CN115072877A - Ecological filter wall and application thereof - Google Patents
Ecological filter wall and application thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115072877A CN115072877ACN202210651796.1ACN202210651796ACN115072877ACN 115072877 ACN115072877 ACN 115072877ACN 202210651796 ACN202210651796 ACN 202210651796ACN 115072877 ACN115072877 ACN 115072877A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- plants
- ecological filter
- filter wall
- fibers
- wall
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription55
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription31
- 238000003911water pollutionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 238000011065in-situ storageMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 241000196324EmbryophytaSpecies0.000claimsdescription90
- 241000195493CryptophytaSpecies0.000claimsdescription17
- 229920002748Basalt fiberPolymers0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000002657fibrous materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription8
- 244000025254Cannabis sativaSpecies0.000claimsdescription7
- 239000004952PolyamideSubstances0.000claimsdescription7
- 229920002647polyamidePolymers0.000claimsdescription7
- 244000205574Acorus calamusSpecies0.000claimsdescription5
- 229920000049Carbon (fiber)Polymers0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000004917carbon fiberSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000002689soilSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 229920000742CottonPolymers0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 235000005273Canna coccineaNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- 240000008555Canna flaccidaSpecies0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003575carbonaceous materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 241000748223AlismaSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 244000291564Allium cepaSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 240000001592Amaranthus caudatusSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000009328Amaranthus caudatusNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000017166Bambusa arundinaceaNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000017491Bambusa tuldaNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000011996Calamus deerratusNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 241001233914Chelidonium majusSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 241000234435LiliumSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004677NylonSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000014676Phragmites communisNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 244000082204Phyllostachys viridisSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000015334Phyllostachys viridisNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 241001223864Sphyraena barracudaSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 240000001398Typha domingensisSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920002978VinylonPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011425bambooSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052909inorganic silicateInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001778nylonPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000728polyesterPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004575stoneSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 241000195967AnthocerosSpecies0.000claims1
- 241000282330Procyon lotorSpecies0.000claims1
- 241000607720SerratiaSpecies0.000claims1
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethaneChemical compoundCVNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 244000005700microbiomeSpecies0.000abstractdescription15
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription14
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000002195synergetic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description14
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000description14
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000description14
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description12
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphorusChemical compound[P]OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description12
- 239000003344environmental pollutantSubstances0.000description12
- 229910052698phosphorusInorganic materials0.000description12
- 239000011574phosphorusSubstances0.000description12
- 231100000719pollutantToxicity0.000description12
- 229910052757nitrogenInorganic materials0.000description6
- XKMRRTOUMJRJIA-UHFFFAOYSA-Nammonia nh3Chemical compoundN.NXKMRRTOUMJRJIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description5
- 239000000945fillerSubstances0.000description5
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description5
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description4
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000description4
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description4
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethyl methacrylateChemical compoundCOC(=O)C(C)=CVVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229920005372Plexiglas®Polymers0.000description3
- MMDJDBSEMBIJBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[NH6+3]Chemical compound[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[NH6+3]MMDJDBSEMBIJBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 238000007667floatingMethods0.000description3
- 239000011521glassSubstances0.000description3
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description3
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000description3
- 229910002651NO3Inorganic materials0.000description2
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-NNitrateChemical compound[O-][N+]([O-])=ONHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000001914filtrationMethods0.000description2
- 239000003501hydroponicsSubstances0.000description2
- 230000000813microbial effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000001546nitrifying effectEffects0.000description2
- 235000015097nutrientsNutrition0.000description2
- 230000028327secretionEffects0.000description2
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description2
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000002028BiomassSubstances0.000description1
- 241001503578Phaeoceros laevisSpecies0.000description1
- 241000589516PseudomonasSpecies0.000description1
- 229910000831SteelInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000000370acceptorSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007227biological adhesionEffects0.000description1
- 230000036983biotransformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000000356contaminantSubstances0.000description1
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000005202decontaminationMethods0.000description1
- 230000003588decontaminative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description1
- 238000004090dissolutionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002708enhancing effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000003912environmental pollutionMethods0.000description1
- 230000029142excretionEffects0.000description1
- 230000012010growthEffects0.000description1
- 238000003306harvestingMethods0.000description1
- 238000010348incorporationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012423maintenanceMethods0.000description1
- 230000014759maintenance of locationEffects0.000description1
- 238000006864oxidative decomposition reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000002957persistent organic pollutantSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008635plant growthEffects0.000description1
- 231100000614poisonToxicity0.000description1
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000746purificationMethods0.000description1
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000005067remediationMethods0.000description1
- 239000010865sewageSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000010959steelSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002352surface waterSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003440toxic substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/32—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage characterised by the animals or plants used, e.g. algae
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/30—Aerobic and anaerobic processes
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/30—Aerobic and anaerobic processes
- C02F3/301—Aerobic and anaerobic treatment in the same reactor
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/30—Aerobic and anaerobic processes
- C02F3/302—Nitrification and denitrification treatment
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/32—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage characterised by the animals or plants used, e.g. algae
- C02F3/322—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage characterised by the animals or plants used, e.g. algae use of algae
- C02F3/325—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage characterised by the animals or plants used, e.g. algae use of algae as symbiotic combination of algae and bacteria
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/34—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage characterised by the microorganisms used
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02W—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO WASTEWATER TREATMENT OR WASTE MANAGEMENT
- Y02W10/00—Technologies for wastewater treatment
- Y02W10/10—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Hydrology & Water Resources (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Ecology (AREA)
- Purification Treatments By Anaerobic Or Anaerobic And Aerobic Bacteria Or Animals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及水体污染治理技术领域,尤其涉及一种生态过滤墙及其应用。The invention relates to the technical field of water pollution control, in particular to an ecological filter wall and its application.
背景技术Background technique
在地表水处理过程中,江、河、湖泊中的污染物处理较为困难,其水流量大,水质波动频繁,因此最好采用对水体自身的生态不会造成影响的原位处理技术。现有的水体原位处理技术有人工浮岛、水下森林、生态护坡等。人工浮岛主要是通过植物生长过程中对水体中氮磷的吸收作用,然而单纯依靠植物根系对污染物的吸收,难以达到高效去除水中污染物的目的。与此同时,人工浮岛寿命短、抗风浪性能较差且受季节影响大,在使用过程中也受到各个方面的限制。水下森林是通过根、茎、叶直接吸收污水中的营养物质把大量营养物质固定在其生物体内,同时植物的根部中可释放大量的溶解氧,保持水体高溶氧状态,达到净化水质的目的。水下森林技术适宜在水流流速较低,水位变化小的水体中使用,且沉水植物生长速度较快时还需要进行及时收割,增加了后期维护成本。生态护坡中的水生植物能够减缓水流流速并对其中颗粒态污染物起到过滤和拦截的作用,繁茂的植被和土壤也能吸收水体中的污染物。但是生态护坡只能对水面较窄的水体有较好的污染物去除效果,且其仅发挥了植物对水体的净化作用,微生物在其中发挥的作用微乎其微,导致污染物的整体去除效能不高。In the process of surface water treatment, it is difficult to treat pollutants in rivers, rivers and lakes. The water flow is large and the water quality fluctuates frequently. Therefore, it is best to use in-situ treatment technology that will not affect the ecology of the water body itself. The existing in-situ treatment technologies for water bodies include artificial floating islands, underwater forests, and ecological slope protection. Artificial floating islands mainly absorb nitrogen and phosphorus in the water during the growth of plants. However, it is difficult to efficiently remove pollutants in water by simply relying on the absorption of pollutants by plant roots. At the same time, artificial floating islands have short lifespan, poor wind and wave resistance, and are greatly affected by seasons, and are also limited in various aspects during use. Underwater forests directly absorb nutrients in sewage through roots, stems, and leaves to fix a large amount of nutrients in their organisms. At the same time, a large amount of dissolved oxygen can be released from the roots of plants, maintaining a high dissolved oxygen state in the water body and purifying water. Purpose. Underwater forest technology is suitable for use in water bodies with low flow velocity and small changes in water level, and when submerged plants grow rapidly, timely harvesting is required, which increases maintenance costs in the later period. The aquatic plants in the ecological slope protection can slow down the water flow speed and filter and intercept the particulate pollutants. The lush vegetation and soil can also absorb the pollutants in the water body. However, ecological slope protection can only have a good pollutant removal effect on water bodies with narrow water surface, and it only plays a role in the purification of water bodies by plants, and microorganisms play a minimal role in it, resulting in a low overall removal efficiency of pollutants.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对上述技术问题,本发明提供一种生态过滤墙及其应用,以具有吸附/过滤、生物转化和植物吸收功能的生态过滤墙,实现对受污染水体的修复,该技术具有构型灵活、模块化程度高、去污能力强且人工痕迹小等优点。In view of the above technical problems, the present invention provides an ecological filter wall and its application, which can achieve the restoration of polluted water bodies with an ecological filter wall with functions of adsorption/filtration, biotransformation and plant absorption. The technology has the advantages of flexible configuration, modular It has the advantages of high chemical degree, strong decontamination ability and small artificial trace.
为实现上述目的,本发明采取的技术方案为:To achieve the above object, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一方面,本发明提供一种用于防治水污染的生态过滤墙,包括墙体、掺杂于所述墙体中的纤维、栽种于所述墙体顶端的挺水植物和栽种于所述墙体至少一侧外立面的沉水植物。In one aspect, the present invention provides an ecological filter wall for preventing and controlling water pollution, comprising a wall body, fibers mixed in the wall body, emergent plants planted on the top of the wall body, and an emergent plant planted on the wall body Submerged plants on at least one side of the body.
作为优选地实施方式,所述墙体的材料选自碳材料、聚酰胺纤维材料、聚酯纤维材料、生物基质材料、无机硅酸盐材料、尼龙材料和维尼纶材料中的一种或几种。As a preferred embodiment, the material of the wall is selected from one or more of carbon materials, polyamide fiber materials, polyester fiber materials, biological matrix materials, inorganic silicate materials, nylon materials and vinylon materials .
作为优选地实施方式,所述掺杂于所述墙体中的纤维选自玄武岩纤维、碳纤维、改性纤维和棉花纤维中的一种或几种;As a preferred embodiment, the fibers doped in the wall are selected from one or more of basalt fibers, carbon fibers, modified fibers and cotton fibers;
优选地,所述纤维的掺杂量为3~9mg/g;Preferably, the doping amount of the fibers is 3-9 mg/g;
优选地,所述纤维的长度为5~10cm。Preferably, the length of the fibers is 5-10 cm.
在本发明的技术方案中,所述植物的种类由水体的水质及气候确定;In the technical solution of the present invention, the type of the plant is determined by the water quality and climate of the water body;
作为优选地实施方式,所述挺水植物选自水培或在含土基质中生长的具有较强吸收氮磷能力且根系泌氧能力较强的挺水类植物中的一种或多种;具体可列举出千屈菜、鸢尾、泽泻、慈姑、藨草、美人蕉、菖蒲、旱伞竹、芦苇、香蒲、水葱、翠芦莉、再力花、梭鱼草和铜钱草等。As a preferred embodiment, the emergent plants are selected from one or more of the emergent plants grown in hydroponics or soil-containing substrates with strong nitrogen and phosphorus absorption capacity and strong root oxygen excretion capacity; Specifically, celandine, iris, Alisma, Cigu, thorn grass, canna, calamus, parasol bamboo, reed, cattail, scallion, green lily, Zaili flower, barracuda, and copper coin grass, etc. can be listed.
作为优选地实施方式,所述沉水植物选自水培或在含土基质中生长的适应各种水深且泌氧能力较强的沉水类植物中的一种或多种,具体可列举出菹草、矮苦草、水蕴草、狸藻、川蔓藻、金鱼藻、黑藻、轮叶黑藻、大茨藻和狐尾藻等。As a preferred embodiment, the submerged plants are selected from one or more of hydroponics or submerged plants grown in soil-containing substrates that are adapted to various water depths and have strong oxygen secretion capabilities. Pseudomonas serrata, dwarf bitter grass, water Yuncao, Uriconas algae, Swan algae, Hornwort algae, Black algae, Black algae, Daci algae and Foxtail algae, etc.
作为优选地实施方式,所述墙体的顶端和至少一侧外立面上开设有植物种植孔,所述植物种植孔内设置有植物种植篮;所述挺水植物或沉水植物栽种于所述植物种植篮内;As a preferred embodiment, plant planting holes are opened on the top of the wall and on at least one side of the outer facade, and plant planting baskets are arranged in the plant planting holes; the emergent plants or submerged plants are planted in the in the planting basket of said plants;
优选地,所述植物种植篮内设置有用于固定所述挺水植物或沉水植物的石头或含土基质。Preferably, a stone or soil-containing substrate for fixing the emergent or submerged plants is arranged in the planting basket.
作为优选地实施方式,所述植物种植篮内还放置有纤维;在本发明的技术方案中,所述纤维从水体中原位富集功能菌群,富集的微生物与植物间通过协同作用加强对污染物的去除;As a preferred embodiment, fibers are also placed in the plant growing basket; in the technical solution of the present invention, the fibers are in situ enriched with functional flora from the water body, and the enriched microorganisms and the plants are strengthened through synergy. removal of contaminants;
优选地,所述纤维选自玄武岩纤维、碳纤维、改性纤维和棉花纤维中的一种或几种。Preferably, the fibers are selected from one or more of basalt fibers, carbon fibers, modified fibers and cotton fibers.
作为优选地实施方式,所述植物种植孔的直径为5~15cm,每个植物种植孔中种植1~3棵挺水植物或沉水植物;As a preferred embodiment, the diameter of the plant planting hole is 5-15 cm, and 1-3 emergent plants or submerged plants are planted in each plant planting hole;
优选地,所述植物种植孔在墙体上的开孔密度由所述挺水植物或沉水植物的种植密度决定;所述植物的种植密度一般为30~60株/m2。Preferably, the opening density of the plant planting holes on the wall is determined by the planting density of the emergent plants or submerged plants; the planting density of the plants is generally 30-60 plants/m2 .
在本发明的技术方案中,所述生态过滤墙应用过程中,其竖直浸入水体中,由此确定其顶端和外立面;In the technical solution of the present invention, during the application process of the ecological filter wall, it is vertically immersed in the water body, thereby determining its top and outer facade;
优选地,所述生态过滤墙的厚度由水体的污染程度决定,优选为0.3m~1m。生态过滤墙在水体中所占体积率可根据水质污染情况确定,一般为10%~40%。Preferably, the thickness of the ecological filter wall is determined by the pollution degree of the water body, and is preferably 0.3 m to 1 m. The volume ratio of the ecological filter wall in the water body can be determined according to the water pollution, generally 10% to 40%.
在本发明的技术方案中,所述生态过滤墙使用过程中完全插入水中,可以通过钢结构进行固定,顶端种植的挺水植物露出水面,外立面种植的沉水植物在水面以下。In the technical solution of the present invention, the ecological filter wall is completely inserted into the water during use, and can be fixed by a steel structure, the emergent plants planted at the top are exposed to the water surface, and the submerged plants planted on the facade are below the water surface.
作为优选地实施方式,所述生态过滤墙由多个生态过滤墙块体在竖直方向上堆叠组装而成;在某些具体的实施方式中,所述单个生态过滤墙块体的规格为:长0.5~5m,宽0.3m~0.5m,厚0.3~1m,所述单个生态过滤墙块体的厚度即为生态过滤墙的厚度;其中,仅所述生态过滤墙顶部的生态过滤墙块体的顶端开设有种植孔;在本发明的技术方案中,可以根据水体的深度用捆扎绳将多个生态过滤墙块体垂直贯通连接。As a preferred embodiment, the ecological filter wall is assembled by stacking a plurality of ecological filter wall blocks in the vertical direction; in some specific embodiments, the specifications of the single ecological filter wall block are: The length is 0.5-5m, the width is 0.3m-0.5m, and the thickness is 0.3-1m. The thickness of the single ecological filter wall block is the thickness of the ecological filter wall; wherein, only the ecological filter wall block at the top of the ecological filter wall A planting hole is opened at the top of the water body; in the technical scheme of the present invention, a plurality of ecological filter wall blocks can be connected vertically through a binding rope according to the depth of the water body.
另一方面,本发明提供上述生态过滤墙在治理受污染水体中的应用。In another aspect, the present invention provides the application of the above-mentioned ecological filter wall in the treatment of polluted water bodies.
优选地,在污染河流或湖泊的原位修复中的应用。Preferably, the application in the in situ remediation of polluted rivers or lakes.
上述技术方案具有如下优点或者有益效果:The above technical scheme has the following advantages or beneficial effects:
本发明提供一种基于挺水植物和沉水植物的墙体中掺杂有纤维的生态过滤墙及其应用,本发明在墙体顶端种植挺水植物,至少一侧外立面种植沉水植物,并掺入纤维原位驯养富集水体中的土著功能微生物,通过微生物和植物的协同作用增强污染去除能力,并具有一定的景观效果。其中,墙体可以通过基体材料的模块化生产,出厂后在施工现场即可便捷组装使用,减少了人为施工痕迹,使用后无需拆除,在长期维持水体水质稳定的同时,也可以完善水体的生态景观体系。The invention provides an ecological filter wall based on emergent plants and submerged plants doped with fibers in the wall and its application. The present invention plants emergent plants at the top of the wall and submerged plants are planted on at least one side of the outer facade. , and incorporates the indigenous functional microorganisms in the in situ domesticated and enriched water body with fibers, which enhances the pollution removal ability through the synergistic effect of microorganisms and plants, and has a certain landscape effect. Among them, the wall can be produced by the modularization of the base material, which can be easily assembled and used on the construction site after leaving the factory, reducing the traces of artificial construction, and does not need to be dismantled after use. While maintaining the stability of the water quality for a long time, it can also improve the ecology of the water body. landscape system.
相对于现有技术,本发明具备以下优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
1.掺杂于墙体中的纤维材料具有成本低、力学性能好、对微生物有较好的亲和性、无环境污染等优点,将部分纤维掺入墙体基体中可以提高生态过滤墙的微生物量,再将部分纤维材料放置在植物种植篮中,植物种植篮中存在好氧和缺氧的微环境,有利于纤维材料上附着的微生物的脱氮作用;1. The fiber material doped in the wall has the advantages of low cost, good mechanical properties, good affinity for microorganisms, and no environmental pollution. The incorporation of some fibers into the wall matrix can improve the ecological filter wall. Microorganisms, and then place part of the fiber material in the planting basket, there are aerobic and anoxic microenvironments in the planting basket, which is conducive to the denitrification of microorganisms attached to the fiber material;
2.挺水植物种植在生态过滤墙的顶端,可有效吸收水体中的氮磷等污染物质,为微生物的生长提供载体,并通过根系泌氧为生物填料和纤维材料表面的微生物提供自上而下,由高到低的溶氧梯度,丰富微生物群落结构,进而强化微生物对污染物的去除效果;2. Emergent plants are planted at the top of the ecological filter wall, which can effectively absorb nitrogen and phosphorus and other pollutants in the water body, provide a carrier for the growth of microorganisms, and provide top-to-bottom supply for microorganisms on the surface of biological fillers and fiber materials through oxygen secretion by roots. Under the dissolved oxygen gradient from high to low, the microbial community structure is enriched, thereby enhancing the removal effect of microorganisms on pollutants;
3.沉水植物种植在生态过滤墙的外立面,其产生的氧气为墙体上富集的功能微生物提供电子受体,促进水体有机污染物的氧化分解,生态过滤墙本身的厚度会在墙体两侧形成稳定的溶氧梯度,进而在不同的氧浓度区域完成不同形态氮的去除;同时沉水植物可以提高水体的溶解氧浓度,抑制水体有毒物质的反应,为水生生物营造良好的水生态环境;3. Submerged plants are planted on the outer facade of the ecological filter wall, and the oxygen produced by them provides electron acceptors for functional microorganisms enriched on the wall, and promotes the oxidative decomposition of organic pollutants in the water body. The thickness of the ecological filter wall itself will be A stable dissolved oxygen gradient is formed on both sides of the wall, and then different forms of nitrogen are removed in different oxygen concentration areas; at the same time, submerged plants can increase the dissolved oxygen concentration in the water body, inhibit the reaction of toxic substances in the water body, and create a good environment for aquatic organisms. water ecological environment;
4.本发明提供的生态过滤强以碳材料、生物基质材料等填料作为墙体的基体材料,具有比表面积大、孔隙结构稳定、亲水性好、生物附着性强、吸附能力较强等特点,可以短时间内增加生态过滤墙内微生物生物量,强化污染物转化,有效提高生态过滤墙对污染物的去除率。4. The ecological filtration provided by the present invention uses carbon materials, biological matrix materials and other fillers as the matrix materials of the wall, which has the characteristics of large specific surface area, stable pore structure, good hydrophilicity, strong biological adhesion, and strong adsorption capacity. It can increase the microbial biomass in the ecological filter wall in a short time, strengthen the transformation of pollutants, and effectively improve the removal rate of pollutants by the ecological filter wall.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是实施例1中的生态过滤墙构建的水污染处理模拟反应器D的结构图。1 is a structural diagram of a water pollution treatment simulation reactor D constructed by an ecological filter wall in Example 1.
图2是实施例1-3中的生态过滤墙的结构图。FIG. 2 is a structural diagram of an ecological filter wall in Examples 1-3.
图3是实施例1中的生态过滤墙构建的水污染处理模拟反应器对氨氮的去除效果图。3 is a diagram showing the removal effect of ammonia nitrogen by a water pollution treatment simulated reactor constructed by an ecological filter wall in Example 1.
图4是实施例1中的生态过滤墙构建的水污染处理模拟反应器对硝氮的去除效果图。4 is a diagram showing the removal effect of nitrate and nitrogen by the simulated reactor for water pollution treatment constructed by the ecological filter wall in Example 1.
图5是实施例1中的生态过滤墙构建的水污染处理模拟反应器对总磷的去除效果图。5 is a diagram showing the removal effect of total phosphorus by the simulated reactor for water pollution treatment constructed by the ecological filter wall in Example 1.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下述实施例仅仅是本发明的一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。因此,以下提供的本发明实施例中的详细描述并非旨在限制要求保护的本发明的范围,而是仅仅表示本发明的选定实施例。基于本发明的实施例,本领域技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明的保护范围。The following embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of the embodiments. Accordingly, the detailed descriptions of the embodiments of the invention provided below are not intended to limit the scope of the invention as claimed, but are merely representative of selected embodiments of the invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art without creative work fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
在本发明中,若非特指,所有的设备和原料等均可从市场购得或是本行业常用的。下述实施例中的方法,如无特别说明,均为本领域的常规方法。In the present invention, unless otherwise specified, all equipment and raw materials can be purchased from the market or commonly used in the industry. The methods in the following examples, unless otherwise specified, are conventional methods in the art.
实施例1:Example 1:
本实施例以长×宽×高为350mm×350mm×360mm的长方体有机玻璃容器构建反应器D并模拟水污染处理,反应器内有效容积为30L,结构如图1所示,玻璃容器内设置四块有机玻璃挡板III用以固定生态过滤墙,玻璃容器左侧面底部设置有进水口I、玻璃容器右侧面距离底部32cm处设置有出水口II;In this example, a cuboid organic glass container with a length × width × height of 350 mm × 350 mm × 360 mm is used to construct a reactor D and simulate water pollution treatment. The effective volume in the reactor is 30 L, and the structure is shown in Figure 1. A piece of plexiglass baffle III is used to fix the ecological filter wall, the bottom of the left side of the glass container is provided with a water inlet I, and the right side of the glass container is provided with a water outlet II at a distance of 32 cm from the bottom;
生态过滤墙的结构如图2所示,该生态过滤墙的墙体2-1由聚酰胺纤维构成,玄武岩纤维2-3掺杂于墙体2-1中,掺杂量为3mg/g,长度为5cm;该墙体的顶端和右侧面上开设有植物种植孔,内置直径为50mm,高为75mm的镂空植物种植篮,植物种植篮中种植有植物2-2,植物种植篮底部放有砾石用以固定植物,植物的根系处还放置有5cm长的玄武岩纤维。The structure of the ecological filter wall is shown in Figure 2. The wall 2-1 of the ecological filter wall is made of polyamide fiber, and the basalt fiber 2-3 is doped in the wall 2-1, and the doping amount is 3mg/g. The length is 5cm; the top and right side of the wall are provided with plant planting holes, and a hollow plant planting basket with a diameter of 50mm and a height of 75mm is built in. The plant planting basket is planted with 2-2 plants, and the bottom of the plant planting basket is placed There are gravels to fix the plants, and 5cm long basalt fibers are placed at the roots of the plants.
本实施例中,生态过滤墙由三块生态过滤墙块体(350mm×100mm×80 mm)竖直叠放组装而成,最上方的生态过滤墙块体的上表面种植的植物为挺水植物菖蒲,种植密度为115棵/m2;三块生态过滤墙块体叠放后的右侧面种植的植物为沉水植物黑藻,种植密度为140棵/m2;组装后的过滤墙的大小为350 mm×100mm×240mm,In this embodiment, the ecological filter wall is assembled by vertically stacking three ecological filter wall blocks (350mm×100mm×80mm), and the plants planted on the upper surface of the uppermost ecological filter wall block are emergent plants calamus, the planting density is 115 trees/m2 ; the plants planted on the right side of the three ecological filter wall blocks after stacking are submerged black algae, and the planting density is 140 trees/m2 ; The size is 350mm×100mm×240mm,
模拟处理过程中,将上述组装好的生态过滤墙按照种植沉水植物的侧面朝向出水口放置于有机玻璃容器构建的反应器D中,并用有机玻璃挡板预设的位置固定好,进水为30L配水,水质参考劣Ⅴ类水质,设定水力停留时间为3d。During the simulation process, the above-mentioned assembled ecological filter wall was placed in the reactor D constructed by the plexiglass container according to the side of the planted submerged plants facing the water outlet, and fixed with the preset position of the plexiglass baffle. 30L water distribution, the water quality is inferior to Class V water quality, and the hydraulic retention time is set to 3d.
效果测试:Effect test:
本实施例测试了上述反应器D系统运行稳定后出水的氨氮、硝氮、总磷去除效果。In this example, the removal effects of ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen and total phosphorus in the effluent after the stable operation of the above-mentioned reactor D system were tested.
本实施例还设置了对照组反应器A、B、C:The present embodiment also sets the control group reactors A, B, and C:
反应器A中的生态过滤墙为聚酰胺纤维构成的墙体;The ecological filter wall in the reactor A is a wall composed of polyamide fibers;
反应器B中的生态过滤墙由聚酰胺纤维构成的墙体和掺杂于墙体的玄武岩纤维构成,纤维掺杂量同反应器D;The ecological filter wall in the reactor B is composed of a wall composed of polyamide fibers and basalt fibers doped into the wall, and the amount of fiber doping is the same as that of the reactor D;
反应器C中的生态过滤墙由聚酰胺纤维构成墙体,且顶端种植挺水植物菖蒲,种植密度同反应器D;The ecological filter wall in the reactor C is made up of polyamide fibers, and the emergent plant calamus is planted at the top, and the planting density is the same as that of the reactor D;
反应器A、B、C、D的测试结果图见图3、图4和图5:The test results of reactors A, B, C, and D are shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5:
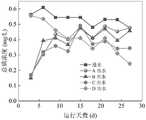
从图3可以看出,进水氨氮的浓度为4.0±0.8mg/L,生态过滤墙的氨氮去除率最终稳定在95%以上,最高可达到100%,而反应器A、B和C的氨氮平均去除率仅为23.8%、26.8%和32.0%;It can be seen from Figure 3 that the concentration of ammonia nitrogen in the influent is 4.0 ± 0.8 mg/L, the ammonia nitrogen removal rate of the ecological filter wall is finally stabilized at more than 95%, and the highest can reach 100%, while the ammonia nitrogen in reactors A, B and C The average removal rate is only 23.8%, 26.8% and 32.0%;
从图4可以看出,进水的硝氮浓度为6.3±0.7mg/L,四个反应器出水的硝氮含量都处于较低的水平,主要是因为反应器A、B、C中的溶解氧浓度偏低,有利于反硝化菌充分发挥作用;添加了沉水植物的生态过滤墙反应器D提高了水体中的溶解氧浓度,但是由于生态过滤墙另一侧处于缺氧状态,反应器中依然存在反硝化菌的所以出水硝氮的浓度也可以维持在较低的水平;It can be seen from Figure 4 that the nitrate nitrogen concentration in the influent is 6.3±0.7 mg/L, and the nitrate nitrogen content in the effluent of the four reactors is at a low level, mainly because of the dissolution in reactors A, B, and C. The low oxygen concentration is conducive to the full effect of denitrifying bacteria; the ecological filter wall reactor D added with submerged plants increases the dissolved oxygen concentration in the water body, but because the other side of the ecological filter wall is in an anoxic state, the reactor There are still denitrifying bacteria in the effluent, so the concentration of nitrate and nitrogen in the effluent can also be maintained at a low level;
从图5可以看出,进水总磷浓度为0.54±0.04mg/L,添加了植物的生态过滤墙对水中总磷的去除效果明显优于未种植植物的两组,A、B、C、D四组反应器运行27天对总磷的去除率分别为2.19%、6.14%、29.3%和47.84%。总磷的去除主要是由于植物对磷的吸收,生物填料的吸附效果并不显著。反应器运行初期,种植了沉水植物的反应器D出水中的总磷含量很高,可能是因为植物还没有适应反应器中的环境,反应器运行一段时间后,出水中的总磷浓度明显下降。It can be seen from Figure 5 that the total phosphorus concentration in the influent is 0.54±0.04mg/L, and the removal effect of the ecological filter wall with plants on the total phosphorus in the water is obviously better than that of the two groups without plants, A, B, C, The removal rates of total phosphorus in four groups of reactors running for 27 days were 2.19%, 6.14%, 29.3% and 47.84%, respectively. The removal of total phosphorus was mainly due to the absorption of phosphorus by plants, and the adsorption effect of biological fillers was not significant. In the early stage of the reactor operation, the total phosphorus content in the effluent of the reactor D where the submerged plants were planted was very high. It may be because the plants have not yet adapted to the environment in the reactor. After the reactor runs for a period of time, the total phosphorus concentration in the effluent is obvious decline.
通过上述效果实施可以看出,本发明能够利用生物填料为微生物的附着提供载体,种植植物后,反应器中单侧的溶解氧浓度显著提高,富集了更多的硝化菌,增强了硝化能力,与此同时,未种植沉水植物一侧的溶氧浓度较低,可以为反硝化菌提供合适的生存场所。种植沉水植物后丰富了生物填料中微生物的多样性,使得系统的运行效果更加稳定,极大的提高了污染物的去除效能。It can be seen from the implementation of the above effects that the present invention can use biological fillers to provide a carrier for the attachment of microorganisms. After planting plants, the dissolved oxygen concentration on one side of the reactor is significantly increased, more nitrifying bacteria are enriched, and the nitrifying ability is enhanced. At the same time, the dissolved oxygen concentration on the side without submerged plants is lower, which can provide a suitable living place for denitrifying bacteria. After planting submerged plants, the diversity of microorganisms in the biological filler is enriched, the operation effect of the system is more stable, and the removal efficiency of pollutants is greatly improved.
实施例2:Example 2:
本实施例用生态过滤墙用于静态湖泊的原位修复,生态过滤墙为:In this embodiment, the ecological filter wall is used for the in-situ restoration of the static lake, and the ecological filter wall is:
由聚酰胺纤维构成墙体,厚度为30cm;The wall is made of polyamide fiber with a thickness of 30cm;
玄武岩纤维掺杂于墙体中,掺杂比例为3mg/g,纤维长度为5cm;Basalt fiber is doped into the wall, the doping ratio is 3mg/g, and the fiber length is 5cm;
栽种于墙体顶端的挺水植物菖蒲,种植密度为38株/m2;The emergent plant calamus planted on the top of the wall, the planting density is 38 plants/m2;
栽种于墙体右侧面即出水侧的沉水植物黑藻,种植密度为12株/m2;The submerged plant black algae planted on the right side of the wall, that is, the water outlet side, with a planting density of 12 plants/m2 ;
本实施例中,墙体的顶端和右侧面开设有直径为10cm的植物种植孔,种植孔内放置植物种植篮,种植篮底部放入砾石用以固定菖蒲和黑藻,且在植物的根系处放入长为5cm的玄武岩纤维。In this embodiment, plant planting holes with a diameter of 10 cm are opened on the top and right side of the wall, and plant planting baskets are placed in the planting holes. A basalt fiber with a length of 5 cm was placed there.
实施例3Example 3
本实施例用生态过滤墙用于受污染河流的原位修复,生态过滤墙同实施例 2,不同之处在于,掺杂于墙体的纤维和植物的根系处放入的纤维为碳纤维,挺水植物为美人蕉,沉水植物为矮苦草。In this example, the ecological filter wall is used for the in-situ restoration of the polluted river. The ecological filter wall is the same as Example 2, except that the fibers mixed in the wall and the fibers placed in the roots of the plants are carbon fibers. The water plant is canna, and the submerged plant is dwarf bitter grass.
以上所述仅是本发明的优选实施方式,应当指出:对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明原理的前提下,还可以做出若干改进和润饰,这些改进和润饰也应视为本发明的保护范围。The above is only the preferred embodiment of the present invention, it should be pointed out that: for those skilled in the art, without departing from the principle of the present invention, several improvements and modifications can also be made, and these improvements and modifications are also It should be regarded as the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210651796.1ACN115072877B (en) | 2022-06-10 | 2022-06-10 | An ecological filter wall and its application |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210651796.1ACN115072877B (en) | 2022-06-10 | 2022-06-10 | An ecological filter wall and its application |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115072877Atrue CN115072877A (en) | 2022-09-20 |
| CN115072877B CN115072877B (en) | 2024-03-22 |
Family
ID=83252212
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210651796.1AActiveCN115072877B (en) | 2022-06-10 | 2022-06-10 | An ecological filter wall and its application |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115072877B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115465954A (en)* | 2022-09-21 | 2022-12-13 | 珠江水利委员会珠江水利科学研究院 | A hydraulic self-adaptive plant three-dimensional filter wall and its water purification treatment system and method for purifying farmland drainage |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105948263A (en)* | 2016-05-18 | 2016-09-21 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Multifunctional ecological purifying wall system and application thereof |
| CN107879478A (en)* | 2017-11-15 | 2018-04-06 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | The ecological bed water remediation method of artificial-strengthening |
| CN109987714A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Suspended ecological restoration water cube for water black and odor control and water quality improvement |
| CN109987711A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Submersible ecological restoration water cube for water black and odor control and water quality improvement |
| CN109987713A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Submersible ecological restoration water cube for black and odor control and water quality improvement |
- 2022
- 2022-06-10CNCN202210651796.1Apatent/CN115072877B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105948263A (en)* | 2016-05-18 | 2016-09-21 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Multifunctional ecological purifying wall system and application thereof |
| CN107879478A (en)* | 2017-11-15 | 2018-04-06 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | The ecological bed water remediation method of artificial-strengthening |
| CN109987714A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Suspended ecological restoration water cube for water black and odor control and water quality improvement |
| CN109987711A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Submersible ecological restoration water cube for water black and odor control and water quality improvement |
| CN109987713A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2019-07-09 | 姚竣耀 | Submersible ecological restoration water cube for black and odor control and water quality improvement |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115465954A (en)* | 2022-09-21 | 2022-12-13 | 珠江水利委员会珠江水利科学研究院 | A hydraulic self-adaptive plant three-dimensional filter wall and its water purification treatment system and method for purifying farmland drainage |
| CN115465954B (en)* | 2022-09-21 | 2023-08-29 | 珠江水利委员会珠江水利科学研究院 | A hydraulic adaptive plant three-dimensional filter wall and its water purification treatment system and method for purifying farmland drainage |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115072877B (en) | 2024-03-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN209024276U (en) | A new type of combined ecological floating bed | |
| CN202322497U (en) | Multifunctional clear water carrier system | |
| CN105347495A (en) | Combined ecological floating bed for water quality improvement of heavily contaminated water body | |
| CN113105070B (en) | Ecological filtering water treatment system and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN107162199B (en) | Energy-saving ecological resource recovery type ecological restoration integrated system and application thereof | |
| CN100457653C (en) | Method for purifying biological settled bed water quality | |
| CN107585868A (en) | Water depth cleaning system | |
| CN204874037U (en) | Ecological chinampa device of coupling aeration | |
| CN107364973B (en) | Sewage treatment system, application thereof and sewage treatment method | |
| CN113371839B (en) | Construction method of underwater forest for ecological restoration of water body | |
| CN115072877A (en) | Ecological filter wall and application thereof | |
| KR100449138B1 (en) | Biofilter sewage treatment method using highly hydrophilic filter media | |
| CN211871749U (en) | Solar ecological floating island | |
| CN109879536B (en) | Rural domestic sewage purification system and purification method | |
| CN1785849A (en) | Bio settling bed method of purifying water quality | |
| CN203999153U (en) | A kind of sun power microkinetic is from pouring dry type ecological floating island | |
| CN108545834A (en) | A kind of row mouthful wet land technique system | |
| CN110467265A (en) | A kind of comprehensive reactor of waste water ecological control | |
| CN214990581U (en) | Ecological remediation system for point source pollution | |
| CN212770083U (en) | Unpowered water purification device | |
| CN108529755A (en) | Activated sludge biological film repairs the system and method for nutrition water body with plant society | |
| CN208948955U (en) | A kind of row mouthful wet land technique system | |
| CN207435252U (en) | The natural catalytic oxidation pool | |
| JP2003112191A (en) | Water quality improving system | |
| CN209522739U (en) | Fountain cooperates with the landscape device of building purification sewage with microorganism and water plant |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |