CN115201760A - Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combination - Google Patents
Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combinationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115201760A CN115201760ACN202210561790.5ACN202210561790ACN115201760ACN 115201760 ACN115201760 ACN 115201760ACN 202210561790 ACN202210561790 ACN 202210561790ACN 115201760 ACN115201760 ACN 115201760A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- clutter
- output signal
- dimension
- doppler
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/28—Details of pulse systems
- G01S7/285—Receivers
- G01S7/292—Extracting wanted echo-signals
- G01S7/2923—Extracting wanted echo-signals based on data belonging to a number of consecutive radar periods
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/35—Details of non-pulse systems
- G01S7/352—Receivers
- G01S7/354—Extracting wanted echo-signals
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/41—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00 using analysis of echo signal for target characterisation; Target signature; Target cross-section
- G01S7/414—Discriminating targets with respect to background clutter
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A90/00—Technologies having an indirect contribution to adaptation to climate change
- Y02A90/10—Information and communication technologies [ICT] supporting adaptation to climate change, e.g. for weather forecasting or climate simulation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于雷达信号处理领域,具体涉及一种强海杂波信号抑制方法。The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing, and in particular relates to a strong sea clutter signal suppression method.
背景技术Background technique
海杂波是局部海平面对雷达发射信号的后向散射回波,受到风浪等多重因素的影响.利 用海杂波的特性分析海平面状况,实现海平面目标的探测具有重要的理论意义和实用价 值.海杂波背景下的小目标检测是目前的研究热点和难点。目前海杂波背景下的小目标检 测由于高频雷达海杂波对目标检测干扰性强,存在海面目标检测的准确性差的问题。Sea clutter is the backscattered echo of local sea level to radar transmission signals, which is affected by multiple factors such as wind and waves. It is of great theoretical significance and practicality to use the characteristics of sea clutter to analyze sea level conditions and realize the detection of sea level targets. Value. Small target detection under the background of sea clutter is the current research focus and difficulty. At present, the detection of small targets in the background of sea clutter has the problem of poor accuracy of sea surface target detection due to the strong interference of high-frequency radar sea clutter to target detection.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明目的是为了解决现有海杂波背景下,海面目标检测的准确性差的问题,提出了 一种基于多域联合的强海杂波抑制方法。The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem of poor accuracy of sea surface target detection under the background of existing sea clutter, and propose a strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain joint.
本发明所述的基于多域联合的海杂波抑制方法,包括:The multi-domain joint-based sea clutter suppression method according to the present invention includes:
步骤一、根据雷达回波信号和天线阵列结构,获取天线每个阵列所有的输出信号;Step 1: Obtain all the output signals of each array of the antenna according to the radar echo signal and the structure of the antenna array;
步骤二、对天线每个阵列每个输出信号进行分解,获取每个输出信号中的复指数分量, 提取复指数分量中的多普勒维信息、距离维信息和角度维信息;
步骤三、利用所述多普勒维信息,利用ROOT循环对消算法,将输出信号中复指数分量消除;Step 3, utilize the Doppler dimension information, utilize the ROOT cycle cancellation algorithm to eliminate the complex exponential component in the output signal;
步骤四、采用子空间分解法,对复指数分量的输出信号按照距离维和多普勒维进行时 间相关性杂波分量去除;Step 4, adopt the subspace decomposition method, carry out the time-dependent clutter component removal to the output signal of the complex exponential component according to the distance dimension and the Doppler dimension;
步骤五、采用空时自适应处理算法,对去除杂波的输出信号中按照多普勒维、距离维 和角度维对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号进行空间相关性残余杂波去除,完成基于多 域联合的强海杂波的抑制。Step 5: Use the space-time adaptive processing algorithm to remove the spatial correlation residual clutter according to the Doppler dimension, the distance dimension and the angle dimension of the clutter-removed output signal. Suppression of strong sea clutter in multi-domain joint.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤一中,根据雷达回波信号和天线阵列结构,获取天线每个阵 列所有的输出信号的方法为:Further, in the present invention, in
发射阵列中第n个发射阵元的发射信号:The transmit signal of the nth transmit element in the transmit array:
其中,E是总发射能量,T是雷达脉冲持续时间,N为天线阵列总个数,基带波形φn(t):where E is the total transmitted energy, T is the radar pulse duration, N is the total number of antenna arrays, and the baseband waveform φn (t):
其中,为基带波形φn(t)的伴随矩阵,设电磁波在自由空间中独立传播,双向传播 时,选择第一个天线阵元作为参考点,对于任意目标,天线第m个接收阵元的接收回波ym(t)为:in, is the adjoint matrix of the baseband waveform φn (t). Assuming that the electromagnetic wave propagates independently in free space, when it propagates in both directions, the first antenna element is selected as the reference point. For any target, the received response of the mth receiving element of the antenna is The wave ym (t) is:
其中,ξ表示目标的复数反射系数,fd,n表示多普勒频率,fd,n=2vtfn/c,vt指代 目标的径向速度;fn为第n个发射天线的工作频率,τn,T和τm,R分别是发送和接收时 间延迟;Among them, ξ represents the complex reflection coefficient of the target, fd,n represents the Doppler frequency, fd,n =2vt fn /c, vt refers to the radial velocity of the target; fn is the nth transmitting antenna The operating frequency of τn,T and τm,R are the transmit and receive time delays, respectively;
其中,dT为发射阵列的阵元间距,dR为接收阵列的阵元间距,τ0=2r/c,θ代表 目标的角度,从法线方向到目标方向测量,r代表目标距离接收阵列的距离,c是光 速;Among them, dT is the array element spacing of the transmitting array, dR is the array element spacing of the receiving array, τ0 =2r/c, θ represents the angle of the target, measured from the normal direction to the target direction, r represents the target distance from the receiving array distance, c is the speed of light;
在接收阵列中,对接收信号经N个匹配滤波器分解,获得N个隔离的传输信号, 则第m个接收天线的第n个输出:In the receiving array, the received signal is decomposed by N matched filters to obtain N isolated transmission signals, then the nth output of the mth receiving antenna is:
fd表示多普勒频率。fd represents the Doppler frequency.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤二中,提取复指数分量中的多普勒维信息、距离维信息和 角度维信息的具体方法为:Further, in the present invention, in
令相位差fdτ0=0:Let the phase difference fd τ0 =0:
分别提取三个e指数因子,为输出信号的多普勒维复指数分量,为输出 信号的距离维复指数分量,为输出信号的角度维复指数分量。Extract three e-index factors, respectively, is the Doppler-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal, is the distance-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal, is the angular-dimension complex exponential component of the output signal.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤三中,将输出信号中复指数分量消除的具体方法为:Further, in the present invention, in step 3, the specific method for eliminating complex exponential components in the output signal is:
步骤三一、在输出信号的多普勒维复指数分量中寻找频谱的峰值及其对应的频率;Step 31: Find the peak value of the frequency spectrum and its corresponding frequency in the Doppler-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal;
步骤三二、建立能量误差函数,在[0,2π]上搜索使能量误差函数值最小的角度对每个输 出信号中的复指数分量初始相位进行估计;Step 32, establish the energy error function, search the angle that makes the energy error function value minimum on [0,2π] to estimate the initial phase of the complex exponential component in each output signal;
步骤三二、利用步骤三一寻找到的频谱的峰值及其对应的频率和估计的初始相位对输 出信号复指数分量消除,并判断该次消除是否达到迭代次数阈值,若是,完成输出信号中 复指数分量消除,否则,返回执行步骤三一,所述迭代次数阈值根据输出信号的信杂比确 定。Step 32: Use the peak value of the spectrum found in step 31, its corresponding frequency and the estimated initial phase to eliminate the complex exponential component of the output signal, and determine whether the elimination reaches the threshold of the number of iterations. If so, complete the complex exponential component in the output signal. The exponential component is eliminated, otherwise, go back to step 31, and the threshold for the number of iterations is determined according to the signal-to-noise ratio of the output signal.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤三一中,在[0,2π]上搜索使能量误差函数最小的角度对初始 相位进行估计的过程为:Further, in the present invention, in step 31, the process of estimating the initial phase by searching for the angle that minimizes the energy error function on [0,2π] is:
建立能量误差函数ε(φ):Establish the energy error function ε(φ):
其中,x(n)为单个距离门的多普勒谱,n对应多普勒单元、A为整个多普勒谱的谱线最高峰值,f为该峰值对应的频率,是待去除的复信号初始相位;Among them, x(n) is the Doppler spectrum of a single range gate, n corresponds to the Doppler unit, A is the highest peak of the spectral line of the entire Doppler spectrum, f is the frequency corresponding to the peak, is the initial phase of the complex signal to be removed;
对初始相位的估计:Estimate of initial phase:
为初始相位估计值。 is the initial phase estimate.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤四中,采用子空间分解法,对复指数分量的输出信号按照距 离维和多普勒维进行时间相关性杂波分量去除的过程为:Further, in the present invention, in step 4, adopt subspace decomposition method, the process that the output signal of complex exponential component is carried out according to distance dimension and Doppler dimension is carried out the process of time-dependent clutter component removal is:
从消除复指数分量的输出信号中提取含有目标信号距离门的回波列向量信号ST(k),k =0,1,2,……N-1;Extract the echo column vector signal ST (k) containing the distance gate of the target signal from the output signal of eliminating the complex exponential component, k = 0, 1, 2, ... N-1;
ST=[ST(0),ST(1),ST(2),……,ST(N-1)]TST = [ST (0), ST (1), ST (2),..., ST (N-1)]T
Si=[Si(0),Si(1),Si(2),……,Si(N-1)]TSi =[Si (0),Si (1),Si (2),...,Si (N-1)]T
其中,Si为与目标相邻的距离单元的回波列向量集合,集合中包含M个列向量;ST为含有目标信号距离门的回波列向量集合;上角标T表示向量转置;Among them, Si is the echo column vector set of the distance unit adjacent to the target, and the set contains M column vectors; ST is the echo column vector set containing the target signal distance gate; the superscript T represents the vector transposition ;
协方差矩阵为:The covariance matrix is:
其中,参数γi的求解公式为:Among them, the solution formula of parameter γi is:
上角标T代表矩阵转置,上角标H代表共轭转置;The superscript T represents the matrix transpose, and the superscript H represents the conjugate transpose;
对协方差矩阵RN×N进行特征分解:Eigendecomposition of the covariance matrix RN×N :
RN×N=WΣWHRN×N = WΣWH
获取特征值,选取特征值中最大的P个特征值,其中W表示窗函数的最优解,Σ为加和符号;Obtain the eigenvalues, and select the largest P eigenvalues among the eigenvalues, where W represents the optimal solution of the window function, and Σ is the summation symbol;
将所述P个特征值对应的特征矢量作为基底组成的线性空间作为杂波子空间,将含有 目标信号的回波列向量投影到“杂波子空间”对杂波列向量进行估计,并利用估计的杂波列 向量对消除复指数分量的输出信号进行杂波去除。The linear space composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the P eigenvalues is used as the base as the clutter subspace, and the echo column vector containing the target signal is projected to the "clutter subspace" to estimate the clutter column vector, and the estimated clutter column vector is used. The clutter column vector performs clutter removal on the output signal with complex exponential components removed.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤三一中,步骤五中,采用空时自适应处理算法,对去除杂波 的输出信号中按照多普勒维、距离维和角度维对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号进行空 间相关性残余杂波去除的具体过程为:Further, in the present invention, in step 31 and
对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号按照多普勒维和距离维顺序堆成一个列向量,构 成一个MN×1维的空时观测向量;The output signal of removing the time-correlated clutter component is stacked into a column vector according to the order of Doppler dimension and distance dimension, forming a space-time observation vector of MN×1 dimension;
具体拼接过程为:The specific splicing process is as follows:
s(f,θ)=ves(f,θ)s(f,θ)=ves(f,θ)
其中vec(·)为向量化操作,二维数据按列的顺序堆成一列;s(f,θ)为去除杂波后的输出 信号;将所述据去除杂波后的输出信号表示成空时导向矢量:Among them, vec( ) is a vectorization operation, and the two-dimensional data are stacked into a column in the order of columns; s(f, θ) is the output signal after removing clutter; the output signal after removing clutter is represented as empty Time Steering Vector:
其中,为克罗内克积(Kronecker),aN(f)为时间导向矢量,vM(θ)为时间导向矢量, 利用STAP算法将空域向量替换成对应的空时向量:in, is the Kronecker product, aN (f) is the time-steering vector, vM (θ) is the time-steering vector, and the STAP algorithm is used to replace the space domain vector with the corresponding space-time vector:
其中,为杂波的空时协方差矩阵。in, is the space-time covariance matrix of the clutter.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤三一中,窗函数的最优解W为:Further, in the present invention, in step 31, the optimal solution W of the window function is:
本发明采用了三个维度联合的全空间自适应处理进行杂波抑制后,杂波抑制效果要比 基于单一多普勒维度的ROOT循环对消,以及基于多普勒维-距离维的子空间投影发要好很 多,海杂波和地物杂波的成分也基本完全去除,信噪比(以噪声幅度最大值为基准)为13.40dB。After the invention adopts the combined full-space adaptive processing of three dimensions to suppress clutter, the effect of clutter suppression is better than that of ROOT cycle cancellation based on a single Doppler dimension, and a sub-domain based on Doppler dimension and distance dimension. The spatial projection is much better, and the components of sea clutter and ground clutter are basically completely removed, and the signal-to-noise ratio (based on the maximum noise amplitude) is 13.40dB.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明所述方法流程图;Fig. 1 is the method flow chart of the present invention;
图2是雷达天线发射信号系统示意图;Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of a radar antenna transmitting signal system;
图3是雷达天线接收信号系统示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of a radar antenna receiving signal system;
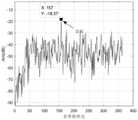
图4是未采用子空间投影法海杂波抑制效果图;Fig. 4 is the effect diagram of sea clutter suppression without subspace projection method;
图5是采用子空间投影法抑制海杂波后的效果图;Fig. 5 is the effect diagram after adopting the subspace projection method to suppress sea clutter;
图6是实测数据第158个多普勒单元的一维距离像目标信号示意图;6 is a schematic diagram of the one-dimensional range image target signal of the 158th Doppler unit of the measured data;
图7是实测数据第158个多普勒单元的一维距离像旁瓣信号示意图;7 is a schematic diagram of the one-dimensional range image sidelobe signal of the 158th Doppler unit of the measured data;
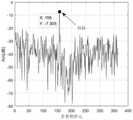
图8是未采用全空时自适应处理抑制海杂波的效果图;Fig. 8 is the effect diagram of suppressing sea clutter without adopting full space-time adaptive processing;
图9是采用全空时自适应处理抑制海杂波后的效果图。Fig. 9 is the effect diagram after adopting full space-time adaptive processing to suppress sea clutter.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地 描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本 发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他 实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present invention, rather than all the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative work shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
需要说明的是,在不冲突的情况下,本发明中的实施例及实施例中的特征可以相互组 合。It should be noted that the embodiments of the present invention and the features of the embodiments may be combined with each other under the condition of no conflict.
具体实施方式一:下面结合图1说明本实施方式,本实施方式所述基于多域联合的海 杂波抑制方法,包括:Embodiment 1: The present embodiment will be described below with reference to FIG. 1. The sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain joint described in this embodiment includes:
步骤一、根据雷达回波信号和天线阵列结构,获取天线每个阵列所有的输出信号;Step 1: Obtain all the output signals of each array of the antenna according to the radar echo signal and the structure of the antenna array;
步骤二、对天线每个阵列每个输出信号进行分解,获取每个输出信号中的复指数分量, 提取复指数分量中的多普勒维信息、距离维信息和角度维信息;
步骤三、利用所述多普勒维信息,利用ROOT循环对消算法,将输出信号中复指数分量消除;Step 3, utilize the Doppler dimension information, utilize the ROOT cycle cancellation algorithm to eliminate the complex exponential component in the output signal;
步骤四、采用子空间分解法,对复指数分量的输出信号按照距离维和多普勒维进行时 间相关性杂波分量去除;Step 4, adopt the subspace decomposition method, carry out the time-dependent clutter component removal to the output signal of the complex exponential component according to the distance dimension and the Doppler dimension;
步骤五、采用空时自适应处理算法,对去除杂波的输出信号中按照多普勒维、距离维 和角度维对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号进行空间相关性残余杂波去除,完成基于多 域联合的强海杂波的抑制。Step 5: Use the space-time adaptive processing algorithm to remove the spatial correlation residual clutter according to the Doppler dimension, the distance dimension and the angle dimension of the clutter-removed output signal. Suppression of strong sea clutter in multi-domain joint.
进一步地,结合图2和图3说明本实施方式,本实施方式中,步骤一中,根据雷达回波信号和天线阵列结构,获取天线每个阵列所有的输出信号的方法为:Further, this embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 2 and FIG. 3. In this embodiment, in
发射阵列中第n个发射阵元的发射信号:The transmit signal of the nth transmit element in the transmit array:
其中,E是总发射能量,T是雷达脉冲持续时间,N为天线阵列总个数,基带波形φn(t):where E is the total transmitted energy, T is the radar pulse duration, N is the total number of antenna arrays, and the baseband waveform φn (t):
其中,为基带波形φn(t)的伴随矩阵,设电磁波在自由空间中独立传播,双向传 播时,选择第一个天线阵元作为参考点,对于任意目标,天线第m个接收阵元的接收回波ym(t)为:in, is the adjoint matrix of the baseband waveform φn (t). Assuming that the electromagnetic wave propagates independently in free space, when it propagates in both directions, the first antenna element is selected as the reference point. For any target, the received response of the mth receiving element of the antenna is The wave ym (t) is:
其中,ξ表示目标的复数反射系数,fd,n表示多普勒频率,fd,n=2vtfn/c,vt指 代目标的径向速度;fn为第n个发射天线的工作频率,τn,T和τm,R分别是发送和接收 时间延迟;Among them, ξ represents the complex reflection coefficient of the target, fd,n represents the Doppler frequency, fd,n =2vt fn /c, vt refers to the radial velocity of the target; fn is the nth transmitting antenna The operating frequency of τn,T and τm,R are the transmit and receive time delays, respectively;
其中,dT为发射阵列的阵元间距,dR为接收阵列的阵元间距,τ0=2r/c,θ代 表目标的角度,从法线方向到目标方向测量,r代表目标距离接收阵列的距离,c是 光速;Among them, dT is the array element spacing of the transmitting array, dR is the array element spacing of the receiving array, τ0 =2r/c, θ represents the angle of the target, measured from the normal direction to the target direction, r represents the target distance from the receiving array distance, c is the speed of light;
在接收阵列中(接收阵列与发射阵列及信号对应),对接收信号经N个匹配滤波 器分解,获得N个隔离的传输信号,则第m个接收天线的第n个输出:In the receiving array (the receiving array corresponds to the transmitting array and the signal), the received signal is decomposed by N matched filters to obtain N isolated transmission signals, then the nth output of the mth receiving antenna:
fd表示多普勒频率。fd represents the Doppler frequency.
进一步地,本实施方式中,步骤二中,提取复指数分量中的多普勒维信息、距离维信 息和角度维信息的具体方法为:Further, in the present embodiment, in
令相位差fdτ0=0:Let the phase difference fd τ0 =0:
分别提取三个e指数因子,为输出信号的多普勒维复指数分量,为输出 信号的距离维复指数分量,为输出信号的角度维复指数分量。Extract three e-index factors, respectively, is the Doppler-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal, is the distance-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal, is the angular-dimension complex exponential component of the output signal.
进一步地,本发明中,步骤三中,将输出信号中复指数分量消除的具体方法为:Further, in the present invention, in step 3, the specific method for eliminating complex exponential components in the output signal is:
步骤三一、在输出信号的多普勒维复指数分量中寻找频谱的峰值及其对应的频率;Step 31: Find the peak value of the frequency spectrum and its corresponding frequency in the Doppler-dimensional complex exponential component of the output signal;
步骤三二、建立能量误差函数,在[0,2π]上搜索使能量误差函数值最小的角度对每个输 出信号中的复指数分量初始相位进行估计;Step 32, establish the energy error function, search the angle that makes the energy error function value minimum on [0,2π] to estimate the initial phase of the complex exponential component in each output signal;
步骤三二、利用步骤三一寻找到的频谱的峰值及其对应的频率和估计的初始相位对输 出信号复指数分量消除,并判断该次消除是否达到迭代次数阈值,若是,完成输出信号中 复指数分量消除,否则,返回执行步骤三一,所述迭代次数阈值根据输出信号的信杂比确 定。Step 32: Use the peak value of the spectrum found in step 31, its corresponding frequency and the estimated initial phase to eliminate the complex exponential component of the output signal, and determine whether the elimination reaches the threshold of the number of iterations. If so, complete the complex exponential component in the output signal. The exponential component is eliminated, otherwise, go back to step 31, and the threshold for the number of iterations is determined according to the signal-to-noise ratio of the output signal.
进一步地,本实施方式中,步骤三一中,在[0,2π]上搜索使能量误差函数最小的角度对 初始相位进行估计的过程为:Further, in this embodiment, in step 31, the process of estimating the initial phase by searching for the angle that minimizes the energy error function on [0,2π] is:
建立能量误差函数ε(φ):Establish the energy error function ε(φ):
其中,x(n)为单个距离门的多普勒谱,n对应多普勒单元,A为整个多普勒谱的谱线最高峰值,f为该峰值对应的频率,是待去除的复信号初始相位;Among them, x(n) is the Doppler spectrum of a single range gate, n corresponds to the Doppler unit, A is the highest peak of the spectral line of the entire Doppler spectrum, f is the frequency corresponding to the peak, is the initial phase of the complex signal to be removed;
对初始相位的估计:Estimate of initial phase:
为初始相位估计值。 is the initial phase estimate.
进一步地,本实施方式中,步骤四中,采用子空间分解法,对复指数分量的输出信号 按照距离维和多普勒维进行时间相关性杂波分量去除的过程为:Further, in the present embodiment, in step 4, the subspace decomposition method is adopted, and the process of removing the time-dependent clutter component to the output signal of the complex exponential component according to the distance dimension and the Doppler dimension is:
从消除复指数分量的输出信号中提取含有目标信号距离门的回波列向量信号ST(k),k =0,1,2,……U-1;Extract the echo column vector signal ST (k) containing the distance gate of the target signal from the output signal of eliminating the complex exponential component, k = 0, 1, 2, ... U-1;
ST=[ST(0),ST(1),ST(2),……,ST(U-1)]TST = [ST (0), ST (1), ST (2),..., ST (U-1)]T
Si=[Si(0),Si(1),Si(2),……,Si(U-1)]TSi =[Si (0),Si (1),Si (2),...,Si (U-1)]T
其中,Si为与目标相邻的距离单元的回波列向量集合,集合中包含V个列向量; ST为含有目标信号距离门的回波列向量集合;上角标T表示向量转置;Among them, Si is the set of echo column vectors of the distance unit adjacent to the target, and the set contains V column vectors; ST is the set of echo column vectors containing the target signal distance gate; the superscript T represents the vector transposition ;
协方差矩阵为:The covariance matrix is:
其中,参数γi的求解公式为:Among them, the solution formula of parameter γi is:
上角标T代表矩阵转置,上角标H代表共轭转置;The superscript T represents the matrix transpose, and the superscript H represents the conjugate transpose;
对协方差矩阵RU×U进行特征分解:Eigendecomposition of the covariance matrix RU×U :
RU×U=WΣWHRU×U = WΣWH
获取特征值,选取特征值中最大的P个特征值,其中W表示窗函数的最优解,Σ为加和符号;Obtain the eigenvalues, and select the largest P eigenvalues among the eigenvalues, where W represents the optimal solution of the window function, and Σ is the summation symbol;
将所述P个特征值对应的特征矢量作为基底组成的线性空间作为杂波子空间,将含有 目标信号的回波列向量投影到“杂波子空间”对杂波列向量进行估计,并利用估计的杂波列 向量对消除复指数分量的输出信号进行杂波去除。The linear space composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the P eigenvalues is used as the base as the clutter subspace, and the echo column vector containing the target signal is projected to the "clutter subspace" to estimate the clutter column vector, and the estimated clutter column vector is used. The clutter column vector performs clutter removal on the output signal with complex exponential components removed.
进一步地,本实施方式中,步骤三一中,步骤五中,采用空时自适应处理算法,对去除杂波的输出信号中按照多普勒维、距离维和角度维对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号进行空间相关性残余杂波去除的具体过程为:Further, in this embodiment, in step 31 and
对去除时间相关性杂波分量输出信号按照多普勒维和距离维顺序堆成一个列向量,构 成一个MN×1维的空时观测向量;The output signal of removing the time-correlated clutter component is stacked into a column vector according to the order of Doppler dimension and distance dimension, forming a space-time observation vector of MN×1 dimension;
具体拼接过程为:The specific splicing process is as follows:
s(f,θ)=ves(f,θ)s(f,θ)=ves(f,θ)
其中vec(·)为向量化操作,二维数据按列的顺序堆成一列;s(f,θ)为去除杂波后的输出 信号;将所述据去除杂波后的输出信号表示成空时导向矢量:Among them, vec( ) is a vectorization operation, and the two-dimensional data are stacked into a column in the order of columns; s(f, θ) is the output signal after removing clutter; the output signal after removing clutter is represented as empty Time Steering Vector:
其中,为克罗内克积(Kronecker),aN(f)为时间导向矢量,vM(θ)为时间导向矢量, 利用STAP算法将空域向量替换成对应的空时向量:in, is the Kronecker product, aN (f) is the time-steering vector, vM (θ) is the time-steering vector, and the STAP algorithm is used to replace the space domain vector with the corresponding space-time vector:
其中,为杂波的空时协方差矩阵。in, is the space-time covariance matrix of the clutter.
进一步地,本实施方式中,步骤三一中,窗函数的最优解W为:Further, in this embodiment, in step 31, the optimal solution W of the window function is:
本发明所述多域联合抑制海杂波方法,可以尽最大可能的利用好海杂波在多个维度上 的相关性,达到抑制杂波及检测目标的最佳效果。考虑到现代雷达图谱存在三个重要维度 ——快时间维,慢时间维,角度维。基于这三种维度的客观存在,在此分析比较了基于单 一维度(慢时间维)的ROOT循环对消,基于两个维度联合作用(慢时间维和快时间维) 的子空间投影法,以及基于三个维度(慢时间维,快时间维和角度维)联合作用的空时自 适应处理方法(STAP方法)。The multi-domain joint sea clutter suppression method of the present invention can make best use of the correlation of sea clutter in multiple dimensions to achieve the best effect of suppressing clutter and detecting targets. Considering that there are three important dimensions in modern radar maps - fast time dimension, slow time dimension, and angle dimension. Based on the objective existence of these three dimensions, the ROOT loop cancellation based on a single dimension (slow time dimension), the subspace projection method based on the joint action of two dimensions (slow time dimension and fast time dimension), and the Three dimensions (slow time dimension, fast time dimension and angle dimension) combined action of space-time adaptive processing method (STAP method).
一个现代体制的一般性雷达系统,发射阵列共有N个阵元,接收阵列共有M个阵元。如图2所示,在这个模型中,不仅可以把N个元素视为N个发射阵列阵元天线对同一目标 的照射,亦可以视为某个发射源对N个不同目标照射后产生不同的反射信号波,设发射 阵列的阵元间距为dT,接收阵列的阵元间距为dR。发射阵列中第n个发射天线的工作频率 为fn,基带信号的形式记为则第n个发射阵元的发射信号可以表示为A general radar system of a modern system has a total of N elements in the transmitting array and M elements in the receiving array. As shown in Figure 2, in this model, N elements can not only be regarded as the irradiation of the same target by N transmitting array element antennas, but also can be regarded as a certain emission source irradiating N different targets to produce different To reflect the signal wave, set the array element spacing of the transmitting array as dT , and the array element spacing of the receiving array as dR . The operating frequency of the nth transmitting antenna in the transmitting array is fn , and the form of the baseband signal is denoted as Then the transmit signal of the nth transmit array element can be expressed as
其中E是总发射能量,T是雷达脉冲持续时间,我们假设基带波形满足正交条件where E is the total transmitted energy and T is the radar pulse duration, we assume the baseband waveform meet the orthogonal condition
假设电磁波在自由空间中独立传播。我们考虑双向传播情况,并选择第一个阵元作为参 考点。因此,对于任意目标,第m个接收阵元的接收回波可以写为:It is assumed that electromagnetic waves propagate independently in free space. We consider the bidirectional propagation case and choose the first array element as the reference point. Therefore, for any target, the received echo of the mth receiving element can be written as:
其中,ξ表示目标的复数反射系数,fd,n表示多普勒频率,即fd,n=2vtfn/c,vt指代目标的径向速度。当然,在第二种背景下,fd,n还可以表示为n个不同的运动目标对 应的多普勒频率。此外,τn,T和τm,R分别是发送和接收时间延迟,如下式给出:Among them, ξ represents the complex reflection coefficient of the target, fd,n represents the Doppler frequency, that is, fd,n =2vt fn /c, and vt refers to the radial velocity of the target. Of course, in the second context, fd,n can also be expressed as Doppler frequencies corresponding to n different moving targets. Furthermore, τn,T and τm,R are the transmit and receive time delays, respectively, given by:
其中,τ0=2r/c,θ代表目标的角度(从法线方向到目标方向测量),r代表目标 距离接收阵列的距离;在接收阵列中,测量的信号被下变频,匹配过滤和存储。接 收到的信号可以被N个匹配滤波器分解,产生N个隔离的传输信号。在匹配滤波之 后,第m个接收天线的第n个输出是:where τ0 =2r/c, θ represents the angle of the target (measured from the normal direction to the target direction), and r represents the distance of the target from the receiving array; in the receiving array, the measured signal is down-converted, matched filtered and stored . The received signal can be decomposed by N matched filters, resulting in N isolated transmitted signals. After matched filtering, the nth output of the mth receive antenna is:
一般来说,慢速运动目标的速度,在雷达极短的采样时间间隔中,并不会积累成较大的 位移。从信号处理的角度讲,就是慢速目标对应的多普勒频率,在距离延时中,积累出的 相位差fdτ0≈0,这也就是为什么我们常称脉冲内的采样为“快时间”,因此式4可以继续化简为Generally speaking, the speed of the slow moving target will not accumulate into a large displacement in the very short sampling time interval of the radar. From the point of view of signal processing, it is the Doppler frequency corresponding to the slow target. In the distance delay, the accumulated phase difference fd τ0 ≈0, which is why we often call the sampling in the pulse "fast"time", so Equation 4 can be simplified to
分析上式,除去第一个常数因子,可分解为三个e指数因子,各自分别代表了一个重要 信息,其中代表慢时间维(多普勒维),代表快时间维(距离维),代表角度维,基于这三个维度,提出了三种不同的杂波抑制方法。Analyzing the above formula, removing the first constant factor, it can be decomposed into three e-exponential factors, each of which represents an important information, where represents the slow time dimension (Doppler dimension), represents the fast time dimension (distance dimension), represents the angle dimension, and based on these three dimensions, three different clutter suppression methods are proposed.
首先,基于慢时间维的ROOT循环对消算法。高频地波雷达的回波信号在经过电离层 相位污染校正后,展宽的一阶Bragg峰得到锐化,会出现局部较大值的特点,洋流与海风的作用使海杂波左右两侧的谱峰同向偏移。在理想条件下,如果发射机和接收机部署在很近的位置,包含杂波在内的回波信号可以当做不同频率的复指数信号线性组合;传统的ROOT循环对消算法就是估计出这些频率分布在目标频率附近,具有不同幅度和初相的复指数信号分量。通过循环迭代,每估计出一个复指数分量的幅度、频率和初相,就将该分 量从原始时域信号中减去,以此来实现杂波抑制。First, the ROOT cycle cancellation algorithm based on slow time dimension. After the echo signal of the high-frequency ground wave radar is corrected by the ionospheric phase pollution, the broadened first-order Bragg peak is sharpened, and there will be a local large value. The peaks are shifted in the same direction. Under ideal conditions, if the transmitter and receiver are deployed in close proximity, the echo signal including clutter can be regarded as a linear combination of complex exponential signals of different frequencies; the traditional ROOT cycle cancellation algorithm is to estimate these frequencies Complex exponential signal components with different amplitudes and initial phases distributed around the target frequency. Through loop iteration, each time the amplitude, frequency and initial phase of a complex exponential component are estimated, the component is subtracted from the original time domain signal to achieve clutter suppression.
对幅度A的估计,是通过在多普勒维,寻找频谱的峰值和位置,将找到的这个峰值,认定为待去除复指数信号的幅度,而谱峰位置,则认定为待去除复指数信号的频率f,而初始相位则是通过在[0,2π]上搜索,使得“能量误差函数”最小的角度来确定,“能量误差 函数”的表达式:The estimation of the amplitude A is to find the peak and position of the spectrum in the Doppler dimension, and the found peak is identified as the amplitude of the complex exponential signal to be removed, and the position of the spectral peak is identified as the complex exponential signal to be removed. frequency f, while the initial phase It is determined by searching on [0,2π] to make the angle that minimizes the "energy error function". The expression of the "energy error function" is:
即初始相位的估计值为:That is, the estimated value of the initial phase is:
其中,x(n)为单个距离门的多普勒普,n对应多普勒单元,n=1,2,……N,A和f是估计出的幅度和频率。在估计出复指数信号的幅度、频率和初相后,就得到了第一个待去除分量,将此分量从原始信号中减去,就可以实现杂波抑制。Among them, x(n) is the Doppler of a single range gate, n corresponds to the Doppler unit, n=1, 2,...N, A and f are the estimated amplitude and frequency. After estimating the amplitude, frequency and initial phase of the complex exponential signal, the first component to be removed is obtained, and this component is subtracted from the original signal to achieve clutter suppression.
在上一步的基础上,下一步是基于慢时间维和快时间维联合的海杂波抑制方法——子 空间分解法,在数学里又叫做矩阵的对角化或者叫做特征值分解。利用这一矩阵变换方法, 将信号列向量集的协方差矩阵,进行特征分解。就可以得到,由代表杂波分量特征矢量为 基底,组成的“杂波子空间”;以及代表噪声分量的特征矢量为基底,组成的“噪声子空间”。 再利用特征矢量相互正交的性质,将含有目标的回波信号进行投影得到杂波分量,从而去 除杂波,实现海杂波抑制的目的。算法的核心思想是:当待研究的距离范围较短时,海杂 波在距离维度上具有较强的相关性。具体求解方法大致是:将目标所在距离门,以及周围 的若干个只含有海杂波,不含目标信号的距离门,组成一个列向量集,并求解其特征值分 解,拿到所有的特征值和特征向量。众所周知,高频地波雷达接收到的目标回波信号,具 有“低信杂比”,“高信噪比”和“高杂噪比”三个特征,换句话说,就是杂波分量的能量要远强于目标信号和噪声。我们知道,协方差矩阵特征值分解后得到的特征值,其大小就代表着对应分量的能量或振幅,所以,我们认为,以较大的特征值所对应的特征矢量为基底,组成的矢量空间为“杂波子空间”;以其余特征矢量为基底组成的矢量空间,则被视为“噪声子空间”。由于目标信号和噪声与杂波信号比起来,幅度都小很多,为了方便研究, 我们可以把目标信号和噪声放在一起,统称为“噪声子空间”。On the basis of the previous step, the next step is the sea clutter suppression method based on the combination of slow time dimension and fast time dimension - subspace decomposition method, which is also called diagonalization of matrix or eigenvalue decomposition in mathematics. Using this matrix transformation method, the covariance matrix of the signal column vector set is eigendecomposed. It can be obtained that the "clutter subspace" is composed of the eigenvector representing the clutter component as the base; and the "noise subspace" composed of the eigenvector representing the noise component as the base. The clutter component is obtained by projecting the echo signal containing the target, so as to remove the clutter and achieve the purpose of sea clutter suppression. The core idea of the algorithm is: when the distance range to be studied is short, the sea clutter has a strong correlation in the distance dimension. The specific solution method is roughly as follows: the distance gate where the target is located, and several surrounding distance gates that only contain sea clutter but not the target signal, form a column vector set, and solve its eigenvalue decomposition to get all the eigenvalues and eigenvectors. As we all know, the target echo signal received by the high-frequency ground wave radar has three characteristics of "low signal-to-noise ratio", "high signal-to-noise ratio" and "high noise-to-noise ratio", in other words, the energy of the clutter component much stronger than the target signal and noise. We know that the size of the eigenvalues obtained by decomposing the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix represents the energy or amplitude of the corresponding components. Therefore, we believe that the vector space composed of the eigenvectors corresponding to the larger eigenvalues is the basis. is the "clutter subspace"; the vector space composed of the remaining eigenvectors is regarded as the "noise subspace". Since the amplitude of the target signal and noise is much smaller than that of the clutter signal, for the convenience of research, we can put the target signal and noise together, collectively referred to as "noise subspace".
接着,将同时含有目标和海杂波的距离单元回波中,把能投影到“杂波子空间”的分 量去除,就可以达到抑制海杂波的目的。可以看出,子空间投影法是以杂波与噪声及目标 不相关/相互独立为前提的。因为相互独立的存在,使得含目标的距离门回波列向量中,投 影到杂波子空间的部分完全代表海杂波,再将其剔除就可以完成杂波抑制。Then, in the range unit echo containing both target and sea clutter, the components that can be projected into the "clutter subspace" can be removed, so as to achieve the purpose of suppressing sea clutter. It can be seen that the subspace projection method is based on the premise that clutter, noise and target are uncorrelated/independent. Because of the existence of mutual independence, the part projected to the clutter subspace in the range gate echo column vector containing the target completely represents the sea clutter, and then clutter suppression can be accomplished by eliminating it.
设ST(k)为含有目标信号距离门的回波列向量信号,k=0,1,2,……U-1。{Si(k)}为其相邻 距离单元的回波列向量集合,集合中总共包含V个列向量,即i=1,2,…,V,则有Let ST (k) be the echo column vector signal containing the target signal range gate, k = 0, 1, 2, ... U-1. {Si (k)} is the set of echo column vectors of adjacent distance units, and the set contains V column vectors in total, i.e. i=1, 2,...,V, then there are
ST=[ST(0),ST(1),ST(2),……,ST(U-1)]TST = [ST (0), ST (1), ST (2),..., ST (U-1)]T
Si=[Si(0),Si(1),Si(2),……,Si(U-1)]TSi =[Si (0),Si (1),Si (2),...,Si (U-1)]T
协方差矩阵的表达式为:The expression of the covariance matrix is:
其中,参数γi的求解公式为Among them, the solution formula of parameter γi is
上角标T代表矩阵转置,上角标H代表共轭转置The superscript T stands for matrix transpose, and the superscript H stands for conjugate transpose
将协方差矩阵RU×U进行特征分解,即Eigendecompose the covariance matrix RU×U , that is
RU×U=W∑WHRU×U = W∑WH
其中W代表U×U的酉矩阵,其中包含所有的特征矢量,而Σ为对角线为特征值,其余位置是0的对角矩阵。在回波中杂波相对噪声具有很高的能量,因此矩阵Σ中较大的几个特征值所对应的特征矢量表示的是,杂波信号从某个特殊角度阐述领域中,各个离散的“分量”。由这些特征矢量为基底组成的线性空间就被叫做“杂波子空间”;与之相对的就 是“噪声子空间”。所以,将含有目标信号的回波列向量投影到“杂波子空间”,就可以估 算出杂波列向量,两个向量做减法就可以去除杂波。Among them, W represents the unitary matrix of U×U, which contains all the eigenvectors, and Σ is the diagonal matrix of which the diagonal is the eigenvalue, and the rest positions are 0. The clutter in the echo has high energy relative to the noise, so the eigenvectors corresponding to the larger eigenvalues in the matrix Σ represent that the clutter signal elucidates the field from a special angle, each discrete " quantity". The linear space composed of these eigenvectors is called "clutter subspace"; the opposite is "noise subspace". Therefore, by projecting the echo column vector containing the target signal into the "clutter subspace", the clutter column vector can be estimated, and the clutter can be removed by subtracting the two vectors.
基于慢时间维、快时间维和角度维三个维度联合的海杂波抑制方法,全空时自适应处 理。在数据具有显著空时特性时,空时自适应处理(STAP)往往能取得一定的效果。最一般 的全自适应STAP对整个数据块的阵元,距离和脉冲三个维度同时进行处理。The sea clutter suppression method based on the three dimensions of slow time dimension, fast time dimension and angle dimension is combined with full space-time adaptive processing. When the data has significant space-time characteristics, space-time adaptive processing (STAP) can often achieve certain results. The most general fully adaptive STAP processes the array elements, distance and pulse dimensions of the entire data block simultaneously.
假设一个距离门的二维数据块为X,其维度为V×U,通常X包含了内部和外部噪声B, 杂波分量C以及潜在的目标回波分量S,即X=S+C+B。Suppose the two-dimensional data block of a distance gate is X, and its dimension is V×U, usually X contains internal and external noise B, clutter component C and potential target echo component S, that is, X=S+C+B .
将二维数据X内的列向量按照慢时间顺序堆砌成一个列向量,就构成一个MN×1维的 空时观测向量,也叫做空时快拍。在一个积累周期之内,有多少距离门就有多少这样的空 时快拍。理所当然的,空时快拍数据也有它对应的空时导向矢量。它的维度也是MN×1,The column vectors in the two-dimensional data X are stacked into a column vector in slow time sequence, and a space-time observation vector of MN×1 dimension is formed, which is also called a space-time snapshot. Within an accumulation cycle, there are as many space-time snapshots as there are distance gates. Of course, the space-time snapshot data also has its corresponding space-time steering vector. Its dimension is also MN×1,
经典STAP算法不过是MVDR算法的展宽,在形式上完全一样,只要将其中的空域 向量替换成对应的空时向量即可得到;The classic STAP algorithm is just a broadening of the MVDR algorithm, which is exactly the same in form, as long as the space vector is replaced with the corresponding space-time vector;
与单纯的多普勒维或快慢时间域联合算法相比,全空时联合域处理算法(3D-STAP)在理 论上可以获得更高的处理性能上限。在构造协方差时,我们要选取与处理目标相邻近的几 个距离——角度拉直向量来构造,但是我们要考虑到,目标信号在距离单元上并不是单一 孤立点,是存在旁瓣的,换句话说,是存在一定宽度的,如图6和图7所示。而旁瓣和信 号主峰是存在相关性的,这种相关性会影响我们抑制杂波的效果,因此,我们采用滑窗的 方式,框选住目标距离以及上下各k个距离门(窗口宽度为2k+1),选取临近的距离-角度 拉直向量,要排除窗内的向量。Compared with the pure Doppler dimension or the fast-slow time-domain joint algorithm, the total space-time joint domain processing algorithm (3D-STAP) can theoretically obtain a higher processing performance upper limit. When constructing the covariance, we need to select several distance-angle straightening vectors adjacent to the processing target to construct, but we need to consider that the target signal is not a single isolated point on the distance unit, but there are side lobes , in other words, there is a certain width, as shown in Figures 6 and 7. There is a correlation between the side lobes and the main peak of the signal, which will affect our effect of suppressing clutter. Therefore, we use the sliding window method to select the target distance and the upper and lower k distance gates (the window width is 2k+1), select the adjacent distance-angle straightening vector, to exclude the vector in the window.
具体实施例:Specific examples:
经过第一阶段,ROOT循环对消算法的处理。我们对图2的实测数据进行测试,进行多次循环对消,任选一个距离单元的多普勒谱为展示效果用例,对消4次后,我们发现右 侧的布拉格峰和中间的地物杂波谱峰得到明显抑制,但目标信号的强度仍然低于杂波对消 6次后,地物杂波已经得到彻底消除,海杂波的谱峰也不能淹没过目标,代表目标的谱线 已经成为了整个频谱的最高峰,此时对消的效果已经达到了最好。After the first stage, the ROOT cycle cancellation algorithm is processed. We tested the measured data in Figure 2, performed multiple cyclic cancellations, and selected the Doppler spectrum of one range unit as the display effect use case. After 4 times of cancellation, we found the Bragg peak on the right and the ground objects in the middle. The clutter spectral peaks are obviously suppressed, but the intensity of the target signal is still lower than that of the clutter. It has become the highest peak of the entire spectrum, and the cancellation effect has reached the best at this time.
子空间投影法。我们选取包含目标的距离门上下各10个距离单元,共计40个列向量 来计算相关性。抑制结果如图4和图5所示。Subspace projection method. We select 10 distance units above and below the distance gate containing the target, a total of 40 column vectors to calculate the correlation. The inhibition results are shown in Figures 4 and 5.
采用了多普勒维和距离维联合的子空间投影法,杂波抑制效果要比基于单一多普勒维 度的ROOT循环对消要好很多,海杂波和地物杂波的成分几乎完全去除,但是以信噪比为 代价的,信噪比(以噪声幅度最大值为基准)为9.24dBUsing the subspace projection method combining Doppler dimension and distance dimension, the effect of clutter suppression is much better than that of ROOT cycle cancellation based on a single Doppler dimension, and the components of sea clutter and ground clutter are almost completely removed. But at the expense of the signal-to-noise ratio, the signal-to-noise ratio (based on the maximum noise amplitude) is 9.24dB
STAP抑制杂波的效果如图8和图9所示The effect of STAP on clutter suppression is shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9
我们选取原完整数据,20至70距离门的所有向量进行相同的处理,分布在海杂波附 近的慢速动目标纷纷在海杂波得到抑制后,以散点的形式显现在RD图像上。We selected the original complete data, and processed all the vectors from 20 to 70 range gates in the same way. The slow-moving targets distributed near the sea clutter were all displayed on the RD image in the form of scatter points after the sea clutter was suppressed.
采用了三个维度联合的全空间自适应处理进行杂波抑制后,杂波抑制效果要比基于单 一多普勒维度的ROOT循环对消,以及基于多普勒维-距离维的子空间投影发要好很多,海 杂波和地物杂波的成分也基本完全去除,信噪比(以噪声幅度最大值为基准)为13.40dB。After using the three-dimensional joint full-space adaptive processing for clutter suppression, the clutter suppression effect is better than the ROOT cycle cancellation based on a single Doppler dimension, and the subspace projection based on Doppler dimension-range dimension. The hair is much better, and the components of sea clutter and ground clutter are basically completely removed, and the signal-to-noise ratio (based on the maximum noise amplitude) is 13.40dB.
虽然在本文中参照了特定的实施方式来描述本发明,但是应该理解的是,这些实施例 仅仅是本发明的原理和应用的示例。因此应该理解的是,可以对示例性的实施例进行许多 修改,并且可以设计出其他的布置,只要不偏离所附权利要求所限定的本发明的精神和范 围。应该理解的是,可以通过不同于原始权利要求所描述的方式来结合不同的从属权利要 求和本文中所述的特征。还可以理解的是,结合单独实施例所描述的特征可以使用在其他 所述实施例中。Although the invention has been described herein with reference to specific embodiments, it should be understood that these embodiments are merely illustrative of the principles and applications of the invention. It should therefore be understood that many modifications may be made to the exemplary embodiments and other arrangements can be devised without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. It will be appreciated that the features described in the various dependent claims and herein may be combined in different ways than are described in the original claims. It will also be appreciated that features described in connection with a single embodiment may be used in other described embodiments.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210561790.5ACN115201760B (en) | 2022-05-23 | 2022-05-23 | Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combination |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210561790.5ACN115201760B (en) | 2022-05-23 | 2022-05-23 | Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combination |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115201760Atrue CN115201760A (en) | 2022-10-18 |
| CN115201760B CN115201760B (en) | 2025-03-25 |
Family
ID=83575121
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210561790.5AActiveCN115201760B (en) | 2022-05-23 | 2022-05-23 | Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combination |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115201760B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119322317A (en)* | 2024-09-26 | 2025-01-17 | 南京理工大学 | High-frequency space-earth wave radar sea clutter suppression method based on space-time domain cascade processing |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103926572A (en)* | 2014-03-28 | 2014-07-16 | 西安电子科技大学 | Clutter rejection method of self-adaption subspace for non-sidelooking airborne array radar |
| KR102073692B1 (en)* | 2018-08-20 | 2020-02-05 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Radar receiver and clutter suppression method of thereof |
| CN111965612A (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2020-11-20 | 西安电子科技大学 | A clutter suppression method based on subspace projection |
| CN114296047A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-04-08 | 中仪知联(无锡)工业自动化技术有限公司 | A static ground object clutter cancellation method based on spatial filtering |
- 2022
- 2022-05-23CNCN202210561790.5Apatent/CN115201760B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103926572A (en)* | 2014-03-28 | 2014-07-16 | 西安电子科技大学 | Clutter rejection method of self-adaption subspace for non-sidelooking airborne array radar |
| KR102073692B1 (en)* | 2018-08-20 | 2020-02-05 | 한화시스템 주식회사 | Radar receiver and clutter suppression method of thereof |
| CN111965612A (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2020-11-20 | 西安电子科技大学 | A clutter suppression method based on subspace projection |
| CN114296047A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-04-08 | 中仪知联(无锡)工业自动化技术有限公司 | A static ground object clutter cancellation method based on spatial filtering |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 刘伟奇: "基于多维度联合的高频地波雷达强海杂波抑制方法", 硕士电子期刊, 15 September 2024 (2024-09-15)* |
| 姚迪;张鑫;杨强;邓维波;陈秋实;: "基于空间多波束的高频地波雷达电离层杂波抑制算法", 电子与信息学报, no. 12, 15 December 2017 (2017-12-15)* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119322317A (en)* | 2024-09-26 | 2025-01-17 | 南京理工大学 | High-frequency space-earth wave radar sea clutter suppression method based on space-time domain cascade processing |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115201760B (en) | 2025-03-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9363024B2 (en) | Method and system for estimation and extraction of interference noise from signals | |
| US10228449B2 (en) | Method and system for jointly separating noise from signals | |
| Yoon et al. | High-resolution through-the-wall radar imaging using beamspace MUSIC | |
| Li et al. | An efficient algorithm for time delay estimation | |
| US8824544B2 (en) | Method and system for recovery of missing spectral information in wideband signal | |
| CN104678372B (en) | OFDM radar super-resolution distance and angle value combined estimation method | |
| CN104865568B (en) | Sparse reconstruction-based broadband radar high-speed group-target resolving method | |
| US10393869B2 (en) | Sub-Nyquist radar processing using doppler focusing | |
| CN103091661A (en) | Broadband signal arriving direction estimation method based on iteration spectral reconfiguration | |
| CN110045337B (en) | Radio Frequency Interference Suppression Method for High Frequency Ground Wave Radar Based on Tension Quantum Space Projection | |
| CN110320490A (en) | A kind of radio wave arrival direction estimating method under the conditions of no direct signal | |
| CN115226129B (en) | Passive sensing device based on intelligent reflective surface and sensing method thereof | |
| CN112379333A (en) | High-frequency radar sea clutter suppression method based on space-time dimension orthogonal projection filtering | |
| CN111665469B (en) | Underwater multipath signal parameter estimation method based on spatial time-frequency distribution | |
| CN116559793A (en) | Radar interference suppression method, radar interference suppression device and storage medium | |
| CN115201760A (en) | Strong sea clutter suppression method based on multi-domain combination | |
| CN106019290B (en) | Weighted broadband time reversal operator decomposition multi-target acoustic imaging method | |
| Turk et al. | High-resolution signal processing techniques for through-the-wall imaging radar systems | |
| CN108896963B (en) | Airborne Radar Space-Time Adaptive Dimensionality Reduction Processing Method | |
| CN109597034A (en) | A kind of space-time adaptive processing method based on Euclidean distance | |
| US20030052820A1 (en) | Method and device for space-time estimation of one or more transmitters | |
| Naishadham et al. | State-space spectral estimation of characteristic electromagnetic responses in wideband data | |
| Kelly et al. | RFI suppression and sparse image formation for UWB SAR | |
| CN106405509B (en) | The piecemeal processing method of space-time adaptive signal | |
| CN116540175A (en) | Signal AOA and TOA joint estimation direction finding method based on dimension reduction multiple signal classification algorithm |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |