CN115670757A - A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effect - Google Patents
A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effectDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115670757A CN115670757ACN202211391451.3ACN202211391451ACN115670757ACN 115670757 ACN115670757 ACN 115670757ACN 202211391451 ACN202211391451 ACN 202211391451ACN 115670757 ACN115670757 ACN 115670757A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- main body
- stress stimulation
- pore structure
- bone
- stimulation effect
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及骨科植入器械领域,具体涉及一种具有界面应力刺激效应的椎间融合器。The invention relates to the field of orthopedic implant instruments, in particular to an intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulation effect.
背景技术Background technique
随着人们日常生活、工作等习惯的改变,腰椎间盘退行性疾病已经成为临床上常见的病症之一,并且发病趋势越来越年轻化,当服用抗炎镇痛药物、佩戴腰围支具等保守治疗效果不明显时,通常需要进行手术治疗。脊柱融合术是目前临床上治疗腰椎间盘退行性疾病的最常用及有效方式,该术式通过植入融合器将两个或两个以上的椎骨融合在一起,从而限制或防止相邻的两个椎体之间的相对运动,减少与这些椎骨的相对运动有关的疼痛,最终目的是诱导形成骨性融合。融合器作为手术治疗的关键器械,在植入后需要提供稳定性、诱导骨细胞分化增值、恢复脊柱前凸、提高融合节段的稳定性等功能。With the changes in people's daily life and work habits, lumbar disc degenerative disease has become one of the common clinical diseases, and the onset tends to be younger and younger. When treatment is not effective, surgery is usually required. Spinal fusion is currently the most common and effective way to treat degenerative lumbar disc disease clinically. This operation fuses two or more vertebrae together by implanting a fusion device, thereby restricting or preventing two adjacent vertebrae from intervertebral fusion. Relative motion between vertebral bodies, reducing pain associated with relative motion of these vertebrae, with the ultimate goal of inducing bony fusion. As a key device for surgical treatment, the fusion device needs to provide stability, induce osteocyte differentiation and proliferation, restore lordosis, and improve the stability of the fusion segment after implantation.
目前融合器使用的材料主要为钛合金和聚醚醚酮(PEEK)两种,其中,钛合金型融合器具有优异的力学性能和良好的生物相容性,能够提供良好的即时稳定性,应用也最为广泛;但是钛合金的弹性模量约为110GPa,远高于人体皮质骨的弹性模量,因此容易产生应力遮挡,进而造成松动和下沉等情况。聚醚醚酮(PEEK)材料的弹性模量介于人体皮质骨和松质骨之间,与钛合金相比,应力遮挡较小;但是聚醚醚酮生物活性较差,会形成纤维连接,较难与骨组织形成骨性融合,长期植入也存在松动的风险。At present, the materials used in fusion devices are mainly titanium alloy and polyether ether ketone (PEEK). Among them, titanium alloy fusion devices have excellent mechanical properties and good biocompatibility, and can provide good instant stability. It is also the most widely used; however, the elastic modulus of titanium alloy is about 110GPa, which is much higher than that of human cortical bone, so it is easy to produce stress shielding, which in turn causes loosening and sinking. The elastic modulus of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) material is between human cortical bone and cancellous bone. Compared with titanium alloy, the stress shielding is smaller; however, PEEK has poor biological activity and will form fibrous connections. It is difficult to form bony fusion with bone tissue, and there is also a risk of loosening in long-term implantation.
研究表明,微动结构可以在界面处给予椎骨一定的应力刺激,适当的应力刺激有利于骨细胞增值分化,达到快速形成稳定的骨性融合的目的。调研发现,目前临床使用的商用融合器产品,几乎均不具备相应的应力刺激功能。Studies have shown that the fretting structure can give a certain amount of stress stimulation to the vertebrae at the interface, and appropriate stress stimulation is conducive to the proliferation and differentiation of bone cells, achieving the purpose of quickly forming stable bone fusion. The survey found that almost none of the commercial fusion devices currently used in clinical practice have the corresponding stress stimulation function.
综上所述,亟需一款具有界面应力刺激效应的椎间融合器,刺激椎骨与融合器接触作用界面快速形成骨性融合,以有效减小松动和下沉In summary, there is an urgent need for an intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulation effect, which can stimulate the contact interface between the vertebrae and the fusion device to quickly form bony fusion, so as to effectively reduce loosening and subsidence
发明内容Contents of the invention
为解决上述问题,本发明提供一种具有界面应力刺激效应的椎间融合器。融合器通过其表面特殊的微孔结构使其具有一定的微动特性,通过植入后初期的微动变形刺激融合器与椎骨接触作用界面的应力,促进界面骨细胞增殖分化和融合,随着后期椎骨和融合器界面组织生长程度和融合的增强,该界面微动效应逐渐减弱消失,因而能够保证融合器的稳定连接功能。In order to solve the above problems, the present invention provides an intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulation effect. The special microporous structure on the surface of the cage makes it have certain fretting characteristics. The initial fretting deformation after implantation stimulates the stress on the contact interface between the cage and the vertebrae, and promotes the proliferation, differentiation and fusion of bone cells at the interface. In the late stage, the growth degree and fusion of the interface between the vertebrae and the fusion cage are enhanced, and the fretting effect of the interface gradually weakens and disappears, thus ensuring the stable connection function of the fusion cage.
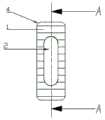
一种具有界面应力刺激效应的椎间融合器,包括主体,主体呈箱型,主体前端有圆形倒角,主体中间设有植骨窗,植骨窗两端呈圆弧形,植骨窗中间为矩形,主体的上下表面设有固定齿,固定齿内部为孔隙结构。An intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulation effect, comprising a main body, the main body is box-shaped, the front end of the main body has a circular chamfer, a bone graft window is arranged in the middle of the main body, the two ends of the bone graft window are arc-shaped, and the bone graft window The center is rectangular, the upper and lower surfaces of the main body are provided with fixed teeth, and the interior of the fixed teeth is a pore structure.
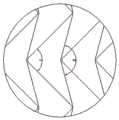
所述孔隙结构的最小单元为内凹的四边形结构,整体形状类似于箭头形,所述∠1的角度为60゜~90゜,∠1与∠2的角度比值为0.4-0.75,孔隙结构能在150-200μm范围内的微动。The smallest unit of the pore structure is a concave quadrilateral structure, the overall shape is similar to an arrow shape, the angle of ∠1 is 60゜~90゜, the ratio of the angle between ∠1 and ∠2 is 0.4-0.75, the pore structure can Fretting in the range of 150-200μm.
所述孔隙结构的孔径为400-800μm,孔径优选600μm,孔隙结构的孔隙率为60%-80%,孔隙率优选60%,使融合器与椎骨接触的界面处的刚度与皮质骨弹性模量接近,同时能提供更多的骨生长空间。The pore size of the pore structure is 400-800 μm, preferably 600 μm, the porosity of the pore structure is 60%-80%, the porosity is preferably 60%, so that the stiffness and the elastic modulus of the cortical bone at the interface where the cage contacts the vertebra close, while providing more room for bone growth.
所述固定齿横截面形状为直角三角形。The cross-sectional shape of the fixed tooth is a right triangle.
所述主体的材质为医用钛合金。The material of the main body is medical titanium alloy.
本发明的效果是:Effect of the present invention is:
该融合器的主体上下表面的固定齿内部结构为孔隙结构,能够在融合器与椎骨的界面处产生约150-200μm范围的微动,给椎骨适当的应力刺激,有利于骨细胞增值分化,加速形成骨性融合,当骨细胞生长填满微孔结构之后,该微动效应随之逐渐减弱消失,保证融合器的稳定性。The internal structure of the fixed teeth on the upper and lower surfaces of the main body of the fusion cage is a porous structure, which can produce micro-movements in the range of about 150-200 μm at the interface between the fusion cage and the vertebrae, giving proper stress stimulation to the vertebrae, which is conducive to the proliferation and differentiation of bone cells, and accelerates Bone fusion is formed. When the bone cells grow and fill the microporous structure, the fretting effect gradually weakens and disappears, ensuring the stability of the fusion device.
孔隙结构适合骨细胞向内生长,其60%-80%的孔隙率使融合器的刚度更接近椎体的皮质骨,400-800μm的孔径适合骨细胞攀附生长。The pore structure is suitable for the inward growth of bone cells, and its 60%-80% porosity makes the rigidity of the cage closer to the cortical bone of the vertebral body, and the pore size of 400-800 μm is suitable for the growth of bone cells.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明的立体结构示意图;Fig. 1 is the three-dimensional structure schematic diagram of the present invention;
图2为图1的俯视图;Fig. 2 is the top view of Fig. 1;
图3为图2中的A-A剖视图;Fig. 3 is A-A sectional view among Fig. 2;
图4为图3的B处局部放大视图;Fig. 4 is a partially enlarged view of place B of Fig. 3;
图5为本发明的孔隙结构最小单元的示意图;5 is a schematic diagram of the smallest unit of the pore structure of the present invention;
图6为图1的侧视图;Fig. 6 is the side view of Fig. 1;
其中:1-固定齿,2-植骨窗,3-融合器主体,4-圆形倒角;5-孔隙结构。Among them: 1-fixed tooth, 2-bone graft window, 3-cage body, 4-circular chamfer; 5-pore structure.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
如图1至图6所示,一种具有界面应力刺激效应的椎间融合器,包括主体3,主体呈箱型,主体3前端有圆形倒角4,主体3中间设有植骨窗2,植骨窗2两端呈圆弧形,植骨窗2中间为矩形,主体3的上下表面设有固定齿1,固定齿1内部为孔隙结构5。As shown in Figures 1 to 6, an intervertebral fusion device with an interface stress stimulation effect includes a main body 3, which is box-shaped, with a round chamfer 4 at the front end of the main body 3, and a
所述孔隙结构5的最小单元为内凹的四边形结构,整体形状类似于箭头形,所述∠1的角度为60゜~90゜,∠1与∠2的角度比值为0.4-0.75,孔隙结构5能在150-200μm范围内的微动。The smallest unit of the
所述孔隙结构5的孔径为400-800μm,孔径优选600μm,孔隙结构5的孔隙率为60%-80%,孔隙率优选60%,使融合器与椎骨接触的界面处的刚度与皮质骨弹性模量接近,同时能提供更多的骨生长空间。The pore diameter of the
所述主体3长度为20-32mm,主体3宽度为8-12mm,主体3高度为6-16mm;主体3长度优选为22mm,主体3宽度优选为8mm,主体3高度优选为6mm。The length of the main body 3 is 20-32mm, the width of the main body 3 is 8-12mm, and the height of the main body 3 is 6-16mm; the length of the main body 3 is preferably 22mm, the width of the main body 3 is preferably 8mm, and the height of the main body 3 is preferably 6mm.
所述植骨窗2的圆弧形的圆弧半径为1.5-3mm,圆弧半径优选为2mm;圆弧形的圆弧角度为120゜-180゜,圆弧角度优选为180゜;所述矩形长度为10-16mm,矩形长度优选为10mm,矩形宽度为4-6mm,矩形宽度优选为4mm。The arc-shaped arc radius of the
所述固定齿1横截面形状为直角三角形,所述三角形长度为1.5-2mm,所述三角形优选长度为2mm,所述三角形高度为0.4-0.6mm,所述三角形优选高度为0.6mm。The cross-sectional shape of the
所述固定齿1的数量为8-14个。The number of said fixed
所述主体3的材质为医用钛合金。The material of the main body 3 is medical titanium alloy.
本发明的工作机理:Working mechanism of the present invention:
融合器具有较高的机械强度,表现出类似于自然骨的承载特性,恢复脊柱的生理前凸以及稳定,植骨窗2中可以填充第三方供体的同种异体骨材料或者来自患者的自体骨材料,以提供较强的骨诱导性能,以促进骨细胞的增值分化。The fusion cage has high mechanical strength, exhibits load-bearing properties similar to natural bone, and restores the physiological lordosis and stability of the spine. The
融合器上下表面的固定齿1内部为孔隙结构5,该孔隙结构5在融合器与椎骨接触的界面处给予椎骨一定的应力刺激,有利于骨细胞分化增长,加速形成骨性融合,同时降低了界面结构刚度,减小了界面应力遮挡。当骨细胞生长填满固定齿1的内部孔隙结构5并继续分化生长时,融合器的微动特性就会消失,最终形成刚性融合。孔隙结构5的放射透明性便于术后观察融合效果。The interior of the
孔隙结构5的孔径设置为400-800μm,孔径优选600μm,孔隙率为60%-80%,孔隙率优选60%,使融合器与椎骨接触的界面处的刚度与皮质骨弹性模量接近,同时能提供更多的骨生长空间。The aperture of the
植骨窗2中可以填充第三方供体的同种异体骨材料或者来自患者的自体骨材料,以提供较强的骨诱导性能,以促进骨细胞的增值分化。The
固定齿1能在融合器植入体内后帮助固定,防止移位.The
融合器前端具有圆形倒角4,方便手术过程中植入。The front end of the fusion device has a rounded chamfer 4 to facilitate implantation during the operation.
融合器具有较大的与椎骨相接触的表面积,粗糙的表面更有利于骨细胞附着。The fusion cage has a large surface area in contact with the vertebrae, and the rough surface is more conducive to bone cell attachment.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211391451.3ACN115670757A (en) | 2022-11-08 | 2022-11-08 | A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effect |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211391451.3ACN115670757A (en) | 2022-11-08 | 2022-11-08 | A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effect |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115670757Atrue CN115670757A (en) | 2023-02-03 |
Family
ID=85049609
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211391451.3APendingCN115670757A (en) | 2022-11-08 | 2022-11-08 | A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effect |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115670757A (en) |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101268963A (en)* | 2008-04-15 | 2008-09-24 | 叶晓健 | Adjustable intervertebral fusion device and holding device |
| CN102525624A (en)* | 2011-12-26 | 2012-07-04 | 周建明 | Interbody fusion cage |
| CN106729977A (en)* | 2017-01-12 | 2017-05-31 | 上海锐植医疗器械有限公司 | A kind of bioactivity Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| CN106955174A (en)* | 2016-11-30 | 2017-07-18 | 重庆润泽医药有限公司 | A kind of elastic Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| CN107753157A (en)* | 2017-10-20 | 2018-03-06 | 常州华森医疗器械有限公司 | Cervical fusion cage |
| CN109009579A (en)* | 2018-06-29 | 2018-12-18 | 何清义 | A kind of round bar shape XLIF Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| WO2021032698A1 (en)* | 2019-08-16 | 2021-02-25 | Biodinamics Ag | Titanium cage with extended support platform |
- 2022
- 2022-11-08CNCN202211391451.3Apatent/CN115670757A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101268963A (en)* | 2008-04-15 | 2008-09-24 | 叶晓健 | Adjustable intervertebral fusion device and holding device |
| CN102525624A (en)* | 2011-12-26 | 2012-07-04 | 周建明 | Interbody fusion cage |
| CN106955174A (en)* | 2016-11-30 | 2017-07-18 | 重庆润泽医药有限公司 | A kind of elastic Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| CN106729977A (en)* | 2017-01-12 | 2017-05-31 | 上海锐植医疗器械有限公司 | A kind of bioactivity Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| CN107753157A (en)* | 2017-10-20 | 2018-03-06 | 常州华森医疗器械有限公司 | Cervical fusion cage |
| CN109009579A (en)* | 2018-06-29 | 2018-12-18 | 何清义 | A kind of round bar shape XLIF Invasive lumbar fusion device |
| WO2021032698A1 (en)* | 2019-08-16 | 2021-02-25 | Biodinamics Ag | Titanium cage with extended support platform |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 钱志辉, 吴思杰, 王强, 等: "仿生张拉机械腿及其抗冲击性能仿真分析", 吉林大学学报(工学版), 12 September 2019 (2019-09-12), pages 758 - 764* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20220273459A1 (en) | Method and spacer device for spanning a space formed upon removal of an intervertebral disc | |
| US6458159B1 (en) | Disc prosthesis | |
| US6736850B2 (en) | Vertebral pseudo arthrosis device and method | |
| US6800092B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for intervertebral implant anchorage | |
| JP5307827B2 (en) | Intervertebral implant | |
| CN201529176U (en) | Embedded bone trabecula intervertebral fusion device used for anastomosing vertebra | |
| US10751194B2 (en) | Bionic dislocation-proof artificial lumbar vertebrae and disc complex | |
| CN204839838U (en) | Artifical neck intervertebral disc false body | |
| CN111920553B (en) | Intervertebral fusion device with protrusions | |
| CN101999951A (en) | Memory alloy artificial cervical intervertebral disc | |
| CN211156492U (en) | Flexible artificial intervertebral disc | |
| CN115670757A (en) | A kind of intervertebral fusion device with interface stress stimulating effect | |
| MXPA02001032A (en) | Improved disc prosthesis. | |
| TWM273326U (en) | Prosthetic cage for spinal fusion | |
| CN220025315U (en) | Metal 3D printed extreme outer side approach lumbar interbody fusion cage | |
| CN217448144U (en) | 3D prints trabecular bone self-locking type interbody fusion cage | |
| CN204909742U (en) | Cervical vertebra uncinate vertebral joint fusion cage | |
| CN211271424U (en) | Allogeneic cortical cancellous bone embedded cervical interbody fusion cage | |
| TWM585598U (en) | Intervertebral fusion device | |
| CN111419481B (en) | Titanium mesh fusion device for spinal intervertebral fusion and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114668562A (en) | A novel bioactive zero-notch cervical fusion cage | |
| CN116421367A (en) | Metal 3D printed extreme outer side approach lumbar interbody fusion cage | |
| CN117179975A (en) | A bionic anterior intervertebral fusion device that matches the endplate structure and mechanical properties | |
| CN2390563Y (en) | internal fixator for cervical spine | |
| RU2281732C2 (en) | Vertebra's body implant |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |