwiou分别代表加权二元交叉熵损失和加权交并损失,主要损失Lmain是计算特征图Di与真值图G之间的损失,辅助损失Laux是计算特征图Ti与真值图G之间的损失。Among them, Lwbce and Lwiou represent the weighted binary cross-entropy loss and weighted intersection loss respectively, the main loss Lmain is the loss between the calculation feature map Di and the true value map G, and the auxiliary lossLaux is the calculation feature map T The loss betweeni and the ground truth graph G.
一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割方法,具体步骤为:A polyp segmentation method based on dual boundary guided attention exploration, the specific steps are:
对原始图像提取主干特征形成特征图;Extract the backbone features from the original image to form a feature map;
融合特征图的相邻两层上下文特征信息,再对融合后的特征信息利用不同扩张速率的扩张卷积获取广泛特征,将多个广泛特征进行聚合获得初步预测分割结果;Fusion of adjacent two layers of contextual feature information of the feature map, and then use dilated convolutions with different expansion rates to obtain extensive features for the fused feature information, and aggregate multiple extensive features to obtain preliminary prediction segmentation results;
根据初步预测分割结果抑制背景干扰以及捕捉细节信息,获取细节特征图;According to the preliminary prediction and segmentation results, suppress background interference and capture detailed information to obtain detailed feature maps;
基于初步预测分割结果和细节特征图通过采用既定策略获得真实息肉边界。Based on the preliminary predicted segmentation results and detailed feature maps, the real polyp boundaries are obtained by adopting established strategies.
经由上述的技术方案可知,本发明公开了一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割方法及系统,与现有技术相比,具有以下优点:It can be known from the above technical solutions that the present invention discloses a method and system for polyp segmentation based on dual boundary-guided attention exploration. Compared with the prior art, it has the following advantages:
1、本发明利用PVTv2主干提取网络从结肠镜图像中提取更加强大的主干特征,表现出更强的全局信息提取能力和更好的输入干扰鲁棒性;1. The present invention uses the PVTv2 backbone extraction network to extract more powerful backbone features from colonoscopy images, showing stronger global information extraction capabilities and better input interference robustness;
2、本发明通过多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA对各个阶段的特征进行聚合增强,从不同的接收区域获得最广泛的特征,以适应息肉多尺度的变化,从而获得了更加丰富的局部和全局特征;2. The present invention aggregates and enhances the features of each stage through the multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA, and obtains the widest range of features from different receiving areas to adapt to the multi-scale changes of polyps, thereby obtaining richer local and global features ;
3、本发明利用底层细节增强模块LDE提取更多的底层细节信息以促进提升整体模型的性能,在抑制背景干扰的同时实现更加精细化的息肉分割结果;3. The present invention uses the underlying detail enhancement module LDE to extract more underlying detail information to promote the performance of the overall model, and achieve more refined polyp segmentation results while suppressing background interference;
4、本发明将输出的特征通过双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE利用了一种从粗到细的策略以实现逐层逼近真实息肉边界。4. The present invention guides the output features through the double boundary. The DBE uses a coarse-to-fine strategy to approach the real polyp boundary layer by layer.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据提供的附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are only It is an embodiment of the present invention, and those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings according to the provided drawings without creative work.
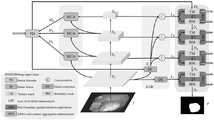
图1为本发明中基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割系统的网络结构图;Fig. 1 is the network structure diagram of the polyp segmentation system based on dual boundary guidance attention exploration among the present invention;
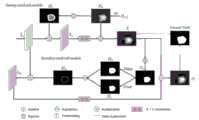
图2为本发明中多尺度上下文聚合增强模块结构图;FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of a multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module in the present invention;
图3为本发明中底层细节增强模块结构图;Fig. 3 is a structural diagram of the bottom layer detail enhancement module in the present invention;
图4为本发明中双重边界引导注意力探索模块结构图;Fig. 4 is a structural diagram of a dual-boundary guided attention exploration module in the present invention;
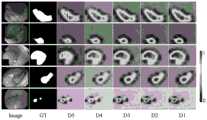
图5为本发明与其他典型模型方法进行定性比较的结果图;Fig. 5 is the result figure that the present invention carries out qualitative comparison with other typical model methods;
图6为本发明中不同阶段的双重边界引导注意力探索模块的输出特性的可视化图。Fig. 6 is a visualization of the output characteristics of the dual boundary-guided attention exploration module at different stages in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
本发明实施例公开了一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割系统,如图1所示,包括PVTv2主干提取网络、多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA、底层细节增强模块LDE和双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE,PVTv2主干提取网络用于从结肠镜图像中提取更加强大的主干特征,并为后续的解码阶段提供更多的前景信息;多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA用于解决息肉多尺度特征适应性问题,通过多个不同扩张速率扩张卷积,从不同的接收域获取更广泛的特征;底层细节增强模块LDE用于解决息肉与周围组织相似性问题,通过提取更多的底层细节信息以促进提升整体模型的性能,得到了更加精细化的息肉分割结果;双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE用于解决边界模糊问题,采用了一种从粗到细的策略以实现逐层逼近真实息肉边界。The embodiment of the present invention discloses a polyp segmentation system based on dual boundary-guided attention exploration, as shown in Figure 1, including PVTv2 backbone extraction network, multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA, underlying detail enhancement module LDE and dual boundary-guided attention Force exploration module DBE, PVTv2 backbone extraction network is used to extract more powerful backbone features from colonoscopy images, and provide more foreground information for the subsequent decoding stage; multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA is used to solve polyp multi-scale features For the adaptive problem, a wider range of features can be obtained from different receptive fields through multiple dilation rate expansion convolutions; the underlying detail enhancement module LDE is used to solve the similarity problem between polyps and surrounding tissues, by extracting more underlying detail information to Promote the improvement of the performance of the overall model, and obtain more refined polyp segmentation results; the dual boundary guided attention exploration module DBE is used to solve the boundary blur problem, and adopts a coarse-to-fine strategy to approach the real polyp boundary layer by layer .
在本实施例中,本发明中PVTv2主干提取网络输出四个多尺度金字塔特征X1、X2、X3和X4,相比于传统CNN方法更加关注局部信息,PVTv2表现出更强的全局信息提取能力和更好的输入干扰鲁棒性,其中输出的特征X1包含丰富的细节信息,如纹理、边界和颜色等细节信息,而X2、X3和X4具有丰富的语义信息。In this embodiment, the PVTv2 backbone extraction network in the present invention outputs four multi-scale pyramid features X1 , X2 , X3 and X4 . Compared with the traditional CNN method, which pays more attention to local information, PVTv2 shows stronger global Information extraction ability and better input disturbance robustness, where the output featureX1 contains rich detail information such as texture, boundary and color, whileX2 ,X3 andX4 have rich semantic information.
在本实施例中,如图2所示,多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA可以帮助获得更详细的局部和全局特征信息,通过相邻高低层特征信息的相互作用来补充位置和空间信息。具体来说,对两个来自不同层的特征图使用1×1卷积将特征通道降低为32,以降低计算资源,然后对较低层的特征进行降采样后与较高层特征进行连接并送入四组具有不同扩张率的扩张卷积分支,不同分支的扩张率分别设置为(1,2,4,8),以获得更多的上下文信息,每个分支包含三组卷积块,每组卷积块将标准卷积分解为3×1卷积,接着再进行1×3卷积,那么通过这种因子分解卷积在相同数量的滤波器下,可以节省33%的参数。最后,将四个分支的特征连接在一起作为MCA模块的输出。In this embodiment, as shown in Figure 2, the multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA can help to obtain more detailed local and global feature information, and complement the location and space information through the interaction of adjacent high-level and low-level feature information. Specifically, 1×1 convolution is used on two feature maps from different layers to reduce the feature channels to 32 to reduce computing resources, and then the lower layer features are down-sampled and concatenated with the higher layer features and sent to Enter four groups of dilated convolution branches with different expansion rates, and the expansion rates of different branches are set to (1, 2, 4, 8) respectively to obtain more context information. Each branch contains three sets of convolution blocks, each The group convolution block decomposes the standard convolution into a 3×1 convolution, and then performs a 1×3 convolution, so that the factorized convolution can save 33% of the parameters under the same number of filters. Finally, the features of the four branches are concatenated together as the output of the MCA module.
在本实施例中,如图3所示,底层细节增强模块LDE用来提取更加丰富的细节信息,息肉的外观通常与周围正常组织非常相似,然而低级别特征图X1通常包含更多例如纹理、边界和颜色等细节信息,因此,通过底层细节增强模块来提取更加丰富的细节信息。底层细节增强模块LDE包括两个部分,第一部分是一个细节融合子模块,通过初步预测结果图的辅助作用来降低底层特征中的背景信息的干扰,之后通过降采样的方式将更多的细节信息与高级特征进行融合;第二部分是一个细节提取子模块,采用通道注意力和空间注意力串联使用的方式来从不同维度捕获息肉的包含纹理、边界和颜色细节信息。In this embodiment, as shown in Figure 3, the underlying detail enhancement module LDE is used to extract richer detail information. The appearance of polyps is usually very similar to the surrounding normal tissue, but the low-level feature map X1 usually contains more such as texture Details such as , boundary and color, therefore, extract richer details through the underlying detail enhancement module. The bottom-level detail enhancement module LDE consists of two parts. The first part is a detail fusion sub-module, which reduces the interference of background information in the bottom-level features through the auxiliary function of the preliminary prediction result map, and then down-samples more detailed information. Fusion with advanced features; the second part is a detail extraction sub-module, which uses channel attention and spatial attention in series to capture polyp texture, boundary and color detail information from different dimensions.
在本实施例中,如图1所示,双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE采用了一种从粗到细的逐层逼近的策略,根据前一个尺度的预测结果和细节增强特征,通过三元掩码子模块从粗糙的不确定区域获得更多真实息肉区域,接着通过边界掩码子模块从细致的边界区域探索更加精细的息肉边界,在经过级联方式构建的有四个双重边界引导注意力探索模块,通过逐层探索不确定区域和边界区域以实现层层逼近真实息肉边界。In this embodiment, as shown in Figure 1, the dual boundary-guided attention exploration module DBE adopts a layer-by-layer approximation strategy from coarse to fine. The mask submodule obtains more real polyp regions from the rough uncertain region, and then explores finer polyp boundaries from the fine boundary regions through the boundary mask submodule, and there are four double boundaries in the cascaded construction to guide attention exploration Module, by exploring the uncertain region and boundary region layer by layer to achieve layer-by-layer approximation to the real polyp boundary.
在本实施例中,如图4所示,双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE包括两个部分,第一部分是一个三元掩码子模块,具体将特征图划分为三个区域,分别是前景、背景和不确定区域,对不同区域赋予不同的权重值,为了强调不确定区域而在不确定区域的像素设置为最高权重1,为了平衡高响应区域而在前景区域的像素设置为0,为了抑制背景区域的干扰而在背景区域的像素设置为最低权值-1;第二部分是一个边界掩码子模块,先对第一部分三元掩码子模块输出的特征图转化成二进制掩码,接着通过形态学上的操作对二进制掩码进行形态学膨胀和腐蚀操作,对经过膨胀和腐蚀操作的掩码进行按元素相减操作,以生成最终的边界掩码图。In this embodiment, as shown in Figure 4, the dual-boundary guided attention exploration module DBE includes two parts, the first part is a ternary mask sub-module, which specifically divides the feature map into three regions, namely foreground and background And the uncertain area, assign different weight values to different areas, in order to emphasize the uncertain area, the pixels in the uncertain area are set to the
在图4中上层三元掩码子模块将前一个尺度的预测结果经过上采样得到Du,接着转化成三元掩码Dt与底层细节增强模块LDE对应的输出特征Li按元素相乘,获得的结果经过3×3卷积后与Du按照元素相加,来获得三元掩码子模块的输出特征图Ti,具体描述如下:In Fig. 4, the upper layer ternary mask submodule upsamples the prediction result of the previous scale to obtain Du , and then converts it into a ternary mask Dt and multiplies the corresponding output feature Li of the bottom layer detail enhancement module LDE element by element, The obtained result is added element-wise to Du after 3×3 convolution to obtain the output feature map Ti of the ternary mask sub-module. The specific description is as follows:
其中,代表按元素相乘,fi代表3×3卷积,三元掩码Dt被描述为:in, stands for element-wise multiplication, fi stands for 3×3 convolution, and the ternary mask Dt is described as:
其中,αl和αh代表划分三元掩码的两个阈值,i代表特征图中第i个像素点。Among them, αl and αh represent the two thresholds for dividing the triplet mask, and i represents the i-th pixel in the feature map.
下层边界掩码子模块从之前三元掩码子模块的输出特征图Ti提取边界信息,输出特征图Ti转换成阈值为0.5的二进制掩码Ds,接着对Ds进行形态学操作生成边界掩码Dm,边界掩码Dm与之前三元掩码子模块的输入特征图Li按元素相乘,获得的结果经过3×3卷积后与Ti按照元素相加,来获得边界掩码子模块的输出特征图Di,具体描述如下:The lower boundary mask sub-module extracts boundary information from the output feature map Ti of the previous ternary mask sub-module, and converts the output feature map Ti into a binary mask Ds with a threshold value of 0.5, and then performs morphological operations on Ds to generate a boundary mask Code Dm , the boundary mask Dm is multiplied element-wise with the input feature mapLi of the previous ternary mask submodule, and the obtained result is added to Ti element-wise after 3×3 convolution to obtain the boundary mask The output feature map Di of the module is specifically described as follows:
其中,边界掩码Dm被描述为:where the boundary mask Dm is described as:
Dm=Dilate(Ds)-Erode(Ds);Dm =Dilate(Ds )-Erode(Ds );
其中,Dilate和Erode分别代表形态学膨胀和腐蚀操作。Among them, Dilate and Erode represent morphological expansion and erosion operations, respectively.
在本实施例中,本发明的损失函数设计为加权IoU损失函数与加权二进制交叉熵BCE损失函数的结合,每个双重边界引导注意力探索模块的两个子模块的输出和初步预测图采用深度监督的方法作为优化目标,总督损失函数定义如下:In this embodiment, the loss function of the present invention is designed as a combination of the weighted IoU loss function and the weighted binary cross-entropy BCE loss function, and the outputs of the two sub-modules and the preliminary prediction map of each double boundary guided attention exploration module adopt deep supervision As the optimization objective of the method, the governor loss function is defined as follows:
L=Lmain+Laux;L=Lmain +Laux ;
其中,Lmain和Laux分别代表主要损失和辅助损失,主要损失Lmain和辅助损失Laux分别被描述为:Among them, Lmain and Laux represent the main loss and auxiliary loss respectively, and the main loss Lmain and auxiliary loss Laux are described as:
其中,主要损失Lmain是计算特征图Di与真值图G之间的损失,辅助损失Laux是计算特征图Ti与真值图G之间的损失。Among them, the main loss Lmain is the loss between the calculated feature map Di and the true value map G, and the auxiliary loss Laux is the loss between the calculated feature map Ti and the true value map G.
在本实施例中,本发明还包括采用平均骰子相似系数mDice、平均交并比mIoU和平均绝对误差MAE来定量评价息肉的分割性能,各指标具体表述为:In this embodiment, the present invention also includes using the average dice similarity coefficient mDice, the average intersection and union ratio mIoU, and the average absolute error MAE to quantitatively evaluate the segmentation performance of polyps, and each index is specifically expressed as:
平均骰子相似系数mDice公式如下:The average dice similarity coefficient mDice formula is as follows:
平均交并比mIoU公式如下:The average IoU formula is as follows:
平均绝对误差MAE公式如下:The mean absolute error MAE formula is as follows:
Dm=Dilate(Ds)-Erode(Ds);Dm =Dilate(Ds )-Erode(Ds );
其中,TP表示真阳性,FP表示假阳性,FN表示假阴性,n表示测试图像的数量,和pi表示总n个像素中第i个像素的预测和相应的真值。Among them, TP represents true positive, FP represents false positive, FN represents false negative, n represents the number of test images, andpi denote the prediction and corresponding ground truth for the i-th pixel out of the total n pixels.
具体地,为了评估提出的方法的分割性能,在5个息肉分割数据上进行了实验,包括Kvasir-SEG、CVC-ClinicDB、CVC-ColonDB、ETIS和CVC-T,对该数据集的描述如下:Specifically, in order to evaluate the segmentation performance of the proposed method, experiments were carried out on 5 polyp segmentation data, including Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ClinicDB, CVC-ColonDB, ETIS and CVC-T, and the description of the data set is as follows:
Kvasir-SEG:该数据集由1000张息肉图像及其相应的地面真实息肉掩码组成,由内窥镜专家注释。Kvasir-SEG中包含的图像的分辨率从332×487到1920×1072像素不等。Kvasir-SEG: This dataset consists of 1000 polyp images and their corresponding ground truth polyp masks, annotated by endoscopy experts. The images included in Kvasir-SEG have resolutions ranging from 332 × 487 to 1920 × 1072 pixels.
CVC-ClinicDB:该数据集也被称为CVC-612,包含来自25个结肠镜视频中的612张开放获取的图像,分辨率为384×288。每个图像都有其相关的手动注释的地面真相,覆盖了息肉。CVC-ClinicDB: This dataset, also known as CVC-612, contains 612 open-access images from 25 colonoscopy videos at a resolution of 384×288. Each image has its associated manually annotated ground truth, overlaid with polyps.
CVC-ColonDB:该数据集由15个结肠镜视频中的380个图像组成。图像分辨率为574×500。CVC-ColonDB: This dataset consists of 380 images from 15 colonoscopy videos. The image resolution is 574×500.
ETIS:该数据集包含从34个结肠镜视频中截取的196张图像,图像分辨率为1225×996。ETIS: This dataset contains 196 images cropped from 34 colonoscopy videos with an image resolution of 1225×996.
CVC-T:该数据集是EndoScene的一个子集,包含来自36名患者44个结肠镜序列的60张图像,图像分辨率为574×500。CVC-T: This dataset is a subset of EndoScene and contains 60 images from 44 colonoscopy sequences in 36 patients with an image resolution of 574×500.
为了进行公平的比较,本发明实验遵循和其余方法一样的原则,在训练集中总共使用了1450张训练图像,其中900张图像来自Kvasir-SEG,550张图像来自CVC-ClinicDB。在测试集中总共使用了798张测试图像,其中100张图像来自Kvasir-SEG,62张图像来自CVC-ClinicDB。同时其他三个数据集都用于测试,分别包括CVC-ColonBD、ETIS和CVC-T中的380、196和62张图像。具体以上五个息肉数据集的信息如下表1所示。In order to make a fair comparison, the experiment of the present invention follows the same principle as other methods, and a total of 1450 training images are used in the training set, of which 900 images are from Kvasir-SEG and 550 images are from CVC-ClinicDB. A total of 798 test images are used in the test set, of which 100 images are from Kvasir-SEG and 62 images are from CVC-ClinicDB. At the same time, the other three datasets are used for testing, including 380, 196 and 62 images in CVC-ColonBD, ETIS and CVC-T, respectively. The specific information of the above five polyp data sets is shown in Table 1 below.
表1息肉数据集信息Table 1 Polyp dataset information
本发明采用三种实验来验证基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割系统的性能,包括定性和定量实验以及消融研究。在实验中,将本实施例的方法与6个不同的方法进行比较,包括最先进的方法,包括UNet、UNet++、SFA、PraNet、SANet和CaraNet,同时,在5个不同的息肉分割数据集上对3个评价指标进行分析比较。为了公平比较,这些方法的分割图是直接提供的原始代码生成的。The present invention uses three kinds of experiments to verify the performance of the polyp segmentation system based on dual boundary-guided attention exploration, including qualitative and quantitative experiments and ablation studies. In the experiments, the method of this example is compared with 6 different methods, including state-of-the-art methods, including UNet, UNet++, SFA, PraNet, SANet and CaraNet, on 5 different polyp segmentation datasets The three evaluation indicators were analyzed and compared. For a fair comparison, the segmentation maps of these methods are generated directly from the original code provided.
从图5中可以看出本实施例的方法和不同竞争方法之间的可视化比较可以定性的看出,很明显,与其他竞争方法比较,本实施例的方法能够更加精准的分割息肉区域,并在多个具有挑战性的方面表现更加出色。As can be seen from Figure 5, the visual comparison between the method of this embodiment and different competing methods can be seen qualitatively. Obviously, compared with other competing methods, the method of this embodiment can more accurately segment the polyp region, and Perform even better on multiple challenging aspects.
表2和表3列出了本实施例的方法在5个不同数据集上与6种不同竞争方法进行统计比较的定量结果。Table 2 and Table 3 list the quantitative results of statistical comparison between the method of this example and 6 different competing methods on 5 different data sets.
表2不同方法在CVC-ClinicDB和Kvasir-SEG息肉数据集上的实验结果对比Table 2 Comparison of experimental results of different methods on CVC-ClinicDB and Kvasir-SEG polyp datasets
考虑到训练集是从CVC-ClinicDB和Kvasir-SEG中选择的,因此首先对该方法的学习能力进行定量分析。如表2所示,本实施例的方法在两个数据集上的各种指标都是最优的。本实施例的方法的mDice在CVC-ClinicDB和Kvasir-SEG中结果分别为93.9%和92.2%,Considering that the training set is selected from CVC-ClinicDB and Kvasir-SEG, the learning ability of the method is firstly analyzed quantitatively. As shown in Table 2, the method of this embodiment is optimal in various indicators on the two data sets. The results of mDice of the method of this embodiment in CVC-ClinicDB and Kvasir-SEG are respectively 93.9% and 92.2%,
为了验证本实施例提出的方法的泛化性能,在三个不可见数据集(CVC-ColonDB、ETIS和CVC-T)上进行了测试。如表3所示,与6种竞争方法相比,本实施例的模型实现了良好的泛化性能。特别的,在具有挑战性的数据集CVC-ColonDB和ETIS上,本实施例的方法的泛化能力实现了显著的提升。在CVC-ColonDB上,mDice分别领先CaraNet和SANet 5.1%和7.1%。在ETIS方面,分别超过CaraNet和SANet5.9%和5.6%。在CVC-T上,超过SANet1.5%。In order to verify the generalization performance of the method proposed in this example, tests were carried out on three unseen datasets (CVC-ColonDB, ETIS and CVC-T). As shown in Table 3, compared with the six competing methods, the model of this embodiment achieves good generalization performance. In particular, on the challenging data sets CVC-ColonDB and ETIS, the generalization ability of the method in this embodiment has been significantly improved. On CVC-ColonDB, mDice leads CaraNet and SANet by 5.1% and 7.1%, respectively. In terms of ETIS, it exceeds CaraNet and SANet by 5.9% and 5.6%, respectively. On CVC-T, it exceeds SANet1.5%.
为了验证模型中每个组成部分的有效性,对双重边界引导注意力探索模块DBE、多尺度上下文聚合增强模块MCA和底层细节增强模块LDE进行消融实验。主干网络的基线是由PVTv2和PD组成的,标准模型是由“Baseline+MCA+LDE+DBE”组成。通过从标准模型中移除或更改不同模块来评估不同模块的有效性。“w/o MCA”、“w/o LDE”和“w/o DBE”分别代表从标准模型中去除MCA、LDE或DBE。实验结果如下表3所示。In order to verify the effectiveness of each component in the model, ablation experiments are performed on the dual boundary-guided attention exploration module DBE, the multi-scale context aggregation enhancement module MCA and the underlying detail enhancement module LDE. The baseline of the backbone network is composed of PVTv2 and PD, and the standard model is composed of "Baseline+MCA+LDE+DBE". Evaluate the effectiveness of different modules by removing or changing them from the standard model. "w/o MCA", "w/o LDE" and "w/o DBE" represent the removal of MCA, LDE or DBE from the Standard Model, respectively. The experimental results are shown in Table 3 below.
表3不同息肉数据集上的消融实验结果Table 3 Results of ablation experiments on different polyp datasets
DBE的消融研究:为了研究DBE模块的有效性,对不同阶段的DBE模块的输出特性进行可视化。如图6所示,区域越红,网络需要给予的关注就越多。可以观察到随着阶段的推移它逐步细化息肉边界,并探索出更多的息肉信息。这说明DBE模块从粗到细的策略能够有效的增强模糊边缘信息。为了定量的分析DBE模块的有效性,训练了一个缺少DBE模块的版本“w/oDBE”。将DBE模块全部移除,并用按元素相加的操作代替。实验结果见表3。与标准模型相比,不含DBE的模型在五个数据集上的表现急剧下降。在CVC-ClinicDB、Kvasir-SEG、CVC-ColonDB、ETIS和CVC-T上,与标准的完整模型DBENet的性能相比,缺少DBE可使mDice分别降低了0.8%、0.6%、1.7%、1.6%和2.1%。Ablation Study of DBE: To study the effectiveness of the DBE module, the output characteristics of the DBE module at different stages are visualized. As shown in Figure 6, the redder the region, the more attention the network needs to give. It can be observed that as the stage progresses, it gradually refines the polyp boundary and explores more polyp information. This shows that the coarse-to-fine strategy of the DBE module can effectively enhance the fuzzy edge information. In order to quantitatively analyze the effectiveness of the DBE module, a version "w/oDBE" lacking the DBE module is trained. Remove the DBE module entirely and replace it with an element-wise addition operation. The experimental results are shown in Table 3. Compared with the standard model, the performance of the model without DBE drops sharply on the five datasets. On CVC-ClinicDB, Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ColonDB, ETIS, and CVC-T, the absence of DBE reduces mDice by 0.8%, 0.6%, 1.7%, and 1.6%, respectively, compared to the performance of the standard full model DBENet and 2.1%.
MCA的消融研究:相似的,为了定量的分析MCA模块的有效性,训练了一个缺少MCA模块的版本“w/o MCA”。将MCA模块全部移除,并直接融合前三个高层的上下文信息(即X2、X3和X4)。表3的结果显示,与标准模型相比,不含MCA的模型在CVC-ColonDB和ETIS数据集上的mDice分别下降1.0%和0.5%。特别的,CVC-ColonDB和ETIS数据集是具有挑战性的不可见数据集,这说明MCA对于多尺度的泛化能力有所增强。MCA Ablation Study: Similarly, in order to quantitatively analyze the effectiveness of the MCA module, a version "w/o MCA" lacking the MCA module was trained. All the MCA modules are removed, and the context information of the first three high-level layers (ie X2 , X3 and X4 ) are directly fused. The results in Table 3 show that compared with the standard model, the mDice of the model without MCA drops by 1.0% and 0.5% on the CVC-ColonDB and ETIS datasets, respectively. In particular, the CVC-ColonDB and ETIS datasets are challenging unseen datasets, which shows that the generalization ability of MCA for multi-scale is enhanced.
LDE的消融研究:为了证明LDE的能力,训练了一个缺少LDE模块的版本“w/o LDE”。如表3显示,与标准模型相比,移除LDE会导致在五个数据集上的表现都略有下降。在CVC-ClinicDB、Kvasir-SEG、CVC-ColonDB、ETIS和CVC-T这五个数据集上,移除LDE可使mDice分别降低了0.5%、0.4%、0.6%、0.1%和1.0%。由此可见,LDE模块对于模型的分割能力有所提升。Ablation Study of LDE: To demonstrate the capability of LDE, a version "w/o LDE" lacking the LDE module is trained. As shown in Table 3, removing LDE results in slightly lower performance on all five datasets compared to the standard model. On the five datasets of CVC-ClinicDB, Kvasir-SEG, CVC-ColonDB, ETIS and CVC-T, removing LDE can reduce mDice by 0.5%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.1% and 1.0%, respectively. It can be seen that the LDE module has improved the segmentation ability of the model.
一种基于双重边界引导注意力探索的息肉分割方法,具体步骤为:A polyp segmentation method based on dual boundary guided attention exploration, the specific steps are:
对原始图像提取主干特征形成特征图;Extract the backbone features from the original image to form a feature map;
融合特征图的相邻两层上下文特征信息,再对融合后的特征信息利用不同扩张速率的扩张卷积获取广泛特征,将多个广泛特征进行聚合获得初步预测分割结果;Fusion of adjacent two layers of contextual feature information of the feature map, and then use dilated convolutions with different expansion rates to obtain extensive features for the fused feature information, and aggregate multiple extensive features to obtain preliminary prediction segmentation results;
根据初步预测分割结果抑制背景干扰以及捕捉细节信息,获取细节特征图;According to the preliminary prediction and segmentation results, suppress background interference and capture detailed information to obtain detailed feature maps;
基于初步预测分割结果和细节特征图通过采用既定策略获得真实息肉边界。Based on the preliminary predicted segmentation results and detailed feature maps, the real polyp boundaries are obtained by adopting established strategies.
本说明书中各个实施例采用递进的方式描述,每个实施例重点说明的都是与其他实施例的不同之处,各个实施例之间相同相似部分互相参见即可。Each embodiment in this specification is described in a progressive manner, each embodiment focuses on the difference from other embodiments, and the same and similar parts of each embodiment can be referred to each other.
对所公开的实施例的上述说明,使本领域专业技术人员能够实现或使用本发明。对这些实施例的多种修改对本领域的专业技术人员来说将是显而易见的,本文中所定义的一般原理可以在不脱离本发明的精神或范围的情况下,在其它实施例中实现。因此,本发明将不会被限制于本文所示的这些实施例,而是要符合与本文所公开的原理和新颖特点相一致的最宽的范围。The above description of the disclosed embodiments is provided to enable any person skilled in the art to make or use the invention. Various modifications to these embodiments will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art, and the general principles defined herein may be implemented in other embodiments without departing from the spirit or scope of the invention. Therefore, the present invention will not be limited to the embodiments shown herein, but is to be accorded the widest scope consistent with the principles and novel features disclosed herein.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211632343.0ACN115841495B (en) | 2022-12-19 | 2022-12-19 | Polyp segmentation method and system based on double boundary guiding attention exploration |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211632343.0ACN115841495B (en) | 2022-12-19 | 2022-12-19 | Polyp segmentation method and system based on double boundary guiding attention exploration |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115841495Atrue CN115841495A (en) | 2023-03-24 |
| CN115841495B CN115841495B (en) | 2025-09-19 |
Family
ID=85578863
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211632343.0AActiveCN115841495B (en) | 2022-12-19 | 2022-12-19 | Polyp segmentation method and system based on double boundary guiding attention exploration |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115841495B (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117132774A (en)* | 2023-08-29 | 2023-11-28 | 河北师范大学 | Multi-scale polyp segmentation method and system based on PVT |
| CN117765251A (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2024-03-26 | 安徽大学 | Bladder tumor segmentation method based on pyramid vision converter |
| CN117830226A (en)* | 2023-12-05 | 2024-04-05 | 广州恒沙云科技有限公司 | Boundary constraint-based polyp segmentation method and system |
| CN118037756A (en)* | 2024-04-11 | 2024-05-14 | 江西师范大学 | Boundary-target enhancement-based colonoscope polyp segmentation method |
| CN119048530A (en)* | 2024-10-28 | 2024-11-29 | 江西师范大学 | Polyp image segmentation method and system based on detail restoration network |
| CN119494840A (en)* | 2024-08-26 | 2025-02-21 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A polyp segmentation method based on edge-guided and deep-supervised PVT |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112465827A (en)* | 2020-12-09 | 2021-03-09 | 北京航空航天大学 | Contour perception multi-organ segmentation network construction method based on class-by-class convolution operation |
| KR102332088B1 (en)* | 2021-01-13 | 2021-12-01 | 가천대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus and method for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images through polyp boundary aware using detailed upsampling encoder-decoder networks |
| CN114724031A (en)* | 2022-04-08 | 2022-07-08 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Corn insect pest area detection method combining context sensing and multi-scale mixed attention |
- 2022
- 2022-12-19CNCN202211632343.0Apatent/CN115841495B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112465827A (en)* | 2020-12-09 | 2021-03-09 | 北京航空航天大学 | Contour perception multi-organ segmentation network construction method based on class-by-class convolution operation |
| KR102332088B1 (en)* | 2021-01-13 | 2021-12-01 | 가천대학교 산학협력단 | Apparatus and method for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images through polyp boundary aware using detailed upsampling encoder-decoder networks |
| CN114724031A (en)* | 2022-04-08 | 2022-07-08 | 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 | Corn insect pest area detection method combining context sensing and multi-scale mixed attention |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| HAICHAO MA 等: "DBE-Net: Dual Boundary-Guided Attention Exploration Network for Polyp Segmentation", 《DIAGNOSTICS》, vol. 13, no. 5, 27 February 2023 (2023-02-27)* |
| 刘家畅: "基于改进FCN的遥感影像语义分割与景观格局变化分析", 《中国优秀硕士论文全文数据库(电子期刊)基础科学辑》, 15 April 2021 (2021-04-15)* |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117132774A (en)* | 2023-08-29 | 2023-11-28 | 河北师范大学 | Multi-scale polyp segmentation method and system based on PVT |
| CN117132774B (en)* | 2023-08-29 | 2024-03-01 | 河北师范大学 | Multi-scale polyp segmentation method and system based on PVT |
| CN117765251A (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2024-03-26 | 安徽大学 | Bladder tumor segmentation method based on pyramid vision converter |
| CN117765251B (en)* | 2023-11-17 | 2024-08-06 | 安徽大学 | Bladder tumor segmentation method based on pyramid vision converter |
| CN117830226A (en)* | 2023-12-05 | 2024-04-05 | 广州恒沙云科技有限公司 | Boundary constraint-based polyp segmentation method and system |
| CN118037756A (en)* | 2024-04-11 | 2024-05-14 | 江西师范大学 | Boundary-target enhancement-based colonoscope polyp segmentation method |
| CN119494840A (en)* | 2024-08-26 | 2025-02-21 | 杭州电子科技大学 | A polyp segmentation method based on edge-guided and deep-supervised PVT |
| CN119048530A (en)* | 2024-10-28 | 2024-11-29 | 江西师范大学 | Polyp image segmentation method and system based on detail restoration network |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115841495B (en) | 2025-09-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115841495A (en) | Polyp segmentation method and system based on double-boundary guiding attention exploration | |
| Zhu et al. | Brain tumor segmentation in MRI with multi-modality spatial information enhancement and boundary shape correction | |
| Alom et al. | Skin cancer segmentation and classification with NABLA-N and inception recurrent residual convolutional networks | |
| Liu et al. | Skin lesion segmentation based on improved u-net | |
| CN114820635A (en) | Polyp segmentation method combining attention U-shaped network and multi-scale feature fusion | |
| CN115393584B (en) | Method for establishing a multi-task ultrasound thyroid nodule segmentation and classification model, segmentation and classification method, and computer equipment | |
| CN114677349B (en) | Image segmentation method and system for enhancing edge information of encoding and decoding end and guiding attention | |
| Bagheri et al. | Skin lesion segmentation based on mask RCNN, Multi Atrous Full‐CNN, and a geodesic method | |
| CN113658201A (en) | Deep learning colorectal cancer polyp segmentation device based on enhanced multi-scale features | |
| Li et al. | CIFG-Net: Cross-level information fusion and guidance network for Polyp Segmentation | |
| CN118071767A (en) | Breast ultrasound image segmentation method based on global boundary enhancement | |
| Yuan et al. | MMUNet: Morphological feature enhancement network for colon cancer segmentation in pathological images | |
| CN115249302B (en) | Intestinal wall blood vessel segmentation method based on multi-scale contextual information and attention mechanism | |
| Chen et al. | SegT: Separated edge-guidance transformer network for polyp segmentation | |
| Yuan et al. | A bi-directionally fused boundary aware network for skin lesion segmentation | |
| CN114842030B (en) | Bladder tumor image segmentation method adopting multi-scale semantic matching | |
| CN119963576A (en) | A three-dimensional coronary artery image segmentation method and system | |
| CN119151968A (en) | Polyp image segmentation method based on boundary clue depth fusion | |
| Wang et al. | A novel dataset and a deep learning method for mitosis nuclei segmentation and classification | |
| CN118366153A (en) | Cell nucleus segmentation method based on large model guided cascade encoding segmentation network | |
| Chen et al. | SegT: A novel separated edge-guidance transformer network for polyp segmentation | |
| CN115439495B (en) | Intestinal polyp boundary segmentation method based on sparse connectivity and global feature enhancement | |
| CN117115188A (en) | Polyp image segmentation method based on pixel dynamic aggregation and local perception enhancement | |
| Jian et al. | A two-stage refinement network for nuclei segmentation in histopathology images | |
| Li et al. | VCE-Net: A New Type of Real-time Polyp Segmentation Network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |