CN115671304A - A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115671304A CN115671304ACN202211366587.9ACN202211366587ACN115671304ACN 115671304 ACN115671304 ACN 115671304ACN 202211366587 ACN202211366587 ACN 202211366587ACN 115671304 ACN115671304 ACN 115671304A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- hyaluronic acid
- carboxybutyl
- melatonin
- prodrug
- reperfusion injury
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Polysaccharides And Polysaccharide Derivatives (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于药物新型给药系统研究领域,特别涉及一种治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物及其制备方法。The invention belongs to the research field of new drug delivery systems, in particular to a step-by-step targeted polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and a preparation method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
肾脏缺血再灌注损伤是肾脏组织缺血再灌注后,其组织细胞代谢障碍,从而导致肾脏结构和功能的破坏造成的急性肾损伤。近年研究发现,肾小管上皮细胞是急性肾损伤发生及发展的主要靶细胞。急性肾损伤可引起肾小管上皮细胞损伤、凋亡、坏死以及脱落,而肾小管内脱落的细胞易与尚未脱落的受激细胞通过粘附分子的相互作用,粘附成团,堵塞管腔,使管内压升高,进一步造成肾小球滤过率下降。其病理生理机制存在损伤级联反应,主要包括氧化应激、炎症反应、凋亡、细胞内钙超载等,其中氧化应激及其所诱导的细胞损伤、凋亡在急性肾损伤中的作用尤为瞩目。当呼吸链被抑制后再次恢复氧供时,线粒体会快速产生大量的ROS,过度氧化应激和细胞内钙超载是导致线粒体通透性转换孔大量开放的主要原因。线粒体通透性转换孔的大量开放易引起线粒体外膜破裂,继而形成线粒体水肿,并且释放大量的促调亡因子,如细胞色素C。外渗的细胞色素C与Caspase 9和Apaf1形成复合物,同时被激活。激活的Caspase 9可激活凋亡执行蛋白Caspase 3,并最终导致细胞凋亡。Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury is an acute kidney injury caused by renal tissue ischemia-reperfusion, and its tissue cell metabolism disorder, which leads to the destruction of kidney structure and function. Recent studies have found that renal tubular epithelial cells are the main target cells for the occurrence and development of acute kidney injury. Acute kidney injury can cause renal tubular epithelial cell damage, apoptosis, necrosis, and detachment, and the exfoliated cells in the renal tubule tend to interact with the stimulated cells that have not yet shed, adhere to form a group, and block the lumen. This increases the intravascular pressure and further reduces the glomerular filtration rate. There is an injury cascade reaction in its pathophysiological mechanism, which mainly includes oxidative stress, inflammatory response, apoptosis, intracellular calcium overload, etc. Among them, oxidative stress and the induced cell damage and apoptosis play a particularly important role in acute kidney injury. attention. When the oxygen supply is restored after the respiratory chain is inhibited, the mitochondria will rapidly generate a large amount of ROS. Excessive oxidative stress and intracellular calcium overload are the main reasons for the massive opening of mitochondrial permeability transition pores. A large number of openings of mitochondrial permeability transition pores can easily cause the rupture of mitochondrial outer membrane, and then form mitochondrial edema, and release a large number of pro-apoptotic factors, such as cytochrome C. Extravasated cytochrome c forms a complex with caspase 9 and Apaf1 and is simultaneously activated. Activated Caspase 9 can activate the apoptosis execution protein Caspase 3, and eventually lead to apoptosis.
线粒体是ROS产生和清除的主要场所,同时也是ROS损伤的主要作用靶点。由于线粒体DNA(mitochondrial DNA,mtDNA)缺乏保护性组蛋白,DNA修复机制不完善,又紧邻呼吸链,对ROS极其敏感,容易引起突变。而mtDNA突变可引起氧化磷酸化功能受损产生大量ROS,进一步促进mtDNA突变,形成恶性循环,进而导致细胞氧供不足,出现线粒体功能障碍,而采用抗氧化剂预处理可提供肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用。因此,从逆转肾小管上皮细胞线粒体的氧化应激损伤过程入手,寻找一种有效的治疗RIRI的手段具有十分重要的研究价值与临床意义。Mitochondria are the main site of ROS production and clearance, and also the main target of ROS damage. Because mitochondrial DNA (mitochondrial DNA, mtDNA) lacks protective histones, its DNA repair mechanism is imperfect, and it is close to the respiratory chain, it is extremely sensitive to ROS and easily causes mutations. However, mtDNA mutation can cause damage to oxidative phosphorylation function and generate a large amount of ROS, which further promotes mtDNA mutation and forms a vicious cycle, which in turn leads to insufficient oxygen supply to cells and mitochondrial dysfunction. Antioxidant pretreatment can protect against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. protective effect. Therefore, it is of great research value and clinical significance to find an effective means of treating RIRI starting from reversing the oxidative stress injury process of renal tubular epithelial cell mitochondria.
目前临床上抗氧化剂的品种很多,如姜黄素、维生素、氨基酸及其衍生物、ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸、褪黑素等,但总体疗效往往不尽如人意,这主要是由于所用药物均存在不同程度的肾外效应,进入机体后不能集中作用于受损靶细胞线粒体,即药物浓度过低,无法达到有效治疗浓度。因此,如何使尽可能多的抗氧化药物分布于肾脏组织,实现肾小管上皮细胞及胞内线粒体的主动靶向递送,提高治疗药物浓度,是急性肾损伤抗氧化治疗的关键。At present, there are many kinds of antioxidants clinically, such as curcumin, vitamins, amino acids and their derivatives, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, melatonin, etc., but the overall curative effect is often unsatisfactory, which is mainly due to the fact that the drugs used are all There are different degrees of extrarenal effects, and after entering the body, it cannot concentrate on the mitochondria of damaged target cells, that is, the drug concentration is too low to reach an effective therapeutic concentration. Therefore, how to distribute as many antioxidant drugs as possible in kidney tissue, realize the active targeted delivery of renal tubular epithelial cells and intracellular mitochondria, and increase the concentration of therapeutic drugs is the key to the antioxidant treatment of acute kidney injury.
褪黑素是一种由松果体分泌的吲哚类激素,具有许多重要的生物学功能,如抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、清除体内自由基等作用。近年研究表明褪黑素可通过抗氧化和抗炎等方式减轻缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤,还可通过与NLRC4炎性小体相互作用,调节急性肾损伤相关炎症反应。但其受限于半衰期短、体内易被代谢等问题,且其对肾脏组织细胞缺乏选择特异性,往往疗效不尽如人意。因此,有必要采用制剂手段从提高体内循环时间、改变药物体内分布等方面出发改善褪黑素用于缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤靶向抗氧化治疗效果。Melatonin is an indole hormone secreted by the pineal gland, which has many important biological functions, such as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, anti-tumor, and scavenging free radicals in the body. Recent studies have shown that melatonin can reduce acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion through anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation, and can also regulate inflammation related to acute kidney injury by interacting with NLRC4 inflammasome. However, it is limited by short half-life, easy to be metabolized in the body, etc., and it lacks selection specificity for kidney tissue cells, so the curative effect is often not satisfactory. Therefore, it is necessary to use preparation methods to improve the effect of melatonin on the targeted antioxidant therapy of acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion from the aspects of increasing the circulation time in the body and changing the distribution of the drug in the body.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明旨在至少部分地克服现有技术中存在的上述和/或其他潜在的问题:提供一种安全、高效的治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物、其制备方法及应用。The present invention aims to at least partly overcome the above-mentioned and/or other potential problems in the prior art: to provide a safe and efficient step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, its preparation method and application.
本发明的第一个目的是提供一种治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物,由(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦、褪黑素和不同聚合度的透明质酸嫁接而成,高分子前体药物的化学结构式如下:The first object of the present invention is to provide a step-by-step targeted macromolecule prodrug for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, consisting of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide, melatonin and different polymers Grafted from high-strength hyaluronic acid, the chemical structural formula of the polymer prodrug is as follows:
其中,n的取值范围为5~20。Wherein, the value range of n is 5-20.
本发明的第二个目的是提供所述治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的制备方法,步骤如下:The second object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing the step-by-step targeted polymer prodrug for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, the steps are as follows:
1)将(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸水溶液,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,用去离子水持续透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,离心取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物;1) Add (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide, 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl Base) carbodiimide hydrochloride, heat and stir to dissolve the reactant completely, then add hyaluronic acid aqueous solution dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir to continue the reaction for 48 hours, put the reaction product in a dialyzer with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500 bag, continue dialysis with deionized water for 48 hours, collect the suspension in the dialysis bag, centrifuge to get the supernatant and freeze-dry to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid grafted thing;
2)将(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,用去离子水持续透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,离心取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物。2) Add (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add N-hydroxysuccinimide, 1-ethyl-(3 -Dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, heat and stir to dissolve the reactant completely, add melatonin, heat and stir to continue the reaction for 48 hours, and place the reaction product in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500 , continued dialysis with deionized water for 48 hours, collected the suspension in the dialysis bag, centrifuged to get the supernatant and freeze-dried to obtain (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin Polymer prodrugs.
作为优化。所述透明质酸的聚合度为5~20。as an optimization. The degree of polymerization of the hyaluronic acid is 5-20.
本发明的第三个目的是提供所述治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的应用,作为原料用于制备治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的药物。The third object of the present invention is to provide the application of the step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury as a raw material for preparing a drug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的有益效果是:高分子前体药物属于聚合物疗法的范畴,其主要特征是将治疗药物通过共价键与亲水性大分子聚合物载体相连,这样会极大地改变原形药物的理化性质和体内行为。相比于游离药物,高分子前体药物能显著延长了血液循环间、改善组织分布和累积、提高药物的生物利用度。该类药物的设计一般需要遵循以下几个原则:1、化学键在细胞外应有足够的稳定性,以延长前药系统在体内的半衰期;2、一旦进入细胞内,化学键(在酸、碱、酶等条件下不稳定)应迅速被破坏降解,释出完整的药物分子;3、作为载体的聚合物应在血液循环中有足够的稳定性。本发明基于高分子前体药物的上述特性,通过将褪黑素与亲水性大分子聚合物相连,改善药物体内半衰期和分布,实现褪黑素的肾小管上皮细胞主动靶向递送。The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the polymer prodrug belongs to the category of polymer therapy, and its main feature is that the therapeutic drug is connected with a hydrophilic macromolecular polymer carrier through a covalent bond, which will greatly change the physical and chemical properties of the original drug. properties and behavior in vivo. Compared with free drugs, polymer prodrugs can significantly prolong blood circulation, improve tissue distribution and accumulation, and increase drug bioavailability. The design of this class of drugs generally needs to follow the following principles: 1. The chemical bond should have sufficient stability outside the cell to prolong the half-life of the prodrug system in vivo; 2. Once it enters the cell, the chemical bond (in acid, alkali, Unstable under conditions such as enzymes) should be quickly destroyed and degraded to release the complete drug molecule; 3. The polymer used as the carrier should have sufficient stability in blood circulation. Based on the above characteristics of the polymer prodrug, the invention improves the half-life and distribution of the drug in vivo by linking melatonin with a hydrophilic macromolecular polymer, and realizes active targeted delivery of melatonin to renal tubular epithelial cells.
黏附因子CD44在正常肾脏组织内表达较少,但在急性肾损伤发生时肾小管上皮细胞上表达异常增加,这为急性肾损伤的主动靶向治疗提供了可能。透明质酸是一种存在于细胞外基质和滑液中的具有生物相容性和生物可降解性的天然阴离子多糖,是黏附因子CD44的特异性配体之一,可与受体黏附因子CD44特异性结合以透明质酸为载体,将褪黑素靶向提送至肾脏损伤细胞中。考虑到肾损伤时肾功能的减弱,肾小管上皮细胞膜上的megalin-cubilin受体介导的内吞作用可能也随之下降,而CD44受体可特异性上调,进而可确保药物在肾小管上皮细胞中的有效分布。在此基础上,进一步进行线粒体靶向基团的修饰。三苯基膦是目前研究最为成功的线粒体靶向分子,其含有三个苯环可增加分子表面积,形成离域正电荷,可有效穿透线粒体双层疏水膜。在三苯基膦的作用下,将主动转运进入肾小管上皮细胞中的褪黑素进一步输送至线粒体以起到清除过多ROS、改善线粒体通透性和肿胀,有效逆转肾小管上皮细胞的氧化应激损伤,实现对缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤的高效靶向治疗。本发明提供的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物,可以用于肾缺血再灌注损伤治疗。该高分子前体药物可通过透明质酸与肾小管上皮细胞表面特异性表达的CD44受体结合,增加褪黑素在肾小管上皮细胞内的分布;进入细胞的高分子前体药物在线粒体靶向分子(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦的介导下,进一步增加褪黑素在靶细胞线粒体中的分布,通过降低线粒体产生的ROS,有效逆转肾小管上皮细胞的氧化应激损伤,实现对急性肾损伤的靶向治疗。Adhesion factor CD44 is less expressed in normal kidney tissue, but its expression is abnormally increased on renal tubular epithelial cells when acute kidney injury occurs, which provides the possibility for active targeted therapy of acute kidney injury. Hyaluronic acid is a biocompatible and biodegradable natural anionic polysaccharide existing in the extracellular matrix and synovial fluid. It is one of the specific ligands of the adhesion factor CD44 and can bind to the receptor adhesion factor CD44 Specific binding uses hyaluronic acid as a carrier to deliver melatonin to damaged kidney cells. Considering the weakening of renal function during renal injury, the endocytosis mediated by the megalin-cubilin receptor on the renal tubular epithelial cell membrane may also decrease, and the CD44 receptor can be specifically up-regulated, which in turn ensures that the drug can be transported to the renal tubular epithelium. Effective distribution in cells. On this basis, the mitochondrial targeting group was further modified. Triphenylphosphine is currently the most successful mitochondrial targeting molecule. It contains three benzene rings that can increase the surface area of the molecule and form a delocalized positive charge, which can effectively penetrate the double-layer hydrophobic membrane of mitochondria. Under the action of triphenylphosphine, melatonin, which is actively transported into renal tubular epithelial cells, is further transported to mitochondria to remove excess ROS, improve mitochondrial permeability and swelling, and effectively reverse the oxidation of renal tubular epithelial cells Stress injury, to achieve high-efficiency targeted therapy for acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion. The (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug provided by the invention can be used for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. The high-molecular prodrug can bind to the CD44 receptor specifically expressed on the surface of renal tubular epithelial cells through hyaluronic acid, and increase the distribution of melatonin in renal tubular epithelial cells; the high-molecular prodrug entering the cell targets mitochondria Mediated by the molecule (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide, it further increases the distribution of melatonin in the mitochondria of target cells, and effectively reverses the oxidative stress of renal tubular epithelial cells by reducing the ROS produced by mitochondria Injury, to achieve targeted therapy for acute kidney injury.
所述(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物可靶向肾小管上皮细胞及胞内细胞器,提高药物在肾脏病灶的药物浓集量,从而提高药物治疗效率,本发明药物能从逆转肾小管上皮细胞的氧化应激损伤过程入手,获得一种安全、高效的缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤靶向治疗新途径。The (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin macromolecular prodrug can target renal tubular epithelial cells and intracellular organelles, increasing the drug concentration of the drug in renal lesions , so as to improve the therapeutic efficiency of the drug. The drug of the present invention can start with reversing the oxidative stress injury process of renal tubular epithelial cells, and obtain a safe and efficient new approach for targeted therapy of acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的合成路线图。Fig. 1 is a synthetic route diagram of step-by-step targeted polymer prodrugs for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
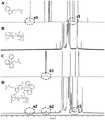
图2为治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的核磁氢谱。Figure 2 is the H NMR spectrum of the step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
图3为治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的肾小管上皮细胞靶向分布图片。Fig. 3 is a picture of the target distribution of renal tubular epithelial cells of step-by-step targeted polymer prodrugs for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
图4为治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的线粒体靶向分布图片。Fig. 4 is a picture of mitochondrial targeting distribution of step-by-step targeted polymer prodrugs for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
图5为载荧光标记物吲哚菁绿的治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的体内分布图片。Fig. 5 is a picture of the in vivo distribution of the step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug loaded with fluorescent marker indocyanine green for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
图6为治疗肾缺血再灌注损伤的逐级靶向高分子前体药物的药效学结果。Fig. 6 is the pharmacodynamic results of step-by-step targeted polymer prodrugs for the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面用具体实施例对本发明做进一步详细说明,但本发明不仅局限于以下具体实施例。The present invention will be described in further detail below with specific examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following specific examples.
下列各实施例中,逐级靶向高分子前体药物,即(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的制备方法,按照两步方法实现,其合成路线图如图1所示:首先通过(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦上的羧基与透明质酸上羟基发生酯化反应合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物,其次褪黑素与(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物上的羧基发生酯化反应合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物。下面具体对其两步合成过程进行描述:In the following examples, the step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug, i.e. the preparation method of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug, follows two steps The method is realized, and its synthetic route diagram is as shown in Figure 1: first, the carboxyl group on the (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and the hydroxyl group on the hyaluronic acid are esterified to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenyl Phenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft, followed by melatonin and (4-carboxybutyl) carboxyl on the triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft is synthesized by esterification (4-carboxybutyl ) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug. The two-step synthesis process is described in detail below:
1、(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物的合成1. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft
称取88.6mg(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到10mL无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸水溶液(含透明质酸总量400mg),加热搅拌持续反应48小时,待反应结束后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,去离子水透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物。Weigh 88.6 mg (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and add it to 10 mL of anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5 mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6 mg 1-ethyl-(3 -Dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, heat and stir at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely, then add hyaluronic acid aqueous solution (containing 400 mg of hyaluronic acid total amount) dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir The reaction was continued for 48 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction product was placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, and dialyzed with deionized water for 48 hours. Freeze-dry to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft.
2、(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的合成2. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
取步骤1)中的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入46.4mg褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,用去离子水持续透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,离心取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物。Take the (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft in step 1) and add it to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6mg 1-Ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, heated and stirred at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely, added 46.4mg of melatonin, heated and stirred for 48 hours, and the reaction The product was placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, and was continuously dialyzed with deionized water for 48 hours. The suspension in the dialysis bag was collected, centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation and freeze-dried to obtain (4-carboxy Butyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug.
下面通过各实施例展示本发明的具体技术效果,以便于本领域技术人员更好地理解本发明。The specific technical effects of the present invention are shown below through various embodiments, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention.
实施例1Example 1
1.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的合成1. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
第一步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物,精密称取88.6mg(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到10mL无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸(聚合度为5,200mg)水溶液,加热搅拌持续反应48小时,待反应结束后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,去离子水透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物。The first step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft, accurately weigh 88.6mg (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and add to 10mL anhydrous dimethyl Add 34.5 mg of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 57.6 mg of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride to the sulfoxide, heat and stir at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely , then add hyaluronic acid (polymerization degree is 5, 200mg) aqueous solution dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir and continue to react for 48 hours, after the reaction finishes, the reaction product is placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, deionized After 48 hours of water dialysis, the suspension in the dialysis bag was collected, centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken for freeze-drying to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft.
第二步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物,取步骤1)中的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mgN-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入46.4mg褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,完成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸与褪黑素的嫁接。利用核磁共振仪对(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物的结构进行确证。The second step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft, get (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid in step 1) Add the acid graft to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6mg 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride, Heat and stir at 60° C. to completely dissolve the reactants, add 46.4 mg of melatonin, and heat and stir for 48 hours to complete the grafting of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid and melatonin. The structure of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft was confirmed by NMR.
实施例2Example 2
1.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的合成1. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
第一步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物,精密称取88.6mg(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到10mL无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸(聚合度为10,400mg)水溶液,加热搅拌持续反应48小时,待反应结束后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,去离子水透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物。The first step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft, accurately weigh 88.6mg (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and add to 10mL anhydrous dimethyl Add 34.5 mg of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 57.6 mg of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride to the sulfoxide, heat and stir at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely , then add hyaluronic acid (polymerization degree is 10, 400mg) aqueous solution dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir and continue to react for 48 hours, after the reaction is finished, the reaction product is placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, deionized After 48 hours of water dialysis, the suspension in the dialysis bag was collected, centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken for freeze-drying to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft.
第二步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物,取步骤1)中的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入46.4mg褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,完成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸与褪黑素的嫁接。利用核磁共振仪对(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物的结构进行确证。The second step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft, get (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid in step 1) Add the acid graft to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5 mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6 mg 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride , heated and stirred at 60°C to dissolve the reactants completely, added 46.4 mg of melatonin, and heated and stirred for 48 hours to complete the grafting of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid and melatonin . The structure of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft was confirmed by NMR.
实施例3Example 3
1.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的合成1. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
第一步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物,精密称取88.6mg(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到10mL无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸(聚合度为15,600mg)水溶液,加热搅拌持续反应48小时,待反应结束后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,去离子水透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物。The first step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft, accurately weigh 88.6mg (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and add to 10mL anhydrous dimethyl Add 34.5 mg of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 57.6 mg of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride to the sulfoxide, heat and stir at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely , then add hyaluronic acid (polymerization degree is 15, 600mg) aqueous solution dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir and continue to react for 48 hours, after the reaction is finished, the reaction product is placed in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500, deionized After 48 hours of water dialysis, the suspension in the dialysis bag was collected, centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken for freeze-drying to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft.
第二步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物,取步骤1)中的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入46.4mg褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,完成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸与褪黑素的嫁接。利用核磁共振仪对(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物的结构进行确证。The second step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft, get (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid in step 1) Add the acid graft to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5 mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6 mg 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride , heated and stirred at 60°C to dissolve the reactants completely, added 46.4 mg of melatonin, and heated and stirred for 48 hours to complete the grafting of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid and melatonin . The structure of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft was confirmed by NMR.
实施例4Example 4
1.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的合成1. Synthesis of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
第一步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物,精密称取88.6mg(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦加入到10mL无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,然后向混合溶液中逐滴加入透明质酸(聚合度为20,800mg)水溶液,加热搅拌持续反应48小时,待反应结束后,将反应产物置于截留分子量为3500的透析袋中,去离子水透析48h,收集透析袋中的混悬液,于14000rpm离心10min,取其上清液进行冷冻干燥,即得(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物。The first step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft, accurately weigh 88.6mg (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide and add to 10mL anhydrous dimethyl Add 34.5 mg of N-hydroxysuccinimide and 57.6 mg of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride to the sulfoxide, heat and stir at 60°C to dissolve the reactant completely , then add hyaluronic acid (polymerization degree is 20, 800mg) aqueous solution dropwise to the mixed solution, heat and stir and continue to react for 48 hours. After 48 hours of water dialysis, the suspension in the dialysis bag was collected, centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken for freeze-drying to obtain (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid graft.
第二步合成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物,取步骤1)中的(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸嫁接物加入到无水二甲基亚砜中,再加入34.5mg N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺、57.6mg 1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺盐酸盐,60℃加热搅拌使反应物完全溶解,加入46.4mg褪黑素,加热搅拌持续反应48小时后,完成(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸与褪黑素的嫁接。利用核磁共振仪对(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素嫁接物的结构进行确证。取(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物10mg溶于0.5mL氘代水中,使其最终浓度为20mg/mL,用核磁共振仪记录核磁共振氢谱。结果如图2所示,(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的核磁氢谱中可见(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦与褪黑素特征峰(a,b)。The second step is to synthesize (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft, get (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid in step 1) Add the acid graft to anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, then add 34.5 mg N-hydroxysuccinimide, 57.6 mg 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride , heated and stirred at 60°C to dissolve the reactants completely, added 46.4 mg of melatonin, and heated and stirred for 48 hours to complete the grafting of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid and melatonin . The structure of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin graft was confirmed by NMR. Take (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug 10mg and dissolve it in 0.5mL deuterated water so that the final concentration is 20mg/mL, and record it with a nuclear magnetic resonance instrument H NMR spectrum. Result as shown in Figure 2, visible (4-carboxybutyl) triphenyl bromide Phosphine and melatonin characteristic peaks (a, b).
2.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的细胞靶向性2. Cell targeting of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
将人肾小管上皮细胞以5.0×104个细胞/孔的密度接种到24孔板中,孵育24小时后,采用双氧水刺激细胞构建体外氧化应激损伤细胞模型,荧光探针异硫氰酸荧光素标记高分子前体药物,考察(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物在肾小管上皮细胞中的摄取差异。结果如图3所示,(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物在氧化应激损伤细胞中的分布显著高于其在正常细胞中的分布,且游离透明质酸会竞争性影响(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的细胞摄取。Human renal tubular epithelial cells were seeded into a 24-well plate at a density of 5.0×104 cells/well, and after incubation for 24 hours, the cells were stimulated with hydrogen peroxide to construct a cell model of oxidative stress injury in vitro, and the fluorescent probe was fluoresced by isothiocyanate To investigate the uptake of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug in renal tubular epithelial cells. The results are shown in Figure 3, the distribution of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug in oxidative stress damaged cells was significantly higher than that in normal cells The distribution of free hyaluronic acid will competitively affect the cellular uptake of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug.
3.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的细胞内线粒体靶向性3. Intracellular mitochondrial targeting of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin macromolecular prodrug
将人肾小管上皮细胞以5.0×104个细胞/孔的密度接种到24孔板中,孵育24小时,荧光探针异硫氰酸荧光素标记高分子前体药物,考察(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的线粒体分布特性,以未经(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦修饰的透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物为对照。孵育2h后,加入线粒体荧光探针溶液,染色30min,荧光倒置显微镜下观察高分子前体药物于线粒体共定位情况。结果如图4所示,相比于透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物(P=0.06),(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物(P=0.91)于线粒体的共定位比例更高,线粒体靶向性更好。Human renal tubular epithelial cells were seeded into 24-well plates at a density of 5.0×104 cells/well and incubated for 24 hours. The fluorescent probe was labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate to detect the polymer prodrug (4-carboxybutylene Based on the mitochondrial distribution characteristics of triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug, the hyaluronic acid-melatonin without (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide modification Polymer prodrugs were used as controls. After incubation for 2 hours, the mitochondrial fluorescent probe solution was added, stained for 30 minutes, and the colocalization of the polymer prodrug in the mitochondria was observed under a fluorescent inverted microscope. The results are shown in Figure 4, compared to hyaluronic acid-melatonin macromolecular prodrug (P=0.06), (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin is higher Molecular prodrugs (P=0.91) had a higher ratio of co-localization in mitochondria and better mitochondrial targeting.
4.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的体内分布4. In vivo distribution of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug
采用吲哚菁绿标记(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物的体内分布情况。采用无创动脉夹夹闭肾动脉构建缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤动物模型,高分子前体药物溶液0.2mL,注射后不同时间点处死动物,取各组织脏器于小动物活体成像仪下观察高分子前体药物在各组织脏器的荧光信号分布情况。结果如图5所示,高分子前体药物主要分布于肾脏组织,且肾脏的分布量要远高于其他各组织。In vivo distribution of (4-carboxybutyl) triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin macromolecular prodrug labeled with indocyanine green. The animal model of acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion was established by clamping the renal artery with a non-invasive arterial clip, and the polymer prodrug solution was injected into 0.2mL, and the animals were sacrificed at different time points after injection, and the tissues and organs were taken under the small animal in vivo imager Observe the distribution of fluorescent signals of polymer prodrugs in various tissues and organs. The results are shown in Figure 5, the polymer prodrug is mainly distributed in the kidney tissue, and the distribution amount in the kidney is much higher than that in other tissues.
5.(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物对急性肾损伤的治疗作用5. Therapeutic effect of (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug on acute kidney injury
采用无创动脉夹夹闭肾动脉构建缺血再灌注引起的急性肾损伤动物模型后,尾静脉给药,评价肾功能变化及病理特征。将C57BL/6小鼠随机分为正常组、急性肾损伤组、急性肾损伤+褪黑素组、急性肾损伤+透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物组和急性肾损伤+(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物组,在给药24h后测定动物肾功能指标(血肌酐、尿素氮)并制备肾脏组织病理切片。结果如图6所示,(4-羧丁基)三苯基溴化膦-透明质酸-褪黑素高分子前体药物组模型动物肾功能(血肌酐、尿素氮)得到显著改善。The animal model of acute kidney injury caused by ischemia-reperfusion was established by clamping the renal artery with a non-invasive arterial clip, and administered through the tail vein to evaluate the changes of renal function and pathological characteristics. C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into normal group, acute kidney injury group, acute kidney injury+melatonin group, acute kidney injury+hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug group and acute kidney injury+(4 -Carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin macromolecular prodrug group, after 24 hours of administration, the renal function indexes (serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) of the animals were measured and renal histopathological sections were prepared. The results are shown in Figure 6, the renal function (serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) of the model animals in the (4-carboxybutyl)triphenylphosphine bromide-hyaluronic acid-melatonin polymer prodrug group was significantly improved.
以上仅是本发明的特征实施范例,对本发明保护范围不构成任何限制。凡采用同等交换或者等效替换而形成的技术方案,均落在本发明权利保护范围之内。The above are only characteristic implementation examples of the present invention, and do not constitute any limitation to the protection scope of the present invention. All technical solutions formed by equivalent exchange or equivalent replacement fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211366587.9ACN115671304A (en) | 2022-11-01 | 2022-11-01 | A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211366587.9ACN115671304A (en) | 2022-11-01 | 2022-11-01 | A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115671304Atrue CN115671304A (en) | 2023-02-03 |
Family
ID=85047472
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211366587.9AWithdrawnCN115671304A (en) | 2022-11-01 | 2022-11-01 | A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115671304A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116059169A (en)* | 2023-02-07 | 2023-05-05 | 余姚市人民医院 | A kind of vascular endothelial cell targeting drug-loaded micelles and its preparation method and application |
| CN119632958A (en)* | 2025-02-12 | 2025-03-18 | 中国科学院南海海洋研究所 | Application of 3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in the preparation of drugs for treating H/R injury of vascular endothelial cells |
- 2022
- 2022-11-01CNCN202211366587.9Apatent/CN115671304A/ennot_activeWithdrawn
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116059169A (en)* | 2023-02-07 | 2023-05-05 | 余姚市人民医院 | A kind of vascular endothelial cell targeting drug-loaded micelles and its preparation method and application |
| CN119632958A (en)* | 2025-02-12 | 2025-03-18 | 中国科学院南海海洋研究所 | Application of 3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in the preparation of drugs for treating H/R injury of vascular endothelial cells |
| CN119632958B (en)* | 2025-02-12 | 2025-07-01 | 中国科学院南海海洋研究所 | Application of 3, 5-dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in preparation of medicines for treating vascular endothelial cell H/R injury |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN105534957B (en) | A kind of core-shell structure nanometer particle of reduction/enzyme/pH multiple responses drug release | |
| CN102380103B (en) | Mannose-modified thiolated chitosan quaternary ammonium salt nanoparticle, preparing method and application thereof | |
| CN115671304A (en) | A step-by-step targeting polymer prodrug for treating renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and preparation method thereof | |
| CN109044963B (en) | A kind of preparation method of pH-sensitive nano hydrogel for injection | |
| CN110742856B (en) | Nanogel drug carrier for targeted delivery and consumption of a large amount of H2O2 while releasing CO, preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN107184987B (en) | A lipoic acid-modified targeting integrin αvβ3 nano-polypeptide carrier and its preparation method and application | |
| Zhang et al. | Dual crosslinking of folic acid-modified pectin nanoparticles for enhanced oral insulin delivery | |
| CN105748439A (en) | Ph-responsive nanometer drug delivery system based on dendrimers modified by short-chain alkane and preparation method and application of drug delivery system | |
| CN109999197B (en) | Tumor-targeted nano-composite, preparation method and application thereof in precise sonodynamic-mediated tumor treatment | |
| CN110652594A (en) | Multi-target-point therapeutic micelle for regulating and controlling Alzheimer disease microenvironment and preparation method thereof | |
| CN105001426B (en) | A kind of polyaminoacid graft copolymer with tumor-targeting and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114712311B (en) | Preparation of a silk fibroin peptide self-assembled drug-loaded nanoparticle and its renal protection | |
| CN104434792B (en) | Polymer micelle and preparation method thereof and antineoplastic pharmaceutical compositions, preparation and preparation method thereof | |
| CN104398504B (en) | A pharmaceutical composition of deoxypodophyllotoxins and its preparation method and preparation | |
| CN110812489B (en) | Dual-stage targeting polymer prodrug for treating acute kidney injury and preparation method thereof | |
| CN109985249B (en) | ROS-sensitive tumor-targeted gene delivery system and preparation method thereof | |
| CN119679961A (en) | Protein nanoparticles for treating ulcerative colitis, preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN106606783A (en) | Drug delivery system for targeting co-delivery of photosensitizer and chemotherapeutic drug | |
| CN108524951A (en) | A kind of Sorafenib nanometer formulation with liver tumour targeting | |
| CN105254780B (en) | A kind of bionical derivative of cation type chitosan and its application | |
| CN116036011B (en) | Preparation and application of bionic bladder-perfusable nano-drug hydrogel system for bladder cancer treatment | |
| CN109954144B (en) | Bi-level pH-responsive nanoparticles based on modified poly-β-urethane materials and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114652846B (en) | Enzyme-sensitive, tumor active targeting and intracellular quick drug release polymer prodrug, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN102462846B (en) | Chlorotoxin-modified glioma targeting gene delivery compound and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114276390B (en) | A dithiocarbamate derivative nanomedicine for anti-tumor drug delivery and its preparation method and application |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| WW01 | Invention patent application withdrawn after publication | ||
| WW01 | Invention patent application withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20230203 |