CN115372926A - Method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic features of moving object - Google Patents
Method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic features of moving objectDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115372926A CN115372926ACN202211004917.XACN202211004917ACN115372926ACN 115372926 ACN115372926 ACN 115372926ACN 202211004917 ACN202211004917 ACN 202211004917ACN 115372926 ACN115372926 ACN 115372926A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- echo signal
- moving target
- scattering point
- radar
- equivalent model
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription48
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 230000033001locomotionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000claimsdescription13
- 230000014509gene expressionEffects0.000claimsdescription13
- 238000001228spectrumMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription8
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000003595spectral effectEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000004804windingMethods0.000claims4
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000claims2
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000claims2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description8
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description8
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description6
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description5
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 238000012512characterization methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005610quantum mechanicsEffects0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001052transient effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/41—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00 using analysis of echo signal for target characterisation; Target signature; Target cross-section
- G01S7/415—Identification of targets based on measurements of movement associated with the target
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明实施例涉及雷达技术领域,特别涉及一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法、装置、设备及介质。Embodiments of the present invention relate to the field of radar technology, and in particular to a method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target.
背景技术Background technique
运动目标在高速飞行时会与周围的大气发生剧烈摩擦,导致空气电离产生等离子体,形成包覆在运动目标周围的等离子体绕流场。等离子体绕流场会与入射的电磁波产生相互作用,从而改变运动目标的电磁特性,给雷达探测、跟踪和识别高速运动目标带来极大困难。因此,为了消除等离子体绕流场对运动目标电磁特性的影响,需要对运动目标以及包覆在运动目标周围的等离子体绕流场的回波信号进行速度补偿,得到补偿后的回波信号,然后再从补偿后的回波信号中提取目标的电磁特征。When the moving target flies at high speed, it will rub against the surrounding atmosphere violently, which will cause air ionization to generate plasma, and form a plasma flow field around the moving target. The plasma flow field will interact with the incident electromagnetic wave, thereby changing the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target, which will bring great difficulties to radar detection, tracking and identification of high-speed moving targets. Therefore, in order to eliminate the influence of the plasma flow field on the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target, it is necessary to perform speed compensation on the echo signal of the moving target and the plasma flow field wrapped around the moving target, and obtain the compensated echo signal. Then the electromagnetic characteristics of the target are extracted from the compensated echo signal.
相关技术中,在对运动目标以及等离子体绕流场的回波信号进行速度补偿时,通常将运动目标和等离子体绕流场作为一个整体,补偿速度均使用运动目标的估计速度。但是,运动目标的估计速度与等离子体绕流场的速度分布有较大差异,导致对等离子体绕流场的速度补偿失准,因而无法准确获得运动目标以及等离子体绕流场的回波信号,导致从该回波信号中提取出的运动目标的电磁特征不准确。In the related art, when performing speed compensation on the echo signals of the moving target and the plasma flow field, the moving target and the plasma flow field are usually taken as a whole, and the estimated speed of the moving target is used for the compensation speed. However, there is a large difference between the estimated velocity of the moving target and the velocity distribution of the plasma surrounding the flow field, resulting in inaccurate compensation for the velocity of the plasma surrounding the flow field, so that the echo signals of the moving target and the plasma surrounding the flow field cannot be accurately obtained , resulting in inaccurate electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target extracted from the echo signal.
基于此,目前亟待需要一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法、装置、设备及介质来解决上述技术问题。Based on this, there is an urgent need for a method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of moving objects to solve the above technical problems.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明实施例提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法、装置、设备及介质,能够准确提取运动目标的电磁特征。Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target, which can accurately extract electromagnetic features of a moving target.
第一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法,包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target, including:
基于运动目标的运动参数,对所述运动目标进行仿真计算,得到包覆所述运动目标的等离子体绕流场;其中,所述等离子体绕流场内的不同区域具有相对于雷达不同的第二径向速度,所述运动参数包括所述运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度,所述第一径向速度与所述第二径向速度不同;Based on the motion parameters of the moving target, the moving target is simulated and calculated to obtain the plasma flow field covering the moving target; wherein, different regions in the plasma flow field have different first-order values relative to the radar Two radial velocities, the motion parameters include a first radial velocity of the moving target relative to the radar, the first radial velocity is different from the second radial velocity;
基于所述运动目标和所述等离子体绕流场,构建简化等效模型;其中,所述简化等效模型包括一个第一散射点和多个第二散射点,所述第一散射点代表所述运动目标,不同所述第二散射点代表所述等离子体绕流场内的不同区域;Based on the moving target and the plasma flow field, a simplified equivalent model is constructed; wherein, the simplified equivalent model includes a first scatter point and a plurality of second scatter points, and the first scatter point represents all For the moving target, the different second scattering points represent different regions in the plasma surrounding flow field;
响应于利用所述雷达向所述简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号;Obtaining a final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model in response to using the radar to transmit electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model;
对所述最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到所述运动目标的电磁特征。Feature extraction is performed on the final echo signal to obtain electromagnetic features of the moving target.
在一种可能的设计中,所述响应于利用所述雷达向所述简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号,包括:In a possible design, the response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model includes:
响应于利用所述雷达向所述简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到由所述第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由所述第二散射点返回的第二回波信号;Obtaining a first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and a second echo signal returned by the second scattering point in response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model;
利用所述第一径向速度对所述第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;performing speed compensation on the first echo signal by using the first radial velocity to obtain a third echo signal;
针对每个所述第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;For each second scattering point, using the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point, performing speed compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal;
将得到的第三回波信号和所有第四回波信号进行矢量相加,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号。The obtained third echo signal and all the fourth echo signals are vector-added to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model.
在一种可能的设计中,所述电磁波为线性调频波LFM;所述线性调频波LFM的信号表达式为:In a possible design, the electromagnetic wave is a linear frequency modulation wave LFM; the signal expression of the linear frequency modulation wave LFM is:
式中,TP为脉冲宽度;k为线性调频信号的斜率,B为信号带宽;fc为信号载频,为线性调频波LFM的快时间,范围是In the formula, TP is the pulse width; k is the slope of the linear frequency modulation signal, B is the signal bandwidth; fc is the signal carrier frequency, is the fast time of the chirp LFM, the range is
在一种可能的设计中,由所述第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由每个所述第二散射点返回的第二回波信号的表达式为:In a possible design, the expression of the first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and the second echo signal returned by each of the second scattering points is:
式中,R为所述散射点到雷达的距离,V为所述散射点相对于所述雷达的径向速度,R0为所述散射点到所述雷达的初始距离,c为光速,A为所述散射点的幅度。In the formula, R is the distance from the scattering point to the radar, V is the radial velocity of the scatter point relative to the radar, R0 is the initial distance from the scatter point to the radar, c is the speed of light, and A is the amplitude of the scatter point.
在一种可能的设计中,由每个所述散射点的径向速度引起的相位误差为:In a possible design, the phase error caused by the radial velocity of each said scattering point is:
所述利用所述第一径向速度对所述第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号,包括:Using the first radial velocity to perform velocity compensation on the first echo signal to obtain a third echo signal includes:
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对所述第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;Using e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on the first echo signal to obtain a third echo signal;
所述针对每个所述第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号,包括:For each of the second scattering points, using the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point to perform speed compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal, include:
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对每个所述第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;Using e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on each of the second echo signals to obtain a fourth echo signal;
所述第三回波信号和所述第四回波信号的表达式为:The expressions of the third echo signal and the fourth echo signal are:
在一种可能的设计中,所述运动目标的电磁特征包括频谱特征和一维距离像;In a possible design, the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target include spectral characteristics and a one-dimensional range profile;
所述对所述最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到所述运动目标的电磁特征,包括:The feature extraction of the final echo signal to obtain the electromagnetic features of the moving target includes:
对所述最终回波信号进行短时傅里叶变换,得到所述运动目标的频谱特征;performing a short-time Fourier transform on the final echo signal to obtain the spectral features of the moving target;
对所述最终回波信号进行混频和去倾斜处理,得到第三回波信号;对所述第三回波信号进行逆傅里叶变换,得到所述运动目标的一维距离像。Perform frequency mixing and de-tilt processing on the final echo signal to obtain a third echo signal; perform inverse Fourier transform on the third echo signal to obtain a one-dimensional range image of the moving target.
第二方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置,包括:In the second aspect, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a device for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target, including:
计算模块,用于基于运动目标的运动参数,对所述运动目标进行仿真计算,得到包覆所述运动目标的等离子体绕流场;其中,所述等离子体绕流场内的不同区域具有相对于雷达不同的第二径向速度,所述运动参数包括所述运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度,所述第一径向速度与所述第二径向速度不同;The calculation module is used to simulate and calculate the moving target based on the moving parameters of the moving target, and obtain the plasma flow field covering the moving target; wherein, different regions in the plasma flow field have relative a second radial velocity different from the radar, the motion parameters include a first radial velocity of the moving target relative to the radar, the first radial velocity is different from the second radial velocity;
构建模块,用于基于所述运动目标和所述等离子体绕流场,构建简化等效模型;其中,所述简化等效模型包括一个第一散射点和多个第二散射点,所述第一散射点代表所述运动目标,不同所述第二散射点代表所述等离子体绕流场内的不同区域;A construction module, configured to construct a simplified equivalent model based on the moving target and the plasma flow field; wherein, the simplified equivalent model includes a first scattering point and a plurality of second scattering points, and the first One scatter point represents the moving target, and the different second scatter points represent different regions in the plasma flow field;
获得模块,用于响应于利用所述雷达向所述简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号;an obtaining module, configured to obtain a final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model in response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model;
提取模块,用于对所述最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到所述运动目标的电磁特征。The extraction module is configured to perform feature extraction on the final echo signal to obtain electromagnetic features of the moving target.
在一种可能的设计中,所述获得模块用于执行如下操作:In a possible design, the obtaining module is configured to perform the following operations:
响应于利用所述雷达向所述简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到由所述第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由所述第二散射点返回的第二回波信号;Obtaining a first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and a second echo signal returned by the second scattering point in response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model;
利用所述第一径向速度对所述第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;performing speed compensation on the first echo signal by using the first radial velocity to obtain a third echo signal;
针对每个所述第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;For each second scattering point, using the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point, performing speed compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal;
将得到的第三回波信号和所有第四回波信号进行矢量相加,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号。The obtained third echo signal and all the fourth echo signals are vector-added to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model.
第三方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种电子设备,包括存储器和处理器,所述存储器中存储有计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述计算机程序时,实现本说明书任一实施例所述的方法。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present invention also provides an electronic device, including a memory and a processor, wherein a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the processor executes the computer program, the computer program described in any embodiment of this specification can be realized. described method.
第四方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,当所述计算机程序在计算机中执行时,令计算机执行本说明书任一实施例所述的方法。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed in a computer, the computer is instructed to execute the method described in any embodiment of this specification .
本发明实施例提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法、装置、设备及介质,该方法首先基于运动目标的运动参数进行仿真计算,得到包覆该运动目标的等离子体绕流场,该等离子体绕流场具有多个区域,不同区域的物理参数分布以及不同区域相对于雷达的第二径向速度不同,且运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度与所述第二径向速度不同;然后,基于运动目标以及等离子体绕流场不同区域的差异,构建运动目标和等离子体绕流场的简化等效模型,将运动目标等效为第一散射点,将等离子体绕流场内的不同区域分别等效为独立地第二散射点;再然后响应于利用雷达向该简化等效模型发送电磁波,也即向每个散射点发送电磁波,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号,也即所有散射点回波信号组合而成的回波信号,由于每个散射点对应的回波信号更精确,因此其组合而成的回波信号更精确,利用该回波信号进行特征提取,得到的运动目标的电磁特征更准确。Embodiments of the present invention provide a method, device, equipment, and medium for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target. The method first performs simulation calculation based on the moving parameters of the moving target to obtain the plasma flow field surrounding the moving target. The plasma The flow field around the body has multiple regions, the distribution of physical parameters in different regions and the second radial velocity relative to the radar in different regions are different, and the first radial velocity of the moving target relative to the radar is different from the second radial velocity ; Then, based on the difference between the moving target and different regions of the plasma flow field, a simplified equivalent model of the moving target and the plasma flow field is constructed, the moving target is equivalent to the first scattering point, and the plasma flow field The different regions of are equivalent to independent second scattering points respectively; then in response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model, that is, to send electromagnetic waves to each scattering point, the final echo of the simplified equivalent model is obtained signal, that is, the echo signal formed by the combination of echo signals of all scattering points. Since the echo signal corresponding to each scattering point is more accurate, the combined echo signal is more accurate, and the echo signal is used for characterization Extraction, the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target are more accurate.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are For some embodiments of the present invention, those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings based on these drawings without creative work.
图1是本发明一实施例提供的运动目标电磁特征的提取方法的结构示意图;1 is a schematic structural diagram of a method for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2是本发明一实施例提供的简化等效模型示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of a simplified equivalent model provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图3是图2所示的简化等效模型相对于雷达观测方向的示意图;Fig. 3 is a schematic diagram of the simplified equivalent model shown in Fig. 2 relative to the radar observation direction;
图4是本发明一实施例提供的未采用本申请方法提取出的时域频谱;Fig. 4 is the time-domain spectrum provided by an embodiment of the present invention that is not extracted by the method of the present application;
图5是本发明一实施例提供的未采用本申请方法提取出的一维距离像;Fig. 5 is a one-dimensional range image provided by an embodiment of the present invention that is not extracted by the method of the present application;
图6是本发明一实施例提供的采用本申请方法提取出的一维距离像;Fig. 6 is a one-dimensional distance image extracted by the method of the present application provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图7是本发明一实施例提供的一种电子设备的硬件架构图;FIG. 7 is a hardware architecture diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8是本发明一实施例提供的一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置结构图。Fig. 8 is a structural diagram of a device for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving object provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例,基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of them. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative work belong to the protection of the present invention. scope.
如前所述,相关技术无法从运动目标以及等离子体绕流场的回波信号中准确提取运动目标的电磁特征。As mentioned above, the relevant technologies cannot accurately extract the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target from the echo signals of the moving target and the plasma flow field.
针对这一问题,发明人发现这是由于现有方法通常认为等离子体绕流场与运动目标相对静止,但实际两者速度相差较大,且等离子体绕流场本身也具有不均匀分布的特性。因此,若均采用目标的运动速度对回波信号进行补偿,会导致等离子体绕流场的速度补偿失准,不能得到准确的回波信号,进而影响提取出的目标电磁特征的准确性,使雷达测量过程中出现频谱展宽和一维距离像散焦等现象,严重影响雷达的探测和跟踪。In response to this problem, the inventors found that this is because the existing methods generally believe that the plasma flow field and the moving target are relatively static, but the actual velocity difference between the two is large, and the plasma flow field itself also has the characteristics of uneven distribution . Therefore, if the echo signal is compensated by the moving speed of the target, the speed compensation of the plasma around the flow field will be inaccurate, and the accurate echo signal cannot be obtained, which will affect the accuracy of the extracted electromagnetic characteristics of the target. Spectrum broadening and one-dimensional range image defocusing occur during radar measurement, which seriously affect radar detection and tracking.
基于此,发明人提出分别计算运动目标和等离子体绕流场的回波信号,从而得到较为准确的回波信号,进而提取出准确的目标特征。Based on this, the inventor proposes to separately calculate the echo signals of the moving target and the plasma flow field, so as to obtain relatively accurate echo signals, and then extract accurate target features.
下面描述以上构思的具体实现方式。The specific implementation of the above idea is described below.
请参考图1,本发明实施例提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法,该方法包括:Please refer to FIG. 1, an embodiment of the present invention provides a method for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target, the method includes:
步骤100,基于运动目标的运动参数,对运动目标进行仿真计算,得到包覆运动目标的等离子体绕流场;其中,等离子体绕流场内的不同区域具有相对于雷达不同的第二径向速度,运动参数包括运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度,第一径向速度与第二径向速度不同;
步骤102,基于运动目标和等离子体绕流场,构建简化等效模型;其中,简化等效模型包括一个第一散射点和多个第二散射点,第一散射点代表运动目标,不同第二散射点代表等离子体绕流场内的不同区域;
步骤104,响应于利用雷达向简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到简化等效模型的最终回波信号;
步骤106,对最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到运动目标的电磁特征。
本发明实施例中,首先基于运动目标的运动参数进行仿真计算,得到包覆该运动目标的等离子体绕流场,该等离子体绕流场具有多个区域,不同区域的物理参数分布以及不同区域相对于雷达的第二径向速度不同,且运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度与所述第二径向速度不同;然后,基于运动目标以及等离子体绕流场不同区域的差异,构建运动目标和等离子体绕流场的简化等效模型,将运动目标等效为第一散射点,将等离子体绕流场内的不同区域分别等效为独立地第二散射点;再然后响应于利用雷达向该简化等效模型发送电磁波,也即向每个散射点发送电磁波,得到所述简化等效模型的最终回波信号,也即所有散射点回波信号组合而成的回波信号,由于每个散射点对应的回波信号更精确,因此其组合而成的回波信号更精确,利用该回波信号进行特征提取,得到的运动目标的电磁特征更准确。In the embodiment of the present invention, the simulation calculation is first performed based on the motion parameters of the moving target, and the plasma flow field covering the moving target is obtained. The plasma flow field has multiple regions, the distribution of physical parameters in different regions and the distribution of different regions The second radial velocity relative to the radar is different, and the first radial velocity of the moving target relative to the radar is different from the second radial velocity; then, based on the difference between the moving target and different regions of the plasma flow field, construct The simplified equivalent model of the moving target and the plasma flow field, the moving target is equivalent to the first scattering point, and the different regions in the plasma flow field are respectively equivalent to independent second scattering points; and then responding to Using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model, that is, to send electromagnetic waves to each scattering point, to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model, that is, the echo signal formed by combining the echo signals of all scattering points, Since the echo signal corresponding to each scattering point is more accurate, the combined echo signal is more accurate. Using the echo signal for feature extraction, the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target obtained are more accurate.
下面描述图1所示的各个步骤的执行方式。The execution manner of each step shown in FIG. 1 is described below.
首先,针对步骤100,基于运动目标的运动参数,对运动目标进行仿真计算,得到包覆运动目标的等离子体绕流场;其中,等离子体绕流场内的不同区域具有相对于雷达不同的第二径向速度,运动参数包括运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度,第一径向速度与第二径向速度不同。First, for
在该步骤中,运动目标可以是任意形状,例如球形等,运动目标的运动参数包括目标的飞行高度、飞行速度和攻角等,有了这些参数,就可以准确地仿真出由于目标运动产生的等离子体绕流场以及等离子体绕流场的物理参数分布,物理参数包括绕流场不同区域的速度、电子密度、温度和压强等。根据物理参数分布可以将等离子体绕流场划分为多个区域,每个区域的物理参数分布均不相同,且每个区域相对于雷达的第二径向速度不同,由于上述不同,等离子体绕流场中每个区域的电磁特性不同,因此,需要单独对每个区域的电磁特性进行分析。In this step, the moving target can be in any shape, such as a sphere, etc. The moving parameters of the moving target include the flying height, flying speed and angle of attack of the target. With these parameters, it is possible to accurately simulate the The plasma flow field and the distribution of physical parameters of the plasma flow field. The physical parameters include the velocity, electron density, temperature and pressure in different regions of the flow field. According to the distribution of physical parameters, the plasma flow field can be divided into multiple regions. The distribution of physical parameters in each region is different, and the second radial velocity of each region relative to the radar is different. Due to the above differences, the plasma flow field The electromagnetic properties of each area in the flow field are different, therefore, the electromagnetic properties of each area need to be analyzed separately.
然后,针对步骤102,基于运动目标和等离子体绕流场,构建简化等效模型;其中,简化等效模型包括一个第一散射点和多个第二散射点,第一散射点代表运动目标,不同第二散射点代表等离子体绕流场内的不同区域。Then, for
在该步骤中,简化等效模型的构建是基于运动目标的电磁特性和等离子体绕流场不同区域的电磁特性之间的差异确定的,根据电磁特性的差异,分别将运动目标和等离子体绕流场的不同区域等效为第一散射点和第二散射点,以利于单独对每一个散射点进行计算,得到更为准确的回波信号。In this step, the construction of the simplified equivalent model is determined based on the difference between the electromagnetic characteristics of the moving target and the electromagnetic characteristics of different regions of the plasma flow field. Different regions of the flow field are equivalent to the first scattering point and the second scattering point, so as to facilitate the calculation of each scattering point separately and obtain more accurate echo signals.
再然后,针对步骤104,响应于利用雷达向简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到简化等效模型的最终回波信号。Then, for
在一些实施方式中,该步骤的具体过程包括:In some embodiments, the specific process of this step includes:
步骤A1,响应于利用雷达向简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到由第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由第二散射点返回的第二回波信号;Step A1, in response to using the radar to send electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model, obtaining a first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and a second echo signal returned by the second scattering point;
步骤A2,利用第一径向速度对第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;Step A2, using the first radial velocity to perform velocity compensation on the first echo signal to obtain a third echo signal;
步骤A3,针对每个第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;Step A3, for each second scattering point, use the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point to perform velocity compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal;
步骤A4,将得到的第三回波信号和所有第四回波信号进行矢量相加,得到简化等效模型的最终回波信号。Step A4, performing vector addition of the obtained third echo signal and all fourth echo signals to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model.
在一些实施方式中,步骤A1中雷达发送的电磁波为性调频波LFM;In some embodiments, the electromagnetic wave sent by the radar in step A1 is a frequency modulated wave LFM;
该线性调频波LFM的信号表达式为:The signal expression of the linear frequency modulation wave LFM is:
式中,TP为脉冲宽度;k为线性调频信号的斜率,B为信号带宽;fc为信号载频,为线性调频波LFM的快时间,范围是In the formula, TP is the pulse width; k is the slope of the linear frequency modulation signal, B is the signal bandwidth; fc is the signal carrier frequency, is the fast time of the chirp LFM, the range is
电磁波入射到每一个散射点后,经散射点反射后形成雷达回波。其中,由第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由每个第二散射点返回的第二回波信号的表达式为:After the electromagnetic wave is incident on each scattering point, the radar echo is formed after being reflected by the scattering point. Among them, the expression of the first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and the second echo signal returned by each second scattering point is:
式中,R为散射点到雷达的距离,V为散射点相对于雷达的径向速度,R0为散射点到雷达的初始距离,c为光速,A为散射点的幅度。In the formula, R is the distance from the scattering point to the radar, V is the radial velocity of the scattering point relative to the radar,R0 is the initial distance from the scattering point to the radar, c is the speed of light, and A is the amplitude of the scattering point.
在该步骤中,由于散射点径向速度的影响,雷达接收到的回波信号存在相位误差,相位误差的表达式如下所示:In this step, due to the influence of the radial velocity of the scattering point, there is a phase error in the echo signal received by the radar, and the expression of the phase error is as follows:
因此,在步骤A2、A3中,需要分别对第一回波信号和第二回波信号进行速度补偿,具体地补偿方法为:Therefore, in steps A2 and A3, speed compensation needs to be performed on the first echo signal and the second echo signal respectively, and the specific compensation method is as follows:
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;Use e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on the first echo signal to obtain the third echo signal;
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对每个第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;Use e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on each second echo signal to obtain the fourth echo signal;
第三回波信号和第四回波信号的表达式为:The expressions of the third echo signal and the fourth echo signal are:
在上述步骤中,由于使用每一个散射点的径向速度分别各自的回波信号进行补偿,因此,补偿得到的回波信号更为准确。由补偿后的回波信号进行矢量相加,得到的最终回波信号具有较高的精度。In the above steps, since the radial velocity of each scattering point is used for compensation respectively, the echo signal obtained by compensation is more accurate. The final echo signal obtained by vector addition of the compensated echo signals has high precision.
最后,针对步骤106,对最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到运动目标的电磁特征。Finally, for
在该步骤中,运动目标的电磁特征包括频谱特征和一维距离像。In this step, the electromagnetic features of the moving target include frequency spectrum features and one-dimensional range images.
针对频谱特征,雷达探测的目标回波信号都是瞬变、不平稳的,含有许多瞬时频率分量,为了获得各分量瞬时频率,Gabor受到量子力学的启发,建议用时间和频率两维坐标来表示信号,于1946年以高斯函数作为展开函数对信号进行分解,提出了Gabor展开。他使用一个很窄的窗函数取出信号,并求其Fourier变换,该频谱称为局部频谱,他的工作引申出短时Fourier变换(Short-time Fourier transform,STFT),是信号的时频二维表示。STFT的定义式为:In view of the spectrum characteristics, the target echo signals detected by radar are all transient and unstable, and contain many instantaneous frequency components. In order to obtain the instantaneous frequency of each component, Gabor, inspired by quantum mechanics, suggested using two-dimensional coordinates of time and frequency to represent In 1946, the Gaussian function was used as the expansion function to decompose the signal, and the Gabor expansion was proposed. He used a very narrow window function to extract the signal, and calculated its Fourier transform, which is called the local spectrum. His work derived the short-time Fourier transform (Short-time Fourier transform, STFT), which is the two-dimensional time-frequency of the signal express. The definition of STFT is:
式中,g(t)是一“窄的”窗函数,*代表复数共轭,s(u)代表回波信号。In the formula, g(t) is a "narrow" window function, * represents the complex conjugate, and s(u) represents the echo signal.
基于上述原理,对最终回波信号进行短时傅里叶变换,即可得到运动目标的频谱特征;Based on the above principles, short-time Fourier transform is performed on the final echo signal to obtain the spectral characteristics of the moving target;
针对一维距离像,根据线性调频波形(LFM)理论,经混频和去倾斜处理后,LFM雷达单个发射脉冲对应的接收回波同目标散射中心随径向距离的分布(即一维距离像)之间是傅里叶逆变换关系。For the one-dimensional range image, according to the linear frequency modulated waveform (LFM) theory, after the frequency mixing and de-tilt processing, the distribution of the received echo corresponding to the single transmission pulse of the LFM radar with the radial distance of the target scattering center (that is, the one-dimensional range image ) is the inverse Fourier transform relationship.
基于上述原理,对最终回波信号进行混频和去倾斜处理,得到第三回波信号后,再对第三回波信号进行逆傅里叶变换,即可得到运动目标的一维距离像。Based on the above principles, the final echo signal is mixed and de-tilted to obtain the third echo signal, and then the third echo signal is subjected to inverse Fourier transform to obtain the one-dimensional range image of the moving target.
下面以一个具体实施例来证明本申请方法的效果:Prove the effect of the application method with a specific embodiment below:
如图2所示,为本实施例提供的简化等效模型示意图,从图中可以看出,运动目标为高速飞行的球体,球体周围为等离子体绕流场,绕流场包括不同的区域,运动目标和每个区域分别被等效为不同的散射点,各散射点的RCS(幅度)和径向速度如表1所示:As shown in Figure 2, it is a schematic diagram of a simplified equivalent model provided by this embodiment. It can be seen from the figure that the moving target is a sphere flying at high speed, and the surrounding flow field of plasma is surrounded by plasma, and the flow field includes different regions. The moving target and each region are equivalent to different scattering points, and the RCS (amplitude) and radial velocity of each scattering point are shown in Table 1:
表1各散射点的RCS(幅度)和径向速度Table 1 RCS (amplitude) and radial velocity of each scattering point
如图3所示,为图2所示的简化等效模型相对于雷达观测方向的示意图,从图中可以看出,各散射点距离雷达观测方向的初始距离均为800km,当雷达以中心频率为5GHz、带宽5MHz的条件向该简化等效模型发射电磁波时,若不对接收到的回波信号进行速度补偿,则提取到的时域频谱如图4所示,从图4可以看出,雷达回波具有较宽的频谱,说明雷达回波受到了等离子体绕流场的干扰,在不进行速度补偿的情况下,提取到的一维距离像如图5所示,从图5可以看出,一维距离像存在严重的散焦现象。而采用本申请方法对回波信号进行速度补偿后,提取出的一维距离像如图6所示,从图中可以看出,一维距离像的散焦现象已经消失。As shown in Figure 3, it is a schematic diagram of the simplified equivalent model shown in Figure 2 relative to the radar observation direction. It can be seen from the figure that the initial distance of each scattering point from the radar observation direction is 800km. When the electromagnetic wave is transmitted to the simplified equivalent model under the conditions of 5GHz and bandwidth of 5MHz, if no velocity compensation is performed on the received echo signal, the extracted time-domain spectrum is shown in Figure 4. It can be seen from Figure 4 that the radar The echo has a wide frequency spectrum, indicating that the radar echo is disturbed by the plasma flow field. Without velocity compensation, the extracted one-dimensional distance image is shown in Figure 5. It can be seen from Figure 5 that , there is serious defocusing phenomenon in the one-dimensional range image. However, after speed compensation is performed on the echo signal by the method of the present application, the extracted one-dimensional range image is shown in FIG. 6 . It can be seen from the figure that the defocus phenomenon of the one-dimensional range image has disappeared.
由该实施例可以看出,本申请方法能够准确提取运动目标的电磁特征。It can be seen from this embodiment that the method of the present application can accurately extract the electromagnetic features of the moving target.
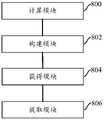
如图7、图8所示,本发明实施例提供了一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置。装置实施例可以通过软件实现,也可以通过硬件或者软硬件结合的方式实现。从硬件层面而言,如图7所示,为本发明实施例提供的一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置所在电子设备的一种硬件架构图,除了图7所示的处理器、内存、网络接口、以及非易失性存储器之外,实施例中装置所在的电子设备通常还可以包括其他硬件,如负责处理报文的转发芯片等等。以软件实现为例,如图8所示,作为一个逻辑意义上的装置,是通过其所在电子设备的CPU将非易失性存储器中对应的计算机程序读取到内存中运行形成的。As shown in FIG. 7 and FIG. 8 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a device for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target. The device embodiments can be implemented by software, or by hardware or a combination of software and hardware. From the hardware level, as shown in Figure 7, it is a hardware architecture diagram of the electronic equipment where the device for extracting the electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target provided by the embodiment of the present invention, except for the processor, memory, and network shown in Figure 7 In addition to the interface and the non-volatile memory, the electronic device where the device in the embodiment is located may generally include other hardware, such as a forwarding chip responsible for processing messages, and the like. Taking software implementation as an example, as shown in Figure 8, as a device in a logical sense, it is formed by reading the corresponding computer program in the non-volatile memory into the memory and running it through the CPU of the electronic device where it is located.
本实施例提供的一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置,包括:A device for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target provided in this embodiment includes:
计算模块800,用于基于运动目标的运动参数,对运动目标进行仿真计算,得到包覆运动目标的等离子体绕流场;其中,等离子体绕流场内的不同区域具有相对于雷达不同的第二径向速度,运动参数包括运动目标相对于雷达的第一径向速度,第一径向速度与第二径向速度不同;The
构建模块802,用于基于运动目标和等离子体绕流场,构建简化等效模型;其中,简化等效模型包括一个第一散射点和多个第二散射点,第一散射点代表运动目标,不同第二散射点代表等离子体绕流场内的不同区域;The
获得模块804,用于响应于利用雷达向简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到简化等效模型的最终回波信号;An obtaining
提取模块806,用于对最终回波信号进行特征提取,得到运动目标的电磁特征。The
在本发明实施例中,计算模块800可用于执行上述方法实施例中的步骤102,构建模块802可用于执行上述方法实施例中的步骤102,获得模块804可用于执行上述方法实施例中的步骤104,提取模块806可用于执行上述方法实施例中的步骤106。In the embodiment of the present invention, the
在一些实施方式中,获得模块804用于执行:In some implementations, the obtaining
响应于利用雷达向简化等效模型发送电磁波,得到由第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由第二散射点返回的第二回波信号;obtaining a first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and a second echo signal returned by the second scattering point in response to sending electromagnetic waves to the simplified equivalent model by using the radar;
利用第一径向速度对第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;performing velocity compensation on the first echo signal by using the first radial velocity to obtain a third echo signal;
针对每个第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;For each second scattering point, using the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point, performing speed compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal;
将得到的第三回波信号和所有第四回波信号进行矢量相加,得到简化等效模型的最终回波信号。The obtained third echo signal and all the fourth echo signals are vector-added to obtain the final echo signal of the simplified equivalent model.
在一些实施方式中,电磁波为线性调频波LFM;线性调频波LFM的信号表达式为:In some embodiments, the electromagnetic wave is a linear frequency modulation wave LFM; the signal expression of the linear frequency modulation wave LFM is:
式中,TP为脉冲宽度;k为线性调频信号的斜率,B为信号带宽;fc为信号载频,为线性调频波LFM的快时间,范围是In the formula, TP is the pulse width; k is the slope of the linear frequency modulation signal, B is the signal bandwidth; fc is the signal carrier frequency, is the fast time of the chirp LFM, the range is
在一些实施方式中,由第一散射点返回的第一回波信号和由每个第二散射点返回的第二回波信号的表达式为:In some embodiments, the expression of the first echo signal returned by the first scattering point and the second echo signal returned by each second scattering point is:
式中,R为散射点到雷达的距离,V为散射点相对于雷达的径向速度,R0为散射点到雷达的初始距离,c为光速,A为散射点的幅度。In the formula, R is the distance from the scattering point to the radar, V is the radial velocity of the scattering point relative to the radar,R0 is the initial distance from the scattering point to the radar, c is the speed of light, and A is the amplitude of the scattering point.
在一些实施方式中,由每个散射点的径向速度引起的相位误差为:In some embodiments, the phase error due to the radial velocity of each scatter point is:
利用第一径向速度对第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号,包括:Using the first radial velocity to perform velocity compensation on the first echo signal to obtain the third echo signal, including:
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对第一回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第三回波信号;Use e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on the first echo signal to obtain the third echo signal;
针对每个第二散射点,利用当前第二散射点的第二径向速度,对由当前第二散射点返回的第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号,包括:For each second scattering point, use the second radial velocity of the current second scattering point to perform speed compensation on the second echo signal returned by the current second scattering point to obtain a fourth echo signal, including:
用e-j2π(-Δψ(t))对每个第二回波信号进行速度补偿,得到第四回波信号;Use e-j2π(-Δψ(t)) to perform speed compensation on each second echo signal to obtain the fourth echo signal;
第三回波信号和第四回波信号的表达式为:The expressions of the third echo signal and the fourth echo signal are:
在一些实施方式中,运动目标的电磁特征包括频谱特征和一维距离像;提取模块806用于执行:In some implementations, the electromagnetic features of the moving target include spectral features and a one-dimensional range image; the
对最终回波信号进行短时傅里叶变换,得到运动目标的频谱特征;Perform short-time Fourier transform on the final echo signal to obtain the frequency spectrum characteristics of the moving target;
对最终回波信号进行混频和去倾斜处理,得到第三回波信号;对第三回波信号进行逆傅里叶变换,得到运动目标的一维距离像。Perform frequency mixing and de-tilt processing on the final echo signal to obtain the third echo signal; perform inverse Fourier transform on the third echo signal to obtain the one-dimensional range image of the moving target.
可以理解的是,本发明实施例示意的结构并不构成对一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置的具体限定。在本发明的另一些实施例中,一种运动目标电磁特征的提取装置可以包括比图示更多或者更少的部件,或者组合某些部件,或者拆分某些部件,或者不同的部件布置。图示的部件可以以硬件、软件或者软件和硬件的组合来实现。It can be understood that the structure illustrated in the embodiment of the present invention does not constitute a specific limitation on a device for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving object. In other embodiments of the present invention, a device for extracting electromagnetic features of a moving target may include more or fewer components than shown in the figure, or combine certain components, or split certain components, or arrange different components . The illustrated components may be realized in hardware, software, or a combination of software and hardware.
上述装置内的各模块之间的信息交互、执行过程等内容,由于与本发明方法实施例基于同一构思,具体内容可参见本发明方法实施例中的叙述,此处不再赘述。The information interaction and execution process among the modules in the above-mentioned device are based on the same concept as the method embodiment of the present invention, and the specific content can refer to the description in the method embodiment of the present invention, and will not be repeated here.
本发明实施例还提供了一种电子设备,包括存储器和处理器,所述存储器中存储有计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述计算机程序时,实现本发明任一实施例中的一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法。An embodiment of the present invention also provides an electronic device, including a memory and a processor, wherein a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the processor executes the computer program, a movement in any embodiment of the present invention is realized Extraction method of target electromagnetic features.
本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质上存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序在被处理器执行时,使所述处理器执行本发明任一实施例中的一种运动目标电磁特征的提取方法。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium, the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the processor executes any implementation of the present invention. A method for extracting electromagnetic features of moving targets in the example.
具体地,可以提供配有存储介质的系统或者装置,在该存储介质上存储着实现上述实施例中任一实施例的功能的软件程序代码,且使该系统或者装置的计算机(或CPU或MPU)读出并执行存储在存储介质中的程序代码。Specifically, a system or device equipped with a storage medium may be provided, on which a software program code for realizing the functions of any of the above embodiments is stored, and the computer (or CPU or MPU of the system or device) ) to read and execute the program code stored in the storage medium.
在这种情况下,从存储介质读取的程序代码本身可实现上述实施例中任何一项实施例的功能,因此程序代码和存储程序代码的存储介质构成了本发明的一部分。In this case, the program code itself read from the storage medium can realize the function of any one of the above-mentioned embodiments, so the program code and the storage medium storing the program code constitute a part of the present invention.
用于提供程序代码的存储介质实施例包括软盘、硬盘、磁光盘、光盘(如CD-ROM、CD-R、CD-RW、DVD-ROM、DVD-RAM、DVD-RW、DVD+RW)、磁带、非易失性存储卡和ROM。可选择地,可以由通信网络从服务器计算机上下载程序代码。Examples of storage media for providing program code include floppy disks, hard disks, magneto-optical disks, optical disks (such as CD-ROM, CD-R, CD-RW, DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, DVD+RW), Tape, non-volatile memory card, and ROM. Alternatively, the program code can be downloaded from a server computer via a communication network.
此外,应该清楚的是,不仅可以通过执行计算机所读出的程序代码,而且可以通过基于程序代码的指令使计算机上操作的操作系统等来完成部分或者全部的实际操作,从而实现上述实施例中任意一项实施例的功能。In addition, it should be clear that not only by executing the program code read by the computer, but also by making the operating system on the computer complete part or all of the actual operations through instructions based on the program code, so as to realize the function of any one of the embodiments.
此外,可以理解的是,将由存储介质读出的程序代码写到插入计算机内的扩展板中所设置的存储器中或者写到与计算机相连接的扩展模块中设置的存储器中,随后基于程序代码的指令使安装在扩展板或者扩展模块上的CPU等来执行部分和全部实际操作,从而实现上述实施例中任一实施例的功能。In addition, it can be understood that the program code read from the storage medium is written into the memory provided in the expansion board inserted into the computer or written into the memory provided in the expansion module connected to the computer, and then based on the program code The instruction causes the CPU installed on the expansion board or the expansion module to perform some or all of the actual operations, thereby realizing the functions of any one of the above-mentioned embodiments.
需要说明的是,在本文中,诸如第一和第二之类的关系术语仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的情况下,由语句“包括一个…”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备中还存在另外的相同因素。It should be noted that in this article, relational terms such as first and second are only used to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, and do not necessarily require or imply that there is a relationship between these entities or operations. There is no such actual relationship or sequence. Furthermore, the term "comprises", "comprises" or any other variation thereof is intended to cover a non-exclusive inclusion such that a process, method, article, or apparatus comprising a set of elements includes not only those elements, but also includes elements not expressly listed. other elements of or also include elements inherent in such a process, method, article, or device. Without further limitations, an element defined by the phrase "comprising a" does not exclude the presence of additional same elements in the process, method, article or apparatus comprising said element.
最后应说明的是:以上实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that: the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, rather than to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: it can still be Modifications are made to the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments, or equivalent replacements are made to some of the technical features; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the various embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211004917.XACN115372926B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | A method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211004917.XACN115372926B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | A method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115372926Atrue CN115372926A (en) | 2022-11-22 |
| CN115372926B CN115372926B (en) | 2025-04-18 |
Family
ID=84068110
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211004917.XAActiveCN115372926B (en) | 2022-08-22 | 2022-08-22 | A method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic characteristics of a moving target |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115372926B (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5486833A (en)* | 1993-04-02 | 1996-01-23 | Barrett; Terence W. | Active signalling systems |
| CN110531331A (en)* | 2019-03-31 | 2019-12-03 | 西安电子科技大学 | Plasma coats target radar returns modeling and simulating method |
| CN110595724A (en)* | 2019-09-10 | 2019-12-20 | 中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所 | A magnetic fluid flow control test device |
| CN110927687A (en)* | 2019-11-09 | 2020-03-27 | 中国电波传播研究所(中国电子科技集团公司第二十二研究所) | A Meteor Detection Method Based on Incoherent Scattering Radar |
- 2022
- 2022-08-22CNCN202211004917.XApatent/CN115372926B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5486833A (en)* | 1993-04-02 | 1996-01-23 | Barrett; Terence W. | Active signalling systems |
| CN110531331A (en)* | 2019-03-31 | 2019-12-03 | 西安电子科技大学 | Plasma coats target radar returns modeling and simulating method |
| CN110595724A (en)* | 2019-09-10 | 2019-12-20 | 中国空气动力研究与发展中心超高速空气动力研究所 | A magnetic fluid flow control test device |
| CN110927687A (en)* | 2019-11-09 | 2020-03-27 | 中国电波传播研究所(中国电子科技集团公司第二十二研究所) | A Meteor Detection Method Based on Incoherent Scattering Radar |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 张群;胡健;罗迎;陈怡君;: "微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展", 雷达学报, no. 05, 8 August 2018 (2018-08-08)* |
| 郭杰;殷红成;满良: "无源散射单元电磁散射特性可控方法综述", 系统工程与电子技术, no. 004, 31 December 2019 (2019-12-31)* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115372926B (en) | 2025-04-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN109164428B (en) | Radar digital simulation system and method | |
| CN108051812A (en) | Satellite-borne SAR moving target detecting method based on two-dimension speed search | |
| CN112639523B (en) | Radar detection method and related device | |
| Orduyilmaz et al. | Machine learning-based radar waveform classification for cognitive EW | |
| CN116449326B (en) | Broadband multi-target translational parameter estimation and compensation method | |
| CN117368877A (en) | Radar image clutter suppression and target detection method based on generation countermeasure learning | |
| CN115372926A (en) | Method, device, equipment and medium for extracting electromagnetic features of moving object | |
| WO2022217407A1 (en) | Signal processing method and apparatus, and readable storage medium | |
| WO2019188509A1 (en) | Radar image processing device, radar image processing method, and storage medium | |
| CN113721204A (en) | Primary information simulation method and system for radar system | |
| CN117554913A (en) | A method for distinguishing plasma sheath radar echoes from other target radar echoes | |
| CN115291179B (en) | Squint SAR two-dimensional resolution analysis method, electronic device and storage medium | |
| Zhang et al. | Robust direction‐of‐arrival estimation based on sparse asymptotic minimum variance | |
| CN114200445B (en) | Helicopter radar pitch angle estimation method and device based on time-frequency characteristics | |
| CN105068076A (en) | Atmospheric radar image interpolation method and device based on Fourier spectrum analysis | |
| CN108594229A (en) | The compensation method of Doppler effect two dimension, device and storage medium in satellite-borne SAR arteries and veins | |
| CN114910898A (en) | Speed measuring method, device and related equipment | |
| CN114002651B (en) | Method and device for estimating radar pitching viewing angle of aircraft in real time and storage medium | |
| Ghio et al. | Inverse radon transform scaling via spin rate estimation for resident space object size assessment | |
| Wang et al. | A method for solving LiDAR waveform decomposition parameters based on a variable projection algorithm | |
| Liu et al. | Radar signal waveform recognition based on convolutional denoising autoencoder | |
| CN113960601A (en) | Method for estimating parameters of video SAR (synthetic aperture radar) simulation moving target | |
| Kim et al. | Moving target detection on an iron‐bridge using phase analysis for automotive FMCW radar | |
| CN106324577A (en) | High resolution radar detection point aggregation method based on standard deviation ellipse | |
| CN119959890B (en) | A SAR sea scene deception jamming method and system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |