CN115150110A - Method for access authentication, related device, equipment and readable storage medium - Google Patents
Method for access authentication, related device, equipment and readable storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115150110A CN115150110ACN202110339645.8ACN202110339645ACN115150110ACN 115150110 ACN115150110 ACN 115150110ACN 202110339645 ACN202110339645 ACN 202110339645ACN 115150110 ACN115150110 ACN 115150110A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- client
- authentication
- authentication server
- message
- key
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/08—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for authentication of entities
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/06—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for supporting key management in a packet data network
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/06—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols the encryption apparatus using shift registers or memories for block-wise or stream coding, e.g. DES systems or RC4; Hash functions; Pseudorandom sequence generators
- H04L9/0643—Hash functions, e.g. MD5, SHA, HMAC or f9 MAC
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0816—Key establishment, i.e. cryptographic processes or cryptographic protocols whereby a shared secret becomes available to two or more parties, for subsequent use
- H04L9/0838—Key agreement, i.e. key establishment technique in which a shared key is derived by parties as a function of information contributed by, or associated with, each of these
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0861—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0869—Generation of secret information including derivation or calculation of cryptographic keys or passwords involving random numbers or seeds
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/08—Key distribution or management, e.g. generation, sharing or updating, of cryptographic keys or passwords
- H04L9/0891—Revocation or update of secret information, e.g. encryption key update or rekeying
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及接入认证的领域,尤其涉及一种接入认证的方法、相关装置、设备以及计算机可读存储介质。The present invention relates to the field of access authentication, and in particular, to a method, related apparatus, equipment and computer-readable storage medium for access authentication.
背景技术Background technique
终端设备在接入网络时一般会进行一个接入认证,接入认证一般有两个目的:第一是验证双方的身份,身份验证的本质是证明双方拥有某个长期共享密钥;第二是双方协商出会话密钥,以便于以后的通信都使用会话密钥来对通信数据进行加密。The terminal device generally performs an access authentication when accessing the network. The access authentication generally has two purposes: the first is to verify the identities of the two parties. The essence of the authentication is to prove that the two parties have a long-term shared key; The two parties negotiate a session key, so that subsequent communications use the session key to encrypt communication data.
为了解决以太网内通信各方的认证和安全问题,安全协议工程师提出了802.1X协议,该协议作为局域网端口的一个普通接入机制在以太网中被广泛应用。因此,一般采用802.1X认证系统来进行接入互联网设备的认证。在802.1X认证系统中存在客户端、接入端以及认证服务器三个角色,为了实现客户端、接入端以及认证服务器之间认证信息的交换,802.1X认证系统通常采用可扩展认证协议(Extensible authentication protocol,EAP)来实现认证信息的封装和转发。在认证通过之前,802.1X认证系统只允许基于互联网的扩展认证协议(Extensible Authentication Protocol Over LAN,EAPOL)的数据通过设备的接入端端口,而接入端与认证服务器之间一般采用可扩展认证协议透传方式(EAP OverRADIUS,EAPOR)来实现EAP报文的透传,认证通过后,正常的数据可以顺利通过以太网端口,客户端和接入端之间的通信数据会用协商出来的会话密钥进行加密处理。In order to solve the authentication and security problems of all communication parties in the Ethernet, the security protocol engineer proposed the 802.1X protocol, which is widely used in Ethernet as a common access mechanism for LAN ports. Therefore, the 802.1X authentication system is generally used to authenticate devices connected to the Internet. In the 802.1X authentication system, there are three roles: the client, the access terminal and the authentication server. In order to realize the exchange of authentication information between the client, the access terminal and the authentication server, the 802.1X authentication system usually adopts the Extensible Authentication Protocol (Extensible Authentication Protocol). authentication protocol, EAP) to realize the encapsulation and forwarding of authentication information. Before the authentication is passed, the 802.1X authentication system only allows the data of the Internet-based Extensible Authentication Protocol Over LAN (EAPOL) to pass through the access port of the device, and the extensible authentication is generally used between the access end and the authentication server. The protocol transparent transmission mode (EAP OverRADIUS, EAPOR) is used to realize the transparent transmission of EAP packets. After the authentication is passed, the normal data can pass through the Ethernet port smoothly, and the communication data between the client and the access end will use the negotiated session. The key is encrypted.
目前在802.1X认证协议中采用的认证方案可以分为两类:一类为基于非对称密码的认证协议,比如EAP-TLS;另一类为基于对称密码的认证协议,比如EAP-AKA。随着接入认证技术的不断发展,如何解决基于对称密码体制的接入认证方案难以实现前向安全性的问题是技术人员关注的问题。The authentication schemes currently used in the 802.1X authentication protocol can be divided into two categories: one is an authentication protocol based on asymmetric ciphers, such as EAP-TLS; the other is an authentication protocol based on symmetric ciphers, such as EAP-AKA. With the continuous development of access authentication technology, how to solve the problem that the access authentication scheme based on the symmetric cryptosystem is difficult to achieve forward security is a problem that technicians pay attention to.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的方法,解决了基于纯对称密码的接入认证方案难以实现前向安全性的问题。The embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication method, which solves the problem that the access authentication scheme based on pure symmetric cipher is difficult to achieve forward security.
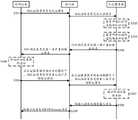
第一方面,本申请实施例提供一种接入认证的方法,包括:客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息;在所述认证服务器基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,所述客户端接收所述认证服务器发送的网络认证消息;在所述客户端基于所述网络认证消息验证所述认证服务器身份合法的情况下,所述客户端基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥;所述客户端删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数;其中,所述客户端存储有基于哈希函数更新后的第一密钥参数。这样,客户端和认证服务器每次基于更新前的长期密钥(更新前的第一密钥参数)协商出会话密钥后,会将更新前的长期密钥删除,由于哈希运算难以求逆,即使攻击者获取更新后的长期密钥也无法恢复更新前的长期密钥,进而无法获取历史协商的会话密钥,保证了会话密钥的前向安全性,从而无法解密客户端与其它网络设备历史通信数据,保证了数据安全。In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication method, including: a client sends a user authentication message to an authentication server; when the authentication server verifies that the identity of the client is legal based on the user authentication message , the client receives the network authentication message sent by the authentication server; when the client verifies that the identity of the authentication server is legal based on the network authentication message, the client is based on the random number of the client, The network authentication message and the first key parameter before the update of the client obtain the session key; the client deletes the first key parameter before the update; wherein, the client stores a hash-based The updated first key parameter of the function. In this way, each time the client and the authentication server negotiate the session key based on the long-term key before the update (the first key parameter before the update), they will delete the long-term key before the update, because the hash operation is difficult to invert. , even if the attacker obtains the updated long-term key, the long-term key before the update cannot be recovered, and thus cannot obtain the historically negotiated session key, which ensures the forward security of the session key, and thus cannot decrypt the client and other networks. The historical communication data of the device ensures data security.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述客户端删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数之前,包括:所述客户端根据公式Ic=Index+1,得到更新后的第一计数值;所述Ic为所述更新后的第一计数值,所述Index为更新前的第一计数值;第一计数值用于表征所述客户端的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数;所述客户端根据公式SIc=HASH(SIc-1),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数;所述SIc为所述客户端更新后的第一密钥参数,所述SIc-1为所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数。这样,客户端将第一计数值与第一密钥参数通过哈希函数的更新次数联系起来,有利于认证服务器在更新其第一密钥参数时以所述第一计数值为参考来确定其第一密钥参数需要进行哈希运算的次数,保证了认证服务器和客户端拥有的长期密钥的一致性(认证服务器和客户端的第一密钥参数相同),有利于提高客户端和认证服务器协商会话密钥的成功率。In a possible implementation manner, before the client deletes the first key parameter before the update, the method includes: the client obtains the updated first count value according to the formula Ic=Index+1; The Ic is the first count value after the update, and the Index is the first count value before the update; the first count value is used to represent the number of times that the first key parameter of the client is updated based on the hash function; The client obtains its updated first key parameter according to the formula SIc =HASH(SIc-1 ); the SIc is the updated first key parameter of the client, and the SIc- 1 is the first key parameter of the client before updating. In this way, the client associates the first count value with the number of updates of the first key parameter through the hash function, which is beneficial for the authentication server to use the first count value as a reference when updating its first key parameter. The number of times that the first key parameter needs to be hashed, which ensures the consistency of the long-term keys owned by the authentication server and the client (the first key parameters of the authentication server and the client are the same), which is beneficial to improve the performance of the client and the authentication server. The success rate of negotiating the session key.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述网络认证消息包括所述认证服务器的消息参数;所述客户端基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥,包括:所述客户端从所述认证服务器的消息参数中获取置位标识Re_sync;若所述Re_sync=1,所述客户端将第一计数值置零,并执行所述客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息的步骤;所述第一计数值用于表征所述客户端的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数;若所述Re_sync=0,所述客户端基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥。这样,在客户端计数器的计数能力达到其阈值(比如最大计数能力)以及第一密钥参数继续通过哈希函数更新的情况下,将第一计数值置0,有利于在计数器的计数能力范围内对第一密钥参数的更新次数进行记录,保证认证服务器和客户端的第一密钥参数相同,提高客户端与认证服务器会话密钥的精确性。In a possible implementation manner, the network authentication message includes a message parameter of the authentication server; the client is based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message, and the first value before the client is updated. Obtaining the session key from the key parameter includes: the client obtains the set identifier Re_sync from the message parameter of the authentication server; if the Re_sync=1, the client sets the first count value to zero, and executes the The client sends a user authentication message to the authentication server; the first count value is used to represent the number of times that the client's first key parameter is updated based on the hash function; if the Re_sync=0, the client The terminal obtains the session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message, and the first key parameter before the client is updated. In this way, when the counting capability of the client counter reaches its threshold (such as the maximum counting capability) and the first key parameter continues to be updated through the hash function, the first count value is set to 0, which is beneficial in the range of the counter's counting capability. The number of updates of the first key parameter is recorded internally to ensure that the first key parameter of the authentication server and the client is the same, and the accuracy of the session key between the client and the authentication server is improved.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息,包括:所述客户端基于所述客户端的身份标识、更新前的第一计数值以及所述客户端的随机数,得到所述客户端的消息参数;所述客户端基于所述客户端的消息参数和所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成所述客户端的消息认证码;所述客户端的消息认证码用于所述认证服务器验证所述客户端身份的合法性;所述客户端将用户认证消息发送给所述认证服务器;所述用户认证消息包括所述客户端的消息参数和所述客户端的消息认证码。这样,有利于认证服务器直接基于用户认证消息中客户端的消息认证码验证客户端的合法性,减小认证服务器的计算资源,从而提高认证服务器的工作性能。In a possible implementation manner, the client sends a user authentication message to the authentication server, including: the client is based on the identity of the client, the first count value before updating, and the random number of the client, Obtain the message parameter of the client; the client generates the message authentication code of the client based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client; the message authentication code of the client is used for the authentication The server verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the client; the client sends a user authentication message to the authentication server; the user authentication message includes the client's message parameters and the client's message authentication code. In this way, it is beneficial for the authentication server to verify the legitimacy of the client directly based on the message authentication code of the client in the user authentication message, thereby reducing the computing resources of the authentication server, thereby improving the working performance of the authentication server.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述网络认证消息包括所述认证服务器的消息参数;所述客户端基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥之前,包括:所述客户端基于所述认证服务器的消息参数、所述客户端的消息参数以及所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成第一消息认证码;所述客户端判断所述第一消息认证码与所述认证服务器的消息认证码是否一致;若判断为是,所述客户端判断所述认证服务器的身份合法;若判断为否,所述客户端判断所述认证服务器的身份非法,并终止所述客户端与所述认证服务器之间的接入认证。这样,客户端通过其生成的第一消息认证码来验证认证服务器身份的合法性,相较于使用数字证书验证身份合法性的方式,节约了大量的传输开销和计算开销,从而提高了客户端的工作性能。In a possible implementation manner, the network authentication message includes a message parameter of the authentication server; the client is based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message, and the first value before the client is updated. Before the key parameter obtains the session key, it includes: the client generates a first message authentication code based on the message parameter of the authentication server, the message parameter of the client, and the second key parameter of the client; the client generates a first message authentication code; The terminal determines whether the first message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the authentication server; if it is determined to be yes, the client determines that the identity of the authentication server is legal; if it is determined to be no, the client determines that the The identity of the authentication server is illegal, and the access authentication between the client and the authentication server is terminated. In this way, the client verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the authentication server through the first message authentication code generated by the client, which saves a lot of transmission overhead and computing overhead compared with the method of using the digital certificate to verify the legitimacy of the identity, thereby improving the client's performance. work performance.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的方法,包括:认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息;在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,所述认证服务器基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥;所述第三密钥参数与所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数相同;所述认证服务器删除其更新前的第一密钥参数;其中,所述认证服务器存储有基于哈希函数更新后的第一密钥参数;所述认证服务器向接入端发送网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥;所述网络认证消息用于所述客户端验证所述认证服务器的身份是否合法以及生成会话密钥。这样,这样,客户端和认证服务器每次基于更新前的长期密钥(更新前的第一密钥参数)协商出会话密钥后,会将更新前的长期密钥删除,由于哈希运算难以求逆,即使攻击者获取更新后的长期密钥也无法恢复更新前的长期密钥,进而无法获取历史协商的会话密钥,从而无法解密客户端与其它网络设备历史通信数据,保证了数据安全的前向性。In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication method, including: an authentication server receiving a user authentication message sent by a client; and in the case of verifying that the identity of the client is legal based on the user authentication message, the The authentication server obtains the session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message; the third key parameter is the same as the first key parameter before the client is updated; The authentication server deletes the first key parameter before the update; wherein, the authentication server stores the updated first key parameter based on the hash function; the authentication server sends the network authentication message and encrypted The latter session key; the network authentication message is used by the client to verify whether the identity of the authentication server is legal and to generate a session key. In this way, each time the client and the authentication server negotiate the session key based on the long-term key before the update (the first key parameter before the update), they will delete the long-term key before the update. Inverse, even if the attacker obtains the updated long-term key, he cannot recover the long-term key before the update, and thus cannot obtain the historically negotiated session key, thereby unable to decrypt the historical communication data between the client and other network devices, ensuring data security. forwardness.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述用户认证消息包括所述客户端的消息参数;所述认证服务器基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥,包括:所述认证服务器从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;第一计数值用于表征所述客户端的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数;若所述更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,所述认证服务器将第二计数值置0,并执行所述认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息的步骤;若所述更新前的第一计数值小于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,所述认证服务器基于所述第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥。这样,在认证服务器计数器的计数能力达到其阈值(比如最大计数能力)以及第一密钥参数继续通过哈希函数更新的情况下,将第二计数值置0,有利于在计数器的计数能力范围内对第一密钥参数的更新次数进行记录,保证认证服务器和客户端的第一密钥参数相同,提高客户端与认证服务器会话密钥的精确性。In a possible implementation manner, the user authentication message includes a message parameter of the client; the authentication server obtains the session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server, and the user authentication message , including: the authentication server obtains the first count value before updating from the message parameter of the client; the first count value is used to represent the number of times that the first key parameter of the client is updated based on the hash function; The first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server, the authentication server sets the second count value to 0, and executes the steps of the authentication server receiving the user authentication message sent by the client; if the The first count value before the update is smaller than the count threshold of the authentication server, and the authentication server obtains the session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server, and the user authentication message. In this way, when the counting capability of the authentication server counter reaches its threshold (such as the maximum counting capability) and the first key parameter continues to be updated through the hash function, the second count value is set to 0, which is beneficial in the range of the counting capability of the counter. The number of updates of the first key parameter is recorded internally to ensure that the first key parameter of the authentication server and the client is the same, and the accuracy of the session key between the client and the authentication server is improved.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述用户认证消息包括所述客户端的消息参数;认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息之后,包括:所述认证服务器从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;第一计数值用于表征所述客户端的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数;所述认证服务器判断所述更新前的第一计数值是否大于或等于更新前的第二计数值;第二计数值用于表征所述认证服务器的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数;若判断为否,所述认证服务器终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证;若判断为是,所述认证服务器基于所述客户端的消息参数以及所述认证服务器的第二密钥参数生成第二消息认证码;所述认证服务器判断所述第二消息认证码与所述客户端的消息认证码是否一致;若判断为是,所述认证服务器判断所述客户端的身份合法;若判断为否,所述认证服务器判断所述客户端的身份非法,并终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证。这样,认证服务器通过判断更新前的第一计数值是否大于或小于更新前的第二计数值以及第二消息认证码来验证客户端身份的合法性,相较于使用数字证书验证身份合法性的方式,节约了大量的传输开销和计算开销,从而提高了认证服务器的工作性能。In a possible implementation manner, the user authentication message includes a message parameter of the client; after the authentication server receives the user authentication message sent by the client, the method includes: the authentication server obtains an update from the message parameter of the client The first count value before the update; the first count value is used to represent the number of times that the first key parameter of the client is updated based on the hash function; the authentication server determines whether the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the update The second count value is used to represent the number of times that the first key parameter of the authentication server is updated based on the hash function; if the judgment is no, the authentication server terminates the authentication server and the client access authentication between terminals; if it is determined to be yes, the authentication server generates a second message authentication code based on the message parameters of the client and the second key parameter of the authentication server; the authentication server determines that the first message authentication code is Whether the message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the client; if the judgment is yes, the authentication server judges that the identity of the client is legal; if the judgment is no, the authentication server judges that the identity of the client is illegal, and Terminate the access authentication between the authentication server and the client. In this way, the authentication server verifies the legitimacy of the client's identity by judging whether the first count value before the update is greater or less than the second count value before the update and the second message authentication code. In this way, a lot of transmission overhead and calculation overhead are saved, thereby improving the working performance of the authentication server.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述认证服务器基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥之前,包括:所述认证服务器根据公式SIndex=HASH(Index-Is)(SIs)得到第三密钥参数;所述SIndex为所述第三密钥参数,所述Index为更新前的第一计数值,所述SIs为所述认证服务器更新前的第一密钥参数;所述认证服务器根据公式Is=Index+1,得到更新后的第二计数值;所述Is为所述更新后的第二计数值;所述认证服务器根据公式SIs=HASH(SIndex),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数;所述SIs为认证服务器更新后的第一密钥参数,所述SIs与所述客户端更新后的第一密钥参数SIc相同。这样,认证服务器通过计算第三密钥参数,使得认证服务器可以基于第三密钥参数通过哈希函数更新其第一密钥参数,解决了认证服务器更新前的第一密钥参数与客户端更新前的第一密钥参数不一致的问题,从而保证了认证服务器计算的会话密钥和客户端计算的会话密钥相同,提高了客户端接入认证的成功率。In a possible implementation manner, before the authentication server obtains the session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message, the method includes: the authentication server obtains the session key according to the formula SIndex = HASH(Index-Is) (SIs ) obtains the third key parameter; the SIndex is the third key parameter, the Index is the first count value before the update, and the SIs is the authentication server the first key parameter before the update; the authentication server obtains the updated second count value according to the formula Is=Index+1; the Is is the updated second count value; the authentication server obtains the updated second count value according to the formula SIs =HASH(SIndex ), obtain the updated first key parameter; the SIs is the updated first key parameter of the authentication server, and the SIs and the updated first key parameter of the client The key parameter SIc is the same. In this way, the authentication server calculates the third key parameter, so that the authentication server can update its first key parameter through the hash function based on the third key parameter, which solves the problem between the first key parameter before the authentication server is updated and the client update Therefore, it is ensured that the session key calculated by the authentication server and the session key calculated by the client are the same, and the success rate of the client access authentication is improved.
第三方面,本申请实施例提供一种接入认证的方法,包括:接入端接收认证服务器发送的网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥;所述网络认证消息用于客户端验证所述认证服务器的身份是否合法以及生成会话密钥;所述接入端将所述加密后的会话密钥进行解密,得到解密后的会话密钥;所述接入端将所述网络认证消息发送给所述客户端。这样,接入端拥有了基于更新前的第一密钥参数、客户端的随机数以及认证服务器的随机数生成的会话密钥;由于第一密钥参数会基于哈希函数更新,且哈希函数不可求逆;因此,即使攻击者获取更新后的长期密钥也无法恢复更新前的长期密钥,进而无法获取历史协商的会话密钥,保证了会话密钥的前向安全性,从而无法解密客户端与其它网络设备历史通信数据,保证了数据安全。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication method, including: an access terminal receives a network authentication message and an encrypted session key sent by an authentication server; the network authentication message is used by the client to verify the Verifying whether the identity of the server is legal and generating a session key; the access terminal decrypts the encrypted session key to obtain the decrypted session key; the access terminal sends the network authentication message to the client. In this way, the access terminal has the session key generated based on the first key parameter before the update, the random number of the client and the random number of the authentication server; since the first key parameter will be updated based on the hash function, and the hash function It is irreversible; therefore, even if the attacker obtains the updated long-term key, he cannot recover the long-term key before the update, and thus cannot obtain the historically negotiated session key, which ensures the forward security of the session key, so that it cannot be decrypted. Historical communication data between the client and other network devices ensures data security.
第四方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的装置,包括:In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an apparatus for access authentication, including:
认证消息发送单元,用于向认证服务器发送用户认证消息;an authentication message sending unit, configured to send a user authentication message to the authentication server;
认证消息接收单元,用于在所述认证服务器基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,接收所述认证服务器发送的网络认证消息;an authentication message receiving unit, configured to receive a network authentication message sent by the authentication server when the authentication server verifies that the identity of the client is legal based on the user authentication message;
会话密钥生成单元,用于基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥;a session key generation unit, configured to obtain a session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the client is updated;
删除单元,用于删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数。A deletion unit, configured to delete the first key parameter before the update.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus for access authentication further includes:
第一更新单元,用于根据公式Ic=Index+1,得到更新后的第一计数值;The first update unit is used to obtain the updated first count value according to the formula Ic=Index+1;
第二更新单元,用于根据公式SIc=HASH(SIc-1),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。The second updating unit is configured to obtain the updated first key parameter according to the formula SIc =HASH(SIc-1 ).
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述会话密钥生成单元,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the session key generation unit includes:
标识获取单元,用于从所述认证服务器的消息参数中获取置位标识Re_sync;an identification obtaining unit, used for obtaining the set identification Re_sync from the message parameter of the authentication server;
置零单元,用于在所述Re_sync=1的情况下,将第一计数值置零,并执行所述客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息的步骤;a zero-setting unit, configured to set the first count value to zero under the condition of Re_sync=1, and execute the step of sending a user authentication message from the client to the authentication server;
生成单元,用于在所述Re_sync=0的情况下,基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥。A generating unit, configured to obtain a session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the client is updated in the case of the Re_sync=0.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述认证消息发送单元,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the authentication message sending unit includes:
消息参数生成单元,用于基于所述客户端的身份标识、更新前的第一计数值以及所述客户端的随机数,得到所述客户端的消息参数;a message parameter generating unit, configured to obtain the message parameter of the client based on the identity of the client, the first count value before updating and the random number of the client;
第一认证码生成单元,用于基于所述客户端的消息参数和所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成所述客户端的消息认证码;a first authentication code generating unit, configured to generate a message authentication code of the client based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client;
发送单元,用于将用户认证消息发送给所述认证服务器。A sending unit, configured to send a user authentication message to the authentication server.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus for access authentication further includes:
第二认证码生成单元,用于所述会话密钥生成单元基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥之前,基于所述认证服务器的消息参数、所述客户端的消息参数以及所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成第一消息认证码;The second authentication code generation unit is used for the session key generation unit to obtain the session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the update of the client, based on the generating the first message authentication code with the message parameter of the authentication server, the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client;
判断单元,用于判断所述第一消息认证码与所述认证服务器的消息认证码是否一致;a judgment unit, configured to judge whether the first message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the authentication server;
终止单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为否的情况下,终止所述客户端与所述认证服务器之间的接入认证。A terminating unit, configured to terminate the access authentication between the client and the authentication server when the judgment unit judges no.
第五方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的装置,包括:In a fifth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an apparatus for access authentication, including:
认证消息接收单元,用于接收客户端发送的用户认证消息;an authentication message receiving unit, configured to receive a user authentication message sent by the client;
会话密钥生成单元,用于在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥;a session key generation unit, configured to obtain a session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message under the condition that the identity of the client is valid based on the user authentication message ;
删除单元,用于删除其更新前的第一密钥参数;a deletion unit, used to delete the first key parameter before the update;
发送单元,用于向接入端发送网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥。The sending unit is used for sending the network authentication message and the encrypted session key to the access end.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述会话密钥生成单元,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the session key generation unit includes:
第一获取单元,用于从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;a first obtaining unit, configured to obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
置零单元,用于若所述更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,将第二计数值置0;a zero setting unit, configured to set the second count value to 0 if the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server;
执行单元,用于执行所述认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息的步骤;an execution unit, configured to execute the step of the authentication server receiving the user authentication message sent by the client;
第一生成单元,用于若所述更新前的第一计数值小于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,基于所述第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥。a first generating unit, configured to obtain a session based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message if the first count value before the update is less than the count threshold of the authentication server key.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus for access authentication further includes:
第二获取单元,用于从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;a second obtaining unit, configured to obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
第一判断单元,用于判断所述更新前的第一计数值是否大于或等于更新前的第二计数值;a first judging unit for judging whether the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the second count value before the update;
终止单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为否后,终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证;a terminating unit, configured to terminate the access authentication between the authentication server and the client after the judging unit judges no;
第二生成单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为是后,基于所述客户端的消息参数以及所述认证服务器的第二密钥参数生成第二消息认证码;a second generating unit, configured to generate a second message authentication code based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the authentication server after the judgment unit judges that it is yes;
第二判断单元,用于判断所述第二消息认证码与所述客户端的消息认证码是否一致。A second judging unit, configured to judge whether the second message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the client.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus for access authentication further includes:
计算单元,用于根据公式SIndex=HASH(Index-Is)(SIs)得到第三密钥参数;a calculation unit, for obtaining the third key parameter according to the formula SIndex =HASH(Index-Is) (SIs );
第一更新单元,用于根据公式Is=Index+1,得到更新后的第二计数值;The first update unit is used to obtain the updated second count value according to the formula Is=Index+1;
第二更新单元,用于根据公式SIs=HASH(SIndex),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。The second updating unit is configured to obtain the updated first key parameter according to the formulaSis =HASH(SIndex ).
第六方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的装置,包括:In a sixth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an apparatus for access authentication, including:
接收单元,用于接收认证服务器发送的网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥;a receiving unit, configured to receive the network authentication message and the encrypted session key sent by the authentication server;
解密单元,用于将所述加密后的会话密钥进行解密,得到解密后的会话密钥;a decryption unit for decrypting the encrypted session key to obtain the decrypted session key;
发送单元,用于将所述网络认证消息发送给所述客户端。A sending unit, configured to send the network authentication message to the client.
第七方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的设备,包括存储器和处理器;In a seventh aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication device, including a memory and a processor;
其中,所述存储器用于存储程序代码,所述处理器用于调用所述存储器存储的程序代码,执行上述第一方面及其各种可能的实现方式中接入认证的方法。Wherein, the memory is used for storing program code, and the processor is used for calling the program code stored in the memory to execute the access authentication method in the first aspect and various possible implementation manners thereof.
第八方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的设备,包括存储器和处理器;In an eighth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication device, including a memory and a processor;
其中,所述存储器用于存储程序代码,所述处理器用于调用所述存储器存储的程序代码,执行上述第二方面及其各种可能的实现方式中接入认证的方法。Wherein, the memory is used for storing program code, and the processor is used for calling the program code stored in the memory to execute the access authentication method in the second aspect and various possible implementation manners thereof.
第九方面,本申请实施例提供了一种接入认证的设备,包括存储器和处理器;In a ninth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an access authentication device, including a memory and a processor;
其中,所述存储器用于存储程序代码,所述处理器用于调用所述存储器存储的程序代码,执行上述第三方面及其各种可能的实现方式中接入认证的方法。Wherein, the memory is used for storing program code, and the processor is used for calling the program code stored in the memory to execute the access authentication method in the third aspect and various possible implementation manners thereof.
第十方面,本申请实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时,实现上述第一方面至第三方面任一方面及其各种可能的实现方式中接入认证的方法。In a tenth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, where the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, implements any one of the first to third aspects above Methods of access authentication in aspects and various possible implementations thereof.
第十一方面,本申请实施例提供了一种计算机程序,该计算机程序包括指令,当所述计算机程序被计算机执行时,使得客户端可以执行上述第一方面及其各种可能实现的方式中第客户端所执行的流程、或认证服务器可以执行上述第二方面及其各种可能实现的方式中认证服务器所执行的流程、或接入端可以执行上述第三方面及其各种可能的实现方式中接入端所执行的流程。In an eleventh aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer program, the computer program including instructions, when the computer program is executed by a computer, enables a client to execute the above-mentioned first aspect and various possible implementation manners thereof The process performed by the first client, or the authentication server may perform the process performed by the authentication server in the second aspect and its various possible implementations, or the access terminal may perform the third aspect and its various possible implementations. The process performed by the access end in the mode.
第十二方面,本申请实施例提供了一种芯片系统,该芯片系统包括处理器,用于支持客户端实现第一方面及其各种可能方式中的方法所涉及的功能、或认证服务器实现第二方面及其各种可能方式中的方法所涉及的功能、或接入端实现上述第三方面及其各种可能的实现方式中的方法所涉及的功能。In a twelfth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a chip system, where the chip system includes a processor for supporting a client to implement the functions involved in the methods in the first aspect and its various possible manners, or an authentication server to implement The functions involved in the method in the second aspect and its various possible manners, or the access terminal implements the functions involved in the method in the third aspect and its various possible implementation manners.
在一种可能的设计中,所述芯片系统还包括存储器,所述存储器用于保存客户端或认证服务器或接入端必要的程序指令和数据。该芯片系统,可以由芯片构成,也可以包含芯片和其它分立器件。In a possible design, the chip system further includes a memory, and the memory is used for storing necessary program instructions and data of the client or the authentication server or the access end. The chip system may be composed of chips, or may include chips and other discrete devices.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面对本申请实施例用到的附图进行介绍。The accompanying drawings used in the embodiments of the present application will be introduced below.
图1是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证场景示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an access authentication scenario provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2是本申请实施例提供的一种基于非对称密码体制的接入认证方法流程图;2 is a flowchart of an access authentication method based on an asymmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3是本申请实施例提供的一种基于对称密码体制的接入认证的方法流程图;3 is a flowchart of a method for access authentication based on a symmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图4是本申请实施例提供的另一种基于对称密码体制的接入认证的方法流程图;4 is a flowchart of another method for access authentication based on a symmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图5是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证系统计数器重置机制的流程图;FIG. 5 is a flowchart of an access authentication system counter reset mechanism provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图6是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图;6 is a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for access authentication provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图7是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图;7 is a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for access authentication provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图8是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for access authentication provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图9是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图10是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图;FIG. 10 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图11是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图。FIG. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合本申请实施例中的附图,对本申请实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述。显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本申请一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。在本文中提及“实施例”意味着,结合实施例描述的特定特征、结构或者特性可以包含在本实施例申请的至少一个实施例中。在说明书中的各个位置出现该短语并不一定均是相同的实施例,也不是与其它实施例互斥的独立的或是备选的实施例。本领域技术人员可以显式地和隐式地理解的是,本文所描述的实施例可以与其它实施例相结合。基于本申请中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本申请保护的范围。The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present application. Obviously, the described embodiments are only a part of the embodiments of the present application, but not all of the embodiments. Reference herein to an "embodiment" means that a particular feature, structure, or characteristic described in connection with the embodiment may be included in at least one embodiment of the present embodiment application. The appearances of this phrase in various places in the specification are not necessarily all referring to the same embodiment, nor are they separate or alternative embodiments that are mutually exclusive with other embodiments. Those skilled in the art will understand, both explicitly and implicitly, that the embodiments described herein may be combined with other embodiments. Based on the embodiments in the present application, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present application.
本申请的说明书和权利要求书及所述附图中术语“第一”、“第二”、“第三”等是区别于不同的对象,而不是用于描述特定顺序。此外,术语“包括”和“具有”以及它们的任何变形,意图在于覆盖不排他的包含。例如,包含了一系列步骤或单元,或者可选地,还包括没有列出的步骤或单元,或者可选地还包括这些过程、方法、产品或设备固有的其它步骤或单元。The terms "first", "second", "third", etc. in the description and claims of the present application and the drawings are used to distinguish different objects, and are not used to describe a specific order. Furthermore, the terms "comprising" and "having", and any variations thereof, are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion. For example, a series of steps or units are included, or optionally, steps or units not listed, or optionally other steps or units inherent to the process, method, product, or apparatus are included.
附图中仅示出了与本申请相关的部分而非全部内容。在更加详细地讨论示例性实施例之前,应当提到的是,一些示例性实施例被描述成作为流程图描绘的处理或方法。虽然流程图将各项操作(或步骤)描述成顺序的处理,但是其中的许多操作可以并行地、并发地或者同时实施。此外,各项操作的顺序可以被重新安排。当其操作完成时所述处理可以被终止,但是还可以具有未包括在附图中的附加步骤。所述处理可以对应于方法、函数、规程、子例程、子程序等等。The drawings show only some but not all of the content related to the present application. Before discussing the exemplary embodiments in greater detail, it should be mentioned that some of the exemplary embodiments are described as processes or methods depicted as flowcharts. Although a flowchart depicts various operations (or steps) as a sequential process, many of the operations may be performed in parallel, concurrently, or concurrently. Additionally, the order of operations can be rearranged. The process may be terminated when its operation is complete, but may also have additional steps not included in the figures. The processes may correspond to methods, functions, procedures, subroutines, subroutines, and the like.
在本说明书中使用的术语“部件”、“模块”、“系统”、“单元”等用于表示计算机相关的实体、硬件、固件、硬件和软件的组合、软件或执行中的软件。例如,单元可以是但不限于在处理器上运行的进程、处理器、对象、可执行文件、执行线程、程序和/或分布在两个或多个计算机之间。此外,这些单元可从在上面存储有各种数据结构的各种计算机可读介质执行。单元可例如根据具有一个或多个数据分组(例如来自与本地系统、分布式系统和/或网络间的另一单元交互的第二单元数据。例如,通过信号与其它系统交互的互联网)的信号通过本地和/或远程进程来通信。The terms "component," "module," "system," "unit," etc. used in this specification are used to refer to a computer-related entity, hardware, firmware, a combination of hardware and software, software, or software in execution. For example, an element may be, but is not limited to, a process running on a processor, a processor, an object, an executable, a thread of execution, a program, and/or distributed between two or more computers. In addition, these units can execute from various computer readable media having various data structures stored thereon. A unit may, for example, be based on a signal with one or more data packets (eg, data from a second unit interacting with another unit between local systems, distributed systems, and/or networks. For example, the Internet interacting with other systems via signals) Communicate through local and/or remote processes.
本申请实施例中的客户端可以为终端设备等能够连接互联网或其它LAN资源的电子设备、服务器、以太网交换机、接入点以及网络访问服务器等设备;认证服务器促进试图访问网络的实体认证的网络设备;接入端可以为具有连接客户端与认证服务器功能的网络设备。The client in this embodiment of the present application may be an electronic device such as a terminal device that can connect to the Internet or other LAN resources, a server, an Ethernet switch, an access point, a network access server, and other devices; the authentication server facilitates the authentication of entities trying to access the network. Network device; the access end can be a network device with the function of connecting the client and the authentication server.
请参见图1,图1是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证场景示意图;在图1所示的接入认证场景中,包括客户端100、接入端200、认证服务器300以及互联网400。在客户端100接入互联网400之前,要向认证服务器进行认证。客户端100和认证服务器300之间通过EAP报文传递认证消息,并通过接入端200将EAP报文透传给对方,并协商出会话密钥;最后,再由认证服务器300将所述会话密钥发送给接入端200,客户端100的接入认证完毕。Please refer to FIG. 1, which is a schematic diagram of an access authentication scenario provided by an embodiment of the present application; the access authentication scenario shown in FIG. 1 includes a client 100, an access terminal 200, an authentication server 300, and an Internet 400 . Before the client 100 accesses the Internet 400, it needs to authenticate to the authentication server. The authentication message is transmitted between the client 100 and the authentication server 300 through the EAP packet, and the EAP packet is transparently transmitted to the other party through the access terminal 200, and a session key is negotiated; finally, the authentication server 300 transmits the session key. The key is sent to the access terminal 200, and the access authentication of the client terminal 100 is completed.
上述图1实施例中客户端100的接入认证主要有两种方案,一种是非对称密码的认证方案,另外一种是对称密码的认证方案。对于对称密码的接入认证方案,本申请实施例结合图2进行具体说明。请参见图2,图2是本申请实施例提供的一种基于非对称密码体制的接入认证方法流程图。基于非对称密码的认证方案通常基于数字证书体制。在客户端与服务器的通信模式下,服务器需要有一个权威方发放的数字证书,客户端需要拥有能够验证该数字证书合法性的根证书。由于客户端和认证服务器双方都拥有共同的信任锚点,因此二者可以进行单向接入认证或者双向接入认证。在某些场景下,例如开放Web访问,通常执行单向接入认证,即:客户端需要验证服务器身份的合法性;在另一些场景下,例如接入企业网场景,通常需要执行双向接入认证,即:服务器也需要验证客户端是否为一个合法的用户客户端,通常采用EAP-TLS来进行设备的接入认证。本申请实施例以客户端为终端设备进行接入认证为例,进行说明。在本实施例中,终端设备、认证服务器以及接入端三者之间认证信息的交互都是通过诸如EAP等数据包发送的,终端设备与认证服务器之间认证信息的传输都是通过接入端进行透传的,且数据包在认证服务器与接入端之间、接入端与终端设备之间的传输都有诸如EAPOL、EAPOR等传输协议支持,本实施例仅做举例说明,不做限制。下面,结合图2对终端设备进行接入认证的具体流程进行展开说明:There are mainly two schemes for the access authentication of the client 100 in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 1 , one is an authentication scheme of asymmetric encryption, and the other is an authentication scheme of symmetric encryption. For the access authentication scheme of the symmetric cipher, the embodiment of the present application will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 2 . Referring to FIG. 2, FIG. 2 is a flowchart of an access authentication method based on an asymmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application. Authentication schemes based on asymmetric cryptography are usually based on digital certificate systems. In the communication mode between the client and the server, the server needs to have a digital certificate issued by an authoritative party, and the client needs to have a root certificate that can verify the validity of the digital certificate. Since both the client and the authentication server have a common trust anchor, they can perform one-way access authentication or two-way access authentication. In some scenarios, such as open web access, one-way access authentication is usually performed, that is, the client needs to verify the legitimacy of the server's identity; in other scenarios, such as access to an enterprise network, two-way access is usually required. Authentication, that is, the server also needs to verify whether the client is a legitimate user client, usually using EAP-TLS for device access authentication. The embodiments of the present application are described by taking the client performing access authentication as a terminal device as an example. In this embodiment, the interaction of authentication information between the terminal device, the authentication server, and the access terminal is all sent through data packets such as EAP, and the transmission of authentication information between the terminal device and the authentication server is through the access The data packets are transparently transmitted between the authentication server and the access terminal, and the transmission between the access terminal and the terminal device is supported by transmission protocols such as EAPOL and EAPOR. This embodiment is only for illustration, not for limit. Below, in conjunction with Fig. 2, the specific process that terminal equipment performs access authentication will be described:
步骤S201:终端设备向认证服务器发送认证请求。Step S201: The terminal device sends an authentication request to the authentication server.
具体地,所述认证请求包括终端设备可以实现的算法列表以及客户端随机数(Client Random Value);其中,Client Random Value用于认证服务器计算主密钥(MasterKey,MK)。示例性的,所述认证请求可以为终端设备在TLS协议下的客户端问候消息(Client-Hello消息),本申请实施例不做限制。示例性的,终端设备将所述认证请求封装在EAP数据包中进行传输,终端设备首先将所述EAP数据包发送给接入端,再由接入端将所述EAP数据包透传给认证服务器;对于终端设备将认证请求封装在数据包中使用的协议可以为EAP协议也可以为其它协议,本申请实施例仅做举例说明,不做限制。示例性的,终端设备将该EAP数据包发送给接入端可以基于EAPOL协议,也可以基于其它协议,本申请实施例不做限制;接入端将该EAP数据包透传给认证服务器可以基于EAPOR协议,也可以基于其他通信协议,本申请实施例不做限制。Specifically, the authentication request includes a list of algorithms that can be implemented by the terminal device and a client random value (Client Random Value); wherein, the Client Random Value is used for the authentication server to calculate a master key (MasterKey, MK). Exemplarily, the authentication request may be a client hello message (Client-Hello message) of the terminal device under the TLS protocol, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. Exemplarily, the terminal device encapsulates the authentication request in an EAP data packet for transmission, the terminal device first sends the EAP data packet to the access end, and then the access end transparently transmits the EAP data packet to the authentication The server; the protocol used by the terminal device to encapsulate the authentication request in the data packet may be the EAP protocol or other protocols, and the embodiments of this application are only illustrative and do not limit it. Exemplarily, the terminal device may send the EAP data packet to the access end based on the EAPOL protocol, or may be based on other protocols, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application; the access end transparently transmits the EAP data packet to the authentication server may be based on The EAPOR protocol may also be based on other communication protocols, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
步骤S202:认证服务器向终端设备发送响应消息。Step S202: The authentication server sends a response message to the terminal device.
具体地,所述响应消息包括认证服务器的数字证书(Server-Certificate)、服务器问候消息(Server-Hello)、服务端密钥交换协议(Server Key-Exchange)以及认证服务器随机数(SreverRandom Value)。其中,Server-Certificate用于终端设备验证该认证服务器的身份是否合法;Server-Hello基于所述认证请求中终端设备可实现的算法列表得到的,用于指示终端设备在此次接入认证中所需要的算法;Server Key-Exchange包括认证服务器的密钥参数ga,所述密钥参数ga用于认证服务器和终端设备推导出预主密钥(PMK);Server Random Value用于认证服务器计算主密钥(Master Key,MK)。Specifically, the response message includes a digital certificate (Server-Certificate) of the authentication server, a server hello message (Server-Hello), a server key exchange protocol (Server Key-Exchange) and an authentication server random number (SreverRandom Value). Among them, Server-Certificate is used by the terminal device to verify whether the identity of the authentication server is legal; Server-Hello is obtained based on the list of algorithms that the terminal device can implement in the authentication request, and is used to indicate the terminal device in this access authentication. The required algorithm; Server Key-Exchange includes the key parameterga of the authentication server, and the key parameterga is used for the authentication server and the terminal device to derive the pre-master key (PMK); Server Random Value is used for the authentication server to calculate Master key (Master Key, MK).
步骤S203:终端设备校验认证服务器的数字证书。Step S203: The terminal device verifies the digital certificate of the authentication server.
具体地,终端设备通过验证Server-Certificate来确定认证服务器身份的合法性,若认证服务器的身份不合法,终端设备则终止此次认证。本申请实施例以终端设备和认证服务器进行双向身份验证为例进行说明,在双向验证情况下,认证服务器需要发送数字证书Server-Certificate给客户端,客户端需要发送自己的数字证书Client-Certificate给认证服务器。每一个Certificate含有两部分内容,一部分是权威方对蕴含身份信息的“签名公钥”的签名,另一部分是签名公钥所有者拿着对应的“签名密钥”对特定消息的签名。因此可以证明自己的签名公钥是合法的以及自己拥有合法签名公钥对应的签名密钥,从而可以证明自己的身份是合法的。数字证书是由证书授权中心(CertificateAuthority,CA)颁发的,认证服务器将其产生密钥对中的公共密钥(公钥)以及部分身份信息传送给CA,CA在核实认证服务器的身份等必要操作后向认证服务器发送一个数字证书,所述数字证书包含认证服务器的部分身份信息、公钥信息以及CA的签名等信息。终端设备在本机对应的根证书对该数字证书进行对比验证,对比一致,则说明认证服务器的身份合法。示例性的,终端设备将根证书与数字证书进行对比认证可以为终端设备验证根证书中的公钥和数字证书中的公钥是否一致,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做任何限制。Specifically, the terminal device determines the validity of the identity of the authentication server by verifying the Server-Certificate, and if the identity of the authentication server is not legal, the terminal device terminates this authentication. The embodiment of this application takes the two-way authentication between the terminal device and the authentication server as an example for description. In the case of two-way authentication, the authentication server needs to send the digital certificate Server-Certificate to the client, and the client needs to send its own digital certificate Client-Certificate to the client. Authentication server. Each certificate contains two parts, one part is the signature of the authoritative party on the "signature public key" containing the identity information, and the other part is the signature of the public key owner holding the corresponding "signature key" to a specific message. Therefore, you can prove that your public key for signature is legal and that you have the signature key corresponding to the public key for legal signature, so you can prove that your identity is legal. A digital certificate is issued by a certificate authority (CA). The authentication server transmits the public key (public key) and part of the identity information in the key pair it generates to the CA, and the CA verifies the identity of the authentication server and other necessary operations. Afterwards, a digital certificate is sent to the authentication server, and the digital certificate includes information such as part of the authentication server's identity information, public key information, and CA's signature. The terminal device compares and verifies the digital certificate with the root certificate corresponding to the local machine. If the comparison is consistent, the identity of the authentication server is legal. Exemplarily, the terminal device can verify whether the public key in the root certificate is consistent with the public key in the digital certificate by comparing the root certificate with the digital certificate.
步骤S204:在认证服务器身份合法的情况下,终端设备向认证服务器发送第一反馈消息。Step S204: In the case that the identity of the authentication server is legal, the terminal device sends a first feedback message to the authentication server.
具体地,所述第一反馈消息包括终端设备的数字证书(Client-Certificate)、客户端(终端设备)密钥交换协议(Client Key-Exchange)以及终端设备支持的加密类型(Change Cipher-Spec)。其中,Client-Certificate用于认证服务器认证终端设备的身份是否合法;Client Key-Exchange包括终端设备的密钥参数gb,所述密钥参数gb用于认证服务器和终端设备推导出预主密钥(PMK)。与步骤S201和步骤S203类似,第一反馈消息可以封装在EAP数据包中,且所述EAP数据包在终端设备和接入端之间的传输可以基于EAPOL协议,EAP数据包在接入端和认证服务器之间的传输协议可以为EAPOR协议,本申请实施例仅做举例说明,不做限制。Specifically, the first feedback message includes a digital certificate (Client-Certificate) of the terminal device, a client (terminal device) key exchange protocol (Client Key-Exchange), and an encryption type (Change Cipher-Spec) supported by the terminal device . Wherein, Client-Certificate is used for the authentication server to verify whether the identity of the terminal device is legal; Client Key-Exchange includes the key parameter gb of the terminal device, and the key parameter gb is used for the authentication server and the terminal device to deduce the pre-master secret key (PMK). Similar to step S201 and step S203, the first feedback message may be encapsulated in an EAP data packet, and the transmission of the EAP data packet between the terminal device and the access terminal may be based on the EAPOL protocol, and the EAP data packet is transmitted between the access terminal and the access terminal. The transmission protocol between the authentication servers may be the EAPOR protocol, and the embodiment of the present application is only used for illustration and does not limit it.
步骤S205:认证服务器校验终端设备的数字证书。Step S205: The authentication server verifies the digital certificate of the terminal device.
具体地,认证服务器通过校验Client-Certificate来确定终端设备身份的合法性;若不合法,认证服务器则终止此次认证。认证服务器验证Client-Certificate的过程可以参考步骤S203终端设备验证Server-Certificate的过程,本申请实施例不再赘述。Specifically, the authentication server determines the legitimacy of the identity of the terminal device by verifying the Client-Certificate; if not, the authentication server terminates the authentication. For the process of verifying the Client-Certificate by the authentication server, reference may be made to the process of verifying the Server-Certificate by the terminal device in step S203, which is not repeated in this embodiment of the present application.
步骤S206:在终端设备身份合法的情况下,认证服务器向终端设备发送第二反馈信息。Step S206: In the case that the identity of the terminal device is legal, the authentication server sends the second feedback information to the terminal device.
具体地,所述第二反馈信息包括认证服务器制定客户端的加密类型(ChangeCipher-Spec)以及Finish消息;所述Finish消息用于指示认证服务器向其发送TLS-ACK消息。与上述步骤一样,第二反馈消息也是封装在如EAP等数据报中,并通过接入端透传给认证服务器。Specifically, the second feedback information includes the encryption type (ChangeCipher-Spec) specified by the authentication server of the client and a Finish message; the Finish message is used to instruct the authentication server to send a TLS-ACK message to it. Similar to the above steps, the second feedback message is also encapsulated in a datagram such as EAP, and transparently transmitted to the authentication server through the access end.
步骤S207:终端设备推导预主密钥。Step S207: The terminal device derives the pre-master key.
具体地,终端设备基于Server-Hello所指定的通信算法,使用密钥参数ga和密钥参数gb计算预主密钥(Pre Master Secret,PMK),所述PMK为gab。Specifically, the terminal device uses the key parameter ga and the key parameter gb to calculatea Pre Master Secret (PMK) based on the communication algorithm specified by Server-Hello, where the PMK is gab .
步骤S208:终端设备推导主密钥。Step S208: the terminal device derives the master key.
具体地,终端设备推导主密钥MK的方式是:终端设备基于Server-Hello所指定的通信算法,使用Client Random Value、Srever Random Value以及PMK推导计算出MK。Specifically, the way for the terminal device to deduce the master key MK is: the terminal device derives and calculates the MK based on the communication algorithm specified by Server-Hello using Client Random Value, Srever Random Value and PMK.
步骤S209:认证服务器推导预主密钥。Step S209: the authentication server deduces the pre-master key.
具体地,认证服务器基于Server-Hello所指定的通信算法,使用密钥参数ga和密钥参数gb计算预主密钥(Pre Master Secret,PMK),所述PMK为gab。Specifically, the authentication server uses the key parameter ga and the key parameter gb to calculatea Pre Master Secret (PMK) based on the communication algorithm specified by Server-Hello, where the PMK is gab .
步骤S210:认证服务器推导主密钥。Step S210: The authentication server deduces the master key.
具体地,认证服务器推导主密钥MK的方式是:认证服务器基于Server-Hello所指定的通信算法,使用Client Random Value、Srever Random Value以及PMK推导计算出MK。Specifically, the way that the authentication server deduces the master key MK is: the authentication server deduces and calculates the MK by using Client Random Value, Srever Random Value and PMK based on the communication algorithm specified by Server-Hello.
步骤S211:终端设备向认证服务器发送TLS-ACK消息。Step S211: The terminal device sends a TLS-ACK message to the authentication server.
具体地,TLS-ACK消息是基于第二反馈消息中的Finish消息发出的,TLS-ACK消息用于指示认证服务器向接入端发送同意接入消息(Access-Accept消息)。Specifically, the TLS-ACK message is sent based on the Finish message in the second feedback message, and the TLS-ACK message is used to instruct the authentication server to send an access consent message (Access-Accept message) to the access end.
步骤S212:认证服务器向接入端发送Access-Accept消息。Step S212: The authentication server sends an Access-Accept message to the access terminal.
具体地,所述Access-Accept消息用于指示接入端接入认证成功,所述Access-Accept消息包括MK。Specifically, the Access-Accept message is used to indicate that the access authentication is successful, and the Access-Accept message includes the MK.
步骤S213:终端设备、接入端和认证服务器协商会话密钥。Step S213: The terminal device, the access terminal and the authentication server negotiate a session key.
具体地,终端设备、接入端和认证服务器基于密钥协商协议,使用相关的算法和MK协商出会话密钥。Specifically, the terminal device, the access terminal, and the authentication server negotiate a session key with the MK by using a related algorithm based on the key agreement protocol.
步骤S214:接入端向终端设备发送EAP-Success消息。Step S214: the access end sends an EAP-Success message to the terminal device.
具体地,所述EAP-Success消息用于指示终端设备,接入认证成功,整个接入认证过程结束;在接入认证结束后,终端设备与接入端之间数据的传输可用会话密钥进行加密。Specifically, the EAP-Success message is used to indicate to the terminal device that the access authentication is successful, and the entire access authentication process ends; after the access authentication ends, the data transmission between the terminal device and the access terminal can be performed with a session key encryption.
本申请实施例,认证服务器和终端设备通过相关认证信息的传输计算推导出了PMK和MK;然后,终端设备、认证服务器和接入端三方通过MK和相关密钥协商协议得到会话密钥。由于采用了非对称密码机制,通信双方仅需要维护共同信任的根证书,无需提前预置任何两两独立共享的信息,就可以实现双向认证,建立安全通道,灵活可扩展,协商出来的会话密钥具有前向安全性;另外,预主密钥gab没有在信道上传输,链路上的窃听者无法根据ga和gb计算得到gab,因此,无法获得会话密钥,从而可以确保会话密钥的安全性。并且由于传输的密钥参数ga,gb都被签名,因此无法被中间人调包篡改;从而,能够保证通信会话密钥的真实性和前向安全性。In the embodiment of the present application, the authentication server and the terminal device derive the PMK and MK through the calculation of related authentication information transmission; then, the terminal device, the authentication server and the access terminal obtain the session key through the MK and the relevant key agreement protocol. Due to the use of an asymmetric cryptographic mechanism, both parties only need to maintain a mutually trusted root certificate, without pre-setting any information shared independently by each pair, to achieve two-way authentication, establish a secure channel, and be flexible and extensible. The negotiated session password The key has forward security; in addition, the pre-master key gab is not transmitted on the channel, the eavesdropper on the link cannot calculate gab according to ga and gb , therefore, the session key cannot be obtained, so as to ensure Session key security. And since the transmitted key parameters ga , gb are signed, they cannot be tampered with by the middleman; thus, the authenticity and forward security of the communication session key can be guaranteed.
在上述图2的实施例中,接入认证的方法采用了非对称密码机制,通信双方仅需要维护共同信任的根证书,无需提前预置任何两两独立共享的信息,就可以实现双向认证,建立安全通道,灵活可扩展,且该方案协商出来的会话密钥具有前向安全性。但是,该方法中的客户端需要验证多个证书以及验证签名,而数字证书的验证不仅会带来较大的传输开销(单个X.509证书至少500B,证书链的尺寸会达到几KB)、较大的计算开销(证书链长度平均2-3级,需要多次签名验证和一次D-H密钥计算,非对称的计算开销大于非对称几千到上万倍),还会带来较大的芯片成本,如非对称密码算法实现代码占整个安全算法代码的60%。因此,对于资源受限的物联网(Internet of Things,IoT)设备并不适用,如在带宽受限(某些IoT设备通信的最大传输单元最大为127B或64B)场景下,传输数字证书会带来拆包分片、多包传输的延迟等问题。In the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 2 , the asymmetric cryptographic mechanism is used for the access authentication method, and the two communicating parties only need to maintain the root certificate of mutual trust, without presetting any information that is independently shared by each pair in advance, so that two-way authentication can be realized. A secure channel is established, which is flexible and extensible, and the session key negotiated by this scheme has forward security. However, the client in this method needs to verify multiple certificates and verify the signature, and the verification of the digital certificate will not only bring a large transmission overhead (a single X.509 certificate is at least 500B, and the size of the certificate chain will reach several KB), Large computational overhead (the average length of the certificate chain is 2-3 levels, multiple signature verifications and one D-H key calculation are required, and the asymmetric computational overhead is thousands to tens of thousands of times larger than that of the asymmetric) Chip cost, such as asymmetric cryptographic algorithm implementation code accounts for 60% of the entire security algorithm code. Therefore, it is not suitable for resource-constrained Internet of Things (IoT) devices. For example, in the scenario of limited bandwidth (the maximum transmission unit of some IoT device communication is up to 127B or 64B), the transmission of digital certificates will carry It can solve problems such as unpacking and fragmentation, delay of multi-packet transmission, etc.
为了解决上述问题,本申请实施例提供了另外一种接入认证的方法;请参见图3,图3是本申请实施例提供的一种基于对称密码体制的接入认证的方法流程图;本申请实施例以客户端为终端设备、认证端为认证服务器为例,进行举例说明。在本实施例中,终端设备、认证服务器以及接入端三者之间认证信息的交互都是通过诸如EAP等数据包发送的,终端设备与认证服务器之间认证信息的传输都是通过接入端进行透传的,且数据包在认证服务器与接入端之间、接入端与终端设备之间的传输都有诸如EAPOL、EAPOR等传输协议支持,对于数据包和传输协议的种类,本实施例仅做举例说明,不做限制。下面,结合图3对终端设备进行接入认证的具体流程进行展开说明:In order to solve the above problems, an embodiment of the present application provides another method for access authentication; please refer to FIG. 3, which is a flowchart of an access authentication method based on a symmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application; The application embodiment takes the client as the terminal device and the authentication end as the authentication server as an example for illustration. In this embodiment, the interaction of authentication information between the terminal device, the authentication server, and the access terminal is all sent through data packets such as EAP, and the transmission of authentication information between the terminal device and the authentication server is through the access The data packet is transparently transmitted between the authentication server and the access terminal, and the transmission between the access terminal and the terminal device is supported by transmission protocols such as EAPOL and EAPOR. For the types of data packets and transmission protocols, this The embodiments are only for illustration and not for limitation. Below, in conjunction with FIG. 3, the specific process of performing access authentication on the terminal device will be described:
步骤S301:终端设备向认证服务器发送认证请求。Step S301: The terminal device sends an authentication request to the authentication server.
具体地,所述认证请求用于指示所述终端设备的身份,在所述认证请求中包括网络访问标识符(Network Access Identifier,NAI),所述NAI是终端设备在网络认证中的唯一标识,认证服务器可以使用NAI来标识所述终端设备。所述请求认证通过封装在诸如EAP数据包中进行传输的,传输的方式为:终端设备将所述EAP数据报传输给接入端,再由接入端传输给认证服务器,所述数据包是基于诸如EAPOL或EAPOR等传输协议进行传输的,本申请实施例仅作举例说明。Specifically, the authentication request is used to indicate the identity of the terminal device, and the authentication request includes a network access identifier (Network Access Identifier, NAI), where the NAI is the unique identifier of the terminal device in network authentication, The authentication server may use the NAI to identify the terminal device. The request for authentication is transmitted through encapsulation in, for example, an EAP data packet, and the transmission method is as follows: the terminal device transmits the EAP data packet to the access terminal, and then the access terminal transmits the EAP data packet to the authentication server. The data packet is: For transmission based on a transmission protocol such as EAPOL or EAPOR, the embodiments of the present application are only used for illustration.
步骤S302:认证服务器基于所述认证请求获取认证向量。Step S302: The authentication server obtains an authentication vector based on the authentication request.
具体地,认证服务器接收到终端设备的NAI后,获取终端设备的认证向量的具体流程为:Specifically, after the authentication server receives the NAI of the terminal device, the specific process of acquiring the authentication vector of the terminal device is as follows:
1、认证服务器向认证中心(Authentication Centre,AuC)发送获取认证向量的请求;所述获取认证向量的请求包括终端设备的NAI。1. The authentication server sends a request for acquiring an authentication vector to an authentication center (Authentication Centre, AuC); the request for acquiring an authentication vector includes the NAI of the terminal device.
2、AuC基于特定的算法使用所述终端设备的NAI与共享密钥推导计算出认证向量;其中,所述共享密钥是终端设备与AuC共享的长期共享密钥,推导计算认证向量的特定算法也是AuC与终端设备事先确定的。2. AuC uses the NAI of the terminal device and the shared key to derive and calculate the authentication vector based on a specific algorithm; wherein, the shared key is the long-term shared key shared by the terminal device and the AuC, and the specific algorithm for calculating the authentication vector is derived It is also determined in advance by the AuC and the terminal device.
3、AuC将所述认证向量发送给认证服务器。3. The AuC sends the authentication vector to the authentication server.
所述认证向量至少包括随机数AT_RAND和网络认证令牌AT_AUTH以及预期回应(Expected Response,XRES);其中,所述AT_RAND用于生成会话密钥,所述AT_AUTH用于终端设备验证认证服务器身份的合法性,所述XRES用于认证服务器验证终端设备身份的合法性。The authentication vector at least includes a random number AT_RAND, a network authentication token AT_AUTH and an expected response (Expected Response, XRES); wherein, the AT_RAND is used to generate a session key, and the AT_AUTH is used for the terminal device to verify the legality of the authentication server identity The XRES is used by the authentication server to verify the legitimacy of the identity of the terminal device.
步骤S303:认证服务器基于所述认证向量获得会话密钥。Step S303: The authentication server obtains a session key based on the authentication vector.
具体地,认证服务器获得会话密钥的具体方式为:认证服务器基于特定的算法使用共享密钥和所述AT_RAND推导计算会话密钥;其中,推导计算所述会话密钥的特定算法是认证服务器和通信设备事先约定好的;示例性的,所述特定算法可以为数据加密标准(DataEncryption Standard,DES)等算法,本申请实施例不做限制。另外,所述会话密钥包括加密密钥(Cipher Key,CK)和完整性密钥(Integrity Key,IK),CK和IK是由长期密钥和所述AT_RAND经过不同的运算得到的。Specifically, the specific method for the authentication server to obtain the session key is: the authentication server uses the shared key and the AT_RAND to derive and calculate the session key based on a specific algorithm; wherein, the specific algorithm for deriving and calculating the session key is the authentication server and the AT_RAND. The communication device is pre-agreed; exemplarily, the specific algorithm may be an algorithm such as a data encryption standard (Data Encryption Standard, DES), which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. In addition, the session key includes an encryption key (Cipher Key, CK) and an integrity key (Integrity Key, IK), and CK and IK are obtained from the long-term key and the AT_RAND through different operations.
步骤S304:认证服务器向终端设备发送第一用户身份验证请求。Step S304: The authentication server sends a first user identity verification request to the terminal device.
示例性的,所述第一用户身份验证请求(User Authentication Request)可以以EAP等数据包的形式发送给终端设备,本申请实施例不做限制。第一用户身份验证请求包括所述随机数AT_RAND、所述网络认证令牌AT_AUTH以及第一消息验证码AT_MAC;其中,所述第一消息验证码AT_MAC为终端设备利用IK对所述第一用户身份验证请求的EAP数据包进行完整性运算而得到的,该第一消息验证码AT_MAC用于指示所述第一用户身份验证请求的发送方为认证服务器。Exemplarily, the first user authentication request (User Authentication Request) may be sent to the terminal device in the form of a data packet such as EAP, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The first user identity verification request includes the random number AT_RAND, the network authentication token AT_AUTH and the first message verification code AT_MAC; wherein, the first message verification code AT_MAC is the identification of the first user by the terminal device using IK The first message verification code AT_MAC is obtained by performing an integrity operation on the EAP data packet of the authentication request, and is used to indicate that the sender of the first user authentication request is an authentication server.
步骤S305:终端设备验证认证服务器的身份。Step S305: The terminal device verifies the identity of the authentication server.
具体地,终端设备接收到第一用户身份验证请求后,通过第一消息验证码AT_MAC判断第一用户身份验证请求的发送方是否为认证服务器;若为否,终端设备则终止此次接入认证;若为是,终端设备验证认证服务器身份的合法性。终端设备验证认证服务器身份合法性的具体方法为:终端设备通过长期密钥验证用户身份验证请求中网络认证令牌AT_AUTH的合法性;如果合法,则说明认证服务器的身份合法;若为否,则说明认证服务器的身份不合法,终端设备终止此次接入认证。Specifically, after receiving the first user identity verification request, the terminal device uses the first message verification code AT_MAC to determine whether the sender of the first user identity verification request is an authentication server; if not, the terminal device terminates this access authentication ; If yes, the terminal device verifies the legitimacy of the authentication server identity. The specific method for the terminal device to verify the legitimacy of the authentication server identity is: the terminal device verifies the legitimacy of the network authentication token AT_AUTH in the user authentication request through the long-term key; if it is legal, it means the authentication server's identity is legal; if not, then It indicates that the identity of the authentication server is invalid, and the terminal device terminates the access authentication.
步骤S306:在认证服务器身份合法的情况下,终端设备向认证服务器发送第二用户身份验证请求。Step S306: In the case that the identity of the authentication server is legal, the terminal device sends a second user identity verification request to the authentication server.
具体地,在验证认证服务器身份合法后,客户端基于第一用户身份验证请求中的网络认证令牌AT_AUTH以及长期密钥推导计算出客户端的身份令牌RES,并通过第一用户身份验证请求中的AT_RAND和长期密钥推导计算出会话密钥。其中,所述会话密钥与步骤S303中的会话密钥相同,认证服务器用于推导计算会话密钥的算法与步骤S303中认证服务器推导计算会话密钥的算法相同。然后,终端设备向认证服务器发送第二用户身份验证请求,所述第二用户身份验证请求中包括RES,并使用推导计算出的会话密钥中的IK对第二用户身份验证的EAP数据包进行完整性运算,得到第二用户身份认证的第二消息验证码AT_MAC。Specifically, after verifying that the identity of the authentication server is legal, the client deduces and calculates the client's identity token RES based on the network authentication token AT_AUTH and the long-term key in the first user's identity verification request. The AT_RAND and long-term key derivation calculate the session key. The session key is the same as the session key in step S303, and the algorithm used by the authentication server to derive and calculate the session key is the same as the algorithm used by the authentication server to derive and calculate the session key in step S303. Then, the terminal device sends a second user authentication request to the authentication server, the second user authentication request includes the RES, and uses the IK in the derived session key to perform the second user authentication on the EAP data packet. The integrity operation is performed to obtain the second message verification code AT_MAC for the second user identity authentication.
步骤S307:认证服务器验证终端设备的身份。Step S307: The authentication server verifies the identity of the terminal device.
具体地,认证服务器接收到第二用户身份验证请求后,通过第二消息验证码AT_MAC判断第二用户身份验证请求的发送方是否为终端设备;若为否,认证服务器则终止此次接入认证;若为是,认证服务器验证终端设备身份的合法性。认证服务器验证终端设备身份合法性的具体方法为:认证服务器比较RES与自己存储的XRES是否相等;若相等,则说明终端设备的身份合法;若不相等,则说明终端设备的身份不合法,认证服务器终止此次接入认证。Specifically, after receiving the second user's identity verification request, the authentication server determines whether the sender of the second user's identity verification request is a terminal device through the second message verification code AT_MAC; if not, the authentication server terminates this access authentication ; If yes, the authentication server verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the terminal device. The specific method for the authentication server to verify the legitimacy of the identity of the terminal device is as follows: the authentication server compares whether the RES is equal to the XRES stored by itself; if they are equal, it means that the identity of the terminal device is legal; The server terminates this access authentication.
步骤S308:认证服务器向接入端发送同意接入消息。Step S308: The authentication server sends an access approval message to the access terminal.
具体地,所述同意接入消息(Access-Accept消息)包括所述会话密钥。这样,接入端和通信设备(客户端)拥有了会话密钥,在接入认证完成后,终端设备与接入端之间的数据的传输可以用所述会话密钥进行加密和解密。Specifically, the access approval message (Access-Accept message) includes the session key. In this way, the access terminal and the communication device (client) have the session key, and after the access authentication is completed, the data transmission between the terminal device and the access terminal can be encrypted and decrypted using the session key.
步骤S309:接入端向通信设备发送EAP-Success消息。Step S309: the access terminal sends an EAP-Success message to the communication device.
具体地,所述EAP-Success消息用于指示终端设备,接入认证成功,整个接入认证过程结束;在接入认证结束后,终端设备与接入端之间数据的传输可用会话密钥进行加密和解密。Specifically, the EAP-Success message is used to indicate to the terminal device that the access authentication is successful, and the entire access authentication process ends; after the access authentication ends, the data transmission between the terminal device and the access terminal can be performed with a session key Encrypt and decrypt.
本申请实施例,客户端(通信设备)和认证服务器双方的身份认证是通过双方拥有的长期共享密钥来实现的,客户端和认证服务器分别通过预置的长期共享密钥来推导计算出会话密钥,再通过认证服务器将对话密钥发送给接入端,使得接入端和客户端都拥有相同的对话密钥,完成客户端接入认证的过程。与上述图2实施例中接入认证的方法相比,本实施例所述的接入认证方法不需要验证多个数字证书以及验证签名,从而减小了客户端和认证服务器的传输开销和计算开销,从而提高了客户端和认证服务器设备的工作性能。In this embodiment of the present application, the identity authentication of the client (communication device) and the authentication server is realized by the long-term shared key owned by both parties, and the client and the authentication server respectively deduce and calculate the session by using the preset long-term shared key. The authentication server sends the session key to the access terminal, so that both the access terminal and the client have the same session key, and the client access authentication process is completed. Compared with the access authentication method in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 2, the access authentication method described in this embodiment does not need to verify multiple digital certificates and verify signatures, thereby reducing the transmission overhead and calculation of the client and the authentication server. overhead, thereby improving the performance of the client and authentication server devices.
在上述图3实施例所述的基于对称密码体制的接入认证方法,通信设备和认证服务器不需要验证多个数字证书以及验证签名,从而减小了通信设备和认证服务器的传输开销和计算开销。但是,该接入认证方法不具备前向安全性,即:攻击者在未来某个时刻获取了通信设备和认证服务器共享的长期密钥,便可以通过所述长期密钥恢复出会话密钥,从而恢复出通信双方的通信数据,影响通信数据传输的安全性。In the access authentication method based on the symmetric cryptosystem described in the embodiment of FIG. 3, the communication device and the authentication server do not need to verify multiple digital certificates and verify the signature, thereby reducing the transmission overhead and computing overhead of the communication device and the authentication server . However, this access authentication method does not have forward security, that is, if the attacker obtains the long-term key shared by the communication device and the authentication server at some point in the future, the session key can be recovered by using the long-term key. Thereby, the communication data of both communication parties is recovered, which affects the security of communication data transmission.
为了解决上述问题,本申请实施例提供了另一种接入认证的方法。请参见图4,图4是本申请实施例提供的另一种基于对称密码体制的接入认证的方法流程图;本申请实施例以终端设备为客户端、认证端为认证服务器为例,进行举例说明。在本申请实施例中,客户端与认证服务器之间消息或信息发送是通过接入端的网络设备进行转发或透传的,且本申请实施例中的消息或信息的发送是基于例如EAP之类的数据包进行发送的,且在客户端与接入端或认证服务器与接入端之间,所述数据包的发送是基于例如EAPOR或EAPOL等协议支持的,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。下面,结合附图对具体流程进行说明:In order to solve the above problem, the embodiment of the present application provides another method for access authentication. Please refer to FIG. 4. FIG. 4 is a flowchart of another method for access authentication based on a symmetric cryptosystem provided by an embodiment of the present application. The embodiment of the present application takes the terminal device as the client and the authentication end as the authentication server as an example. for example. In this embodiment of the present application, the sending of messages or information between the client and the authentication server is forwarded or transparently transmitted through the network device of the access end, and the sending of messages or information in the embodiments of the present application is based on, for example, EAP. The data packets are sent between the client and the access terminal or between the authentication server and the access terminal, and the sending of the data packets is supported based on protocols such as EAPOR or EAPOL, and the embodiment of this application is only for illustration. , without restrictions. Below, in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, the specific process will be described:
步骤S401:客户端基于哈希函数更新其第一密钥参数。Step S401: The client updates its first key parameter based on the hash function.
具体地,在基于对称密码体制的接入认证系统中,客户端和认证服务器共享长期密钥(sk,S);其中,S为长期密钥中的第一密钥参数,sk为长期密钥中的第二密钥参数,第二密钥参数sk保持不变,第一密钥参数S会通过哈希函数进行更新。为了记录第一密钥参数S的更新次数,在客户端的设备和认证服务器各设置有一个计数器分别记录客户端和认证服务器的S的更新次数,用第一计数值Ic和第二计数值Is分别表征客户端和认证服务器的第一密钥参数基于哈希函数更新的次数。首先,客户端的设备基于公式Ic=Index+1得到更新后的第一计数值Ic,所述Index为更新前的第一计数值,第一计数值用于表征客户端基于哈希函数更新其第一密钥参数的次数;然后根据公式SIc=HASH(SIc-1)得到客户端更新后的第一密钥参数;其中,所述SIc所述客户端更新后的第一密钥参数,所述SIc-1为所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数。这样,当客户端下一次生成会话密钥时,可以使用所述SIc生成会话密钥。Specifically, in an access authentication system based on a symmetric cryptosystem, the client and the authentication server share a long-term key (sk, S); where S is the first key parameter in the long-term key, and sk is the long-term key In the second key parameter, the second key parameter sk remains unchanged, and the first key parameter S will be updated through the hash function. In order to record the number of updates of the first key parameter S, a counter is set on each of the client device and the authentication server to record the number of updates of S of the client and the authentication server, respectively. The first count value Ic and the second count value Is are respectively The number of times the first key parameter characterizing the client and the authentication server is updated based on the hash function. First, the device of the client obtains the updated first count value Ic based on the formula Ic=Index+1, the Index is the first count value before the update, and the first count value is used to represent that the client updates its first count value based on the hash function. A number of key parameters; then obtain the updated first key parameter of the client according to the formula SIc =HASH(SIc-1 ); wherein, the SIc updated first key parameter of the client , the SIc-1 is the first key parameter of the client before updating. In this way, when the client generates the session key next time, the SIc can be used to generate the session key.
需要说明的是,本申请实施例中,客户端更新长期密钥的过程可以在步骤S402客户端向认证服务器发送用户身份认证信息的步骤之前,也可以在步骤S412客户端删除其更新前的第一密钥参数的步骤之前,对于步骤S401顺序的排列,本申请实施例仅做举例说明,不做限制。It should be noted that, in this embodiment of the present application, the process of updating the long-term key by the client may be performed before the step of sending the user identity authentication information to the authentication server in step S402, or the client may delete the first key before the update in step S412. Before the step of a key parameter, the order of step S401 is only described in the embodiment of the present application, and is not limited.
步骤S402:客户端向认证服务器发送用户身份认证消息。Step S402: The client sends a user identity authentication message to the authentication server.
具体地,客户端基于客户端的随机数RandC、客户端的身份标识IDC以及更新前的第一计数值Index,计算所述客户端的消息参数M1;示例性的,所述客户端的消息参数M1的计算方式可以为M1=IDC||Index||RandC,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。在计算得到消息参数M1之后,客户端基于所述M1以及客户端的sk计算得到客户端的消息认证码authC;示例性的,所述authC的计算方法可以基于哈希杂凑算法得到,即:authC=HMAC(sk,M1),本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。然后,客户端将计算得到的authC以及M1通过用户身份认证消息(User Authentication)发送给接入端,经过接入端透传给认证服务器。Specifically, the client calculates the message parameter M1 of the client based on the random number RandC of the client, the identity IDC of the client, and the first count value Index before the update; exemplarily, the message parameter M of the client The calculation method of1 may be M1 =IDC ||Index||RandC , and the embodiment of the present application is only for illustration and not limited. After calculating the message parameter M1, the client calculates and obtains the message authentication code authCof the client based on the M1 and the skof the client; exemplarily, the calculation method of the authC can be obtained based on a hash algorithm, that is, : authC =HMAC(sk, M1 ), the embodiment of the present application is only for illustration and not limited. Then, the client sends the calculated authC and M1 to the access terminal through a user authentication message (User Authentication), and transparently transmits it to the authentication server through the access terminal.
步骤S403:认证服务器基于所述用户身份认证消息验证客户端身份的合法性。Step S403: The authentication server verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the client based on the user identity authentication message.
具体地,认证服务器基于所述用户身份认证消息中的M1获取Index,获取的方式为:认证服务器通过M1的计算公式来获取Index;示例性的,若M1=IDC||Index||RandC,由于M1的计算公式是客户端和认证服务器双方事先约定好的,认证服务器通过所述计算公式得到Index、IDC以及RandC。然后,认证服务器验证客户端身份的合法性,具体过程为:认证服务器首先判断Index是否大于或等于第二计数值Is;若判断为否,则客户端的身份是非法的,认证服务器终止此次接入认证;若判断为是,认证服务器基于M1和第二密钥参数sk计算得到第一认证码auth′C;其中,auth′C的计算方式与authC相同,为客户端和认证服务器事先约定好的;示例性的,若authC的计算公式为authC=HMAC(sk,M1),则认证服务器也使用相同的计算公式auth′C=HMAC(sk,M1)。在计算得到auth′C后,认证服务器验证auth′C=authC是否成立,若不成立,则说明客户端的身份不合法,认证服务器终止此次接入认证过程;若合法,则说明客户端的身份合法。Specifically, the authentication server obtains the Index based on M1 in the user identity authentication message, and the obtaining method is as follows: the authentication server obtains the Index through the calculation formula of M1 ; exemplarily, if M1 =IDC ||Index| |RandC , since the calculation formula of M1 is pre-agreed by both the client and the authentication server, the authentication server obtains Index, IDC and RandC through the calculation formula. Then, the authentication server verifies the legitimacy of the client's identity. The specific process is as follows: the authentication server first judges whether the Index is greater than or equal to the second count value Is; if the judgment is no, the identity of the client is illegal, and the authentication server terminates the connection. If it is judged to be yes, the authentication server calculates and obtains the first authentication code auth'C based on M1 and the second key parameter sk; wherein, the calculation method of auth'C is the same as that of authC , and it is the same as that of the client and the authentication server in advance. It is agreed; exemplarily, if the calculation formula of authC is authC =HMAC(sk, M1 ), the authentication server also uses the same calculation formula auth′C =HMAC(sk, M1 ). After calculating auth'C , the authentication server verifies whether auth'C = authC is established. If not, it means that the identity of the client is illegal, and the authentication server terminates the access authentication process; if it is legal, it means that the identity of the client is legal. .
步骤S404:在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,所述认证服务器判断更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值。Step S404: In the case of verifying that the identity of the client is legitimate based on the user authentication message, the authentication server determines that the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server.
具体地,认证服务器判断第二计数值是否需要重置的过程为:认证服务器判断Index是否大于或等于认证服务器的计数阈值;所述计数阈值是认证服务器存储的计数器的阈值ThresholdValue;示例性的,所述ThresholdValue可以为计数器计数最大长度的0.75倍的整数,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。若Index是大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,认证服务器和客户端进入计数器重置流程;若Index小于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,认证服务器和客户端的计数器不需要重置。Specifically, the process of the authentication server judging whether the second count value needs to be reset is: the authentication server judges whether the Index is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server; the count threshold is the threshold ThresholdValue of the counter stored by the authentication server; exemplarily, The ThresholdValue may be an integer that is 0.75 times the maximum count length of the counter, and the embodiment of the present application is only for illustration and not limited. If the Index is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server, the authentication server and the client enter the counter reset process; if the Index is less than the count threshold of the authentication server, the counters of the authentication server and the client do not need to be reset.
步骤S405:在认证服务器判断第二计数值不需要重置的情况下,认证服务器基于第三密钥参数、认证服务器的随机数以及用户认证消息得到会话密钥。Step S405: When the authentication server determines that the second count value does not need to be reset, the authentication server obtains the session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message.
具体地,认证服务器在判断其计数器不进入重置流程后,即第二计数值不需要置0后,根据公式SIndex=HASH(Index-Is)(SIs)得到第三密钥参数;所述SIndex为所述第三密钥参数,所述SIs为所述认证服务器更新前的第一密钥参数;这样,第三密钥参数与客户端更新前的第一密钥参数是相同的,第三密钥参数计算的哈希函数与客户端更新计算的第一密钥参数的哈希函数相同,是认证服务器和客户端事先约定好的。此外,认证服务器根据公式Is=Index+1得到更新后的第二计数值,使得更新后的第二计数值与更新后的第一计数值相同,以此来保证客户端和认证服务器双方的计数器的计数值的一致性,所述Is为更新后的第二计数值。然后,认证服务器通过公式SIs=HASH(SIndex)得到认证服务器更新后的第一密钥参数,使得所述认证服务器和客户端更新后的第一密钥参数相同,保证客户端和认证服务器共享的长期密钥相同;其中,SIs为认证服务器更新后的第一密钥参数。在计算出更新后的第一密钥参数后,认证服务器删除其更新前的第一密钥参数。认证服务器在计算出SIndex后,基于SIndex、认证服务器的随机数RandS以及RandC得到会话密钥Sessionkey;其中,Sessionkey的算法是认证服务器和客户端事先协商好的;示例性的,Sessionkey的算法可以为基于HMAC的密钥派生函数,即:Sessionkey=HKDF(SIndex,RandC||RandS),本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。Specifically, after judging that its counter does not enter the reset process, that is, after the second count value does not need to be set to 0, the authentication server obtains the third key parameter according to the formula SIndex =HASH(Index-Is) (SIs ); The SIndex is the third key parameter, and the SIs is the first key parameter before the authentication server is updated; in this way, the third key parameter is the same as the first key parameter before the client is updated Yes, the hash function calculated by the third key parameter is the same as the hash function of the first key parameter calculated by the client update, and is pre-agreed by the authentication server and the client. In addition, the authentication server obtains the updated second count value according to the formula Is=Index+1, so that the updated second count value is the same as the updated first count value, so as to ensure the counters of both the client and the authentication server. The consistency of the count value, the Is is the updated second count value. Then, the authentication server obtains the updated first key parameter of the authentication server through the formula SIs =HASH(SIndex ), so that the updated first key parameter of the authentication server and the client is the same, ensuring that the client and the authentication server are the same. The shared long-term keys are the same; where SIs is the updated first key parameter of the authentication server. After calculating the updated first key parameter, the authentication server deletes the first key parameter before the update. After the authentication server calculates the SIndex , it obtains the session key Sessionkey based on the SIndex , the random numbers RandS and RandC of the authentication server; wherein, the algorithm of the Sessionkey is negotiated by the authentication server and the client in advance; exemplarily, the Sessionkey The algorithm may be an HMAC-based key derivation function, that is: Sessionkey=HKDF(SIndex , RandC || RandS ), and the embodiments of this application are only for illustration and do not limit.
步骤S406:认证服务器向接入端发送网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥。Step S406: The authentication server sends the network authentication message and the encrypted session key to the access terminal.
具体地,设置重置位Re_sync=0,Re_sync=0用于指示客户端的计数器不需要置0;在设置Re_sync=0后,认证服务器基于所述Re_sync和RandS计算得到认证服务器的消息参数M2;示例性的,所述M2的计算公式可以为M2=Re_sync||RandS,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。认证服务器在计算出M2之后,认证服务器基于客户端的消息参数M1、认证服务器的消息参数M2以及认证服务器的第二密钥参数sk生成认证服务器的消息认证码authS,所述authS的计算函数与authc相同,为客户端和认证服务器实现约定好的;示例性的,若authC=HMAC(sk,M1),则authS的计算函数也为HMAC,即authS=HMAC(sk,M1||M2)。然后,认证服务器将包含M2和authS的网络认证消息(Network Authentication)发送给接入端,并将会话密钥Sessionkey通过接入端和认证服务器事先约定的加密算法以及密钥Key进行加密,得到加密后的会话密钥[Sessionkey]Key,并将[Sessionkey]Key发送给接入端。Specifically, the reset bit Re_sync=0 is set, and Re_sync=0 is used to indicate that the counter of the client does not need to be set to 0; after setting Re_sync=0, the authentication server calculates and obtains the message parameter M2 of the authentication server based on the Re_sync and RandS ; Exemplarily, the calculation formula of M2 may be M2=Re_sync||RandS , and the embodiment of the present application is only for illustration and not for limitation. After the authentication server calculates M2, the authentication server generates the message authentication code authS of the authentication server based on the message parameter M1 of the client, the message parameter M2 of the authentication server, and the second key parameter sk of the authentication server. The calculation function of the authS Same as authc , it is agreed for the client and the authentication server; exemplarily, if authC =HMAC(sk, M1 ), then the calculation function of authS is also HMAC, that is, authS =HMAC(sk, M1 || M2). Then, the authentication server sends the network authentication message (Network Authentication) containing M2 and authS to the access terminal, and encrypts the session key Sessionkey through the encryption algorithm and the key Key agreed in advance between the access terminal and the authentication server to obtain Encrypted session key [Sessionkey]Key , and send [Sessionkey]Key to the access terminal.
步骤S407:接入端将加密后的会话密钥进行解密,得到解密后的会话密钥。Step S407: the access terminal decrypts the encrypted session key to obtain the decrypted session key.
步骤S408:接入端将网络认证消息发送给客户端。Step S408: the access end sends the network authentication message to the client.
步骤S409:客户端基于所述网络认证消息验证所述认证服务器的身份是否合法。Step S409: The client verifies whether the identity of the authentication server is legal based on the network authentication message.
具体地,客户端基于所述网络认证消息中M2、客户端的消息参数M1以及客户端的第二密钥参数sk生成第二消息认证码auth′S;所述第二消息认证码的计算函数与认证服务器的消息认证码的计算函数相同;示例性的,若认证服务器的消息认证码的生成函数为authS=HMAC(sk,M1||M2),则第二消息认证码的生成函数也为auth′S=HMAC(sk,M1||M2),本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。然后,客户端比较auth′S与authS是否相同,若相同,则说明认证服务器的身份合法;若不同,则说明认证服务器的身份非法,客户端终止认证服务器与客户端之间的接入认证。客户端比较auth′S与authS是否相同,实质上是在比较客户端的第二密钥参数和认证服务器的第二密钥参数是否相同,以及认证服务器和客户端计算消息认证码的函数相同,进而通过客户端和认证服务器的共享长期密钥的一致性来验证认证服务器的身份的合法性。相较上述图2实施例中,客户端和认证服务器通过数字证书验证身份的合法性,本实施例节省了大量的传输资源和计算资源;相较于上述图3实施例中,认证服务器通过向AuC获取网络认证令牌来进行验证身份的合法性,本实施例的步骤更加简便。Specifically, the client generates a second message authentication code auth'S based on M2 in the network authentication message, the message parameter M1 of the client, and the second key parameter sk of the client; the calculation function of the second message authentication code and the authentication The calculation function of the message authentication code of the server is the same; exemplarily, if the generation function of the message authentication code of the authentication server is authS =HMAC(sk, M1 ||M2), then the generation function of the second message authentication code is also auth′S =HMAC(sk, M1 || M2), the embodiments of the present application are only for illustration, and do not limit. Then, the client compares whether auth'S and authS are the same. If they are the same, it means that the identity of the authentication server is legal; if they are different, it means that the identity of the authentication server is illegal, and the client terminates the access authentication between the authentication server and the client. . When the client compares whether auth'S and authS are the same, it is essentially comparing whether the second key parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the authentication server are the same, and the functions of the authentication server and the client to calculate the message authentication code are the same, Further, the legitimacy of the identity of the authentication server is verified through the consistency of the shared long-term key between the client and the authentication server. Compared with the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 2, the client and the authentication server verify the legitimacy of identities through digital certificates, this embodiment saves a lot of transmission resources and computing resources; compared with the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 3, the authentication server The AuC obtains the network authentication token to verify the legitimacy of the identity, and the steps in this embodiment are simpler.
步骤S410:客户端通过置位标识判断是否将第一计数值重置。Step S410: The client determines whether to reset the first count value by using the set flag.
具体地,客户端基于所述网络认证消息中的M2获取置位标识Re_sync和认证服务器的随机数RandS;示例性的,若M2=Re_sync||RandS,M2可以根据该公式求解得到Re_sync和RandS。客户端根据Re_sync的值来判断是否需要将第一计数值置0;若Re_sync=1,客户端进入计数器置0的流程;Re_sync=0,则第一计数值不需要置0。Specifically, the client obtains the location identifier Re_sync and the random number RandS of the authentication server based on M2 in the network authentication message; exemplarily, if M2=Re_sync||RandS , M2 can obtain Re_sync and Re_sync according to this formula. RandS. The client determines whether the first count value needs to be set to 0 according to the value of Re_sync; if Re_sync=1, the client enters the process of setting the counter to 0; if Re_sync=0, the first count value does not need to be set to 0.
步骤S411:在第一计数值不置0的情况下,客户端基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥。Step S411: In the case where the first count value is not set to 0, the client obtains a session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the client is updated.
具体地,客户端在判断其计数器不进入置0流程后,基于RandC、从网络认证消息中获取的RandS以及客户端更新前的第一密钥参数SIc-1得到会话密钥;实现了接入端、客户端以及认证服务器都能得到相同的会话密钥SessionKey。示例性的,会话密钥的计算公式可以为SessionKey=HKDF(SIc-1,RandC||RandS),本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。Specifically, the client obtains the session key based on RandC , the RandS obtained from the network authentication message, and the first key parameter SIc-1 before the client is updated after judging that the counter does not enter the set-to-zero process; In this way, the access terminal, the client and the authentication server can get the same session key SessionKey. Exemplarily, the calculation formula of the session key may be SessionKey=HKDF(SIc-1 , RandC || RandS ), and the embodiment of the present application is for illustration only and not for limitation.
步骤S412:客户端删除更新前的第一密钥参数。Step S412: The client deletes the first key parameter before the update.
具体地,在计算得到会话密钥SessionKey后,客户端删除其更新前的第一密钥参数,保留其更新后的第一密钥参数。Specifically, after calculating and obtaining the session key SessionKey, the client deletes the first key parameter before the update, and retains the first key parameter after the update.
本申请实施例,本申请实施例采用对称密码体制的接入认证方法,相较于上述图2实施例中的非对称密码体制中的接入认证方法,本申请实施例中的接入认证系统内的认证服务器对客户端进行身份认证时,仅需判断更新前的第一计数值大于或等于更新前的第二计数值以及认证服务器生成的第二消息认证码是否与客户端的消息认证码相同即可实现认证服务器对客户端的验证;同样的,客户端对认证服务器身份的验证仅需判断客户端生成的第一消息认证码是否与认证服务器的消息认证码相同即可实现客户端对认证服务器身份的验证;相较于上述图2实施例中认证服务器与客户端之间身份合法性的验证需要验证多个数字证书及其签名,本申请实施例中认证服务器与客户端之间的身份验证由于没有数字证书的传输和验证,节约了大量的传输资源和计算资源,从而提高了接入认证系统的工作性能。另外,相较于上述图3实施例中攻击者可以通过获取客户端或认证服务器的长期共享密钥,进而通过该密钥恢复出客户端以往通信数据,从而造成数据泄露的安全性问题,本实施例通过更新长期密钥,并在每次生成会话密钥后删除更新前的长期密钥,使得长期密钥具有前向性,从而使得攻击者无法获取过去更新前的长期密钥,进而恢复出过去的会话密钥,从而窃取过往的数据,避免了数据泄露的问题。The embodiment of the present application adopts the access authentication method of the symmetric cryptosystem in the embodiment of the present application. Compared with the access authentication method in the asymmetric cryptosystem in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. When the authentication server in the authentication server performs identity authentication on the client, it only needs to judge whether the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the second count value before the update and whether the second message authentication code generated by the authentication server is the same as the client's message authentication code. The authentication server can verify the client; similarly, the client can verify the identity of the authentication server only by judging whether the first message authentication code generated by the client is the same as the message authentication code of the authentication server. Verification of identity; Compared with the verification of identity legitimacy between the authentication server and the client in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 2, multiple digital certificates and their signatures need to be verified, and the authentication between the authentication server and the client in the embodiment of the present application. Since there is no transmission and verification of digital certificates, a lot of transmission resources and computing resources are saved, thereby improving the work performance of the access authentication system. In addition, compared with the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 3, an attacker can obtain the long-term shared key of the client or the authentication server, and then use the key to restore the client's previous communication data, thereby causing the security problem of data leakage. The embodiment updates the long-term key and deletes the long-term key before the update after each session key is generated, so that the long-term key is forward-looking, so that the attacker cannot obtain the long-term key before the update in the past, and then recovers The past session key is released, thereby stealing past data and avoiding the problem of data leakage.
综上所述,在本申请实施例中所述的接入认证系统中,客户端和认证服务器采用正向哈希链的方式生成哈希节点,即:(Ic=0,S0)→(Ic=1,S1)……→(Ic=i,Si)→(Ic=i+1,Si+1)→……组成一条正向的哈希链。由于哈希函数的不可逆性质,根据长期密钥Si+1以及Si+1=HASH(Si)任何攻击者也无法求出Si;此外,由于在Ic=i阶段时,当使用完Si后,会立即删除Si,所以当Ic=i+1的阶段时,任何攻击者也无法求出Si,进而无法获得在Ic=i时对应的会话密钥;从而,在保证较小的传输开销和计算开销的前提下,又提高会话密钥的安全性和前向性,使得客户端的设备的数据泄露的概率大大降低。To sum up, in the access authentication system described in the embodiments of the present application, the client and the authentication server use a forward hash chain to generate hash nodes, that is: (Ic=0, S0 )→( Ic=1, S1 )...→(Ic=i, Si )→(Ic=i+1, Si+1 )→... form a forward hash chain. Due to the irreversible nature of the hash function, according to the long-term key Si+1 and Si+1 =HASH(Si ), any attacker cannot obtain Si ; After Si, Si will be deleted immediately, so when Ic=i +1, any attacker cannot find Si, and then cannot obtain the corresponding session key when Ic=i ; On the premise of small transmission overhead and calculation overhead, the security and forwardness of the session key are improved, so that the probability of data leakage of the client's device is greatly reduced.
在上述图4所述的实施例中的步骤S404和步骤S410,客户端和认证服务器需要分别判断第一计数值和第二计数值是否需要重置,若需要重置,则客户端和认证服务器的计数器进入重置机制的流程;下面,结合图5,对客户端和认证服务器的计数器进入重置机制的流程进行说明。请参见图5,图5是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证系统计数器重置机制的流程图;在本申请实施例中,客户端与认证服务器之间消息或信息发送是通过接入端的网络设备进行转发或透传的,且本申请实施例中的消息或信息的发送是基于例如EAP之类的数据包进行发送的,且在客户端与接入端或认证服务器与接入端之间,所述数据包的发送是基于例如EAPOR或EAPOL等协议支持的,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。下面,结合附图,对该流程进行详细说明;In steps S404 and S410 in the embodiment described in FIG. 4 above, the client and the authentication server need to judge whether the first count value and the second count need to be reset respectively. The flow of the counter entering the reset mechanism; the following, in conjunction with FIG. 5 , describes the flow of the counter of the client and the authentication server entering the reset mechanism. Please refer to FIG. 5. FIG. 5 is a flowchart of an access authentication system counter reset mechanism provided by an embodiment of the present application; It is forwarded or transparently transmitted by the network device of the terminal, and the message or information in this embodiment of the present application is sent based on data packets such as EAP, and is transmitted between the client and the access terminal or between the authentication server and the access terminal. In between, the sending of the data packets is supported based on protocols such as EAPOR or EAPOL, and the embodiments of the present application are only used for illustration and are not limited. Below, in conjunction with accompanying drawing, this process is described in detail;
步骤S501:客户端基于哈希函数更新其第一密钥参数。Step S501: The client updates its first key parameter based on the hash function.
具体地,步骤S501可以参考上述图4实施例中的步骤S401,本实施例不再赘述。需要说明的是,步骤S501可以在步骤S502客户端向认证服务器发送身份认证信息的步骤之前,也可以在客户端删除其更新的第一密钥参数之前,对于步骤S501的顺序排列,本申请实施例仅作举例说明,不做限制。Specifically, for step S501, reference may be made to step S401 in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 4 , which is not repeated in this embodiment. It should be noted that, in step S501, before the step of sending the identity authentication information to the authentication server in step S502, or before the client deletes its updated first key parameter, the order of step S501 is implemented in this application. The example is for illustration only and not for limitation.
步骤S502:客户端向认证服务器发送用户身份认证消息。Step S502: the client sends a user identity authentication message to the authentication server.
步骤S503:认证服务器基于所述用户身份认证消息验证客户端身份的合法性。Step S503: The authentication server verifies the legitimacy of the identity of the client based on the user identity authentication message.
步骤S504:在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,所述认证服务器判断更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值。Step S504: In the case of verifying that the identity of the client is legitimate based on the user authentication message, the authentication server determines that the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server.
步骤S502~步骤S504请参考上述图4实施例中的步骤S402~步骤S404,本申请实施例不做限制。For steps S502 to S504, please refer to steps S402 to S404 in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 4, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
步骤S505:在认证服务器判断第二数值需要重置的情况下,认证服务器向客户端发送网络认证消息。Step S505: When the authentication server determines that the second value needs to be reset, the authentication server sends a network authentication message to the client.
具体地,认证服务器在判断其计数器需要进入重置的情况下,根据公式Is′=0,使得第二计数值为0;所述Is′为更新后的第二计数值;然后,认证服务器根据公式new_SIs=HASH(Index+1-Is)(SIs),得到认证服务器更新后的第一密钥参数(Is为更新前的第二计数值),通过所述公式,使得new_SIs与客户端更新后的第一密钥参数相同,保证了客户端与认证服务器长期共享密钥的完整性。此外,认证服务器设置重置位Re_sync=1,Re_sync=1用于指示客户端的计数器需要置0;然后生成认证服务器的消息参数M2以及认证服务器的消息认证码authS,M2和authS的生成方法可以参考上述图4实施例中的步骤S406,本实施例不再赘述。然后,认证服务器通过接入端将包括authS和M2的网络认证消息发送给客户端。Specifically, when judging that the counter needs to be reset, the authentication server makes the
步骤S506:客户端基于所述网络认证消息验证所述认证服务器的身份是否合法。Step S506: The client verifies whether the identity of the authentication server is legal based on the network authentication message.
步骤S507:客户端通过置位标识判断是否将第一计数值重置。Step S507: The client determines whether to reset the first count value by using the set flag.
步骤S506~步骤S507可以参考上述图4实施例中步骤S409~步骤S410,本申请实施例不再赘述。For steps S506 to S507, reference may be made to steps S409 to S410 in the above-mentioned embodiment of FIG. 4 , and details are not repeated in this embodiment of the present application.
步骤S508:在客户端通过置位标识判断第一计数值需要置0的情况下,客户端更新其第一密钥参数。Step S508: In the case that the client determines that the first count value needs to be set to 0 through the set flag, the client updates its first key parameter.
具体地,在客户端通过Re_sync=1判断第一计数值需要置0时,客户端将第一计数值置零,置0后的第一计数值用于表征其当前第一密钥参数的更新次数。Specifically, when the client determines that the first count value needs to be set to 0 through Re_sync=1, the client sets the first count value to zero, and the first count value after setting 0 is used to represent the update of its current first key parameter frequency.
步骤S509:客户端删除其更新前的第一密钥参数。Step S509: The client deletes the first key parameter before the update.
本申请实施例,认证服务器在判断更新前的第一计数值大于或等于认证服务器计数器的阈值前提下,进入计数器重置流程。在客户端和认证服务器的计数器在达到其最大计数能力(计数器的计数阈值)的情况下,通过将计数值置0,使得计数器可以周期性地表征认证服务器和客户端的第一密钥参数通过哈希函数的更新次数;与此同时,客户端和认证服务器的第一密钥参数在更新,并未随着第一计数值和第二计数值的置零而停止更新从而保证了长期密钥(第一密钥参数)的前向安全性,即使在第一计数值和第二计数值置0的情况下,攻击者也不能获取过去的长期密钥,并恢复出历史会话密钥,进而无法对通过历史会话密钥传输的数据进行解密,保证了数据的安全性。In this embodiment of the present application, the authentication server enters a counter reset process on the premise that the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the threshold value of the authentication server counter. When the counters of the client and the authentication server reach their maximum counting capability (counting threshold of the counter), by setting the count value to 0, the counters can periodically represent the first key parameters of the authentication server and the client. At the same time, the first key parameters of the client and the authentication server are being updated, and they do not stop updating with the setting of the first count value and the second count value to zero, thus ensuring the long-term key ( The forward security of the first key parameter), even when the first count value and the second count value are set to 0, the attacker cannot obtain the past long-term key and recover the historical session key, and thus cannot Decrypt the data transmitted through the historical session key to ensure the security of the data.
上述详细阐述了本申请实施例的方法,下面提供本实施例的相关装置、设备、计算机可读存储介质、计算机程序以及芯片系统。The methods of the embodiments of the present application are described in detail above, and the related apparatuses, devices, computer-readable storage media, computer programs, and chip systems of the present embodiments are provided below.
请参见图6,图6是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图,所述接入认证的装置6可以为上述实施例中的客户端的设备,所述接入认证的装置6可以包括认证消息发送单元601、认证消息接收单元602、会话密钥生成单元603以及删除单元604,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 6. FIG. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication apparatus provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication apparatus 6 may be the equipment of the client in the above-mentioned embodiment. The device 6 may include an authentication
认证消息发送单元601,用于向认证服务器发送用户认证消息;An authentication
认证消息接收单元602,用于在所述认证服务器基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,接收所述认证服务器发送的网络认证消息;An authentication
会话密钥生成单元603,用于基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥;a session
删除单元604,用于删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数。A
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置6,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus 6 for access authentication further includes:
第一更新单元,用于根据公式Ic=Index+1,得到更新后的第一计数值;The first update unit is used to obtain the updated first count value according to the formula Ic=Index+1;
第二更新单元,用于根据公式SIc=HASH(SIc-1),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。The second updating unit is configured to obtain the updated first key parameter according to the formula SIc =HASH(SIc-1 ).
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述会话密钥生成单元603,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the session
标识获取单元,用于从所述认证服务器的消息参数中获取置位标识Re_sync;an identification obtaining unit, used for obtaining the set identification Re_sync from the message parameter of the authentication server;
置零单元,用于在所述Re_sync=1的情况下,将第一计数值置零,并执行所述客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息的步骤;a zero-setting unit, configured to set the first count value to zero under the condition of Re_sync=1, and execute the step of sending a user authentication message from the client to the authentication server;
生成单元,用于在所述Re_sync=0的情况下,基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥。A generating unit, configured to obtain a session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the client is updated in the case of the Re_sync=0.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述认证消息发送单元601,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the authentication
消息参数生成单元,用于基于所述客户端的身份标识、更新前的第一计数值以及所述客户端的随机数,得到所述客户端的消息参数;a message parameter generating unit, configured to obtain the message parameter of the client based on the identity of the client, the first count value before updating and the random number of the client;
第一认证码生成单元,用于基于所述客户端的消息参数和所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成所述客户端的消息认证码;a first authentication code generating unit, configured to generate a message authentication code of the client based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client;
发送单元,用于将用户认证消息发送给所述认证服务器。A sending unit, configured to send a user authentication message to the authentication server.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置6,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the apparatus 6 for access authentication further includes:
第二认证码生成单元,用于所述会话密钥生成单元基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥之前,基于所述认证服务器的消息参数、所述客户端的消息参数以及所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成第一消息认证码;The second authentication code generation unit is used for the session key generation unit to obtain the session key based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the update of the client, based on the generating the first message authentication code with the message parameter of the authentication server, the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client;
判断单元,用于判断所述第一消息认证码与所述认证服务器的消息认证码是否一致;a judgment unit, configured to judge whether the first message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the authentication server;
终止单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为否的情况下,终止所述客户端与所述认证服务器之间的接入认证。A terminating unit, configured to terminate the access authentication between the client and the authentication server when the judgment unit judges no.
请参见图7,图7是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图,所述接入认证的装置7可以为上述实施例中的客户端的设备,所述接入认证的装置7可以包括认证消息接收单元701、会话密钥生成单元702、删除单元703以及发送单元704,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 7 . FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication apparatus provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication apparatus 7 may be the equipment of the client in the foregoing embodiment. The apparatus 7 may include an authentication
认证消息接收单元701,用于接收客户端发送的用户认证消息;An authentication
会话密钥生成单元702,用于在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥;The session
删除单元703,用于删除其更新前的第一密钥参数;Deleting
发送单元704,用于向接入端发送网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥。The sending
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述会话密钥生成单元702,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the session
第一获取单元,用于从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;a first obtaining unit, configured to obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
置零单元,用于若所述更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,将第二计数值置0;a zero setting unit, configured to set the second count value to 0 if the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server;
执行单元,用于执行所述认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息的步骤;an execution unit, configured to execute the step of the authentication server receiving the user authentication message sent by the client;
第一生成单元,用于若所述更新前的第一计数值小于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,基于所述第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥。a first generating unit, configured to obtain a session based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server and the user authentication message if the first count value before the update is less than the count threshold of the authentication server key.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置7,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the access authentication device 7 further includes:
第二获取单元,用于从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;a second obtaining unit, configured to obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
第一判断单元,用于判断所述更新前的第一计数值是否大于或等于更新前的第二计数值;a first judging unit for judging whether the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the second count value before the update;
终止单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为否后,终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证;a terminating unit, configured to terminate the access authentication between the authentication server and the client after the judging unit judges no;
第二生成单元,用于在所述判断单元判断为是后,基于所述客户端的消息参数以及所述认证服务器的第二密钥参数生成第二消息认证码;a second generating unit, configured to generate a second message authentication code based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the authentication server after the judgment unit judges that it is yes;
第二判断单元,用于判断所述第二消息认证码与所述客户端的消息认证码是否一致。A second judging unit, configured to judge whether the second message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the client.
在一种可能实现的方式中,所述接入认证的装置7,还包括:In a possible implementation manner, the access authentication device 7 further includes:
计算单元,用于根据公式SIndex=HASH(Index-Is)(SIs)得到第三密钥参数;a calculation unit, for obtaining the third key parameter according to the formula SIndex =HASH(Index-Is) (SIs );
第一更新单元,用于根据公式Is=Index+1,得到更新后的第二计数值;The first update unit is used to obtain the updated second count value according to the formula Is=Index+1;
第二更新单元,用于根据公式SIs=HASH(SIndex),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。The second updating unit is configured to obtain the updated first key parameter according to the formulaSis =HASH(SIndex ).
请参见图8,图8是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的装置的结构示意图,所述接入认证的装置8可以为上述实施例中的客户端的设备,所述接入认证的装置8可以包括接收单元801、解密单元802以及发送单元803,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 8. FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication apparatus provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication apparatus 8 may be the equipment of the client in the foregoing embodiment. The apparatus 8 may include a receiving
接收单元801,用于接收认证服务器发送的网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥;A receiving
解密单元802,用于将所述加密后的会话密钥进行解密,得到解密后的会话密钥;
发送单元803,用于将所述网络认证消息发送给所述客户端。The sending
请参见图9,图9是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图,所述接入认证的设备9可以为上述图4和图5实施例中客户端的终端设备,所述接入认证的设备9可以包括存储器901、通信模块902和处理器903,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 9. FIG. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication device 9 may be the terminal device of the client in the above-mentioned embodiments of FIG. 4 and FIG. 5. Therefore, The access authentication device 9 may include a
存储器901用于存储程序代码。The
处理器903用于调用存储器存储的程序代码执行如下步骤:The
通过通信模块902向认证服务器发送用户认证消息;Send a user authentication message to the authentication server through the
在所述认证服务器基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,通过通信模块902接收所述认证服务器发送的网络认证消息;In the case that the authentication server verifies that the identity of the client is legal based on the user authentication message, receiving the network authentication message sent by the authentication server through the
在所述客户端基于所述网络认证消息验证所述认证服务器身份合法的情况下,基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥;In the case that the client verifies that the identity of the authentication server is legal based on the network authentication message, obtain a session based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the update of the client key;
删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数。Delete the first key parameter before the update.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器903删除所述更新前的第一密钥参数之前,包括:In a possible implementation manner, before the
根据公式Ic=Index+1,得到更新后的第一计数值;According to the formula Ic=Index+1, the updated first count value is obtained;
根据公式SIc=HASH(SIc-1),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。According to the formula SIc =HASH(SIc-1 ), the updated first key parameter is obtained.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器903基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the
从所述认证服务器的消息参数中获取置位标识Re_sync;Obtain the set identifier Re_sync from the message parameter of the authentication server;
若所述Re_sync=1,将第一计数值置零,并执行所述客户端向认证服务器发送用户认证消息的步骤;If the Re_sync=1, set the first count value to zero, and execute the step of the client sending a user authentication message to the authentication server;
若所述Re_sync=0,基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥。If the Re_sync=0, the session key is obtained based on the random number of the client, the network authentication message and the first key parameter before the client is updated.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器903通过通信模块902向认证服务器发送用户认证消息,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the
基于所述客户端的身份标识、更新前的第一计数值以及所述客户端的随机数,得到所述客户端的消息参数;Obtain the message parameter of the client based on the identity of the client, the first count value before the update, and the random number of the client;
基于所述客户端的消息参数和所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成所述客户端的消息认证码;generating a message authentication code of the client based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the client;
通过通信模块902将用户认证消息发送给所述认证服务器。The user authentication message is sent to the authentication server through the
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器903基于所述客户端的随机数、所述网络认证消息以及所述客户端更新前的第一密钥参数得到会话密钥之前,包括:In a possible implementation manner, before the
基于所述认证服务器的消息参数、所述客户端的消息参数以及所述客户端的第二密钥参数生成第一消息认证码;generating a first message authentication code based on the message parameter of the authentication server, the message parameter of the client, and the second key parameter of the client;
判断所述第一消息认证码与所述认证服务器的消息认证码是否一致;Judging whether the first message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the authentication server;
若判断为是,判断所述认证服务器的身份合法;If it is judged to be yes, judge that the identity of the authentication server is legal;
若判断为否,判断所述认证服务器的身份非法,并终止所述客户端与所述认证服务器之间的接入认证。If the judgment is negative, it is judged that the identity of the authentication server is illegal, and the access authentication between the client and the authentication server is terminated.
请参见图10,图10是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图,所述接入认证的设备10可以为上述图4和图5实施例中的认证服务器,所述接入认证的设备10可以包括存储器1001、通信模块1002和处理器1003,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 10 . FIG. 10 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication device 10 may be the authentication server in the above-mentioned embodiments of FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 . The device 10 for access authentication may include a
存储器1001用于存储程序代码。The
处理器1003用于调用存储器存储的程序代码执行如下步骤:The
通过通信模块1002接收客户端发送的用户认证消息;Receive the user authentication message sent by the client through the
在基于所述用户认证消息验证所述客户端身份合法的情况下,基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥;Obtaining a session key based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server, and the user authentication message under the condition that the identity of the client is valid based on the user authentication message;
删除其更新前的第一密钥参数;delete the first key parameter before the update;
向接入端发送网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥。Send the network authentication message and the encrypted session key to the access end.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器1003基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥,包括:In a possible implementation manner, the
从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;Obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
若所述更新前的第一计数值大于或等于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,将第二计数值置0,并执行所述认证服务器接收客户端发送的用户认证消息的步骤;If the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the count threshold of the authentication server, set the second count value to 0, and execute the step of the authentication server receiving the user authentication message sent by the client;
若所述更新前的第一计数值小于所述认证服务器的计数阈值,基于所述第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥。If the first count value before the update is smaller than the count threshold of the authentication server, a session key is obtained based on the third key parameter, the random number of the authentication server, and the user authentication message.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器1003通过通信模块1002接收客户端发送的用户认证消息之后,包括:In a possible implementation manner, after the
从所述客户端的消息参数中获取更新前的第一计数值;Obtain the first count value before the update from the message parameter of the client;
判断所述更新前的第一计数值是否大于或等于更新前的第二计数值;Determine whether the first count value before the update is greater than or equal to the second count value before the update;
若判断为否,终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证;If the judgment is negative, terminate the access authentication between the authentication server and the client;
若判断为是,基于所述客户端的消息参数以及所述认证服务器的第二密钥参数生成第二消息认证码;If it is determined to be yes, generate a second message authentication code based on the message parameter of the client and the second key parameter of the authentication server;
判断所述第二消息认证码与所述客户端的消息认证码是否一致;Judging whether the second message authentication code is consistent with the message authentication code of the client;
若判断为是,判断所述客户端的身份合法;If it is judged to be yes, judge that the identity of the client is legal;
若判断为否,判断所述客户端的身份非法,并终止所述认证服务器与所述客户端之间的接入认证。If the judgment is negative, it is judged that the identity of the client is illegal, and the access authentication between the authentication server and the client is terminated.
在一种可能实现的方式中,处理器1003基于第三密钥参数、所述认证服务器的随机数以及所述用户认证消息得到会话密钥之前,包括:In a possible implementation manner, before the
根据公式SIndex=HASH(Index-Is)(SIs)得到第三密钥参数;Obtain the third key parameter according to the formula SIndex =HASH(Index-Is) (SIs );
所述认证服务器根据公式Is=Index+1,得到更新后的第二计数值;The authentication server obtains the updated second count value according to the formula Is=Index+1;
所述认证服务器根据公式SIs=HASH(SIndex),得到其更新后的第一密钥参数。The authentication server obtains its updated first key parameter according to the formula SIs =HASH(SIndex ).
请参见图11,图11是本申请实施例提供的一种接入认证的设备的结构示意图,所述接入认证的设备11可以为上述图4和图5实施例中的认证服务器,所述接入认证的设备11可以包括存储器1101、通信模块1102和处理器1103,其中,各个单元的详细描述如下:Please refer to FIG. 11 . FIG. 11 is a schematic structural diagram of an access authentication device provided by an embodiment of the present application. The access authentication device 11 may be the authentication server in the above-mentioned embodiments of FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 . The device 11 for access authentication may include a
存储器1101用于存储程序代码。The
处理器1103用于调用存储器存储的程序代码执行如下步骤:The
通过通信模块1102接收认证服务器发送的网络认证消息以及加密后的会话密钥;Receive the network authentication message and the encrypted session key sent by the authentication server through the
将所述加密后的会话密钥进行解密,得到解密后的会话密钥;Decrypting the encrypted session key to obtain the decrypted session key;
通过通信模块1102将所述网络认证消息发送给所述客户端。The network authentication message is sent to the client through the
本申请实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时,实现上述实施例及其各种可能的实现方式中的接入认证的方法。An embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, where a computer program is stored in the computer-readable storage medium, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the interfaces in the foregoing embodiment and various possible implementation manners thereof are implemented. method of entering authentication.
本申请实施例提供了一种计算机程序,该计算机程序包括指令,当所述计算机程序被计算机执行时,使得客户端可以执行上述实施例及其各种可能实现的方式中客户端所执行的流程、或认证服务器可以执行上述实施例及其各种可能实现的方式中认证服务器所执行的流程、或接入端可以执行上述实施例及其各种可能的实现方式中接入端所执行的流程。The embodiments of the present application provide a computer program, the computer program includes instructions, when the computer program is executed by a computer, so that the client can execute the processes executed by the client in the foregoing embodiments and various possible implementation manners thereof , or the authentication server may execute the process performed by the authentication server in the foregoing embodiment and its various possible implementation manners, or the access terminal may execute the procedure performed by the access terminal in the foregoing embodiment and its various possible implementation manners .
本申请实施例提供了一种芯片系统,该芯片系统包括处理器,用于支持客户端实现上述实施例及其各种可能方式中的方法所涉及的功能、或认证服务器实现上述实施例及其各种可能方式中的方法所涉及的功能、或接入端实现上述实施例及其各种可能的实现方式中的方法所涉及的功能。An embodiment of the present application provides a chip system, where the chip system includes a processor, and is configured to support a client to implement the functions involved in the methods in the foregoing embodiments and various possible manners, or an authentication server to implement the foregoing embodiments and their methods. The functions involved in the methods in the various possible manners, or the access terminal implements the functions involved in the methods in the foregoing embodiments and various possible implementation manners.
在一种可能的设计中,所述芯片系统还包括存储器,所述存储器用于保存第一设备或第二设备必要的程序指令和数据。该芯片系统,可以由芯片构成,也可以包含芯片和其它分立器件。In a possible design, the chip system further includes a memory for storing necessary program instructions and data of the first device or the second device. The chip system may be composed of chips, or may include chips and other discrete devices.
需要说明的是,上述实施例中的存储器,可以是只读存储器(read-only memory,ROM)或可存储静态信息和指令的其它类型的静态存储设备,随机存储器(random accessmemory,RAM)或者可存储信息和指令的其它类型的动态存储设备,也可以是电可擦可编程只读存储器(Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory,EEPROM)、只读光盘(Compact Disc Read-Only Memory,CD-ROM)或其它光盘存储、光碟存储(包括压缩光碟、激光碟、光碟、数字通用光碟、蓝光光碟等)、磁盘存储介质或者其它磁存储设备、或者能够用于携带或存储具有指令或数据结构形式的期望的程序代码并能够由计算机存取的任何其它介质,但不限于于此。存储器可以是独立存在,通过总线于处理器相连接。存储器可以和处理器集成在一起。It should be noted that, the memory in the above-mentioned embodiments may be a read-only memory (ROM) or other types of static storage devices that can store static information and instructions, a random access memory (RAM) or a random access memory (RAM). Other types of dynamic storage devices that store information and instructions can also be Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), Compact Disc Read-Only Memory (CD-ROM) or other optical disc storage, optical disc storage (including compact disc, laser disc, optical disc, digital versatile disc, blu-ray disc, etc.), magnetic disk storage medium or other magnetic storage device, or capable of being used to carry or store desired in the form of instructions or data structures program code and any other medium that can be accessed by a computer, but is not limited thereto. The memory may exist independently and be connected to the processor through a bus. The memory can be integrated with the processor.
上述实施例中的处理器,可以是通用中央处理器(CPU),微处理器,特定应用集成电路(application-specific integrated circuit,ASIC),或一个或多个用于控制以上方案程序执行的集成电路。The processor in the above-mentioned embodiments may be a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU), a microprocessor, an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), or one or more integrated circuits for controlling the execution of programs in the above solutions. circuit.
对于前述各方法实施例,为了简单描述,故将其都表达为一系列的动作组合,但是本领域的技术人员应该知悉,本申请并不受所描述的动作顺序的限制,因为依据本申请,某些步骤可能可以采用其它顺序或者同时进行。其次,本领域技术人员也应该知悉,说明书中所描述的实施例均属于优选实施例,所涉及的动作和模块并不一定是本申请所必须的。For the foregoing method embodiments, for the sake of simple description, they are all expressed as a series of action combinations, but those skilled in the art should know that the present application is not limited by the described action sequence, because according to the present application, Certain steps may be performed in other orders or simultaneously. Secondly, those skilled in the art should also know that the embodiments described in the specification are all preferred embodiments, and the actions and modules involved are not necessarily required by the present application.
在本申请所提供的几个实施例中,应该理解到,所揭露的装置,可通过其它方式实现。例如,以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,例如上述单元的划分,仅仅为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式,例如多个单元或组件可以结合或者可以集成到另一个系统,或一些特征可以忽略,或不执行。In the several embodiments provided in this application, it should be understood that the disclosed apparatus may be implemented in other manners. For example, the device embodiments described above are only illustrative. For example, the division of the above-mentioned units is only a logical function division. In actual implementation, there may be other division methods. For example, multiple units or components may be combined or integrated. to another system, or some features can be ignored, or not implemented.
上述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者不是也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,既可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部单元来实现本实施例方案的目的。The units described above as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and components shown as units may or may not be physical units, and may be located in one place or distributed to multiple network units. Some or all of the units may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution in this embodiment.
另外,在本申请各实施例中的各功能单元可以集成在一个处理单元中,也可以是各个单元单独物理存在,也可以是两个或两个以上单元集成在一个单元中。上述集成单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能单元的形式实现。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present application may be integrated into one processing unit, or each unit may exist physically alone, or two or more units may be integrated into one unit. The above-mentioned integrated unit may be implemented in the form of hardware, or may be implemented in the form of software functional units.
上述集成的单元如果以软件功能单元的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,可以存储在一个计算机可读存储介质中。基于这样理解,本申请的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分或者该技术方案的全部或部分可以以软件的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以为个人计算机、服务器或者网络设备等,具体可以是计算机设备中的处理器)执行本申请各个实施例上述方法的全部或部分步骤。其中,前述的存储介质可包括:U盘、移动硬盘、磁碟、光盘、只读存储器(read-only memory,ROM)或者随机存取存储器(random access memory,RAM)等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。If the above-mentioned integrated units are implemented in the form of software functional units and sold or used as independent products, they may be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. Based on this understanding, the technical solution of the present application can be embodied in the form of software in essence, or the part that contributes to the prior art, or all or part of the technical solution, and the computer software product is stored in a storage medium, including Several instructions are used to cause a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc., specifically a processor in the computer device) to execute all or part of the steps of the foregoing methods in various embodiments of the present application. Wherein, the aforementioned storage medium may include: U disk, mobile hard disk, magnetic disk, optical disk, read-only memory (read-only memory, ROM) or random access memory (random access memory, RAM) and other various programs that can store program codes medium.
以上所述,以上实施例仅用以说明本申请的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本申请进行了详细的说明,本领域的技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本申请各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。As mentioned above, the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present application, but not to limit them; although the present application has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those skilled in the art should understand that: The technical solutions described in the embodiments are modified, or some technical features thereof are equivalently replaced; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application.
Claims (13)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110339645.8ACN115150110A (en) | 2021-03-30 | 2021-03-30 | Method for access authentication, related device, equipment and readable storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110339645.8ACN115150110A (en) | 2021-03-30 | 2021-03-30 | Method for access authentication, related device, equipment and readable storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115150110Atrue CN115150110A (en) | 2022-10-04 |
Family
ID=83403550
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110339645.8APendingCN115150110A (en) | 2021-03-30 | 2021-03-30 | Method for access authentication, related device, equipment and readable storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115150110A (en) |
- 2021
- 2021-03-30CNCN202110339645.8Apatent/CN115150110A/enactivePending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10079813B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for secure network enclaves | |
| CN100388244C (en) | Method and system for remotely changing communication password | |
| CN101459506B (en) | Cipher key negotiation method, system, customer terminal and server for cipher key negotiation | |
| WO2018045817A1 (en) | Mobile network authentication method, terminal device, server and network authentication entity | |
| CN112165386B (en) | Data encryption method and system based on ECDSA | |
| TW201014314A (en) | Techniques for secure channelization between UICC and a terminal | |
| WO2010078755A1 (en) | Method and system for transmitting electronic mail, wlan authentication and privacy infrastructure (wapi) terminal thereof | |
| CN114268439A (en) | Identity-based authentication key negotiation method based on lattice | |
| TWI804179B (en) | Quantum safe key exchange scheme | |
| EP4270866A1 (en) | Identity authentication method and apparatus, device, chip, storage medium, and program | |
| WO2022135391A1 (en) | Identity authentication method and apparatus, and storage medium, program and program product | |
| CN117201000A (en) | Mass data secure communication method, equipment and medium based on temporary key agreement | |
| CN115484038A (en) | A data processing method and device thereof | |
| CN111836260A (en) | Authentication information processing method, terminal and network device | |
| CN118540163A (en) | Quantum security enhancement method for national security SSL VPN protocol | |
| CN118540165A (en) | Quantum security enhancement method for national security IPSec VPN protocol | |
| CN119382897A (en) | A method and system for quickly building a national secret encryption channel | |
| WO2021032304A1 (en) | Gateway devices and methods for performing a site-to-site communication | |
| WO2022135394A1 (en) | Identity authentication method and apparatus, storage medium, program, and program product | |
| WO2022135387A1 (en) | Identity authentication method and apparatus | |
| CN118713920A (en) | A method for verifying access security of an Internet of Things device | |
| CN114760040A (en) | Identity authentication method and device | |
| Niemiec et al. | Authentication in virtual private networks based on quantum key distribution methods | |
| US20240129115A1 (en) | Generating post-quantum pre-shared keys | |
| WO2022135386A1 (en) | Method and device for identity authentication |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |