CN114968099A - NVM (non-volatile memory) access method and NVM controller - Google Patents
NVM (non-volatile memory) access method and NVM controllerDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114968099A CN114968099ACN202210539163.1ACN202210539163ACN114968099ACN 114968099 ACN114968099 ACN 114968099ACN 202210539163 ACN202210539163 ACN 202210539163ACN 114968099 ACN114968099 ACN 114968099A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- address
- microinstruction
- page
- user command
- block
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0629—Configuration or reconfiguration of storage systems
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/0671—In-line storage system
- G06F3/0673—Single storage device
- G06F3/0679—Non-volatile semiconductor memory device, e.g. flash memory, one time programmable memory [OTP]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Memory System Of A Hierarchy Structure (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及固态存储设备(Solid Storage Device,SSD),更具体地,本发明涉及存储器控制器中块/页地址检查微指令的执行。The present invention relates to solid state storage devices (SSD), and more particularly, the present invention relates to the execution of block/page address checking microinstructions in memory controllers.
背景技术Background technique
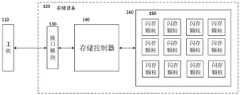
同机械式硬盘相类似,固态存储设备(SSD)也是用于计算机系统的大容量、非易失性存储设备。固态存储设备一般以例如的闪存(Flash)的非易失存储器(NVM,Non VolatileMemory)作为存储介质。如图1所示,为现有技术的存储系统的框图。其中主要包括主机系统110和固态存储设备120。其中,固态存储设备120包括接口模块130,存储控制器140,以及由多个闪存颗粒150组成的Flash阵列160。其中,接口模块130主要用于实现与主机系统通信的接口协议,例如SATA(Serial Advanced Technology Attachment,串行高级技术附件)、USB(Universal Serial Bus,通用串行总线)、PCIE(Peripheral Component InterconnectExpress,快速外围组件互连)、NVMe(NVM Express)、SCSI(Small Computer SystemInterface,小型计算机系统接口)、iSCSI(internet Small Computer System Interface,因特网小型计算机系统接口)、IDE(Integrated Drive Electronics,集成驱动器电子)等。通过接口模块130,固态存储设备呈现给主机系统的是拥有一定逻辑地址空间或物理地址空间的标准存储设备。存储控制器140是整个存储设备的控制核心,主要负责接口模块130与闪存阵列160之间的控制信号及数据的传输、闪存管理、主机逻辑地址到闪存物理地址的转换或映射、磨损均衡、和/或坏块管理等。可由软件、硬件、固件或者其组合的多种方式实现存储控制器140。Similar to mechanical hard drives, solid-state storage devices (SSDs) are high-capacity, non-volatile storage devices used in computer systems. A solid-state storage device generally uses a non-volatile memory (NVM, Non Volatile Memory) such as a flash memory (Flash) as a storage medium. As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a block diagram of a storage system in the prior art. It mainly includes the
存储控制器140通过向闪存阵列160中的闪存颗粒150发送命令来访问闪存颗粒150。访问闪存颗粒150的命令包括,例如,读出、编程和/或擦除等。按页向闪存颗粒150写入或读出数据。闪存颗粒150提供了预定的页大小,每个页的大小是例如2KB、4KB、8KB或16KB。The
主机110的文件系统或设备驱动也按照预定大小的数据块来访问存储设备。预定大小的数据块可被称为块(block)、页(page)或区段(sector)。这里数据块的大小同闪存颗粒150的页大小相同或不同。The file system or device driver of the
在公开号为CN1414468A的中国专利申请中,提供了通过执行微指令序列来处理CPU(Central Processing Unit,中央处理单元)指令的方案。当CPU要处理特定指令时,转换逻辑电路将特定指令转换成与之对应的微指令序列,通过执行微指令序列来实现特定指令的功能。微指令序列或者微指令序列的模板存储在ROM(Read Only Memory,只读存储器)中。在将特定指令转换成微指令序列过程中,可对微指令序列模板进行填充,使之与特定指令相对应。In the Chinese patent application with publication number CN1414468A, a solution for processing CPU (Central Processing Unit, central processing unit) instructions by executing a sequence of micro-instructions is provided. When the CPU needs to process a specific instruction, the conversion logic circuit converts the specific instruction into a corresponding microinstruction sequence, and implements the function of the specific instruction by executing the microinstruction sequence. The microinstruction sequence or the template of the microinstruction sequence is stored in a ROM (Read Only Memory, read only memory). In the process of converting a specific instruction into a microinstruction sequence, the microinstruction sequence template can be filled to correspond to the specific instruction.
存储器目标(Target)是闪存颗粒150封装内的共享芯片使能(CE,Chip Enable)信号的一个或多个逻辑单元(Logic Unit)。每个逻辑单元具有逻辑单元号(LUN,Logic UnitNumber)。NAND闪存封装内可包括一个或多个管芯(Die)。典型地,逻辑单元对应于单一的管芯。逻辑单元可包括多个平面(Plane)。逻辑单元内的多个平面可以并行存取,而NAND闪存芯片内的多个逻辑单元可以彼此独立地执行命令和报告状态。在可从http://www.micron.com/~/media/Documents/Products/Other%20Documents/ONF I3_0Gold.ashx获得的“Open NAND Flash Interface Specification(Revision 3.0)”中,提供了关于目标(target)、逻辑单元、LUN、平面(Plane)的含义。The memory target (Target) is one or more logic units (Logic Unit) in the package of the
公开号为CN102177556A的中国专利申请公开了一种闪存转换层(FTL),其展示了用于FTL的并行单元的查找表的例子。由于闪存芯片中的逻辑单元(Logic Unit)可以并行方式存取,因而,并行单元可以是逻辑单元。逻辑单元内可包括多个平面(Plane),并行单元也可为平面。Chinese Patent Application Publication No. CN102177556A discloses a flash translation layer (FTL), which shows an example of a lookup table for parallel cells of the FTL. Since the logic units (Logic Units) in the flash memory chip can be accessed in parallel, the parallel units can be logic units. The logic unit may include multiple planes, and the parallel unit may also be a plane.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
在一些应用场景中,NVM的页大小不同于应用所请求的页大小。例如操作系统的IO访问请求的数据单元大小为512字节,而NVM的页大小为4KB、8KB或16KB。为响应一个IO访问请求而从NVM读出数据后,大量被读出的数据并未被当前的IO请求所使用。但由于数据访问的局部性或其他原因,从NVM中被读出的数据可能在随后的IO访问请求中被使用。因而在需要从闪存颗粒读出数据时,希望有灵活的方式判断数据是否已存在于存储控制器的缓存中。数据被缓存的原因有多种,希望判断数据是否已存在于存储控制器的缓存中的方式能够适应不同的原因。并且被期待的是,存储设备的用户能够参与缓存利用的灵活控制,而不是依赖于存储控制器判断数据是否被缓存。In some application scenarios, the page size of the NVM is different from the page size requested by the application. For example, the data unit size of the IO access request of the operating system is 512 bytes, while the page size of the NVM is 4KB, 8KB or 16KB. After reading data from NVM in response to an IO access request, a large amount of the read data is not used by the current IO request. However, due to the locality of data access or other reasons, the data read from the NVM may be used in subsequent IO access requests. Therefore, when data needs to be read from the flash memory particles, it is desirable to have a flexible way to judge whether the data already exists in the cache of the storage controller. There are various reasons for data being cached, and it is hoped that the way of judging whether the data already exists in the cache of the storage controller can be adapted to different reasons. And it is expected that users of storage devices can participate in flexible control of cache utilization, rather than relying on the storage controller to determine whether data is cached.
为实现上述目的,本发明通过微指令序列的执行来响应来自主机或用户的命令。通过微指令执行单元对微指令序列的执行,向闪存颗粒发出操作命令和/或接收从闪存颗粒读出的数据或其他信息。存储设备的用户通过对微指令序列的编程、更新和/或修改,能够参与对存储控制器的缓存利用的灵活控制。To achieve the above objects, the present invention responds to commands from a host or a user through the execution of microinstruction sequences. Through the execution of the microinstruction sequence by the microinstruction execution unit, an operation command is issued to the flash memory particle and/or data or other information read out from the flash memory particle is received. The user of the storage device can participate in flexible control of the cache utilization of the storage controller by programming, updating and/or modifying the sequence of microinstructions.
根据本发明的第一个方面,提供了一种访问NVM的方法,包括:处理指示读NVM的第一用户命令,检查所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址是否相同,其中,所述第二用户命令指示读NVM,所述第二用户命令出现于所述第一用户命令之前,且所述第二命令与所述第一用户命令访问相同的第一并行单元;若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,从与所述第一并行单元对应的第一缓存中读出数据,用来响应所述第一用户命令。According to a first aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for accessing an NVM, comprising: processing a first user command instructing to read the NVM, and checking that the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command correspond to the second user command Whether the block address and page address are the same, where the second user command instructs to read the NVM, the second user command appears before the first user command, and the second command is the same as the first user command Access the same first parallel unit; if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, from the first cache corresponding to the first parallel unit Data is read out in response to the first user command.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,进一步包括:若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不同,向NVM发出NVM读命令。An embodiment according to the first aspect of the present invention further includes: if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, issuing an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,为访问第一并行单元的第一用户命令提供第一缓存,为访问第二并行单元的第一用户命令提供第二缓存。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, a first buffer is provided for the first user command accessing the first parallel unit, and a second buffer is provided for the first user command accessing the second parallel unit.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,响应于所述第二用户命令,将从NVM中读出与所述第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址对应的数据写入所述第一缓存。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, in response to the second user command, data corresponding to the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command are read from the NVM and written into the first cache.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,设置标志寄存器;以及若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不同,清除标志寄存器。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, a flag register is set; and if the The block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, and the flag register is cleared.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,跳转执行第一微指令序列,以从与所述第一并行单元对应的第一缓存中读出数据;以及若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不同,跳转执行第二微指令序列,以向NVM发出NVM读命令。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, the first microinstruction sequence is executed by jumping , to read data from the first cache corresponding to the first parallel unit; and if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, skip the The second sequence of microinstructions is executed to issue an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,响应于所述第一用户命令,若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不同,进一步从NVM中读出与所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址对应的数据,并写入所述第一缓存。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, in response to the first user command, if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command , and further read data corresponding to the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command from the NVM, and write it into the first cache.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述第一用户命令对应第一区段地址,所述第二用户命令对应第二区段地址。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, the first user command corresponds to a first segment address, and the second user command corresponds to a second segment address.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述第一用户命令指示获取第一地址范围的数据,所述第二用户命令指示获取第二地址范围的数据。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, the first user command instructs to acquire data of a first address range, and the second user command instructs to acquire data of a second address range.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,响应于所述第二用户命令,从NVM中读出与所述第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址对应的页数据写入所述第一缓存,所述页数据包括第一区段数据与第二区段数据。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, in response to the second user command, the page data corresponding to the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command is read from the NVM and written into the In the first cache, the page data includes first segment data and second segment data.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,进一步包括:处理指示读NVM的第三用户命令,根据所述第三用户命令访问第二并行单元,将从NVM中读出与所述第三用户命令对应的块地址和页地址对应的数据写入第二缓存。An embodiment according to the first aspect of the present invention further comprises: processing a third user command instructing to read the NVM, accessing the second parallel unit according to the third user command, reading out from the NVM and the third user command The data corresponding to the block address and the page address corresponding to the command are written into the second cache.
根据本发明的第一方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述标志寄存器被设置,跳转执行第一微指令序列,以从与所述第一并行单元对应的第一缓存中读出数据;以及若所述标志寄存器被清除,跳转执行第二微指令序列,以向NVM发出NVM读命令。According to an embodiment of the first aspect of the present invention, if the flag register is set, jump to execute a first microinstruction sequence to read data from a first cache corresponding to the first parallel unit; and if the flag register is cleared, jumping to execute a second sequence of microinstructions to issue an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第二方面,还提供了一种访问NVM的方法,包括:处理指示读NVM的第一用户命令,检查所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址是否相同,其中,所述第二用户命令指示写NVM,所述第二用户命令出现于所述第一用户命令之前,且所述第二命令与所述第一用户命令访问相同的并行单元;若所述第一用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,从与所述并行单元对应的缓存中读出数据,用来响应所述第一用户命令。According to a second aspect of the present invention, a method for accessing an NVM is also provided, comprising: processing a first user command instructing to read the NVM, and checking that the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command correspond to the second user command Whether the block address and page address are the same, wherein the second user command instructs to write to the NVM, the second user command appears before the first user command, and the second command is the same as the first user command Access the same parallel unit; if the block address and page address corresponding to the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, read data from the cache corresponding to the parallel unit for in response to the first user command.
根据本发明的第二方面的一个实施方式,进一步包括:若所述用户命令对应的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不同,向NVM发出NVM读命令。An embodiment according to the second aspect of the present invention further includes: if the block address and page address corresponding to the user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, issuing an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第三方面,还提供了一种NVM控制器,包括:微指令存储器,用于存储微指令序列;微指令执行单元,用于对微指令进行译码并执行微指令所对应的操作;程序计数器,用于指示微指令存储器中微指令的存储位置;通用寄存器组,其中通过所述微指令序列中的微指令能够访问所述通用寄存器组中的寄存器;用户命令存储器,用于存储用户命令;上下文存储器,用于存储微指令序列对应的上下文信息。According to a third aspect of the present invention, an NVM controller is also provided, including: a microinstruction memory for storing microinstruction sequences; a microinstruction execution unit for decoding the microinstructions and executing the corresponding microinstructions operation; a program counter, used to indicate the storage location of microinstructions in the microinstruction memory; a general-purpose register group, wherein the registers in the general-purpose register group can be accessed by the microinstructions in the microinstruction sequence; the user command memory, used for Stores user commands; context memory is used to store context information corresponding to micro-instruction sequences.
根据本发明的第三方面的一个实施方式,其中,依据程序计数器,所述微指令执行单元从微指令存储器中获取第一微指令;所述微指令执行单元对第一微指令进行解码,当第一微指令是读地址检查微指令时,所述微指令执行单元,依据读地址检查微指令的偏移值访问用户命令存储器,获取第一块地址与第一页地址;所述微指令执行单元,访问上下文存储器,获得当前微指令序列的上下文信息中存储的第二块地址与第二页地址;所述微指令执行单元比较第一块地址与第二块地址,第一页地址与第二页地址,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,所述微指令执行单元则依据所述读地址检查微指令的寄存器索引设置通用寄存器组中由所述寄存器索引所指示的通用寄存器。According to an embodiment of the third aspect of the present invention, wherein, according to the program counter, the microinstruction execution unit obtains the first microinstruction from the microinstruction memory; the microinstruction execution unit decodes the first microinstruction, and when When the first microinstruction is a read address check microinstruction, the microinstruction execution unit accesses the user command memory according to the offset value of the read address inspection microinstruction, and obtains the first block address and the first page address; the microinstruction executes The unit accesses the context memory to obtain the second block address and the second page address stored in the context information of the current microinstruction sequence; the microinstruction execution unit compares the first block address and the second block address, and the first page address and the first page address Two page addresses, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the microinstruction execution unit checks the register index setting of the microinstruction according to the read address. The general purpose register in the register bank indicated by the register index.
根据本发明的第三方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,所述微指令执行单元则依据所述读地址检查微指令的寄存器索引清除通用寄存器组中由所述寄存器索引所指示的通用寄存器;以及所述微指令执行单元使所述程序计数器递增。According to an embodiment of the third aspect of the present invention, if the first block address and the second block address are different, or the first page address and the second page address are different, the microinstruction execution unit executes the microinstruction according to the A read address checking the register index of the microinstruction clears the general register in the general register set indicated by the register index; and the microinstruction execution unit increments the program counter.
根据本发明的第三方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述微指令执行单元访问用户命令存储器,进一步获取第一并行单元地址;所述微指令执行单元访问用户命令存储器,依据所述第一并行单元地址获得当前微指令序列的上下文信息中存储的第二块地址与第二页地址。According to an embodiment of the third aspect of the present invention, the microinstruction execution unit accesses the user command memory, and further acquires the address of the first parallel unit; the microinstruction execution unit accesses the user command memory, according to the first parallel The unit address obtains the second block address and the second page address stored in the context information of the current microinstruction sequence.
根据本发明的第三方面的一个实施方式,其中,响应于用户命令存储器中的用户命令而发起微指令序列的执行,依据所述用户命令所访问的并行单元而为所述微指令序列执行第一上下文存储器,所述微指令执行单元访问第一上下文存储器,获得当前微指令序列的上下文信息中存储的第二块地址与第二页地址。An embodiment according to the third aspect of the present invention, wherein the execution of the microinstruction sequence is initiated in response to a user command in the user command memory, and the first microinstruction sequence is executed for the microinstruction sequence according to the parallel unit accessed by the user command. a context memory, the microinstruction execution unit accesses the first context memory to obtain the second block address and the second page address stored in the context information of the current microinstruction sequence.
根据本发明的第四方面,还提供了一种NVM控制器,包括:微指令存储器,用于存储微指令序列;微指令执行单元,用于对微指令进行译码并执行微指令所对应的操作;程序计数器,用于指示微指令存储器中微指令的存储位置;用户命令存储器,用于存储用户命令;上下文存储器,用于存储微指令序列对应的上下文信息。According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, an NVM controller is also provided, including: a microinstruction memory for storing microinstruction sequences; and a microinstruction execution unit for decoding the microinstructions and executing the corresponding microinstructions operation; program counter, used to indicate the storage location of microinstructions in the microinstruction memory; user command memory, used to store user commands; context memory, used to store the context information corresponding to the microinstruction sequence.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,依据程序计数器,所述微指令执行单元从微指令存储器中获取第一微指令,所述微指令执行单元对第一微指令进行解码,当第一微指令是读地址检查微指令时,所述微指令执行单元,依据读地址检查微指令的偏移值访问用户命令存储器,获取第一块地址与第一页地址;所述微指令执行单元,访问上下文存储器,获得当前微指令序列的上下文信息中存储的第二块地址与第二页地址;所述微指令执行单元比较第一块地址与第二块地址,第一页地址与第二页地址,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,所述微指令执行单元则依据所述读地址检查微指令的第一地址设置所述程序计数器;若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,所述微指令执行单元使所述程序计数器递增为第二地址。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, according to the program counter, the microinstruction execution unit acquires the first microinstruction from the microinstruction memory, and the microinstruction execution unit decodes the first microinstruction, and when When the first microinstruction is a read address check microinstruction, the microinstruction execution unit accesses the user command memory according to the offset value of the read address inspection microinstruction, and obtains the first block address and the first page address; the microinstruction executes The unit accesses the context memory to obtain the second block address and the second page address stored in the context information of the current microinstruction sequence; the microinstruction execution unit compares the first block address and the second block address, and the first page address and the first page address Two page addresses, wherein, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the microinstruction execution unit checks the first address of the microinstruction according to the read address The address sets the program counter; if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the microinstruction execution unit increments the program counter to the second address.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,依据程序计数器,所述微指令执行单元从微指令存储器中获取第一微指令,所述微指令执行单元对第一微指令进行解码,当第一微指令是读地址检查微指令时,所述微指令执行单元,依据读地址检查微指令的偏移值访问用户命令存储器,获取第一块地址与第一页地址;所述微指令执行单元,访问上下文存储器,获得当前微指令序列的上下文信息中存储的第二块地址与第二页地址;所述微指令执行单元比较第一块地址与第二块地址,第一页地址与第二页地址,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,所述微指令执行单元则依据所述读地址检查微指令的第一地址设置所述程序计数器;若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,所述微指令执行单元使所述程序计数器递增为第二地址。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, according to the program counter, the microinstruction execution unit acquires the first microinstruction from the microinstruction memory, and the microinstruction execution unit decodes the first microinstruction, and when When the first microinstruction is a read address check microinstruction, the microinstruction execution unit accesses the user command memory according to the offset value of the read address inspection microinstruction, and obtains the first block address and the first page address; the microinstruction executes The unit accesses the context memory to obtain the second block address and the second page address stored in the context information of the current microinstruction sequence; the microinstruction execution unit compares the first block address and the second block address, and the first page address and the first page address Two page addresses, wherein, if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the microinstruction execution unit checks the first address of the microinstruction according to the read address The address sets the program counter; if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the microinstruction execution unit increments the program counter to the second address.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述上下文存储器中进一步存储在处理所述用户命令之前在NVM的第二块地址与第二页地址中读出的数据。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the context memory further stores data read out from the second block address and the second page address of the NVM before processing the user command.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述上下文存储器中进一步存储在处理所述用户命令之前向NVM的第二块地址与第二页地址中写入的数据。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the context memory further stores data written to the second block address and the second page address of the NVM before processing the user command.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述微指令存储器从所述第一地址开始存储用于从缓存中获取数据的微指令序列。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the microinstruction memory stores a microinstruction sequence for fetching data from the cache from the first address.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述微指令存储器从所述第二地址开始存储用于向NVM发出NVM读命令的微指令序列。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the microinstruction memory stores a microinstruction sequence for issuing an NVM read command to the NVM from the second address.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述微指令存储器从所述第一地址开始存储用于向NVM发出NVM读命令的微指令序列。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the microinstruction memory stores, starting from the first address, a microinstruction sequence for issuing an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第四方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述微指令存储器从所述第二地址开始存储用于从缓存中获取数据的微指令序列。According to an embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the microinstruction memory stores a microinstruction sequence for fetching data from the cache starting from the second address.
根据本发明的第五方面,还提供了一种在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法,包括:取出第一微指令;对所述第一微指令进行解码,确定所述第一微指令是读地址检查微指令,其中所述读地址检查微指令包括寄存器索引与偏移值,所述寄存器索引用于指示存储所述读地址检查指令执行结果的标志寄存器,所述偏移值用于指示用户命令的存储位置;依据所述偏移值获取所述用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;依据所述读地址检查微指令的上下文信息获取第二块地址与第二页地址,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,则依据寄存器索引设置标志寄存器;所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则依据寄存器索引清除标志寄存器。According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller, comprising: fetching a first microinstruction; decoding the first microinstruction to determine the first microinstruction A microinstruction is a read address check microinstruction, wherein the read address check microinstruction includes a register index and an offset value, the register index is used to indicate a flag register that stores the execution result of the read address check instruction, and the offset The value is used to indicate the storage location of the user command; the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command are obtained according to the offset value; the second block address and the first page address are obtained by checking the context information of the microinstruction according to the read address. The second page address, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the flag register is set according to the register index; the first block address and the second block address are are different, or the address of the first page is different from the address of the second page, the flag register is cleared according to the register index.
根据本发明的第六方面,还提供了一种在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法,包括:取出所述读地址检查微指令,其中所述读地址检查微指令包括寄存器索引与偏移值,所述寄存器索引用于指示存储所述读地址检查指令执行结果的标志寄存器,所述偏移值用于指示用户命令的存储位置;对所述读地址检查微指令进行解码;依据所述偏移值获取所述用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;依据所述读地址检查微指令的上下文信息获取第二块地址与第二页地址,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,则依据寄存器索引设置标志寄存器;若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则依据寄存器索引清除标志寄存器。According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller, comprising: fetching the read address check microinstruction, wherein the read address check microinstruction includes a register index and an offset value, the register index is used to indicate a flag register that stores the execution result of the read address check instruction, and the offset value is used to indicate the storage location of the user command; the read address check microinstruction is decoded; Obtain the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command according to the offset value; check the context information of the microinstruction according to the read address to obtain the second block address and the second page address, if the first block address and the second page address are obtained. The block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, then the flag register is set according to the register index; if the first block address and the second block address are different, or the first page address and the If the addresses of the two pages are different, the flag register is cleared according to the register index.
根据本发明的第六方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述第二块地址与第二页地址是发生于所述用户命令之前的用户命令所对应的访问NVM的块地址和页地址。According to an embodiment of the sixth aspect of the present invention, the second block address and the second page address are the block address and page address for accessing the NVM corresponding to the user command that occurs before the user command.
根据本发明的第六方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述用户命令指示读取NVM的第一块地址以及第一页地址所对应的存储位置的数据。According to an embodiment of the sixth aspect of the present invention, the user command instructs to read the first block address of the NVM and the data of the storage location corresponding to the first page address.
根据本发明的第六方面的一个实施方式,其中,其余用户命令是指示从NVM读出数据的命令或向NVM写入数据的命令。An embodiment according to the sixth aspect of the present invention, wherein the remaining user commands are commands instructing to read data from the NVM or commands to write data to the NVM.
根据本发明的第七方面,还提供了一种在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法,包括:取出所述读地址检查微指令,其中所述读地址检查微指令包括寄存器索引与偏移值,所述寄存器索引用于指示存储所述读地址检查指令执行结果的标志寄存器,所述偏移值用于指示用户命令的存储位置;对所述读地址检查微指令进行解码;依据所述偏移值获取所述用户命令对应的第一并行单元地址、第一块地址与第一页地址;依据所述第一并行单元地址获取第二块地址与第二页地址,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,则依据寄存器索引设置标志寄存器;若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则依据寄存器索引清除标志寄存器。According to a seventh aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller, comprising: fetching the read address check microinstruction, wherein the read address check microinstruction includes a register index and an offset value, the register index is used to indicate a flag register that stores the execution result of the read address check instruction, and the offset value is used to indicate the storage location of the user command; the read address check microinstruction is decoded; Obtain the first parallel unit address, the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command according to the offset value; obtain the second block address and the second page address according to the first parallel unit address, wherein, If the address of the first block is the same as the address of the second block, and the address of the first page is the same as the address of the second page, the flag register is set according to the register index; if the address of the first block and the address of the second block are different, or the If the address of one page is different from the address of the second page, the flag register is cleared according to the register index.
根据本发明的第七方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述第二块地址与第二页地址是发生于所述用户命令之前的其余用户命令所对应的访问NVM的块地址和页地址。According to an embodiment of the seventh aspect of the present invention, the second block address and the second page address are block addresses and page addresses for accessing the NVM corresponding to the remaining user commands that occur before the user command.
根据本发明的第七方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述用户命令指示读取NVM的第一块地址以及第一页地址所对应的存储位置的数据。According to an embodiment of the seventh aspect of the present invention, the user command instructs to read the first block address of the NVM and the data of the storage location corresponding to the first page address.
根据本发明的第七方面的一个实施方式,其中,所述其余用户命令是指示从NVM读出数据的命令或向NVM写入数据的命令。An embodiment according to the seventh aspect of the present invention, wherein the remaining user commands are commands instructing to read data from the NVM or commands to write data to the NVM.
根据本发明的第八方面,还提供了一种在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法,包括:取出所述读地址检查微指令,其中所述读地址检查微指令包括寄存器索引与偏移值,所述寄存器索引用于指示存储所述读地址检查指令执行结果的标志寄存器,所述偏移值用于指示用户命令的存储位置,所述读地址检查指令还包括第一地址;对所述读地址检查微指令进行解码;依据所述偏移值获取所述用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;依据所述读地址检查微指令的上下文信息获取第二块地址与第二页地址,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,则将所述NVM接口控制器的程序计数器设置为所述第一地址;其中从所述第一地址开始存储从缓存中获取数据的微指令序列。According to an eighth aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller, comprising: fetching the read address check microinstruction, wherein the read address check microinstruction includes a register index and an offset value, the register index is used to indicate a flag register that stores the execution result of the read address check instruction, the offset value is used to indicate the storage location of the user command, and the read address check instruction also includes a first address ; Decode the read address check microinstruction; obtain the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command according to the offset value; obtain the second block according to the context information of the read address check microinstruction address and second page address, wherein, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the program counter of the NVM interface controller is set to the a first address; wherein a microinstruction sequence for retrieving data from the cache is stored from the first address.
根据本发明的第八方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则将所述NVM接口控制器的程序计数器设置为第二地址;其中所述第二地址开始存储向NVM发出NVM读命令的微指令序列。According to an embodiment of the eighth aspect of the present invention, if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the program of the NVM interface controller is changed to The counter is set to a second address; wherein the second address begins to store the sequence of microinstructions that issue an NVM read command to the NVM.
根据本发明的第八方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,所述方法进一步包括:依据寄存器索引设置标志寄存器。According to an embodiment of the eighth aspect of the present invention, wherein, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the method further includes: setting according to a register index flag register.
根据本发明的第八方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,所述方法进一步包括:依据寄存器索引清除标志寄存器。According to an embodiment of the eighth aspect of the present invention, if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the method further includes: clearing according to a register index flag register.
根据本发明的第九方面,还提供了一种在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法,包括:取出所述读地址检查微指令,其中所述读地址检查微指令包括寄存器索引与偏移值,所述寄存器索引用于指示存储所述读地址检查指令执行结果的标志寄存器,所述偏移值用于指示用户命令的存储位置,所述读地址检查指令还包括第一地址;对所述读地址检查微指令进行解码;依据所述偏移值获取所述用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;依据所述读地址检查微指令的上下文信息获取第二块地址与第二页地址,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则将所述NVM接口控制器的程序计数器设置为所述第一地址;其中从所述第一地址开始存储向NVM发出NVM读命令的微指令序列。According to a ninth aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller, comprising: fetching the read address check microinstruction, wherein the read address check microinstruction includes a register index and an offset value, the register index is used to indicate a flag register that stores the execution result of the read address check instruction, the offset value is used to indicate the storage location of the user command, and the read address check instruction also includes a first address ; Decode the read address check microinstruction; obtain the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command according to the offset value; obtain the second block according to the context information of the read address check microinstruction address and the second page address, if the first block address and the second block address are the same, and the first page address and the second page address are different, set the program counter of the NVM interface controller to the first address; wherein the microinstruction sequence for issuing the NVM read command to the NVM is stored from the first address.
根据本发明的第九方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,则将所述NVM接口控制器的程序计数器设置为第二地址;其中所述第二地址开始存储从缓存中获取数据的微指令序列。According to an implementation of the ninth aspect of the present invention, if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the program of the NVM interface controller is changed to The counter is set to a second address; wherein the second address begins to store the sequence of microinstructions to fetch data from the cache.
根据本发明的第九方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址相同,且第一页地址与第二页地址相同,所述方法进一步包括:依据寄存器索引设置标志寄存器。According to an embodiment of the ninth aspect of the present invention, if the first block address is the same as the second block address, and the first page address is the same as the second page address, the method further includes: setting according to a register index flag register.
根据本发明的第九方面的一个实施方式,其中,若所述第一块地址与第二块地址不同,或第一页地址与第二页地址不同,所述方法进一步包括:依据寄存器索引清除标志寄存器。According to an embodiment of the ninth aspect of the present invention, if the first block address is different from the second block address, or the first page address is different from the second page address, the method further includes: clearing according to a register index flag register.
根据本发明的第十方面,提供一种包含计算机程序代码的计算机程序,当被载入计算机系统并在计算机系统上执行时,所述计算机程序代码使所述计算机系统执行上面所述的方法。According to a tenth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a computer program comprising computer program code which, when loaded into and executed on a computer system, causes the computer system to perform the above-described method.
根据本发明的第十一方面,提供一种包括程序代码的程序,当被载入存储设备并在存储设备上执行时,所述计程序代码使所述存储设备执行上面所述的方法。According to an eleventh aspect of the present invention, there is provided a program comprising program code which, when loaded into and executed on a storage device, causes the storage device to perform the above-described method.
通过本发明的技术方案,能够灵活判断数据是否已存在于存储控制器的缓存中,存储设备的用户能够参与缓存利用的灵活控制,而不依赖于存储控制器判断数据是否被缓存。Through the technical solution of the present invention, it is possible to flexibly judge whether data already exists in the cache of the storage controller, and the user of the storage device can participate in the flexible control of cache utilization without relying on the storage controller to judge whether the data is cached.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过阅读下文优选实施方式的详细描述,各种其他的优点和益处对于本领域普通技术人员将变得清楚明了。附图仅用于示出优选实施方式的目的,而并不认为是对本发明的限制。而且在整个附图中,用相同的参考符号表示相同的部件。其中在附图中,参考数字之后的字母标记指示多个相同的部件,当泛指这些部件时,将省略其最后的字母标记。在附图中:Various other advantages and benefits will become apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art upon reading the following detailed description of the preferred embodiments. The drawings are for the purpose of illustrating preferred embodiments only and are not to be considered limiting of the invention. Also, the same components are denoted by the same reference numerals throughout the drawings. Wherein in the drawings, the letter marks after the reference numerals indicate a plurality of the same components, and the last letter marks thereof will be omitted when referring to these components in general. In the attached image:
图1示出了现有技术的存储系统的框图;Figure 1 shows a block diagram of a prior art storage system;
图2示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的存储器控制器的处理微指令的部件的结构框图;FIG. 2 shows a structural block diagram of a component of a memory controller that processes micro-instructions according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的块/页读地址检查微指令的格式的示意图;3 shows a schematic diagram of the format of a block/page read address check microinstruction according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4-1示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图;4-1 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4-2示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图;4-2 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4-3示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图;4-3 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图5示出了根据本发明另一实施方式的访问NVM的方法流程图;5 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing NVM according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图6A示出了根据本发明的另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法的流程图;6A shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller according to an embodiment of another aspect of the present invention;
图6B示出了根据本发明另一方面的另一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法及其后续操作的流程图;6B shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller and subsequent operations thereof according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图7A示出了根据本发明另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法的流程图;以及7A shows a flowchart of a method of executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller according to an embodiment of another aspect of the present invention; and
图7B示出了根据本发明另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法及其后续操作的流程图。7B shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller and its subsequent operations according to an embodiment of another aspect of the present invention.
在附图中,使用相同或类似的标号来指代相同或类似的元素。In the drawings, the same or similar reference numbers are used to refer to the same or similar elements.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和具体的实施方式对本发明作进一步的描述。The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
图2示出了根据本发明一个实施方式的存储器控制器的处理微指令的部件的结构框图。为实现对微指令的处理,存储设备的存储器控制器可包括微指令执行单元210、命令队列220、接口控制器230、微指令存储器240、上下文存储器260和/或通用寄存器250。FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of the structure of the components of the memory controller processing microinstructions according to one embodiment of the present invention. To implement the processing of microinstructions, the memory controller of the storage device may include
微指令存储器240用于存储微指令。微指令执行单元210从微指令存储器240中读取并执行微指令。微指令使得微指令执行单元210通过接口控制器230向闪存颗粒发出访问闪存颗粒的命令,包括,例如,读出、编程、擦除、暂停、读取闪存颗粒特征和/或读设置闪存颗粒特征等命令。微指令也使得微指令执行单元210通过接口控制器230获得从闪存颗粒读出的数据。一条微指令或多条微指令可对应于读出、编程、擦除和/或暂停等访问闪存颗粒的命令之一。微指令还包括分支、跳转微指令,其使得微指令执行单元改变执行微指令的顺序。微指令还包括块/页读地址检查微指令。后文中将结合图3详细介绍块/页读地址检查微指令。
微指令存储器240中可存储一段或多段微指令序列。作为举例,在图2的微指令存储器240中,存储了n段微指令序列,包括微指令序列1、微指令序列2……以及微指令序列n。微指令序列1、微指令序列2……以及微指令序列n的每段包括多条微指令。One or more sequences of microinstructions may be stored in the
在微指令序列中的多条微指令可由微指令执行单元210执行。每段微指令序列拥有自己的执行状态,从而每段微指令的执行可被暂停和恢复。微指令执行单元210能够暂停正在执行的微执行序列,并选择执行其他微指令序列。也可以在微指令序列中提供让步微指令,当执行到让步微指令时,微指令执行单元210可调度并执行其他微指令序列。微指令执行单元210暂停正在执行的微指令序列,或者执行让步微指时,正在执行的微指令序列的执行状态被保存;当微指令执行单元恢复微指令序列的执行时,读出被保存的执行状态,从而继续被恢复的微指令序列的执行。A plurality of microinstructions in a sequence of microinstructions may be executed by
接口控制器230同闪存颗粒相耦合,用于向闪存颗粒发出访问闪存颗粒的命令,包括,例如,读出、编程、擦除、暂停和/或恢复等;也用于获得从闪存颗粒读出的数据。The
命令队列220用于缓存来自用户或上层系统的命令。来自用户或上层系统的命令可包括读出、写入、删除、标记为无效等命令,还可以包括读取存储设备状态、读取/设置闪存颗粒特征等命令,以及也可以包括用户自定义命令。命令队列220可由存储器、先进先出存储器寄存器堆等实现。微指令执行单元210可访问命令队列220。例如,在执行微指令时,依据微指令,微指令执行单元210访问命令队列220。
在处理命令队列220中的命令时,获取与该命令对应的微指令序列,并由微指令执行单元210执行该微指令序列,以完成对命令队列220中的命令的处理。可由转换电路(未示出)实现从处理命令队列220中的命令到微指令序列的转换。也可以由微指令执行单元210实现从处理命令队列220中的命令到微指令序列的转换。在获取微指令序列的过程中,可以基于命令队列220中的命令对微指令序列进行填充或适配,以使微指令序列同命令队列220中的命令相适应。微指令序列还控制微指令执行单元210访问并处理命令队列220中的命令。并依据命令队列220中的命令来选择执行对应的微指令序列。When processing a command in the
通用寄存器250耦合到微指令执行单元210,用于保存和提供微指令序列的执行状态。微指令序列的执行状态包括程序计数器(PC)、通用寄存器(GR)、物理地址寄存器和/或定时器等。程序计数器用于指示微指令序列中当前执行的微指令地址。物理地址寄存器用于指示微指令序列访问的闪存颗粒的地址。A
上下文存储器260用于保存微指令序列的执行状态。上下文存储器260保存的微指令序列的执行状态可包括通用寄存器250的内容。在上下文存储器260中,可保存一条或多条微指令序列的执行状态。在上下文存储器260中保存了状态信息的微指令序列,可被调度恢复执行。通过将上下文存储器260中保存的对应于一条微指令序列的状态信息恢复到通用寄存器250中,微指令执行单元210可恢复该微指令序列的执行。将执行的微指令序列称作线程。同一微指令序列在每次执行时拥有自己的执行状态,从而可基于同一微指令序列创建多个线程。在上下文存储器260中,为每个线程存储执行状态。The
在根据本发明的实施例中,基于所要访问的并行单元来创建或使用线程。例如使用第1线程来访问第1并行单元,和/或使用第2线程来访问第2并行单元。在一个例子中,上下文存储器260可容纳的线程数量同图2的处理微指令的部件所耦合的闪存颗粒的并行单元的数量相同;为每一个并行单元分配或保留线程;当处理对一个并行单元的请求时,调度与该并行单元相对应的线程。在一个例子中,上下文存储器260可容纳的线程数量小于同图2的处理微指令的部件所耦合的并行单元的数量。当处理对一个并行单元的请求时,使用已分配来处理该并行单元的线程或者分配新线程来处理该请求。In an embodiment according to the invention, threads are created or used based on the parallel unit to be accessed. For example, the first thread is used to access the first parallel unit, and/or the second thread is used to access the second parallel unit. In one example, the number of threads that the
提供并行单元缓存来存储从并行单元读出或向并行单元写入的数据。为每个线程提供并行单元缓存。并行单元缓存的大小对应于闪存颗粒150(参见图1)的页大小。提供更大尺寸的并行单元缓存对提高性能是有利的。在一个例子中,在上下文存储器260中提供并行单元缓存。在另一个例子中,由DRAM或其他外部于图2的处理微指令的部件的存储器来提供并行单元缓存。A parallel unit cache is provided to store data read from or written to the parallel unit. Provides a parallel cell cache for each thread. The size of the parallel cell cache corresponds to the page size of flash granules 150 (see FIG. 1). It is advantageous to provide a larger size parallel unit cache to improve performance. In one example, parallel cell caching is provided in
图3示出了根据本发明实施例的块/页读地址检查微指令的格式。块/页读地址检查微指令包括操作码(OpCode)字段、寄存器(Reg)字段与偏移值(Offset)字段。操作码字段通过特定标识符或值指示微指令是块/页读地址检查微指令。寄存器字段指示该块/页读地址检查微指令所修改的通用寄存器(参见图2,通用寄存器250)的名字或编号。偏移值字段指示该块/页读地址检查微指令所对应的命令在命令队列220(参见图2)中的位置。在一个例子中,偏移值字段指示待检查的命令在命令队列220中的存储位置。例如,待检查的命令是当前正在处理的命令之前被处理的读命令或编程命令。Figure 3 illustrates the format of a block/page read address check microinstruction according to an embodiment of the present invention. The block/page read address check microinstruction includes an operation code (OpCode) field, a register (Reg) field and an offset value (Offset) field. The opcode field indicates by a specific identifier or value that the microinstruction is a block/page read address check microinstruction. The register field indicates the name or number of the general register (see Figure 2, general register 250) modified by this block/page read address check microinstruction. The offset value field indicates the position in the command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) of the command corresponding to the block/page read address check microinstruction. In one example, the offset value field indicates where in the
在一个例子中,在基地址上累加偏移值字段指示的值,获得命令在命令队列220中的存储位置。注意到在该块/页读地址检查微指令中并未包括基地址字段,而是为线程或各个微指令提供全局的基地址寄存器或基地址索引,使得在执行该块/页读地址检查微指令时可获得基地址。在另一个例子中,单独使用偏移值字段获得命令在命令队列220中的存储位置。在依然另一个例子中,偏移值字段指示带检查的命令与当前正在处理的命令的偏移。在又一个例子中,偏移值字段是寄存器地址或编号,从而得以通过微指令序列的执行来修改寄存器的内容来在运行时修改偏移值信息。In one example, the value indicated by the offset value field is accumulated at the base address to obtain the storage location of the command in the
在命令队列220内的命令中,提供该命令所访问的并行单元地址、块地址与页地址,从而基于并行单元地址、块地址与页地址可确定特定的闪存颗粒150(参见图1)的特定块与页。例如,由user_cmd[base+offset].block_page_address表示在命令队列220(参照图2)中由偏移值字段索引的命令所提供的块地址与页地址的组合。In a command within
在根据本发明的实施例中,为各线程提供可作为线程上下文的块地址寄存器与页地址寄存器,用于分别存储块地址与页地址。可由多种方式存储块地址与页地址,例如,将块地址与页地址组合存放于同一寄存器。例如,由block_page_address表示作为某一线程上下文的块地址与页地址的组合。属于同一线程的微指令,可访问作为线程上下文的块地址与页地址。In an embodiment according to the present invention, each thread is provided with a block address register and a page address register, which can be used as thread contexts, for storing the block address and the page address, respectively. The block and page addresses can be stored in various ways, for example, by combining the block and page addresses in the same register. For example, a combination of a block address and a page address as a thread context is represented by block_page_address. Microinstructions belonging to the same thread can access the block address and page address as the thread context.
在执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令时,微指令执行单元210(参见图2)比较作为线程上下文的块地址与页地址与该线程所处理的命令队列220中的命令的块地址与页地址是否相同,如果相同,在该块/页读地址检查微指令的寄存器(Reg)字段所指示的通用寄存器置位。如果作为线程上下文的块地址与页地址与该线程所处理的命令队列220中的命令的块地址与页地址不同,将该块/页读地址检查微指令的寄存器(Reg)字段所指示的通用寄存器清除。寄存器置位操作可对应于在寄存器的特定位置写入逻辑“1”或逻辑“0”,寄存器清除操作在寄存器的特定位置中写入的值与寄存器置位操作相反。作为举例,块/页读地址检查微指令的语义表示如下:GR[Reg]=(block_page_address==user_cmd[base+offset].block_page_address)?1:0。当block_page_address与user_cmd[base+offset].block_page_address相同时,将通用寄存器GR[Reg]设置为1,否则设置为0。When executing a block/page read address checking microinstruction according to the present invention, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2) compares the block address and page address that are the context of the thread with the block of commands in the
在根据本发明的实施例中,还提供条件分支微指令。条件分支微指令在执行时,检查指定的通用寄存器。依据指定的通用寄存器被置位或清除,条件分支微指令将程序计数器(PC)设置为两个不同的值之一,以指示微指令执行单元210从微指令存储器240的不同位置获取下一条要执行的微指令。In embodiments according to the invention, conditional branch microinstructions are also provided. The conditional branch microinstruction checks the specified general-purpose register when it executes. The conditional branch microinstruction sets the program counter (PC) to one of two different values depending on whether the designated general-purpose register is set or cleared to instruct the
在根据本发明的又一实施例中,将块/页读地址检查微指令与条件分支微指令的操作相结合,而提供融合微指令。融合微指令,除了操作码(OpCode)字段、寄存器(Reg)字段与偏移值(Offset)字段外,还包括分支目标字段。In yet another embodiment according to the present invention, the operation of the block/page read address check microinstruction is combined with the operation of the conditional branch microinstruction to provide a fused microinstruction. The fusion microinstruction, in addition to the opcode (OpCode) field, the register (Reg) field and the offset value (Offset) field, also includes a branch target field.
在执行融合微指令时,微指令执行单元210(参见图2)比较作为线程上下文的块地址与页地址与该线程所处理的命令队列220中的命令的块地址与页地址是否相同。依据比较结果,将程序计数器(PC)设置为不同的值,以指示微指令执行单元210从微指令存储器的不同位置获取下一条要执行的微指令。例如,在比较结果为真时,指示微指令执行单元210从当前微指令的下一条微指令地址处获取要执行的微指令;而在比较结果为假时,指示微指令执行单元210从分支目标字段指示的地址处获取要执行的微指令。以此方式,不必再使用分离的块/页读地址检查微指令与条件分支微指令,而将条件分支语义融合到执行块/页读地址检查微指令中,从而减少微指令序列的长度,并减少微指令序列在微指令存储器240中占用的存储空间。When executing a fused microinstruction, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) compares whether the block address and page address as the thread context are the same as the block address and page address of the command in the
在根据本发明的另一实施例中,在执行又一融合微指令时,微指令执行单元210(参见图2)比较作为线程上下文的块地址与页地址与该线程所处理的命令队列220中的命令的块地址与页地址是否相同。依据比较结果,将程序计数器(PC)设置为不同的值,以指示微指令执行单元210从微指令存储器的不同位置获取下一条要执行的微指令;并且,将该块/页读地址检查微指令的寄存器(Reg)字段所指示的通用寄存器置位或清除。In another embodiment according to the present invention, when executing yet another fused microinstruction, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) compares the block address and page address as the thread context with the
图4-1示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图。4-1 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing an NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention.
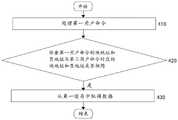
如图4-1所示,访问NVM的方法包括:步骤410:处理第一用户命令;步骤420:检查第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址是否相同;步骤430:如果第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,从第一缓存中取得数据。As shown in Figure 4-1, the method for accessing the NVM includes: Step 410: Process the first user command; Step 420: Check whether the block address and page address of the first user command and the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command The same; Step 430: If the block address and page address of the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, obtain data from the first cache.
在步骤410,作为举例,第一用户命令是第一读命令,开始处理第一读命令。返回参看图2,从命令队列220中取得下一待处理器的命令,并确定其为第一读命令。微指令执行单元210执行相应的微指令序列来处理第一读命令。在步骤420,微指令执行单元210执行根据本发明提供的块/页读地址检查微指令(也参见图3),来判断第一读命令的块地址和/或页地址与第二用户命令的块地址和/或页地址是否相同。第二用户命令是微指令执行单元210在处理第一读命令之前从命令队列210获取并处理的命令。若相同,进行到步骤430,从缓存中取得第一读指令所需的数据。在根据本发明的实施例中,第二用户命令可以是读命令或写命令,在处理第二用户命令时,与第二用户命令的块地址和/或页地址对应的数据被搬运到缓存中。因而当第一读命令与第二用户命令具有相同的块地址和/或页地址时,第一读命令所需要的数据已经存在于缓存中,从缓存中能够获得第一读命令要读取的数据,并无需再发出NVM读命令,从而加快了第一读命令的处理速度。In
图4-2示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图。4-2 shows a flowchart of a method of accessing an NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图4-2所示,访问NVM的方法包括:步骤410:处理第一用户命令;步骤420:检查第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址是否相同;步骤430:如果第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,从第一缓存中取得数据。在图4-2中示出的访问NVM的方法进一步包括步骤440:如果第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不相同,向NVM发出NVM读命令。As shown in Figure 4-2, the method for accessing the NVM includes: Step 410: Process the first user command; Step 420: Check whether the block address and page address of the first user command and the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command The same; Step 430: If the block address and page address of the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, obtain data from the first cache. The method of accessing the NVM shown in FIG. 4-2 further includes step 440: if the block address and page address of the first user command are different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, issuing an NVM read command to the NVM .
图4-3示出了根据本发明的一个实施方式的访问NVM的方法的流程图。4-3 show a flowchart of a method of accessing an NVM according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图4-3所示,访问NVM的方法包括:步骤410:处理第一用户命令;步骤420:检查第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址是否相同;步骤430:如果第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址相同,从第一缓存中取得数据;步骤440:如果第一用户命令的块地址和页地址与第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址不相同,向NVM发出NVM读命令。在图4-3中示出的访问NVM的方法,在步骤440向NVM发出NVM读命令后,进一步包括步骤450:从NVM读出数据,将数据写入第一缓存。As shown in Figure 4-3, the method for accessing the NVM includes: Step 410: Process the first user command; Step 420: Check whether the block address and page address of the first user command and the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command Step 430: If the block address and page address of the first user command are the same as the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, obtain data from the first cache; Step 440: If the block address and page address of the first user command are the same as The page address is different from the block address and page address corresponding to the second user command, and an NVM read command is issued to the NVM. In the method for accessing the NVM shown in FIG. 4-3, after the NVM read command is issued to the NVM in
在步骤450中,响应于第二用户命令,将从NVM中读出与所述第二用户命令对应的块地址和页地址对应的数据写入所述第一缓存。In
在进一步的实施例中,为NVM的每个并行单元(LUN)分配专用的缓存,从而在访问缓存时(例如向缓存搬运数据,或将数据从缓存搬出),能够容易获得缓存的地址,并降低了缓存管理的开销。In a further embodiment, a dedicated cache is allocated for each parallel unit (LUN) of the NVM, so that when accessing the cache (eg, moving data to or from the cache), the address of the cache can be easily obtained, and Reduced cache management overhead.
实施例1Example 1
在根据本发明的实施例1中,在NVM的页中包括多个扇区,第一读命令与第二用户命令访问相同并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址,但访问的扇区不同,其中第一命令访问第一扇区而第二用户命令访问第二扇区。第二用户命令是读命令,且在第一读命令之前被放入命令队列(参看图2,命令队列220)。尽管第二用户命令读取的是第二扇区的数据,但NVM接口能够按页大小传输数据,在根据第二用户命令访问NVM时,将包括第二扇区的整页数据传输到缓存中。随后第一读命令被放入命令队列220。通过执行微指令来处理第一读命令(参见图4-1,步骤410)。执行块/页读地址检查微指令,比较第一读命令与第二用户命令的块地址与页地址(参见图4-1,步骤420),发现第一读命令的块地址与第二用户命令的块地址相同,以及第一读命令的页地址与第二用户命令的页地址相同。这意味着由于第二用户命令的执行,第一读命令所需要的数据已经被搬移到缓存中。作为举例,执行块/页读地址检查微指令,依据比较结果,在通用寄存器(参看图2,通用寄存器250)中设置标志。下一微指令依据所设置的标志,决定执行与步骤430对应的微指令。因而,继续执行微指令来从缓存中取得数据(参见图4-1,步骤430)。以此方式,无需再向NVM发出数据读取命令即可获得要访问的数据,节省了第一读命令的执行时间,提高了效率。In
实施例2Example 2
在根据本发明的实施例2中,页为读取NVM的基本单元,第一读命令与第二用户命令访问相同并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址。第二用户命令是读命令,且在第一读命令之前被放入命令队列(参看图2,命令队列220)。因而第一读命令与第二用户命令是对相同地址的连续的读命令。在根据在前的第二用户命令访问NVM时,将整页数据传输到缓存中。随后第一读命令被放入命令队列220。通过执行微指令来处理第一读命令(参见图4-1,步骤410)。执行块/页读地址检查微指令,比较第一读命令与第二用户命令的块地址与页地址(步骤420),发现第一读命令的块地址与第二用户命令的块地址相同,以及第一读命令的页地址与第二用户命令的页地址相同。这意味着由于第二用户命令的执行,第一读命令所需要的数据已经被搬移到缓存中。因而,继续执行微指令来从缓存中取得数据(步骤430)。以此方式,无需再向NVM发出数据读取命令即可获得要访问的数据,节省了第一读命令的执行时间,提高了效率。In Embodiment 2 according to the present invention, a page is the basic unit for reading NVM, and the first read command and the second user command access the same parallel unit and carry the same block address and page address. The second user command is a read command and is placed in the command queue (see Figure 2, command queue 220) before the first read command. Therefore, the first read command and the second user command are consecutive read commands to the same address. The entire page of data is transferred into the cache when the NVM is accessed according to the second preceding user command. The first read command is then placed into
实施例3Example 3
在根据本发明的实施例3中,页为读取NVM的基本单元,第一读命令与第二用户命令访问相同并行单元。但第一读命令与第二用户命令携带的块地址和/或页地址不同。第二用户命令是读命令,且在第一读命令之前被放入命令队列(参看图2,命令队列220)。在根据在前的第二用户命令访问NVM时,将整页数据传输到缓存中。随后第一读命令被放入命令队列220。通过执行微指令来处理第一读命令(参见图4-3,步骤410)。执行块/页读地址检查微指令,比较第一读命令与第二用户命令的块地址与页地址(步骤420),发现第一读命令的块地址与第二用户命令的块地址不同,或者第一读命令的页地址与第二用户命令的页地址不同。因而第一读命令所需要的数据以很大几率并不在缓存中。作为举例,执行块/页读地址检查微指令,依据比较结果,在通用寄存器(参看图2,通用寄存器250)中设置标志。下一微指令依据所设置的标志,决定执行与步骤440对应的微指令。因而,继续执行微指令来向NVM发出NVM读命令(步骤440)。微指令通过操作接口控制器(参看图2,接口控制器230)来发出NVM读命令。以及通过执行微指令来接收从NVM读出的数据并将数据写入缓存中(步骤450)。当在第一读命令之后出现在命令队列(参看图2,命令队列220)的第三用户命令的块地址与页地址同第一读命令的块地址与页地址分别相同时,意味着第三用户命令所要访问的数据已经存在于缓冲。可从缓存中获取第三用户命令所需的数据而无需再向NVM发出数据读取命令。In Embodiment 3 according to the present invention, a page is the basic unit for reading NVM, and the first read command and the second user command access the same parallel unit. But the block address and/or page address carried by the first read command and the second user command are different. The second user command is a read command and is placed in the command queue (see Figure 2, command queue 220) before the first read command. The entire page of data is transferred into the cache when the NVM is accessed according to the second preceding user command. The first read command is then placed into
图5示出了根据本发明另一实施方式的访问NVM的方法流程图。通过执行微指令序列,使得微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行在图5中展示的访问NVM的方法。FIG. 5 shows a flowchart of a method for accessing an NVM according to another embodiment of the present invention. By executing the microinstruction sequence, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) is caused to perform the method of accessing the NVM shown in FIG. 5 .
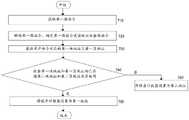
如图5所示,访问NVM的方法包括:步骤510:处理第一读命令;步骤520:从NVM读出第一数据,将第一数据写入第一缓存;步骤530:处理第二读命令:步骤540:检查第一读命令的块地址和页地址与第二读命令的块地址和页地址是否相同;步骤550:如果第一读命令的块地址和页地址与第二读命令的块地址和页地址相同,从第一缓存中取得第一数据;步骤560:如果第一读命令的块地址和页地址与第二读命令的块地址和页地址不相同,发出NVM读命令;步骤570:取得从NVM读出的第二数据,将第二数据写入缓存。As shown in FIG. 5, the method for accessing the NVM includes: Step 510: process the first read command; Step 520: read the first data from the NVM, and write the first data into the first cache; Step 530: process the second read command : Step 540: Check whether the block address and page address of the first read command are the same as the block address and page address of the second read command; Step 550: If the block address and page address of the first read command are the same as the block address and page address of the second read command The address is the same as the page address, and the first data is obtained from the first cache; Step 560: If the block address and page address of the first read command are different from the block address and page address of the second read command, issue an NVM read command; Step 570: Acquire the second data read from the NVM, and write the second data into the cache.
在步骤510,在命令队列220(如图2所示)中出现未处理的第一读命令时,通过执行微指令序列来处理第一读命令。在步骤520,通过执行微指令序列来依据第一读命令从NVM读出数据,并将读出的数据写入缓存。在一个例子中,依据第一读命令从NVM读出数据时,也执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令,并确定第一读命令的块地址与页地址不同于在前的读/写命令的块地址和页地址,从而依据第一读命令向NVM发送NVM读命令。在另一个例子中,依据第一读命令是命令队列220(参看图2)中仅有的读命令或写命令,从而确定缓存中不存在第一读命令所需的数据。在步骤530,响应于命令队列中出现第二读命令,通过执行微指令序列来处理第二读命令。在步骤540,执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令,并确定第二读命令的块地址与页地址与在前的读/写命令(在本例中,为第一读命令)的块地址和页地址是否相同。At
若第二读命令的块地址与页地址与第一读命令的块地址与页地址分别相同,意味着第二读命令所需的数据已经由对第一读命令的执行而被搬运到缓存中,在步骤550,通过执行相应的微指令从缓存中取得第二读命令所需的数据。在进一步的例子中,对第一读命令的处理尚未完成,暂时挂起对第二读命令的处理,并设置在由第一读命令取回数据后,恢复对第二读命令的处理,并从缓存中取得第二读命令所需的数据。If the block address and page address of the second read command are the same as the block address and page address of the first read command, it means that the data required by the second read command has been transferred to the cache by executing the first read command. , in
若第二读命令的块地址与页地址与第一读命令的块地址与页地址不同,意味着第二读命令所需的数据在缓存中的可能性极低,在步骤560,通过执行微指令向NVM发出NVM读命令。在步骤570,通过执行微指令取得从NVM读出的数据,并将数据写入缓存。If the block address and page address of the second read command are different from the block address and page address of the first read command, it means that the possibility that the data required by the second read command is in the cache is extremely low. The instruction issues an NVM read command to the NVM. In
通过以下的具体实施例详细描述:Described in detail through the following specific embodiments:
实施例4Example 4
在根据本发明的实施例4中,命令队列220(参看图2)中在前的第一用户命令是写命令,在后的第二用户命令是读命令。第一用户命令与第二用户命令访问相同的并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第一用户命令,通过执行微指令序列将第一用户命令要写入的数据搬运到缓存中,并通过接口控制器230(参看图2)向NVM发出NVM编程命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第二用户命令,通过微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令确定第一用户命令与第二用户命令访问的块地址与页地址分别相同。据此判断第二用户命令所需的数据存在于缓存中,并通过执行微指令从缓存中取得数据。In Embodiment 4 according to the present invention, the first user command at the front in the command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) is a write command, and the second user command at the end is a read command. The first user command and the second user command access the same parallel unit and carry the same block address and page address. In response to the appearance of the unprocessed first user command in the
实施例5Example 5
在根据本发明的实施例5中,命令队列220(参看图2)中在前的第一用户命令是写命令,在后的第二用户命令是读命令。第一用户命令与第二用户命令访问相同的并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址。第一用户命令要写入一整页数据,而第二用户命令读出页数据的部分。由第二用户命令中携带的地址范围来指示要读出的页数据的部分。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第一用户命令,通过执行微指令序列将第一用户命令要写入的整页数据搬运到缓存中,并通过接口控制器230(参看图2)向NVM发出NVM编程命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第二用户命令,通过微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令确定第一用户命令与第二用户命令访问的块地址与页地址分别相同。据此判断第二用户命令所需的数据存在于缓存中,并通过执行微指令从缓存中取得所需的部分页数据。In Embodiment 5 according to the present invention, the preceding first user command in the command queue 220 (refer to FIG. 2 ) is a write command, and the succeeding second user command is a read command. The first user command and the second user command access the same parallel unit and carry the same block address and page address. The first user command is to write an entire page of data, and the second user command is to read a portion of the page data. The portion of the page data to be read is indicated by the address range carried in the second user command. In response to the appearance of the unprocessed first user command in the
实施例6Example 6
在根据本发明的实施例6中,命令队列220(参看图2)中在前的第一用户命令是读命令,在第一用户命令之后的第二用户命令是读ID命令,在第二用户命令之后的第三用户命令是读命令。第一用户命令与第三用户命令访问相同的并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第一用户命令,通过执行微指令序列将第一用户命令要写入的数据搬运到缓存中,并通过接口控制器230(参看图2)向NVM发出NVM编程命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第二用户命令,通过执行微指令序列向NVM发出NVM读ID命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第三用户命令,通过微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令确定第一用户命令与第二用户命令访问的块地址与页地址不同,以及再次执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令确定第一用户命令与第三用户命令访问的块地址与页地址分别相同。据此判断第三用户命令所需的数据存在于缓存中,并通过执行微指令从缓存中取得数据。In Embodiment 6 according to the present invention, the first user command preceding in the command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) is a read command, the second user command following the first user command is a read ID command, and the second user command after the first user command is a read ID command. The third user command after the command is a read command. The first user command and the third user command access the same parallel unit and carry the same block address and page address. In response to the appearance of the unprocessed first user command in the
实施例7Example 7
在根据本发明的实施例7中,命令队列220(参看图2)中在前的第一用户命令是读命令,在第一用户命令之后的第二用户命令是Set Feature命令,在第二用户命令之后的第三用户命令是读命令。第一用户命令与第三用户命令访问相同的并行单元,并携带相同的块地址与页地址。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第一用户命令,通过执行微指令序列将第一用户命令要写入的数据搬运到缓存中,并通过接口控制器230(参看图2)向NVM发出NVM编程命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第二用户命令,通过执行微指令序列向NVM发出NVM Set Feature命令。响应于命令队列220中出现未处理的第三用户命令,通过执行微指令确定命令队列中的第二用户命令将使得第三用户命令所期待的数据不同于第一用户命令所读到的数据,因而不再执行根据本发明的块/页读地址检查微指令或者忽略块/页读地址检查微指令的检查结果,并依据第三用户命令向NVM发出NVM读命令。In Embodiment 7 according to the present invention, the first user command preceding in the command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) is a read command, the second user command following the first user command is a Set Feature command, and the second user command after the first user command is a Set Feature command. The third user command after the command is a read command. The first user command and the third user command access the same parallel unit and carry the same block address and page address. In response to the appearance of the unprocessed first user command in the
图6A示出了根据本发明的另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法的流程图。6A shows a flowchart of a method of executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller according to one embodiment of another aspect of the present invention.
如图6A所示,在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法包括:步骤610:获取第一微指令;步骤620:解码第一微指令,确定第一微指令是读地址检查微指令;步骤630:获取用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;步骤640:检查第一块地址和第一页地址与已存储块地址和页地址是否相同,如果相同的话,则进入步骤650:设置标志寄存器;如果不相同的话,则进入步骤660:清除标志寄存器。As shown in FIG. 6A , the method for executing the read address check microinstruction in the NVM interface controller includes: step 610 : obtaining the first microinstruction; step 620 : decoding the first microinstruction, and determining that the first microinstruction is the read address check microinstruction instruction; Step 630: Obtain the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command; Step 640: Check whether the first block address and the first page address are the same as the stored block address and page address, if they are the same, enter Step 650 : set the flag register; if not, proceed to step 660 : clear the flag register.
在步骤610,微指令执行单元210依据通用寄存器250中的程序计数器(PC)而从微指令存储器240(参见图2)的指定位置取出块/页读地址检查微指令微指令。作为举例,块/页读地址检查微指令是用于处理读命令的微指令序列中的一条微指令。在步骤620,微指令执行单元210解码从微指令存储器240中读到的微指令,并且确定该微指令为块/页读地址检查微指令。在步骤630,微指令执行单元210依据块/页读地址检查微指令的偏移值字段(参看图3)访问命令队列220,并从中获取当前读命令之前的第一命令的块地址与页地址。微指令执行单元210还从上下文存储器260中获取当前读命令的块地址与页地址。在步骤640,微指令执行单元210比较第一命令的块地址与页地址与当前读命令的块地址与页地址是否均分别相同。若相同,在步骤650,微指令执行单元210依据块/页读地址检查微指令的Reg字段(参见图3)提供的通用寄存器索引设置通用寄存器250中的标志寄存器;若不相同,在步骤660,微指令执行单元210依据块/页读地址检查微指令的Reg字段(参见图3)提供的通用寄存器索引清除通用寄存器250中的标志寄存器。At
在上面的例子中,微指令执行单元210从上下文存储器260中获取当前读命令的块地址与页地址。In the above example, the
可选地,在根据本发明的另一实施例中,块/页读地址检查微指令中提供第二偏移值字段,用以指示当前读命令在命令队列220(参看图2)中的存储位置。并且微指令执行单元210依据第二偏移值字段从命令队列220中取得当前读命令的块地址与页地址,并与由第一偏移值字段所指示的第一命令的块地址与页地址进行比较。Optionally, in another embodiment according to the present invention, a second offset value field is provided in the block/page read address check microinstruction to indicate the storage of the current read command in the command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) Location. And the
依然可选地,在根据本发明的又一实施例中,微指令执行单元210(参看图2)维护上下文标识符,用以标识微指令序列的上下文,特别是微指令序列的上下文在上下文存储器260(参看图2)中的存储位置。从而无需在每条微指令中指示上下文标识符。微指令执行单元210依据上下文标识符,从上下文存储器260中取得当前读指令的块地址与页地址。Still optionally, in yet another embodiment according to the present invention, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) maintains a context identifier to identify the context of the microinstruction sequence, especially the context of the microinstruction sequence is stored in the context memory. 260 (see Figure 2). This eliminates the need to indicate a context identifier in every microinstruction. The
依然可选地,在根据本发明的又一实施例中,命令队列220(参看图2)中的未处理的命令引起微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行微指令序列,在命令中提供上下文标识符,用以标识微指令序列的上下文,特别是微指令序列的上下文在上下文存储器260(参看图2)中的存储位置。并将命令中携带的块地址与页地址存储在上下文存储260中。在执行块/页地址检查微指令时,微指令执行单元210(参看图2)依据上下文标识符,从上下文存储器260中取得当前读指令的块地址与页地址。Still optionally, in yet another embodiment in accordance with the present invention, an unprocessed command in command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) causes microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) to execute a sequence of microinstructions provided in the command. The context identifier is used to identify the context of the microinstruction sequence, especially the storage location of the context of the microinstruction sequence in the context memory 260 (refer to FIG. 2 ). The block address and page address carried in the command are stored in the
依然可选地,在根据本发明的又一实施例中,命令队列220(参看图2)中的未处理的命令引起微指令执行单元210(参看图2)执行微指令序列,在命令中提供并行单元标识符,并使用并行单元标识符来标识微指令序列的上下文,特别是微指令序列的上下文在上下文存储器260(参看图2)中的存储位置。从而为访问相同并行单元的命令分配相同的上下文。以及将命令中携带的块地址与页地址存储在上下文存储260中。在执行块/页地址检查微指令时,微指令执行单元210依据并行单元标识符,从上下文存储器260中取得当前读指令的块地址与页地址。Still optionally, in yet another embodiment in accordance with the present invention, an unprocessed command in command queue 220 (see FIG. 2 ) causes microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) to execute a sequence of microinstructions provided in the command. The parallel unit identifier, and the parallel unit identifier is used to identify the context of the microinstruction sequence, in particular the storage location of the context of the microinstruction sequence in the context memory 260 (see FIG. 2 ). Thus, commands accessing the same parallel unit are assigned the same context. And the block address and page address carried in the command are stored in the
依然可选地,在根据本发明的又一实施例中,微指令执行单元210(参看图2)维护线程标识符,用以标识微指令序列所属的线程。以及在上下文存储器260(参看图2)中存储线程的上下文信息。并且依据线程标识符确定线程上下文在上下文存储器260中的存储位置。微指令执行单元210依据线程标识符,从上下文存储器260中取得当前读指令的块地址与页地址。Still optionally, in yet another embodiment according to the present invention, the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) maintains a thread identifier to identify the thread to which the microinstruction sequence belongs. And the context information of the thread is stored in the context memory 260 (see FIG. 2). And the storage location of the thread context in the
图6B示出了根据本发明另一方面的另一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法及其后续操作的流程图。FIG. 6B shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller and its subsequent operations according to another embodiment of the present invention.
如图6B所示,在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令后,还依据读地址检查微指令的执行结果,执行步骤680从第一缓存读出数据;或者执行步骤670:从NVM读出第二数据,将第二数据写入第一缓存。As shown in FIG. 6B , after the read address check microinstruction is executed in the NVM interface controller, the execution result of the read address check microinstruction is also executed, and step 680 is executed to read data from the first cache; or step 670 is executed: read from the NVM The second data is output, and the second data is written into the first cache.
在步骤680中,块/页读地址检查微指令的后续微指令(例如,分支微指令)检查标志寄存器,依据标志寄存器被置位,相应修改程序计数器(PC)的值,使得微指令执行单元依据更新的程序计数器(PC)的值取得下一条微指令,并通过执行该下一条微指令以及后续微指令序列,从缓存中读出当前读命令所需要的数据。在步骤670中,块/页读地址检查微指令的后续微指令(例如,分支微指令)检查标志寄存器,依据标志寄存器被清除,相应修改程序计数器PC的值,使得微指令执行单元依据更新的程序计数器PC的值取得下一条微指令,并通过执行该下一条微指令以及后续微指令序列,向NVM发出NVM读命令,取得从NVM读出的数据并写入缓存。In
图7A示出了根据本发明另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法的流程图。7A shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller according to one embodiment of another aspect of the present invention.
如图7A所示,在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法包括:步骤710:获取第一微指令;步骤720:解码第一微指令,确定第一微指令是读地址检查微指令;步骤730:获取用户命令对应的第一块地址与第一页地址;步骤740:检查第一块地址和第一页地址与已存储第二块地址和第二页地址是否相同,如果相同的话,则进入步骤750:将程序计数器设置为第一地址;如果不相同的话,则进入步骤760:将程序计数器设置为第二地址。As shown in FIG. 7A , the method for executing the read address check microinstruction in the NVM interface controller includes: Step 710: obtain the first microinstruction; Step 720: decode the first microinstruction, and determine that the first microinstruction is the read address check microinstruction instruction; Step 730: Obtain the first block address and the first page address corresponding to the user command; Step 740: Check whether the first block address and the first page address are the same as the stored second block address and second page address, if they are the same If yes, go to step 750: set the program counter to the first address; if not, go to step 760: set the program counter to the second address.
在步骤710,微指令执行单元210依据通用寄存器250中的程序计数器(PC)而从微指令存储器240(参见图2)的指定位置取出第一微指令。在步骤720,微指令执行单元210解码从微指令存储器240中读到的第一微指令,并且确定该第一微指令为块/页读地址检查微指令。在步骤730,微指令执行单元210依据块/页读地址检查微指令的偏移值字段(参看图3)访问命令队列220,并从中获取当前读命令之前的第一命令的块地址与页地址。微指令执行单元210还从上下文存储器260中获取当前读命令的块地址与页地址。在步骤740,微指令执行单元210比较第一命令的块地址与页地址与当前读命令的块地址与页地址是否均分别相同。若相同,在步骤750,微指令执行单元210将通用寄存器250中的程序计数器(PC)设置为第一值;若不相同,在步骤760,微指令执行单元210将通用寄存器250中的程序计数器(PC)设置为第二值。至此,块/页读地址检查微指令执行完成。At
图7B示出了根据本发明另一方面的一个实施方式的在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令的方法及其后续操作的流程图。7B shows a flowchart of a method for executing a read address check microinstruction in an NVM interface controller and its subsequent operations according to an embodiment of another aspect of the present invention.
如图7B所示,在NVM接口控制器中执行读地址检查微指令后,还依据读地址检查微指令的执行结果,执行步骤步骤770:从程序计数器指示的地址获取第二微指令。As shown in FIG. 7B , after the read address check microinstruction is executed in the NVM interface controller, the execution result of the microinstruction is also checked according to the read address, and step 770 is performed: obtaining the second microinstruction from the address indicated by the program counter.
在步骤770中,微指令执行单元210(参见图2)依据更新的程序计数器PC的值取得下一条微指令,并通过执行该下一条微指令以及后续微指令序列,当在步骤750将程序计数器PC的值设置为第一值时,微指令执行单元通过执行该下一条微指令以及后续微指令序列,从缓存中读出当前读命令所需要的数据;当在步骤760将程序计数器PC的值设置为第二值时,微指令执行单元通过执行该下一条微指令以及后续微指令序列,向NVM发出NVM读命令,取得从NVM读出的数据并写入缓存。In step 770 , the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) obtains the next microinstruction according to the updated value of the program counter PC, and executes the next microinstruction and the subsequent microinstruction sequence, when the program counter is reset in
在可选的实施例中,通过执行块/页读地址检查微指令,在微指令执行单元210(参见图2)将程序计数器(PC)设置为第一值时,还依据块/页读地址检查微指令的Reg字段(参见图3)提供的通用寄存器索引置位通用寄存器250中的标志寄存器;在微指令执行单元210将程序计数器(PC)设置为第二值时,还依据块/页读地址检查微指令的Reg字段(参见图3)提供的通用寄存器索引清除通用寄存器250中的标志寄存器。In an alternative embodiment, the microinstruction is checked by executing the block/page read address, and when the microinstruction execution unit 210 (see FIG. 2 ) sets the program counter (PC) to the first value, the block/page read address is also checked Checking the general register index provided by the microinstruction's Reg field (see Figure 3) sets the flags register in the
本发明中NVM的例子是闪存。所属领域技术人员将意识到本发明的实施例也可应用于其他类型的存储介质,例如相变存储器、电阻存储器、铁电存储器等。An example of NVM in the present invention is flash memory. Those skilled in the art will appreciate that embodiments of the present invention are also applicable to other types of storage media, such as phase change memory, resistive memory, ferroelectric memory, and the like.
根据本发明的一个方面,本发明还提供一种包含计算机程序代码的计算机程序,当被载入计算机系统并在计算机系统上执行时,所述计算机程序代码使所述计算机系统执行上面所述的方法。According to one aspect of the present invention, the present invention also provides a computer program comprising computer program code which, when loaded into and executed on a computer system, causes the computer system to perform the above-described method.
根据本发明的另一个方面,还提供一种包括程序代码的程序,当被载入存储设备并在存储设备上执行时,所述计程序代码使所述存储设备执行上面所述的方法。According to another aspect of the present invention, there is also provided a program comprising program code which, when loaded into and executed on a storage device, causes the storage device to perform the above-described method.
通过本发明的技术方案,能够灵活判断数据是否已存在于存储控制器的缓存中,存储设备的用户能够参与缓存利用的灵活控制,而不依赖于存储控制器判断数据是否被缓存。Through the technical solution of the present invention, it is possible to flexibly judge whether data already exists in the cache of the storage controller, and the user of the storage device can participate in the flexible control of cache utilization without relying on the storage controller to judge whether the data is cached.
应该理解,框图和流程图的每个框以及框图和流程图的框的组合可以分别由包括计算机程序指令的各种装置来实施。这些计算机程序指令可以加载到通用计算机、专用计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备上以产生机器,从而在计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备上执行的指令创建了用于实现一个或多个流程图框中指定的功能的装置。It will be understood that each block of the block diagrams and flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams and flowchart illustrations, respectively, can be implemented by various means including computer program instructions. These computer program instructions can be loaded on a general purpose computer, special purpose computer or other programmable data control device to produce a machine such that the instructions executed on the computer or other programmable data control device create a flow diagram for implementing one or more blocks device with the function specified in .
这些计算机程序指令还可以存储在可以引导计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备的计算机可读存储器中从而以特定方式起作用,从而能够利用存储在计算机可读存储器中的指令来制造包括用于实现一个或多个流程图框中所指定功能的计算机可读指令的制品。计算机程序指令还可以加载到计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备上以使得在计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备上执行一系列的操作步骤,从而产生计算机实现的过程,进而在计算机或其他可编程数据控制设备上执行的指令提供了用于实现一个或多个流程图框中所指定功能的步骤。These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer readable memory that can direct a computer or other programmable data control device to function in a particular manner, such that the instructions stored in the computer readable memory can be used to manufacture including for implementing a Articles of manufacture of computer readable instructions for the functions specified in the flowchart block or blocks. Computer program instructions can also be loaded onto a computer or other programmable data control device to cause a series of operational steps to be performed on the computer or other programmable data control device, resulting in a computer-implemented process, which in turn is performed on the computer or other programmable data control device The instructions executing on the control device provide steps for implementing the functions specified in one or more of the flowchart blocks.
因而,框图和流程图的框支持用于执行指定功能的装置的组合、用于执行指定功能的步骤的组合和用于执行指定功能的程序指令装置的组合。还应该理解,框图和流程图的每个框以及框图和流程图的框的组合可以由执行指定功能或步骤的、基于硬件的专用计算机系统实现,或由专用硬件和计算机指令的组合实现。Thus, blocks of the block diagrams and flowchart illustrations support combinations of means for performing the specified functions, combinations of steps for performing the specified functions and combinations of program instruction means for performing the specified functions. It will also be understood that each block of the block diagrams and flowchart illustrations, and combinations of blocks in the block diagrams and flowchart illustrations, can be implemented by special purpose hardware-based computer systems that perform the specified functions or steps, or by combinations of special purpose hardware and computer instructions.
上述的不同块、操作以及技术的至少一部分可以被执行,通过使用硬件,控制设备执行固件指令,控制设备执行软件指令,或者及其任意组合。当采用执行固件以及软件指令的控制设备执行时,软件或固件指令可以被存储在任意计算机可读存储介质中,例如磁盘,光盘或者其他存储介质,在RAM或者ROM或者flash存储器,控制设备,硬盘,光盘,磁盘等等。同样地,软件和固件指令可以被传输到用户或者系统,通过任意已知的或者期望的传输方式包括,例如,在计算机可读盘或者其他便携式计算机存储机制或者通过通信媒介。通信媒介典型地具体化计算机可读指令,数据结构,序模块或者在已调制数据信号中的其它数据例如载波或者其他传输机制。通过示例,并非限制,通信介质包括有线介质例如有线网络或者单线连接,以及无线媒介,例如声、无线频率,红外以及其它无线介质。从而,软件和固件指令可以被传输给用户或者系统,通过通信信道,例如电话线,DSL线,电缆电视线,光纤线缆,无线信道,因特网,等等(通过便携式存储介质提供这样的软件,其被看作是相同的或者可互换的)。软件或者固件指令可以包括机器可读指令,这些可读指令在由控制设备执行时,导致控制设备执行不同动作。当在硬件中执行时,硬件可以包括一个或多个离散组件,集成电路,应用的集成电路(ASIC),等等。At least some of the various blocks, operations, and techniques described above may be performed using hardware, a control device executing firmware instructions, a control device executing software instructions, or any combination thereof. When executed using a control device that executes firmware and software instructions, the software or firmware instructions may be stored in any computer-readable storage medium, such as a magnetic disk, optical disk or other storage medium, in RAM or ROM or flash memory, control device, hard disk , CD-ROM, Disk, etc. Likewise, software and firmware instructions may be transmitted to a user or system by any known or desired means of transmission, including, for example, on a computer-readable disk or other portable computer storage mechanism or through a communication medium. Communication media typically embody computer readable instructions, data structures, sequence modules, or other data in a modulated data signal such as a carrier wave or other transport mechanism. By way of example, and not limitation, communication media includes wired media such as a wired network or single-wire connection, and wireless media such as acoustic, radio frequency, infrared, and other wireless media. Thus, software and firmware instructions may be transmitted to a user or system over a communication channel, such as a telephone line, DSL line, cable television line, fiber optic cable, wireless channel, the Internet, etc. (providing such software over a portable storage medium, are considered the same or interchangeable). The software or firmware instructions may include machine-readable instructions that, when executed by the control device, cause the control device to perform various actions. When implemented in hardware, the hardware may include one or more discrete components, integrated circuits, application integrated circuits (ASICs), and the like.
需要理解的是,本发明可以以纯软件、纯硬件、固件以及上述的各种组合来实现。硬件例如可以是控制设备、专用集成电路、大规模集成电路等等。It should be understood that the present invention may be implemented in pure software, pure hardware, firmware, and various combinations of the above. The hardware may be, for example, a control device, an application specific integrated circuit, a large scale integrated circuit, or the like.
虽然当前发明参考的示例被描述,其只是为了解释的目的而不是对本发明的限制,对实施方式的改变,增加和/或删除可以被做出而不脱离本发明的范围。Although the examples with reference to the present invention are described for purposes of explanation only and not limitation of the invention, changes, additions and/or deletions to the embodiments may be made without departing from the scope of the invention.
这些实施方式所涉及的、从上面描述和相关联的附图中呈现的教导获益的领域中的技术人员将认识到这里记载的本发明的很多修改和其他实施方式。因此,应该理解,本发明不限于公开的具体实施方式,旨在将修改和其他实施方式包括在所附权利要求书的范围内。尽管在这里采用了特定的术语,但是仅在一般意义和描述意义上使用它们并且不是为了限制的目的而使用。Many modifications and other embodiments of the inventions set forth herein will come to mind to those skilled in the art to which these embodiments pertain having the benefit of the teachings presented in the foregoing descriptions and the associated drawings. Therefore, it is to be understood that the inventions are not to be limited to the specific embodiments disclosed, but that modifications and other embodiments are intended to be included within the scope of the appended claims. Although specific terms are employed herein, they are used in a generic and descriptive sense only and not for purposes of limitation.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210539163.1ACN114968099A (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | NVM (non-volatile memory) access method and NVM controller |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210539163.1ACN114968099A (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | NVM (non-volatile memory) access method and NVM controller |
| CN201610009789.6ACN106951374B (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | Method for checking block page address and apparatus thereof |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610009789.6ADivisionCN106951374B (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | Method for checking block page address and apparatus thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114968099Atrue CN114968099A (en) | 2022-08-30 |
Family
ID=59465862
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610009789.6AActiveCN106951374B (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | Method for checking block page address and apparatus thereof |
| CN202210539163.1APendingCN114968099A (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | NVM (non-volatile memory) access method and NVM controller |
Family Applications Before (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201610009789.6AActiveCN106951374B (en) | 2016-01-06 | 2016-01-06 | Method for checking block page address and apparatus thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (2) | CN106951374B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116188247A (en)* | 2023-02-06 | 2023-05-30 | 格兰菲智能科技有限公司 | Register information processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109508205B (en)* | 2017-09-15 | 2024-04-05 | 北京忆恒创源科技股份有限公司 | NVM chip supporting in-situ operation, operation method thereof and solid-state storage device |
| CN111488298A (en)* | 2017-12-29 | 2020-08-04 | 贵阳忆芯科技有限公司 | Method and device for optimizing execution sequence of NVM interface commands |
| CN111736779B (en)* | 2018-04-25 | 2022-01-11 | 上海忆芯实业有限公司 | Method and device for optimizing execution of NVM interface command |
| CN110580227B (en)* | 2018-06-07 | 2024-04-12 | 北京忆恒创源科技股份有限公司 | Adaptive NVM command generation method and device |
| CN111400988B (en)* | 2018-12-27 | 2023-08-22 | 北京忆芯科技有限公司 | Bump (Bump) pad layout method for integrated circuit chip |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4156278A (en)* | 1977-11-22 | 1979-05-22 | Honeywell Information Systems Inc. | Multiple control store microprogrammable control unit including multiple function register control field |
| US4768148A (en)* | 1986-06-27 | 1988-08-30 | Honeywell Bull Inc. | Read in process memory apparatus |
| US5117487A (en)* | 1988-08-26 | 1992-05-26 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for accessing microprocessor and microinstruction control type microprocessor including pointer register |
| US5274829A (en)* | 1986-11-05 | 1993-12-28 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Information processing apparatus having micro instructions stored both in on-chip ROM and off-chip memory |
| CN101477443A (en)* | 2008-01-03 | 2009-07-08 | 上海奇码数字信息有限公司 | NAND control system and control method |
| CN102207916A (en)* | 2011-05-30 | 2011-10-05 | 西安电子科技大学 | Instruction prefetch-based multi-core shared memory control equipment |
| CN104916315A (en)* | 2014-03-14 | 2015-09-16 | 株式会社东芝 | semiconductor storage device |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4161026A (en)* | 1977-11-22 | 1979-07-10 | Honeywell Information Systems Inc. | Hardware controlled transfers to microprogram control apparatus and return via microinstruction restart codes |
| US4156906A (en)* | 1977-11-22 | 1979-05-29 | Honeywell Information Systems Inc. | Buffer store including control apparatus which facilitates the concurrent processing of a plurality of commands |
| SE515718C2 (en)* | 1994-10-17 | 2001-10-01 | Ericsson Telefon Ab L M | Systems and methods for processing memory data and communication systems |
| JP3486690B2 (en)* | 1995-05-24 | 2004-01-13 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | Pipeline processor |
| CN100583059C (en)* | 2007-12-28 | 2010-01-20 | 祥硕科技股份有限公司 | Data access integration method and its system |
| CN101876944B (en)* | 2009-11-26 | 2012-02-15 | 威盛电子股份有限公司 | Dynamic random access memory controller and control method |
| CN101887398B (en)* | 2010-06-25 | 2012-08-29 | 浪潮(北京)电子信息产业有限公司 | Method and system for dynamically enhancing input/output (I/O) throughput of server |
| US8359528B2 (en)* | 2010-07-23 | 2013-01-22 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Parity look-ahead scheme for tag cache memory |
| CN101916227B (en)* | 2010-08-13 | 2015-04-01 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | RLDRAM SIO storage access control method and device |
| US8793442B2 (en)* | 2012-02-08 | 2014-07-29 | International Business Machines Corporation | Forward progress mechanism for stores in the presence of load contention in a system favoring loads |
| WO2013147820A1 (en)* | 2012-03-29 | 2013-10-03 | Intel Corporation | System and method for managing persistence with a multi-level memory hierarchy including non-volatile memory |
| US9026699B2 (en)* | 2013-09-23 | 2015-05-05 | Seagate Technology Llc | Command execution using existing address information |
- 2016
- 2016-01-06CNCN201610009789.6Apatent/CN106951374B/enactiveActive
- 2016-01-06CNCN202210539163.1Apatent/CN114968099A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4156278A (en)* | 1977-11-22 | 1979-05-22 | Honeywell Information Systems Inc. | Multiple control store microprogrammable control unit including multiple function register control field |
| US4768148A (en)* | 1986-06-27 | 1988-08-30 | Honeywell Bull Inc. | Read in process memory apparatus |
| US5274829A (en)* | 1986-11-05 | 1993-12-28 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Information processing apparatus having micro instructions stored both in on-chip ROM and off-chip memory |
| US5117487A (en)* | 1988-08-26 | 1992-05-26 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Method for accessing microprocessor and microinstruction control type microprocessor including pointer register |
| CN101477443A (en)* | 2008-01-03 | 2009-07-08 | 上海奇码数字信息有限公司 | NAND control system and control method |
| CN102207916A (en)* | 2011-05-30 | 2011-10-05 | 西安电子科技大学 | Instruction prefetch-based multi-core shared memory control equipment |
| CN104916315A (en)* | 2014-03-14 | 2015-09-16 | 株式会社东芝 | semiconductor storage device |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116188247A (en)* | 2023-02-06 | 2023-05-30 | 格兰菲智能科技有限公司 | Register information processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN116188247B (en)* | 2023-02-06 | 2024-04-12 | 格兰菲智能科技有限公司 | Register information processing method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN106951374B (en) | 2022-06-10 |
| CN106951374A (en) | 2017-07-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106951374B (en) | Method for checking block page address and apparatus thereof | |
| US9785545B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for providing dual memory access to non-volatile memory | |
| KR102663304B1 (en) | Read handling in zoned namespace devices | |
| TWI709854B (en) | Data storage device and method for accessing logical-to-physical mapping table | |
| JP6224253B2 (en) | Speculative prefetching of data stored in flash memory | |
| TWI592865B (en) | Data reading method, data writing method and storage controller using the same | |
| US11210226B2 (en) | Data storage device and method for first processing core to determine that second processing core has completed loading portion of logical-to-physical mapping table thereof | |
| EP2546755A2 (en) | Flash controller hardware architecture for flash devices | |
| JP6021759B2 (en) | Memory system and information processing apparatus | |
| EP3608790B1 (en) | Modifying nvme physical region page list pointers and data pointers to facilitate routing of pcie memory requests | |
| KR20200016075A (en) | Apparatus and method for searching valid data in memory system | |
| US20130019050A1 (en) | Flexible flash commands | |
| CN108628759B (en) | Method and device for executing NVM commands out of sequence | |
| CN108874301A (en) | data storage device and operation method thereof | |
| CN110119361B (en) | Memory controller and method of operating the same | |
| US8332575B2 (en) | Data management systems, methods and computer program products using a phase-change random access memory for selective data maintenance | |
| CN110806900A (en) | Memory access instruction processing method and processor | |
| CN108572932A (en) | Multi-plane NVM command fusion method and device | |
| US10866755B2 (en) | Two stage command buffers to overlap IOMMU map and second tier memory reads | |
| TW202011411A (en) | Flash memory controller and associated accessing method and electronic device | |
| KR20240138021A (en) | Memory device and method for scheduling block request | |
| CN112416818A (en) | Apparatus and method for managing firmware through runtime overlay | |
| US10572382B2 (en) | Method of operating data storage device and method of operating data processing system including the same | |
| CN118626246A (en) | Storage device and method for scheduling block requests |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |