CN115514273A - Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor - Google Patents
Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115514273A CN115514273ACN202211143002.7ACN202211143002ACN115514273ACN 115514273 ACN115514273 ACN 115514273ACN 202211143002 ACN202211143002 ACN 202211143002ACN 115514273 ACN115514273 ACN 115514273A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- speed
- phase
- position angle
- rotor position
- rotating speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P21/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of electric machines by vector control, e.g. by control of field orientation
- H02P21/14—Estimation or adaptation of machine parameters, e.g. flux, current or voltage
- H02P21/18—Estimation of position or speed
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P25/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of AC motor or by structural details
- H02P25/02—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of AC motor or by structural details characterised by the kind of motor
- H02P25/022—Synchronous motors
- H02P25/024—Synchronous motors controlled by supply frequency
- H02P25/026—Synchronous motors controlled by supply frequency thereby detecting the rotor position
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using DC to AC converters or inverters
- H02P27/08—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using DC to AC converters or inverters with pulse width modulation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P6/00—Arrangements for controlling synchronous motors or other dynamo-electric motors using electronic commutation dependent on the rotor position; Electronic commutators therefor
- H02P6/14—Electronic commutators
- H02P6/16—Circuit arrangements for detecting position
- H02P6/18—Circuit arrangements for detecting position without separate position detecting elements
- H02P6/182—Circuit arrangements for detecting position without separate position detecting elements using back-emf in windings
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P2207/00—Indexing scheme relating to controlling arrangements characterised by the type of motor
- H02P2207/05—Synchronous machines, e.g. with permanent magnets or DC excitation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Control Of Motors That Do Not Use Commutators (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明公开一种三相永磁同步电机全速域无位置传感器控制方法,属于发电、变电或配电的技术领域。The invention discloses a position sensorless control method in the full speed range of a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor, which belongs to the technical field of power generation, power transformation or power distribution.
背景技术Background technique
三相永磁同步电机结构简单、调速性能优异,在家用电器、风力发电、电动汽车、电动轮船和航空航天等诸多领域有广泛的应用前景。三相永磁同步电机通常采用磁场定向技术实现调速,对机械式转子位置传感器依赖性较大。一方面,机械式转子位置传感器价格比较高昂,在洗衣机和空调等一些对成本敏感的领域中的应用受到了限制;另一方面,机械式转子位置传感器对环境温度、湿度和安装方式有特殊的要求,这也限制了它在多数场合的实际应用。综合考虑,取消转子位置传感器对三相永磁同步电驱动系统的发展至关重要,在这种情况下,无位置传感器控制技术应运而生,无位置传感器控制技术又简称为无位置控制技术。当前,无位置控制系统在家电领域已经获得了成功的应用,但是也存在如下三个问题亟待解决:(1)调速性能慢,这是因为采用了大量的观测器和滤波器观测转子位置,因而相比于有位置控制而言调速性能严重退化,滤波器的引入往往还需要相位补偿;(2)观测的转子位置存在波动,这是因为随着观测器和滤波器的大量使用,各功能模块之间阻抗匹配失调,从而引起非线性振荡;(3)高低速无位置传感器控制在快速切换方面存在困难,其本质还是因转子位置观测器的动态响应较慢。因此,为了实现在全速范围内无位置控制、扩大三相永磁同步电驱动系统的应用范围,迫切需要发展高动态无位置控制技术。The three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor has a simple structure and excellent speed regulation performance, and has broad application prospects in many fields such as household appliances, wind power generation, electric vehicles, electric ships, and aerospace. Three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors usually use field-oriented technology to achieve speed regulation, which relies heavily on mechanical rotor position sensors. On the one hand, the price of the mechanical rotor position sensor is relatively high, and its application in some cost-sensitive fields such as washing machines and air conditioners is limited; on the other hand, the mechanical rotor position sensor has special requirements for ambient temperature, humidity and installation methods. requirements, which also limits its practical application in most occasions. Considering comprehensively, the elimination of the rotor position sensor is crucial to the development of the three-phase permanent magnet synchronous electric drive system. In this case, the position sensorless control technology emerges at the historic moment, and the position sensorless control technology is also referred to as the positionless control technology for short. At present, the positionless control system has been successfully applied in the field of home appliances, but there are still three problems to be solved urgently: (1) The speed regulation performance is slow, because a large number of observers and filters are used to observe the rotor position, Therefore, compared with position control, the speed regulation performance is seriously degraded, and the introduction of filters often requires phase compensation; (2) There are fluctuations in the observed rotor position, because with the extensive use of observers and filters, each Impedance mismatch between functional modules causes nonlinear oscillation; (3) There are difficulties in fast switching between high and low speed position sensorless control, which is essentially due to the slow dynamic response of the rotor position observer. Therefore, in order to realize positionless control in the full speed range and expand the application range of three-phase permanent magnet synchronous electric drive system, it is urgent to develop high dynamic positionless control technology.
现有的全速域无位置控制技术有以下三个缺陷:(1)在低速域通常采用高频脉动信号注入法,而在低速域采用高频脉动信号注入法会产生高频噪音以及电磁干扰,给电机带来额外的发热损耗;(2)在低速域向中高速域过渡时,需要综合考虑高频脉动信号注入法获得的有效位置信息和中高速域观测的位置信号获取中高速域的给定转速,一方面,高频脉动信号注入法提取有效位置信息需要的多个滤波器影响整个控制方法的动态响应性能,另一方面,中高速域常用的滑模观测法存在的抖动问题既影响整个控制方法的动态响应性能又影响算法的平稳过渡;(3)将转速区间划分为零低速、低速、中高速三个区间,对每个转速区间采用不同的无位置算法,判断电机初始转速所属区间后采用对应的无位置算法,不同转速区间下无位置控制算法的切换给系统带来不稳定性,应用不同无位置算法所增加的编码工作加重了数字控制器的运算负担,算法复杂。The existing positionless control technology in the full-speed domain has the following three defects: (1) The high-frequency pulse signal injection method is usually used in the low-speed domain, and the high-frequency pulse signal injection method in the low-speed domain will generate high-frequency noise and electromagnetic interference. Bring additional heat loss to the motor; (2) When transitioning from the low-speed domain to the medium-high speed domain, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the effective position information obtained by the high-frequency pulse signal injection method and the position signal obtained by the medium-high speed domain observation. Fixed speed, on the one hand, the multiple filters required to extract effective position information by the high-frequency pulse signal injection method affect the dynamic response performance of the entire control method; The dynamic response performance of the entire control method also affects the smooth transition of the algorithm; (3) Divide the speed interval into three intervals: zero-low speed, low speed, and medium-high speed, and use different positionless algorithms for each speed interval to determine the motor’s initial speed. After the interval, the corresponding positionless algorithm is adopted. The switching of the positionless control algorithm under different speed intervals brings instability to the system. The increased coding work of applying different positionless algorithms increases the computational burden of the digital controller, and the algorithm is complex.
本发明旨在提出一种三相永磁同步电机全速域无位置传感器器控制方法以克服上述缺陷。The present invention aims to propose a position sensorless control method in the full speed range of a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor to overcome the above-mentioned defects.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是针对以上所述背景技术的局限性,提出一种三相永磁同步电机全速域无位置传感器控制方法,摈弃划分不同转速区间后根据实时转速切换至不同无位置控制算法的思路,先采用斜坡给定转速变频起动电机,再采用反电动势模型法实现全速域无位置控制,实现动态响应无位置控制并平稳调节电机转速的发明目的,解决现有永磁同步电机全速域无位置传感器控制技术算法复杂、难以兼顾动态响应和稳态精度的技术问题。The purpose of the present invention is to propose a position sensorless control method in the full speed range of a three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor in view of the limitations of the above-mentioned background technology, and abandon the idea of dividing different speed ranges and switching to different positionless control algorithms according to the real-time speed , first use the slope given speed variable frequency starter motor, and then use the back electromotive force model method to realize the full speed range without position control, realize the invention purpose of dynamic response without position control and smoothly adjust the motor speed, and solve the problem of the existing permanent magnet synchronous motor without position in the full speed range The algorithm of sensor control technology is complex, and it is difficult to take into account the technical problems of dynamic response and steady-state accuracy.
本发明为实现上述发明目的采用如下技术方案:基于一种反电动势实时计算算法、反电动势归一化、考虑切换时序的正交锁相环实现全速域内的无位置控制。其中,反电动势实时计算算法不包含电流微分项,并能有效减少对电机参数的依赖,它无需迭代即可实现无差拍观测反电动势,解决了目前反电动势观测算法计算量大、动态响应慢和运算复杂的问题。进一步地,在不使用滤波器的情况下直接对反电动势观测值进行归一化处理,结合锁相环系统计算转子转速和转子位置。本发明的锁相环技术考虑了低速和中高速无位置控制的切换时序,可实现电机从零速或极低速起动并可即时切换至中高速域无位置控制。The present invention adopts the following technical solution to achieve the above invention object: based on a back EMF real-time calculation algorithm, back EMF normalization, and a quadrature phase-locked loop that considers the switching sequence to realize positionless control in the full speed range. Among them, the back EMF real-time calculation algorithm does not include the current differential item, and can effectively reduce the dependence on the motor parameters. It can realize the back EMF measurement without iteration, which solves the problem of the current back EMF observation algorithm, which has a large amount of calculation and slow dynamic response. and computationally complex problems. Furthermore, without using a filter, the observed value of the back electromotive force is directly normalized, and the rotor speed and rotor position are calculated in combination with the phase-locked loop system. The phase-locked loop technology of the present invention considers the switching sequence of low-speed and medium-high speed without position control, and can realize the motor starting from zero speed or very low speed and can switch to medium-high speed without position control immediately.
首先该发明利用了一种三相PMSM的反电动势实时计算算法,其具体表达式为:First of all, the invention utilizes a real-time calculation algorithm of back electromotive force of a three-phase PMSM, and its specific expression is:
式(1)中,iα,iβ分别为电机定子电流在静止坐标系(α-β坐标系)α轴和β轴上的分量;uα,uβ分别为电机输入电压在静止坐标系α轴和β轴上的分量;Lq为交轴电感;Rs为电机定子每相绕组的电阻;ωe为电角速度;eα,eβ为α-β坐标系下的一种扩展反电动势,且满足:In formula (1), iα , iβ are the components of the motor stator current on the α-axis and β-axis of the stationary coordinate system (α-β coordinate system) respectively; uα , uβ are the motor input voltage in the stationary coordinate system Components on theα -axis andβ -axis; Lq is the quadrature axis inductance; Rs is the resistance of each phase winding of the motor stator; ωe is the electrical angular velocity; Electromotive force, and satisfy:
式(2)中,Ld为直轴电感,id,iq分别为电机定子电流在d-q坐标系d轴和q轴上的分量,p为电机极对数,ψf为永磁体磁链,θe代表了电机转子的位置信息。In formula (2), Ld is the direct axis inductance, id and iq are the components of the motor stator current on the d-axis and q-axis of the dq coordinate system, respectively, p is the number of pole pairs of the motor, and ψf is the flux linkage of the permanent magnet , θe represents the position information of the motor rotor.
进一步地,求出扩展反电动势幅值Eamp:Further, calculate the extended back electromotive force amplitude Eamp :
进一步地,对扩展反电动势eα,eβ进行标幺化处理:Further, the extended back electromotive force eα , eβ is per unitized:
进一步地,将标幺化的扩展反电动势输入到锁相环(Phase-locked Loop,PLL),并与锁相环输出的转子信息进行如下运算:Further, the p.u. extended back electromotive force is input into a phase-locked loop (PLL), and the following operation is performed with the rotor information output by the phase-locked loop:
式(5)中,为锁相环提取的转子位置角,由于:In formula (5), The rotor position angle extracted for the PLL, due to:
所以在稳态下,可近似认为Δθ为锁相环输出转子位置角与扩展反电动势观测位置角θe之间的差值。锁相环能够实现对扩展反电动势观测位置角θe的无静差跟踪,具有较好的无位置控制稳态性能。Therefore, in the steady state, Δθ can be approximately considered as the phase-locked loop output rotor position angle and the difference between the extended back EMF observation position angleθe . The phase-locked loop can realize static error-free tracking of the extended back-EMF observation position angle θe , and has better steady-state performance without position control.
当电机运行在零速或极低速时,由于反电动势以及定子电流很小,有用信号的信噪比很低,造成转子位置和转速检测误差大,电机起动过程中容易失步甚至起动失败。为解决上述问题,本发明提出一种起动阶段与中高速阶段良好衔接的方法,可具体描述为:When the motor is running at zero speed or very low speed, the signal-to-noise ratio of the useful signal is very low due to the small counter electromotive force and stator current, resulting in a large error in the detection of the rotor position and speed, and the motor is prone to out-of-step or even failure during starting. In order to solve the above problems, the present invention proposes a method for good connection between the start-up phase and the medium-high speed phase, which can be specifically described as:
起动阶段,生成一个给定斜坡转速ωstart,并覆盖锁相环的PI控制器输出,同时限制转速PI输出幅值用于实现低速恒流启动。给定斜坡转速ωstart是一个从0开始自增运算的数值,经过锁相环的积分环节得到给定变化的位置角θstart,θstart只是一个虚拟的转子位置角,并不能反映转子起动阶段的实际位置,其作用在于生成一个起动旋转磁场。由于该旋转磁场的角速度与ωstart相等,而ωstart从零速到低速域增加,由于ωstart变化较慢,所以即使提供的θstart不是精确的位置信号,电机也能跟随ωstart起动。In the starting phase, a given ramp speed ωstart is generated and overwrites the output of the PI controller of the phase-locked loop. At the same time, the amplitude of the PI output of the speed is limited for low-speed constant-current startup. The given ramp speed ωstart is a value that is self-increased from 0. After the integral link of the phase-locked loop, the given changing position angle θstart is obtained. θstart is only a virtual rotor position angle and cannot reflect the rotor starting stage. The actual position of , its role is to generate a starting rotating magnetic field. Since the angular velocity of the rotating magnetic field is equal to ωstart , and ωstart increases from zero speed to low speed, and since ωstart changes slowly, the motor can start following ωstart even if the provided θstart is not an accurate position signal.
为实现电机由起动阶段向中高速阶段切换,需设置一个切换信号K以及转速切换阈值ωswitch。ωswitch可取10~30rad/s,若取值太小,反电动势很小,切换后得到的转子信息估算误差依然很大,容易造成起动失败,若取值太大,由于θstart在较高转速下与实际位置角误差较大,电机转速还未达到ωswitch就出现失步的风险。当ωstart<ωswitch时,电机处于起动阶段,切换信号K=0。当ωstart>ωswitch时,代表起动阶段已完成,触发切换信号K=1,锁相环系统接收到该信号后,ωstart不再覆盖锁相环的PI输出,而是将ωstart的数值赋给PI调节器的积分初值,锁相环的PI输出将从ωstart开始进行自治调节,经过积分环节后输出也会自治调节逐步接近真实的转子位置角;同时,进一步放开转速PI控制器的输出限幅。In order to switch the motor from the starting stage to the medium-high speed stage, it is necessary to set a switching signal K and a speed switching threshold ωswitch . ωswitch can be 10~30rad /s, if the value is too small, the counter electromotive force is very small, and the estimation error of the rotor information obtained after switching is still large, which will easily cause starting failure. The error between the lower and actual position angle is large, and there is a risk of out-of-step before the motor speed reaches ωswitch . When ωstart <ωswitch , the motor is in the starting phase, and the switching signal K=0. When ωstart >ωswitch , it means that the starting phase has been completed, and the trigger switch signal K=1. After the phase-locked loop system receives this signal, ωstart no longer covers the PI output of the phase-locked loop, but the value of ωstart The integral initial value assigned to the PI regulator, the PI output of the phase-locked loop will self-regulate starting from ωstart , Output after integration It will also be adjusted autonomously to gradually approach the real rotor position angle; at the same time, the output limit of the speed PI controller will be further released.
由于切换发生时,锁相环PI的输出是从ωstart开始,因此实现了两种模式的平稳切换,不会因为与ωswitch相差较大而造成切换时发生抖振等问题。Since the output of the phase-locked loop PI starts from ωstart when switching occurs, the smooth switching of the two modes is realized without The large difference from ωswitch causes problems such as chattering when switching.
切换完成以后,电机进入中高速阶段,锁相环估算的转速信号一方面作用于反电动势实时计算,另一方面用于转速闭环调节。通过改变转速环的转速参考值ωref实现电机的调速控制。After the switching is completed, the motor enters the medium-high speed stage, and the speed signal estimated by the phase-locked loop On the one hand, it acts on the real-time calculation of the counter electromotive force, and on the other hand, it is used for the closed-loop adjustment of the speed. The speed regulation control of the motor is realized by changing the speed reference value ωref of the speed loop.
进一步地,锁相环包括:Further, the phase-locked loop includes:
鉴相器,其一个输入端接收通过归一化扩展反电动势获取转子位置角观测信息,其另一个输入端接收目标转子位置角信号,输出目标转子位置角与通过归一化扩展反电动势获取的转子位置角的差值;A phase detector, one of its input terminals receives the rotor position angle observation information obtained by normalizing the extended back electromotive force, and its other input terminal receives the target rotor position angle signal, and outputs the target rotor position angle and the obtained by normalizing the extended back electromotive force. The difference in rotor position angle;
PI控制器,其第一输入端与鉴相器的输出端连接,其第二输入端接收切换信号,其第三输入端在切换信号表征给定斜坡转速信号达到切换阈值时接收斜坡转速信号;PI controller, its first input terminal is connected to the output terminal of the phase detector, its second input terminal receives the switching signal, and its third input terminal receives the ramp speed signal when the switching signal represents a given ramp speed signal reaching the switching threshold;
切换开关,其一个输入端接PI控制器的输出端,其另一个输入端接收给定斜坡转速信号,其控制端接收切换信号,在切换信号表征给定斜坡转速信号未达到切换阈值时传输给定斜坡转速信号至积分器的输入端以及转速外环,在切换信号表征给定斜坡转速信号达到切换阈值时传输PI控制器输出信号至积分器的输入端以及转速外环;及,A changeover switch, one of its input terminals is connected to the output terminal of the PI controller, the other input terminal receives a given ramp speed signal, and its control terminal receives a switching signal, and when the switching signal indicates that the given ramp speed signal does not reach the switching threshold, it is transmitted to setting the ramp speed signal to the input terminal of the integrator and the speed outer loop, and transmitting the PI controller output signal to the input terminal of the integrator and the speed outer loop when the switching signal represents that the given ramp speed signal reaches the switching threshold; and,
积分器,其输入端接切换开关的输出端,输出目标转子位置角信号至电流内环以及转速外环。The integrator, whose input terminal is connected to the output terminal of the switch, outputs the target rotor position angle signal to the current inner loop and the rotational speed outer loop.
本发明采用上述技术方案,具有以下优势:The present invention adopts above-mentioned technical scheme, has the following advantages:
(1)本发明将一种反电动势实时计算算法与锁相环技术联合使用,将两者的优势结合,避免传统扩展反电动势观测算法带来的电流微分误差,仅需电阻和交轴电感两个电机参数,有效减少对电机参数的依赖,无需迭代即可实现无差拍观测反电动势,在不使用滤波器的情况下直接对反电动势观测值进行归一化处理,既克服目前反电动势观测算法计算量大、动态响应慢和运算复杂的缺陷,也解决低通滤波带来相位延迟误差的问题,再通过锁相环处理归一化电动势后得到的转子位置角信息,能够估算出较为准确的转子位置信息,使得无位置控制系统的稳态性能和动态性能都有所改善。(1) The present invention combines a real-time calculation algorithm of back EMF with phase-locked loop technology, combines the advantages of the two, avoids the current differential error caused by the traditional extended back EMF observation algorithm, and only needs two components of resistance and quadrature axis inductance One motor parameter, which effectively reduces the dependence on motor parameters, realizes back-EMF observation without iteration, and directly normalizes the back-EMF observation value without using a filter, which overcomes the current back-EMF observation The algorithm has the defects of large amount of calculation, slow dynamic response and complex calculation, and also solves the problem of phase delay error caused by low-pass filtering, and then processes the rotor position angle information obtained after normalizing the electromotive force through the phase-locked loop, which can estimate more accurately The rotor position information can improve the steady-state performance and dynamic performance of the positionless control system.
(2)本发明在零速或极低速采用斜坡给定转速变频起动,相比于高频信号注入法具有动态响应高的优势,所采用的锁相环技术考虑低速和中高速无位置控制的切换时序,,可实现电机从零速或极低速起动并可即时切换至中高速域的无位置控制,在软件算法上更加简单,大大减少代码冗余繁杂,减轻数字控制器的运算负担,具有算法简单、兼顾动态响应和稳态精度、适合中低端数字控制器编程的特点,可有效拓展无转子位置控制技术的应用范围。(2) The present invention adopts slope given speed variable frequency starting at zero speed or very low speed, which has the advantage of high dynamic response compared to the high frequency signal injection method, and the phase locked loop technology adopted considers low speed and medium and high speed without position control The switching sequence can realize the positionless control of the motor starting from zero speed or very low speed and switching to the medium and high speed domain in real time. It is simpler in software algorithm, greatly reduces code redundancy and complexity, and reduces the calculation burden of digital controller. It has the advantages of The algorithm is simple, both dynamic response and steady-state accuracy are considered, and it is suitable for the programming of low-end digital controllers, which can effectively expand the application range of rotorless position control technology.
(3)本发明提出的起动阶段向中高速阶段柔性切换方法,能够实现起动阶段向中高速阶段即时过渡,甚至可以在电机起动时就设定一个高目标转速,电机从起动到目标转速可连贯完成,保证无位置控制的快速性。(3) The flexible switching method from the starting stage to the medium and high speed stage proposed by the present invention can realize the instant transition from the starting stage to the medium and high speed stage, and even set a high target speed when the motor is started, and the motor can be continuous from the start to the target speed Complete, guaranteeing the rapidity of position-free control.
(4)本发明提出的无位置控制方法不仅适用于隐极式电机,同样适用于凸极式电机,在永磁同步电机的无位置控制中具有普适性。(4) The positionless control method proposed by the present invention is not only suitable for hidden pole motors, but also suitable for salient pole motors, and has universal applicability in the positionless control of permanent magnet synchronous motors.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是三相PMSM无位置控制的系统框图。Fig. 1 is a system block diagram of three-phase PMSM without position control.
图2是本发明所利用的一种扩展反电动势实时计算算法原理图。Fig. 2 is a principle diagram of an extended counter electromotive force real-time calculation algorithm utilized in the present invention.
图3是本发明利用的锁相环算法原理图。Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the phase-locked loop algorithm utilized in the present invention.
图4是电机零速起动升至200rpm时的实验波形图。Figure 4 is the experimental waveform diagram when the motor starts at zero speed and rises to 200rpm.
图5是电机转速由200rpm升至750rpm的实验波形图。Fig. 5 is the experimental waveform diagram of the motor speed rising from 200rpm to 750rpm.
图6是电机转速由750rpm降至200rpm的实验波形图。Fig. 6 is an experimental waveform diagram of the motor speed decreasing from 750rpm to 200rpm.
图7是电机转速在200rpm时的扩展反电动势波形图。Fig. 7 is the extended back electromotive force waveform diagram when the motor speed is 200rpm.
图8是电机转速在750rpm时的扩展反电动势波形图。Figure 8 is the extended back EMF waveform diagram when the motor speed is at 750rpm.
图9是电机转速从零速起动升至200rpm再升至750rpm的转速波形图。Fig. 9 is a waveform diagram of the motor speed rising from zero speed starting to 200rpm and then rising to 750rpm.
图10是电机转速从750rpm降至200rpm再降至0的转速波形图。Fig. 10 is a waveform diagram of the motor speed decreasing from 750rpm to 200rpm and then to 0.
具体实施方式detailed description
为了将本发明的实施方法与技术优势阐述得更加清晰易懂,下面结合附图对本发明的技术方案进行详细说明。In order to explain the implementation method and technical advantages of the present invention more clearly and easily, the technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
三相PMSM无位置控制的系统框图如图1所示,该系统的闭环控制主要包含转速外环,电流内环以及锁相环。给定转速ωref送入转速外环,与反馈转速作差后,经过转速PI调节器输出iqref的指令值,idref的指令值设置为0。dq轴的指令值idref、iqref送入电流内环,与反馈电流id、iq作差后,经过电流PI调节器输出控制电压ud和uq。ud和uq根据观测的位置角经过Park逆变换得到α-β坐标系下的uα和uβ,uα和uβ采用合适的PWM技术(如SVPWM,空间矢量脉宽调制)得到三相定子坐标系中的变量uA、uB、uC,经过比较与驱动电路后,生成控制逆变器开关管导通/关断的驱动信号,从而生成控制电机运动状态的三相电流iA、iB、iC。对三相电流iA、iB、iC进行采样并做Clark变换得到α-β坐标系下的iα和iβ,一方面iα和iβ根据观测的位置角经过Park变换得到d-q坐标系下的id、iq,然后将id、iq作为反馈电流送入电流PI调节器实现电流闭环控制。另一方面,iα、iβ、uα和uβ一起作为扩展反电动势实时计算算法的输入,再加上观测转速扩展反电动势eα和eβ将被实时计算得到。将扩展反电动势eα和eβ进行标幺化处理,得到包含转子位置信息的三角函数sinθe和cosθe。将sinθe和cosθe送入PLL,经过PLL提取估算出转速一方面估算转速会反馈至转速PI调节器,实现转速闭环控制,另一方面,估算转速经过积分环节得到观测的位置角起动与中高速切换系统用来控制电机零速或极低速起动,并实现起动后向中高速阶段柔性切换的功能。PLL输出的估算转速以及积分后的观测位置角是无位置控制系统中最关键的两个参量,它们估算的精确与否直接影响到无位置控制系统性能的好坏。The system block diagram of three-phase PMSM without position control is shown in Figure 1. The closed-loop control of the system mainly includes the outer speed loop, the inner current loop and the phase-locked loop. The given speed ωref is sent to the outer ring of the speed, and the feedback speed After making a difference, the command value of iqref is output through the speed PI regulator, and the command value of idref is set to 0. The command valuesidref andiqref of the dq axis are sent to the current inner loop, and after making a difference with the feedback current id andiq , the control voltagesud anduq are output through the current PI regulator. ud and uq according to the observed position angle Uα and u β in the α-β coordinate system are obtained through Park inverse transformation, u αand u βuseappropriate PWM technology (such as SVPWM, space vector pulse width modulation) to obtain the variables uA , uB , uC , after comparison and driving circuit, generate the driving signal to control the on/off of the inverter switch tube, thereby generating the three-phase current iA , iB , iC that control the motion state of the motor. Sampling the three-phase currents iA , iB , and iC and performing Clark transformation to obtain iα and iβ in the α-β coordinate system. On the one hand, iα and iβ are based on the observed position angle After Park transformation, id and iq in the dq coordinate system are obtained, and then id and iq are sent as feedback current to the current PI regulator to realize current closed-loop control. On the other hand, iα , iβ , uα and uβ together serve as the input of the extended back-emf real-time calculation algorithm, together with the observed rotational speed The extended back EMF eα and eβ will be calculated in real time. The extended counter electromotive force eα and eβ are converted into per unit, and the trigonometric functions sinθe and cosθe including the rotor position information are obtained. Send sinθe and cosθe to PLL, and estimate the rotational speed through PLL extraction Estimating speed on the one hand It will be fed back to the speed PI regulator to realize the closed-loop control of the speed. On the other hand, the estimated speed The observed position angle is obtained through the integration link The starting and medium-to-high-speed switching system is used to control the motor to start at zero speed or very low speed, and realize the function of flexible switching to the medium-to-high speed stage after starting. Estimated speed of PLL output and the integrated observation position angle They are the two most critical parameters in the positionless control system, and the accuracy of their estimation directly affects the performance of the positionless control system.
本发明所利用的一种扩展反电动势实时计算算法原理如图2所示。以凸极式PMSM为例,重写扩展反电动势观测模型:The principle of an extended counter electromotive force real-time calculation algorithm used in the present invention is shown in FIG. 2 . Taking the salient pole PMSM as an example, rewrite the extended back EMF observation model:
从式(8)中可知,要想求出扩展反电动势eα和eβ,需要输入的变量为uα、uβ、iα、iβ和ωe,其中,ωe可由锁相环估算的转速得到,即uα和uβ由电流PI调节器输出的ud和uq经过Park逆变换得到,表达式为:It can be known from formula (8) that in order to obtain the extended back electromotive force eα and eβ , the variables that need to be input are uα , uβ , iα , iβ and ωe , where ωe can be estimated by the phase-locked loop speed of get, ie uα and uβ are obtained by inverse Park transformation of ud and uq output by the current PI regulator, and the expressions are:
式(9)中的为锁相环观测的位置角iα和iβ由电机三相电流进行采样并做Clark变换得到,表达式为:In formula (9) is the position angle observed by the phase-locked loop iα and iβ are obtained by sampling the three-phase current of the motor and performing Clark transformation, and the expressions are:
得到扩展反电动势实时计算算法所需的输入变量后,根据图2所示的扩展反电动势实时计算算法即可得到扩展反电动势的观测值和其具体描述为:After obtaining the input variables required by the real-time calculation algorithm of the extended back-emf, the observed value of the extended back-emf can be obtained according to the real-time calculation algorithm of the extended back-emf shown in Figure 2 and Its specific description is:
第一乘法器M1对α-β坐标系下的电机电流iα和定子绕组电阻Rs进行乘法运算,输出乘积结果至第一加法器A1;第二乘法器M2对α-β坐标系下的电机电流iβ和定子绕组电阻Rs进行乘法运算,输出乘积结果至第三加法器A3;第三乘法器M3对锁相环估算的电角速度和交轴电感Lq进行乘法运算,输出乘积结果至第四乘法器M4;第五乘法器M5对iα以及第三乘法器输出的结果进行乘法运算,输出乘积结果至第三加法器A3;第一加法器A1对第一乘法器输出的乘积结果以及第四乘法器输出的乘积结果进行累加运算,输出累加结果至第二加法器A2;第三加法器A3对第二乘法器输出的乘积结果以及第五乘法器输出的乘积结果进行累加运算,输出累加结果至第四加法器A4;第二加法器A2对第一加法器输出的累加结果以及α-β坐标系下的电压uα进行累加运算,输出α-β坐标系下的扩展反电动势的观测值第四累加器对第三累加器输出的累加结果以及α-β坐标系下的电压uβ进行累加运算,输出α-β坐标系下的扩展反电动势的观测值The first multiplier M1 multiplies the motor current iα in the α-β coordinate system and the stator winding resistance Rs , and outputs the product result to the first adder A1; the second multiplier M2 performs a multiplication operation on the α-β coordinate system The motor current iβ and the stator winding resistance Rs are multiplied, and the result of the product is output to the third adder A3; the third multiplier M3 calculates the electrical angular velocity estimated by the phase-locked loop Carry out multiplication with the quadrature axis inductance Lq , and output the product result to the fourth multiplier M4; the fifth multiplier M5 multiplies iα and the result output by the third multiplier, and outputs the product result to the third adder A3; The first adder A1 performs accumulation operation on the multiplication result output by the first multiplier and the multiplication result output by the fourth multiplier, and outputs the accumulation result to the second adder A2; the third adder A3 outputs the product of the second multiplier The result and the multiplication result output by the fifth multiplier are accumulated, and the accumulated result is output to the fourth adder A4; the second adder A2 performs the accumulation result output by the first adder and the voltage uα under the α-β coordinate system Accumulation operation, output the observed value of the extended back electromotive force in the α-β coordinate system The fourth accumulator accumulates the accumulated result output by the third accumulator and the voltage uβ in the α-β coordinate system, and outputs the observed value of the extended back electromotive force in the α-β coordinate system
从该算法可以清楚得知,传统扩展反电动势中的电流微分项被ωeiα或ωeiβ取代,这样就避免了微分误差和迭代运算,使得位置角信息估算更准确。It can be clearly seen from the algorithm that the current differential term in the traditional extended back EMF is replaced by ωe iα or ωe iβ , which avoids differential errors and iterative operations, and makes the position angle information estimation more accurate.
本发明所利用的锁相环算法原理如图3所示,其具体描述为:The phase-locked loop algorithm principle that the present invention utilizes is as shown in Figure 3, and its specific description is:
第六乘法器M6对扩展反电动势观测器输出的取反并和扩展反电动势幅值的倒数进行乘法运算,其目的在于对扩展反电动势进行标幺化处理,从而将扩展反电动势转换为包含位置角信息的三角函数同理,第七乘法器M7对扩展反电动势观测器输出的和扩展反电动势幅值的倒数进行乘法运算,输出乘积的结果为第八乘法器M8对第六乘法器输出的结果和锁相环输出的观测位置角取余弦函数的结果进行乘法运算。第九乘法器M9对第七乘法器输出的结果和锁相环输出的观测位置角取正弦函数的结果进行乘法运算。第五加法器A5对第八乘法器输出的结果和第九乘法器输出的结果进行作差运算,并将计算结果送入锁相环系统的比例积分调节器(PI调节器)。PI调节器输出的结果为锁相环系统估算的转速当锁相环系统的切换信号K=1时,估算转速经过积分环节输出观测位置角当锁相环系统的切换信号K=0时,此时控制系统还处于起动阶段,锁相环系统内部生成的起动给定斜坡转速ωstart会代替估算转速进入积分环节。当锁相环系统的切换信号K=1时,锁相环系统由到的传递函数可表示为:The sixth multiplier M6 expands the output of the back electromotive force observer Negate and sum the reciprocal of the extended back EMF magnitude Perform multiplication, the purpose of which is to process the extended back EMF per unit, thereby converting the extended back EMF into a trigonometric function including position angle information In the same way, the seventh multiplier M7 is output to the extended back EMF observer and the reciprocal of the magnitude of the extended back EMF Multiplication is performed, and the result of the output product is The result of the output of the eighth multiplier M8 to the sixth multiplier and the observed position angle of the phase-locked loop output Take the result of the cosine function Perform multiplication. The result of the ninth multiplier M9 to the output of the seventh multiplier and the observed position angle of the phase-locked loop output Take the result of the sine function Perform multiplication. The fifth adder A5 performs difference operation to the result output by the eighth multiplier and the result output by the ninth multiplier, and calculates the result Feed to the proportional-integral regulator (PI regulator) of the phase-locked loop system. The result output by the PI regulator is the speed estimated by the phase-locked loop system When the switching signal K=1 of the phase-locked loop system, the estimated speed After the integration link, the observed position angle is output When the switching signal K of the phase-locked loop system is K=0, the control system is still in the start-up phase, and the given ramp speed ωstart generated inside the phase-locked loop system will replace the estimated speed Enter the points section. When the switching signal K of the phase-locked loop system=1, the phase-locked loop system consists of arrive The transfer function of can be expressed as:
式(11)中ωn决定PI调节器的带宽。锁相环的性能往往受转速环和电流环的动态性能的影响,对于Kp、Ki的选取,需从整个控制系统考虑,Kp过小,会导致估算转速的变化跟不上转速环的响应速度,从而导致系统失控;Kp过大,会导致估算转速的精度与实际转速相差过大,稳态性能降低。Ki一般选取较大值,可以保证在转速大幅度阶跃信号下无位置控制的可靠性。In formula (11) ωn determines the bandwidth of the PI regulator. The performance of the phase-locked loop is often affected by the dynamic performance of the speed loop and the current loop. For the selection of Kp and Ki , the entire control system needs to be considered. If Kp is too small, the change of the estimated speed will not keep up with the speed loop. If Kp is too large, the difference between the accuracy of the estimated speed and the actual speed will be too large, and the steady-state performance will be reduced. Ki generally chooses a larger value, which can ensure the reliability of no-position control under a large-scale step signal of the speed.
本发明所提出的零速或极低速恒流变频起动方法和起动阶段向中高速阶段柔性切换方法,具体描述为:The zero-speed or extremely low-speed constant-current variable-frequency starting method and the flexible switching method from the starting stage to the medium-high speed stage proposed by the present invention are specifically described as follows:
起动阶段,锁相环的切换信号K=0,向转速PI调节器输出限幅信号,从而限制起动电流,由于PI调节器在起动阶段饱和,所以输出电流恒定。此外,锁相环系统内部生成的起动给定斜坡转速ωstart做自加运算,可表示为:In the starting phase, the switching signal K of the phase-locked loop is 0, and the limiting signal is output to the PI regulator of the rotational speed, thereby limiting the starting current. Since the PI regulator is saturated in the starting phase, the output current is constant. In addition, the starting given ramp speed ωstart generated inside the phase-locked loop system is used for self-addition operation, which can be expressed as:
ωstart=ωstart′+atk (12)ωstart = ωstart ′+atk (12)
上式中,ωstart′为处理器上一次计算得到的给定转速值,tk为处理器计算周期,a为自增系数,在计算周期不变的情况下,a的取值决定了ωstart的增长速率。In the above formula, ωstart ′ is the given speed value calculated by the processor last time, tk is the calculation cycle of the processor, and a is the self-increment coefficient. When the calculation cycle remains unchanged, the value of a determines ω The growth rate ofstart .
在起动阶段,锁相环输出的观测位置角用来指示SVPWM算法让电机生成圆形旋转磁场,且磁场旋转速度等于ωstart/p,p为电机的极对数。由于磁场旋转速度从0开始缓慢增加,可以带动电机跟随该旋转磁场起动。In the start-up phase, the observed position angle output by the phase-locked loop It is used to instruct the SVPWM algorithm to make the motor generate a circular rotating magnetic field, and the rotating speed of the magnetic field is equal to ωstart /p, where p is the number of pole pairs of the motor. Since the rotation speed of the magnetic field increases slowly from 0, the motor can be driven to start following the rotating magnetic field.
设定ωstart=A时(A为转速切换阈值,可取10~30rad/s),锁相环系统进入切换点,内部生成切换信号K=1,此时锁相环输出的观测位置角将由估算转速代替起动阶段的ωstart后经积分环节得到,且放开转速PI调节器限幅。在起动阶段,由于反电动势和定子电流很小造成估算转速误差较大,所以并未作用于控制系统,但随着起动转速的建立,实际转速逐渐接近ωstart,扩展反电动势估算位置角也逐渐接近θstart,此时将ωstart的数值赋给锁相环PI调节器的积分初值,让估算转速从ωstart开始自治调节,经过积分环节得到的观测位置角也开始向扩展反电动势估算的位置角平滑切换。由于在切换点,有且接近θstart,所以观测位置角能在转速波动不大的情况下,从θstart向平滑过渡。When ωstart = A (A is the speed switching threshold, which can be 10~30rad/s), the phase-locked loop system enters the switching point, and the internally generated switching signal K=1. At this time, the observed position angle output by the phase-locked loop is will be estimated by the speed Instead of ωstart in the starting phase, it is obtained through the integral link, and the limit of the speed PI regulator is released. During the starting phase, the estimated speed due to the small back EMF and stator current The error is large, so It does not act on the control system, but with the establishment of the starting speed, the actual speed gradually approaches ωstart , and the estimated position angle of the expanded back EMF is also gradually approaching θstart , at this time, the value of ωstart is assigned to the integral initial value of the phase-locked loop PI regulator, so that the estimated speed Self-regulated from ωstart , Observation position angle obtained through integration link also begins to extend the back-EMF estimation to the position angle Smooth switching. Since at the switching point, there is and close to θstart , so the observed position angle It can move from θstart to Smooth transition.
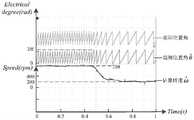
为验证本发明的实际有效性,本发明基于STM32数字控制器搭建实验平台进行验证。图4为4对极三相PMSM从0开始起动升速至200rpm的实验波形图,从图中可以清楚看到起动过程中,观测位置角很快就与实际位置角保持同相位,证明起动具有很好的可靠性。将起动阶段向中高速阶段过渡的切换点设置在100rpm,从图中可以看到,当观测转速达到100rpm后,短时间里有略微下降,说明锁相环跟踪的转速由ωstart变为后,控制系统仍然需要一定时间做出调整,不过调整时间内,观测转速并未出现抖动,说明切换过程较为平滑。进入到中高速阶段后,观测转速快速上升至200rpm。In order to verify the actual effectiveness of the present invention, the present invention builds an experimental platform based on the STM32 digital controller for verification. Figure 4 is the experimental waveform diagram of the 4-pair three-phase PMSM starting from 0 and increasing the speed to 200rpm. From the figure, it can be clearly seen that during the starting process, the observed position angle quickly maintains the same phase as the actual position angle, which proves that the starting has Very good reliability. Set the switching point for the transition from the starting stage to the medium-high speed stage at 100rpm. It can be seen from the figure that when the observed speed reaches 100rpm, there is a slight drop in a short time, indicating that the speed tracked by the phase-locked loop changes from ωstart to After that, the control system still needs a certain amount of time to make adjustments, but within the adjustment time, the observed speed does not jitter, indicating that the switching process is relatively smooth. After entering the middle and high speed stage, the observation speed rises rapidly to 200rpm.
图5和图6分别给出了三相PMSM从200rpm升速至750rpm和从750rpm降速至200rpm的实验波形图。从两图中可得知,无论是升速还是降速,暂态过程只有约0.4s,证明本发明在调速过程的动态响应良好,且观测位置角始终与实际位置角同相位,证明本发明观测的位置信息精确,稳态性能良好。Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the experimental waveforms of three-phase PMSM speed up from 200rpm to 750rpm and speed down from 750rpm to 200rpm respectively. It can be seen from the two figures that the transient process is only about 0.4s whether it is speed up or down, which proves that the dynamic response of the present invention is good in the speed regulation process, and the observed position angle is always in the same phase as the actual position angle, which proves that the present invention The position information observed by the invention is accurate, and the steady-state performance is good.
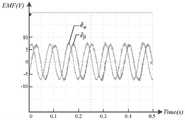
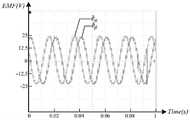
图7和图8分别给出了三相PMSM在200rpm和750rpm时的扩展反电动势波形。从图中可以看出和波形上为较为平滑的正弦波,其中观测转速为200rpm时,扩展反电动势幅值约为7.5V,观测转速为750rpm时,扩展反电动势幅值约为25V。由于数字控制器处理性能限制,锁相环系统的采样周期设置为1ms,在较高转速下,扩展反电动势一个周期内得到锁相环系统更新的观测位置角数量相对更少,所以会出现较小的阶梯波形,如果缩短锁相环的采样周期,则高转速下的扩展反电动势波形会更加平滑。Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the extended back EMF waveforms of the three-phase PMSM at 200rpm and 750rpm, respectively. It can be seen from the figure and The waveform is a relatively smooth sine wave. When the observed speed is 200rpm, the amplitude of the extended back EMF is about 7.5V, and when the observed speed is 750rpm, the amplitude of the extended back EMF is about 25V. Due to the limitation of the processing performance of the digital controller, the sampling period of the phase-locked loop system is set to 1 ms. At a higher speed, the number of observed position angles updated by the phase-locked loop system within one cycle of the extended back electromotive force is relatively small, so there will be relatively small Small staircase waveform, if the sampling period of the phase-locked loop is shortened, the extended back EMF waveform at high speed will be smoother.
图9和图10分别给出了三相PMSM从零升至200rpm再升至750rpm的转速图以及从750rpm降至200rpm再降至零速的转速图。从图中可以看到本发明在全速域无位置控制中兼顾动态响应和稳态精度,在中低端电机控制器中具有一定的工程应用价值。Fig. 9 and Fig. 10 respectively show the rotation speed diagram of the three-phase PMSM rising from zero to 200rpm to 750rpm and the rotation speed diagram from 750rpm to 200rpm and then to zero speed. It can be seen from the figure that the present invention takes both dynamic response and steady-state accuracy into account in the positionless control in the full speed range, and has certain engineering application value in low-end motor controllers.
以上实施例仅为说明本发明的技术思想,不能以此限定本发明的保护范围,凡是按照本发明提出的技术思想,在技术方案基础上所做的任何改动,均落入本发明保护范围之内。The above embodiments are only to illustrate the technical ideas of the present invention, and cannot limit the protection scope of the present invention with this. All technical ideas proposed according to the present invention, any changes made on the basis of technical solutions, all fall within the protection scope of the present invention. Inside.
Claims (8)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211143002.7ACN115514273A (en) | 2022-09-20 | 2022-09-20 | Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211143002.7ACN115514273A (en) | 2022-09-20 | 2022-09-20 | Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115514273Atrue CN115514273A (en) | 2022-12-23 |
Family
ID=84504414
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211143002.7APendingCN115514273A (en) | 2022-09-20 | 2022-09-20 | Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115514273A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118826563A (en)* | 2024-08-19 | 2024-10-22 | 浙江大学先进电气装备创新中心 | Position sensorless control method for high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor based on prediction idea |
- 2022
- 2022-09-20CNCN202211143002.7Apatent/CN115514273A/enactivePending
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118826563A (en)* | 2024-08-19 | 2024-10-22 | 浙江大学先进电气装备创新中心 | Position sensorless control method for high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor based on prediction idea |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107046387B (en) | Variable PID parameter current loop starting method of permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| Gou et al. | Integral sliding mode control for starting speed sensorless controlled induction motor in the rotating condition | |
| CN102684592B (en) | Torque and flux linkage control method for permanent synchronous motor | |
| CN108155838A (en) | A kind of rotating speed method for tracing based on permanent magnet synchronous motor open loop | |
| CN107508521B (en) | A speed sensorless control method and system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| CN112671298B (en) | Improved PLL non-inductive control algorithm for permanent magnet synchronous motor control | |
| CN113676088B (en) | Speed sensorless control method of permanent magnet synchronous motor with harmonic suppression | |
| CN110429891B (en) | Position-sensor-free permanent magnet motor direct-drive power generation control method | |
| WO2022237829A1 (en) | Motor control method, control system, and storage medium | |
| CN110011587A (en) | A sensorless vector control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on multi-parameter identification | |
| CN108494308A (en) | A kind of control method of quick lock in asynchronous machine rotor frequency | |
| CN111181458A (en) | Surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation method based on extended Kalman filter | |
| CN110971166A (en) | Obtaining method and control system of rotor position of permanent magnet synchronous generator | |
| CN108880377A (en) | A kind of method for estimating rotating speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor based on novel phaselocked loop | |
| CN115242154B (en) | Self-adaptive smooth switching method for I-f starting to position sliding mode observer | |
| CN115514273A (en) | Full-speed-domain position-sensorless control method for three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| CN113328659B (en) | PI parameter setting method for rotating speed ring of permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| CN114465530A (en) | Speed control method and system of permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| CN112865654A (en) | Torque maximum utilization control system and method for permanent magnet magnetic concentration type synchronous reluctance motor | |
| CN116208053B (en) | Control system and method for permanent magnet synchronous motor | |
| Liang et al. | A compensation method for rotor position estimation of PMSM based on pulsating high frequency injection | |
| CN115378333B (en) | Sliding mode angle self-adaptive compensation method based on current loop output | |
| CN102386839B (en) | Synchronous motor vector controller based on reactive power observer and control method | |
| CN116232158A (en) | SynRM high-quality resonance dead beat prediction current control method | |
| CN111800039B (en) | Rotor position information confirming method, vector control method and device of synchronous motor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |