CN115205667A - A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s - Google Patents
A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5sDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115205667A CN115205667ACN202210920891.7ACN202210920891ACN115205667ACN 115205667 ACN115205667 ACN 115205667ACN 202210920891 ACN202210920891 ACN 202210920891ACN 115205667 ACN115205667 ACN 115205667A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- module
- convolution
- training
- fish
- channel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V20/00—Scenes; Scene-specific elements
- G06V20/05—Underwater scenes
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V2201/07—Target detection
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及计算机视觉目标检测领域,具体涉及一种基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测方法。The invention relates to the field of computer vision target detection, in particular to a dense target detection method based on YOLOv5s.
背景技术Background technique
视觉目标检测旨在定位和识别图像中存在的物体,属于计算机视觉领域的经典任务之一,也是许多计算机视觉任务的前提与基础,在自动驾驶、视频监控、水产养殖、智慧农业等领域具有重要的理论研究意义和实际应用价值。随着深度学习技术的飞速发展,目标检测取得了巨大的进展。以往的人工检测方式准确率差,效率低,耗时耗力。随着图像处理技术的不断发展,传统的机器学习通过支持向量机,进行分类识别,该方法检测结果准确率不高,且容易造成漏检误检等情况。近年来,对于诸多领域内存在密集目标的情况,采用计算机视觉技术结合深度学习方法进行检测逐渐成为主流,目标检测识别算法它通过卷积神经网络来自动提取目标特征,相较于以往的方法,具有更快的检测速度和更高的检测准确率。Visual object detection aims at locating and recognizing objects in images. It is one of the classic tasks in the field of computer vision, and it is also the premise and foundation of many computer vision tasks. The theoretical research significance and practical application value. With the rapid development of deep learning technology, object detection has made great progress. The previous manual detection methods have poor accuracy, low efficiency, time-consuming and labor-intensive. With the continuous development of image processing technology, traditional machine learning uses support vector machines to classify and identify. In recent years, for the situation of dense targets in many fields, the use of computer vision technology combined with deep learning methods for detection has gradually become the mainstream. The target detection and recognition algorithm automatically extracts target features through convolutional neural networks. Compared with previous methods, It has faster detection speed and higher detection accuracy.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对上述存在的问题,提出一种基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测模型。采用该模型能够较好的满足密集目标检测检测任务的需求。In view of the above problems, a dense target detection model based on YOLOv5s is proposed. The model can better meet the needs of dense target detection and detection tasks.
为了实现上述目的,本发明采用的技术方案如下:一种基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测方法,包括如下步骤:In order to achieve the above purpose, the technical solution adopted in the present invention is as follows: a dense target detection method based on YOLOv5s, comprising the following steps:
1)将检测装置置于投饵船前端检测鱼群数量情况,所述检测装置包括摄像装置和照明装置;所述摄像装置用于拍摄鱼群进行数量检测;所述照明装置保持常亮用于水下照明;1) Place the detection device at the front end of the bait-casting boat to detect the number of fish schools, and the detection device includes a camera device and a lighting device; the camera device is used for photographing fish schools for quantity detection; the lighting device is kept on for constant light. underwater lighting;
2)构建鱼类数据集D2,划分训练集Dtrain和验证集Dtest;2) construct fish data set D2, divide training set Dtrain and verification set Dtest ;
3)构建YOLOv5s网络模型,所述YOLOv5s网络模型包括Input、Backbone、Neck、Prediction;所述Input包括Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放;所述Backbone包括Focus模块、SPP模块和C3模块;所述颈部网络Neck包括FPN模块、PAN模块、C3模块;所述Prediction包括Bounding box损失函数和NMS;3) construct YOLOv5s network model, described YOLOv5s network model includes Input, Backbone, Neck, Prediction; Described Input includes Mosaic data enhancement, adaptive anchor frame calculation, adaptive picture zoom; Described Backbone includes Focus module, SPP module and C3 module; described neck network Neck includes FPN module, PAN module, C3 module; described Prediction includes Bounding box loss function and NMS;
4)修改主干网络卷积模块,将主干网络卷积模块修改为RepVGG Block模块;4) Modify the backbone network convolution module, and modify the backbone network convolution module to the RepVGG Block module;
5)修改主干网络结构,在RepVGG模块与SPP模块之间插入SA注意力机制;5) Modify the backbone network structure and insert the SA attention mechanism between the RepVGG module and the SPP module;
6)修改YOLOv5s颈部网络的上采样方式,将最邻近上采样改为CARAFE上采样方式;6) Modify the upsampling method of the YOLOv5s neck network, and change the nearest neighbor upsampling to the CARAFE upsampling method;
7)将评价目标框和预测框的类损失和置信度损失的损失函数Focal Loss修改为Varifocal Loss损失函数;7) Modify the loss function Focal Loss of evaluating the class loss and confidence loss of the target frame and the prediction frame to the Varifocal Loss loss function;
8)对鱼类数据集D2进行迁移训练,得到训练权重w;即用GIOU_Loss作为损失函数,当模型损失曲线趋近于0且无明显波动时,停止训练,得到训练权重w,否则继续训练;8) Perform migration training on the fish dataset D2 to obtain the training weight w; that is, use GIOU_Loss as the loss function, when the model loss curve approaches 0 and there is no obvious fluctuation, stop the training, and obtain the training weight w, otherwise continue training;
9)输入图像,进行鱼群检测,将获取到的鱼群图像输入到训练权重为w的模型中,模型根据权重自动识别鱼群数量。9) Input an image, perform fish school detection, and input the obtained fish school image into a model with a training weight of w, and the model automatically identifies the number of fish schools according to the weight.
进一步地,上述步骤2)包括如下步骤:Further, above-mentioned step 2) comprises the steps:
2.1)从鱼类公共数据集选取N张,构建数据集D1;2.1) Select N pieces from the fish public data set to construct the data set D1;
2.2)使用标注工具Labelimg对数据集D1中每一张图像中的鱼类进行标注,构建鱼类数据集D2;2.2) Use the labeling tool Labelimg to label the fish in each image in the dataset D1 to construct the fish dataset D2;
2.3)按照比例将鱼类数据集D2划分为训练集Dtrain和验证集Dtest。2.3) Divide the fish dataset D2 into a training set Dtrain and a validation set Dtest according to the proportion.
进一步地,上述步骤4)包括如下步骤:Further, above-mentioned step 4) comprises the steps:
4.1)训练多分支模型:在训练时,为每一个3×3卷积层添加平行的1×1卷积分支与恒等映射分支;4.1) Training a multi-branch model: During training, add parallel 1×1 convolution branches and identity mapping branches to each 3×3 convolutional layer;
4.2)将多分支模型等价转换为单路模型:将1×1卷积看成卷积核中有很多0的3×3卷积,恒等映射是一个特殊1×1卷积;根据卷积的可加性原理,每个RepVGG Block模块三个分支则可以合并为一个3×3卷积;4.2) Equivalently convert the multi-branch model to a one-way model: regard the 1×1 convolution as a 3×3 convolution with many 0s in the convolution kernel, and the identity map is a special 1×1 convolution; according to the volume According to the principle of product additivity, the three branches of each RepVGG Block module can be combined into a 3×3 convolution;
4.3)结构参数重构:通过实际数据流,将多分支网络的权值转移到简单网络中。4.3) Structural parameter reconstruction: Through the actual data flow, the weights of the multi-branch network are transferred to the simple network.
进一步地,上述步骤5)包括如下步骤:Further, above-mentioned step 5) comprises the steps:
5.1)特征分组:假设输入特征为X∈RC×H×W,其中C、H、W分别表示通道数、高度和宽度,特征分组会将输入X沿着通道维度拆分为g组,使得每个子功能在训练过程中逐渐捕获特定的语义响应;5.1) Feature grouping: Assuming that the input feature is X∈RC×H×W , where C, H, and W represent the number of channels, height and width, respectively, the feature grouping will split the input X into g groups along the channel dimension, so that Each sub-feature gradually captures a specific semantic response during training;
5.2)使用通道注意力机制,捕获通道相关性信息,计算公式如下:5.2) Using the channel attention mechanism to capture channel correlation information, the calculation formula is as follows:
X′k1=σ(W1s+b1)·Xk1X′k1 =σ(W1 s+b1 )·Xk1
式中:s表示信道统计,Xk1为在通道维度被分成的一个分支,X′k1表示通道注意力的最终输出,σ为sigmoid激活函数,W1与b1是形状为C/2G×1×1的参数。In the formula: s represents the channel statistics, Xk1 is a branch divided in the channel dimension, X′k1 represents the final output of the channel attention, σ is the sigmoid activation function, W1 and b1 are the shape of C/2G×1 ×1 parameter.
5.3)使用空间注意力机制,捕获空间相关性信息,计算公式见下:5.3) Use the spatial attention mechanism to capture spatial correlation information. The calculation formula is as follows:
X′k2=σ(W2·GN(XK2)+b2)·Xk2X′k2 =σ(W2 ·GN(XK2 )+b2 )·Xk2
式中:Xk2为在通道维度被分成的一个分支,X′k2表示空间注意力的最终输出,W2与b2是形状为C/2G×1×1的参数,GN表示组归一化方法;where Xk2 is a branch divided in the channel dimension, X′k2 represents the final output of spatial attention, W2 and b2 are parameters of shape C/2G×1×1, GN represents group normalization method;
5.4)聚合:在完成通道注意力、空间注意力计算后,对两种注意力进行集成,通过Concat进行融合得到:X′k=[X′k1,X′k2]∈RC/2G×H×W,采用通道置换操作(channel shuffle)进行组间通信。5.4) Aggregation: After completing the calculation of channel attention and spatial attention, the two kinds of attention are integrated and fused through Concat: X′k = [X′k1 , X′k2 ]∈RC/2G×H ×W , using channel shuffle for inter-group communication.
进一步地,上述步骤6)中,包括如下步骤:Further, in above-mentioned step 6), comprise the following steps:
6.1)特征图通道压缩:假设上采样倍率为σ,对于形状为C×H×W的输入特征图,其中C、H、W分别表示通道数、高度和宽度,用1×1卷积将它的通道数压缩到Cm;6.1) Feature map channel compression: Assuming that the upsampling magnification is σ, for an input feature map with a shape of C×H×W, where C, H, and W represent the number of channels, height and width, respectively, use 1×1 convolution to convolve it. The number of channels compressed to Cm ;
6.2)内容编码及上采样核预测:对步骤6.1)压缩后的输入特征图,利用的卷积层预测上采样核,假设上采样的卷积核为kup×kup,输入通道数为Cm,输出通道数为将通道维在空间维展开,得到形状为的上采样核;6.2) Content encoding and upsampling kernel prediction: For the compressed input feature map in step 6.1), use The convolutional layer predicts the upsampling kernel, assuming that the upsampling convolution kernel is kup ×kup , the number of input channels is Cm , and the number of output channels is Expand the channel dimension in the space dimension to get the shape as The upsampling kernel of ;
6.3)上采样核归一化:对步骤6.2)得到的上采样核每个通道kup×kup利用softmax进行归一化,使得卷积核权重和为1;对于输出特征图中的每个位置,将其映射回输入特征图,取出以之为中心的kup×kup的区域,和预测出的该点的上采样核作点积,得到输出值;相同位置的不同通道共享同一个上采样核。6.3) Normalization of the upsampling kernel: normalize each channel kup ×kup of the upsampling kernel obtained in step 6.2) using softmax, so that the sum of the convolution kernel weights is 1; for each channel in the output feature map position, map it back to the input feature map, take out the kup ×kup area centered on it, and do a dot product with the predicted upsampling kernel of the point to get the output value; different channels at the same position share the same Upsampling kernel.
进一步地,上述步骤7)中,所述Varifocal Loss损失函数公式如下:Further, in the above step 7), the Varifocal Loss loss function formula is as follows:
式中:p是预测的IACS,q是目标IoU得分,对于正样本,q是预测包围框和gt框之间的IoU,对于负样本,q为0。where p is the predicted IACS, q is the target IoU score, for positive samples, q is the IoU between the predicted bounding box and gt box, and for negative samples, q is 0.
进一步地,上述步骤8)中,所述GIoU_Loss损失函数转换公式如下:Further, in the above step 8), the GIoU_Loss loss function conversion formula is as follows:
式中:where:
IoU表示两个重叠矩形框之间的交并比;I表示两个矩形的重叠部分,U表示的是两个矩形面积之和Ap+Ag掉两个矩形相交面积I,Ac是两个矩形的最小外界面积。IoU represents the intersection ratio between two overlapping rectangles; I represents the overlapping part of the two rectangles, U represents the sum of the areas of the two rectangles, Ap + Ag minus the intersection area I of the two rectangles, and Ac is the two rectangles. The minimum outer area of a rectangle.
本发明提供一种基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测方法,采用了融合了RepVGG模块,注意力机制和CARAFE上采样模块的检测模型。该方法能够有效提高在密集目标图像检测任务中的综合性能,极大提高检测准确性,对自动驾驶、视频监控、水产养殖业的发展具有重要意义。The present invention provides a dense target detection method based on YOLOv5s, which adopts a detection model integrating RepVGG module, attention mechanism and CARAFE upsampling module. This method can effectively improve the comprehensive performance in the task of dense target image detection, greatly improve the detection accuracy, and is of great significance to the development of autonomous driving, video surveillance, and aquaculture.
附图说明Description of drawings
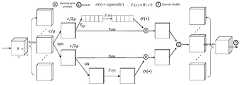
图1为本发明中基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测方法流程图。FIG. 1 is a flowchart of the dense target detection method based on YOLOv5s in the present invention.
图2为本发明中YOLOv5s网络结构图。FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of the YOLOv5s network in the present invention.
图3为本发明中主干网络RepVGG Block模块结构图。FIG. 3 is a structural diagram of a backbone network RepVGG Block module in the present invention.
图4为本发明中SA注意力机制结构图。FIG. 4 is a structural diagram of the SA attention mechanism in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图以及具体实施例对本发明做进一步的说明,需要指出的是,下面仅以一种优选的技术方案对本发明的技术方案以及设计原理进行详细阐述,但本发明的保护范围并不限于此。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that the technical solution and design principle of the present invention are described in detail below only with a preferred technical solution, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to this.
所述实施例为本发明的优选的实施方式,但本发明并不限于上述实施方式,在不背离本发明的实质内容的情况下,本领域技术人员能够做出的任何显而易见的改进、替换或变型均属于本发明的保护范围。The embodiments are preferred embodiments of the present invention, but the present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments, and any obvious improvement, replacement or All modifications belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
本发明提供的一种基于YOLOv5s的密集目标检测方法流程见图1,包括如下步骤:The flow chart of a method for dense target detection based on YOLOv5s provided by the present invention is shown in Figure 1, which includes the following steps:
1)将检测装置置于投饵船前端检测鱼群数量情况,所述检测装置包括摄像装置和照明装置;所述摄像装置用于拍摄鱼群进行数量检测;所述照明装置保持常亮用于水下照明;1) Place the detection device at the front end of the bait-casting boat to detect the number of fish schools, and the detection device includes a camera device and a lighting device; the camera device is used for photographing fish schools for quantity detection; the lighting device is kept on for constant light. underwater lighting;
2)构建鱼类数据集D2,划分训练集Dtrain和验证集Dtest;2) construct fish data set D2, divide training set Dtrain and verification set Dtest ;
3)构建YOLOv5s网络模型,YOLOv5s网络结构图见图2,所述YOLOv5s网络模型包括Input、Backbone、Neck、Prediction;所述Input包括Mosaic数据增强、自适应锚框计算、自适应图片缩放;所述Backbone包括Focus模块、SPP模块和C3模块;所述颈部网络包括FPN模块、PAN模块、C3模块;所述Prediction包括Bounding box损失函数和NMS;其中,所述主干网络C3模块其结构分为两支,一支使用多个Bottleneck堆叠和3个标准卷积层,另一支仅经过一个基本卷积模块,最后将两支进行concat操作;3) Build a YOLOv5s network model, the YOLOv5s network structure diagram is shown in Figure 2, and the YOLOv5s network model includes Input, Backbone, Neck, Prediction; the Input includes Mosaic data enhancement, adaptive anchor frame calculation, and adaptive image scaling; the Backbone includes Focus module, SPP module and C3 module; described neck network includes FPN module, PAN module, C3 module; described Prediction includes Bounding box loss function and NMS; wherein, the structure of described backbone network C3 module is divided into two parts One branch uses multiple Bottleneck stacks and 3 standard convolutional layers, the other only passes through a basic convolution module, and finally the two branches are concat operated;
4)修改主干网络卷积模块,将主干网络卷积模块修改为RepVGG Block模块;4) Modify the backbone network convolution module, and modify the backbone network convolution module to the RepVGG Block module;
5)修改主干网络结构,在RepVGG模块与SPP模块之间插入SA注意力机制;5) Modify the backbone network structure and insert the SA attention mechanism between the RepVGG module and the SPP module;
6)修改YOLOv5s颈部网络的上采样方式,将最邻近上采样改为CARAFE上采样方式。6) Modify the upsampling method of the YOLOv5s neck network, and change the nearest neighbor upsampling to the CARAFE upsampling method.
7)将评价目标框和预测框的类损失和置信度损失的损失函数Focal Loss修改为Varifocal Loss。7) Modify the loss function Focal Loss for evaluating the class loss and confidence loss of the target frame and the prediction frame to Varifocal Loss.
8)对鱼类数据集D2进行迁移训练,得到训练权重w;即用GIOU_Loss作为损失函数,当模型损失曲线趋近于0且无明显波动时,停止训练,得到训练权重w,否则继续训练;8) Perform migration training on the fish data set D2 to obtain the training weight w; that is, use GIOU_Loss as the loss function, when the model loss curve approaches 0 and there is no obvious fluctuation, stop the training, and obtain the training weight w, otherwise continue training;
9)输入图像,进行鱼类检测,将获取到的鱼类图像输入到训练权重为w的模型中,模型根据权重自动识别鱼类数量。9) Input the image, perform fish detection, and input the obtained fish image into the model with training weight w, and the model automatically identifies the number of fish according to the weight.
作为本发明的优选实施例,步骤2)包括如下步骤:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, step 2) comprises the following steps:
2.1)从鱼类公共数据集选取N张,构建数据集D1;2.1) Select N pieces from the fish public data set to construct the data set D1;
2.2)使用标注工具Labelimg对数据集D1的中每一张图像中的鱼类进行标注,构建鱼类数据集D2;2.2) Use the labeling tool Labelimg to label the fish in each image in the dataset D1 to construct the fish dataset D2;
2.3)按比例将鱼类数据集D2划分为训练集Dtrain和验证集Dtest。2.3) Divide the fish dataset D2 into a training set Dtrain and a validation set Dtest in proportion.
作为本发明的优选实施例,RepVGG Block卷积结构如图3所示,上述步骤4)包括如下步骤:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the RepVGG Block convolution structure is shown in Figure 3, and the above step 4) includes the following steps:
4.1)训练多分支模型。在训练时,为每一个3×3卷积层添加平行的1×1卷积分支与恒等映射分支。4.1) Train a multi-branch model. During training, parallel 1×1 convolution branches and identity mapping branches are added to each 3×3 convolutional layer.
4.2)将多分支模型等价转换为单路模型。将1×1卷积看成卷积核中有很多0的3×3卷积,恒等映射是一个特殊1×1卷积。根据卷积的可加性原理,每个RepVGG Block模块三个分支则可以合并为一个3×3卷积。4.2) Equivalently convert the multi-branch model to a one-way model. Think of the 1×1 convolution as a 3×3 convolution with many 0s in the convolution kernel, and the identity map is a special 1×1 convolution. According to the additivity principle of convolution, the three branches of each RepVGG Block module can be combined into a 3×3 convolution.
4.3)结构参数重构。通过实际数据流,将多分支网络的权值转移到简单网络中。4.3) Structure parameter reconstruction. The weights of the multi-branch network are transferred to the simple network through the actual data flow.
作为本发明的优选实施例,SA模块结构见图4,上述步骤5)包括如下步骤:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the SA module structure is shown in Figure 4, and the above step 5) includes the following steps:
5.1)特征分组,假设输入特征为X∈RC×H×W,其中C、H、W分别表示通道数、高度和宽度,特征分组会将输入X沿着通道维度拆分为g组,使得每个子功能在训练过程中逐渐捕获特定的语义响应;5.1) Feature grouping, assuming that the input feature is X∈RC×H×W , where C, H, and W represent the number of channels, height and width, respectively, and the feature grouping will split the input X into g groups along the channel dimension, so that Each sub-feature gradually captures a specific semantic response during training;
5.2)使用通道注意力机制。捕获通道相关性信息,计算公式如下:5.2) Use channel attention mechanism. Capture channel correlation information, the calculation formula is as follows:
X′k1=σ(W1s+b1)·Xk1X′k1 =σ(W1 s+b1 )·Xk1
式中:s表示信道统计,Xk1为在通道维度被分成的一个分支,X′k1表示通道注意力的最终输出,σ为sigmoid激活函数,W1与b1是形状为C/2G×1×1的参数。In the formula: s represents the channel statistics, Xk1 is a branch divided in the channel dimension, X′k1 represents the final output of the channel attention, σ is the sigmoid activation function, W1 and b1 are the shape of C/2G×1 ×1 parameter.
5.3)使用空间注意力机制。捕获空间相关性信息,计算公式见下:5.3) Use spatial attention mechanism. Capture spatial correlation information, the calculation formula is as follows:
X′k2=σ(W2·GN(XK2)+b2)·Xk2X′k2 =σ(W2 ·GN(XK2 )+b2 )·Xk2
式中:Xk2表示在通道维度被分成的一个分支,X′k2表示空间注意力的最终输出,W2与b2是形状为C/2G×1×1的参数,GN表示组归一化方法。where Xk2 represents a branch divided in the channel dimension, X′k2 represents the final output of spatial attention, W2 and b2 are parameters of shape C/2G×1×1, GN represents group normalization method.
5.4)聚合。在完成前面两种注意力计算后,对其进行集成,首先通过简单的Concat进行融合得到:X′k=[X′k1,X′k2]∈RC/2G×H×W。最后采用通道置换操作(channel shuffle)进行组间通信。5.4) Aggregation. After completing the first two attention calculations, they are integrated, firstly obtained by simple Concat fusion: X′k = [X′k1 , X′k2 ]∈RC/2G×H×W . Finally, the channel shuffle operation is used for inter-group communication.
作为本发明的优选实施例,上述步骤6)包括如下步骤:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the above step 6) includes the following steps:
6.1)特征图通道压缩,假设上采样倍率为σ,对于形状为C×H×W的输入特征图,其中C、H、W分别表示通道数、高度和宽度,用1×1卷积将它的通道数压缩到Cm,减少后续步骤计算量。6.1) Feature map channel compression, assuming that the upsampling magnification is σ, for the input feature map with shape C×H×W, where C, H, W represent the number of channels, height and width respectively, use 1×1 convolution to convolve it. The number of channels is compressed to Cm , reducing the amount of computation in subsequent steps.
6.2)内容编码及上采样核预测,对于第一步中压缩后的输入特征图,利用的卷积层来预测上采样核,假设上采样的卷积核为kup×kup,输入通道数为Cm,输出通道数为将通道维在空间维展开,得到形状为的上采样核。6.2) Content encoding and upsampling kernel prediction, for the compressed input feature map in the first step, use topredict theupsamplingkernel by using the convolutional layer of Expand the channel dimension in the space dimension to get the shape as upsampling kernel.
6.3)上采样核归一化,对得到的上采样核每个通道kup×kup利用softmax进行归一化,使得卷积核权重和为1。对于输出特征图中的每个位置,我们将其映射回输入特征图,取出以之为中心的kup×kup的区域,和预测出的该点的上采样核作点积,得到输出值。相同位置的不同通道共享同一个上采样核。6.3) Normalization of the upsampling kernel, using softmax for each channel kup ×kup of the obtained upsampling kernel, so that the sum of the convolution kernel weights is 1. For each position in the output feature map, we map it back to the input feature map, take out the kup × kup region centered on it, and do a dot product with the predicted upsampling kernel of that point to get the output value . Different channels at the same location share the same upsampling kernel.
作为本发明的优选实施例,上述步骤7)中的Varifocal Loss损失函数公式如下:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the Varifocal Loss loss function formula in the above step 7) is as follows:
其中,p是预测的IACS,q是目标IoU得分,对于正样本,q是预测包围框和gt框之间的IoU,对于负样本,q为0。where p is the predicted IACS, q is the target IoU score, for positive samples, q is the IoU between the predicted bounding box and gt box, and for negative samples, q is 0.
作为本发明的优选实施例,步骤8)中的GIoU_Loss损失函数转换公式如下:As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the GIoU_Loss loss function conversion formula in step 8) is as follows:
式中,In the formula,
IoU表示两个重叠矩形框之间的交并比;I表示两个矩形的重叠部分,U表示的是两个矩形面积之和Ap+Ag掉两个矩形相交面积I,Ac是两个矩形的最小外界面积。IoU represents the intersection ratio between two overlapping rectangles; I represents the overlapping part of the two rectangles, U represents the sum of the areas of the two rectangles, Ap + Ag minus the intersection area I of the two rectangles, and Ac is the two rectangles. The minimum outer area of a rectangle.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210920891.7ACN115205667A (en) | 2022-08-02 | 2022-08-02 | A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210920891.7ACN115205667A (en) | 2022-08-02 | 2022-08-02 | A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115205667Atrue CN115205667A (en) | 2022-10-18 |
Family
ID=83586088
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210920891.7APendingCN115205667A (en) | 2022-08-02 | 2022-08-02 | A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115205667A (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116343045A (en)* | 2023-03-30 | 2023-06-27 | 南京理工大学 | Lightweight SAR image ship target detection method based on YOLO v5 |
| CN116958907A (en)* | 2023-09-18 | 2023-10-27 | 四川泓宝润业工程技术有限公司 | Method and system for inspecting surrounding hidden danger targets of gas pipeline |
| CN116994118A (en)* | 2023-08-16 | 2023-11-03 | 河北科技大学 | Neural network, method and device for target detection |
| CN117132767A (en)* | 2023-10-23 | 2023-11-28 | 中国铁塔股份有限公司湖北省分公司 | Small target detection method, device, equipment and readable storage medium |
| CN117237794A (en)* | 2023-09-04 | 2023-12-15 | 淮阴工学院 | A marine life detection method and system based on PNC-YOLOv7 |
| CN117274192A (en)* | 2023-09-20 | 2023-12-22 | 重庆市荣冠科技有限公司 | A pipeline magnetic leakage defect detection method based on improved YOLOv5 |
| CN117496475A (en)* | 2023-12-29 | 2024-02-02 | 武汉科技大学 | A target detection method and system applied to autonomous driving |
| CN118314451A (en)* | 2024-03-29 | 2024-07-09 | 金陵科技学院 | Unmanned boat feeding method for target fish schools based on temporal network algorithm |
| CN119810988A (en)* | 2025-03-12 | 2025-04-11 | 南京信息工程大学 | An intelligent security monitoring system based on YOLOv8 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113762081A (en)* | 2021-08-09 | 2021-12-07 | 江苏大学 | Granary pest detection method based on YOLOv5s |
- 2022
- 2022-08-02CNCN202210920891.7Apatent/CN115205667A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113762081A (en)* | 2021-08-09 | 2021-12-07 | 江苏大学 | Granary pest detection method based on YOLOv5s |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| 任克勤,等.: "基于 YOLOv5的试管检测算法", 《现代计算机》, vol. 28, no. 7, 10 April 2022 (2022-04-10), pages 1 - 2* |
| 周裔扬,等.: "基于 YOLOv5 的移动机器人目标检测算法的研究", 《装备制造技术》, 31 August 2021 (2021-08-31), pages 1* |
| 赵兴博,等.: "适用于 FPGA 的轻量实时视频人脸检测", 《现代计算机》, vol. 28, no. 8, 25 April 2022 (2022-04-25), pages 2* |
| 颜小红: "基于深度学习的水下目标检测方法研究", 《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技辑》, 15 March 2022 (2022-03-15), pages 3* |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116343045B (en)* | 2023-03-30 | 2024-03-19 | 南京理工大学 | Lightweight SAR image ship target detection method based on YOLO v5 |
| CN116343045A (en)* | 2023-03-30 | 2023-06-27 | 南京理工大学 | Lightweight SAR image ship target detection method based on YOLO v5 |
| CN116994118A (en)* | 2023-08-16 | 2023-11-03 | 河北科技大学 | Neural network, method and device for target detection |
| CN117237794A (en)* | 2023-09-04 | 2023-12-15 | 淮阴工学院 | A marine life detection method and system based on PNC-YOLOv7 |
| CN116958907A (en)* | 2023-09-18 | 2023-10-27 | 四川泓宝润业工程技术有限公司 | Method and system for inspecting surrounding hidden danger targets of gas pipeline |
| CN116958907B (en)* | 2023-09-18 | 2023-12-26 | 四川泓宝润业工程技术有限公司 | Method and system for inspecting surrounding hidden danger targets of gas pipeline |
| CN117274192A (en)* | 2023-09-20 | 2023-12-22 | 重庆市荣冠科技有限公司 | A pipeline magnetic leakage defect detection method based on improved YOLOv5 |
| CN117132767A (en)* | 2023-10-23 | 2023-11-28 | 中国铁塔股份有限公司湖北省分公司 | Small target detection method, device, equipment and readable storage medium |
| CN117132767B (en)* | 2023-10-23 | 2024-03-19 | 中国铁塔股份有限公司湖北省分公司 | Small target detection method, device, equipment and readable storage medium |
| CN117496475A (en)* | 2023-12-29 | 2024-02-02 | 武汉科技大学 | A target detection method and system applied to autonomous driving |
| CN117496475B (en)* | 2023-12-29 | 2024-04-02 | 武汉科技大学 | Target detection method and system applied to automatic driving |
| CN118314451A (en)* | 2024-03-29 | 2024-07-09 | 金陵科技学院 | Unmanned boat feeding method for target fish schools based on temporal network algorithm |
| CN119810988A (en)* | 2025-03-12 | 2025-04-11 | 南京信息工程大学 | An intelligent security monitoring system based on YOLOv8 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115205667A (en) | A Dense Object Detection Method Based on YOLOv5s | |
| CN111126472B (en) | An Improved Target Detection Method Based on SSD | |
| CN108805070A (en) | A kind of deep learning pedestrian detection method based on built-in terminal | |
| CN114283469B (en) | Improved YOLOv4-tiny target detection method and system | |
| CN114220035A (en) | Rapid pest detection method based on improved YOLO V4 | |
| CN111767927A (en) | A lightweight license plate recognition method and system based on fully convolutional network | |
| CN114202672A (en) | A small object detection method based on attention mechanism | |
| CN110334705A (en) | A Language Recognition Method for Scene Text Images Combining Global and Local Information | |
| CN113435269A (en) | Improved water surface floating object detection and identification method and system based on YOLOv3 | |
| CN112348036A (en) | Adaptive Object Detection Method Based on Lightweight Residual Learning and Deconvolution Cascade | |
| CN110348376A (en) | A kind of pedestrian's real-time detection method neural network based | |
| CN115082855A (en) | Pedestrian occlusion detection method based on improved YOLOX algorithm | |
| CN116485860A (en) | Monocular depth prediction algorithm based on multi-scale progressive interaction and aggregation cross attention features | |
| WO2024108857A1 (en) | Deep-learning-based method for small target detection in unmanned aerial vehicle scenario | |
| CN117456167A (en) | Target detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8s | |
| CN113536896B (en) | Insulator defect detection method, device and storage medium based on improved Faster RCNN | |
| CN113743505A (en) | An improved SSD object detection method based on self-attention and feature fusion | |
| CN116469100A (en) | A method for semantic segmentation of dual-band images based on Transformer | |
| CN114998879B (en) | Fuzzy license plate recognition method based on event camera | |
| CN113505640A (en) | Small-scale pedestrian detection method based on multi-scale feature fusion | |
| CN114743023B (en) | An image detection method of wheat spider based on RetinaNet model | |
| CN115410087A (en) | Transmission line foreign matter detection method based on improved YOLOv4 | |
| CN111680705A (en) | MB-SSD Method and MB-SSD Feature Extraction Network for Object Detection | |
| CN116416244A (en) | Crack detection method and system based on deep learning | |
| CN117315752A (en) | Training method, device, equipment and medium for face emotion recognition network model |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |