CN115154259A - Method and device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic equipment - Google Patents
Method and device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115154259A CN115154259ACN202210866363.8ACN202210866363ACN115154259ACN 115154259 ACN115154259 ACN 115154259ACN 202210866363 ACN202210866363 ACN 202210866363ACN 115154259 ACN115154259 ACN 115154259A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- value
- determining
- elastic coefficient
- chest
- acceleration
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61H—PHYSICAL THERAPY APPARATUS, e.g. DEVICES FOR LOCATING OR STIMULATING REFLEX POINTS IN THE BODY; ARTIFICIAL RESPIRATION; MASSAGE; BATHING DEVICES FOR SPECIAL THERAPEUTIC OR HYGIENIC PURPOSES OR SPECIFIC PARTS OF THE BODY
- A61H31/00—Artificial respiration by a force applied to the chest; Heart stimulation, e.g. heart massage
- A61H31/004—Heart stimulation
- A61H31/006—Power driven
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Rehabilitation Therapy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Percussion Or Vibration Massage (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医疗器械领域,特别是涉及一种胸外按压参数的确定方法及装置、存储介质和电子设备。The invention relates to the field of medical devices, in particular to a method and device for determining chest compression parameters, a storage medium and electronic equipment.
背景技术Background technique
心脏骤停,是指由于心律失常和/或心脏有效搏动消失而直接导致心脏泵血功能机械活动突然停止,造成全身血液循环中断、呼吸停止和意识丧失的濒临死亡状态。心肺复苏是挽救心脏骤停患者生命的基石,在心搏骤停的大部分时间内,必须通过有效的胸外按压产生足够的血流,给关键器官和组织输送氧气和代谢底物;能否恢复自主循环取决于心肺复苏期输送给心肌氧和血流量。Cardiac arrest refers to a near-death state in which the mechanical activity of the pumping function of the heart is directly stopped due to arrhythmia and/or the disappearance of the effective heartbeat, resulting in interruption of blood circulation, respiratory arrest and loss of consciousness. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the cornerstone of life-saving cardiac arrest patients. During most of the time of cardiac arrest, adequate blood flow must be generated through effective chest compressions to deliver oxygen and metabolic substrates to critical organs and tissues; recovery is possible Spontaneous circulation depends on oxygen and blood flow to the myocardium during CPR.
在胸外按压期,通过按压胸骨,胸骨下陷,使位于胸骨和脊柱之间心脏受到挤压将血液泵出心脏,同时,胸外按压产生胸腔内外血管系统压力梯度,血管收到“挤压”,将血液向前推动,使其流向胸外压力较低的动脉。静脉瓣和动脉瓣的存在阻止了血液逆流,保证血液在按压期间单向流动。在胸腔回弹放松期,由于胸廓具有弹性,利用储存在其内的按压动能被动扩张,胸廓扩张使胸腔内产生相对于大气压的负压,促进静脉回流、增加胸泵前负荷,血液从静脉系统“回流到泵内-心脏”,为下一次按压时泵出做好准备。During the chest compression period, by pressing the sternum, the sternum is depressed, so that the heart between the sternum and the spine is squeezed and the blood is pumped out of the heart. , which pushes the blood forward so that it flows to the lower-pressure arteries outside the chest. The presence of venous and arterial valves prevents reverse flow of blood and ensures unidirectional flow of blood during compressions. During the thoracic rebound and relaxation period, due to the elasticity of the thorax, the compression kinetic energy stored in it is used to passively expand. The expansion of the thoracic cavity generates a negative pressure relative to the atmospheric pressure, which promotes venous return and increases the preload of the thoracic pump. Blood flows from the venous system. "Back into the pump - heart", ready to pump out on the next compression.
临床大数据已证实,高质量的胸外按压才能改善心脏骤停患者的复苏成功率,为此,目前国际指南均要求严格控制胸外按压的质量,并对各项胸外按压的质量参数提出了具体指标。已有胸外按压反馈装置能够对人工按压过程中的数据进行采集、分析和反馈,从而为胸外按压的评判和指导提供依据。然而,目前胸外按压反馈装置仅测量装置本身的位移,装置本身的位移在一些特殊情况下与胸腔变形位移是不一样的,比如在软床上按压和/或在救护车内按压等。如此反馈的信息对于施救过程的进行是没有帮助的,甚至可能产生错误的指引。准确确定胸外按压参数,减少误判、错判,进而准确地进行胸外按压信息的反馈,是本领域始终致力解决的重要技术问题。Clinical big data has confirmed that only high-quality chest compressions can improve the resuscitation success rate of cardiac arrest patients. For this reason, current international guidelines require strict control of the quality of chest compressions, and put forward the quality parameters of various chest compressions. specific indicators. The existing chest compression feedback device can collect, analyze and feed back the data during the manual compression process, so as to provide a basis for the evaluation and guidance of chest compression. However, current chest compression feedback devices only measure the displacement of the device itself, and the displacement of the device itself is different from the deformation displacement of the chest in some special cases, such as compression on a soft bed and/or compression in an ambulance. Such feedback information is not helpful for the rescue process, and may even lead to wrong guidance. Accurately determining chest compression parameters, reducing misjudgments and misjudgments, and then accurately feeding back chest compression information is an important technical problem that the field has always strived to solve.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
有鉴于此,本申请实施例为解决背景技术中存在的至少一个问题而提供一种胸外按压参数的确定方法及装置、存储介质和电子设备。In view of this, the embodiments of the present application provide a method and apparatus for determining chest compression parameters, a storage medium and an electronic device to solve at least one problem existing in the background art.
第一方面,本申请实施例提供了一种胸外按压参数的确定方法,所述方法包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a method for determining chest compression parameters, the method comprising:
获取由压力传感器采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器采集的加速度数据;Acquire the pressure data collected by the pressure sensor and the acceleration data collected by the acceleration sensor;
根据加速度数据确定按压深度;Determine the compression depth according to the acceleration data;
根据压力数据和按压深度确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值。A measure of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the compressed patient is determined from the pressure data and the depth of compressions.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,所述方法还包括:In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional implementation manner, the method further includes:
判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件;Determine whether the current measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition;
如果不满足,则根据胸腔弹性系数测量值与胸腔弹性系数干预值的比值以及所述按压深度,确定按压深度修正值。If not satisfied, the compression depth correction value is determined according to the ratio of the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity to the intervention value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity and the compression depth.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment,
所述方法还包括:The method also includes:
判断所述加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求;judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets a preset requirement;
如果不符合,则根据所述压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值,确定按压深度修正值。If not, then according to the pressure data and the intervening value of the elasticity coefficient of the thoracic cavity, the correction value of the compression depth is determined.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment,
所述胸腔弹性系数干预值通过以下步骤确定:The thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient intervention value is determined by the following steps:
如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中的至少一次判断所述胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果为满足,则根据结果为满足时对应的所述胸腔弹性系数测量值确定当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数,且所述胸腔弹性系数干预值等于所述当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数;If the result of judging whether the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition is satisfied at least once in the process of performing chest compression on the currently compressed patient, the determination is made according to the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity corresponding to when the result is satisfied. The thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of the currently compressed patient, and the intervening value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient is equal to the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient;
如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中判断所述胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果始终为不满足,则所述胸腔弹性系数干预值等于预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值。If the result of judging whether the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity satisfies the preset condition is always unsatisfied during the chest compression process on the currently compressed patient, the intervention value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity is equal to the pre-stored reference value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity .
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment,
所述判断当前的所述胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件,包括:The judging whether the current measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies a preset condition includes:
判断当前的所述胸腔弹性系数测量值与预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值之间的差距是否满足预设条件。It is judged whether the difference between the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity and the pre-stored reference value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies a preset condition.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,所述判断所述加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:With reference to the first aspect of the present application, in an optional implementation manner, the judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets a preset requirement includes:
确定所述压力数据的变化规律;determining the variation law of the pressure data;
确定所述横向加速度是否存在变化规律;determining whether there is a variation law in the lateral acceleration;
根据所述压力数据的变化规律与所述横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断所述加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求。According to the corresponding relationship between the variation rule of the pressure data and the variation rule of the lateral acceleration, it is determined whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets a preset requirement.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment,
所述确定所述压力数据的变化规律,包括:确定所述压力数据变化的频率;The determining of the variation law of the pressure data includes: determining the frequency of variation of the pressure data;
所述确定所述横向加速度是否存在变化规律,包括:确定所述横向加速度变化的频率;The determining whether the lateral acceleration has a variation law includes: determining the frequency of the lateral acceleration variation;
所述根据所述压力数据的变化规律与所述横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断所述加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:若所述压力数据变化的频率与所述横向加速度变化的频率一致或部分一致,则所述加速度数据中的横向加速度符合预设要求;否则,不符合预设要求。The judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements according to the corresponding relationship between the variation rule of the pressure data and the variation rule of the lateral acceleration includes: if the frequency of the variation of the pressure data is the same as that of the lateral acceleration. If the frequencies of the lateral acceleration changes are consistent or partially consistent, the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements; otherwise, it does not meet the preset requirements.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,所述确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值为确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值;其中,With reference to the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment, the determination of the measured value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient is to determine the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient; wherein,
所述确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:确定在预设时间周期内所述压力数据中的最大压力值和所述按压深度中的最大按压深度值,将所述最大压力值与所述最大按压深度值的比值确定为所述等效胸腔弹性系数测量值。The determining the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient includes: determining a maximum pressure value in the pressure data and a maximum compression depth value in the compression depth within a preset time period, and converting the maximum pressure value into the compression depth. The ratio of the value to the maximum compression depth value is determined as the equivalent thoracic elastic modulus measurement.
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,所述确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值为确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值;其中,With reference to the first aspect of the present application, in an optional embodiment, the determination of the measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient is determined as the real-time measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the compressed patient; wherein,
所述确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:将所述压力数据对时间的求导值与所述按压深度对时间的求导值的比值确定为所述实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。The determining the real-time thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient measurement value of the compressed patient includes: determining the ratio of the pressure data-to-time derivation value to the compression depth-versus-time derivation value as the real-time thoracic cavity elastic coefficient measurement value .
结合本申请的第一方面,在一可选实施方式中,所述方法还包括:In conjunction with the first aspect of the present application, in an optional implementation manner, the method further includes:
根据所述实时胸腔弹性系数测量值确定相应的分析结果;Determine a corresponding analysis result according to the real-time thoracic cavity elastic coefficient measurement value;
根据所述相应的分析结果向用户提供反馈信息。Feedback information is provided to the user according to the corresponding analysis results.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供了一种胸外按压参数的确定装置,包括:In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a device for determining chest compression parameters, including:
数据获取模块,用于获取由压力传感器采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器采集的加速度数据;a data acquisition module for acquiring the pressure data collected by the pressure sensor and the acceleration data collected by the acceleration sensor;
数据处理模块,用于根据加速度数据确定按压深度;根据压力数据和按压深度确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值。The data processing module is used for determining the compression depth according to the acceleration data; and determining the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the compressed patient according to the pressure data and the compression depth.
第三方面,本申请一实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质存储有指令,当所述指令由电子设备的处理器执行时,使得所述电子设备能够执行上述第一方面中任意一项提供的胸外按压参数的确定方法。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, where the computer-readable storage medium stores instructions, and when the instructions are executed by a processor of an electronic device, the electronic device can be executed The method for determining chest compression parameters provided by any one of the above first aspects.
第四方面,本申请一实施例提供了一种电子设备,所述电子设备包括:In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an electronic device, the electronic device comprising:
处理器;processor;
用于存储计算机可执行指令的存储器;memory for storing computer-executable instructions;
所述处理器,用于执行所述计算机可执行指令,以实现上述第一方面中任意一项所述的胸外按压参数的确定方法。The processor is configured to execute the computer-executable instructions to implement the method for determining chest compression parameters according to any one of the first aspect above.
本申请实施例所提供的胸外按压参数的确定方法及装置、存储介质和电子设备,通过获取由压力传感器采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器采集的加速度数据;根据加速度数据确定按压深度;根据压力数据和按压深度确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值;如此,可以在一定程度上反映出患者的胸腔状况,为救治提供依据;对于患者身处非适当的心肺复苏环境时,胸腔弹性系数的测量也能够为胸外按压参数、尤其是按压深度的确定提供帮助,有利于准确反馈胸外按压信息。The method and device for determining chest compression parameters, the storage medium and the electronic device provided by the embodiments of the present application, by acquiring the pressure data collected by the pressure sensor and the acceleration data collected by the acceleration sensor; determining the compression depth according to the acceleration data; according to the pressure The data and compression depth determine the measured value of the thoracic elastic coefficient of the compressed patient; in this way, it can reflect the patient's thoracic condition to a certain extent and provide a basis for treatment; when the patient is in an inappropriate CPR environment, the thoracic elastic coefficient Measurements can also help determine chest compression parameters, especially compression depth, and facilitate accurate feedback of chest compression information.
本申请附加的方面和优点将在下面的描述中部分给出,部分将从下面的描述中变得明显,或通过本申请的实践了解到。Additional aspects and advantages of the present application will be set forth, in part, in the following description, and in part will be apparent from the following description, or learned by practice of the present application.
附图说明Description of drawings
此处所说明的附图用来提供对本申请的进一步理解,构成本申请的一部分,本申请的示意性实施例及其说明用于解释本申请,并不构成对本申请的不当限定。在附图中:The drawings described herein are used to provide further understanding of the present application and constitute a part of the present application. The schematic embodiments and descriptions of the present application are used to explain the present application and do not constitute an improper limitation of the present application. In the attached image:
图1为本申请一实施例采用的胸外按压反馈装置的硬件结构示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a hardware structure of a chest compression feedback device adopted in an embodiment of the application;
图2a和图2b为胸外按压反馈装置的使用场景示意图;2a and 2b are schematic diagrams of usage scenarios of the chest compression feedback device;
图3为本申请一实施例提供的胸外按压参数的确定方法的流程示意图;3 is a schematic flowchart of a method for determining chest compression parameters according to an embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请一实施例提供的胸外按压参数的确定装置的结构框图;4 is a structural block diagram of an apparatus for determining chest compression parameters provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图5为本申请一实施例提供的电子设备的结构框图。FIG. 5 is a structural block diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的技术方案和有益效果能够更加明显易懂,下面通过列举具体实施例的方式进行详细说明。其中,附图不一定是按比例绘制的,局部特征可以被放大或缩小,以更加清楚的显示局部特征的细节;除非另有定义,本文所使用的技术和科学术语与本申请所属的技术领域中的技术和科学术语的含义相同。In order to make the technical solutions and beneficial effects of the present invention more obvious and easy to understand, the following detailed description is given by way of specific embodiments. Wherein, the accompanying drawings are not necessarily drawn to scale, and local features may be enlarged or reduced to more clearly show the details of local features; unless otherwise defined, the technical and scientific terms used herein are related to the technical field to which this application belongs. The technical and scientific terms in the text have the same meaning.
除另作定义外,本申请所涉及的技术术语或者科学术语应具有本申请所属技术领域具备一般技能的人所理解的一般含义。在本申请中的“一”、“一个”、“一种”、“该”、“这些”等类似的词并不表示数量上的限制,它们可以是单数或者复数。在本申请中所涉及的术语“包括”、“包含”、“具有”及其任何变体,其目的是涵盖不排他的包含;例如,包含一系列步骤或模块(单元)的过程、方法和系统、产品或设备并未限定于列出的步骤或模块(单元),而可包括未列出的步骤或模块(单元),或者可包括这些过程、方法、产品或设备固有的其他步骤或模块(单元)。在本申请中所涉及的“多个”是指两个或两个以上。“和/或”描述关联对象的关联关系,表示可以存在三种关系,例如,“A和/或B”可以表示:单独存在A,同时存在A和B,单独存在B这三种情况。在本申请中所涉及的术语“第一”、“第二”、“第三”等,只是对相似对象进行区分,并不代表针对对象的特定排序。Unless otherwise defined, the technical or scientific terms involved in this application shall have the general meaning understood by a person with ordinary skills in the technical field to which this application belongs. Words like "a", "an", "an", "the", "these" and the like in this application do not denote quantitative limitations, and they may be singular or plural. The terms "comprising", "comprising", "having" and any variations thereof referred to in this application are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion; for example, processes, methods and The system, product or device is not limited to the listed steps or modules (units), but may include unlisted steps or modules (units), or may include other steps or modules inherent to these processes, methods, products or devices (unit). As used in this application, "plurality" refers to two or more. "And/or" describes the association relationship between associated objects, indicating that there can be three kinds of relationships. For example, "A and/or B" can mean that A exists alone, A and B exist at the same time, and B exists alone. The terms "first", "second", "third", etc. involved in this application are only for distinguishing similar objects, and do not represent a specific order for the objects.
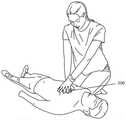
本申请提供的方法实施例可以在终端、计算机或者类似的运算装置中执行。比如在胸外按压反馈装置上执行,该胸外按压反馈装置的结构可以参考图1,该胸外按压反馈装置的使用场景可以参考图2a和图2b。如图所示,患者仰卧于平地上或用胸外按压板垫于其肩背下,施救人员可采用跪式等不同体位处于患者身体的一侧,施救人员将胸外按压反馈装置100安放在患者胸腔上方,施救人员双手放置在胸外按压反馈仪100之上实施徒手心肺复苏。施救人员应尽量保证持续有效的胸外按压,快速有力,中间不间断。The method embodiments provided in this application may be executed in a terminal, a computer or a similar computing device. For example, it is performed on a chest compression feedback device, the structure of the chest compression feedback device may refer to FIG. 1 , and the usage scenarios of the chest compression feedback device may refer to FIGS. 2 a and 2 b . As shown in the figure, the patient is lying on his back on the ground or the chest compression pad is placed under his shoulders and back. It is placed above the patient's chest, and the rescuer's hands are placed on the chest
实际胸外按压的情况往往是复杂多样的,比如,患者的身体情况会各有不同,同样的压力大小对于不同的患者效果是不一样的;再比如,患者身处的环境各有不同,如果患者躺在软床上,施救人员施加较小的压力就可以产生较大的位移,然而产生的位移有一部分是软床被压缩导致的,并不能真实反映胸腔变形情况;如果患者躺在救护车内,救护车的移动也会对胸外按压反馈仪100的测量结果造成影响。The actual chest compression situation is often complex and diverse. For example, the physical condition of the patient will be different, and the same pressure will have different effects on different patients; The patient is lying on the soft bed, and the rescuer can generate a large displacement by applying less pressure. However, part of the displacement is caused by the compression of the soft bed, which cannot truly reflect the deformation of the thoracic cavity; if the patient is lying in an ambulance In addition, the movement of the ambulance will also affect the measurement results of the chest
基于此,本申请实施例提出了一种胸外按压参数的确定方法,采用压力传感器和加速度传感器分别采集压力数据和加速度数据,进而计算患者的胸腔弹性系数,为胸外按压信息的反馈提供参考信息。Based on this, an embodiment of the present application proposes a method for determining chest compression parameters, which uses a pressure sensor and an acceleration sensor to collect pressure data and acceleration data respectively, and then calculates the patient's thoracic elasticity coefficient to provide a reference for feedback of chest compression information information.
图3为本实施例提供的胸外按压参数的确定方法的流程示意图,如图所示,该方法包括:3 is a schematic flowchart of a method for determining chest compression parameters provided by the present embodiment. As shown in the figure, the method includes:
步骤301、获取由压力传感器采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器采集的加速度数据;Step 301: Acquire pressure data collected by a pressure sensor and acceleration data collected by an acceleration sensor;
步骤302、根据加速度数据确定按压深度;
步骤303、根据压力数据和按压深度确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值。Step 303: Determine the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the compressed patient according to the pressure data and the compression depth.
可以理解的,本实施例通过压力传感器和加速度传感器分别采集了压力数据和加速度数据,进而通过计算得到了被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数,如此,可以在一定程度上反映出患者的胸腔状况,为救治提供依据;对于患者身处非适当的心肺复苏环境时,胸腔弹性系数的测量也能够为胸外按压参数、尤其是按压深度的确定提供帮助,有利于准确反馈胸外按压信息。It can be understood that in this embodiment, the pressure data and the acceleration data are collected by the pressure sensor and the acceleration sensor, respectively, and then the thoracic elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient is obtained through calculation. In this way, the thoracic condition of the patient can be reflected to a certain extent, which is: Provide evidence for treatment; when the patient is in an inappropriate CPR environment, the measurement of the thoracic elasticity coefficient can also provide help for the determination of chest compression parameters, especially the compression depth, and is conducive to accurate feedback of chest compression information.
请继续参考图1,胸外按压反馈装置100可以包括:壳体170、压力传感器110、加速度传感器120、处理单元130、存储单元140、以及反馈单元160等。其中,壳体170将各部件封装在内部,保护各部件不受损失,并且使得整个装置便于携带。压力传感器110,被配置为采集压力数据;该压力数据反映了在各采集时刻施救人员所施加的按压力的大小。加速度传感器120,被配置为采集加速度数据;该加速度数据反映了在各采集时刻患者胸腔面胸骨加速度的变化,包括胸腔被按压所致的下陷加速度和胸腔回弹期的回弹加速度等。处理单元130,被配置为获取由压力传感器110采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器120采集的加速度数据,并根据获取到的压力数据和加速度数据进行时间节点的确定和质量参数的计算。处理单元130根据计算得到的质量参数指示反馈单元160向用户提供反馈信息。当然,处理单元130也可以将质量参数传输给外部设备,如计算机或其他医疗装置等,以通过外部设备向用户提供反馈信息;外部设备可以向位于远端的用户实时提供该反馈消息,也可以进行数据存储和/或分析等,以供稍后复查救助期间内所进行的动作。反馈单元160在处理单元130的指示下,完成具体的信息反馈工作。这里,反馈单元160所进行的反馈工作有助于向用户提供通知、指示、和/或提醒;反馈单元160可以以任何合适的形式进行反馈,包括但不限于:视觉反馈,如通过指示灯的亮起/关闭、闪烁、不同颜色等向用户反馈不同的信息内容,又如通过显示屏幕向用户展示相关信息;声音反馈,如提醒音、语音指示;触觉反馈,如震动等。Please continue to refer to FIG. 1 , the chest
其中,压力传感器110采集压力数据和加速度传感器120采集加速度数据的时钟同步,或者二者的采集过程使用同一时钟记录。采集数据的时间趋近于实时采集。根据采集到的各压力数据和各加速度数据以及采集数据的时间,可以得到压力变化曲线和加速度变化曲线。进一步的,还可以根据采集到的各加速度数据和采集数据的时间得到位移变化曲线和/或速度变化曲线。The clocks of the pressure data collected by the
作为一种可选的实施方式,步骤302具体包括:根据压力数据和加速度数据确定本次胸外按压的按压开始时间点和对应的按压下降期结束时间点;根据按压开始时间点和对应的按压下降期结束时间点确定本次按压下降期及按压下降期时长;根据在本次的按压下降期内的加速度数据以及本次的按压下降期时长确定本次的按压深度。As an optional implementation manner, step 302 specifically includes: determining, according to the pressure data and acceleration data, the compression start time point of the chest compression and the corresponding compression drop period end time point; according to the compression start time point and the corresponding compression The ending time point of the descending period determines the current pressing descending period and the duration of the pressing descending period; the current pressing depth is determined according to the acceleration data in the current pressing descending period and the current pressing descending period length.
胸外按压过程中的各时间节点,例如包括以下至少之一:按压开始时间点(记为t0)、按压下降期结束时间点(记为t1)、胸腔回弹开始时间点(记为t2)、以及胸腔回弹上升期结束时间点(记为t3);可以理解的,由于胸外按压过程一般包括多次按压,正常情况下以每次按压开始至下次按压开始作为一个按压周期,或称“一次按压”,则上述各时间节点为各次按压的按压周期内包含的各时间节点;对于整个胸外按压过程,具体可以包括多个上述各时间节点,例如包括:第一次按压的开始时间点、第一次按压的按压下降期结束时间点、第一次按压的胸腔回弹开始时间点、第一次按压的胸腔回弹上升期结束时间点、第二次按压的开始时间点、第二次按压的按压下降期结束时间点、第二次按压的胸腔回弹开始时间点、第二次按压的胸腔回弹上升期结束时间点、第三次按压的开始时间点……为便于描述,本文使用“本次”代表上述中的任意一次,使用“下次”代表发生在“本次”之后的且与“本次”时间最临近的下一次,使用“上次”代表发生在“本次”之前的且与“本次”时间最临近的上一次,使用“最近一次”代表与当前时刻最为临近的一次。由于在正常情况下,下次按压开始代表了本次按压周期结束,因此在确定本次按压周期时,还可能需要利用下次的按压开始时间点;这里将下次的按压开始时间点记为t4。Each time node in the chest compression process, for example, includes at least one of the following: the compression start time point (denoted as t0), the end time point of the compression descending period (denoted as t1), and the chest cavity rebound start time point (denoted as t2) , and the end time point of the chest cavity rebound rising period (marked as t3); it is understandable that since the chest compression process generally includes multiple compressions, under normal circumstances, the start of each compression to the beginning of the next compression is regarded as a compression cycle, or is called "one compression", the above time nodes are the time nodes included in the compression cycle of each compression; for the entire chest compression process, it may specifically include a plurality of the above time nodes, for example, including: the first compression The start time point, the end time point of the compression descending period of the first compression, the start time point of the chest cavity recoil of the first compression, the end time point of the chest cavity recoil rising period of the first compression, the start time point of the second compression period , the end time point of the compression descending period of the second compression, the start time point of the chest cavity rebound of the second compression, the end time point of the chest cavity rebound rising period of the second compression, the start time point of the third compression... For ease of description, in this article, "this time" is used to represent any one of the above, "next time" is used to represent the next time that occurs after "this time" and is closest to the time of "this time", and "last time" is used to represent the occurrence The last time before "this time" and closest to the time of "this time", use "the most recent time" to represent the time closest to the current time. Because under normal circumstances, the start of the next compression represents the end of the current compression cycle, so when determining the current compression cycle, it may also be necessary to use the next compression start time point; here, the next compression start time point is recorded as t4.
作为一种可选的实施方式,根据压力数据和加速度数据确定本次胸外按压的按压开始时间点和对应的按压下降期结束时间点,包括:将压力数据由零或接近零的波谷值变化成满足预设条件的高位压力值的时间点确定为按压开始时间点;并且具体将压力数据为满足预设条件的高位压力值且由加速度数据经处理后得到的速度数据由正向速度变化成零的时间点确定为所述按压下降期结束时间点。As an optional implementation manner, determining the compression start time point and the corresponding compression drop period end time point of the chest compression according to the pressure data and the acceleration data includes: changing the pressure data from a trough value of zero or close to zero. The time point at which the high pressure value that meets the preset condition is determined as the pressing start time point; and the pressure data is the high pressure value that meets the preset condition and the velocity data obtained by processing the acceleration data is changed from the forward velocity to The time point of zero is determined as the end time point of the compression drop period.
这里,考虑到如果在某两次按压之间存在滞留压,那么压力数据可能不会下降为零,此时将接近零的波谷值视为未施加压力的情况。应当理解,在压力变化曲线上,压力数据位于波谷值往往是容易识别的,压力数据由高位压力值下降,逐渐接近零但未到零时反弹,则这一过程中的最小值即为接近零的波谷值。此外,为了降低识别误差,还可以通过设置零位点位阈值范围的方式确定接近零的波谷值,例如在预设的零位点位阈值范围内的波谷值为接近零的波谷值。Here, considering that the pressure data may not drop to zero if there is a stagnant pressure between certain two compressions, a valley value close to zero is considered as a case where no pressure is applied. It should be understood that on the pressure change curve, it is often easy to identify the pressure data at the trough value. The pressure data decreases from the high pressure value and gradually approaches zero but rebounds before reaching zero. The minimum value in this process is close to zero. trough value. In addition, in order to reduce the identification error, the valley value close to zero can also be determined by setting the threshold value range of the zero position, for example, the valley value within the preset threshold value range of the null position is a value close to zero.
如此,本次的按压开始时间点t0,以及下次的按压开始时间点记为t4,均可以采用上述步骤确定。In this way, the current pressing start time t0 and the next pressing start time t4 can be determined by using the above steps.
在胸外按压过程中,施救人员在患者胸腔上施加的按压力一般是瞬时增大,即变化成高位压力值,这在压力变化曲线上也是容易识别的。进一步为了避免设备将搭扶、倚靠等非按压力产生的压力值错误的识别为按压力,可以通过设置高位阈值的方式确定高位压力值,如将压力数据超过高位阈值确定为满足预设条件,将压力数据超过高位阈值的时刻确定为变化成满足预设条件的高位压力值的时间点。During the chest compression process, the compression force exerted by the rescuer on the patient's chest generally increases instantaneously, that is, changes to a high pressure value, which is also easy to identify on the pressure change curve. Further, in order to prevent the device from erroneously identifying the pressure value generated by the non-pressing force such as leaning and leaning as the pressing force, the high-level pressure value can be determined by setting the high-level threshold value. The time point when the pressure data exceeds the high level threshold value is determined as the time point when the pressure data changes to the high level pressure value satisfying the preset condition.
在实际应用中,当压力传感器监测的按压压力高于零位压力电位且处于高位时,识别为本次的按压开始时间点t0,此时间点作为后续胸腔被按压所致的下陷加速度测量按压深度Dp的计算开始时间点。In practical applications, when the compression pressure monitored by the pressure sensor is higher than the zero pressure potential and is at a high level, it is identified as the compression start time point t0, and this time point is used as the subsidence acceleration caused by the subsequent chest compression to measure the compression depth Dp calculation start time point.
本申请实施例中,将施加按压力的方向定义为正向,将胸腔回弹的方向定义为反向。在此基础上,可以理解的,正向速度指的是方向与按压方向一致的速度;相应的,反向速度指的是方向与胸腔回弹方向一致的速度。In the embodiments of the present application, the direction in which the pressing force is applied is defined as the forward direction, and the direction in which the thoracic cavity rebounds is defined as the reverse direction. On this basis, it can be understood that the forward speed refers to the speed in which the direction is consistent with the pressing direction; correspondingly, the reverse speed refers to the speed in which the direction is consistent with the direction of the rib cage.
在实际应用中,当压力传感器监测的按压压力处于高位且由加速度数据经处理后得到的速度数据由正向速度变化成零的时间点,识别为本次的按压下降期结束时间点t1。In practical applications, when the pressing pressure monitored by the pressure sensor is at a high level and the speed data obtained after processing the acceleration data changes from the forward speed to zero, it is identified as the end time t1 of the current pressing drop period.
如此,可以得到本次按压下降期为从t0到t1的时间区间,并且可以计算出本次的按压下降期时长T1=t1-t0。根据从t0到t1的时间区间内的加速度数据以及T1可以确定本次的按压深度。实际应用中,可以通过在该按压下降期时长内对本次按压下降期的加速度积分,可以得到速度V(t),具体采用下面的公式(1)进行计算:In this way, it can be obtained that the current pressing down period is a time interval from t0 to t1, and the current pressing down period duration T1=t1-t0 can be calculated. The current pressing depth can be determined according to the acceleration data in the time interval from t0 to t1 and T1. In practical applications, the velocity V(t) can be obtained by integrating the acceleration of this pressing down period within the duration of the pressing down period. Specifically, the following formula (1) is used for calculation:
在此基础上,通过在该按压下降期时长内对本次按压下降期的加速度进行二次积分,可以得到本次的按压深度Dp。具体的,在通过上述公式(1)计算得到速度V(t)之后,再采用下面的公式(2)对速度V(t)进行积分,得到按压深度Dp:On this basis, the current pressing depth Dp can be obtained by integrating the acceleration of this pressing falling period twice within the pressing falling period duration. Specifically, after the speed V(t) is obtained by calculating the above formula (1), the following formula (2) is used to integrate the speed V(t) to obtain the pressing depth Dp:
其中,加速度a是对采集得到的加速度数据进行滤波处理后的加速度。对加速度数据进行滤波处理,具体可以包括:通过高通滤波,滤除加速度数据中的重力加速度g的直流信号,从而消除因检测重力加速度g偏移而造成的基线漂移;还可以包括:经过低通滤波,滤除高频干扰和/或噪声信号。Among them, the acceleration a is the acceleration after filtering the collected acceleration data. The filtering processing of the acceleration data may specifically include: filtering out the DC signal of the gravitational acceleration g in the acceleration data through high-pass filtering, thereby eliminating the baseline drift caused by detecting the offset of the gravitational acceleration g; it may also include: passing through a low-pass filter Filtering to filter out high frequency interference and/or noise signals.
如此,可以获得按压深度随时间的变化曲线,如此,可以获得按压速度随时间变化的曲线,也可以称为“速度变化曲线”;还可以获得按压深度随时间的变化曲线,也可以称为“位移变化曲线”。。In this way, the change curve of the pressing depth with time can be obtained, in this way, the curve of the change of the pressing speed with time can be obtained, which can also be called "speed change curve"; the change curve of the pressing depth with time can also be obtained, which can also be called " Displacement Variation Curve". .
采用下面的公式(3)进行计算,可以得到胸腔弹性系数:Using the following formula (3) for calculation, the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity can be obtained:
胸腔弹性系数=压力/按压深度 公式(3)Chest elasticity coefficient = pressure / compression depth Formula (3)
作为一种可选的实施方式,确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,和/或确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。As an optional embodiment, determining the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the compressed patient includes: determining the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the equivalent chest cavity of the compressed patient, and/or determining the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity in real time of the compressed patient.
其中,确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:确定在预设时间周期内压力数据中的最大压力值和按压深度中的最大按压深度值,将压力数据中的最大压力值与按压深度中的最大按压深度值的比值确定为等效胸腔弹性系数测量值。Wherein, determining the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elastic coefficient of the compressed patient includes: determining the maximum pressure value in the pressure data and the maximum compression depth value in the compression depth within a preset time period, and comparing the maximum pressure value in the pressure data with the maximum pressure value in the pressure data. The ratio of the maximum compression depth values among the compression depths was determined as the equivalent thoracic elastic modulus measurement.
这里,通过最大压力值除以最大按压深度值,可以得到等效胸腔弹性系数测量值;即,将胸腔假设为线性弹性体,胸腔弹性系数在按压范围内不变。可以理解的,随着测量时间的不断变化,或者根据计算时间段的选取不同,等效胸腔弹性系数测量值也可以包含多个值;比如,在当前时刻,压力变化曲线上的最大压力值为P1,位移变化曲线上的最大按压深度值为Dp1,那么,此时的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值为P1÷Dp1;经过一段时间后,压力变化曲线上出现了新的最大压力值为P2,显然P2大于P1,那么,此时的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值为P2÷Dp1;或者,位移变化曲线上出现了新的最大按压深度值为Dp2,显然Dp2大于Dp1,那么,此时的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值为P1÷Dp2;或者,经过一段时间后,压力变化曲线上的新的最大压力值为P2,并且,位移变化曲线上的最大按压深度值为Dp2,那么,此时的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值为P2÷Dp2。Here, by dividing the maximum pressure value by the maximum compression depth value, the equivalent thoracic elastic coefficient measurement can be obtained; that is, the thorax is assumed to be a linear elastic body, and the thoracic elastic coefficient does not change within the compression range. It is understandable that with the continuous change of the measurement time, or according to the selection of different calculation time periods, the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient may also contain multiple values; for example, at the current moment, the maximum pressure value on the pressure change curve is P1, the maximum compression depth value on the displacement change curve is Dp1, then the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient at this time is P1÷Dp1; after a period of time, a new maximum pressure value P2 appears on the pressure change curve, Obviously, P2 is greater than P1, then the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient at this time is P2÷Dp1; or, a new maximum compression depth value Dp2 appears on the displacement curve, obviously Dp2 is greater than Dp1, then, at this time, etc. The measured value of the effective thoracic elasticity coefficient is P1÷Dp2; or, after a period of time, the new maximum pressure value on the pressure change curve is P2, and the maximum compression depth value on the displacement change curve is Dp2, then, at this time, the The equivalent thoracic elastic modulus measure is P2÷Dp2.
这里,预设时间周期可以为一次按压周期,即从t0到t4。此时,等效胸腔弹性系数测量值可以称为单次按压的胸腔弹性系数测量值。Here, the preset time period may be one pressing period, that is, from t0 to t4. At this point, the equivalent thoracic elastic coefficient measurement may be referred to as the single-compression thoracic elastic coefficient measurement.
不同人体的胸腔弹性系数可能存在较大差异,即便是对于同一个人,实际人体的胸腔弹性系数也并不是一个一成不变的恒定值。随着人体的生长变化,胸骨的软硬程度也可能有所变化。因此,等效胸腔弹性系数测量值有助于对患者当下的胸腔弹性情况做出反映。The elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity of different human bodies may be quite different. Even for the same person, the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity of the actual human body is not a constant value. As the body grows, the stiffness of the breastbone may also change. Therefore, the measurement of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient helps to reflect the current thoracic elasticity of the patient.
此外,确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:将压力数据对时间的求导值与按压深度对时间的求导值的比值确定为实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。比如,想要确定被按压患者在时间tn处的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值,首先根据压力变化曲线确定Pn是时间tn处的压力,根据位移变化曲线确定Dpn是时间tn处的按压深度;那么,时间tn处的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值=(dPn/dt)÷(dDpn/dt)。可以理解的,压力数据对时间的求导值指的是当自变量t的增量趋于零时,因变量P的增量与自变量t的增量之商的极限;dPn/dt基本等于在压力变化曲线上时间tn处的斜率。相应的,按压深度对时间的求导值指的是当自变量t的增量趋于零时,因变量Dp的增量与自变量t的增量之商的极限;dDpn/dt基本等于在位移变化曲线上时间tn处的斜率。In addition, determining the real-time thoracic elastic coefficient measurement value of the compressed patient includes: determining a ratio of a derivation value of the pressure data with respect to time to a derivation value of the compression depth with respect to time as the real-time thoracic cavity elastic coefficient measurement value. For example, to determine the real-time thoracic elastic coefficient measurement value of a compressed patient at time tn , first determine that Pn is the pressure at time tn according to the pressure change curve, and Dpn is the pressure at time tn according to the displacement change curve Compression depth; then, real-time thoracic elastic modulus measurement at time tn = (dPn /dt)÷(dDpn /dt). It can be understood that the derivation value of pressure data against time refers to the limit of the quotient of the increment of the dependent variable P and the increment of the independent variable t when the increment of the independent variable t tends to zero; dPn /dt basically is equal to the slope at time tn on the pressure profile. Correspondingly, the derivation value of pressing depth to time refers to the limit of the quotient of the increment of the dependent variable Dp and the increment of the independent variable t when the increment of the independent variable t tends to zero; dDpn /dt is basically equal to The slope at time tn on the displacement curve.
这里,通过压力对时间求导除以位移对时间求导,可以得到实时胸腔弹性系数测量值;即,不将胸腔假设为线性弹性体,还可以得到胸腔弹性系数的实时数据。Here, the real-time measurement of the thoracic elastic coefficient can be obtained by dividing the pressure-to-time derivation by the displacement-to-time derivation; that is, real-time data of the thoracic elastic coefficient can be obtained without assuming the thorax as a linear elastic body.
不仅如此,随着按压深度的变化,人体的胸腔弹性系数也随时变化,实时胸腔弹性系数测量值有助于了解患者胸骨的实时情况,如判断是否遭受到外力损伤,胸骨发生骨折、断裂、肺萎陷等。如果实时胸腔弹性系数测量值发生骤变,可以向用户反馈并发出提醒。Not only that, with the change of the compression depth, the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity of the human body also changes at any time. The real-time measurement of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity helps to understand the real-time situation of the patient’s sternum, such as judging whether it has suffered external force damage, sternum fracture, fracture, lung collapse etc. If there is a sudden change in the real-time thoracic elastic coefficient measurement, feedback and alerts can be sent to the user.
在实际应用中,上述方法还包括:根据实时胸腔弹性系数测量值确定相应的分析结果;根据相应的分析结果向用户提供反馈信息。这里,分析结果例如分析患者是否发生胸骨损伤等。如此,有利于判断突发事件,比如及时地反馈出胸骨发生骨折的情况。In practical applications, the above method further includes: determining a corresponding analysis result according to the real-time measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity; and providing feedback information to the user according to the corresponding analysis result. Here, the analysis result, for example, analyzes whether the patient has a sternal injury or the like. In this way, it is helpful to judge emergencies, such as timely feedback of the fracture of the sternum.
在实际应用中,可以对等效胸腔弹性系数测量值和实时胸腔弹性系数测量值进行存储和/或传输,从而有利于对患者的身体情况进行分析。例如,可以通过胸腔弹性系数测量值反映患者的胸骨的软硬情况;胸腔弹性系数测量值越低,胸骨越柔软,从而在施加相对较小的压力的情况下即可发生所需的形变;反之,胸腔弹性系数测量值越高,胸骨越硬,为了实现符合要求的按压深度需要施加更大的按压压力。此外,不同群体的胸腔弹性系数存在一定的差异,记录多位患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值还将具有统计意义,比如,可以获知中国人中胸腔弹性系数处于各不同数值范围内的人口比例;可以理解的,还可以基于获取的胸腔弹性系数测量值对胸腔弹性系数参考值进行修正。In practical applications, the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elastic coefficient and the real-time measured value of the thoracic elastic coefficient can be stored and/or transmitted, thereby facilitating the analysis of the patient's physical condition. For example, a measurement of thoracic elasticity can reflect the softness and stiffness of a patient's sternum; the lower the measurement of thoracic elasticity, the softer the sternum, allowing the desired deformation to occur with relatively little pressure; conversely , the higher the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity, the harder the sternum, and the greater the compression pressure required to achieve the required compression depth. In addition, there are certain differences in the thoracic elasticity coefficient of different groups, and it will be statistically significant to record the measured values of the thoracic elasticity coefficient of multiple patients. It is understood that the reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient can also be modified based on the obtained measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient.
作为一种可选的实施方式,所述方法还包括:根据胸腔弹性系数测量值,确定按压深度修正值。As an optional implementation manner, the method further includes: determining a compression depth correction value according to the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity.
可选的,判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件;如果不满足,则根据胸腔弹性系数测量值与胸腔弹性系数干预值的比值以及所述按压深度,确定按压深度修正值。Optionally, it is judged whether the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies a preset condition; if not, the correction value of the compression depth is determined according to the ratio of the measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient to the intervention value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient and the compression depth.
这里,当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值不满足预设条件可以理解为当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值明显不正确,不属于人类正常的胸腔弹性系数范围。Here, it can be understood that the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity does not meet the preset condition, and it can be understood that the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity is obviously incorrect and does not belong to the normal range of the elastic coefficient of the human thoracic cavity.
具体的,判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件,可以包括:判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值与预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值之间的差距是否满足预设条件。其中,预设条件例如设置为偏离胸腔弹性系数参考值的50%以上;当然,本申请并不限于此。Specifically, judging whether the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition may include: judging whether the difference between the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient and the pre-stored reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition. Wherein, the preset condition is, for example, set to deviate by more than 50% of the reference value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity; of course, the present application is not limited to this.
应当理解,胸腔弹性系数参考值可以由设备工程师或者由用户预先存储在胸外按压参数的确定装置内,其具体数值可以根据统计数据或者根据经验值确定。其中,当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值具体可以选用当前的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,而不是实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。换言之,判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件,具体为判断当前的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件。It should be understood that the reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient may be pre-stored in the apparatus for determining chest compression parameters by an equipment engineer or a user, and its specific value may be determined according to statistical data or empirical values. The current measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity may specifically be the measurement value of the current equivalent elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity, rather than the real-time measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity. In other words, judging whether the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition is specifically judging whether the current measured value of the equivalent elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition.
进一步的,在根据胸腔弹性系数测量值,确定按压深度修正值的步骤中,均可以选用等效胸腔弹性系数测量值。Further, in the step of determining the correction value of the compression depth according to the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity, an equivalent measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity may be selected.
在获得按压深度修正值后,可以将该按压深度修正值作为输出值进行输出,以便于用户获得更加贴近实际情况的按压深度。After the pressing depth correction value is obtained, the pressing depth correction value may be output as an output value, so that the user can obtain a pressing depth that is closer to the actual situation.
可选的,判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件;如果满足,则表示当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是正常的被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数,可以根据当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值确定当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数。Optionally, it is judged whether the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition; if so, it means that the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient is the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of a normal compressed patient, and the measured value of the current thoracic cavity elastic coefficient can be determined according to the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient. Determines the thoracic elasticity coefficient of the currently compressed patient.
具体地,可以将当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值记为当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数;此外,也可以将多次判断结果为满足的多个当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值的平均值确定为当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数。Specifically, the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity may be recorded as the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the currently compressed patient; in addition, the average value of multiple current measured values of the elastic coefficient of the current thoracic cavity for which multiple judgment results are satisfied may be determined as the current elastic coefficient of the chest cavity. The elastic coefficient of the chest cavity of the compressed patient.
如果判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值满足预设条件,则无需修正按压深度,可以将前述根据加速度数据确定的按压深度作为输出值进行输出。If it is determined that the current measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition, it is not necessary to correct the compression depth, and the aforementioned compression depth determined according to the acceleration data may be output as an output value.
胸腔弹性系数干预值可以通过以下步骤确定:如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中的至少一次判断胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果为满足,则根据结果为满足时对应的胸腔弹性系数测量值确定当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数,且胸腔弹性系数干预值等于当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数;如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中判断胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果始终为不满足,则胸腔弹性系数干预值等于预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值。The intervening value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient can be determined by the following steps: if the result of judging whether the measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition is satisfied at least once in the process of performing chest compression on the currently compressed patient, then according to the result, corresponding The measured value of the thoracic elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient determines the thoracic elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient, and the intervening value of the thoracic elastic coefficient is equal to the thoracic elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient; The result of whether the value satisfies the preset condition is always unsatisfied, and the intervention value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient is equal to the pre-stored reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient.
可以理解的,如果检测到胸腔弹性系数明显偏小,则基本可以判断此时为在柔软的可按压表面上(如在软床上)按压,即按压深度偏深、压力偏小。那么,这种情况胸腔弹性系数测量值是不准确的,需要采用胸腔弹性系数干预值等比例的确定按压深度修正值,以将该按压深度修正值作为输出值进行输出,以便于用户获得更加贴近实际情况的按压深度。It is understandable that if it is detected that the elasticity coefficient of the thoracic cavity is significantly lower, it can be basically determined that the compression is performed on a soft compressible surface (eg, on a soft bed), that is, the compression depth is deeper and the pressure is lower. Then, in this case, the measured value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient is inaccurate. It is necessary to determine the correction value of the compression depth in the same proportion as the intervention value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient, so as to output the corrected value of the compression depth as an output value, so that the user can obtain a closer The actual compression depth.
比如,通过检测得到的胸腔弹性系数测量值为5N/mm,确定的胸腔弹性系数干预值为10N/mm,则采用胸腔弹性系数干预值10N/mm进行修正计算,确定按压深度修正值等于根据加速度数据确定的按压深度*5N/mm÷10N/mm。For example, if the measured value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient obtained through detection is 5N/mm, and the determined intervening value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient is 10N/mm, then the intervening value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient of 10N/mm is used for correction calculation, and it is determined that the correction value of the compression depth is equal to that according to the acceleration The compression depth determined by the data*5N/mm÷10N/mm.
对于胸外按压一直在软床上进行的情况,在胸外按压过程中判断胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果将会出现始终为不满足,此种情况直接采用预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值来修正按压深度;而对于在胸外按压过程中,患者被从平地抬到软床上(当然,本申请也不排除患者被从软床抬到平地上),在胸外按压过程中会存在至少一预设时长范围内胸腔弹性系数测量值是满足预设条件的,那么可以根据该预设时长范围内的胸腔弹性系数测量值确定胸腔弹性系数干预值,从而确定按压深度修正值。For the case where chest compression is always performed on the soft bed, the result of judging whether the measured value of the thoracic elastic coefficient meets the preset conditions during the chest compression process will always be unsatisfied. In this case, the pre-stored thoracic elastic coefficient is directly used. The reference value is used to correct the compression depth; while during chest compressions, the patient is lifted from a flat floor to a soft bed (of course, this application does not exclude that the patient is lifted from a soft bed to a flat floor), during chest compressions If the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity satisfies the preset condition within at least one preset time period, the intervention value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity can be determined according to the measured value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity within the preset time period, thereby determining the correction value of the compression depth.
作为一种可选的实施方式,上述方法还包括:判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求;如果不符合,则根据压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值,确定按压深度修正值。As an optional implementation manner, the above method further includes: judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets a preset requirement; if not, determining a compression depth correction value according to the pressure data and the intervention value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient.
其中,胸腔弹性系数干预值可以采用如前所述的步骤确定。并且,其中,当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值具体可以选用当前的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,而不是实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。The intervening value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity can be determined by using the steps described above. Moreover, the current measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity may specifically select the current measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the equivalent thoracic cavity, rather than the real-time measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity.
作为一种可选的实施方式,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:确定压力数据的变化规律;确定横向加速度是否存在变化规律;根据压力数据的变化规律与横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求。As an optional implementation manner, judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements includes: determining the variation rule of the pressure data; determining whether there is a variation rule in the lateral acceleration; according to the variation rule of the pressure data and the variation of the lateral acceleration The corresponding relationship between the laws is used to determine whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements.
可以理解的,由于在胸外按压过程中一般要进行多次按压,因此压力数据是存在一定变化规律的。具体的,在每一次按压周期的开始,压力数据先变化成满足预设条件的高位压力值,即对应于施救者用力施压的阶段;而后,压力数据由满足预设条件的高位压力值变化成零或接近零的波谷值,即施救者撤除压力、胸腔回弹的阶段。如果横向加速度也存在变化规律,并且与压力数据的变化规律相同,或者至少存在关联,那么横向加速度可能是由于施救者的按压未严格沿着竖直方向进行导致的,此时可认为加速度数据中的横向加速度符合预设要求,无需对按压深度进行修正。此外,如果按压过程中加速度数据没有横向加速度分量或者仅有很少的横向加速度分量(具体可以通过横向加速度分量是否超过预设横向加速度分量阈值来判断),也应当认为横向加速度符合预设要求,无需对按压深度进行修正。反之,如果横向加速度分量超过预设横向加速度分量阈值,且没有变化规律或虽有变化规律但与压力数据的变化规律没有关联,则判断横向加速度不符合预设要求,根据加速度数据确定的按压深度是不准确的,需要根据压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值确定按压深度修正值。It is understandable that since multiple compressions are generally performed during the chest compression process, there is a certain variation law in the pressure data. Specifically, at the beginning of each pressing cycle, the pressure data first changes to a high pressure value that satisfies the preset condition, that is, corresponding to the stage when the rescuer exerts pressure; then, the pressure data is changed from the high pressure value that satisfies the preset condition Changes to zero or near-zero trough values, that is, the stage when the rescuer removes the pressure and the thoracic cavity rebounds. If the lateral acceleration also has a variation law and is the same as, or at least correlated with, the pressure data, then the lateral acceleration may be caused by the rescuer's pressing not strictly in the vertical direction, and the acceleration data can be considered at this time. The lateral acceleration in , meets the preset requirements and does not need to be corrected for the compression depth. In addition, if the acceleration data has no lateral acceleration component or only a small lateral acceleration component during the pressing process (specifically, it can be judged by whether the lateral acceleration component exceeds the preset lateral acceleration component threshold), it should also be considered that the lateral acceleration meets the preset requirements. No correction for compression depth is required. Conversely, if the lateral acceleration component exceeds the preset lateral acceleration component threshold, and there is no variation rule or there is a variation rule but is not related to the variation rule of the pressure data, it is judged that the lateral acceleration does not meet the preset requirements, and the pressing depth determined according to the acceleration data is determined. It is inaccurate, and it is necessary to determine the compression depth correction value according to the pressure data and the intervention value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient.
具体可选的,确定压力数据的变化规律,可以包括:确定压力数据变化的频率;确定横向加速度是否存在变化规律,可以包括:确定横向加速度变化的频率。基于此,根据压力数据的变化规律与横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:若压力数据变化的频率与横向加速度变化的频率一致或部分一致,则加速度数据中的横向加速度符合预设要求;否则,不符合预设要求。这里,频率一致或部分一致,也即二者的周期性相同或部分相同。Specifically, optionally, determining the variation rule of the pressure data may include: determining the frequency of variation of the pressure data; determining whether there is a variation rule in the lateral acceleration may include: determining the frequency of the lateral acceleration variation. Based on this, according to the corresponding relationship between the change law of the pressure data and the change law of the lateral acceleration, it is determined whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements, including: if the frequency of the pressure data change is consistent with the frequency of the lateral acceleration change or If they are partially consistent, the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements; otherwise, it does not meet the preset requirements. Here, the frequencies are identical or partly identical, that is, the periodicity of the two is identical or partly identical.
当然,本申请并不限于此,作为一种替代的实施方式,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,也可以包括:根据加速度数据确定横向位移;判断横向位移是否超出预设阈值;如果超出,则根据压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值,确定按压深度修正值。可以理解的,如果出现超出预设阈值的横向位移,则基本也可表明患者是在救护车、移动病床等移动装置上,而不是在静止状态下。Of course, the present application is not limited to this. As an alternative embodiment, judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements may also include: determining the lateral displacement according to the acceleration data; judging whether the lateral displacement exceeds a preset threshold; If it exceeds, the compression depth correction value is determined based on the pressure data and the intervening value of the elastic coefficient of the chest cavity. It can be understood that if there is a lateral displacement exceeding the preset threshold, it can basically also indicate that the patient is on a mobile device such as an ambulance, a mobile hospital bed, etc., rather than in a stationary state.
根据压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值,确定按压深度修正值,具体例如为:将压力数据与胸腔弹性系数干预值的比值确定为按压深度修正值。并且,可以将该按压深度修正值作为输出值进行输出。Determine the compression depth correction value according to the pressure data and the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient intervention value, for example, determine the ratio of the pressure data to the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient intervention value as the compression depth correction value. Then, the pressing depth correction value may be output as an output value.
胸外按压反馈装置100正常使用时一般平放在患者胸口进行按压,按压过程中加速度信号理论上只有很少的横向加速度分量。如果在按压过程中检测到了不规律的横向加速度(即与按压节奏不同的横向加速度),则判断为当前处于非静止状态,例如随着救护车移动,这种情况下加速度传感器测量的加速度数据将无法真实反映患者胸腔面胸骨加速度的变化。因此,如果还是像常态下一样,将根据加速度数据确定的按压深度作为输出值输出,将导致用户无法了解实际的按压深度情况,容易造成误判;此时,本申请实施例通过确定按压深度修正值,并将该按压深度修正值作为输出值进行输出,便于用户获得更加贴近实际情况的按压深度。例如,没有任何横向加速度,也没有任何横向位移时,认为患者没有出现移动,无需修正按压深度;在检测到横向加速度时,计算横向位移,并判断横向位移是否超出预设阈值,如果超出则认为患者当前处于非静止状态,则按压深度修正值被确定为等于按压压力/胸腔弹性系数。其中,胸腔弹性系数可以参考前述描述,这里不再赘述。During normal use, the chest
在此基础上,本申请实施例还提供了一种胸外按压参数的确定装置;请参考图5,胸外按压反馈装置100’包括:On this basis, the embodiment of the present application also provides a device for determining chest compression parameters; please refer to FIG. 5 , the chest compression feedback device 100' includes:
数据获取模块101,用于获取由压力传感器采集的压力数据和由加速度传感器采集的加速度数据;The data acquisition module 101 is used for acquiring the pressure data collected by the pressure sensor and the acceleration data collected by the acceleration sensor;
数据处理模块102,用于根据加速度数据确定按压深度;根据压力数据和按压深度确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值。The data processing module 102 is configured to determine the compression depth according to the acceleration data; and determine the measured value of the thoracic elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient according to the pressure data and the compression depth.
可以理解的,这里的胸外按压反馈装置100’可以为上述胸外按压反馈装置100,或者为上述胸外按压反馈装置100的一部分。It can be understood that the chest compression feedback device 100' here may be the above-mentioned chest
作为一种可选的实施方式,数据处理模块102,还用于判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件;如果不满足,则根据胸腔弹性系数测量值与胸腔弹性系数干预值的比值以及所述按压深度,确定按压深度修正值。As an optional implementation, the data processing module 102 is further configured to determine whether the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition; and the compression depth, a compression depth correction value is determined.
作为一种可选的实施方式,数据处理模块102,还用于判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求;如果不符合,则根据压力数据和胸腔弹性系数干预值,确定按压深度修正值。As an optional implementation manner, the data processing module 102 is further configured to determine whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements; if not, determine the correction value of the compression depth according to the pressure data and the intervention value of the elasticity coefficient of the chest cavity .
作为一种可选的实施方式,数据处理模块102,用于确定胸腔弹性系数干预值,具体用于如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中的至少一次判断胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果为满足,则根据结果为满足时对应的胸腔弹性系数测量值确定当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数,且胸腔弹性系数干预值等于当前被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数;如果在对当前被按压患者进行胸外按压过程中判断胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件的结果始终为不满足,则胸腔弹性系数干预值等于预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值。As an optional implementation manner, the data processing module 102 is configured to determine an intervention value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient, and is specifically used to determine whether the measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient satisfies at least one time in the process of performing chest compressions on the currently compressed patient. If the result of the preset condition is satisfied, the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient is determined according to the corresponding measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient when the result is satisfied, and the intervening value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient is equal to the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the currently compressed patient; The result of judging whether the measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies the preset condition during the chest compression process of the currently compressed patient is always unsatisfied, and the intervening value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient is equal to the pre-stored reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient.
作为一种可选的实施方式,判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值是否满足预设条件,包括:判断当前的胸腔弹性系数测量值与预先存储的胸腔弹性系数参考值之间的差距是否满足预设条件。As an optional implementation manner, judging whether the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies a preset condition includes: judging whether the gap between the current measured value of the thoracic cavity elastic coefficient and a pre-stored reference value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient satisfies a preset condition condition.
作为一种可选的实施方式,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:确定压力数据的变化规律;确定横向加速度是否存在变化规律;根据压力数据的变化规律与横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求。As an optional implementation manner, judging whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements includes: determining the variation rule of the pressure data; determining whether there is a variation rule in the lateral acceleration; according to the variation rule of the pressure data and the variation of the lateral acceleration The corresponding relationship between the laws is used to determine whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements.
作为一种可选的实施方式,确定压力数据的变化规律,包括:确定压力数据变化的频率;确定横向加速度是否存在变化规律,包括:确定横向加速度变化的频率;根据压力数据的变化规律与横向加速度的变化规律之间的对应关系,判断加速度数据中的横向加速度是否符合预设要求,包括:若压力数据变化的频率与横向加速度变化的频率一致或部分一致,则加速度数据中的横向加速度符合预设要求;否则,不符合预设要求。As an optional implementation manner, determining the variation rule of the pressure data includes: determining the frequency of the variation of the pressure data; determining whether there is a variation rule of the lateral acceleration, including: determining the frequency of the variation of the lateral acceleration; Correspondence between the changing laws of acceleration, to determine whether the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the preset requirements, including: if the frequency of pressure data changes is consistent or partially consistent with the frequency of lateral acceleration changes, then the lateral acceleration in the acceleration data meets the requirements. Default requirement; otherwise, the default requirement is not met.
作为一种可选的实施方式,确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值为确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值;其中,确定被按压患者的等效胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:确定在预设时间周期内压力数据中的最大压力值和按压深度中的最大按压深度值,将最大压力值与最大按压深度值的比值确定为等效胸腔弹性系数测量值。As an optional embodiment, determining the measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient is determined as the measured value of the equivalent thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the compressed patient; wherein, determining the measured value of the equivalent thoracic cavity elastic coefficient of the compressed patient includes: Determine the maximum pressure value in the pressure data and the maximum compression depth value in the compression depth within the preset time period, and determine the ratio of the maximum pressure value to the maximum compression depth value as the measured value of the equivalent thoracic elasticity coefficient.
作为一种可选的实施方式,确定被按压患者的胸腔弹性系数测量值为确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值;其中,确定被按压患者的实时胸腔弹性系数测量值,包括:将压力数据对时间的求导值与按压深度对时间的求导值的比值确定为实时胸腔弹性系数测量值。As an optional implementation manner, determining the measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient is determined as the real-time thoracic cavity elastic coefficient measured value of the compressed patient; wherein, determining the real-time measured value of the thoracic cavity elasticity coefficient of the compressed patient includes: The ratio of the derivative of data versus time to the derivative of compression depth versus time is determined as the real-time thoracic elastic coefficient measurement.
作为一种可选的实施方式,数据处理模块102,还用于根据实时胸腔弹性系数测量值确定相应的分析结果,根据相应的分析结果向用户提供反馈信息。胸外按压反馈装置100’还包括:反馈模块103,用于在数据处理模块102的控制下提供相应的反馈信息。As an optional implementation manner, the data processing module 102 is further configured to determine a corresponding analysis result according to the real-time measurement value of the elastic coefficient of the thoracic cavity, and provide feedback information to the user according to the corresponding analysis result. The chest compression feedback device 100' further includes: a feedback module 103 for providing corresponding feedback information under the control of the data processing module 102.
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质。该计算机可读存储介质存储有指令,当该指令由电子设备的处理器执行时,使得电子设备能够执行如上述任一实施例的胸外按压参数的确定方法中的步骤。Embodiments of the present application also provide a computer-readable storage medium. The computer-readable storage medium stores instructions that, when executed by the processor of the electronic device, enable the electronic device to perform the steps in the method for determining chest compression parameters according to any of the foregoing embodiments.
本申请实施例可以是系统、方法和/或计算机程序产品。计算机程序产品可以包括计算机可读存储介质,其上载有用于使处理器实现本申请的各个方面的计算机可读程序指令。计算机程序产品可以以一种或多种程序设计语言的任意组合来编写用于执行本申请实施例操作的程序代码,程序设计语言包括面向对象的程序设计语言,诸如Java、C++等,还包括常规的过程式程序设计语言,诸如“C”语言或类似的程序设计语言。程序代码可以完全地在用户计算设备上执行、部分地在用户设备上执行、作为一个独立的软件包执行、部分在用户计算设备上部分在远程计算设备上执行、或者完全在远程计算设备或服务器上执行。在涉及远程计算机的情形中,远程计算机可以通过任意种类的网络—包括局域网(LAN)或广域网(WAN)—连接到用户计算机,或者,可以连接到外部计算机(例如利用因特网服务提供商来通过因特网连接)。在一些实施例中,通过利用计算机可读程序指令的状态信息来个性化定制电子电路,例如可编程逻辑电路、现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)或可编程逻辑阵列(PLA),该电子电路可以执行计算机可读程序指令,从而实现本申请的各个方面。Embodiments of the present application may be systems, methods and/or computer program products. The computer program product may include a computer-readable storage medium having computer-readable program instructions loaded thereon for causing a processor to implement various aspects of the present application. The computer program product may be written in any combination of one or more programming languages to write program codes for performing the operations of the embodiments of the present application. The programming languages include object-oriented programming languages, such as Java, C++, etc., as well as conventional procedural programming language, such as "C" language or similar programming language. The program code may execute entirely on the user computing device, partly on the user device, as a stand-alone software package, partly on the user computing device and partly on a remote computing device, or entirely on the remote computing device or server execute on. In the case of a remote computer, the remote computer may be connected to the user's computer through any kind of network, including a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN), or may be connected to an external computer (eg, using an Internet service provider through the Internet connect). In some embodiments, custom electronic circuits, such as programmable logic circuits, field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), or programmable logic arrays (PLAs), can be personalized by utilizing state information of computer readable program instructions. Computer readable program instructions are executed to implement various aspects of the present application.
计算机可读存储介质可以采用一个或多个可读介质的任意组合。可读介质可以是可读信号介质或者可读存储介质。计算机可读存储介质是可以保持和存储由指令执行设备使用的指令的有形设备。可读存储介质例如可以包括但不限于电、磁、光、电磁、红外线、或半导体的系统、装置或器件,或者任意以上的组合。可读存储介质的更具体的例子(非穷举的列表)包括:便携式计算机盘、硬盘、随机存取存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、可擦式可编程只读存储器(EPROM或闪存)、静态随机存取存储器(SRAM)、便携式压缩盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、数字多功能盘(DVD)、记忆棒、软盘、机械编码设备、例如其上存储有指令的打孔卡或凹槽内凸起结构、以及上述的任意合适的组合。这里所使用的计算机可读存储介质不被解释为瞬时信号本身,诸如无线电波或者其他自由传播的电磁波、通过波导或其他传输媒介传播的电磁波(例如,通过光纤电缆的光脉冲)、或者通过电线传输的电信号。A computer-readable storage medium can employ any combination of one or more readable media. The readable medium may be a readable signal medium or a readable storage medium. A computer-readable storage medium is a tangible device that can hold and store instructions for use by an instruction execution device. The readable storage medium may include, for example, but not limited to, electrical, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor systems, apparatuses or devices, or a combination of any of the above. More specific examples (non-exhaustive list) of readable storage media include: portable computer disks, hard disks, random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), erasable programmable read only memory (EPROM or Flash memory), static random access memory (SRAM), portable compact disk read only memory (CD-ROM), digital versatile disk (DVD), memory sticks, floppy disks, mechanically encoded devices, such as punch holes on which instructions are stored Card or in-groove raised structures, and any suitable combination of the above. Computer-readable storage media, as used herein, are not to be construed as transient signals per se, such as radio waves or other freely propagating electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic waves propagating through waveguides or other transmission media (eg, light pulses through fiber optic cables), or through electrical wires transmitted electrical signals.
这里所描述的计算机可读程序指令可以从计算机可读存储介质下载到各个计算/处理设备,或者通过网络、例如因特网、局域网、广域网和/或无线网下载到外部计算机或外部存储设备。网络可以包括铜传输电缆、光纤传输、无线传输、路由器、防火墙、交换机、网关计算机和/或边缘服务器。每个计算/处理设备中的网络适配卡或者网络接口从网络接收计算机可读程序指令,并转发该计算机可读程序指令,以供存储在各个计算/处理设备中的计算机可读存储介质中。The computer readable program instructions described herein may be downloaded to various computing/processing devices from a computer readable storage medium, or to an external computer or external storage device over a network such as the Internet, a local area network, a wide area network, and/or a wireless network. The network may include copper transmission cables, fiber optic transmission, wireless transmission, routers, firewalls, switches, gateway computers, and/or edge servers. A network adapter card or network interface in each computing/processing device receives computer-readable program instructions from a network and forwards the computer-readable program instructions for storage in a computer-readable storage medium in each computing/processing device .
这里参照根据本申请实施例的方法、装置(系统)和计算机程序产品的流程图和/或框图描述了本申请的各个方面。应当理解,流程图和/或框图的每个方框以及流程图和/或框图中各方框的组合,都可以由计算机可读程序指令实现。Aspects of the present application are described herein with reference to flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams of methods, apparatus (systems) and computer program products according to embodiments of the present application. It will be understood that each block of the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, and combinations of blocks in the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, can be implemented by computer readable program instructions.
这些计算机可读程序指令可以提供给通用计算机、专用计算机或其它可编程数据处理装置的处理器,从而生产出一种机器,使得这些指令在通过计算机或其它可编程数据处理装置的处理器执行时,产生了实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作的装置。也可以把这些计算机可读程序指令存储在计算机可读存储介质中,这些指令使得计算机、可编程数据处理装置和/或其他设备以特定方式工作,从而,存储有指令的计算机可读介质则包括一个制造品,其包括实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作的各个方面的指令。These computer readable program instructions may be provided to a processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to produce a machine that causes the instructions when executed by the processor of the computer or other programmable data processing apparatus , resulting in means for implementing the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowchart and/or block diagrams. These computer readable program instructions can also be stored in a computer readable storage medium, these instructions cause a computer, programmable data processing apparatus and/or other equipment to operate in a specific manner, so that the computer readable medium on which the instructions are stored includes An article of manufacture comprising instructions for implementing various aspects of the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowchart and/or block diagrams.
也可以把计算机可读程序指令加载到计算机、其它可编程数据处理装置、或其它设备上,使得在计算机、其它可编程数据处理装置或其它设备上执行一系列操作步骤,以产生计算机实现的过程,从而使得在计算机、其它可编程数据处理装置、或其它设备上执行的指令实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作。Computer readable program instructions can also be loaded onto a computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other equipment to cause a series of operational steps to be performed on the computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other equipment to produce a computer-implemented process , thereby causing instructions executing on a computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other device to implement the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowcharts and/or block diagrams.
本申请实施例还提供了一种电子设备。图5所示为本申请一实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图。如图所示,该电子设备500包括:一个或多个处理器501和存储器502;存储器502中存储有计算机可执行指令;处理器501,用于执行计算机可执行指令,以实现如上述任一实施例的胸外按压参数的确定方法中的步骤。The embodiments of the present application also provide an electronic device. FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in the figure, the electronic device 500 includes: one or more processors 501 and a memory 502; the memory 502 stores computer-executable instructions; the processor 501 is configured to execute the computer-executable instructions to implement any of the above Steps in the method for determining chest compression parameters of an embodiment.
处理器501可以是中央处理单元(CPU)或者具有数据处理能力和/或指令执行能力的其他形式的处理单元,并且可以控制电子设备中的其他组件以执行期望的功能。The processor 501 may be a central processing unit (CPU) or other form of processing unit having data processing capabilities and/or instruction execution capabilities, and may control other components in the electronic device to perform desired functions.
存储器502可以包括一个或多个计算机程序产品,计算机程序产品可以包括各种形式的计算机可读存储介质,例如易失性存储器和/或非易失性存储器。易失性存储器例如可以包括随机存取存储器(RAM)和/或高速缓冲存储器(cache)等。非易失性存储器例如可以包括只读存储器(ROM)、硬盘、闪存等。在计算机可读存储介质上可以存储一个或多个计算机程序指令,处理器1501可以运行程序指令,以实现上文的本申请的各个实施例的文本识别方法中的步骤以及/或者其他期望的功能。Memory 502 may include one or more computer program products, which may include various forms of computer-readable storage media, such as volatile memory and/or non-volatile memory. Volatile memory may include, for example, random access memory (RAM) and/or cache memory, among others. Non-volatile memory may include, for example, read only memory (ROM), hard disk, flash memory, and the like. One or more computer program instructions may be stored on the computer-readable storage medium, and the processor 1501 may execute the program instructions to implement the steps and/or other desired functions of the text recognition methods of the various embodiments of the present application above. .
在一个示例中,电子设备500还可以包括:输入装置和输出装置,这些组件通过总线系统和/或其他形式的连接机构(图中未示出)互连。In one example, the electronic device 500 may further include: input means and output means, these components are interconnected by a bus system and/or other forms of connection mechanisms (not shown in the figure).
此外,输入装置还可以包括例如键盘、鼠标、麦克风等等。输出装置可以向外部输出各种信息,例如可以包括例如显示器、扬声器、打印机、以及通信网络及其所连接的远程输出设备等等。In addition, the input device may also include, for example, a keyboard, a mouse, a microphone, and the like. The output device may output various information to the outside, and may include, for example, a display, a speaker, a printer, a communication network and a remote output device connected thereto, and the like.
当然,为了简化,图5中仅示出了该电子设备500中与本申请有关的组件中的一部分,省略了诸如总线、输入装置/输出接口等组件。除此之外,根据具体应用情况,电子设备500还可以包括任何其他适当的组件。Of course, for simplicity, only a part of the components in the electronic device 500 related to the present application are shown in FIG. 5 , and components such as a bus, an input device/output interface and the like are omitted. Besides, the electronic device 500 may also include any other appropriate components according to the specific application.
需要说明的是,本申请实施例提供的胸外按压参数的确定方法实施例、胸外按压参数的确定装置实施例、计算机可读存储介质实施例和电子设备实施例属于同一构思;各实施例所记载的技术方案中各技术特征之间,在不冲突的情况下,可以任意组合。It should be noted that the embodiments of the method for determining chest compression parameters, the embodiment of the device for determining chest compression parameters, the embodiments of the computer-readable storage medium, and the embodiments of the electronic device provided by the embodiments of the present application belong to the same concept; The technical features in the described technical solutions can be arbitrarily combined under the condition that there is no conflict.
应当理解,以上实施例均为示例性的,不用于包含权利要求所包含的所有可能的实施方式。在不脱离本公开的范围的情况下,还可以在以上实施例的基础上做出各种变形和改变。同样的,也可以对以上实施例的各个技术特征进行任意组合,以形成可能没有被明确描述的本发明的另外的实施例。因此,上述实施例仅表达了本发明的几种实施方式,不对本发明专利的保护范围进行限制。It should be understood that the above embodiments are all exemplary and are not intended to include all possible implementations contained in the claims. Various modifications and changes may also be made on the basis of the above embodiments without departing from the scope of the present disclosure. Likewise, various technical features of the above embodiments can also be arbitrarily combined to form additional embodiments of the present invention that may not be explicitly described. Therefore, the above embodiments only represent several embodiments of the present invention, and do not limit the protection scope of the patent of the present invention.
Claims (13)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210866363.8ACN115154259B (en) | 2022-07-22 | 2022-07-22 | Device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210866363.8ACN115154259B (en) | 2022-07-22 | 2022-07-22 | Device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115154259Atrue CN115154259A (en) | 2022-10-11 |
| CN115154259B CN115154259B (en) | 2025-06-24 |
Family
ID=83496940
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210866363.8AActiveCN115154259B (en) | 2022-07-22 | 2022-07-22 | Device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115154259B (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116312952A (en)* | 2023-05-10 | 2023-06-23 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Chest compression feedback method, device, readable storage medium and program product |
| CN118415871A (en)* | 2024-07-04 | 2024-08-02 | 浙江大学医学院附属第二医院 | CPR pressing device motor control method, device and CPR pressing device |
| CN120259980A (en)* | 2025-06-03 | 2025-07-04 | 福州大学附属省立医院 | A standardized monitoring method and system for cardiopulmonary resuscitation operation process |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102973402A (en)* | 2012-11-09 | 2013-03-20 | 中国人民解放军第三军医大学 | Method and auxiliary device of determining cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters during process of cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| CN104274172A (en)* | 2013-07-08 | 2015-01-14 | 深圳迈瑞生物医疗电子股份有限公司 | Monitoring method and system for external chest compression depth and defibrillator |
| CN106037769A (en)* | 2016-05-19 | 2016-10-26 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Method for sensing occurrence of fracture in cardio-pulmonary resuscitation process and compression apparatus |
| CN107625627A (en)* | 2017-09-07 | 2018-01-26 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院卫生装备研究所 | A kind of CPR accessory system |
| CN108205941A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-26 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of real-time detection method of thoracic cavity coefficient of elasticity and external chest compression reponse system |
| KR20190057555A (en)* | 2017-11-20 | 2019-05-29 | 강원대학교산학협력단 | System and Method for Monitoring Mechanical Impedance During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation |
| US20200000680A1 (en)* | 2018-06-29 | 2020-01-02 | Zoll Medical Corporation | Systems and Methods for Providing Resuscitation Guidance based on Physical Features of a Patient Measured During an Acute Care Event |
| CN113632175A (en)* | 2019-01-31 | 2021-11-09 | Zoll医疗公司 | System and method for determining compression depth and providing feedback during active compression decompression |
- 2022
- 2022-07-22CNCN202210866363.8Apatent/CN115154259B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102973402A (en)* | 2012-11-09 | 2013-03-20 | 中国人民解放军第三军医大学 | Method and auxiliary device of determining cardiopulmonary resuscitation quality parameters during process of cardiopulmonary resuscitation |
| CN104274172A (en)* | 2013-07-08 | 2015-01-14 | 深圳迈瑞生物医疗电子股份有限公司 | Monitoring method and system for external chest compression depth and defibrillator |
| CN106037769A (en)* | 2016-05-19 | 2016-10-26 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Method for sensing occurrence of fracture in cardio-pulmonary resuscitation process and compression apparatus |
| CN107625627A (en)* | 2017-09-07 | 2018-01-26 | 中国人民解放军军事医学科学院卫生装备研究所 | A kind of CPR accessory system |
| KR20190057555A (en)* | 2017-11-20 | 2019-05-29 | 강원대학교산학협력단 | System and Method for Monitoring Mechanical Impedance During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation |
| CN108205941A (en)* | 2018-01-04 | 2018-06-26 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | A kind of real-time detection method of thoracic cavity coefficient of elasticity and external chest compression reponse system |
| US20200000680A1 (en)* | 2018-06-29 | 2020-01-02 | Zoll Medical Corporation | Systems and Methods for Providing Resuscitation Guidance based on Physical Features of a Patient Measured During an Acute Care Event |
| CN113632175A (en)* | 2019-01-31 | 2021-11-09 | Zoll医疗公司 | System and method for determining compression depth and providing feedback during active compression decompression |
| US20220110827A1 (en)* | 2019-01-31 | 2022-04-14 | Zoll Medical Corporation | Systems and Methods for Determining Compression Depth and Providing Feedback During Active Compression Decompressions |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116312952A (en)* | 2023-05-10 | 2023-06-23 | 苏州尚领医疗科技有限公司 | Chest compression feedback method, device, readable storage medium and program product |
| CN118415871A (en)* | 2024-07-04 | 2024-08-02 | 浙江大学医学院附属第二医院 | CPR pressing device motor control method, device and CPR pressing device |
| CN120259980A (en)* | 2025-06-03 | 2025-07-04 | 福州大学附属省立医院 | A standardized monitoring method and system for cardiopulmonary resuscitation operation process |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115154259B (en) | 2025-06-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN115154259A (en) | Method and device for determining chest compression parameters, storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| US12220211B2 (en) | Processing impedance signals for breath detection | |
| US12310917B2 (en) | Assisting a CPR treatment | |
| EP3407781B1 (en) | Sensor-based detection of changes in health and ventilation thresholds | |
| US11672730B2 (en) | Chest compliance directed chest compressions | |
| CN108135485A (en) | Lung conditions are assessed by speech analysis | |
| EP2787746A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for improving the audibility of specific sounds to a user | |
| JP7369702B2 (en) | High frequency parapet oscillator | |
| WO2024016909A1 (en) | Chest compression feedback method and apparatus, storage medium, and electronic device | |
| US20220110827A1 (en) | Systems and Methods for Determining Compression Depth and Providing Feedback During Active Compression Decompressions | |
| US12226204B2 (en) | Body motion determination system and biological state monitoring system | |
| CN114983794B (en) | Risk feedback device for chest compression, storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| KR20190058289A (en) | Detecting respiratory rates in audio using an adaptive low-pass filter | |
| EP4278960A1 (en) | Non-invasive blood pressure measurement | |
| EP4534021A1 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, information processing system, and information processing program | |
| CN114098794A (en) | Method and device for detecting human health status | |
| Syryamkin et al. | A system for automated monitoring of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation procedure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |