CN115757634A - Real-time synchronization system and method for mass data - Google Patents
Real-time synchronization system and method for mass dataDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115757634A CN115757634ACN202211501389.9ACN202211501389ACN115757634ACN 115757634 ACN115757634 ACN 115757634ACN 202211501389 ACN202211501389 ACN 202211501389ACN 115757634 ACN115757634 ACN 115757634A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- message
- incremental
- queue
- rules
- real
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription57
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000claimsdescription30
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000claimsdescription14
- 238000001914filtrationMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000012795verificationMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000005012migrationEffects0.000description11
- 238000013508migrationMethods0.000description11
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description9
- 230000008878couplingEffects0.000description4
- 238000010168coupling processMethods0.000description4
- 238000005859coupling reactionMethods0.000description4
- 238000005192partitionMethods0.000description4
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description3
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000010076replicationEffects0.000description2
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description2
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002452interceptive effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000007781pre-processingMethods0.000description1
- 238000009420retrofittingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001960triggered effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及数据处理技术领域,尤其是涉及一种海量数据的实时同步系统及方法。The invention relates to the technical field of data processing, in particular to a real-time synchronization system and method for massive data.
背景技术Background technique
随着互联网技术更新迭代、用户量的激增,平台已不满足日常使用,需对平台进行重构,重构时如果涉及到数据库的改造,则需对原平台的数据进行全量迁移和增量迁移,而数据库重构则可能涉及表调整、字段类型等情况。因此,在迁移数据时不能直接对表进行复制,需要根据数据进行转换、拆分等操作。With the update and iteration of Internet technology and the surge in the number of users, the platform is no longer suitable for daily use, and the platform needs to be restructured. If the reconstruction involves the transformation of the database, the data of the original platform needs to be fully migrated and incrementally migrated. , while database refactoring may involve table adjustments, field types, and more. Therefore, when migrating data, you cannot directly copy the table, and you need to perform operations such as conversion and splitting based on the data.
为保证平台的稳定性,通常使用增量迁移方式。现有增量迁移常用的方案主要有:定时任务模式、流量复制模式和埋点模式。基于增量迁移要求数据的实时性和平台的解耦性等,在增量数据量非常大的情况下,无法实现大量数据的实时同步,上述方案均不满足平台增量迁移的要求。In order to ensure the stability of the platform, incremental migration is usually used. The commonly used solutions for existing incremental migration mainly include: scheduled task mode, traffic replication mode, and buried point mode. Incremental migration requires real-time data and platform decoupling. When the amount of incremental data is very large, real-time synchronization of a large amount of data cannot be achieved. None of the above solutions meets the requirements of incremental migration of the platform.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一种海量数据的实时同步系统及方法,以解决现有技术无法满足大量数据增量迁移时的实时性和解耦性要求的技术问题。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a real-time synchronization system and method for massive data, so as to solve the technical problem that the existing technology cannot meet the real-time and decoupling requirements when a large amount of data is incrementally migrated.
本发明的目的,可以通过如下技术方案实现:The purpose of the present invention can be achieved through the following technical solutions:
一种海量数据的实时同步系统,包括:A real-time synchronization system for massive data, including:
源数据库、Canal集群、消息队列集群、增量同步系统、目标数据库;Source database, Canal cluster, message queue cluster, incremental synchronization system, target database;
其中,所述源数据库产生增量日志;Wherein, the source database generates an incremental log;
所述Canal集群监听所述源数据库并获取增量日志,根据所述增量日志生成增量数据,并将所述增量数据作为消息记录推送至所述消息队列集群;The Canal cluster monitors the source database and obtains an incremental log, generates incremental data according to the incremental log, and pushes the incremental data to the message queue cluster as a message record;
所述消息队列集群接收所述Canal集群推送的消息记录;The message queue cluster receives the message record pushed by the Canal cluster;
所述增量同步系统监听所述消息队列集群并获取消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费,对所述消息子队列中的消息记录进行处理后存入所述目标数据库;The incremental synchronization system monitors the message queue cluster and obtains message records, distributes the message records to the corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rules, and processes the message records in the message sub-queues Store in the target database after processing;
所述目标数据库保存所述增量同步系统处理后的消息记录。The target database saves the message records processed by the incremental synchronization system.
本发明还提供了一种海量数据的实时同步方法,应用在一种海量数据的实时同步系统上,所述方法包括:The present invention also provides a real-time synchronization method for massive data, which is applied to a real-time synchronization system for massive data, and the method includes:
利用Canal获取源数据库的增量日志,根据所述增量日志生成增量数据,并将所述增量数据作为消息记录推送至所述消息队列集群;Using Canal to obtain the incremental log of the source database, generate incremental data according to the incremental log, and push the incremental data to the message queue cluster as a message record;
利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费;Obtaining message records in the message queue by using an incremental synchronization system, and distributing the message records to corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to preset distribution rules;
利用增量同步系统对所述消息子队列中的消息记录进行处理后存入目标数据库。The message records in the message sub-queue are processed by the incremental synchronization system and stored in the target database.
可选地,所述预设分发规则包括:Optionally, the preset distribution rules include:
前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则;Pre- and post-table association rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules;
其中,所述前后置表关联规则根据当前增量同步的表分发消息记录,所述表字段值关联规则根据表中的字段分发消息记录,所述单表并发消费规则是将单张表根据字段取模将消息记录并行分发。Wherein, the pre- and post-table association rules distribute message records according to the table that is currently incrementally synchronized, the table field value association rules distribute message records according to the fields in the table, and the single-table concurrent consumption rule distributes a single table according to the fields Modulo distributes message records in parallel.
可选地,包括:根据优先级使用所述前后置表关联规则、所述表字段值关联规则和所述单表并发消费规则中的至少一个;Optionally, the method includes: using at least one of the preceding and preceding table association rules, the table field value association rules, and the single-table concurrent consumption rules according to priority;
其中,所述表字段值关联规则、所述前后置表关联规则、所述单表并发消费规则的优先级从高到低。Wherein, the priorities of the table field value association rules, the preceding and following table association rules, and the single-table concurrent consumption rules are from high to low.
可选地,利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录之后还包括:Optionally, after using the incremental synchronization system to obtain the message records in the message queue, it also includes:
若消息记录为更新操作时,则进入过滤模块验证。If the message record is an update operation, enter the filtering module for verification.
可选地,过滤模块验证包括:Optionally, filter module verification includes:
S11:判断是否配置了消息过滤规则,若是,执行S12,若否,执行步骤“根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费”;S11: Determine whether a message filtering rule is configured, if yes, perform S12, if not, perform the step "distribute the message record to the corresponding message sub-queue for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rule";
S12:验证消息记录是否需要进行过滤,若是,结束操作,若否,执行步骤“根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费”。S12: Verify whether the message records need to be filtered, if yes, end the operation, if not, perform the step of "distributing the message records to the corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rules".
可选地,还包括:Optionally, also include:
根据预设异常条件判断消息记录是否异常,若异常,将异常的消息记录加入重试队列并进行重试操作。Determine whether the message record is abnormal according to the preset abnormal conditions. If it is abnormal, add the abnormal message record to the retry queue and perform the retry operation.
可选地,将异常的消息记录加入重试队列并进行重试操作之后还包括:Optionally, after adding the abnormal message record to the retry queue and performing the retry operation, it also includes:
当重试操作次数达到预设阈值时,将异常的消息记录进行异常入库操作。When the number of retry operations reaches the preset threshold, the abnormal message will be recorded for abnormal warehousing operation.
可选地,利用Canal集群获取源数据库的增量日志之前还包括:Optionally, before using the Canal cluster to obtain the incremental log of the source database, it also includes:
部署Canal集群,部署消息队列,通过Canal配置文件配置需要同步的表和推送的消息队列地址。Deploy the Canal cluster, deploy the message queue, and configure the table to be synchronized and the address of the message queue to be pushed through the Canal configuration file.
可选地,利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录之前还包括:Optionally, before using the incremental synchronization system to obtain the message records in the message queue, it also includes:
部署增量同步系统,配置预设分发规则。Deploy an incremental synchronization system and configure preset distribution rules.
本发明提供了一种海量数据的实时同步系统及方法,其中方法包括:利用Canal获取源数据库的增量日志,根据所述增量日志生成增量数据,并将所述增量数据作为消息记录推送至消息队列;利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费;利用增量同步系统对所述消息子队列中的消息记录进行处理后存入目标数据库。The present invention provides a real-time synchronization system and method for massive data, wherein the method includes: using Canal to obtain the incremental log of the source database, generating incremental data according to the incremental log, and recording the incremental data as a message Push to the message queue; use the incremental synchronization system to obtain the message records in the message queue, and distribute the message records to the corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rules; use the incremental synchronization system to The message records in the message subqueue are processed and stored in the target database.
有鉴如此,本发明带来的有益效果是:In view of this, the beneficial effects brought by the present invention are:
本发明利用Canal监听源数据库并获取增量日志,根据增量日志生成增量数据并推送至消息队列,把重点放在数据上,不需要关注上层业务应用,避免跟业务有关联,具有高解耦性;根据配置的预设分发规则,增量同步系统将消息记录分发到具体的消息子队列,灵活配置数据消费,能加快消息消费,保证大量数据同步的实时性;通过重试机制和异常提醒机制,保证增量同步数据的一致性。The invention uses Canal to monitor the source database and obtain incremental logs, generates incremental data according to the incremental logs and pushes them to the message queue, focuses on the data, does not need to pay attention to upper-level business applications, and avoids being related to the business, with high resolution Coupling; according to the configured preset distribution rules, the incremental synchronization system distributes message records to specific message subqueues, and flexibly configures data consumption, which can speed up message consumption and ensure real-time synchronization of large amounts of data; through retry mechanism and exception The reminder mechanism ensures the consistency of incremental synchronization data.
附图说明Description of drawings
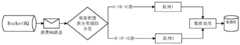
图1为本发明系统装置的结构示意图;Fig. 1 is the structural representation of system device of the present invention;
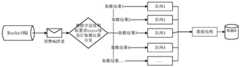
图2为本发明方法实施例的流程示意图一;Fig. 2 is a schematic flow diagram 1 of a method embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明方法实施例的流程示意图二;Fig. 3 is the second schematic flow diagram of the method embodiment of the present invention;
图4为本发明方法实施例的前后置表关联规则流程示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic flow chart of the front and back table association rules of the method embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明方法实施例的表字段值关联规则流程示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic flow chart of table field value association rules in the method embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明方法实施例的单表并发消费规则流程示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic flow chart of a single-table concurrent consumption rule in a method embodiment of the present invention;
图7为本发明方法含过滤和异常重试的流程示意图;Fig. 7 is a schematic flow diagram of the method of the present invention including filtering and abnormal retry;
图8为本发明方法另一实施例的流程示意图。Fig. 8 is a schematic flowchart of another embodiment of the method of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明实施例提供了一种海量数据的实时同步系统及方法,以解决现有技术无法满足大量数据增量迁移时的实时性和解耦性要求的技术问题。Embodiments of the present invention provide a real-time synchronization system and method for massive data to solve the technical problem that the prior art cannot meet the real-time and decoupling requirements of incremental migration of massive data.
为了便于理解本发明,下面将参照相关附图对本发明进行更全面的描述。附图中给出了本发明的首选实施例。但是,本发明可以以许多不同的形式来实现,并不限于本文所描述的实施例。相反地,提供这些实施例的目的是使对本发明的公开内容更加透彻全面。In order to facilitate the understanding of the present invention, the present invention will be described more fully below with reference to the associated drawings. A preferred embodiment of the invention is shown in the drawings. However, the present invention can be embodied in many different forms and is not limited to the embodiments described herein. Rather, these embodiments are provided so that the disclosure of the present invention will be thorough and complete.
除非另有定义,本文所使用的所有的技术和科学术语与属于本发明的技术领域的技术人员通常理解的含义相同。本文中在本发明的说明书中所使用的术语只是为了描述具体的实施例的目的,不是旨在于限制本发明。本文所使用的术语“及/或”包括一个或多个相关的所列项目的任意的和所有的组合。Unless otherwise defined, all technical and scientific terms used herein have the same meaning as commonly understood by one of ordinary skill in the technical field of the invention. The terms used herein in the description of the present invention are for the purpose of describing specific embodiments only, and are not intended to limit the present invention. As used herein, the term "and/or" includes any and all combinations of one or more of the associated listed items.
本发明主要针对增量迁移和实时同步第三方系统的数据;增量迁移为在全量迁移期间,在旧平台又产生新增、修改、删除数据,这样需要对这一系列数据进行增量同步。为保证平台稳定性,新平台上线方案一般不会采取直接切割,一般采取逐步放量等方式,在运行稳定后才进行全部切割。在这期间旧平台产生的数据也需要实时同步至新平台,保证数据的实时性和有效性。The present invention is mainly aimed at incremental migration and real-time synchronization of data in third-party systems; incremental migration means adding, modifying, and deleting data on the old platform during the full migration period, which requires incremental synchronization of this series of data. In order to ensure the stability of the platform, the online plan of the new platform generally does not adopt direct cuts, but generally adopts methods such as gradual increase in volume, and all cuts are carried out after the operation is stable. During this period, the data generated by the old platform also needs to be synchronized to the new platform in real time to ensure the real-time and validity of the data.
实现增量迁移,目前常用的技术方案主要包括:To achieve incremental migration, the currently commonly used technical solutions mainly include:
(1)定时任务模式:通过数据库同步或接口获取数据;定时根据时间参数获取数据同步至新平台,该方法实时性不高,还需考虑性能瓶颈。(1) Timing task mode: Obtain data through database synchronization or interface; regularly obtain data according to time parameters and synchronize to the new platform. This method is not real-time, and performance bottlenecks need to be considered.
(2)流量复制模式:该方式为复制旧平台流量,在新平台增加一样的接口来处理数据,该方式虽然能保证数据实时性,但需对旧平台的业务处理非常熟悉,才能保证整个业务请求处理的数据都可以与旧平台一致。(2) Traffic replication mode: This method is to copy the traffic of the old platform, and add the same interface to process data on the new platform. Although this method can ensure real-time data, it needs to be very familiar with the business processing of the old platform to ensure the entire business The data processed by the request can be consistent with the old platform.
(3)埋点模式:该方式通过在底层数据操作时,通过调用接口或其他方式通知新平台有数据操作,新平台再对数据处理。该模式需要改造旧平台。(3) Buried point mode: This method notifies the new platform that there is data operation by calling the interface or other methods when the underlying data is operated, and the new platform processes the data. This model requires retrofitting legacy platforms.
基于增量迁移要求数据的实时性和平台的解耦性等,在增量数据量非常大的情况下,上述方案都不满足平台增量迁移的要求。现有技术中也有基于Canal同步的方案,但为保证数据消费的顺序性,无法做到大量数据的实时同步。Based on the real-time data and platform decoupling required by incremental migration, none of the above solutions can meet the requirements of platform incremental migration when the amount of incremental data is very large. There are also solutions based on Canal synchronization in the prior art, but in order to ensure the order of data consumption, real-time synchronization of a large amount of data cannot be achieved.
请参阅图1,本发明提供了一种海量数据的实时同步系统的实施例,包括:Please refer to Fig. 1, the present invention provides a kind of embodiment of the real-time synchronization system of mass data, including:
源数据库、Canal集群、消息队列集群、增量同步系统、目标数据库;Source database, Canal cluster, message queue cluster, incremental synchronization system, target database;
其中,所述源数据库产生增量日志;Wherein, the source database generates an incremental log;
所述Canal集群监听所述源数据库并获取增量日志,根据所述增量日志生成增量数据,并将所述增量数据作为消息记录推送至所述消息队列集群;The Canal cluster monitors the source database and obtains an incremental log, generates incremental data according to the incremental log, and pushes the incremental data to the message queue cluster as a message record;
所述消息队列集群接收所述Canal集群推送的消息记录;The message queue cluster receives the message record pushed by the Canal cluster;
所述增量同步系统监听所述消息队列集群并获取消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费,对所述消息子队列中的消息记录进行处理后存入所述目标数据库;The incremental synchronization system monitors the message queue cluster and obtains message records, distributes the message records to the corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rules, and processes the message records in the message sub-queues Store in the target database after processing;
所述目标数据库保存所述增量同步系统处理后的消息记录。The target database saves the message records processed by the incremental synchronization system.
本发明提供的海量数据的实时同步方法,基于Canal和消息队列实现海量数据的实时同步,包括:The real-time synchronization method of massive data provided by the present invention realizes the real-time synchronization of massive data based on Canal and message queue, including:
(1)Canal监听源数据库Binlog增量日志,生成JSON格式数据推送消息队列;(1) Canal monitors the Binlog incremental log of the source database and generates a JSON format data push message queue;
(2)增量同步系统消费消息队列中的消息记录;(2) The incremental synchronization system consumes the message records in the message queue;
(3)根据消息过滤规则对数据进行过滤;(3) Filter the data according to the message filtering rules;
(4)根据预设分发规则进行分发处理,发送至对应的子队列进行消费处理。针对不同业务和不同的数据量配置合适的分发规则进行同步,达到数据实时同步;其中,预设分发规则包括前后置表关系规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则;(4) Perform distribution processing according to preset distribution rules, and send to corresponding sub-queues for consumption processing. Configure appropriate distribution rules for different businesses and different data volumes for synchronization to achieve real-time data synchronization; among them, the preset distribution rules include pre- and post-table relationship rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules;
(5)若出现异常,则启用重试机制,把相关异常数据加入重试队列,进行重试操作。(5) If an exception occurs, enable the retry mechanism, add relevant abnormal data to the retry queue, and perform retry operations.
请参阅图2和图3,本发明还提供了一种海量数据的实时同步方法的实施例,应用在一种海量数据的实时同步系统上,所述方法包括:Please refer to Fig. 2 and Fig. 3, the present invention also provides the embodiment of a kind of real-time synchronization method of massive data, applied on a kind of real-time synchronization system of massive data, described method comprises:
利用Canal获取源数据库的增量日志,根据所述增量日志生成增量数据,并将所述增量数据作为消息记录推送至消息队列;Utilize Canal to obtain the incremental log of the source database, generate incremental data according to the incremental log, and push the incremental data to the message queue as a message record;
利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费;Obtaining message records in the message queue by using an incremental synchronization system, and distributing the message records to corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to preset distribution rules;
利用增量同步系统对所述消息子队列中的消息记录进行处理后存入目标数据库。The message records in the message sub-queue are processed by the incremental synchronization system and stored in the target database.
在步骤S100中,利用增量数据订阅与消费服务Canal监听源数据库产生的Binlog日志,并获取源数据库的Binlog增量日志,本实施例通过Canal获取源数据库Binlog增量日志中的操作记录,将操作记录值转成JSON格式的字符串生成增量数据,将增量数据作为消息记录推送至消息队列中。In step S100, use the incremental data subscription and consumption service Canal to monitor the Binlog log generated by the source database, and obtain the Binlog incremental log of the source database. In this embodiment, the Canal is used to obtain the operation records in the Binlog incremental log of the source database. The value of the operation record is converted into a string in JSON format to generate incremental data, and the incremental data is pushed to the message queue as a message record.
本实施例基于Canal获取源数据库产生的Binlog增量日志,将数据的变化值推送至消息队列(支持RocketMQ、Kafka、RabbitMQ)中。为保证读取Binlog的顺序性和写入MQ消息的顺序性,可以配置单Topic、单Queue模式。This embodiment is based on the Binlog incremental log generated by Canal to obtain the source database, and pushes the change value of the data to the message queue (supporting RocketMQ, Kafka, RabbitMQ). To ensure the order of reading Binlog and writing MQ messages, you can configure single Topic and single Queue mode.
需要说明的是,配置单Topic、单Queue模式为Canal框架默认配置,可以通过Canal的canal.properties文件配置,具体配置如下:It should be noted that the configuration of single topic and single queue mode is the default configuration of the Canal framework, which can be configured through the canal.properties file of Canal. The specific configuration is as follows:
#配置模式tcp,kafka,rocketMQ,rabbitMQ#Configuration mode tcp, kafka, rocketMQ, rabbitMQ
canal.serverMode=rocketMQ;canal.serverMode = rocketMQ;
#配置mq的group地址、group、topic及tag#Configure the group address, group, topic and tag of mq
rocketmq.producer.group=CANCAL;rocketmq.producer.group=CANCAL;
rocketmq.customized.trace.topic=smarthome_topic;rocketmq.customized.trace.topic = smarthome_topic;
rocketmq.namespace=***;rocketmq.namespace=***;
rocketmq.namesrv.addr=http://xxxxxx;rocketmq.namesrv.addr = http://xxxxxx;
rocketmq.tag=data_tag;rocketmq.tag = data_tag;
在步骤S200中,利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录,根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费。In step S200, the incremental synchronization system is used to acquire message records in the message queue, and the message records are distributed to corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to preset distribution rules.
本实施例中,增量同步系统监听消息记录,进行并发消费。增量同步系统配置的预设分发规则可以包括:In this embodiment, the incremental synchronization system monitors message records for concurrent consumption. The preset distribution rules for incremental synchronization system configuration can include:
前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则;其中,前后置表关联规则根据当前增量同步的表分发消息记录,表字段值关联规则根据表中的字段分发消息记录,单表并发消费规则是将单张表根据字段取模将消息记录并行分发。Pre- and post-table association rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules; among them, the pre- and post-table association rules distribute message records according to the table that is currently incrementally synchronized, and the table field value association rules distribute message records according to the fields in the table. The single-table concurrent consumption rule is to take a single table according to the field modulo and distribute the message records in parallel.
具体地,前后置表关联规则为根据当前增量同步的表进行分类,基础表放入主队列同步,然后根据业务表中是否存在前置表的数据进行分类,如A表中有B表中的关联数据,则B表为A表的前置表,将可以A表、B表这两张表作为一个分类。Specifically, the association rules of front and back tables are to classify according to the table that is currently incrementally synchronized, put the basic table into the main queue for synchronization, and then classify according to whether there is data in the front table in the business table, for example, there are tables in table B in table A The associated data, then table B is the pre-table of table A, and the two tables of table A and table B can be used as a classification.
需要说明的是,主队列为监听消息记录的消息队列,该主队列可以有多个并发的子队列,然后子队列再有子队列,前一级子队列是后一级子队列的父队列。It should be noted that the main queue is a message queue for listening to message records. The main queue can have multiple concurrent sub-queues, and then sub-queues have sub-queues. The previous sub-queue is the parent queue of the subsequent sub-queue.
前后置表关联规则将当前增量数据中需要同步的表进行分类,根据配置表的关联规则进行分类分发,将基础表放入主队列同步,根据业务配置表判断基础表是否存在前置表,若存在,将基础表和该基础表的所有前置表作为一个分类,即将基础表和前置表加入同一个消息子队列中。The pre- and post-table association rules classify the tables that need to be synchronized in the current incremental data, classify and distribute according to the association rules of the configuration table, put the basic table into the main queue for synchronization, and judge whether the basic table has a pre-table according to the business configuration table. If it exists, take the basic table and all preceding tables of the basic table as a category, that is, add the basic table and preceding tables to the same message subqueue.
请参阅图4,例如,A表中有B表中的关联数据,B表中有C表中的关联数据,则B表为A表的前置表,C表为B表的前置表,且C表同时也是A表的前置表,即A表(基础表)的前置表有B表和C表,将A表、B表和C表这三张表作为同一个分类分发到消息队列1中。前后置表关联规则中,根据前后置表关系分发消息记录,如消息队列1配置了A表、B表和C表,则将A表、B表和C表的操作记录自动转发至消息队列1进行处理。Please refer to Figure 4. For example, if table A contains associated data in table B, and table B contains associated data in table C, then table B is the pre-table of table A, and table C is the pre-table of table B. And table C is also the front table of table A, that is, the front table of table A (basic table) has table B and table C, and the three tables of table A, table B and table C are distributed to the message as the same classification in
可以理解的是,图4中,B表为C表的后置业务关联表,A表同时为B表、C表的后置业务关联表。It can be understood that, in FIG. 4 , Table B is the subsequent service association table of Table C, and Table A is the subsequent service association table of Table B and Table C at the same time.
需要说明的是,根据实际的业务配置表,基础表与前置表之间的关联数据可以有一级或更多级。It should be noted that, according to the actual business configuration table, there may be one or more levels of associated data between the basic table and the pre-table.
具体地,表字段值关联规则为根据表中的某些字段进行分类,如新增用户A,涉及后续跟该用户有关的业务数据都推送至相同的消费队列中,保证该用户下的所有业务数据的顺序消费,不会出现并发消费导致数据错乱。Specifically, the table field value association rule is to classify according to certain fields in the table. For example, if a new user A is added, all subsequent business data related to this user will be pushed to the same consumption queue to ensure that all services under this user The sequential consumption of data does not cause data confusion due to concurrent consumption.
请参阅图5,表字段值关联规则根据表字段值分发消息记录,获取消息记录中配置的表字段值和消息队列数量进行取模运算,确定消息记录要转发的消息队列。具体规则可以为:根据配置的分类字段进行取模运算,例如,根据用户ID值分类,RocketMQ配置了8个Queue消费队列,取模运算规则为通过用户ID获取HASH值除以8取余,则可以获取该条消息记录需要分发到具体的哪个队列中,再根据RocketMQ的MessageQueueSelector接口实现指定消息发送到具体的指定Queue消费队列中。Please refer to Figure 5. The table field value association rule distributes message records according to the table field values, obtains the table field values configured in the message records and the number of message queues, and performs modulo calculations to determine the message queues to which the message records are to be forwarded. The specific rules can be: perform modulo calculations based on the configured classification fields. For example, RocketMQ configures 8 Queue consumption queues according to the classification of user ID values. You can obtain the specific queue to which the message record needs to be distributed, and then send the specified message to the specific specified Queue consumption queue according to the MessageQueueSelector interface of RocketMQ.
具体地,单表并发消费规则根据配置的表名,把所有该表的记录都分发至并发消费队列中,并通过指定的字段分配值分发到不同的Queue中,保证同一条记录的有序性。Specifically, the single-table concurrent consumption rule distributes all the records of the table to the concurrent consumption queue according to the configured table name, and distributes them to different Queues through the specified field assignment value to ensure the order of the same record .
请参阅图6,当增量同步的某张表(简称同步表)数据量大或者出现积压情况时,通过增量同步系统配置单张表并发规则进行并发消费,并配置并发表的一个非空字段进行取模分发到不同的消息队列Queue中,在并发消费的同时,保证同一条记录的有序性。规则可以为:若同步表的所有前置业务表在同一个父队列中,并且该同步表无后置业务关联表,则可以配置该同步表到并发消费队列中进行并发消费。例如,图4中的A表,A表的前置业务表为B表和C表,当B表和C表在同一个父队列中,并且A表不是其他表的前置业务表即A表无后置业务关联表,当A表的数据量大或者出现积压情况时,根据A表的某个非空字段进行取模将A表分发到对应的子队列中进行并发消费。Please refer to Figure 6. When a certain table (referred to as the synchronization table) for incremental synchronization has a large amount of data or has a backlog, configure the concurrency rules for a single table through the incremental synchronization system for concurrent consumption, and configure and publish a non-empty Fields are modeled and distributed to different message queues to ensure the order of the same record while concurrently consuming. The rule can be: if all the front business tables of the synchronization table are in the same parent queue, and the synchronization table has no post business association table, then the synchronization table can be configured to be consumed concurrently in the concurrent consumption queue. For example, in table A in Figure 4, the preceding business tables of table A are table B and table C, when table B and table C are in the same parent queue, and table A is not the preceding business table of other tables, that is, table A There is no post-installed business association table. When the amount of data in table A is large or there is a backlog, model A is taken according to a non-empty field in table A and table A is distributed to the corresponding sub-queue for concurrent consumption.
本实施例中,前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则这三种分发规则,可以单独使用,也可以根据优先级组合使用前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则中的至少两个,表字段值关联规则、前后置表关联规则、单表并发消费规则的优先级从高到低。即可以将前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则任意两两组合或全部组合,例如,A表和B表是关联表,则需使用前后置表关联规则,若B表数据量大,则还需使用单表并发消费规则,这种情况对应的是同时使用前后置表关联规则和单表并发消费规则。若前后置表关联规则和表字段值关联规则同时使用时,则表字段值关联规则优先。In this embodiment, the three distribution rules, the pre- and post-table association rules, the table field value association rules, and the single-table concurrent consumption rules, can be used alone, or can be used in combination according to the priority. and at least two of the single-table concurrent consumption rules, the priority of table field value association rules, front and rear table association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules is from high to low. That is, you can combine any pair or all of the front and back table association rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules. For example, if table A and B are associated tables, you need to use the front and rear table association rules. If B If the amount of table data is large, it is necessary to use the single-table concurrent consumption rule. This situation corresponds to the simultaneous use of the front and back table association rules and the single-table concurrent consumption rule. If the front and rear table association rules and table field value association rules are used at the same time, the table field value association rules take precedence.
在基于原有canal中间件和MQ(Message Queue,消息队列)方式做不到大数据量的实时同步情况下,本实施例通过设置前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则和单表并发消费规则,结合实际情况分析对整体同步程序做出改进,能保证同步数据的实时性和有效性。In the case that the real-time synchronization of a large amount of data cannot be achieved based on the original canal middleware and MQ (Message Queue, message queue), this embodiment sets the front and back table association rules, table field value association rules and single table concurrent consumption Rules, combined with actual situation analysis to improve the overall synchronization program, can ensure the real-time and effectiveness of synchronization data.
本实施例结合MQ特性,建立主、子队列机制,根据主队列对数据进行相关预处理,在接收某消息记录时,对该消息记录进行分发规则的适配,为该消息记录匹配对应的某个或某些分发规则,解析后再根据增量同步系统提供的消息分发规则对消息记录进行分发处理,将该消息记录分发至相关的子队列进行处理,达到快速消费,实现实时同步,增量同步系统提供3种分发规则,可以单独使用,也可以组合使用。This embodiment combines the characteristics of MQ, establishes the main and sub-queue mechanism, and performs relevant preprocessing on the data according to the main queue. After parsing one or some distribution rules, the message records are distributed and processed according to the message distribution rules provided by the incremental synchronization system, and the message records are distributed to the relevant sub-queues for processing to achieve fast consumption, real-time synchronization, incremental The synchronization system provides 3 distribution rules, which can be used alone or in combination.
需要说明的是,MQ特性为异步、解耦、削峰,主要通过消息队列的顺序消息、并发消费、消息延迟组合建立主子队列。It should be noted that the characteristics of MQ are asynchronous, decoupling, and peak shaving, and the main and subqueues are mainly established through the combination of sequential messages, concurrent consumption, and message delay of message queues.
本实施例中,利用增量同步系统获取消息队列中的消息记录之后还包括:若消息记录为更新操作时,则进入过滤模块验证。由于旧平台(源数据库)对某条记录可能只更新一个或者多个不重要的字段,新平台(目标数据库)用不到该字段或者无用的值,则可以配置消息过滤规则对消息记录进行过滤,当消息记录对应的某个表、某些字段存在更新时,自动忽略该记录,避免对数据库进行查询和操作,这样能加快数据同步的效率。In this embodiment, after using the incremental synchronization system to obtain the message records in the message queue, it further includes: if the message records are update operations, then enter the filtering module for verification. Since the old platform (source database) may only update one or more unimportant fields for a certain record, and the new platform (target database) does not use this field or useless values, you can configure message filtering rules to filter message records , when a table or some fields corresponding to a message record is updated, the record is automatically ignored to avoid querying and operating the database, which can speed up the efficiency of data synchronization.
请参阅图7,过滤模块验证具体包括:Please refer to Figure 7, the filtering module verification specifically includes:
S11:判断是否配置了消息过滤规则,若是,执行S12,若否,执行步骤“根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费”;S11: Determine whether a message filtering rule is configured, if yes, perform S12, if not, perform the step "distribute the message record to the corresponding message sub-queue for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rule";
S12:验证消息记录是否需要进行过滤,若是,结束操作,若否,执行步骤“根据预设分发规则将所述消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中进行并发消费”。S12: Verify whether the message records need to be filtered, if yes, end the operation, if not, perform the step of "distributing the message records to the corresponding message sub-queues for concurrent consumption according to the preset distribution rules".
需要说明的是,根据实际同步情况来说,数据库的插入操作(insert)和删除操作(delete)是必须执行的,不能进行过滤;但是更新操作(update)时可能存在不需要关注的字段,因此,当消息记录为update操作时,可以针对性地过滤某些消息记录。It should be noted that, according to the actual synchronization situation, the insert operation (insert) and delete operation (delete) of the database must be performed, and cannot be filtered; however, there may be fields that do not need to be concerned during the update operation (update), so , when the message record is an update operation, some message records can be filtered in a targeted manner.
本实施例还包括:根据预设异常条件判断消息记录是否异常,若异常,将异常的消息记录加入重试队列并进行重试操作。当出现某条消息记录(数据)获取不到关联值等异常情况时,通过制定异常触发重试机制,根据预设异常条件判断消息记录是否异常,若异常,将异常数据发送到重试队列并进行重试操作。当重试操作次数达到配置的重试次数(预设阈值)后,若还存在异常的消息记录,则将异常的消息路进行异常入库操作,以便分析和处理异常数据。This embodiment also includes: judging whether the message record is abnormal according to the preset abnormal condition, and if abnormal, adding the abnormal message record to the retry queue and performing a retry operation. When there is an abnormal situation such as a certain message record (data) cannot obtain the associated value, by formulating an abnormal trigger retry mechanism, it is judged whether the message record is abnormal according to the preset abnormal conditions. If it is abnormal, the abnormal data is sent to the retry queue and Do a retry operation. When the number of retry operations reaches the configured number of retries (preset threshold), if there is still an abnormal message record, the abnormal message path will be abnormally stored in order to analyze and process the abnormal data.
需要说明的是,重试队列是MQ中的概念,但是本实施例中的重试队列不是使用MQ的重试队列,是定义了一个正常队列为重试队列,主要用来当消息记录同步出现异常情况下,可以根据自定义的异常触发该消息记录,将该消息记录放入该重试队列进行重试触发。It should be noted that the retry queue is a concept in MQ, but the retry queue in this embodiment is not a retry queue using MQ, but a normal queue is defined as a retry queue, which is mainly used when message records appear synchronously Under abnormal circumstances, the message record can be triggered according to the custom exception, and the message record can be put into the retry queue for retry triggering.
需要说明的是,MQ为Message Queue-消息队列,MQ消息为消息队列中的消息记录,MQ是一种应用程序对应用程序的消息通信,一端只管往队列不断发布信息,另一端只管往队列中读取消息,发布者不需要关心读取消息的谁,读取消息者不需要关心发布消息的是谁,各干各的互不干扰。常见的消息队列有:RabbitMQ、RocketMQ、Kafka。It should be noted that MQ is Message Queue-message queue, and MQ messages are message records in the message queue. MQ is a kind of application-to-application message communication. One end only releases information to the queue continuously, and the other end only releases information to the queue. To read the message, the publisher does not need to care about who reads the message, and the reader does not need to care about who publishes the message, each doing its own thing without interfering with each other. Common message queues are: RabbitMQ, RocketMQ, Kafka.
本实施例中,利用Canal集群获取源数据库的增量日志之前还包括:部署Canal集群,部署消息队列,通过Canal配置文件配置需要同步的表和推送的消息队列地址。利用增量同步系统获取所述消息队列中的消息记录之前还包括:部署增量同步系统,配置预设分发规则。In this embodiment, before using the Canal cluster to obtain the incremental log of the source database, it also includes: deploying the Canal cluster, deploying the message queue, and configuring the table to be synchronized and the address of the message queue to be pushed through the Canal configuration file. Before using the incremental synchronization system to obtain the message records in the message queue, it also includes: deploying the incremental synchronization system, and configuring preset distribution rules.
本实施例中,需部署消息队列、Canal集群,通过Canal配置文件配置需要同步的表和推送的消息队列地址。具体地,Canal配置canal.serverMode=RocketMQ/Kafka/RabbitMQ方式,并配置canal.mq.servers=MQ集群地址。Canal配置canal.mq.dynamicTopic=需要同步的表,并配置canal.mq.partition=全量导出时MySql记录的partition值。部署增量同步系统,配置预设分发规则,根据业务配置前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则、单表并发消费规则。In this embodiment, a message queue and a Canal cluster need to be deployed, and the table to be synchronized and the address of the message queue to be pushed are configured through the Canal configuration file. Specifically, Canal configures canal.serverMode=RocketMQ/Kafka/RabbitMQ mode, and configures canal.mq.servers=MQ cluster address. Canal configures canal.mq.dynamicTopic = the table that needs to be synchronized, and configures canal.mq.partition = the partition value recorded by MySql when exporting in full. Deploy an incremental synchronization system, configure preset distribution rules, and configure front and rear table association rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules according to business configuration.
本实施例提供的海量数据的实时同步方法,利用Canal监听源数据库并获取增量日志,根据增量日志生成增量数据并推送至消息队列,把重点放在数据上,不需要关注上层业务应用,避免跟业务有关联,具有高解耦性;根据配置的预设分发规则,增量同步系统将消息记录分发到具体的消息子队列,灵活配置数据消费,能加快消息消费,保证大量数据同步的实时性;通过重试机制和异常提醒机制,保证增量同步数据的一致性。The real-time synchronization method for massive data provided in this embodiment uses Canal to monitor the source database and obtain incremental logs, generates incremental data based on incremental logs and pushes them to the message queue, focusing on data without paying attention to upper-level business applications , to avoid being associated with the business, with high decoupling; according to the configured preset distribution rules, the incremental synchronization system distributes message records to specific message subqueues, and flexibly configures data consumption, which can speed up message consumption and ensure a large amount of data synchronization The real-time performance; through the retry mechanism and exception reminder mechanism, the consistency of incremental synchronization data is guaranteed.
请参阅图8,本发明提供的一种海量数据的实时同步方法的另一实施例,整体流程详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 8, another embodiment of a real-time synchronization method for massive data provided by the present invention, the overall process is described in detail as follows:
(1)部署消息队列,部署Canal集群;(1) Deploy message queues and deploy Canal clusters;
(2)Canal配置canal.serverMode=RocketMQ/Kafka/RabbitMQ方式,并配置canal.mq.servers=MQ集群地址;(2) Canal configures canal.serverMode=RocketMQ/Kafka/RabbitMQ mode, and configures canal.mq.servers=MQ cluster address;
(3)Canal配置canal.mq.dynamicTopic=需要同步的表,并配置canal.mq.partition=全量导出时MySql记录的partition值;(3) Canal configures canal.mq.dynamicTopic = the table that needs to be synchronized, and configures canal.mq.partition = the partition value recorded by MySql when exporting in full;
(4)部署增量同步系统,配置消息记录分发规则,根据业务配置表关联规则、字段关联规则、单表并发消费规则;(4) Deploy an incremental synchronization system, configure message record distribution rules, and configure table association rules, field association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules according to the business;
(5)开启程序,主队列进行Canal监听和MQ消费;(5) Start the program, and the main queue performs Canal monitoring and MQ consumption;
(6)若配置了消息过滤规则,判断是否需要对消息记录进行过滤,若需要,再根据消息过滤规则对数据进行过滤,将消息记录分发至并发的消息子队列,进行并发消费;(6) If the message filtering rules are configured, judge whether the message records need to be filtered, if necessary, then filter the data according to the message filtering rules, and distribute the message records to the concurrent message sub-queues for concurrent consumption;
(7)增量同步系统对消息子队列中的数据(消息记录)进行相关转换和处理,将源数据库的字段值转换成目标数据库对应的字段值,并进行入库操作。(7) The incremental synchronization system converts and processes the data (message records) in the message subqueue, converts the field values of the source database into the corresponding field values of the target database, and performs storage operations.
需要说明的是,一般情况下,在将原平台的数据增量迁移到新平台的过程中,源数据库与目标数据库的字段值可能存在不同,因此,需要将源数据库的字段值转换成目标数据库的字段值。It should be noted that, in general, in the process of incrementally migrating data from the original platform to the new platform, the field values of the source database and the target database may be different. Therefore, it is necessary to convert the field values of the source database to the target database field value.
本发明重点基于MQ消费时队列分发规则改造,通过消费消息队列的消息记录,增量同步系统根据前后置表关联规则、表字段值关联规则、单表并发消费规则等多种分发规则将消息记录分发到对应的消息子队列中,达到海量数据的实时同步。The focus of the present invention is based on the transformation of the queue distribution rules during MQ consumption. Through the message records of the consumption message queue, the incremental synchronization system records the messages according to various distribution rules such as the front and rear table association rules, table field value association rules, and single-table concurrent consumption rules. Distributed to the corresponding message sub-queue to achieve real-time synchronization of massive data.
本发明通过增量同步系统配置预设分发规则,由主队列进行消息分发,根据配置的规则分发到具体的子队列,灵活配置数据消费,加快消息消费,保证数据同步的实时性。通过Canal监听数据库,把重点放在数据上,不需要关注上层业务应用,避免跟业务有关联,具有高解耦性。通过重试机制和异常提醒机制,保证增量同步数据的一致性。The invention configures preset distribution rules through the incremental synchronization system, distributes messages by the main queue, distributes them to specific sub-queues according to the configured rules, flexibly configures data consumption, speeds up message consumption, and ensures real-time data synchronization. Monitor the database through Canal, focus on the data, do not need to pay attention to the upper-level business application, avoid being related to the business, and have high decoupling. Through the retry mechanism and exception reminder mechanism, the consistency of incremental synchronization data is guaranteed.
所属领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到,为描述的方便和简洁,上述描述的系统,装置和单元的具体工作过程,可以参考前述方法实施例中的对应过程,在此不再赘述。Those skilled in the art can clearly understand that for the convenience and brevity of the description, the specific working process of the above-described system, device and unit can refer to the corresponding process in the foregoing method embodiment, which will not be repeated here.
在本申请所提供的实施例中,应该理解到,所揭露的系统,装置和方法,可以通过其它的方式实现。例如,以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,例如,所述单元的划分,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式,例如多个单元或组件可以结合或者可以集成到另一个系统,或一些特征可以忽略,或不执行。另一点,所显示或讨论的相互之间的耦合或直接耦合或通信连接可以是通过一些接口,装置或单元的间接耦合或通信连接,可以是电性,机械或其它的形式。In the embodiments provided in this application, it should be understood that the disclosed systems, devices and methods may be implemented in other ways. For example, the device embodiments described above are only illustrative. For example, the division of the units is only a logical function division. In actual implementation, there may be other division methods. For example, multiple units or components can be combined or May be integrated into another system, or some features may be ignored, or not implemented. In another point, the mutual coupling or direct coupling or communication connection shown or discussed may be through some interfaces, and the indirect coupling or communication connection of devices or units may be in electrical, mechanical or other forms.
所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部单元来实现本实施例方案的目的。The units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components shown as units may or may not be physical units, that is, they may be located in one place, or may be distributed to multiple network units. Part or all of the units can be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution of this embodiment.
另外,在本发明各个实施例中的各功能单元可以集成在一个处理单元中,也可是各个单元单独物理存在,也可以两个或两个以上单元集成在一个单元中。上述集成的单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能单元的形式实现。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present invention may be integrated into one processing unit, or each unit may physically exist separately, or two or more units may be integrated into one unit. The above-mentioned integrated units can be implemented in the form of hardware or in the form of software functional units.
所述集成的单元如果以软件功能单元的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,可以存储在一个计算机可读取存储介质中。基于这样的理解,本发明的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分或者该技术方案的全部或部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,服务器,或者网络设备等)执行本发明各个实施例所述方法的全部或部分步骤。而前述的存储介质包括:U盘、移动硬盘、只读存储器(ROM,Read-OnlyMemory)、随机存取存储器(RAM,Random Access Memory)、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。If the integrated unit is realized in the form of a software function unit and sold or used as an independent product, it can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. Based on this understanding, the essence of the technical solution of the present invention or the part that contributes to the prior art or all or part of the technical solution can be embodied in the form of a software product, and the computer software product is stored in a storage medium , including several instructions to make a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc.) execute all or part of the steps of the method described in each embodiment of the present invention. The aforementioned storage medium includes: U disk, mobile hard disk, read-only memory (ROM, Read-Only Memory), random access memory (RAM, Random Access Memory), magnetic disk or optical disk, and other media that can store program codes.
以上实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。The above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, rather than to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: it can still be described in the foregoing embodiments Modifications are made to the recorded technical solutions, or equivalent replacements are made to some of the technical features; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211501389.9ACN115757634B (en) | 2022-11-28 | 2022-11-28 | A real-time synchronization system and method for massive data |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211501389.9ACN115757634B (en) | 2022-11-28 | 2022-11-28 | A real-time synchronization system and method for massive data |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115757634Atrue CN115757634A (en) | 2023-03-07 |
| CN115757634B CN115757634B (en) | 2025-03-11 |
Family
ID=85339347
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211501389.9AActiveCN115757634B (en) | 2022-11-28 | 2022-11-28 | A real-time synchronization system and method for massive data |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115757634B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119003313A (en)* | 2024-10-24 | 2024-11-22 | 客思服(杭州)科技有限公司 | Homologous Binlog message routing method |
| CN119066123A (en)* | 2024-07-26 | 2024-12-03 | 九恒星(武汉)信息技术有限公司 | A data synchronization method, system, device and storage medium under microservice architecture |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107783975A (en)* | 2016-08-24 | 2018-03-09 | 北京京东尚科信息技术有限公司 | The method and apparatus of distributed data base synchronization process |
| WO2019047479A1 (en)* | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | 广东省建设信息中心 | General multi-source heterogenous large-scale data synchronization system |
| WO2020147392A1 (en)* | 2019-01-16 | 2020-07-23 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method and system for data synchronization between databases |
| CN112307037A (en)* | 2019-07-26 | 2021-02-02 | 北京京东振世信息技术有限公司 | Data synchronization method and device |
- 2022
- 2022-11-28CNCN202211501389.9Apatent/CN115757634B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107783975A (en)* | 2016-08-24 | 2018-03-09 | 北京京东尚科信息技术有限公司 | The method and apparatus of distributed data base synchronization process |
| WO2019047479A1 (en)* | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | 广东省建设信息中心 | General multi-source heterogenous large-scale data synchronization system |
| WO2020147392A1 (en)* | 2019-01-16 | 2020-07-23 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method and system for data synchronization between databases |
| CN112307037A (en)* | 2019-07-26 | 2021-02-02 | 北京京东振世信息技术有限公司 | Data synchronization method and device |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119066123A (en)* | 2024-07-26 | 2024-12-03 | 九恒星(武汉)信息技术有限公司 | A data synchronization method, system, device and storage medium under microservice architecture |
| CN119003313A (en)* | 2024-10-24 | 2024-11-22 | 客思服(杭州)科技有限公司 | Homologous Binlog message routing method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115757634B (en) | 2025-03-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN103516585B (en) | Method and system for distributing messages according to priorities | |
| CN100531055C (en) | Data synchronous system and its method | |
| US10122665B2 (en) | Distributed synchronization data in a message management service | |
| CN115757634A (en) | Real-time synchronization system and method for mass data | |
| CN112182001A (en) | Method, apparatus and medium for incremental synchronization of database to dynamic ES index library | |
| CN100449543C (en) | Method and device for storing logs | |
| CN101894348B (en) | Self-expanded online transaction system and implementing method thereof | |
| US9858306B2 (en) | Archiving to a single database table information located across multiple tables | |
| CN111552885B (en) | System and method for realizing automatic real-time message pushing operation | |
| CN112685499B (en) | A method, device and equipment for synchronizing process data of work business flow | |
| CN106951552A (en) | A kind of user behavior data processing method based on Hadoop | |
| CN111582955A (en) | Promotional information display method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN108536743A (en) | A kind of Combat Command System database in phase system | |
| CN111131368A (en) | Message pushing method and device | |
| JP2004531839A (en) | Unified messaging with separate media component storage | |
| WO2025124475A1 (en) | Event dispatching optimization method and device under super-large-scale kubernetes cluster | |
| CN118861057A (en) | Real-time data processing method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116521652B (en) | Method, system and medium for realizing migration of distributed heterogeneous database based on DataX | |
| CN110019045A (en) | Method and device is landed in log | |
| CN104869056B (en) | A Synchronization Method of Institution-Personnel Data Based on Relation-Data Separation | |
| CN113407491B (en) | Data processing method and device | |
| WO2016150111A1 (en) | Data processing method, device and system based on call reminder | |
| CN115202979A (en) | A kind of SQL real-time monitoring method, system, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN111563123A (en) | Live warehouse metadata real-time synchronization method | |
| CN116431366B (en) | Behavior path analysis method, system, storage terminal, server terminal and client terminal |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |