CN115478046A - A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture system - Google Patents
A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115478046A CN115478046ACN202211205861.4ACN202211205861ACN115478046ACN 115478046 ACN115478046 ACN 115478046ACN 202211205861 ACN202211205861 ACN 202211205861ACN 115478046 ACN115478046 ACN 115478046A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- cells
- bsa
- residual amount
- cell preparation
- reducing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription36
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription30
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription24
- 235000003642hungerNutrition0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 230000037351starvationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription21
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsabstractdescription20
- 238000004140cleaningMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 230000010261cell growthEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000claimsdescription23
- 239000007640basal mediumSubstances0.000claimsdescription16
- 239000002504physiological saline solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription11
- 230000007910cell fusionEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000abstractdescription6
- 229960005486vaccineDrugs0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000003908quality control methodMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000004927fusionEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 238000012258culturingMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description67
- 239000012091fetal bovine serumSubstances0.000description14
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description11
- 230000029087digestionEffects0.000description10
- 108091003079Bovine Serum AlbuminProteins0.000description9
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description6
- 210000002901mesenchymal stem cellAnatomy0.000description6
- 210000003954umbilical cordAnatomy0.000description6
- 229940098773bovine serum albuminDrugs0.000description4
- 238000013401experimental designMethods0.000description4
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description4
- 230000012010growthEffects0.000description3
- 208000010544human prion diseaseDiseases0.000description3
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000description3
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000description3
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description3
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description3
- 210000000130stem cellAnatomy0.000description3
- 206010020751HypersensitivityDiseases0.000description2
- 208000024777Prion diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 230000003833cell viabilityEffects0.000description2
- 238000011109contaminationMethods0.000description2
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description2
- 241000283690Bos taurusSpecies0.000description1
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description1
- AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-NN-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]-2-[[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methylamino]pyrimidine-5-carboxamideChemical compoundO=C(CCNC(=O)C=1C=NC(=NC=1)NCC1=CC(=CC=C1)OC(F)(F)F)N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 208000018756Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 241000700605VirusesSpecies0.000description1
- 238000004115adherent cultureMethods0.000description1
- 239000013566allergenSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007815allergyEffects0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 210000000988bone and boneAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000004271bone marrow stromal cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 208000005881bovine spongiform encephalopathyDiseases0.000description1
- 210000000845cartilageAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000004113cell cultureMethods0.000description1
- 239000006143cell culture mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 229940030156cell vaccineDrugs0.000description1
- 238000012136culture methodMethods0.000description1
- 210000004748cultured cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 230000004069differentiationEffects0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description1
- 210000003038endotheliumAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 235000020774essential nutrientsNutrition0.000description1
- 230000008014freezingEffects0.000description1
- 238000007710freezingMethods0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description1
- 238000011081inoculationMethods0.000description1
- 210000003041ligamentAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004185liverAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- 210000003205muscleAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000004165myocardiumAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000005036nerveAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000001778pluripotent stem cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000008092positive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000035755proliferationEffects0.000description1
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 239000008354sodium chloride injectionSubstances0.000description1
- 210000002435tendonAnatomy0.000description1
- 229960004854viral vaccineDrugs0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0652—Cells of skeletal and connective tissues; Mesenchyme
- C12N5/0662—Stem cells
- C12N5/0665—Blood-borne mesenchymal stem cells, e.g. from umbilical cord blood
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N5/00—Undifferentiated human, animal or plant cells, e.g. cell lines; Tissues; Cultivation or maintenance thereof; Culture media therefor
- C12N5/06—Animal cells or tissues; Human cells or tissues
- C12N5/0602—Vertebrate cells
- C12N5/0652—Cells of skeletal and connective tissues; Mesenchyme
- C12N5/0662—Stem cells
- C12N5/0668—Mesenchymal stem cells from other natural sources
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2500/00—Specific components of cell culture medium
- C12N2500/90—Serum-free medium, which may still contain naturally-sourced components
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2509/00—Methods for the dissociation of cells, e.g. specific use of enzymes
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Developmental Biology & Embryology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于生物细胞学领域,尤其涉及一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法。The invention belongs to the field of biological cytology, and in particular relates to a method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in a serum culture system.
背景技术Background technique
人脐带间充质干细胞(Mesenchymal Stem Cells,MSCs)是指存在于新生儿脐带组织中的一种多功能干细胞,有较高的分化潜能,可向多个方向进行分化。它在骨、软骨、肌肉、肌腱、韧带、神经、肝、内皮和心肌等组织工程方面具有广阔的临床应用前景。传统的人脐带间充质干细胞培养液,是含10%FBS(fetal bovine serum,胎牛血清)的培养基,FBS能够维持人脐带间充质干细胞体外培养的干细胞特性,对于人脐带间充质干细胞的贴壁、分裂和增殖有着重要作用。且胎牛血清是病毒性疫苗生产过程中必不可少的营养成分。但胎牛血清中含有BSA(Bovine Serum Albumin,牛血清白蛋白),在干细胞成品疫苗中,BSA作为一种异源蛋白对接种疫苗的患者的健康可能造成潜在的危害,作为过敏原引起过敏反应,尤其是对过敏体质人群和儿童危害极大;同时,BSA可能携带一定种类的动物性病毒,如具有传播TSE(Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy,可传染性海绵状脑病)和BSE(Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy,疯牛病)的潜在危险。因此《中国生物制品规程》对其进行质控,要求每人份疫苗中残余牛血清白蛋白的含量不得高于50ng/剂。Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (Mesenchymal Stem Cells, MSCs) refer to a kind of pluripotent stem cells existing in neonatal umbilical cord tissue, which have high differentiation potential and can differentiate in multiple directions. It has broad clinical application prospects in tissue engineering of bone, cartilage, muscle, tendon, ligament, nerve, liver, endothelium and cardiac muscle. The traditional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell culture medium is a medium containing 10% FBS (fetal bovine serum, fetal bovine serum). FBS can maintain the stem cell characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells cultured in vitro. For human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells Adherence, division and proliferation of stem cells play an important role. And fetal bovine serum is an essential nutrient in the production of viral vaccines. However, fetal bovine serum contains BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin, bovine serum albumin). In the finished stem cell vaccine, BSA, as a heterologous protein, may cause potential harm to the health of vaccinated patients and cause allergic reactions as an allergen , especially to people with allergies and children; at the same time, BSA may carry certain kinds of animal viruses, such as TSE (Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy) and BSE (Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy, mad cow disease) potential danger. Therefore, the "China Biological Products Regulations" conducts quality control on it, requiring that the content of residual bovine serum albumin in each vaccine should not exceed 50ng/dose.
传统含血清的细胞制剂培养方式,得到的成品中BSA残留高达137.99ng/剂,远大于50ng/剂,不符合《中国生物制品规程》对疫苗的质控要求。The traditional serum-containing cell preparation culture method, the BSA residue in the finished product is as high as 137.99ng/dose, far greater than 50ng/dose, which does not meet the quality control requirements of the "China Biological Products Regulations" for vaccines.
发明内容Contents of the invention
针对现有技术的缺点,本发明的目的在于提供一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法,该方法使得血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA的含量明显降低,满足《中国生物制品规程》对疫苗的质控要求,即每人份疫苗中残余牛血清白蛋白的含量不得高于50ng/剂。In view of the shortcomings of the prior art, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in the serum culture system, which can significantly reduce the content of cell preparation BSA in the serum culture system, and meet the requirements of the "China Biological Products Regulations" The quality control requirements for vaccines, that is, the content of residual bovine serum albumin in each dose of vaccine should not exceed 50ng/dose.
为实现上述目的,本发明的技术方案为:To achieve the above object, the technical solution of the present invention is:
一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法,包括以下步骤:A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in a serum culture system, comprising the following steps:
S1:清洗:在细胞制剂消化收集前,细胞生长融合率达到80%-90%,将细胞与完全培养基分开,采用生理盐水清洗细胞;S1: Cleaning: Before the cell preparation is digested and collected, the cell growth and fusion rate reaches 80%-90%, the cells are separated from the complete medium, and the cells are washed with normal saline;
S2:饥饿培养:将清洗后的细胞在基础培养基内饥饿培养0-20h(不包括0),然后清洗、消化、收集细胞;S2: Starvation culture: starve the washed cells in the basal medium for 0-20h (excluding 0), then wash, digest, and collect the cells;
其中,完全培养基为FBS和基础培养基的混合培养基。Wherein, the complete medium is a mixed medium of FBS and basal medium.
优选地,所述步骤S1和S2中,采用100-400ml生理盐水清洗细胞。Preferably, in the steps S1 and S2, the cells are washed with 100-400ml of physiological saline.
优选地,所述步骤S1和S2中,采用生理盐水清洗细胞1-3次。Preferably, in the steps S1 and S2, the cells are washed with physiological saline for 1-3 times.
优选地,在所述步骤S1和S2中,采用250ml生理盐水清洗细胞1次。Preferably, in the steps S1 and S2, the cells are washed once with 250 ml of physiological saline.
优选地,其特征在于,在所述步骤S2中,将清洗后的细胞在基础培养基内饥饿培养16-18h。Preferably, it is characterized in that, in the step S2, starvation culture the washed cells in the basal medium for 16-18 hours.
优选地,所述完全培养基中含有10%FBS。Preferably, the complete medium contains 10% FBS.
优选地,所述步骤S2中,清洗后的细胞在培养瓶中贴壁培养,将培养瓶放入37℃,5%CO2培养箱中培养0-20h。Preferably, in the step S2, the washed cells are cultured adherently in a culture flask, and the culture flask is placed in a 37° C., 5% CO2 incubator for 0-20 h.
优选地,所述细胞制剂中BSA的含量低于30ng/剂,优选地,低于22.05ng/剂。Preferably, the content of BSA in the cell preparation is lower than 30ng/dose, preferably lower than 22.05ng/dose.
本发明由于采用以上技术方案,使其与现有技术相比具有以下的优点和积极效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages and positive effects due to the adoption of the above technical scheme:
本申请在细胞消化收集前进行生理盐水清洗加血清饥饿后,再进行消化收集。采用本申请的方法得到的细胞中BSA残留量明显降低,满足《中国生物制品规程》对疫苗的质控要求,解决了血清培养体系中细胞BSA残留量高的问题。In this application, before the cells are digested and collected, they are washed with normal saline and starved for serum, and then digested and collected. The residual amount of BSA in the cells obtained by the method of the present application is significantly reduced, which meets the quality control requirements of the "China Biological Products Regulations" for vaccines, and solves the problem of high residual amount of BSA in cells in the serum culture system.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为实施例1中生理盐水清洗参数实验设计结果图;Fig. 1 is the experimental design result figure of physiological saline cleaning parameter in
图2为实施例1中血清饥饿实验设计结果图;Fig. 2 is the design result figure of serum starvation experiment in
图3为实施例1中清洗参数结合血清饥饿时间实验设计结果图;Fig. 3 is the experimental design result diagram of cleaning parameters combined with serum starvation time in
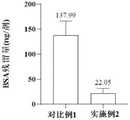
图4为实施例2和对比例1处理后的细胞制剂的BSA含量结果图。4 is a graph showing the BSA content results of the cell preparations treated in Example 2 and Comparative Example 1.
具体实施方式detailed description
以下结合附图和具体实施例对本发明提出的一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法作进一步详细说明。根据下面说明,本发明的优点和特征将更清楚。A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in the serum culture system proposed by the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific examples. The advantages and features of the present invention will become clearer from the following description.
本发明针对现有技术的缺点,提出一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法,包括以下步骤:The present invention aims at the shortcoming of prior art, proposes a kind of method that reduces the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in the serum culture system, comprises the following steps:
S1:清洗:在细胞制剂收集前,细胞生长融合率达到80%-90%,将细胞与完全培养基分开,采用生理盐水清洗细胞;S1: Cleaning: Before the cell preparation is collected, the cell growth and fusion rate reaches 80%-90%, separate the cells from the complete medium, and wash the cells with normal saline;
S2:饥饿培养:将清洗后的细胞在基础培养基内饥饿培养0-20h,然后清洗、消化、收集细胞;S2: starvation culture: starve the washed cells in the basal medium for 0-20h, then wash, digest and collect the cells;
其中,完全培养基为FBS和基础培养基的混合培养基。Wherein, the complete medium is a mixed medium of FBS and basal medium.
本发明的方法适合采用血清培养体系的细胞,对于细胞来源不限定,只要其可以采用血清培养即可。The method of the present invention is suitable for cells in a serum culture system, and the source of the cells is not limited as long as they can be cultured in serum.
本发明涉及到生理盐水清洗细胞,以及基础培养基饥饿培养三个重要的工艺参数,以下实施例1中从生理盐水的清洗用量、清洗次数和饥饿培养时间三个重要参数进行探究。The present invention relates to three important process parameters of washing cells with physiological saline and starvation culture of basal medium. In the following Example 1, the three important parameters of washing amount of physiological saline, washing times and starvation culture time are explored.
在本发明实施例1-2和对比例1中细胞培养均采用培养瓶贴壁培养方式,培养的细胞种类为人脐带间充质干细胞,采用的培养瓶为十层瓶(厂家:CORNIG),细胞接种密度为1.215×104个细胞/cm2,冻存的细胞代次均为P6,采用的生理盐水为0.9%氯化钠注射液,采用的基础培养基购买于(生产厂家:Gibco),完全培养基为基础培养基和FBS(生产厂家:Gibco)的混合液,其中FBS占有完全培养基的10%。In Example 1-2 of the present invention and Comparative Example 1, cell culture all adopts culture flask adherent culture mode, and the kind of cultured cell is human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell, and the culture bottle that adopts is ten-layer flask (manufacturer: CORNIG), and the cell The inoculation density was 1.215×104 cells/cm2 , the passages of frozen cells were all P6, the normal saline used was 0.9% sodium chloride injection, and the basal medium used was purchased from (manufacturer: Gibco), The complete medium is a mixture of basal medium and FBS (manufacturer: Gibco), wherein FBS accounts for 10% of the complete medium.
实施例1Example 1
1、对清洗用量和清洗次数进行实验设计1. Experimental design for cleaning dosage and cleaning times
在细胞制剂收集消化前,细胞的生长融合率达到80%-90%时,设置不同的生理盐水用量及不同的清洗次数清洗细胞表面,再进行后续消化收集,即将培养瓶中的完全培养基全部倒出,分别采用100ml、250ml、400ml清洗培养瓶中的细胞,清洗1-3次,再进行后续消化收集细胞,将细胞按1×107个细胞/ml,1ml/管进行冻存,检测其BSA含量,故数据统计图(图1、图2、图3)BSA含量的单位为ng/ml。Before the collection and digestion of cell preparations, when the growth and fusion rate of cells reaches 80%-90%, set different amounts of normal saline and different washing times to clean the cell surface, and then carry out subsequent digestion and collection, that is, all the complete medium in the culture bottle Pour it out, wash the cells in the culture flask with 100ml, 250ml, and 400ml respectively, wash 1-3 times, and then perform subsequent digestion to collect the cells, freeze the cells at 1×107 cells/ml, 1ml/tube, and detect Its BSA content, so the unit of the BSA content in the data statistical chart (Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3) is ng/ml.
实验设置如表1所示:The experimental settings are shown in Table 1:
实验结果如图1所示,从图1中可以看出,生理盐水使用量为100ml时注射液成品中BSA残留量最高,生理盐水使用量为250ml、400ml时注射液成品中BSA残留量较低且相差不大,但考虑到使用400ml生理盐水会增加操作时长,风险较大,导致可操作性差,故清洗用量优选为250ml。从清洗次数考虑,同250ml生理盐水用量的条件下,分别清洗1次、2次、3次时BSA残留量相差不大,在大批量生产中,清洗3次会增加污染风险,极大增加细胞收集时的操作时长,进而会影响细胞活率,所以清洗参数优选为生理盐水清洗1-2次。The experimental results are shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the residual amount of BSA in the finished injection is the highest when the amount of physiological saline is 100ml, and the residual amount of BSA in the finished injection is lower when the amount of physiological saline is 250ml and 400ml And the difference is not big, but considering that the use of 400ml normal saline will increase the operation time, the risk is greater, resulting in poor operability, so the cleaning dosage is preferably 250ml. Considering the number of washings, under the condition of the same amount of 250ml normal saline, the residual amount of BSA is not much different when washing 1 time, 2 times, and 3 times respectively. In mass production, washing 3 times will increase the risk of contamination and greatly increase the number of cells. The operation time during collection will affect the cell viability, so the washing parameters are preferably washed with normal saline 1-2 times.
2、饥饿培养实验设计及结果2. Starvation culture experiment design and results
在细胞制剂收集消化前,细胞的生长融合率达到80%-90%时,将培养瓶内完全培养基全部倒出,用250ml生理盐水清洗1次,倒出,再加入与原完全培养基等量的不含10%FBS的基础培养基,放入37℃,5%CO2培养箱中饥饿培养,分别培养14h、16h、18h、20h后,进行后续清洗、消化收集细胞,将细胞按1×107个细胞/ml,1ml/管进行冻存,检测其BSA含量。实验设计如表2(饥饿时间为0的实验组为空白对照,即不进行饥饿操作):Before the cell preparation is collected and digested, when the growth and fusion rate of the cells reaches 80%-90%, pour out all the complete medium in the culture bottle, wash it once with 250ml normal saline, pour it out, and then add the original complete medium, etc. A large amount of basal medium without 10% FBS was placed in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator for starvation culture, and after culturing for 14h, 16h, 18h, and 20h respectively, subsequent washing and digestion were performed to collect the cells, and the cells were pressed for 1 ×107 cells/ml, frozen in 1ml/tube, and tested for BSA content. The experimental design is shown in Table 2 (the experimental group with a starvation time of 0 is the blank control, that is, no starvation operation):
实验结果如图2表示:饥饿培养很大程度上降低了BSA的残留,分别设置14h、16h、18h、20h的饥饿时间,从16h之后,BSA残留量进入平台期;考虑生产中若饥饿20h,换液或收集时需要凌晨操作,可操作性较弱,故血清饥饿时间优选为16-18h。在此基础上结合清洗参数进行再次实验探究。The experimental results are shown in Figure 2: starvation culture greatly reduces the residue of BSA, and the starvation time of 14h, 16h, 18h, and 20h is set respectively. After 16h, the residual amount of BSA enters the plateau stage; It needs to be operated in the early morning when the liquid is changed or collected, and the operability is weak, so the serum starvation time is preferably 16-18h. On this basis, combined with the cleaning parameters, the experiment was carried out again.
3、清洗参数结合饥饿培养实验设计及结构:3. Cleaning parameters combined with starvation culture experiment design and structure:
在细胞制剂收集前,细胞的生长融合率达到80%-90%时,将培养瓶内完全培养基全部倒出,按如下设计用生理盐水清洗细胞表面,倒出,再加入与原完全培养基等量的不含10%FBS的基础培养基,放入37℃,5%CO2培养箱中培养,培养16h-18h后,将基础培养基全部倒出,按如下设计用生理盐水清洗细胞表面后倒出,再加入消化液进行后续消化收集,将细胞按1×107个细胞/ml,1ml/管进行冻存,检测其BSA含量。实验组别设计如表3所示:Before the collection of cell preparations, when the growth and fusion rate of the cells reaches 80%-90%, pour out all the complete medium in the culture bottle, wash the cell surface with physiological saline according to the following design, pour it out, and then add the original complete medium The same amount of basal medium without 10% FBS was placed in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator for culture. After 16h-18h of culture, all the basal medium was poured out, and the cell surface was washed with physiological saline according to the following design Then pour it out, then add digestion solution for subsequent digestion and collection, freeze the cells at 1×107 cells/ml, 1ml/tube, and detect the BSA content. The experimental group design is shown in Table 3:
实验结构如图3所示,BSA残留量各组均有浮动但差异不大,同时考虑到实际生产中清洗两次会增加污染风险,增加操作时长进而影响细胞活率,可操作性较弱;因此组别6的清洗参数较为理想,即血清饥饿16-18h,饥饿培养前用250ml生理盐水清洗一次,消化收集前用250ml生理盐水清洗一次。The experimental structure is shown in Figure 3. The residual amount of BSA in each group fluctuates but the difference is not significant. At the same time, considering that cleaning twice in actual production will increase the risk of contamination, increase the operation time and affect the cell viability, and the operability is weak; Therefore, the cleaning parameters of
实施例2Example 2
基于上述的分析,一种降低血清培养体系中细胞制剂BSA残留量的方法,优选的实施方案为:在含血清体系的细胞制剂制备中,细胞收集前同时满足细胞生长融合率达到80%-90%,将原有含胎牛血清的完全培养基全部倒出,使用250ml生理盐水小心清洗一次细胞表面以清除残留的完全培养基,倒出全部生理盐水(此为清洗过程),加入与原先完全培养基等量的不含血清的基础培养基,放入37℃,5%CO2培养箱中培养16-18h后(此为血清饥饿过程),然后再采用250ml生理盐水小心清洗一次细胞表面以清除残留的基础培养基,倒出全部生理盐水,进行后续的消化收集。Based on the above analysis, a method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in the serum culture system, the preferred embodiment is: in the preparation of the cell preparation containing the serum system, before the cells are collected, the cell growth and fusion rate must reach 80%-90% at the same time. %, pour out all the original complete medium containing fetal bovine serum, use 250ml normal saline to carefully wash the cell surface once to remove the remaining complete medium, pour out all the normal saline (this is the cleaning process), add the original complete medium Culture medium The same amount of serum-free basal medium was placed in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator and cultured for 16-18 hours (this is a serum starvation process), and then the cell surface was carefully washed once with 250ml of normal saline to Remove the residual basal medium, pour out all the normal saline, and carry out subsequent digestion and collection.
采用此方法,连续生产4批细胞制剂,按注射液成品规格冻存,即1×107个细胞/ml,10ml/袋,此规格为一剂,冻存后测量细胞制剂的BSA含量,故数据统计图(图4)中BSA含量单位为ng/剂。Using this method, 4 batches of cell preparations were continuously produced and stored frozen according to the specifications of the finished injection, i.e. 1×107 cells/ml, 10ml/bag. This specification was one dose, and the BSA content of the cell preparation was measured after freezing. The unit of BSA content in the data statistical graph (Fig. 4) is ng/dose.
对比例1Comparative example 1
在细胞消化收集前,细胞生长融合率达到80%-90%,将完全培养基全部倒出,采用100mL生理盐水清洗细胞1次,然后进行后续的消化收集。测量细胞制剂的BSA含量。Before cell digestion and collection, the cell growth and fusion rate reached 80%-90%, all the complete medium was poured out, and the cells were washed once with 100 mL of normal saline, and then subsequent digestion and collection were performed. The BSA content of the cell preparations was measured.
比较实施例2和对比例1的细胞制剂的BSA,实施例2的细胞制剂BSA的含量明显降低,BSA含量的平均值为22.05ng/剂,而对于没有进行血清饥饿培养和清洗的对比例1,BSA含量的平均值为137.99ng/剂。BSA含量的结果如附图4所示。Comparing the BSA of the cell preparations of Example 2 and Comparative Example 1, the content of the cell preparation BSA of Example 2 was significantly reduced, and the average value of the BSA content was 22.05ng/dose, while for the comparative example 1 that did not carry out serum starvation culture and cleaning , the average value of BSA content was 137.99ng/dose. The results of the BSA content are shown in Figure 4.
对比例1和实施例2的细胞制剂的规格均为1×107个细胞/ml,10ml/袋。The specifications of the cell preparations in Comparative Example 1 and Example 2 are both 1×107 cells/ml, 10ml/bag.
上面结合附图对本发明的实施方式作了详细说明,但是本发明并不限于上述实施方式。即使对本发明做出各种变化,倘若这些变化属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则仍落入在本发明的保护范围之中。The embodiments of the present invention have been described in detail above with reference to the accompanying drawings, but the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments. Even if various changes are made to the present invention, if these changes fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and equivalent technologies, they still fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211205861.4ACN115478046A (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211205861.4ACN115478046A (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115478046Atrue CN115478046A (en) | 2022-12-16 |
Family
ID=84393766
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211205861.4APendingCN115478046A (en) | 2022-09-30 | 2022-09-30 | A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115478046A (en) |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100068191A1 (en)* | 2008-08-14 | 2010-03-18 | Alla Danilkovich | Purified mesenchymal stem cell compositions and methods of purifying mesenchymal stem cell compositions |
| CN101892192A (en)* | 2010-07-12 | 2010-11-24 | 北京汉氏联合生物技术有限公司 | Cell culture method capable of reducing heterologous protein residue in cell products |
- 2022
- 2022-09-30CNCN202211205861.4Apatent/CN115478046A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100068191A1 (en)* | 2008-08-14 | 2010-03-18 | Alla Danilkovich | Purified mesenchymal stem cell compositions and methods of purifying mesenchymal stem cell compositions |
| CN101892192A (en)* | 2010-07-12 | 2010-11-24 | 北京汉氏联合生物技术有限公司 | Cell culture method capable of reducing heterologous protein residue in cell products |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| PAN XUE, ET AL.: "Highly Sensitive Chemiluminescent Analysis of Residual Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) Based on a Pair of Specific Monoclonal Antibodies and Peroxyoxalate–glyoxaline–PHPPA Dimer Chemiluminescent System in Vaccines", APPLIED BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY, vol. 166, 11 February 2012 (2012-02-11), pages 1604 - 1614, XP035018131, DOI: 10.1007/s12010-012-9567-1* |
| 方玉,冯晓明,奚廷斐: "组织工程医疗产品中残留牛血清白蛋白的检验常见问题", 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, vol. 12, no. 32, 5 August 2008 (2008-08-05), pages 6347 - 6350* |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6405304B2 (en) | Adipose-derived stem cell production system and method | |
| Li et al. | Transplantation of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell-induced neural stem cells to treat spinal cord injury | |
| CN111542350B (en) | Systems and methods for preparing adipose-derived stem cells | |
| US20060110825A1 (en) | Process for the preparation of stem cells from human muscle tissue and adipose tissue, and stem cell obtainable by this process | |
| JP2013524856A (en) | Dosage unit formulation of autologous dermal fibroblasts | |
| CN109893541B (en) | Application of menstrual blood stem cell-derived exosomes in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of intrauterine adhesions | |
| CN104762257B (en) | A kind of method preparing mescenchymal stem cell from umbilical cord | |
| CN111876378A (en) | Method for efficiently separating and culturing myocardial cells and myocardial fibroblasts of suckling mice | |
| WO2019161590A1 (en) | Mesenchymal stem cell suspension and preparation method therefor and application thereof | |
| CN111973632B (en) | Stem cell preparation for treating diabetes and preparation method thereof | |
| CN117157389A (en) | Preparation method and application of mesenchymal stem cells of hair follicle | |
| CN114672456B (en) | Method for improving extracellular vesicle secretion efficiency of adipose-derived stem cells by utilizing ultrasonic stimulation and application | |
| CN111534477A (en) | Method for culturing primary epithelial stem cell balls of lung tissue of mouse | |
| CN101173247A (en) | A method for cultivating osteoclasts using mesenchymal stem cells combined with cytokines | |
| CN115478046A (en) | A method for reducing the residual amount of cell preparation BSA in serum culture system | |
| WO2019237812A1 (en) | Adipose tissue digestive juice and method for rapidly obtaining stromal vascular fraction cells | |
| CN116240167A (en) | A preparation method for extracting dental pulp stem cells | |
| CN114276980A (en) | A method for culturing pancreatic islet cells suitable for clinical application | |
| WO2022056991A1 (en) | Mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord, and preparation method therefor and use thereof | |
| CN106591223A (en) | Separation and primary culture method for human skin fibroblasts | |
| CN106676063A (en) | Separate culture method for human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells | |
| CN112237589A (en) | Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell active matter and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN110592008A (en) | Culture method of canine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells | |
| CN110742906A (en) | Application of mesenchymal stem cell paracrine factor in preparation of pain medicine | |
| CN118909925B (en) | A high-throughput method for constructing skeletal muscle organoids |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |