CN115276891A - Data transmission method, device and readable storage medium - Google Patents
Data transmission method, device and readable storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115276891A CN115276891ACN202110483034.0ACN202110483034ACN115276891ACN 115276891 ACN115276891 ACN 115276891ACN 202110483034 ACN202110483034 ACN 202110483034ACN 115276891 ACN115276891 ACN 115276891A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- packet
- data packet
- header
- packets
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0056—Systems characterized by the type of code used
- H04L1/0057—Block codes
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0056—Systems characterized by the type of code used
- H04L1/0057—Block codes
- H04L1/0058—Block-coded modulation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/004—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received by using forward error control
- H04L1/0056—Systems characterized by the type of code used
- H04L1/0064—Concatenated codes
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L1/00—Arrangements for detecting or preventing errors in the information received
- H04L1/0078—Avoidance of errors by organising the transmitted data in a format specifically designed to deal with errors, e.g. location
- H04L1/0079—Formats for control data
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及通信技术领域,尤其涉及一种数据传输方法、装置及可读存储介质。The present application relates to the technical field of communication, and in particular to a data transmission method, device and readable storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
网络编码技术是一种通过对若干个大小相同的数据包进行编码获得编码数据包(简称为编码包),并通过对足够的编码数据包进行译码恢复原数据包的方法。因为编码数据包融合了若干个原数据包的信息,所以接收端可以用编码数据包来恢复原数据包。该技术是一种可以有效改善无线通信系统传输性能的方法。The network coding technology is a method of obtaining encoded data packets (referred to as encoded packets) by encoding several data packets of the same size, and recovering the original data packets by decoding enough encoded data packets. Because the coded data packet combines the information of several original data packets, the receiving end can use the coded data packet to restore the original data packet. This technology is a method that can effectively improve the transmission performance of a wireless communication system.
现有通信系统中,虽然反馈重传实现了有效的差错控制,如媒体接入控制(mediaaccess control,MAC)层的混合自动重传请求(hybrid automatic repeat request,HARQ)机制和无线链路控制(radio link control,RLC)层的自动重传请求重传机制联合保证了传输的可靠性。但是随着通信技术的演进及发展,新一代无线接入技术(new radio accesstechnology,NR/5G)对系统的可靠性、有效性等提出了更高的需求,反馈重传机制也面临着诸多问题,比如多播或者广播场景中频繁的反馈导致的开销大及性能损失问题,突发连续错误场景、双连接或者多连接拥堵场景下的性能损失严重等问题。由于网络编码技术是一种前向纠错技术,其通过对原始数据包进行编码并预先增加冗余来对抗无线传输中的丢包或性能损失等问题,可以减少反馈开销,所以网络编码为新一代无线接入技术提供了一种保证传输可靠性的不同解决思路。In the existing communication system, although the feedback retransmission realizes effective error control, such as the hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) mechanism of the media access control (media access control, MAC) layer and the radio link control ( The automatic retransmission request retransmission mechanism of the radio link control (RLC) layer jointly ensures the reliability of the transmission. However, with the evolution and development of communication technology, the new generation of wireless access technology (new radio access technology, NR/5G) puts forward higher requirements on the reliability and effectiveness of the system, and the feedback retransmission mechanism is also facing many problems. , such as high overhead and performance loss caused by frequent feedback in multicast or broadcast scenarios, serious performance loss in burst and continuous error scenarios, dual connections or multi-connection congestion scenarios, etc. Since the network coding technology is a forward error correction technology, it can reduce the feedback overhead by coding the original data packets and adding redundancy in advance to combat packet loss or performance loss in wireless transmission, so network coding is a new A generation of wireless access technology provides a different solution to ensure transmission reliability.
然而,因为网络编码技术要求原数据的大小均相同,而现有NR协议中,任何一层对应的业务数据单元(service data unit,SDU)或者协议数据单元(protocol data unit,PDU)大小都无法保证是相同的,所以现有NR协议无法支持网络编码技术。However, because the network coding technology requires the size of the original data to be the same, in the existing NR protocol, the size of the service data unit (service data unit, SDU) or protocol data unit (protocol data unit, PDU) corresponding to any layer cannot be The guarantees are the same, so existing NR protocols cannot support network coding techniques.
如何使网络编码技术在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下获得应用是当前亟待解决的问题。How to make the network coding technology not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the size of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different, is an urgent problem to be solved.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请实施例提供一种数据传输方法、装置及可读存储介质,可以使网络编码技术在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小的场景下也可以获得应用。Embodiments of the present application provide a data transmission method, device, and readable storage medium, which can enable network coding technology to be applied in scenarios that do not depend on the size of an SDU or PDU.
下面从不同的方面介绍本申请,应理解的是,下面的不同方面的实施方式和有益效果可以互相参考。The following introduces the present application from different aspects, and it should be understood that the implementation manners and beneficial effects of the following different aspects can refer to each other.
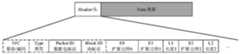
第一方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第一设备获取N个第一数据包,再传输获取到的该N个第一数据包;第一设备对获取到的该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。换句话说,每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据与数据单元的映射关系。或者说,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数,且M和N的大小关系不做限定,即M可以小于N,也可以大于N。In a first aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: a first device obtains N first data packets, and then transmits the obtained N first data packets; After encoding the first data packets and adding the encoded packet header, M second data packets are obtained, and the M second data packets are transmitted. Wherein, the sizes of the N first data packets are equal. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. In other words, the header of each first data packet includes the mapping relationship between the data of the first data packet and the data unit. In other words, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. The header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, which is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. The encoded packet header includes an encoding factor field. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both N and M are positive integers, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, that is, M may be smaller than N or larger than N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备是编码端或发送端。第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如用户设备(user equipment,UE)。Optionally, the first device is an encoding end or a sending end. The first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as user equipment (user equipment, UE).
可选的,该N个第一数据包和该M个第二数据包之间的对应关系可以是预定义的,或者,配置给第二设备(即,接收端)的。比如,可以通过将该对应关系携带在该N个第一数据包和/或该M个第二数据包来告知第二设备。具体的,该对应关系可以携带在该N个第一数据包的包头和/或该M个第二数据包的包头。Optionally, the correspondence between the N first data packets and the M second data packets may be predefined, or configured for the second device (ie, the receiving end). For example, the second device may be notified by carrying the corresponding relationship in the N first data packets and/or the M second data packets. Specifically, the corresponding relationship may be carried in headers of the N first data packets and/or headers of the M second data packets.
本申请中的预定义可以理解为定义、预先定义、存储、预存储、预协商、预配置、固化、或预烧制。Predefined in this application can be understood as defining, predefining, storing, prestoring, prenegotiating, preconfiguring, curing, or prefiring.
可见,本方案通过在获得原数据包(即上述第一数据包)后一方面直接发送原数据包来保证接收端的低延时。另一方面对原数据包进行网络编码,在网络编码后发送冗余编码包(即上述第二数据包),因为冗余编码包的编码数据可以恢复出原数据包(这是因为编码数据是由原数据包经过网络编码后得到),并且原数据包中有完整的包头信息,所以即使在传输过程中多个原数据包丢失,也可以根据冗余编码包恢复出原数据包,再根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,对原数据包的数据进行分割和级联的逆处理,从而恢复出PDU/SDU数据。因此,本方案不仅可以使网络编码技术在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小的场景下也可以获得应用,从而在现有NR协议中支持网络编码技术,还可以降低时延。此外,即使在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失和重传时延。It can be seen that this solution guarantees low delay at the receiving end by directly sending the original data packet after obtaining the original data packet (that is, the first data packet). On the other hand, the original data packet is network encoded, and the redundant encoded packet (ie, the second data packet) is sent after network encoding, because the encoded data of the redundant encoded packet can restore the original data packet (this is because the encoded data is It is obtained from the original data packet after network encoding), and the original data packet has complete header information, so even if multiple original data packets are lost during transmission, the original data packet can be recovered according to the redundant encoded packet, and then according to The segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header of the original data packet performs inverse processing of the segmentation and concatenation of the data of the original data packet, thereby recovering the PDU/SDU data. Therefore, this solution not only enables the network coding technology to be applied in scenarios that do not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, thereby supporting the network coding technology in the existing NR protocol, but also reducing the delay. In addition, PDUs or SDUs can be recovered even when multiple original data packets are lost, reducing performance loss and retransmission delay.
结合第一方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头还包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the first aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and/ Or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet.
可见,本方案通过在包头中增加指示信息来指示该包头所在的数据包是原数据包还是编码包,有利于译码端/接收端区分接收到的数据包是原数据包还是编码包,从而采用不同的方式对接收到的数据包进行解析、译码等操作,以得到PDU/SDU。It can be seen that this solution indicates whether the data packet where the packet header is located is the original data packet or the encoded packet by adding indication information in the packet header, which is beneficial to the decoding end/receiving end to distinguish whether the received data packet is the original data packet or the encoded packet, thereby Different methods are used to analyze and decode the received data packets to obtain PDU/SDU.
第二方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第二设备获取P个数据包,并对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。In a second aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the second device obtains P data packets, and decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets, the The P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets.
其中,N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括编码因子字段。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据部分对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。换句话说,每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据与数据单元的映射关系。或者说,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P、K、以及N均为正整数,P大于或等于N,K小于或等于P,K小于或等于N。Wherein, the sizes of the N first data packets are equal. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. Each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. The encoded packet header of each second data packet includes an encoding factor field. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data part of the first data packet. In other words, the header of each first data packet includes the mapping relationship between the data of the first data packet and the data unit. In other words, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. P, K, and N are all positive integers, P is greater than or equal to N, K is less than or equal to P, and K is less than or equal to N.
进一步的,第二设备再根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。Further, the second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第二设备是译码端或接收端。第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the second device is a decoding end or a receiving end. The second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
可选的,该N个第一数据包和该M个第二数据包之间的对应关系可以是预定义的,或者,从发送端获取的。比如,该对应关系可以携带在该N个第一数据包和/或该M个第二数据包中。具体的,该对应关系可以携带在该N个第一数据包的包头和/或该M个第二数据包的包头。Optionally, the correspondence between the N first data packets and the M second data packets may be predefined, or acquired from the sending end. For example, the corresponding relationship may be carried in the N first data packets and/or the M second data packets. Specifically, the corresponding relationship may be carried in headers of the N first data packets and/or headers of the M second data packets.
示例的,该对应关系携带在该M个第二数据包的包头。该对应关系通过用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息来指示。Exemplarily, the corresponding relationship is carried in headers of the M second data packets. The corresponding relationship is indicated by identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet.
本申请中的预定义可以理解为定义、预先定义、存储、预存储、预协商、预配置、固化、或预烧制。Predefined in this application can be understood as defining, predefining, storing, prestoring, prenegotiating, preconfiguring, curing, or prefiring.
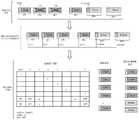
结合第二方面,在一种可能的设计中,对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,包括:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。In combination with the second aspect, in a possible design, decoding the P data packets to obtain the decoded N first data packets includes: according to the length of each data packet in the P data packets And the length threshold, determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets; adopt the parsing method of the original data packets to resolve each first data packet in the K first data packets Baotou, obtaining the serial number of the first data packet, and adopting the parsing method of the coded packet to analyze the coded packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets, and obtaining the coding factor field; according to the K first data packets The sequence number of the sequence number and the indication of the encoding factor field in the packet header of the P-K second data packets constitute a coefficient factor matrix; the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets are performed using the coefficient factor matrix Jointly decode to obtain decoded N-K first data packets. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The decoded N-K first data packets and the K first data packets belong to the N first data packets.
可选的,在该N个第一数据包和/或该M个第二数据包中携带该N个第一数据包和该M个第二数据包之间的对应关系。具体的,该对应关系可以携带在该N个第一数据包的包头和/或该M个第二数据包的包头。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该M个第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the N first data packets and/or the M second data packets carry the correspondence between the N first data packets and the M second data packets. Specifically, the corresponding relationship may be carried in headers of the N first data packets and/or headers of the M second data packets. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, headers of the M second data packets may include identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packets to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可以理解的是,由于第二数据包较第一数据包多了包头,第二数据包的长度比第一数据包长。因而,可以基于数据包的长度来确定该数据包是第一数据包还是第二数据包。It can be understood that, since the second data packet has more headers than the first data packet, the length of the second data packet is longer than that of the first data packet. Thus, it can be determined based on the length of the data packet whether the data packet is the first data packet or the second data packet.
具体的,可以通过长度阈值来确定。该长度阈值的设定可以区分出第一数据包和第二数据包即可。Specifically, it can be determined through a length threshold. The setting of the length threshold only needs to distinguish the first data packet from the second data packet.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包,包括:比较该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与该编码包长度阈值L1的大小关系;如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度等于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(编码包);如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(原数据包);从而从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. According to the length of each data packet in the P data packets and the length threshold, determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets, including: comparing each of the P data packets The size relationship between the length of a data packet and the encoded packet length threshold L1; if the length of a certain data packet in the P data packets is equal to the encoded packet length threshold L1, then it is determined that the data packet is the second data packet (encoded packet) ); If the length of a certain data packet in these P data packets is less than this encoded packet length threshold L1, then determine that this data packet is the first data packet (original data packet); thereby determine K from these P data packets first data packets and P-K second data packets.
可选的,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包,包括:比较该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与该原数据包长度阈值L2的大小关系;如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于或等于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(原数据包);如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度大于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(编码包);从而从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2. According to the length of each data packet in the P data packets and the length threshold, determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets, including: comparing each of the P data packets The size relationship between the length of the data packets and the original data packet length threshold L2; if the length of a certain data packet in the P data packets is less than or equal to the original data packet length threshold L2, then it is determined that the data packet is the first data packet Packet (original data packet); If the length of a certain data packet in these P data packets is greater than this former data packet length threshold value L2, then determine that this data packet is the second data packet (coded packet); thereby from these P data packets K first data packets and P-K second data packets are determined in the packets.
可见,本方案提供一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header carried by the original data packet Segment and concatenate information to recover PDU/SDU, which can reduce the performance loss of NR system.
结合第二方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,以上译码步骤中可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。With reference to the second aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each first data packet above further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and/ Or, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, and the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information for indicating that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet . In this way, in the above decoding step, it is possible to determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded data packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the header, and then adopt a corresponding parsing method for the header of the data packet to parse.
可见,本方案提供另一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少性能损失和重传时延。It can be seen that this solution provides another decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header of the original data packet Segmentation and concatenation information, so as to restore PDU/SDU, which can reduce performance loss and retransmission delay.
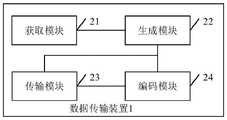
第三方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第一设备或第一设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系,该每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号;传输模块,用于传输该获取模块获取到的N个第一数据包;编码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;该传输模块,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数,且M和N的大小关系不做限定,即M可以小于N,也可以大于N。In a third aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be a first device or a chip in the first device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire N first data packets, the N first data packets are equal in size, each first data packet includes a header and data, and the header of each first data packet Including segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit, each The packet header of the first data packet also includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet; the transmission module is used to transmit the N first data packets obtained by the acquisition module; encoding A module, configured to encode the N first data packets acquired by the acquisition module and obtain M second data packets after adding the header of the encoded packet, the header of the encoded packet includes a coding factor field; the transmission module is also used to transmit The M second data packets. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both N and M are positive integers, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, that is, M may be smaller than N or larger than N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
结合第三方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the third aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and/ Or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet.
第四方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第二设备或第二设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,该每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括编码因子字段;译码模块,用于对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,该每个第一数据包的包头还包括该第一数据包的数据部分对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系;还原模块,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P和K均为正整数,K小于或等于P。P大于或等于N。In a fourth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be the second device or a chip in the second device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire P data packets, the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets, each first data packet includes a packet header and data, the The header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet, and each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, and each second The coded packet header of the data packet includes a coding factor field; the decoding module is used to decode the P data packets to obtain N first data packets after decoding, and the N first data packets are equal in size, The packet header of each first data packet also includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data part of the first data packet, and the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate that the data of the first data packet is related to the Correspondence of at least one data unit; a restore module, configured to restore the data of the N first data packets into At least one data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both P and K are positive integers, and K is less than or equal to P. P is greater than or equal to N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
结合第四方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述译码模块,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。With reference to the fourth aspect, in a possible design, the above-mentioned decoding module is specifically configured to: determine K out of the P data packets according to the length of each of the P data packets and the length threshold The first data packet and the P-K second data packets; the packet header of each first data packet in the K first data packets is parsed by using the analysis method of the original data packet, and the sequence number of the first data packet is obtained, and encoded The packet analysis method parses the encoded packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets to obtain the encoding factor field; according to the sequence numbers of the K first data packets and the encoding in the packet header of the P-K second data packets The indication of the factor field constitutes a coefficient factor matrix; the coded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets are jointly decoded by using the coefficient factor matrix to obtain N-K first data packets after decoding . Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The decoded N-K first data packets and the K first data packets belong to the N first data packets.
如何根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包,可以参考第二方面中的描述,在此不予展开。How to determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets according to the length of each data packet in the P data packets and the length threshold, you can refer to the description in the second aspect, It will not be expanded here.
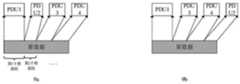
结合第四方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,译码模块可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,一个第一数据包的数据包括一个或多个数据段,一个数据段包括一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。换句话说,原数据包中的数据包括一个或多个数据段,每个数据段来自不同的PDU/SDU,一个数据段是一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。With reference to the fourth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; each The encoded packet header of the second data packet includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet. In this way, the decoding module can determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the header, and then use a corresponding analysis method to analyze the header of the data packet. In an implementation manner of any aspect above, the data of a first data packet includes one or more data segments, and one data segment includes all or part of a PDU/SDU. In other words, the data in the original data packet includes one or more data segments, each data segment comes from a different PDU/SDU, and a data segment is all or part of a PDU/SDU.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该第一数据包的数据中的最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。第一数据包的数据中数据段的排列方式可以按照PDU/SDU的序列号大小,从小到大排列,即序列号最小的PDU/SDU作为第一个数据段,中间数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号依次增加,序列号最大的PDU/SDU作为最后一个数据段。第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号也可以乱序排列。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating the data unit corresponding to the first data segment (or start data segment) and/or the last data segment (or end data segment) in the data of the first data packet Whether the information is divided, or the information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided; the data indicating that the first data packet includes Whether the i-th data segment of the first data packet is the last data segment in the data of the first data packet (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . The arrangement of the data segments in the data of the first data packet can be arranged according to the serial number of the PDU/SDU, from small to large, that is, the PDU/SDU with the smallest serial number is used as the first data segment, and the PDU/SDU corresponding to the middle data segment The serial numbers of the serial numbers increase in turn, and the PDU/SDU with the largest serial number is used as the last data segment. The serial numbers of the PDUs/SDUs corresponding to the data segments in the data of the first data packet may also be arranged in random order.
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和块标识(Block ID)字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,块标识(Block ID)字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the header of each first data packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a block identification (Block ID) field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or is used to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, and the block identification (Block ID) field is used to indicate the identification of the data block, and this data block includes the Block ID field in the first packet.
进一步的,通过在第二数据包的包头也携带该块标识,可以通过该块标识指示编码得到该第二数据包的多个第一数据包。Further, by carrying the block identifier in the packet header of the second data packet, the block identifier can be used to indicate that multiple first data packets of the second data packet are obtained by encoding.
可见,本方案通过指示每个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段指示其长度,有利于译码端根据原数据包(即上述第一数据包)的包头的指示对原数据(即上述第一数据包的数据)进行分割和级联,以恢复出一个或多个PDU/SDU。It can be seen that, by indicating whether each data segment is the last data segment, and indicating its length for each data segment, this scheme is beneficial to the decoding end for the original The data (that is, the data of the above-mentioned first data packet) is divided and concatenated to recover one or more PDUs/SDUs.
上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元的序列号,或者该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any of the above aspects, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: the first data segment (or initial data segment) and/or the last data segment (or end data segment) in the data of the first data packet segment) corresponding to the sequence number of the data unit, or the maximum sequence number and/or minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet; indicating the i-th data included in the data of the first data packet Whether the segment is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
可见,本方案通过在包头中指示起始数据段和/或末尾数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号,可以指示出多个第一数据包的数据中数据段所来自的PDU/SDU,以使译码端能够将不同的数据段恢复成PDU/SDU。It can be seen that, by indicating the sequence number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the start data segment and/or the end data segment in the packet header, this solution can indicate the PDU/SDU from which the data segment in the data of multiple first data packets comes, so as to It enables the decoding end to recover different data segments into PDU/SDU.
上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该第一个数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any of the above aspects, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment (or in other words, the data of the first data packet Whether there is a next data segment after the first data segment) and whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided); indicates that the first data Whether the i-th data segment included in the data of the packet is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and indicating the i-th Information about the length of the data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
可见,本方案通过指示第一数据包的数据中起始数据段和末尾数据段对应的数据单元是否完整,并为每个数据段都设置1bit的扩展比特字段来指示该数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段设置一个长度字段来指示其长度,有利于译码端根据原数据包的包头的指示对原数据进行分割和级联,以恢复出一个或多个PDU/SDU。It can be seen that this solution indicates whether the data units corresponding to the start data segment and the end data segment in the data of the first data packet are complete, and sets a 1-bit extended bit field for each data segment to indicate whether the data segment is the last one Data segment, and set a length field for each data segment to indicate its length, which is beneficial for the decoding end to segment and concatenate the original data according to the header of the original data packet to recover one or more PDU/SDU .
上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段的个数的信息;以及指示每个数据段的长度的信息。In an implementation manner of any of the above aspects, the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information includes: the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating the first data segment (or initial data segment) in the data of the first data packet and/or Or information about whether the data unit corresponding to the last data segment (or the last data segment) is divided, or indicates the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet information indicating whether to be divided; information indicating the number of data segments included in the data of the first packet; and information indicating the length of each data segment.
应理解,如果第一数据包的总长度可以确定,第一数据包的包头长度也可以确定,则上述分割和级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该第一数据包的总长度、该第一数据包的包头长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段总数。It should be understood that if the total length of the first data packet can be determined, and the length of the header of the first data packet can also be determined, then the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information can only include the length of each data segment in theDnum -1 data segments , instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be obtained by the total length of the first data packet, the header length of the first data packet and Dnum -1 The length of the data segment is calculated. Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first packet.
可见,本方案通过指示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数,无需针对每个数据段都指示其是否是最后一个数据段,可以节省开销。It can be seen that in this solution, by indicating the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet, it is not necessary to indicate whether each data segment is the last data segment, which can save overhead.
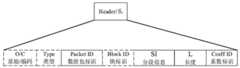
上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是块标识(Block ID)字段或包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,则用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息包括编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、和编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中的至少一项即可。编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)的长度为8bit,用于指示码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。In an implementation manner of any one of the above aspects, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet. The identification information used to indicate that the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a block identification (Block ID) field or includes at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first in the encoding window The sequence number of the first data packet, the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. It should be understood that if the window length of the encoding window is configured semi-statically, the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet includes the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window , and at least one of the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. The encoding factor field (such as the Coeff ID field) has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the row index of the codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, and the like.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和Packet ID字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a Packet ID field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the sequence number of the data packet. The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located.
可见,本方案提供的编码包包头既可以是重新设计的,其含义清晰;也可以是复用现有的编码包包头中的字段,不仅可以保证译码端的正确译码,还可以提高兼容性。It can be seen that the encoded packet header provided by this solution can be redesigned with clear meaning; it can also reuse the fields in the existing encoded packet header, which can not only ensure correct decoding at the decoding end, but also improve compatibility .
上述任一方面的一种实现方式中,第一数据包的序列号顺序递增。和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头中还包括该第二数据包的序列号。第二数据包的序列号也顺序递增。其中,因为原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头中携带有自己的序列号,编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中既可以携带自己的序列号,也可以不携带自己的序列号,所以针对序列号的实现方式有以下几种:(1)编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中不携带序列号,即编码包包头中不存在Packet ID字段,此时原数据包(即第一数据包)的序列号顺序编号。(2)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套编号系统),且编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号不重复。(3)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号分别有自己的一套编号系统,互不影响。(4)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套序列号),且允许编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号重复使用,可使用包头的指示信息来区分原数据包和编码包。In an implementation manner of any one of the above aspects, the sequence number of the first data packet is incremented sequentially. And/or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes the sequence number of the second data packet. The sequence number of the second data packet is also sequentially incremented. Wherein, because the header of the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) carries its own serial number, the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) can either carry its own serial number or not carry its own serial number. Therefore, there are several implementations for the serial number: (1) the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) does not carry the serial number, that is, there is no Packet ID field in the encoded packet header. The sequence numbers of the original data packets (that is, the first data packet) are sequentially numbered. (2) The sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of numbering system), and the sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are not repeated. (3) The sequence number of the encoded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet have their own set of numbering systems respectively, which do not affect each other. (4) The serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of serial numbers), and the serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are allowed to be reused, and the instruction information in the header can be used to Distinguish between raw data packets and encoded packets.
可见,本方案针对序列号设计不同的方案,灵活多样。It can be seen that this solution designs different solutions for the serial number, which is flexible and diverse.
第五方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第一设备获取N个第一数据包,并对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。In the fifth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method includes: the first device obtains N first data packets, encodes the N first data packets, and adds the encoded packet headers to obtain M second For a data packet, the header of the encoded packet includes an encoding factor field; the first device transmits the M second data packets. Wherein, the sizes of the N first data packets are equal. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备是编码端或发送端。第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the first device is an encoding end or a sending end. The first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
可选的,用于编码的编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,后M-N行构成的子矩阵可以包括码本中的一行或多行,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。也就是说,采用该编码系数矩阵编码得到的M个编码数据中前N个编码数据包只包含单个原数据包的信息,后M-N个编码数据融合了多个原数据包的信息。Optionally, the sub-matrix formed by the first N rows in the encoding coefficient matrix used for encoding is an identity matrix, and the sub-matrix formed by the last M-N rows may include one or more rows in the codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook , Cauchy codebook, random codebook, etc. That is to say, among the M coded data obtained by encoding with the coding coefficient matrix, the first N coded data packets only contain the information of a single original data packet, and the last M-N coded data combine the information of multiple original data packets.
可见,本方案通过不直接传输原数据包(即上述第一数据包),而是对原数据包进行编码,来保证第一设备传输的数据包的大小相等。本方案还通过在原数据包中携带包头信息,所以即使在传输过程中多个原数据包丢失,也可以根据编码包(即上述第二数据包)恢复出原数据包,再根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,对原数据包的数据进行分割和级联的逆处理,从而恢复出PDU/SDU数据。因此,本方案可以在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如现有NR协议中,支持网络编码技术,并且即使在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。It can be seen that in this solution, the size of the data packets transmitted by the first device is guaranteed to be equal by encoding the original data packets instead of directly transmitting the original data packets (that is, the above-mentioned first data packets). This solution also carries packet header information in the original data packet, so even if multiple original data packets are lost during the transmission process, the original data packet can be restored according to the encoded packet (ie, the second data packet above), and then according to the original data packet The segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header performs inverse processing of the segmentation and concatenation of the data of the original data packet, thereby recovering the PDU/SDU data. Therefore, this solution can support network coding technology in scenarios that do not depend on the size of SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different, such as in the existing NR protocol, and even in multiple original data In case of packet loss, PDU or SDU can also be recovered to reduce performance loss.
第六方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第二设备获取P个数据包,并对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该P个数据包均是编码包,每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P、N、M均为正整数,P大于或等于N且小于或等于M,即N≤P≤M。In a sixth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the second device acquires P data packets, and decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets, the The P data packets are all encoded packets, and each data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, and the encoded packet header includes an encoding factor field; wherein, the N first data packets are equal in size, and each first data packet includes header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. P, N, and M are all positive integers, and P is greater than or equal to N and less than or equal to M, that is, N≤P≤M.
进一步的,第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。Further, the second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第二设备是译码端或接收端。第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the second device is a decoding end or a receiving end. The second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
结合第六方面,在一种可能的设计中,对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,包括:采用编码包的解析方式解析该P个数据包的编码包包头获得每个编码包包头携带的编码因子字段,利用该P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P个数据包的编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。In combination with the sixth aspect, in a possible design, decoding the P data packets to obtain the decoded N first data packets includes: parsing the P data packets in a coded packet parsing manner The encoding factor field carried by each encoded packet header is obtained from the encoded packet header, and the coefficient factor matrix is formed by using the indication of the encoding factor field in the encoded packet header of the P data packets; the encoded data of the P data packets is obtained by using the coefficient factor matrix Decoding is performed to obtain N first data packets after decoding. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
可见,本方案提供一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header carried by the original data packet Segment and concatenate information to recover PDU/SDU, which can reduce the performance loss of NR system.
第七方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第一设备或第一设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等;编码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;传输模块,用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。In a seventh aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be a first device or a chip in the first device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire N first data packets, the N first data packets are equal in size; an encoding module, configured to encode the N first data packets acquired by the acquisition module M second data packets are obtained after adding a coded packet header, the coded packet header includes a coding factor field; a transmission module, configured to transmit the M second data packets. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
第八方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第二设备或第二设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取P个数据包,该P个数据包均是编码包,每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;译码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包;还原模块,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P大于或等于N,N为正整数,P为正整数。In an eighth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be the second device or a chip in the second device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire P data packets, the P data packets are coded packets, each data packet includes a coded packet header and encoded data, and the coded packet header includes a coding factor field; decoding module, used to decode the P data packets obtained by the acquisition module, and obtain N first data packets after decoding; The segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit. Wherein, the sizes of the N first data packets are equal. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. P is greater than or equal to N, N is a positive integer, and P is a positive integer.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
结合第八方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述译码模块,具体用于:采用编码包的解析方式解析该P个数据包的编码包包头获得每个编码包包头携带的编码因子字段,利用该P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P个数据包的编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。In combination with the eighth aspect, in a possible design, the above-mentioned decoding module is specifically used to: parse the headers of the encoded packets of the P data packets by means of analyzing the encoded packets to obtain the encoding factor field carried by the header of each encoded packet, Utilize the indication of the encoding factor field in the encoding factor field of the P data packets to form a coefficient factor matrix; use the coefficient factor matrix to decode the encoded data of the P data packets, and obtain N first data packets after decoding . Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,一个第一数据包的数据包括一个或多个数据段,一个数据段包括一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。换句话说,原数据包中的数据包括一个或多个数据段,每个数据段来自不同的PDU/SDU,一个数据段是一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the data of a first data packet includes one or more data segments, and one data segment includes all or part of a PDU/SDU. In other words, the data in the original data packet includes one or more data segments, each data segment comes from a different PDU/SDU, and a data segment is all or part of a PDU/SDU.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该第一数据包的数据中的最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。第一数据包的数据中数据段的排列方式可以按照PDU/SDU的序列号大小,从小到大排列,即序列号最小的PDU/SDU作为第一个数据段,中间数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号依次增加,序列号最大的PDU/SDU作为最后一个数据段。第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号也可以乱序排列。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating the data unit corresponding to the first data segment (or start data segment) and/or the last data segment (or end data segment) in the data of the first data packet Whether the information is divided, or the information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided; the data indicating that the first data packet includes Whether the i-th data segment of the first data packet is the last data segment in the data of the first data packet (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . The arrangement of the data segments in the data of the first data packet can be arranged according to the serial number of the PDU/SDU, from small to large, that is, the PDU/SDU with the smallest serial number is used as the first data segment, and the PDU/SDU corresponding to the middle data segment The serial numbers of the serial numbers increase in turn, and the PDU/SDU with the largest serial number is used as the last data segment. The serial numbers of the PDUs/SDUs corresponding to the data segments in the data of the first data packet may also be arranged in random order.
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元的序列号,或者该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the segmentation and concatenation information includes: the first data segment (or initial data segment) and/or the last data segment in the data of the first data packet The sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the segment (or the end data segment), or the maximum sequence number and/or minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet; the data indicating that the first data packet includes Whether the i-th data segment is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and indicate the length of the i-th data segment Information. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该第一个数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment (or in other words, the first data segment Whether there is a next data segment after the first data segment in the data of a data packet) and whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided); Information indicating whether the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割和级联信息包括:上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段的个数的信息;以及指示每个数据段的长度的信息。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information includes: the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating that the first data segment (or initial data segment) in the data of the first data packet data segment) and/or the information about whether the data unit corresponding to the last data segment (or the last data segment) is divided, or indicates that the sequence number in the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is the largest and/or the sequence information indicating whether the data unit with the smallest number is divided; information indicating the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet; and information indicating the length of each data segment.
应理解,如果第一数据包的总长度可以确定,第一数据包的包头长度也可以确定,则上述分割和级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该第一数据包的总长度、该第一数据包的包头长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段总数。It should be understood that if the total length of the first data packet can be determined, and the length of the header of the first data packet can also be determined, then the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information can only include the length of each data segment in theDnum -1 data segments , instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be obtained by the total length of the first data packet, the header length of the first data packet and Dnum -1 The length of the data segment is calculated. Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first packet.
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述M个第二数据包中包括N个第一类编码包和M-N个第二类编码包。其中第一类编码包的编码系数子矩阵是单位阵,第二类编码包的编码系数子矩阵是非单位阵。第一类编码包的编码系数子矩阵和第二类编码包的编码系数子矩阵形成一个编码系数矩阵。编码系数矩阵用于对该N个第一数据包进行编码。上述M个第二数据包中每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是块标识字段或包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the M second data packets include N first-type encoded packets and M-N second-type encoded packets. The coding coefficient sub-matrix of the first type of coding packet is an identity matrix, and the coding coefficient sub-matrix of the second type of coding packet is a non-identity matrix. The coding coefficient sub-matrix of the first type of coding packet and the coding coefficient sub-matrix of the second type of coding packet form a coding coefficient matrix. The encoding coefficient matrix is used to encode the N first data packets. The encoded packet header of each of the M second data packets includes identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet. The identification information used to indicate that the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a block identification field or includes at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first first data in the encoding window The sequence number of the packet, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括第二指示信息、类型(Type)字段以及PacketID字段中的一项或多项。第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may further include one or more items of second indication information, a type (Type) field, and a PacketID field. The second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the sequence number of the data packet. The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located.
上述第五至第八任一方面的一种实现方式中,第一数据包的序列号顺序递增。和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头中还包括该第二数据包的序列号。第二数据包的序列号也顺序递增。其中,因为原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头中携带有自己的序列号,编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中既可以携带自己的序列号,也可以不携带自己的序列号,所以针对序列号的实现方式有以下几种:(1)编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中不携带序列号,即编码包包头中不存在Packet ID字段,此时原数据包(即第一数据包)的序列号顺序编号。(2)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套编号系统),且编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号不重复。(3)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号分别有自己的一套编号系统,互不影响。(4)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套序列号),且允许编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号重复使用,可使用包头的指示信息来区分原数据包和编码包。In an implementation manner of any one of the fifth to eighth aspects above, the sequence number of the first data packet is incremented sequentially. And/or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes the sequence number of the second data packet. The sequence number of the second data packet is also sequentially incremented. Wherein, because the header of the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) carries its own serial number, the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) can either carry its own serial number or not carry its own serial number. Therefore, there are several implementations for the serial number: (1) the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) does not carry the serial number, that is, there is no Packet ID field in the encoded packet header. The sequence numbers of the original data packets (that is, the first data packet) are sequentially numbered. (2) The sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of numbering system), and the sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are not repeated. (3) The sequence number of the encoded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet have their own set of numbering systems respectively, which do not affect each other. (4) The serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of serial numbers), and the serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are allowed to be reused, and the instruction information in the header can be used to Distinguish between raw data packets and encoded packets.
可见,本方案针对序列号设计不同的方案,灵活多样。It can be seen that this solution designs different solutions for the serial number, which is flexible and diverse.
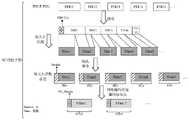
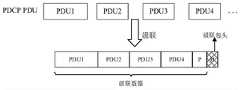
第九方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第一设备获取级联数据包,并根据该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包;第一设备传输该N个第一数据包;第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;第二设备传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数,且M和N的大小关系不做限定,j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。In a ninth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the first device acquires concatenated data packets, and generates N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets; the first device transmits the N first data packets Data packets: the first device encodes the N first data packets and adds headers of the encoded packets to obtain M second data packets; the second device transmits the M second data packets. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment except the start data segment and the end data segment among the plurality of data segments is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both N and M are positive integers, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, and the value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N].
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
可选的,第一设备是编码端或发送端。第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the first device is an encoding end or a sending end. The first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
可见,本方案对多个PDU/SDU进行级联,以获得一个级联数据,并添加级联包包头得到一个级联数据包,再对级联数据包进行等大小分割得到一定数量的原数据(第一数据包的数据),继而通过加包头获得原数据包(即上述第一数据包),并对原数据包进行编码和加编码包包头后获得编码包(即上述第二数据包),从而在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如现有NR协议中,支持网络编码技术,并且在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。此外,本方案无需对每个原数据包都添加级联的字段指示,而是通过统一的级联包包头进行级联信息的指示,可以节省包头的开销。It can be seen that this scheme concatenates multiple PDUs/SDUs to obtain a concatenated data, and adds a concatenated packet header to obtain a concatenated data packet, and then divides the concatenated data packets into equal sizes to obtain a certain amount of original data (the data of the first data packet), then obtain the original data packet (i.e. the above-mentioned first data packet) by adding the packet header, and obtain the encoded packet (i.e. the above-mentioned second data packet) after encoding the original data packet and adding the encoded packet header , so that it does not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the size of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different. For example, in the existing NR protocol, network coding technology is supported, and when multiple original data packets are lost The PDU or SDU can also be restored in the next case, reducing performance loss. In addition, this solution does not need to add a concatenated field indication to each original data packet, but uses a unified concatenated packet header to indicate the concatenated information, which can save the overhead of the packet header.
结合第九方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包还包头包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the ninth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each first data packet above further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and/ Or, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, and the encoded packet header of each second data packet also includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded Bag.
第十方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第二设备获取P个数据包,并对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和N-K个第二数据包;第二设备按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包,并根据该级联包包头包括的该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。该级联数据包包括该级联包包头和该级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。K和P均为正整数,且K小于或等于P。P大于或等于N,j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。In a tenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the second device obtains P data packets, and decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets, the The P data packets include K first data packets and N-K second data packets; the second device restores the data of the N first data packets into one The data packets are concatenated, and the concatenated data is divided into multiple data units according to the concatenation information of the multiple data units included in the concatenated data included in the header of the concatenated packet. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packets into N equal parts. The concatenated data packet includes the concatenated packet header and the concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment in the plurality of data segments other than the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both K and P are positive integers, and K is less than or equal to P. P is greater than or equal to N, and the value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N].
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
可选的,第二设备是译码端或接收端。第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the second device is a decoding end or a receiving end. The second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
结合第十方面,在一种可能的设计中,对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,包括:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。In combination with the tenth aspect, in a possible design, decoding the P data packets to obtain the decoded N first data packets includes: according to the length of each of the P data packets And the length threshold, determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets; adopt the parsing method of the original data packets to resolve each first data packet in the K first data packets Baotou, obtaining the serial number of the first data packet, and adopting the parsing method of the coded packet to analyze the coded packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets, and obtaining the coding factor field; according to the K first data packets The sequence number of the sequence number and the indication of the encoding factor field in the packet header of the P-K second data packets constitute a coefficient factor matrix; the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets are performed using the coefficient factor matrix Jointly decode to obtain decoded N-K first data packets. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The decoded N-K first data packets and the K first data packets belong to the N first data packets.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。第一设备从P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包的实现方式可参考第二方面的相应描述,此处不展开说明。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. Alternatively, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2. For an implementation manner in which the first device determines K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets, reference may be made to the corresponding description of the second aspect, and no further description is given here.
可选的,在该第一数据包和/或该第二数据包中携带该第一数据包和该第二数据包之间的对应关系。具体的,该对应关系可以携带在该第一数据包的包头和/或该第二数据包的包头。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the correspondence between the first data packet and the second data packet is carried in the first data packet and/or the second data packet. Specifically, the corresponding relationship may be carried in the header of the first data packet and/or the header of the second data packet. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, the packet header of the second data packet may include identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可见,本方案提供一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header carried by the original data packet Segment and concatenate information to recover PDU/SDU, which can reduce the performance loss of NR system.
结合第十方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,以上译码步骤中可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。With reference to the tenth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each first data packet above further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and/ Or, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, and the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate the second indication information where the second indication information is located. Data packets are encoded packets. In this way, in the above decoding step, it is possible to determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded data packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the header, and then adopt a corresponding parsing method for the header of the data packet to parse.
可见,本方案提供一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header carried by the original data packet Segment and concatenate information to recover PDU/SDU, which can reduce the performance loss of NR system.
第十一方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第一设备或第一设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取级联数据包;生成模块,用于根据该获取模块获取到的该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包;传输模块,用于传输该生成模块生成的N个第一数据包;编码模块,用于对该生成模块生成的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;该传输模块,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。In an eleventh aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, where the data transmission device may be a first device or a chip in the first device. The data transmission device includes: an acquiring module, configured to acquire concatenated data packets; a generating module, configured to generate N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets acquired by the acquiring module; a transmitting module, configured to transmit the generated The N first data packets generated by the module; the encoding module is used to encode the N first data packets generated by the generating module and add the header of the encoded packet to obtain M second data packets; the transmission module is also used for Transmit the M second data packets. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment in the plurality of data segments other than the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. Both N and M are positive integers. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N].
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
结合第十一方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the eleventh aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, each second data packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, the coded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate the second indication information where the second indication information is located. The second data packet is an encoded packet.
第十二方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第二设备或第二设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;译码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等;还原模块,用于按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包;分割模块,还用于根据该级联包包头包括的该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。该级联数据包包括该级联包包头和该级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。P和K均为正整数,K小于或等于P。P大于或等于N。In a twelfth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be a second device or a chip in the second device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire P data packets, the P data packets including K first data packets and P-K second data packets; a decoding module, configured to acquire the P data packets from the acquisition module Decode the P data packets, obtain N first data packets after decoding, the data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the packet header sizes of the N first data packets are equal; the restore module uses According to the order of the serial numbers of the N first data packets, the data of the N first data packets is restored into a concatenated data packet; The data includes concatenation information of multiple data units, and the concatenated data is divided into multiple data units. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packets into N equal parts. The concatenated data packet includes the concatenated packet header and the concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment in the plurality of data segments other than the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N]. Both P and K are positive integers, and K is less than or equal to P. P is greater than or equal to N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
结合第十二方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述译码模块,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。With reference to the twelfth aspect, in a possible design, the above-mentioned decoding module is specifically configured to: determine K from the P data packets according to the length of each of the P data packets and the length threshold. A first data packet and P-K second data packets; adopt the analysis method of the original data packet to resolve the packet header of each first data packet in the K first data packets, obtain the serial number of the first data packet, and use The encoding packet analysis method is to analyze the encoding packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets to obtain the encoding factor field; according to the serial numbers of the K first data packets and the headers of the P-K second data packets The indication of the encoding factor field forms a coefficient factor matrix; using the coefficient factor matrix to jointly decode the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets, and obtain the decoded N-K first data packets Bag. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The decoded N-K first data packets and the K first data packets belong to the N first data packets.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. Alternatively, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2.
结合第十二方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,译码模块可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。With reference to the twelfth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, each second data packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, the coded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate the second indication information where the second indication information is located. The second data packet is an encoded packet. In this way, the decoding module can determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded data packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the packet header, and then use a corresponding analysis method to analyze the packet header of the data packet .
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的数据段的个数的信息;以及指示该级联数据包括的每个数据段的长度的信息。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the concatenation information includes: indicating the start data segment (that is, the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (that is, the last data segment) of the concatenated data. A data segment) whether the data unit corresponding to the data segment is divided, or information indicating whether the data unit with the largest serial number and/or the smallest serial number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is divided; indicating that the concatenation information on the number of data segments included in the data; and information indicating the length of each data segment included in the concatenated data.
应理解,如果级联数据包的总长度可以确定(如半静态配置)、级联包包头的长度也可以确定,则上述级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该级联数据包的总长度、该级联包包头的长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Dnum表示级联数据包括的数据段总数。It should be understood that if the total length of the concatenated data packet can be determined (such as semi-static configuration), and the length of the header of the concatenated packet can also be determined, then the above concatenated information can only include each data in Dnum -1 data segments The length of the segment, instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be passed through the total length of the concatenated data packet, the length of the concatenated packet header and Dnum - The length of 1 data segment is calculated. Dnum indicates the total number of data segments included in the concatenated data.
可见,本方案提供的级联包包头设计,在级联包包头内带Dnum(即级联数据包括的数据段个数)个长度字段,来指示每个数据段的长度,可以不在每个原数据包的包头中携带Dnum个长度字段,从而节省头开销。It can be seen that the design of the concatenated packet header provided by this program has Dnum (that is, the number of data segments included in the concatenated data) length fields in the concatenated packet header to indicate the length of each data segment. The packet header of the original data packet carries Dnum length fields, thereby saving header overhead.
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段的信息;以及指示该第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该级联数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the concatenation information includes: indicating the start data segment (that is, the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (that is, the last data segment) of the concatenated data. A data segment) whether the data unit corresponding to the data segment is divided, or information indicating whether the data unit with the largest serial number and/or the smallest serial number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is divided; indicating that the concatenation Information about whether the i-th data segment included in the data is the last data segment; and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the concatenated data, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
可见,本方案提供一种可能的级联包包头设计来携带级联信息,以支持在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如现有NR协议中,应用网络编码技术。It can be seen that this solution provides a possible concatenation packet header design to carry concatenation information to support scenarios that do not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different, such as the current In the NR protocol, network coding technology is applied.
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据中起始数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该起始数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该级联数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the above concatenation information includes: indicating whether the initial data segment in the concatenated data is the last data segment (or in other words, the first data segment in the concatenated data Whether there is a next data segment after the first data segment) and whether the data unit corresponding to the initial data segment is complete (complete means that it has not been divided, and incomplete means that it is divided); indicate the i-th data included in the concatenated data Whether the first data segment is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the concatenated data); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the concatenated data, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
可见,本方案在级联包包头中为每一个数据段都指示该数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段指示其长度,有利于译码端根据级联包包头的指示对级联数据进行分割,以恢复出多个PDU/SDU。It can be seen that this scheme indicates whether the data segment is the last data segment for each data segment in the header of the concatenated packet, and indicates its length for each data segment, which is beneficial to the decoding end according to the indication of the header of the concatenated packet. The concatenated data is segmented to recover multiple PDUs/SDUs.
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联数据包括多个完整数据单元级联得到的数据以及填充比特。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple complete data units and padding bits.
可选的,上述级联包包头还包括填充信息,该填充信息包括该填充比特的长度。Optionally, the header of the concatenated packet further includes padding information, and the padding information includes the length of the padding bits.
可见,本方案的级联数据中每个数据段都是一个PDU/SDU,此时译码端获得级联数据包后,分割级联数据即可得到PDU/SDU。It can be seen that each data segment in the concatenated data in this solution is a PDU/SDU. At this time, after the decoding end obtains the concatenated data packet, the PDU/SDU can be obtained by dividing the concatenated data.
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述编码包包头还包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是块标识字段或包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the encoded packet header further includes identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet. The identification information used to indicate that the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a block identification field or includes at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first first data in the encoding window The sequence number of the packet, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window.
可见,本方案提供的编码包包头既可以是重新设计的,其含义清晰;也可以是复用原有编码包包头中的字段,并新增一个字段来指示数据包的种类(编码包还是原数据包),不仅可以保证译码端的正确译码,还可以提高兼容性。It can be seen that the encoded packet header provided by this solution can be redesigned with clear meaning; it can also reuse the fields in the original encoded packet header, and add a new field to indicate the type of data packet (encoded packet or original data packet), not only can ensure correct decoding at the decoding end, but also improve compatibility.
上述第九至第十二任一方面的一种实现方式中,第一数据包的序列号顺序递增。和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头中还包括该第二数据包的序列号。第二数据包的序列号也顺序递增。其中,因为原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头中携带有自己的序列号,编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中既可以携带自己的序列号,也可以不携带自己的序列号,所以针对序列号的实现方式有以下几种:(1)编码包(即第二数据包)的编码包包头中不携带序列号,即编码包包头中不存在Packet ID字段,此时原数据包(即第一数据包)的序列号顺序编号。(2)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套编号系统),且编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号不重复。(3)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号分别有自己的一套编号系统,互不影响。(4)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套序列号),且允许编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号重复使用,可使用包头的指示信息来区分原数据包和编码包。In an implementation manner of any one of the ninth to twelfth aspects above, the sequence number of the first data packet is incremented sequentially. And/or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes the sequence number of the second data packet. The sequence number of the second data packet is also sequentially incremented. Wherein, because the header of the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) carries its own serial number, the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) can either carry its own serial number or not carry its own serial number. Therefore, there are several implementations for the serial number: (1) the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) does not carry the serial number, that is, there is no Packet ID field in the encoded packet header. The sequence numbers of the original data packets (that is, the first data packet) are sequentially numbered. (2) The sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of numbering system), and the sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet are not repeated. (3) The sequence number of the encoded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet have their own set of numbering systems respectively, which do not affect each other. (4) The serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of serial numbers), and the serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are allowed to be reused, and the instruction information in the header can be used to Distinguish between raw data packets and encoded packets.
可见,本方案针对序列号设计不同的方案,灵活多样。It can be seen that this solution designs different solutions for the serial number, which is flexible and diverse.
第十三方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第一设备获取级联数据包,并根据该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等;第一设备再对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的序列号。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。In a thirteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the first device obtains concatenated data packets, and generates N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets, and the N first data packets The size of the data is equal, and the size of the headers of the N first data packets is equal; the first device encodes the N first data packets and adds the headers of the encoded packets to obtain M second data packets, and the headers of the encoded packets include A coding factor field; the first device transmits the M second data packets. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment except the start data segment and the end data segment among the plurality of data segments is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N]. M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
可选的,第一设备是编码端或发送端。第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the first device is an encoding end or a sending end. The first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
可选的,用于编码的编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,后M-N行构成的子矩阵可以包括码本中的一行或多行,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。也就是说,采用该编码系数矩阵编码得到的M个编码数据中前N个编码数据包只包含单个原数据包的信息,后M-N个编码数据融合了多个原数据包的信息。Optionally, the sub-matrix formed by the first N rows in the encoding coefficient matrix used for encoding is an identity matrix, and the sub-matrix formed by the last M-N rows may include one or more rows in the codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook , Cauchy codebook, random codebook, etc. That is to say, among the M coded data obtained by encoding with the coding coefficient matrix, the first N coded data packets only contain the information of a single original data packet, and the last M-N coded data combine the information of multiple original data packets.
可见,本方案通过不直接传输原数据包(即上述第一数据包),而是对原数据包进行编码,来保证第一设备传输的数据包的大小相等。本方案还通过在原数据包中携带包头信息,所以即使在传输过程中多个原数据包丢失,也可以根据编码包(即上述第二数据包)恢复出原数据包,再根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,对原数据包的数据进行分割和级联的逆处理,从而恢复出PDU/SDU数据,减少性能损失。此外,本方案无需对每个原数据包都添加级联的字段指示,而是通过统一的级联包包头进行级联信息的指示,可以节省包头的开销。It can be seen that in this solution, the size of the data packets transmitted by the first device is guaranteed to be equal by encoding the original data packets instead of directly transmitting the original data packets (that is, the above-mentioned first data packets). This solution also carries packet header information in the original data packet, so even if multiple original data packets are lost during the transmission process, the original data packet can be restored according to the encoded packet (ie, the second data packet above), and then according to the original data packet The segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header performs the inverse processing of the segmentation and concatenation of the original data packet data, thereby recovering the PDU/SDU data and reducing performance loss. In addition, this solution does not need to add a concatenated field indication to each original data packet, but uses a unified concatenated packet header to indicate the concatenated information, which can save the overhead of the packet header.
第十四方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第二设备获取P个数据包,并对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该P个数据包均是编码包,每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等;第二设备按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包,并根据该级联包包头包括的该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的序列号。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。P大于N,N和P均为正整数。In a fourteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the second device obtains P data packets, and decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets, The P data packets are all coded packets, each data packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, the coded packet header includes a coding factor field, the data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the N first data packets The headers of the packets are equal in size; the second device restores the data of the N first data packets into a concatenated data packet according to the order of the sequence numbers of the N first data packets, and according to the The concatenated data includes concatenated information of multiple data units, and the concatenated data is divided into multiple data units. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment except the start data segment and the end data segment among the plurality of data segments is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N]. P is greater than N, and both N and P are positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
可选的,第二设备是译码端或接收端。第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the second device is a decoding end or a receiving end. The second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
结合第十四方面,在一种可能的设计中,对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,包括:采用编码包的解析方式解析该P个数据包的编码包包头获得每个编码包包头携带的编码因子字段,利用该P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P个数据包的编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。In combination with the fourteenth aspect, in a possible design, decoding the P data packets to obtain the decoded N first data packets includes: parsing the P data packets by means of encoding packets The encoding factor field carried by each encoded packet header is obtained, and the coefficient factor matrix is formed by using the indication of the encoding factor field in the encoded packet header of the P data packets; the coefficient factor matrix is used to encode the P data packets The data is decoded to obtain N first data packets after decoding. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
可见,本方案提供一种译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a decoding process and operation, in order to correctly decode the original data packet when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N), and according to the packet header carried by the original data packet Segment and concatenate information to recover PDU/SDU, which can reduce the performance loss of NR system.
第十五方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第一设备或第一设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取级联数据包;生成模块,用于根据该获取模块获取到的该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包;传输模块,用于传输该生成模块生成的N个第一数据包;编码模块,用于对该生成模块生成的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段;该传输模块,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的序列号。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。In a fifteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be a first device or a chip in the first device. The data transmission device includes: an acquiring module, configured to acquire concatenated data packets; a generating module, configured to generate N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets acquired by the acquiring module; a transmitting module, configured to transmit the generated The N first data packets generated by the module; the encoding module is used to encode the N first data packets generated by the generation module and add the encoded packet header to obtain M second data packets, the encoded packet header includes the encoding factor field; the transmission module is also used to transmit the M second data packets. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment in the plurality of data segments other than the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N].
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
第十六方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第二设备或第二设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;译码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等;还原模块,用于按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包;分割模块,还用于根据该级联包包头包括的该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的序列号。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。In a sixteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be the second device or a chip in the second device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire P data packets, the P data packets including K first data packets and P-K second data packets; a decoding module, configured to acquire the P data packets from the acquisition module Decode the P data packets, obtain N first data packets after decoding, the data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the packet header sizes of the N first data packets are equal; the restore module uses According to the order of the serial numbers of the N first data packets, the data of the N first data packets are restored into a concatenated data packet; The data includes concatenation information of multiple data units, and the concatenated data is divided into multiple data units. Wherein, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments. Wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit. Each data segment in the plurality of data segments other than the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained by dividing the concatenated data packet into N equal parts. The packet header of each first data packet includes the sequence number of the first data packet. The first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N].
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。上述级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。原数据是指原数据包中的数据。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU. The size of the above-mentioned concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
结合第十六方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述译码模块,具体用于:采用编码包的解析方式解析该P个数据包的编码包包头获得每个编码包包头携带的编码因子字段,利用该P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P个数据包的编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。In combination with the sixteenth aspect, in a possible design, the above-mentioned decoding module is specifically used to: analyze the encoded packet headers of the P data packets by using the encoded packet analysis method to obtain the encoding factor field carried by the header of each encoded packet , use the indication of the coding factor field in the coding packet header of the P data packets to form a coefficient factor matrix; use the coefficient factor matrix to decode the coded data of the P data packets, and obtain the decoded N first data Bag. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的数据段的个数的信息;以及指示该级联数据包括的每个数据段的长度的信息。In an implementation manner of any of the above-mentioned thirteenth to sixteenth aspects, the above-mentioned concatenation information includes: indicating the start data segment (that is, the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (that is, the first data segment) of the concatenated data. The information on whether the data unit corresponding to the last data segment) is split, or the information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is split; information about the number of data segments included in the concatenated data; and information indicating the length of each data segment included in the concatenated data.
应理解,如果级联数据包的总长度可以确定(如半静态配置)、级联包包头的长度也可以确定,则上述级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该级联数据包的总长度、该级联包包头的长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Dnum表示级联数据包括的数据段总数。It should be understood that if the total length of the concatenated data packet can be determined (such as semi-static configuration), and the length of the header of the concatenated packet can also be determined, then the above concatenated information can only include each data in Dnum -1 data segments The length of the segment, instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be passed through the total length of the concatenated data packet, the length of the concatenated packet header and Dnum - The length of 1 data segment is calculated. Dnum indicates the total number of data segments included in the concatenated data.
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段的信息;以及指示该第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该级联数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any of the above-mentioned thirteenth to sixteenth aspects, the above-mentioned concatenation information includes: indicating the start data segment (that is, the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (that is, the first data segment) of the concatenated data. The information on whether the data unit corresponding to the last data segment) is split, or the information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is split; Information about whether the i-th data segment included in the linked data is the last data segment; and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the concatenated data, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联信息包括:指示该级联数据中起始数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该起始数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该级联数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。In an implementation manner of any one of the above-mentioned thirteenth to sixteenth aspects, the above-mentioned concatenation information includes: indicating whether the initial data segment in the concatenated data is the last data segment (or in other words, the first data segment in the concatenated data Whether there is a next data segment after a data segment) and whether the data unit corresponding to the initial data segment is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided); indicates that the concatenated data includes the first Information about whether the i data segment is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i th data segment included in the concatenated data); and information indicating the length of the i th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the concatenated data, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述级联数据包括多个完整数据单元级联得到的数据以及填充比特。In an implementation manner of any one of the thirteenth to sixteenth aspects above, the concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple complete data units and padding bits.
可选的,上述级联包包头还包括填充信息,该填充信息包括该填充比特的长度。Optionally, the header of the concatenated packet further includes padding information, and the padding information includes the length of the padding bits.
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述编码包包头还包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是块标识字段或包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。In an implementation manner of any one of the thirteenth to sixteenth aspects above, the encoded packet header further includes identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet. The identification information used to indicate that the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a block identification field or includes at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first first data in the encoding window The sequence number of the packet, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window.
上述第十三至第十六任一方面的一种实现方式中,第一数据包的序列号顺序递增。和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头中还包括该第二数据包的序列号。第二数据包的序列号也顺序递增。In an implementation manner of any one of the thirteenth to sixteenth aspects above, the sequence number of the first data packet is incremented sequentially. And/or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes the sequence number of the second data packet. The sequence number of the second data packet is also sequentially incremented.
第十七方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第一设备获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等;第一设备传输该N个第一数据包;第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包。该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N、M以及Q均为正整数,Q小于或等于N。In a seventeenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the first device acquires N first data packets, and the sizes of the N first data packets are not completely equal; the first device transmits the N first data packets A data packet; the first device encodes the N first data packets and adds headers of the encoded packets to obtain M second data packets; the first device transmits the M second data packets. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation information of the data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. The N first data packets correspond to the Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding. The Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. The packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field or an offset field. The offset field is used to indicate the offset number of the sequence number of the first data packet relative to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet corresponding to the first data packet. Wherein, the first data packet is an original data packet, and the second data packet is an encoded packet. N, M and Q are all positive integers, and Q is less than or equal to N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备是编码端或发送端。第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the first device is an encoding end or a sending end. The first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
可选的,原数据包(即上述第一数据包)的包头中编码因子字段指示的行向量中只有一个元素等于1,其他元素均为0。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段的值相同。Optionally, only one element in the row vector indicated by the encoding factor field in the packet header of the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) is equal to 1, and the other elements are all 0. If multiple original data packets correspond to an equivalent original data packet, the values of the Coeff ID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same.
可见,本方案提供一种纯分割场景下支持网络编码的数据传输方法,不仅可以在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下应用,比如可以兼容NR协议,还能在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a data transmission method that supports network coding in a pure segmentation scenario, and can be applied not only in scenarios that do not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different, for example, it can be Compatible with the NR protocol, it can also restore PDU or SDU even when multiple original data packets are lost, reducing performance loss.
结合第十七方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头还包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the seventeenth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet.
第十八方面,本申请提供一种数据传输方法,该方法包括:第二设备获取P个数据包,并对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等;第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个或多个数据单元。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包。该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。P大于或等于N,N大于或等于Q,P、N以及Q均为正整数。In an eighteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission method, the method comprising: the second device acquires P data packets, and decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets, The P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets, and the sizes of the N first data packets are not completely equal; the second device according to each first data packet in the N first data packets The segmentation information included in the packet header of the data packet restores the data of the N first data packets into one or more data units. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation information of the data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. The N first data packets correspond to the Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding. The Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. The packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field or an offset field. The offset field is used to indicate the offset number of the sequence number of the first data packet relative to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet corresponding to the first data packet. P is greater than or equal to N, N is greater than or equal to Q, and P, N, and Q are all positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第二设备是编码端或发送端。第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。Optionally, the second device is an encoding end or a sending end. The second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE.
结合第十八方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头包括编码因子字段。对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个等效原数据包,包括:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示和该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。With reference to the eighteenth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each first data packet includes a coding factor field. Decoding the P data packets to obtain decoded N equivalent original data packets includes: determining from the P data packets according to the length of each of the P data packets and the length threshold Go out K first data packets and P-K second data packets; Adopt the analytic mode of original data packet to analyze the header of each first data packet in these K first data packets, obtain the serial number of this first data packet, And adopt the parsing mode of encoding packet to analyze the encoded packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets, and obtain the encoding factor field; according to the indication of the encoding factor field in the header of the K first data packets and the P-K The indication of the encoding factor field in the encoding packet header of the second data packet constitutes a coefficient factor matrix; the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets are jointly decoded by using the coefficient factor matrix to obtain Decoded N first data packets. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
可选的,原数据包(即上述第一数据包)的包头中编码因子字段指示的行向量中只有一个元素等于1,其他元素均为0。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段的值相同。Optionally, only one element in the row vector indicated by the encoding factor field in the packet header of the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) is equal to 1, and the other elements are all 0. If multiple original data packets correspond to an equivalent original data packet, the values of the Coeff ID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same.
可选的,在该第二数据包的包头携带该Q个等效原数据包和该第二数据包之间的对应关系。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the header of the second data packet carries the correspondence between the Q equivalent original data packets and the second data packet. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, the header of the second data packet may include identification information for indicating Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可见,本方案针对第一数据包的包头包括编码因子字段的情况,提供一种可能的译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a possible decoding process and operation for the case where the packet header of the first data packet includes a coding factor field, so that it can be correct when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N). The original data packet is decoded, and the PDU/SDU is recovered according to the segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header of the original data packet, thereby reducing the performance loss of the NR system.
结合第十八方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括偏移字段,该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个等效原数据包,包括:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段以及该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。With reference to the eighteenth aspect, in a possible design, the header of each first data packet above further includes an offset field, and the offset field is used to indicate that the sequence number of the first data packet is relative to the first data packet. The offset number corresponding to the sequence number of the original data packet corresponding to the packet. Decoding the P data packets to obtain decoded N equivalent original data packets includes: determining from the P data packets according to the length of each of the P data packets and the length threshold K first data packets and P-K second data packets are produced; the packet header of each first data packet in the K first data packets is analyzed by using the analysis method of the original data packet, and the serial number and the sequence number of the first data packet are obtained Offset field, and adopt the parsing mode of coded packet to analyze the encoded packet header of the second data packet in the P-K second data packets, and obtain the encoding factor field; according to the first data packet in the header of the K first data packets The sequence number and the offset field and the indication of the encoding factor field in the encoded packet header of the P-K second data packets form a coefficient factor matrix; the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K The first data packets are jointly decoded to obtain N first data packets after decoding.
可选的,在该第二数据包的包头携带该Q个等效原数据包和该第二数据包之间的对应关系。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the header of the second data packet carries the correspondence between the Q equivalent original data packets and the second data packet. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, the header of the second data packet may include identification information for indicating Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。第一设备从P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包的实现方式可参考第二方面的相应描述,此处不展开说明。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. Alternatively, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2. For an implementation manner in which the first device determines K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets, reference may be made to the corresponding description of the second aspect, and no further description is given here.
可见,本方案针对第一数据包的包头包括偏移字段的情况,提供一种可能的译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that this solution provides a possible decoding process and operation for the case where the packet header of the first data packet includes an offset field, so that it can be correct when the data packet received by the decoding end is full rank (rank=N). The original data packet is decoded, and the PDU/SDU is recovered according to the segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header of the original data packet, thereby reducing the performance loss of the NR system.
结合第十八方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头中包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,以上译码步骤中可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。With reference to the eighteenth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate where the second indication information is located The second data packet is an encoded packet. In this way, in the above decoding step, it is possible to determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded data packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the header, and then adopt a corresponding parsing method for the header of the data packet to parse.
第十九方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第一设备或第一设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等;传输模块,用于传输该N个第一数据包;编码模块,用于对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;该传输模块,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包。该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。N、M以及Q均为正整数,Q小于或等于N。In a nineteenth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be a first device or a chip in the first device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire N first data packets, the sizes of the N first data packets are not completely equal; a transmission module, configured to transmit the N first data packets; an encoding module, used M second data packets are obtained after encoding the N first data packets and adding headers of the encoded packets; the transmission module is also used to transmit the M second data packets. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation information of the data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. The N first data packets correspond to the Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding. The Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. The packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field or an offset field. The offset field is used to indicate the offset number of the sequence number of the first data packet relative to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet corresponding to the first data packet. N, M and Q are all positive integers, and Q is less than or equal to N.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,原数据包(即上述第一数据包)的包头中编码因子字段指示的行向量中只有一个元素等于1,其他元素均为0。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段的值相同。Optionally, only one element in the row vector indicated by the encoding factor field in the packet header of the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) is equal to 1, and the other elements are all 0. If multiple original data packets correspond to an equivalent original data packet, the values of the Coeff ID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same.
结合第十九方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头还包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。With reference to the nineteenth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet.
第二十方面,本申请提供一种数据传输装置,该数据传输装置可以是第二设备或第二设备中的芯片。该数据传输装置包括:获取模块,用于获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;译码模块,用于对该获取模块获取到的P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等;还原模块,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个或多个数据单元。其中,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包。该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。P大于或等于N,N大于或等于Q,P、N以及Q均为正整数。In a twentieth aspect, the present application provides a data transmission device, and the data transmission device may be the second device or a chip in the second device. The data transmission device includes: an acquisition module, configured to acquire P data packets, the P data packets including K first data packets and P-K second data packets; a decoding module, configured to acquire the P data packets from the acquisition module The P data packets are decoded to obtain N first data packets after decoding, and the sizes of the N first data packets are not completely equal; The segmentation information included in the packet header of the first data packet restores the data of the N first data packets into one or more data units. Wherein, each first data packet includes a header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation information of the data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet. The header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. The N first data packets correspond to the Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding. The Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. The packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field or an offset field. The offset field is used to indicate the offset number of the sequence number of the first data packet relative to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet corresponding to the first data packet. P is greater than or equal to N, N is greater than or equal to Q, and P, N, and Q are all positive integers.
可选的,上述数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the above data unit is a PDU or an SDU.
结合第二十方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头包括编码因子字段。上述译码模块,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示和该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。With reference to the twentieth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each first data packet includes a coding factor field. The above-mentioned decoding module is specifically used to: determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets according to the length and the length threshold of each data packet in the P data packets; The analysis method of the original data packet analyzes the header of each first data packet in the K first data packets, obtains the serial number of the first data packet, and uses the analysis method of the encoded packet to analyze the P-K second data packets. The encoded packet header of the second data packet obtains the encoding factor field; according to the indication of the encoding factor field in the header of the K first data packets and the indication of the encoding factor field in the encoded packet header of the P-K second data packets, constitute A coefficient factor matrix: using the coefficient factor matrix to jointly decode the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
可选的,原数据包(即上述第一数据包)的包头中编码因子字段指示的行向量中只有一个元素等于1,其他元素均为0。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段的值相同。Optionally, only one element in the row vector indicated by the encoding factor field in the packet header of the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) is equal to 1, and the other elements are all 0. If multiple original data packets correspond to an equivalent original data packet, the values of the Coeff ID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same.
结合第二十方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括偏移字段,该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。上述译码模块,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段以及该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。With reference to the twentieth aspect, in a possible design, the header of each first data packet above further includes an offset field, and the offset field is used to indicate that the sequence number of the first data packet is relative to the first data packet. The offset number corresponding to the sequence number of the original data packet corresponding to the packet. The above-mentioned decoding module is specifically used to: determine K first data packets and P-K second data packets from the P data packets according to the length and the length threshold of each data packet in the P data packets; The parsing method of the original data packet parses the packet header of each first data packet in the K first data packets, obtains the sequence number and offset field of the first data packet, and parses the P-K first data packets by using the parsing method of the encoded packet The encoded packet header of the second data packet in the two data packets obtains the encoding factor field; according to the sequence number and the offset field of the first data packet in the header of the K first data packets and the encoding of the P-K second data packets The indication of the encoding factor field in the packet header constitutes a coefficient factor matrix; the coded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets are jointly decoded by using the coefficient factor matrix to obtain N decoded first packet. Wherein, the rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N.
可选的,在该第二数据包的包头携带该Q个等效原数据包和该第二数据包之间的对应关系。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the header of the second data packet carries the correspondence between the Q equivalent original data packets and the second data packet. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, the header of the second data packet may include identification information for indicating Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. Alternatively, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2.
结合第二十方面,在一种可能的设计中,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;和/或,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头中包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,上述译码模块可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。With reference to the twentieth aspect, in a possible design, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; and /or, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate where the second indication information is located The second data packet is an encoded packet. In this way, the above-mentioned decoding module can determine whether the data packet is an original data packet or an encoded data packet according to the first indication information and/or the second indication information in the packet header, and then use a corresponding parsing method to analyze the packet header of the data packet. parse.
上述第十七至第二十任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述分割信息包括:该第一数据包的数据在该数据对应的数据单元中的位置信息,和指示该第一数据包的数据的长度的信息。In an implementation manner of any one of the seventeenth to twentieth aspects above, the segmentation information includes: position information of the data of the first data packet in the data unit corresponding to the data, and information indicating the first data packet Information about the length of the data.
可见,本方案通过在第一数据包的包头中携带该第一数据包的数据在PDU/SDU的位置信息,和其长度,有利于译码端将多个第一数据包的数据级联起来以恢复PDU/SDU。It can be seen that, by carrying the position information of the data of the first data packet in the PDU/SDU and its length in the header of the first data packet, this solution is beneficial for the decoding end to concatenate the data of multiple first data packets to recover the PDU/SDU.
上述第十七至第二十任一方面的一种实现方式中,上述编码包包头还包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息是块标识字段或包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。In an implementation manner of any one of the seventeenth to twentieth aspects above, the encoded packet header further includes identification information for indicating Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet. The identification information used to indicate that the Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a block identification field or includes at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first first in the encoding window The sequence number of the packet, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window.
应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,则用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息包括编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、和编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中的至少一项即可。编码包包头中的编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)的长度为8bit,用于指示码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。It should be understood that if the window length of the encoding window is configured semi-statically, the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet includes the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window , and at least one of the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. The encoding factor field (such as the Coeff ID field) in the header of the encoded packet has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the row index of the codebook. The codebook here can be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, etc.
上述第十七至第二十任一方面的一种实现方式中,第一数据包的序列号顺序递增。和/或,每个第二数据包的编码包包头中还包括该第二数据包的序列号。第二数据包的序列号也顺序递增。In an implementation manner of any one of the seventeenth to twentieth aspects above, the sequence number of the first data packet is incremented sequentially. And/or, the encoded packet header of each second data packet further includes the sequence number of the second data packet. The sequence number of the second data packet is also sequentially incremented.
第二十一方面,本申请提供一种通信装置,该通信装置可以包括处理器和存储器,可选的包括收发器。其中,该存储器用于存储计算机程序,该收发器用于收发各种数据包或信号,该计算机程序包括程序指令,当该处理器运行该程序指令时,使得该通信装置执行上述第一方面、或上述第二方面、或上述第五方面、或上述第六方面、或上述第九方面、或上述第十方面、或上述第十三方面、或上述第十四方面、或上述第十七方面、或上述第十八方面、或其中任一方面的任意一种可能的实现方式描述的数据传输方法。其中,收发器可以为通信装置中的射频模块,或,射频模块和天线的组合,或,芯片或电路的输入输出接口。In a twenty-first aspect, the present application provides a communication device, where the communication device may include a processor and a memory, and may optionally include a transceiver. Wherein, the memory is used to store a computer program, and the transceiver is used to send and receive various data packets or signals, the computer program includes program instructions, and when the processor executes the program instructions, the communication device executes the above first aspect, or The above-mentioned second aspect, or the above-mentioned fifth aspect, or the above-mentioned sixth aspect, or the above-mentioned ninth aspect, or the above-mentioned tenth aspect, or the above-mentioned thirteenth aspect, or the above-mentioned fourteenth aspect, or the above-mentioned seventeenth aspect, Or the data transmission method described in the eighteenth aspect above, or any possible implementation manner of any one of the aspects. Wherein, the transceiver may be a radio frequency module in the communication device, or a combination of a radio frequency module and an antenna, or an input and output interface of a chip or a circuit.
第二十二方面,本申请提供一种可读存储介质,该可读存储介质上存储有程序指令,当其在计算机上运行时,使得计算机执行上述第一方面、或上述第二方面、或上述第五方面、或上述第六方面、或上述第九方面、或上述第十方面、或上述第十三方面、或上述第十四方面、或上述第十七方面、或上述第十八方面、或其中任一方面的任意一种可能的实现方式描述的数据传输方法。In a twenty-second aspect, the present application provides a readable storage medium, on which program instructions are stored, and when run on a computer, the computer executes the above first aspect, or the above second aspect, or The fifth aspect above, or the sixth aspect above, or the ninth aspect above, or the tenth aspect above, or the thirteenth aspect above, or the fourteenth aspect above, or the seventeenth aspect above, or the eighteenth aspect above , or the data transmission method described in any possible implementation manner of any aspect thereof.
第二十三方面,本申请提供一种包含程序指令的程序产品,当其运行时,使得上述第一方面、或上述第二方面、或上述第五方面、或上述第六方面、或上述第九方面、或上述第十方面、或上述第十三方面、或上述第十四方面、或上述第十七方面、或上述第十八方面、或其中任一方面的任意一种可能的实现方式描述的数据传输方法被执行。In the twenty-third aspect, the present application provides a program product containing program instructions, which, when run, make the above-mentioned first aspect, or the above-mentioned second aspect, or the above-mentioned fifth aspect, or the above-mentioned sixth aspect, or the above-mentioned The ninth aspect, or the above tenth aspect, or the above thirteenth aspect, or the above fourteenth aspect, or the above seventeenth aspect, or the above eighteenth aspect, or any possible implementation of any of them The described data transfer method is implemented.
第二十四方面,本申请提供一种装置,该装置可以以芯片的形式实现,也可以为设备的形式,该装置包括处理器。该处理器用于读取并执行存储器中存储的程序,以执行上述第一方面、第二方面、第五方面、第六方面、第九方面、第十方面、第十三方面、第十四方面、第十七方面、第十八方面中的一项或多项,或,其中任一方面的任意可能的实现方式中的一项或多项提供的数据传输方法。可选的,该装置还包括存储器,该存储器与该处理器通过电路连接。进一步可选的,该装置还包括通信接口,该处理器与该通信接口连接。该通信接口用于接收待处理的数据包和/或信息,该处理器从该通信接口获取该数据包和/或信息,并对该数据包和/或信息进行处理,并通过该通信接口输出处理结果。该通信接口可以是输入输出接口。In a twenty-fourth aspect, the present application provides an apparatus, which may be implemented in the form of a chip or in the form of equipment, and the apparatus includes a processor. The processor is used to read and execute the program stored in the memory to implement the first aspect, the second aspect, the fifth aspect, the sixth aspect, the ninth aspect, the tenth aspect, the thirteenth aspect, and the fourteenth aspect , one or more of the seventeenth aspect, and the eighteenth aspect, or, the data transmission method provided by one or more of any possible implementation manners of any one of the aspects. Optionally, the device further includes a memory, and the memory is connected to the processor through a circuit. Further optionally, the device further includes a communication interface, and the processor is connected to the communication interface. The communication interface is used to receive the data packet and/or information to be processed, and the processor obtains the data packet and/or information from the communication interface, processes the data packet and/or information, and outputs the data packet and/or information through the communication interface process result. The communication interface may be an input-output interface.
可选的,上述的处理器与存储器可以是物理上相互独立的单元,或者,存储器也可以和处理器集成在一起。Optionally, the above-mentioned processor and memory may be physically independent units, or the memory may also be integrated with the processor.
第二十五方面,本申请提供一种通信系统,该通信系统包括上述任一方面中的第一设备和上述任一方面中的第二设备。In a twenty-fifth aspect, the present application provides a communication system, where the communication system includes the first device in any one of the above aspects and the second device in any one of the above aspects.
实施本申请实施例,可以在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如现有NR协议中,支持网络编码技术,即使在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。Implementing the embodiment of the present application can support network coding technology in scenarios that do not depend on the size of SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different. PDU or SDU can also be recovered in the case of data packet loss, reducing performance loss.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本申请实施例的技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所使用的附图作简单地介绍。In order to illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application more clearly, the accompanying drawings used in the description of the embodiments will be briefly introduced below.
图1a是本申请实施例提供的一种多个DU共用一个CU的网络架构示意图;Figure 1a is a schematic diagram of a network architecture in which multiple DUs share one CU provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图1b是本申请实施例提供的一种CU和DU的协议层功能的示意图;FIG. 1b is a schematic diagram of protocol layer functions of a CU and DU provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2是本申请实施例提供的应用场景示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of an application scenario provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3是本申请实施例提供的通信系统的简化示意图;FIG. 3 is a simplified schematic diagram of a communication system provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图4是随机线性网络编码的示意图;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of random linear network coding;
图5是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第一种示意流程图;FIG. 5 is a first schematic flowchart of a data transmission method provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图6是本申请实施例提供的协议栈的示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a protocol stack provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图7是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第一种示意图;FIG. 7 is a first schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图8是本申请实施例提供的PDU/SDU与第一数据包的数据的映射关系示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of the mapping relationship between PDU/SDU and the data of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图9是本申请实施例提供的PDU/SDU与第一数据包中的数据段的位置关系示意图;9 is a schematic diagram of the positional relationship between the PDU/SDU and the data segment in the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图10a是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图一;Fig. 10a is a first schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图10b是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图二;Fig. 10b is a second schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图11是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图三;FIG. 11 is a third schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图12是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图四;FIG. 12 is a fourth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图13是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图五;FIG. 13 is a schematic diagram five of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图14是本申请实施例提供的编码包包头的第一种示意图;Fig. 14 is a schematic diagram of the first type of encoded packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图15是本申请实施例提供的编码包包头的第二种示意图;Fig. 15 is a second schematic diagram of the header of the encoded packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图16是本申请实施例提供的译码端数据传输流程示意图;Fig. 16 is a schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the decoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图17是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第二种示意流程图;Fig. 17 is a second schematic flowchart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图18是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第二种示意图;FIG. 18 is a second schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图19是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头和编码包包头的示意图;Fig. 19 is a schematic diagram of the header of the first data packet and the header of the encoded packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图20是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第三种示意流程图;FIG. 20 is a third schematic flow chart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图21是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第三种示意图;FIG. 21 is a third schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图22是本申请实施例提供的级联数据包中级联包包头的位置示意图;Fig. 22 is a schematic diagram of the position of the header of the concatenated packet in the concatenated data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图23是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第四种示意图;Fig. 23 is a fourth schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图24是本申请实施例提供的添加填充比特的级联数据包中级联包包头的位置示意图;Fig. 24 is a schematic diagram of the position of the header of the concatenated packet in the concatenated data packet with padding bits added according to the embodiment of the present application;
图25是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图一;Fig. 25 is a first schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图26a是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图二;Figure 26a is a second schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图26b是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图三;Figure 26b is a schematic diagram of the third format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图27是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图四;Figure 27 is a schematic diagram of the fourth format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图28是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图六;Figure 28 is a sixth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图29是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第四种示意流程图;Fig. 29 is a fourth schematic flowchart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图30是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第五种示意图;Fig. 30 is a fifth schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图31a是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图七;Fig. 31a is a schematic diagram 7 of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图31b是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图八;Fig. 31b is a schematic diagram eight of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application;
图32是本申请实施例提供的一种构造系数因子矩阵的示意图;Fig. 32 is a schematic diagram of constructing a coefficient factor matrix provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图33是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置1的一结构示意图;FIG. 33 is a schematic structural diagram of the
图34是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置1的另一结构示意图;FIG. 34 is another schematic structural diagram of the
图35是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置2的一结构示意图;FIG. 35 is a schematic structural diagram of the
图36是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置2的另一结构示意图;FIG. 36 is another schematic structural diagram of the
图37是本申请实施例提供的通信装置的结构示意图。Fig. 37 is a schematic structural diagram of a communication device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本申请实施例中的附图,对本申请实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述。The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present application.
为了便于清楚描述本申请实施例的技术方案,在本申请的实施例中,采用了“第一”、“第二”等字样对功能和作用基本相同的相同项或相似项进行区分。例如,第一信息和第二信息仅仅是为了区分不同的信息,并不对其先后顺序进行限定。本领域技术人员可以理解“第一”、“第二”等字样并不对数量和执行次序进行限定,并且“第一”、“第二”等字样也并不限定一定不同。In order to clearly describe the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application, in the embodiments of the present application, words such as "first" and "second" are used to distinguish the same or similar items with basically the same function and effect. For example, the first information and the second information are only for distinguishing different information, and the sequence thereof is not limited. Those skilled in the art can understand that words such as "first" and "second" do not limit the number and execution order, and words such as "first" and "second" do not necessarily limit the difference.
本申请实施例中,“至少一个”是指一个或者多个,“多个”是指两个或两个以上。“和/或”,描述关联对象的关联关系,表示可以存在三种关系,例如,A和/或B,可以表示:单独存在A,同时存在A和B,单独存在B的情况,其中A,B可以是单数或者复数。字符“/”一般表示前后关联对象是一种“或”的关系。“以下至少一项(个)”或其类似表达,是指的这些项中的任意组合,包括单项(个)或复数项(个)的任意组合。例如,a,b,或c中的至少一项(个),可以表示:a,b,c;a和b;a和c;b和c;或a和b和c。其中a,b,c可以是单个,也可以是多个。In the embodiments of the present application, "at least one" means one or more, and "multiple" means two or more. "And/or" describes the association relationship of associated objects, indicating that there may be three types of relationships, for example, A and/or B, which can mean: A exists alone, A and B exist simultaneously, and B exists alone, where A, B can be singular or plural. The character "/" generally indicates that the contextual objects are an "or" relationship. "At least one of the following" or similar expressions refer to any combination of these items, including any combination of single or plural items. For example, at least one item (unit) of a, b, or c may represent: a, b, c; a and b; a and c; b and c; or a and b and c. Where a, b, c can be single or multiple.
可以理解,在本申请中,“当…时”、“若”以及“如果”均指在某种客观情况下装置会做出相应的处理,并非是限定时间,且也不要求装置实现时一定要有判断的动作,也不意味着存在其它限定。It can be understood that in this application, "when", "if" and "if" all mean that the device will make corresponding processing under certain objective circumstances, and it is not a time limit, and it is not required that the device implements a certain The act of judgment does not mean that there are other restrictions.
本申请中的“同时”可以理解为在相同的时间点,也可以理解为在一段时间段内,还可以理解为在同一个周期内,具体可以结合上下文进行理解。"Simultaneously" in this application can be understood as at the same time point, within a certain period of time, or within the same period, which can be specifically understood in conjunction with the context.
本申请中对于使用单数表示的元素旨在用于表示“一个或多个”,而并非表示“一个且仅一个”,除非有特别说明。In this application, an element expressed in the singular is intended to mean "one or more" rather than "one and only one", unless otherwise specified.
另外,本文中术语“系统”和“网络”在本文中常被可互换使用。Additionally, the terms "system" and "network" are often used herein interchangeably.
可以理解,在本申请各实施例中,“与A相应的B”表示B与A相关联,根据A可以确定B。但还应理解,根据A确定B并不意味着仅仅根据A确定B,还可以根据A和/或其它信息确定B。It can be understood that in each embodiment of the present application, "B corresponding to A" means that B is associated with A, and B can be determined according to A. However, it should also be understood that determining B according to A does not mean determining B only according to A, and B may also be determined according to A and/or other information.
为便于理解本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法,下面将对本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的系统架构和应用场景进行说明。可理解的,本申请实施例描述的系统架构和应用场景是为了更加清楚的说明本申请实施例的技术方案,并不构成对于本申请实施例提供的技术方案的限定。In order to facilitate understanding of the data transmission method provided in the embodiment of the present application, the system architecture and application scenarios of the data transmission method provided in the embodiment of the present application will be described below. It can be understood that the system architecture and application scenarios described in the embodiments of the present application are for more clearly illustrating the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application, and do not constitute limitations on the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application.
无线通信系统中包括通信设备,通信设备间可以利用空口资源进行无线通信。其中,通信设备可以包括网络设备和终端设备,网络设备还可以称为基站设备。空口资源可以包括时域资源、频域资源、码资源和空间资源中至少一个。The wireless communication system includes communication devices, and the communication devices can use air interface resources to perform wireless communication. Wherein, the communication device may include a network device and a terminal device, and the network device may also be called a base station device. The air interface resources may include at least one of time domain resources, frequency domain resources, code resources and space resources.
本申请实施例涉及到的网络设备包括接入网设备,例如基站(base station,BS),BS可以是网络侧的一种用于发射或接收信号的实体,也是一种部署在无线接入网中能够和终端进行无线通信的设备。基站(BS)可以是固定的,也可以是移动的。其中,基站可能有多种形式,比如宏基站、微基站、中继站和接入点等。示例性地,本申请实施例涉及到的基站可以是5G中的基站或LTE中演进的基站(Evolved Node B,eNB)。其中,5G中的基站还可以称为发送接收点(transmission reception point,TRP)或5G基站(Next-Generation Node B,gNB)。基站还可以与如下名称进行替换,比如:节点B(NodeB)、发射点(transmittingpoint,TP)、主站MeNB、辅站SeNB、多制式无线(MSR)节点、家庭基站、网络控制器、接入节点、无线节点、传输节点、收发节点、基带单元(baseband unit,BBU)、射频拉远单元(remoteradio unit,RRU)、有源天线单元(AAU)、射频头(RRH)、中心单元(CU)、分布单元(DU)、定位节点等。本申请实施例中,用于实现网络设备的功能的装置可以是网络设备;也可以是能够支持网络设备实现该功能的装置,例如芯片系统、或通信模块、或调制解调器等,该装置可以被安装在网络设备中。在本申请实施例提供的技术方案中,以用于实现网络设备的功能的装置是网络设备,以网络设备是基站为例,描述本申请实施例提供的技术方案。基站可以支持相同或不同接入技术的网络。本申请的实施例对网络设备所采用的具体技术和具体设备形态不做限定。The network equipment involved in the embodiment of the present application includes access network equipment, such as a base station (base station, BS). The BS can be an entity used to transmit or receive signals on the network side, and is also an entity deployed on the wireless access network. A device capable of wireless communication with a terminal. A base station (BS) can be fixed or mobile. Among them, the base station may have various forms, such as a macro base station, a micro base station, a relay station, and an access point. Exemplarily, the base station involved in the embodiment of the present application may be a base station in 5G or an evolved base station (Evolved Node B, eNB) in LTE. Wherein, the base station in 5G may also be referred to as a transmission reception point (transmission reception point, TRP) or a 5G base station (Next-Generation Node B, gNB). The base station can also be replaced with the following names, such as: Node B (NodeB), transmitting point (transmitting point, TP), primary station MeNB, secondary station SeNB, multi-standard radio (MSR) node, home base station, network controller, access Node, wireless node, transmission node, transceiver node, baseband unit (baseband unit, BBU), remote radio unit (remoteradio unit, RRU), active antenna unit (AAU), radio head (RRH), central unit (CU) , distribution unit (DU), positioning nodes, etc. In this embodiment of the application, the device used to realize the function of the network device may be a network device; it may also be a device capable of supporting the network device to realize the function, such as a chip system, or a communication module, or a modem, etc., and the device can be installed in network equipment. In the technical solution provided by the embodiment of the present application, the technical solution provided by the embodiment of the present application is described by taking the apparatus for realizing the function of the network device as the network device and taking the network device as the base station as an example. Base stations can support networks of the same or different access technologies. The embodiment of the present application does not limit the specific technology and specific device form adopted by the network device.
在一些部署中,接入网设备(例如:gNB)可以包括集中式单元(centralized unit,CU)和分布式单元(distributed unit,DU)。gNB还可以包括射频单元(radio unit,RU)。CU和DU可以理解为是对基站从逻辑功能角度的划分,CU和DU在物理上可以分离,也可以部署在一起。例如,多个DU可以共用一个CU或者一个DU也可以连接多个CU,CU和DU之间可以通过F1接口相连。示例性的,参见图1a,图1a是本申请实施例提供的一种多个DU共用一个CU的网络架构示意图。如图1a所示,核心网和RAN互连通信,RAN中的基站分离成CU和DU,多个DU共用一个CU。图1a所示的网络架构可以应用于5G通信系统,也可以与LTE系统共享一个或多个部件或资源。包括CU节点和DU节点的接入网设备将协议层拆分开,部分协议层的功能放在CU集中控制,剩下部分或全部协议层的功能分布在DU中,由CU集中控制DU。作为一种实现方式,参见图1b,图1b是本申请实施例提供的一种CU和DU的协议层功能的示意图。如图1b所示,CU部署有协议栈中的无线资源控制(radio resource control,RRC)层,分组数据汇聚协议(packet data convergence protocol,PDCP)层,以及业务数据适应协议(servicedata adaptation protocol,SDAP)层;DU部署有协议栈中的无线链路控制(radio linkcontrol,RLC)层,媒体接入控制(medium access control,MAC)层,以及物理层(physicallayer,PHY)。从而,CU具有RRC、PDCP和SDAP的处理能力。DU具有RLC、MAC和PHY的处理能力。可以理解的是,上述功能的切分仅为一个示例,不构成对CU和DU的限定。也就是说,CU和DU之间还可以有其他功能切分的方式,示例性的,将RLC层的部分功能和RLC层以上的协议层的功能设置在CU,将RLC层的剩余功能和RLC层以下的协议层的功能设置在DU。例如,还可以按照通话业务、语音业务或短信业务的业务类型或者其他系统需求对CU或者DU的功能进行划分。示例性的,CU或者DU的功能按照时延划分,可以将处理时间需要满足时延要求的功能设置在DU,不需要满足时延要求的功能设置在CU。例如,CU也可以具有核心网的一个或多个功能,一个或者多个CU可以集中设置,也可以分离设置。例如,CU可以设置在网络侧方便集中管理,DU可以具有多个射频功能,也可以将射频功能拉远设置。In some deployments, an access network device (for example: gNB) may include a centralized unit (centralized unit, CU) and a distributed unit (distributed unit, DU). The gNB may also include a radio unit (radio unit, RU). CU and DU can be understood as the division of base stations from the perspective of logical functions. CU and DU can be physically separated or deployed together. For example, multiple DUs can share one CU or one DU can also be connected to multiple CUs, and the CUs and DUs can be connected through the F1 interface. For example, refer to FIG. 1a . FIG. 1a is a schematic diagram of a network architecture in which multiple DUs share one CU according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 1a, the core network and the RAN communicate with each other, the base station in the RAN is separated into CU and DU, and multiple DUs share one CU. The network architecture shown in Figure 1a can be applied to a 5G communication system, and can also share one or more components or resources with an LTE system. Access network equipment including CU nodes and DU nodes separates the protocol layer, and the functions of some protocol layers are centrally controlled by the CU, while the rest or all functions of the protocol layer are distributed in the DU, and the CU centrally controls the DU. As an implementation manner, refer to FIG. 1b, which is a schematic diagram of protocol layer functions of a CU and a DU provided in an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 1b, the CU is deployed with the radio resource control (radio resource control, RRC) layer in the protocol stack, the packet data convergence protocol (packet data convergence protocol, PDCP) layer, and the service data adaptation protocol (servicedata adaptation protocol, SDAP) ) layer; the DU is deployed with a radio link control (radio link control, RLC) layer, a medium access control (medium access control, MAC) layer, and a physical layer (physical layer, PHY) in the protocol stack. Thus, the CU has the processing capability of RRC, PDCP and SDAP. DU has the processing capability of RLC, MAC and PHY. It can be understood that the division of the above functions is only an example, and does not constitute a limitation on CUs and DUs. That is to say, there may be other ways of splitting functions between CU and DU. For example, some functions of the RLC layer and functions of the protocol layer above the RLC layer are set in the CU, and the remaining functions of the RLC layer and RLC The functions of the protocol layer below the layer are set in DU. For example, the functions of the CU or DU may also be divided according to the service types of call service, voice service or short message service or other system requirements. Exemplarily, the functions of the CU or DU are divided according to the delay, and the functions whose processing time needs to meet the delay requirement can be set in the DU, and the functions that do not need to meet the delay requirement can be set in the CU. For example, a CU may also have one or more functions of the core network, and one or more CUs may be configured centrally or separately. For example, the CU can be set on the network side to facilitate centralized management, and the DU can have multiple radio functions, or the radio functions can be set remotely.
CU的功能可以由一个实体来实现也可以由不同的实体实现。例如,可以对CU的功能进行进一步切分,例如,将控制面(controlplane,CP)和用户面(userplane,UP)分离,即CU的控制面(CU-CP)和CU的用户面(CU-UP)。例如,CU-CP和CU-UP可以由不同的功能实体来实现,该CU-CP和CU-UP可以与DU相耦合,共同完成基站的功能。一种可能的方式中,CU-CP负责控制面功能,主要包含RRC和PDCP控制面PDCP-C。PDCP-C主要负责控制面数据的加解密,完整性保护,数据传输等中的一项或多项。CU-UP负责用户面功能,主要包含SDAP和PDCP用户面PDCP-U。其中SDAP主要负责将核心网的数据进行处理并将数据流(flow)映射到承载。PDCP-U主要负责数据面的加解密,完整性保护,头压缩,序列号维护,数据传输等中的一项或多项。其中CU-CP和CU-UP通过E1接口连接。CU-CP代表接入网设备通过Ng接口和核心网连接。CU-CP通过F1-C(控制面)和DU连接。CU-UP通过F1-U(用户面)和DU连接。当然还有一种可能的实现是PDCP-C也在CU-UP。由于RRC层的信息最终会变成PHY层的信息,或者,由PHY层的信息转变而来,因而,在这种架构下,高层信令,如RRC层信令或PDCP层信令,也可以认为是由DU发送的,或者,由DU+RU发送的。可以理解的是,接入网设备可以为CU节点、或DU节点、或包括CU节点和DU节点的设备。The functions of the CU can be implemented by one entity or by different entities. For example, the functions of the CU can be further divided, for example, the control plane (controlplane, CP) and the user plane (userplane, UP) are separated, that is, the control plane (CU-CP) of the CU and the user plane (CU-CP) of the CU (CU-CP). UP). For example, the CU-CP and CU-UP can be implemented by different functional entities, and the CU-CP and CU-UP can be coupled with the DU to jointly complete the functions of the base station. In a possible way, the CU-CP is responsible for the control plane function, mainly including RRC and PDCP control plane PDCP-C. PDCP-C is mainly responsible for one or more of control plane data encryption and decryption, integrity protection, and data transmission. CU-UP is responsible for user plane functions, mainly including SDAP and PDCP user plane PDCP-U. Among them, the SDAP is mainly responsible for processing the data of the core network and mapping the data flow (flow) to the bearer. PDCP-U is mainly responsible for one or more of data plane encryption and decryption, integrity protection, header compression, serial number maintenance, and data transmission. Among them, CU-CP and CU-UP are connected through E1 interface. The CU-CP represents the access network equipment and connects to the core network through the Ng interface. CU-CP is connected with DU through F1-C (control plane). CU-UP is connected to DU through F1-U (user plane). Of course, another possible implementation is that PDCP-C is also in CU-UP. Since the information of the RRC layer will eventually become the information of the PHY layer, or be transformed from the information of the PHY layer, under this framework, high-level signaling, such as RRC layer signaling or PDCP layer signaling, can also be It is considered to be sent by DU, or sent by DU+RU. It can be understood that the access network device may be a CU node, or a DU node, or a device including a CU node and a DU node.
本申请实施例涉及的终端设备还可以称为终端、用户设备(user equipment,UE)、移动台(mobile station,MS)、移动终端(mobile terminal,MT)等,其可以是用户侧的一种用于接收或发射信号的实体,如手机;其可以部署在陆地上,包括室内或室外、手持或车载;也可以部署在水面上(如轮船等);还可以部署在空中(例如飞机、气球和卫星上等)。终端设备可以是用户设备(user equipment,UE),其中,UE包括具有无线通信功能的手持式设备、车载设备、可穿戴设备或计算设备。示例性地,UE可以是手机(mobile phone)、平板电脑或带无线收发功能的电脑。终端设备还可以是虚拟现实(virtual reality,VR)终端设备、增强现实(augmented reality,AR)终端设备、工业控制中的无线终端、无人驾驶中的无线终端、远程医疗中的无线终端、智能电网中的无线终端、智慧城市(smart city)中的无线终端、智慧家庭(smart home)中的无线终端等等。本申请实施例中,用于实现终端的功能的装置可以是终端;也可以是能够支持终端实现该功能的装置,例如芯片系统、或通信模块、或调制解调器等,该装置可以被安装在终端中。本申请实施例中,芯片系统可以由芯片构成,也可以包括芯片和其他分立器件。本申请实施例提供的技术方案中,以用于实现终端的功能的装置是终端,以终端是UE为例,描述本申请实施例提供的技术方案。本申请的实施例对终端设备所采用的具体技术和具体设备形态不做限定。The terminal equipment involved in this embodiment of the present application may also be referred to as a terminal, a user equipment (UE), a mobile station (mobile station, MS), a mobile terminal (mobile terminal, MT), etc., and it may be a user-side An entity used to receive or transmit signals, such as a mobile phone; it can be deployed on land, including indoor or outdoor, handheld or vehicle-mounted; it can also be deployed on water (such as ships, etc.); it can also be deployed in the air (such as aircraft, balloons, etc.) and satellites, etc.). The terminal device may be user equipment (user equipment, UE), where the UE includes a handheld device, a vehicle-mounted device, a wearable device, or a computing device with a wireless communication function. Exemplarily, the UE may be a mobile phone (mobile phone), a tablet computer or a computer with a wireless transceiver function. The terminal device can also be a virtual reality (virtual reality, VR) terminal device, an augmented reality (augmented reality, AR) terminal device, a wireless terminal in industrial control, a wireless terminal in unmanned driving, a wireless terminal in telemedicine, a smart Wireless terminals in power grids, wireless terminals in smart cities, wireless terminals in smart homes, and so on. In the embodiment of the present application, the device for realizing the function of the terminal may be a terminal; it may also be a device capable of supporting the terminal to realize the function, such as a chip system, or a communication module, or a modem, etc., and the device may be installed in the terminal . In the embodiment of the present application, the system-on-a-chip may be composed of chips, or may include chips and other discrete devices. In the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application, the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application are described by taking the terminal as an example in which the device for realizing the functions of the terminal is a terminal and the terminal is a UE. The embodiment of the present application does not limit the specific technology and specific device form adopted by the terminal device.
可选的,UE也可以用于充当基站。例如,UE可以充当调度实体,其在车辆外联(vehicle-to-everything,V2X)、设备到设备(device-to-device,D2D)或点对点(peer topeer,P2P)等中的UE之间提供侧行链路信号。Optionally, the UE can also be used as a base station. For example, the UE can act as a dispatching entity, which provides a network connection between UEs in vehicle-to-everything (V2X), device-to-device (D2D) or peer-to-peer (P2P), etc. Sidelink signal.
本申请实施例提供的技术方案可以应用于通信设备间的无线通信。通信设备间的无线通信可以包括:网络设备和终端间的无线通信、网络设备和网络设备间的无线通信以及终端和终端间的无线通信。在本申请实施例中,术语“无线通信”还可以简称为“通信”,术语“通信”还可以描述为“数据传输”、“信息传输”或“传输”。The technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application may be applied to wireless communication between communication devices. Wireless communication between communication devices may include: wireless communication between network devices and terminals, wireless communication between network devices and network devices, and wireless communication between terminals. In this embodiment of the present application, the term "wireless communication" may also be referred to as "communication" for short, and the term "communication" may also be described as "data transmission", "information transmission" or "transmission".
本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法主要针对长期演进(long term evolution,LTE)或NR等协议框架,可应用于多种移动通信场景中。比如,基站和用户设备(UserEquipment,UE)之间、或UE和UE之间独立组网(Standalone,SA)场景的点对点传输、基站和用户设备的多跳/中继(relay)传输、多个基站和用户设备的双连接(Dual Connectivity,DC)或多连接等场景。参见图2,图2是本申请实施例提供的应用场景示意图。如图2所示,图2示出了四种应用场景,分别是点对点单连接、多跳单连接、双连接、以及多跳多连接。应理解的,本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法可以应用于图2所示的各种应用场景中,还应理解,图2仅是示例性的,从业务场景角度而言,本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法还适用于诸多场景,包括但不限于诸如扩展现实(extended reality,XR)业务中的数据编码、上行大容量场景等。此外,图2不对适用于本申请的网络架构产生限制,并且本申请不限制上行、下行、接入链路、回传(backhaul)链路、侧链路(Sidelink)等传输。The data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application is mainly aimed at protocol frameworks such as long term evolution (long term evolution, LTE) or NR, and can be applied in various mobile communication scenarios. For example, point-to-point transmission between a base station and a user equipment (User Equipment, UE), or between a UE and a UE in an independent networking (Standalone, SA) scenario, multi-hop/relay (relay) transmission between a base station and a user equipment, multiple Scenarios such as dual connectivity (Dual Connectivity, DC) or multiple connections between the base station and the user equipment. Referring to FIG. 2, FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of an application scenario provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 2, FIG. 2 shows four application scenarios, which are point-to-point single connection, multi-hop single connection, dual connection, and multi-hop multi-connection. It should be understood that the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application can be applied to various application scenarios shown in FIG. 2 . It should also be understood that FIG. 2 is only exemplary. The data transmission method provided is also applicable to many scenarios, including but not limited to data encoding in extended reality (extended reality, XR) services, uplink large-capacity scenarios, and the like. In addition, FIG. 2 does not limit the network architecture applicable to this application, and this application does not limit transmissions such as uplink, downlink, access link, backhaul (backhaul) link, and sidelink (Sidelink).
参见图3,图3是本申请实施例提供的通信系统的简化示意图。为了简单起见,图3仅示出了基站110、UE 120以及网络130。基站110包括接口111和处理器112。处理器112可选地可以存储程序114。基站110可选地可以包括存储器113。存储器113可选地可以存储程序115。UE 120包括接口121和处理器122。处理器122可选地可以存储程序124。UE 120可选地可以包括存储器123。存储器123可选地可以存储程序125。这些组件一起工作,以提供本申请中描述的各种功能。例如,处理器112和接口121一起工作以提供基站110与UE 120之间的无线连接。处理器122和接口121共同作用,实现UE 120的下行传输和/或上行传输。Referring to FIG. 3 , FIG. 3 is a simplified schematic diagram of a communication system provided by an embodiment of the present application. For simplicity, FIG. 3 only shows base station 110,
网络130可以包括一个或多个网络节点130a、130b,以提供核心网功能。网络节点130a、130b可以是5G核心网节点,或更早一代(例如4G、3G或2G)核心网节点。例如,网络130a、130b可以是接入管理功能(AMF)、移动性管理实体(MME)等。网络130还可以包括公共交换电话网络(PSTN)、分组数据网络、光网络、互联网协议(IP)网络中的一个或多个网络节点。广域网(WAN)、局域网(LAN)、无线局域网(WLAN)、有线网络、无线网络、城域网和其他网络,以使UE 120和/或基站110之间能够进行通信。The
处理器(例如,处理器112和/或处理器122)可包括一个或多个处理器并实现为计算设备的组合。处理器(例如,处理器112和/或处理器122)可分别包括以下一种或多种:微处理器、微控制器、数字信号处理器(DSP)、数字信号处理设备(DSPD)、专用集成电路(ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)、可编程逻辑器件(PLD)、选通逻辑、晶体管逻辑、分立硬件电路、处理电路或其它合适的硬件、固件和/或硬件和软件的组合,用于执行本申请中所描述的各种功能。处理器(例如,处理器112和/或处理器122)可以是通用处理器或专用处理器。例如,处理器112和/或处理器122可以是基带处理器或中央处理器。基带处理器可用于处理通信协议和通信数据。中央处理器可用于使基站110和/或UE 120执行软件程序,并处理软件程序中的数据。A processor (eg,
接口(例如,接口111和/或121)可包括用于实现与一个或多个计算机设备(例如,UE、BS和/或网络节点)之间的通信。在一些实施例中,接口可以包括用于耦合有线连接的电线、或用于耦合无线收发器的管脚、或用于无线连接的芯片和/或管脚。在一些实施例中,接口可以包括发射器、接收器、收发器和/或天线。接口可以被配置为使用任何可用的协议(例如3GPP标准)。Interfaces (eg, interfaces 111 and/or 121 ) may include devices for enabling communication with one or more computer devices (eg, UEs, BSs, and/or network nodes). In some embodiments, the interface may include wires for coupling a wired connection, or pins for coupling a wireless transceiver, or chips and/or pins for a wireless connection. In some embodiments, an interface may include a transmitter, receiver, transceiver and/or antenna. The interface can be configured to use any available protocol (eg 3GPP standard).
本申请中的程序在广义上用于表示软件。软件的非限制性示例是程序代码、程序、子程序、指令、指令集、代码、代码段、软件模块、应用程序、软件应用程序等。程序可以在处理器和/或计算机中运行,以使基站110和/或UE 120执行本申请中描述的各种功能和/或过程。A program in this application is used in a broad sense to mean software. Non-limiting examples of software are program code, programs, subroutines, instructions, instruction sets, codes, code segments, software modules, applications, software applications, and the like. The program can run in the processor and/or the computer to make the base station 110 and/or the
内存(例如存储器113和/或存储器123)可存储由处理器112、122在执行软件时操纵的数据。存储器113、123可以使用任何存储技术实现。例如,存储器可以是处理器和/或计算机能够访问的任何可用存储介质。存储介质的非限制性示例包括:RAM、ROM、EEPROM、CD-ROM、可移动介质、光盘存储器、磁盘存储介质、磁存储设备、闪存、寄存器、状态存储器、远程挂载存储器、本地或远程存储器组件,或能够携带或存储软件、数据或信息并可由处理器/计算机访问的任何其它介质。Memory (eg,
内存(例如存储器113和/或存储器123)和处理器(例如处理器112和/或处理器122)可以分开设置或集成在一起。存储器可以用于与处理器连接,使得处理器能够从存储器中读取信息,在存储器中存储和/或写入信息。存储器113可以集成在处理器112中。存储器123可以集成在处理器122中。处理器(例如处理器113和/或处理器123)和存储器(例如处理器112和/或处理器122)可以设置在集成电路中(例如,该集成电路可以设置在UE或基站或其他网络节点中)。The memory (such as the
上述内容简要阐述了本申请实施例的系统架构和可能的应用场景,为更好地理解本申请实施例的技术方案,下面将简要介绍网络编码。The above content briefly describes the system architecture and possible application scenarios of the embodiment of the present application. In order to better understand the technical solution of the embodiment of the present application, the network coding will be briefly introduced below.
常用的网络编码方案包括随机线性网络编码(random linear network coding,RLNC)、卷积网络编码(convolutional network coding,CNC)等。下面以RLNC为例进行简要说明。RLNC方案以数据块(一个数据块中包括若干个大小相同的原数据)为单元,通过构建编码系数矩阵对原数据进行编码得到一组编码数据包。编码数据包的大小与数据块中原数据包的大小相同。通常,编码系数矩阵中的系数在有限域,如伽罗华域(Galois Field,GF)中随机选取。参见图4,图4是随机线性网络编码的示意图。如图4所示,编码系数矩阵(即图4中的A(W+R)×W)大小为(W+R)×W,即(W+R)行W列,通过对一个包含W个原数据的数据块(图4中的XW×1)进行网络编码,得到W+R个编码数据(图4中的Y(W+R)×1),对应的码率(冗余)表示为W/(W+R)。其中,编码系数矩阵在GF(q)域中随机选择系数,q表示伽罗华域的大小,伽罗华域的取值为区间[0,q-1]。W和R均是正整数。应理解,RLNC方案中,编码数据块(这里的编码数据块是指对一个包含W个原数据的数据块进行网络编码得到W+R个编码数据)之间没有关联,即编码操作对每个独立的数据块进行,每个数据块的冗余(码率)可以相同,也可以不相同。编码端/发送端对生成的W+R个编码数据统一加包头信息后发送,译码端/接收端接收到W个正确且线性无关的编码数据包时,即可正确译码并恢复出W个原数据。这是因为编码数据包融合了若干个原数据的信息,所以接收端可以用编码数据包来恢复原数据。在本申请实施例中,术语“编码数据包”还可以简称为“编码包”,两者可替换使用。Commonly used network coding schemes include random linear network coding (random linear network coding, RLNC), convolutional network coding (convolutional network coding, CNC) and so on. The following takes RLNC as an example for a brief description. The RLNC scheme takes a data block (a data block includes several original data of the same size) as a unit, and encodes the original data by constructing a coding coefficient matrix to obtain a set of coded data packets. The size of the encoded packet is the same as the size of the original packet in the data block. Usually, the coefficients in the coding coefficient matrix are randomly selected in a finite field, such as a Galois Field (Galois Field, GF). Referring to FIG. 4, FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of random linear network coding. As shown in Figure 4, the size of the encoding coefficient matrix (that is, A(W+R)×W in Figure 4) is (W+R)×W, that is, (W+R) rows and W columns, by The data block of the original data (XW×1 in Figure 4) is network-encoded to obtain W+R coded data (Y(W+R)×1 in Figure 4), and the corresponding code rate (redundancy) represents It is W/(W+R). Among them, the encoding coefficient matrix randomly selects coefficients in the GF(q) field, q represents the size of the Galois field, and the value of the Galois field is in the interval [0,q-1]. Both W and R are positive integers. It should be understood that in the RLNC scheme, there is no correlation between encoded data blocks (the encoded data blocks here refer to performing network encoding on a data block containing W original data to obtain W+R encoded data), that is, the encoding operation is performed on each Independent data blocks are performed, and the redundancy (code rate) of each data block may be the same or different. The encoding end/sending end adds header information to the generated W+R encoded data and sends them. When the decoding end/receiving end receives W correct and linearly independent encoded data packets, it can correctly decode and recover W raw data. This is because the coded data packet combines information of several original data, so the receiving end can use the coded data packet to restore the original data. In this embodiment of the present application, the term "encoded data packet" may also be referred to as "encoded packet" for short, and the two may be used interchangeably.
由于干扰、噪声等因素,当译码端/接收端接收到的正确且线性无关的编码数据包个数小于W时,译码端/接收端无法进行译码,此时反馈给编码端/发送端正确译码还需要的编码数据包个数,编码端/发送端根据反馈信息发送对应个数的编码数据包,该编码数据包与下一个数据块的编码无关。Due to interference, noise and other factors, when the number of correct and linearly independent encoded data packets received by the decoding end/receiving end is less than W, the decoding end/receiving end cannot decode. At this time, the feedback is given to the encoding end/sending The encoding end/transmitter sends the corresponding number of encoded data packets according to the feedback information, and the encoded data packets have nothing to do with the encoding of the next data block.
因为网络编码需要原数据的大小均相同,而NR协议中,任何一层对应的业务数据单元(service data unit,SDU)或者协议数据单元(protocol data unit,PDU)大小都无法保证是相同的,所以NR协议无法直接支持网络编码技术。Because network coding requires the same size of the original data, and in the NR protocol, the size of the service data unit (service data unit, SDU) or protocol data unit (protocol data unit, PDU) corresponding to any layer cannot be guaranteed to be the same. Therefore, the NR protocol cannot directly support network coding technology.
因此,本申请实施例提供一种数据传输方法,编码端通过对每个原数据添加包头,并将PDU或者SDU进行分割和级联后的信息添加到该包头中获得包括包头的原数据包,再对原数据包进行网络编码生成编码数据并对该编码数据添加编码包头后发送;译码端则根据接收正确的原数据包和编码包进行译码,通过包头携带的分割和级联信息,将原数据恢复出PDU/SDU信息;不仅可以使网络编码技术在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小的场景下也可以获得应用,从而可以在现有NR协议中支持网络编码技术,即使在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失,提高传输的可靠性。Therefore, the embodiment of the present application provides a data transmission method. The encoding end adds a packet header to each original data, and adds the information after dividing and concatenating the PDU or SDU to the packet header to obtain the original data packet including the packet header. Then perform network encoding on the original data packet to generate encoded data and add an encoded packet header to the encoded data before sending it; the decoding end decodes according to the received correct original data packet and encoded packet, and through the segmentation and concatenation information carried by the packet header, Restore the original data to PDU/SDU information; not only can the network coding technology be applied in scenarios that do not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, so that the network coding technology can be supported in the existing NR protocol, even in multiple original PDU or SDU can also be recovered in the case of data packet loss, reducing performance loss and improving transmission reliability.
下面将结合更多的附图对本申请提供的技术方案进行详细说明。The technical solutions provided by the present application will be described in detail below in conjunction with more drawings.
本申请提供的技术方案通过四个实施例来详细说明。其中,实施例一阐述PDU/SDU经过分割和/或级联操作后得到的原数据非等大小情况下,如何进行网络编码并传输两类数据包(原数据包和编码包)、以及如何设计两类数据包的包头。实施例二阐述对PDU/SDU经过分割和/或级联操作后得到的原数据非等大小情况下,如何进行网络编码并保证传输的数据包的大小相等、以及如何设计包头。实施例三阐述对多个PDU/SDU先级联再加包头和填充操作,再等大小分割后,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。实施例四阐述仅对PDU/SDU进行分割操作后,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。可理解的,本申请实施例一至实施例四所描述的技术方案可以任一组合形成新的实施例且所涉及概念或方案相同或相似的部分可以相互参考或组合。下面分别对各个实施例进行详细说明。The technical solution provided by this application is described in detail through four examples. Among them,
可选的,本申请提供的技术方案可通过第一设备和第二设备来实现。其中,第一设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE;第二设备既可以是网络设备,如基站;也可以是终端设备,如UE。本申请的所有实施例均以第一设备作为编码端(或发送端)来描述,第二设备作为译码端(或接收端)来描述;但在实际应用中,第一设备也可以作为译码端(或接收端),第二设备作为编码端(或发送端);本申请对此不作限定。另外,在一次数据传输过程中,假设第一设备是编码端,第二设备是译码端;在另一次数据传输过程中,第一设备可以是译码端,第二设备是编码端,或者第一设备还是编码端,第二设备还是译码端。换句话说,编码端和译码端是针对通信双方而言,在一次通信过程中,通信的一方是编码端,另一方就是译码端。Optionally, the technical solutions provided in this application may be implemented by the first device and the second device. Wherein, the first device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE; the second device may be a network device, such as a base station, or a terminal device, such as a UE. All the embodiments of this application are described with the first device as the encoding end (or sending end), and the second device as the decoding end (or receiving end); however, in practical applications, the first device can also be used as the decoding end The code end (or receiving end), and the second device serves as the encoding end (or sending end); this application does not limit it. In addition, in a data transmission process, it is assumed that the first device is an encoding end, and the second device is a decoding end; in another data transmission process, the first device can be a decoding end, and the second device is an encoding end, or The first device is still the encoding end, and the second device is also the decoding end. In other words, the encoding end and the decoding end are for the two parties in communication. In a communication process, the communicating party is the encoding end, and the other party is the decoding end.
实施例一Embodiment one
本申请实施例一主要介绍在NR协议中引入网络编码的一种可能的数据传输方法,该方法既传输原数据包也传输编码包,并且介绍PDU/SDU经过分割和/或级联操作后得到的原数据非等大小情况下,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。
参见图5,图5是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第一种示意流程图。如图5所示,该数据传输方法包括但不限于以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 5 , FIG. 5 is a first schematic flowchart of a data transmission method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 5, the data transmission method includes but is not limited to the following steps:
S101,第一设备获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系,每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。S101. The first device obtains N first data packets, the N first data packets are equal in size, each first data packet includes a header and data, and the header of each first data packet includes the header of the first data packet The segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the corresponding relationship between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit, and the packet header of each first data packet also includes The data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet.
S102,第一设备传输该N个第一数据包。S102. The first device transmits the N first data packets.
S103,第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包。S103. The first device encodes the N first data packets and adds headers of the encoded packets to obtain M second data packets.
S104,第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。S104. The first device transmits the M second data packets.
可选的,本申请实施例中的第一数据包可以称为原数据包,第二数据包可以称为编码包。原数据包可以理解为未经过网络编码的数据包,编码包可以理解为经过网络编码后的数据包。本申请实施例中的数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the first data packet in this embodiment of the present application may be called an original data packet, and the second data packet may be called an encoded packet. The original data packet can be understood as a data packet that has not undergone network encoding, and the encoded packet can be understood as a data packet that has undergone network encoding. The data unit in this embodiment of the present application is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备对至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)进行分割和/或级联等处理获得N个原数据,再对每个原数据加包头得到第一数据包(即原数据包),其中每个第一数据包的大小都相同。为了降低时延,第一设备可以每得到一个第一数据包就传输该第一数据包,并将该第一数据包缓存在存储器(这里的存储器是指存储空间,比如缓存)中。当该存储器中的第一数据包的个数达到网络编码所需的数据包个数(本申请实施例假设网络编码所需的数据包个数,即数据块大小为N)时,再对该存储器中缓存的N个第一数据包进行网络编码,生成M个编码数据。其中这N个第一数据包的大小相等,这M个编码数据的大小也相等,并且任一个编码数据的大小与任一个第一数据包的大小也相等。第一设备对每个编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包),并传输该第二数据包。M个编码数据加编码包包头后可得到M个第二数据包(即编码包)。其中,本申请对网络编码的方式不做限定,既可以是前述图4所示的随机线性网络编码,也可以是通过编码窗(编码窗的窗长为N)的窗头和窗尾指针的滑动,来实现的卷积网络编码或者块网络编码,这里不展开说明。N和M均为正整数,且M和N的大小关系不做限定,即M可以小于N,也可以大于N,还可以等于N。Optionally, the first device divides and/or concatenates at least one data unit (PDU or SDU) to obtain N original data, and then adds a header to each original data to obtain the first data packet (that is, the original data packet ), where each first packet is the same size. In order to reduce the delay, the first device may transmit the first data packet every time it obtains the first data packet, and cache the first data packet in a memory (here, the memory refers to a storage space, such as a cache). When the number of the first data packets in the memory reaches the number of data packets required for network coding (the embodiment of the present application assumes the number of data packets required for network coding, that is, the size of the data block is N), then the Network coding is performed on the N first data packets buffered in the memory to generate M coded data. The size of the N first data packets is equal, the size of the M encoded data is also equal, and the size of any encoded data is also equal to the size of any first data packet. The first device adds an encoded packet header to each encoded data to obtain a second data packet (that is, an encoded packet), and transmits the second data packet. M second data packets (ie, encoded packets) can be obtained after adding the encoded packet header to the M encoded data. Among them, this application does not limit the way of network coding, it can be the random linear network coding shown in the above-mentioned figure 4, or it can be through the window head and window tail pointer of the coding window (the window length of the coding window is N). Sliding to realize the convolutional network coding or block network coding, which will not be explained here. Both N and M are positive integers, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, that is, M may be smaller than N, larger than N, or equal to N.
可见,第二数据包(即编码包)比第一数据包(即原数据包)多一个编码包包头,即编码包的编码数据和原数据包大小相等,也就是说,本申请实施例传输的编码包(第二数据包)和原数据包(第一数据包)不等大小,一定程度上节约了原数据包的包头开销。It can be seen that the second data packet (i.e., the encoded packet) has one more encoded packet header than the first data packet (i.e., the original data packet), that is, the encoded data of the encoded packet is equal in size to the original data packet, that is to say, the transmission of the embodiment of the present application The encoded packet (second data packet) and the original data packet (first data packet) are not equal in size, which saves the header overhead of the original data packet to a certain extent.
可选的,本申请实施例对上述步骤S102和上述步骤S103的执行顺序不做限定。比如上述步骤S102既可以在上述步骤S103之前执行,也可以在上述步骤S103之后执行,还可以与上述步骤S103同时/并行执行。Optionally, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the execution order of the above step S102 and the above step S103. For example, the above step S102 may be executed before the above step S103, may also be executed after the above step S103, and may also be executed simultaneously/parallelly with the above step S103.
可选的,上述每个第一数据包(即原数据包)包括包头和数据(即上述原数据)。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据(即上述原数据)对应的至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)的分割和级联信息,换句话说,每个原数据包的包头中包括该原数据包的数据与PDU/SDU的映射关系。或者说,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)的对应关系。每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括第一指示信息和数据包标识(Packet ID)字段。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包。数据包标识字段用于指示第一数据包的序列号。应理解,第一数据包的序列号可以按照从小到大顺序编号,或顺序递增。也就是说,第一设备获取到的第一个第一数据包的序列号为1,第二个第一数据包的序列号为2,以此类推。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned first data packets (ie, the original data packet) includes a packet header and data (ie, the above-mentioned original data). The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit (PDU or SDU) corresponding to the data of the first data packet (ie, the above-mentioned original data), in other words, each original data packet The packet header includes the mapping relationship between the data of the original data packet and the PDU/SDU. In other words, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and at least one data unit (PDU or SDU). The header of each first data packet may further include first indication information and a data packet identification (Packet ID) field. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is contained is an original data packet. The data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. It should be understood that the sequence numbers of the first data packets may be numbered sequentially from small to large, or in ascending order. That is to say, the sequence number of the first first data packet acquired by the first device is 1, the sequence number of the second first data packet is 2, and so on.
可选的,上述每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据(这里的编码数据是多个第一数据包经过网络编码后得到)。每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括编码因子字段,还可以包括第二指示信息。第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned second data packets includes an encoded packet header and encoded data (the encoded data here is obtained after network encoding of multiple first data packets). The encoded packet header of each second data packet includes an encoding factor field, and may also include second indication information. The second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet.
可选的,上述步骤S101至步骤S104可以由第一设备中的网络编码(networkcoding,NC)功能子层实现,该NC功能子层还可以用来实现网络编码功能。其中,该NC功能子层可以位于分组数据汇聚协议(packet data convergence protocol,PDCP)层与无线链路控制(radio link control,RLC)层之间,也可以位于RLC层与媒体接入控制(media accesscontrol,MAC)层之间,还可以位于MAC层与物理层(physicallayer,PHY)之间。当考虑NC功能子层时,结合具体的场景,NC功能子层可以在gNB的CU侧,也可以在gNB的DU侧,本申请实施例对此不做限定。或者,可以将NC功能嵌入到具体的某一层中,如可以将NC功能嵌入到自适应回传协议(backhaul adaptation protocol,BAP)层、或PDCP层、或RLC层、或MAC层等,则上述步骤S101至步骤S104可以由第一设备中具有NC功能的层实现。第一设备中具有NC功能的层既可以对协议层的PDU进行网络编码,也可以对SDU进行网络编码。当NC功能嵌入到PDCP层时,该NC功能可以位于头压缩和完整性保护功能之间,也可以位于加密功能之后,添加PDCP头之前。Optionally, the above step S101 to step S104 may be implemented by a network coding (network coding, NC) functional sublayer in the first device, and the NC functional sublayer may also be used to implement the network coding function. Wherein, the NC function sublayer may be located between the packet data convergence protocol (packet data convergence protocol, PDCP) layer and the radio link control (radio link control, RLC) layer, or may be located between the RLC layer and the media access control (media) layer. between the access control (MAC) layers, and may also be located between the MAC layer and the physical layer (physical layer, PHY). When considering the NC function sublayer, in combination with specific scenarios, the NC function sublayer may be on the CU side of the gNB, or on the DU side of the gNB, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. Alternatively, the NC function may be embedded in a specific layer, for example, the NC function may be embedded in a backhaul adaptation protocol (BAP) layer, or a PDCP layer, or an RLC layer, or a MAC layer, etc., then The above step S101 to step S104 may be implemented by a layer having an NC function in the first device. The layer having the NC function in the first device can perform network coding on the PDU of the protocol layer, and can also perform network coding on the SDU. When the NC function is embedded in the PDCP layer, the NC function can be located between the header compression and integrity protection functions, or after the encryption function and before adding the PDCP header.
示例性的,以NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间为例,参见图6,图6是本申请实施例提供的协议栈的示意图。如图6所示,在PDCP和RLC层引入了NC功能子层,来实现网络编码功能。NC功能子层接收PDCP层传输来的PDCP PDU,并将其拆分合并为NC层的SDU(即原数据包的数据),通过加包头H(即原数据包的包头),可以获得包括包头H的NC PDU(即原数据包),并传输到RLC层。对若干个NC PDU进行网络编码,可以得到编码数据,并加编码包头获得包括编码包头的编码包,作为不同于原数据包的NC PDU发送到RLC层。换句话说,RLC层可以接收到两种类型的数据包,一种是NC功能子层传下来的原数据包,另一种是NC功能子层传下来的编码包。NC功能子层传下来的两种NC PDU(或两种数据包)都可以完全兼容RLC层的功能,即RLC层将NC功能子层传下来的NC PDU视为PDCP PDU进行处理和操作。示例性的,协议栈中也可以不单独定义一个NC功能子层,而是对PDCP层的功能进行扩展,保证PDCP层具有NC的前述功能,即对PDCP PDU进行分割和/或级联等操作生成原数据包和编码数据包,均作为NC PDU向RLC层传输。应理解,NC功能子层位于其他层之间、与NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间类似,而NC功能嵌入到某一层中时,NC功能与已有功能进行合并。Exemplarily, it is taken that the NC function sublayer is located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer as an example, see FIG. 6 , which is a schematic diagram of a protocol stack provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 6, the NC function sublayer is introduced in the PDCP and RLC layers to realize the network coding function. The NC function sublayer receives the PDCP PDU transmitted by the PDCP layer, and splits and merges it into the SDU of the NC layer (that is, the data of the original data packet). By adding the header H (that is, the header of the original data packet), the packet header can be obtained. H's NC PDU (that is, the original data packet) and transmit it to the RLC layer. Perform network coding on several NC PDUs to obtain coded data, and add coded headers to obtain coded packets including coded headers, and send them to the RLC layer as NC PDUs different from the original data packets. In other words, the RLC layer can receive two types of data packets, one is the original data packet passed down from the NC functional sublayer, and the other is the encoded packet passed down from the NC functional sublayer. The two types of NC PDUs (or two types of data packets) passed down from the NC function sublayer are fully compatible with the functions of the RLC layer, that is, the RLC layer treats the NC PDUs passed down from the NC function sublayer as PDCP PDUs for processing and operation. Exemplarily, an NC function sublayer may not be defined separately in the protocol stack, but the functions of the PDCP layer may be extended to ensure that the PDCP layer has the aforementioned functions of the NC, that is, operations such as segmentation and/or concatenation of PDCP PDUs Generate the original data packet and the coded data packet, and transmit them to the RLC layer as NC PDU. It should be understood that the NC function sublayer is located between other layers, similar to the NC function sublayer located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer, and when the NC function is embedded in a certain layer, the NC function is merged with the existing function.
为更好地理解上述步骤S101至上述步骤S104所述的流程,下面以一个示例来说明上述步骤S101至上述步骤S104所示的编码端数据传输流程。In order to better understand the process described in the above step S101 to the above step S104, an example is used below to illustrate the data transmission process at the encoding end shown in the above step S101 to the above step S104.
示例性的,参见图7,图7是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第一种示意图。如图7所示,以NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间为例。假设NC功能子层依次接收到PDCP PDU1~4,根据NC功能子层中对原数据包的大小要求(其中原数据包的大小可以是半静态配置,也可以是收端(或译码端、或第二设备)提前告知发端(或编码端、或第一设备)的),对PDCP PDU1~4进行分割和/或级联操作,依次得到原数据包Pkt1~Pkt4的数据(如图7中的Data1~Data4)。再对得到的每个数据添加包头(如图7中的Header),获得包括包头的原数据包;一方面将原数据包作为NC功能子层的NC PDU直接传输至下一层,另一方面将原数据包缓存在NC功能子层的编码器的缓存区(buffer)中。当buffer中的原数据包达到编码器所需的数据包个数时(这里假设编码器所需的数据包个数为4),将buffer中的4个原数据包进行网络编码生成编码数据EData1和EData2。应理解,对4个原数据包进行网络编码生成的编码数据的个数可以小于或等于原数据包的个数,也可以大于原数据包的个数。对每个编码数据添加编码包包头(如图7中的NC_Header),得到包括包头的编码包(如图7中的EPkt1和EPkt2)并作为NC功能子层的PDU进行发送。应理解,发送编码包时可以只发送得到的部分编码包(比如发送EPkt1,不发送EPkt2),也可以发送得到的全部编码包。还应理解,这里分割和/或级联得到的原数据不一定是等大小的,但需要保证每个原数据包(包括数据Data和包头Header)的大小相等,也就是说原数据包的包头Header非等大小。For example, refer to FIG. 7 . FIG. 7 is a first schematic diagram of a data transmission process at an encoding end provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 7 , it is taken as an example that the NC function sublayer is located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer. Assuming that the NC functional sublayer receives PDCP PDU1-4 in sequence, according to the size requirements of the original data packet in the NC functional sublayer (the size of the original data packet can be semi-statically configured, or it can be the receiving end (or decoding end, or the second device) to inform the sender (or the encoding end, or the first device) in advance), to divide and/or concatenate PDCP PDU1-4, and obtain the data of the original data packets Pkt1-Pkt4 in sequence (as shown in Figure 7 Data1~Data4). Then add a header to each data obtained (Header as shown in Figure 7), and obtain the original data packet including the header; on the one hand, the original data packet is directly transmitted to the next layer as the NC PDU of the NC function sublayer, on the other hand The original data packet is cached in the buffer area (buffer) of the encoder of the NC function sublayer. When the original data packets in the buffer reach the number of data packets required by the encoder (here, it is assumed that the number of data packets required by the encoder is 4), network encode the 4 original data packets in the buffer to generate encoded data EData1 and EData2. It should be understood that the number of encoded data generated by performing network encoding on the four original data packets may be less than or equal to the number of original data packets, and may also be greater than the number of original data packets. Add a coded packet header (such as NC_Header in Figure 7) to each coded data to obtain coded packets including the header (such as EPkt1 and EPkt2 in Figure 7) and send it as a PDU of the NC function sublayer. It should be understood that when sending the encoded packets, only part of the obtained encoded packets may be sent (for example, EPkt1 is sent and EPkt2 is not sent), or all the obtained encoded packets may be sent. It should also be understood that the original data obtained by splitting and/or concatenating here are not necessarily equal in size, but it is necessary to ensure that the size of each original data packet (including data Data and header Header) is equal, that is to say, the header of the original data packet Header is not equal in size.
可见,本申请实施例提供了一种NR协议栈下的网络编码方案,保证了NC功能子层或NC功能与其他层的适配和兼容性,并通过在获得原数据包(即上述第一数据包)后一方面直接发送原数据包来保证接收端的低延时,即接收端可以基于接收到的原数据包恢复出NC功能子层的上一层PDU,即接收端正确接收。另一方面将原数据包缓存在编码器的buffer中等待进行网络编码(这是因为buffer中的原数据包需要达到编码器所需的数据包个数),在网络编码后发送冗余编码包,因为冗余编码包的编码数据可以恢复出原数据包(这是因为编码数据是由原数据包经过网络编码后得到),并且原数据包中有完整的包头信息,所以即使在传输过程中多个原数据包丢失,也可以根据冗余编码包恢复出原数据包,再根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,对原数据包的数据进行分割和级联的逆处理,从而恢复出上一层的PDU/SDU数据。因此,本申请实施例不仅可以在现有NR协议中支持网络编码技术,还可以降低时延;此外,即使在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application provides a network coding scheme under the NR protocol stack, which ensures the adaptation and compatibility between the NC function sublayer or the NC function and other layers, and obtains the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first Data packet) On the other hand, the original data packet is directly sent to ensure the low delay of the receiving end, that is, the receiving end can recover the upper layer PDU of the NC function sub-layer based on the received original data packet, that is, the receiving end receives it correctly. On the other hand, cache the original data packets in the buffer of the encoder and wait for network encoding (this is because the original data packets in the buffer need to reach the number of data packets required by the encoder), and send redundant encoded packets after network encoding , because the encoded data of the redundant encoded packet can restore the original data packet (this is because the encoded data is obtained by the original data packet after network encoding), and the original data packet has complete header information, so even in the transmission process If multiple original data packets are lost, the original data packets can also be recovered according to the redundant coded packets, and then the data of the original data packets can be segmented and concatenated according to the segmentation and concatenation information carried in the header of the original data packets. Thereby recovering the PDU/SDU data of the upper layer. Therefore, the embodiment of the present application can not only support the network coding technology in the existing NR protocol, but also reduce the delay; in addition, even when multiple original data packets are lost, the PDU or SDU can be recovered to reduce performance loss.
上述内容详细阐述了编码端的数据传输流程,为了保证译码端能够根据正确接收的原数据包和编码包恢复出PDU/SDU,下面将结合编码端的数据传输流程详细介绍第一数据包(即原数据包)的包头和第二数据包(即编码包)的编码包包头的实现方式。其中,第一数据包中包头的格式可采用下述实现方式1.1至实现方式1.4中任一种,实现方式1.1至实现方式1.4也可以任一组合形成新的实现方式且所涉及概念或方案相同或相似的部分可以相互参考或组合。第二数据包中编码包包头的格式可采用下述实现方式2.1和实现方式2.2中任一种,实现方式2.1至实现方式2.2也可以任一组合形成新的实现方式且所涉及概念或方案相同或相似的部分可以相互参考或组合。The above content elaborates the data transmission process of the encoding end in detail. In order to ensure that the decoding end can recover the PDU/SDU according to the correctly received original data packet and encoded packet, the following will introduce the first data packet in detail in combination with the data transmission process of the encoding end. data packet) and the second data packet (that is, the coded packet) of the coded packet header. Wherein, the format of the packet header in the first data packet can adopt any of the following implementations 1.1 to 1.4, and any combination of implementations 1.1 to 1.4 can also be used to form a new implementation and the concepts or solutions involved are the same or similar parts may be mutually referenced or combined. The format of the encoded packet header in the second data packet can adopt any of the following implementation methods 2.1 and 2.2, and any combination of implementation methods 2.1 to 2.2 can also be used to form a new implementation method, and the concepts or solutions involved are the same or similar parts may be mutually referenced or combined.
1、第一数据包的包头1. The header of the first data packet
可选的,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,为便于描述,下文将第一数据包中的数据称为原数据,也就是说本申请实施例中“原数据”与“第一数据包(原数据包)中的数据”可替换使用。一个第一数据包的数据包括一个或多个数据段,一个数据段包括一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。换句话说,原数据包中的数据包括一个或多个数据段,每个数据段来自不同的PDU/SDU,一个数据段是一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。参见图8,图8是本申请实施例提供的PDU/SDU与第一数据包的数据的映射关系示意图。如图8所示,图8示出了两种典型的PDU/SDU与原数据的映射关系。第一种典型的PDU/SDU与原数据的映射关系如图8的8a所示,一个PDU/SDU被分割成多个原数据;第二种典型的PDU/SDU与原数据的映射关系如图8的8b所示,多个PDU/SDU的全部或部分构成一个原数据。Optionally, each first data packet includes a header and data. For the convenience of description, the data in the first data packet is referred to as original data hereinafter, that is to say, "original data" and "first data" in this embodiment of the application "Data in the packet (original data packet)" can be used instead. The data of a first data packet includes one or more data segments, and one data segment includes all or part of a PDU/SDU. In other words, the data in the original data packet includes one or more data segments, each data segment comes from a different PDU/SDU, and a data segment is all or part of a PDU/SDU. Referring to FIG. 8 , FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of a mapping relationship between a PDU/SDU and data in a first data packet provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 8, FIG. 8 shows the mapping relationship between two typical PDUs/SDUs and original data. The first typical mapping relationship between PDU/SDU and original data is shown in 8a of Figure 8, one PDU/SDU is divided into multiple original data; the second typical mapping relationship between PDU/SDU and original data is shown in Figure 8 As shown in 8b of 8, all or part of multiple PDUs/SDUs constitute one original data.
可选的,图8示出的映射关系中第一数据包包括的数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号顺序递增,但实际应用中第一数据包包括的数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号也可以乱序。应理解,第一数据包包括的数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号顺序递减,与顺序递增的方式类似,此处不再展开说明。参见图9,图9是本申请实施例提供的PDU/SDU与第一数据包中的数据段的位置关系示意图。其中,图9针对上述图8的8b情况,即图9针对多个PDU/SDU的全部或部分构成一个原数据(第一数据包的数据)的情况。如图9的9a所示,第一数据包的数据中数据段的排列方式可以按照PDU/SDU的序列号大小,从小到大排列,即序列号最小的PDU/SDU作为第一个数据段,中间数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号依次增加,序列号最大的PDU/SDU作为最后一个数据段。应理解,图9的9a所示与上述图8的8b所示的映射关系相同。如图9的9b所示,第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号可以乱序排列,比如第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号分别是1,3,4,2。此时,第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU就是PDU/SDU 1,最后一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU就是PDU/SDU2。应理解,图9的9b仅是示例,第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号还可以有其他排列方式,如3,1,4,2或1,4,2,3等等。Optionally, the sequence number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment included in the first data packet in the mapping relationship shown in FIG. Numbers can also be out of order. It should be understood that the serial number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment included in the first data packet is decremented sequentially, which is similar to the manner of sequentially incremented, and no further description is given here. Referring to FIG. 9, FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of the positional relationship between the PDU/SDU and the data segment in the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. Wherein, Fig. 9 is directed to the case of 8b in Fig. 8 above, that is, Fig. 9 is directed to the case where all or part of multiple PDUs/SDUs form one original data (data of the first data packet). As shown in 9a of Figure 9, the arrangement of the data segments in the data of the first data packet can be arranged according to the size of the serial number of the PDU/SDU, from small to large, that is, the PDU/SDU with the smallest serial number is used as the first data segment, The serial number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the middle data segment increases sequentially, and the PDU/SDU with the largest serial number is taken as the last data segment. It should be understood that the mapping relationship shown in 9a of FIG. 9 is the same as that shown in 8b of FIG. 8 above. As shown in 9b of Figure 9, the serial numbers of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet can be arranged out of order, for example, the serial numbers of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet are respectively 1,3,4,2. At this time, the PDU/SDU corresponding to the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is PDU/
下面结合图8所示的映射关系和图9所示的位置关系,对第一数据包的包头的实现方式进行详细说明。The implementation of the header of the first data packet will be described in detail below in combination with the mapping relationship shown in FIG. 8 and the positional relationship shown in FIG. 9 .
实现方式1.1Implementation method 1.1
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识(Packet ID)字段、以及分割和级联信息,可选的还包括第一指示信息。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是原始/编码(original/coded,O/C)字段,应理解,第一指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。第一数据包的包头中Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第一数据包(原数据包)的序列号(sequence number,SN)。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和块标识(Block ID)字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。块标识(Block ID)字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification (Packet ID) field, segmentation and concatenation information, and optionally also includes first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet, and the representation form of the first indication information in the header may be an original/coded (O/C) field, It should be understood that the first indication information may also be expressed as a field with another name, and this embodiment of the present application does not limit the name of the field. The Packet ID field in the packet header of the first data packet is used to indicate the sequence number (sequence number, SN) of the first data packet (original data packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a block identification (Block ID) field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). A block identification (Block ID) field is used to indicate an identification of a data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该第一数据包的数据中的最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。应理解,当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9a所示,则该第一数据包的包头既可以选择指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段和/或最后一个数据段对应的数据单元是否被分割,也可以选择指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割。当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9b所示,则该第一数据包的包头选择指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating the data unit corresponding to the first data segment (or start data segment) and/or the last data segment (or end data segment) in the data of the first data packet Whether the information is divided, or the information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided; the data indicating that the first data packet includes Whether the i-th data segment of the first data packet is the last data segment in the data of the first data packet (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . It should be understood that when the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9a of FIG. 9 , the header of the first data packet You can choose to indicate whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment and/or the last data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided, or you can choose to indicate the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet Whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number is split. When the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9b of Figure 9, the selection of the header of the first data packet indicates the Whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided.
应理解,本申请中“指示…是否…的信息”可以通过若干个比特,如1比特,来指示,当这若干个比特所取的不同值可以分别指出“是”和“否”的情况。“指示……长度的信息”可以通过该长度的具体值,或者,通过和该长度对应的索引来指示,也即,本申请中的“指示”可以为显式指示,也可以为隐式指示,本申请不做限定。It should be understood that the "information indicating whether..." in this application can be indicated by several bits, such as 1 bit, when the different values taken by these several bits can respectively indicate "yes" and "no". "Information indicating the length" can be indicated by a specific value of the length, or by an index corresponding to the length, that is, the "instruction" in this application can be an explicit indication or an implicit indication , which is not limited in this application.
下面通过几个示例来介绍在实现方式1.1下第一数据包中包头的几种可能格式。Several possible formats of the packet header in the first data packet in the implementation mode 1.1 are introduced below through several examples.
示例1:参见图10a,图10a是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图一。如图10a所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,开始分段(Segment_start,S_start)字段和/或结束分段(Segment_end,S_end)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extensionbit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段以及Block ID字段。Example 1: Refer to FIG. 10a, which is a first schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 10a, the header of the first data packet includes: Packet ID field, start segment (Segment_start, S_start) field and/or end segment (Segment_end, S_end) field, one or more extension bits (extensionbit, indicating is the E) field, and one or more length (length, L) fields; optionally including the O/C field, the Type field, and the Block ID field.
其中,因为编码端(上述第一设备)既传输了原数据包(即上述第一数据包)也传输了编码包(即上述第二数据包),所以为了区分原数据包和编码包,可以引入1bit的O/C字段。当该O/C字段的取值为0时,表示该O/C字段所在的数据包是原数据包,当该O/C字段的取值为1时,表示该O/C字段所在的数据包是编码包;或者,当该O/C字段的取值为1时,表示该O/C字段所在的数据包是原数据包,当该O/C字段的取值为0时,表示该O/C字段所在的数据包是编码包。应理解,本申请实施例中第一数据包的包头包括的O/C字段设置为第一值(比如0),用来指示该O/C字段所在的第一数据包是原数据包。Wherein, because the coding end (the above-mentioned first device) not only transmits the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) but also transmits the coded packet (that is, the above-mentioned second data packet), so in order to distinguish the original data packet and the coded packet, you can Introduce 1bit O/C field. When the value of the O/C field is 0, it means that the data packet where the O/C field is located is the original data packet; when the value of the O/C field is 1, it means that the data packet where the O/C field is located The packet is an encoded packet; or, when the value of the O/C field is 1, it means that the data packet in which the O/C field is located is the original data packet; when the value of the O/C field is 0, it means that the The packet where the O/C field is located is an encoded packet. It should be understood that in the embodiment of the present application, the O/C field included in the header of the first data packet is set to a first value (such as 0), which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the O/C field is located is the original data packet.
Type字段是可选字段,表示数据包的SN范围或Packet ID字段长度,比如,1bit可以表征两种长度的SN或Packet ID字段长度,2bit表征四种长度的SN或Packet ID字段长度。示例性的,以Type字段的长度为1比特为例,Type字段取值为0时,表示Packet ID字段的长度为6bit;Type字段取值为1时,表示Packet ID字段的长度为14bit。The Type field is an optional field, indicating the SN range of the data packet or the length of the Packet ID field. For example, 1 bit can represent the length of the SN or Packet ID field of two lengths, and 2 bits can represent the length of the SN or Packet ID field of four lengths. Exemplarily, taking the length of the Type field as 1 bit as an example, when the value of the Type field is 0, it means that the length of the Packet ID field is 6 bits; when the value of the Type field is 1, it means that the length of the Packet ID field is 14 bits.
Packet ID字段用于表示该Packet ID字段所在数据包的序列号,数据包的序列号范围可根据Type字段确定。当Packet ID字段的长度为n bit时,序列号范围是0~2n-1。The Packet ID field is used to indicate the serial number of the data packet where the Packet ID field is located, and the range of the serial number of the data packet can be determined according to the Type field. When the length of the Packet ID field is n bits, the sequence number ranges from 0 to 2n -1.
Block ID字段是可选字段,表示数据块的标识(identifier,ID)。这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。The Block ID field is an optional field, and represents an identifier (identifier, ID) of a data block. This data block includes the first data packet where the Block ID field is located.
一种实现方式中,S_start字段的长度为1bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否被分割,或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU中序列号最小的PDU/SDU是否被分割。换句话说,S_start字段可以用来判断原数据包的数据部分起始数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否被分割,以使接收端(或译码端,或第二设备)恢复时确定是否需要级联。其中,S_start字段取值为0,表示未被分割,S_start字段取值为1,表示被分割;或者,S_start字段取值为1,表示未被分割,S_start字段取值为0,表示被分割。In one implementation, the length of the S_start field is 1 bit, which is used to indicate whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided, or to indicate the data segment in the data of the first data packet Whether the PDU/SDU with the smallest sequence number in the corresponding PDU/SDU is divided. In other words, the S_start field can be used to determine whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the initial data segment of the data part of the original data packet is segmented, so that the receiving end (or the decoding end, or the second device) can determine whether a stage is needed when recovering. couplet. Wherein, the value of the S_start field is 0, indicating that it is not divided, and the value of the S_start field is 1, indicating that it is divided; or, the value of the S_start field is 1, indicating that it is not divided, and the value of the S_start field is 0, indicating that it is divided.
另一种实现方式中,S_start字段的长度为1bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否完整(完整即未被分割,不完整即为被分割,被分割就表示第一个数据段是一个PDU/SDU的部分),或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU中序列号最小的PDU/SDU是否完整。In another implementation, the length of the S_start field is 1 bit, which is used to indicate whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided, Being segmented means that the first data segment is part of a PDU/SDU), or it is used to indicate whether the PDU/SDU with the smallest sequence number in the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is complete.
一种实现方式中,S_end字段的长度为1bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中最后一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否被分割,或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU中序列号最大的PDU/SDU是否被分割。换句话说,S_end字段可以用来判断原数据包的数据部分末尾数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否被分割,以使接收端(或译码端,或第二设备)恢复时确定是否需要级联。其中,S_end字段取值为0,表示未被分割,S_start字段取值为1,表示被分割;或者,S_end字段取值为1,表示未被分割,S_end字段取值为0,表示被分割。应理解,第一数据包的包头中可以只存在S_start字段和S_end字段中的一个,也可以两个字段都存在。In one implementation, the length of the S_end field is 1 bit, which is used to indicate whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the last data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided, or to indicate whether the data segment in the data of the first data packet corresponds to Whether the PDU/SDU with the largest sequence number among the PDUs/SDUs is divided. In other words, the S_end field can be used to determine whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment at the end of the data part of the original data packet is segmented, so that the receiving end (or decoding end, or the second device) can determine whether concatenation is required when recovering . Wherein, the value of the S_end field is 0, indicating that it is not divided, and the value of the S_start field is 1, indicating that it is divided; or, the value of the S_end field is 1, indicating that it is not divided, and the value of the S_end field is 0, indicating that it is divided. It should be understood that only one of the S_start field and the S_end field may exist in the packet header of the first data packet, or both fields may exist.
另一种实现方式中,S_end字段的长度为1bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中最后一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU是否完整(完整即未被分割,不完整即为被分割,被分割就表示最后一个数据段是一个PDU/SDU的部分且是该PDU/SDU的前部分),或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的PDU/SDU中序列号最大的PDU/SDU是否完整。In another implementation, the length of the S_end field is 1 bit, which is used to indicate whether the PDU/SDU corresponding to the last data segment in the data of the first data packet is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided, and is Segmentation means that the last data segment is part of a PDU/SDU and is the front part of the PDU/SDU), or used to indicate the PDU/SDU with the largest sequence number in the PDU/SDU corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet Whether the SDU is complete.
一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段表示为E1,E2,E3,…,EDnum。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数。E1表示第一数据包的数据中第1个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,或者第一数据包的数据中第1个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段;E2表示第一数据包的数据中第2个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,或者第一数据包的数据中第2个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段;E3表示第一数据包的数据中第3个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,或者第一数据包的数据中第3个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段;以此类推。Ei表示第一数据包的数据中第i个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,或者第一数据包的数据中第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段,i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。其中,每个扩展比特字段的长度为1bit。当该1bit取值为0时,表示是最后一个数据段或不存在下一个数据段,第一数据包的包头再累计一个长度字段后结束;当该1bit取值为1时,表示不是最后一个数据段或存在下一个数据段,第一数据包的包头也累计一个L字段,之后第一数据包的包头还会累计下一个E字段和对应的L字段。或者反之,即当该1bit取值为1时,表示是最后一个数据段或不存在下一个数据段,第一数据包的包头再累计一个长度字段后结束;当该1bit取值为0时,表示不是最后一个数据段或存在下一个数据段,第一数据包的包头也累计一个L字段,之后第一数据包的包头还会累计下一个E字段和对应的L字段。应理解,每个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段后都紧跟一个长度(length,L)字段。One or more extension bit (extension bit, denoted as E) fields are denoted as E1, E2, E3, . . . , EDnum . Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet. E1 indicates whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment, or whether there is a next data segment after the first data segment in the data of the first data packet; E2 indicates the data of the first data packet Whether the second data segment in the data is the last data segment, or whether there is a next data segment after the second data segment in the data of the first data packet; E3 indicates whether the third data segment in the data of the first data packet is The last data segment, or whether there is a next data segment after the third data segment in the data of the first data packet; and so on. Ei indicates whether the i-th data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment, or whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment in the data of the first data packet, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . Wherein, the length of each extended bit field is 1 bit. When the value of this 1 bit is 0, it means that it is the last data segment or there is no next data segment, and the header of the first data packet will end after accumulating a length field; when the value of this 1 bit is 1, it means that it is not the last one The data segment may have a next data segment, and the packet header of the first data packet also accumulates an L field, and then the packet header of the first data packet also accumulates the next E field and the corresponding L field. Or vice versa, that is, when the value of the 1 bit is 1, it means that it is the last data segment or there is no next data segment, and the header of the first data packet will end after accumulating a length field; when the value of the 1 bit is 0, Indicates that it is not the last data segment or there is a next data segment. The header of the first data packet also accumulates an L field, and then the header of the first data packet also accumulates the next E field and the corresponding L field. It should be understood that each extension bit (extension bit, denoted as E) field is followed by a length (length, L) field.
一个或多个长度(length,L)字段表示为L1,L2,L3,…,LDnum。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数。L1表示第一数据包的数据中第1个数据段的长度;L2表示第一数据包的数据中第2个数据段的长度;L3表示第一数据包的数据中第3个数据段的长度;以此类推。Li表示第一数据包的数据中第i个数据段的长度,i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。应理解,如果第一数据包的总长度可以确定,第一数据包的包头长度也可以确定,则i的取值可以是1≤i≤Dnum-1,也就是说,第一数据包的包头中可以指示Dnum-1个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该第一数据包的总长度、该第一数据包的包头长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。可见,此种方式可以节省一个长度字段,节省开销。One or more length (length, L) fields are represented as L1, L2, L3, . . . , LDnum . Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet. L1 represents the length of the first data segment in the data of the first data packet; L2 represents the length of the second data segment in the data of the first data packet; L3 represents the length of the third data segment in the data of the first data packet ; and so on. Li represents the length of the i-th data segment in the data of the first data packet, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . It should be understood that if the total length of the first data packet can be determined, and the header length of the first data packet can also be determined, then the value of i can be 1≤i≤Dnum -1, that is, the first data packet The length of Dnum -1 data segments can be indicated in the header, and the length of the remaining data segment can be determined by the total length of the first data packet, the length of the header of the first data packet and the length of Dnum -1 data segments The length is calculated. It can be seen that this method can save a length field and save overhead.
应理解,图10a仅是示例,图10a中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图10a中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should be understood that FIG. 10a is only an example, and the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 10a may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 10a are also not limited.
示例2:参见图10b,图10b是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图二。如图10b所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,分段信息(segmentinformation,SI)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。Example 2: Refer to FIG. 10b. FIG. 10b is a second schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 10b, the header of the first data packet includes: a Packet ID field, a segment information (segmentinformation, SI) field, one or more extension bit (extension bit, denoted as E) fields, and one or more length (length, L) field; optionally includes O/C field, Type field and Block ID field.
其中,图10b中SI字段的长度为2bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段和最后一个数据段对应的数据单元是否被分割,或者该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割。比如,当SI字段为00(十进制0)时,表示第一个数据段和最后一个数据段对应的数据单元都没有被分割(或者表示序列号最大和序列号最小的数据单元都没有被分割);当SI字段为01(十进制1)时,表示第一个数据段对应的数据单元被分割(或序列号最小的数据单元被分割),最后一个数据段对应的数据单元没有被分割(或序列号最大的数据单元没有被分割);当SI字段为10(十进制2)时,表示第一个数据段对应的数据单元没有被分割(或序列号最小的数据单元没有被分割),最后一个数据段对应的数据单元被分割(或序列号最大的数据单元被分割);当SI字段为11(十进制3)时,表示第一个数据段和最后一个数据段对应的数据单元都被分割(或者表示序列号最大和序列号最小的数据单元都没有被分割)。又如,当SI字段为11(十进制3)时,表示第一个数据段和最后一个数据段对应的数据单元都没有被分割(或者表示序列号最大和序列号最小的数据单元都没有被分割);当SI字段为10(十进制2)时,表示第一个数据段对应的数据单元被分割(或序列号最小的数据单元被分割),最后一个数据段对应的数据单元没有被分割(或序列号最大的数据单元没有被分割);当SI字段为01(十进制1)时,表示第一个数据段对应的数据单元没有被分割(或序列号最小的数据单元没有被分割),最后一个数据段对应的数据单元被分割(或序列号最大的数据单元被分割);当SI字段为00(十进制0)时,表示第一个数据段和最后一个数据段对应的数据单元都被分割(或者表示序列号最大和序列号最小的数据单元都没有被分割)。应理解,本申请实施例对SI字段的取值和含义的对应关系不做限定。Among them, the length of the SI field in Figure 10b is 2 bits, which is used to indicate whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment and the last data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided, or whether the data in the data of the first data packet Whether the data units with the largest serial number and the smallest serial number among the data units corresponding to the segment are divided. For example, when the SI field is 00 (decimal 0), it means that the data units corresponding to the first data segment and the last data segment are not divided (or the data units with the largest serial number and the smallest serial number are not divided) ; When the SI field is 01 (decimal 1), it means that the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is divided (or the data unit with the smallest serial number is divided), and the data unit corresponding to the last data segment is not divided (or the sequence The data unit with the largest number has not been divided); when the SI field is 10 (decimal 2), it means that the data unit corresponding to the first data segment has not been divided (or the data unit with the smallest serial number has not been divided), and the last data The data unit corresponding to the segment is divided (or the data unit with the largest serial number is divided); when the SI field is 11 (decimal 3), it means that the data units corresponding to the first data segment and the last data segment are divided (or Indicates that neither the data unit with the largest serial number nor the smallest serial number is split). For another example, when the SI field is 11 (decimal 3), it means that the data units corresponding to the first data segment and the last data segment have not been divided (or the data units with the largest serial number and the smallest serial number have not been divided. ); when the SI field is 10 (decimal 2), it means that the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is divided (or the data unit with the smallest serial number is divided), and the data unit corresponding to the last data segment is not divided (or The data unit with the largest serial number has not been divided); when the SI field is 01 (decimal 1), it means that the data unit corresponding to the first data segment has not been divided (or the data unit with the smallest serial number has not been divided), and the last The data unit corresponding to the data segment is divided (or the data unit with the largest serial number is divided); when the SI field is 00 (decimal 0), it means that the data units corresponding to the first data segment and the last data segment are divided ( Or it means that neither the data unit with the largest sequence number nor the smallest sequence number is split). It should be understood that the embodiment of the present application does not limit the correspondence between the values and meanings of the SI field.
第一数据包的包头中其他字段(O/C字段,Packet ID字段,一个或多个扩展比特(表示为E)字段,一个或多个长度字段,Type字段,Block ID字段)的含义参考前述图10a中相应字段的含义,此处不再赘述。The meaning of other fields (O/C field, Packet ID field, one or more extended bits (expressed as E) field, one or more length fields, Type field, Block ID field) in the header of the first data packet refers to the aforementioned The meanings of the corresponding fields in FIG. 10a will not be repeated here.
应理解,图10b仅是示例,图10b中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图10b中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should be understood that FIG. 10b is only an example, and the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 10b may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 10b are also not limited.
可见,实现方式1.1中为每一个数据段都设置1bit的扩展比特字段来指示该数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段设置一个长度字段来指示其长度,有利于译码端根据原数据包的包头的指示对原数据进行分割和级联,以恢复出一个或多个PDU/SDU。另外,实现方式1.1通过2个比特分别指示第一数据包的数据中起始数据段和末尾数据段对应的数据单元是否被分割,可以节省开销。It can be seen that in the implementation mode 1.1, a 1-bit extended bit field is set for each data segment to indicate whether the data segment is the last data segment, and a length field is set for each data segment to indicate its length, which is beneficial to the decoding end The original data is segmented and concatenated according to the header of the original data packet to recover one or more PDUs/SDUs. In addition, in the implementation mode 1.1, 2 bits are used to respectively indicate whether the data units corresponding to the start data segment and the end data segment in the data of the first data packet are divided, which can save overhead.
实现方式1.2Implementation method 1.2
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识(Packet ID)字段、以及分割和级联信息,可选的还包括第一指示信息。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第一指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。第一数据包的包头中Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第一数据包(原数据包)的序列号(SN)。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和块标识(Block ID)字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。块标识(Block ID)字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification (Packet ID) field, segmentation and concatenation information, and optionally also includes first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet, and the representation form of the first indication information in the packet header may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the first indication information may also be For fields with other names, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the names of the fields. The Packet ID field in the packet header of the first data packet is used to indicate the sequence number (SN) of the first data packet (original data packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a block identification (Block ID) field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). A block identification (Block ID) field is used to indicate an identification of a data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元的序列号,或者该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该第一数据包的数据中最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。应理解,当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9a所示,则该第一数据包的包头既可以选择指示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段和/或最后一个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号,也可以选择指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号。当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9b所示,则该第一数据包的包头选择指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: the data unit corresponding to the first data segment (or initial data segment) and/or the last data segment (or last data segment) in the data of the first data packet Sequence number, or the maximum sequence number and/or minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet; indicating whether the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet is the first data Information about the last data segment in the data of the packet (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . It should be understood that when the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9a of FIG. 9 , the header of the first data packet Either the serial number indicating the data unit corresponding to the first data segment and/or the last data segment in the data of the first data packet can be selected, or the serial number indicating the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet can be selected. Maximum serial number and/or minimum serial number. When the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9b of Figure 9, the selection of the header of the first data packet indicates the The maximum sequence number and/or the minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet.
参见图11,图11是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图三。如图11所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,开始序列号(SN_begin)字段和/或结束序列号(SN_end)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。Referring to FIG. 11 , FIG. 11 is a third schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 11, the header of the first data packet includes: Packet ID field, start sequence number (SN_begin) field and/or end sequence number (SN_end) field, one or more extension bits (extension bit, expressed as E) field, and one or more length (length, L) fields; optionally including O/C field, Type field and Block ID field.
其中,SN_begin字段用于表示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号,或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最小序列号。换句话说,SN_begin字段可以用来指示原数据包的数据部分起始段对应的PDU/SDU的SN。Wherein, the SN_begin field is used to indicate the sequence number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the first data segment in the data of the first data packet, or is used to indicate the minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet. In other words, the SN_begin field can be used to indicate the SN of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the beginning segment of the data part of the original data packet.
SN_end字段用于表示第一数据包的数据中最后一个数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号,或者用于表示第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号。换句话说,SN_end字段可以用来指示原数据包的数据部分末尾段对应的PDU/SDU的SN。应理解,第一数据包的包头中可以只存在SN_begin字段和SN_end字段中的一个,也可以两个字段都存在。The SN_end field is used to indicate the sequence number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the last data segment in the data of the first data packet, or to indicate the maximum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet. In other words, the SN_end field can be used to indicate the SN of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the end segment of the data part of the original data packet. It should be understood that only one of the SN_begin field and the SN_end field may exist in the packet header of the first data packet, or both fields may exist.
可选的,SN_begin字段和SN_end字段可以替换成一个或多个序列号字段。这一个或多个序列号字段表示为SN1,SN2,SN3,…,SNDnum。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数。一个序列号字段表示第一数据包的数据中一个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号。SN1表示第一数据包的数据中第1个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号;SN2表示第一数据包的数据中第2个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号;SN3表示第一数据包的数据中第3个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号;以此类推。SNi表示第一数据包的数据中第i个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号,i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。换句话说,上述分割和级联信息包括的不再是第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段和/或最后一个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号,或者该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元的最大序列号和/或最小序列号;而是第一数据包的数据中每个数据段对应的数据单元的序列号。Optionally, the SN_begin field and the SN_end field can be replaced with one or more sequence number fields. The one or more sequence number fields are denoted as SN1, SN2, SN3, . . . , SNDnum . Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet. A sequence number field indicates a sequence number of a data unit corresponding to a data segment in the data of the first data packet. SN1 represents the serial number of the data unit corresponding to the first data segment in the data of the first data packet; SN2 represents the serial number of the data unit corresponding to the second data segment in the data of the first data packet; SN3 represents the first data packet The sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the third data segment in the data; and so on. SNi represents the sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the i-th data segment in the data of the first data packet, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum . In other words, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes no longer the serial number of the data unit corresponding to the first data segment and/or the last data segment in the data of the first data packet, or the data of the first data packet The maximum sequence number and/or the minimum sequence number of the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the middle; but the sequence number of the data unit corresponding to each data segment in the data of the first data packet.
还应理解,第一数据包的包头中其他字段(O/C字段,Packet ID字段,一个或多个扩展比特(表示为E)字段,一个或多个长度字段,Type字段,Block ID字段)的含义可参考前述图10a中相应字段的描述,此处不再赘述。It should also be understood that other fields (O/C field, Packet ID field, one or more extended bits (expressed as E) field, one or more length fields, Type field, Block ID field) in the header of the first data packet For the meaning of , refer to the description of the corresponding fields in FIG. 10a above, and details are not repeated here.
应理解,图11仅是示例,图11中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图11中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should be understood that FIG. 11 is only an example, and the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 11 may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 11 are also not limited.
可见,实现方式1.2通过在包头中指示起始数据段和/或末尾数据段对应的PDU/SDU的序列号,可以指示出多个第一数据包的数据中数据段是否来自不同的PDU/SDU,以使译码端能够将不同的数据段组合成完整的PDU/SDU。It can be seen that the implementation mode 1.2 can indicate whether the data segments in the data of multiple first data packets come from different PDUs/SDUs by indicating the sequence number of the PDU/SDU corresponding to the start data segment and/or the end data segment in the packet header , so that the decoding end can combine different data segments into a complete PDU/SDU.
实现方式1.3Implementation method 1.3
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识(Packet ID)字段、以及分割和级联信息,可选的还包括第一指示信息。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第一指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。第一数据包的包头中Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第一数据包(原数据包)的序列号(SN)。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和块标识(Block ID)字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。块标识(Block ID)字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification (Packet ID) field, segmentation and concatenation information, and optionally also includes first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet, and the representation form of the first indication information in the packet header may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the first indication information may also be For fields with other names, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the names of the fields. The Packet ID field in the packet header of the first data packet is used to indicate the sequence number (SN) of the first data packet (original data packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a block identification (Block ID) field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). A block identification (Block ID) field is used to indicate an identification of a data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该第一个数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该第一数据包的数据中最后一个数据段(或者说,该第一数据包的数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该第一数据包的数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment (or in other words, after the first data segment in the data of the first data packet Whether there is a next data segment) and whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided); indicates the i-th data included in the first data packet Whether the first data segment is the last data segment in the data of the first data packet (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the data of the first data packet); and indicating the i-th data segment Information about the length of a data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the data of the first data packet, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
参见图12,图12是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图四。如图12所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,扩展比特0(extension bit 0,表示为E0)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。Referring to FIG. 12 , FIG. 12 is a fourth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 12, the header of the first data packet includes: a Packet ID field, an extension bit 0 (extension bit 0, expressed as E0) field, one or more extension bits (extension bit, expressed as E) fields, and a or multiple length (length, L) fields; optionally including O/C field, Type field and Block ID field.
其中,扩展比特0(表示为E0)字段的长度为2bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段是否是最后一个数据段和该第一个数据段对应的数据单元是否完整。换句话说,E0字段表示原数据包的数据部分起始数据段后是否存在下一个数据段以及该起始数据段是否完整。比如,当E0字段为00(十进制0)时,表示第一个数据段是最后一个数段段(即不包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元完整;当E0字段为01(十进制1)时,表示表示第一个数据段是最后一个数段段(即不包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元不完整;当E0字段为10(十进制2)时,表示表示第一个数据段不是最后一个数段段(即包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元完整;当E0字段为11(十进制3)时,表示表示第一个数据段不是最后一个数段段(即包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元不完整。应理解,本申请实施例对E0字段的取值和含义的对应关系不做限定,即E0字段的取值和含义可以有其他对应关系。又如,当E0字段为11(十进制3)时,表示第一个数据段是最后一个数段段(即不包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元完整;当E0字段为10(十进制2)时,表示表示第一个数据段是最后一个数段段(即不包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元不完整;当E0字段为01(十进制1)时,表示表示第一个数据段不是最后一个数段段(即包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元完整;当E0字段为00(十进制0)时,表示表示第一个数据段不是最后一个数段段(即包含下一个数据段),且该第一个数据段对应的数据单元不完整。Wherein, the length of the extended bit 0 (expressed as E0) field is 2 bits, which is used to indicate whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment and whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete . In other words, the E0 field indicates whether there is a next data segment after the initial data segment of the data part of the original data packet and whether the initial data segment is complete. For example, when the E0 field is 00 (decimal 0), it means that the first data segment is the last number segment (that is, the next data segment is not included), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete; when the E0 field When it is 01 (decimal 1), it means that the first data segment is the last number segment (that is, the next data segment is not included), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is incomplete; when the E0 field is 10 ( In decimal 2), it means that the first data segment is not the last number segment (that is, contains the next data segment), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete; when the E0 field is 11 (decimal 3), Indicates that the first data segment is not the last number segment (that is, contains the next data segment), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is incomplete. It should be understood that the embodiment of the present application does not limit the corresponding relationship between the value and meaning of the E0 field, that is, the value and meaning of the E0 field may have other corresponding relationships. As another example, when the E0 field is 11 (decimal 3), it means that the first data segment is the last number segment (that is, the next data segment is not included), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete; when E0 When the field is 10 (decimal 2), it means that the first data segment is the last number segment (that is, the next data segment is not included), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is incomplete; when the E0 field is 01 (decimal 1), it means that the first data segment is not the last segment (that is, contains the next data segment), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is complete; when the E0 field is 00 (decimal 0) , indicating that the first data segment is not the last number segment (that is, contains the next data segment), and the data unit corresponding to the first data segment is incomplete.
应理解,因为E0字段已经指示了第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段是否是最后一个数据段,所以图12所示包头的扩展比特(表示为E)字段可从E2开始,长度字段仍然从L1开始,且L1字段位于E0字段后。还应理解,第一数据包的包头中其他字段(O/C字段,Packet ID字段,一个或多个扩展比特(表示为E)字段,一个或多个长度字段,Type字段,Block ID字段)的含义参考前述图10a中相应字段的含义,此处不再赘述。It should be understood that because the E0 field has indicated whether the first data segment in the data of the first data packet is the last data segment, the extended bit (expressed as E) field of the header shown in Figure 12 can start from E2, and the length field It still starts from L1, and the L1 field is located after the E0 field. It should also be understood that other fields (O/C field, Packet ID field, one or more extended bits (expressed as E) field, one or more length fields, Type field, Block ID field) in the header of the first data packet For the meaning of , please refer to the meanings of the corresponding fields in FIG. 10 a , which will not be repeated here.
应理解,图12仅是示例,图12中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图12中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should be understood that FIG. 12 is only an example, and the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 12 may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 12 are also not limited.
可见,实现方式1.3通过2比特来指示第一数据包的数据中起始数据段和末尾数据段对应的数据单元是否完整,并为每个数据段都设置1bit的扩展比特字段来指示该数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段设置一个长度字段来指示其长度,有利于译码端根据原数据包的包头的指示对原数据进行分割和级联,以恢复出一个或多个PDU/SDU。It can be seen that the implementation mode 1.3 uses 2 bits to indicate whether the data units corresponding to the start data segment and the end data segment in the data of the first data packet are complete, and set a 1-bit extended bit field for each data segment to indicate the data segment Whether it is the last data segment, and a length field is set for each data segment to indicate its length, which is beneficial for the decoding end to divide and concatenate the original data according to the indication of the header of the original data packet, so as to recover one or more PDU/SDU.
实现方式1.4Implementation method 1.4
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识(Packet ID)字段、以及分割和级联信息,可选的还包括第一指示信息。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第一指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。第一数据包的包头中Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第一数据包(原数据包)的序列号(SN)。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和块标识(Block ID)字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。块标识(Block ID)字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the header of each first data packet includes a data packet identification (Packet ID) field, segmentation and concatenation information, and optionally also includes first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet, and the representation form of the first indication information in the packet header may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the first indication information may also be For fields with other names, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the names of the fields. The Packet ID field in the packet header of the first data packet is used to indicate the sequence number (SN) of the first data packet (original data packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a block identification (Block ID) field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). A block identification (Block ID) field is used to indicate an identification of a data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
可选的,上述分割和级联信息包括:指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段(或起始数据段)和/或最后一个数据段(或末尾数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段的个数(记为Dnum)的信息;以及指示每个数据段的长度的信息。应理解,当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9a所示,则该第一数据包的包头既可以选择指示该第一数据包的数据中第一个数据段和/或最后一个数据段对应的数据单元是否被分割,也可以选择指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割。当第一数据包的数据包括多个数据段时,如果这多个数据段与数据单元(PDU/SDU)的位置关系如图9的9b所示,则该第一数据包的包头指示该第一数据包的数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割。还应理解,如果第一数据包的总长度可以确定,第一数据包的包头长度也可以确定,则上述分割和级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该第一数据包的总长度、该第一数据包的包头长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Dnum表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段总数。Optionally, the above segmentation and concatenation information includes: indicating the data unit corresponding to the first data segment (or start data segment) and/or the last data segment (or end data segment) in the data of the first data packet Whether it is divided, or information indicating whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided; information on the number of included data segments (denoted as Dnum ); and information indicating the length of each data segment. It should be understood that when the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9a of FIG. 9 , the header of the first data packet You can choose to indicate whether the data unit corresponding to the first data segment and/or the last data segment in the data of the first data packet is divided, or you can choose to indicate the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the data of the first data packet Whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number is split. When the data of the first data packet includes a plurality of data segments, if the positional relationship between the plurality of data segments and the data unit (PDU/SDU) is as shown in 9b of Figure 9, the header of the first data packet indicates the first Whether the data unit with the largest sequence number and/or the smallest sequence number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the data of a data packet is divided. It should also be understood that if the total length of the first data packet can be determined, and the length of the header of the first data packet can also be determined, then the above-mentioned segmentation and concatenation information can only include the number of each data segment in theDnum -1 data segments Length, instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be passed through the total length of the first data packet, the header length of the first data packet and Dnum -1 The length of the data segment is calculated. Dnum represents the total number of data segments included in the data of the first packet.
参见图13,图13是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图五。如图13所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,S_start字段和/或S_end字段,分段数(segmentnumber,表示为Seg_N)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。Referring to FIG. 13 , FIG. 13 is a fifth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 13, the header of the first data packet includes: Packet ID field, S_start field and/or S_end field, segment number (segmentnumber, expressed as Seg_N) field, and one or more length (length, L) fields ; Optionally include O/C field, Type field and Block ID field.
其中,Seg_N字段的长度可以为4bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数(记为Dnum)。4bit可以表示十进制数值0-15,其最大可指示16个数据段。比如,Seg_N字段取值为0时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为1(即Dnum=1);Seg_N字段取值为1时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为2(即Dnum=2);Seg_N字段取值为2时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为3(即Dnum=3),以此类推,Seg_N字段取值为15时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为16(即Dnum=16),即Dnum=Seg_N字段的值+1。或者,Seg_N字段取值为0时,表示预留;Seg_N字段取值为1时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为1(即Dnum=1);Seg_N字段取值为2时,表示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数为2(即Dnum=2),以此类推,即Dnum=Seg_N字段的值。应理解,一个数据段来自于一个PDU/SDU,不同数据段来自于不同PDU/SDU,所以Seg_N字段还可以理解为第一数据包的数据所对应的PDU/SDU个数。还应理解,包头中长度字段的个数等于Seg_N字段指示的数据段个数。Wherein, the length of the Seg_N field may be 4 bits, which is used to indicate the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet (denoted as Dnum ). 4bit can represent the decimal value 0-15, and it can indicate a maximum of 16 data segments. For example, when the value of the Seg_N field is 0, it means that the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet is 1 (that is, Dnum =1); when the value of the Seg_N field is 1, it means that the data of the first data packet includes The number of data segments included is 2 (i.e. Dnum =2); when the value of the Seg_N field is 2, it means that the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet is 3 (i.e. Dnum =3), so By analogy, when the value of the Seg_N field is 15, it means that the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet is 16 (that is, Dnum =16), that is, Dnum =the value of the
应理解,O/C字段,Packet ID字段,S_start字段和S_end字段,一个或多个长度字段,Type字段,以及Block ID字段的含义参考前述图10a中相应字段的含义,此处不再赘述。It should be understood that, for the meanings of the O/C field, Packet ID field, S_start field and S_end field, one or more length fields, Type field, and Block ID field, refer to the meanings of the corresponding fields in FIG. 10a, and will not be repeated here.
应理解,图13仅是示例,图13中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图13中第一数据包的包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should be understood that FIG. 13 is only an example, and the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 13 may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the first data packet in FIG. 13 are also not limited.
可见,实现方式1.4中通过Seg_N字段来指示第一数据包的数据中包括的数据段个数,无需针对每个数据段都设置一个扩展比特(表示为E)字段来指示其是否是最后一个数据段,可以节省开销。It can be seen that in the implementation mode 1.4, the Seg_N field is used to indicate the number of data segments included in the data of the first data packet, and there is no need to set an extended bit (denoted as E) field for each data segment to indicate whether it is the last data segment, which saves overhead.
2、第二数据包的编码包包头2. The encoded packet header of the second data packet
实现方式2.1Implementation method 2.1
可选的,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。编码数据是多个原数据包经过网络编码后得到。每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息、以及编码因子字段(如系数标识(Coeff ID)字段),可选的还包括第二指示信息。其中,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。该第二指示信息在编码包包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第二指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息可以包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,则用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息包括编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、和编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中的至少一项即可。编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)的长度为8bit,用于指示255行码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。应理解,本申请中编码因子字段与Coeff ID字段可相互替换使用。Optionally, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. The encoded data is obtained by network encoding of multiple original data packets. The encoded packet header of each second data packet includes identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet, and a coding factor field (such as a coefficient identification (Coeff ID) field), optional It also includes second indication information. Wherein, the second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. The form of the second indication information in the header of the encoded packet may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the second indication information may also be expressed as a field with another name, and the embodiment of the present application does not limit the name of the field. The identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet may include at least two of the following items: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, and the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window , the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. It should be understood that if the window length of the encoding window is configured semi-statically, the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet includes the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window , and at least one of the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. The encoding factor field (such as the Coeff ID field) has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the row index of the 255-row codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, or the like. It should be understood that in this application, the encoding factor field and the Coeff ID field can be used interchangeably.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和Packet ID字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a Packet ID field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located.
其中,因为原数据包(第一数据包)的包头中携带有自己的序列号,编码包(第二数据包)的编码包包头中既可以携带自己的序列号,也可以不携带自己的序列号,所以针对序列号的实现方式有以下几种:(1)编码包的编码包包头中不携带序列号,即编码包包头中不存在Packet ID字段,此时原数据包(第一数据包)的序列号顺序编号。(2)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套编号系统),且编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号不重复;比如原数据包的序列号为1-20,编码包的序列号从21开始顺序递增。(3)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号分别有自己的一套编号系统,互不影响。(4)编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号都顺序编号(共用一套序列号),且允许编码包的序列号与原数据包的序列号重复使用,可使用O/C字段来区分原数据包和编码包。比如,原数据包的序列号为1-20,编码包的序列号为11-15。Wherein, because the header of the original data packet (the first data packet) carries its own serial number, the encoded packet header of the encoded packet (the second data packet) can either carry its own serial number or not carry its own sequence number, so there are several implementations for the serial number as follows: (1) The encoded packet header of the encoded packet does not carry the serial number, that is, there is no Packet ID field in the encoded packet header. At this time, the original data packet (the first data packet ) serial numbers are numbered sequentially. (2) The serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of numbering system), and the serial number of the encoded packet is not repeated with the serial number of the original data packet; for example, the serial number of the original data packet is 1-20, the serial number of the coded package increases sequentially from 21. (3) The sequence number of the encoded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet have their own set of numbering systems respectively, which do not affect each other. (4) The serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are numbered sequentially (share a set of serial numbers), and the serial number of the encoded packet and the serial number of the original data packet are allowed to be reused, and the O/C field can be used to Distinguish between raw data packets and encoded packets. For example, the sequence numbers of the original data packets are 1-20, and the sequence numbers of the encoded packets are 11-15.
参见图14,图14是本申请实施例提供的编码包包头的第一种示意图。如图14所示,编码包包头包括:系数标识(Coeff ID)字段,以及窗长(Window Length,表示为Win_L)字段、网络编码数据包开始(NC_Packet_Start)字段、网络编码数据包结束(NC_Packet_End)字段中至少两个;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Packet ID字段。Referring to FIG. 14 , FIG. 14 is a schematic diagram of the first type of encoded packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 14, the coded packet header includes: a coefficient identification (Coeff ID) field, a window length (Window Length, expressed as Win_L) field, a network coding data packet start (NC_Packet_Start) field, a network coding data packet end (NC_Packet_End) At least two fields; optional O/C field, Type field and Packet ID field.
其中,本申请实施例中编码包包头包括的O/C字段设置为第二值(比如1),用来指示该O/C字段所在的第二数据包是原数据包。Type字段和Packet ID字段的含义可参考前述图10a中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。如果编码包包头中不存在Type字段,则Packet ID字段的长度可以为8bit。Coeff ID字段的长度为8bit,用于表示255行码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。Wherein, in the embodiment of the present application, the O/C field included in the header of the encoded packet is set to a second value (such as 1), which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the O/C field is located is the original data packet. For the meanings of the Type field and the Packet ID field, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the preceding FIG. 10a , which will not be repeated here. If the Type field does not exist in the header of the encoded packet, the length of the Packet ID field can be 8 bits. The length of the Coeff ID field is 8 bits, and is used to represent the row index of the 255-row codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, or the like.
窗长(表示为Win_L)字段的长度为8bit,用于表示编码窗的窗长,或者说表示用于网络编码的数据块的大小。其中,编码窗的窗长或用于网络编码的数据块的大小,以数据包为粒度,8bit最多表示255个数据包,即编码窗的窗长最大为255个数据包,或者用于网络编码的数据块的大小最大为255个数据包。The length of the window length (represented as Win_L) field is 8 bits, and is used to indicate the window length of the encoding window, or in other words, the size of the data block used for network encoding. Among them, the window length of the encoding window or the size of the data block used for network encoding is based on the data packet as the granularity, and 8 bits represent at most 255 data packets, that is, the maximum window length of the encoding window is 255 data packets, or it is used for network encoding The size of the data block is at most 255 packets.
NC_Packet_Start字段的长度为8bit,用于表示编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号。The NC_Packet_Start field has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the sequence number of the first first data packet in the coding window.
NC_Packet_End字段的长度为8bit,用于表示编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。The NC_Packet_End field has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the sequence number of the last first data packet in the coding window.
应理解,NC_Packet_Start字段、NC_Packet_End字段、Win_L字段中三者有其二即可唯一确定编码窗中的原数据包。如果Win_L字段半静态配置,则有NC_Packet_Start字段和NC_Packet_End字段中任一个即可。It should be understood that any two of the NC_Packet_Start field, the NC_Packet_End field, and the Win_L field can uniquely determine the original data packet in the encoding window. If the Win_L field is configured semi-statically, any one of the NC_Packet_Start field and the NC_Packet_End field is sufficient.
还应理解,图14仅是示例,图14中编码包包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图14中编码包包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should also be understood that FIG. 14 is only an example, and the fields included in the encoded packet header in FIG. 14 may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the encoded packet in FIG. 14 are also not limited.
可见,实现方式2.1中重新设计一种编码包包头的格式,以支持译码端的正确译码。It can be seen that in the implementation mode 2.1, a format of the header of the encoded packet is redesigned to support correct decoding at the decoding end.
实现方式2.2Implementation method 2.2
可选的,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。编码数据是多个原数据包经过网络编码后得到。每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息、以及编码因子字段(如系数标识(Coeff ID)字段),可选的还包括第二指示信息。其中,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。该第二指示信息在编码包包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第二指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息在编码包包头中的表现形式可以是块标识(Block ID)字段。Optionally, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. The encoded data is obtained by network encoding of multiple original data packets. The encoded packet header of each second data packet includes identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet, and a coding factor field (such as a coefficient identification (Coeff ID) field), optional It also includes second indication information. Wherein, the second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. The form of the second indication information in the header of the encoded packet may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the second indication information may also be expressed as a field with another name, and the embodiment of the present application does not limit the name of the field. The form of the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet in the header of the encoded packet may be a block identification (Block ID) field.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括类型(Type)字段和Packet ID字段中的一项或多项。类型(Type)字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may further include one or more items of a type (Type) field and a Packet ID field. The type (Type) field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet, such as 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent 4 The length of SN (or Packet ID field length). The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located.
参见图15,图15是本申请实施例提供的编码包包头的第二种示意图。如图15所示,编码包包头包括:系数标识(Coeff ID)字段,以及块标识(Block ID)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Packet ID字段。其中,O/C字段、Type字段、以及Packet ID字段的含义可参考前述图10a中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Coeff ID字段的含义可参考前述图14中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Block ID字段用于表示数据块的标识,这个数据块用于编码得到该Block ID字段所在的第二数据包。Referring to FIG. 15 , FIG. 15 is a second schematic diagram of the encoded packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 15 , the coded packet header includes: a coefficient identification (Coeff ID) field, and a block identification (Block ID) field; optionally includes an O/C field, a Type field and a Packet ID field. For the meanings of the O/C field, the Type field, and the Packet ID field, reference may be made to the corresponding description in FIG. 10 a , and details are not repeated here. For the meaning of the Coeff ID field, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the aforementioned FIG. 14 , which will not be repeated here. The Block ID field is used to indicate the identifier of the data block, and this data block is used to encode the second data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
还应理解,图15仅是示例,图15中编码包包头包括的各个字段还可以有其他名称,本申请实施例对此不做限定。图15中编码包包头包括的各个字段的长度和排列顺序也不做限定。It should also be understood that FIG. 15 is only an example, and the fields included in the encoded packet header in FIG. 15 may also have other names, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The length and sequence of the fields included in the header of the encoded packet in FIG. 15 are also not limited.
可见,实现方式2.2中通过复用原有编码包包头中的Coeff ID字段、Block ID字段、Type字段、以及Packet ID字段,并新增一个O/C字段来指示数据包的种类(编码包还是原数据包),不仅可以保证译码端的正确译码,还可以提高兼容性。It can be seen that in the implementation mode 2.2, the Coeff ID field, the Block ID field, the Type field, and the Packet ID field in the original encoded packet header are reused, and an O/C field is added to indicate the type of the data packet (encoded packet or Original data packet), not only can ensure the correct decoding of the decoding end, but also can improve compatibility.
可选的,虽然第一设备分别传输了N个第一数据包(即原数据包)和M个第二数据包(即编码包),但因为干扰、噪声等因素,第一设备传输的数据包不一定都能被第二设备正确接收,也就是说,在传输过程中可能发生丢包的情况。所以,当第二设备接收到至少N个正确且线性无关的数据包时,才能正确译码并恢复出N个第一数据包。Optionally, although the first device has respectively transmitted N first data packets (ie, original data packets) and M second data packets (ie, coded packets), due to factors such as interference and noise, the data transmitted by the first device The packets may not all be correctly received by the second device, that is, packet loss may occur during transmission. Therefore, when the second device receives at least N correct and linearly independent data packets, it can correctly decode and restore the N first data packets.
下面详细介绍译码端的数据传输流程。The following describes the data transmission process at the decoding end in detail.
S105,第二设备获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。S105. The second device acquires P data packets, where the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets.
S106,第二设备对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。S106. The second device decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets.
S107,第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。S107. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,第二设备接收到P个数据包,或从存储空间(如buffer)中读取到P个数据包,P是正整数,且大于或等于N。可见,当P等于N时,可以减少冗余开销。应理解,第二设备可以一次性接收到P个数据包,将其按序存储在存储空间中;也可以分多次接收,将每次接收到的数据包按序存储在存储空间中。在接收到的数据包个数等于P后,可执行译码操作,即步骤S106。Optionally, the second device receives P data packets, or reads P data packets from a storage space (such as a buffer), where P is a positive integer greater than or equal to N. It can be seen that when P is equal to N, redundancy overhead can be reduced. It should be understood that the second device may receive P data packets at one time and store them in the storage space in sequence; it may also receive in multiple times and store the data packets received each time in the storage space in sequence. After the number of received data packets is equal to P, the decoding operation can be performed, that is, step S106.
可选的,因为原数据包的包头和编码包包头的解析方式不相同,所以第二设备在解析原数据包的包头和编码包包头获得其中的信息之前,判断接收到的P个数据包中哪些是原数据包哪些是编码包。第二设备判断接收到的数据包是编码包还是原数据包的方式有两种:Optionally, because the headers of the original data packets and the headers of the encoded packets are parsed in different ways, the second device judges the received P packets before analyzing the headers of the original data packets and the headers of the encoded packets to obtain the information therein. Which are original data packets and which are encoded packets. There are two ways for the second device to judge whether the received data packet is an encoded packet or an original data packet:
一种实现方式中,第二设备比较P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与编码包长度阈值L1的大小关系。如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度等于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(即编码包)。如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包)。或者,第二设备比较P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与该原数据包长度阈值L2的大小关系。如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于或等于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包)。如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度大于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(即编码包)。其中,编码包长度阈值L1可以是预设的,也可以是半静态配置的,还可以收发双方提前协商的。同理,原数据包长度阈值L2可以是预设的,也可以是半静态配置的,还可以收发双方提前协商的。In an implementation manner, the second device compares the size relationship between the length of each of the P data packets and the encoded packet length threshold L1. If the length of a certain data packet among the P data packets is equal to the coded packet length threshold L1, it is determined that the data packet is the second data packet (ie, a coded packet). If the length of a certain data packet among the P data packets is smaller than the coded packet length threshold L1, it is determined that the data packet is the first data packet (ie, the original data packet). Alternatively, the second device compares the size relationship between the length of each of the P data packets and the original data packet length threshold L2. If the length of a certain data packet among the P data packets is less than or equal to the original data packet length threshold L2, it is determined that the data packet is the first data packet (ie, the original data packet). If the length of a certain data packet among the P data packets is greater than the original data packet length threshold L2, it is determined that the data packet is the second data packet (ie, an encoded packet). Wherein, the coded packet length threshold L1 may be preset, may also be configured semi-statically, or may be negotiated in advance by the sending and receiving parties. Similarly, the original data packet length threshold L2 can be preset, semi-statically configured, or negotiated in advance between the sending and receiving parties.
另一种实现方式中,如果上述第一数据包的包头和上述第二数据包的编码包包头中均携带指示信息(即O/C字段),则第二设备针对P个数据包中的每个数据包,可以读取该数据包的第一个比特(即O/C字段),确定该数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包)还是第二数据包(即编码包)。In another implementation, if both the header of the first data packet and the header of the encoded packet of the second data packet carry indication information (that is, the O/C field), the second device for each of the P data packets A data packet, the first bit of the data packet (ie the O/C field) can be read to determine whether the data packet is the first data packet (ie the original data packet) or the second data packet (ie the coded packet).
如果该数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包),则第二设备采用原数据包的解析方式解析该数据包的包头,获得该数据包的序列号。如果该数据包是第二数据包(即编码包),则第二设备采用编码包的解析方式解析该数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段(即CoeffID字段)和用于指示编码得到该数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。K和P均为正整数,且K小于或等于P。第二设备按照该K个第一数据包的序列号从小到大排序、该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示、以及任一个第二数据包的包头中用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息,构成系数因子矩阵。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。第二设备采用该系数因子矩阵对P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。应理解,译码得到的N-K个第一数据包和K个第一数据包加起来就是N个第一数据包。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据部分对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。第二设备再根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将这N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。其中,K小于或等于N。用于指示编码得到该数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是Block ID字段,或包括编码窗的窗长、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、以及编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中至少两项。If the data packet is the first data packet (ie, the original data packet), the second device parses the packet header of the data packet by using the analysis method of the original data packet, and obtains the serial number of the data packet. If the data packet is a second data packet (i.e., a coded packet), the second device uses the parsing method of the coded packet to parse the coded packet header of the data packet, obtains the coding factor field (ie, the CoeffID field) and is used to indicate that the code is obtained by obtaining the coded packet. Identification information of the first N data packets of the data packets. Wherein, the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets. Each first data packet includes a packet header and data, and each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. Both K and P are positive integers, and K is less than or equal to P. The second device sorts the sequence numbers of the K first data packets from small to large, the indication of the encoding factor field in the header of the encoded packet of the P-K second data packets, and the indication in the header of any second data packet The identification information of the N first data packets of the second data packet is obtained by encoding to form a coefficient factor matrix. The rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The second device jointly decodes the coded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets by using the coefficient factor matrix to obtain decoded N-K first data packets. It should be understood that the N-K first data packets obtained by decoding and the K first data packets add up to N first data packets. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data part of the first data packet, and the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate that the data of the first data packet is related to the at least one Correspondence between data units. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets. Wherein, K is less than or equal to N. The identification information used to indicate the first N data packets encoded to obtain the data packet is the Block ID field, or includes the window length of the encoding window, the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window, and the last block in the encoding window. There are at least two items in the sequence number of a first data packet.
为更好地理解上述步骤S105至上述步骤S107所述的流程,下面以一个示例来说明上述步骤S105至上述步骤S107所示的译码端数据传输流程。In order to better understand the process described in the above step S105 to the above step S107, an example is used below to illustrate the data transmission process at the decoding end shown in the above step S105 to the above step S107.
示例性的,参见图16,图16是本申请实施例提供的译码端数据传输流程示意图。当编码端(即第一设备)对N个原数据包进行编码并加编码包包头,得到M个编码包,发送给译码端(即第二设备)。这里假设由于信道衰落、干扰等因素,原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3丢失。相应地,译码端(即第二设备)可以判断出原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3错误被擦除或者丢失,其判断方式可以是译码端(即第二设备)未接收到序列号为2和3的原数据包。这里还假设M=2,P=N。因此,译码端(即第二设备)可以通过接收正确的原数据包和编码包进行联合译码,恢复出丢失的原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3。如图16所示,因为编码端(即第一设备)总共传输的原数据包个数为N,在传输过程中原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3错误被擦除,所以还需要接收正确的至少2个编码包(如图16中的EPkt1和EPkt2)来联合接收正确的N-2个原数据包进行译码。如果编码包包头按照前述实现方式2.1设计,假设编码包包头包括编码窗的窗长和编码窗中起始原数据包的序列号,则译码端(即第二设备)解析每个编码包(如图16中的EPkt1和EPkt2)的编码包包头,获取编码窗的窗长(即Win_L字段,可半静态配置,即不在编码包包头中携带)和编码窗中起始原数据包的序列号、以及Coeff ID字段。如果编码包包头按照前述实现方式2.2设计,包括Block ID字段,则译码端(即第二设备)解析每个编码包(如图16中的EPkt1和EPkt2)的编码包包头,获取Block ID字段以及Coeff ID字段。译码端(即第二设备)再解析每个原数据包获取每个原数据包的序列号,并根据N-2个原数据包的序列号和2个编码包的Coeff ID字段,构造系数因子矩阵(如图16所示的系数因子矩阵,该系数因子矩阵的列从左到右对应原数据包的序列号从小到大排列)。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)为N。译码端(即第二设备)再对每个编码包进行去编码包包头的操作,获取每个编码包的编码数据,再根据系数因子矩阵对编码包的编码数据和原数据包进行排序,保证系数因子矩阵与其的对应关系(如图16中接收正确的数据包)。译码端(即第二设备)采用高斯消元等典型译码算法译码,恢复出丢失的原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3。译码端(即第二设备)对译码后的原数据包(即图16中的Pkt2和Pkt3)解析包头获取分割和级联信息,并对接收正确的N-2个原数据包解析包头获取分割和级联信息,去除N个原数据包中每个原数据包的包头,根据每个原数据包的包头中的分割和级联信息,对N个原数据包的数据进行分割和级联的逆向操作,构成一个或多个PDCP PDU/SDU。图16中,Header表示原数据包的包头,Data表示原数据,NC_Header表示编码包包头,EData表示编码数据,Pkt表示原数据包,EPkt表示编码包。For example, refer to FIG. 16 , which is a schematic diagram of a data transmission process at the decoding end provided by an embodiment of the present application. When the encoding end (ie, the first device) encodes N original data packets and adds encoded packet headers, M encoded packets are obtained and sent to the decoding end (ie, the second device). It is assumed here that the original data packets Pkt2 and Pkt3 are lost due to factors such as channel fading and interference. Correspondingly, the decoding end (i.e. the second device) can judge that the original data packets Pkt2 and Pkt3 are erased or lost by mistake, and the judgment method can be that the decoding end (i.e. the second device) does not receive the
可选的,由于传输过程中的丢包问题,译码端(即第二设备)可能译码成功,也可能译码失败,这里针对译码成功和译码失败这两种情况分别设计反馈消息。针对译码端译码成功(比如,译码端正确恢复出丢失的原数据包)的情况,译码端(即第二设备)可以采用1比特来反馈确认(acknowledge,ACK)信息。针对译码端译码失败(比如,译码端无法正确恢复出丢失的原数据包)的情况,译码端(即第二设备)反馈需要重传的编码包个数、和译码的原数据包范围。Optionally, due to the packet loss problem during transmission, the decoding end (that is, the second device) may succeed in decoding or fail in decoding. Here, feedback messages are designed for the two cases of successful decoding and decoding failure. . For the situation that the decoding end succeeds in decoding (for example, the decoding end recovers the lost original data packet correctly), the decoding end (that is, the second device) may use 1 bit to feed back acknowledgment (acknowledge, ACK) information. For the situation where the decoding end fails to decode (for example, the decoding end cannot correctly recover the lost original data packet), the decoding end (that is, the second device) feeds back the number of encoded packets that need to be retransmitted, and the original number of decoded packets. packet range.
其中,译码端(即第二设备)可通过反馈秩(rank)数,或者需要的rank数(比如,采用6bit来指示,可指示最多64个包)来指示需要重传的编码包个数。rank数,表示译码端(即第二设备)正确接收到的数据包个数,P减去rank数即为需要重传的编码包个数。需要的rank数可用于直接指示需要重传的编码包个数。Among them, the decoding end (that is, the second device) can indicate the number of encoded packets that need to be retransmitted by feeding back the rank number, or the required rank number (for example, using 6 bits to indicate, which can indicate up to 64 packets) . The rank number indicates the number of data packets correctly received by the decoding end (that is, the second device), and P minus the rank number is the number of encoded packets that need to be retransmitted. The required rank number can be used to directly indicate the number of encoded packets that need to be retransmitted.
一种实现方式中,译码的原数据包范围可通过编码窗的窗长(该变量可半静态配置,可通过8bit进行指示)、编码窗中起始原数据包(即第一数据包)的序列号、编码窗中末尾原数据包(即第一数据包)的序列号中任意两项进行指示。应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,译码的原数据包范围可通过编码窗中起始原数据包的序列号、编码窗中末尾原数据包的序列号中的任一项联合编码窗的窗长来指示,或者直接通过编码窗中起始原数据包和末尾原数据包的序列号来指示。还应理解,对于编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号共用一套编号的情况,译码端(即第二设备)在反馈译码的原数据包范围时,将一串连续编号中编码包的序列号剔除,只指示原数据包的序列号。对于编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号分别用一套编号的情况,译码端(即第二设备)在反馈译码的原数据包范围时,只需关注原数据包的编号范围即可。In one implementation, the range of the decoded original data packet can be determined by the window length of the encoding window (this variable can be configured semi-statically and can be indicated by 8 bits), the initial original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) in the encoding window Any two of the sequence number and the sequence number of the original data packet at the end of the encoding window (that is, the first data packet) are indicated. It should be understood that if the window length of the coding window is semi-statically configured, the range of the original data packet to be decoded can be determined by any one of the sequence number of the original data packet at the beginning of the coding window and the sequence number of the original data packet at the end of the coding window It can be indicated by the window length of the joint encoding window, or directly by the sequence numbers of the initial original data packet and the end original data packet in the encoding window. It should also be understood that, for the case where the sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet share a set of numbers, when the decoding end (i.e. the second device) feeds back the range of the decoded original data packet, it will include a series of consecutive numbers The sequence number of the encoded packet is removed, and only the sequence number of the original data packet is indicated. For the case where the sequence number of the coded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet use a set of numbers respectively, the decoding end (that is, the second device) only needs to pay attention to the number range of the original data packet when feeding back the range of the decoded original data packet That's it.
另一种实现方式中,如果编码包包头中存在block ID字段,译码的原数据包范围可通过block ID字段进行反馈。此时可以省去编码窗的窗长、编码窗中起始原数据包和末尾原数据包的序列号。In another implementation manner, if there is a block ID field in the header of the encoded packet, the range of the decoded original data packet can be fed back through the block ID field. At this time, the window length of the encoding window, the sequence numbers of the initial original data packet and the end original data packet in the encoding window can be omitted.
可选的,如果编码包(即第二数据包)与原数据包(即第一数据包)分开独立编号,即编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号采用两套编号系统,则编码端(即第一设备)仅允许原数据包进入编码器的缓存区(buffer)。此时,译码端(即第二设备)可以维护两个buffer,一个buffer用来存储原数据包,另一个buffer用来存储编码包。译码端(即第二设备)也可以仅维护一个buffer,通过O/C字段对数据包的类型进行区分。Optionally, if the encoded packet (i.e. the second data packet) is numbered independently from the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet), that is, the sequence number of the encoded packet and the sequence number of the original data packet adopt two sets of numbering systems, then the encoding The end (that is, the first device) only allows the original data packet to enter the buffer area (buffer) of the encoder. At this time, the decoding end (that is, the second device) can maintain two buffers, one buffer is used to store the original data packet, and the other buffer is used to store the encoded packet. The decoding end (that is, the second device) may also maintain only one buffer, and distinguish the types of data packets through the O/C field.
如果编码包(即第二数据包)与原数据包(即第一数据包)联合顺序编号,即编码包的序列号和原数据包的序列号共用一套编号系统,则编码端(即第一设备)仅对原数据包进行编码。If the encoding packet (i.e. the second data packet) and the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) are sequentially numbered, that is, the sequence number of the encoding packet and the sequence number of the original data packet share a set of numbering system, then the encoding end (i.e. the first data packet) A device) only encodes the original data packet.
可选的,编码端(即第一设备)既可以是基站,也可以是UE;译码端(即第二设备)既可以是UE,也可以是基站。当编码端(即第一设备)和译码端(即第二设备)中一端是基站,另一端是UE时,基站可在UE的上行传输之前,通过无线资源控制(radio resource control,RRC)消息或者MAC控制元素(MAC Control Element,MAC CE)消息指示UE上行传输的编码策略。该RRC消息或MAC CE消息可以指示UE的编码方式,如bit级编码还是包级编码;或者指示不同的编码方案,如块编码还是卷积网络编码。Optionally, the coding end (that is, the first device) can be either a base station or a UE; the decoding end (that is, the second device) can be either a UE or a base station. When one of the encoding end (that is, the first device) and the decoding end (that is, the second device) is a base station, and the other end is a UE, the base station may use radio resource control (radio resource control, RRC) before the uplink transmission of the UE. The message or the MAC Control Element (MAC Control Element, MAC CE) message indicates the UE uplink transmission coding policy. The RRC message or MAC CE message may indicate the encoding method of the UE, such as bit-level encoding or packet-level encoding; or indicate different encoding schemes, such as block encoding or convolutional network encoding.
可见,本申请实施例提供了原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头和编码包包头的字段设计,并通过译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并且根据原数据包的包头携带的分割和级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application provides the header of the original data packet (i.e. the first data packet) and the field design of the header of the encoded packet, and through the decoding process and operation, it is hoped that the data packet received by the decoding end has a full rank (rank= In the case of N), the original data packet can be correctly decoded, and the PDU/SDU can be recovered according to the segmentation and concatenation information carried in the header of the original data packet, thereby reducing the performance loss of the NR system.
实施例二Embodiment two
本申请实施例二主要介绍在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如NR协议中,引入网络编码的另一种可能的数据传输方法,该方法只传输编码包,并且介绍PDU/SDU经过分割和/或级联操作后得到的原数据非等大小情况下,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。
应理解,本申请实施例二的整体流程与前述实施例一的整体流程类似,不同之处在于:本申请实施例二对原数据包进一步封装编码包包头,确保传输的所有数据包的大小相等。换句话说,本申请实施例二只传输编码包,不传输原数据包。It should be understood that the overall process of the second embodiment of the present application is similar to the overall process of the aforementioned first embodiment, the difference is that the second embodiment of the present application further encapsulates the encoded header of the original data packet to ensure that all transmitted data packets are of equal size . In other words, in
参见图17,图17是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第二种示意流程图。如图17所示,该数据传输方法包括但不限于以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 17 , FIG. 17 is a second schematic flowchart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 17, the data transmission method includes but is not limited to the following steps:
S201,第一设备获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。S201. The first device obtains N first data packets, the N first data packets are equal in size, each first data packet includes a header and data, and the header of each first data packet includes the header of the first data packet The segmentation and concatenation information of the at least one data unit corresponding to the data, where the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit.
S202,第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。S202. The first device encodes the N first data packets and adds encoded packet headers to obtain M second data packets, where the encoded packet headers include a coding factor field.
S203,第一设备传输该M个第二数据包,其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。S203. The first device transmits the M second data packets, where the first data packets are original data packets and the second data packets are encoded packets.
可选的,本申请实施例中的第一数据包可以称为原数据包,第二数据包可以称为编码包。原数据包可以理解为未经过网络编码的数据包,编码包可以理解为经过网络编码后的数据包。本申请实施例中的数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the first data packet in this embodiment of the present application may be called an original data packet, and the second data packet may be called an encoded packet. The original data packet can be understood as a data packet that has not undergone network encoding, and the encoded packet can be understood as a data packet that has undergone network encoding. The data unit in this embodiment of the present application is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备对至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)进行分割和/或级联等处理获得N个原数据,再对每个原数据加包头得到第一数据包(即原数据包),其中每个第一数据包的大小都相同。一种实现方式中,为了降低时延,第一设备每得到一个第一数据包(即原数据包)就将其缓存在存储器(这里的存储器是指存储空间,如缓存)中,并对该第一数据包进行编码(比如,将该第一数据包乘以行向量,该行向量中只有一个元素为1,其余元素为0),得到一个编码数据(该编码数据就是该第一数据包),再对该编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包)并传输。当该存储器中的第一数据包的个数达到网络编码所需的数据包个数(本申请实施例假设网络编码所需的数据包个数,即数据块大小为N)时,再对该存储器中缓存的N个第一数据包进行网络编码,生成M-N个编码数据。第一设备对该M-N个编码数据中每个编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包)。第一设备可以每得到一个第二数据包就传输该第二数据包。其中这M-N个编码数据都融合了N个原数据包的信息。这N个第一数据包的大小相等,这M-N个编码数据的大小也相等,并且任一个编码数据的大小与任一个第一数据包的大小也相等。Optionally, the first device divides and/or concatenates at least one data unit (PDU or SDU) to obtain N original data, and then adds a header to each original data to obtain the first data packet (that is, the original data packet ), where each first packet is the same size. In an implementation manner, in order to reduce the delay, each time the first device obtains a first data packet (ie, the original data packet), it caches it in a memory (here, the memory refers to a storage space, such as a cache), and The first data packet is encoded (for example, the first data packet is multiplied by a row vector, only one element in the row vector is 1, and the remaining elements are 0) to obtain an encoded data (the encoded data is the first data packet ), and then add the encoded packet header to the encoded data to obtain the second data packet (ie encoded packet) and transmit it. When the number of the first data packets in the memory reaches the number of data packets required for network coding (the embodiment of the present application assumes the number of data packets required for network coding, that is, the size of the data block is N), then the The N first data packets buffered in the memory are network-encoded to generate M-N encoded data. The first device adds a coded packet header to each of the M-N coded data to obtain a second data packet (ie, a coded packet). The first device may transmit the second data packet every time it obtains the second data packet. The M-N coded data are all fused with the information of the N original data packets. The size of the N first data packets is equal, the size of the M-N encoded data is also equal, and the size of any encoded data is also equal to the size of any first data packet.
另一种实现方式中,第一设备每得到一个第一数据包(即原数据包)就将其缓存在存储器(这里的存储器是指存储空间,如缓存)中。当该存储器中的第一数据包的个数达到网络编码所需的数据包个数(本申请实施例假设网络编码所需的数据包个数,即数据块大小为N)时,再对该存储器中缓存的N个第一数据包进行网络编码,生成M个编码数据,其中这N个第一数据包的大小相等,这M个编码数据的大小也相等,并且任一个编码数据的大小与任一个第一数据包的大小也相等。其中,对N个第一数据包进行网络编码可以理解为:将该N个第一数据包作为N行1列的矩阵,与编码系数矩阵做矩阵乘积。该编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,后M-N行构成的子矩阵可以包括码本中的一行或多行,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。前N个编码数据中一个编码数据就是一个原数据包,后M-N个编码数据中每个编码数据都融合了N个原数据包的信息。本申请对网络编码的方式不做限定,既可以是卷积网络编码也可以是块网络编码等。第一设备对每个编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包)。第一设备可以每得到一个第二数据包就传输该第二数据包。In another implementation manner, each time the first device obtains a first data packet (ie, the original data packet), it caches it in a memory (here, the memory refers to a storage space, such as a cache). When the number of the first data packets in the memory reaches the number of data packets required for network coding (the embodiment of the present application assumes the number of data packets required for network coding, that is, the size of the data block is N), then the The N first data packets buffered in the memory are network-encoded to generate M encoded data, wherein the sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the sizes of the M encoded data are also equal, and the size of any encoded data is equal to The sizes of any first data packets are also equal. Wherein, performing network coding on the N first data packets may be understood as: taking the N first data packets as a matrix with N rows and one column, and performing matrix product with the coding coefficient matrix. The submatrix formed by the first N rows in the encoding coefficient matrix is an identity matrix, and the submatrix formed by the last M-N rows can include one or more rows in the codebook, where the codebook can be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook etc. One coded data in the first N coded data is an original data packet, and each coded data in the next M-N coded data is fused with information of N original data packets. This application does not limit the way of network coding, which can be either convolutional network coding or block network coding. The first device adds an encoded packet header to each encoded data to obtain a second data packet (ie an encoded packet). The first device may transmit the second data packet every time it gets the second data packet.
可选的,第一设备对N个第一数据包进行网络编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,可以理解为:一方面,每得到一个第一数据包就直接加编码包包头,获得一个第二数据包,N个第一数据包加编码包包头就得到N个第二数据包。另一方面,将N个第一数据包作为N行1列的矩阵,与编码系数矩阵做矩阵乘积,得到M-N个第二数据包。该编码系数矩阵中的一行是码本中的一行,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。其中,N和M均为正整数,且M大于N。可见,第一设备传输的数据包(这里只有编码包)的大小相等。Optionally, the first device performs network encoding on the N first data packets and adds encoded packet headers to obtain M second data packets, which can be understood as: On the one hand, each time a first data packet is obtained, the encoded packet is directly added Packet header, one second data packet is obtained, and N second data packets are obtained by adding the encoded packet header to N first data packets. On the other hand, take the N first data packets as a matrix with N rows and one column, and perform matrix product with the coding coefficient matrix to obtain M-N second data packets. A row in the coding coefficient matrix is a row in a codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, or the like. Wherein, both N and M are positive integers, and M is greater than N. It can be seen that the data packets (only encoded packets here) transmitted by the first device are equal in size.
可选的,上述步骤S201至步骤S203可以由第一设备中单独的NC功能子层实现,也可以由具有NC功能的层实现,具体可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the above step S201 to step S203 may be implemented by a separate NC function sublayer in the first device, or may be implemented by a layer having an NC function. For details, please refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, which will not be repeated here. repeat.
可选的,为更好地理解上述步骤S201至上述步骤S203所述的流程,下面以一个示例来说明上述步骤S201至上述步骤S203所示的编码端数据传输流程。Optionally, in order to better understand the process described in the above step S201 to the above step S203, an example is used below to illustrate the data transmission process at the encoding end shown in the above step S201 to the above step S203.
示例性的,参见图18,图18是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第二种示意图。如图18所示,以NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间为例。假设NC功能子层依次接收到PDCP PDU1~4,根据NC功能子层中对原数据包的大小要求(其中原数据包的大小可以是半静态配置,也可以是收端(或译码端、或第二设备)提前告知发端(或编码端、或第一设备)的),对PDCP PDU1~4进行分割和/或级联操作,依次得到原数据包Pkt1~Pkt4的数据(如图18中的Data1~Data4)。再对得到的每个数据添加原数据包包头(如图18中的Header),获得原数据包,并将原数据包缓存在NC功能子层的编码器的缓存区(buffer)中等待编码。当buffer中的原数据包达到编码器所需的数据包个数时,假设编码器所需的数据包个数为4,然后将buffer中的4个原数据包进行网络编码并加编码包包头(如图18中的NC_Header),得到编码包并作为NC功能子层的PDU进行发送。因为网络编码所采用的编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,后M-N行构成的子矩阵包括码本中的一行或多行,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。所以,图18所示的编码数据可分为两类,一类是只包含单个原数据包的信息(比如图18中的Data1~Data4),另一类是包含多个原数据包的信息(比如图18中的EData1和EData2)。应理解,发送编码包时可以只发送得到的部分编码包,也可以发送得到的全部编码包。还应理解,这里分割和/或级联得到的原数据不一定是等大小的,但需要保证每个原数据包(包括数据Data和包头Header)的大小相等,也就是说原数据包的包头Header非等大小。For example, refer to FIG. 18 . FIG. 18 is a second schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 18 , it is taken as an example that the NC function sublayer is located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer. Assuming that the NC functional sublayer receives PDCP PDU1-4 in sequence, according to the size requirements of the original data packet in the NC functional sublayer (the size of the original data packet can be semi-statically configured, or it can be the receiving end (or decoding end, or the second device) to inform the sender (or the encoding end, or the first device) in advance), to divide and/or concatenate PDCP PDU1~4, and obtain the data of the original data packets Pkt1~Pkt4 in sequence (as shown in Figure 18 Data1~Data4). Then add the original data packet header to each obtained data (Header in Figure 18), obtain the original data packet, and cache the original data packet in the buffer area (buffer) of the encoder of the NC function sublayer to wait for encoding. When the original data packets in the buffer reach the number of data packets required by the encoder, assuming that the number of data packets required by the encoder is 4, then network encode the 4 original data packets in the buffer and add the encoded packet header (such as NC_Header in Figure 18), the coded packet is obtained and sent as a PDU of the NC functional sublayer. Because the sub-matrix composed of the first N rows in the coding coefficient matrix used in network coding is a unit matrix, the sub-matrix composed of the last M-N rows includes one or more rows in the codebook, where the codebook can be Vandermonde codebook, Cauchy codebook, random codebook, etc. Therefore, the coded data shown in Figure 18 can be divided into two categories, one is information containing only a single original data packet (such as Data1 to Data4 in Figure 18), and the other is information containing multiple original data packets ( Such as EData1 and EData2 in Figure 18). It should be understood that when sending the encoded packets, only part of the obtained encoded packets may be sent, and all obtained encoded packets may also be sent. It should also be understood that the original data obtained by splitting and/or concatenating here are not necessarily equal in size, but it is necessary to ensure that the size of each original data packet (including data Data and header Header) is equal, that is to say, the header of the original data packet Header is not equal in size.
可选的,上述每个第一数据包(即原数据包)包括包头和数据(即上述原数据)。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据(即上述原数据)对应的至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)的分割和级联信息,换句话说,每个原数据包的包头中包括该原数据包的数据与PDU/SDU的映射关系。或者说,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)的对应关系。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned first data packets (ie, the original data packet) includes a packet header and data (ie, the above-mentioned original data). The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit (PDU or SDU) corresponding to the data of the first data packet (ie, the above-mentioned original data), in other words, each original data packet The packet header includes the mapping relationship between the data of the original data packet and the PDU/SDU. In other words, the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate the correspondence between the data of the first data packet and at least one data unit (PDU or SDU).
可选的,每个第二数据包(即编码包)包括编码包包头和编码数据(这里的编码数据是第一数据包经过网络编码后得到)。编码包包头包括编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段),用于指示码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。因为编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,所以前N个编码包的编码包包头中携带的CoeffID字段,指示的是该单位阵中的一行,也就是说,前N个编码包的编码包包头中Coeff ID字段指示行向量只有一个元素为1,其他元素为0。应理解,因为本申请实施例中仅传输一种类型的数据包,即只传输编码包,所以可以不通过指示信息来指示传输的数据包是原数据包还是编码包。也就是说,本申请实施例中编码包包头中可以不包括O/C字段。Optionally, each second data packet (that is, an encoded packet) includes an encoded packet header and encoded data (the encoded data here is obtained after the first data packet is network-encoded). The header of the encoded packet includes an encoding factor field (such as a Coeff ID field), which is used to indicate the row index of the codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, or the like. Because the sub-matrix formed by the first N rows in the encoding coefficient matrix is an identity matrix, the CoeffID field carried in the header of the encoding packet of the first N encoding packets indicates a row in the identity matrix, that is, the first N encoding packets The Coeff ID field in the encoded packet header of the packet indicates that only one element of the row vector is 1, and the other elements are 0. It should be understood that in this embodiment of the present application, only one type of data packet is transmitted, that is, only encoded packets are transmitted, so indication information may not be used to indicate whether the transmitted data packets are original data packets or encoded packets. That is to say, in the embodiment of the present application, the header of the coded packet may not include the O/C field.
可选的,虽然每个编码包都包括编码包包头和编码数据,但因为编码系数矩阵中前N行构成的子矩阵是单位阵,后M-N行构成的子矩阵包括码本中的一行或多行(这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等),所以编码数据可以理解为两类,一类是只包含单个原数据包的信息,另一类是融合了多个原数据包的信息。相应地,本申请实施例中的M个编码包(即第二数据包)也可以理解为两类,分别为第一类编码包和第二类编码包。第一类编码包的编码系数子矩阵是单位阵,第二类编码包的编码系数子矩阵是非单位阵,故M个编码包(即第二数据包)包括N个第一类编码包和M-N个第二类编码包。其中,第一类编码包的编码系数子矩阵和第二类编码包的编码系数子矩阵形成一个编码系数矩阵,该编码系数矩阵用于对N个第一数据包进行编码。Optionally, although each coded packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, because the submatrix formed by the first N rows in the coded coefficient matrix is a unit matrix, the submatrix formed by the last M-N rows includes one or more rows in the codebook line (the codebook here can be Vandermonde codebook, Cauchy codebook, random codebook, etc.), so the encoded data can be understood as two types, one type contains only the information of a single original data packet, and the other type is a fusion of Information about multiple original data packets. Correspondingly, the M coded packets (that is, the second data packets) in the embodiment of the present application can also be understood as two types, namely, the first type of encoded packets and the second type of encoded packets. The coding coefficient sub-matrix of the first type of coding packet is a unit matrix, and the coding coefficient sub-matrix of the second type of coding packet is a non-identity matrix, so M coding packets (ie, the second data packet) include N first-type coding packets and M-N A second type of encoding package. Wherein, the coding coefficient sub-matrix of the first type of coding packet and the coding coefficient sub-matrix of the second type of coding packet form a coding coefficient matrix, and the coding coefficient matrix is used for coding the N first data packets.
可选的,在本申请实施例中,由于第一设备对原数据包(即第一数据包)进一步添加了编码包包头来保证传输的所有数据包的大小一致,所以原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头中可以省去O/C字段、Type字段、Packet ID字段、Block ID字段中的部分或全部,通过其他字段指示分割和级联信息;而编码包包头的实现方式可以参考前述实施例一中实现方式2.1和实现方式2.2,此处不再赘述。换句话说,原数据包(即第一数据包)中包头携带的分割和级联信息可参考前述实施例一中实现方式1.1至实现方式1.4的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, in this embodiment of the application, since the first device further adds a coded packet header to the original data packet (i.e., the first data packet) to ensure that all transmitted data packets have the same size, the original data packet (i.e., the first data packet) In the header of a data packet), some or all of the O/C field, Type field, Packet ID field, and Block ID field can be omitted, and the segmentation and concatenation information can be indicated through other fields; and the implementation of the encoded packet header can refer to The implementation mode 2.1 and the implementation mode 2.2 in the foregoing first embodiment will not be repeated here. In other words, for the segmentation and concatenation information carried in the packet header of the original data packet (ie, the first data packet), reference may be made to the corresponding descriptions of Implementation Mode 1.1 to Implementation Mode 1.4 in
示例性的,参见图19,图19是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头和编码包包头的示意图。如图19所示,编码包包头(图19中的NC_Header)采用实现方式2.2的格式,其包括Coeff ID字段和Block ID字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段以及Packet ID字段。其中,图19中的O/C字段用于表示该O/C字段所在的数据包中的数据是原数据包(即上述第一数据包)还是编码数据。第一数据包的包头(图19中的Header)包括分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息可由S_start字段和/或S_end字段、一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段携带。应理解,图19仅是示例,编码包包头还可以采用实现方式2.1的格式,第一数据包中包头包括的分割和级联信息还可以由其他字段携带,具体参考前述实施一中实现方式1.1至实现方式1.4的相应描述。还应理解,图19所示各个字段的含义可参考前述实施例一中的描述,此处不再赘述。其中,图19中的Data表示第一数据包的数据(或原数据),Pkt表示第一数据包(原数据包),EData表示编码数据,EPkt表示编码包。For example, refer to FIG. 19 . FIG. 19 is a schematic diagram of a header of a first data packet and a header of an encoded packet provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 19 , the coded packet header (NC_Header in FIG. 19 ) adopts the format of implementation 2.2, which includes a Coeff ID field and a Block ID field; optionally includes an O/C field, a Type field, and a Packet ID field. Wherein, the O/C field in FIG. 19 is used to indicate whether the data in the data packet in which the O/C field is located is the original data packet (that is, the above-mentioned first data packet) or encoded data. The header of the first data packet (Header in Figure 19) includes segmentation and concatenation information, which can be composed of S_start field and/or S_end field, one or more extension bits (extension bit, represented as E) field , and carry one or more length (length, L) fields. It should be understood that Figure 19 is only an example, and the header of the encoded packet can also adopt the format of Implementation 2.1, and the segmentation and concatenation information included in the header of the first data packet can also be carried by other fields. For details, refer to Implementation 1.1 in the first implementation. To the corresponding description of implementation 1.4. It should also be understood that, for the meaning of each field shown in FIG. 19 , reference may be made to the description in the foregoing
可见,本申请实施例通过两层头信息(即NC_Header和Header)来封装原数据包,很好地包含了分割和级联信息。另外,由于中间会对一层头信息(即Header)的原数据包进行编码,因此两层头信息的添加是分步完成的,不能一次性完成。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application uses two layers of header information (ie, NC_Header and Header) to encapsulate the original data packet, which well includes segmentation and concatenation information. In addition, since the original data packet of one layer of header information (that is, Header) is encoded in the middle, the addition of two layers of header information is completed step by step and cannot be completed at one time.
可选的,虽然第一设备传输了M(M>N)个第二数据包(即编码包),但因为干扰、噪声等因素,第一设备传输的数据包不一定都能被第二设备正确接收,也就是说,在传输过程中可能发生丢包的情况。所以,当第二设备接收到至少N个正确且线性无关的数据包时,才能正确译码并恢复出N个第一数据包(即原数据包)。下述步骤S204至步骤S206将详细介绍译码端的数据传输流程。Optionally, although the first device has transmitted M (M>N) second data packets (that is, coded packets), due to interference, noise and other factors, the data packets transmitted by the first device may not be all received by the second device. Received correctly, that is, packet loss may occur during transmission. Therefore, when the second device receives at least N correct and linearly independent data packets, it can correctly decode and restore N first data packets (ie, original data packets). The following steps S204 to S206 will introduce the data transmission process at the decoding end in detail.
S204,第二设备获取P个数据包,该P个数据包均是编码包,每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。S204. The second device acquires P data packets, the P data packets are coded packets, each data packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, and the coded packet header includes a coding factor field.
S205,第二设备对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。S205. The second device decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets. The N first data packets are equal in size, and each first data packet includes a packet header and data. Each The packet header of a first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet, and the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate that the data of the first data packet is related to the at least one data unit corresponding relationship.
S206,第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。S206. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,第二设备接收到P个数据包,或从存储空间(如buffer)中读取到P个数据包,这P个数据包均是编码包。P、N、M均为正整数,P大于或等于N且小于或等于M,即N≤P≤M。可见,当P等于N时,可以减少冗余开销。应理解,第二设备可以一次性接收到P个数据包,将其按序存储到存储空间中;也可以分多次接收,将每次接收到的数据包按序存储在存储空间中。在接收到的数据包个数等于P后,可执行译码操作,即步骤S205。Optionally, the second device receives P data packets, or reads P data packets from a storage space (such as a buffer), and the P data packets are all encoded packets. P, N, and M are all positive integers, and P is greater than or equal to N and less than or equal to M, that is, N≤P≤M. It can be seen that when P is equal to N, redundancy overhead can be reduced. It should be understood that the second device may receive P data packets at one time, and store them in the storage space in sequence; or may receive in multiple times, and store the data packets received each time in the storage space in sequence. After the number of received data packets is equal to P, the decoding operation can be performed, that is, step S205.
可选的,第二设备采用编码包的解析方式解析P个数据包中每个数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段),再利用这P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。第二设备去除该P个数据包的编码包包头,得到P个编码数据,采用该系数因子矩阵对这P个编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息,该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将这N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。Optionally, the second device parses the coded packet header of each data packet in the P data packets using the coded packet parsing method to obtain the coding factor field (ie Coeff ID field), and then utilizes the coded packet header of the P data packets The indications in the Coding Factor field constitute the coefficient factor matrix. The rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The second device removes the headers of the encoded packets of the P data packets to obtain P encoded data, uses the coefficient factor matrix to decode the P encoded data, and obtains decoded N first data packets. The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation and concatenation information of at least one data unit corresponding to the data of the first data packet, and the segmentation and concatenation information is used to indicate that the data of the first data packet and the at least one data unit unit correspondence. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into at least one data unit according to the segmentation and concatenation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,译码端(即第二设备)可能译码成功,也可能译码失败,所以针对译码成功和译码失败这两种情况分别设计反馈消息。该反馈消息的具体实现方式可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the decoding end (that is, the second device) may succeed in decoding or fail in decoding, so feedback messages are respectively designed for the two cases of successful decoding and decoding failure. For the specific implementation manner of the feedback message, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
可选的,由于本申请实施例中只传输编码包,所以本申请实施例可以只对编码包进行编号。此时,只需保证编码包的序列号顺序编号即可,比如编码包的序列号顺序递增。Optionally, since only encoded packets are transmitted in the embodiment of the present application, the embodiment of the present application may only number the encoded packets. At this time, it is only necessary to ensure that the serial numbers of the encoded packets are numbered sequentially, for example, the serial numbers of the encoded packets are incremented sequentially.
可选的,基站可通过RRC消息或者MAC CE消息指示UE上行传输的编码策略。该RRC消息或MAC CE消息可以指示UE的编码方式,或者指示不同的编码方案。Optionally, the base station may indicate the coding strategy of the UE for uplink transmission through an RRC message or a MAC CE message. The RRC message or the MAC CE message may indicate the encoding mode of the UE, or indicate different encoding schemes.
可见,本申请实施例通过对原数据包进一步添加编码包包头,来保证编码端(即第一设备)传输的数据包的大小相等。本申请实施例可以在物理层传输块(transport block,TB)大小为数据包整数倍的情况下,有利于分别识别出每个数据包的位置,并有利于通过循环冗余校验(cyclic redundancy check,CRC)判断每个数据包是否正确,如果正确即可向上层递交,最大化网络编码的效率和性能。It can be seen that, in the embodiment of the present application, by further adding an encoded packet header to the original data packet, it is ensured that the size of the data packets transmitted by the encoding end (that is, the first device) is equal. In the embodiment of the present application, when the size of the physical layer transport block (transport block, TB) is an integer multiple of the data packet, it is beneficial to identify the position of each data packet separately, and it is beneficial to pass the cyclic redundancy check (cyclic redundancy check). check, CRC) to judge whether each data packet is correct, and if it is correct, it can be submitted to the upper layer to maximize the efficiency and performance of network coding.
实施例三Embodiment three
本申请实施例三主要介绍在NR协议中引入网络编码的又一种可能的数据传输方法,该方法既传输原数据包也传输编码包,并且介绍在PDU/SDU进行级联操作和等大小分割后,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。The third embodiment of this application mainly introduces another possible data transmission method that introduces network coding into the NR protocol. This method transmits both the original data packet and the encoded packet, and introduces the concatenation operation and equal-size segmentation in the PDU/SDU Finally, how to perform network coding and data transmission, and how to design the header.
应理解,本申请实施例三与前述实施例一和前述实施例二在流程上的区别是:本申请实施例三先将多个PDU/SDU进行级联,然后在等大小分割,得到的原数据(即原数据包的数据)等大小;而前述实施例一和前述实施例二是直接对一个或多个PDU/SDU进行非等大小分割和级联操作,其得到的原数据(即原数据包的数据)不一定等大小。It should be understood that the difference between the third embodiment of the present application and the
参见图20,图20是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第三种示意流程图。如图20所示,该数据传输方法包括但不限于以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 20 , FIG. 20 is a third schematic flowchart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 20, the data transmission method includes but is not limited to the following steps:
S301,第一设备获取级联数据包,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据,该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据,其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分,该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元,该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。S301. The first device obtains a concatenated data packet, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data, and the concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments, wherein the start data segment and the end data segment At least one of them is all or part of a data unit, each data segment except the start data segment and the end data segment in the plurality of data segments is a data unit, and the concatenated packet header includes the concatenated data including Concatenation information of multiple data units of .
S302,第一设备根据该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等,该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。S302. The first device generates N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are equal. The N first data packets The data of the jth first data packet in the packet is the jth data obtained after the concatenated data packet is divided into N equal parts, each first data packet includes a header and data, and the header of each first data packet includes the The sequence number of the first packet.
S303,第一设备传输该N个第一数据包。S303. The first device transmits the N first data packets.
S304,第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包。S304. The first device encodes the N first data packets and adds headers of the encoded packets to obtain M second data packets.
S305,第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。S305. The first device transmits the M second data packets.
可选的,本申请实施例中的第一数据包可以称为原数据包,第二数据包可以称为编码包。原数据包可以理解为未经过网络编码的数据包,编码包可以理解为经过网络编码后的数据包。本申请实施例中的数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the first data packet in this embodiment of the present application may be called an original data packet, and the second data packet may be called an encoded packet. The original data packet can be understood as a data packet that has not undergone network encoding, and the encoded packet can be understood as a data packet that has undergone network encoding. The data unit in this embodiment of the present application is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备获取级联数据包的方式有两种。一种实现方式中,第一设备对多个PDU/SDU的部分或全部进行级联,并添加级联包包头,保证得到的级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍,具体可以是N倍,N是正整数。第一设备在得到级联数据包后,对该级联数据包进行等大小分割,分成N份数据,并对该N份数据中的每份数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。其中,级联包包头既可以位于级联数据的第一个比特之前,也可以位于级联数据的最后一个比特之后。也就是说,级联包包头既可以放在级联数据包的头部,也可以放在级联数据包的尾部。Optionally, there are two manners for the first device to obtain the concatenation data packet. In one implementation, the first device concatenates some or all of the multiple PDUs/SDUs, and adds a concatenation packet header to ensure that the size of the obtained concatenation data packet is an integer multiple of the original data size, which can be specifically N times, N is a positive integer. After the first device obtains the concatenated data packet, it divides the concatenated data packet into equal sizes, divides it into N parts of data, and adds a header to each of the N parts of data to obtain the first data packet (i.e., the original data Bag). Wherein, the header of the concatenated packet can be located before the first bit of the concatenated data, or after the last bit of the concatenated data. That is to say, the header of the concatenated packet can be placed at the head of the concatenated data packet or at the end of the concatenated data packet.
针对级联包包头位于级联数据的最后一个比特后的情况,也就是说,级联包包头位于最后一个第一数据包中,上述步骤S304还可以为:第一设备每获得一个PDU/SDU,就判断该PDU/SDU的大小是否大于或等于原数据大小。如果该PDU/SDU的大小大于或等于原数据大小,则直接将该PDU/SDU按照原数据大小进行分割,得到一个原数据,再对原数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。如果该PDU/SDU被分割后的剩余部分大小小于原数据大小,则当第一设备获得下一个PDU/SDU后,将该PDU/SDU被分割后的剩余部分与下一个PDU/SDU进行级联,然后再按照原数据大小进行分割,得到另一个原数据,再对该另一个原数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包);依次类推。如果该PDU/SDU被分割后的剩余部分大小大于或等于小于原数据大小,则再次对该PDU/SDU被分割后的剩余部分按照原数据大小进行分割,直到该PDU/SDU经过一次或多次分割后的剩余部分大小小于原数据大小为止。一次分割可以得到一个原数据,对一个原数据添加包头可得到一个第一数据包。如果该PDU/SDU的大小小于原数据大小,则第一设备等待下一个PDU/SDU,在获得下一个PDU/SDU后,将该PDU/SDU与该下一个PDU/SDU进行级联,然后判断级联后的PDU/SDU的大小是否大于或等于原数据大小。如果级联后的PDU/SDU的大小大于或等于原数据大小,则第一设备将该级联后的PDU/SDU按照原数据大小进行分割,得到一个原数据,再对原数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。如果级联后的PDU/SDU的大小小于原数据大小,则第一设备等待第三个PDU/SDU,然后在获得第三个PDU/SDU后,将该级联后的PDU/SDU与第三个PDU/SDU进行级联,直到经过一次或多次级联后的PDU/SDU的大小大于或等于原数据大小为止。也就是说,第一设备可以将级联和分割操作并行/同时执行。For the case where the header of the concatenated packet is located after the last bit of the concatenated data, that is to say, the header of the concatenated packet is located in the last first data packet, the above step S304 can also be: the first device acquires a PDU/SDU , it is judged whether the size of the PDU/SDU is greater than or equal to the original data size. If the size of the PDU/SDU is greater than or equal to the size of the original data, then directly divide the PDU/SDU according to the size of the original data to obtain an original data, and then add a packet header to the original data to obtain the first data packet (i.e. the original data packet ). If the size of the remaining part after the PDU/SDU is divided is smaller than the size of the original data, after the first device obtains the next PDU/SDU, the remaining part after the division of the PDU/SDU is concatenated with the next PDU/SDU , and then divide according to the size of the original data to obtain another original data, and then add a header to the other original data to obtain the first data packet (ie, the original data packet); and so on. If the size of the remaining part after the PDU/SDU is divided is greater than or equal to the size of the original data, then the remaining part of the PDU/SDU is divided according to the size of the original data again until the PDU/SDU has passed through one or more times The size of the remaining part after division is smaller than the size of the original data. One original data can be obtained by one division, and a first data packet can be obtained by adding a packet header to one original data. If the size of the PDU/SDU is smaller than the original data size, the first device waits for the next PDU/SDU, and after obtaining the next PDU/SDU, concatenates the PDU/SDU with the next PDU/SDU, and then judges Whether the size of the concatenated PDU/SDU is greater than or equal to the original data size. If the size of the concatenated PDU/SDU is greater than or equal to the size of the original data, the first device divides the concatenated PDU/SDU according to the size of the original data to obtain an original data, and then adds a header to the original data to obtain The first data packet (ie, the original data packet). If the size of the concatenated PDU/SDU is smaller than the original data size, the first device waits for the third PDU/SDU, and after obtaining the third PDU/SDU, combines the concatenated PDU/SDU with the third Each PDU/SDU is concatenated until the size of the PDU/SDU after one or more concatenations is greater than or equal to the original data size. That is, the first device can perform concatenation and division operations in parallel/simultaneously.
其中,原数据大小可以半静态配置,或者可以半静态配置编码包大小和N(N是网络编码所需的数据包个数(即数据块大小)或者说计划编码的数据包个数)。原数据包的包头大小固定,则可以基于编码包大小、原数据包的包头大小、以及N,计算出原数据大小(原数据大小=编码包大小-原数据包的包头大小)和级联数据包的大小(级联数据包的大小=N*原数据大小)。Among them, the original data size can be semi-statically configured, or the encoded packet size and N can be semi-statically configured (N is the number of data packets required for network encoding (ie, the size of the data block) or the number of planned encoded data packets). The header size of the original data packet is fixed, then the original data size (original data size=encoded packet size-the header size of the original data packet) and concatenated data can be calculated based on the size of the encoded packet, the header size of the original data packet, and N Packet size (size of concatenated data packet=N*original data size).
另一种实现方式中,第一设备对多个PDU/SDU的全部进行级联,并添加填充(padding)比特和级联包包头,保证得到的级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍,具体可以是N倍,N是正整数。换句话说,此实现方式中级联的PDU/SDU是完整的,边界的PDU/SDU不会被分割,而是通过填充比特的方式来补充缺少的bit数,从而构成一个级联数据,并通过对级联数据加级联包包头,获得一个包括级联包包头的级联数据包。也就是说,此种实现方式下的级联数据包括多个PDU/SDU以及填充比特。第一设备在得到级联数据包后,对该级联数据包进行等大小分割,分成N份数据,并对该N份数据中的每份数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。第一设备在得到级联数据包后,对该级联数据包进行等大小分割,分成N份数据,并对该N份数据中的每份数据添加包头,得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。其中,级联包包头既可以位于级联数据的第一个比特之前,也可以位于级联数据的最后一个比特之后。也就是说,级联包包头既可以放在级联数据包的头部,也可以放在级联数据包的尾部。In another implementation, the first device concatenates all of the multiple PDUs/SDUs, and adds padding bits and concatenated packet headers to ensure that the size of the concatenated data packet obtained is an integer of the original data size times, specifically N times, where N is a positive integer. In other words, in this implementation, the concatenated PDU/SDU is complete, and the boundary PDU/SDU will not be divided, but the missing bits will be supplemented by filling bits to form a concatenated data, and A concatenated data packet including a concatenated packet header is obtained by adding a concatenated packet header to the concatenated data. That is to say, the concatenated data in this implementation manner includes multiple PDUs/SDUs and padding bits. After the first device obtains the concatenated data packet, it divides the concatenated data packet into equal sizes, divides it into N parts of data, and adds a header to each of the N parts of data to obtain the first data packet (i.e., the original data Bag). After the first device obtains the concatenated data packet, it divides the concatenated data packet into equal sizes, divides it into N parts of data, and adds a header to each of the N parts of data to obtain the first data packet (i.e., the original data Bag). Wherein, the header of the concatenated packet can be located before the first bit of the concatenated data, or after the last bit of the concatenated data. That is to say, the header of the concatenated packet can be placed at the head of the concatenated data packet or at the end of the concatenated data packet.
针对级联包包头位于级联数据的最后一个比特后的情况,也就是说,级联包包头位于最后一个第一数据包中,上述步骤S304中第一设备也可以将级联和分割操作并行/同时执行。与前述实现方式不同之处在于:当第一设备获得N-1个第一数据包后,在确定第N个原数据时,该第N个原数据中包括一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分、和填充比特、以及级联包包头。也就是说,边界的PDU/SDU不会被分割,而是通过填充比特的方式来补充缺少的bit数。其中,原数据是指原数据包中的数据。For the case where the header of the concatenated packet is located after the last bit of the concatenated data, that is to say, the header of the concatenated packet is located in the last first data packet, the first device in the above step S304 may also perform the concatenation and division operations in parallel / execute simultaneously. The difference from the aforementioned implementation is that: after the first device obtains N-1 first data packets, when determining the Nth original data, the Nth original data includes all or part of a PDU/SDU, and padding bits, and concatenated packet headers. That is to say, the PDU/SDU at the boundary will not be divided, but the missing bits will be supplemented by filling bits. Wherein, the original data refers to the data in the original data packet.
可选的,为了降低时延,第一设备可以每得到一个第一数据包就传输该第一数据包,并将该第一数据包缓存在存储器(这里的存储器是指存储空间,如缓存)中。N份数据添加包头后可得到N个第一数据包,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,这N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且这N个第一数据包的包头大小也相等。这N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据,j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。也就是说,该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第1份数据至第N份数据分别添加包头后,得到第1个第一数据包至第N个第一数据包。当该存储器中的第一数据包的个数达到网络编码所需的数据包个数(本申请实施例假设网络编码所需的数据包个数,即数据块大小为N)时,再对该存储器中缓存的N个第一数据包进行网络编码,生成M个编码数据。其中这M个编码数据的大小相等,并且任一个编码数据的大小与任一个第一数据包的大小也相等。第一设备对每个编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包),并传输该第二数据包。M个编码数据加编码包包头后可得到M个第二数据包(即编码包)。其中,本申请对网络编码的方式不做限定。N和M均为正整数,且M和N的大小关系不做限定,即M可以小于N,也可以大于N,还可以等于N。Optionally, in order to reduce the delay, the first device may transmit the first data packet every time it obtains a first data packet, and cache the first data packet in a memory (the memory here refers to a storage space, such as a cache) middle. N first data packets can be obtained after headers are added to N parts of data. Each first data packet includes a header and data. The data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the header sizes of the N first data packets are also the same equal. The data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained after the concatenated data packets are divided into N equal parts, and the value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N]. That is to say, the first data packet to the Nth data packet obtained after the concatenated data packet is divided into N equal parts are respectively added with headers to obtain the first first data packet to the Nth first data packet. When the number of the first data packets in the memory reaches the number of data packets required for network coding (the embodiment of the present application assumes the number of data packets required for network coding, that is, the size of the data block is N), then the Network coding is performed on the N first data packets buffered in the memory to generate M coded data. The size of the M pieces of coded data is equal, and the size of any one of the coded data is also equal to the size of any one of the first data packets. The first device adds an encoded packet header to each encoded data to obtain a second data packet (that is, an encoded packet), and transmits the second data packet. M second data packets (ie, encoded packets) can be obtained after adding the encoded packet header to the M encoded data. Wherein, the present application does not limit the way of network coding. Both N and M are positive integers, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, that is, M may be smaller than N, larger than N, or equal to N.
可见,第二数据包(即编码包)比第一数据包(即原数据包)多一个编码包包头,即编码包的编码数据和原数据包大小相等,也就是说,本申请实施例传输的编码包(即第二数据包)和原数据包(即第一数据包)不等大小,一定程度上节约了原数据包的包头开销。It can be seen that the second data packet (i.e., the encoded packet) has one more encoded packet header than the first data packet (i.e., the original data packet), that is, the encoded data of the encoded packet is equal in size to the original data packet, that is to say, the transmission of the embodiment of the present application The encoded packet (that is, the second data packet) and the original data packet (that is, the first data packet) are of different sizes, which saves the header overhead of the original data packet to a certain extent.
可选的,本申请实施例对上述步骤S303和上述步骤S304的执行顺序不做限定。比如上述步骤S303既可以在上述步骤S304之前执行,也可以在上述步骤S304之后执行,还可以与上述步骤S304同时/并行执行。Optionally, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the execution order of the above step S303 and the above step S304. For example, the above step S303 may be executed before the above step S304, may also be executed after the above step S304, and may also be executed simultaneously/parallelly with the above step S304.
可选的,上述级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据,其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元(即PDU/SDU)的全部或部分,该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个完整的数据单元(即PDU/SDU)。因为该级联数据对应的多个数据单元中第一个数据单元(如,序列号最小的数据单元)不一定放在该级联数据的起始位置,同理,最后一个数据单元(如,序列号最大的数据单元)也不一定放在该级联数据的末尾位置;具体放置位置,只要发端(或编码端,或第一设备)和收端(或译码端,或第二设备)双方均知晓即可,具体可通过协议预定义,或是,发端知会收端等方式,具体不予限定。所以,起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分,多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个完整的数据单元,可以理解为:该级联数据对应的多个数据单元中除序列号最小和序列号最大的数据单元外的每个数据单元都是完整的。序列号最小的数据单元和序列号最大的数据单元是否完整需根据实际情况判断。Optionally, the foregoing concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The concatenated data includes the data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments, wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit (i.e. PDU/SDU), and among the multiple data segments except Each data segment except the start data segment and the end data segment is a complete data unit (ie PDU/SDU). Because the first data unit (for example, the data unit with the smallest sequence number) among the multiple data units corresponding to the concatenated data is not necessarily placed at the starting position of the concatenated data, similarly, the last data unit (for example, The data unit with the largest serial number) is not necessarily placed at the end of the concatenated data; the specific placement position, as long as the sending end (or encoding end, or the first device) and the receiving end (or decoding end, or the second device) It is enough for both parties to know, and the details can be pre-defined through the agreement, or the sender notifies the receiver, etc., and the details are not limited. Therefore, at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit, and each data segment in the multiple data segments except the start data segment and the end data segment is a complete data unit, It can be understood that: among the multiple data units corresponding to the concatenated data, every data unit except the data units with the smallest serial number and the largest serial number is complete. Whether the data unit with the smallest serial number and the data unit with the largest serial number are complete needs to be judged according to the actual situation.
可选的,上述级联数据包的级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元(即PDU/SDU)的级联信息。其中,针对级联数据包括多个完整的PDU/SDU以及填充比特的情况,可以在级联包包头中引入一个字段,来指示填充信息(比如填充比特的长度)。如果已知级联包包头的大小、每个完整PDU/SDU的大小、以及原数据大小,网络编码所需的数据包个数(N)半静态配置,则可以推算出填充比特的长度,此时可以不在级联包包头中引入字段来指示填充信息。Optionally, the concatenation packet header of the concatenation data packet includes concatenation information of multiple data units (ie, PDU/SDU) included in the concatenation data. Wherein, for the case where the concatenated data includes multiple complete PDUs/SDUs and padding bits, a field may be introduced in the header of the concatenated packet to indicate padding information (such as the length of padding bits). If the size of the concatenated packet header, the size of each complete PDU/SDU, and the original data size are known, and the number of data packets (N) required for network coding is configured semi-statically, the length of the padding bits can be calculated. It is not necessary to introduce a field in the header of the concatenated packet to indicate padding information.
可选的,上述步骤S301至步骤S305可以由第一设备中单独的NC功能子层实现,也可以由具有NC功能的层实现,具体可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the above step S301 to step S305 may be implemented by a separate NC function sublayer in the first device, or may be implemented by a layer having an NC function. For details, please refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, which will not be repeated here. repeat.
可选的,为更好地理解上述步骤S301至上述步骤S305所述的流程,下面以两个示例来说明上述步骤S301至上述步骤S305所示的编码端数据传输流程。Optionally, in order to better understand the process described in the above step S301 to the above step S305, the following two examples are used to illustrate the data transmission process at the encoding end shown in the above step S301 to the above step S305.
示例性的,参见图21,图21是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第三种示意图。如图21所示,以NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间为例。假设NC功能子层依次接收到PDCP PDU1~5。编码端(即第一设备)根据原数据大小和计划编码的数据包个数(即N),对PDCP PDU1、PDCP PDU2等依次级联,直到满足编码的长度需求(即满足N乘以原数据大小的值减去级联包包头的大小)。这里通过取PDCP PDU5的一部分联合PDCP PDU1~4级联构成级联数据,并通过加级联包包头(如图21中的H),构成级联数据包。从而保证得到的级联数据包的大小为原数据大小的整数倍。编码端(即第一设备)再按照原数据大小对级联数据包进行等大小分割,获得若干个原数据(如图21中的Data1~Data5)。编码端(即第一设备)再对获得的每个原数据添加原数据包包头(如图21中的Header),获得包括包头的原数据包(如图21中的Pkt1~Pkt5);一方面将原数据包作为NC功能子层的NC PDU直接传输至下一层,另一方面将原数据包缓存在NC功能子层的编码器的缓存区(buffer)中。当buffer中的原数据包达到编码器所需的数据包个数时,假设编码器所需的数据包个数为5,然后将buffer中的5个原数据包进行网络编码生成编码数据EData1和EData2。应理解,对5个原数据包进行网络编码生成的编码数据的个数可以小于或等于原数据包的个数,也可以大于原数据包的个数。对每个编码数据添加编码包包头(如图21中的NC_Header),得到编码包(如图21中的EPkt1和EPkt2)并作为NC功能子层的PDU进行发送。应理解,发送编码包时可以只发送得到的部分编码包(比如发送EPkt1,不发送EPkt2),也可以发送得到的全部编码包。For example, refer to FIG. 21 , which is a third schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 21 , it is taken as an example that the NC function sublayer is located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer. It is assumed that the NC functional sublayer receives PDCP PDU1-5 in sequence. The coding end (that is, the first device) cascades PDCP PDU1, PDCP PDU2, etc. in sequence according to the size of the original data and the number of data packets to be coded (that is, N) until the length requirement of the coding is met (that is, N is multiplied by the original data size value minus the size of the concatenated packet header). Here, a part of PDCP PDU5 is concatenated with PDCP PDU1-4 to form concatenated data, and a concatenated data packet is formed by adding a concatenated packet header (as shown in H in Figure 21). Therefore, it is ensured that the size of the obtained concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. The encoding end (that is, the first device) divides the concatenated data packets into equal sizes according to the size of the original data to obtain several original data (such as Data1-Data5 in FIG. 21 ). The encoding end (i.e. the first device) adds an original data packet header (such as Header in Figure 21) to each original data obtained, and obtains an original data packet including the header (Pkt1~Pkt5 in Figure 21); on the one hand The original data packet is directly transmitted to the next layer as the NC PDU of the NC function sublayer, and on the other hand, the original data packet is buffered in the buffer area (buffer) of the encoder of the NC function sublayer. When the original data packets in the buffer reach the number of data packets required by the encoder, assuming that the number of data packets required by the encoder is 5, then network encode the 5 original data packets in the buffer to generate encoded data EData1 and EData2. It should be understood that the number of encoded data generated by performing network encoding on five original data packets may be less than or equal to the number of original data packets, and may also be greater than the number of original data packets. Add a coded packet header (such as NC_Header in Figure 21) to each coded data to obtain coded packets (such as EPkt1 and EPkt2 in Figure 21) and send it as a PDU of the NC functional sublayer. It should be understood that when sending the encoded packets, only part of the obtained encoded packets may be sent (for example, EPkt1 is sent and EPkt2 is not sent), or all the obtained encoded packets may be sent.
其中,级联包包头既可以位于级联数据的第一个bit之前,也可以位于级联数据的最后一个bit之后。也就是说,级联包包头既可以放在级联数据包的头部,也可以放在级联数据包的尾部。图21示出了级联包包头位于级联数据包头部的情况,相应地,译码端(或收端、或第二设备)可以对一个级联数据包,从左侧包头的第一个比特开始解析。Wherein, the header of the concatenated packet can be located before the first bit of the concatenated data, or after the last bit of the concatenated data. That is to say, the header of the concatenated packet can be placed at the head of the concatenated data packet or at the end of the concatenated data packet. Figure 21 shows the situation that the header of the concatenated packet is located at the header of the concatenated data packet. Correspondingly, the decoding end (or receiving end, or the second device) can, for a concatenated data packet, start from the first Bits start parsing.
参见图22,图22是本申请实施例提供的级联数据包中级联包包头的位置示意图。如图22所示,级联数据位于级联包包头之前,译码端(或收端、或第二设备)通过反向解析级联包包头,可以更好地保证实时性。具体地,编码端(即第一设备)根据原数据大小和计划编码的数据包个数(即N),对PDCP PDU1、PDCP PDU2等依次级联,同时更新级联包包头(如图22中的H)中的信息。当级联到最后一个PDCP PDU(如图22中PDCP PDU5)时,结合级联包包头(如图22中的H)的大小,同步确定最后一个级联的PDCP PDU大小(如图22中PDCP PDU5的部分),最后级联构成一个级联数据包。该级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。相应地,译码端(或收端、或第二设备)可以对级联数据包的末尾(即级联包包头H)进行解析,其中级联包包头H的数据是从级联数据包最后1bit开始反向解析。Referring to FIG. 22 , FIG. 22 is a schematic diagram of the position of the header of the concatenated packet in the concatenated data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 22 , the concatenated data is located before the header of the concatenated packet, and the decoding end (or receiving end, or the second device) can better ensure real-time performance by reversely parsing the header of the concatenated packet. Specifically, the coding end (that is, the first device) sequentially concatenates PDCP PDU1, PDCP PDU2, etc. according to the size of the original data and the number of data packets to be coded (that is, N), and at the same time updates the header of the concatenated packet (as shown in Figure 22 information in H). When concatenating to the last PDCP PDU (such as PDCP PDU5 in Figure 22), combined with the size of the concatenated packet header (such as H in Figure 22), the size of the last concatenated PDCP PDU (such as PDCP PDU in Figure 22) is determined synchronously. part of PDU5), and finally concatenated to form a concatenated data packet. The size of the concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. Correspondingly, the decoding end (or receiving end, or the second device) can analyze the end of the concatenated data packet (ie, the header H of the concatenated packet), wherein the data of the header H of the concatenated packet is from the end of the concatenated data packet 1bit starts reverse parsing.
示例性的,参见图23,图23是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第四种示意图。其中,图23与前述图21的主要区别在于级联设计,图23中级联的PDU/SDU是完整的(如图23中级联的PDCP PDU1~4),边界的PDU/SDU不会被分割,而缺少的bit数则通过填充比特的方式来补充(如图23中的P),获得一个级联数据,通过加级联包包头(如图23中的H),获得一个级联数据包,其大小等于原数据大小的整数倍,其倍数可以半静态配置。应理解,图23中编码端得到级联数据包后的操作与前述图21中编码端的操作相同,此处不再赘述。同理,为了不用等待获得所有的PDU/SDU之后才进行级联和分割操作,可以将级联包包头放在级联数据包的末尾,相应地,译码端从最后1bit开始反向解析级联包包头。For example, refer to FIG. 23 , which is a fourth schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application. Among them, the main difference between Figure 23 and the aforementioned Figure 21 is the cascading design. The concatenated PDU/SDU in Figure 23 is complete (as shown in the concatenated PDCP PDU1~4 in Figure 23), and the border PDU/SDU will not be The missing bits are supplemented by filling bits (as shown in P in Figure 23) to obtain a concatenated data, and a concatenated data is obtained by adding a concatenated packet header (as shown in Figure 23 H). Packet, whose size is equal to an integer multiple of the original data size, and its multiple can be configured semi-statically. It should be understood that the operation of the encoding end in FIG. 23 after obtaining the concatenated data packets is the same as the operation of the encoding end in FIG. 21 described above, and will not be repeated here. In the same way, in order not to wait for all the PDUs/SDUs to be concatenated and split, the header of the concatenated packet can be placed at the end of the concatenated data packet. Correspondingly, the decoding end starts from the last 1 bit to reversely analyze the level Joint package Baotou.
参见图24,图24是本申请实施例提供的添加填充比特的级联数据包中级联包包头的位置示意图。如图24所示,级联数据位于级联包包头之前,译码端(或收端、或第二设备)通过反向解析级联包包头,可以更好地保证实时性。具体地,编码端(即第一设备)根据原数据大小和计划编码的数据包个数(即N),对PDCP PDU1、PDCP PDU2等依次级联,同时更新级联包包头(如图24中的H)中的信息。当最后一个PDCP PDU(如图22中PDCP PDU4)级联后,结合级联包包头(如图24中的H)的大小,同步确定填充比特的大小(如图24中P),最后将填充比特添加到最后一个PDCP PDU后,并添加级联包包头(如图24中的H),构成一个级联数据包。该级联数据包的大小是原数据大小的整数倍。相应地,译码端(或收端、或第二设备)可以对级联数据包的末尾(即级联包包头H)进行解析,其中级联包包头H的数据是从级联数据包最后1bit开始反向解析。Referring to FIG. 24 , FIG. 24 is a schematic diagram of the position of the header of the concatenated packet in the concatenated data packet with padding bits added according to the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 24 , the concatenated data is located before the header of the concatenated packet, and the decoding end (or receiving end, or the second device) can better ensure real-time performance by reversely parsing the header of the concatenated packet. Specifically, the coding end (that is, the first device) sequentially concatenates PDCP PDU1, PDCP PDU2, etc. according to the size of the original data and the number of data packets to be coded (that is, N), and at the same time updates the header of the concatenated packet (as shown in Figure 24 information in H). When the last PDCP PDU (as shown in PDCP PDU4 in Figure 22) is concatenated, combined with the size of the concatenated packet header (as shown in H in Figure 24), the size of the filling bits (as shown in Figure 24 P) is synchronously determined, and finally the padding Bits are added to the last PDCP PDU, and a concatenated packet header (as shown in H in Figure 24) is added to form a concatenated data packet. The size of the concatenated data packet is an integer multiple of the size of the original data. Correspondingly, the decoding end (or receiving end, or the second device) can analyze the end of the concatenated data packet (ie, the header H of the concatenated packet), wherein the data of the header H of the concatenated packet is from the end of the concatenated data packet 1bit starts reverse parsing.
可见,本申请实施例对多个PDU/SDU进行级联,并在边界处进行分割或填充比特,以获得一个级联数据,并添加级联包包头得到一个级联数据包,再对级联数据包进行等大小分割得到一定数量的原数据(第一数据包的数据),继而通过加包头获得原数据包,并对原数据包进行编码和加编码包包头后获得编码包,从而在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下,比如现有NR协议中,支持网络编码技术。此外,本申请实施例无需对每个原数据包都添加级联的字段指示,而是通过统一的级联包包头进行级联信息的指示,可以节省包头的开销。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application concatenates multiple PDUs/SDUs, and divides or fills bits at the boundary to obtain a concatenated data, and adds a concatenated packet header to obtain a concatenated data packet, and then concatenates The data packet is divided into equal sizes to obtain a certain amount of original data (the data of the first data packet), and then the original data packet is obtained by adding a header, and the original data packet is encoded and the encoded packet is added. Depending on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different. In scenarios such as the existing NR protocol, network coding technology is supported. In addition, in the embodiment of the present application, there is no need to add a concatenation field indication to each original data packet, but to indicate the concatenation information through a unified concatenation packet header, which can save the overhead of the packet header.
上述内容详细阐述了编码端的数据传输流程,为了保证译码端能够根据正确接收的原数据包和编码包恢复出PDU/SDU,下面将结合编码端的数据传输流程详细介绍级联数据包的级联包包头、第一数据包(即原数据包)的包头、以及第二数据包(即编码包)的编码包包头的实现方式。其中,级联包包头的格式可采用下述实现方式3.1至实现方式3.3中任一种,实现方式3.1至实现方式3.3也可以任一组合形成新的实现方式且所涉及概念或方案相同或相似的部分可以相互参考或组合。The above content elaborates the data transmission process of the encoding end in detail. In order to ensure that the decoding end can recover the PDU/SDU according to the correctly received original data packet and encoding packet, the following will introduce the cascading of concatenated data packets in detail in combination with the data transmission process of the encoding end. The implementation of the header of the packet, the header of the first data packet (ie, the original data packet), and the header of the encoded packet of the second data packet (ie, the encoded packet). Among them, the format of the concatenated packet header can adopt any of the following implementation methods 3.1 to 3.3, and any combination of implementation methods 3.1 to 3.3 can also be used to form a new implementation method, and the concepts or solutions involved are the same or similar Parts of the sections may refer to each other or be combined.
实现方式3.1Implementation method 3.1
可选的,上述级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元(即PDU/SDU)的级联信息。该级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的数据段的个数(记为Dnum)的信息;以及指示该级联数据包括的每个数据段的长度的信息。应理解,如果级联数据包的总长度可以确定(如半静态配置)、级联包包头的长度也可以确定,则上述级联信息中可以只包括Dnum-1个数据段中每个数据段的长度,而不是包括Dnum个数据段中每个数据段的长度,剩下的一个数据段的长度可通过该级联数据包的总长度、该级联包包头的长度以及Dnum-1个数据段的长度计算得出。Optionally, the foregoing concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units (ie, PDU/SDU) included in the concatenated data. The concatenation information includes: indicating whether the data unit corresponding to the start data segment (i.e. the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (i.e. the last data segment) of the concatenation data is divided, or indicates the Information about whether the data unit with the largest serial number and/or the smallest serial number among the data units corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is divided; information indicating the number of data segments (denoted as Dnum ) included in the concatenated data; and information indicating the length of each data segment included in the concatenated data. It should be understood that if the total length of the concatenated data packet can be determined (such as semi-static configuration), and the length of the header of the concatenated packet can also be determined, then the above concatenated information can only include each data in Dnum -1 data segments The length of the segment, instead of including the length of each data segment in Dnum data segments, the length of the remaining data segment can be passed through the total length of the concatenated data packet, the length of the concatenated packet header and Dnum - The length of 1 data segment is calculated.
参见图25,图25是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图一。如图25所示,该级联包包头包括:开始分段(Segment_start,S_start)字段和/或结束分段(Segment_end,S_end)字段,分段数(segmentnumber,表示为Seg_N)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段。图25中级联包包头的各个字段的含义可参考前述实施例一中相应字段的含义,此处不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 25 , FIG. 25 is a first schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 25, the header of the concatenated packet includes: a start segment (Segment_start, S_start) field and/or an end segment (Segment_end, S_end) field, a segment number (segmentnumber, represented as Seg_N) field, and one or Multiple length (length, L) fields. For the meaning of each field of the concatenated packet header in FIG. 25 , please refer to the meaning of the corresponding field in the foregoing
可见,实现方式3.1中级联包包头内的长度字段更少,可以节省头开销。这是因为因为分割会导致更多的数据段产生,而通常数据单元的个数比数据段的个数更少,所以节省开销;此外,等长的原数据包的包头和数据比变长情况更易处理,复杂度低。It can be seen that, in the implementation mode 3.1, there are fewer length fields in the header of the concatenated packet, which can save header overhead. This is because segmentation will lead to more data segments, and usually the number of data units is less than the number of data segments, so the overhead is saved; in addition, the header and data of the original data packet of equal length are longer than the case of variable length Easier to handle and less complex.
实现方式3.2Implementation method 3.2
可选的,上述级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元(即PDU/SDU)的级联信息。该级联信息包括:指示该级联数据的起始数据段(即第一个数据段)和/或末尾数据段(即最后一个数据段)对应的数据单元是否被分割的信息,或者指示该级联数据中数据段对应的数据单元中序列号最大和/或序列号最小的数据单元是否被分割的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该级联数据的最后一个数据段的信息;以及指示该第i个数据段的长度的信息。其中,i是正整数,且i的取值为1至该级联数据包括的数据段总数Dnum,即i为正整数且1≤i≤Dnum。Optionally, the foregoing concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units (ie, PDU/SDU) included in the concatenated data. The concatenation information includes: indicating whether the data unit corresponding to the start data segment (i.e. the first data segment) and/or the end data segment (i.e. the last data segment) of the concatenation data is divided, or indicates the Information about whether the data unit with the largest serial number and/or the smallest serial number in the data unit corresponding to the data segment in the concatenated data is divided; indicates whether the i-th data segment included in the concatenated data is the last of the concatenated data information of the data segment; and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment. Wherein, i is a positive integer, and the value of i ranges from 1 to the total number of data segments Dnum included in the concatenated data, that is, i is a positive integer and 1≤i≤Dnum .
参见图26a,图26a是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图二。参见图26a,该级联包包头包括:开始分段(Segment_start,S_start)字段和/或结束分段(Segment_end,S_end)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段。图26a的各个子字段的含义可参考前述实施例一的图10a中相同字段的描述,此处不再赘述。参见图26b,图26b是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图三。参见图26b,该级联包包头包括:分段信息(segmentinformation,SI)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段。其中,图26b的各个子字段的含义可参考前述实施例一的图10b中相同字段的描述,此处不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 26a, FIG. 26a is a second schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. Referring to Fig. 26a, the header of the concatenated packet includes: a start segment (Segment_start, S_start) field and/or an end segment (Segment_end, S_end) field, one or more extension bits (extension bit, represented as E) field, and One or more length (length, L) fields. For the meaning of each subfield in FIG. 26a , refer to the description of the same field in FIG. 10a in the first embodiment, and details are not repeated here. Referring to FIG. 26b, FIG. 26b is a third schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. Referring to FIG. 26b, the header of the concatenated packet includes: a segment information (segmentinformation, SI) field, one or more extension bit (extension bit, denoted as E) fields, and one or more length (length, L) fields. Wherein, the meaning of each subfield in FIG. 26b can refer to the description of the same field in FIG. 10b in the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
实现方式3.3Implementation method 3.3
可选的,上述级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元(即PDU/SDU)的级联信息。该级联信息包括:指示该级联数据中起始数据段是否是最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据中第一个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)以及该起始数据段对应的数据单元是否完整(完整即为未被分割,不完整即为被分割)的信息;指示该级联数据包括的第i个数据段是否是该级联数据的最后一个数据段(或者说,该级联数据包括的第i个数据段后是否存在下一个数据段)的信息;以及指示第i个数据段的长度的信息。Optionally, the foregoing concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units (ie, PDU/SDU) included in the concatenated data. The concatenation information includes: indicating whether the initial data segment in the concatenated data is the last data segment (or in other words, whether there is a next data segment after the first data segment in the concatenated data) and the initial data segment Information about whether the corresponding data unit is complete (complete means not divided, incomplete means divided); indicates whether the i-th data segment included in the concatenated data is the last data segment of the concatenated data (or , information about whether there is a next data segment after the i-th data segment included in the concatenated data; and information indicating the length of the i-th data segment.
参见图27,图27是本申请实施例提供的级联包包头的格式示意图四。如图27所示,该级联包包头包括:扩展比特0(extension bit 0,表示为E0)字段,一个或多个扩展比特(extension bit,表示为E)字段,以及一个或多个长度(length,L)字段。其中,图27的各个子字段的含义可参考前述实施例一的图12中相应字段的描述,此处不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 27 , FIG. 27 is a fourth schematic diagram of the format of the concatenated packet header provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 27, the header of the concatenated packet includes: an extension bit 0 (extension bit 0, denoted as E0) field, one or more extension bit (extension bit, denoted as E) fields, and one or more length ( length, L) field. Wherein, the meaning of each subfield in FIG. 27 can refer to the description of the corresponding field in FIG. 12 in the first embodiment, and will not be repeated here.
可见,实现方式3.2和实现方式3.3在级联包包头中为每一个数据段都设置1bit的扩展比特字段来指示该数据段是否是最后一个数据段,并为每一个数据段设置一个长度字段来指示其长度,有利于译码端根据级联包包头的指示对级联数据进行分割,以恢复出多个PDU/SDU。It can be seen that in the implementation mode 3.2 and the implementation mode 3.3, a 1-bit extended bit field is set for each data segment in the concatenated packet header to indicate whether the data segment is the last data segment, and a length field is set for each data segment to Indicating its length is beneficial for the decoding end to divide the concatenated data according to the indication of the header of the concatenated packet, so as to recover multiple PDUs/SDUs.
可选的,上述每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号,可选的还包括第一指示信息。该第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包。其中,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第一指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。第一数据包的序列号可以由Packet ID字段来指示。应理解,第一数据包的序列号可以按照从小到大顺序编号。也就是说,第一设备生成的第一个第一数据包的序列号为1,第二个第一数据包的序列号为2,以此类推。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括Type字段和Block ID字段中的一项或多项。Type字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围,比如1比特可以表示2种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度);2比特可以表示4种长度的SN(或Packet ID字段长度)。Block ID字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned first data packets includes a packet header and data. The packet header of each first data packet includes the serial number of the first data packet, and optionally also includes first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is contained is an original data packet. Wherein, the form of the first indication information in the packet header may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the first indication information may also be expressed as a field with another name, and the embodiment of the present application does not limit the name of the field. The sequence number of the first data packet may be indicated by the Packet ID field. It should be understood that the sequence numbers of the first data packets may be numbered in ascending order. That is to say, the sequence number of the first first data packet generated by the first device is 1, the sequence number of the second first data packet is 2, and so on. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may also include one or more items of the Type field and the Block ID field. The Type field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the sequence number of the data packet. For example, 1 bit can represent SN (or Packet ID field length) of 2 lengths; 2 bits can represent SN of 4 lengths SN (or Packet ID field length). The Block ID field is used to indicate the identifier of the data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
参见图28,图28是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图六。如图28所示,第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。其中,第一数据包的包头中各个字段的含义可参考前述实施例一中相应字段的含义,此处不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 28 , FIG. 28 is a sixth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 28 , the header of the first data packet includes: a Packet ID field, optionally including an O/C field, a Type field and a Block ID field. Wherein, the meaning of each field in the header of the first data packet can refer to the meaning of the corresponding field in the first embodiment above, and will not be repeated here.
可选的,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据(这里的编码数据是第一数据包经过网络编码后得到)。每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息、以及编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段),可选的还包括第二指示信息。第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。该第二指示信息在编码包包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段,应理解,第二指示信息也可以表现为其他名称的字段,本申请实施例对字段的名称不做限定。该用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是Block ID字段,或者包括以下至少两项:编码窗的窗长、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。还应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,则用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息可以包括编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、和编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中的至少一项即可。编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)的长度为8bit,用于指示255行码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。Optionally, each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data (the encoded data here is obtained after the first data packet is network-encoded). The coded packet header of each second data packet includes identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet, and a coding factor field (such as a Coeff ID field), and optionally also includes a second Instructions. The second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. The form of the second indication information in the header of the encoded packet may be an O/C field. It should be understood that the second indication information may also be expressed as a field with another name, and the embodiment of the present application does not limit the name of the field. The identification information used to indicate that the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a Block ID field, or includes at least two of the following items: the window length of the encoding window, the first first data packet in the encoding window sequence number, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window. It should also be understood that if the window length of the encoding window is configured semi-statically, the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet may include the first first data packet in the encoding window At least one of the sequence number and the sequence number of the last first data packet in the coding window is sufficient. The encoding factor field (such as the Coeff ID field) has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the row index of the 255-row codebook, where the codebook may be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, or the like.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括Type字段和Packet ID字段中的一项或多项。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。其中,编码包和原数据包的序列号的实现方式可参考前述实施例一中相应描述,此处不再赘述。具体地,编码包包头的实现方式也可参考前述实施例一中实现方式2.1和实现方式2.2的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may also include one or more items of the Type field and the Packet ID field. The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Wherein, the implementation of the sequence numbers of the encoded packet and the original data packet can refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and will not be repeated here. Specifically, for the implementation manner of the encoded packet header, reference may also be made to the corresponding descriptions of the implementation manner 2.1 and the implementation manner 2.2 in the first embodiment, and details are not repeated here.
可选的,虽然第一设备分别传输了N个第一数据包(即原数据包)和M个第二数据包(即编码包),但因为干扰、噪声等因素,第一设备传输的数据包不一定都能被第二设备正确接收,也就是说,在传输过程中可能发生丢包的情况。所以,当第二设备接收到至少N个正确且线性无关的数据包时,才能正确译码并恢复出N个第一数据包。Optionally, although the first device has respectively transmitted N first data packets (ie, original data packets) and M second data packets (ie, coded packets), due to factors such as interference and noise, the data transmitted by the first device The packets may not all be correctly received by the second device, that is, packet loss may occur during transmission. Therefore, when the second device receives at least N correct and linearly independent data packets, it can correctly decode and restore the N first data packets.
下面详细介绍译码端的数据传输流程。The following describes the data transmission process at the decoding end in detail.
S306,第二设备获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和N-K个第二数据包。S306. The second device obtains P data packets, where the P data packets include K first data packets and N-K second data packets.
S307,第二设备对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。S307. The second device decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets.
S308,第二设备按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包,并根据该级联包包头包括的形成该级联数据的多个数据单元,即该级联数据包括的多个数据单元,的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。S308. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into a concatenated data packet according to the sequence numbers of the N first data packets, and forms the concatenated data packet according to the header of the concatenated packet. The concatenation information of multiple data units of the data, that is, the multiple data units included in the concatenated data, divides the concatenated data into multiple data units.
可选的,第二设备接收到P个数据包,或从存储空间(如buffer)中读取到P个数据包,P是正整数,且大于或等于N。可见,当P等于N时,可以减少冗余开销。应理解,第二设备可以一次性接收到P个数据包,将其按序存储在存储空间中;也可以分多次接收,将每次接收到的数据包按序存储在存储空间中。在接收到的数据包个数等于P后,可执行译码操作,即步骤S307。Optionally, the second device receives P data packets, or reads P data packets from a storage space (such as a buffer), where P is a positive integer greater than or equal to N. It can be seen that when P is equal to N, redundancy overhead can be reduced. It should be understood that the second device may receive P data packets at one time and store them in the storage space in sequence; it may also receive in multiple times and store the data packets received each time in the storage space in sequence. After the number of received data packets is equal to P, the decoding operation can be performed, that is, step S307.
可选的,第二设备判断接收到的数据包是编码包还是原数据包的方式参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。如果某个数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包),则第二设备采用原数据包的解析方式解析该数据包的包头,获得该数据包的序列号。如果某个数据包是第二数据包(即编码包),则第二设备采用编码包的解析方式解析该数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段)和用于指示编码得到该数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。K和P均为正整数,且K小于或等于P。第二设备按照该K个第一数据包的序列号从小到大排序、该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示、以及任一个第二数据包的包头中用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息,构成系数因子矩阵。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。第二设备采用该系数因子矩阵对P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。应理解,译码得到的N-K个第一数据包和K个第一数据包加起来就是N个第一数据包。第二设备按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包。该级联数据包中包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据,其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分,该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。第二设备根据该级联包包头中的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。应理解,由于级联数据中可能有部分数据段不是完整的数据单元,所以仅对该级联数据进行分割后得到的多个数据单元中也可能存在一个完整数据单元的部分,此时按照级联包包头的指示(比如,S_start字段和S_end字段的指示),将分割得到的不完整的数据单元与其他级联数据中不完整的数据单元进行级联,以恢复出完整的数据单元。Optionally, for the manner in which the second device determines whether the received data packet is an encoded packet or an original data packet, refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here. If a certain data packet is the first data packet (that is, the original data packet), the second device parses the header of the data packet by using the analysis method of the original data packet, and obtains the serial number of the data packet. If a certain data packet is a second data packet (i.e., an encoded packet), the second device uses the parsing method of an encoded packet to parse the encoded packet header of the data packet, obtains the encoding factor field (i.e., the Coeff ID field) and is used to indicate the encoding The identification information of the N first data packets of the data packet is obtained. Wherein, the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets. Each first data packet includes a packet header and data, and each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. Both K and P are positive integers, and K is less than or equal to P. The second device sorts the sequence numbers of the K first data packets from small to large, the indication of the encoding factor field in the header of the P-K second data packets, and the indication encoding in the header of any second data packet to obtain The identification information of the N first data packets of the second data packet constitutes a coefficient factor matrix. The rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The second device jointly decodes the coded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets by using the coefficient factor matrix to obtain decoded N-K first data packets. It should be understood that the N-K first data packets obtained by decoding and the K first data packets add up to N first data packets. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into a concatenated data packet according to the sequence numbers of the N first data packets. The concatenation data packet includes a concatenation packet header and concatenation data. The concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments, wherein at least one of the start data segment and the end data segment is all or part of a data unit, and among the multiple data segments, except the start data segment and the end data segment Each data segment outside the data segment is a data unit. The header of the concatenated packet includes concatenated information of multiple data units included in the concatenated data. The second device divides the concatenated data into multiple data units according to the concatenated information in the header of the concatenated packet. It should be understood that since some data segments in the concatenated data may not be complete data units, there may also be a part of a complete data unit among the multiple data units obtained after only dividing the concatenated data. The indication of the header of the concatenated packet (for example, the indication of the S_start field and the S_end field), concatenates the incomplete data unit obtained by segmentation with the incomplete data unit in other concatenated data, so as to recover the complete data unit.
其中,K小于或等于N。用于指示编码得到该数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息是Block ID字段,或包括编码窗的窗长、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、以及编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中至少两项。Wherein, K is less than or equal to N. The identification information used to indicate the first N data packets encoded to obtain the data packet is the Block ID field, or includes the window length of the encoding window, the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window, and the last block in the encoding window. There are at least two items in the sequence number of a first data packet.
可选的,译码端(即第二设备)可能译码成功,也可能译码失败,所以针对译码成功和译码失败这两种情况分别设计反馈消息。该反馈消息的具体实现方式可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the decoding end (that is, the second device) may succeed in decoding or fail in decoding, so feedback messages are respectively designed for the two cases of successful decoding and decoding failure. For the specific implementation manner of the feedback message, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
可选的,针对原数据包和编码包的分开独立编号方式和联合顺序编号方式,其在编码端(即第一设备)和译码端(即第二设备)的存储参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, for the separate independent numbering method and joint sequential numbering method of the original data packet and the encoded packet, the storage at the encoding end (ie, the first device) and the decoding end (ie, the second device) refers to the first embodiment above The corresponding descriptions are not repeated here.
可选的,基站可通过RRC消息或者MAC CE消息指示UE上行传输的编码策略。该RRC消息或MAC CE消息可以指示UE的编码方式,或者指示不同的编码方案。Optionally, the base station may indicate the coding strategy of the UE for uplink transmission through an RRC message or a MAC CE message. The RRC message or the MAC CE message may indicate the encoding mode of the UE, or indicate different encoding schemes.
可见,本申请实施例提供了级联包包头、原数据包(即第一数据包)的包头、以及编码包包头的字段设计,并通过译码流程和操作,以期译码端接收到的数据包满秩(rank=N)的情况下能够正确译码出原数据包,并根据原数据包的序列号大小进行级联得到级联数据包,再根据级联数据包中级联包包头携带的级联信息,从而恢复出PDU/SDU,进而可以减少NR系统的性能损失。此外,本申请实施例仅在级联包包头中携带级联信息,可以节省包头的开销。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application provides the header of the concatenated packet, the header of the original data packet (that is, the first data packet), and the field design of the header of the encoded packet, and through the decoding process and operation, it is expected that the data received by the decoding end When the packet is full rank (rank=N), the original data packet can be correctly decoded, and the concatenated data packet can be obtained by concatenating according to the sequence number of the original data packet, and then according to the concatenated packet header carried in the concatenated data packet The concatenation information of the PDU/SDU can be recovered, thereby reducing the performance loss of the NR system. In addition, in the embodiment of the present application, only the concatenation information is carried in the header of the concatenation packet, which can save the overhead of the header.
作为一个可选实施例,本申请实施例三还可以结合前述实施例二形成一个新的实施例。在前述实施例三的基础上结合前述实施例二得到的技术方案与前述实施例三所述技术方案的区别在于:(1)前述实施例三结合前述实施例二所得技术方案可以不传输原数据包,只传输编码包;(2)前述实施例三结合前述实施例二所得技术方案对原数据包进一步封装编码包包头,确保传输的所有数据包的大小相等。As an optional embodiment,
具体地,前述实施例三的结合前述实施例二所得技术方案包括但不限于以下步骤:Specifically, the technical solution obtained in combination with the foregoing
S1,第一设备获取级联数据包,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据,该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据,其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分,该多个数据段中除起始数据段和末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元,该级联包包头包括级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。其中,级联包包头的设计参考前述实施例三中相应的描述,此处不再赘述。S1. The first device acquires a concatenated data packet, the concatenated data packet includes a concatenated packet header and concatenated data, and the concatenated data includes data obtained by concatenating multiple data segments, wherein the start data segment and the end data segment At least one of them is all or part of a data unit, each data segment in the multiple data segments except the start data segment and the end data segment is a data unit, and the concatenated packet header includes the concatenated data. Concatenation information for multiple data units. Wherein, the design of the header of the concatenated packet refers to the corresponding description in the foregoing third embodiment, and details are not repeated here.
S2,第一设备根据该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等,该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。其中,第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的序列号。S2, the first device generates N first data packets according to the concatenated data packets, each first data packet includes a packet header and data, the data sizes of the N first data packets are equal, and the N first data packets The size of the packet headers is equal, and the data of the j-th first data packet among the N first data packets is the j-th piece of data obtained after the concatenated data packet is divided into N equal parts. The value of j is an integer in the interval [1, N]. Wherein, the header of the first data packet includes the serial number of the first data packet.
S3,第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,M大于N,N和M均为正整数,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。此时,编码包包头的设计参考前述实施例二中相应描述,此处不再赘述。S3. The first device encodes the N first data packets and adds encoded packet headers to obtain M second data packets, where M is greater than N, and both N and M are positive integers, and the encoded packet headers include an encoding factor field. At this time, for the design of the header of the encoded packet, refer to the corresponding description in the foregoing second embodiment, and details are not repeated here.
S4,第一设备传输该M个第二数据包,其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。S4. The first device transmits the M second data packets, where the first data packets are original data packets and the second data packets are encoded packets.
S5,第二设备获取P个数据包,该P个数据包均是编码包,每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段,P为正整数。S5. The second device obtains P data packets, the P data packets are coded packets, each data packet includes a coded packet header and coded data, the coded packet header includes a coding factor field, and P is a positive integer.
S6,第二设备对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,译码方式参考前述实施例二中步骤S205的描述,此处不再赘述。S6. The second device decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets. Wherein, for the decoding method, refer to the description of step S205 in the second embodiment above, which will not be repeated here.
S7,第二设备按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包,并根据该级联包包头包括的形成该级联数据的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,步骤S7参考前述实施例三中步骤S308的描述,此处不再赘述。S7. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into a concatenated data packet according to the order of the sequence numbers of the N first data packets, and forms the concatenated data according to the header of the concatenated packet. The concatenation information of multiple data units of data, the concatenated data is divided into multiple data units. Wherein, for step S7, refer to the description of step S308 in the third embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
可见,本申请实施例通过对原数据包进一步添加编码包包头,来保证编码端(即第一设备)传输的数据包的大小相等。本申请实施例可以在物理层传输块(TB)大小为数据包整数倍的情况下,有利于分别识别出每个数据包的位置,并有利于通过CRC判断每个数据包是否正确,如果正确即可向上层递交,最大化网络编码的效率和性能。此外,本申请实施例无需对每个原数据包都添加级联的字段指示,而是通过统一的级联包包头进行级联信息的指示,可以节省包头的开销。It can be seen that, in the embodiment of the present application, by further adding an encoded packet header to the original data packet, it is ensured that the size of the data packets transmitted by the encoding end (that is, the first device) is equal. In the embodiment of the present application, when the size of the physical layer transport block (TB) is an integer multiple of the data packet, it is beneficial to identify the position of each data packet separately, and it is beneficial to judge whether each data packet is correct through CRC, and if it is correct It can be submitted to the upper layer to maximize the efficiency and performance of network coding. In addition, in the embodiment of the present application, there is no need to add a concatenation field indication to each original data packet, but to indicate the concatenation information through a unified concatenation packet header, which can save the overhead of the packet header.
实施例四Embodiment Four
本申请实施例四主要介绍在NR协议中引入网络编码的再又一种可能的数据传输方法,该方法既传输原数据包也传输编码包,并且介绍仅对PDU/SDU进行分割操作后,如何进行网络编码和数据传输、以及如何设计包头。
应理解,本申请实施例四与前述实施例一至前述实施例三在流程上的区别是:本申请实施例四只对PDU/SDU进行分割,不级联;而前述实施例一至前述实施例三都可以对PDU/SDU进行分割和级联两个操作。It should be understood that the difference in process between
参见图29,图29是本申请实施例提供的数据传输方法的第四种示意流程图。如图29所示,该数据传输方法包括但不限于以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 29 , FIG. 29 is a fourth schematic flowchart of the data transmission method provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 29, the data transmission method includes but is not limited to the following steps:
S401,第一设备获取N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等,每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息,每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段,该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。S401. The first device acquires N first data packets, the sizes of the N first data packets are not exactly equal, each first data packet includes a header and data, and the header of each first data packet includes the first The division information of the data unit corresponding to the data of the data packet, the packet header of each first data packet further includes a data packet identification field, and the data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet.
S402,第一设备传输该N个第一数据包。S402. The first device transmits the N first data packets.
S403,第一设备对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包,该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包,该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等,每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段,该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。S403, the first device encodes the N first data packets and adds encoded packet headers to obtain M second data packets, the N first data packets correspond to Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding, the The size of the Q equivalent original data packets is equal, and the packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field or an offset field, and the offset field is used to indicate that the sequence number of the first data packet is relative to the first data The offset number corresponding to the sequence number of the original data packet corresponding to the packet.
S404,第一设备传输该M个第二数据包。S404. The first device transmits the M second data packets.
可选的,本申请实施例中的第一数据包可以称为原数据包,第二数据包可以称为编码包。原数据包可以理解为未经过网络编码的数据包,编码包可以理解为经过网络编码后的数据包。本申请实施例中的数据单元是PDU或SDU。Optionally, the first data packet in this embodiment of the present application may be called an original data packet, and the second data packet may be called an encoded packet. The original data packet can be understood as a data packet that has not undergone network encoding, and the encoded packet can be understood as a data packet that has undergone network encoding. The data unit in this embodiment of the present application is a PDU or an SDU.
可选的,第一设备按照预设大小对至少一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)进行分割,得到N个原数据(原数据指原数据包中的数据)。如果某个数据单元的大小小于或等于该预设大小,则无需对其进行分割,直接作为一个原数据。如果某个数据单元经过一次或多次分割后剩余部分的大小小于该预设大小,则将该剩余部分作为一个原数据,并从下一个数据单元(PDU或SDU)中分割出一部分(该部分的大小也小于该预设大小),作为另一个原数据,使这两个原数据分别加上包头后的大小之和等于该预设大小与包头大小之和。因此,该N个原数据中有部分原数据是等大小的,另外部分原数据不等大小。第一设备再对每个原数据加包头得到第一数据包(即原数据包)。N个原数据分别加包头得到N个第一数据包,由于这N个原数据不等大小,所以这N个第一数据包也不等大小。为了降低时延,第一设备可以每得到一个第一数据包就传输该第一数据包,并将该第一数据包缓存在存储器(这里的存储器是指存储空间,也可以是缓存)中。当该存储器中第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的个数达到网络编码所需的数据包个数(本申请实施例假设网络编码所需的数据包个数,即数据块大小,为Q)时,再对该存储器中缓存的N个第一数据包进行网络编码,生成M个编码数据。其中,第一设备在对N个第一数据包进行网络编码时,将这N个第一数据包形成Q个等大小的等效原数据包,并对该Q个等效原数据包进行网络编码。一个等效原数据包包括一个或多个第一数据包。如果某个第一数据包的大小小于该预设大小与包头大小之和,则可以将相邻两个或多个小于该预设大小的第一数据包形成一个等效原数据包,一个等效数据包的大小等于该预设大小与包头大小之和。应理解,一个等效数据包中可能包括多个第一数据包的包头。第一设备对每个编码数据加编码包包头,得到第二数据包(即编码包),并传输该第二数据包。M个编码数据加编码包包头后可得到M个第二数据包(即编码包)。其中,本申请对网络编码的方式不做限定。N、M、Q均为正整数,Q小于或等于N,M和N的大小关系不做限定,即M可以小于N,也可以大于N,还可以等于N。Optionally, the first device divides at least one data unit (PDU or SDU) according to a preset size to obtain N original data (original data refers to data in an original data packet). If the size of a certain data unit is less than or equal to the preset size, it does not need to be divided, and it is directly used as a piece of original data. If the size of the remaining part of a data unit after one or more divisions is smaller than the preset size, the remaining part will be regarded as an original data, and a part (this part) will be divided from the next data unit (PDU or SDU) The size is also smaller than the preset size), as another original data, so that the sum of the sizes of the two original data plus the header is equal to the sum of the preset size and the header size. Therefore, some of the original data in the N pieces of original data have equal sizes, and other parts of the original data have different sizes. The first device then adds a packet header to each original data to obtain the first data packet (ie, the original data packet). Packet headers are added to the N original data respectively to obtain N first data packets. Since the N original data are of different sizes, the N first data packets are also of different sizes. In order to reduce the delay, the first device may transmit the first data packet every time it obtains the first data packet, and cache the first data packet in a memory (here, the memory refers to a storage space, and may also be a cache). When the number of equivalent original data packets corresponding to the first data packet in the memory reaches the number of data packets required for network coding (the embodiment of the present application assumes that the number of data packets required for network coding, that is, the size of the data block, is Q), then perform network coding on the N first data packets buffered in the memory to generate M coded data. Wherein, when performing network coding on the N first data packets, the first device forms the N first data packets into Q equivalent original data packets of equal size, and performs network encoding on the Q equivalent original data packets. coding. An equivalent original data packet includes one or more first data packets. If the size of a certain first data packet is smaller than the sum of the preset size and the header size, two or more adjacent first data packets smaller than the preset size can be formed into an equivalent original data packet, one equal The size of the effective data packet is equal to the sum of the preset size and the size of the header. It should be understood that one equivalent data packet may include headers of multiple first data packets. The first device adds an encoded packet header to each encoded data to obtain a second data packet (that is, an encoded packet), and transmits the second data packet. M second data packets (ie, encoded packets) can be obtained after adding the encoded packet header to the M encoded data. Wherein, the present application does not limit the way of network coding. N, M, and Q are all positive integers, Q is less than or equal to N, and the size relationship between M and N is not limited, that is, M can be smaller than N, larger than N, or equal to N.
可见,第二数据包(即编码包)比等效原数据包多一个编码包包头,即编码包的编码数据和等效原数据包大小相等,也就是说,本申请实施例传输的编码包(第二数据包)和原数据包(第一数据包)不等大小,并且N个原数据包也不等大小,一定程度上节约了原数据包的包头开销。It can be seen that the second data packet (that is, the encoded packet) has one more encoded packet header than the equivalent original data packet, that is, the encoded data of the encoded packet is equal in size to the equivalent original data packet, that is to say, the encoded packet transmitted in the embodiment of the present application (the second data packet) and the original data packet (the first data packet) have different sizes, and the N original data packets have different sizes, which saves the header overhead of the original data packet to a certain extent.
可选的,本申请实施例对上述步骤S402和上述步骤S403的执行顺序不做限定。比如上述步骤S402既可以在上述步骤S403之前执行,也可以在上述步骤S403之后执行,还可以与上述步骤S403同时/并行执行。Optionally, the embodiment of the present application does not limit the execution order of the above step S402 and the above step S403. For example, the above step S402 may be executed before the above step S403, may also be executed after the above step S403, and may also be executed simultaneously/parallelly with the above step S403.
可选的,上述步骤S401至步骤S404可以由第一设备中单独的NC功能子层实现,也可以由具有NC功能的层实现,具体可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the above step S401 to step S404 may be implemented by a separate NC function sublayer in the first device, or may be implemented by a layer having an NC function. For details, please refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, which will not be repeated here. repeat.
可选的,为更好地理解上述步骤S401至上述步骤S404所述的流程,下面以一个示例来说明上述步骤S401至上述步骤S404所示的编码端数据传输流程。Optionally, in order to better understand the process described in the above step S401 to the above step S404, an example is used below to illustrate the data transmission process at the encoding end shown in the above step S401 to the above step S404.
示例性的,参见图30,图30是本申请实施例提供的编码端数据传输流程的第五种示意图。如图30所示,以NC功能子层位于PDCP层和RLC层之间为例。假设NC功能子层依次接收到PDCP PDU1和PDCP PDU2。编码端(即第一设备)按照预设大小对PDCP PDU1和PDCP PDU2进行分割,得到6个原数据(如图30中的Data1~6)。其中,Data1~3以及Data6的大小相等,Data4和Data5的大小不等,但Data4和Data5分别加上包头(即图30中的Header)后与Data1~3和Data6中任一个加包头后的大小相等。Data4是PDCP PDU1经过前3次等大小分割后剩余的部分,Data5是PDCP PDU2的头部。再对每个原数据添加包头(即图30中的Header),获得包括包头的原数据包;一方面将原数据包作为NC功能子层的NC PDU直接传输至下一层,另一方面将原数据包缓存在NC功能子层的编码器的缓存区(buffer)中。6个原数据分别加包头得到6个原数据包(如图30中的Pkt1~6),这6个原数据包对应用于编码的5个等大小的等效原数据包。当buffer中缓存的原数据包对应的等效原数据包的个数达到编码器所需的数据包个数时(这里假设编码器所需的数据包个数为5),将buffer中的6个原数据包转换成5个等大小的等效原数据包后,对这5个等大小的等效原数据包进行网络编码,生成编码数据EData1和EData2。应理解,对这5个等效原数据包进行网络编码生成的编码数据的个数可以小于等效原数据包的个数,也可以大于等效原数据包的个数。最后对每个编码数据添加编码包包头(如图30中的NC_Header),得到包括包头的编码包(如图30中的EPkt1和EPkt2)并作为NC功能子层的PDU进行发送。应理解,发送编码包时可以只发送得到的部分编码包(比如发送EPkt1,不发送EPkt2),也可以发送得到的全部编码包。For example, refer to FIG. 30 , which is a fifth schematic diagram of the data transmission process at the encoding end provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 30 , it is taken as an example that the NC function sublayer is located between the PDCP layer and the RLC layer. It is assumed that the NC functional sublayer receives PDCP PDU1 and PDCP PDU2 in sequence. The encoding end (that is, the first device) divides PDCP PDU1 and PDCP PDU2 according to a preset size to obtain 6 pieces of original data (Data1-6 in FIG. 30 ). Among them, the sizes of Data1~3 and Data6 are equal, and the sizes of Data4 and Data5 are different, but the size of Data4 and Data5 after adding the header (that is, the Header in Figure 30) is the same as that of any one of Data1~3 and Data6 after adding the header equal. Data4 is the remaining part of PDCP PDU1 after the first three equal-size divisions, and Data5 is the header of PDCP PDU2. Then add a packet header (i.e. Header in Figure 30) to each original data to obtain the original data packet including the header; on the one hand, the original data packet is directly transmitted to the next layer as the NC PDU of the NC function sublayer; on the other hand, the The original data packet is buffered in the buffer of the encoder of the NC functional sublayer. Six original data packets are respectively added with packet headers to obtain six original data packets (Pkt1-6 in Fig. 30), and these six original data packets correspond to five equivalent original data packets of equal size used for encoding. When the number of equivalent original data packets corresponding to the original data packets cached in the buffer reaches the number of data packets required by the encoder (here, it is assumed that the number of data packets required by the encoder is 5), the 6 in the buffer After the original data packets are converted into five equivalent original data packets of equal size, network coding is performed on these five equivalent original data packets of equal size to generate encoded data EData1 and EData2. It should be understood that the number of encoded data generated by performing network encoding on the five equivalent original data packets may be smaller than or greater than the number of equivalent original data packets. Finally, add a coded packet header (such as NC_Header in Figure 30) to each coded data to obtain coded packets including the header (such as EPkt1 and EPkt2 in Figure 30) and send it as a PDU of the NC function sublayer. It should be understood that when sending the encoded packets, only part of the obtained encoded packets may be sent (for example, EPkt1 is sent and EPkt2 is not sent), or all the obtained encoded packets may be sent.
可选的,上述每个第一数据包(即原数据包)包括包头和数据(即上述原数据)。每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元(PDU或SDU)的分割信息。其中,一个第一数据包的数据对应一个PDU/SDU的全部或部分。该分割信息包括:第一数据包的数据在该数据对应的数据单元中的位置信息,和指示该第一数据包的数据的长度的信息。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned first data packets (ie, the original data packet) includes a packet header and data (ie, the above-mentioned original data). The packet header of each first data packet includes segmentation information of the data unit (PDU or SDU) corresponding to the data of the first data packet. Wherein, the data of one first data packet corresponds to all or part of one PDU/SDU. The segmentation information includes: position information of the data of the first data packet in the data unit corresponding to the data, and information indicating the length of the data of the first data packet.
可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还包括Packet ID字段,可选的还可以包括第一指示信息。第一指示信息用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包,该第一指示信息在包头中的表现形式可以是O/C字段。数据包标识字段用于指示第一数据包的序列号。应理解,第一数据包的序列号可以按照从小到大顺序编号,或顺序递增。也就是说,第一设备获取到的第一个第一数据包的序列号为1,第二个第一数据包的序列号为2,以此类推。每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)或偏移(offset)字段,该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。可选的,每个第一数据包的包头还可以包括Type字段和Block ID字段中的一项或多项。Type字段用于指示数据包标识字段的长度,或者用于指示数据包的序列号的范围。Block ID字段用于指示数据块的标识,这个数据块包括该Block ID字段所在的第一数据包。Optionally, the packet header of each first data packet further includes a Packet ID field, and optionally may also include first indication information. The first indication information is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is contained is an original data packet, and a form of the first indication information in a packet header may be an O/C field. The data packet identification field is used to indicate the sequence number of the first data packet. It should be understood that the sequence numbers of the first data packets may be numbered sequentially from small to large, or in ascending order. That is to say, the sequence number of the first first data packet acquired by the first device is 1, the sequence number of the second first data packet is 2, and so on. The packet header of each first data packet also includes a coding factor field (such as a Coeff ID field) or an offset (offset) field, and the offset field is used to indicate that the sequence number of the first data packet corresponds to the first data packet The offset number equivalent to the sequence number of the original packet. Optionally, the header of each first data packet may also include one or more items of the Type field and the Block ID field. The Type field is used to indicate the length of the data packet identification field, or to indicate the range of the serial number of the data packet. The Block ID field is used to indicate the identifier of the data block, and this data block includes the first data packet in which the Block ID field is located.
参见图31a,图31a是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图七。如图31a所示,该第一数据包的包头(Header)包括:Packet ID字段,分段信息(segmentinformation,SI)字段,长度(Length,L)字段,以及Coeff ID字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。参见图31b,图31b是本申请实施例提供的第一数据包的包头格式示意图八。如图31b所示,该第一数据包的包头包括:Packet ID字段,SI字段,长度(Length,L)字段,以及偏移(offset)字段;可选的包括O/C字段,Type字段和Block ID字段。应理解,第一数据包的包头中O/C字段设置为第一值,用于指示该第一数据包是原数据包。第一值可以是1或0。Referring to FIG. 31a, FIG. 31a is a schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application VII. As shown in Figure 31a, the header (Header) of this first data packet comprises: Packet ID field, segmentation information (segmentinformation, SI) field, length (Length, L) field, and Coeff ID field; Optionally include O /C field, Type field and Block ID field. Referring to FIG. 31b, FIG. 31b is an eighth schematic diagram of the header format of the first data packet provided by the embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 31b, the header of this first data packet includes: Packet ID field, SI field, length (Length, L) field, and offset (offset) field; Optionally include O/C field, Type field and Block ID field. It should be understood that the O/C field in the header of the first data packet is set to the first value, which is used to indicate that the first data packet is an original data packet. The first value can be 1 or 0.
其中,原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段指示的行向量中只有一个元素等于1,其他元素均为0。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中CoeffID字段的值相同。图31b中offset字段的长度可以为8bit,用于表示原数据包的序列号相对于等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。图31a和图31b中SI字段的长度为2bit,用于表示第一数据包的数据在该数据对应的数据单元中的位置信息,其取值和含义如下述表1所示。图31a和图31b中其他字段的含义,可参考前述实施例一中相同字段的含义。Among them, in the row vector indicated by the Coeff ID field in the packet header of the original data packet, only one element is equal to 1, and the other elements are all 0. If multiple original data packets correspond to one equivalent original data packet, the values of the CoeffID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same. The length of the offset field in FIG. 31b may be 8 bits, which is used to indicate the offset number of the sequence number of the original data packet relative to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet. The length of the SI field in FIG. 31a and FIG. 31b is 2 bits, which is used to indicate the position information of the data of the first data packet in the data unit corresponding to the data, and its values and meanings are shown in Table 1 below. For meanings of other fields in FIG. 31a and FIG. 31b , reference may be made to the meanings of the same fields in
表1Table 1
可选的,上述每个第二数据包(即编码包)包括编码包包头和编码数据(这里的编码数据是第一数据包经过网络编码后得到)。每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息、以及编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段),可选的还可以包括第二指示信息。第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息是BlockID字段,或者包括以下至少两项:指示编码窗的窗长的信息、编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号。应理解,如果编码窗的窗长是半静态配置的,则用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息包括编码窗中第一个第一数据包的序列号、和编码窗中最后一个第一数据包的序列号中的至少一项即可。编码包包头中的编码因子字段(如Coeff ID字段)的长度为8bit,用于指示255行码本的行索引,这里的码本可以是范德蒙码本、柯西码本、随机码本等。Optionally, each of the above-mentioned second data packets (ie, encoded packets) includes an encoded packet header and encoded data (the encoded data here is obtained after the first data packet is network-encoded). The coded packet header of each second data packet includes the identification information used to indicate the Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet, and a coding factor field (such as a Coeff ID field), and may optionally include Second instruction message. The second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. The identification information used to indicate that the Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet is a BlockID field, or include at least two of the following: information indicating the window length of the encoding window, the first first data in the encoding window The sequence number of the packet, the sequence number of the last first packet in the encoding window. It should be understood that if the window length of the encoding window is configured semi-statically, the identification information used to indicate the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet includes the sequence number of the first first data packet in the encoding window , and at least one of the sequence number of the last first data packet in the encoding window. The encoding factor field (such as the Coeff ID field) in the header of the encoded packet has a length of 8 bits and is used to indicate the row index of the 255-row codebook. The codebook here can be a Vandermonde codebook, a Cauchy codebook, a random codebook, etc.
可选的,上述编码包包头还可以包括Type字段和Packet ID字段中的一项或多项。编码包包头中的Packet ID字段用于指示该Packet ID字段所在第二数据包(编码包)的SN。其中,编码包和原数据包的序列号的实现方式可参考前述实施例一中相应描述,此处不再赘述。具体地,编码包包头的实现方式也可参考前述实施例一中实现方式2.1和实现方式2.2的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the header of the encoded packet may also include one or more items of the Type field and the Packet ID field. The Packet ID field in the header of the encoded packet is used to indicate the SN of the second data packet (encoded packet) where the Packet ID field is located. Wherein, the implementation of the sequence numbers of the encoded packet and the original data packet can refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and will not be repeated here. Specifically, for the implementation manner of the encoded packet header, reference may also be made to the corresponding descriptions of the implementation manner 2.1 and the implementation manner 2.2 in the first embodiment, and details are not repeated here.
可选的,虽然第一设备分别传输了N个第一数据包(即原数据包)和M个第二数据包(即编码包),但因为干扰、噪声等因素,第一设备传输的数据包不一定都能被第二设备正确接收,也就是说,在传输过程中可能发生丢包的情况。所以,当第二设备接收到至少N个正确且线性无关的数据包时,才能正确译码并恢复出N个第一数据包。下述步骤S405至步骤S407将详细介绍译码端的数据传输流程。Optionally, although the first device has respectively transmitted N first data packets (ie, original data packets) and M second data packets (ie, coded packets), due to factors such as interference and noise, the data transmitted by the first device The packets may not all be correctly received by the second device, that is, packet loss may occur during transmission. Therefore, when the second device receives at least N correct and linearly independent data packets, it can correctly decode and restore the N first data packets. The following steps S405 to S407 will introduce the data transmission process at the decoding end in detail.
S405,第二设备获取P个数据包,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。S405. The second device acquires P data packets, where the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets.
S406,第二设备对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。S406. The second device decodes the P data packets to obtain decoded N first data packets.
S407,第二设备根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个或多个数据单元。S407. The second device restores the data of the N first data packets into one or more data units according to the segmentation information included in the packet header of each of the N first data packets.
可选的,第二设备接收到P个数据包,或从存储空间(如buffer)中读取到P个数据包,P是正整数,且大于或等于N。可见,当P等于N时,可以减少冗余开销。应理解,第二设备可以一次性接收到P个数据包,将其按序存储在存储空间中;也可以分多次接收,将每次接收到的数据包按序存储在存储空间中。在接收到的数据包个数等于P后,可执行译码操作,即步骤S406。Optionally, the second device receives P data packets, or reads P data packets from a storage space (such as a buffer), where P is a positive integer greater than or equal to N. It can be seen that when P is equal to N, redundancy overhead can be reduced. It should be understood that the second device may receive P data packets at one time and store them in the storage space in sequence; it may also receive in multiple times and store the data packets received each time in the storage space in sequence. After the number of received data packets is equal to P, the decoding operation can be performed, that is, step S406.
可选的,第二设备判断接收到的数据包是编码包还是原数据包的方式参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, for the manner in which the second device determines whether the received data packet is an encoded packet or an original data packet, refer to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
一种实现方式中,针对第一数据包的包头包括编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段)的情况(即前述图31a所示包头格式),如果某个数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包),则第二设备采用原数据包的解析方式解析该数据包的包头获得编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段)。如果某个数据包是第二数据包(即编码包),则第二设备采用编码包的解析方式解析该数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段)和用于指示编码得到该数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。如果多个原数据包对应一个等效原数据包,则该多个原数据包的包头中Coeff ID字段的值相同。对于这P个数据包(或K个第一数据包)中包长小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和的数据包,判断这些数据包中编码因子字段的值是否相同,将编码因子字段的值相同的数据包进行等效级联(应理解,这里的等效级联并不是指真正的级联,而是将编码因子字段的值相同的多个数据包作为一个完整数据包,或者说,将编码因子字段的值相同的多个数据包与等效的第三数据包建立映射关系),得到等效的第三数据包。其中,能够等效级联成一个第三数据包的原数据包的序列号连续。如果该等效的第三数据包的长度小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则认为该等效的第三数据包不完整,则丢弃等效级联成该第三数据包的所有第一数据包(即原数据包)。如果该等效的第三数据包的长度等于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则认为该等效的第三数据包完整,即正确接收。应理解,如果该等效的第三数据包的长度等于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则该等效的第三数据包就是等效原数据包。In one implementation, for the case where the packet header of the first data packet includes a coding factor field (i.e. the Coeff ID field) (i.e. the header format shown in FIG. 31a), if a certain data packet is the first data packet (i.e. the original data packet), the second device parses the packet header of the data packet in the same way as the original data packet to obtain the encoding factor field (that is, the Coeff ID field). If a certain data packet is a second data packet (i.e., an encoded packet), the second device uses the parsing method of an encoded packet to parse the encoded packet header of the data packet, obtains the encoding factor field (i.e., the Coeff ID field) and is used to indicate the encoding The identification information of Q equivalent original data packets of the data packet is obtained. Wherein, the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets. The Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. If multiple original data packets correspond to an equivalent original data packet, the values of the Coeff ID fields in the packet headers of the multiple original data packets are the same. For the data packets whose packet length is less than the sum of the above-mentioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet in these P data packets (or K first data packets), it is judged whether the values of the encoding factor fields in these data packets are the same, and the The data packets with the same value of the encoding factor field are equivalently concatenated (it should be understood that the equivalent concatenation here does not refer to the real concatenation, but multiple data packets with the same value of the encoding factor field as a complete data package, or in other words, establish a mapping relationship between a plurality of data packets with the same value of the encoding factor field and an equivalent third data packet), to obtain an equivalent third data packet. Wherein, the sequence numbers of the original data packets that can be equivalently concatenated into a third data packet are continuous. If the length of the equivalent third data packet is less than the sum of the above-mentioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is considered to be incomplete, and the equivalent concatenation into the third data packet is discarded. All the first data packets (ie original data packets) of the packet. If the length of the equivalent third data packet is equal to the sum of the aforementioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is considered complete, that is, received correctly. It should be understood that if the length of the equivalent third data packet is equal to the sum of the preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is the equivalent original data packet.
另一种实现方式,针对第一数据包的包头包括偏移字段(即offset字段)的情况(即前述图31b所示包头格式),如果某个数据包是第一数据包(即原数据包),则第二设备采用原数据包的解析方式解析该数据包的包头该数据包的序列号和偏移字段。如果某个数据包是第二数据包(即编码包),则第二设备采用编码包的解析方式解析该数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段(即Coeff ID字段)和用于指示编码得到该数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。对于这P个数据包(或K个第一数据包)中包长小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和的数据包,判断这些数据包的序列号分别减去各自包头中offset字段的值所得差值是否相等,将差值相等的数据包进行等效级联(应理解,这里的等效级联并不是指真正的级联,而是将编码因子字段的值相同的多个数据包作为一个完整数据包,或者说,将编码因子字段的值相同的多个数据包与等效的第三数据包建立映射关系),得到等效的第三数据包。其中,能够等效级联成一个第三数据包的原数据包的序列号连续。如果该等效的第三数据包的长度小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则认为该等效的第三数据包不完整,则丢弃等效级联成该第三数据包的所有第一数据包(即原数据包)。如果该等效的第三数据包的长度等于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则认为该等效的第三数据包完整,即正确接收。应理解,如果该等效的第三数据包的长度等于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则该等效的第三数据包就是等效原数据包。Another implementation, for the case where the packet header of the first data packet includes an offset field (ie, the offset field) (ie, the packet header format shown in Figure 31b), if a certain data packet is the first data packet (ie, the original data packet ), the second device parses the sequence number and offset fields of the header of the data packet in the same manner as the original data packet. If a certain data packet is a second data packet (i.e., an encoded packet), the second device uses the parsing method of an encoded packet to parse the encoded packet header of the data packet, obtains the encoding factor field (i.e., the Coeff ID field) and is used to indicate the encoding The identification information of Q equivalent original data packets of the data packet is obtained. Wherein, the P data packets include K first data packets and P-K second data packets. For the data packets in the P data packets (or the K first data packets) whose packet length is less than the sum of the above-mentioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet, it is judged that the sequence numbers of these data packets are respectively subtracted from the offset in the respective headers field values are equal, and the data packets with equal differences are equivalently concatenated (it should be understood that the equivalent concatenation here does not refer to the real concatenation, but the value of the coding factor field is much the same data packets as a complete data packet, or in other words, establish a mapping relationship between multiple data packets with the same value of the encoding factor field and an equivalent third data packet), to obtain an equivalent third data packet. Wherein, the sequence numbers of the original data packets that can be equivalently concatenated into a third data packet are continuous. If the length of the equivalent third data packet is less than the sum of the above-mentioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is considered to be incomplete, and the equivalent concatenation into the third data packet is discarded. All the first data packets (ie original data packets) of the packet. If the length of the equivalent third data packet is equal to the sum of the aforementioned preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is considered complete, that is, received correctly. It should be understood that if the length of the equivalent third data packet is equal to the sum of the preset size and the header size of the original data packet, then the equivalent third data packet is the equivalent original data packet.
可选的,假设K个第一数据包(即原数据包)等效级联成(或对应)T个等效原数据包,T小于或等于K且T为正整数。当第二设备正确接收到的等效原数据包和编码包(即第二数据包)的总个数(T+P-K)大于或等于N时,第二设备按照该T个等效原数据包的序列号从小到大排序、该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示、以及任一个第二数据包的包头中用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息构成系数因子矩阵。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。第二设备采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包(或T个等效原数据包)进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。第二设备获得译码后的N个第一数据包(即原数据包)后,根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个或多个数据单元。其中,该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包,该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据,每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据。K、P、以及Q均为正整数,K小于或等于P,N≤P≤N+M,Q小于或等于N。Optionally, it is assumed that K first data packets (ie, original data packets) are equivalently concatenated into (or correspond to) T equivalent original data packets, where T is less than or equal to K and T is a positive integer. When the total number (T+P-K) of the equivalent original data packets and encoded packets (i.e. the second data packets) correctly received by the second device is greater than or equal to N, the second device according to the T equivalent original data packets The sequence numbers of the P-K second data packets are sorted from small to large, the indication of the encoding factor field in the header of the encoded packet of the P-K second data packets, and the header of any second data packet is used to indicate the Q number of the second data packet obtained by encoding, etc. The identification information of the original data packet constitutes a coefficient factor matrix. The rank of the coefficient factor matrix is equal to N. The second device uses the coefficient factor matrix to jointly decode the encoded data of the P-K second data packets and the K first data packets (or T equivalent original data packets), and obtain the decoded Nth a packet. After the second device obtains the decoded N first data packets (i.e. the original data packets), according to the segmentation information included in the packet header of each first data packet in the N first data packets, the N first data packets The data of a packet is reduced to one or more data units. Wherein, the N first data packets correspond to Q equivalent original data packets used for encoding, and the Q equivalent original data packets are equal in size. Each first data packet includes a packet header and data, and each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. K, P, and Q are all positive integers, K is less than or equal to P, N≤P≤N+M, and Q is less than or equal to N.
为更好地理解上述步骤S406的译码流程,下面以一个示例来举例说明。In order to better understand the decoding process of step S406 above, an example is used as an example below.
示例性的,参见图32,图32是本申请实施例提供的一种构造系数因子矩阵的示意图。假设序列号为3和4的原数据包(即Pkt3和Pkt4)对应一个等效原数据包,序列号为5和6的原数据包(即Pkt5和Pkt6)对应另一等效原数据包。这里假设由于信道衰落、干扰等因素,原数据包Pkt2和Pkt3丢失。一种实现方式中,Pkt3和Pkt4中Coeff ID字段的值相同,Pkt5和Pkt6中Coeff ID字段的值相同,Pkt3和Pkt5中Coeff ID字段的值不相同。数据块大小,即用于编码的等效原数据包个数Q为半静态配置。由于原数据包Pkt3丢失,而译码端(即第二设备)接收到的Pkt4的包长又小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,并且接收到的原数据包中没有与Pkt4的Coeff ID字段的值相同的原数据包,所以译码端(即第二设备)丢弃Pkt4,即译码端(即第二设备)认为Pkt3和Pkt4都丢失了,即Pkt3和Pkt4对应的等效原数据包丢失。也就是说,译码端(即第二设备)在构造系数因子矩阵时忽略Pkt4中携带的CoeffID字段。由于译码端(即第二设备)接收到的Pkt5和Pkt6的Coeff ID字段的值相同,且Pkt5和Pkt6的长度之和等于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,则译码端(即第二设备)认为正确接收到Pkt5和Pkt6,或者认为Pkt5和Pkt6对应的等效原数据包未丢失。也就是说,译码端(即第二设备)在构造系数因子矩阵时将Pkt5和Pkt6视为一个完整数据包,只提取其中一个的Coeff ID字段。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)为Q。其中,因为图33中丢失了2个等效原数据包(即序列号为2和3的等效原数据包),则需要至少2个编码包来联合译码。For example, refer to FIG. 32 , which is a schematic diagram of constructing a factor matrix of coefficients provided by an embodiment of the present application. Assume that the original data packets with
另一种实现方式中,数据块大小,即用于编码的等效原数据包个数Q为半静态配置。如图33所示,译码端(即第二设备)接收到的Pkt5中offset字段的值为1,Pkt6中offset字段的值为2。由于Pkt5的序列号(5)减去自己包头中offset字段的值(1)所得差值为4(5-1=4),Pkt6的序列号(6)减去自己包头中offset字段的值(2)所得差值为4(6-2=4),则译码端(即第二设备)认为正确接收到Pkt5和Pkt6,且Pkt5和Pkt6等效级联成一个序列号为4的等效原数据包。因为原数据包Pkt3丢失,而译码端(即第二设备)接收到的Pkt4的包长又小于上述预设大小与原数据包的包头大小之和,并且接收到的原数据包中没有原数据包的序列号减去自己包头中offset字段的值所得的差值与Pkt4的序列号(4)减去自己包头中offset字段的值(1)所得差值(4-1=3)相同,所以译码端(即第二设备)丢弃Pkt4,即译码端(即第二设备)认为Pkt3和Pkt4都丢失了,即Pkt3和Pkt4对应的等效原数据包(该等效原数据包的序列号为3)丢失。译码端(即第二设备)按照等效原数据包的序列号和编码包的Coeff ID字段构造系数因子矩阵(如图33所示的系数因子矩阵,该系数因子矩阵的列从左到右对应等效原数据包的序列号从小到大排列)。该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)为Q。其中,因为图33中丢失了2个等效原数据包(即序列号为2和3的等效原数据包),则需要至少2个编码包来联合译码。In another implementation manner, the data block size, that is, the number Q of equivalent original data packets used for encoding is configured semi-statically. As shown in FIG. 33 , the value of the offset field in Pkt5 received by the decoding end (that is, the second device) is 1, and the value of the offset field in Pkt6 is 2. Since the sequence number (5) of Pkt5 subtracts the value (1) of the offset field in the header of the Pkt5, the resulting difference is 4 (5-1=4), and the sequence number (6) of Pkt6 subtracts the value of the offset field in the header of the packet ( 2) The resulting difference is 4 (6-2=4), then the decoding end (i.e. the second device) thinks that Pkt5 and Pkt6 are received correctly, and Pkt5 and Pkt6 are equivalently concatenated into an equivalent sequence number of 4 original packet. Because the original data packet Pkt3 is lost, and the packet length of Pkt4 received by the decoding end (that is, the second device) is smaller than the sum of the above preset size and the header size of the original data packet, and there is no original data packet in the received original data packet. The difference obtained by subtracting the value of the offset field in the packet header from the sequence number of the data packet is the same as the difference (4-1=3) obtained by subtracting the value (1) of the offset field in the packet header from the sequence number of Pkt4 (4), So the decoding end (i.e. the second device) discards Pkt4, that is, the decoding end (i.e. the second device) thinks that both Pkt3 and Pkt4 are lost, that is, the equivalent original data packet corresponding to Pkt3 and Pkt4 (the equivalent original data packet The serial number is 3) missing. The decoding end (i.e. the second device) constructs a coefficient factor matrix according to the sequence number of the equivalent original data packet and the Coeff ID field of the encoded packet (the coefficient factor matrix shown in Figure 33, the columns of the coefficient factor matrix are from left to right The sequence numbers corresponding to the equivalent original data packets are arranged from small to large). The rank of the coefficient factor matrix is Q. Wherein, because two equivalent original data packets (that is, equivalent original data packets with
可选的,译码端(即第二设备)可能译码成功,也可能译码失败,所以针对译码成功和译码失败这两种情况分别设计反馈消息。该反馈消息的具体实现方式可参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, the decoding end (that is, the second device) may succeed in decoding or fail in decoding, so feedback messages are respectively designed for the two cases of successful decoding and decoding failure. For the specific implementation manner of the feedback message, reference may be made to the corresponding description in the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
可选的,针对原数据包和编码包的分开独立编号方式和联合顺序编号方式,其在编码端(即第一设备)和译码端(即第二设备)的存储参考前述实施例一中的相应描述,此处不再赘述。Optionally, for the separate independent numbering method and joint sequential numbering method of the original data packet and the encoded packet, the storage at the encoding end (ie, the first device) and the decoding end (ie, the second device) refers to the first embodiment above The corresponding descriptions are not repeated here.
可选的,基站可通过RRC消息或者MAC CE消息指示UE上行传输的编码策略。该RRC消息或MAC CE消息可以指示UE的编码方式,或者指示不同的编码方案。Optionally, the base station may indicate the coding strategy of the UE for uplink transmission through an RRC message or a MAC CE message. The RRC message or the MAC CE message may indicate the encoding mode of the UE, or indicate different encoding schemes.
可见,本申请实施例提供一种纯分割场景下支持网络编码的数据传输方法,不仅在不依赖于SDU或PDU大小,即不同SDU或PDU大小可以相同,也可以不同,的场景下可以应用,比如可以兼容NR协议,还能在多个原数据包丢失的情况下也能恢复出PDU或SDU,减少性能损失。It can be seen that the embodiment of the present application provides a data transmission method that supports network coding in a pure segmentation scenario, which is not only applicable to scenarios that do not depend on the size of the SDU or PDU, that is, the sizes of different SDUs or PDUs can be the same or different. For example, it can be compatible with the NR protocol, and can also restore PDUs or SDUs when multiple original data packets are lost, reducing performance loss.
上述内容详细阐述了本申请的方法,为便于更好地实施本申请实施例的上述方案,本申请实施例还提供了相应的装置或设备。The above content elaborates the method of the present application in detail. In order to better implement the above solutions of the embodiments of the present application, the embodiments of the present application also provide corresponding devices or equipment.
本申请实施例可以根据上述方法示例对第一设备和第二设备进行功能模块的划分,例如,可以对应各个功能划分各个功能模块,也可以将两个或两个以上的功能集成在一个处理模块中。上述集成的模块既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能模块的形式实现。需要说明的是,本申请实施例中对模块的划分是示意性的,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式。下面将结合图33至图37详细描述本申请实施例的数据传输装置。In this embodiment of the present application, the functional modules of the first device and the second device can be divided according to the above method examples. For example, each functional module can be divided corresponding to each function, or two or more functions can be integrated into one processing module. middle. The above-mentioned integrated modules can be implemented in the form of hardware or in the form of software function modules. It should be noted that the division of modules in the embodiment of the present application is schematic, and is only a logical function division, and there may be other division methods in actual implementation. The data transmission device according to the embodiment of the present application will be described in detail below with reference to FIG. 33 to FIG. 37 .
在采用集成的单元的情况下,参见图33,图33是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置1的一结构示意图。该数据传输装置1可以为第一设备或者可以设置于第一设备中的芯片或电路。如图33所示,该数据传输装置1包括:获取模块11、传输模块12、以及编码模块13。In the case of using an integrated unit, refer to FIG. 33 , which is a schematic structural diagram of the
第一种设计中,获取模块11,用于获取N个第一数据包;传输模块12,用于传输该获取模块11获取到的N个第一数据包;编码模块13,用于对该获取模块11获取到的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;该传输模块12,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。该每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段。该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数。In the first design, the obtaining
应理解,第一种设计中该数据传输装置1可对应执行前述实施例一,并且该数据传输装置1中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例一中第一设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例一中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that in the first design, the
第二种设计中,获取模块11,用于获取N个第一数据包;编码模块13,用于对该获取模块11获取到的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;传输模块12,用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。M大于N,N和M均为正整数。In the second design, the obtaining
应理解,第二种设计中该数据传输装置1可对应执行前述实施例二,并且该数据传输装置1中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例二中第一设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例二中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that in the second design, the
第三种设计中,获取模块11,用于N个第一数据包;传输模块12,用于传输该获取模块11获取到的N个第一数据包;编码模块13,用于对该获取模块11获取到的N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;该传输模块12,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。该每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段。该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包,该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。该每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N、M以及Q均为正整数,Q小于或等于N。In the third design, the
应理解,第三种设计中该数据传输装置1可对应执行前述实施例四,并且该数据传输装置1中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例四中第一设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例四中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that in the third design, the
其中,上述三种设计中,上述获取模块11和上述编码模块13可以集成为一个模块,例如处理模块。上述传输模块12还可以称为收发模块。Wherein, in the above three designs, the
参见图34,图34是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置1的另一结构示意图。该数据传输装置1可以为第一设备或者可以设置于第一设备中的芯片或电路。如图34所示,该数据传输装置1包括:获取模块21、生成模块22、传输模块23、以及编码模块24。Referring to FIG. 34 , FIG. 34 is another schematic structural diagram of the
获取模块21,用于获取级联数据包;生成模块22,用于根据该获取模块21获取到的该级联数据包生成N个第一数据包;传输模块23,用于传输该生成模块22生成的N个第一数据包;编码模块24,用于对该N个第一数据包进行编码并加编码包包头后得到M个第二数据包;该传输模块23,还用于传输该M个第二数据包。其中,该级联数据包包括级联包包头和级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。该级联包包头包括该级联数据包括的多个数据单元的级联信息。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是该级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。N和M均为正整数。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。The obtaining
其中,上述获取模块21、上述生成模块22、以及上述编码模块24可以集成为一个模块,例如处理模块。上述传输模块23还可以称为收发模块。Wherein, the
应理解,该数据传输装置1可对应执行前述实施例三,并且该数据传输装置1中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例三中第一设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例三中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that the
参见图35,图35是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置2的一结构示意图。该数据传输装置2可以为第二设备或者可以设置于第二设备中的芯片或电路。如图35所示,该数据传输装置2包括:获取模块31、译码模块32、以及还原模块33。Referring to FIG. 35 , FIG. 35 is a schematic structural diagram of the
第一种设计中,获取模块31,用于获取P个数据包;译码模块32,用于对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包;还原模块33,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括数据包标识字段。该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包的大小相等。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据部分对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P和K均为正整数,K小于或等于P。P大于或等于N。In the first design, the
可选的,上述译码模块32,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。Optionally, the above-mentioned
可选的,在该N个第一数据包和/或该M个第二数据包中携带该N个第一数据包和该M个第二数据包之间的对应关系。具体的,该对应关系可以携带在该N个第一数据包的包头和/或该M个第二数据包的包头。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该M个第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的N个第一数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the N first data packets and/or the M second data packets carry the correspondence between the N first data packets and the M second data packets. Specifically, the corresponding relationship may be carried in headers of the N first data packets and/or headers of the M second data packets. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, headers of the M second data packets may include identification information for indicating the N first data packets obtained by encoding the second data packets to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可选的,上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。上述译码模块32,还具体用于:比较该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与该编码包长度阈值L1的大小关系;如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度等于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(编码包);如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于该编码包长度阈值L1,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(原数据包);从而从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the coded packet length threshold L1. The above-mentioned
可选的,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。上述译码模块32,还具体用于:比较该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度与该原数据包长度阈值L2的大小关系;如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度小于或等于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第一数据包(原数据包);如果该P个数据包中某个数据包的长度大于该原数据包长度阈值L2,则确定该数据包是第二数据包(编码包);从而从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。Optionally, the aforementioned length threshold is the original data packet length threshold L2. The above-mentioned
可选的,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包。Optionally, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet.
可选的,每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。Optionally, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, which is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is contained is an encoded packet.
这样,以上译码模块32可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。In this way, the
应理解,该数据传输装置2可对应执行前述实施例一,并且该数据传输装置2中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例一中第二设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例一中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that the
第二种设计中,获取模块31,用于获取P个数据包;译码模块32,用于对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包;还原模块33,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割和级联信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成至少一个数据单元。其中,该P个数据包均是编码包。每个数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该编码包包头包括编码因子字段。该N个第一数据包的大小相等。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的数据对应的至少一个数据单元的分割和级联信息。该分割和级联信息用于指示该第一数据包的数据与该至少一个数据单元的对应关系。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P大于或等于N,N为正整数,P为正整数。In the second design, the
可选的,上述译码模块32,具体用于:采用编码包的解析方式解析该P个数据包的编码包包头获得每个编码包包头携带的编码因子字段,利用该P个数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P个数据包的编码数据进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。Optionally, the above-mentioned
应理解,该数据传输装置2可对应执行前述实施例二,并且该数据传输装置2中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例二中第二设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例二中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that the
第三种设计中,获取模块31,用于获取P个数据包;译码模块32,用于对该P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包,该N个第一数据包的大小不完全相等;还原模块33,用于根据该N个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头包括的分割信息,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个或多个数据单元。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头中包括该第一数据包的数据对应的数据单元的分割信息。该每个第一数据包的包头还包括数据包标识字段。该数据包标识字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包对应用于编码的Q个等效原数据包,该Q个等效原数据包的大小相等。该每个第一数据包的包头还包括编码因子字段或偏移字段。该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。P大于或等于N,N大于或等于Q,P、N以及Q均为正整数。In the third design, the obtaining
可选的,上述每个第一数据包的包头包括编码因子字段。上述译码模块32,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示和该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。Optionally, the packet header of each first data packet includes a coding factor field. The above-mentioned
可选的,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括偏移字段,该偏移字段用于指示该第一数据包的序列号相对于该第一数据包对应的等效原数据包的序列号的偏移数。上述译码模块32,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的包头中第一数据包的序列号和偏移字段、和该P-K个第二数据包的编码包包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包。上述长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,上述长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。Optionally, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes an offset field, and the offset field is used to indicate that the sequence number of the first data packet is relative to the sequence of the equivalent original data packet corresponding to the first data packet Number of offsets. The above-mentioned
可选的,在该第二数据包的包头携带该Q个等效原数据包和该第二数据包之间的对应关系。这样,可以基于该对应关系来获得上述系数因子矩阵。可选的,可以在该第二数据包的包头包括用于指示编码得到该第二数据包的Q个等效原数据包的标识信息来指示该对应关系。Optionally, the header of the second data packet carries the correspondence between the Q equivalent original data packets and the second data packet. In this way, the above-mentioned coefficient factor matrix can be obtained based on the corresponding relationship. Optionally, the header of the second data packet may include identification information for indicating Q equivalent original data packets obtained by encoding the second data packet to indicate the corresponding relationship.
可选的,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包;每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头中包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。这样,以上译码模块32可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。Optionally, the packet header of each first data packet above also includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet; each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and For the encoded data, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate that the second data packet in which the second indication information is located is an encoded packet. In this way, the
应理解,该数据传输装置2可对应执行前述实施例四,并且该数据传输装置2中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例四中第二设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例四中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that the
其中,上述三种设计中,上述获取模块31、上述译码模块32、以及上述还原模块33可以集成为一个模块,例如处理模块。上述获取模块31可以包括收发单元,用于收发数据包或信息等。Among the above three designs, the
参见图36,图36是本申请实施例提供的数据传输装置2的另一结构示意图。该数据传输装置2可以为第二设备或者可以设置于第二设备中的芯片或电路。如图36所示,该数据传输装置2包括:获取模块41、译码模块42、还原模块43、以及分割模块44。Referring to FIG. 36 , FIG. 36 is another schematic structural diagram of the
获取模块41,用于获取P个数据包;译码模块42,用于对该获取模块41获取到的P个数据包进行译码,获得译码后的N个第一数据包;还原模块43,用于按照该N个第一数据包的序列号大小顺序,将该N个第一数据包的数据还原成一个级联数据包;分割模块44,还用于根据该级联包包头包括的形成该级联数据的多个数据单元的级联信息,将该级联数据分割成多个数据单元。其中,该P个数据包中包括K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包。每个第一数据包包括包头和数据。该每个第一数据包的包头包括该第一数据包的序列号。该N个第一数据包的数据大小相等,且该N个第一数据包的包头大小相等。该N个第一数据包中第j个第一数据包的数据是级联数据包经过N等分后得到的第j份数据。该级联数据包包括该级联包包头和该级联数据。该级联数据包括多个数据段级联得到的数据。其中起始数据段和末尾数据段中的至少一个是一个数据单元的全部或部分。该多个数据段中除该起始数据段和该末尾数据段外的每个数据段是一个数据单元。其中,第一数据包是原数据包,第二数据包是编码包。j的取值为区间[1,N]中的整数。P和K均为正整数,K小于或等于P。P大于或等于N。The obtaining
可选的,上述译码模块42,具体用于:根据该P个数据包中每个数据包的长度以及长度阈值,从该P个数据包中确定出K个第一数据包和P-K个第二数据包;采用原数据包的解析方式解析该K个第一数据包中每个第一数据包的包头,获得该第一数据包的序列号,并采用编码包的解析方式解析该P-K个第二数据包中第二数据包的编码包包头,获得编码因子字段;根据该K个第一数据包的序列号、和该P-K个第二数据包的包头中编码因子字段的指示,构成系数因子矩阵;采用该系数因子矩阵对该P-K个第二数据包的编码数据和该K个第一数据包进行联合译码,获得译码后的N-K个第一数据包。其中,该系数因子矩阵的秩(rank)等于N。该译码后的N-K个第一数据包和该K个第一数据包属于N个第一数据包。其中,该长度阈值是编码包长度阈值L1。或者,该长度阈值是原数据包长度阈值L2。Optionally, the above-mentioned
可选的,上述每个第一数据包的包头还包括第一指示信息,用于指示该第一指示信息所在的第一数据包是原数据包。Optionally, the packet header of each of the above first data packets further includes first indication information, which is used to indicate that the first data packet in which the first indication information is located is an original data packet.
每个第二数据包包括编码包包头和编码数据,可选的,该每个第二数据包的编码包包头包括第二指示信息,该第二指示信息用于指示该第二指示信息所在的第二数据包是编码包。Each second data packet includes an encoded packet header and encoded data. Optionally, the encoded packet header of each second data packet includes second indication information, and the second indication information is used to indicate where the second indication information is located. The second data packet is an encoded packet.
这样,以上译码模块32可以根据包头中的第一指示信息和/或第二指示信息来确定该数据包是原数据包还是编码数据包,进而采用相对应的解析方式对该数据包的包头进行解析。In this way, the
其中,上述获取模块41、上述译码模块42、上述还原模块43、以及上述分割模块44可以集成为一个模块,例如处理模块。上述获取模块41可以包括收发单元,用于收发数据包或信息等。Wherein, the above-mentioned
应理解,该数据传输装置2可对应执行前述实施例三,并且该数据传输装置2中的各个单元的上述操作或功能分别为了实现前述实施例三中第二设备的相应操作,其技术效果参见前述实施例三中的技术效果,为了简洁,在此不再赘述。It should be understood that the
可选的,以上各实施例的编码模块可以对应于编码器,译码模块可以对应于译码器。编码器或译码器可以由硬件电路或软件来实现。除编码模块和译码模块,以及和收发单元对应的模块之外的模块的功能可以由处理器来实现。Optionally, the encoding module in the above embodiments may correspond to an encoder, and the decoding module may correspond to a decoder. Encoders or decoders can be implemented by hardware circuits or software. The functions of the modules other than the encoding module, the decoding module, and the module corresponding to the transceiver unit may be implemented by the processor.
参见图37,图37是本申请实施例提供的通信装置的结构示意图。如图37所示,本申请实施例提供的通信装置1000可用于实现上述方法实施例中描述的方法,可以参见上述方法实施例中的说明。该通信装置1000可以是前述第一设备和前述第二设备中的任意一种。Referring to FIG. 37, FIG. 37 is a schematic structural diagram of a communication device provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 37 , the
通信装置1000包括一个或多个处理器1001。处理器1001可以是通用处理器或者专用处理器等。例如可以是基带处理器、或中央处理器。基带处理器可以用于对通信协议以及通信数据进行处理,中央处理器可以用于对装置(如,通信设备、基站或芯片等)进行控制,执行软件程序,处理软件程序的数据。该装置可以包括收发单元,用以实现信号的输入(接收)和输出(发送)。例如,装置可以为芯片,该收发单元可以是芯片的输入和/或输出电路,或者通信接口。该芯片可以用于通信设备或接入网设备(比如基站)。又如,装置可以为通信设备(比如UE)或接入网设备(比如基站),该收发单元可以为收发器,射频芯片等。The
通信装置1000包括一个或多个处理器1001,该一个或多个处理器1001可实现前述任一实施例中第一设备、或第二设备的方法。The
可选的,处理器1001除了实现前述任一实施例的方法,还可以实现其他功能。Optionally, the
可选的,一种设计中,处理器1001也可以包括指令1003,所述指令可以在所述处理器上被运行,使得通信装置1000执行上述任一方法实施例中描述的方法。Optionally, in one design, the
在又一种可能的设计中,通信装置1000也可以包括电路,所述电路可以实现前述任一方法实施例中第一设备或第二设备的功能。In yet another possible design, the
在又一种可能的设计中,通信装置1000中可以包括一个或多个存储器1002,其上存有指令1004,所述指令可在所述处理器上被运行,使得通信装置1000执行上述任一方法实施例中描述的方法。可选的,所述存储器中还可以存储有数据。可选的处理器中也可以存储指令和/或数据。例如,所述一个或多个存储器1002可以存储上述实施例中所描述的第一数据包,或者上述实施例中所涉及的其他信息。所述处理器和存储器可以单独设置,也可以集成在一起。In yet another possible design, the
在又一种可能的设计中,通信装置1000还可以包括收发单元1005以及天线1006,或者,包括通信接口。收发单元1005可以称为收发机、收发电路、或者收发器等,用于通过天线1006实现装置的收发功能。所述通信接口(图中未示出),可以用于核心网设备和接入网设备,或是,接入网设备和接入网设备之间的通信。可选的,该通信接口可以为有线通信的接口,比如光纤通信的接口。In yet another possible design, the
处理器1001可以称为处理单元,对装置(比如通信设备)进行控制。The
应理解,在本申请实施例中的处理器可以是中央处理单元(central processingunit,CPU),该处理器还可以是其他通用处理器、数字信号处理器(digital signalprocessor,DSP)、专用集成电路(application specific integrated circuit,ASIC)、现成可编程门阵列(field programmable gate array,FPGA)或者其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件等。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者该处理器也可以是任何常规的处理器等。It should be understood that the processor in the embodiment of the present application may be a central processing unit (central processing unit, CPU), and the processor may also be other general processors, digital signal processors (digital signal processor, DSP), application specific integrated circuits ( Application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), off-the-shelf programmable gate array (field programmable gate array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc. A general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor, or the processor may be any conventional processor, or the like.
还应理解,本申请实施例中的存储器可以是易失性存储器或非易失性存储器,或可包括易失性和非易失性存储器两者。其中,非易失性存储器可以是只读存储器(read-only memory,ROM)、可编程只读存储器(programmable ROM,PROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(erasable PROM,EPROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(electrically EPROM,EEPROM)或闪存。易失性存储器可以是随机存取存储器(random access memory,RAM),其用作外部高速缓存。通过示例性但不是限制性说明,许多形式的随机存取存储器(random accessmemory,RAM)可用,例如静态随机存取存储器(static RAM,SRAM)、动态随机存取存储器(DRAM)、同步动态随机存取存储器(synchronous DRAM,SDRAM)、双倍数据速率同步动态随机存取存储器(double data rate SDRAM,DDR SDRAM)、增强型同步动态随机存取存储器(enhanced SDRAM,ESDRAM)、同步连接动态随机存取存储器(synchlink DRAM,SLDRAM)和直接内存总线随机存取存储器(direct rambus RAM,DR RAM)。It should also be understood that the memory in the embodiments of the present application may be a volatile memory or a nonvolatile memory, or may include both volatile and nonvolatile memories. Among them, the non-volatile memory can be read-only memory (read-only memory, ROM), programmable read-only memory (programmable ROM, PROM), erasable programmable read-only memory (erasable PROM, EPROM), electrically programmable Erases programmable read-only memory (electrically EPROM, EEPROM) or flash memory. Volatile memory can be random access memory (RAM), which acts as external cache memory. By way of illustration and not limitation, many forms of random access memory (RAM) are available such as static random access memory (static RAM (SRAM), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), synchronous dynamic random access memory (RAM), Access memory (synchronous DRAM, SDRAM), double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (double data rate SDRAM, DDR SDRAM), enhanced synchronous dynamic random access memory (enhanced SDRAM, ESDRAM), synchronous connection dynamic random access memory (synchlink DRAM, SLDRAM) and direct memory bus random access memory (direct rambus RAM, DR RAM).
上述实施例,可以全部或部分地通过软件、硬件(如电路)、固件或其他任意组合来实现。当使用软件实现时,上述实施例可以全部或部分地以计算机程序产品的形式实现。所述计算机程序产品包括一个或多个计算机指令或计算机程序。在计算机上加载或执行所述计算机指令或计算机程序时,全部或部分地产生按照本申请实施例所述的流程或功能。所述计算机可以为通用计算机、专用计算机、计算机网络、或者其他可编程装置。所述计算机指令可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,或者从一个计算机可读存储介质向另一个计算机可读存储介质传输,例如,所述计算机指令可以从一个网站站点、计算机、服务器或数据中心通过有线,例如光纤,或是无线,例如红外、无线、微波等,方式向另一个网站站点、计算机、服务器或数据中心进行传输。所述计算机可读存储介质可以是计算机能够存取的任何可用介质或者是包含一个或多个可用介质集合的服务器、数据中心等数据存储设备。所述可用介质可以是磁性介质(例如,软盘、硬盘、磁带)、光介质(例如,DVD)、或者半导体介质。半导体介质可以是固态硬盘。The above-mentioned embodiments may be implemented in whole or in part by software, hardware (such as circuits), firmware, or other arbitrary combinations. When implemented using software, the above-described embodiments may be implemented in whole or in part in the form of computer program products. The computer program product comprises one or more computer instructions or computer programs. When the computer instruction or computer program is loaded or executed on the computer, the processes or functions according to the embodiments of the present application will be generated in whole or in part. The computer may be a general purpose computer, a special purpose computer, a computer network, or other programmable devices. The computer instructions may be stored in or transmitted from one computer-readable storage medium to another computer-readable storage medium, for example, the computer instructions may be transmitted from a website, computer, server or data center Transmission to another website site, computer, server or data center through wired, such as optical fiber, or wireless, such as infrared, wireless, microwave, etc. The computer-readable storage medium may be any available medium that can be accessed by a computer, or a data storage device such as a server or a data center that includes one or more sets of available media. The available media may be magnetic media (eg, floppy disk, hard disk, magnetic tape), optical media (eg, DVD), or semiconductor media. The semiconductor medium may be a solid state drive.
本申请实施例还提供一种计算机程序产品,该计算机程序产品包括计算机程序代码,当该计算机程序代码在计算机上运行时,使得该计算机执行前述实施例所描述的第一设备的方法步骤;或者当该计算机程序代码在计算机上运行时,使得该计算机执行前述实施例所描述的第二设备的方法步骤。An embodiment of the present application also provides a computer program product, where the computer program product includes computer program code, and when the computer program code is run on a computer, the computer is made to execute the method steps of the first device described in the foregoing embodiments; or When the computer program code is run on the computer, the computer is made to execute the method steps of the second device described in the foregoing embodiments.
本申请实施例还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质上存储有程序指令,当其在计算机上运行时,使得该计算机执行前述实施例所描述的第一设备的方法步骤;或者当该计算机程序代码在计算机上运行时,使得该计算机执行前述实施例所描述的第二设备的方法步骤。The embodiment of the present application also provides a computer-readable storage medium, the computer-readable storage medium stores program instructions, and when it is run on a computer, it causes the computer to execute the method steps of the first device described in the foregoing embodiments ; or when the computer program code is run on the computer, causing the computer to execute the method steps of the second device described in the foregoing embodiments.
本申请实施例还提供一种装置,该装置可以为芯片。该芯片包括处理器。该处理器用于读取并执行存储器中存储的计算机程序,以执行前述任一实施例的任意可能的实现方式中的方法。可选的,该芯片还包括存储器,该存储器与该处理器通过电路或电线连接。进一步可选的,该芯片还包括通信接口,该处理器与该通信接口连接。该通信接口用于接收待处理的数据和/或信号,该处理器从该通信接口获取该数据和/或信号,并对该数据和/或信号进行处理,并通过该通信接口输出处理结果。该通信接口可以是输入输出接口。The embodiment of the present application also provides a device, and the device may be a chip. The chip includes a processor. The processor is configured to read and execute the computer program stored in the memory, so as to execute the method in any possible implementation manner of any of the foregoing embodiments. Optionally, the chip further includes a memory, and the memory is connected to the processor through a circuit or wires. Further optionally, the chip further includes a communication interface, and the processor is connected to the communication interface. The communication interface is used to receive data and/or signals to be processed, and the processor obtains the data and/or signals from the communication interface, processes the data and/or signals, and outputs processing results through the communication interface. The communication interface may be an input-output interface.
可选的,上述的处理器与存储器可以是物理上相互独立的单元,或者,存储器也可以和处理器集成在一起。Optionally, the above-mentioned processor and memory may be physically independent units, or the memory may also be integrated with the processor.
本申请的另一实施例中,还提供一种通信系统,该通信系统包括第一设备和第二设备。该第一设备和该第二设备可以执行前述任一实施例中的方法。In another embodiment of the present application, a communication system is further provided, and the communication system includes a first device and a second device. The first device and the second device may execute the method in any of the preceding embodiments.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例方法中的全部或部分流程,该流程可以由计算机程序来指令相关的硬件完成,该程序可存储于计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可包括如上述各方法实施例的流程。而前述的存储介质包括:ROM或随机存储记忆体RAM、磁碟或者光盘等各种可存储程序代码的介质。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the processes in the methods of the above embodiments are realized. The processes can be completed by computer programs to instruct related hardware. The programs can be stored in computer-readable storage media. When the programs are executed , may include the processes of the foregoing method embodiments. The aforementioned storage medium includes: ROM or random access memory RAM, magnetic disk or optical disk, and other various media that can store program codes.
以上所述,仅为本申请的具体实施方式,但本申请的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本申请揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到变化或替换,都应涵盖在本申请的保护范围之内。因此,本申请的保护范围应以所述权利要求的保护范围为准。The above is only a specific implementation of the application, but the scope of protection of the application is not limited thereto. Anyone familiar with the technical field can easily think of changes or substitutions within the technical scope disclosed in the application. Should be covered within the protection scope of this application. Therefore, the protection scope of the present application should be determined by the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (28)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110483034.0ACN115276891A (en) | 2021-04-30 | 2021-04-30 | Data transmission method, device and readable storage medium |
| PCT/CN2022/089568WO2022228467A1 (en) | 2021-04-30 | 2022-04-27 | Data transmission method and apparatus, and readable storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110483034.0ACN115276891A (en) | 2021-04-30 | 2021-04-30 | Data transmission method, device and readable storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115276891Atrue CN115276891A (en) | 2022-11-01 |
Family
ID=83745621
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110483034.0APendingCN115276891A (en) | 2021-04-30 | 2021-04-30 | Data transmission method, device and readable storage medium |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115276891A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2022228467A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023046029A1 (en)* | 2021-09-26 | 2023-03-30 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus, and readable storage medium |
| WO2024139382A1 (en)* | 2022-12-29 | 2024-07-04 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Delay information management method and related apparatus |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119232500B (en)* | 2024-12-02 | 2025-02-28 | 四川英创力电子科技股份有限公司 | Automatic processing method of engineering data based on data storage server |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105991625B (en)* | 2015-03-06 | 2020-11-06 | 电信科学技术研究院 | A method and device for data transmission |
| WO2017004814A1 (en)* | 2015-07-08 | 2017-01-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | User equipment and network side equipment, and method of determining processing mode for data packet |
| US10034200B2 (en)* | 2015-10-23 | 2018-07-24 | Motorola Mobility Llc | Iteratively transmitting random linear network encoded packets from multiple transmission nodes |
| WO2018133020A1 (en)* | 2017-01-20 | 2018-07-26 | 广东欧珀移动通信有限公司 | Data transmission method, device, transmitting end, receiving end, and system |
| CN109691061A (en)* | 2017-02-10 | 2019-04-26 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | A kind of method and apparatus for transmitting data |
| US11350305B2 (en)* | 2019-01-09 | 2022-05-31 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for processing data in wireless communication system |
- 2021
- 2021-04-30CNCN202110483034.0Apatent/CN115276891A/enactivePending
- 2022
- 2022-04-27WOPCT/CN2022/089568patent/WO2022228467A1/ennot_activeCeased
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023046029A1 (en)* | 2021-09-26 | 2023-03-30 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus, and readable storage medium |
| WO2024139382A1 (en)* | 2022-12-29 | 2024-07-04 | 荣耀终端有限公司 | Delay information management method and related apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2022228467A1 (en) | 2022-11-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3576329B1 (en) | Communication method and device | |
| WO2022228467A1 (en) | Data transmission method and apparatus, and readable storage medium | |
| CN109150419A (en) | A kind of communication means and its device | |
| CN114157400B (en) | Codebook processing method and codebook processing device | |
| WO2021012727A1 (en) | Data transmission method and device, and storage medium | |
| WO2023005909A1 (en) | Timeout packet loss method and apparatus in network coding scenario, and readable storage medium | |
| EP4161138A1 (en) | Coding method and device | |
| JP2022002406A (en) | UEs used for channel coding, methods and equipment in base stations | |
| CN112636879B (en) | Method and device for code block processing based on hybrid automatic repeat request | |
| JP2022046754A (en) | Method and device in user equipment and base station used for channel coding | |
| US20240235762A1 (en) | Data transmission method and apparatus, and readable storage medium | |
| CN115885480A (en) | Information processing device, encoding method, and decoding method | |
| US11539470B2 (en) | Re-transmission control method, radio terminal, and radio base station | |
| US20240129068A1 (en) | Communication method and apparatus | |
| KR101647373B1 (en) | Method of retransmitting Data using Random Linear Coding in a Wireless Access System | |
| WO2014110812A1 (en) | Information transmission method and device | |
| CN115968538A (en) | Information processing device and information processing method | |
| WO2014190819A1 (en) | Method, intermediate node, and terminal for information transmission | |
| WO2025118504A1 (en) | Methods, apparatus, systems, computer-readable storege media, and computer program products of communication | |
| WO2025073084A1 (en) | Apparatuses and methods for retransmissions using cross-transport block check blocks | |
| US20250125904A1 (en) | Apparatus and methods for source coding and channel coding of low entropy signals | |
| CN115276896A (en) | Data processing method, device and system | |
| WO2022050019A1 (en) | Information processing device and decoding method | |
| WO2025140431A1 (en) | Sequence processing method and communication apparatus | |
| CN117426060A (en) | Communication method and communication device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |