CN115544902A - Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method - Google Patents
Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification methodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115544902A CN115544902ACN202211502787.2ACN202211502787ACN115544902ACN 115544902 ACN115544902 ACN 115544902ACN 202211502787 ACN202211502787 ACN 202211502787ACN 115544902 ACN115544902 ACN 115544902A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- risk level
- risk
- sample data
- data set
- level identification
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/20—Design optimisation, verification or simulation
- G06F30/27—Design optimisation, verification or simulation using machine learning, e.g. artificial intelligence, neural networks, support vector machines [SVM] or training a model
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/21—Design or setup of recognition systems or techniques; Extraction of features in feature space; Blind source separation
- G06F18/214—Generating training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/10—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2119/00—Details relating to the type or aim of the analysis or the optimisation
- G06F2119/02—Reliability analysis or reliability optimisation; Failure analysis, e.g. worst case scenario performance, failure mode and effects analysis [FMEA]
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P90/00—Enabling technologies with a potential contribution to greenhouse gas [GHG] emissions mitigation
- Y02P90/30—Computing systems specially adapted for manufacturing
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及药品风险监管技术领域,更具体地,涉及一种药店风险等级识别模型生成方法、药店风险等级识别方法、装置、电子设备和存储介质。The present application relates to the technical field of drug risk supervision, and more specifically, relates to a method for generating a pharmacy risk level identification model, a pharmacy risk level identification method, a device, an electronic device, and a storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
对药品销售的监管不到位可能致使重大药品安全事故发生。因此,为了能够及时发现药店存在的风险事件,需要对药店进行风险管理。Inadequate supervision of drug sales may lead to major drug safety accidents. Therefore, in order to be able to detect the risk events in the pharmacy in time, it is necessary to carry out risk management on the pharmacy.
在对药店进行风险管理的过程中,无可避免地需要确定药店的风险级别,而在相关技术中,药店风险等级的确定一般依赖于工作人员的个人经验,其结果具有一定的主观性,使得药店风险等级的识别精度较差。In the process of risk management for pharmacies, it is inevitable to determine the risk level of pharmacies, but in related technologies, the determination of risk levels of pharmacies generally depends on the personal experience of the staff, and the results are somewhat subjective, making The identification accuracy of pharmacy risk level is poor.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本申请提供了一种药店风险等级识别模型生成方法、药店风险等级识别方法、装置、电子设备和可读存储介质。In view of this, the present application provides a pharmacy risk level identification model generation method, a pharmacy risk level identification method, a device, an electronic device and a readable storage medium.
本申请的一个方面提供了一种药店风险等级识别模型生成方法,包括:采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,上述历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性;基于上述第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个上述药店的历史风险等级标签,确定上述第一样本数据集的第一信息熵;基于样本数据子集和上述历史风险等级标签来处理上述第一信息熵,得到上述样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,上述第一样本数据集包括多个上述样本数据子集,多个上述样本数据子集与多个上述风险特征属性一一对应;基于与多个上述风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值;以及基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个上述风险权值和上述历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。One aspect of the present application provides a method for generating a pharmacy risk level identification model, including: collecting historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies to obtain a first sample data set, wherein the above-mentioned historical business behavior data includes multiple risk characteristic attributes ; Based on the number of samples in the first sample data set and the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies, determine the first information entropy of the first sample data set; process based on the sample data subset and the historical risk level labels The above-mentioned first information entropy obtains the information gain rate of the above-mentioned sample data subset, wherein, the above-mentioned first sample data set includes a plurality of the above-mentioned sample data subsets, and the above-mentioned multiple sample data subsets are equal to the multiple above-mentioned risk characteristic attributes One-to-one correspondence; multiple risk weights are determined based on multiple information gain rates corresponding to multiple above-mentioned risk characteristic attributes; and based on the Bayesian algorithm, multiple above-mentioned risk weights and the above-mentioned historical risk level labels are used to generate Risk level identification model.
本申请的另一个方面提供了一种药店风险等级识别方法,包括:采集目标药店的目标业务行为数据,得到第一目标数据集;以及利用风险等级识别模型来处理上述第一目标数据集,得到上述目标药店的风险等级识别结果;其中,上述风险等级识别模型包括使用如上所述的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法来生成的。Another aspect of the present application provides a method for identifying a risk level of a pharmacy, including: collecting target business behavior data of a target pharmacy to obtain a first target data set; and using a risk level identification model to process the first target data set to obtain The above-mentioned risk level identification result of the target pharmacy; wherein, the above-mentioned risk level identification model is generated by using the above-mentioned pharmacy risk level identification model generation method.
本申请的另一个方面提供了一种药店风险等级识别模型生成装置,包括:第一采集模块,用于采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,上述历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性;第一确定模块,用于基于上述第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个上述药店的历史风险等级标签,确定上述第一样本数据集的第一信息熵;第一处理模块,用于基于样本数据子集和上述历史风险等级标签来处理上述第一信息熵,得到上述样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,上述第一样本数据集包括多个上述样本数据子集,多个上述样本数据子集与多个上述风险特征属性一一对应;第二确定模块,用于基于与多个上述风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值;以及第一生成模块,用于基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个上述风险权值和上述历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。Another aspect of the present application provides a pharmacy risk level identification model generation device, including: a first collection module, used to collect historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies to obtain a first sample data set, wherein the above-mentioned historical business The behavior data includes a plurality of risk characteristic attributes; the first determination module is configured to determine the first information of the first sample data set based on the number of samples in the first sample data set and the historical risk level labels of a plurality of the above-mentioned pharmacies Entropy; a first processing module, configured to process the above-mentioned first information entropy based on the sample data subset and the above-mentioned historical risk level label to obtain the information gain rate of the above-mentioned sample data subset, wherein the above-mentioned first sample data set includes multiple The above-mentioned sample data subsets, the plurality of the above-mentioned sample data subsets are in one-to-one correspondence with the plurality of the above-mentioned risk characteristic attributes; determining a plurality of risk weights; and a first generating module, configured to generate a risk level identification model based on a Bayesian algorithm by using the plurality of risk weights and the historical risk level labels.
本申请的另一个方面提供了一种药店风险等级识别装置,包括:第二采集模块,用于采集目标药店的目标业务行为数据,得到第一目标数据集;以及第二处理模块,用于利用风险等级识别模型来处理上述第一目标数据集,得到上述目标药店的风险等级识别结果;其中,上述风险等级识别模型包括使用如上所述的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法来生成的。Another aspect of the present application provides a drugstore risk level identification device, including: a second collection module, used to collect target business behavior data of a target pharmacy to obtain a first target data set; and a second processing module, used to use A risk level identification model is used to process the first target data set to obtain the risk level identification result of the target pharmacy; wherein, the risk level identification model is generated by using the method for generating a pharmacy risk level identification model as described above.
本申请的另一方面提供了一种电子设备,包括:一个或多个处理器;存储器,用于存储一个或多个指令,其中,当上述一个或多个指令被上述一个或多个处理器执行时,使得上述一个或多个处理器实现如上所述的方法。Another aspect of the present application provides an electronic device, including: one or more processors; memory for storing one or more instructions, wherein, when the above one or more instructions are executed by the above one or more processors When executed, the above-mentioned one or more processors are made to implement the above-mentioned method.
本申请的另一方面提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,存储有计算机可执行指令,上述指令在被执行时用于实现如上所述的方法。Another aspect of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium storing computer-executable instructions, which are used to implement the above-mentioned method when executed.
根据本申请的实施例,在进行风险等级识别模型的生成时,可以基于采集得到的第一样本数据集和历史风险等级标签来计算该第一样本数据集的第一信息熵,再基于第一信息熵来确定各个风险特征属性的信息增益率,然后,可以利用各个风险特征属性的信息增益率来确定各个风险特征属性的风险权值,该风险权值可以与基于贝叶斯算法确定的概率模型进行结合,以得到风险等级识别模型。通过对熵权法和贝叶斯算法的改进,即使用信息增益率取代信息增益作为风险权值的计算依据,并在贝叶斯算法中加入了利用风险权值进行加权运算的操作,可以有效降低样本不均衡对模型识别精度的影响,通过使用模型进行风险等级识别的方法,可以至少部分地克服相关技术中药店风险等级的识别精度较差的问题,可以有效降低实施成本,提高风险等级识别精度。According to an embodiment of the present application, when generating a risk level identification model, the first information entropy of the first sample data set can be calculated based on the collected first sample data set and historical risk level labels, and then based on The first information entropy is used to determine the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute, and then, the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute can be used to determine the risk weight of each risk characteristic attribute, and the risk weight can be determined based on the Bayesian algorithm The probability model of the risk level is combined to obtain the risk level identification model. By improving the entropy weight method and the Bayesian algorithm, that is, using the information gain rate instead of the information gain as the basis for calculating the risk weight, and adding the operation of using the risk weight to carry out weighted operations in the Bayesian algorithm, it can effectively To reduce the impact of sample imbalance on model identification accuracy, by using the model for risk level identification, the problem of poor identification accuracy of pharmacy risk levels in related technologies can be at least partially overcome, which can effectively reduce implementation costs and improve risk level identification. precision.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过以下参照附图对本申请实施例的描述,本申请的上述以及其他目的、特征和优点将更为清楚,在附图中:Through the following description of the embodiments of the application with reference to the accompanying drawings, the above and other purposes, features and advantages of the application will be more clear, in the accompanying drawings:
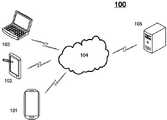
图1示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的可以应用药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法及装置的示例性系统架构。Fig. 1 schematically shows an exemplary system architecture in which a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy or a method and device for identifying a risk level for a pharmacy can be applied according to an embodiment of the present application.
图2示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 2 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
图3示意性示出了根据本申请另一实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 3 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to another embodiment of the present application.
图4示意性示出了根据本申请又一实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 4 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to yet another embodiment of the present application.
图5示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别方法的流程图。Fig. 5 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for identifying a risk level of a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
图6示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成装置的框图。Fig. 6 schematically shows a block diagram of a device for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
图7示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别装置的框图。Fig. 7 schematically shows a block diagram of a drugstore risk level identification device according to an embodiment of the present application.
图8示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的适于实现药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法的电子设备的框图。Fig. 8 schematically shows a block diagram of an electronic device adapted to implement a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy or a method for identifying a risk level for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式detailed description
以下,将参照附图来描述本申请的实施例。但是应该理解,这些描述只是示例性的,而并非要限制本申请的范围。在下面的详细描述中,为便于解释,阐述了许多具体的细节以提供对本申请实施例的全面理解。然而,明显地,一个或多个实施例在没有这些具体细节的情况下也可以被实施。此外,在以下说明中,省略了对公知结构和技术的描述,以避免不必要地混淆本申请的概念。Hereinafter, embodiments of the present application will be described with reference to the drawings. However, it should be understood that these descriptions are only exemplary and not intended to limit the scope of the present application. In the following detailed description, for purposes of explanation, numerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the embodiments of the present application. It may be evident, however, that one or more embodiments may be practiced without these specific details. Also, in the following description, descriptions of well-known structures and techniques are omitted to avoid unnecessarily obscuring the concept of the present application.
在此使用的术语仅仅是为了描述具体实施例,而并非意在限制本申请。在此使用的术语“包括”、“包含”等表明了所述特征、步骤、操作和/或部件的存在,但是并不排除存在或添加一个或多个其他特征、步骤、操作或部件。The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only, and is not intended to limit the application. The terms "comprising", "comprising", etc. used herein indicate the presence of stated features, steps, operations and/or components, but do not exclude the presence or addition of one or more other features, steps, operations or components.
在此使用的所有术语(包括技术和科学术语)具有本领域技术人员通常所理解的含义,除非另外定义。应注意,这里使用的术语应解释为具有与本说明书的上下文相一致的含义,而不应以理想化或过于刻板的方式来解释。All terms (including technical and scientific terms) used herein have the meanings commonly understood by those skilled in the art, unless otherwise defined. It should be noted that the terms used herein should be interpreted to have a meaning consistent with the context of this specification, and not be interpreted in an idealized or overly rigid manner.
在使用类似于“A、B和C等中至少一个”这样的表述的情况下,一般来说应该按照本领域技术人员通常理解该表述的含义来予以解释(例如,“具有A、B和C中至少一个的系统”应包括但不限于单独具有A、单独具有B、单独具有C、具有A和B、具有A和C、具有B和C、和/或具有A、B、C的系统等)。在使用类似于“A、B或C等中至少一个”这样的表述的情况下,一般来说应该按照本领域技术人员通常理解该表述的含义来予以解释(例如,“具有A、B或C中至少一个的系统”应包括但不限于单独具有A、单独具有B、单独具有C、具有A和B、具有A和C、具有B和C、和/或具有A、B、C的系统等)。Where expressions such as "at least one of A, B, and C, etc." are used, they should generally be interpreted as those skilled in the art would normally understand the expression (for example, "having A, B, and C A system of at least one of "shall include, but not be limited to, systems with A alone, B alone, C alone, A and B, A and C, B and C, and/or A, B, C, etc. ). Where an expression such as "at least one of A, B, or C, etc." is used, it should generally be interpreted in accordance with the meaning that those skilled in the art would normally understand the expression (for example, "having A, B, or C A system of at least one of "shall include, but not be limited to, systems with A alone, B alone, C alone, A and B, A and C, B and C, and/or A, B, C, etc. ).
在本申请的技术方案中,所涉及的用户个人信息的获取,存储和应用等,均符合相关法律法规的规定,采取了必要保密措施,且不违背公序良俗。In the technical solution of this application, the acquisition, storage and application of the user's personal information involved are in compliance with relevant laws and regulations, necessary confidentiality measures have been taken, and they do not violate public order and good customs.
在本申请的技术方案中,在获取或采集用户个人信息之前,均获取了用户的授权或同意。In the technical solution of this application, before obtaining or collecting the user's personal information, the authorization or consent of the user is obtained.
对药品销售的监管不到位可能致使重大药品安全事故发生。例如,如果有用户购买含麻药品超量,则将该用品用于非法行为的风险就较高。因此,为了能够及时发现药店存在的风险事件,需要对药店进行风险管理。Inadequate supervision of drug sales may lead to major drug safety accidents. For example, if a user purchases an overdose of a drug containing narcotics, there is a higher risk that the item will be used for illegal activities. Therefore, in order to be able to detect the risk events in the pharmacy in time, it is necessary to carry out risk management on the pharmacy.
在对药店进行风险管理的过程中,无可避免地需要确定药店的风险级别,然而,由于现有的药店的进销存系统和仓库管理系统没有统一的标准,不同药店的系统之间信息孤岛现象严重,导致相关部门无法实时检测药店的风险级别。目前,针对药店的风险级别的主要检测手段依赖于工作人员到店检查经营漏洞、登记违规项以及人工记录检查结果,但这种工作方式主要依赖于工作人员的人为经验,检查结果存在一定的主观性,且即使耗费了大量的人力和物力资源,也无法及时发现药店存在的风险事件,药店风险等级的识别精度较差。In the process of risk management for pharmacies, it is inevitable to determine the risk level of pharmacies. However, due to the lack of uniform standards for the existing pharmacy inventory system and warehouse management system, information islands between different pharmacy systems The phenomenon is so serious that the relevant departments cannot detect the risk level of the pharmacy in real time. At present, the main detection method for the risk level of pharmacies relies on the staff to check the business loopholes, register violations and manually record the inspection results. However, this working method mainly relies on the human experience of the staff, and the inspection results are somewhat subjective. Even if a lot of manpower and material resources are spent, it is impossible to detect the risk events in the pharmacy in time, and the identification accuracy of the risk level of the pharmacy is poor.
有鉴于此,本申请的实施例提供了一种药店风险等级识别模型生成方法、药店风险等级识别方法、装置、电子设备和可读存储介质。其中,药店风险等级识别模型生成方法包括:采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性;基于第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第一样本数据集的第一信息熵;基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来处理第一信息熵,得到样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,第一样本数据集包括多个样本数据子集,多个样本数据子集与多个风险特征属性一一对应;基于与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值;以及基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。In view of this, the embodiments of the present application provide a pharmacy risk level identification model generation method, a pharmacy risk level identification method, a device, an electronic device, and a readable storage medium. Among them, the generation method of the pharmacy risk level identification model includes: collecting historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies to obtain the first sample data set, wherein the historical business behavior data includes a plurality of risk characteristic attributes; based on the first sample data set The number of samples and the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies determine the first information entropy of the first sample data set; process the first information entropy based on the sample data subset and historical risk level labels to obtain the information gain of the sample data subset rate, wherein the first sample data set includes a plurality of sample data subsets, and the plurality of sample data subsets are in one-to-one correspondence with a plurality of risk characteristic attributes; based on a plurality of information gain ratios corresponding to a plurality of risk characteristic attributes , determining multiple risk weights; and using multiple risk weights and historical risk level labels to generate a risk level identification model based on the Bayesian algorithm.
图1示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的可以应用药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法及装置的示例性系统架构。需要注意的是,图1所示仅为可以应用本申请实施例的系统架构的示例,以帮助本领域技术人员理解本申请的技术内容,但并不意味着本申请实施例不可以用于其他设备、系统、环境或场景。Fig. 1 schematically shows an exemplary system architecture in which a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy or a method and device for identifying a risk level for a pharmacy can be applied according to an embodiment of the present application. It should be noted that Figure 1 is only an example of the system architecture to which the embodiment of the present application can be applied, to help those skilled in the art understand the technical content of the present application, but it does not mean that the embodiment of the present application cannot be used in other device, system, environment or scenario.
如图1所示,根据该实施例的系统架构100可以包括终端设备101、102、103,网络104和服务器105。As shown in FIG. 1 , a
终端设备101、102、103可以是各种电子设备,包括但不限于智能手机、平板电脑、膝上型便携计算机和台式计算机等等。终端设备101、102、103上可以存储有药店的业务行为数据,或者,终端设备101、102、103可以通过有线或无线通信链路从外部存储设备中获取药店的业务行为数据。The
网络104用以在终端设备101、102、103和服务器105之间提供通信链路的介质。网络104可以包括各种连接类型,例如有线和/或无线通信链路等等。The
服务器105可以是提供各种服务的服务器,例如对用户利用终端设备101、102、103实施的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法提供计算资源及存储资源的支持。作为可选的实施方式,服务器也可以是云服务器,又称为云计算服务器或云主机,是云计算服务体系中的一项主机产品,以解决了传统物理主机与VPS服务(“VirtualPrivate Server”,或简称“VPS”)中,存在的管理难度大,业务扩展性弱的缺陷。服务器也可以为分布式系统的服务器,或者是结合了区块链的服务器。The
需要说明的是,本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法一般可以由服务器105执行。相应地,本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成装置或药店风险等级识别装置一般可以设置于服务器105中。本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法也可以由不同于服务器105且能够与终端设备101、102、103和/或服务器105通信的服务器或服务器集群执行。相应地,本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成装置或药店风险等级识别装置也可以设置于不同于服务器105且能够与终端设备101、102、103和/或服务器105通信的服务器或服务器集群中。或者,本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法也可以由终端设备101、102、或103执行,或者也可以由不同于终端设备101、102、或103的其他终端设备执行。相应地,本申请实施例所提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成装置或药店风险等级识别装置也可以设置于终端设备101、102、或103中,或设置于不同于终端设备101、102、或103的其他终端设备中。It should be noted that the method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy or the method for identifying a risk level for a pharmacy provided in the embodiment of the present application can generally be executed by the
例如,在进行风险等级识别模型的生成时,用户可以通过终端设备101从外部设备中获取历史业务行为数据,将该历史业务行为数据发送给服务器105后,服务器105可以执行本申请实施例提供的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法来生成风险等级识别模型。For example, when generating a risk level identification model, the user can obtain historical business behavior data from an external device through the
应该理解,图1中的终端设备、网络和服务器的数目仅仅是示意性的。根据实现需要,可以具有任意数目的终端设备、网络和服务器。It should be understood that the numbers of terminal devices, networks and servers in Fig. 1 are only illustrative. According to the implementation needs, there can be any number of terminal devices, networks and servers.
图2示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 2 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
如图2所示,该方法包括操作S201~S205。As shown in Fig. 2, the method includes operations S201-S205.
在操作S201,采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性。In operation S201, historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies are collected to obtain a first sample data set, wherein the historical business behavior data includes multiple risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S202,基于第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第一样本数据集的第一信息熵。In operation S202, based on the number of samples in the first sample data set and the historical risk level labels of a plurality of pharmacies, a first information entropy of the first sample data set is determined.
在操作S203,基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来处理第一信息熵,得到样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,第一样本数据集包括多个样本数据子集,多个样本数据子集与多个风险特征属性一一对应。In operation S203, the first information entropy is processed based on the sample data subset and the historical risk level label to obtain the information gain rate of the sample data subset, wherein the first sample data set includes multiple sample data subsets, and multiple sample data sets The data subsets are in one-to-one correspondence with multiple risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S204,基于与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值。In operation S204, a plurality of risk weights are determined based on a plurality of information gain rates corresponding one-to-one to a plurality of risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S205,基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。In operation S205, a risk level identification model is generated by using multiple risk weights and historical risk level labels based on the Bayesian algorithm.
根据本申请的实施例,多个药店可以指具有相同的主营业务的多个药店,主营业务可以指处方药品经营业务、非处方药品经营业务、中草药经营业务等。采集具有相同主营业务的多个药店的历史行为数据,可以使得不同药店的历史业务行为数据中所包含的风险特征属性属于同一维度。According to the embodiment of the present application, multiple pharmacies may refer to multiple pharmacies with the same main business, and the main business may refer to prescription drug business, non-prescription drug business, Chinese herbal medicine business, etc. Collecting the historical behavior data of multiple pharmacies with the same main business can make the risk characteristic attributes contained in the historical business behavior data of different pharmacies belong to the same dimension.
根据本申请的实施例,历史业务行为数据中包含的风险特征属性可以包括进销存数据的完备性、近效期药品的数量、执业药师考勤数据、许可证数据、电子处方完备性和含麻药品登记情况等。历史业务行为数据中的每一条数据可以和以上任意一项风险特征属性相关,例如,近效期药品这一风险特征属性可以与药品的进销存数据相关,具体与进销存数据中的药片生成日期数据、药片有效期数据等相关。According to the embodiment of the present application, the risk characteristic attributes contained in the historical business behavior data may include the completeness of purchase, sales and inventory data, the quantity of medicines with near expiration date, licensed pharmacist attendance data, license data, electronic prescription completeness and Drug registration status, etc. Each piece of data in the historical business behavior data can be related to any one of the above risk characteristic attributes. For example, the risk characteristic attribute of a drug with a short-term expiration date can be related to the purchase, sales and inventory data of the drug, specifically the tablet in the purchase, sales and inventory data. Generate date data, tablet expiration date data, etc.
根据本申请的实施例,药店的历史风险等级标签可以包括基于该药店的历史业务行为数据中的每一条记录所确定的标签值,该标签值可以认为标定,也可以是基于现有的标签生成方法来确定,在此不作限定。According to the embodiment of this application, the historical risk level label of the pharmacy may include a label value determined based on each record in the historical business behavior data of the pharmacy. method to determine, not limited here.
根据本申请的实施例,风险等级的数量及划分标准可以根据具体应用场景进行选择,在此不作限定。在一些实施例中,在多个药店的历史风险等级标签是基于不同的划分标准来确定的情况下,在执行操作S202的方法之前,还可以包括将多个药店的历史风险等级标签统一为某一标准下的风险等级标签的操作。According to the embodiment of the present application, the number of risk levels and classification criteria can be selected according to specific application scenarios, which are not limited here. In some embodiments, in the case that the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies are determined based on different classification criteria, before performing the method of operation S202, it may also include unifying the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies into a certain The operation of the risk level label under a standard.
根据本申请的实施例,第一信息熵可以用于描述第一样本数据集的不确定程度。第一信息熵可以根据第一样本数据集中每个风险等级的出现次数来确定,如公式(1)所示:According to an embodiment of the present application, the first information entropy may be used to describe the degree of uncertainty of the first sample data set. The first information entropy can be determined according to the number of occurrences of each risk level in the first sample data set, as shown in formula (1):
在式(1)中,S表示第一样本数据集;E(S)可以表示第一信息熵;n1可以表示风险等级的数量;N1可以表示第一样本数据集中样本的数量,每个样本可以表示为历史业务行为数据中的一条记录;N1[i]可以表示第i个风险等级出现的次数。In formula (1), S represents the first sample data set; E(S) can represent the first information entropy; n1 can represent the number of risk levels; N1 can represent the number of samples in the first sample data set, each A sample can be represented as a record in historical business behavior data; N1[i] can represent the number of occurrences of the i-th risk level.
根据本申请的实施例,第一样本数据集S可以包括多个样本数据子集S1,…,Sm,其中,m表示风险特征属性的数量,第i个样本数据子集Si可以和第i个风险特征属性相关。According to an embodiment of the present application, the first sample data set S may include multiple sample data subsets S1 ,...,Sm , where m represents the number of risk characteristic attributes, and the i-th sample data subset Si may be The i-th risk characteristic attribute is related.
根据本申请的实施例,信息增益率可以是将信息增益消除偏好属性后得到的,通过利用信息增益率来计算权值,可以避免因样本的不均衡而带来的对样本数量较多的特征的偏好。According to the embodiment of the present application, the information gain rate can be obtained by eliminating the preference attribute from the information gain. By using the information gain rate to calculate the weight, it is possible to avoid the characteristics of a large number of samples caused by the imbalance of samples. Preferences.
根据本申请的实施例,风险等级识别模型可以是基于概率模型生成的,该概率模型可以包含至少一个由贝叶斯算法确定的函数,多个风险权值和历史风险等级标签可以作为参数填入该至少一个函数中,以得到风险等级识别模型。According to an embodiment of the present application, the risk level identification model can be generated based on a probability model, and the probability model can include at least one function determined by the Bayesian algorithm, and multiple risk weights and historical risk level labels can be filled in as parameters In the at least one function, a risk level identification model is obtained.
根据本申请的实施例,在进行风险等级识别模型的生成时,可以基于采集得到的第一样本数据集和历史风险等级标签来计算该第一样本数据集的第一信息熵,再基于第一信息熵来确定各个风险特征属性的信息增益率,然后,可以利用各个风险特征属性的信息增益率来确定各个风险特征属性的风险权值,该风险权值可以与基于贝叶斯算法确定的概率模型进行结合,以得到风险等级识别模型。通过对熵权法和贝叶斯算法的改进,即使用信息增益率取代信息增益作为风险权值的计算依据,并在贝叶斯算法中加入了利用风险权值进行加权运算的操作,可以有效降低样本不均衡对模型识别精度的影响,通过使用模型进行风险等级识别的方法,可以至少部分地克服相关技术中药店风险等级的识别精度较差的问题,可以有效降低实施成本,提高风险等级识别精度。According to an embodiment of the present application, when generating a risk level identification model, the first information entropy of the first sample data set can be calculated based on the collected first sample data set and historical risk level labels, and then based on The first information entropy is used to determine the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute, and then, the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute can be used to determine the risk weight of each risk characteristic attribute, and the risk weight can be determined based on the Bayesian algorithm The probability model of the risk level is combined to obtain the risk level identification model. By improving the entropy weight method and the Bayesian algorithm, that is, using the information gain rate instead of the information gain as the basis for calculating the risk weight, and adding the operation of using the risk weight to carry out weighted operations in the Bayesian algorithm, it can effectively To reduce the impact of sample imbalance on model identification accuracy, by using the model for risk level identification, the problem of poor identification accuracy of pharmacy risk levels in related technologies can be at least partially overcome, which can effectively reduce implementation costs and improve risk level identification. precision.
下面参考图3~图4,结合具体实施例对图2所示的方法做进一步说明。The method shown in FIG. 2 will be further described in conjunction with specific embodiments below with reference to FIGS. 3 to 4 .
根据本申请的实施例,操作S203可以包括如下操作:According to an embodiment of the present application, operation S203 may include the following operations:
对于每个样本数据子集,基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来确定样本数据子集的第二信息熵和样本数据子集针对第一样本数据集的条件熵;基于条件熵和第一信息熵,确定样本数据子集的信息增益;以及基于样本数据子集的信息增益和第二信息熵,确定样本数据子集的信息增益率。For each sample data subset, determine the second information entropy of the sample data subset and the conditional entropy of the sample data subset for the first sample data set based on the sample data subset and the historical risk level label; an information entropy, determining an information gain of the sample data subset; and determining an information gain rate of the sample data subset based on the information gain of the sample data subset and a second information entropy.
根据本申请的实施例,每一项风险特征属性可以包括多个子特征属性,例如,对于电子处方完备性这一风险特征属性,可以包括电子处方的开方人、药品种类及数量、使用注意事项等子特征属性。According to the embodiment of this application, each risk characteristic attribute may include multiple sub-characteristic attributes. For example, for the risk characteristic attribute of electronic prescription completeness, it may include the person who prescribes the electronic prescription, the type and quantity of the drug, and precautions for use. and other sub-feature attributes.
根据本申请的实施例,对于样本数据子集Si,其针对第一样本数据集的条件熵可以由样本数据子集Si中每一个子特征属性出现的次数,即每一个子特征属性被判定为各个风险等级的次数来确定,如公式(2)所示:According to the embodiment of the present application, for the sample data subset Si , its conditional entropy for the first sample data set can be determined by the number of occurrences of each sub-feature attribute in the sample data subset Si , that is, each sub-feature attribute It is determined by the number of times it is judged as each risk level, as shown in formula (2):
在式(2)中,E(S|Si)可以表示样本数据子集Si针对第一样本数据集S的条件熵;N3[j][k]可以表示样本数据子集Si的第j个子特征属性被判定为第k个风险等级的次数;n2可以表示对应于样本数据子集Si的风险特征属性包含的子特征属性的数量;N2[j]可以表示第j个子特征属性的出现次数;N2可以表示样本数据子集Si中包含的样本数量。In formula (2), E(S|Si ) can represent the conditional entropy of the sample data subset Si for the first sample data set S; N3[j][k] can represent the conditional entropy of the sample data subset Si The number of times that the j-th sub-feature attribute is judged as the k-th risk level; n2 can represent the number of sub-feature attributes contained in the risk feature attribute corresponding to the sample data subset Si ; N2[j] can represent the j-th sub-feature attribute The number of occurrences; N2 can represent the number of samples contained in the sample data subset Si .
根据本申请的实施例,在式(2)中,对于任意的j和k的取值,满足N2[j]≠0且N3[j][k]≠0,即在进行条件熵的计算时,仅对具有数据记录的子特征属性及相应的风险等级进行统计。According to the embodiment of this application, in formula (2), for any value of j and k, N2[j]≠0 and N3[j][k]≠0 are satisfied, that is, when calculating the conditional entropy , only count the sub-feature attributes with data records and the corresponding risk levels.
根据本申请的实施例,样本数据子集Si的信息增益可以通过公式(3)计算得到:According to the embodiment of the present application, the information gain of the sample data subset Si can be calculated by formula (3):
在式(3)中,g'(S|Si)可以表示样本数据子集Si的信息增益。In formula (3), g'(S|Si ) can represent the information gain of the sample data subset Si .
根据本申请的实施例,由于信息增益会随着包含的样本数量的增多而增大,使得基于信息增益计算得到的风险权值在面对不同数量的样本时的表达能力较差,因此,可以通过引入与信息增益具有相同趋势的惩罚项,即第二信息熵来计算信息增益率,并通过信息增益率来计算风险权值的方式,来避免上述影响。According to the embodiment of the present application, since the information gain increases with the number of included samples, the risk weight calculated based on the information gain has poor expressiveness when faced with different numbers of samples. Therefore, it can be The above effects are avoided by introducing a penalty term with the same tendency as information gain, that is, the second information entropy to calculate the information gain rate, and calculate the risk weight value through the information gain rate.
根据本申请的实施例,对于样本数据子集Si,其第二信息熵可以由该样本数据子集Si中每一个子特征属性出现的次数来确定,如公式(4)所示:According to the embodiment of the present application, for the sample data subset Si , its second information entropy can be determined by the number of occurrences of each sub-feature attribute in the sample data subset Si , as shown in formula (4):
在式(4)中,E(Si)可以表示样本数据子集Si的第二信息熵。In formula (4), E(Si ) may represent the second information entropy of the sample data subset Si .
根据本申请的实施例,样本数据子集Si的信息增益率可以通过公式(5)计算得到:According to the embodiment of the present application, the information gain rate of the sample data subset Si can be calculated by formula (5):
在式(5)中,gr'(S|Si)可以表示样本数据子集Si的信息增益率。In formula (5), gr '(S|Si ) canrepresent the information gain rate of the sample data subset S i.
根据本申请的实施例,在操作S204中,基于多个信息增益率来确定样本数据子集Si的风险权值可以如公式(6)所示:According to an embodiment of the present application, in operation S204, determining the risk weight of the sample data subset Si based on multiple information gain ratios may be as shown in formula (6):
在式(6)中,wi可以表示样本数据子集Si的风险权值。In formula (6), wi can represent the risk weight of the sample data subset Si .
根据本申请的实施例,通过采用利用信息增益率来计算风险权值的方式,可以避免因样本的不均衡带来的对样本数量多的特征的偏好,从而提高风险权值的表达能力及风险等级识别模型的鲁棒性。According to the embodiment of the present application, by using the information gain rate to calculate the risk weight, it is possible to avoid the preference for features with a large number of samples due to the imbalance of the sample, thereby improving the expressiveness and risk of the risk weight. Robustness of grade recognition models.
根据本申请的实施例,操作S205可以包括如下操作:According to an embodiment of the present application, operation S205 may include the following operations:
基于多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定多个风险等级中每个风险等级的历史概率;对于每个风险等级,基于多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定多个风险特征属性中每个风险特征属性的后验概率;以及基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值、多个历史概率和多个后验概率来生成风险等级识别模型。Based on the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies, determine the historical probability of each risk level in multiple risk levels; for each risk level, determine each risk in multiple risk characteristic attributes based on the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies The posterior probability of the feature attribute; and based on the Bayesian algorithm, using multiple risk weights, multiple historical probabilities, and multiple posterior probabilities to generate a risk level identification model.
根据本申请的实施例,第i个风险等级的历史概率可以指第i个风险等级出现的次数与多个风险等级出现的总次数的比值,即第一样本数据集中被标定为第i个风险等级的样本的数量与第一样本数据集的总数量的比值,如公式(7)所示:According to an embodiment of the present application, the historical probability of the i-th risk level may refer to the ratio of the number of occurrences of the i-th risk level to the total number of occurrences of multiple risk levels, that is, the first sample data set is marked as the i-th The ratio of the number of samples of the risk level to the total number of the first sample data set, as shown in formula (7):
在式(7)中,Pi可以表示第i个风险等级的历史概率;N3[i]可以表示第一样本数据集中被标定为第i个风险等级的样本的数量。In formula (7), Pi can represent the historical probability of the i-th risk level; N3[i] can represent the number of samples marked as the i-th risk level in the first sample data set.
根据本申请的实施例,第i个风险等级下,第j个风险特征属性的后验概率可以通过公式(8)计算得到:According to the embodiment of the present application, under the i-th risk level, the posterior probability of the j-th risk characteristic attribute can be calculated by formula (8):
在式(8)中,可以表示第i个风险等级下,第j个风险特征属性的后验概率;N4[i][j]可以表示第i个风险等级下,第j个风险特征属性的出现次数。In formula (8), It can represent the posterior probability of the j-th risk characteristic attribute under the i-th risk level; N4[i][j] can represent the occurrence times of the j-th risk characteristic attribute under the i-th risk level.
根据本申请的实施例,基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值、多个历史概率和多个后验概率来生成的风险等级识别模型可以是一个函数模型,其输入为需要识别的药店的业务行为数据,输出为识别得到的风险等级。According to the embodiment of the present application, based on the Bayesian algorithm, the risk level identification model generated by using multiple risk weights, multiple historical probabilities, and multiple posterior probabilities can be a function model, and its input is the pharmacy that needs to be identified The business behavior data of , the output is the identified risk level.
根据本申请的实施例,以需要识别的药店的业务行为数据为X={a1,a2,...,aM}为例,风险等级识别模型可以如公式(9)所示:According to the embodiment of this application, taking the business behavior data of the pharmacy that needs to be identified as X={a1 ,a2 ,...,aM } as an example, the risk level identification model can be shown in formula (9):
在式(9)中,FXMAP可以表示识别得到的风险等级;P(FXi)可以表示第i个风险等级的历史概率,可以通过公式(7)计算得到;P(aj|FX)可以表示在需要识别的药店的业务行为数据X第i个风险等级下第j个风险特征属性为aj的概率,可以通过公式(8)计算得到。In formula (9), FXMAP can represent the identified risk level; P(FXi ) can represent the historical probability of the i-th risk level, which can be calculated by formula (7); P(aj |FX) can be Indicates the probability that the j-th risk characteristic attribute is aj under the i-th risk level of the business behavior data X of the pharmacy that needs to be identified, which can be calculated by formula (8).
图3示意性示出了根据本申请另一实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 3 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to another embodiment of the present application.
如图3所示,该方法包括操作S301~S306。As shown in Fig. 3, the method includes operations S301-S306.
在操作S301,采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性。In operation S301, historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies are collected to obtain a first sample data set, wherein the historical business behavior data includes multiple risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S302,对第一样本数据集进行数据增强处理,得到第二样本数据集。In operation S302, data enhancement processing is performed on the first sample data set to obtain a second sample data set.
在操作S303,基于第二样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第二样本数据集的第一信息熵。In operation S303, based on the number of samples in the second sample data set and the historical risk level labels of the plurality of pharmacies, the first information entropy of the second sample data set is determined.
在操作S304,基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来处理第一信息熵,得到样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,第二样本数据集包括多个样本数据子集,多个样本数据子集与多个风险特征属性一一对应。In operation S304, the first information entropy is processed based on the sample data subset and the historical risk level label to obtain the information gain rate of the sample data subset, wherein the second sample data set includes a plurality of sample data subsets, and a plurality of sample data The subsets are in one-to-one correspondence with multiple risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S305,基于与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值。In operation S305, a plurality of risk weights are determined based on a plurality of information gain rates corresponding one-to-one to a plurality of risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S306,基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。In operation S306, based on the Bayesian algorithm, a risk level identification model is generated using multiple risk weights and historical risk level labels.
根据本申请的实施例,操作S301和操作S303~S306的方法可以根据操作S201~S205的方法来实现,将操作S201~S205中的第一样本数据集更换为第二样本数据集即可,在此不再赘述。According to the embodiment of the present application, the method of operation S301 and operation S303~S306 can be realized according to the method of operation S201~S205, just replace the first sample data set in operation S201~S205 with the second sample data set, I won't repeat them here.
根据本申请的实施例,在操作S302中,经数据增强后,第二样本数据集的样本数量可以大于第一样本数据集的样本数量,从而可以减少样本不均衡的影响,提高生成的风险等级识别模型的鲁棒性。According to an embodiment of the present application, in operation S302, after data enhancement, the number of samples in the second sample data set may be greater than that in the first sample data set, thereby reducing the impact of sample imbalance and increasing the risk of generation Robustness of grade recognition models.
根据本申请的实施例,操作S302可以包括如下操作:According to an embodiment of the present application, operation S302 may include the following operations:
对第一样本数据集中的样本进行分类,得到属于第一类别的多个第一样本和属于第二类别的多个第二样本,其中,第一类别的样本数量大于第二类别的样本数量;对于每个第二样本,利用K近邻算法从第一样本数据集中确定多个第三样本;根据多个第三样本所属的类别,基于第二样本生成至少一个第四样本;以及基于多个第一样本和多个第四样本,生成第二样本数据集。Classify the samples in the first sample data set to obtain a plurality of first samples belonging to the first category and a plurality of second samples belonging to the second category, wherein the number of samples of the first category is greater than the number of samples of the second category Quantity; for each second sample, utilize the K nearest neighbor algorithm to determine a plurality of third samples from the first sample data set; according to the category to which the plurality of third samples belong, at least one fourth sample is generated based on the second sample; and based on The plurality of first samples and the plurality of fourth samples generate a second sample data set.
根据本申请的实施例,对第一样本数据集中的样本进行分类时可以采用任意的无监督聚类算法来实现,在此不作限定。According to the embodiment of the present application, any unsupervised clustering algorithm may be used to classify the samples in the first sample data set, which is not limited herein.
根据本申请的实施例,第一类别可以指聚类后具有最多样本数量的类别,第二类别可以包括聚类后除该第一类别外的其他所有类别。相应的,第一类别的样本数量大于第二类别的样本数量可以理解为第一类别的样本数量比第二类包中任意一个类别的样本数量更多。According to an embodiment of the present application, the first category may refer to the category with the largest number of samples after clustering, and the second category may include all other categories after clustering except the first category. Correspondingly, the number of samples of the first category is greater than the number of samples of the second category can be understood as the number of samples of the first category is greater than the number of samples of any category in the second category.
根据本申请的实施例,利用K近邻算法确定的多个第三样本可以指在特征空间中,与第二样本最接近的多个样本,即第二样本的多个最近邻。According to an embodiment of the present application, the plurality of third samples determined by using the K-nearest neighbor algorithm may refer to the plurality of samples closest to the second sample in the feature space, that is, the plurality of nearest neighbors of the second sample.
根据本申请的实施例,第三样本可以与第二样本属于同一类别,即属于第二类别,也可以与第二样本属于不同类别,即属于第一类别。根据多个第三样本所属的类别,基于第二样本生成至少一个第四样本可以理解为根据多个第三样本属于第一类别或第二类别的统计结果,选择对应的策略来基于第二样本生成至少一个第四样本。According to the embodiment of the present application, the third sample may belong to the same category as the second sample, that is, belong to the second category, or may belong to a different category from the second sample, that is, belong to the first category. According to the category to which multiple third samples belong, generating at least one fourth sample based on the second sample can be understood as selecting a corresponding strategy based on the statistical results of multiple third samples belonging to the first category or the second category. At least one fourth sample is generated.
根据本申请的实施例,对于第二样本px,利用K近邻算法可以从第一样本数据集中确定b个第三样本。在b个第三样本中属于第一类别的样本数量小于第二预设阈值的情况下,可以将该第二样本px定义为安全样本,相应可以采用安全处理策略来处理第二样本px,例如,可以直接将第二样本px确定为所生成的第四样本。该第二预设阈值可以根据具体应用场景进行设定,例如可以设置为b/2,在此不作限定。在b个第三样本中属于第一类别的样本数量大于或等于第二预设阈值的情况下,可以将该第二样本px定义为危险样本,相应可以采用危险处理策略来处理第二样本px,例如,可以先从b个第三样本中确定至少一个第五样本,如s个第五样本,再基于至少一个第五样本和第二样本来生成至少一个第四样本,如公式(10)所示:According to the embodiment of the present application, for the second sample px , b third samples can be determined from the first sample data set by using the K nearest neighbor algorithm. In the case that the number of samples belonging to the first category among the b third samples is less than the second preset threshold, the second sample px can be defined as a safe sample, and a safe processing strategy can be used to process the second sample px accordingly , for example, the second sample px may be directly determined as the generated fourth sample. The second preset threshold can be set according to specific application scenarios, for example, it can be set to b/2, which is not limited here. In the case that the number of samples belonging to the first category among the b third samples is greater than or equal to the second preset threshold, the second sample px can be defined as a dangerous sample, and a risky treatment strategy can be used to process the second sample accordingly px , for example, at least one fifth sample may be firstly determined from b third samples, such as s fifth samples, and then at least one fourth sample may be generated based on at least one fifth sample and the second sample, as shown in the formula ( 10) as shown:
在式(10)中,px'可以表示第四样本;rand(0,1)可以表示利用随机数算法从区间[0,1]中选择一个随机数;ps,i可以表示第i个第五样本;d(ps,i-px)可以表示第i个第五样本与第二样本之间的距离。In formula (10), px ' can represent the fourth sample; rand(0,1) can represent a random number selected from the interval [0,1] using a random number algorithm; ps,i can represent the i-th The fifth sample; d(ps,i −px ) may represent the distance between the i-th fifth sample and the second sample.
根据本申请的实施例,通过如上数据增强方法,对于少数类样本,可以使用代表在少数类样本边界上的危险样本来合成新的样本数据,加入到少数类样本中,从而可以有效避免样本不均衡对模型性能的影响。According to the embodiment of the present application, through the above data enhancement method, for the minority class samples, the dangerous samples representing the boundary of the minority class samples can be used to synthesize new sample data, which can be added to the minority class samples, so that the samples can be effectively avoided. Balance the impact on model performance.
根据本申请的实施例,第二样本数据集可以由原本的多个第一样本,以及分别由每一个第二样本所生产的第四样本构成。在利用第二样本数据集进行药店风险等级识别模型的生成时,使用第二样本数据集S'对将公式(1)~(9)中的第一样本数据集S进行替换即可,在此不再赘述。According to an embodiment of the present application, the second sample data set may be composed of a plurality of original first samples and a fourth sample produced from each second sample. When using the second sample data set to generate the pharmacy risk level identification model, use the second sample data set S' to replace the first sample data set S in formulas (1)~(9), in This will not be repeated here.
图4示意性示出了根据本申请又一实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法的流程图。Fig. 4 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to yet another embodiment of the present application.
如图4所示,该方法包括操作S401~S404。As shown in Fig. 4, the method includes operations S401-S404.
在操作S401,采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性。In operation S401, historical business behavior data of multiple pharmacies are collected to obtain a first sample data set, wherein the historical business behavior data includes multiple risk characteristic attributes.
在操作S402,判断第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量是否大于第一预设阈值。在确定第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量小于或等于第一预设阈值的情况下,执行操作S403;在确定第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量大于第一预设阈值的情况下,执行操作S404。In operation S402, it is determined whether the number of samples included in the first sample data set is greater than a first preset threshold. When it is determined that the number of samples contained in the first sample data set is less than or equal to the first preset threshold, perform operation S403; when it is determined that the number of samples contained in the first sample data set is greater than the first preset threshold, Execute operation S404.
在操作S403,利用熵权法和贝叶斯算法,基于第一样本数据集和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。In operation S403, a risk level identification model is generated based on the first sample data set and the historical risk level labels by using the entropy weight method and the Bayesian algorithm.
在操作S404,利用第一样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,以生成风险等级识别模型。In operation S404, an initial network model is trained using the first sample data set to generate a risk level identification model.
根据本申请的实施例,第一预设阈值可以根据具体应用场景来确定,例如,该第一预设阈值可以设置为训练得到具有较高鲁棒性的模型所需要的最低样本数量。According to an embodiment of the present application, the first preset threshold may be determined according to a specific application scenario, for example, the first preset threshold may be set as the minimum number of samples required for training to obtain a model with higher robustness.
根据本申请的实施例,在确定第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量小于或等于第一预设阈值的情况下,利用熵权法和贝叶斯算法,基于第一样本数据集和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型可以理解为:在第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量小于或等于第一预设阈值的情况下,利用操作S202~S205的方法或操作S302~S306的方法来生成风险等级识别模型,在此不再赘述。According to an embodiment of the present application, when it is determined that the number of samples contained in the first sample data set is less than or equal to the first preset threshold, the entropy weight method and the Bayesian algorithm are used, based on the first sample data set and history The risk level label to generate the risk level identification model can be understood as: in the case that the number of samples contained in the first sample data set is less than or equal to the first preset threshold, using the method of operation S202~S205 or the method of operation S302~S306 to generate a risk level identification model, which will not be repeated here.
根据本申请的实施例,利用第一样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,以生成风险等级识别模型可以是基于预设学习参数,利用第一样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,得到风险等级识别模型。According to an embodiment of the present application, using the first sample data set to train the initial network model to generate a risk level identification model may be based on preset learning parameters, using the first sample data set to train the initial network model to obtain the risk level Identify the model.
作为一种可选的实施方式,在利用第一样本数据集进行训练时还可以包括对第一样本数据集进行预处理的过程。该预处理的过程例如可以包括:对第一样本数据集进行数据增强处理,得到第二样本数据集;以及对第二样本数据集中的样本数据作归一化处理,得到第三样本数据集。在完成预处理后,可以基于预设学习参数,利用第三样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,得到风险等级识别模型。As an optional implementation manner, when using the first sample data set for training, a process of preprocessing the first sample data set may also be included. The preprocessing process may include, for example: performing data enhancement processing on the first sample data set to obtain a second sample data set; and performing normalization processing on the sample data in the second sample data set to obtain a third sample data set . After the preprocessing is completed, based on the preset learning parameters, the third sample data set can be used to train the initial network model to obtain a risk level identification model.
根据本申请的实施例,对第一样本数据集进行数据增强处理,得到第二样本数据集可以采用如操作S302的方法来实现,在此不再赘述。According to the embodiment of the present application, performing data enhancement processing on the first sample data set to obtain the second sample data set may be implemented by a method such as operation S302, which will not be repeated here.
根据本申请的实施例,对第二样本数据集中的样本数据作归一化处理,得到第三样本数据集可以是将第二样本数据集中的样本特征归一化,如公式(11)所示:According to an embodiment of the present application, performing normalization processing on the sample data in the second sample data set to obtain the third sample data set may be to normalize the sample features in the second sample data set, as shown in formula (11) :
在式(11)中,可以表示归一化后的样本特征,f可以表示归一化前的样本特征,MAX(n)可以表示归一化前的样本特征的最大值。In formula (11), can represent the sample features after normalization, f can represent the sample features before normalization, and MAX(n) can represent the maximum value of the sample features before normalization.
图5示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别方法的流程图。Fig. 5 schematically shows a flowchart of a method for identifying a risk level of a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
如图5所示,该方法包括操作S501~S502。As shown in Fig. 5, the method includes operations S501~S502.
在操作S501,采集目标药店的目标业务行为数据,得到第一目标数据集。In operation S501, collect target business behavior data of a target pharmacy to obtain a first target data set.
在操作S502,利用风险等级识别模型来处理第一目标数据集,得到目标药店的风险等级识别结果。In operation S502, the risk level identification model is used to process the first target data set to obtain a risk level identification result of the target pharmacy.
根据本申请的实施例,目标药店与用于模型生成时的多个药店可以具有相同的主营业务,以使得目标药店的目标业务行为数据中所包含的风险特征属性与训练时的历史行为数据中所包含的风险特征属性属于同一维度。According to the embodiment of the present application, the target pharmacy and the multiple pharmacies used for model generation may have the same main business, so that the risk characteristic attributes contained in the target business behavior data of the target pharmacy are consistent with the historical behavior data during training. The risk characteristic attributes contained in belong to the same dimension.
根据本申请的实施例,风险等级识别模型包括使用操作S201~S205的方法或操作S301~S306的方法而生成的风险等级识别概率模型,或者,使用操作S401~S404的方法来生成的风险等级识别网络模型。药店风险等级识别方法中的风险等级识别模型生成方法部分具体可以参考药店风险等级识别模型生成方法部分,在此不再赘述。According to the embodiment of the present application, the risk level identification model includes a risk level identification probability model generated by using the method of operation S201~S205 or operation S301~S306, or a risk level identification model generated by using the method of operation S401~S404 network model. For details on the generation method of the risk level identification model in the risk level identification method for pharmacies, please refer to the section on the generation method of the risk level identification model for pharmacies, and details will not be repeated here.
根据本申请的实施例,在风险等级识别模型为风险等级识别概率模型的情况下,操作S502可以包括如下操作:According to an embodiment of the present application, when the risk level identification model is a risk level identification probability model, operation S502 may include the following operations:
从风险等级识别概率模型中获取与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个风险权值、多个历史概率和多个后验概率,其中,历史概率包括多个风险等级中每个风险等级的历史概率,后验概率包括多个风险等级的每个风险等级下,多个风险特征属性中每个风险特征属性的后验概率;对于每个风险等级,基于风险等级下的与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个后验概率和第一目标数据集,确定与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个条件概率;利用多个风险权值来对多个条件概率进行加权求和,得到风险等级的最大后验概率;以及基于分别与多个风险等级对应的多个最大后验概率,确定风险等级识别结果。Obtain multiple risk weights, multiple historical probabilities, and multiple posterior probabilities corresponding to multiple risk characteristic attributes from the risk level identification probability model, where the historical probability includes the risk level of each risk level in the multiple risk levels Historical probability, the posterior probability includes the posterior probability of each risk characteristic attribute in multiple risk characteristic attributes under each risk level of multiple risk levels; for each risk level, based on the risk level and multiple risk characteristics A plurality of posterior probabilities corresponding to one attribute and the first target data set, determine a plurality of conditional probabilities corresponding to a plurality of risk characteristic attributes; use a plurality of risk weights to carry out weighted summation of a plurality of conditional probabilities, obtaining the maximum posterior probability of the risk level; and determining the risk level identification result based on the multiple maximum posterior probabilities respectively corresponding to the multiple risk levels.
根据本申请的实施例,从风险等级识别概率模型中可以获取得到多个风险权值w1,…,wm,多个历史概率P1,…,Pm,和多个后验概率P ̂1(S|S1),…,P ̂1(S|Sm),…,P ̂n1(S|S1),…,P ̂n1(S|Sm)。According to the embodiment of the present application, multiple risk weights w1 ,...,wm , multiple historical probabilities P1 ,...,Pm , and multiple posterior probabilities P ̂ can be obtained from the risk level identification probability model1 (S|S1 ),…,P̂ 1 (S|Sm ),…,P̂ n1 (S|S1 ),…,P̂ n1 (S|Sm ).
根据本申请的实施例,从目标业务行为数据中确定的第一目标数据集可以表示为X={a1,a2,...,aM}。可以使用P(FXi|a1,a2,...,aM)表示第一目标数据集X={a1,a2,...,aM}属于第i个风险等级的概率。当属于第i个风险等级的概率P(FXi|a1,a2,...,aM)最大时,则可以确定风险等级识别结果表示目标药店的风险等级为第i个风险等级。According to the embodiment of the present application, the first target data set determined from the target business behavior data may be expressed as X={a1 , a2 , . . . , aM }. P(FXi |a1 ,a2 ,...,aM ) can be used to represent the probability that the first target data set X={a1 ,a2 ,...,aM } belongs to the i-th risk level . When the probability P(FXi |a1 ,a2 ,...,aM ) belonging to the i-th risk level is the largest, it can be determined that the risk level identification result indicates that the risk level of the target pharmacy is the i-th risk level.
根据本申请的实施例,最大后验概率对应的风险等级可以如公式(12)所示:According to the embodiment of this application, the risk level corresponding to the maximum posterior probability can be shown in formula (12):
在式(12)中,FXMAP可以表示最大后验概率对应的风险等级;P(FXi|a1,a2,...,aM)可以表示第i个风险等级下各个风险特征属性的条件概率,可以通过公式(13)计算得到:In formula (12), FXMAP can represent the risk level corresponding to the maximum posterior probability; P(FXi |a1 ,a2 ,...,aM ) can represent each risk characteristic attribute under the i-th risk level The conditional probability of can be calculated by formula (13):
在式(13)中,P(a1,a2,...,aM|FXi)可以表示第i个风险等级下,风险特征属性为X={a1,a2,...,aM}的后验概率;P(a1,a2,...,aM)可以表示为第一目标数据集的全概率。In formula (13), P(a1 ,a2 ,...,aM |FXi ) can represent that under the i-th risk level, the risk characteristic attribute is X={a1 ,a2 ,... ,aM } the posterior probability; P(a1 ,a2 ,...,aM ) can be expressed as the full probability of the first target data set.
根据本申请的实施例,结合公式(12)和(13)及乘法定理,即可得到如公式(9)所示的风险等级识别模型。将第一目标数据集代入公式(9)中,即可确定最大后验概率对应的风险等级,即风险等级识别结果。According to the embodiment of the present application, combining formulas (12) and (13) and the multiplication theorem, the risk level identification model shown in formula (9) can be obtained. Substituting the first target data set into formula (9), the risk level corresponding to the maximum posterior probability can be determined, that is, the risk level identification result.
根据本申请的实施例,在风险等级识别模型为风险等级网络概率模型的情况下,操作S502可以包括如下操作:According to an embodiment of the present application, when the risk level identification model is a risk level network probability model, operation S502 may include the following operations:
对第一目标数据集作归一化处理,得到第二目标数据集;以及将第二目标数据集输入风险等级识别网络模型中,得到风险等级识别结果。Normalizing the first target data set to obtain a second target data set; and inputting the second target data set into a risk level identification network model to obtain a risk level identification result.
根据本申请的实施例,归一化处理的过程可以如公式(11)所示。According to the embodiment of the present application, the normalization process may be as shown in formula (11).
根据本申请的实施例,在得到风险等级识别结果后,还可以根据确定的风险等级进行风险预警。例如,可以设置一个阈值等级,在确定的目标药店的风险等级大于该阈值等级时,可以向相关人员或部门的电子设备发送风险预警信息,以便及时发现问题,避免风险事件的发生。According to the embodiment of the present application, after the risk level identification result is obtained, risk warning may also be performed according to the determined risk level. For example, a threshold level can be set, and when the risk level of the determined target pharmacy is greater than the threshold level, risk warning information can be sent to the electronic equipment of relevant personnel or departments, so as to detect problems in time and avoid the occurrence of risk events.
图6示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别模型生成装置的框图。Fig. 6 schematically shows a block diagram of a device for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application.
如图6所示,药店风险等级识别模型生成装置600可以包括第一采集模块610、第一确定模块620、第一处理模块630、第二确定模块640和第一生成模块650。As shown in FIG. 6 , the pharmacy risk level identification
第一采集模块610,用于采集多个药店的历史业务行为数据,得到第一样本数据集,其中,历史业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性。The
第一确定模块620,用于基于第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第一样本数据集的第一信息熵。The
第一处理模块630,用于基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来处理第一信息熵,得到样本数据子集的信息增益率,其中,第一样本数据集包括多个样本数据子集,多个样本数据子集与多个风险特征属性一一对应。The
第二确定模块640,用于基于与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个信息增益率,确定多个风险权值。The second determining
第一生成模块650,用于基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值和历史风险等级标签来生成风险等级识别模型。The
根据本申请的实施例,在进行风险等级识别模型的生成时,可以基于采集得到的第一样本数据集和历史风险等级标签来计算该第一样本数据集的第一信息熵,再基于第一信息熵来确定各个风险特征属性的信息增益率,然后,可以利用各个风险特征属性的信息增益率来确定各个风险特征属性的风险权值,该风险权值可以与基于贝叶斯算法确定的概率模型进行结合,以得到风险等级识别模型。通过对熵权法和贝叶斯算法的改进,即使用信息增益率取代信息增益作为风险权值的计算依据,并在贝叶斯算法中加入了利用风险权值进行加权运算的操作,可以有效降低样本不均衡对模型识别精度的影响,通过使用模型进行风险等级识别的方法,可以至少部分地克服相关技术中药店风险等级的识别精度较差的问题,可以有效降低实施成本,提高风险等级识别精度。According to an embodiment of the present application, when generating a risk level identification model, the first information entropy of the first sample data set can be calculated based on the collected first sample data set and historical risk level labels, and then based on The first information entropy is used to determine the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute, and then, the information gain rate of each risk characteristic attribute can be used to determine the risk weight of each risk characteristic attribute, and the risk weight can be determined based on the Bayesian algorithm The probability model of the risk level is combined to obtain the risk level identification model. By improving the entropy weight method and the Bayesian algorithm, that is, using the information gain rate instead of the information gain as the basis for calculating the risk weight, and adding the operation of using the risk weight to carry out weighted operations in the Bayesian algorithm, it can effectively To reduce the impact of sample imbalance on model identification accuracy, by using the model for risk level identification, the problem of poor identification accuracy of pharmacy risk levels in related technologies can be at least partially overcome, which can effectively reduce implementation costs and improve risk level identification. precision.
根据本申请的实施例,第一处理模块630包括第一处理单元、第二处理单元和第三处理单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the
第一处理单元,用于对于每个样本数据子集,基于样本数据子集和历史风险等级标签来确定样本数据子集的第二信息熵和样本数据子集针对第一样本数据集的条件熵。The first processing unit is configured to, for each sample data subset, determine the second information entropy of the sample data subset and the condition of the sample data subset for the first sample data set based on the sample data subset and the historical risk level label entropy.
第二处理单元,用于基于条件熵和第一信息熵,确定样本数据子集的信息增益。The second processing unit is configured to determine the information gain of the sample data subset based on the conditional entropy and the first information entropy.
第三处理单元,用于基于样本数据子集的信息增益和第二信息熵,确定样本数据子集的信息增益率。The third processing unit is configured to determine an information gain rate of the sample data subset based on the information gain of the sample data subset and the second information entropy.
根据本申请的实施例,药店风险等级识别模型生成装置600还可以包括第三处理模块。According to the embodiment of the present application, the pharmacy risk level identification
第三处理模块,用于对第一样本数据集进行数据增强处理,得到第二样本数据集。The third processing module is configured to perform data enhancement processing on the first sample data set to obtain the second sample data set.
根据本申请的实施例,第一确定模块620包括第一确定单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the first determining
第一确定单元,用于基于第二样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第二样本数据集的第一信息熵。The first determination unit is configured to determine the first information entropy of the second sample data set based on the number of samples in the second sample data set and the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies.
根据本申请的实施例,样本数据子集中包括第二样本数据集中与每个风险特征属性对应的样本。According to an embodiment of the present application, the sample data subset includes samples corresponding to each risk characteristic attribute in the second sample data set.
根据本申请的实施例,药店风险等级识别模型生成装置600还可以包括第三确定模块和第二生成模块。According to the embodiment of the present application, the pharmacy risk level identification
第三确定模块,用于确定第一样本数据集中包含的样本数量。A third determining module, configured to determine the number of samples included in the first sample data set.
第二生成模块,用于在样本数量大于第一预设阈值的情况下,利用第一样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,以生成风险等级识别模型。The second generation module is configured to use the first sample data set to train the initial network model to generate a risk level identification model when the number of samples is greater than the first preset threshold.
根据本申请的实施例,第二生成模块包括第一生成子模块、第二生成子模块和第三生成子模块。According to an embodiment of the present application, the second generation module includes a first generation submodule, a second generation submodule, and a third generation submodule.
第一生成子模块,用于对第一样本数据集进行数据增强处理,得到第二样本数据集。The first generation submodule is used to perform data enhancement processing on the first sample data set to obtain the second sample data set.
第二生成子模块,用于对第二样本数据集中的样本数据作归一化处理,得到第三样本数据集。The second generation sub-module is used to normalize the sample data in the second sample data set to obtain the third sample data set.
第三生成子模块,用于基于预设学习参数,利用第三样本数据集来训练初始网络模型,得到风险等级识别模型。The third generation sub-module is configured to use the third sample data set to train the initial network model based on preset learning parameters to obtain a risk level identification model.
根据本申请的实施例,第三处理模块或第二生成子模块包括第四处理单元、第五处理单元、第六处理单元和第七处理单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the third processing module or the second generating sub-module includes a fourth processing unit, a fifth processing unit, a sixth processing unit and a seventh processing unit.
第四处理单元,用于对第一样本数据集中的样本进行分类,得到属于第一类别的多个第一样本和属于第二类别的多个第二样本,其中,第一类别的样本数量大于第二类别的样本数量。A fourth processing unit, configured to classify the samples in the first sample data set to obtain a plurality of first samples belonging to the first category and a plurality of second samples belonging to the second category, wherein the samples of the first category The number is greater than the sample size of the second category.
第五处理单元,用于对于每个第二样本,利用K近邻算法从第一样本数据集中确定多个第三样本。The fifth processing unit is configured to, for each second sample, determine a plurality of third samples from the first sample data set by using the K-nearest neighbor algorithm.
第六处理单元,用于根据多个第三样本所属的类别,基于第二样本生成至少一个第四样本。A sixth processing unit, configured to generate at least one fourth sample based on the second sample according to categories to which the plurality of third samples belong.
第七处理单元,用于基于多个第一样本和多个第四样本,生成第二样本数据集。A seventh processing unit, configured to generate a second sample data set based on the plurality of first samples and the plurality of fourth samples.
根据本申请的实施例,第六处理单元包括第一处理子单元、第二处理子单元和第三处理子单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the sixth processing unit includes a first processing subunit, a second processing subunit, and a third processing subunit.
第一处理子单元,用于在多个第三样本中属于第一类别的样本数量小于第二预设阈值的情况下,确定第四样本为第二样本。The first processing subunit is configured to determine the fourth sample as the second sample when the number of samples belonging to the first category among the plurality of third samples is less than a second preset threshold.
第二处理子单元,用于在多个第三样本中属于第一类别的样本数量大于或等于第二预设阈值的情况下,从第三样本中确定至少一个第五样本。The second processing subunit is configured to determine at least one fifth sample from the third samples when the number of samples belonging to the first category among the plurality of third samples is greater than or equal to a second preset threshold.
第三处理子单元,用于基于至少一个第五样本和第二样本来生成至少一个第四样本。The third processing subunit is configured to generate at least one fourth sample based on the at least one fifth sample and the second sample.
根据本申请的实施例,第一确定模块620包括第二确定单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the
第二确定单元,用于在样本数量小于或等于第一预设阈值的情况下,基于第一样本数据集中的样本数量和多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定第一样本数据集的第一信息熵。The second determination unit is configured to determine the number of samples in the first sample data set based on the number of samples in the first sample data set and the historical risk level labels of multiple pharmacies when the number of samples is less than or equal to the first preset threshold. The first information entropy.
根据本申请的实施例,第一生成模块650包括第一生成单元、第二生成单元和第三生成单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the
第一生成单元,用于基于多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定多个风险等级中每个风险等级的历史概率。The first generation unit is configured to determine the historical probability of each risk level in the plurality of risk levels based on the historical risk level labels of the plurality of pharmacies.
第二生成单元,用于对于每个风险等级,基于多个药店的历史风险等级标签,确定多个风险特征属性中每个风险特征属性的后验概率。The second generating unit is configured to, for each risk level, determine the posterior probability of each risk characteristic attribute in the plurality of risk characteristic attributes based on the historical risk level labels of the plurality of pharmacies.
第三生成单元,用于基于贝叶斯算法,利用多个风险权值、多个历史概率和多个后验概率来生成风险等级识别模型。The third generating unit is configured to generate a risk level identification model based on a Bayesian algorithm by using multiple risk weights, multiple historical probabilities, and multiple posterior probabilities.
需要说明的是,本申请的实施例中药店风险等级识别模型生成装置部分与本申请的实施例中药店风险等级识别模型生成方法部分是相对应的,药店风险等级识别模型生成装置部分的描述具体参考药店风险等级识别模型生成方法部分,在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the part of the pharmacy risk level identification model generation device in the embodiment of the application corresponds to the pharmacy risk level identification model generation method part in the embodiment of the application, and the description of the pharmacy risk level identification model generation device part is specific Refer to the section on the generation method of the pharmacy risk level identification model, and will not repeat it here.
图7示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的药店风险等级识别装置的框图。Fig. 7 schematically shows a block diagram of a drugstore risk level identification device according to an embodiment of the present application.
如图7所示,药店风险等级识别装置700可以包括第二采集模块710和第二处理模块720。As shown in FIG. 7 , the drugstore risk
第二采集模块710,用于采集目标药店的目标业务行为数据,得到第一目标数据集。The
第二处理模块720,用于利用风险等级识别模型来处理第一目标数据集,得到目标药店的风险等级识别结果。The
根据本申请的实施例,风险等级识别模型可以包括使用如上的药店风险等级识别模型生成方法来生成,在此不再赘述。According to an embodiment of the present application, the risk level identification model may be generated by using the method for generating a risk level identification model of a pharmacy as described above, which will not be repeated here.
根据本申请的实施例,风险等级识别模型包括风险等级识别概率模型或风险等级识别网络模型。According to an embodiment of the present application, the risk level identification model includes a risk level identification probability model or a risk level identification network model.
根据本申请的实施例,目标业务行为数据包括多个风险特征属性。According to an embodiment of the present application, the target business behavior data includes a plurality of risk characteristic attributes.
根据本申请的实施例,第二处理模块720包括第八处理单元、第九处理单元、第十处理单元和第十一处理单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the
第八处理单元,用于在风险等级识别模型为风险等级识别概率模型的情况下,从风险等级识别概率模型中获取与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个风险权值、多个历史概率和多个后验概率,其中,历史概率包括多个风险等级中每个风险等级的历史概率,后验概率包括多个风险等级的每个风险等级下,多个风险特征属性中每个风险特征属性的后验概率。The eighth processing unit is used to obtain a plurality of risk weights and a plurality of historical probabilities corresponding to a plurality of risk characteristic attributes from the risk level identification probability model when the risk level identification model is a risk level identification probability model and multiple posterior probabilities, wherein the historical probability includes the historical probability of each risk level in multiple risk levels, and the posterior probability includes each risk feature in multiple risk feature attributes under each risk level of multiple risk levels The posterior probability of the attribute.
第九处理单元,用于对于每个风险等级,基于风险等级下的与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个后验概率和第一目标数据集,确定与多个风险特征属性一一对应的多个条件概率。The ninth processing unit is configured to, for each risk level, determine the one-to-one correspondence with the multiple risk feature attributes based on the multiple posterior probabilities under the risk level and the first target data set that correspond to the multiple risk feature attributes one-to-one. Multiple conditional probabilities for .
第十处理单元,用于利用多个风险权值来对多个条件概率进行加权求和,得到风险等级的最大后验概率。The tenth processing unit is configured to use multiple risk weights to weight and sum multiple conditional probabilities to obtain the maximum posterior probability of the risk level.
第十一处理单元,用于基于分别与多个风险等级对应的多个最大后验概率,确定风险等级识别结果。An eleventh processing unit, configured to determine a risk level identification result based on multiple maximum posterior probabilities respectively corresponding to the multiple risk levels.
根据本申请的实施例,第二处理模块720包括第十二处理单元和第十三处理单元。According to an embodiment of the present application, the
第十二处理单元,用于在风险等级识别模型为风险等级识别网络模型的情况下,对第一目标数据集作归一化处理,得到第二目标数据集。A twelfth processing unit, configured to perform normalization processing on the first target data set to obtain a second target data set when the risk level identification model is a risk level identification network model.
第十三处理单元,用于将第二目标数据集输入风险等级识别网络模型中,得到风险等级识别结果。A thirteenth processing unit, configured to input the second target data set into the risk level identification network model to obtain a risk level identification result.
需要说明的是,本申请的实施例中药店风险等级识别装置部分与本申请的实施例中药店风险等级识别方法部分是相对应的,药店风险等级识别装置部分的描述具体参考药店风险等级识别方法部分,在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the part of the pharmacy risk level identification device in the embodiment of the present application corresponds to the pharmacy risk level identification method part in the embodiment of the present application, and the description of the pharmacy risk level identification device part specifically refers to the pharmacy risk level identification method part and will not be repeated here.
根据本申请的实施例的模块、子模块、单元、子单元中的任意多个、或其中任意多个的至少部分功能可以在一个模块中实现。根据本申请实施例的模块、子模块、单元、子单元中的任意一个或多个可以被拆分成多个模块来实现。根据本申请实施例的模块、子模块、单元、子单元中的任意一个或多个可以至少被部分地实现为硬件电路,例如现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)、可编程逻辑阵列(PLA)、片上系统、基板上的系统、封装上的系统、专用集成电路(ASIC),或可以通过对电路进行集成或封装的任何其他的合理方式的硬件或固件来实现,或以软件、硬件以及固件三种实现方式中任意一种或以其中任意几种的适当组合来实现。或者,根据本申请实施例的模块、子模块、单元、子单元中的一个或多个可以至少被部分地实现为计算机程序模块,当该计算机程序模块被运行时,可以执行相应的功能。According to the embodiments of the present application, any multiple of the modules, sub-modules, units, and sub-units, or at least part of the functions of any multiple of them may be implemented in one module. Any one or more of the modules, sub-modules, units, and sub-units according to the embodiments of the present application may be divided into multiple modules for implementation. Any one or more of modules, submodules, units, and subunits according to the embodiments of the present application may be at least partially implemented as hardware circuits, such as field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), programmable logic arrays (PLA), system-on-chip, system-on-substrate, system-on-package, application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), or hardware or firmware that may be implemented by any other reasonable means of integrating or packaging circuits, or in a combination of software, hardware, and firmware Any one of these implementations or an appropriate combination of any of them. Alternatively, one or more of the modules, submodules, units, and subunits according to the embodiments of the present application may be at least partially implemented as computer program modules, and when the computer program modules are executed, corresponding functions may be performed.
例如,第一采集模块610、第一确定模块620、第一处理模块630、第二确定模块640和第一生成模块650,或者,第二采集模块710和第二处理模块720中的任意多个可以合并在一个模块/单元/子单元中实现,或者其中的任意一个模块/单元/子单元可以被拆分成多个模块/单元/子单元。或者,这些模块/单元/子单元中的一个或多个模块/单元/子单元的至少部分功能可以与其他模块/单元/子单元的至少部分功能相结合,并在一个模块/单元/子单元中实现。根据本申请的实施例,第一采集模块610、第一确定模块620、第一处理模块630、第二确定模块640和第一生成模块650,或者,第二采集模块710和第二处理模块720中的至少一个可以至少被部分地实现为硬件电路,例如现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)、可编程逻辑阵列(PLA)、片上系统、基板上的系统、封装上的系统、专用集成电路(ASIC),或可以通过对电路进行集成或封装的任何其他的合理方式等硬件或固件来实现,或以软件、硬件以及固件三种实现方式中任意一种或以其中任意几种的适当组合来实现。或者,第一采集模块610、第一确定模块620、第一处理模块630、第二确定模块640和第一生成模块650,或者,第二采集模块710和第二处理模块720中的至少一个可以至少被部分地实现为计算机程序模块,当该计算机程序模块被运行时,可以执行相应的功能。For example, the
图8示意性示出了根据本申请实施例的适于实现药店风险等级识别模型生成方法或药店风险等级识别方法的电子设备的框图。图8示出的电子设备仅仅是一个示例,不应对本申请实施例的功能和使用范围带来任何限制。Fig. 8 schematically shows a block diagram of an electronic device adapted to implement a method for generating a risk level identification model for a pharmacy or a method for identifying a risk level for a pharmacy according to an embodiment of the present application. The electronic device shown in FIG. 8 is only an example, and should not limit the functions and application scope of the embodiment of the present application.
如图8所示,根据本申请实施例的计算机电子设备800包括处理器801,其可以根据存储在只读存储器(ROM)802中的程序或者从存储部分808加载到随机访问存储器(RAM)803中的程序而执行各种适当的动作和处理。处理器801例如可以包括通用微处理器(例如CPU)、指令集处理器和/或相关芯片组和/或专用微处理器(例如,专用集成电路(ASIC)),等等。处理器801还可以包括用于缓存用途的板载存储器。处理器801可以包括用于执行根据本申请实施例的方法流程的不同动作的单一处理单元或者是多个处理单元。As shown in FIG. 8 , a computer
在RAM 803中,存储有电子设备800操作所需的各种程序和数据。处理器 801、ROM802以及RAM 803通过总线804彼此相连。处理器801通过执行ROM 802和/或RAM 803中的程序来执行根据本申请实施例的方法流程的各种操作。需要注意,所述程序也可以存储在除ROM 802和RAM 803以外的一个或多个存储器中。处理器801也可以通过执行存储在所述一个或多个存储器中的程序来执行根据本申请实施例的方法流程的各种操作。In the
根据本申请的实施例,电子设备800还可以包括输入/输出(I/O)接口805,输入/输出(I/O)接口805也连接至总线804。电子设备800还可以包括连接至I/O接口805的以下部件中的一项或多项:包括键盘、鼠标等的输入部分806;包括诸如阴极射线管(CRT)、液晶显示器(LCD)等以及扬声器等的输出部分807;包括硬盘等的存储部分808;以及包括诸如LAN卡、调制解调器等的网络接口卡的通信部分809。通信部分809经由诸如因特网的网络执行通信处理。驱动器810也根据需要连接至I/O接口805。可拆卸介质811,诸如磁盘、光盘、磁光盘、半导体存储器等等,根据需要安装在驱动器810上,以便于从其上读出的计算机程序根据需要被安装入存储部分808。According to the embodiment of the present application, the
本申请还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质可以是上述实施例中描述的设备/装置/系统中所包含的;也可以是单独存在,而未装配入该设备/装置/系统中。上述计算机可读存储介质承载有一个或者多个程序,当上述一个或者多个程序被执行时,实现根据本申请实施例的方法。The present application also provides a computer-readable storage medium. The computer-readable storage medium may be included in the device/apparatus/system described in the above embodiments; it may also exist independently without being assembled into the device/system. device/system. The above-mentioned computer-readable storage medium carries one or more programs, and when the above-mentioned one or more programs are executed, the method according to the embodiment of the present application is implemented.
根据本申请的实施例,计算机可读存储介质可以是非易失性的计算机可读存储介质。例如可以包括但不限于:便携式计算机磁盘、硬盘、随机访问存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、可擦式可编程只读存储器(EPROM或闪存)、便携式紧凑磁盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、光存储器件、磁存储器件、或者上述的任意合适的组合。在本申请中,计算机可读存储介质可以是任何包含或存储程序的有形介质,该程序可以被指令执行系统、装置或者器件使用或者与其结合使用。According to the embodiment of the present application, the computer-readable storage medium may be a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium. Examples may include, but are not limited to: portable computer diskettes, hard disks, random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), portable compact disk read-only memory (CD- ROM), optical storage devices, magnetic storage devices, or any suitable combination of the above. In the present application, a computer-readable storage medium may be any tangible medium that contains or stores a program that can be used by or in conjunction with an instruction execution system, apparatus, or device.
例如,根据本申请的实施例,计算机可读存储介质可以包括上文描述的ROM 802和/或RAM 803和/或ROM 802和RAM 803以外的一个或多个存储器。For example, according to an embodiment of the present application, a computer-readable storage medium may include one or more memories other than the above-described
附图中的流程图和框图,图示了按照本申请各种实施例的系统和方法的可能实现的体系架构、功能和操作。在这点上,流程图或框图中的每个方框可以代表一个模块、程序段、或代码的一部分,上述模块、程序段、或代码的一部分包含一个或多个用于实现规定的逻辑功能的可执行指令。也应当注意,在有些作为替换的实现中,方框中所标注的功能也可以以不同于附图中所标注的顺序发生。例如,两个接连地表示的方框实际上可以基本并行地执行,它们有时也可以按相反的顺序执行,这依所涉及的功能而定。也要注意的是,框图或流程图中的每个方框、以及框图或流程图中的方框的组合,可以用执行规定的功能或操作的专用的基于硬件的系统来实现,或者可以用专用硬件与计算机指令的组合来实现。本领域技术人员可以理解,本申请的各个实施例和/或权利要求中记载的特征可以进行多种组合和/或结合,即使这样的组合或结合没有明确记载于本申请中。特别地,在不脱离本申请精神和教导的情况下,本申请的各个实施例和/或权利要求中记载的特征可以进行多种组合和/或结合。所有这些组合和/或结合均落入本申请的范围。The flowchart and block diagrams in the figures illustrate the architecture, functionality, and operation of possible implementations of systems and methods according to various embodiments of the present application. In this regard, each block in a flowchart or block diagram may represent a module, program segment, or portion of code that includes one or more logical functions for implementing specified executable instructions. It should also be noted that, in some alternative implementations, the functions noted in the block may occur out of the order noted in the figures. For example, two blocks shown in succession may, in fact, be executed substantially concurrently, or they may sometimes be executed in the reverse order, depending upon the functionality involved. It should also be noted that each block in the block diagrams or flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams or flowchart illustrations, can be implemented by a dedicated hardware-based system that performs the specified function or operation, or can be implemented by a A combination of dedicated hardware and computer instructions. Those skilled in the art can understand that various combinations and/or combinations can be made of the features described in the various embodiments and/or claims of the present application, even if such combinations or combinations are not explicitly recorded in the present application. In particular, without departing from the spirit and teaching of the present application, various combinations and/or combinations can be made of the features described in the various embodiments and/or claims of the present application. All such combinations and/or combinations fall within the scope of the present application.
以上对本申请的实施例进行了描述。但是,这些实施例仅仅是为了说明的目的,而并非为了限制本申请的范围。尽管在以上分别描述了各实施例,但是这并不意味着各个实施例中的措施不能有利地结合使用。本申请的范围由所附权利要求及其等同物限定。不脱离本申请的范围,本领域技术人员可以做出多种替代和修改,这些替代和修改都应落在本申请的范围之内。The embodiments of the present application have been described above. However, these examples are for illustrative purposes only and are not intended to limit the scope of the application. Although the various embodiments have been described separately above, this does not mean that the measures in the various embodiments cannot be advantageously used in combination. The scope of the application is defined by the claims appended hereto and their equivalents. Those skilled in the art can make various substitutions and modifications without departing from the scope of the present application, and these substitutions and modifications should all fall within the scope of the present application.
Claims (17)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211502787.2ACN115544902A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
| CN202310658494.1ACN116484750A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Pharmacy risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211502787.2ACN115544902A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310658494.1ADivisionCN116484750A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Pharmacy risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115544902Atrue CN115544902A (en) | 2022-12-30 |
Family
ID=84722276
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211502787.2APendingCN115544902A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
| CN202310658494.1APendingCN116484750A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Pharmacy risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202310658494.1APendingCN116484750A (en) | 2022-11-29 | 2022-11-29 | Pharmacy risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (2) | CN115544902A (en) |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104809233A (en)* | 2015-05-12 | 2015-07-29 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Attribute weighting method based on information gain ratios and text classification methods |
| CN105045825A (en)* | 2015-06-29 | 2015-11-11 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Structure extended polynomial naive Bayes text classification method |
| CN105760889A (en)* | 2016-03-01 | 2016-07-13 | 中国科学技术大学 | Efficient imbalanced data set classification method |
| CN108229826A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-29 | 中国计量大学 | A kind of net purchase risk class appraisal procedure based on improvement bayesian algorithm |
| CN108876166A (en)* | 2018-06-27 | 2018-11-23 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Financial risk authentication processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN111582315A (en)* | 2020-04-09 | 2020-08-25 | 上海淇毓信息科技有限公司 | Sample data processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN112017061A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-12-01 | 北京淇瑀信息科技有限公司 | Financial risk prediction method and device based on Bayesian deep learning and electronic equipment |
| CN114511760A (en)* | 2022-02-14 | 2022-05-17 | 中国农业银行股份有限公司 | Sample equalization method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN114693188A (en)* | 2022-05-31 | 2022-07-01 | 四川骏逸富顿科技有限公司 | Risk supervision method, system and equipment for drug retail industry |
| CN115129607A (en)* | 2022-07-19 | 2022-09-30 | 中国电力科学研究院有限公司 | Power grid security analysis machine learning model testing method, device, equipment and medium |
| CN115222177A (en)* | 2021-04-23 | 2022-10-21 | 索信达(北京)数据技术有限公司 | Service data processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
- 2022
- 2022-11-29CNCN202211502787.2Apatent/CN115544902A/enactivePending
- 2022-11-29CNCN202310658494.1Apatent/CN116484750A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104809233A (en)* | 2015-05-12 | 2015-07-29 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Attribute weighting method based on information gain ratios and text classification methods |
| CN105045825A (en)* | 2015-06-29 | 2015-11-11 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | Structure extended polynomial naive Bayes text classification method |
| CN105760889A (en)* | 2016-03-01 | 2016-07-13 | 中国科学技术大学 | Efficient imbalanced data set classification method |
| CN108229826A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-29 | 中国计量大学 | A kind of net purchase risk class appraisal procedure based on improvement bayesian algorithm |
| CN108876166A (en)* | 2018-06-27 | 2018-11-23 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Financial risk authentication processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN111582315A (en)* | 2020-04-09 | 2020-08-25 | 上海淇毓信息科技有限公司 | Sample data processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN112017061A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-12-01 | 北京淇瑀信息科技有限公司 | Financial risk prediction method and device based on Bayesian deep learning and electronic equipment |
| CN115222177A (en)* | 2021-04-23 | 2022-10-21 | 索信达(北京)数据技术有限公司 | Service data processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN114511760A (en)* | 2022-02-14 | 2022-05-17 | 中国农业银行股份有限公司 | Sample equalization method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN114693188A (en)* | 2022-05-31 | 2022-07-01 | 四川骏逸富顿科技有限公司 | Risk supervision method, system and equipment for drug retail industry |
| CN115129607A (en)* | 2022-07-19 | 2022-09-30 | 中国电力科学研究院有限公司 | Power grid security analysis machine learning model testing method, device, equipment and medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN116484750A (en) | 2023-07-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112507936B (en) | Image information auditing method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| Sowah et al. | Decision support system (DSS) for fraud detection in health insurance claims using genetic support vector machines (GSVMs) | |
| CN113626607B (en) | Abnormal work order identification method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN111785384A (en) | Artificial intelligence-based abnormal data identification method and related equipment | |
| CN114462532A (en) | Model training method, method, device, equipment and medium for predicting transaction risk | |
| CN112131322B (en) | Time sequence classification method and device | |
| CN111966886B (en) | Object recommendation method, object recommendation device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111639706A (en) | Personal risk portrait generation method based on image set and related equipment | |
| CN111783039B (en) | Risk determination method, device, computer system and storage medium | |
| CN108428001B (en) | Credit score prediction method and device | |
| US20230197230A1 (en) | Hierarchy-aware adverse reaction embeddings for signal detection | |
| Ganguly et al. | A review of the role of causality in developing trustworthy ai systems | |
| CN114781832A (en) | Course recommendation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113469519B (en) | Business event attribution analysis method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN114708461A (en) | Multi-modal learning model-based classification method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114756669A (en) | Intelligent analysis method and device for problem intention, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN115222427A (en) | Fraud risk identification method and related equipment based on artificial intelligence | |
| CN114840660A (en) | Service recommendation model training method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114638299A (en) | Intelligent zombie license identification method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114610980A (en) | Network public opinion based black product identification method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114493142A (en) | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for matching support policies with enterprises | |
| WO2019223082A1 (en) | Customer category analysis method and apparatus, and computer device and storage medium | |
| CN118504752A (en) | Determination method of transaction risk prediction model, transaction risk prediction method, device, equipment, storage medium and program product | |
| CN115544902A (en) | Drugstore risk level identification model generation method and pharmacy risk level identification method | |
| CN116401606A (en) | Fraud identification method, device, equipment and medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20221230 | |
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |