CN114998592A - Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioning - Google Patents
Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioningDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114998592A CN114998592ACN202210693795.3ACN202210693795ACN114998592ACN 114998592 ACN114998592 ACN 114998592ACN 202210693795 ACN202210693795 ACN 202210693795ACN 114998592 ACN114998592 ACN 114998592A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- candidate
- target
- mask
- instance segmentation
- target image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/20—Image preprocessing
- G06V10/26—Segmentation of patterns in the image field; Cutting or merging of image elements to establish the pattern region, e.g. clustering-based techniques; Detection of occlusion
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/20—Image preprocessing
- G06V10/25—Determination of region of interest [ROI] or a volume of interest [VOI]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/764—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using classification, e.g. of video objects
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V20/00—Scenes; Scene-specific elements
- G06V20/70—Labelling scene content, e.g. deriving syntactic or semantic representations
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本公开的示例实施例总体涉及计算机视觉领域,特别地涉及用于实例分割的方法、装置、设备和计算机可读存储介质。Example embodiments of the present disclosure relate generally to the field of computer vision, and in particular, to methods, apparatus, devices, and computer-readable storage media for instance segmentation.
背景技术Background technique
在计算机视觉处理任务中,图像的实例分割指的是将在图像中检测到的对象实例进行像素级别分离。实例分割可以在对象检测基础上执行,即,在检测出图像中的对象实例后,还将对象实例的像素标识出来。图像的实例分割在视频监控、自动驾驶、图像创作、工业质检等诸多场景下均有应用。In computer vision processing tasks, instance segmentation of images refers to the pixel-level separation of object instances detected in an image. Instance segmentation can be performed on the basis of object detection, that is, after an object instance in an image is detected, the pixels of the object instance are also identified. Instance segmentation of images has applications in many scenarios such as video surveillance, autonomous driving, image creation, and industrial quality inspection.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
在本公开的第一方面,提供了一种实例分割的方法。该方法包括:利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,从目标图像提取特征图;基于特征图确定针对目标图像的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从目标图像分割出候选对象实例;基于特征图和多个候选掩码确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分;以及至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从目标图像分割出目标对象实例。In a first aspect of the present disclosure, a method for instance segmentation is provided. The method includes: extracting a feature map from a target image by using a self-attention mechanism based on an offset window; determining a plurality of candidate masks for the target image based on the feature map, and the candidate masks are used to segment candidate object instances from the target image; Determine a plurality of mask confidence scores corresponding to the plurality of candidate masks based on the feature map and the plurality of candidate masks; and determine at least one target mask for the target image based on at least the plurality of mask confidence scores, and the target mask uses It is used to segment the target object instance from the target image.
在本公开的第二方面,提供了一种用于实例分割的装置。该装置包括:特征提取模块,被配置为利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,从目标图像提取特征图;候选掩码确定模块,被配置为基于特征图确定针对目标图像的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从目标图像分割出候选对象实例;掩码置信度确定模块,被配置为基于特征图和多个候选掩码确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分;以及目标掩码确定模块,被配置为至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从目标图像分割出目标对象实例。In a second aspect of the present disclosure, an apparatus for instance segmentation is provided. The apparatus includes: a feature extraction module configured to extract a feature map from a target image using an offset window-based self-attention mechanism; a candidate mask determination module configured to determine a plurality of candidate masks for the target image based on the feature map code, the candidate mask is used to segment the candidate object instance from the target image; the mask confidence determination module is configured to determine a plurality of mask confidence scores corresponding to the plurality of candidate masks based on the feature map and the plurality of candidate masks and a target mask determination module configured to determine at least one target mask for the target image based at least on the plurality of mask confidence scores, the target mask being used to segment the target object instance from the target image.
在本公开的第三方面,提供了一种电子设备。该设备包括:至少一个处理单元;以及至少一个存储器,至少一个存储器被耦合到至少一个处理单元并且存储用于由至少一个处理单元执行的指令。指令在由至少一个处理单元执行时使设备执行第一方面的方法。In a third aspect of the present disclosure, an electronic device is provided. The apparatus includes: at least one processing unit; and at least one memory coupled to the at least one processing unit and storing instructions for execution by the at least one processing unit. The instructions, when executed by at least one processing unit, cause an apparatus to perform the method of the first aspect.
在本公开的第四方面,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质。该计算机可读存储介质上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现第一方面的方法。In a fourth aspect of the present disclosure, a computer-readable storage medium is provided. A computer program is stored on the computer-readable storage medium, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the method of the first aspect is implemented.
应当理解,本发明内容部分中所描述的内容并非旨在限定本公开的实施例的关键特征或重要特征,也不用于限制本公开的范围。本公开的其它特征将通过以下的描述而变得容易理解。It should be understood that what is described in this Summary section is not intended to limit key features or important features of the embodiments of the present disclosure, nor is it intended to limit the scope of the present disclosure. Other features of the present disclosure will become readily understood from the following description.
附图说明Description of drawings
结合附图并参考以下详细说明,本公开各实施例的上述和其他特征、优点及方面将变得更加明显。在附图中,相同或相似的附图标记表示相同或相似的元素,其中:The above and other features, advantages and aspects of various embodiments of the present disclosure will become more apparent when taken in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and with reference to the following detailed description. In the drawings, the same or similar reference numbers refer to the same or similar elements, wherein:
图1示出了能够在其中实现本公开的实施例的示例环境的示意图;1 shows a schematic diagram of an example environment in which embodiments of the present disclosure can be implemented;
图2示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的实例分割模型的示例结构的框图;2 shows a block diagram of an example structure of an instance segmentation model according to some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图3示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的骨干网络的部分网络层处的自注意力机制的示意图;3 shows a schematic diagram of a self-attention mechanism at a part of the network layer of a backbone network according to some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图4示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的针对目标图像的示例候选边界框;4 illustrates example candidate bounding boxes for a target image, according to some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图5示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的基于模型组合的示例架构的框图;5 illustrates a block diagram of an example architecture based on model composition according to some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图6示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的模型训练和应用架构的框图;6 illustrates a block diagram of a model training and application architecture in accordance with some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图7示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的实例分割的过程的流程图;7 shows a flowchart of a process of instance segmentation according to some embodiments of the present disclosure;
图8示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的用于实例分割的装置的框图;以及Figure 8 shows a block diagram of an apparatus for instance segmentation according to some embodiments of the present disclosure; and
图9示出了其中可以实施本公开的一个或多个实施例的电子设备的框图。9 shows a block diagram of an electronic device in which one or more embodiments of the present disclosure may be implemented.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将参照附图更详细地描述本公开的实施例。虽然附图中示出了本公开的某些实施例,然而应当理解的是,本公开可以通过各种形式来实现,而且不应该被解释为限于这里阐述的实施例,相反,提供这些实施例是为了更加透彻和完整地理解本公开。应当理解的是,本公开的附图及实施例仅用于示例性作用,并非用于限制本公开的保护范围。Embodiments of the present disclosure will be described in more detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. While certain embodiments of the present disclosure are shown in the drawings, it should be understood that the present disclosure may be embodied in various forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein, but rather are provided for a more thorough and complete understanding of the present disclosure. It should be understood that the drawings and embodiments of the present disclosure are only for exemplary purposes, and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present disclosure.
在本公开的实施例的描述中,术语“包括”及其类似用语应当理解为开放性包含,即“包括但不限于”。术语“基于”应当理解为“至少部分地基于”。术语“一个实施例”或“该实施例”应当理解为“至少一个实施例”。术语“一些实施例”应当理解为“至少一些实施例”。下文还可能包括其他明确的和隐含的定义。In the description of embodiments of the present disclosure, the term "comprising" and the like should be understood as open-ended inclusion, ie, "including but not limited to". The term "based on" should be understood as "based at least in part on". The terms "one embodiment" or "the embodiment" should be understood to mean "at least one embodiment". The term "some embodiments" should be understood to mean "at least some embodiments." Other explicit and implicit definitions may also be included below.
可以理解的是,本技术方案所涉及的数据(包括但不限于数据本身、数据的获得或使用)应当遵循相应法律法规及相关规定的要求。It can be understood that the data involved in this technical solution (including but not limited to the data itself, the acquisition or use of the data) shall comply with the requirements of the corresponding laws and regulations and relevant regulations.
可以理解的是,在使用本公开各实施例公开的技术方案之前,均应当根据相关法律法规通过适当的方式对本公开所涉及个人信息的类型、使用范围、使用场景等告知用户并获得用户的授权。It can be understood that, before using the technical solutions disclosed in the embodiments of the present disclosure, the user should be informed of the type, scope of use, and use scenario of the personal information involved in the present disclosure in an appropriate manner in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, and the user's authorization should be obtained. .
例如,在响应于接收到用户的主动请求时,向用户发送提示信息,以明确地提示用户,其请求执行的操作将需要获得和使用到用户的个人信息,从而使得用户可以根据提示信息来自主地选择是否向执行本公开技术方案的操作的电子设备、应用程序、服务器或存储介质等软件或硬件提供个人信息。For example, in response to receiving a user's active request, a prompt message is sent to the user to explicitly prompt the user that the requested operation will require the acquisition and use of the user's personal information, so that the user can independently according to the prompt information Choose whether to provide personal information to software or hardware such as electronic devices, applications, servers, or storage media that perform operations of the technical solutions of the present disclosure.
作为一种可选的但非限制性的实现方式,响应于接收到用户的主动请求,向用户发送提示信息的方式,例如可以是弹窗的方式,弹窗中可以以文字的方式呈现提示信息。此外,弹窗中还可以承载供用户选择“同意”或“不同意”向电子设备提供个人信息的选择控件。As an optional but non-limiting implementation, in response to receiving a user's active request, the method of sending prompt information to the user, for example, can be a pop-up window, and the prompt information can be presented in the form of text in the pop-up window. . In addition, the pop-up window may also carry a selection control for the user to choose "agree" or "disagree" to provide personal information to the electronic device.
可以理解的是,上述通知和获得用户授权过程仅是示意性的,不对本公开的实现方式构成限定,其他满足相关法律法规的方式也可应用于本公开的实现方式中。It can be understood that the above process of notifying and obtaining user authorization is only illustrative, and does not limit the implementation of the present disclosure, and other methods that satisfy relevant laws and regulations can also be applied to the implementation of the present disclosure.
如本文中所使用的,术语“模型”可以从训练数据中学习到相应的输入与输出之间的关联关系,从而在训练完成后可以针对给定的输入,生成对应的输出。模型的生成可以基于机器学习技术。深度学习是一种机器学习算法,通过使用多层处理单元来处理输入和提供相应输出。神经网络模型是基于深度学习的模型的一个示例。在本文中,“模型”也可以被称为“机器学习模型”、“学习模型”、“机器学习网络”或“学习网络”,这些术语在本文中可互换地使用。As used herein, the term "model" can learn the correlation between the corresponding input and output from the training data, so that the corresponding output can be generated for a given input after the training is completed. The generation of the model can be based on machine learning techniques. Deep learning is a machine learning algorithm that uses multiple layers of processing units to process inputs and provide corresponding outputs. A neural network model is an example of a deep learning based model. A "model" may also be referred to herein as a "machine learning model," "learning model," "machine learning network," or "learning network," and these terms are used interchangeably herein.
“神经网络”是一种基于深度学习的机器学习网络。神经网络能够处理输入并且提供相应输出,其通常包括输入层和输出层以及在输入层与输出层之间的一个或多个隐藏层。在深度学习应用中使用的神经网络通常包括许多隐藏层,从而增加网络的深度。神经网络的各个层按顺序相连,从而前一层的输出被提供作为后一层的输入,其中输入层接收神经网络的输入,而输出层的输出作为神经网络的最终输出。神经网络的每个层包括一个或多个节点(也称为处理节点或神经元),每个节点处理来自上一层的输入。A "neural network" is a deep learning-based machine learning network. Neural networks are capable of processing inputs and providing corresponding outputs, which typically include input and output layers and one or more hidden layers between the input and output layers. Neural networks used in deep learning applications often include many hidden layers, thereby increasing the depth of the network. The layers of the neural network are connected in sequence so that the output of the previous layer is provided as the input of the latter layer, where the input layer receives the input of the neural network and the output of the output layer is the final output of the neural network. Each layer of a neural network consists of one or more nodes (also called processing nodes or neurons), each of which processes input from the previous layer.
通常,机器学习大致可以包括三个阶段,即训练阶段、测试阶段和应用阶段(也称为推理阶段)。在训练阶段,给定的模型可以使用大量的训练数据进行训练,不断迭代更新参数值,直到模型能够从训练数据中获得一致的满足预期目标的推理。通过训练,模型可以被认为能够从训练数据中学习从输入到输出之间的关联(也称为输入到输出的映射)。训练后的模型的参数值被确定。在测试阶段,将测试输入应用到训练后的模型,测试模型是否能够提供正确的输出,从而确定模型的性能。在应用阶段,模型可以被用于基于训练得到的参数值,对实际的输入进行处理,确定对应的输出。Generally, machine learning can roughly include three stages, namely training stage, testing stage and application stage (also called inference stage). During the training phase, a given model can be trained using a large amount of training data, iteratively updating parameter values until the model can obtain consistent inferences from the training data that meet the expected goals. Through training, a model can be thought of as being able to learn associations from input to output (also known as input-to-output mapping) from the training data. The parameter values of the trained model are determined. During the testing phase, the performance of the model is determined by applying the test input to the trained model and testing whether the model can provide the correct output. In the application phase, the model can be used to process the actual input based on the parameter values obtained by training to determine the corresponding output.
图1示出了能够在其中实现本公开的实施例的示例环境100的示意图。在环境100中,实例分割系统110被配置为实现对输入的目标图像105执行实例分割。实例分割指的是将在图像中检测到的对象实例进行像素级别分离。例如,针对目标图像105中检测到的任一对象实例,生成对应的掩码(mask),其指示目标图像105中的哪些像素属于该对象实例,哪些像素不属于该对象实例。在一些示例中,可以生成二值化掩码,其可以将目标图像105中属于特定对象实例的像素标注为1、并将不属于特定对象实例的像素标注为0,或者反之。FIG. 1 shows a schematic diagram of an
如图1所示,实例分割系统110可以生成实例分割后的图像125,其中不同类别的人的像素分别被标注。As shown in FIG. 1 , the
在一些实施例中,实例分割过程还可以涉及对象检测,或者还可以涉及对象分类。对象检测是从目标图像105中检测出感兴趣的对象实例。对象分类指的是将检测到的对象实例进行分类。例如,图1中实例分割后的图像125还标识有所分割的每个对象实例的类别,即“正常行人”、“带拐杖的人”和“坐轮椅的人”。注意,这里的类别仅是示例,在一些实施例中,对象实例还可以按更细的类别划分,例如划分为“人”、“轮椅”和“拐杖”等。在一些情况下,目标图像105中可能具有属于同一类别的多个对象实例,并且实例分割的过程要将每个对象实例进行分离。In some embodiments, the instance segmentation process may also involve object detection, or may also involve object classification. Object detection is the detection of object instances of interest from the
在一些实施例中,实例分割系统110可以利用实例分割模型120来执行对目标图像105的实例分割。实例分割模型120例如可以是基于机器学习或深度学习技术配置和训练得到的模型。In some embodiments,
已经提出了一些基于机器学习的模型用于自动的图像实例分割。这些模型大多数依赖于在图像处理任务中比较常见的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构来实现。然而,这些模型在实例分割方面的性能,包括分割的准确度等方面仍有待提高。Several machine learning based models have been proposed for automatic image instance segmentation. Most of these models rely on convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures that are more common in image processing tasks. However, the performance of these models in instance segmentation, including segmentation accuracy, still needs to be improved.
在一些实例分割场景中,可能会涉及到针对某些特殊对象的实例分割,这些对象在不同的图像捕获情况下可能会在图像中给出诸多分割难点,从而导致实例分割结果不够准确。例如,有些图像中可能会包含残障人士,而残障人士通常会携带辅助工具,例如视力损伤人士会携带拐杖,行动障碍人士会乘坐轮椅,等等。这类人士的准确检测和分割在很多应用中是非常有意义的。例如,在自动驾驶应用中,如果在交通场景中发现残障人士,可能需要基于此来执行特殊的策略。然而,残障人士的实例分割面临的一些问题在于,需要准确检测出人与辅助设施的交互,但辅助设施却又比较容易被遮挡,从而造成不准确的分割或对象分类等。除了涉及残障人士的图像实例分割之外,在其他场景中可能也存在类似的问题,特别是在存在较小的对象、或者对象遮挡较严重的情况。In some instance segmentation scenarios, instance segmentation for some special objects may be involved. These objects may present many segmentation difficulties in the image under different image capture conditions, resulting in inaccurate instance segmentation results. For example, some images may include people with disabilities who often carry assistive devices, such as crutches for people with visual impairments, wheelchairs for people with mobility impairments, and so on. Accurate detection and segmentation of such persons is of great interest in many applications. For example, in an autonomous driving application, if a disabled person is found in a traffic scene, special strategies may need to be implemented based on this. However, some of the problems faced by instance segmentation for people with disabilities are that the interaction between people and auxiliary facilities needs to be accurately detected, but auxiliary facilities are relatively easily occluded, resulting in inaccurate segmentation or object classification, etc. In addition to image instance segmentation involving people with disabilities, similar problems may exist in other scenarios, especially when there are small objects, or when objects are heavily occluded.
因此,期望能够提供改进的实例分割方案,能够在各种场景下,包括在遮挡严重或对象尺寸较小时,均获得准确的实例分割结果。Therefore, it is expected to provide an improved instance segmentation scheme, which can obtain accurate instance segmentation results in various scenarios, including severe occlusion or small object size.
在本公开的示例实施例中,提供了一种改进的实例分割方案。根据该方案,利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,从目标图像提取特征图。基于所提取的特征图,确定针对目标图像的多个候选掩码。基于所提取的特征图和多个候选掩码确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分。至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,以用于从目标图像分割出目标对象实例。根据本公开的实施例,通过利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,使得可以提取到目标图像中关于不同尺寸的对象的特征信息。此外,通过衡量候选掩码的置信度得分,可以获得更准确的掩码来实现实例分割。由此,可以提高在各种场景下实例分割的准确度。In an example embodiment of the present disclosure, an improved instance segmentation scheme is provided. According to this scheme, feature maps are extracted from target images using an offset window-based self-attention mechanism. Based on the extracted feature maps, multiple candidate masks for the target image are determined. Multiple mask confidence scores corresponding to multiple candidate masks are determined based on the extracted feature maps and multiple candidate masks. At least one target mask for the target image is determined for segmenting the target object instance from the target image based at least on the plurality of mask confidence scores. According to the embodiments of the present disclosure, by using the self-attention mechanism based on the offset window, it is possible to extract feature information about objects of different sizes in the target image. Furthermore, by measuring the confidence scores of the candidate masks, more accurate masks can be obtained for instance segmentation. Thus, the accuracy of instance segmentation in various scenarios can be improved.
以下将继续参考附图描述本公开的一些示例实施例。Some example embodiments of the present disclosure will be described below with continued reference to the accompanying drawings.
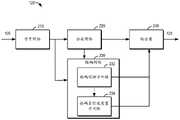
图2示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的实例分割模型120的示例结构的框图。该实例分割模型120可以被应用在图1的环境100中,用于对输入的目标图像105执行实例分割,以确定实例分割后的图像125。如图2所述,实例分割模型120包括骨干网络210、分类网络220、掩码网络230和输出层240。FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of an example structure of an
骨干网络210被配置为执行针对目标图像105的特征提取,以提取目标图像105的特征图(feature map)。特征图能够描述目标图像105中的有用特征信息,特别是有助于实现实例分割的特征信息。在本公开的实施例中,骨干网络210被配置为利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制来执行针对目标图像105的特征提取。The
自注意力机制是机器学习技术中常用的处理机制。在图像处理应用中,自注意力机制可以有助于关注图像中对于目标任务更有用的特征信息。在很多常规实例分割模型中,骨干网络通常采用基于CNN的网络结构。虽然在CNN的网络结构中可能也会引入自注意力机制,但这些机制通常具有固定窗口大小。在本公开的实施例中,基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制将通过在不同网络层之间偏移用于自注意力机制的窗口,达到利用变化的窗口大小来遍历图像。在一些实施例中,骨干网络210可以基于转换器(Transformer),特别是基于Swin转换器(Swin Transformer)来实现基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制。Self-attention mechanism is a commonly used processing mechanism in machine learning technology. In image processing applications, the self-attention mechanism can help to focus on the feature information in the image that is more useful for the target task. In many conventional instance segmentation models, the backbone network usually adopts a CNN-based network structure. Although self-attention mechanisms may also be introduced in the network structure of CNNs, these mechanisms usually have a fixed window size. In an embodiment of the present disclosure, the offset window-based self-attention mechanism will traverse the image with varying window sizes by offsetting the windows used for the self-attention mechanism between different network layers. In some embodiments, the
图3示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的骨干网络210中的第L网络层和第(L+1)网络层处的自注意力机制的示意图。这两个网络层可以是骨干网络210的Swin转换器块的一部分。特征图310是第L网络层的输入,该输入例如可以是第L网络层之前的网络层对目标图像105处理后得到的中间特征图或者是模型的输入(在第L网络层是第一网络层的情况下);并且特征图320是第L网络层输出的中间特征图。3 shows a schematic diagram of the self-attention mechanism at the Lth network layer and the (L+1)th network layer in the
特征图310和320可以被划分为固定大小的多个分块302。在第L网络处,对特征图310,按自注意力窗口304的大小来划分特征图310,以应用自注意力机制,即计算每个窗口内的特征信息的重要程度,并基于重要程度来进行特征信息的聚合。在第(L+1)网络层处,自注意力窗口304在多个方向(例如,上、下、左、右)上偏移,从而获得新的自注意力窗口。这些新的自注意力窗口具有不同尺寸。针对特征图320,在新的自注意力窗口内应用自注意力机制。Feature maps 310 and 320 may be divided into multiple partitions 302 of fixed size. At the Lth network, the
在一些实施例中,骨干网络310可以基于复合骨干网络V2(CBNetV2),其包括级联的多个Swin转换器块。在一些实施例中,多个Swin转换器块可以具有相同或不同的结构。在一些实施例中,骨干网络310可以基于Dual-Swin-T的结构,其包括Swin-T类型的两个级联的Swin转换器块。在一些实施例中,骨干网络310可以基于Dual-Swin-S的结构,其包括Swin-S类型的两个级联的Swin转换器块。In some embodiments, the
在许多情况下,骨干网络对于实例分割的结果具有重要作用。骨干网络能够提取出更具有代表性的特征图,将意味着后续的实例分割结果会更好。以下表1给出了根据本公开的一些实施例的骨干网络的不同结构的性能比较。在表1中,以平均精确度(averageprecision,AP)作为性能度量指标,其中AP、APS、APM和APL指的是在相同数据集上针对不同类型的检测目标所确定的平均精确度(AP针对数据集中的所有目标,APS针对数据集中的小尺寸目标,APM针对数据集中的中等尺寸目标,APL针对数据集中的大尺寸目标)。In many cases, the backbone network plays an important role in the result of instance segmentation. The backbone network can extract more representative feature maps, which will mean that the subsequent instance segmentation results will be better. Table 1 below presents a performance comparison of different structures of the backbone network according to some embodiments of the present disclosure. In Table 1, the average precision (AP) is used as the performance metric, where AP,APS ,APM andAPL refer to the average precision determined for different types of detection targets on the same dataset (AP is for all objects in the dataset, APS is for small-sized objects in the dataset, APM is for medium-sized objects in the dataset, and APL is for large-sized objects in the dataset).
表1骨干网络的不同结构的性能Table 1 Performance of different structures of backbone network
从表1可以看出,基于Swin-T的骨干网络已能够获得较高精确度,而在相同训练轮数(epoch)下基于Dual-Swin-T的骨干网络还能够获得进一步的精度提升。此外,在相同网络结构下(基于Dual-Swin-T),执行更多训练轮数也能获得一定的性能提升。It can be seen from Table 1 that the backbone network based on Swin-T has been able to obtain higher accuracy, and the backbone network based on Dual-Swin-T can obtain further accuracy improvement under the same number of training epochs (epoch). In addition, under the same network structure (based on Dual-Swin-T), performing more training rounds can also obtain a certain performance improvement.
在骨干网络210提取的特征图基础上,掩码网络230被配置为基于特征图来确定用于从目标图像105分割候选对象实例的多个候选掩码(mask)。在本文中,掩码可以指示目标图像105中的属于对应对象实例的像素。例如,掩码可以包括二值化掩码,其中以1值指示对应的像素属于对象实例,0值指示对应的像素不属于对象实例;或者反之。Based on the feature maps extracted by
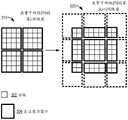
在一些实施例中,可以基于特征图确定目标图像105中的多个候选边界框(bounding box),并确定针对多个候选边界框的多个候选掩码。每个候选边界框用于界定目标图像105中可能存在对象实例的图像区域,也称为感兴趣区域(RoI)。每个候选掩码用于对对应的候选边界框分割出候选对象实例。In some embodiments, multiple candidate bounding boxes in the
在一些实施例中,分类网络220被配置为基于骨干网络210提取的特征图来确定目标图像105中的多个候选边界框(bounding box),如图4所示,可以生成多个候选边界框,以用于框定不同的图像区域。在一些实施例中,分类网络220可以被配置为确定预定数目的候选边界框,并确定预定数目的候选边界框对应的分类置信度得分。分类置信度得分指示候选边界框内的对象实例可以被分类到预定类别的置信度。例如,可以设置多个预定类别,并确定每个候选边界框所框定的图像区域中是否存在某个预定类别的对象实例。如果该候选边界框的位置选取比较准确,例如框定了属于对象实例的大部分图像区域,那么分类置信度得分较高;否则,分类置信度得分较低。In some embodiments, the
在一些实施例中,分类网络220可以被配置为从预定数目(例如,N个)的候选边界框中选择分类置信度得分较高的多个候选边界框(例如,前k个候选边界框),其中N和k可以根据具体应用进行设置。以此方式,可以基于分类置信度得分筛选掉一部分不太可靠的候选边界框。分类网络220可以输出所选择的多个候选边界框的分类置信度得分,以及这些候选边界框在目标图像105中的坐标信息。In some embodiments,
分类网络220可以基于各种网络结构来构建。在一些实施例中,分类网络220可以被配置为基于区域卷积神经网络(R-CNN),其包括一个或多个卷积层、一个或多个全连接(FC)层等。在该示例中,分类网络220有时也称为R-CNN头(R-CNN head)。在其他实施例中,分类网络220还可以基于其他网络结构,只要能够实现对象实例的分类以及边界框的选择即可。
在一些实施例中,掩码网络230可以针对由分类网络220选择的多个候选边界框,基于对应的特征图来执行候选掩码的确定。例如,掩码网络230可以确定k个候选边界框的候选掩码。在针对这些掩码确定候选掩码时,可能无法确定这些候选掩码是否准确。特别地,如果基于分类网络220推荐的候选边界框来确定候选掩码,那么这些候选掩码的置信度通常会有分类网络220所确定的分类置信度得分来衡量。然而,分类置信度得分通常是从对图像中的对象实例的分类准确度角度来衡量的。在一些情况下可能会出现候选边界框界定不准确,从而导致分类置信度得分较高,而所确定的掩码却无法精确分割对象实例的情况(例如,候选边界框界定出对象实例以及无关的图像部分,或者候选边界框仅界定出对象实例中有助于图像分类的特征部分)。In some embodiments,
在本公开的实施例中,提出了对候选掩码的置信度进行独立衡量。具体地,掩码网络230包括掩码预测子网络232和掩码置信度度量子网络234。掩码预测子网络232被配置为基于目标图像105的特征图来确定针对目标网络的多个候选掩码,例如基于分类网络220确定的候选边界框来确定对应的多个候选掩码。掩码预测子网络232可以基于各种网络结构来构建。在一些实施例中,掩码预测子网络232被构建为包括一个或多个卷积层、一个或多个全连(FC)层等。在一些示例中,掩码预测子网络232有时也称为掩码头(mask head)。In the embodiments of the present disclosure, it is proposed to independently measure the confidence of the candidate masks. Specifically, the
掩码置信度度量子网络234被配置为基于目标图像105的特征图和多个候选掩码,确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分。掩码置信度得分用于衡量对应的掩码的质量,即是否能够准确分割出对应的候选对象实例。The mask confidence
在一些实施例中,掩码置信度度量子网络234可以被配置为预测候选掩码与实际的真值掩码之间的交并比(intersection of union,IoU),即描述两个掩码之间的重合度。IoU越高,意味着候选掩码的掩码置信度得分越高;反之,IoU越低,意味着候选掩码的掩码置信度得分较低。掩码置信度度量子网络234可以基于各种网络结构来构建。在一些实施例中,掩码置信度度量子网络234被构建为包括一个或多个卷积层、一个或多个全连接(FC)层等。在一些示例中,掩码置信度度量子网络234有时也称为掩码IoU头(MaskIoU head)。In some embodiments, the mask confidence
通过衡量多个候选掩码的掩码置信度得分,可以确定出置信度更高的候选掩码。在一些实施例中,掩码预测子网络232和掩码置信度度量子网络234将各自的输出提供给输出层240。输出层240被配置为至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像105的至少一个目标掩码。目标掩码用于从目标图像105(例如,从对应候选边界框分割出目标对象实例)分割出目标对象实例,即获得实例分割后的图像125。By measuring the mask confidence scores of multiple candidate masks, a candidate mask with higher confidence can be determined. In some embodiments,
在一些实施例中,分类网络220也将其输出(即,多个候选边界框的分类置信度得分)提供给输出层240。输出层240被配置为基于与多个候选边界框(例如,k个候选边界框)对应的分类置信度得分和掩码置信度得分,确定针对目标图像105的至少一个目标掩码。在一些实施例中,可以通过组合分类置信度得分和掩码置信度得分,来确定与多个候选边界框对应的多个候选掩码的最终置信度得分,并基于最终置信度得分来选择一个或多个目标掩码。例如,可以基于最终置信度得分与阈值置信度得分的比较,来选择超过阈值置信度得分的候选掩码作为目标掩码。由此,可以选择出更准确的掩码用于从目标图像105分割出准确的对象实例。In some embodiments,
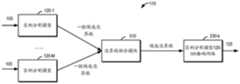
在一些实施例中,在候选边界框的选定时,还可以利用多个实例分割模型来筛选候选边界框,以便融合得到边界框的更好的预测结果。图5示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的基于模型组合的示例架构的框图。实例分割系统110可以这样的模型组合来执行针对目标图像105的实例分割。In some embodiments, when candidate bounding boxes are selected, multiple instance segmentation models may also be used to screen candidate bounding boxes, so as to obtain better prediction results of bounding boxes through fusion. 5 illustrates a block diagram of an example architecture based on model composition according to some embodiments of the present disclosure. The
在图5的实施例中,实例分割系统110利用实例分割模型120-1、……、实例分割模型120-M(其中M是大于等于2的整数)来生成目标图像105的多个候选边界框。多个实例分割模型120-1、……、120-M可以统称为或单独称为实例分割模型120。In the embodiment of FIG. 5 ,
每个实例分割模型120-i(i=1、……、M)可以包括如图2所示的类似结构。不同的实例分割模型120-i可以具有不同的模型配置(例如,网络层类型、数目等不同)和/或经过不同的训练过程训练得到。例如,实例分割模型120-1中的骨干网络可以基于Dual-Swin-T的结构,而实例分割模型120-M中的骨干网络可以基于Dual-Swin-S的结构。Each instance segmentation model 120-i (i=1, . . . , M) may include a similar structure as shown in FIG. 2 . Different instance segmentation models 120-i may have different model configurations (eg, different types and numbers of network layers, etc.) and/or be trained through different training processes. For example, the backbone network in instance segmentation model 120-1 may be based on the structure of Dual-Swin-T, while the backbone network in instance segmentation model 120-M may be based on the structure of Dual-Swin-S.
每个实例分割模型120-i可以分别从目标图像105提取特征图,并基于特征图来确定一组候选边界框,例如确定k个候选边界框。实例分割系统110包括边界框融合模型510,其被配置为通过融合来自多个实例分割模型120-i的多组候选边界框,来确定针对目标图像105的多个候选边界框。在一些实施例中,每个实例分割模型120-i中的分类网络可以基于特征图来确定具有较高置信度的一组候选边界框。在一些实施例中,边界框融合模型510可以被配置为利用加权边界框融合(weighted boxes fusion,WBF)机制来组合来自多个实例分割模型120-i的多组候选边界框,例如对多组候选边界框中对应的候选边界框进行加权融合,以获得最终的多个候选边界框。所得到的多个候选边界框可以更准确定位出目标图105中的对象实例。通过利用多个实例分割模型的骨干网络和分类网络进行候选边界框的选择,并融合候选边界框,可以进一步提高实例分割的准确度。Each instance segmentation model 120-i may extract feature maps from the
边界框融合模型510可以将所确定的多个候选边界框输入到多个实例分割模型中的目标实例分割模型(假设是实例分割模型120-t)中的掩码网络230-k。掩码网络230-k被配置为从多个候选边界框中确定用于对象实例分割的多个候选掩码,多个候选掩码的掩码置信度得分,并进而可以选择出目标掩码用于从目标图像105中分割出目标对象实例。Bounding
在一些实施例中,目标实例分割模型120-t可以是多个实例分割模型中具有较高性能的模型。例如,目标实例分割模型120-t的性能指标度量可以超过其他实例分割模型的性能指标度量。用于衡量模型性能的性能指标例如可以是模型的平均精确度(AP)、平均准确度(accuracy)等。例如,可以利用验证数据集来确定各个实例分割模型的性能,并选择性能较好的目标实例分割模型用于确定掩码。In some embodiments, the target instance segmentation model 120-t may be a model with higher performance among the plurality of instance segmentation models. For example, the performance metric metric of the target instance segmentation model 120-t may exceed the performance metric metrics of other instance segmentation models. The performance indicators used to measure the performance of the model may be, for example, the average precision (AP), average accuracy (accuracy) of the model, and the like. For example, the validation dataset can be used to determine the performance of each instance segmentation model, and the target instance segmentation model with better performance can be selected for mask determination.
以上讨论了实例分割模型120在实例分割任务中的具体操作。作为基于机器学习或深度学习的模型,在投入模型应用前,实例分割模型120还需要经过模型训练阶段,以确定模型中各项处理所利用的参数值。在图5的基于模型组合的实施例中,针对每个实例分割模型120-i,均可以经过类似的模型训练过程来获得经训练的模型。The specific operation of the
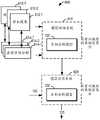
图6示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的模型训练和应用环境100的示意图。在图6的环境600中,期望训练和使用实例分割模型120,用于实现实例分割任务。Figure 6 shows a schematic diagram of a model training and
如图6所示,环境600包括模型训练系统610和模型应用系统620。在图1的示例实施例,模型训练系统610被配置利用训练数据来训练实例分割模型120。训练数据可以包括多个样本图像612-1、612-2、……612-T以及对应的标注信息,即各个样本图像对应的真值实例分割614-1、614-2、……614-T,其中T为大于等于1的整数。为便于讨论,样本图像统称为或单独称为样本图像612,真值实例分割统称为或单独称为真值实例分割614。样本图像612与对应真值实例分割614可以组成样本对,其中真值实例分割614可以指示样本图像612中目标对象实例的分类结果以及属于目标对象实例的图像区域。As shown in FIG. 6 ,
在训练前,实例分割模型120的参数值集合可以是被初始化的,或者是可以通过预训练过程而获得经预训练的参数值。经过训练过程,实例分割模型120的参数值被更新和调整。模型训练系统610可以利用各种模型训练技术,例如随机梯度下降、交叉熵损失、反向传播等,来实现对实例分割模型120的训练。通过训练,使实例分割模型120能够从训练数据中学习到如何对输入的图像执行实例分割,对象分类等。Before training, the set of parameter values of the
在训练完成后,实例分割模型120具有训练后的参数值集合。基于这样的参数值,实例分割模型120能够实现实例分割。在图1中,经训练的实例分割模型120可以被提供给模型应用系统620。模型应用系统620例如可以是图1的实例分割系统110。模型应用系统610可以接收输入的待分类的目标图像105。模型应用系统620可以被配置为利用训练后的实例分割模型120来执行对目标图像105的实例分割,以获得实例分割后的图像125。After training is complete, the
在图6中,模型训练系统610和模型应用系统620可以是任何具有计算能力的系统,例如各种计算设备/系统、终端设备、服务器等。终端设备可以是任意类型的移动终端、固定终端或便携式终端,包括移动手机、台式计算机、膝上型计算机、笔记本计算机、上网本计算机、平板计算机、媒体计算机、多媒体平板、或者前述各项的任意组合,包括这些设备的配件和外设或者其任意组合。服务器包括但不限于大型机、边缘计算节点、云环境中的计算设备,等等。In FIG. 6 , the
应当理解,图6示出的环境中的部件和布置仅是示例,适于用于实现本公开所描述的示例实施例的计算系统可以包括一个或多个不同的部件、其他部件和/或不同的布置方式。例如,虽然被示出为是分离的,但模型训练系统610和模型应用系统620可以集成在相同系统或设备。本公开的实施例在此方面不受限制。It should be understood that the components and arrangements in the environment illustrated in FIG. 6 are only examples and that a computing system suitable for implementing the example embodiments described in this disclosure may include one or more different components, other components and/or different arrangement. For example, although shown as separate,
应当理解,仅出于示例性的目的描述环境600中各个元素的结构和功能,而不暗示对于本公开的范围的任何限制。It should be understood that the structure and function of the various elements in
损失函数在模型训练过程中很重要。由于其设计空间大的问题,设计一个好的损失函数通常是具有挑战性的,并且设计一个适用于不同任务和数据集的损失函数则更具挑战性。在一些实施例中,在实例分割模型的训练中,通常基于交叉熵损失(cross-entropyloss)来设计损失函数用于模型训练。在本公开的一些实施例中,为了进一步提高实例分割模型的性能,提出了基于多项式损失(PolyLoss)函数来训练实例分割模型120,例如图5的实施例中的一个或多个实例分割模型。多项式损失函数将模型训练的损失函数看作是多项式函数的线性组合。在一些实施例中,可以基于Poly-1 Loss来训练实例分割模型120,利用用于替换实例分割模型120中针对分类网络220的损失函数。Poly-1 Loss函数例如可以被表示为如下:The loss function is important in the model training process. Designing a good loss function is often challenging due to its large design space, and it is even more challenging to design a loss function suitable for different tasks and datasets. In some embodiments, in the training of an instance segmentation model, a loss function is typically designed based on a cross-entropy loss for model training. In some embodiments of the present disclosure, in order to further improve the performance of the instance segmentation model, it is proposed to train the
LPoly-1=-log Pt+∈1(1-Pt) (1)LPoly-1 = -log Pt +∈1 (1-Pt ) (1)
其中LPoly-1表示Poly-1 Loss,Pt表示正在训练的实例分割模型120针对输入图像预测该图像属于目标类别的概率;∈1可以是预设值,例如∈1可以被设置为-1。where LPoly-1 represents Poly-1 Loss, and Pt represents the probability that the
应当理解,除多项式损失函数外,在训练实例分割模型120时还可以针对掩码网络的损失函数。在训练过程中,可以基于多个损失函数来执行针对实例分割模型120的端到端训练。实例分割模型120的训练目标可以被设置为使得多个损失函数的值最小化或者降低到较小值(例如,小于预设阈值)。可以利用各种训练技术,基于损失函数来训练实例分割模型120。It should be understood that in addition to the polynomial loss function, the loss function of the mask network may also be targeted when training the
在一些实施例中,在训练实例分割模型120时,为更好的模型性能,还可以基于随机权重平均(Stochastic Weights Averaging,SWA)来训练实例分割模型120。具体地,在将实例分割模型120训练已达到预定的训练目标(例如,损失函数最小化或者降低到预设阈值)后,对实例分割模型120继续执行额外的多个训练周期(例如,多个训练轮次)的训练。例如,可以利用循环学习,在训练数据基础上继续训练实例分割模型120。在每个训练周期中,记录实例分割模型120的更新参数值集合。通过组合多个训练后期的多个更新参数值集合(例如,将对应参数的多个值求平均,得到该参数的平均值),得到实例分割模型120的目标参数值集合。目标参数值集合可以提供更高的模型性能。基于SWA的模型训练过程仅增加一定的训练时间,但并不会增加实例分割模型120在应用阶段的时间消耗,同时还能够提供更高的模型性能。In some embodiments, when training the
以下表2示出了根据本公开的不同实施例构建的实例分割模型的性能比较。在表2中,AP、AP50、AP75、APS、APM和APL指的是在相同数据集上针对不同类型的检测目标所确定的平均精确度,常规基准模型指的是利于常规CNN骨干网络的模型;本公开的基准模型指的是基于Swin Transformer-T骨干网络的模型;在本公开的基准模型基础上还测试了在多种改进模型的性能。Table 2 below shows a performance comparison of instance segmentation models constructed according to different embodiments of the present disclosure. In Table 2, AP, AP50 , AP75 ,APS ,APM andAPL refer to the average accuracies determined for different types of detection targets on the same dataset, and the conventional benchmark model refers to the The model of the CNN backbone network; the benchmark model of the present disclosure refers to the model based on the Swin Transformer-T backbone network; the performance of various improved models is also tested on the basis of the benchmark model of the present disclosure.
表2骨干网络的不同结构的性能Table 2 Performance of different structures of backbone network
从表2可以看出,在一些示例实施例中提出的基准模型可以相较常规基准模型带来较大的性能提升。此外,不同实施例中提出的新网络结构或训练方法还能够进一步提升模型性能。例如,基于PolyLoss损失函数训练的实例分割模型与基于Swin-S的模型相比,能够带来0.83AP的性能提升。It can be seen from Table 2 that the benchmark model proposed in some example embodiments can bring a larger performance improvement compared to the conventional benchmark model. In addition, new network structures or training methods proposed in different embodiments can further improve model performance. For example, the instance segmentation model trained based on the PolyLoss loss function can bring a performance improvement of 0.83AP compared to the model based on Swin-S.
图7示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的实例分割的过程700的流程图。过程700例如可以被实现在图1的实例分割系统110或图6的模型应用系统620处。FIG. 7 shows a flowchart of a
在框710,实例分割系统110利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,从目标图像提取特征图。At
在框720,实例分割系统110基于特征图确定针对目标图像的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从目标图像分割出候选对象实例。At
在框730,实例分割系统110基于特征图和多个候选掩码确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分。At
在框740,实例分割系统110至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从目标图像分割出目标对象实例。At
在一些实施例中,确定多个候选掩码包括:基于特征图确定目标图像中的多个候选边界框;以及确定针对多个候选边界框的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从对应的候选边界框分割出候选对象实例。In some embodiments, determining the plurality of candidate masks includes: determining a plurality of candidate bounding boxes in the target image based on the feature maps; and determining a plurality of candidate masks for the plurality of candidate bounding boxes, the candidate masks being used for extracting from corresponding The candidate bounding boxes of , segment candidate object instances.
在一些实施例中,确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码包括:确定多个候选边界框对应的多个分类置信度得分,分类置信度得分指示候选边界框内的对象实例被分类到预定类别的置信度;以及基于多个分类置信度得分和多个掩码置信度得分,从多个候选掩码确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从对应候选边界框分割出目标对象实例。In some embodiments, determining at least one target mask for the target image includes determining a plurality of classification confidence scores corresponding to the plurality of candidate bounding boxes, the classification confidence scores indicating that object instances within the candidate bounding boxes are classified into a predetermined category and based on the plurality of classification confidence scores and the plurality of mask confidence scores, determining at least one target mask for the target image from the plurality of candidate masks, the target mask being used to segment out the corresponding candidate bounding boxes The target object instance.
在一些实施例中,从目标对象提取特征图包括:利用经训练的多个实例分割模型分别从目标图像提取多个特征图。在一些实施例中,确定多个候选边界框包括:利用多个实例分割模型分别基于各自提取的特征图确定多组候选边界框,以及通过融合多组候选边界框来确定多个候选边界框。In some embodiments, extracting a feature map from the target object includes extracting a plurality of feature maps from the target image using the trained plurality of instance segmentation models, respectively. In some embodiments, determining the plurality of candidate bounding boxes includes: using a plurality of instance segmentation models to determine a plurality of candidate bounding boxes based on the respective extracted feature maps, and determining the plurality of candidate bounding boxes by fusing the plurality of candidate bounding boxes.
在一些实施例中,确定多个候选掩码包括:利用多个实例分割模型中的目标实例分割模型来确定多个候选掩码。In some embodiments, determining the plurality of candidate masks includes utilizing a target instance segmentation model of the plurality of instance segmentation models to determine the plurality of candidate masks.
在一些实施例中,目标实例分割模型的性能指标度量超过多个实例分割模型中的其他实例分割模型的性能指标度量。In some embodiments, the performance metric metric of the target instance segmentation model exceeds the performance metric metrics of other instance segmentation models in the plurality of instance segmentation models.
在一些实施例中,过程700通过利用经训练的实例分割模型(例如,实例分割模型120)来执行,实例分割模型基于多项式损失函数来训练。In some embodiments,
在一些实施例中,过程700通过利用经训练的实例分割模型来执行,在实例分割模型的训练过程中执行以下:在达到预定的训练目标后,对实例分割模型执行多个训练周期的训练,得到多个更新参数值集合;以及通过组合多个更新参数值集合来确定实例分割模型的目标参数值集合。In some embodiments, the
图8示出了根据本公开的一些实施例的用于实例分割的装置800的示意性结构框图。装置800可以被实现为或者被包括在实例分割系统110或图6的模型应用系统620中。装置800中的各个模块/组件可以由硬件、软件、固件或者它们的任意组合来实现。FIG. 8 shows a schematic structural block diagram of an
如图所示,装置800包括特征提取模块810,被配置为利用基于偏移窗口的自注意力机制,从目标图像提取特征图,装置800还包括候选掩码确定模块820,被配置为基于特征图确定针对目标图像的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从目标图像分割出候选对象实例。装置800还包括掩码置信度确定模块830,被配置为基于特征图和多个候选掩码确定多个候选掩码对应的多个掩码置信度得分;以及目标掩码确定模块840,被配置为至少基于多个掩码置信度得分确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从目标图像分割出目标对象实例。As shown in the figure, the
在一些实施例中,掩码置信度确定模块820包括:候选边界框确定模块,被配置为基于特征图确定目标图像中的多个候选边界框;以及基于边界框的掩码确定模块,被配置为确定针对多个候选边界框的多个候选掩码,候选掩码用于从对应的候选边界框分割出候选对象实例。In some embodiments, the mask
在一些实施例中,目标掩码确定模块包括:分类置信度确定模块,被配置为确定多个候选边界框对应的多个分类置信度得分,分类置信度得分指示候选边界框内的对象实例被分类到预定类别的置信度;以及基于多得分的目标掩码确定模块,被配置为基于多个分类置信度得分和多个掩码置信度得分,从多个候选掩码确定针对目标图像的至少一个目标掩码,目标掩码用于从对应候选边界框分割出目标对象实例。In some embodiments, the target mask determination module includes a classification confidence determination module configured to determine a plurality of classification confidence scores corresponding to the plurality of candidate bounding boxes, the classification confidence scores indicating that object instances within the candidate bounding boxes are Confidence of classification to a predetermined class; and a multi-score-based target mask determination module configured to determine at least a target image for the target image from the plurality of candidate masks based on the plurality of classification confidence scores and the plurality of mask confidence scores A target mask used to segment target object instances from corresponding candidate bounding boxes.
在一些实施例中,特征图提取模块810被包括:基于多模型的特征图提取模块,被配置为利用经训练的多个实例分割模型分别从目标图像提取多个特征图。在一些实施例中,候选边界框确定模块包括:基于多模型的候选边界框确定模块,被配置为利用多个实例分割模型分别基于各自提取的特征图确定多组候选边界框;以及边界框融合模块,被配置为通过融合多组候选边界框来确定多个候选边界框。In some embodiments, the feature
在一些实施例中,候选掩码确定模块820包括:基于目标模型的候选掩码确定模块,被配置为利用多个实例分割模型中的目标实例分割模型来确定多个候选掩码。In some embodiments, the candidate
在一些实施例中,目标实例分割模型的性能指标度量超过多个实例分割模型中的其他实例分割模型的性能指标度量。In some embodiments, the performance metric metric of the target instance segmentation model exceeds the performance metric metrics of other instance segmentation models in the plurality of instance segmentation models.
在一些实施例中,利用经训练的实例分割模型(例如,实例分割模型120)来实现特征提取模块810、候选掩码确定模块820、掩码置信度确定模块830和目标掩码确定模块840,实例分割模型基于多项式损失函数来训练。In some embodiments,
在一些实施例中,利用经训练的实例分割模型来实现特征提取模块810、候选掩码确定模块820、掩码置信度确定模块830和目标掩码确定模块840。在实例分割模型的训练过程中执行以下:在达到预定的训练目标后,对实例分割模型执行多个训练周期的训练,得到多个更新参数值集合;以及通过组合多个更新参数值集合来确定实例分割模型的目标参数值集合。In some embodiments, the
图9示出了其中可以实施本公开的一个或多个实施例的电子设备900的框图。应当理解,图9所示出的电子设备900仅仅是示例性的,而不应当构成对本文所描述的实施例的功能和范围的任何限制。图9所示出的电子设备900可以用于图1的实例分割系统、和/或图6的模型应用系统620和/或模型训练系统610。FIG. 9 shows a block diagram of an
如图9所示,电子设备900是通用计算设备的形式。电子设备900的组件可以包括但不限于一个或多个处理器或处理单元910、存储器920、存储设备960、一个或多个通信单元940、一个或多个输入设备950以及一个或多个输出设备990。处理单元910可以是实际或虚拟处理器并且能够根据存储器920中存储的程序来执行各种处理。在多处理器系统中,多个处理单元并行执行计算机可执行指令,以提高电子设备900的并行处理能力。As shown in FIG. 9,
电子设备900通常包括多个计算机存储介质。这样的介质可以是电子设备900可访问的任何可以获得的介质,包括但不限于易失性和非易失性介质、可拆卸和不可拆卸介质。存储器920可以是易失性存储器(例如寄存器、高速缓存、随机访问存储器(RAM))、非易失性存储器(例如,只读存储器(ROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(EEPROM)、闪存)或它们的某种组合。存储设备960可以是可拆卸或不可拆卸的介质,并且可以包括机器可读介质,诸如闪存驱动、磁盘或者任何其他介质,其可以能够用于存储信息和/或数据(例如用于训练的训练数据)并且可以在电子设备900内被访问。
电子设备900可以进一步包括另外的可拆卸/不可拆卸、易失性/非易失性存储介质。尽管未在图9中示出,可以提供用于从可拆卸、非易失性磁盘(例如“软盘”)进行读取或写入的磁盘驱动和用于从可拆卸、非易失性光盘进行读取或写入的光盘驱动。在这些情况中,每个驱动可以由一个或多个数据介质接口被连接至总线(未示出)。存储器920可以包括计算机程序产品925,其具有一个或多个程序模块,这些程序模块被配置为执行本公开的各种实施例的各种方法或动作。
通信单元940实现通过通信介质与其他电子设备进行通信。附加地,电子设备900的组件的功能可以以单个计算集群或多个计算机器来实现,这些计算机器能够通过通信连接进行通信。因此,电子设备900可以使用与一个或多个其他服务器、网络个人计算机(PC)或者另一个网络节点的逻辑连接来在联网环境中进行操作。The
输入设备950可以是一个或多个输入设备,例如鼠标、键盘、追踪球等。输出设备990可以是一个或多个输出设备,例如显示器、扬声器、打印机等。电子设备900还可以根据需要通过通信单元940与一个或多个外部设备(未示出)进行通信,外部设备诸如存储设备、显示设备等,与一个或多个使得用户与电子设备900交互的设备进行通信,或者与使得电子设备900与一个或多个其他电子设备通信的任何设备(例如,网卡、调制解调器等)进行通信。这样的通信可以经由输入/输出(I/O)接口(未示出)来执行。
根据本公开的示例性实现方式,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机可执行指令,其中计算机可执行指令被处理器执行以实现上文描述的方法。根据本公开的示例性实现方式,还提供了一种计算机程序产品,计算机程序产品被有形地存储在非瞬态计算机可读介质上并且包括计算机可执行指令,而计算机可执行指令被处理器执行以实现上文描述的方法。According to an exemplary implementation of the present disclosure, there is provided a computer-readable storage medium having computer-executable instructions stored thereon, wherein the computer-executable instructions are executed by a processor to implement the method described above. According to an exemplary implementation of the present disclosure, there is also provided a computer program product tangibly stored on a non-transitory computer-readable medium and comprising computer-executable instructions executed by a processor to implement the method described above.
这里参照根据本公开实现的方法、装置、设备和计算机程序产品的流程图和/或框图描述了本公开的各个方面。应当理解,流程图和/或框图的每个方框以及流程图和/或框图中各方框的组合,都可以由计算机可读程序指令实现。Aspects of the present disclosure are described herein with reference to flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams of methods, apparatus, devices, and computer program products implemented in accordance with the present disclosure. It will be understood that each block of the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, and combinations of blocks in the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, can be implemented by computer readable program instructions.
这些计算机可读程序指令可以提供给通用计算机、专用计算机或其他可编程数据处理装置的处理单元,从而生产出一种机器,使得这些指令在通过计算机或其他可编程数据处理装置的处理单元执行时,产生了实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作的装置。也可以把这些计算机可读程序指令存储在计算机可读存储介质中,这些指令使得计算机、可编程数据处理装置和/或其他设备以特定方式工作,从而,存储有指令的计算机可读介质则包括一个制造品,其包括实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作的各个方面的指令。These computer readable program instructions may be provided to the processing unit of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to produce a machine that causes the instructions when executed by the processing unit of the computer or other programmable data processing apparatus , resulting in means for implementing the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowchart and/or block diagrams. These computer readable program instructions can also be stored in a computer readable storage medium, these instructions cause a computer, programmable data processing apparatus and/or other equipment to operate in a specific manner, so that the computer readable medium on which the instructions are stored includes An article of manufacture comprising instructions for implementing various aspects of the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowchart and/or block diagrams.
可以把计算机可读程序指令加载到计算机、其他可编程数据处理装置、或其他设备上,使得在计算机、其他可编程数据处理装置或其他设备上执行一系列操作步骤,以产生计算机实现的过程,从而使得在计算机、其他可编程数据处理装置、或其他设备上执行的指令实现流程图和/或框图中的一个或多个方框中规定的功能/动作。Computer-readable program instructions can be loaded onto a computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other equipment to cause a series of operational steps to be performed on the computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other equipment to produce a computer-implemented process, Thereby, instructions executing on a computer, other programmable data processing apparatus, or other device are caused to carry out the functions/acts specified in one or more blocks of the flowchart and/or block diagrams.
附图中的流程图和框图显示了根据本公开的多个实现的系统、方法和计算机程序产品的可能实现的体系架构、功能和操作。在这点上,流程图或框图中的每个方框可以代表一个模块、程序段或指令的一部分,模块、程序段或指令的一部分包含一个或多个用于实现规定的逻辑功能的可执行指令。在有些作为替换的实现中,方框中所标注的功能也可以以不同于附图中所标注的顺序发生。例如,两个连续的方框实际上可以基本并行地执行,它们有时也可以按相反的顺序执行,这依所涉及的功能而定。也要注意的是,框图和/或流程图中的每个方框、以及框图和/或流程图中的方框的组合,可以用执行规定的功能或动作的专用的基于硬件的系统来实现,或者可以用专用硬件与计算机指令的组合来实现。The flowchart and block diagrams in the Figures illustrate the architecture, functionality, and operation of possible implementations of systems, methods and computer program products according to various implementations of the present disclosure. In this regard, each block in the flowchart or block diagrams may represent a module, segment, or portion of instructions, which comprises one or more executables for implementing the specified logical function(s) instruction. In some alternative implementations, the functions noted in the blocks may occur out of the order noted in the figures. For example, two blocks in succession may, in fact, be executed substantially concurrently, or the blocks may sometimes be executed in the reverse order, depending upon the functionality involved. It is also noted that each block of the block diagrams and/or flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams and/or flowchart illustrations, can be implemented in dedicated hardware-based systems that perform the specified functions or actions , or can be implemented in a combination of dedicated hardware and computer instructions.
以上已经描述了本公开的各实现,上述说明是示例性的,并非穷尽性的,并且也不限于所公开的各实现。在不偏离所说明的各实现的范围和精神的情况下,对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说许多修改和变更都是显而易见的。本文中所用术语的选择,旨在最好地解释各实现的原理、实际应用或对市场中的技术的改进,或者使本技术领域的其他普通技术人员能理解本文公开的各个实现方式。While various implementations of the present disclosure have been described above, the foregoing description is exemplary, not exhaustive, and not limiting of the disclosed implementations. Numerous modifications and variations will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art without departing from the scope and spirit of the described implementations. The terminology used herein was chosen to best explain the principles of the various implementations, the practical application or improvement over the technology in the marketplace, or to enable others of ordinary skill in the art to understand the various implementations disclosed herein.
Claims (18)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210693795.3ACN114998592A (en) | 2022-06-18 | 2022-06-18 | Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioning |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210693795.3ACN114998592A (en) | 2022-06-18 | 2022-06-18 | Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioning |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114998592Atrue CN114998592A (en) | 2022-09-02 |
Family
ID=83034522
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210693795.3APendingCN114998592A (en) | 2022-06-18 | 2022-06-18 | Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioning |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114998592A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115171029A (en)* | 2022-09-09 | 2022-10-11 | 山东省凯麟环保设备股份有限公司 | Unmanned-driving-based method and system for segmenting instances in urban scene |
| CN115760901A (en)* | 2022-11-11 | 2023-03-07 | 哲库科技(上海)有限公司 | Image processing method, electronic device and chip |
| CN116843897A (en)* | 2023-06-16 | 2023-10-03 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Training method of segmentation model, image segmentation method, device, equipment and medium |
| CN117132607A (en)* | 2023-10-27 | 2023-11-28 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Image segmentation model processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN119068000A (en)* | 2024-08-23 | 2024-12-03 | 安徽启新明智科技有限公司 | Material sorting device and system based on instance segmentation |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110503097A (en)* | 2019-08-27 | 2019-11-26 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Training method, device and the storage medium of image processing model |
| CN111932545A (en)* | 2020-07-14 | 2020-11-13 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | Image processing method, target counting method and related device thereof |
| EP3872704A2 (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-09-01 | Beijing Baidu Netcom Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | Header model for instance segmentation, instance segmentation model, image segmentation method and apparatus |
| US20210326656A1 (en)* | 2020-04-15 | 2021-10-21 | Adobe Inc. | Panoptic segmentation |
| CN114332457A (en)* | 2021-08-24 | 2022-04-12 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Image instance segmentation model training, image instance segmentation method and device |
| WO2022077917A1 (en)* | 2020-10-14 | 2022-04-21 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Instance segmentation model sample screening method and apparatus, computer device and medium |
- 2022
- 2022-06-18CNCN202210693795.3Apatent/CN114998592A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110503097A (en)* | 2019-08-27 | 2019-11-26 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Training method, device and the storage medium of image processing model |
| US20210326656A1 (en)* | 2020-04-15 | 2021-10-21 | Adobe Inc. | Panoptic segmentation |
| CN111932545A (en)* | 2020-07-14 | 2020-11-13 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | Image processing method, target counting method and related device thereof |
| WO2022077917A1 (en)* | 2020-10-14 | 2022-04-21 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | Instance segmentation model sample screening method and apparatus, computer device and medium |
| EP3872704A2 (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-09-01 | Beijing Baidu Netcom Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | Header model for instance segmentation, instance segmentation model, image segmentation method and apparatus |
| CN114332457A (en)* | 2021-08-24 | 2022-04-12 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Image instance segmentation model training, image instance segmentation method and device |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| CERPA A等: "Ensemble Learning to Perform Instance Segmentation over Synthetic Data", INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON VISUAL COMPUTING, vol. 13018, 1 January 2022 (2022-01-01), pages 313 - 324* |
| XU X等: "An Improved Swin Transformer-Based Model for Remote Sensing Object Detection and Instance Segmentation", REMOTE SENSING, vol. 13, no. 23, 25 November 2021 (2021-11-25), pages 4779* |
| 王子愉;袁春;黎健成;: "利用可分离卷积和多级特征的实例分割", 软件学报, no. 04, 15 April 2019 (2019-04-15)* |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115171029A (en)* | 2022-09-09 | 2022-10-11 | 山东省凯麟环保设备股份有限公司 | Unmanned-driving-based method and system for segmenting instances in urban scene |
| CN115171029B (en)* | 2022-09-09 | 2022-12-30 | 山东省凯麟环保设备股份有限公司 | Unmanned-driving-based method and system for segmenting instances in urban scene |
| CN115760901A (en)* | 2022-11-11 | 2023-03-07 | 哲库科技(上海)有限公司 | Image processing method, electronic device and chip |
| CN116843897A (en)* | 2023-06-16 | 2023-10-03 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Training method of segmentation model, image segmentation method, device, equipment and medium |
| CN117132607A (en)* | 2023-10-27 | 2023-11-28 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Image segmentation model processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN119068000A (en)* | 2024-08-23 | 2024-12-03 | 安徽启新明智科技有限公司 | Material sorting device and system based on instance segmentation |
| CN119068000B (en)* | 2024-08-23 | 2025-06-10 | 安徽启新明智科技有限公司 | Material sorting device and system based on instance segmentation |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Rao et al. | Vision-based automated crack detection using convolutional neural networks for condition assessment of infrastructure | |
| Mukhoti et al. | Evaluating bayesian deep learning methods for semantic segmentation | |
| CN113056743B (en) | Training a neural network for vehicle re-identification | |
| CN114998592A (en) | Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for instance partitioning | |
| CN108171233B (en) | Method and apparatus for object detection using region-based deep learning model | |
| US9965719B2 (en) | Subcategory-aware convolutional neural networks for object detection | |
| US10943096B2 (en) | High-quality training data preparation for high-performance face recognition systems | |
| CN107169421B (en) | Automobile driving scene target detection method based on deep convolutional neural network | |
| US9971942B2 (en) | Object detection in crowded scenes using context-driven label propagation | |
| US20200005022A1 (en) | Method, terminal, and storage medium for tracking facial critical area | |
| US10860837B2 (en) | Deep multi-task learning framework for face detection, landmark localization, pose estimation, and gender recognition | |
| CN114245912B (en) | System, computer program product, or method for evaluating and reducing perceptual errors | |
| US20150169989A1 (en) | Foreground object detection from multiple images | |
| CN110096929A (en) | Object Detection Based on Neural Network | |
| CN115797736B (en) | Object detection model training and object detection method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN110414299B (en) | A computer vision-based kinship analysis method for monkey faces | |
| WO2018232592A1 (en) | SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION TAKING INTO ACCOUNT AN EVENT WITH COMPLETE CONVOLUTION | |
| US9842274B2 (en) | Extending data-driven detection to the prediction of object part locations | |
| CN113762327B (en) | Machine learning method, machine learning system and non-transitory computer readable medium | |
| US12373980B2 (en) | Method and system for localization with supervision | |
| CN114693997A (en) | Image description generation method, device, equipment and medium based on transfer learning | |
| US11688175B2 (en) | Methods and systems for the automated quality assurance of annotated images | |
| US12254631B2 (en) | Dual-level model for segmentation | |
| WO2023109361A1 (en) | Video processing method and system, device, medium and product | |
| Wang et al. | G-NET: Accurate lane detection model for autonomous vehicle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |