CN115587945A - High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium - Google Patents
High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115587945A CN115587945ACN202211240751.1ACN202211240751ACN115587945ACN 115587945 ACN115587945 ACN 115587945ACN 202211240751 ACN202211240751 ACN 202211240751ACN 115587945 ACN115587945 ACN 115587945A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- image
- dynamic infrared
- high dynamic
- frequency
- processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/70—Denoising; Smoothing
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/40—Image enhancement or restoration using histogram techniques
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/50—Image enhancement or restoration using two or more images, e.g. averaging or subtraction
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/73—Deblurring; Sharpening
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T5/00—Image enhancement or restoration
- G06T5/90—Dynamic range modification of images or parts thereof
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10048—Infrared image
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20024—Filtering details
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20172—Image enhancement details
- G06T2207/20192—Edge enhancement; Edge preservation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20212—Image combination
- G06T2207/20221—Image fusion; Image merging
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及红外图像细节增强技术领域,特别涉及一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法、系统及计算机存储介质。The invention relates to the technical field of infrared image detail enhancement, in particular to a high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
红外热成像系统因其特有的温差成像方式,可以实现在黑夜,甚至大雾等恶劣条件下提供视频图像而被广泛应用于军事侦察、工业生产等领域。目前,红外机芯可输出位宽达14Bit灰度等级的红外图像,而普通显示设备仅能显示8Bit灰度等级的红外图像,14Bit红外图像的灰度范围远超过普通显示设备的响应范围,所以这样的图像被称为高动态范围图像。为了可以在显示设备中实时观察红外图像,必须将14Bit原始红外图像的动态范围压缩至8Bit。能量变化平缓的景物,生成图像的灰度分布会集中在较狭窄的区间内,而能量变化剧烈的景物所生成图像的灰度会散落在范围较宽的区间。对于高动态范围图像红外图像处理,关键在于将14Bit图像中的信息转化到人眼可观察到的8Bit图像中同时还要保持图像原有的细节信息,具备较好的对比度以供人眼观察。Infrared thermal imaging system is widely used in military reconnaissance, industrial production and other fields because of its unique temperature difference imaging method, which can provide video images in the dark and even in harsh conditions such as fog. At present, the infrared core can output infrared images with a bit width of 14Bit grayscale, while ordinary display devices can only display infrared images with 8Bit grayscale, and the grayscale range of 14Bit infrared images is far beyond the response range of ordinary display devices, so Such images are called high dynamic range images. In order to observe the infrared image in real time on the display device, the dynamic range of the 14Bit original infrared image must be compressed to 8Bit. For scenes with gentle energy changes, the grayscale distribution of the generated images will be concentrated in a narrow range, while for scenes with severe energy changes, the grayscales of images generated will be scattered in a wider range. For infrared image processing of high dynamic range images, the key is to convert the information in the 14Bit image into the 8Bit image that can be observed by the human eye while maintaining the original details of the image and having a better contrast for human observation.
现有的红外图像增强技术中,有基于双边滤波的动态范围分割算法,但双边滤波器在图像灰度变化比较剧烈的边缘易出现梯度翻转现象,图像将出现光晕伪像,且容易出现伪边缘;有基于引导滤波的DDE算法,算法采用引导滤波代替双边滤波的方法,既保留图像细节信息又避免梯度翻转现象。由于算法采用设定参数的方法,场景自适应性较差,有基于引导滤波的自适应红外图像细节增强算法,通过直方图分布信息为基础层图像确定自适应门限,去除图像中无效灰度值,使得基础层图像能更好地显示有效信息,但算法去噪效果较差,当图像包含大面积天空背景时,处理后的图像包含大量噪声干扰。In the existing infrared image enhancement technology, there is a dynamic range segmentation algorithm based on bilateral filtering, but the bilateral filter is prone to gradient reversal at the edge where the gray level of the image changes sharply, and the image will appear halo artifacts, and it is prone to artifacts. Edge; there is a DDE algorithm based on guided filtering, which uses guided filtering instead of bilateral filtering, which not only preserves image detail information but also avoids gradient reversal. Since the algorithm adopts the method of setting parameters, the scene adaptability is poor. There is an adaptive infrared image detail enhancement algorithm based on guided filtering, which determines the adaptive threshold for the base layer image through the histogram distribution information, and removes the invalid gray value in the image. , so that the base layer image can better display effective information, but the denoising effect of the algorithm is poor. When the image contains a large area of sky background, the processed image contains a lot of noise interference.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供了一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法、系统及计算机存储介质,用以解决现有技术中图像出现光晕伪像,容易出现伪边缘和去噪效果较差,图像包含大面积天空背景时,处理后的图像包含大量噪声干扰等问题。Embodiments of the present invention provide a high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system, and computer storage medium, which are used to solve halo artifacts in images in the prior art, which are prone to false edges and have poor denoising effects, and images contain large When the sky background is covered, the processed image contains a lot of noise interference and other problems.
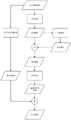
一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法,包括:On the one hand, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image, including:
利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像;Use guided filtering to denoise the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a denoised image;
利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像;Using Gaussian filtering to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, and using the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image;
根据人眼视觉特性获得对比度提升函数;A contrast enhancement function is obtained according to the visual characteristics of the human eye;
利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像;performing enhancement processing on the high-frequency image by using the contrast enhancement function to obtain an enhanced detail image;
对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像;performing brightness-maintaining dual-platform histogram dimming processing on the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a dimmed image;
对所述调光后图像与所述增强后细节图像进行加权融合。Weighted fusion is performed on the dimmed image and the enhanced detail image.
在一种可能的实现方式中,利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像,包括:根据高动态红外原始图像与引导图像确定引导滤波的权重系数和偏置系数;根据所述引导图像、权重系数和偏置系数对所述高动态红外原始图像进行滤波处理,获得所述去噪图像。In a possible implementation manner, the denoising process is performed on the high dynamic infrared original image by using guided filtering to obtain the denoised image, including: determining a weight coefficient and a bias coefficient of the guided filtering according to the original high dynamic infrared image and the guided image; The denoising image is obtained by filtering the high dynamic infrared original image according to the guide image, weight coefficient and offset coefficient.
在一种可能的实现方式中,利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像,包括:设置一个高斯滤波模板mask;利用所述高斯滤波模板mask与高动态红外原始图像进行卷积操作,获取低频图像;利用所述高动态红外原始图像与所述低频图像作差,获取所述高频图像。In a possible implementation manner, Gaussian filtering is used to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, and using the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image includes: setting a Gaussian filter template mask; using the Gaussian filtering template mask to perform a convolution operation with the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a low frequency image; using the high dynamic infrared original image to make a difference with the low frequency image to obtain the high frequency image.
在一种可能的实现方式中,所述对比度提升函数由局部细节调整函数和对比度限制函数的乘积构成。In a possible implementation manner, the contrast enhancement function is composed of a product of a local detail adjustment function and a contrast limitation function.
在一种可能的实现方式中,利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像,包括:将所述对比度提升函数与所述高频图像做乘积;对乘积的结果进行限制,得到所述增强后细节图像。In a possible implementation manner, using the contrast enhancement function to enhance the high-frequency image to obtain the enhanced detail image includes: multiplying the contrast enhancement function by the high-frequency image; multiplying the product The results are limited to obtain the enhanced detail image.
在一种可能的实现方式中,对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像,包括:设置图像统计直方图的上限阈值,得到直方图累计分布函数,所述双平台直方图为直方图累计分布函数分段后得到的两段平台直方图;将两段所述平台直方图各自进行互不干扰的直方图映射,得到调光后图像。In a possible implementation manner, the dual-platform histogram dimming processing with brightness maintenance is performed on the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain the dimmed image, including: setting the upper threshold of the image statistics histogram, and obtaining the histogram cumulative distribution function, the two-platform histogram is a two-stage platform histogram obtained after the cumulative distribution function of the histogram is segmented; each of the two platform histograms is mapped to a non-interfering histogram to obtain a dimmed image.
另一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种高动态红外图像细节增强系统,包括:On the other hand, an embodiment of the present invention provides a high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement system, including:
去噪模块,用于利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像;The denoising module is used to perform denoising processing on the high dynamic infrared original image by using guided filtering to obtain a denoising image;
分层模块,用于利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像;A layering module, configured to use Gaussian filtering to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, and use the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image;
增强模块,用于根据人眼视觉特性获得对比度提升函数,利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像;An enhancement module, configured to obtain a contrast enhancement function according to the visual characteristics of the human eye, and use the contrast enhancement function to perform enhancement processing on the high-frequency image to obtain an enhanced detail image;
调光模块,用于对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像;A dimming module, configured to perform brightness-maintaining dual-platform histogram dimming processing on the original high dynamic infrared image to obtain a dimmed image;
融合模块,用于对所述调光后图像与所述增强后细节图像进行加权融合。A fusion module, configured to perform weighted fusion on the dimmed image and the enhanced detail image.
另一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种计算机存储介质,所述计算机存储介质中存储有多条计算机指令,所述多条计算机指令用于使计算机执行上述的方法。On the other hand, an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer storage medium, where a plurality of computer instructions are stored in the computer storage medium, and the plurality of computer instructions are used to cause a computer to execute the above method.
本发明中的一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法、系统及计算机存储介质,具有以下优点:A high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium in the present invention have the following advantages:
(1)本发明在分层前使用引导滤波对原始图像进行去噪,结合高斯滤波,直接提取抑制噪声后的高频图像,图像数据包含完整的边缘信息;(1) The present invention uses guided filtering to denoise the original image before layering, and in combination with Gaussian filtering, directly extracts the high-frequency image after suppressing the noise, and the image data contains complete edge information;
(2)本发明在高频图像中结合人眼视觉特性,实现了自适应选择增强边缘权重,达到提升较弱细节强度的同时保护原始清晰边缘的效果;(2) The present invention combines the visual characteristics of the human eye in high-frequency images to realize the adaptive selection of enhanced edge weights, and achieve the effect of protecting the original clear edges while improving the strength of weaker details;
(3)本发明直接利用原始图像进行双平台直方图均衡化调光,避免了对原图进行滤波算法后造成的边缘扩散,调光后的图片与加强后的高频图像加权融合可有效减弱伪边缘现象。(3) The present invention directly uses the original image to perform dual-platform histogram equalization dimming, which avoids the edge diffusion caused by the filtering algorithm on the original image, and the weighted fusion of the dimmed image and the enhanced high-frequency image can effectively reduce the Pseudo-edge phenomenon.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单的介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are only These are some embodiments of the present invention. Those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings without creative work.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法的流程图。Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
图2为本发明实施例提供的一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法的对比效果图A。Fig. 2 is a comparison effect diagram A of a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
图3为本发明实施例提供的一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法的对比效果图B。FIG. 3 is a comparison effect diagram B of a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式detailed description
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案清楚、完整地进行描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
申请人对现有技术研究后发现,2009年Branchitta和Francesco提出了基于双边滤波的动态范围分割算法。在此基础上,各国学者提出了与之相似的滤波分层框架算法。在基于双边滤波的动态范围分割算法中,双边滤波将原始图像分为包含低频信息的基础层分量和包含高频信息的细节层分量,通过压缩算法和噪声抑制分别对两层分量进行处理,选择合适的融合比例将两层分量的图像进行融合。分层模式的算法处理,在保留红外图像细节信息的同时增强了红外图像的对比度。但双边滤波器在图像灰度变化比较剧烈的边缘易出现梯度翻转现象,图像将出现光晕伪像,且容易出现伪边缘。为了消除梯度翻转现象并减少整体算法运算时间,Liu等在2014年提出了一种基于引导滤波的DDE算法。DDE算法采用引导滤波代替双边滤波的方法,既保留图像细节信息又避免梯度翻转现象。由于算法采用设定参数的方法导致场景自适应性较差,因此,为了实现自适应场景的参数调节,Zhou等在2018年提出了一种基于引导滤波的自适应红外图像细节增强算法,通过直方图分布信息为基础层图像确定自适应门限,去除图像中无效灰度值,使得基础层图像能更好地显示有效信息。但算法去噪效果较差,当图像包含大面积天空背景时,处理后的图像包含大量噪声干扰。After studying the prior art, the applicant found that Branchitta and Francesco proposed a dynamic range segmentation algorithm based on bilateral filtering in 2009. On this basis, scholars from various countries have proposed a similar filter layered framework algorithm. In the dynamic range segmentation algorithm based on bilateral filtering, bilateral filtering divides the original image into base layer components containing low-frequency information and detail layer components containing high-frequency information, and the two-layer components are processed by compression algorithm and noise suppression respectively. An appropriate fusion ratio is used to fuse the images of the two layer components. The algorithm processing of the layered mode enhances the contrast of the infrared image while retaining the detailed information of the infrared image. However, the bilateral filter is prone to gradient reversal phenomenon on the edge where the gray level of the image changes sharply, and the image will appear halo artifacts, and false edges are prone to appear. In order to eliminate the gradient flip phenomenon and reduce the overall algorithm operation time, Liu et al. proposed a DDE algorithm based on guided filtering in 2014. The DDE algorithm uses guided filtering instead of bilateral filtering, which not only preserves image detail information but also avoids the phenomenon of gradient reversal. Because the algorithm adopts the method of setting parameters, the adaptability of the scene is poor. Therefore, in order to realize the parameter adjustment of the adaptive scene, Zhou et al. proposed an adaptive infrared image detail enhancement algorithm based on guided filtering in 2018. Through the histogram The graph distribution information determines the adaptive threshold for the base layer image, and removes invalid gray values in the image, so that the base layer image can better display effective information. However, the denoising effect of the algorithm is poor. When the image contains a large area of sky background, the processed image contains a lot of noise interference.
针对现有技术中的问题,本发明提供了一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法,通过对高动态红外原始图像先进行去噪处理,再对去噪后的图像分层增强处理的方法,解决处理后图像噪声干扰严重的问题,通过结合人眼视觉特性达到自适应选择增强边缘权重,达到提升较弱细节强度的同时保护原始清晰边缘的效果,通过将调光处理后的图像与增强处理后的图像加权融合减弱处理图片时出现的伪边缘现象。Aiming at the problems in the prior art, the present invention provides a high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, which solves the problem by first denoising the original high dynamic infrared image, and then layering and enhancing the denoised image. The problem of serious image noise interference after processing, by combining the visual characteristics of the human eye to achieve adaptive selection to enhance the edge weight, to achieve the effect of improving the strength of weaker details while protecting the original clear edge, by combining the image after dimming processing with the enhanced processing The image weighted fusion weakens the pseudo-edge phenomenon that occurs when processing images.
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法的流程图。本发明实施例提供了一种高动态红外图像细节增强方法,包括:Fig. 1 is a flow chart of a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image provided by an embodiment of the present invention. An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for enhancing details of a high dynamic infrared image, including:
利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像;Use guided filtering to denoise the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a denoised image;
利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像;Using Gaussian filtering to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, and using the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image;
根据人眼视觉特性获得对比度提升函数;A contrast enhancement function is obtained according to the visual characteristics of the human eye;
利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像;performing enhancement processing on the high-frequency image by using the contrast enhancement function to obtain an enhanced detail image;
对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像;performing brightness-maintaining dual-platform histogram dimming processing on the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a dimmed image;
对所述调光后图像与所述增强后细节图像进行加权融合。Weighted fusion is performed on the dimmed image and the enhanced detail image.
示例性的,利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像,包括:根据高动态红外原始图像与引导图像确定引导滤波的权重系数和偏置系数;根据所述引导图像、权重系数和偏置系数对所述高动态红外原始图像进行滤波处理,获得所述去噪图像。Exemplarily, using guided filtering to perform denoising processing on the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain the denoised image includes: determining the weight coefficient and bias coefficient of the guiding filter according to the high dynamic infrared original image and the guiding image; , weight coefficient and offset coefficient to filter the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain the denoised image.
所述引导滤波是一种具有代表性的边缘保持平滑技术,设去噪后的去噪图像q与引导图像I之间存在线性关系,即:其中,qi表示坐标为i的去噪图像灰度值,Ii表示坐标为i的引导图像灰度值,ωk表示以k坐标位置为中心,r为半径的矩形窗口;ak、bk分别表示引导图像在窗口内的权重系数与偏置系数。引导滤波就是寻找使得高动态红外原始图像p与处理后的去噪图像q差异最小的ak与bk的最优解,因此,需要构造代价函数:E(ak,bk),即E(ak,bk)=∑((akIi+bk-pi)2+εak2)在E(ak,bk)式中,ε表示正则系数,其作用是删除过大的ak,而通过计算可得:The guided filtering is a representative edge-preserving smoothing technique. It is assumed that there is a linear relationship between the denoised image q after denoising and the guided image I, namely: Among them, qi represents the gray value of the denoised image whose coordinate is i, Ii represents the gray value of the guide image whose coordinate is i, ωk represents a rectangular window centered at the k coordinate position and r is the radius; ak , bk respectively represent the weight coefficient and bias coefficient of the guide image in the window. Guided filtering is to find the optimal solution of ak and bk that minimizes the difference between the original high dynamic infrared image p and the denoised image q after processing. Therefore, it is necessary to construct a cost function: E(ak , bk ), that is, E (ak ,bk )=∑((ak Ii +bk -pi )2 +εak2 ) In E(ak ,bk ), ε represents the regularization coefficient, and its function is to delete large ak , and can be obtained by calculation:
其中,|ω|表示窗口内像素数量,σ2与μk分别表示引导图像I在ωk窗口内的方差与均值。表示高动态红外原始图像p在ωk窗口内的均值。最后,在整幅图像内采取窗口操作,最后取均值可以得到滤波后的结果:其中,Among them, |ω| represents the number of pixels in the window, σ2 and μk represent the variance and mean of the guiding image I in the ωk window, respectively. Indicates the mean value of the high dynamic infrared original image p in the ωk window. Finally, take the window operation in the whole image, and finally take the mean value to get the filtered result: in,
利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像,包括:设置一个高斯滤波模板mask;利用所述高斯滤波模板mask与高动态红外原始图像进行卷积操作,获取低频图像;利用所述高动态红外原始图像与所述低频图像作差,获取所述高频图像。Using Gaussian filtering to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, using the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image, including: setting a Gaussian filtering template mask; using the Gaussian filtering template. Convolving the mask with the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain a low frequency image; using the high dynamic infrared original image and the low frequency image as a difference to obtain the high frequency image.
所述高斯滤波模板mask如下所示是一个5*5的满足方差为0.5的高斯滤波模板。The Gaussian filter template mask as shown below is a 5*5 Gaussian filter template with a variance of 0.5.
利用所述高斯滤波模板mask与q去噪图像进行步长为1的卷积操作,获取低频图像q_L,然后利用q与q_L作差,获取高频图像q_H,即:q_H=q-q_L。Use the Gaussian filter template mask and the q denoising image to perform a convolution operation with a step size of 1 to obtain a low-frequency image q_L, and then use the difference between q and q_L to obtain a high-frequency image q_H, that is: q_H=q-q_L.
所述对比度提升函数由局部细节调整函数和对比度限制函数的乘积构成。The contrast boosting function is formed by the product of a local detail adjustment function and a contrast limiting function.
设所述对比度提升函数为β(x,y),利用韦伯比曲线模拟构造局部细节调整函数,实现依据背景光照分量进行对应的细节增强,所述局部细节调整函数为β1(x,y)=1-0.85·sin(q_L'(x,y)·π),考虑在实际应用中,对于高动态红外原始图像中梯度较大的地方无需进行过度增强,真正需要强调的地方在于高动态红外原始图像梯度较小的区域,故而,构造一个对比度限制函数k(x,y),所述对比度限制函数细节调整函数β1(x,y)与对比度限制函数k(x,y)的乘积为最终的对比度提升函数β(x,y),即β(x,y)=β1(x,y)×k(x,y)。采用模拟人眼视觉特性和抑制细节过增强的局部对比度增强函数,可使高对比度地方增强较少,增强图像结果总体比较柔和,视觉效果不至于太锐化,对处于暗区和亮区且细节不明显的像素点具有较强的增强,同时可抑制细节的过增强。上述公式中的q_L'(x,y)和q_H'(x,y)分别为q_L(x,y)和q_H(x,y)归一化后的变量。Assuming that the contrast enhancement function is β(x, y), the Weber ratio curve is used to simulate and construct a local detail adjustment function to realize the corresponding detail enhancement based on the background illumination component, and the local detail adjustment function is β1 (x, y) =1-0.85·sin(q_L'(x,y)·π), considering that in practical applications, there is no need to over-enhance the places with large gradients in the original high-dynamic infrared image, and what really needs to be emphasized is the high-dynamic infrared The area where the gradient of the original image is small, therefore, a contrast-limited function k(x, y) is constructed, and the contrast-limited function The product of the detail adjustment function β1 (x,y) and the contrast limiting function k(x,y) is the final contrast enhancement function β(x,y), that is, β(x,y)=β1 (x,y) ×k(x,y). The local contrast enhancement function that simulates the visual characteristics of the human eye and suppresses the over-enhancement of details can make the high-contrast areas less enhanced, the result of the enhanced image is generally softer, and the visual effect will not be too sharp. For dark and bright areas with details Inconspicuous pixels have strong enhancement, and at the same time, over-enhancement of details can be suppressed. q_L'(x,y) and q_H'(x,y) in the above formula are the normalized variables of q_L(x,y) and q_H(x,y) respectively.
利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像,包括:将所述对比度提升函数与所述高频图像做乘积;对乘积的结果进行限制,得到所述增强后细节图像。Using the contrast enhancement function to enhance the high-frequency image to obtain an enhanced detail image includes: multiplying the contrast enhancement function and the high-frequency image; limiting the result of the product to obtain the enhancement. Post detail image.
将所述对比度提升函数β(x,y)与所述高频图像q_H(x,y)做乘积,并将乘积结果限制在[-20,20]之间,得到q_HE(x,y)作为增强后细节图像。The contrast enhancement function β(x, y) is multiplied by the high-frequency image q_H(x, y), and the result of the product is limited to [-20, 20], and q_HE(x, y) is obtained as Enhanced detail image.
在一种可能的实施例中,对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像,包括:设置图像统计直方图的上限阈值,得到直方图累计分布函数,所述双平台直方图为直方图累计分布函数分段后得到的两段平台直方图;将两段所述平台直方图各自进行互不干扰的直方图映射,得到调光后图像。In a possible embodiment, performing brightness-maintaining dual-platform histogram dimming processing on the high dynamic infrared original image to obtain the dimmed image includes: setting an upper threshold of the image statistical histogram to obtain the histogram cumulative distribution function, the two-platform histogram is a two-stage platform histogram obtained after the cumulative distribution function of the histogram is segmented; each of the two platform histograms is mapped to a non-interfering histogram to obtain a dimmed image.
设置图像统计直方图T为上限阈值,当灰度频数P大于T,则将T值赋给P,否则,P保持不变,此处取T=500,直方图累计分布函数可以表示成下式:以8192作为直方图分段中心点,前8192个灰度级映射至[y8Start,y8Mid],后8192个灰度级映射至[y8Mid,255],其中:y8Range表示8bit图像的动态范围,此处取y8Range=235。两段平台直方图各自进行互不干扰的直方图映射即可得到调光后图像q_base(x,y)。Set the image statistical histogram T as the upper threshold, when the gray frequency P is greater than T, then assign the T value to P, otherwise, P remains unchanged, here T=500, the cumulative distribution function of the histogram can be expressed as the following formula : Taking 8192 as the center point of the histogram segmentation, the first 8192 gray levels are mapped to [y8Start, y8Mid], and the last 8192 gray levels are mapped to [y8Mid, 255], where: y8Range represents the dynamic range of an 8bit image, here y8Range=235. The image q_base(x, y) after dimming can be obtained by performing histogram mapping without interfering with each other on the two platform histograms.
对调光后的图像q_base(x,y)与所述增强后的高频图像q_HE(x,y)加权融合。即:oImg(x,y)=q_base(x,y)+q_HE(x,y);所得oImg(x,y)即为最终的增强红外图像,如图2和图3所示。其中,图2中的a为增强细节前的高动态红外图像,b为增强细节后的高动态红外图像。图3中的a为增强细节前的高动态红外图像,b为增强细节后的高动态红外图像。The light-adjusted image q_base(x, y) is weighted and fused with the enhanced high-frequency image q_HE(x, y). Namely: oImg(x, y)=q_base(x, y)+q_HE(x, y); the obtained oImg(x, y) is the final enhanced infrared image, as shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 . Among them, a in Fig. 2 is the high dynamic infrared image before detail enhancement, and b is the high dynamic infrared image after detail enhancement. A in Figure 3 is the high dynamic infrared image before detail enhancement, and b is the high dynamic infrared image after detail enhancement.
本发明实施例还提供了一高动态红外图像细节增强系统,包括:The embodiment of the present invention also provides a high dynamic infrared image detail enhancement system, including:
去噪模块,用于利用引导滤波对高动态红外原始图像进行去噪处理,获得去噪图像;The denoising module is used to perform denoising processing on the high dynamic infrared original image by using guided filtering to obtain a denoising image;
分层模块,用于利用高斯滤波对所述去噪图像进行图像分层处理,获得低频图像,利用所述低频图像和高动态红外原始图像获得高频图像;A layering module, configured to use Gaussian filtering to perform image layering processing on the denoising image to obtain a low-frequency image, and use the low-frequency image and the original high-dynamic infrared image to obtain a high-frequency image;
增强模块,用于根据人眼视觉特性获得对比度提升函数,利用所述对比度提升函数对所述高频图像进行增强处理,获得增强后细节图像;An enhancement module, configured to obtain a contrast enhancement function according to the visual characteristics of the human eye, and use the contrast enhancement function to perform enhancement processing on the high-frequency image to obtain an enhanced detail image;
调光模块,用于对所述高动态红外原始图像进行亮度保持的双平台直方图调光处理,获得调光后图像;A dimming module, configured to perform brightness-maintaining dual-platform histogram dimming processing on the original high dynamic infrared image to obtain a dimmed image;
融合模块,用于对所述调光后图像与所述增强后细节图像进行加权融合。A fusion module, configured to perform weighted fusion on the dimmed image and the enhanced detail image.
本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机存储介质,所述计算机存储介质中存储有多条计算机指令,所述多条计算机指令用于使计算机执行上述的方法。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer storage medium, where a plurality of computer instructions are stored in the computer storage medium, and the plurality of computer instructions are used to make the computer execute the above method.
尽管已描述了本发明的优选实施例,但本领域内的技术人员一旦得知了基本创造性概念,则可对这些实施例做出另外的变更和修改。所以,所附权利要求意欲解释为包括优选实施例以及落入本发明范围的所有变更和修改。While preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described, additional changes and modifications can be made to these embodiments by those skilled in the art once the basic inventive concept is appreciated. Therefore, it is intended that the appended claims be construed to cover the preferred embodiment as well as all changes and modifications which fall within the scope of the invention.
显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。Obviously, those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications to the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the present invention. Thus, if these modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and equivalent technologies thereof, the present invention also intends to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240751.1ACN115587945A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240751.1ACN115587945A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115587945Atrue CN115587945A (en) | 2023-01-10 |
Family
ID=84779935
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240751.1APendingCN115587945A (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115587945A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116433540A (en)* | 2023-06-15 | 2023-07-14 | 武汉高芯科技有限公司 | Infrared image enhancement method and system |
| CN116703777A (en)* | 2023-06-27 | 2023-09-05 | 武汉网幂科技有限公司 | Image processing method, system, storage medium and electronic device |
| CN116894793A (en)* | 2023-09-08 | 2023-10-17 | 南京道成网络科技有限公司 | Method and device for enhancing image quality |
| CN118446940A (en)* | 2023-02-02 | 2024-08-06 | 蔚来移动科技有限公司 | Clear image acquisition method, device, medium and mobile terminal |
| CN119180763A (en)* | 2024-08-30 | 2024-12-24 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Vehicle-mounted infrared image enhancement processing acceleration method and system based on sky detection |
| CN119444614A (en)* | 2025-01-09 | 2025-02-14 | 元途人工智能(杭州)有限公司 | A method of image detail enhancement based on FPGA |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103177429A (en)* | 2013-04-16 | 2013-06-26 | 南京理工大学 | FPGA (field programmable gate array)-based infrared image detail enhancing system and method |
- 2022
- 2022-10-11CNCN202211240751.1Apatent/CN115587945A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103177429A (en)* | 2013-04-16 | 2013-06-26 | 南京理工大学 | FPGA (field programmable gate array)-based infrared image detail enhancing system and method |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 凡遵林: "亮度保持和细节增强的红外图像增强方法", 《中南大学学报(自然科学版)》, 25 July 2016 (2016-07-25), pages 2* |
| 宋岩峰: "基于双平台直方图的红外图像增强算法", 《红外与激光工程》, 25 April 2008 (2008-04-25), pages 1 - 3* |
| 张永新: "《基于边缘保持滤波的多聚焦图像融合算法研究》", 31 May 2020, pages: 42 - 43* |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118446940A (en)* | 2023-02-02 | 2024-08-06 | 蔚来移动科技有限公司 | Clear image acquisition method, device, medium and mobile terminal |
| WO2024159969A1 (en)* | 2023-02-02 | 2024-08-08 | 蔚来移动科技有限公司 | Method for acquiring clear image, device, medium and mobile terminal |
| CN118446940B (en)* | 2023-02-02 | 2025-09-19 | 蔚来移动科技有限公司 | Clear image acquisition method, device, medium and mobile terminal |
| CN116433540A (en)* | 2023-06-15 | 2023-07-14 | 武汉高芯科技有限公司 | Infrared image enhancement method and system |
| CN116433540B (en)* | 2023-06-15 | 2023-09-29 | 武汉高芯科技有限公司 | Infrared image enhancement method and system |
| CN116703777A (en)* | 2023-06-27 | 2023-09-05 | 武汉网幂科技有限公司 | Image processing method, system, storage medium and electronic device |
| CN116894793A (en)* | 2023-09-08 | 2023-10-17 | 南京道成网络科技有限公司 | Method and device for enhancing image quality |
| CN116894793B (en)* | 2023-09-08 | 2023-11-28 | 南京道成网络科技有限公司 | Method and device for enhancing image quality |
| CN119180763A (en)* | 2024-08-30 | 2024-12-24 | 杭州电子科技大学 | Vehicle-mounted infrared image enhancement processing acceleration method and system based on sky detection |
| CN119444614A (en)* | 2025-01-09 | 2025-02-14 | 元途人工智能(杭州)有限公司 | A method of image detail enhancement based on FPGA |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115587945A (en) | High dynamic infrared image detail enhancement method, system and computer storage medium | |
| Wang et al. | Single image dehazing based on the physical model and MSRCR algorithm | |
| CN107527332B (en) | Low-illumination image color retention enhancement method based on improved Retinex | |
| CN109754377B (en) | A Multi-Exposure Image Fusion Method | |
| CN113256533B (en) | Self-adaptive low-illumination image enhancement method and system based on MSRCR | |
| Zhou et al. | Multi-scale retinex-based adaptive gray-scale transformation method for underwater image enhancement | |
| CN110047055B (en) | An infrared image detail enhancement and denoising method | |
| CN112991197B (en) | A low-light video enhancement method and device based on dark channel detail preservation | |
| CN114331873A (en) | Non-uniform illumination color image correction method based on region division | |
| CN115578297A (en) | A Generalized Attenuation Image Enhancement Method with Adaptive Color Compensation and Detail Optimization | |
| CN112116536A (en) | Low-illumination image enhancement method and system | |
| Zhou et al. | A multifeature fusion method for the color distortion and low contrast of underwater images | |
| CN116309152A (en) | Method, system, device and storage medium for detail enhancement of low-illuminance images | |
| CN104318529A (en) | Method for processing low-illumination images shot in severe environment | |
| CN116993616A (en) | A single low-light scene image enhancement method and enhancement system | |
| CN118261810A (en) | A method for underwater image enhancement of nuclear power plants based on multi-scale pixel fusion | |
| Wu et al. | Reflectance-guided histogram equalization and comparametric approximation | |
| Wang et al. | Single underwater image enhancement based on $ l_ {P} $-norm decomposition | |
| Zou et al. | Image haze removal algorithm using a logarithmic guide filtering and multi-channel prior | |
| CN119379560A (en) | Image defogging method, device, storage medium and electronic device | |
| CN110807748A (en) | New tone mapping image enhancement method based on high dynamic range | |
| CN117649694A (en) | Face detection method, system and device based on image enhancement | |
| Mohammed et al. | An Improved Underwater Image Enhancement Approach for Border Security | |
| Su et al. | Clarity method of low-illumination and dusty coal mine images based on improved amef | |
| Jayanthi et al. | Underwater haze removal using contrast boosted grayscale image |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |