CN115199326A - Method for dynamic disaster of space gangue grouting filling weakening overlying rock after coal mining - Google Patents
Method for dynamic disaster of space gangue grouting filling weakening overlying rock after coal miningDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115199326A CN115199326ACN202210876400.3ACN202210876400ACN115199326ACN 115199326 ACN115199326 ACN 115199326ACN 202210876400 ACN202210876400 ACN 202210876400ACN 115199326 ACN115199326 ACN 115199326A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- gangue
- grouting
- impact
- rock
- filling
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21F—SAFETY DEVICES, TRANSPORT, FILLING-UP, RESCUE, VENTILATION, OR DRAINING IN OR OF MINES OR TUNNELS
- E21F15/00—Methods or devices for placing filling-up materials in underground workings
- E21F15/005—Methods or devices for placing filling-up materials in underground workings characterised by the kind or composition of the backfilling material
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21C—MINING OR QUARRYING
- E21C41/00—Methods of underground or surface mining; Layouts therefor
- E21C41/16—Methods of underground mining; Layouts therefor
- E21C41/18—Methods of underground mining; Layouts therefor for brown or hard coal
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21F—SAFETY DEVICES, TRANSPORT, FILLING-UP, RESCUE, VENTILATION, OR DRAINING IN OR OF MINES OR TUNNELS
- E21F15/00—Methods or devices for placing filling-up materials in underground workings
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E21—EARTH OR ROCK DRILLING; MINING
- E21F—SAFETY DEVICES, TRANSPORT, FILLING-UP, RESCUE, VENTILATION, OR DRAINING IN OR OF MINES OR TUNNELS
- E21F17/00—Methods or devices for use in mines or tunnels, not covered elsewhere
- E21F17/18—Special adaptations of signalling or alarm devices
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mining & Mineral Resources (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Geochemistry & Mineralogy (AREA)
- Geology (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Investigating Strength Of Materials By Application Of Mechanical Stress (AREA)
- Consolidation Of Soil By Introduction Of Solidifying Substances Into Soil (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,属于覆岩动力灾害防控领域。The invention relates to a method for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining, and belongs to the field of preventing and controlling the dynamic disaster of overlying rock.
背景技术Background technique
在煤矿高强扰动开采过程中,顶板岩层在断裂或者移动时,会释放大量弹性能,特别对于坚硬顶板,较普通顶板,坚硬顶板聚集了更多的弹性能,断裂时大量释放,极有可能引发坚硬岩层型动力灾害,造成人员伤亡和巨大的经济损失。针对目前矿井生产面临的坚硬岩层型冲击矿压问题,我国煤矿冲击矿压防治主要包括优开拓布局来进行区域防范以及通过煤层注水、钻孔卸压、煤体卸压爆破、顶板深孔爆破、顶板水力致裂等措施进行局部解危。虽然上述措施能够取得了成效,但并未整体切断岩层应力传递,仍存在较大冲击危险,如何从源头上控制顶板岩层破断冲击成为亟待解决的难题。In the process of high-strength disturbance mining in coal mines, when the roof strata fracture or move, a large amount of elastic energy will be released, especially for hard roofs, compared with ordinary roofs, the hard roofs accumulate more elastic energy, which will be released in large quantities when fractured, which is very likely to cause Hard rock formation type dynamic disasters, causing casualties and huge economic losses. Aiming at the problem of rock burst type rock burst faced by the current mine production, the prevention and control of rock burst in my country's coal mines mainly includes optimal development layout for regional prevention, and through coal seam water injection, drilling pressure relief, coal body pressure relief blasting, roof deep hole blasting, The roof hydraulic cracking and other measures can be used to locally solve the danger. Although the above measures have achieved results, they have not cut off the stress transfer of the rock formation as a whole, and there is still a great risk of impact. How to control the breaking impact of the roof rock formation from the source has become an urgent problem to be solved.
矸石作为煤矿开采中难以避免的固体废弃物在我国大部分矿区都存在着处理难的问题,随着国家对绿色矿山建设要求的提高,一种经济适用的矸石井下充填处理方式展现出了良好发展前景。利用岩层移动过程中上覆岩层内形成的嗣后空间,从地面布置注浆钻孔向离层空间充填矸石注浆材料来支撑上覆岩层并压实下方空隙从而控制诱冲关键层的断裂和运动,从而达到弱化由于诱冲关键层破断引起的动力灾害和减缓地表下沉的目的。因此,研发一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,对于促进煤矿绿色开采和可持续发展具有很强的理论意义和实际意义。As an unavoidable solid waste in coal mining, gangue is difficult to deal with in most mining areas in my country. With the improvement of the country's requirements for green mine construction, an economical and applicable method for underground filling and treatment of gangue has shown good development. prospect. Using the subsequent space formed in the overlying strata during the movement of the strata, the grouting holes are arranged from the ground to fill the abscission space with gangue grouting materials to support the overlying stratum and compact the space below, so as to control the fracture and movement of the key scouring stratum , so as to achieve the purpose of weakening the dynamic disaster caused by the rupture of the key layer of decoupling and slowing down the surface subsidence. Therefore, the development of a method to weaken the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining has strong theoretical and practical significance for promoting green mining and sustainable development of coal mines.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对现有技术的不足之处,提供一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,解决目前矿井矸石难处理的问题,坚硬岩层型动力灾害后果严重的现状,其系统简单,作业灵活,能够处理矸石排放难题,还能有效减小动力灾害发生风险。Aiming at the deficiencies of the prior art, a method for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining is provided, which solves the problem that the current mine gangue is difficult to deal with and the serious consequences of the dynamic disaster of hard rock formation. The system is simple, The operation is flexible, it can deal with the problem of gangue discharge, and it can also effectively reduce the risk of power disasters.
为实现上述技术目的,本发明一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,首先分析矿井煤岩冲击倾向性、坚硬岩层移动变形与致灾能量演变特征,判定冲击危险区域嗣后空间范围;将矿井掘进矸石和洗选矸石进行多级筛分破碎生成细粒径矸石和粗粒径矸石,优化粒径级配后与水混合制成矸石注浆充填材料;采用充填泵和注浆钻孔将矸石料浆泵送至冲击危险区域嗣后空间,依据矸石注浆充填材料的承载压缩性能对诱冲关键层形成支撑作用,减小诱冲关键层弯曲变形量,降低离层区周围弹性应变能积聚与应力集中程度,并减缓诱冲关键层已积聚的能量向下伏煤系岩层释放强度,弱化工作面煤岩体超前支承应力集中程度,进而弱化了冲击灾害发生的风险;最后,通过制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测的监测结果评价注浆充填对覆岩动力灾害的弱化效果。In order to achieve the above technical purpose, the present invention is a method for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining. First, the impact tendency of coal and rock in the mine, the movement and deformation of hard rock layers and the evolution characteristics of disaster-causing energy are analyzed, and the impact danger area is determined. Spatial scope; multi-stage screening and crushing of mine excavation gangue and washing gangue to generate fine-grained gangue and coarse-grained gangue. Slurry drilling pumps the gangue slurry to the subsequent space of the impact risk area. According to the load-bearing and compressive performance of the gangue grouting filling material, it forms a supporting role for the key layer of the induced impact, reduces the bending deformation of the key layer of the induced impact, and reduces the surrounding area of the separation zone. The elastic strain energy accumulation and stress concentration degree, and slow down the release strength of the energy accumulated in the key strata induced by the scour to the underlying coal-measure strata, weaken the advance bearing stress concentration degree of the coal-rock mass at the working face, and thus weaken the risk of impact disasters; , through the monitoring results of grouting monitoring, grouting monitoring, and surface rock movement monitoring to evaluate the weakening effect of grouting and filling on overlying rock dynamic disasters.
具体步骤如下:Specific steps are as follows:
S1、确定矿井冲击危险区域嗣后空间:首先,通过对工作面煤体及上覆坚硬岩层取样,测试煤岩体试样的冲击倾向性风险,综合考虑工作面开采深度、煤层赋存特征、坚硬岩层自身特性因素,确定工作面煤体及上覆坚硬岩层冲击倾向性危险区域范围;然后,采用理论计算和数值模拟的方法,分析冲击倾向性区域的坚硬岩层变形过程中的应变能积聚与释放的演变特征,判定诱发冲击灾害的坚硬岩层为诱冲关键层,进而确定此诱冲关键层以下的离层区、裂隙带以及垮落带为冲击风险区域的嗣后空间(17);S1. Determine the subsequent space of the mine impact risk area: First, test the impact tendency risk of the coal and rock samples by sampling the coal body of the working face and the overlying hard rock layer, comprehensively considering the mining depth of the working face, coal seam occurrence characteristics, hardness The characteristic factors of the rock formation itself are used to determine the scope of the impact-prone danger zone of the coal body in the working face and the overlying hard rock formation; then, the theoretical calculation and numerical simulation methods are used to analyze the accumulation and release of strain energy during the deformation process of the hard rock formation in the impact-prone zone. According to the evolution characteristics, the hard rock layer that induces shock disasters is determined as the key layer of decoy, and then the abscission zone, fissure zone and caving zone below the key layer of decoy are determined as the subsequent space of the shock risk area (17);
S2、制备矸石注浆充填材料:首先将掘进矸石和洗选矸石破碎为0~0.15mm的细粒径矸石和0.15~2mm的粗粒径矸石,按照细粒径矸石与粗粒径矸石的质量比为1:2的配比混合均匀后,加水搅拌均匀制成质量浓度为60%的矸石注浆充填材料;S2. Preparation of gangue grouting filling material: firstly, the excavation gangue and washing gangue are broken into fine-grained gangue of 0-0.15mm and coarse-grained gangue of 0.15-2mm, according to the quality of fine-grained gangue and coarse-grained gangue After mixing evenly with a ratio of 1:2, add water and stir evenly to make a gangue grouting filling material with a mass concentration of 60%;
S3、利用矸石注浆充填材料充填冲击危险区域嗣后空间:首先,确定首个注浆钻孔的位置为距离区段工作面开切眼300m处,并位于工作面倾向宽度的中部;然后,垂直于地面向冲击风险区域嗣后空间(17)施工注浆钻孔;其次,沿着区段工作面走向方向依次间隔300m布置一个注浆钻孔,直至布置到工作面停采线0~300m左右位置;最后,利用充填泵和注浆钻孔将矸石料浆泵送至嗣后空间,矸石料浆注充至嗣后空间后形成承载结构,对诱冲关键层形成支撑作用,阻止了诱冲关键层变形过程中致灾能量积聚,而且嗣后空间的矸石料浆泌水沉积形成垫层材料,从而吸收诱冲关键层向下方煤系地层传递的能量;同时注入的矸石注浆充填材料具有压力,能够压实下方裂隙岩层并扩展孔道,有助于料浆扩散以及填充封堵孔径小于2mm的岩体裂隙;S3. Use gangue grouting filling material to fill the subsequent space in the impact-hazardous area: first, determine the position of the first grouting hole to be 300m away from the incision hole of the section working face, and located in the middle of the inclination width of the working face; then, vertically Construct grouting holes on the ground to the subsequent space (17) of the impact risk area; secondly, arrange a grouting hole at intervals of 300m along the direction of the working face of the section until it is arranged at about 0-300m from the mining stop line of the working face Finally, the gangue slurry is pumped to the subsequent space by the filling pump and the grouting hole, and the gangue slurry is filled into the subsequent space to form a bearing structure, which forms a supporting effect on the key layer of the lure and prevents the deformation of the key layer of the lure. During the process, the disaster-causing energy accumulated, and the gangue slurry in the space was subsequently deposited by bleeding to form cushion material, thereby absorbing the energy transmitted from the key stratum induced by scouring to the coal measure strata below; The fissure rock below is solidified and the channel is expanded, which is helpful for slurry diffusion and filling and sealing of rock mass fissures with a diameter of less than 2mm;
S4、充填弱化覆岩动力灾害效果监测与评价:通过制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测的监测结果来评价覆岩动力灾害弱化效果,其中,制浆监测:监测浆体浓度是否符合预期要求,检测颗粒粒径是否达到破碎效果,以及制浆设备运行状态是否良好;注浆监测:包括注浆速度、注浆压力、和单孔注浆量参数的监测,以此判定是否达到预期效果;地表岩移监测:根据岩层变形及地表变形反馈地表下沉量。S4. Monitoring and evaluation of the dynamic disaster effect of filling weakened overlying rock: The weakening effect of overlying rock dynamic disaster is evaluated through the monitoring results of slurry monitoring, grouting monitoring, and surface rock movement monitoring. Among them, slurry monitoring: monitoring whether the slurry concentration meets the Expected requirements, check whether the particle size achieves the crushing effect, and whether the pulping equipment is in good operating condition; grouting monitoring: including the monitoring of grouting speed, grouting pressure, and single-hole grouting parameters to determine whether the expectations are met Effect; surface rock movement monitoring: feedback the surface subsidence amount according to the deformation of the rock layer and the surface deformation.
进一步,所述的冲击危险区域的充填层位是嗣后空间,嗣后空间是指诱发冲击灾害的诱冲关键层下方的软弱岩层受重力作用下发生滑移和回转变形而产生不同程度的失稳破断,在上覆岩层中形成空隙和裂隙空间的总称,主要包括诱冲关键层下方弯曲下沉带离层区、裂隙带和垮落带。Further, the filling layer of the shock-hazard zone is the subsequent space, and the subsequent space refers to the weak rock layer under the key layer of the shock that induces the shock disaster due to the sliding and rotational deformation under the action of gravity, resulting in different degrees of instability and fracture. , a general term for the formation of voids and fissure spaces in the overlying rock, mainly including the abscission zone, fissure zone and caving zone below the key scouring layer.
进一步,所述的矸石与水混合制备矸石注浆充填材料,0.15~2mm粗粒径的矸石由对辊制砂机破碎得到,过筛的粗粒径矸石由溢流式球磨机经机械研磨得到0~0.15mm细粒径的矸石,为确定粗细粒径矸石和水的合理配比,改变它们之间的含量优化配比制备矸石注浆充填材料,并对其流动度,扩展度进行测试,保证矸石注浆充填材料具有较好的输送性能。Further, the gangue is mixed with water to prepare the gangue grouting filling material, the gangue with a coarse particle size of 0.15-2mm is obtained by crushing a counter-roll sand making machine, and the sieved coarse particle size gangue is obtained by mechanical grinding by an overflow ball mill. For gangue with fine particle size of ~0.15mm, in order to determine the reasonable ratio of coarse and fine particle size gangue and water, change the content between them to optimize the ratio to prepare gangue grouting filling material, and test its fluidity and expansion to ensure that Gangue grouting filling material has good conveying performance.
进一步,所述的矸石与水的合理配比中煤矸石与矿井水的固料质量浓度为60%,粗细粒径矸石质量比1:1。Further, in the reasonable ratio of gangue and water, the solid mass concentration of coal gangue and mine water is 60%, and the mass ratio of coarse and fine particle size gangue is 1:1.
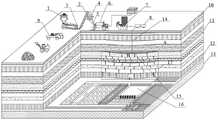
进一步,通过从地面布置注浆钻孔(14)打通地面至离层区(15),选取管道,将制备好的料浆通过充填泵(8)泵送至离层空间(15),离层空间(15)是由煤层开采,破坏了岩体的原平衡状态产生的,离层区的空间会导致诱冲关键层(11)破断,引起表土层(10)下沉,但当充填料浆充填至离层空间(15)时,能有效支撑诱冲关键层(11),减缓诱冲关键层的破断及变形,压实下方软弱岩层,从而大规模处理矸石、弱化冲击灾害的发生以及控制地表下沉。Further, by arranging grouting boreholes (14) from the ground to get through the ground to the layer separation area (15), selecting pipes, and pumping the prepared slurry to the layer separation space (15) through the filling pump (8), the layer separation The space (15) is produced by the mining of coal seams, which destroys the original equilibrium state of the rock mass. The space in the separation zone will cause the key layer (11) to be broken, causing the topsoil layer (10) to sink. When filled to the abscission space (15), it can effectively support the key layer (11), slow down the breakage and deformation of the key layer, and compact the weak rock layer below, so as to deal with gangue on a large scale, weaken the occurrence and control of impact disasters The surface sinks.
有益效果:本方法,包括冲击危险区域的确定、矸石注浆充填材料的制备、冲击危险区域嗣后空间矸石注浆充填、充填弱化覆岩动力灾害效果的监测与评价。嗣后空间矸石充填通过充填作用、支撑作用、压实作用、胶结作用、膨胀作用和减缓作用减缓控制诱冲关键层的位移和突然破断,从而减弱或者消除动力灾害。通过对诱发冲击灾害的诱冲关键层进行判定,并确定诱冲关键层下方的嗣后空间为具有冲击倾向性的危险区域空间;通过钻孔注浆充填方法,从地面打孔,将注浆材料注入具有冲击灾害发生的危险区域空间:离层空间、裂隙带空间、垮落带空间进行矸石注浆充填,充填材料一方面阻止了诱冲关键层的弯曲变形的速度,和诱冲关键层突然迅速破断的情况,进而阻止能够诱发冲击灾害的致灾能量积聚过程,让诱冲关键层因弯曲变形产生的弹性应变能(致灾能量)不达到发生冲击的阈值,另一方面,充填材料在处置了生产矸石的同时具有承载压缩变形,对诱冲关键层变形具有缓冲的作用,让诱冲关键层缓慢变形,不发生突然破断,而是缓慢的发生破坏,释放的冲击力强度大幅度降低了,进而传到工作面的强度也减小了,达到防治冲击灾害的目的该方法系统简单,初期投资小,可以实现连续、机械化、大面积开采,单位成本低,仅为其它充填方式的1/3~1/4,且回采率高,能达到80%~90%,降低了矸石固废地面环境的破坏与污染,是促进煤矿绿色开采和可持续发展的重要技术手段,具有重要的社会意义,进一步推动注浆充填采煤理论和技术的发展,对于类似条件矿井煤炭资源的开采具有典型示范作用。Beneficial effects: The method includes the determination of the impact dangerous area, the preparation of gangue grouting filling material, the subsequent space gangue grouting filling of the impact dangerous area, and the monitoring and evaluation of the dynamic disaster effect of filling weakened overlying rock. Afterwards, the space gangue filling slows down the displacement and sudden break of the key layer to control the scour through filling, support, compaction, cementation, expansion and mitigation, thereby weakening or eliminating dynamic disasters. By judging the key layer of decoy that induces shock disaster, and determining the subsequent space below the key layer of decoy as a dangerous area space with impact tendency; by drilling grouting filling method, drilling holes from the ground, grouting material Injecting into the space of dangerous areas with impact disasters: gangue grouting filling in the abscission space, fissure zone space, and caving zone space. The situation of rapid breaking, thereby preventing the accumulation process of the disaster-causing energy that can induce the impact disaster, so that the elastic strain energy (disaster-causing energy) generated by the bending deformation of the key layer of the impact-induced impact does not reach the threshold of the impact. On the other hand, the filling material is in the When the production gangue is disposed of, it has load-bearing compression deformation, and has a buffering effect on the deformation of the key layer of the lure, so that the key layer of the lure is slowly deformed, not suddenly broken, but slowly destroyed, and the strength of the released impact force is greatly reduced. In addition, the strength transmitted to the working face is also reduced, and the purpose of preventing and controlling shock disasters is achieved. This method is simple in system, small in initial investment, and can realize continuous, mechanized and large-scale mining. The unit cost is low, which is only 1 /3 ~ 1/4, and the recovery rate is high, which can reach 80% ~ 90%, which reduces the damage and pollution of the gangue solid waste ground environment, is an important technical means to promote green mining and sustainable development of coal mines, and has an important social It is of great significance to further promote the development of the theory and technology of grouting and filling coal mining, and has a typical demonstration role for the mining of coal resources in mines with similar conditions.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害效果评价流程图;Fig. 1 is a flow chart of the dynamic disaster effect evaluation of the weakened overlying rock after the coal mining of the present invention by grouting and filling of space gangue;
图2为本发明煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法使用系统示意图;Fig. 2 is the schematic diagram of the application system of the method of using gangue grouting and filling to weaken the dynamic disaster of overlying rock after coal mining of the present invention;
图3为本发明煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法中工作面注浆钻孔布置俯视图。Fig. 3 is a plan view of the arrangement of drilling holes for working face grouting in the method of the present invention for grouting and filling of space gangue for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock after coal mining.
图中:1—震动给料机;2—胶带运输机;3—细颚式破碎机;4—对辊制砂机;5—清水泵;6—球磨机;7—搅拌池;8—充填泵;9—汽车;10—表土层;11—诱冲关键层;12—顶板岩层;13—底板岩层;14—注浆钻孔;15—离层空间;16—采空区;17-嗣后空间;A—煤柱承载区;B—离层区;C—压实区。In the figure: 1—vibrating feeder; 2—belt conveyor; 3—fine jaw crusher; 4—pair roller sand making machine; 5—cleaning water pump; 6—ball mill; 7—mixing tank; 8—filling pump; 9—Automobile; 10—Topsoil layer; 11—Induced scour key layer; 12—Top rock layer; 13—Bottom rock layer; 14—Grouting drilling hole; A—coal pillar bearing area; B—separation area; C—compaction area.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明的实施例做进一步说明。The embodiments of the present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
如图1所示,本发明的一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,分析矿井煤岩冲击倾向性、坚硬岩层移动变形与致灾能量演变特征,判定冲击危险区域的嗣后空间范围;将矿井掘进矸石、洗选矸石进行多级筛分破碎,优化粒径级配后与水混合制备成矸石注浆充填材料;利用注浆钻孔和充填泵将充填料浆泵注至诱冲关键层下方离层区,料浆在泵送压力作用下不断向离层深处流动,同时,也受到岩层阻力,导致料浆粉末颗粒层析沉积,在注浆结束后,沉积灰层形成具有和离层区层状空间近似的坡度线几何形状;其中,充填料浆中的粉末颗粒与水均是不可压缩物料,填充离层空间后,对上方诱冲关键层具有承载支撑能力,抑制其持续发生弯曲下沉,降低离层区周围弹性应变能积聚,减少冲击应力峰值;泵压注浆带有水压作用,在连续高压大流量的注浆条件下,高压浆料不仅对上层岩层起到支撑作用,从而有效的防止上覆岩层继续下沉,而且对下层被破坏岩层具有向下的压力,进而压实下层抗弯承载力较小的岩层。而且,充填料浆与下层岩层共同组合成承载诱冲关键层的充填体结构,重新组合的充填体结构具有压缩性能,能够卸载诱冲关键层传递的弹性应变能,减少应变能向工作面煤岩体传递的强度,大幅降低了工作面应力集中程度,进而弱化了冲击灾害发生的风险;最后通过制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测的监测结果评价注浆充填对覆岩动力灾害的弱化效果。As shown in Figure 1 , a method for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining of the present invention analyzes the impact tendency of coal and rock in the mine, the movement and deformation of hard rock layers and the evolution characteristics of disaster-causing energy, and determines the impact risk area. Subsequent space scope; the gangue excavated in the mine, washed and washed for multi-stage screening and crushing, and mixed with water to prepare the gangue grouting filling material after optimizing the particle size gradation; To the layer separation area below the key layer of scouring, the slurry continuously flows to the depth of the separation layer under the action of pumping pressure, and at the same time, it is also resisted by the rock formation, resulting in the chromatographic deposition of slurry powder particles. The layer formation has a gradient line geometry similar to the layered space in the abscission zone; among them, the powder particles and water in the filling slurry are incompressible materials, and after filling the abscission space, it has bearing and supporting capacity for the key layer above the induced impingement. , suppress its continuous bending and sinking, reduce the accumulation of elastic strain energy around the separation zone, and reduce the peak value of impact stress; pump grouting has the effect of water pressure, under the condition of continuous high pressure and large flow grouting, high pressure slurry not only The upper rock layer plays a supporting role, thereby effectively preventing the overlying rock layer from continuing to sink, and has downward pressure on the lower layer damaged rock layer, thereby compacting the lower layer rock layer with lower flexural bearing capacity. In addition, the filling slurry and the underlying rock layers are combined to form a backfill structure that supports the key strata of induced impingement. The recombined backfill structure has compressive properties, which can unload the elastic strain energy transmitted by the key strata of induced impingement, and reduce the strain energy to the coal at the working face. The strength of the rock mass transfer greatly reduces the stress concentration of the working face, thereby weakening the risk of impact disasters. Finally, the monitoring results of grouting monitoring, grouting monitoring and surface rock movement monitoring are used to evaluate the effect of grouting and filling on the dynamic disaster of overlying rock. weakening effect.
具体步骤如下:Specific steps are as follows:
S1、确定矿井冲击危险区域嗣后空间:首先,通过对工作面煤体及上覆坚硬岩层取样制备标准试件,测试煤岩体试样的冲击倾向性风险,综合考虑工作面开采深度、煤层赋存特征、坚硬岩层自身特性方面因素,确定工作面煤体及上覆坚硬岩层冲击倾向性危险区域范围;然后,采用理论计算和数值模拟的方法对冲击倾向性区域坚硬岩层变形过程中的应变能积聚与释放的特征进行分析,基于坚硬岩层致灾能量阈值判定诱发冲击灾害的诱冲关键层,进而确定诱冲关键层以下的离层区、裂隙区以及垮落区为冲击风险区域嗣后空间17,工作面开采之后,上覆岩层移动变形产生的裂隙空间,此时下方采空区不仅有垮落物,也有注浆充填材料,即注浆钻孔打到垮落带上方,有垮落带裂隙空间沟通就可以把注浆材料充填进去采空区垮落带;S1. Determine the subsequent space of the mine impact risk area: First, prepare standard specimens by sampling the coal mass of the working face and the overlying hard rock layer, test the impact tendency risk of the coal and rock mass samples, and comprehensively consider the mining depth of the working face, coal seam distribution According to factors such as the existing characteristics and the characteristics of the hard rock formation itself, the scope of the impact tendency danger zone of the coal body in the working face and the overlying hard rock formation is determined; The characteristics of accumulation and release are analyzed, and the key layer of decoupling that induces shock disasters is determined based on the hazard-causing energy threshold of hard rock layers, and then the abscission area, fissure area and caving area below the key layer of decoy are determined as the subsequent space of the shock risk area17 , After the working face is mined, the fissure space generated by the movement and deformation of the overlying rock layer. At this time, there are not only caving objects in the gob below, but also grouting filling materials, that is, the grouting hole is drilled above the caving zone, and there is a caving zone. The communication of the fissure space can fill the grouting material into the caving zone of the goaf;
S2、制备矸石注浆充填材料:首先将矸石破碎为0~0.15mm和0.15~2mm两种粒径,按照粒径质量比(0~0.15mm):(0.15~2mm)=1:2的配比进行混合,然后,将混合材料与水搅拌混合制备成质量浓度为60%的矸石注浆充填材料;S2. Preparation of gangue grouting filling material: First, crush the gangue into two particle sizes of 0-0.15mm and 0.15-2mm, according to the ratio of particle size to mass (0-0.15mm): (0.15-2mm)=1:2 Then, the mixed material is stirred and mixed with water to prepare a gangue grouting filling material with a mass concentration of 60%;
S3、如图3所示,利用矸石注浆充填材料充填冲击危险区域嗣后空间:首先,确定首个注浆钻孔的位置为距离区段工作面开切眼300m处,并且在工作面倾向宽度的中间位置;从地面垂直向冲击风险区域嗣后空间17施工注浆钻孔,然后,沿着区段工作面推进方向依次间隔300m布置注浆钻孔,直至布置整个区段工作面的注浆钻孔,注浆钻孔底部位置打到诱冲关键层与软岩移动变形而产生的离层区,等离层区充填完毕,继续往深处打钻,打到工作面采空区垮落带上方进行注浆充填,所以,这个注浆钻孔注入的裂隙空间位置属于嗣后空间;最后,利用充填泵和注浆钻孔将矸石注浆充填材料泵送至嗣后空间,浆材料注充到嗣后空间后形成承载结构,对坚硬岩层具有填充支撑作用,而且充填料浆泌水沉积形成嗣后空间垫层材料,沉积垫层形成的位置主要是将离层区充填满之后在离层空间形成的;当料浆充填到垮落带,泌水后的料浆也会充填垮落带破碎岩体之间的裂隙,并和垮落带破碎岩体聚结形成组合体,但是这种情况,垮落带的充填体距离诱冲关键层较远,对诱冲关键层起到的垫层作用不是特别明显,所以,主要起到垫层作用,能缓冲诱冲关键层弯曲变形的积聚能量,阻止诱冲关键层突然垮断的作用是指离层空间充填的注浆材料所起到的作用,具有缓冲坚硬岩层弯曲变形作用,在阻止坚硬岩层变形过程中能量积聚的同时,利用自身压缩特性吸收部分坚硬岩层向下传递的能量;同时注浆材料压实下方裂隙岩层,扩展孔道,当充填材料填充完大孔径裂隙之后,封堵孔径小于2mm的岩体裂隙,泌水之后,形成沉积层封堵较小裂隙;S3. As shown in Figure 3, use the gangue grouting filling material to fill the subsequent space in the impact danger area: First, determine the position of the first grouting hole to be 300m away from the opening of the working face in the section, and the width of the working face inclination is determined. The middle position of the grouting hole is constructed from the ground to the subsequent space 17 of the impact risk area, and then the grouting holes are arranged at intervals of 300m along the advancing direction of the working face of the section until the grouting drilling of the entire working face of the section is arranged. The bottom position of the grouting hole is drilled to the layer separation area generated by the key layer of scouring and the movement and deformation of the soft rock. After the filling of the plasma layer area is completed, continue to drill deeper to the caving zone of the gob area of the working face. The grouting filling is performed above, so the position of the fissure space injected by this grouting hole belongs to the subsequent space; finally, the filling pump and the grouting hole are used to pump the gangue grouting filling material to the subsequent space, and the grouting material is injected into the subsequent space. After the space is formed, a bearing structure is formed, which has a filling and supporting effect on the hard rock layer, and the filling slurry is bleeded and deposited to form the subsequent space cushion material. When the slurry is filled into the caving zone, the bleeding slurry will also fill the fissures between the broken rock masses in the caving zone, and coalesce with the broken rock mass in the caving zone to form a composite body, but in this case, the caving The filling body of the belt is far away from the key layer of lubricating, so the cushioning effect on the key layer of lubricating is not particularly obvious. The effect of the sudden collapse of the key stratum refers to the effect of the grouting material filled in the abscission space, which has the effect of buffering the bending deformation of the hard rock stratum. The energy transmitted downward by the hard rock layer; at the same time, the grouting material compresses the lower fractured rock layer and expands the channel. When the filling material fills the large-diameter fractures, it seals the rock mass fractures with a diameter of less than 2mm. After bleeding, a sedimentary layer is formed to seal. small cracks;
S4、充填弱化覆岩动力灾害效果的监测与评价:通过制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测结果来评价覆岩动力灾害弱化效果:其中制浆监测浆体浓度是否符合预期要求,检测颗粒粒径否达到破碎效果,此外还包括制浆设备运行状态是否良好;注浆监测主要包括注浆速度、注浆压力、和单孔注浆量,以判断注浆量是否达到预期效果;地表岩移监测根据岩层变形以及地表。S4. Monitoring and evaluation of the effect of filling and weakening the dynamic disaster of the overlying rock: Evaluate the weakening effect of the dynamic disaster of the overlying rock through the results of slurry monitoring, grouting monitoring, and surface rock movement monitoring. Whether the particle size can achieve the crushing effect, in addition to whether the pulping equipment is in good operating condition; grouting monitoring mainly includes grouting speed, grouting pressure, and single-hole grouting amount to judge whether the grouting amount achieves the expected effect; Rock movement monitoring is based on the deformation of the rock formation as well as the surface.
实施例一、本发明目的是针对矿井矸石难处理,覆岩动力灾害后果严重的现状,提供一种煤矿开采嗣后空间矸石注浆充填弱化覆岩动力灾害方法,其中地层结构为表土层10、诱冲关键层11、顶板岩层12;底板岩层13,嗣后空间17区域从上到下包括煤柱承载区A、离层区B和压实区C,其中离层区B上方为离层空间15Embodiment 1. The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for weakening the dynamic disaster of overlying rock by grouting and filling of space gangue after coal mining, aiming at the current situation that mine gangue is difficult to handle and the consequences of overlying rock dynamic disaster are serious, wherein the stratum structure is
具体步骤为:The specific steps are:
①冲击危险区域的确定:通过UDEC数值模拟软件模拟煤层采高、工作面推进对覆岩离层发育演化的规律,判断产生冲击危险的区域,并在现场检测验证冲击危险区域,划分出高应力集中区,并结合其规律,确定工作面回采结束后,未破断处于平衡状态下的诱冲关键层上方为冲击危险区域。①Determination of the impact risk area: Use the UDEC numerical simulation software to simulate the development and evolution of the coal seam mining height and working face advancement to the overburden separation layer, determine the impact risk area, and perform on-site testing to verify the impact risk area, and divide high stress. Concentration area, and combined with its laws, it is determined that after the mining face is completed, the area above the key layer of lubricating impact that is not broken and in a balanced state is the impact danger area.
②矸石注浆充填材料的制备:材料主要为不同粒径的矸石和水,采用单一变量法测试不同矸石粒径、加载速度、初始加载应力对矸石注浆充填材料的影响规律,选取0~0.15mm和0.15~2mm粒径的矸石和水混合制成矸石注浆充填材料。② Preparation of gangue grouting filling material: The materials are mainly gangue and water with different particle sizes. The single variable method is used to test the influence of different gangue particle size, loading speed, and initial loading stress on the gangue grouting filling material. Select 0~0.15 The gangue with a particle size of 0.15-2mm and water is mixed to make a gangue grouting filling material.
③冲击危险区域嗣后空间矸石注浆充填:将注浆钻孔14沿走向布置在工作面中间位置,孔底间距300m,选好矿井充填路线,通过充填泵将矸石注浆充填材料泵送至冲击危险区域嗣后空间17。3. Subsequent gangue grouting filling in the impact risk area: Arrange the
④充填弱化覆岩动力灾害效果的评价:通过制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测结果来评价覆岩动力灾害弱化效果。④ Evaluation of the dynamic disaster effect of filling weakened overlying rock: The weakening effect of overlying rock dynamic disaster is evaluated through the monitoring results of slurry production, grouting monitoring, and surface rock movement monitoring.
所述的嗣后空间17是指煤炭开采后,上覆岩层受重力因素作用会发生不同程度的失稳破断,在采空区16以滑落和回转的形式不规则堆积,上覆岩层破裂产生缝隙以及弯曲下沉产生离层使得离层区B、裂隙区、垮落区中普遍存在空隙,嗣后空间17即广泛地分布于上述空隙中。The subsequent space 17 refers to the fact that after coal mining, the overlying rock layer will be unstable and fractured to varying degrees due to the action of gravity, and the
所述的嗣后空间17,其空隙的大小有所差异,在走向方向上可以将采动影响的区域划分为煤柱支撑区A、离层区B与压实稳定区C,其中离层区的嗣后空间17就分布较多。在垮落带中走向方向上又可根据破碎岩石压实程度的不同划分为自然堆积区、载荷影响区和重新压实区,其中自然堆积区通常为嗣后空间17的主体分布区。The following space 17 has different sizes of gaps, and the area affected by mining can be divided into coal pillar support area A, layer separation area B and compaction stability area C in the direction of strike. Afterwards, space 17 is more distributed. In the strike direction of the caving zone, it can be divided into natural accumulation area, load-affected area and recompaction area according to the degree of compaction of broken rock. The natural accumulation area is usually the main distribution area of the subsequent space 17 .
所述的矸石注浆充填材料的制备,其特征在于所述的矸石与水混合制备矸石注浆充填材料,矸石经由汽车9、振动给料机1、胶带运输机2、颚式破碎机3破碎至5mm以下,而0.15~2mm粒径的矸石由对辊制砂机4破碎得到,过筛的大粒径矸石由溢流式球磨机6经机械研磨得到0~0.15mm粒径的矸石,为确定0~0.15mm、0.15~2mm粒径矸石和清水泵5提供的水的合理配比,改变配比的含量制成矸石注浆充填材料,并对其流动度,扩展度进行测试,保障矸石注浆充填材料的输送性能。The preparation of the gangue grouting filling material is characterized in that the gangue is mixed with water to prepare the gangue grouting filling material, and the gangue is crushed to 5mm or less, and the gangue with a particle size of 0.15-2mm is obtained by crushing the roller sand making machine 4, and the sieved large-diameter gangue is mechanically ground by the
将矸石颗粒与水在搅拌池7中制备矸石注浆充填材料:将矸石与水的合理配比中煤矸石与矿井水的固料质量浓度为60%,粗细矸石质量比1:1。The gangue particles and water are used to prepare gangue grouting filling material in the stirring tank 7: the solid mass concentration of coal gangue and mine water in a reasonable ratio of gangue and water is 60%, and the mass ratio of coarse and fine gangue is 1:1.
采用单一变量法测试不同矸石粒径、加载速度、初始加载应力对矸石注浆充填材料的影响。试验是将矸石粒径分为0~0.15mm、0.15~2mm、2~5mm、5~8mm、8~10mm放入缸筒压实试验装置中,并将万能材料试验系统的加载速率设置为0.5kN/s、1.0kN/s、2.0kN/s、5.0kN/s、10.0kN/s,初始加载应力为0MPa、0.5MPa、1.0MPa、1.5MPa、2.0MPa,研究坚硬岩层型顶板下沉时矸石注浆充填材料的应变能变化,得出矸石注浆充填材料为达到相同变形时消耗的能量越多,矸石的应变就需越小,粒径就需越小,故综合考虑矸石的破碎成本、矸石注浆充填材料的输送性能和能量耗散选择0~0.15mm和0.15~2mm粒径的矸石和水混合制备矸石注浆充填材料。The single-variable method was used to test the effects of different gangue particle size, loading speed and initial loading stress on the gangue grouting filling material. The test is to divide the gangue particle size into 0-0.15mm, 0.15-2mm, 2-5mm, 5-8mm, 8-10mm and put them into the cylinder compaction test device, and set the loading rate of the universal material test system to 0.5 kN/s, 1.0kN/s, 2.0kN/s, 5.0kN/s, 10.0kN/s, the initial loading stress is 0MPa, 0.5MPa, 1.0MPa, 1.5MPa, 2.0MPa, when studying the subsidence of the hard rock type roof The strain energy of the gangue grouting filling material changes, and it is concluded that the more energy the gangue grouting filling material consumes to achieve the same deformation, the smaller the strain of the gangue and the smaller the particle size. Therefore, the crushing cost of the gangue needs to be considered comprehensively. , Transport performance and energy dissipation of gangue grouting filling material Select 0-0.15mm and 0.15-2mm particle size gangue and water to prepare gangue grouting filling material.
所述的制浆监测、注浆监测、地表岩移监测结果来评价覆岩动力灾害弱化效果,其中制浆监测主要为浆体浓度浆液是否符合预期配比和颗粒粒径颗粒是否达到破碎效果监测,此外还包括制浆设备运行状态是否良好监测;注浆监测主要包括注浆速度、注浆压力浆液注入难易程度、和单孔注浆量是否达到预期效果;地表岩移监测根据岩层变形以及地表变形反馈地表下沉量。The results of slurry monitoring, grouting monitoring, and surface rock movement monitoring are used to evaluate the weakening effect of overlying rock dynamic disasters. The slurry monitoring is mainly to monitor whether the slurry concentration meets the expected ratio and whether the particle size and particle size achieve the crushing effect. In addition, it also includes monitoring whether the operating status of the grouting equipment is good; grouting monitoring mainly includes grouting speed, grouting pressure, and the difficulty of grouting injection, and whether the single-hole grouting amount achieves the expected effect; surface rock movement monitoring is based on rock deformation and Surface deformation feedbacks the amount of surface subsidence.
所述的矿井充填路线,通过从地面布置注浆钻孔14打通地面至离层空间15,选取管道,将制备好的料浆通过充填泵8泵送至离层空间15,离层空间15是由煤层开采,破坏了岩体的原平衡状态产生的,离层区的空间会导致诱冲关键层11破断,引起表土层10下沉,但当充填料浆充填至离层空间15时,能有效支撑诱冲关键层11,减缓诱冲关键层的破断及变形,压实下方各软岩层,从而大规模处理矸石、弱化冲击矿压的发生以及控制地表下沉。For the mine filling route, by arranging
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210876400.3ACN115199326B (en) | 2022-07-25 | 2022-07-25 | Dynamic disaster method for weakening overburden rock by grouting, filling and weakening space gangue after mining of coal mine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210876400.3ACN115199326B (en) | 2022-07-25 | 2022-07-25 | Dynamic disaster method for weakening overburden rock by grouting, filling and weakening space gangue after mining of coal mine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115199326Atrue CN115199326A (en) | 2022-10-18 |
| CN115199326B CN115199326B (en) | 2024-04-09 |
Family
ID=83583391
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210876400.3AActiveCN115199326B (en) | 2022-07-25 | 2022-07-25 | Dynamic disaster method for weakening overburden rock by grouting, filling and weakening space gangue after mining of coal mine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115199326B (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115199328A (en)* | 2022-07-25 | 2022-10-18 | 中国矿业大学 | A design method of gangue grouting and filling engineering for space after coal mining |
| CN115539123A (en)* | 2022-10-27 | 2022-12-30 | 陕西绿北国邦环保工程有限公司 | Method for filling coal mine goaf layer by slag stone reinjection |
| CN116146243A (en)* | 2023-02-21 | 2023-05-23 | 山西文龙中美环能科技股份有限公司 | An Intelligent Grouting Method for Overlying Rock Detachment |
| CN116291697A (en)* | 2023-02-06 | 2023-06-23 | 中煤科工开采研究院有限公司 | Grouting filling method based on multi-coal seam mining |
| CN117189228A (en)* | 2023-09-11 | 2023-12-08 | 中国矿业大学 | A multi-level mining space anti-collision collaborative three-dimensional filling mining method |
| CN118407801A (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2024-07-30 | 内蒙古工业大学 | A method for accurate grouting of gangue filling slurry in layers and stages |
| CN118728381A (en)* | 2024-07-03 | 2024-10-01 | 鄂尔多斯市中钰泰德煤炭有限公司 | Technology of using gangue slurry separation grouting to achieve water-retaining coal mining |
| CN119572268A (en)* | 2024-12-02 | 2025-03-07 | 山东科技大学 | Method for treating and preventing slurry collapse of geological structure under separation layer grouting filling exploitation |
| CN119572297A (en)* | 2024-11-19 | 2025-03-07 | 中国矿业大学 | Carbon storage space construction method for negative carbon filling exploitation |
| CN120139880A (en)* | 2025-05-16 | 2025-06-13 | 中国矿业大学 | A method for repairing water-conducting fractures in overburden rock by microwave-induced high-diffusivity slurry consolidation |
| CN120193877A (en)* | 2025-04-18 | 2025-06-24 | 山西能源学院 | Device and method for repairing filling bodies by inducing microbial nanomaterials based on acoustic-thermal effect |
| CN120608729A (en)* | 2025-08-07 | 2025-09-09 | 内蒙古满世煤炭集团罐子沟煤炭有限责任公司 | Intelligent gangue filling control system for extra-thick coal seam |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108708723A (en)* | 2018-05-02 | 2018-10-26 | 中国矿业大学 | Alternately support subtracts heavy method without coal column filling mining for a kind of coal petrography column |
| US20200408094A1 (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2020-12-31 | China University Of Mining And Technology | Mine exploitation based on stoping, separation and filling control |
| CN113339056A (en)* | 2021-06-24 | 2021-09-03 | 中国矿业大学 | Fluidized gangue layer surface subsequent filling system and method |
| CN113605970A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-05 | 中国矿业大学 | Overlying strata isolation grouting filling method for coal gangue underground emission reduction |
| CN113700527A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-26 | 中国矿业大学 | High-strength coal gangue overlying rock isolation grouting filling green mining method for mining working face |
| CN113833467A (en)* | 2021-10-19 | 2021-12-24 | 中勘资源勘探科技股份有限公司 | Method for solving rock burst of coal field mining area through grouting filling |
| CN114472462A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-05-13 | 中煤科工集团西安研究院有限公司 | Underground-aboveground linkage coal gangue disposal system and disposal method |
| CN114542171A (en)* | 2022-02-17 | 2022-05-27 | 徐州格润矿山技术开发有限公司 | A kind of improvement method of overlying rock isolation grouting filling material |
- 2022
- 2022-07-25CNCN202210876400.3Apatent/CN115199326B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108708723A (en)* | 2018-05-02 | 2018-10-26 | 中国矿业大学 | Alternately support subtracts heavy method without coal column filling mining for a kind of coal petrography column |
| US20200408094A1 (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2020-12-31 | China University Of Mining And Technology | Mine exploitation based on stoping, separation and filling control |
| CN113339056A (en)* | 2021-06-24 | 2021-09-03 | 中国矿业大学 | Fluidized gangue layer surface subsequent filling system and method |
| CN113605970A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-05 | 中国矿业大学 | Overlying strata isolation grouting filling method for coal gangue underground emission reduction |
| CN113700527A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-26 | 中国矿业大学 | High-strength coal gangue overlying rock isolation grouting filling green mining method for mining working face |
| CN113833467A (en)* | 2021-10-19 | 2021-12-24 | 中勘资源勘探科技股份有限公司 | Method for solving rock burst of coal field mining area through grouting filling |
| CN114472462A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-05-13 | 中煤科工集团西安研究院有限公司 | Underground-aboveground linkage coal gangue disposal system and disposal method |
| CN114542171A (en)* | 2022-02-17 | 2022-05-27 | 徐州格润矿山技术开发有限公司 | A kind of improvement method of overlying rock isolation grouting filling material |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115199328B (en)* | 2022-07-25 | 2024-05-28 | 中国矿业大学 | A design method for space gangue grouting filling engineering after coal mining |
| CN115199328A (en)* | 2022-07-25 | 2022-10-18 | 中国矿业大学 | A design method of gangue grouting and filling engineering for space after coal mining |
| CN115539123A (en)* | 2022-10-27 | 2022-12-30 | 陕西绿北国邦环保工程有限公司 | Method for filling coal mine goaf layer by slag stone reinjection |
| CN116291697A (en)* | 2023-02-06 | 2023-06-23 | 中煤科工开采研究院有限公司 | Grouting filling method based on multi-coal seam mining |
| CN116146243B (en)* | 2023-02-21 | 2025-08-01 | 山西文龙中美环能科技股份有限公司 | Intelligent grouting method for overlying strata separation layer |
| CN116146243A (en)* | 2023-02-21 | 2023-05-23 | 山西文龙中美环能科技股份有限公司 | An Intelligent Grouting Method for Overlying Rock Detachment |
| CN117189228A (en)* | 2023-09-11 | 2023-12-08 | 中国矿业大学 | A multi-level mining space anti-collision collaborative three-dimensional filling mining method |
| CN117189228B (en)* | 2023-09-11 | 2025-09-05 | 中国矿业大学 | A multi-layer mining method for space anti-collision collaborative three-dimensional filling mining |
| CN118407801A (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2024-07-30 | 内蒙古工业大学 | A method for accurate grouting of gangue filling slurry in layers and stages |
| CN118728381A (en)* | 2024-07-03 | 2024-10-01 | 鄂尔多斯市中钰泰德煤炭有限公司 | Technology of using gangue slurry separation grouting to achieve water-retaining coal mining |
| CN119572297A (en)* | 2024-11-19 | 2025-03-07 | 中国矿业大学 | Carbon storage space construction method for negative carbon filling exploitation |
| CN119572268A (en)* | 2024-12-02 | 2025-03-07 | 山东科技大学 | Method for treating and preventing slurry collapse of geological structure under separation layer grouting filling exploitation |
| CN120193877A (en)* | 2025-04-18 | 2025-06-24 | 山西能源学院 | Device and method for repairing filling bodies by inducing microbial nanomaterials based on acoustic-thermal effect |
| CN120139880A (en)* | 2025-05-16 | 2025-06-13 | 中国矿业大学 | A method for repairing water-conducting fractures in overburden rock by microwave-induced high-diffusivity slurry consolidation |
| CN120608729A (en)* | 2025-08-07 | 2025-09-09 | 内蒙古满世煤炭集团罐子沟煤炭有限责任公司 | Intelligent gangue filling control system for extra-thick coal seam |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115199326B (en) | 2024-04-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115199326A (en) | Method for dynamic disaster of space gangue grouting filling weakening overlying rock after coal mining | |
| Zhang et al. | Enhancement of gas drainage efficiency in a special thick coal seam through hydraulic flushing | |
| Wang et al. | Experimental investigation of rock breakage by a conical pick and its application to non-explosive mechanized mining in deep hard rock | |
| Kang et al. | A combined “ground support-rock modification-destressing” strategy for 1000-m deep roadways in extreme squeezing ground condition | |
| Wang et al. | Case study on pressure-relief mining technology without advance tunneling and coal pillars in longwall mining | |
| Wang et al. | Fracture failure analysis of hard–thick sandstone roof and its controlling effect on gas emission in underground ultra-thick coal extraction | |
| Xuan et al. | Dynamic disaster control under a massive igneous sill by grouting from surface boreholes | |
| Xue et al. | Dynamic disaster control of backfill mining under thick magmatic rock in one side goaf: A case study | |
| WO2024207808A1 (en) | Mining method and apparatus, electronic device and storage medium | |
| Li et al. | Study on stability of stope surrounding rock under repeated mining in close‐distance coal seams | |
| Zou et al. | Mechanism of hydraulic fracturing for controlling strong mining-induced earthquakes induced by coal mining | |
| Li et al. | Measurement and numerical analysis of influence of key stratum breakage on mine pressure in top-coal caving face with super great mining height | |
| CN105781552A (en) | Novel high-gas outburst coal seam stereoscopic punching crosscut coal uncovering method | |
| CN117113715A (en) | Design method for preventing and controlling rock burst of mining area by filling coal-based solid wastes | |
| Yu et al. | Pre-reinforcement grout in fractured rock masses and numerical simulation for optimizing shrinkage stoping configuration | |
| Qiang | Mining subsidence control by solid backfilling under buildings | |
| Gui et al. | Research on preventive technologies for bed-separation water hazard in China coal mines | |
| CN110781597A (en) | A calculation method of roof cutting height based on coal mine roof cutting weakening | |
| Pei et al. | Large deformation mechanism and “stress relief-support reinforcement” synergetic control method of soft rock roadway in the footwall of deep normal fault | |
| Du et al. | Study on the evolution law of fracture field in full‐mechanized caving mining of double system and extrathick coal seam | |
| Bin | Study of “3-step mining” subsidence control in coal mining under buildings | |
| Gray et al. | Longwall behaviour in massive strata | |
| Wu et al. | Mesoscopic influence mechanism of particle fragmentation on compressive deformation of gangue aggregates with different gradations under load | |
| Lee et al. | Laboratory investigation on excavation performance of foam-conditioned weathered granite soil for EPB shield tunnelling | |
| Jing et al. | Mechanism and Control Technology of Lateral Load-Bearing Behavior of a Support System Adjacent to Empty Roadways. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |