CN115547046A - Bus lane variable system control method with absolute priority - Google Patents
Bus lane variable system control method with absolute priorityDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115547046A CN115547046ACN202211207768.7ACN202211207768ACN115547046ACN 115547046 ACN115547046 ACN 115547046ACN 202211207768 ACN202211207768 ACN 202211207768ACN 115547046 ACN115547046 ACN 115547046A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- bus
- signal
- intersection
- vehicle
- vehicles
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription27
- 238000011144upstream manufacturingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription35
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000claimsdescription8
- VVNRQZDDMYBBJY-UHFFFAOYSA-Msodium 1-[(1-sulfonaphthalen-2-yl)diazenyl]naphthalen-2-olateChemical compound[Na+].C1=CC=CC2=C(S([O-])(=O)=O)C(N=NC3=C4C=CC=CC4=CC=C3O)=CC=C21VVNRQZDDMYBBJY-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 241000209094OryzaSpecies0.000claims7
- 235000007164Oryza sativaNutrition0.000claims7
- 235000009566riceNutrition0.000claims7
- 238000004148unit processMethods0.000claims1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description10
- 238000011217control strategyMethods0.000description7
- 230000001934delayEffects0.000description5
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description3
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description3
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description3
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description3
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description3
- 230000035939shockEffects0.000description3
- 230000011664signalingEffects0.000description3
- 229920006395saturated elastomerPolymers0.000description2
- 206010021033HypomenorrhoeaDiseases0.000description1
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description1
- 238000013459approachMethods0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 230000006835compressionEffects0.000description1
- 238000007906compressionMethods0.000description1
- 230000005574cross-species transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 230000003111delayed effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 230000000630rising effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0125—Traffic data processing
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
- G08G1/0137—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions for specific applications
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/07—Controlling traffic signals
- G08G1/08—Controlling traffic signals according to detected number or speed of vehicles
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/20—Monitoring the location of vehicles belonging to a group, e.g. fleet of vehicles, countable or determined number of vehicles
- G08G1/207—Monitoring the location of vehicles belonging to a group, e.g. fleet of vehicles, countable or determined number of vehicles with respect to certain areas, e.g. forbidden or allowed areas with possible alerting when inside or outside boundaries
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及交通运输技术领域,尤其涉及一种公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交车道系统控制方法。The invention relates to the technical field of transportation, in particular to a method for controlling a variable bus lane system in which buses have absolute priority.
背景技术Background technique
在城市公交系统中,除了公交信号优先策略外,公交专用道(dedicated buslane,DBL)是为公共交通提供高质量服务的另一种有效方式。然而,由于城市道路空间限制,DBL的出现严重影响了社会车辆在交叉口处的通行能力。当社会车辆交通需求较高时,由于车道数限制,社会车辆通常会在信号交叉口排成长队,特别是由于绿灯时间有限,过长的车辆队列可能会导致社会车辆在离开交叉口前经历多次停车。由于公交车的到达频率通常低于社会车辆,公交专用道的使用带来城市道路资源使用的不平等性问题。特别是当公交车发车频率较低而社会车辆交通需求较高时,公交车专用车道通常处于闲置状态,普通车道却因为空间受限而产生频繁拥堵。结果是,DBL的使用导致对原有普通车道的压缩,而城市拥堵的形式则转移到普通车道上,特别是当交叉口信号在绿灯期间,可能由于DBL没有公交车,交叉口导致潜在的通行能力被浪费。In the urban public transport system, in addition to the bus signal priority strategy, dedicated bus lanes (DBL) are another effective way to provide high-quality services for public transport. However, due to the space constraints of urban roads, the emergence of DBL seriously affects the traffic capacity of social vehicles at intersections. When the traffic demand of social vehicles is high, due to the limited number of lanes, social vehicles usually form long queues at signalized intersections, especially due to the limited green light time, excessively long vehicle queues may cause social vehicles to go through a long queue before leaving the intersection. parking. Since the arrival frequency of buses is usually lower than that of social vehicles, the use of bus lanes brings about the problem of inequality in the use of urban road resources. Especially when the bus frequency is low and the social vehicle traffic demand is high, the bus lanes are usually idle, but the ordinary lanes are frequently congested due to limited space. The result is that the use of the DBL results in a compression of the original common lane, and the form of urban congestion is shifted to the common lane, especially when the intersection signal is green, possibly due to the lack of buses at the DBL, and the intersection leads to potential traffic Capacity is wasted.
为改善DBL与普通车道之间的道路资源平衡,一些预信号(Pre-signals)控制策略被相继提出。然而,当前预信号控制方法仍存在下述问题:In order to improve the road resource balance between DBL and ordinary lanes, some pre-signals control strategies have been proposed one after another. However, the current pre-signal control method still has the following problems:
⑴现有预信号策略要求预信号必须设置在交叉口上游某足够远的位置,并且要求社会车辆必须在预信号处停车。然而,当交通需求量较大时,预信号处就会形成较长的社会车辆排队队列,此时,很可能因为队列上溢导致上游交叉口堵塞,因此,不适用于所有交叉口。(1) The existing pre-signal strategy requires that the pre-signal must be set at a position far enough upstream of the intersection, and that social vehicles must stop at the pre-signal. However, when the traffic demand is large, a long queue of social vehicles will be formed at the pre-signal. At this time, it is likely that the upstream intersection will be blocked due to queue overflow, so it is not suitable for all intersections.
⑵现有预信号策略下,一些情况下公交车在交叉口必须加入到社会车辆的队列尾部停车,因此,公交车可能会遇到一些额外的延误。(2) Under the existing pre-signaling strategy, in some cases, the bus must join the queue of social vehicles to stop at the intersection, so the bus may encounter some additional delays.
⑶现有预信号策略下,在一个信号周期内,预信号的使用未考虑普通车道上的社会车辆的排队长度。但是,当社会车辆流量较低时,若仍要求车辆在预信号处停车,此时现有预信号策略并不能改善交叉口交通性能,相反会造成车辆额外停车,并导致额外的能耗和尾气排放。(3) Under the existing pre-signaling strategy, within a signal cycle, the use of pre-signaling does not consider the queue length of social vehicles on the ordinary lane. However, when the social vehicle flow is low, if vehicles are still required to stop at the pre-signal, the existing pre-signal strategy cannot improve the traffic performance of the intersection, on the contrary, it will cause extra parking of vehicles, and lead to additional energy consumption and exhaust emission.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明所要解决的技术问题是提供一种能有效提升交叉口交通通行能力、并能降低社会车辆延误和停车次数的公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交车道系统控制方法。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a variable bus lane system control method that can effectively improve the traffic capacity of the intersection and reduce the delay and parking times of social vehicles. The bus has absolute priority.
为解决上述问题,本发明所述的一种公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交车道系统控制方法,包括以下步骤:In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, a kind of bus of the present invention has the variable bus lane system control method of absolute priority, comprises the following steps:
⑴根据下式确定上游车辆长度L;(1) Determine the lengthL of the upstream vehicle according to the following formula;
式中,,取整数值;为交叉口主信号绿灯时长,单位:秒;为两连续通过停车线车辆的平均最小车头时距,单位:秒/辆;,取整数值;为交叉口主信号红灯时长,单位:秒;dq为车辆在静止队列中占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆;In the formula, , taking an integer value; It is the duration of the green light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second; is the average minimum headway of two consecutive vehicles passing the stop line, unit: second/vehicle; , taking an integer value; is the duration of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;dq is the average space occupied by vehicles in the stationary queue, unit: m/vehicle;
⑵在公交专用道距离交叉口的主信号的上游车辆长度为L处设置预信号,主信号与预信号之间的公交专用道区域为可变区域;并在预信号的一侧公交专用道上设置用于检测可变区域内车辆排队长度的传感器Ⅰ,另一侧普通车道上设置用于检测普通车道上车辆排队长度的传感器Ⅱ;同时,在公交车上安装定位传感器;主信号、定位传感器、传感器Ⅰ、传感器Ⅱ以及预信号通过无线网络分别与主控室的数据处理单元相连;⑵The pre-signal is set at the position where the distance from the bus lane to the upstream vehicle of the main signal at the intersection isL , and the area of the bus lane between the main signal and the pre-signal is a variable area; The sensor I used to detect the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area, and the sensor II used to detect the queuing length of vehicles on the ordinary lane on the other side; at the same time, a positioning sensor is installed on the bus; the main signal, positioning sensor, Sensor Ⅰ, sensor Ⅱ and the pre-signal are respectively connected to the data processing unit in the main control room through the wireless network;
⑶针对道路路段实际情况,确定公交专用道预信号上游的临界距离D;(3) Determine the critical distanceD upstream of the bus lane pre-signal for the actual situation of the road section;
⑷将主信号提供的交叉口主信号信号状态、公交车载定位传感器提供的即将到达公交车的位置、传感器Ⅰ提供的可变区域内车辆排队长度、传感器Ⅱ提供的普通车道上车辆排队队长,通过无线网络送入主控室的数据处理单元,由其处理后完成预信号控制。(4) The signal status of the main signal at the intersection provided by the main signal, the position of the arriving bus provided by the positioning sensor on the bus, the queue length of the vehicles in the variable area provided by the sensor I, and the queue length of the vehicles on the ordinary lane provided by the sensor II, It is sent to the data processing unit in the main control room through the wireless network, and the pre-signal control is completed after processing by it.
所述步骤⑶中临界距离D按下述方法确定:In the step (3), the critical distanceD is determined as follows:
(a)若临界距离D内不存在任何交通设施,则(a) If there is no traffic facility within the critical distanceD , then
式中:,为在无任何限制时可变区域内社会车辆最大排队长度,单位:辆;为交叉口主信号红灯开始时公交车与交叉口停车线的距离,单位:米,为可变区域内社会车辆最大排队车辆被完全清空所需的时间,单位:秒;In the formula: , is the maximum queuing length of social vehicles in the variable area when there is no restriction, unit: vehicle; is the distance between the bus and the stop line at the intersection when the main signal red light at the intersection starts, unit: meter, Maximum queuing vehicles for social vehicles in variable regions The time required to be completely cleared, unit: second;
,为社会车辆队列的释放速度;qs为饱和流量,单位:辆/秒;dq为车辆在静止队列中占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆;dc为车辆自由行驶时占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆; , is the release speed of the social vehicle queue;qs is the saturated flow, unit: vehicle/second;dq is the average space occupied by the vehicle in the stationary queue, unit: m/vehicle;dc is the average space occupied by the vehicle when it is free running Space, unit: m/vehicle;
为即将到达公交车距离交叉口停车线的距离,单位:米; is the distance between the coming bus and the stop line at the intersection, unit: meter;
vb为公交车平均车速,单位:米/秒;vb is the average speed of the bus, unit: m/s;
为即将到达公交车距离交叉口停车线的距离为时,交叉口主信号红灯已逝去时长,单位:秒; The distance between the coming bus and the stop line at the intersection is , the elapsed time of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;
,为社会车辆队列的形成速度;q为交通流量,单位:辆/秒; , is the formation speed of the social vehicle queue;q is the traffic flow, unit: vehicle/second;
(b)若临界距离D内存在一上游交叉口,则(b) If there is an upstream intersection within the critical distanceD , then
式中:为目标交叉口与其相邻上游交叉口之间的距离,单位:米;In the formula: is the distance between the target intersection and its adjacent upstream intersection, unit: meter;
为目标交叉口与其相邻上游交叉口交通信号灯绝对偏移量,单位:秒; is the absolute offset of traffic lights between the target intersection and its adjacent upstream intersection, unit: second;
(c)若临界距离D内存在一公交车站,则(c) If there is a bus stop within the critical distanceD , then
式中:tdepart= tstay+tarrive,为公交车离站时间,单位:秒;In the formula:tdepart =tstay +tarrive , which is the departure time of the bus, unit: second;
tstay为公交车在站台的平均停留时间,单位:秒;tstay is the average stay time of the bus at the platform, unit: second;
tarrive= t0+(Rint vb-dstation)/vb,t0为交叉口主信号红灯开始时刻,单位:秒;dstation为公交站与交叉口停车线之间的距离,单位:米。tarrive =t0 +(Rintvb -dstation )/vb ,t0 is the starting time of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;dstation is the distance between the bus station and the stop line at the intersection, Unit: m.
所述步骤⑷中预信号控制按下述方法进行:Pre-signal control in the step (4) is carried out as follows:
交叉口主信号在红灯阶段内,且当普通车道上车辆排队长度小于L时,则预信号显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域;The main signal at the intersection is in the red light phase, and when the queuing length of vehicles on the ordinary lane is less thanL , the pre-signal shows a red light, and social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area;
交叉口主信号在红灯阶段内,且当普通车道上的社会车辆排队长度大于L时:The main signal at the intersection is in the red light phase, and when the queuing length of social vehicles on the ordinary lane is greater thanL :
ⅰ 若临界距离D内有公交车,则预信号对社会车辆显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域;ⅰ If there is a bus within the critical distanceD , the pre-signal will show a red light to the social vehicles, and the social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area;
ⅱ 若临界距离D内无公交车,且可变区域内车辆排队长度小于L,则预信号显示为绿色,允许排在预信号上游的社会车辆进入可变区域;ⅱ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , and the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area is less thanL , the pre-signal will be displayed in green, allowing social vehicles upstream of the pre-signal to enter the variable area;
ⅲ 若临界距离D内无公交车,但可变区域内车辆排队长度等于L,则预信号显示为红色,不允许社会车辆进入可变区域;ⅲ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , but the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area is equal toL , the pre-signal is displayed in red, and social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area;
交叉口主信号在绿灯阶段内,且预信号对社会车辆始终显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域。The main signal at the intersection is in the green light phase, and the pre-signal always shows a red light for social vehicles, and social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area.
本发明与现有技术相比具有以下优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
1、本发明是基于预信号的公交专用道交通控制方法,在无须重大交通基础设施重建的低成本条件下,为低频到达的公交车提供绝对优先权,并同时解决具有DBL的信号交叉口空间资源和时间资源利用不足问题,最终达到提升信号交叉口交通通行能力,并降低社会车辆延误和停车次数的目的。1. The present invention is a traffic control method for bus-only lanes based on pre-signals. Under low-cost conditions without major traffic infrastructure reconstruction, absolute priority is provided for buses arriving at low frequencies, and at the same time, it solves the signal intersection space with DBL Insufficient utilization of resources and time resources can ultimately achieve the purpose of improving traffic capacity at signalized intersections and reducing social vehicle delays and parking times.
2、本发明中在公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交专用道(Variable bus lane withabsolute priority,VBLAP)策略下,所有车辆只可能在原有交叉口停车线处停车。由于社会车辆和公交车在任何时候均无需在预信号处停车,特别是在本发明控制方式下,普通车道上排队的社会车辆在预信号控制下可进一步被允许进入公交专用车道,因此,可降低社会车辆在信号交叉口的延误和停车次数。同时,还可以大大降低车辆排队上溢到上游交叉口的风险。2. In the present invention, under the variable bus lane with absolute priority (VBLAP) strategy in which buses have absolute priority, all vehicles can only stop at the original intersection stop line. Because social vehicles and buses all need not stop at the pre-signal place at any time, especially under the control mode of the present invention, the social vehicles lined up on the common lane can be further allowed to enter the bus-only lane under the pre-signal control, therefore, can Reduce delays and stops for social vehicles at signalized intersections. At the same time, the risk of vehicle queues overflowing to upstream intersections can be greatly reduced.
3、本发明中的VBLAP策略在临界距离的设计下,无论公交车的到达时间如何,都不会对公交车造成额外的延误。公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交车道策略意味着公交车辆对交叉口处的公交专用车道的使用不会受到社会车辆使用的干扰。并且,在交叉口下游,设置车辆合流区,可让社会车辆重新返回普通车道,以提高公交车对公交专用道道路路段使用绝对优先权。3. Under the design of the critical distance, the VBLAP strategy in the present invention will not cause additional delay to the bus regardless of the arrival time of the bus. The variable bus lane strategy, in which buses have absolute priority, means that bus use of the bus lanes at intersections will not be interfered with by social vehicle use. In addition, in the downstream of the intersection, a vehicle merging area is set up to allow social vehicles to return to the ordinary lane, so as to improve the absolute priority of buses to use the bus-only road section.
4、在本发明的VBLAP策略中,在交叉口信号红灯期间,只有当普通车道上的车辆排队长度大于给定的阈值,并且在给定的临界区域内没有公交车出现时,预信号才可切换为绿灯允许社会车辆进入到公交专用道。显然,在建议的VBLAP策略下,当社会车流量较低时,不会造成车辆额外停车。4. In the VBLAP strategy of the present invention, during the red light of the intersection signal, the pre-signal will be activated only when the queue length of vehicles on the common lane is greater than a given threshold and no bus appears in the given critical area. Can be switched to a green light to allow social vehicles to enter the bus lane. Obviously, under the proposed VBLAP strategy, when the social traffic flow is low, it will not cause extra parking of vehicles.
5、在本发明的VBLAP策略中,预信号的信号周期与交叉口主信号原有信号周期相同,并且,交叉口原有信号控制策略不受预信号影响,因此,可实现简单易用的目的。5. In the VBLAP strategy of the present invention, the signal period of the pre-signal is the same as the original signal period of the main signal at the intersection, and the original signal control strategy of the intersection is not affected by the pre-signal, therefore, the purpose of being simple and easy to use can be achieved .
附图说明Description of drawings
下面结合附图对本发明的具体实施方式作进一步详细的说明。The specific implementation manners of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
图1为本发明的VBLAP策略的布局。Figure 1 is the layout of the VBLAP strategy of the present invention.
图中:1—主信号;2—定位传感器;3—传感器Ⅰ;4—传感器Ⅱ;5—数据处理单元。In the figure: 1—main signal; 2—positioning sensor; 3—sensor I; 4—sensor II; 5—data processing unit.
图2为本发明辅助信号的工作流程。Fig. 2 is the workflow of the auxiliary signal of the present invention.
图3为本发明交叉口红灯阶段预信号的运行过程。其中:(a) 当即将到来的公交车位置大于临界距离D,若普通车道社会车辆排队长度小于L,预信号对社会车辆显示红灯,不允许普通车道社会车辆进入可变区域;(b) 当即将到来的公交车位置小于或等于临界距离D,不论普通车道社会车辆的排队长度多大,预信号对社会车辆显示红灯,不允许普通车道社会车辆进入可变区域;(c) 当即将到来的公交车位置大于临界距离D,若普通车道社会车辆排队长度大于L,预信号对社会车辆显示绿灯,允许普通车道上排在预信号上游的社会车辆进入可变区域,直到可变区域车辆队长等于L时,预信号对社会车辆切换为红灯。Fig. 3 is the operation process of the red light stage pre-signal at the intersection of the present invention. Among them: (a) When the position of the upcoming bus is greater than the critical distanceD , if the queue length of social vehicles in the common lane is less thanL , the pre-signal will show a red light to the social vehicles, and the social vehicles in the common lane are not allowed to enter the variable area; (b) When the position of the upcoming bus is less than or equal to the critical distanceD , no matter how long the queuing length of the social vehicles in the ordinary lane is, the pre-signal will show a red light to the social vehicles, and the social vehicles in the ordinary lane are not allowed to enter the variable area; (c) when the coming bus The position of the bus is greater than the critical distanceD , if the queuing length of social vehicles in the ordinary lane is greater thanL , the pre-signal will show a green light to the social vehicles, allowing the social vehicles on the ordinary lane upstream of the pre-signal to enter the variable area until the leader of the variable area vehicle When equal toL , the pre-signal switches to red light for social vehicles.
图4为本发明交叉口绿灯阶段预信号的运行过程。Fig. 4 is the operation process of the pre-signal in the green phase of the intersection of the present invention.
图5为本发明孤立交叉口时空图。Fig. 5 is a space-time diagram of an isolated intersection in the present invention.
图6为本发明上游交叉口存在于临界距离范围内情形。Fig. 6 shows the situation that the upstream intersection of the present invention exists within the critical distance range.
图7为本发明公交车站存在于临界距离范围内情形。Fig. 7 shows the situation that the bus stop exists within the critical distance range according to the present invention.
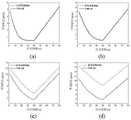
图8为本发明不同流量下使用/不使用VBLAP策略的性能比较。其中:(a)平均排队长度;(b)平均延误;(c)周期内的释放率;(d)总停车次数;(e)剩余排队长度;(f)普通车道上的最大排队长度;(g)交通强度。FIG. 8 is a performance comparison of using/not using the VBLAP strategy under different flow rates in the present invention. where: (a) average queue length; (b) average delay; (c) release rate during the period; (d) total number of stops; (e) remaining queue length; (f) maximum queue length on the common lane; ( g) Traffic intensity.
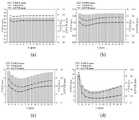
图9为本发明不同交通需求下一个周期内的排队长度。其中:(a) 450(辆/小时);(b) 630(辆/小时);(c) 810(辆/小时);(d) 855(辆/小时)。Fig. 9 is the queue length in the next cycle of different traffic demands according to the present invention. Among them: (a) 450 (vehicle/hour); (b) 630 (vehicle/hour); (c) 810 (vehicle/hour); (d) 855 (vehicle/hour).
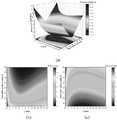
图10为本发明在交叉口红灯时间开始时,可变区域内公交车数量对交通性能的影响。其中:(a)平均排队长度;(b)平均延误;(c)一个周期内的释放率;(d)总停车次数。Fig. 10 shows the influence of the number of buses in the variable area on the traffic performance when the red light time at the intersection starts according to the present invention. where: (a) average queue length; (b) average delay; (c) release rate within a cycle; (d) total number of stops.
图11为本发明在不同饱和度下可变区域长度对交通性能的影响。其中:(a) 0.2;(b) 0.5;(c) 0.8;(d) 1.0。Fig. 11 shows the influence of the variable region length on the traffic performance under different saturation degrees according to the present invention. Where: (a) 0.2; (b) 0.5; (c) 0.8; (d) 1.0.
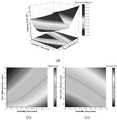
图12为本发明在不同长度可变区域下的车辆排队长度。其中:(a)一个周期内;(b)交叉口信号绿灯阶段;(c)交叉口信号红灯阶段。Fig. 12 is the vehicle queuing length under different length variable regions according to the present invention. Among them: (a) within one cycle; (b) the green light phase of the intersection signal; (c) the red light phase of the intersection signal.
图13为本发明在公交车不同到达概率下的车辆排队长度。其中:(a)一个周期内车辆排队长度;(b)绿灯阶段的车辆排队长度;(c)红灯阶段的车辆排队长度。Fig. 13 is the vehicle queuing length under different arrival probabilities of buses according to the present invention. Among them: (a) the vehicle queue length in one cycle; (b) the vehicle queue length in the green light phase; (c) the vehicle queue length in the red light phase.
具体实施方式detailed description
一种公交具有绝对优先权的可变公交车道系统控制方法,包括以下步骤:A method for controlling a variable bus lane system in which buses have absolute priority, comprising the following steps:
⑴根据下式确定上游车辆长度L;(1) Determine the lengthL of the upstream vehicle according to the following formula;
式中,,取整数值;为交叉口主信号绿灯时长,单位:秒;为两连续通过停车线车辆的平均最小车头时距,单位:秒/辆;,取整数值;为交叉口主信号红灯时长,单位:秒;dq为车辆在静止队列中占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆。In the formula, , taking an integer value; It is the duration of the green light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second; is the average minimum headway of two consecutive vehicles passing the stop line, unit: second/vehicle; , taking an integer value; is the duration of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;dq is the average space occupied by vehicles in the stationary queue, unit: m/vehicle.
⑵在公交专用道距离交叉口的主信号1的上游车辆长度为L处设置预信号,主信号1与预信号之间的公交专用道区域为可变区域;并在预信号的一侧公交专用道上设置用于检测可变区域内车辆排队长度的传感器Ⅰ3,另一侧普通车道上设置用于检测普通车道上车辆排队长度的传感器Ⅱ4;同时,在公交车上安装定位传感器2;主信号1、定位传感器2、传感器Ⅰ3、传感器Ⅱ4以及预信号通过无线网络分别与主控室的数据处理单元5相连。⑵The pre-signal is set at the distanceL of the upstream vehicle length of the
在公交专用道设置预信号后,预信号不影响交叉口的主信号1原有控制策略,且公交车亦不受预信号控制。After the pre-signal is set in the bus-only lane, the pre-signal does not affect the original control strategy of the
⑶针对道路路段实际情况,确定公交专用道预信号上游的临界距离D。具体确定方法如下:(3) According to the actual situation of the road section, determine the critical distanceD upstream of the bus lane pre-signal. The specific determination method is as follows:
(a)若临界距离D内不存在任何交通设施,则(a) If there is no traffic facility within the critical distanceD , then
式中:,为在无任何限制时可变区域内社会车辆最大排队长度,单位:辆;为交叉口主信号红灯开始时公交车与交叉口停车线的距离,单位:米,为可变区域内社会车辆最大排队车辆被完全清空所需的时间,单位:秒;In the formula: , is the maximum queuing length of social vehicles in the variable area when there is no restriction, unit: vehicle; is the distance between the bus and the stop line at the intersection when the main signal red light at the intersection starts, unit: meter, Maximum queuing vehicles for social vehicles in variable regions The time required to be completely cleared, unit: second;
,为社会车辆队列的释放速度;qs为饱和流量,单位:辆/秒;dq为车辆在静止队列中占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆;dc为车辆自由行驶时占据的平均空间,单位:米/辆; , is the release speed of the social vehicle queue;qs is the saturated flow, unit: vehicle/second;dq is the average space occupied by the vehicle in the stationary queue, unit: m/vehicle;dc is the average space occupied by the vehicle when it is free running Space, unit: m/vehicle;
为即将到达公交车距离交叉口停车线的距离,单位:米; is the distance between the coming bus and the stop line at the intersection, unit: meter;
vb为公交车平均车速,单位:米/秒;vb is the average speed of the bus, unit: m/s;
为即将到达公交车距离交叉口停车线的距离为时,交叉口主信号红灯已逝去时长,单位:秒; The distance between the coming bus and the stop line at the intersection is , the elapsed time of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;
,为社会车辆队列的形成速度;q为交通流量,单位:辆/秒; , is the formation speed of the social vehicle queue;q is the traffic flow, unit: vehicle/second;
(b)若临界距离D内存在一上游交叉口,则(b) If there is an upstream intersection within the critical distanceD , then
式中:为目标交叉口与其相邻上游交叉口之间的距离,单位:米;In the formula: is the distance between the target intersection and its adjacent upstream intersection, unit: meter;
为目标交叉口与其相邻上游交叉口交通信号灯绝对偏移量,单位:秒; is the absolute offset of traffic lights between the target intersection and its adjacent upstream intersection, unit: second;
(c)若临界距离D内存在一公交车站,则(c) If there is a bus stop within the critical distanceD , then
式中:tdepart= tstay+tarrive,为公交车离站时间,单位:秒;In the formula:tdepart =tstay +tarrive , which is the departure time of the bus, unit: second;
tstay为公交车在站台的平均停留时间,单位:秒;tstay is the average stay time of the bus at the platform, unit: second;
tarrive= t0+(Rint vb-dstation)/vb,t0为交叉口主信号红灯开始时刻,单位:秒;dstation为公交站与交叉口停车线之间的距离,单位:米。tarrive =t0 +(Rintvb -dstation )/vb ,t0 is the starting time of the red light of the main signal at the intersection, unit: second;dstation is the distance between the bus station and the stop line at the intersection, Unit: m.
⑷将主信号1提供的交叉口主信号信号状态(即红灯,绿灯)、公交车载定位传感器2提供的即将到达公交车的位置、传感器Ⅰ3提供的可变区域内车辆排队长度、传感器Ⅱ4提供的普通车道上车辆排队队长,通过无线网络送入主控室的数据处理单元5,由其处理后完成预信号控制。(4) The main signal status of the intersection provided by the main signal 1 (that is, red light, green light), the location of the upcoming bus provided by the
具体控制方法如下:The specific control method is as follows:
交叉口主信号1在红灯阶段内,且当普通车道上车辆排队长度小于L时,则预信号显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域;The
交叉口主信号1在红灯阶段内,且当普通车道上的社会车辆排队长度大于L时:The intersection
ⅰ 若临界距离D内有公交车,则预信号对社会车辆显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域;ⅰ If there is a bus within the critical distanceD , the pre-signal will show a red light to the social vehicles, and the social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area;
ⅱ 若临界距离D内无公交车,且可变区域内车辆排队长度小于L,则预信号显示为绿色,允许排在预信号上游的社会车辆进入可变区域;ⅱ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , and the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area is less thanL , the pre-signal will be displayed in green, allowing social vehicles upstream of the pre-signal to enter the variable area;
ⅲ 若临界距离D内无公交车,但可变区域内车辆排队长度等于L,则预信号显示为红色,不允许社会车辆进入可变区域;ⅲ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , but the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area is equal toL , the pre-signal is displayed in red, and social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area;
交叉口主信号1在绿灯阶段内,且预信号对社会车辆始终显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域。The
本发明信号控制策略的工作环境如下:The working environment of the signal control strategy of the present invention is as follows:
(1)具有DBL的信号控制交叉口、信号控制人行横道道路路段;(1) Signal-controlled intersections and signal-controlled crosswalk road sections with DBL;
(2)公交低频到达;(2) Low-frequency bus arrival;
(3)普通车道社会车辆交通需求量高。这一策略的底层出发点是,确保公交车在交通信号位置对道路使用的绝对优先权,就好像社会车辆从未在DBL中出现过一样。(3) The traffic demand of social vehicles on ordinary lanes is high. The underlying starting point of this strategy is to ensure that buses have absolute priority for road use at traffic signal locations, as if social vehicles were never present in the DBL.
【信号控制策略】【Signal Control Strategy】
为满足公交车绝对优先的要求,需借助公交车上安装的远程车载无线通信设备,向主控室的数据处理单元5提供DBL中即将到来公交车的位置信息。如图1所示,当即将到来的公交车距离预信号为D时,社会车辆将不允许进入可变区域。在这种情况下,公交车的某个特定位置和预信号之间的距离D被认为是DBL中的一个临界距离,临界距离D的值会随着即将到来的公交车的位置和交叉口的信号状态而变化。临界距离D用以保证在预信号控制下,在可变区域内社会车辆不会在即将到来的公交车前面停车排队。In order to meet the absolute priority of the bus, it is necessary to provide the location information of the upcoming bus in the DBL to the
【基本控制规则】【Basic Control Rules】
图2中展示了预信号控制流程图。在本发明中,预信号置于距离交叉口主信号为L的上游位置,其状态根据以下信息由主控室数据处理单元5综合决定:(1)主信号1提供的交叉口主信号信号状态(即红灯,绿灯),(2)公交车载定位传感器2提供的即将到达公交车的位置,(3) 传感器Ⅰ3提供的可变区域内车辆排队长度,以及(4) 传感器Ⅱ4提供的普通车道上车辆排队队长。Figure 2 shows the pre-signal control flow chart. In the present invention, the pre-signal is placed at an upstream position where the distance from the intersection main signal isL , and its state is comprehensively determined by the main control room
综上所述,本发明中预信号的操作遵循以下规则。To sum up, the operation of the pre-signal in the present invention follows the following rules.
(1) 预信号仅控制普通车道社会车辆是否允许进入可变区域,不影响交叉口主信号1原有控制策略,且公交车亦不受预信号控制。(1) The pre-signal only controls whether social vehicles in ordinary lanes are allowed to enter the variable area, and does not affect the original control strategy of the intersection
(2) 在交叉口主信号红灯阶段内:(2) During the red light phase of the main signal at the intersection:
(a)交叉口主信号1在红灯阶段内,当普通车道上车辆排队长度小于L时,则预信号显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域,如图3(a)所示。(a) During the red light phase of the intersection
(b)交叉口主信号1在红灯阶段内,当普通车道上的社会车辆排队长度大于L时:(b) When the intersection
ⅰ 若临界距离D内有公交车,则预信号对社会车辆显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域,如图3(b)所示;ⅰ If there is a bus within the critical distanceD , the pre-signal will show a red light to the social vehicles, and the social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area, as shown in Figure 3(b);
ⅱ 若临界距离D内无公交车,且可变区域内车辆排队长度小于L,则预信号显示为绿色,允许排在预信号上游的社会车辆进入可变区域,如图3(c)所示;ⅱ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , and the queue length of vehicles in the variable area is less thanL , the pre-signal is displayed in green, allowing the social vehicles upstream of the pre-signal to enter the variable area, as shown in Figure 3(c) ;
ⅲ 若临界距离D内无公交车,但可变区域内车辆排队长度等于L,则预信号显示为红色,不允许社会车辆进入可变区域。ⅲ If there is no bus within the critical distanceD , but the queuing length of vehicles in the variable area is equal toL , the pre-signal is displayed in red, and social vehicles are not allowed to enter the variable area.
(3) 在交叉口主信号绿灯时间内:(3) During the green time of the main signal at the intersection:
为保证公交车绝对优先权、且不影响交叉口主信号1原有信号配时方案及控制策略,交叉口主信号1在绿灯阶段内,预信号对社会车辆始终显示红灯,社会车辆不允许进入可变区域,如图4所示。In order to ensure the absolute priority of buses and not affect the original signal timing scheme and control strategy of intersection
【临界距离的计算】【Calculation of critical distance】
当道路交通状态发生变化时,则会形成冲击波。冲击波定义如下:Shock waves are formed when road traffic conditions change. A shock wave is defined as follows:
(1) (1)
其中,qi和qf分别为初始状态和最终状态的交通流量(辆/秒),ki和kf分别为初始状态和最终状态的交通密度(辆/米),vsw为冲击波速度(米/秒)。Among them,qi andqf are the traffic flow (vehicles/s) in the initial state and the final staterespectively, ki and kfarethe traffic density (vehicles/m) in the initial state and the final state respectively,vsw is the shock wave velocity ( m/s).
在队列释放过程中,初始状态和最终状态分别为qi= 0,ki= 1/dq和qf=qs,kf=1/dc,其中dq是车辆在队列中占据的平均空间(米/辆)。During queue release, the initial and final states areqi = 0,ki = 1/dq andqf =qs ,kf =1/dc , wheredq is the number of vehicles occupied in the queue Average space (m/vehicle).
当交叉口主信号变为绿灯时,队列的释放速度vd通过下式得到When the main signal at the intersection turns green, the release speedvd of the queue is obtained by the following formula
(2) (2)
在队列形成过程中,初始状态和最终状态分别为qi=q,其中q是交通流量(辆/秒),ki=q/vb,qf= 0,kf= 1/dq。由式(1),当交叉口主信号变为绿灯时,队列的形成速度vf可通过下式得到During queue formation, the initial state and final state are respectivelyqi =q , whereq is the traffic flow (vehicles/second),ki=q /vb ,qf = 0, andkf = 1/dq . From formula (1), when the main signal at the intersection turns green, the formation speedvf of the queue can be obtained by the following formula
(3) (3)
图5为一孤立交叉口交通时空图,用于表示社会车辆队列在可变区域内的形成和消散过程。以红灯开始的时刻和交叉口信号的位置为原点,建立坐标系。社会车辆队列的形成速度为vf,释放速度为vd,当交叉口主信号在tc秒后变为绿灯时,车辆队列的启动波与消散波相遇,此时,社会车辆队列形成的拥堵将完全消除。tc可通过下式得到Figure 5 is a traffic space-time diagram of an isolated intersection, which is used to represent the formation and dissipation process of social vehicle queues in the variable region. A coordinate system is established with the time when the red light starts and the position of the intersection signal as the origin. The formation speed of the social vehicle queue isvf , and the release speed isvd . When the main signal at the intersection turns green aftertc seconds, the starting wave of the vehicle queue meets the dissipating wave. At this time, the congestion formed by the social vehicle queue will be completely eliminated.tc can be obtained by
(4) (4)
此时,相应纵坐标位置为At this time, the corresponding ordinate position is
(5) (5)
假设在红灯开始时刻(ti= 0),距离交叉口xi处检测到一辆公交车,它将在交叉口主信号变绿时以速度vb沿着轨迹K通过交叉口。在这种情况下,公交车和交叉口之间的距离xi至少应为Rintvb,此时,预信号保持红灯。Suppose a bus is detected ata distancexi from the intersection at the red light start moment (ti = 0), and it will pass through the intersection with velocityvb along trajectoryK when the main signal at the intersection turns green. In this case, the distancexi between the bus and the intersection should be at leastRintvb , at which point the pre-signal remains red.
从图5时空图中可以看出,如果公交车经过灰色阴影区域,社会车辆会造成额外的排队延误。因此,通过提前检测公交车的位置,可以及时阻止社会车辆进入可变区域(预信号变为红色)。从图中可以看出,公交车在直线上的点以vb的速度启动,然后到达社会车辆的尾部。此时,队列中最后一辆社会车辆刚刚开始以自由速度行驶。因此,直线是公交车不受额外排队延误的关键条件。From the time-space diagram in Figure 5, it can be seen that if the bus passes through the gray shaded area, social vehicles will cause additional queuing delays. Therefore, by detecting the location of the bus in advance, the social vehicle can be prevented from entering the variable area in time (the pre-signal turns red). It can be seen from the figure that the bus starts at a point on the straight line with a speed ofvb , and then reaches the rear of the social vehicle. At this point, the last social vehicle in the queue has just started traveling at free speed. Therefore, a straight line is a key condition for buses not to be delayed by additional queuing.
假设即将到来的公交车的位置是(t0,x0)Suppose the location of the upcoming bus is (t0 ,x0 )
直线a x=vft (6)Lineax =vft (6)
直线b x=vd(t-Rint) (7)straight linebx=vd(t-Rint) (7)
直线c (8)straight linec (8)
直线K x-x0=-vb(t-t0) (9)straight lineK x-x0=-vb(t-t0) (9)
首先,需要确定当公交车到达临界距离时,社会车辆在可变区域形成的队列的长度为xg。First, it needs to be determined that when the bus reaches the critical distance, the length of the queue formed by social vehicles in the variable area isxg .
当可变区域的最后一辆社会车辆获得自由速度时,公交车到达队尾的临界时间tg可以通过联立式(7)和式(9)计算出来:When the last social vehicle in the variable area obtains free speed, the critical timetg for the bus to reach the tail of thequeue can be calculated by the simultaneous formula (7) and formula (9):
(10) (10)
然后可以通过将式(10)代入式(9)得到xg:xg can then be obtained by substituting equation (10) into equation (9):
(11) (11)
设tf为消耗的红灯时间,在此期间形成社会车辆的排队长度xg,那么有:Lettf be the consumed red light time, during which the queuing lengthxg of social vehicles is formed, then:
(12) (12)
因此,预信号和公交车之间的临界距离D可以通过将式(12)代入式(8)来计算:Therefore, the critical distanceD between the pre-signal and the bus can be calculated by substituting Equation (12) into Equation (8):
(13) (13)
其中,k=(xc-xi)/ tc。where,k = (xc -xi )/tc .
此外,若目标交叉口上游道路存在某些交通基础设施,临界距离需要做进一步修改。典型情形如下:In addition, if there is some traffic infrastructure on the upstream road of the target intersection, the critical distance needs to be further modified. A typical situation is as follows:
特殊情形1:临界距离范围内存在一交叉口。Special case 1: There is an intersection within the critical distance range.
如图6所示,临界距离与两相邻交叉口之间的距离da和相位差ta有关。如果tf(Rint-ta,da)≤tf(t0,x0),公交车的运动不受上游交叉口的影响,式(13)仍然适用。如果tf(t0,x0)<tf(Rint-ta,da)≤L/vf,公交车会因为红灯而停在上游交叉口,因此,社会车辆可被允许进入可变区域,增加的排队长度为xg(Rint-ta,da)-xg(t0,x0)。As shown in Figure 6, the critical distance is related to the distanceda and the phase differenceta between two adjacent intersections. Iftf (Rint -ta ,da ) ≤tf (t0 ,x0 ), the movement of the bus is not affected by the upstream intersection, and equation (13) still applies. Iftf (t0 ,x0 ) <tf (Rint -ta ,da ) ≤L /vf , the bus will stop at the upstream intersection because of the red light, so social vehicles can be allowed to enter Variable region, increasing queue lengthxg (Rint -ta ,da ) -xg (t0 ,x0 ).
此时,临界距离可以通过下式确定:At this time, the critical distance can be determined by the following formula:
(14) (14)
其中,k=(xc-xi)/ tc。where,k = (xc -xi )/tc .
特殊情形2:临界距离范围内存在一公交车站。Special case 2: There is a bus stop within the critical distance range.
如图7所示,公交车在站台的停留时间内,社会车辆可以进入可变区域。如果在位置(t0,x0)检测到一辆公交车,那么公交车的到达时间为tarrive= t0+(Rint vb-dstation)/vb,增加的排队长度为xg(tdepart,dstation)-xg(t0,x0),其中dstation为公交站与目标交叉口之间的距离;tdepart= tstay+tarrive为公交车离站时间,tstay为公交车在站台的平均停留时间。As shown in Figure 7, social vehicles can enter the variable area during the residence time of the bus on the platform. If a bus is detected at location (t0 ,x0 ), then the arrival time of the bus istarrive =t0 + (Rintvb -dstation )/vb , increasing the queue length byxg (tdepart ,dstation )-xg (t0 ,x0 ), wheredstation is the distance between the bus station and the target intersection;tdepart =tstay +tarrive is the bus departure time,tstay is the average dwell time of the bus at the platform.
此时,临界距离可以通过下式确定:At this time, the critical distance can be determined by the following formula:
(15) (15)
其中,k=(xc-xi)/ tc。where,k = (xc -xi )/tc .
本发明中将重点评估VBLAP策略使用前后交叉口的交通性能,并根据所得结果,进一步检验VBLAP策略的性能如何受到可能因素的影响,例如,可变区域长度,公交车的到达情况等。The present invention will focus on evaluating the traffic performance of the intersection before and after the use of the VBLAP strategy, and according to the obtained results, further test how the performance of the VBLAP strategy is affected by possible factors, such as the length of the variable area, the arrival of the bus, etc.
【实验参数】【Experimental parameters】
数值实验中使用的主要参数描述如下:The main parameters used in the numerical experiments are described as follows:
交叉口信号周期为80秒,绿灯和红灯时间均为40秒;The intersection signal period is 80 seconds, and the time for green and red lights is 40 seconds;
在有信号控制的交叉口有一条公交专用车道和一条普通车道;There is a bus-only lane and an ordinary lane at signalized intersections;
预信号的信号周期与交叉口信号相同;The signal period of the pre-signal is the same as that of the intersection signal;
每个时间间隔的长度为2秒,这里时间间隔取2秒已被广泛应用于各类交通排队模型中;The length of each time interval is 2 seconds, where the time interval of 2 seconds has been widely used in various traffic queuing models;
数值实验中的所有参数均满足交通强度小于1。All parameters in the numerical experiments satisfy that the traffic intensity is less than 1.
【使用VBLAP策略对交通性能的影响】【Impact of using VBLAP strategy on traffic performance】
为了考察VBLAP策略对信号交叉口交通性能的影响,本发明在相同的交通条件下对使用VBLAP策略前后的交叉口交通性能进行了以下分析。In order to examine the influence of the VBLAP strategy on the traffic performance of signalized intersections, the present invention conducts the following analysis on the traffic performance of the intersection before and after using the VBLAP strategy under the same traffic conditions.
假设在每个交叉口信号周期的红色时间内,停在可变区域的公交车的平均数量为1(即Z=1),公交车到达参数为1/20,这意味着在一个周期内平均有两辆公交车到达。对于社会车辆的不同交通需求,图8显示了使用VBLAP策略前后的交叉口交通性能,其中,可变区域的容量为10辆车。从图8(a)和8(b)可以看出,当社会车辆的需求量较低时,使用VBLAP策略前后的交叉口交通性能在排队长度和延误方面没有明显差异。Assume that during the red time of each intersection signal cycle, the average number of buses parked in the variable area is 1 (i.e.Z = 1), and the bus arrival parameter is 1/20, which means that in a cycle the average There are two buses arriving. For different traffic demands of social vehicles, Fig. 8 shows the intersection traffic performance before and after using the VBLAP strategy, where the capacity of the variable area is 10 vehicles. From Figures 8(a) and 8(b), it can be seen that when the demand of social vehicles is low, there is no significant difference in queue length and delay in the intersection traffic performance before and after using the VBLAP strategy.
但是,随着交通需求的增加,与使用VBLAP策略前相比,VBLAP策略可以显著减少系统中社会车辆的平均排队长度和平均延误。例如,在VBLAP策略下,当社会车辆的需求量为900(辆/时)时,社会车辆的平均延误不超过20秒,而在使用VBLAP策略前,当需求量为900(辆/时)时,平均延误达到80秒。如图8(c)所示,虽然在交叉口饱和状态下,两种策略在一个周期内的释放率大致相当,但在不使用VBLAP策略下的交叉口释放率随着交通需求量增加却不再增长。However, as the traffic demand increases, the VBLAP strategy can significantly reduce the average queue length and average delay of social vehicles in the system compared with before using the VBLAP strategy. For example, under the VBLAP strategy, when the demand of social vehicles is 900 (vehicles/hour), the average delay of social vehicles is no more than 20 seconds. , with an average delay of 80 seconds. As shown in Fig. 8(c), although the release rate of the two strategies in a cycle is roughly equivalent in the state of intersection saturation, the release rate of the intersection without VBLAP strategy does not increase with the increase of traffic demand. grow again.
此外,如图8(d)所示,当社会车辆需求量大时,使用VBLAP策略后社会车辆停车总数总是小于使用前的情形。这一结果的原因是,VBLAP策略可以使社会车辆在主信号绿灯结束时的残留车辆数显著降低,这可以从图8(e)的结果中证实。In addition, as shown in Fig. 8(d), when the social vehicle demand is large, the total number of social vehicle parking after using the VBLAP strategy is always smaller than the situation before using it. The reason for this result is that the VBLAP strategy can significantly reduce the number of residual vehicles of social vehicles at the end of the main signal green light, which can be confirmed from the results in Fig. 8(e).
事实上,绿灯结束时的残留车辆数是交叉口停车数量中一个非常重要的组成部分。此外,图8(f)所示的车辆最大排队长度表明,在交通需求量大的情况下,VBLAP策略可以减少对上游交叉口的溢出效应。In fact, the number of remaining vehicles at the end of the green light is a very important component of the number of stops at intersections. Furthermore, the maximum queuing length of vehicles shown in Fig. 8(f) shows that the VBLAP strategy can reduce the spillover effect to upstream intersections when traffic demand is high.
图8(g)进一步表明,在相同的交通需求下,采用VBLAP策略的交通强度总是低于使用VBLAP策略前的情形。图8(g)的结果表明,当交通流量达到900(辆/时)时,不使用VBLAP策略的交通强度开始接近1,这意味着如果交通需求继续增加,社会车辆在交叉口的排队长度将急剧增加,最终形成拥堵。然而,在使用VBLAP策略后,当流量为900(辆/时)时,交通强度仍小于0.9,直到交通需求大于1080(辆/时)时,交通强度才会达到1。Figure 8(g) further shows that under the same traffic demand, the traffic intensity with VBLAP strategy is always lower than the situation before using VBLAP strategy. The results in Fig. 8(g) show that when the traffic flow reaches 900 (vehicles/hour), the traffic intensity without using the VBLAP strategy begins to approach 1, which means that if the traffic demand continues to increase, the queuing length of social vehicles at the intersection will decrease increased sharply, eventually forming congestion. However, after using the VBLAP strategy, when the flow rate is 900 (vehicles/hour), the traffic intensity is still less than 0.9, and the traffic intensity will not reach 1 until the traffic demand is greater than 1080 (vehicles/hour).
以上结果都表明,当社会车辆在普通车道上的排队长度较小时,VBLAP策略对于减少社会车辆在普通车道上的排队长度和提高交叉口通行能力的效果并不明显,但当社会车辆交通需求较大时,VBLAP策略可以显著提高交叉口的服务性能。The above results show that when the queuing length of social vehicles on the common lane is small, the effect of the VBLAP strategy on reducing the queuing length of social vehicles on the common lane and improving the traffic capacity of the intersection is not obvious, but when the traffic demand of social vehicles is large When large, the VBLAP strategy can significantly improve the service performance at intersections.
图9进一步考察了不同交通需求下使用VBLAP策略前后在一个周期内各时刻的社会车辆排队队长。从结果可以看出,当饱和度较低时,使用VBLAP策略对社会车辆排队队长的改善并不明显。然而,当交通需求量大时,VBLAP策略可以在整个信号周期内显著减少社会车辆在信号交叉口的排队长度。Figure 9 further examines the queue length of social vehicles at each moment in a cycle before and after using the VBLAP strategy under different traffic demands. From the results, it can be seen that when the saturation is low, the improvement of the social vehicle queuing leader by using the VBLAP strategy is not obvious. However, when the traffic demand is high, the VBLAP strategy can significantly reduce the queuing length of social vehicles at signalized intersections throughout the signal period.
图10展示了在交叉口主信号配时、交通需求、可变区域长度和临界距离长度等相同条件下,交叉口主信号红灯开始时停车线前不同数量公交车对交叉口交通性能的影响。图10中的曲线表明,当社会车辆交通需求较大时,停车线前较多数量的公交车将导致交叉口处社会车辆更大的排队长度、延误和停车次数,同时,公交车数量的增加也会对释放率产生负面影响。但是,与使用VBLAP策略前的情形相比,VBLAP策略仍然可以显著改善交叉口交通性能。Figure 10 shows the influence of different numbers of buses before the stop line on the traffic performance of the intersection under the same conditions of intersection main signal timing, traffic demand, variable area length and critical distance length. . The curves in Figure 10 show that when the traffic demand of social vehicles is greater, a larger number of buses in front of the stop line will lead to greater queue lengths, delays, and parking times for social vehicles at intersections. At the same time, the increase in the number of buses It can also negatively affect the release rate. However, the VBLAP strategy can still significantly improve the intersection traffic performance compared to the situation before using the VBLAP strategy.
【可变区域长度对交通性能的影响】【Influence of variable area length on traffic performance】
可变区域的长度可能对VBLAP策略的性能带来影响。为此,本发明进一步考察不同社会车辆交通需求下,可变区域长度对VBLAP策略交通性能的影响,如图11所示,其中Z=1辆。The length of the variable region may have an impact on the performance of the VBLAP strategy. For this reason, the present invention further examines the influence of the length of the variable region on the traffic performance of the VBLAP strategy under different social vehicle traffic demands, as shown in Figure 11, where Z=1 vehicle.
图11(a)和图11(b)结果表明,对于低饱和度交叉口,可变区域长度对社会车辆的平均排队队长和平均延误并没有明显影响。然而,图11(c)和11(d)的结果表明,当饱和度增加到0.8或1时,随着可变区域长度的增加,社会车辆平均排队队长和平均延误均会降低。但当可变区域的长度继续增加时,上述性能指标又开始增加。在图11(d)中可以发现,当可变区域长度达到能容纳7辆车时,饱和度为1的情况下,社会车辆在交叉口的平均排队队长和平均延误均获得其最小值。此外,图11还表明,当社会车辆的交通需求较大时,采用VBLAP策略能有效缓解交通拥堵。这进一步表明在社会车辆交通需求较大时,使用VBLAP策略可以提升交叉口交通通行能力。而且,图11中结果也表明,可变区域长度对社会车辆的总停车次数亦有影响。The results in Fig. 11(a) and Fig. 11(b) show that for low-saturation intersections, the length of the variable area has no significant effect on the average queuing length and average delay of social vehicles. However, the results in Figures 11(c) and 11(d) show that when the saturation increases to 0.8 or 1, both the average queuing length and the average delay of social vehicles decrease as the length of the variable region increases. But when the length of the variable region continues to increase, the above performance indicators start to increase again. In Figure 11(d), it can be found that when the length of the variable area reaches 7 vehicles and the saturation is 1, the average queuing length and average delay of social vehicles at the intersection both obtain their minimum values. In addition, Figure 11 also shows that when the traffic demand of social vehicles is large, the use of VBLAP strategy can effectively alleviate traffic congestion. This further shows that when the social vehicle traffic demand is large, the use of VBLAP strategy can improve the traffic capacity of the intersection. Moreover, the results in Figure 11 also show that the length of the variable area also has an impact on the total parking times of social vehicles.
表1展示了在社会车辆需求量为850辆/时情况下,不同长度可变区域下其他详细交通性能指标。可以看出,除可变区域利用率(U)和交通负载强度(ρ)外,表1中各项指标值均呈现先降后升的趋势。在当前设定的交通状况下,可变区区域容量为7辆车的设计较为理想。Table 1 shows other detailed traffic performance indicators under different length variable areas under the condition that the social vehicle demand is 850 vehicles/hour. It can be seen that, except for the variable area utilization rate (U ) and traffic load intensity (ρ ), the values of all indicators in Table 1 show a trend of first falling and then rising. Under the currently set traffic conditions, the design of the variable area with a capacity of 7 vehicles is ideal.
表1 不同长度可变区域下的性能指标Table 1 Performance indicators under different length variable regions
由于信号交叉口绿灯与红灯交替出现,车辆平均排队队长无法反映出可变区域长度对交叉口社会车辆队列形成和消散过程的影响。为此,结合信号演化状态,图12进一步考察了当交通需求为850辆/时,不同长度可变区域情况下一个周期内车辆排队队长的演化过程,如图12(a)所示。图12(b)和12(c)进一步分别给出了图12(a)中绿灯阶段和红灯阶段的队长变化过程的投影。从图12中可以看出,对于不同长度的可变区域,社会车辆排队队长总是随着绿灯时间的推移而减少,进而在交叉口主信号的红灯时间内排队队长逐渐累积。可以发现,不同长度可变区域总会导致一个周期内各时刻的车辆排队队长不同。Since green lights and red lights appear alternately at signalized intersections, the average queue length of vehicles cannot reflect the influence of variable area length on the formation and dissipation of social vehicle queues at intersections. For this reason, combined with the signal evolution state, Fig. 12 further examines the evolution process of the vehicle queuing leader in a cycle under the condition of different length variable areas when the traffic demand is 850 vehicles/hour, as shown in Fig. 12(a). Figures 12(b) and 12(c) further show the projections of the team leader change process in the green light phase and red light phase in Figure 12(a) respectively. It can be seen from Figure 12 that for variable areas of different lengths, the queue length of social vehicles always decreases with the passage of the green light time, and then gradually accumulates during the red light time of the main signal at the intersection. It can be found that different length variable regions will always lead to different vehicle queuing lengths at each moment in a cycle.
此外,从图12(b)和12(c)可以看出,当可变区域容量设置为6辆车长度时,所提出的VBLAP策略可以在整个信号周期内显著减少社会车辆的排队队长。这进一步表明,恰当的可变区域长度设计更有利于缓解拥堵。Furthermore, it can be seen from Fig. 12(b) and 12(c) that when the variable area capacity is set to 6 vehicle lengths, the proposed VBLAP strategy can significantly reduce the queuing length of social vehicles during the entire signal period. This further shows that the appropriate variable area length design is more conducive to alleviating congestion.
【公交车到达过程对交叉口交通性能的影响】【Influence of bus arrival process on traffic performance at intersections】
在VBLAP策略下,预信号绿灯的激活还取决于公交车的到达过程。具体来说,在交叉口主信号红灯期间,当普通车道上的社会车辆排队队长超过可变区域长度时,如果有公交车到达临界距离,可变区域只能作为公交专用道使用,但当临界距离内没有公交车时,预信号会立即变绿,因此,可变区域会立即切换到普通车道。Under the VBLAP strategy, the activation of the pre-signal green light also depends on the bus arrival process. Specifically, during the red light period of the main signal at the intersection, when the queue length of social vehicles on the ordinary lane exceeds the length of the variable area, if a bus reaches the critical distance, the variable area can only be used as a bus-only lane, but when When there are no buses within the critical distance, the pre-signal will turn green immediately, so the variable area will immediately switch to the normal lane.
假设公交车到达临界距离过程遵循参数为p的Bernoulli实验。图13显示了当公交车到达参数p从0.1增加到0.9时,社会车辆在信号交叉口的排队演变过程,这里,社会车辆需求量为850辆/时,Z=1,可变区域容量为7辆车长度。图中结果表明,随着公交车到达参数p的增加,社会车辆在一个周期内各时刻的平均排队队长均迅速增加。例如,当公交车到达参数p为0.1时,社会车辆在交叉口信号绿灯结束时的排队长度仅为2.570辆;而当公交车到达参数p增加为0.7时,社会车辆在同一时刻的排队长度增加到5.110辆,这意味着在交叉口绿灯结束时至少有5辆车会被滞留。Assume that the process of the bus reaching the critical distance follows the Bernoulli experiment with parameterp . Figure 13 shows the queuing evolution of social vehicles at signalized intersections when the bus arrival parameterp increases from 0.1 to 0.9. Here, the demand for social vehicles is 850 vehicles/hour,Z = 1, and the variable area capacity is 7 vehicle length. The results in the figure show that with the increase of the bus arrival parameterp , the average queuing length of social vehicles at each moment in a cycle increases rapidly. For example, when the bus arrival parameterp is 0.1, the queue length of social vehicles at the end of the intersection signal green light is only 2.570 vehicles; and when the bus arrival parameterp increases to 0.7, the queue length of social vehicles at the same moment increases to 5.110 vehicles, which means at least 5 vehicles will be stranded at the end of the intersection green light.
为衡量公交车的到达过程对系统其他交通性能的影响,表2进一步给出了公交车不同到达参数p下的其他对应性能指标。从表2中可以看出,随着公交车到达参数p的增加,除可变区域最大利用率指标外,其他性能指标都有所提高。图13和表2所示的结果表明,VBLAP策略不适用于公交车高频率到达的专用车道,这也进一步印证了本发明提出的VBLAP策略的适用特点。In order to measure the impact of the bus arrival process on other traffic performance of the system, Table 2 further gives other corresponding performance indicators of the bus under different arrival parametersp . It can be seen from Table 2 that with the increase of the bus arrival parameterp , all other performance indicators are improved except for the variable area maximum utilization indicator. The results shown in Fig. 13 and Table 2 show that the VBLAP strategy is not suitable for the dedicated lanes where buses arrive frequently, which further confirms the applicable characteristics of the VBLAP strategy proposed by the present invention.
表2 不同的公交车到达过程下的性能指标Table 2 Performance indicators under different bus arrival processes
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211207768.7ACN115547046B (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | Control method for variable bus lane system with absolute priority of buses |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211207768.7ACN115547046B (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | Control method for variable bus lane system with absolute priority of buses |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115547046Atrue CN115547046A (en) | 2022-12-30 |
| CN115547046B CN115547046B (en) | 2024-06-11 |
Family
ID=84731675
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211207768.7AActiveCN115547046B (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | Control method for variable bus lane system with absolute priority of buses |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115547046B (en) |
Citations (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010098306A (en)* | 2000-04-29 | 2001-11-08 | 이흥수 | Method and apparatus for collecting traffic information by using a difference method |
| CN102071609A (en)* | 2011-01-11 | 2011-05-25 | 上海市城市建设设计研究院 | Crossing pre-signal lane |
| CN103198680A (en)* | 2013-04-25 | 2013-07-10 | 东南大学 | Green wave coordination control method for multiline public transport in main trunk line |
| CN103236164A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-08-07 | 东南大学 | Vehicle controlling method for guaranteeing public transport vehicle priority passing |
| CN103280112A (en)* | 2013-06-03 | 2013-09-04 | 东南大学 | Road canalization and signal coordination control method improving bus running efficiency |
| CN103295405A (en)* | 2013-07-03 | 2013-09-11 | 东南大学 | Crossing bus traffic priority control method based on special bus advanced area |
| JP2013228942A (en)* | 2012-04-26 | 2013-11-07 | Sumitomo Electric System Solutions Co Ltd | Traffic signal control device and computer program |
| DE102014215857A1 (en)* | 2014-08-11 | 2016-02-11 | Init Innovative Informatikanwendungen In Transport-, Verkehrs- Und Leitsystemen Gmbh | Procedure for guiding public transport passengers |
| CN105869417A (en)* | 2016-06-16 | 2016-08-17 | 兰州理工大学 | Traffic signal control method and system based on combined control |
| CN107016858A (en)* | 2017-05-12 | 2017-08-04 | 东南大学 | The pre-signal control method of Hou Shi areas and dislocation type stop line is flowed to a kind of intersection more |
| CN107067766A (en)* | 2017-06-20 | 2017-08-18 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Put pre-signal control method in a kind of intersection bus left-hand rotation right side |
| AU2017216548A1 (en)* | 2013-03-15 | 2017-09-07 | Balu Subramanya | Advanced parking and intersection management system |
| CN107230361A (en)* | 2017-07-06 | 2017-10-03 | 武汉理工大学 | One kind mixing public transportation lane real-time control system and method |
| WO2018072240A1 (en)* | 2016-10-20 | 2018-04-26 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Direction-variable lane control method for tidal traffic flow on road network |
| CN108122420A (en)* | 2017-12-19 | 2018-06-05 | 长沙理工大学 | A kind of medium-sized dynamic public transportation lane in road is emptied apart from setting method |
| CN109345844A (en)* | 2018-11-05 | 2019-02-15 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A pre-signal control method for the left-change lane of a bus parked at an intersection |
| CN109778599A (en)* | 2019-01-29 | 2019-05-21 | 兰州交通大学 | A method for in-situ intelligent determination of permeability coefficient under mudstone overburden load of high-speed railway foundation |
| KR20200025433A (en)* | 2018-08-30 | 2020-03-10 | (주)동림티엔에스 | Signal control system for bus-only lane |
| CN112735151A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2021-04-30 | 长安大学 | Road intersection multi-partition traffic organization method |
| CN113409599A (en)* | 2021-06-16 | 2021-09-17 | 河南省城乡规划设计研究总院股份有限公司 | Urban public transport priority coordination control method based on information prediction |
| US20220013011A1 (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2022-01-13 | Chang'an University | Method for berth allocation of a multiline bus station and speed guidance of buses |
| CN114419903A (en)* | 2021-12-17 | 2022-04-29 | 东南大学 | A method, device and vehicle for traffic control at intersection of intelligent networked vehicle queue |
| CN114554412A (en)* | 2022-04-26 | 2022-05-27 | 兰州交通大学 | A kind of bus information transmission system and method based on dynamic station |
| CN114913698A (en)* | 2022-04-26 | 2022-08-16 | 东南大学 | Time-space cooperative priority control method for induction and right transfer co-taking of bus signals without special lane |
| CN114944067A (en)* | 2022-05-16 | 2022-08-26 | 浙江海康智联科技有限公司 | Elastic bus lane implementation method based on vehicle-road cooperation |
- 2022
- 2022-09-30CNCN202211207768.7Apatent/CN115547046B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20010098306A (en)* | 2000-04-29 | 2001-11-08 | 이흥수 | Method and apparatus for collecting traffic information by using a difference method |
| CN102071609A (en)* | 2011-01-11 | 2011-05-25 | 上海市城市建设设计研究院 | Crossing pre-signal lane |
| JP2013228942A (en)* | 2012-04-26 | 2013-11-07 | Sumitomo Electric System Solutions Co Ltd | Traffic signal control device and computer program |
| AU2017216548A1 (en)* | 2013-03-15 | 2017-09-07 | Balu Subramanya | Advanced parking and intersection management system |
| CN103198680A (en)* | 2013-04-25 | 2013-07-10 | 东南大学 | Green wave coordination control method for multiline public transport in main trunk line |
| CN103236164A (en)* | 2013-04-28 | 2013-08-07 | 东南大学 | Vehicle controlling method for guaranteeing public transport vehicle priority passing |
| CN103280112A (en)* | 2013-06-03 | 2013-09-04 | 东南大学 | Road canalization and signal coordination control method improving bus running efficiency |
| CN103295405A (en)* | 2013-07-03 | 2013-09-11 | 东南大学 | Crossing bus traffic priority control method based on special bus advanced area |
| DE102014215857A1 (en)* | 2014-08-11 | 2016-02-11 | Init Innovative Informatikanwendungen In Transport-, Verkehrs- Und Leitsystemen Gmbh | Procedure for guiding public transport passengers |
| CN105869417A (en)* | 2016-06-16 | 2016-08-17 | 兰州理工大学 | Traffic signal control method and system based on combined control |
| WO2018072240A1 (en)* | 2016-10-20 | 2018-04-26 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Direction-variable lane control method for tidal traffic flow on road network |
| CN107016858A (en)* | 2017-05-12 | 2017-08-04 | 东南大学 | The pre-signal control method of Hou Shi areas and dislocation type stop line is flowed to a kind of intersection more |
| CN107067766A (en)* | 2017-06-20 | 2017-08-18 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Put pre-signal control method in a kind of intersection bus left-hand rotation right side |
| CN107230361A (en)* | 2017-07-06 | 2017-10-03 | 武汉理工大学 | One kind mixing public transportation lane real-time control system and method |
| CN108122420A (en)* | 2017-12-19 | 2018-06-05 | 长沙理工大学 | A kind of medium-sized dynamic public transportation lane in road is emptied apart from setting method |
| KR20200025433A (en)* | 2018-08-30 | 2020-03-10 | (주)동림티엔에스 | Signal control system for bus-only lane |
| CN109345844A (en)* | 2018-11-05 | 2019-02-15 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A pre-signal control method for the left-change lane of a bus parked at an intersection |
| CN109778599A (en)* | 2019-01-29 | 2019-05-21 | 兰州交通大学 | A method for in-situ intelligent determination of permeability coefficient under mudstone overburden load of high-speed railway foundation |
| US20220013011A1 (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2022-01-13 | Chang'an University | Method for berth allocation of a multiline bus station and speed guidance of buses |
| CN112735151A (en)* | 2020-12-29 | 2021-04-30 | 长安大学 | Road intersection multi-partition traffic organization method |
| CN113409599A (en)* | 2021-06-16 | 2021-09-17 | 河南省城乡规划设计研究总院股份有限公司 | Urban public transport priority coordination control method based on information prediction |
| CN114419903A (en)* | 2021-12-17 | 2022-04-29 | 东南大学 | A method, device and vehicle for traffic control at intersection of intelligent networked vehicle queue |
| CN114554412A (en)* | 2022-04-26 | 2022-05-27 | 兰州交通大学 | A kind of bus information transmission system and method based on dynamic station |
| CN114913698A (en)* | 2022-04-26 | 2022-08-16 | 东南大学 | Time-space cooperative priority control method for induction and right transfer co-taking of bus signals without special lane |
| CN114944067A (en)* | 2022-05-16 | 2022-08-26 | 浙江海康智联科技有限公司 | Elastic bus lane implementation method based on vehicle-road cooperation |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| 杨乔礼: "交叉口信号控制下交通流随机排队模型研究", 《中国博士学位论文全文数据库 工程科技Ⅱ辑》, 15 February 2020 (2020-02-15), pages 034 - 24* |
| 王予瑞: "考虑逆向可变车道的预信号公交优先控制", 《交通运输工程与信息学报》, 6 May 2021 (2021-05-06), pages 68 - 80* |
| 薛靖: "基于预信号的交叉口公交信号优先控制方法研究", 《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 工程科技Ⅱ辑》, 15 January 2022 (2022-01-15), pages 034 - 1060* |
| 邓明君: "基于公交优先与综合待行区的交叉口信号控制研究", 《重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版)》, 14 August 2020 (2020-08-14), pages 36 - 44* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115547046B (en) | 2024-06-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106920403B (en) | A kind of single-point self-adaptation control method based on array radar | |
| CN103794066B (en) | A kind of Bus Priority signal control method without dedicated bus lanes | |
| CN107798868A (en) | A kind of signalized intersections u-turn opening bit selecting method that traffic flow composition influences | |
| CN110910662B (en) | Single-point adaptive traffic signal optimization control method in vehicle-road coordination environment | |
| CN113538935B (en) | An inductive control method for optimizing bus punctuality in the environment without dedicated right of way | |
| CN104504918B (en) | A kind of urban road bus signals mode of priority | |
| CN109712414B (en) | Optimization method of multi-bandwidth trunk road bus control scheme | |
| CN104485005A (en) | Intersection multiline public traffic vehicle priority request conflict coordination control method | |
| CN113096419B (en) | Signal control method for serving vehicles to pass preferentially | |
| CN113506442B (en) | An urban road network traffic signal control method based on expected revenue estimation | |
| CN103680163A (en) | Regional bus signal priority method based on bus demands | |
| CN114155724B (en) | Intersection traffic signal control method in Internet of vehicles environment | |
| CN103065479B (en) | Method and system of controlling traffic signal of public transport priority | |
| CN108364486B (en) | Multi-scene vehicle priority self-adaptive traffic signal control system and working method thereof | |
| CN111932916B (en) | A control method and control system for dynamic emergency lane of urban road | |
| CN109215357B (en) | Priority control method for bus queue cutting at intersection based on speed detection | |
| CN104933877B (en) | Method for controlling bus priority and system based on bus platform parking information | |
| WO2013007075A1 (en) | Method and device for acquiring distributed duration for traffic lights | |
| CN112053580A (en) | Intersection bus signal priority control optimization method | |
| CN114639252A (en) | A method for setting the timing of signal lights for signal-controlled pedestrian crossings | |
| CN115311868A (en) | Bus priority-based trunk line coordination control method and device | |
| CN102063791A (en) | Public transport travelling control method by combining signal control with positioning monitoring | |
| CN105741585B (en) | The track of vehicle smooth control method based on car networking towards fuel-economizing | |
| CN110288844A (en) | A collaborative optimization method for continuous intersections based on vehicle-road communication | |
| CN115547046A (en) | Bus lane variable system control method with absolute priority |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |