CN115373119B - Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment - Google Patents
Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115373119B CN115373119BCN202211317687.2ACN202211317687ACN115373119BCN 115373119 BCN115373119 BCN 115373119BCN 202211317687 ACN202211317687 ACN 202211317687ACN 115373119 BCN115373119 BCN 115373119B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- lens
- optical
- optical axis
- optical lens
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B13/00—Optical objectives specially designed for the purposes specified below
- G02B13/001—Miniaturised objectives for electronic devices, e.g. portable telephones, webcams, PDAs, small digital cameras
- G02B13/0015—Miniaturised objectives for electronic devices, e.g. portable telephones, webcams, PDAs, small digital cameras characterised by the lens design
- G02B13/002—Miniaturised objectives for electronic devices, e.g. portable telephones, webcams, PDAs, small digital cameras characterised by the lens design having at least one aspherical surface
- G02B13/0045—Miniaturised objectives for electronic devices, e.g. portable telephones, webcams, PDAs, small digital cameras characterised by the lens design having at least one aspherical surface having five or more lenses
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Lenses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及光学成像技术领域,尤其涉及一种光学镜头、摄像模组及电子设备。The invention relates to the technical field of optical imaging, in particular to an optical lens, a camera module and electronic equipment.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,随着摄像技术的发展,人们对光学镜头的成像品质要求越来越高,同时轻薄小型化的结构特点也逐渐成为光学镜头的发展趋势。相关技术中,在满足光学镜头轻薄小型化的设计趋势下,难以同时满足人们对光学镜头的高清成像要求。In recent years, with the development of camera technology, people have higher and higher requirements for the imaging quality of optical lenses. At the same time, the structural characteristics of lightness, thinness and miniaturization have gradually become the development trend of optical lenses. In related technologies, it is difficult to meet people's high-definition imaging requirements for optical lenses while satisfying the design trend of optical lenses being thin, light and miniaturized.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例公开了一种光学镜头、摄像模组及电子设备,能够在实现光学镜头的轻薄、小型化设计的同时,提高光学镜头的成像品质。The embodiment of the invention discloses an optical lens, a camera module and electronic equipment, which can improve the imaging quality of the optical lens while realizing the light, thin and miniaturized design of the optical lens.
为了实现上述目的,第一方面,本发明公开了一种光学镜头,所述光学镜头共有五片具有屈折力的透镜,五片所述透镜沿光轴从物侧至像侧依次为第一透镜、第二透镜、第三透镜、第四透镜和第五透镜;In order to achieve the above object, in the first aspect, the present invention discloses an optical lens, the optical lens has five lenses with refractive power, and the five lenses are the first lens in sequence from the object side to the image side along the optical axis , the second lens, the third lens, the fourth lens and the fifth lens;
所述第一透镜具有正屈折力,所述第一透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凸面,所述第一透镜的像侧面于近光轴处为凸面;The first lens has positive refractive power, the object side of the first lens is convex at the near optical axis, and the image side of the first lens is convex at the near optical axis;
所述第二透镜具有负屈折力,所述第二透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凸面,所述第二透镜的像侧面于近光轴处为凹面;The second lens has a negative refractive power, the object side of the second lens is convex at the near optical axis, and the image side of the second lens is concave at the near optical axis;
所述第三透镜具有负屈折力;The third lens has a negative refractive power;
所述第四透镜具有负屈折力,所述第四透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凹面;The fourth lens has a negative refractive power, and the object side of the fourth lens is concave at the near optical axis;
所述第五透镜具有正屈折力,所述第五透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凸面,所述第五透镜的像侧面于近光轴处为凸面;The fifth lens has positive refractive power, the object side of the fifth lens is convex at the near optical axis, and the image side of the fifth lens is convex at the near optical axis;
所述光学镜头满足以下关系式:-6.5<R10/f<-0.1;The optical lens satisfies the following relationship: -6.5<R10/f<-0.1;
其中,R10为所述第五透镜的像侧面于所述光轴处的曲率半径,f为所述光学镜头的焦距。本申请提供的光学镜头中,第一透镜具有正屈折力,起到汇聚光线的作用,有利于大角度的入射光线进入光学系统,使光学系统具有较大的视场角,以满足光学系统对拍摄范围的需求;且第一透镜采用于光轴处双凸的面型,可加强第一透镜的正屈折力,有利于缩短光学系统的总长;第二透镜具有负屈折力,第二透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凸面,第二透镜的像侧面于近光轴处为凹面,有利于矫正光学镜头的畸变,提高成像质量;第三透镜具有负屈折力,可抵消第一透镜或者第二透镜产生的球差以及彗差等像差;第四透镜具备负屈折力,且第四透镜的物侧面于近光轴处为凹面,有利于校正入射光线经过前述透镜所产生的畸变、像散及场曲,提高成像质量;第五透镜具有正屈折力,配合第五透镜于近光轴处的凸凸面型,有利于平衡第四透镜的像差,进一步提升光学镜头的成像质量,同时也有利于进一步收缩光线,从而有利于缩短光学镜头的总长。Wherein, R10 is the radius of curvature of the image side of the fifth lens at the optical axis, and f is the focal length of the optical lens. In the optical lens provided by the present application, the first lens has a positive refractive power and plays the role of converging light, which is conducive to the incident light with a large angle entering the optical system, so that the optical system has a larger field of view to meet the requirements of the optical system. The requirements of the shooting range; and the first lens adopts a biconvex surface at the optical axis, which can strengthen the positive refractive power of the first lens and help shorten the total length of the optical system; the second lens has negative refractive power, and the second lens has a negative refractive power. The object side is convex at the near optical axis, and the image side of the second lens is concave at the near optical axis, which is beneficial to correct the distortion of the optical lens and improve the imaging quality; the third lens has negative refractive power, which can offset the first lens or Aberrations such as spherical aberration and coma generated by the second lens; the fourth lens has negative refractive power, and the object side of the fourth lens is concave at the near optical axis, which is beneficial to correct the distortion generated by the incident light passing through the aforementioned lens, Astigmatism and field curvature improve imaging quality; the fifth lens has positive refractive power, and the convex-convex shape of the fifth lens at the near optical axis is beneficial to balance the aberration of the fourth lens and further improve the imaging quality of the optical lens. At the same time, it is also beneficial to further shrink the light, thereby helping to shorten the total length of the optical lens.
此外,光学镜头满足关系式:-6.5<R10/f<-0.1。满足上述关系式时,能够将第五透镜的像侧面于光轴处的曲率半径、光学镜头的焦距控制在合理的范围内,从而有利于矫正光学镜头的像散、场曲和畸变,压缩光学镜头的光学总长,实现光学镜头轻薄小型化的设计要求。低于上述关系式的下限时,第五透镜的像侧面于光轴处的曲率半径过大,导致第五透镜的面型过于平缓,难以充分地校正像散、场曲和畸变;超过上述关系式的上限时,第五透镜的像侧面于光轴处的曲率半径过小,导致第五透镜的面型弯曲度过大,增加了第五透镜的敏感度,不利于第五透镜的工程制造。In addition, the optical lens satisfies the relationship: -6.5<R10/f<-0.1. When the above relationship is satisfied, the radius of curvature of the image side of the fifth lens at the optical axis and the focal length of the optical lens can be controlled within a reasonable range, which is beneficial to correct the astigmatism, field curvature and distortion of the optical lens, and compress the optical lens. The total optical length of the lens meets the design requirements for light, thin and miniaturized optical lenses. Below the lower limit of the above relationship, the radius of curvature of the image side of the fifth lens at the optical axis is too large, causing the surface of the fifth lens to be too gentle, and it is difficult to fully correct astigmatism, curvature of field and distortion; exceeding the above relationship When the upper limit of the formula is reached, the radius of curvature of the image side of the fifth lens at the optical axis is too small, causing the surface curvature of the fifth lens to be too large, which increases the sensitivity of the fifth lens, which is not conducive to the engineering manufacture of the fifth lens .
第二方面,本发明公开了一种摄像模组,所述摄像模组包括感光芯片和如上述第一方面所述的光学镜头,所述感光芯片设置于所述光学镜头的像侧。具有所述光学镜头的摄像模组能够在降低光学镜头光学总长,实现光学镜头的轻薄、小型化设计的同时,校正光学镜头的畸变、像散及场曲等像差,提高光学镜头的成像品质。In a second aspect, the present invention discloses a camera module. The camera module includes a photosensitive chip and the optical lens as described in the first aspect above, and the photosensitive chip is arranged on the image side of the optical lens. The camera module with the optical lens can reduce the total optical length of the optical lens and realize the light and thin design of the optical lens while correcting aberrations such as distortion, astigmatism and curvature of field of the optical lens and improving the imaging quality of the optical lens .
第三方面,本发明还公开了一种电子设备,所述电子设备包括壳体和如上述第二方面所述的摄像模组,所述摄像模组设于所述壳体。具有所述摄像模组的电子设备,能够在降低光学镜头光学总长,实现光学镜头的轻薄、小型化设计的同时,校正光学镜头的畸变、像散及场曲等像差,提高光学镜头的成像品质。In a third aspect, the present invention also discloses an electronic device, the electronic device includes a casing and the camera module as described in the second aspect above, and the camera module is arranged in the casing. The electronic device with the camera module can correct the distortion, astigmatism, field curvature and other aberrations of the optical lens while reducing the total optical length of the optical lens and realize the light and thin, miniaturized design of the optical lens, so as to improve the imaging performance of the optical lens. quality.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果在于:Compared with prior art, the beneficial effect of the present invention is:
本发明实施例提供的一种光学镜头、摄像模组及电子设备,所述光学镜头采用五片透镜,通过对五片透镜的屈折力、面型进行设计,同时使得光学镜头满足关系式:-6.5<R10/f<-0.1,以将第五透镜的像侧面于光轴处的曲率半径、光学镜头的焦距控制在合理的范围内,从而有利于矫正光学镜头的像散、场曲和畸变,压缩光学镜头的光学总长,实现光学镜头轻薄小型化的设计要求。An optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment provided by the embodiments of the present invention, the optical lens adopts five lenses, and by designing the refractive power and surface shape of the five lenses, the optical lens satisfies the relational expression:- 6.5<R10/f<-0.1, to control the radius of curvature of the image side of the fifth lens at the optical axis and the focal length of the optical lens within a reasonable range, which is beneficial to correct the astigmatism, field curvature and distortion of the optical lens , to compress the total optical length of the optical lens, and realize the design requirements of thinner and smaller optical lens.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例中的技术方案,下面将对实施例中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention, the following will briefly introduce the accompanying drawings that need to be used in the embodiments. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention. For Those of ordinary skill in the art can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings without making creative efforts.
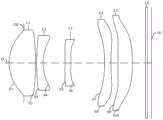
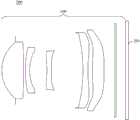
图1是本申请第一实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the first embodiment of the present application;
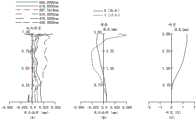
图2是本申请第一实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)及畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 2 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the first embodiment of the present application;
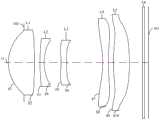
图3是本申请第二实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the second embodiment of the present application;
图4是本申请第二实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 4 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the second embodiment of the present application;
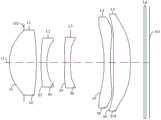
图5是本申请第三实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;Fig. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of the optical lens disclosed in the third embodiment of the present application;
图6是本申请第三实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 6 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the third embodiment of the present application;
图7是本申请第四实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;Fig. 7 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the fourth embodiment of the present application;
图8是本申请第四实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 8 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the fourth embodiment of the present application;
图9是本申请第五实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the fifth embodiment of the present application;
图10是本申请第五实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 10 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the fifth embodiment of the present application;
图11是本申请第六实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;Fig. 11 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the sixth embodiment of the present application;
图12是本申请第六实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 12 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the sixth embodiment of the present application;
图13是本申请第七实施例公开的光学镜头的结构示意图;Fig. 13 is a schematic structural view of the optical lens disclosed in the seventh embodiment of the present application;
图14是本申请第七实施例公开的光学镜头的纵向球差图(mm)、像散曲线图(mm)和畸变曲线图(%);Fig. 14 is the longitudinal spherical aberration diagram (mm), astigmatism curve diagram (mm) and distortion curve diagram (%) of the optical lens disclosed in the seventh embodiment of the present application;
图15是本申请公开的摄像模组的结构示意图;Fig. 15 is a schematic structural view of the camera module disclosed in the present application;
图16是本申请公开的电子设备的结构示意图。FIG. 16 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device disclosed in the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention, not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
请参阅图1,根据本申请的第一方面,本申请公开了一种光学镜头100,该光学镜头100共有五片具有屈折力的透镜,五片透镜沿光轴O从物侧至像侧依次为第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4和第五透镜L5。成像时,光线从第一透镜L1的物侧依次进入第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4和第五透镜L5并最终成像于光学镜头100的成像面101上。Please refer to Fig. 1, according to the first aspect of the present application, the present application discloses an
其中,第一透镜L1具有正屈折力,第二透镜L2具有负屈折力,第三透镜L3具有负屈折力,第四透镜L4具有负屈折力,第五透镜L5具有正屈折力。第一透镜L1的物侧面S1于近光轴O处可为凸面,第一透镜L1的像侧面S2于近光轴O处可为凸面,第二透镜L2的物侧面S3于近光轴O处可为凸面,第二透镜L2的像侧面S4于近光轴O处可为凹面,第三透镜L3的物侧面S5于近光轴O处可为凸面或凹面,第三透镜L3的像侧面S6于近光轴O处可为凸面或凹面,第四透镜L4的物侧面S7于近光轴O处可为凹面,第四透镜L4的像侧面S8于近光轴O处可为凸面或凹面,第五透镜L5的物侧面S9于近光轴O处可为凸面,第五透镜L5的像侧面S10于近光轴O处可为凸面。Wherein, the first lens L1 has positive refractive power, the second lens L2 has negative refractive power, the third lens L3 has negative refractive power, the fourth lens L4 has negative refractive power, and the fifth lens L5 has positive refractive power. The object side S1 of the first lens L1 can be convex at the near optical axis O, the image side S2 of the first lens L1 can be convex at the near optical axis O, and the object side S3 of the second lens L2 can be convex at the near optical axis O It can be convex, the image side S4 of the second lens L2 can be concave at the near optical axis O, the object side S5 of the third lens L3 can be convex or concave at the near optical axis O, and the image side S6 of the third lens L3 It can be convex or concave at the near optical axis O, the object side S7 of the fourth lens L4 can be concave at the near optical axis O, and the image side S8 of the fourth lens L4 can be convex or concave at the near optical axis O, The object side S9 of the fifth lens L5 can be convex at the near optical axis O, and the image side S10 of the fifth lens L5 can be convex at the near optical axis O.
本申请提供的光学镜头100中,第一透镜L1具有正屈折力,起到汇聚光线的作用,有利于大角度的入射光线进入光学系统,使光学系统具有较大的视场角,以满足光学系统对拍摄范围的需求;且第一透镜L1采用于光轴O处双凸的面型,可加强第一透镜L1的正屈折力,有利于缩短光学系统的总长;第二透镜L2具有负屈折力,第二透镜L2的物侧面S3于近光轴O处为凸面,第二透镜L2的像侧面S4于近光轴O处为凹面,有利于矫正光学镜头100的畸变,提高成像质量;第三透镜L3具有负屈折力,可抵消第一透镜L1或者第二透镜L2产生的球差以及彗差等像差;第四透镜L4具备负屈折力,且第四透镜L4的物侧面S7于近光轴O处为凹面,有利于校正入射光线经过前述透镜所产生的畸变、像散及场曲,提高成像质量;第五透镜L5具有正屈折力,配合第五透镜L5于近光轴O处的凸凸面型,有利于平衡第四透镜L4的像差,进一步提升光学镜头100的成像质量,同时也有利于进一步收缩光线,从而有利于缩短光学镜头100的总长。In the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100可应用于手机、平板、行车记录仪、安防监控器等电子设备,则第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4和第五透镜L5的材质可选用塑料,从而使得光学镜头100具有良好的光学效果的同时,使得光学镜头具有良好的轻便性。此外,塑料材质更易于透镜的加工,从而可降低光学镜头的加工成本。In some embodiments, the
在一些实施例中,光学镜头100中透镜的材质也可以为玻璃,具有玻璃材质的透镜能够耐受较高或较低的温度且具有优良的光学效果及较佳的稳定性。In some embodiments, the material of the lens in the
在一些实施例中,光学镜头100中还可设置至少两种不同材质的透镜,例如可采用玻璃透镜及塑料透镜相结合的设计,但具体配置关系可根据实际需求而确定,此处不加以穷举。In some embodiments, at least two lenses of different materials can also be provided in the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100还包括光阑102,光阑102可为孔径光阑或视场光阑,其可设置在光学镜头100的物侧与第一透镜L1的物侧面S1之间。可以理解的是,在其他实施例中,该光阑102也可设置在第二透镜L2的像侧面S4和第三透镜L3的物侧面S5之间,或者,该光阑102也可设置在第一透镜L1和第二透镜L2之间,具体可根据实际情况调整设置,本实施例对此不作具体限定。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100还包括滤光片L6,例如红外带通滤光片,红外带通滤光片设于第五透镜L5的像侧面S10与光学镜头100的成像面101之间,红外带通滤光片可允许预期波长范围内的红外光透过,而处于范围外的其他波长的光线将被滤除而无法透过,从而避免干扰光影响红外光的正常成像。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:-6.5<R10/f<-0.1。其中,R10为第五透镜L5的像侧面S10于光轴O处的曲率半径,f为光学镜头100的焦距。满足上述关系式时,能够将第五透镜L5的像侧面S10于光轴O处的曲率半径、光学镜头100的焦距控制在合理的范围内,从而有利于矫正光学镜头100的像散、场曲和畸变,压缩光学镜头100的光学总长,实现光学镜头100轻薄小型化的设计要求。低于上述关系式的下限时,第五透镜L5的像侧面S10于光轴O处的曲率半径过大,导致第五透镜L5的面型过于平缓,难以充分地校正光学镜头100的像散、场曲和畸变;超过上述关系式的上限时,第五透镜L5的像侧面S10于光轴O处的曲率半径过小,导致第五透镜L5的面型弯曲度过大,增加了第五透镜L5的敏感度,不利于第五透镜L5的工程制造。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.65<∑ET/∑CT<0.75。其中,∑ET为所述第一透镜L1至所述第五透镜L5中,每一片透镜的物侧面的最大有效口径处至像侧面的最大有效口径处于光轴O方向上的距离之和(即第一透镜L1至第五透镜L5共五片透镜的边缘厚度的总和),∑CT为所述第一透镜L1至所述第五透镜L5于所述光轴O上的厚度之和(即第一透镜L1至第五透镜L5共五片透镜的中心厚度的总和)。具体地,∑ET/∑CT可以为0.655、0.661、0.694、0.701、0.725、0.734或0.749等。满足上述关系式时,有利于将光学镜头100五片透镜的中心厚度总和与边缘厚度总和控制在合适范围内,从而能够平衡中心视场与边缘视场光程差,有效改善场曲,减小畸变。∑ET/∑CT≥0.75时,光学镜头100的边缘视场光程大于中心光线光程,会导致光学镜头100的场曲过大,引起外视场图像模糊;∑ET/∑CT≤0.65时,光学镜头100的边缘视场光程小于中心光线光程,同样容易导致光学镜头100的场曲过大,引起外视场图像模糊。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.24<(SAG11+SAG21)/TTL<0.3。其中,TTL为所述第一透镜L1的物侧面S1至所述光学镜头100的成像面101于所述光轴O上的距离(即光学镜头100的光学总长),SAG11为所述第一透镜L1的物侧面S1与所述光轴O的交点至所述第一透镜L1的物侧面S1的最大有效半径处在平行于所述光轴O方向上的距离(即第一透镜L1的物侧面S1的矢高),SAG21为所述第二透镜L2的物侧面S3与所述光轴O的交点至所述第二透镜L2的物侧面S3的最大有效半径处在平行于光轴O方向上的距离(即第二透镜L2的物侧面S3的矢高)。具体地,(SAG11+SAG21)/TTL可以为0.241、0.263、0.277、0.284、0.292或0.299等。满足上述关系式时,有利于控制第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2在整个光学镜头100中的结构占比,有效地降低光学镜头100的光学总长,有利于实现光学镜头100的小型化设计。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:3<AT23/AT12<24。其中,AT23为第二透镜L2的像侧面S4至第三透镜L3的物侧面S5于光轴O上的空气间隙,AT12为第一透镜L1的像侧面S2至第二透镜L2的物侧面S3于光轴O上的空气间隙。具体地,AT23/AT12可以为3.5、5.6、7.1、9.4、12.5、16.7、19.3、22.6、23.9等。满足上述关系式时,有利于汇聚入射光线,让光线平滑过渡到成像面101上。AT23/AT12≥24时,第一透镜L1的像侧面S2至第二透镜L2的物侧面S3于光轴O上的空气间隙过小,第二透镜L2的像侧面S4至第三透镜L3的物侧面S5于光轴O上的空气间隙过大,不利于入射光线的汇聚,还容易导致光线在空间间隙里过于陡峭,无法平滑过渡到成像面101上;AT23/AT12≤3时,第一透镜L1的像侧面S2至第二透镜L2的物侧面S3于光轴O上的空气间隙增大,需额外增加隔圈的设计,导致光学镜头100的重量和成本增大,不利于光学镜头100的小型化,同时加大光学镜头100的组装难度,第二透镜L2的像侧面S4至第三透镜L3的物侧面S5于光轴O上的空气间隙被压缩,不利于光线平滑过渡。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.13<CT3/AT34<0.2。其中,CT3为第三透镜L3于光轴O上的厚度,AT34为第三透镜L3的像侧面S6至第四透镜L4的物侧面S7于光轴O上的空气间隙。具体地,AT23/AT12可以为0.131、0.145、0.162、0.173、0.186、0.191或0.199等。满足上述关系式时,能够合理控制第三透镜L3的厚度以及第三透镜L3至第四透镜L4之间的空气间隙,不仅能让光线平滑地从第三透镜L3出射并以合理的入射角进入到第四透镜L4里,还有利于使得外视场相对亮度比较高,保证像面中心亮度与外视场亮度差距较小。 CT3/AT34≥0.2 时,光线过渡不够平滑,容易出现光线陡峭的情况,CT3/AT34≤0.1时,第三透镜L3中心厚度太薄,不利于第三透镜L3的生产加工,且影响整个光学镜头100的光学解析力,导致成像清晰度下降。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:1.30<MAX45/MIN45<3.55。其中,MAX45为第四透镜L4的像侧面S8至第五透镜L5的物侧面S9在平行于光轴O方向上的最大空气间隙,MIN45为第四透镜L4的像侧面S8至第五透镜L5的物侧面S9在平行于光轴O方向上的最小空气间隙。具体地,MAX45/MIN45可以为1.313、1.321、1.405、1.455、1.589、1.762、2.151、2.591、2.816、3.145、3.337、3.510或3.549等。满足上述关系式时,有利于控制第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5的弯曲程度,避免透镜过于弯曲,能够有效的减小局部象散,降低光学镜头100的整体敏感度,有利于工程制造。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.8<TTL/f<0.9,其中,TTL为所述第一透镜L1的物侧面S1至所述光学镜头100的成像面101于所述光轴O上的距离,f为光学镜头100的焦距。具体地,TTL/f可以为0.815、0.838、0.857、0.861、0.889或0.895等。满足上述关系式时,能够合理控制光学镜头100的焦距以及光学镜头100的光学总长,不仅能实现光学镜头100的小型化,还有利于使得光线更好的汇聚于成像面101上。TTL/f≤0.8时,光学镜头100的光学总长相对于光学镜头100的焦距而言过短,容易加大光学镜头100的敏感度,且不利于光线在成像面101上的汇聚。TTL/f≥0.9时,光学镜头100的光学总长相对于光学镜头100的焦距而言过长,导致光线进入成像面101的主光线角度太大,光学镜头100的边缘光线无法成像在成像面101上,造成成像信息不全,降低成像品质,且不利于实现光学镜头100的小型化设计。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:3.5<f/ΣET<4.5。其中,∑ET为所述第一透镜L1至所述第五透镜L5中,每一片透镜的物侧面的最大有效口径处至像侧面的最大有效口径处于光轴O方向上的距离之和,f为光学镜头100的焦距。具体地,f/ΣET可以为3.51、3.60、3.72、3.95、4.05、4.45或4.49等。当光学镜头的透镜采用树脂、塑料等材料制成时,透镜焦距会随温度变化产生焦点位置的移动(简称温飘),使得光学镜头的透镜组公差敏感度及成像解析率下降,当光学镜头满足上述关系式时,能使得透镜组的结构组合较为紧凑,从而满足光学镜头的小型化设计,并提高加工工艺良率,同时,还能保证光线较好地在成像面上汇聚成像,从而保证良好的成像质量。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.13<BFL/TTL<0.18。其中,BFL为第五透镜L5的像侧面S10至光学镜头100的成像面101于光轴O上的距离,即后焦。具体地,BFL/TTL可以为0.131、0.145、0.157、0.162、0.173或0.179等。满足上述关系式时,有利于实现光学镜头100的小型化设计,保证光学镜头100具有足够的调焦范围,提升摄像模组的组装良率,同时有利于保证光学镜头100具备较大的焦深,能够获取物方更多的深度信息。BFL/TTL≤0.13时,摄像模组组装过程中允许公差范围过小,会导致摄像模组的良率过低,加大生产工艺难度,同时光学镜头100的焦深难以保证,容易导致光学镜头100的成像质量不佳;BFL/TTL≥0.18时,光学镜头100的光学总长过短,光学镜头100被过度压缩,容易导致光学镜头100敏感,加大工艺组装难度。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.18<AT34/TTL<0.3。其中,AT34为第三透镜L3的像侧面S6至第四透镜L4的物侧面S7于光轴O上的空气间隙。具体地,AT34/TTL可以为0.181、0.191、0.205、0.215、0.257或0.296等。满足上述关系式时,有利于降低光学镜头100的组装敏感性,提升组装良率。AT34/TTL≥0.3时,会加大光学镜头100的组装敏感性,降低光学镜头100的生产良率; AT34/TTL≤0.18时,在满足光学镜头100性能的同时势必会造成光学镜头100过长,不利于实现光学镜头100小型化的设计。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:0.8<CT3/CT2<1.5。其中,CT3为第三透镜L3于光轴O上的厚度,CT2为第二透镜L2于光轴O上的厚度。具体地,CT3/CT2可以为0.82、0.88、0.98、1.10、1.17、1.25、1.36或1.48等。满足上述关系式时,有利于提高光学镜头100的解析力,校正光学镜头100的像散量,提高光学镜头100的成像清晰度。CT3/CT2≥1.5时,光学镜头100的像散量过大; CT3/CT2≤0.8时,光学镜头100的解析力下降,影响成像质量。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:1.2<DT12/DT22<1.4。其中,DT12为第一透镜L1的像侧面S2的最大有效半口径,DT22为第二透镜L2的像侧面S4的最大有效半口径。具体地,DT12/DT22可以为1.211、1.226、1.287、1.337、1.360或1.395等。满足上述关系式时,能够将第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2的像侧面的最大有效半口径控制在合理范围内,从而利用第一透镜L1的大口径实现入射光线的角度最大化,利用第二透镜L2的较小口径对入射光线进行收拢和汇聚。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:1.1<DT22/DT31<1.3。其中,DT22为第二透镜L2的像侧面S4的最大有效半口径,DT31为第三透镜L3的物侧面S5的最大有效半口径。具体地,DT22/DT31可以为1.113、1.172、1.213、1.244、1.267、1.289或1.295等。满足上述关系式时,有利于第二透镜L2光线进入到第二透镜L2后得到较好的汇聚,第三透镜L3的物侧面S5的小口径有利于对入射光线再次进行汇聚,压缩光学镜头100体积,有利于光学镜头100的小型化。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:1.5<(DL41+DL51)/Imgh<1.7。其中,DL41为第四透镜L4的物侧面S7的最大有效口径,DL51为第五透镜L5的物侧面S9的最大有效口径,Imgh为最大视场角所对应的像高。具体地,(DL41+DL51)/Imgh可以为1.51、1.53、1.57、1.63、1.67或1.69等。满足上述关系式时,有利于使得光线经过第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5平滑过渡至成像面101。 (DL41+DL51)/Imgh≥1.7时,光线经过第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5时光线过于陡峭,导致光线难以平滑过渡到成像面101上;(DL41+DL51)/Imgh≤1.5时,光线经过第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5平滑过渡后以较大角度过渡到成像面101上,无法与合适芯片匹配导致成像信息差。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:1.55<f1/R1<1.80。其中,R1为第一透镜L1的物侧面S1于光轴O处的曲率半径,f1为第一透镜L1的焦距。具体地,f1/R1可以为1.553、1.591、1.620、1.672、1.733、1.765或1.795等。满足上述关系式时,有利于使得第一透镜L1物侧面S1的曲率半径、像侧面S2的曲率半径与第一透镜L1的焦距相适配,使得光学镜头100具备大视场的特性。f1/R1≤1.55时,光学镜头100的视场角范围过大,增加加工难度;f1/R1≥1.80时,第一透镜L1的焦距与物侧面S1的曲率半径不相适配,导致光学镜头100的成像性能下降,像散量增大。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:-14<R2/f1<-3。其中,R2为第一透镜L1的像侧面S2于光轴O处的曲率半径,f1为第一透镜L1的焦距。具体地,R2/f1可以为-13.9、-13.5、-10.0、-8.7、-6.5、-4.1、-3.5、-3.2或-3.05等。满足上述关系式时,有利于使得第一透镜L1物侧面S1的曲率半径、像侧面S2的曲率半径与第一透镜L1的焦距相适配,使得光学镜头100具备大视场的特性。R2/f1≤-14时,光学镜头100的视场角范围过大,增加加工难度;R1/f1≥-3时,第一透镜L1的焦距与像侧面S2的曲率半径不相适配,导致光学镜头100的成像性能下降,像散量增大。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:-1.6<SAG41/CT4<-0.7。其中,SAG41为第四透镜L4的物侧面S7与光轴O的交点至第四透镜L4的物侧面S7的最大有效半径处在平行于光轴O方向上的距离(即第四透镜L4的物侧面S7的矢高),CT4为第四透镜L4于光轴O上的厚度。具体地,SAG41/CT4可以为-1.59、-1.43、-1.26、-1.10、-1.03、-0.95、-0.87、-0.79或-0.71等。满足上述关系式时,能够将第四透镜L4物侧面S7矢高与第四透镜L4中心厚度控制在合适范围内,以使光线平稳过渡,有利于使得外视场成像相对亮度较大,提高成像质量,同时有利于第四透镜L4的加工成型。 SAG41/ CT4≤-1.6时,第四透镜L4的中心厚度过薄,且第四透镜L4的物侧面S7弯曲度过大,不利于第四透镜L4的加工成型,降低成型良率;SAG41/CT4≥-0.7时,第四透镜L4的物侧面S7弯曲度过小,光线难以平滑过渡,外视场相对亮度过小,导致成像质量降低。In some embodiments, the
一些实施例中,光学镜头100满足以下关系式:-4<SAG42/MIN45<-0.4。其中,SAG42为第四透镜L4的像侧面S8与光轴O的交点至第四透镜L4的像侧面S8的最大有效半径处在平行于光轴O方向上的距离(即第四透镜L4的像侧面S8的矢高),MIN45为第四透镜L4的像侧面S8至第五透镜L5的物侧面S9在平行于光轴O的方向上的最小空气间隙。具体地,SAG42/MIN45可以为-3.9、-3.1、-2.6、-2.3、-1.7、-1.1、-0.6、-0.53、-0.49或-0.42等。满足上述关系式时,有利于校正光学镜头100的外视场畸变,提高光学镜头100的成像质量,同时有利于第四透镜L4的加工成型,提高生产良率。SAG42/MIN45≤-4时,第四透镜L4至第五透镜L5之间的空气间隙太薄,矫正畸变的空间有限,导致矫正效果不佳; SAG42/MIN45≥-0.4时,第四透镜L4的像侧面S8弯曲度与最小空气间隙配比不相适配,不利于畸变校正,同时光线难以平稳过渡,导致光学镜头100的成像质量降低。In some embodiments, the
以下将结合具体参数对本实施例的光学镜头100进行详细说明。The
第一实施例first embodiment
本申请的第一实施例公开的光学镜头100的结构示意图如图1所示,光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。The structural diagram of the
进一步地,第一透镜L1具有正屈折力,第二透镜L2具有负屈折力,第三透镜L3具有负屈折力,第四透镜L4具有负屈折力,第五透镜L5具有正屈折力。Further, the first lens L1 has positive refractive power, the second lens L2 has negative refractive power, the third lens L3 has negative refractive power, the fourth lens L4 has negative refractive power, and the fifth lens L5 has positive refractive power.
更进一步地,第一透镜L1的物侧面S1、像侧面S2于近光轴O处均为凸面;第二透镜L2的物侧面S3、像侧面S4于近光轴O处分别为凸面和凹面;第三透镜L3的物侧面S5、像侧面S6于近光轴O处分别为凹面和凸面;第四透镜L4的物侧面S7、像侧面S8于近光轴O处均为凹面;第五透镜L5的物侧面S9、像侧面S10于近光轴O处均为凸面。Furthermore, the object side S1 and the image side S2 of the first lens L1 are both convex at the near optical axis O; the object side S3 and image side S4 of the second lens L2 are respectively convex and concave at the near optical axis O; The object side S5 and image side S6 of the third lens L3 are respectively concave and convex at the near optical axis O; the object side S7 and image side S8 of the fourth lens L4 are both concave at the near optical axis O; the fifth lens L5 Both the object side S9 and the image side S10 are convex at the near optical axis O.
具体地,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.66mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=37.81°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.52mm、光圈数FNO=2.49为例,光学镜头100的其他参数由下表1给出。其中,沿光学镜头100的光轴O由物侧向像侧的各元件依次按照表1从上至下的各元件的顺序排列。在同一透镜中,面序号较小的表面为该透镜的物侧面,面序号较大的表面为该透镜的像侧面,如面序号1和2分别对应第一透镜L1的物侧面S1和像侧面S2。表1中的Y半径为相应面序号的物侧面或像侧面于近光轴O处的曲率半径。透镜的“厚度”参数列中的第一个数值为该透镜于光轴O上的厚度,第二个数值为该透镜的像侧面至后一表面于光轴O上的距离。光阑102于“厚度”参数列中的数值为光阑102至后一表面顶点(顶点指表面与光轴O的交点)于光轴O上的距离,默认第一透镜L1物侧面到最后一枚透镜像侧面的方向为光轴O的正方向,当该值为负时,表明光阑102设置于后一表面顶点的像侧,若光阑102厚度为正值时,光阑102在后一表面顶点的物侧。可以理解的是,表1中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表1中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。Specifically, taking the focal length f=8.66mm of the
表1Table 1
在第一实施例中,第一透镜L1至第四透镜L4的任意一个透镜的物侧面和像侧面均为非球面,各非球面透镜的面型x可利用但不限于以下非球面公式进行限定:In the first embodiment, the object side and the image side of any one of the first lens L1 to the fourth lens L4 are aspheric surfaces, and the surface type x of each aspheric lens can be defined by but not limited to the following aspheric surface formula :
其中,x为非球面沿光轴方向在高度为h的位置时,距非球面顶点的距离矢高;c为非球面的近轴曲率,c=1/R(即,近轴曲率c为上表1中Y半径R的倒数);K为圆锥系数;Ai是非球面第i项高次项相对应的修正系数。表2给出了可用于第一实施例中各个非球面镜面S1-S10的高次项系数A4、A6、A8、A10、A12、A14 、A16、A18和A20。Among them, x is the distance vector height of the aspheric surface from the apex of the aspheric surface at the position of height h along the optical axis; c is the paraxial curvature of the aspheric surface, c=1/R (that is, the paraxial curvature c is the above table 1 in the reciprocal of Y radius R); K is the cone coefficient;Ai is the correction coefficient corresponding to the i-th high-order item of the aspheric surface. Table 2 shows the high-order term coefficients A4, A6, A8, A10, A12, A14, A16, A18 and A20 that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface S1-S10 in the first embodiment.
表2Table 2
请参阅图2中的(A),图2中的(A)示出了第一实施例中的光学镜头100在波长为435nm、470nm、510nm、587.5615nm、610nm和650nm下的纵向球差图。图2中的(A)中,沿X轴方向的横坐标表示焦点偏移,沿Y轴方向的纵坐标表示归一化视场。由图2中的(A)可以看出,第一实施例中的光学镜头100的球差得到了有效控制,说明本实施例中的光学镜头100的成像质量较好。Please refer to (A) in FIG. 2. (A) in FIG. 2 shows the longitudinal spherical aberration diagrams of the
请参阅图2中的(B),图2中的(B)为第一实施例中的光学镜头100在波长为587.5615nm下的像散曲线图。其中,沿X轴方向的横坐标表示焦点偏移,沿Y轴方向的纵坐标表示像高,单位为mm。像散曲线图中的T表示成像面101在子午方向的弯曲,S表示成像面101在弧矢方向的弯曲,由图2中的(B)可以看出,在该波长下,光学镜头100的像散得到了较好的补偿。Please refer to (B) in FIG. 2 . (B) in FIG. 2 is an astigmatism curve of the
请参阅图2中的(C),图2中的(C)为第一实施例中的光学镜头100在波长为587.5615nm下的畸变曲线图。其中,沿X轴方向的横坐标表示畸变,沿Y轴方向的纵坐标表示像高,单位为mm。由图2中的(C)可以看出,在波长587.5615nm下,该光学镜头100的畸变得到了很好的校正。Please refer to (C) in FIG. 2 . (C) in FIG. 2 is a distortion curve of the
第二实施例second embodiment
请参照图3,图3为本申请第二实施例的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 3 , which is a schematic structural diagram of an
进一步地,在第二实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。同时,在第二实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型一致。Further, in the second embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with the refractive power of each lens in the first embodiment. Meanwhile, in the second embodiment, the surface type of each lens is consistent with the surface type of each lens in the first embodiment.
在第二实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.86mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=37.89°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.68mm、光圈数FNO=2.49为例。该第二实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表3给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述实施例的说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表3中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表3中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the second embodiment, the focal length of the
表3table 3
在第二实施例中,表4给出了可用于第二实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the second embodiment, Table 4 shows the high-order term coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the second embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表4Table 4
请参阅图4,由图4中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图4中的(A)、图4中的(B)以及图4中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to Fig. 4, from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in Fig. 4, it can be seen that the longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism and distortion of the
第三实施例third embodiment
请参照图5,图5示出了本申请第三实施例的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 5 , which shows a schematic structural diagram of an
进一步地,在第三实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。同时,在第三实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型的区别在于:第四透镜L4的像侧面S8于近光轴O处为凸面。Further, in the third embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with that of the first embodiment. Meanwhile, in the third embodiment, the surface shape of each lens differs from that in the first embodiment in that: the image side S8 of the fourth lens L4 is convex at the near optical axis O.
在第三实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.67mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=38.09°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.48mm、光圈数FNO=2.48为例。该第三实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表5给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表5中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表5中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the third embodiment, the focal length of the
表5table 5
在第三实施例中,表6给出了可用于第三实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the third embodiment, Table 6 shows the high-order term coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the third embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表6Table 6
请参阅图6,由图6中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图6中的(A)、图6中的(B)以及图6中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to FIG. 6, from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in FIG. control, so that the
第四实施例Fourth embodiment
请参阅图7,为本申请第四实施例公开的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 7 , which is a schematic structural diagram of the
进一步地,在第四实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。而在第四实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型的区别在于:第四透镜L4的像侧面S8于近光轴O处为凸面。Further, in the fourth embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with the refractive power of each lens in the first embodiment. In the fourth embodiment, the surface shape of each lens differs from that of the first embodiment in that: the image side S8 of the fourth lens L4 is convex at the near optical axis O.
在第四实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.67mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=34.67°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.50mm、光圈数FNO=2.48为例。该第四实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表7给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表7中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表7中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the fourth embodiment, the focal length of the
表7Table 7
在第四实施例中,表8给出了可用于第四实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the fourth embodiment, Table 8 shows the high-order term coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the fourth embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表8Table 8
请参阅图8,由图8中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图8中的(A)、图8中的(B)以及图8中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to FIG. 8, from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in FIG. control, so that the
第五实施例fifth embodiment
请参阅图9,为本申请第五实施例公开的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 9 , which is a schematic structural diagram of the
进一步地,在第五实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。同时,在第五实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型一致。Further, in the fifth embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with the refractive power of each lens in the first embodiment. Meanwhile, in the fifth embodiment, the surface type of each lens is identical to that of each lens in the first embodiment.
在第五实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.68mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=37.69°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.50mm、光圈数FNO=2.49为例。该第五实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表9给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表9中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表9中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the fifth embodiment, the focal length of the
表9Table 9
在第五实施例中,表10给出了可用于第五实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the fifth embodiment, Table 10 shows the higher-order coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the fifth embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表10Table 10
请参阅图10,由图10中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图10中的(A)、图10中的(B)以及图10中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to FIG. 10, from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in FIG. control, so that the
第六实施例Sixth embodiment
请参阅图11,为本申请第六实施例公开的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 11 , which is a schematic structural diagram of the
进一步地,在第六实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。同时,在第六实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型一致。Further, in the sixth embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with that of the first embodiment. Meanwhile, in the sixth embodiment, the surface type of each lens is consistent with the surface type of each lens in the first embodiment.
在第六实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.67mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=37.77°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.48mm、光圈数FNO=2.47为例。该第六实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表11给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表11中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表11中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the sixth embodiment, the focal length of the
表11Table 11
在第六实施例中,表12给出了可用于第六实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the sixth embodiment, Table 12 shows the high-order term coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the sixth embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表12Table 12
请参阅图12,由图12中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图12中的(A)、图12中的(B)以及图12中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to Fig. 12, from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in Fig. 12, it can be seen that the longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism and distortion of the
第七实施例Seventh embodiment
请参阅图13,为本申请第七实施例公开的光学镜头100的结构示意图。光学镜头100包括沿光轴O从物侧向像侧依次设置的光阑102、第一透镜L1、第二透镜L2、第三透镜L3、第四透镜L4、第五透镜L5和滤光片L6。Please refer to FIG. 13 , which is a schematic structural diagram of the
进一步地,在第七实施例中,各个透镜的屈折力与第一实施例中的各个透镜的屈折力一致。同时,在第七实施例中,各个透镜的面型与第一实施例中的各个透镜的面型的区别在于:第三透镜L3的物侧面S5、像侧面S6于近光轴O处分别为凸面和凹面,第四透镜L4的像侧面S8于近光轴O处为凸面。Further, in the seventh embodiment, the refractive power of each lens is consistent with that of the first embodiment. At the same time, in the seventh embodiment, the difference between the surface type of each lens and the surface type of each lens in the first embodiment is that: the object side S5 and the image side S6 of the third lens L3 at the near optical axis O are respectively Convex and concave, the image side S8 of the fourth lens L4 is convex at the near optical axis O.
在第七实施例中,以光学镜头100的焦距f=8.67mm、光学镜头100的视场角FOV=38.09°、光学镜头100的光学总长TTL=7.48mm、光圈数FNO=2.49为例。该第七实施例中的其他各项参数由下列表13给出,且其中各参数的定义可由前述说明中得出,此处不加以赘述。可以理解的是,表13中的Y半径、厚度、焦距的单位均为mm。且表13中各个透镜的折射率、阿贝数、焦距的参考波长为587.6nm。In the seventh embodiment, the focal length of the
表13Table 13
在第七实施例中,表14给出了可用于第七实施例中各个非球面镜面的高次项系数,其中,各个非球面面型可由第一实施例中给出的公式限定。In the seventh embodiment, Table 14 shows the high-order term coefficients that can be used for each aspheric mirror surface in the seventh embodiment, wherein each aspheric surface type can be defined by the formula given in the first embodiment.
表14Table 14
请参阅图14,由图14中的(A)纵向球差图,(B)像散曲线图以及(C)畸变曲线图可知,光学镜头100的纵向球差、像散和畸变均得到良好的控制,从而该实施例的光学镜头100拥有良好的成像品质。此外,关于图14中的(A)、图14中的(B)以及图14中的(C)中各曲线对应的波长可参考第一实施例中关于图2中的(A)、图2中的(B)、图2中的(C)所描述的内容,此处不再赘述。Please refer to FIG. 14 , from the (A) longitudinal spherical aberration diagram, (B) astigmatism curve diagram and (C) distortion curve diagram in FIG. 14 , it can be seen that the longitudinal spherical aberration, astigmatism and distortion of the
请参阅表15,表15为本申请第一实施例至第七实施例中各关系式的比值汇总。Please refer to Table 15. Table 15 is a summary of the ratios of the relational expressions in the first embodiment to the seventh embodiment of the present application.
表15Table 15
请参阅图15,本申请还公开了一种摄像模组200,摄像模组200包括感光芯片201和上述的光学镜头100,感光芯片201设置于光学镜头100的像侧。具有光学镜头100的摄像模组能够在降低光学镜头100光学总长,实现光学镜头100的轻薄、小型化设计的同时,校正光学镜头100的畸变、像散及场曲等像差,提高光学镜头100的成像品质。Referring to FIG. 15 , the present application also discloses a
请参阅图16,本申请还公开了一种电子设备,所述电子设备300包括壳体301和上述的摄像模组200,摄像模组200设于壳体301以获取影像信息。其中,电子设备300可以但不限于手机、平板电脑、笔记本电脑、智能手表、监控器等。可以理解的,具有上述摄像模组200的电子设备300,也具有上述光学镜头100的全部技术效果,即,能够在降低光学镜头100光学总长,实现光学镜头100的轻薄、小型化设计的同时,校正光学镜头100的畸变、像散及场曲等像差,提高光学镜头100的成像品质。Please refer to FIG. 16 , the present application also discloses an electronic device. The
以上对本发明实施例公开的光学镜头、摄像模组及电子设备进行了详细介绍,本文中应用了具体个例对本发明的原理及实施方式进行了阐述,以上实施例的说明只是用于帮助理解本发明的光学镜头、摄像模组及电子设备及其核心思想;同时,对于本领域的一般技术人员,依据本发明的思想,在具体实施方式及应用范围上均会有改变之处,综上,本说明书内容不应理解为对本发明的限制。The optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment disclosed in the embodiments of the present invention have been introduced in detail above. In this paper, specific examples have been used to illustrate the principles and implementation methods of the present invention. The descriptions of the above embodiments are only used to help understand the present invention. Invented optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment and their core ideas; at the same time, for those of ordinary skill in the art, according to the idea of the present invention, there will be changes in the specific implementation and application range. In summary, The contents of this description should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211317687.2ACN115373119B (en) | 2022-10-26 | 2022-10-26 | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211317687.2ACN115373119B (en) | 2022-10-26 | 2022-10-26 | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115373119A CN115373119A (en) | 2022-11-22 |
| CN115373119Btrue CN115373119B (en) | 2023-03-10 |
Family
ID=84074346
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211317687.2AActiveCN115373119B (en) | 2022-10-26 | 2022-10-26 | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115373119B (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116430549B (en)* | 2023-04-06 | 2024-01-12 | 广东旭业光电科技股份有限公司 | Telephoto lens and electronic equipment |
| CN116609924A (en)* | 2023-06-20 | 2023-08-18 | 浙江舜宇光学有限公司 | Optical lens system |
| CN119986981B (en)* | 2025-04-14 | 2025-09-02 | 江西联益光学有限公司 | Optical lens |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104597586A (en)* | 2013-10-31 | 2015-05-06 | 苹果公司 | Small form factor telephoto camera |
| JP2021047315A (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-25 | カンタツ株式会社 | Image capturing lens |
| CN113640953A (en)* | 2019-03-27 | 2021-11-12 | 康达智株式会社 | Camera lens |
| CN114063248A (en)* | 2020-07-29 | 2022-02-18 | 大立光电股份有限公司 | Imaging optical lens assembly, image capturing device and electronic device |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114740604B (en)* | 2022-04-26 | 2023-09-05 | 江西晶超光学有限公司 | Optical systems, camera modules and electronics |
- 2022
- 2022-10-26CNCN202211317687.2Apatent/CN115373119B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104597586A (en)* | 2013-10-31 | 2015-05-06 | 苹果公司 | Small form factor telephoto camera |
| CN113640953A (en)* | 2019-03-27 | 2021-11-12 | 康达智株式会社 | Camera lens |
| JP2021047315A (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2021-03-25 | カンタツ株式会社 | Image capturing lens |
| CN114063248A (en)* | 2020-07-29 | 2022-02-18 | 大立光电股份有限公司 | Imaging optical lens assembly, image capturing device and electronic device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115373119A (en) | 2022-11-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115373119B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| WO2020019705A1 (en) | Camera lens, camera module, and terminal | |
| CN113933968B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN112363302B (en) | Optical systems, camera modules and electronic equipment | |
| CN113552697A (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114296213B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN111812806A (en) | Optical systems, camera modules and electronic equipment | |
| CN114355579A (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN112987256B (en) | Optical system, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN113552695B (en) | Optical zoom system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114415343A (en) | Optical system, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114326026A (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114740599A (en) | Optical systems, camera modules and electronic equipment | |
| CN114114617A (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| CN115390226B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN115480364B (en) | Optical lenses, camera modules and electronic equipment | |
| CN114578525B (en) | Optical system, lens module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114721126B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN113900226B (en) | Optical systems, imaging modules and electronic equipment | |
| CN113933966B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN113741005B (en) | Optical system, imaging module and electronic equipment | |
| CN214845997U (en) | Optical system, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN116027527B (en) | Optical lens, camera module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114326052B (en) | Optical system, image capturing module and electronic equipment | |
| CN114690378B (en) | Optical imaging system, lens module and electronic equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CP03 | Change of name, title or address | ||
| CP03 | Change of name, title or address | Address after:330096 No.699 Tianxiang North Avenue, Nanchang hi tech Industrial Development Zone, Jiangxi Province Patentee after:Jiangxi Oufei Optics Co.,Ltd. Country or region after:China Address before:No. 699 Tianxiang North Avenue, Nanchang High tech Industrial Development Zone, Nanchang City, Jiangxi Province Patentee before:Jiangxi Jingchao optics Co.,Ltd. Country or region before:China |