CN115327834B - Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation device - Google Patents
Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115327834B CN115327834BCN202211264245.6ACN202211264245ACN115327834BCN 115327834 BCN115327834 BCN 115327834BCN 202211264245 ACN202211264245 ACN 202211264245ACN 115327834 BCN115327834 BCN 115327834B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- energy level
- rare earth
- pulse light
- absorption band
- stokes
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/35—Non-linear optics
- G02F1/353—Frequency conversion, i.e. wherein a light beam is generated with frequency components different from those of the incident light beams
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/35—Non-linear optics
- G02F1/3526—Non-linear optics using two-photon emission or absorption processes
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Optical Modulation, Optical Deflection, Nonlinear Optics, Optical Demodulation, Optical Logic Elements (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及量子信息技术领域,特别涉及固态关联光子对产生方法、固态关联光子对产生装置。The invention relates to the technical field of quantum information, in particular to a method for generating a solid-state correlated photon pair and a device for generating a solid-state correlated photon pair.
背景技术Background technique
光子在自由空间和光纤中传输时均会产生损耗,这导致光子信息的长程传输很难实现。想要实现数百公里以上的量子通信,可以采用量子中继方案。实现量子中继的一种可能方案是 Duan-Lukin-Cirac-Zoller (DLCZ) 方案,它主要包含两个核心步骤:第一,让物质系统产生具有量子关联的光子对,该光子对与物质系统具有关联;第二,通过对若干物质系统的关联光子对进行一系列线性光学操作和测量,可以实现子物质系统间的远程纠缠,从而实现量子中继。可见,产生具有量子时间关联的光子对是实现DLCZ的基础步骤。Photons will suffer losses when they are transmitted in free space and optical fibers, which makes it difficult to realize the long-distance transmission of photon information. If you want to realize quantum communication over hundreds of kilometers, you can use the quantum relay scheme. A possible scheme to realize quantum relay is the Duan-Lukin-Cirac-Zoller (DLCZ) scheme, which mainly includes two core steps: first, let the material system generate a photon pair with quantum correlation, and the photon pair is related to the material system Second, by performing a series of linear optical operations and measurements on the correlated photon pairs of several material systems, remote entanglement between sub-material systems can be achieved, thereby realizing quantum relay. It can be seen that the generation of photon pairs with quantum time correlation is the basic step to realize DLCZ.
稀土离子掺杂晶体具有很长的相干时间和很宽的吸收带宽,是有潜力用于实现长寿命时间多模DLCZ方案的一种物理系统。但是,稀土离子掺杂晶体的跃迁偶极矩强度较弱且非均匀展宽较大,导致直接应用原始的DLCZ方案难以产生高效的量子关联光子对。Rare-earth ion-doped crystals have long coherence times and wide absorption bandwidths, and are a potential physical system for realizing long-lived multimode DLCZ schemes. However, the weak transition dipole moment intensity and large non-uniform broadening of rare earth ion-doped crystals make it difficult to directly apply the original DLCZ scheme to generate efficient quantum correlated photon pairs.
近来,有研究报道,将量子存储的原子频率梳(AFC)方案与DLCZ方案相结合,提出了AFC-DLCZ方案,成功用稀土离子掺杂晶体中产生了时间多模的量子关联光子对。但对于Eu等跃迁偶极矩强度很弱的掺杂离子,AFC-DLCZ产生的量子关联光子对的效率和量子关联性仍较低,难以满足应用需求。Recently, it has been reported that the atomic frequency comb (AFC) scheme of quantum storage is combined with the DLCZ scheme, and the AFC-DLCZ scheme is proposed, which successfully generates time-multimode quantum correlated photon pairs in the crystal doped with rare earth ions. However, for dopant ions with very weak transition dipole moment strengths such as Eu, the efficiency and quantum correlation of quantum-correlated photon pairs generated by AFC-DLCZ are still low, which is difficult to meet the application requirements.
发明内容Contents of the invention
有鉴于此,本发明的实施例提出一种固态关联光子对产生方法、固态关联光子对产生装置,以期至少部分地解决上述提及的技术问题中的至少之一。In view of this, embodiments of the present invention propose a solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and a solid-state correlated photon pair generation device, in order to at least partially solve at least one of the above-mentioned technical problems.
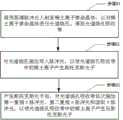
作为本发明的第一方面,提供了一种固态关联光子对产生方法,包括:As a first aspect of the present invention, a method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs is provided, including:
将预泵浦脉冲光入射至稀土离子掺杂晶体,以对稀土离子掺杂晶体进行光谱烧孔,得到光谱烧孔吸收带;稀土离子掺杂晶体中的稀土离子包括第一能级、第二能级、第三能级和第四能级;第一能级、第二能级、第三能级和第四能级为稀土离子的四个超精细能级,第一能级和第二能级的电子组态相同,第三能级和第四能级的电子组态相同,第一能级的能量和第二能级的能量均低于第三能级的能量,第一能级的能量和第二能级的能量均低于第四能级的能量,且第一能级到第三能级的跃迁波长在光学波段;The pre-pump pulse light is incident on the rare earth ion doped crystal to perform spectral hole burning on the rare earth ion doped crystal to obtain the spectral hole burning absorption band; the rare earth ion in the rare earth ion doped crystal includes the first energy level, the second Energy level, third energy level and fourth energy level; the first energy level, second energy level, third energy level and fourth energy level are the four hyperfine energy levels of rare earth ions, the first energy level and the second The electronic configuration of the energy level is the same, the electronic configuration of the third energy level and the fourth energy level are the same, the energy of the first energy level and the energy of the second energy level are lower than the energy of the third energy level, and the energy of the first energy level The energy of the energy and the energy of the second energy level are lower than the energy of the fourth energy level, and the transition wavelength from the first energy level to the third energy level is in the optical band;
对光谱烧孔吸收带施加写入脉冲光,以使光谱烧孔吸收带中的稀土离子产生斯托克斯光子,写入脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率;以及Applying writing pulse light to the spectral hole-burning absorption band, so that the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band generate Stokes photons, and the central frequency of the writing pulse light is equal to that of the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band from the first energy the resonant frequency of the transition from level to fourth energy level; and
产生斯托克斯光子后,对光谱烧孔吸收带依次施加第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光,以使光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子产生反斯托克斯光子,斯托克斯光子和反斯托克斯光子组成关联光子对,其中,第一复相π脉冲光的中心频率和第二复相π脉冲光的中心频率均等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第三能级跃迁的共振频率,读取π脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。After the Stokes photons are generated, the first complex-phase π pulse light, the second complex-phase π pulse light and the reading π pulse light are sequentially applied to the spectral hole-burning absorption band, so that the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band react Stokes photons, Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons form correlated photon pairs, wherein the center frequency of the first complex phase π pulse light and the center frequency of the second complex phase π pulse light are both equal to the spectral burning The resonant frequency of the rare earth ion transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in the hole absorption band, and the center frequency of reading the π pulse light is equal to the transition frequency of the rare earth ion in the hole burning absorption band from the second energy level to the fourth energy level Resonance frequency.
进一步地,固态关联光子对产生方法,还包括:在写入脉冲光与第一复相π脉冲光之间,在第一复相π脉冲光与第二复相π脉冲光之间,以及在第二复相π脉冲光与读取π脉冲光之间,引入射频脉冲光执行动力学解耦合,以延长反斯托克斯光子的寿命。Further, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs also includes: between the writing pulse light and the first complex-phase π pulse light, between the first complex-phase π pulse light and the second complex-phase π pulse light, and between Between the second complex-phase π pulse light and the reading π pulse light, a radio frequency pulse light is introduced to perform dynamic decoupling, so as to prolong the lifetime of the anti-Stokes photons.
进一步地,光谱烧孔吸收带包括宽度为1MHz量级的吸收线,以及位于吸收线两端的宽度为10 MHz量级的透明带,吸收线的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Further, the spectral hole-burning absorption band includes an absorption line with a width of 1 MHz, and a transparent band with a width of 10 MHz at both ends of the absorption line. The center frequency of the absorption line is equal to that of the rare earth ion of the spectral hole-burning absorption band. The resonant frequency of the transition from the first energy level to the fourth energy level.
进一步地,稀土离子掺杂晶体包括稀土离子和宿主晶体,且稀土离子掺杂晶体中的稀土离子处于宿主晶体的非中心对称位置。Further, the rare earth ion-doped crystal includes rare earth ions and a host crystal, and the rare earth ion in the rare earth ion-doped crystal is located at a noncentrosymmetric position of the host crystal.
进一步地,上述固态关联光子对产生方法,还包括:Further, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs further includes:
对稀土离子掺杂晶体施加磁场,以阻止光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第三能级到第二能级跃迁,从而降低噪声。A magnetic field is applied to the rare-earth ion-doped crystal to prevent the transition of the rare-earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band from the third energy level to the second energy level, thereby reducing noise.
进一步地,写入脉冲光与读取π脉冲光以相反方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体,第一复相π脉冲光与第二复相π脉冲光以相同方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体,并且在稀土离子掺杂晶体内,预泵浦脉冲光的传播路径、写入脉冲光的传播路径和第一复相π脉冲光的传播路径传播路径部分重合;Further, the write pulse light and the read π pulse light are collinearly injected into the rare earth ion doped crystal in opposite directions, and the first multiphase π pulse light and the second multiphase π pulse light are collinearly injected into the rare earth ion in the same direction Doping the crystal, and in the rare earth ion doped crystal, the propagation path of the pre-pump pulse light, the propagation path of the writing pulse light and the propagation path of the first complex phase π pulse light partially overlap;
斯托克斯光子的探测方向与反斯托克斯光子的探测方向反向共线。The detection direction of the Stokes photons is anti-collinear to the detection direction of the anti-Stokes photons.
进一步地,斯托克斯光子和反斯托克斯光子组成关联光子对,包括:斯托克斯光子与反斯托克斯光子的交叉二阶关联度的平方大于斯托克斯光子与反斯托克斯光子的自二阶关联度的乘积。Furthermore, the Stokes photon and the anti-Stokes photon form a correlated photon pair, including: the square of the second-order correlation degree of the Stokes photon and the anti-Stokes photon is greater The product of the self-second-order correlations of the Stokes photons.
进一步地,写入脉冲光的带宽小于或者等于吸收线的宽度。Further, the bandwidth of the writing pulse light is smaller than or equal to the width of the absorption line.
进一步地,在得到斯托克光子以及反斯托克斯光子之后,固态关联光子对产生方法还包括:Further, after Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons are obtained, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs also includes:
对斯托克光子以及反斯托克斯光子进行滤光。Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons are filtered.
作为本发明的第二个方面,还提供了一种固态关联光子对产生装置,用于实现上述的固态关联光子对产生方法,包括:As the second aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a solid-state correlated photon pair generation device, which is used to realize the above solid-state correlated photon pair generation method, including:
激光单元,适用于产生预泵浦脉冲光、写入脉冲光、第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光;A laser unit adapted to generate pre-pump pulse light, write pulse light, first complex phase π pulse light, second complex phase π pulse light and read π pulse light;
光子对产生单元,包括稀土离子掺杂晶体,稀土离子掺杂晶体适用于在预泵浦脉冲光的作用下进行光谱烧孔,得到光谱烧孔吸收带,光谱烧孔吸收带中的稀土离子在写入脉冲光的作用下产生斯托克斯光子,光谱烧孔吸收带中的稀土离子在第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光的作用下产生反斯托克斯光子;The photon pair generation unit includes rare earth ion doped crystals, which are suitable for spectral hole burning under the action of pre-pump pulse light to obtain spectral hole burning absorption bands. The rare earth ions in the spectral hole burning absorption bands are in the The Stokes photons are generated under the action of the write pulse light, and the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band react under the action of the first multiphase π pulse light, the second multiphase π pulse light and the read π pulse light. Stokes Photon;
其中,写入脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率;第一复相π脉冲光的中心频率和第二复相π脉冲光的中心频率均等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第三能级跃迁的共振频率,读取π脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Among them, the center frequency of the writing pulse light is equal to the resonant frequency of the transition of the rare earth ion from the first energy level to the fourth energy level in the spectral hole-burning absorption band; the center frequency of the first complex-phase π pulse light and the second complex-phase π-pulse The center frequency of the light is equal to the resonant frequency of the rare earth ion transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in the spectral hole-burning absorption band, and the center frequency of the reading π pulse light is equal to the transition from the second energy level of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band The resonant frequency of the transition to the fourth energy level.
晶体中的稀土离子的跃迁存在非均匀展宽,使得稀土离子在发射斯托克斯光子后,其微观电偶极矩的相位以不同速率演化。在对稀土离子依次施加第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光后,在某一时刻(该时刻由斯托克斯光子的出射时刻和第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光的施加时刻共同决定)各稀土离子的相位又演化到同相,从而形成了一个宏观的电偶极矩,该宏观电偶极矩的偶极辐射即反斯托克斯光子。因此,本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生方法能够使稀土离子产生高效的量子关联光子对,且产生的关联光子对的关联性较高。The transition of rare earth ions in the crystal has non-uniform broadening, which makes the phase of the microscopic electric dipole moments of rare earth ions evolve at different rates after Stokes photons are emitted. After sequentially applying the first complex-phase π pulse light, the second complex-phase π pulse light and the reading π pulse light to the rare earth ions, at a certain moment (this moment is determined by the exit moment of the Stokes photon and the first complex-phase π pulse light, the second complex-phase π pulse light and the application time of reading π pulse light are jointly determined) the phase of each rare earth ion evolves to the same phase, thus forming a macroscopic electric dipole moment, the macroscopic electric dipole moment The dipole radiation of is the anti-Stokes photon. Therefore, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs provided by the embodiments of the present invention can enable rare earth ions to generate highly efficient quantum correlated photon pairs, and the generated correlated photon pairs have high correlation.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1示出了根据本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生方法的流程图;Fig. 1 shows a flowchart of a method for generating a solid-state correlated photon pair according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2示出了根据本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生装置的方框图;Fig. 2 shows a block diagram of a solid-state correlated photon pair generation device provided according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3示出了根据本发明另一实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生装置的方框图;Fig. 3 shows a block diagram of a solid-state correlated photon pair generation device provided according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图4示出了根据本发明另一实施例提供的稀土离子掺杂晶体的能级结构示意图;Figure 4 shows a schematic diagram of the energy level structure of a rare earth ion doped crystal according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图5示出了根据本发明实施例提供的各脉冲光的时间序列示意图。Fig. 5 shows a schematic diagram of time series of pulsed lights provided according to an embodiment of the present invention.
附图标记说明Explanation of reference signs
1-激光单元;1 - laser unit;
10-激光器;11-第一声光调制器;12-第二声光调制器;13-第三声光调制器;10-laser; 11-first acousto-optic modulator; 12-second acousto-optic modulator; 13-third acousto-optic modulator;
2-光子对产生单元;2-photon pair generation unit;
3-滤波单元;3-filtering unit;
311-第一单模光纤;312-第二单模光纤;321-第一滤波片;311-the first single-mode fiber; 312-the second single-mode fiber; 321-the first filter;
322-第二滤波片;331-第一声光调制器开关;332-第二声光调制器开关;341-第一滤波晶体;342-第二滤波晶体。322 - the second filter; 331 - the first AOM switch; 332 - the second AOM switch; 341 - the first filter crystal; 342 - the second filter crystal.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚明白,以下结合具体实施例,并参照附图,对本发明作进一步的详细说明。In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
图1示出了根据本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生方法的流程图。Fig. 1 shows a flowchart of a method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图1所示,上述固态关联光子对产生方法包括步骤S1-步骤S3。As shown in FIG. 1 , the above-mentioned method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs includes step S1-step S3.
步骤S1:将预泵浦脉冲光入射至稀土离子掺杂晶体,以对稀土离子掺杂晶体进行光谱烧孔,得到光谱烧孔吸收带;稀土离子掺杂晶体中的稀土离子包括第一能级、第二能级、第三能级和第四能级;第一能级、第二能级、第三能级和第四能级为稀土离子的四个超精细能级,第一能级和第二能级的电子组态相同,第三能级和第四能级的电子组态相同,第一能级的能量和第二能级的能量均低于第三能级的能量,第一能级的能量和第二能级的能量均低于第四能级的能量,且第一能级到第三能级的跃迁波长在光学波段。Step S1: injecting the pre-pump pulse light into the rare earth ion doped crystal to perform spectral hole burning on the rare earth ion doped crystal to obtain the spectral hole burning absorption band; the rare earth ion in the rare earth ion doped crystal includes the first energy level , the second energy level, the third energy level and the fourth energy level; the first energy level, the second energy level, the third energy level and the fourth energy level are four hyperfine energy levels of rare earth ions, and the first energy level The electronic configuration of the second energy level is the same, the electronic configuration of the third energy level and the fourth energy level are the same, the energy of the first energy level and the energy of the second energy level are lower than the energy of the third energy level, the energy of the third energy level Both the energy of the first energy level and the energy of the second energy level are lower than the energy of the fourth energy level, and the transition wavelength from the first energy level to the third energy level is in the optical band.
步骤S2:对光谱烧孔吸收带施加写入脉冲光,以使光谱烧孔吸收带中的稀土离子产生斯托克斯光子,写入脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Step S2: Apply writing pulse light to the spectral hole-burning absorption band, so that the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band generate Stokes photons, and the center frequency of the writing pulse light is equal to that of the rare earth ions in the spectral hole-burning absorption band from The resonant frequency of the transition from the first energy level to the fourth energy level.
步骤S3:产生斯托克斯光子后,对光谱烧孔依次施加第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光,以使光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子产生反斯托克斯光子,斯托克斯光子和反斯托克斯光子组成关联光子对,其中,第一复相π脉冲光的中心频率和第二复相π脉冲光的中心频率均等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第三能级跃迁的共振频率,读取π脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Step S3: After Stokes photons are generated, the first complex-phase π pulse light, the second complex-phase π pulse light and the reading π pulse light are sequentially applied to the spectral hole burning, so that the rare earth ions in the spectral hole burning absorption band are generated Anti-Stokes photons, Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons form correlated photon pairs, where the center frequency of the first complex-phase π-pulse light and the center frequency of the second complex-phase π-pulse light are both equal to the spectral The resonant frequency of the rare earth ion transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in the hole-burning absorption band, and the center frequency of reading the π pulse light is equal to the transition from the second energy level to the fourth energy level of the rare earth ion in the hole-burning absorption band the resonant frequency.
根据本发明的实施例,稀土离子掺杂晶体中的稀土离子的跃迁存在非均匀展宽,使得光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子在发射斯托克斯光子后,其微观电偶极矩的相位以不同速率演化。在对光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子依次施加第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光和读取π脉冲光(其中,第一复相π脉冲光的中心频率和第二复相π脉冲光的中心频率均等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第三能级跃迁的共振频率,读取π脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率)后,在某一时刻光谱烧孔吸收带的各稀土离子的相位又演化到同相,从而形成了一个宏观的电偶极矩,该宏观电偶极矩的偶极辐射即反斯托克斯光子。因此,本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生方法能够使稀土离子产生高效的量子关联光子对,且产生的关联光子对的关联性较高。According to an embodiment of the present invention, there is non-uniform broadening of the transition of rare earth ions in the rare earth ion doped crystal, so that after the rare earth ions in the spectral hole burning absorption band emit Stokes photons, the phase of their microscopic electric dipole moment is Evolution at different rates. Apply the first complex phase π pulse light, the second complex phase π pulse light and the reading π pulse light sequentially to the rare earth ions in the spectral hole burning absorption band (wherein, the center frequency of the first complex phase π pulse light and the second complex phase π pulse light The center frequency of the phase π pulse light is equal to the resonant frequency of the rare earth ion transition from the first energy level to the third energy level in the spectral hole-burning absorption band, and the center frequency of the read π pulse light is equal to that of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band. After the resonant frequency of the transition from the second energy level to the fourth energy level), the phase of each rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band evolves to the same phase at a certain moment, thus forming a macroscopic electric dipole moment, the macroscopic electric dipole moment The dipole radiation of the dipole moment is the anti-Stokes photon. Therefore, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs provided by the embodiments of the present invention can enable rare earth ions to generate highly efficient quantum correlated photon pairs, and the generated correlated photon pairs have high correlation.
根据本发明的实施例,写入脉冲光的光学脉冲面积小于0.2,以抑制噪声。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the optical pulse area of the write pulse light is smaller than 0.2 to suppress noise.
根据本发明的实施例,斯托克斯光子和反斯托克斯光子组成关联光子对,包括:斯托克斯光子与反斯托克斯光子的交叉二阶关联度的平方大于斯托克斯光子与反斯托克斯光子的自二阶关联度的乘积。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the Stokes photon and the anti-Stokes photon form an associated photon pair, including: the square of the cross second-order correlation degree of the Stokes photon and the anti-Stokes photon is greater than the Stokes The product of the self-second-order correlation of the Stokes photon and the anti-Stokes photon.
根据本发明的实施例,上述固态关联光子对产生方法,还包括:According to an embodiment of the present invention, the above solid-state associated photon pair generation method further includes:
在写入脉冲光与第一复相π脉冲光之间,在第一复相π脉冲光与第二复相π脉冲光之间,以及在第二复相π脉冲光与读取π脉冲光之间,引入射频脉冲光执行动力学解耦合,以延长反斯托克斯光子的寿命。between the write pulse light and the first complex-phase π pulse light, between the first complex-phase π pulse light and the second complex-phase π pulse light, and between the second complex-phase π pulse light and the read π pulse light In between, RF pulsed light is introduced to perform dynamic decoupling to prolong the lifetime of anti-Stokes photons.
根据本发明的实施例,在得到斯托克光子以及反斯托克斯光子之后,固态关联光子对产生方法还包括:According to an embodiment of the present invention, after Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons are obtained, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs further includes:
对斯托克光子以及反斯托克斯光子进行滤光。Stokes photons and anti-Stokes photons are filtered.
根据本发明的实施例,光谱烧孔吸收带包括宽度为1 MHz量级的吸收线,以及位于吸收线两端的宽度为10 MHz量级的透明带,吸收线的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。吸收线内的稀土离子将在后续的脉冲光(第一复相π脉冲光、第二复相π脉冲光、以及读取π脉冲光)的作用下产生关联光子对,透明带将吸收线内的稀土离子与吸收带外稀土离子掺杂晶体中的其他离子隔离开来,使得后续的脉冲光只作用于吸收线中的稀土离子,避免吸收带外的稀土离子的发光,从而降低噪声。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the spectral hole-burning absorption band includes an absorption line with a width on the order of 1 MHz, and transparent bands with a width on the order of 10 MHz located at both ends of the absorption line, and the central frequency of the absorption line is equal to the spectral hole-burning absorption band The resonance frequency of the rare earth ion transition from the first energy level to the fourth energy level. The rare earth ions in the absorption line will generate correlated photon pairs under the action of subsequent pulsed light (the first complex phase π pulse light, the second complex phase π pulse light, and the reading π pulse light), and the transparent zone will absorb The rare earth ions in the absorption band are isolated from other ions in the rare earth ion doped crystal outside the absorption band, so that the subsequent pulse light only acts on the rare earth ions in the absorption line, avoiding the luminescence of the rare earth ions outside the absorption band, thereby reducing noise.
根据本发明的实施例,写入脉冲光与读取π脉冲光以相反方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体,第一复相π脉冲光与第二复相π脉冲光以相同方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体,并且在稀土离子掺杂晶体内,预泵浦脉冲光的传播路径、写入脉冲光的传播路径和第一复相π脉冲光的传播路径部分重合,以满足反斯托克斯光子出射所需的空间相位匹配条件使得反斯托克斯光子可以有效出射,并排除非预期的辐射,减少噪声。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the writing pulse light and the reading π pulse light are collinearly injected into the rare earth ion doped crystal in opposite directions, and the first multiphase π pulse light and the second multiphase π pulse light are collinear in the same direction into the rare earth ion-doped crystal, and in the rare earth ion-doped crystal, the propagation path of the pre-pump pulse light, the propagation path of the writing pulse light and the propagation path of the first complex phase π pulse light are partially overlapped to meet the reflection The spatial phase matching condition required for the emission of Stokes photons enables the effective emission of anti-Stokes photons, and excludes unintended radiation and reduces noise.
斯托克斯光子的探测方向与反斯托克斯光子的探测方向反向共线。The detection direction of the Stokes photons is anti-collinear to the detection direction of the anti-Stokes photons.
根据本发明的实施例在对光谱烧孔吸收带施加写入脉冲光之前,固态关联光子对产生方法还包括:According to an embodiment of the present invention, before applying the writing pulse light to the spectral hole-burning absorption band, the method for generating solid-state correlated photon pairs further includes:
对稀土离子掺杂晶体施加磁场,以阻止光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第三能级到第二能级跃迁,以减少噪声的产生。A magnetic field is applied to the rare-earth ion-doped crystal to prevent the transition of the rare-earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band from the third energy level to the second energy level, so as to reduce the generation of noise.
根据本发明的实施例,稀土离子掺杂晶体包括稀土离子和宿主晶体,且稀土离子掺杂晶体中的稀土离子处于宿主晶体的非中心对称位置。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the rare earth ion-doped crystal includes rare earth ions and a host crystal, and the rare earth ion in the rare earth ion-doped crystal is located at a noncentrosymmetric position of the host crystal.
根据本发明的实施例,稀土离子可以选自Pr,Eu,Yb,或Er,宿主晶体可以选自YSO晶体或YVO晶体。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the rare earth ions may be selected from Pr, Eu, Yb, or Er, and the host crystal may be selected from YSO crystal or YVO crystal.
根据本发明的实施例,写入脉冲光的带宽小于或者等于吸收线的宽度,以使吸收线中的稀土离子可以有效地吸收写入脉冲光。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the bandwidth of the writing pulse light is smaller than or equal to the width of the absorption line, so that the rare earth ions in the absorption line can effectively absorb the writing pulse light.
图2示出了根据本发明实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生装置的方框图。Fig. 2 shows a block diagram of a solid-state correlated photon pair generation device provided according to an embodiment of the present invention.
图3示出了根据本发明另一实施例提供的固态关联光子对产生装置的方框图。如图2-图3所示,该固态关联光子对产生装置包括:激光单元1、光子对产生单元2。Fig. 3 shows a block diagram of a solid-state correlated photon pair generating device according to another embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIGS. 2-3 , the solid-state associated photon pair generating device includes: a
激光单元1适用于产生泵浦光L0,该泵浦光包括预泵浦脉冲光L110、写入脉冲光L101、第一复相π脉冲光L111、第二复相π脉冲光L112和读取π脉冲光L113。The
光子对产生单元2包括稀土离子掺杂晶体,稀土离子掺杂晶体适用于在预泵浦脉冲光L110的作用下进行光谱烧孔,得到光谱烧孔吸收带,光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子在写入脉冲光L101的作用下产生斯托克斯光子L31,光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子在第一复相π脉冲光L111、第二复相π脉冲光L112和读取π脉冲光L113的作用下产生反斯托克斯光子L32。光谱烧孔吸收带可以包括一个1 MHz宽度的吸收线;在吸收线两侧是总宽度为10 MHz的透明带,使吸收线孤立于其他吸收带,吸收线的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级和第四能级跃迁的共振频率。The photon
其中,斯托克斯光子L31和反斯托克斯光子L32组成关联光子对L3。写入脉冲光L101的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率;第一复相π脉冲光L111的中心频率和第二复相π脉冲光L112的中心频率均等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第一能级到第三能级跃迁的共振频率,读取π脉冲光L113中心的频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Wherein, the Stokes photon L31 and the anti-Stokes photon L32 form a correlated photon pair L3. The center frequency of the writing pulse light L101 is equal to the resonant frequency of the transition from the first energy level to the fourth energy level of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band; the center frequency of the first complex-phase π pulse light L111 and the second complex-phase π-pulse The center frequency of the light L112 is equal to the resonant frequency of the transition from the first energy level to the third energy level of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band, and the frequency of the center of the reading π pulse light L113 is equal to the transition from the second energy level of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band The resonant frequency of the transition from the second energy level to the fourth energy level.
根据本发明的实施例,固态关联光子对产生装置还包括滤波单元3,适用于在泵浦光L0的作用下,对关联光子对L3进行滤波。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the solid-state associated photon pair generating device further includes a
如图3所示,激光单元1包括:激光器10、第一声光调制器11、第二声光调制器12、第三声光调制器13。As shown in FIG. 3 , the
激光器10为580nm的激光器,用于产生线宽100kHz以下的预泵浦激光L0。The
第一声光调制器11可以为中心频率为200MHz的声光调制器,适用于调制泵浦光产生写入脉冲光,并将写入脉冲光输出给光子对产生单元2。The first acousto-
第二声光调制器12为200MHz中心频率的声光调制器,用于调制激光L0产生强泵浦脉冲光L11,(强泵浦脉冲光L11包括预泵浦脉冲光L110,第一复相π脉冲光L111、第二复相π脉冲光L112和读取π脉冲光L113)并将强泵浦脉冲光L11输出给光子对产生单元2;其中,预泵浦脉冲光L110用于对光子对产生单元2进行光谱烧孔,制备光谱烧孔吸收带A1,以吸收写入脉冲光L101。The second acousto-
第三声光调制器13为中心频率为200MHz的声光调制器,其在目标频率附近以1MHz的步长进行扫频,用于调制激光L0产生滤波单元3所需的泵浦光L2,并输出给滤波单元3,以使滤波单元3可对关联光子对L3进行滤波。The third acousto-
写入脉冲光L101是谱宽为2MHz、功率在10uW量级的弱光,用于使光子对产生单元2受激产生斯托克斯光子L31,在本实施例中,探测到斯托克斯光子L31的概率设置为0.2%。The writing pulse light L101 is a weak light with a spectral width of 2MHz and a power of 10uW, which is used to stimulate the photon
关联光子对L3的关联性体现在,斯托克斯光子L31与反斯托克斯光子L32的交叉二阶关联度的平方大于斯托克斯光子L31与反斯托克斯光子L32的自二阶关联度的乘积。The correlation of the correlated photon to L3 is reflected in that the square of the second-order correlation degree of the Stokes photon L31 and the anti-Stokes photon L32 is greater than the self-two of the Stokes photon L31 and the anti-Stokes photon L32 The product of order correlation.
光子对产生单元2,为浓度0.01%的151Eu3+掺杂的YSO晶体。The photon
图4示出了根据本发明另一实施例提供的稀土离子掺杂晶体的能级结构示意图。Fig. 4 shows a schematic diagram of the energy level structure of a rare earth ion doped crystal according to another embodiment of the present invention.
如图4所示为151Eu3+:YSO晶体中的151Eu3+离子在强磁场下的部分能级结构,由低到高至少包括第一能级(7F0,3/2超精细能级)、第二能级(7F0,1/2超精细能级)、第三能级(7D0,3/2超精细能级)、第四能级(7D0,5/2超精细能级)。写入脉冲光L101的频率等于151Eu3+离子从第一能级和第四能级跃迁的共振频率;第一复相π脉冲光L111与第二复相π脉冲光L112的中心频率等于151Eu3+离子从第一能级和第三能级跃迁的共振频率;读取π脉冲光L113的中心频率等于151Eu3+离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率;斯托克斯光子L31的中心频率等于151Eu3+离子从第二能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率;反斯托克斯光子L32的中心频率等于151Eu3+离子从第一能级到第四能级跃迁的共振频率。Figure 4 shows the partial energy level structure of151 Eu3+ :151 Eu3+ ions in YSO crystal under strong magnetic field, including at least the first energy level (7 F0 , 3/2 hyperfine energy level), second energy level (7 F0 , 1/2 hyperfine energy level), third energy level (7 D0 , 3/2 hyperfine energy level), fourth energy level (7 D0 , 5 /2 hyperfine level). The frequency of writing pulse light L101 is equal to the resonant frequency of151 Eu3+ ion transition from the first energy level and the fourth energy level; the center frequency of the first complex phase π pulse light L111 and the second complex phase π pulse light L112 is equal to151 The resonance frequency of the Eu3+ ion transition from the first energy level to the third energy level; the center frequency of reading π pulse light L113 is equal to the resonance frequency of the151 Eu3+ ion transition from the second energy level to the fourth energy level; The center frequency of the Stokes photon L31 is equal to the resonant frequency of the151 Eu3+ ion transition from the second energy level to the fourth energy level; the center frequency of the anti-Stokes photon L32 is equal tothe 151 Eu3+ ion transition from the first energy level The resonant frequency of the transition to the fourth energy level.
对稀土离子掺杂晶体施加适当的强磁场,以阻止光谱烧孔吸收带的稀土离子从第三能级到第二能级跃迁。An appropriate strong magnetic field is applied to the rare earth ion-doped crystal to prevent the transition of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band from the third energy level to the second energy level.
继续参考图3,滤波单元3包括:第一单模光纤311及第二单模光纤312、第一滤波片321及第二滤波片322、第一声光调制器开关331及第二声光调制器开关332、第一滤波晶体341及第二滤波晶体342;其中,第一单模光纤311及第二单模光纤312可以选取600nm的单模光纤,适用于接收由光子对产生单元2输出的关联光子对,并滤除关联光子对L3的噪声。Continuing to refer to FIG. 3 , the
第一单模光纤311及第二单模光纤312为600nm的单模光纤,用于接收由光子对产生单元2输出的关联光子对L3,并滤除与关联光子对L3具有不同空间模式的噪声。具体而言,第一单模光纤311适用于滤除与反斯托克斯光子L32具有不同空间模式的噪声,第二单模光纤312适用于滤除与斯托克斯光子L31具有不同空间模式的噪声。The first single-mode
第一滤波片321及第二滤波片322为1nm带宽、透过率大于99%的干涉滤波片,用于滤除波长与关联光子对的波长相差1nm及以上的噪声。具体而言,第一滤波片321适用于滤除波长与反斯托克斯光子L32相差1nm及以上的噪声;第二滤波片322适用于滤除波长与反斯托克斯光子L31相差1nm及以上的噪声。The
第一声光调制器开关331及第二声光调制器开关332为开关速度为15ns,消光比大于10000:1的高速调制晶体,用于滤除时间模式在关联光子对L31和L32各自探测时间窗口之外的噪声。具体而言,第一声光调制器开关331用于滤除时间模式在反斯托克斯光子L32探测时间窗口之外的噪声,第二声光调制器开关332用于滤除时间模式在斯托克斯光子L31探测时间窗口之外的噪声。The first acousto-
第一滤波晶体341及第二滤波晶体342为浓度0.1%,厚度30mm的151Eu3+掺杂的YSO晶体,用于在激光单元1产生的泵浦光L2的光谱烧孔的作用下,在关联光子对L31和L32各自频率附近产生一个1MHz线宽的透明窗口,窗口背景吸收深度大于6,可滤除频率与L31及L32相差频率值1MHz及以上的噪声。具体而言,第一滤波晶体341在反斯托克斯光子L32的频率附近产生一个1MHz线宽的透明窗口。第一滤波晶体341产生的透明窗口的背景吸收深度大于6,用于滤除频率与反斯托克斯光子L32相差频率1MHz及以上的噪声。第二滤波晶体342在斯托克斯光子L31的频率附近产生一个1MHz线宽的透明窗口。第二滤波晶体342产生的透明窗口的背景吸收深度大于6,用于滤除频率与斯托克斯光子L31频率相差1MHz及以上的噪声。The
根据本发明的实施例,光子对产生单元2、第一滤波晶体341及第二滤波晶体342均放置在低温腔中工作,低温腔内的工作温度为3.0K。According to the embodiment of the present invention, the photon
参见图2和图3,为满足相位匹配,泵浦光路和信号光路具有一定的空间配置:Referring to Figure 2 and Figure 3, in order to meet the phase matching, the pump optical path and the signal optical path have a certain spatial configuration:
泵浦光路P1包括写入脉冲光L101、预泵浦脉冲光L110、第一复相π脉冲光L111、第二复相π脉冲光L112和读取π脉冲光L113的光路。The pump optical path P1 includes an optical path of write pulse light L101, pre-pump pulse light L110, first complex phase π pulse light L111, second complex phase π pulse light L112 and read π pulse light L113.
写入脉冲光L101与读取脉冲光L113以相反方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体,预泵浦脉冲光L110、读取π脉冲光L113、第一复相π脉冲光L111与第二复相π脉冲光L112以相同方向共线射入稀土离子掺杂晶体。The write pulse light L101 and the read pulse light L113 are collinearly injected into the rare earth ion doped crystal in opposite directions, the pre-pump pulse light L110, the read π pulse light L113, the first complex phase π pulse light L111 and the second complex phase Phase π pulsed light L112 is collinearly injected into the rare earth ion doped crystal in the same direction.
信号光路P3包括关联光子对L3的光路。关联光子对L3中的斯托克斯光子L31的出射方向与反斯托克斯光子L32的出射方向反向共线,且斯托克斯光子L31的出射方向与写入脉冲光L101的在稀土离子掺杂晶体内的传播路径反向不共线,泵浦光路P1与信号光路P3在稀土离子掺杂晶体内的传播路径的夹角为3°。The signal light path P3 includes the light path of the associated photon pair L3. The outgoing direction of the Stokes photon L31 in the correlated photon pair L3 is anti-collinear to the outgoing direction of the anti-Stokes photon L32, and the outgoing direction of the Stokes photon L31 is in line with the writing pulse light L101 in the rare earth The propagation path in the ion-doped crystal is not collinear in reverse, and the included angle between the propagation paths of the pumping optical path P1 and the signal optical path P3 in the rare earth ion-doped crystal is 3°.
图5示出了根据本发明实施例提供的各脉冲光的时间序列示意图。Fig. 5 shows a schematic diagram of time series of pulsed lights provided according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图5所示,在射入预泵浦脉冲光L110,完成光谱烧孔的吸收带制备之后,依次射入写入脉冲光L101、第一复相π脉冲光L111、第二复相π脉冲光L112和读取π脉冲光L113,以实现具有量子关联的关联光子对L31及L32的产生。在写入脉冲光L101与第一复相π脉冲光L111之间,以及第二复相π脉冲光L112与读取π脉冲光L113之间,插入与基态自旋跃迁共振的射频脉冲光执行动力学解耦D1及D2,延长反斯托克斯光子L32的存储时间。射频脉冲光的中心频率等于光谱烧孔吸收带的的稀土离子的第一能级到第二能级跃迁的共振频率。执行动力学解耦的射频脉冲光的脉冲序列选择为XY4型脉冲,脉冲峰值功率300W,脉宽约20μs,脉冲间隔设置为250μs,总平均存储时间为2 ms。As shown in Figure 5, after the pre-pump pulse light L110 is injected to complete the preparation of the absorption band for spectral hole burning, the writing pulse light L101, the first multi-phase π pulse light L111, and the second multi-phase π pulse are sequentially injected. The light L112 and the reading π-pulse light L113 are used to realize the generation of correlated photon pairs L31 and L32 with quantum correlation. Between the write pulse light L101 and the first complex-phase π pulse light L111, and between the second complex-phase π pulse light L112 and the read π pulse light L113, insert a radio frequency pulse light that resonates with the ground state spin transition to perform power Decoupling D1 and D2 scientifically to prolong the storage time of the anti-Stokes photon L32. The center frequency of the radio frequency pulsed light is equal to the resonant frequency of the transition from the first energy level to the second energy level of the rare earth ion in the spectral hole-burning absorption band. The pulse sequence of radio frequency pulsed light for dynamic decoupling is selected as XY4 type pulse, the pulse peak power is 300W, the pulse width is about 20μs, the pulse interval is set to 250μs, and the total average storage time is 2ms.
以射入写入脉冲光L101的时刻作为时间零点,斯托克斯光子L31的探测时间窗口为T1,反斯托克斯光子L32的探测时间窗口为T2,探测时间窗口T1及T2的长度与第一复相π脉冲光L111和第二复相π脉冲光L222的时间间隔相同,选为20us。第一复相π脉冲光L111的射入时刻选择为1000us,第二复相π脉冲光L112的射入时刻选择为1020 ,读取π脉冲光L113的射入时刻选择为2000 μs。Taking the moment when the writing pulse light L101 is injected as the time zero point, the detection time window of the Stokes photon L31 is T1, the detection time window of the anti-Stokes photon L32 is T2, and the lengths of the detection time windows T1 and T2 are the same as The time interval between the first complex-phase π-pulse light L111 and the second complex-phase π-pulse light L222 is the same, which is selected as 20us. The incident time of the first complex-phase π-pulse light L111 is selected as 1000 μs, the incident time of the second complex-phase π-pulse light L112 is selected as 1020 Å, and the incident time of the readout π-pulse light L113 is selected as 2000 μs.
在上述脉冲时序下,斯托克斯光子L31的出射时刻t1与反斯托克斯光子L32的出射时刻t2满足t1+t2=2020μs。Under the above pulse timing, the emission time t1 of the Stokes photon L31 and the emission time t2 of the anti-Stokes photon L32 satisfy t1+t2=2020 μs.
以上所述的具体实施例,对本发明的目的、技术方案和有益效果进行了进一步详细说明,应理解的是,以上所述仅为本发明的具体实施例而已,并不用于限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The specific embodiments described above have further described the purpose, technical solutions and beneficial effects of the present invention in detail. It should be understood that the above descriptions are only specific embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Within the spirit and principles of the present invention, any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc., shall be included in the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211264245.6ACN115327834B (en) | 2022-10-17 | 2022-10-17 | Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211264245.6ACN115327834B (en) | 2022-10-17 | 2022-10-17 | Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115327834A CN115327834A (en) | 2022-11-11 |
| CN115327834Btrue CN115327834B (en) | 2023-03-10 |
Family
ID=83915319
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211264245.6AActiveCN115327834B (en) | 2022-10-17 | 2022-10-17 | Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115327834B (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3649408B1 (en)* | 2004-04-20 | 2005-05-18 | 独立行政法人科学技術振興機構 | Generation method of entangled photon pairs |
| CN109787082A (en)* | 2017-11-14 | 2019-05-21 | 中国科学技术大学 | Quantum sensor and application thereof based on rare earth ion doped optical crystal |
| CN111856361A (en)* | 2019-04-30 | 2020-10-30 | 中国科学技术大学 | A kind of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and method for detecting energy level structure |
| CN111864511A (en)* | 2020-08-19 | 2020-10-30 | 中国科学技术大学 | Spectrally uncorrelated photon pair source |
| EP3971638A1 (en)* | 2020-09-16 | 2022-03-23 | FRAUNHOFER-GESELLSCHAFT zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Method for generating heralded single-photons |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6350266B2 (en)* | 2014-12-22 | 2018-07-04 | 富士通株式会社 | Single photon generator and single photon generation method |
- 2022
- 2022-10-17CNCN202211264245.6Apatent/CN115327834B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3649408B1 (en)* | 2004-04-20 | 2005-05-18 | 独立行政法人科学技術振興機構 | Generation method of entangled photon pairs |
| CN109787082A (en)* | 2017-11-14 | 2019-05-21 | 中国科学技术大学 | Quantum sensor and application thereof based on rare earth ion doped optical crystal |
| CN111856361A (en)* | 2019-04-30 | 2020-10-30 | 中国科学技术大学 | A kind of nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer and method for detecting energy level structure |
| CN111864511A (en)* | 2020-08-19 | 2020-10-30 | 中国科学技术大学 | Spectrally uncorrelated photon pair source |
| EP3971638A1 (en)* | 2020-09-16 | 2022-03-23 | FRAUNHOFER-GESELLSCHAFT zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Method for generating heralded single-photons |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 《Quantum light storage in rare-earth-ion-doped solids》;华怡林,周宗权,李传锋,郭光灿;《Chinese Physics B》;20180228;第27卷(第2期);全文* |
| 《基于EuCl3·6H2O晶体的光存储》;李宗峰,刘端程,周宗权,李传锋;《物理学报》;20210831;第20卷(第16期);全文* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115327834A (en) | 2022-11-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7184206B2 (en) | Evanescent-field optical amplifiers and lasers | |
| Lauritzen et al. | Approaches for a quantum memory at telecommunication wavelengths | |
| JP5192692B2 (en) | Broadband optical pulse generator and noise-like pulse generator | |
| Yoshida et al. | Measurement of the timing jitter and pulse energy fluctuation of a PLL regeneratively mode-locked fiber laser | |
| CN113206427A (en) | High repetition frequency linear polarization femtosecond mode-locked fiber laser | |
| Booth et al. | Operation of diode laser pumped Tm/sup 3+/ZBLAN upconversion fiber laser at 482 nm | |
| Su et al. | On-demand multimode optical storage in a laser-written on-chip waveguide | |
| CN115713954A (en) | Quantum memory device and method | |
| CN115327834B (en) | Solid-state correlated photon pair generation method and solid-state correlated photon pair generation device | |
| GB2116772A (en) | Emerald laser | |
| CN119649875A (en) | Quantum storage device and quantum storage method based on optical resonant cavity | |
| CN103188019B (en) | Microwave signal source based on dual-wavelength single-frequency fiber laser | |
| CN107393587A (en) | Can the solid state quantum storage device that is multiplexed parallel of multiple degrees of freedom | |
| CN105811053B (en) | Broadband continuous tuning optical carrier microwave filtering device | |
| Sucha et al. | Generation of high-power femtosecond pulses near 1.5 mu m using a color-center laser system | |
| CN101222102B (en) | Device for generating microwave and millimeter wave of linear cavity polarization-preserving optical fiber laser | |
| Pollock et al. | Recent progress in color center lasers | |
| Zhang et al. | Switchable single/dual-wavelength Q-switched all-fiber laser utilizing thulium-doped fiber saturable absorber | |
| CN107171173A (en) | A kind of new technology that laser mode locking is carried out using intermode beat frequency | |
| Marowsky | Recent progress in the development of electrically and optically pumped dye vapor lasers | |
| Lin | Polarisation effects in fibre lasers | |
| CN203166931U (en) | Dual-wavelength single-frequency optical fiber laser-based microwave signal source | |
| CN120279964B (en) | A solid-state quantum storage device based on optical fiber microcavity | |
| CN114520012A (en) | Quantum memory device | |
| CN104009381A (en) | Yb: LYSO laser for Kerr lens mode self-locking |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |