CN115807041A - Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production method - Google Patents
Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115807041A CN115807041ACN202211285941.5ACN202211285941ACN115807041ACN 115807041 ACN115807041 ACN 115807041ACN 202211285941 ACN202211285941 ACN 202211285941ACN 115807041 ACN115807041 ACN 115807041A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- inoculum
- hydrogen
- fermentation
- methanogens
- dark fermentation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E50/00—Technologies for the production of fuel of non-fossil origin
- Y02E50/30—Fuel from waste, e.g. synthetic alcohol or diesel
Landscapes
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及暗发酵技术领域,具体涉及一种抑制厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的方法及制氢方法。The invention relates to the technical field of dark fermentation, in particular to a method for inhibiting the activity of methanogenic bacteria in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and a hydrogen production method.
背景技术Background technique
氢无毒、清洁、燃值高,被普遍认为是一种理想的能源载体,在能源、交通、工业生产领域,有着巨大的市场潜力。Hydrogen is non-toxic, clean, and has a high fuel value. It is generally regarded as an ideal energy carrier. It has huge market potential in the fields of energy, transportation, and industrial production.
氢能虽然具有诸多优点,且有广阔的市场前景,但我国目前氢产能中97%以上是来自化石能源的灰氢或蓝氢,若要真正实现快速健康发展,仍需加大来自可再生能源的绿氢在氢能结构中的占比。在绿氢生产技术中,生物质暗发酵具有条件温和、方法简单、成本低等特点,而我国生物质废物产量巨大,是降低绿氢生产成本、实现规模化应用的切实可行的有效手段,同时还可以解决生物质废物污染所带来的环境问题和社会问题。Although hydrogen energy has many advantages and has broad market prospects, more than 97% of my country's current hydrogen production capacity is gray hydrogen or blue hydrogen from fossil fuels. The proportion of green hydrogen in the hydrogen energy structure. In the green hydrogen production technology, the dark fermentation of biomass has the characteristics of mild conditions, simple method, and low cost. However, the huge amount of biomass waste in my country is a practical and effective means to reduce the cost of green hydrogen production and realize large-scale application. At the same time It can also solve environmental and social problems caused by biomass waste pollution.
目前生物质暗发酵制氢通常以农作物秸秆等生物质废物作为原料,牛粪、秸秆消化液等作为接种物。为了提高产氢效率,暗发酵进行前需要对接种物进行预处理,以抑制接种物中的产甲烷菌,从而提高氢气产率。现有接种物预处理方法包括:在90~100℃下,对接种物进行加热60min左右,使接种物中的梭状芽孢杆菌等产氢菌形成孢子,从而在极端环境下存活下来,而其他的耗氢细菌(如氢营养型产甲烷菌)在该环境下死亡,从而抑制接种物中的产甲烷菌,后期孢子萌发后可提高产氢量。由于孢子萌发需要一定的时间,采用加热方式预处理后的接种物产气高峰延后,且产氢量有待进一步提高。At present, biomass dark fermentation hydrogen production usually uses biomass wastes such as crop straws as raw materials, and cow dung, straw digestion liquid, etc. as inoculum. In order to improve the efficiency of hydrogen production, the inoculum needs to be pretreated before dark fermentation to inhibit the methanogens in the inoculum, thereby increasing the hydrogen production rate. The existing inoculum pretreatment method includes: heating the inoculum at 90-100°C for about 60 minutes, so that the hydrogen-producing bacteria such as Clostridium in the inoculum form spores, thereby surviving in extreme environments, while other The hydrogen-consuming bacteria (such as hydrogenotrophic methanogens) die in this environment, thereby inhibiting the methanogens in the inoculum, and the hydrogen production can be increased after the spores germinate in the later stage. Since the germination of spores takes a certain amount of time, the gas production peak of the inoculum pretreated by heating is delayed, and the hydrogen production needs to be further improved.
发明内容Contents of the invention
(一)发明目的(1) Purpose of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种抑制厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的方法及制氢方法,无需加热即可实现对厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的抑制,处理后的接种物接种后12h左右就可达到产气高峰,同等条件下与加热处理的接种物比,产气高峰提早了三分之一左右,同时,产气高峰产氢量提高了1.5倍左右。The object of the present invention is to provide a method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in the anaerobic fermentation inoculum and a hydrogen production method, which can realize the inhibition of the activity of the methanogens in the anaerobic fermentation inoculum without heating. The gas production peak can be reached in about 12 hours. Compared with the heat-treated inoculum under the same conditions, the gas production peak is about one-third earlier, and at the same time, the hydrogen production at the gas production peak is increased by about 1.5 times.
(二)技术方案(2) Technical solutions
为解决上述问题,本发明的第一方面提供了一种抑制厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的方法,对接种物直接进行离心处理。In order to solve the above problems, the first aspect of the present invention provides a method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in the anaerobic fermentation inoculum, and the inoculum is directly centrifuged.
具体地,所述接种物包括动物粪便或厌氧消化液;Specifically, the inoculum includes animal feces or anaerobic digestate;
所述动物粪便选自牛粪、鸡粪、猪粪中的至少一种;The animal manure is selected from at least one of cow manure, chicken manure, and pig manure;
所述厌氧消化液选自餐厨垃圾厌氧消化液、秸秆厌氧消化液中的至少一种。The anaerobic digestion liquid is selected from at least one of anaerobic digestion liquid of kitchen waste and anaerobic digestion liquid of straw.
优选地,所述接种物为牛粪或秸秆消化液。Preferably, the inoculum is cow dung or straw digestate.
更优选地,以质量百分比计:More preferably, by mass percentage:
所述牛粪的总固体含量为5~7%、挥发性固体含量为4~6%;The total solid content of the cow dung is 5-7%, and the volatile solid content is 4-6%;
所述秸秆消化液的总固体含量为5~7%、挥发性固体含量为4~5%。The total solid content of the straw digestion liquid is 5-7%, and the volatile solid content is 4-5%.
优选地,所述离心处理的具体条件包括:Preferably, the specific conditions of the centrifugation treatment include:
转速为7000~9000g;The speed is 7000~9000g;
时间为10~20min。The time is 10-20 minutes.
优选地,所述离心处理的具体条件包括:Preferably, the specific conditions of the centrifugation treatment include:
离心时向所述接种物中加入铁粉。Iron powder was added to the inoculum during centrifugation.
优选地,所述铁粉的加入量为0.05~0.4g/gVS。Preferably, the iron powder is added in an amount of 0.05-0.4 g/gVS.
通过在离心时加入铁粉不仅增加了第一个产气高峰的氢气产量,在30h内还能形成第二个产气高峰,进一步增加了产气量。Adding iron powder during centrifugation not only increases the hydrogen production of the first gas production peak, but also forms the second gas production peak within 30 hours, further increasing the gas production.
本发明的第二方面,提供了一种暗发酵制氢方法,包括:The second aspect of the present invention provides a method for producing hydrogen by dark fermentation, comprising:
采用上述任一项所述方法处理接种物,得到产甲烷菌得到抑制的接种物;Treat the inoculum by any of the methods described above to obtain an inoculum in which methanogens are inhibited;
将所述产甲烷菌得到抑制的接种物与农作物秸秆按比例混合后进行暗发酵制氢。The inoculum in which the methanogenic bacteria is inhibited is mixed with the crop stalks in proportion to carry out dark fermentation to produce hydrogen.
优选地,所述产甲烷菌得到抑制的接种物与农作物秸秆的质量比为1:1.5~2.5。Preferably, the mass ratio of the inhibited inoculum to the crop straw is 1:1.5-2.5.
优选地,暗发酵的具体条件包括:Preferably, the specific conditions of dark fermentation include:
pH为5~6;pH is 5~6;
温度为34~37℃;The temperature is 34~37℃;
发酵时间为18~30h。The fermentation time is 18-30 hours.
优选地,所述农作物秸秆选自玉米秸秆、稻草、麦秸中的至少一种;Preferably, the crop straw is selected from at least one of corn straw, rice straw and wheat straw;
优选地,所述农作物秸秆使用前进行预处理,预处理的条件具体包括:Preferably, the crop stalks are pretreated before use, and the pretreatment conditions specifically include:
采用质量浓度为0.5~1.5%的硫酸进行预处理;Using sulfuric acid with a mass concentration of 0.5 to 1.5% for pretreatment;
处理温度为100~140℃;The treatment temperature is 100~140℃;
处理时间为5~15min。The processing time is 5-15 minutes.
(三)有益效果(3) Beneficial effects
本发明的上述技术方案具有如下有益的技术效果:The technical solution of the present invention has the following beneficial technical effects:
本发明提供的抑制厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的方法,无需加热即可实现对厌氧发酵接种物中产甲烷菌活性的抑制,处理后的接种物接种后12h左右就可达到产气高峰,同等条件下与加热处理的接种物比,产气高峰提早了三分之一左右,同时,产气高峰产氢量提高了1.5倍左右;The method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in the anaerobic fermentation inoculum provided by the present invention can realize the inhibition of the activity of the methanogens in the anaerobic fermentation inoculum without heating, and the treated inoculum can reach the peak of gas production about 12 hours after inoculation , under the same conditions, compared with the heat-treated inoculum, the gas production peak was about one-third earlier, and at the same time, the hydrogen production at the gas production peak was increased by about 1.5 times;
该方法可随时随地对接种物进行处理,且处理完之后的接种物可即时转移运输,避免了加热后接种物温度过高无法再即时转移的问题;The method can process the inoculum anytime and anywhere, and the processed inoculum can be transferred and transported immediately, avoiding the problem that the temperature of the inoculum after heating is too high and cannot be transferred immediately;
处理后的接种物体积缩小了近一半,更便于运输和/或储存。The processed inoculum was nearly halved in size, making it easier to transport and/or store.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例提供的制氢方法装置示意图;Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a hydrogen production method device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
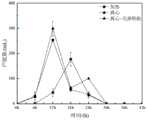
图2为本发明实施例提供的实施例2、3及对比例2的产气量示意图;Fig. 2 is the gas production schematic diagram of
图3为本发明实施例提供的实施例2、3及对比例2的氢气含量示意图;Fig. 3 is the hydrogen content schematic diagram of
图4为本发明实施例提供的实施例2、3及对比例2的产氢量示意图;Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the hydrogen production of Examples 2, 3 and Comparative Example 2 provided by the embodiments of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例提供的实施例2、3及对比例2的累积产氢量示意图。Fig. 5 is a schematic diagram of the cumulative hydrogen production of Examples 2, 3 and Comparative Example 2 provided by the examples of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚明了,下面结合具体实施方式并参照附图,对本发明进一步详细说明。应该理解,这些描述只是示例性的,而并非要限制本发明的范围。此外,在以下说明中,省略了对公知结构和技术的描述,以避免不必要地混淆本发明的概念。In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in combination with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that these descriptions are exemplary only, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Also, in the following description, descriptions of well-known structures and techniques are omitted to avoid unnecessarily obscuring the concept of the present invention.
本发明各实施例所用原料、试剂均为常规市售产品,其中:所用牛粪取自北京大兴区金银岛牧场,TS为6.33%、VS为5.12%;暗发酵底物为粉碎至40目的玉米秸秆,TS为92.78%、VS为85.45%;The raw materials and reagents used in each embodiment of the present invention are conventional commercially available products, wherein: the cow dung used is taken from the Treasure Island Ranch in Daxing District, Beijing, and the TS is 6.33%, and the VS is 5.12%; the dark fermentation substrate is crushed to 40 mesh Corn stalks, TS is 92.78%, VS is 85.45%;
各实施例中,TS表示总固体含量,VS表示挥发性固体含量,测试方法具体包括:In each embodiment, TS represents the total solid content, VS represents the volatile solid content, and the test method specifically includes:
TS的测定:称量空坩埚的质量记作a,将样品放入空坩埚,测量空坩埚与样品的混合质量记做b,将装满样品的坩埚放入100℃的烘箱中烘烤24小时将样品与坩埚取出,放到干燥器皿中冷却干燥,等待1小时,恢复室温,取出称量质量记做c;Determination of TS: Weigh the mass of the empty crucible as a, put the sample into the empty crucible, measure the mixed mass of the empty crucible and the sample as b, put the crucible filled with the sample in an oven at 100°C and bake for 24 hours Take out the sample and the crucible, put it in a desiccator to cool and dry, wait for 1 hour, return to room temperature, take out and weigh the mass and record it as c;
VS的测定:将烘箱中烘烤过后的样品放入马弗炉中在600℃中加热12小时,关闭马弗炉,等待其自然冷却至100℃左右取出放入干燥皿冷却干燥,等待一小时左右恢复至室温,取出称量质量,记此时质量为d;Determination of VS: Put the sample baked in the oven into the muffle furnace and heat it at 600°C for 12 hours, turn off the muffle furnace, wait for it to cool naturally to about 100°C, take it out and put it in a drying dish to cool and dry, wait for one hour Return to room temperature from left to right, take out and weigh the mass, record the mass at this time as d;
TS与VS的计算公式如下:The calculation formulas of TS and VS are as follows:
TS=(c-a)/(b-a)×100%TS=(c-a)/(b-a)×100%
TS=(c-d)/(b-a)×100%。TS=(c-d)/(b-a)×100%.
各实施例所用装置如图1所示,包括反应器1、集气瓶2、集水槽3和恒温水浴4,其中,反应器1置于恒温水浴4中,集气瓶2内存有一定量水,反应器1左侧开口通过止水夹7夹紧,反应器1右端通过第一管路5与集气瓶2左上方连通,且连通口位于瓶内水面上方,集气瓶2右侧通过第二管路6与集水槽3连通,第二管路6位于集气瓶2内的一端探入瓶底且与瓶底具有间隙。The device used in each embodiment is as shown in Figure 1, comprises
实施例1Example 1
(1)将牛粪放入离心机中,在8000g下离心15min,去除液体,得到处理后的接种物;(1) Cow manure is put into the centrifuge, centrifuged at 8000g for 15min, remove the liquid, and obtain the treated inoculum;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,定容至400ml,调节pH值为7.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。暗发酵24h后氢气含量为26.123%,产气量为480ml,其中产氢量为125.39ml,未检测出甲烷。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS substrate and add it into
对比例1Comparative example 1
与实施例1基本相同,唯一不同的是,步骤(2)中所用牛粪未经离心处理直接用于步骤(2)中。厌氧发酵24h后甲烷含量为13.04%,氢气含量仅为0.436%,产气量为335.89ml,甲烷量为43.8ml。Basically the same as Example 1, the only difference is that the cow dung used in step (2) is directly used in step (2) without centrifugation. After 24 hours of anaerobic fermentation, the methane content was 13.04%, the hydrogen content was only 0.436%, the gas production was 335.89ml, and the methane volume was 43.8ml.
由实施例1和对比例1可知,厌氧发酵接种物经离心处理后有效抑制了产甲烷菌活性。From Example 1 and Comparative Example 1, it can be known that the anaerobic fermentation inoculum effectively inhibited the activity of methanogens after centrifugation.
实施例2Example 2
(1)将牛粪放入离心机中,在8000g下离心15min,去除液体,得到处理后的接种物;(1) Cow manure is put into the centrifuge, centrifuged at 8000g for 15min, remove the liquid, and obtain the treated inoculum;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS暗发酵底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,用去离子水定容至400ml,调节pH值为6.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS dark fermentation substrate and add it into
实施例3Example 3
(1)将牛粪放入离心机中并按照0.2g/gVS的加入量加入还原铁粉,在8000g下离心15min,去除液体,得到处理后的接种物;(1) Put the cow dung into the centrifuge and add reduced iron powder according to the addition of 0.2g/gVS, centrifuge at 8000g for 15min, remove the liquid, and obtain the treated inoculum;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS暗发酵底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,用去离子水定容至400ml,调节pH值为6.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS dark fermentation substrate and add it into
对比例2Comparative example 2
(1)将牛粪在90℃下加热60min,得到处理后的接种物;(1) Cow dung was heated at 90°C for 60 minutes to obtain the treated inoculum;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS暗发酵底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,用去离子水定容至400ml,调节pH值为6.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS dark fermentation substrate and add it into
实施例2、3、对比例2均间隔6h测一次产气量和氢气含量,测试结果如图2~4所示:
由图2可以看出,实施例2和3的产气高峰均在暗发酵进行的第12h产生,而对比例2的产气高峰则在18h产生,且实施例2、3的产气量明显高于对比例2,尤其是实施例3的最大产气量为对比例2最大产气量的近2倍;It can be seen from Figure 2 that the gas production peaks of Examples 2 and 3 were both produced at the 12th hour of dark fermentation, while the gas production peaks of Comparative Example 2 were produced at 18 hours, and the gas production volumes of Examples 2 and 3 were significantly higher Compared with Comparative Example 2, especially the maximum gas production of Example 3 is nearly 2 times of the maximum gas production of Comparative Example 2;
经气相色谱测试得知各实施例所产气体由氮气、氢气和二氧化碳组成,不含甲烷;由图3可以看出,实施例2和3所得气体中氢气含量均比对比例2高25%左右;Through gas chromatography test, it is known that the gas produced by each embodiment is composed of nitrogen, hydrogen and carbon dioxide, and does not contain methane; as can be seen from Figure 3, the hydrogen content in the gas obtained in Examples 2 and 3 is about 25% higher than that of Comparative Example 2 ;
由图4可知,实施例2和3的产氢高峰均在暗发酵进行的第12h产生,而对比例2的产氢高峰则在18h产生,且实施例2、3的产氢量明显高于对比例2;It can be seen from Figure 4 that the hydrogen production peaks of Examples 2 and 3 were both produced at the 12th hour of dark fermentation, while the hydrogen production peaks of Comparative Example 2 were produced at 18 hours, and the hydrogen production of Examples 2 and 3 was significantly higher than that of Comparative example 2;
由图5可知,实施例2和3的累积产氢量均高于对比例2。It can be seen from Figure 5 that the cumulative hydrogen production of Examples 2 and 3 is higher than that of Comparative Example 2.
实施例4Example 4
(1)将秸秆发酵液放入离心机中在8000g下离心15min,去除液体,得到处理后的接种物,其中所述秸秆发酵液取自河北省三河市盈盛生物能源科技股份有限公司,TS为6.38±0.03%,VS为4.10±0.05%;(1) Put the straw fermented liquid into a centrifuge and centrifuge at 8000g for 15 minutes to remove the liquid and obtain the treated inoculum, wherein the straw fermented liquid is taken from Yingsheng Bioenergy Technology Co., Ltd., Sanhe City, Hebei Province, TS is 6.38±0.03%, VS is 4.10±0.05%;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS暗发酵底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,用去离子水定容至400ml,调节pH值为6.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS dark fermentation substrate and add it into
对比例3Comparative example 3
(1)将实施例4步骤(1)所用秸秆发酵液在90℃下加热60min,得到处理后的接种物;(1) heating the stalk fermented liquid used in step (1) of Example 4 at 90° C. for 60 min to obtain the treated inoculum;
(2)将15gTS处理后的接种物与30gTS暗发酵底物混合均匀后加入反应器1中,用去离子水定容至400ml,调节pH值为6.0,将恒温水浴4调至36℃并确保恒温水浴4中的水始终没过反应器1中的物料,开始暗发酵产氢。(2) Mix 15g of TS-treated inoculum with 30g of TS dark fermentation substrate and add it into
实施例4、对比例3均间隔6h测一次产气量和氢气含量:
实施例4的产气高峰在暗发酵进行的第12h左右产生,而对比例3的产气高峰则在18h左右产生,且实施例4的产气量明显高于对比例3;The gas production peak of Example 4 was produced at about 12 hours after dark fermentation, while the gas production peak of Comparative Example 3 was produced at about 18 hours, and the gas production of Example 4 was significantly higher than that of Comparative Example 3;
经气相色谱测试得知各实施例所产气体由氮气、氢气和二氧化碳组成,不含甲烷;实施例4所得气体中氢气含量比对比例3高。Gas chromatography tests show that the gas produced in each example is composed of nitrogen, hydrogen and carbon dioxide, and does not contain methane; the hydrogen content in the gas obtained in Example 4 is higher than that in Comparative Example 3.
应当理解的是,本发明的上述具体实施方式仅仅用于示例性说明或解释本发明的原理,而不构成对本发明的限制。因此,在不偏离本发明的精神和范围的情况下所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。此外,本发明所附权利要求旨在涵盖落入所附权利要求范围和边界、或者这种范围和边界的等同形式内的全部变化和修改例。It should be understood that the above specific embodiments of the present invention are only used to illustrate or explain the principle of the present invention, and not to limit the present invention. Therefore, any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention. Furthermore, it is intended that the appended claims of the present invention cover all changes and modifications that come within the scope and metespan of the appended claims, or equivalents of such scope and metesight.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211285941.5ACN115807041A (en) | 2022-10-20 | 2022-10-20 | Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211285941.5ACN115807041A (en) | 2022-10-20 | 2022-10-20 | Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115807041Atrue CN115807041A (en) | 2023-03-17 |
Family
ID=85482752
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211285941.5APendingCN115807041A (en) | 2022-10-20 | 2022-10-20 | Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115807041A (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101914573A (en)* | 2010-07-29 | 2010-12-15 | 江苏大学 | A step-by-step method for producing hydrogen and methane by anaerobic fermentation of cow manure |
| US20110033908A1 (en)* | 2009-08-04 | 2011-02-10 | Dae-Yeol Cheong | Methods for selectively producing hydrogen and methane from biomass feedstocks using an anaerobic biological system |
| CN102559773A (en)* | 2012-03-06 | 2012-07-11 | 北京化工大学 | Method for improving methane-producing performance under synergistic action of mixed quasi-synchronous fermentation of multiple raw materials |
| CN103602715A (en)* | 2013-12-06 | 2014-02-26 | 四川蓉加川大环保工程咨询设计有限公司 | Method for preparing hydrogen from straws |
| CN111268643A (en)* | 2020-02-14 | 2020-06-12 | 江苏理工学院 | Process for accelerating production of hydrogen from organic solid waste by using iron-containing sludge |
| CN113801898A (en)* | 2021-09-15 | 2021-12-17 | 上海交通大学 | A method for producing hydrogen and methane by using multi-material mixed two-stage anaerobic fermentation |
- 2022
- 2022-10-20CNCN202211285941.5Apatent/CN115807041A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110033908A1 (en)* | 2009-08-04 | 2011-02-10 | Dae-Yeol Cheong | Methods for selectively producing hydrogen and methane from biomass feedstocks using an anaerobic biological system |
| CN101914573A (en)* | 2010-07-29 | 2010-12-15 | 江苏大学 | A step-by-step method for producing hydrogen and methane by anaerobic fermentation of cow manure |
| CN102559773A (en)* | 2012-03-06 | 2012-07-11 | 北京化工大学 | Method for improving methane-producing performance under synergistic action of mixed quasi-synchronous fermentation of multiple raw materials |
| CN103602715A (en)* | 2013-12-06 | 2014-02-26 | 四川蓉加川大环保工程咨询设计有限公司 | Method for preparing hydrogen from straws |
| CN111268643A (en)* | 2020-02-14 | 2020-06-12 | 江苏理工学院 | Process for accelerating production of hydrogen from organic solid waste by using iron-containing sludge |
| CN113801898A (en)* | 2021-09-15 | 2021-12-17 | 上海交通大学 | A method for producing hydrogen and methane by using multi-material mixed two-stage anaerobic fermentation |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 李奥等: "原料比例与接种量对猪粪秸秆厌氧干发酵产气率及微生物群落的影响", 中国沼气, vol. 37, no. 06, 31 December 2019 (2019-12-31), pages 3 - 10* |
| 雷国元等: "有机固体废物生物法制氢的研究进展", 化工环保, vol. 27, no. 06, 31 December 2007 (2007-12-31), pages 525 - 531* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1944658B (en) | Method for producing cellulose alcohol by fermenting corncob processing residue | |
| CN114736934B (en) | Method for preparing biogas by promoting anaerobic co-fermentation of livestock manure straw by adding biochar | |
| CN107083401A (en) | A kind of resource utilization method of agricultural organic waste | |
| CN107604011B (en) | Method for improving anaerobic fermentation gas production by using carbon quantum dots as accelerant | |
| CN102533609A (en) | Methane dry fermentation compound bacteria | |
| CN106746398A (en) | A kind of method for improving residual active sludge anaerobic digestion performance | |
| CN102031276B (en) | Method for producing hydrogen by fermenting organism and alkali mat composite pretreated straw fiber raw erial at two steps | |
| CN103159386A (en) | Method for recycling surplus sludge in municipal sewage plant | |
| CN102250967B (en) | A method for preparing biofuel butanol from food waste | |
| CN114906999B (en) | Method for improving sequencing batch anaerobic digestion performance of cow dung by gradient heating method | |
| CN114250250B (en) | A method and application of ethanol combined with biochar to promote methane production from anaerobic fermentation of straw | |
| CN109182389B (en) | A method for improving the efficiency of high-solid anaerobic fermentation of organic waste to produce methane | |
| CN102766661A (en) | Algal residue and livestock/poultry feces coupled anaerobic fermentation method for producing hydrogen | |
| CN115807041A (en) | Method for inhibiting the activity of methanogens in anaerobic fermentation inoculum and hydrogen production method | |
| CN105861576A (en) | Method for producing volatile fatty acid (VFA) from mushroom cultured residue through alkaline fermentation | |
| CN101914576B (en) | Method for producing ethanol and methane by mixed fermentation of paper-making sludge and monosodium glutamate waste liquid | |
| CN110684580A (en) | Preparation method of composite high-energy biomass fuel rod | |
| CN116768189A (en) | Modified biochar for improving anaerobic fermentation methane production efficiency and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116002939A (en) | Method for promoting anaerobic digestion process of sludge through coupling treatment of oxygen and corn straw biogas residue biochar | |
| CN115896184A (en) | Method for improving anaerobic digestion performance of high-organic-load perishable organic solid waste by biogas residue biochar | |
| CN108048492A (en) | A kind of method for improving biomass material anaerobic fermentation gas production amount | |
| CN115125166A (en) | A method for enhancing the anaerobic treatment of kitchen waste by utilizing a conductive carrier to form a Shewanella electroactive biofilm | |
| CN101381072A (en) | A method for producing hydrogen by anaerobic fermentation of sweet sorghum stalks | |
| CN102242158B (en) | Method for producing ethanol with lotus peel powder as raw material by synchronization of saccharification and fermentation | |
| CN118186024A (en) | A method for promoting biogas and methane production by anaerobic fermentation of wheat straw using magnetic biochar |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |