CN114966583A - Maneuvering target coherent detection method and system based on improved coordinate rotation and Lu distribution - Google Patents
Maneuvering target coherent detection method and system based on improved coordinate rotation and Lu distributionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114966583A CN114966583ACN202210072550.9ACN202210072550ACN114966583ACN 114966583 ACN114966583 ACN 114966583ACN 202210072550 ACN202210072550 ACN 202210072550ACN 114966583 ACN114966583 ACN 114966583A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- target
- rotation
- signal
- distribution
- jerk
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/41—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00 using analysis of echo signal for target characterisation; Target signature; Target cross-section
- G01S7/411—Identification of targets based on measurements of radar reflectivity
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/41—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00 using analysis of echo signal for target characterisation; Target signature; Target cross-section
- G01S7/418—Theoretical aspects
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于机动目标检测领域,特别涉及一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法及系统。The invention belongs to the field of mobile target detection, in particular to a method and system for coherent detection of a mobile target based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution.
背景技术Background technique
随着高超音速飞机和超高速无人飞行器等具有高速度、加速度和加加速度的空中灵活机动目标的发展,地面和空中雷达对这类目标的检测和运动参数估计受到越来越广泛的关注。由于高速机动目标具有速度快、运动参数多和低雷达截获面积(Radar Cross-Section,RCS)等特点,使得运动目标检测方法(Moving Target Detection,MTD)方法的探测性能严重下降。因此,为了提高雷达的探测性能,研究提出长时间相参积累的解决方法。然而,积累过程中会出现速度引起的距离徙动(Range Migration,RM)、加速度引起的线性多普勒频率偏移(Linear Doppler Frequency Migration,LDFM)和加加速度引起的二次多普勒频率偏移(Quadratic Doppler Frequency Migration,QDFM)效应,导致积累性能下降。。With the development of flexible and maneuverable airborne targets with high velocity, acceleration and jerk, such as hypersonic aircraft and ultra-high-speed unmanned aerial vehicles, the detection and motion parameter estimation of such targets by ground and airborne radars have received more and more attention. Because high-speed maneuvering targets have the characteristics of high speed, many motion parameters and low Radar Cross-Section (RCS), the detection performance of Moving Target Detection (MTD) method is seriously degraded. Therefore, in order to improve the detection performance of radar, a long-term coherent accumulation solution is proposed. However, velocity-induced Range Migration (RM), acceleration-induced Linear Doppler Frequency Migration (LDFM), and jerk-induced quadratic Doppler frequency shift occur during the accumulation process. The Quadratic Doppler Frequency Migration (QDFM) effect leads to a decrease in the accumulation performance. .
根据目标运动模型的阶数,可以将现有研究方法分为以下三类:(a)匀速运动目标相参积累算法,主要针对目标常规状态下平稳飞行时保持径向速度不变的情况;(b)匀加速运动目标相参积累算法,主要针对目标具有恒定加速度的情况;(c)变加速运动目标相参积累算法,主要针对目标具有加加素的复杂运动状态情况。其中,匀速运动目标相参积累算法目的是为了消除RM,具体方法可分为:参数搜索类和非搜索类。搜索类算法在低SNR条件下可以有效积累,但是计算复杂度高。非搜索类算法虽可以解除距离频率和慢时间的耦合,但是存在无法解决高速目标引起的速度模糊等问题。匀加速运动目标相参积累算法主要是消除LDFM效应,尽管能够在低信噪比下获得最优检测性能,但其巨大的运算量严重限制了实际应用。变加速运动目标相参积累算法主要包含前两种运动,还要消除加加速度带来的QDFM,但若信号出现非线性徙动,积累性能将出现恶化,且存在由于使用曲线拟合估计运动参数,低SNR时参数估计准确度会下降,以造成一定的性能损失,虽有些方案抗噪性能好,但是其中RFT的搜索运算量较大、计算速度较慢。According to the order of the target motion model, the existing research methods can be divided into the following three categories: (a) the coherent accumulation algorithm of the uniform moving target, which is mainly aimed at keeping the radial velocity constant when the target flies smoothly in the normal state; ( b) The coherent accumulation algorithm of moving targets with uniform acceleration is mainly aimed at the situation that the target has a constant acceleration; (c) The coherent accumulation algorithm of moving targets with variable acceleration is mainly aimed at the complex motion state of the target with additive elements. Among them, the purpose of the coherent accumulation algorithm for uniform moving targets is to eliminate RM, and the specific methods can be divided into: parameter search type and non-search type. Search-like algorithms can accumulate efficiently under low SNR conditions, but have high computational complexity. Although the non-search algorithm can decouple the distance frequency and slow time, it cannot solve the problem of speed ambiguity caused by high-speed targets. The uniform acceleration moving target coherent accumulation algorithm mainly eliminates the LDFM effect. Although it can obtain the best detection performance under low signal-to-noise ratio, its huge computational load severely limits its practical application. The variable acceleration moving target coherent accumulation algorithm mainly includes the first two motions, and also eliminates the QDFM caused by the jerk. However, if the signal has nonlinear migration, the accumulation performance will deteriorate, and there is a problem due to the use of curve fitting to estimate the motion parameters. , when the SNR is low, the accuracy of parameter estimation will decrease, resulting in a certain performance loss. Although some schemes have good anti-noise performance, the RFT has a large amount of search operation and a slow calculation speed.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
为此,本发明提供一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法及系统,解决高速目标长时间相参积累时产生的距离徙动和多普勒徙动等问题,在降低计算复杂度的同时,能够保证参数估计性能和效果,便于实际场景应用。Therefore, the present invention provides a method and system for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution, which solves the problems of distance migration and Doppler migration caused by long-term coherent accumulation of high-speed targets. While calculating the complexity, it can ensure the performance and effect of parameter estimation, which is convenient for practical application.
按照本发明所提供的设计方案,提供一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,包含如下内容:According to the design scheme provided by the present invention, a method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution is provided, including the following contents:
对雷达回波信号进行脉冲压缩和二维离散形式变换,并设置旋转搜索角度范围,通过旋转坐标变换使回波轨迹旋转到相同距离单元内来确定最佳旋转搜索角度,根据最佳旋转搜索角度估计目标速度和初始距离;Perform pulse compression and two-dimensional discrete form transformation on the radar echo signal, and set the rotation search angle range, and rotate the echo trajectory to the same distance unit through the rotation coordinate transformation to determine the optimal rotation search angle. According to the optimal rotation search angle Estimate target speed and initial distance;
根据初始距离提取相同距离单元内信号,并利用改进吕分布算法估计出目标加速度和加加速度参数;According to the initial distance, the signal in the same distance unit is extracted, and the target acceleration and jerk parameters are estimated by the improved Lv distribution algorithm;
利用相位函数对目标加速度和加加速度参数进行补偿,以校正加速度引起的线性多普勒频率偏移和加加速度引起的二次多普勒频率偏移,并通过傅里叶变换来实现相参积累。Compensate the target acceleration and jerk parameters with the phase function to correct the linear Doppler frequency shift caused by acceleration and the quadratic Doppler frequency shift caused by jerk, and achieve coherent accumulation through Fourier transform .
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,针对检测过程中雷达发射的线性调频信号,利用高阶多项式模型表征目标运动,并对接收机接收的反射回波信号进行脉冲压缩。As the coherent detection method of a maneuvering target based on the improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, for the chirp signal emitted by the radar during the detection process, a high-order polynomial model is used to characterize the target motion, and the reflected echo received by the receiver is analyzed. The signal is pulse compressed.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,对第k个目标的回波信号进行脉冲压缩过程表示为:其中,表示快时间,Tp为脉冲持续时间,kr=B/Tp为LFM信号调频率,B为发射信号带宽,fc表示载频,tm=m/fp表示慢时间变量,m=0,1,…,M-1为脉冲指数,M为积累脉冲总数, fp=1/Tr为雷达脉冲重复频率,Tr表示脉冲重复间隔,c为电磁波速度,Ac,k为幅度,R0,k、vk、 ak和gk分别表示第k个目标回波信号的初始距离、速度、加速度和加加速度。As the coherent detection method of the maneuvering target based on the improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, the pulse compression process for the echo signal of the k-th target is expressed as: in, represents fast time, Tp is the pulse duration, kr =B/Tp is the frequency modulation frequency of the LFM signal, B is the transmission signal bandwidth, fc represents the carrier frequency, tm =m/fp represents the slow time variable, m= 0,1,…,M-1 is the pulse index, M is the total number of accumulated pulses, fp =1/Tr is the radar pulse repetition frequency, Tr is the pulse repetition interval, c is the electromagnetic wave speed, Ac,k is the amplitude , R0,k , vk , ak and gk represent the initial distance, velocity, acceleration and jerk of the k-th target echo signal, respectively.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,依据雷达参数及目标距离-多普勒频域内目标倾斜角度来确定旋转搜索角度范围。As the coherent detection method of the maneuvering target based on the improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, the rotation search angle range is determined according to the radar parameters and the target range-target inclination angle in the Doppler frequency domain.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,利用对二维离散形式变换后信号进行角度旋转,并对旋转后的信号沿慢时间维度进行能量积分,依据积分后的最大值来获取最佳旋转搜索角度,其中,(m,n)和(m′,n′)分别为信号旋转前、后坐标,为旋转搜索角度。As the method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and distribution of the present invention, further, using Rotate the angle of the signal after the transformation of the two-dimensional discrete form, and integrate the energy of the rotated signal along the slow time dimension, and obtain the optimal rotation search angle according to the maximum value after integration, where (m, n) and (m ', n') are the coordinates before and after the signal rotation, respectively, Search angle for rotation.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,通过构建代价函数来估计并获取最佳旋转搜索角度,其中,代价函数表示为:其中,(m′,n′)分别为信号旋转后坐标,为旋转搜索角度;通过对代价函数进行求解,将最大值对应的旋转角度作为所要求获取的最佳旋转搜索角度。As the coherent detection method of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, the cost function is constructed to estimate and obtain the optimal rotation search angle, wherein the cost function is expressed as: Among them, (m', n') are the coordinates of the signal after rotation, respectively, is the rotation search angle; by solving the cost function, the The rotation angle corresponding to the maximum value is taken as the required optimal rotation search angle.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,针对最佳旋转搜索角度,利用公式来估计目标速度和初始距离其中,为最佳旋转搜索角度,μ为过采样率,ρ表示距离采样单元,Δr表示距离分辨单元,Tr为脉冲间隔时间,nmax表示目标距离最大离散化指数最大值。As the coherent detection method of the maneuvering target based on the improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, for the optimal rotation search angle, use the formula to estimate the target speed and initial distance in, is the optimal rotation search angle, μ is the oversampling rate, ρ is the distance sampling unit,Δr is the distance resolution unit, Tr is the pulse interval time, andnmax is the maximum value of the target distance maximum discretization index.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,针对估计出的目标初始距离,沿慢时间维提取目标慢时间维信号,利用改进吕分布算法中参数对称自相关函数来提取信号中用于计算目标加速度和加加速度的过采样率和距离变量,其中,针对参数对称自相关函数提取过程,首先对信号进行尺度傅里叶变换的解耦合,然后并利用二维傅里叶变换来获取慢时间变量和变延时对应的频率,通过在频率构成的平面内二维傅里叶变换所聚集的峰值坐标来获取过采样率和距离变量。As the method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on the improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, for the estimated initial distance of the target, the target slow time dimension signal is extracted along the slow time dimension, and the parameter symmetric autocorrelation in the improved Lv distribution algorithm is used. function to extract the oversampling rate and distance variables used to calculate the target acceleration and jerk in the signal, wherein, for the extraction process of the parametric symmetric autocorrelation function, the signal is first decoupled from the scale Fourier transform, and then the two-dimensional Fourier transform is used to obtain the frequency corresponding to the slow time variable and variable delay, and the oversampling rate and distance variables are obtained by the peak coordinates gathered by the two-dimensional Fourier transform in the plane composed of frequencies.
作为本发明基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,进一步地,针对多个机动目标相参检测的情形,依次遍历每个机动目标,并依次通过旋转坐标变换和改进吕分布算法估计,直至所有机动目标完成相参检测。As the method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution of the present invention, further, for the situation of coherent detection of multiple maneuvering targets, each maneuvering target is traversed in turn, and the rotation coordinates are transformed and Lv distribution algorithm is modified in turn. Estimate until all maneuvering targets complete the coherent detection.
进一步地,本发明还提供一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,包含:坐标旋转估计模块、吕分布估计模块及相参积累模块,其中,Further, the present invention also provides a method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and distribution, comprising: a coordinate rotation estimation module, a distribution estimation module and a coherence accumulation module, wherein,
坐标旋转估计模块,用于对雷达回波信号进行脉冲压缩和二维离散形式变换,并设置旋转搜索角度范围,通过旋转坐标变换使回波轨迹旋转到相同距离单元内来确定最佳旋转搜索角度,根据最佳旋转搜索角度估计目标速度和初始距离;The coordinate rotation estimation module is used to perform pulse compression and two-dimensional discrete form transformation on the radar echo signal, and set the rotation search angle range. Through the rotation coordinate transformation, the echo trajectory is rotated to the same distance unit to determine the optimal rotation search angle. , estimate the target speed and initial distance according to the optimal rotation search angle;
吕分布估计模块,用于根据初始距离提取相同距离单元内信号,并利用改进吕分布算法估计出目标加速度和加加速度参数;The Lv distribution estimation module is used to extract the signals in the same distance unit according to the initial distance, and use the improved Lv distribution algorithm to estimate the target acceleration and jerk parameters;
相参积累模块,用于利用相位函数对目标加速度和加加速度参数进行补偿,以校正加速度引起的线性多普勒频率偏移和加加速度引起的二次多普勒频率偏移,并通过傅里叶变换来实现相参积累。The coherent accumulation module is used to compensate the target acceleration and jerk parameters with the phase function to correct the linear Doppler frequency shift caused by acceleration and the quadratic Doppler frequency shift caused by jerk, and pass Fourier Leaf transformation to achieve coherent accumulation.
本发明的有益效果:Beneficial effects of the present invention:
本发明针对高速目标长时间相参积累时产生距离徙动(RM)和多普勒徙动等问题,通过在一定范围内搜索坐标轴的最佳旋转角度,利用坐标旋转变换MLRT算法对坐标轴进行角度旋转消除RM效应,同时根据旋转角度计算目标速度和初始距离;进一步,通过沿着慢时间维提取消除RM效应后相同距离单元内的信号,利用MLVD算法对QFM信号处理并估计出目标加速度和加加速度,通过补偿原信号中加速度和加加速度的相位项并利用FFT实现相参积累,具有更低的计算复杂度和较高的检测性能和参数估计性能。并进一步利用Ka波段雷达探测的无人机实测数据进行验证,本案方案具有良好的相参积累能力,能够满足实际应用场景需求,具有较好的应用前景。The invention aims at the problems of distance migration (RM) and Doppler migration when high-speed targets are accumulated for a long time. Perform angle rotation to eliminate the RM effect, and calculate the target speed and initial distance according to the rotation angle; further, by extracting the signal in the same distance unit after eliminating the RM effect along the slow time dimension, use the MLVD algorithm to process the QFM signal and estimate the target acceleration and jerk, by compensating the phase terms of acceleration and jerk in the original signal and using FFT to achieve coherent accumulation, it has lower computational complexity and higher detection performance and parameter estimation performance. It is further verified by using the UAV measured data detected by Ka-band radar. The scheme of this case has a good coherent accumulation ability, can meet the needs of practical application scenarios, and has a good application prospect.
附图说明:Description of drawings:
图1为实施例中基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测流程示意;1 is a schematic diagram of the coherent detection process of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lv distribution in an embodiment;
图2为实施例中坐标旋转变换原理示意;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the principle of coordinate rotation transformation in the embodiment;
图3为实施例中本案MLRT-MLVD算法实现流程示意;3 is a schematic diagram of the implementation process of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in this case in the embodiment;
图4为实施例中不同算法计算复杂度比较示意;Fig. 4 is a schematic diagram of comparing the computational complexity of different algorithms in the embodiment;
图5为实施例中本案MLRT-MLVD算法单目标相参积累结果示意;5 is a schematic diagram of the single-target coherent accumulation result of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in this case in the embodiment;
图6为实施例中SNR=-5dB时不同算法相参积累结果对比示意;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the comparison of the coherent accumulation results of different algorithms when SNR=-5dB in the embodiment;
图7为实施例中本案MLRT-MLVD算法多目标相参积累结果示意;7 is a schematic diagram of the multi-target coherent accumulation result of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in this case in the embodiment;
图8为实施例中不同算法检测概率对比示意;8 is a schematic diagram of the comparison of detection probabilities of different algorithms in an embodiment;
图9为实施例中不同算法速度、加速度和加加速度参数估计误差对比示意;FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram showing the comparison of estimation errors of speed, acceleration and jerk parameters of different algorithms in the embodiment;
图10为实施例中实测数据积累结果示意。FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of the actual measurement data accumulation result in the embodiment.
具体实施方式:Detailed ways:
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚、明白,下面结合附图和技术方案对本发明作进一步详细的说明。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer and more comprehensible, the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and technical solutions.
本发明实施例,提供一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,参见图 1所示,包含如下内容:An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for coherent detection of maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and distribution, as shown in FIG. 1, including the following contents:
S101、对雷达回波信号进行脉冲压缩和二维离散形式变换,并设置旋转搜索角度范围,通过旋转坐标变换使回波轨迹旋转到相同距离单元内来确定最佳旋转搜索角度,根据最佳旋转搜索角度估计目标速度和初始距离;S101. Perform pulse compression and two-dimensional discrete form transformation on the radar echo signal, and set the rotation search angle range, and rotate the echo trajectory to the same distance unit through the rotation coordinate transformation to determine the optimal rotation search angle. Search angle to estimate target speed and initial distance;
S102、根据初始距离提取相同距离单元内信号,并利用改进吕分布算法估计出目标加速度和加加速度参数;S102, extracting the signal in the same distance unit according to the initial distance, and using the improved Lv distribution algorithm to estimate the target acceleration and jerk parameters;
S103、利用相位函数对目标加速度和加加速度参数进行补偿,以校正加速度引起的线性多普勒频率偏移和加加速度引起的二次多普勒频率偏移,并通过傅里叶变换来实现相参积累。S103. Compensate the target acceleration and jerk parameters by using the phase function to correct the linear Doppler frequency shift caused by the acceleration and the quadratic Doppler frequency shift caused by the jerk, and realize the phase by Fourier transform ginseng accumulation.
针对三阶运动模型,基于坐标旋转和吕分布来估计目标运动参数来实现相参积累和目标定位检测,解决对高速目标长时间相参积累时产生距离徙动和多普勒徙动等问题,具有较低的计算复杂度和较高的检测性能和参数估计性能,便于实际场景应用。For the third-order motion model, the target motion parameters are estimated based on coordinate rotation and Lv distribution to achieve coherent accumulation and target positioning detection, and solve the problems of distance migration and Doppler migration when high-speed targets are accumulated for a long time. It has low computational complexity and high detection performance and parameter estimation performance, which is convenient for practical application.
进一步地,针对检测过程中雷达发射的线性调频信号,利用高阶多项式模型表征目标运动,并对接收机接收的反射回波信号进行脉冲压缩。Further, for the chirp signal emitted by the radar during the detection process, a high-order polynomial model is used to characterize the motion of the target, and the reflected echo signal received by the receiver is pulse-compressed.
假设雷达发射常用的线性调频信号(LFM),即:Assume that the radar transmits the usual chirp signal (LFM), namely:
其中,in,
式(1)中表示快时间,Tp为脉冲持续时间;kr=B/Tp为LFM信号调频率,B为发射信号带宽, fc表示载频;tm=m/fp表示慢时间变量,用于衡量信号在脉冲间的传播时间;m=0,1,L,M-1为脉冲指数,M为积累脉冲总数,fp=1/Tr为雷达脉冲重复频率(Pulse RepetitionFrequency,PRF), Tr表示脉冲重复间隔(Pulse Repetition Interval,PRI)。In formula (1) represents fast time, Tp is the pulse duration; kr =B/Tp is the modulation frequency of the LFM signal, B is the bandwidth of the transmitted signal, fc represents the carrier frequency; tm =m/fp represents the slow time variable, used for Measure the propagation time of the signal between pulses; m = 0, 1, L, M-1 is the pulse index, M is the total number of accumulated pulses, fp = 1/Tr is the radar pulse repetition frequency (Pulse Repetition Frequency, PRF), Tr represents the pulse repetition interval (Pulse Repetition Interval, PRI).
实际雷达探测过程中,目标的运动方式不简单地局限于恒定加速度,尤其对于长时间相参积累,复杂机动是难以避免的,例如战斗机和无人机飞行状态突变、巡航导弹末端机动突防等。因此,可用高阶多项式模型表征目标运动更为贴切,可表示为:In the actual radar detection process, the movement mode of the target is not simply limited to constant acceleration, especially for long-term coherent accumulation, complex maneuvers are unavoidable, such as sudden changes in the flight status of fighter jets and UAVs, and terminal maneuver penetration of cruise missiles. . Therefore, it is more appropriate to use a higher-order polynomial model to characterize the target motion, which can be expressed as:
其中,R0,k、vk、ak和gk分别为第k个目标的初始距离、速度、加速度和加加速度。Among them, R0,k , vk , ak and gk are the initial distance, velocity, acceleration and jerk of the k-th target, respectively.
经过接收机接收反射回波后,第k个目标的回波信号可以表示为:After the receiver receives the reflected echo, the echo signal of the k-th target can be expressed as:
其中,c为电磁波速度,A0,k为幅度。经过脉冲压缩后,回波信号可以表示为:Among them, c is the electromagnetic wave velocity, A0,k is the amplitude. After pulse compression, the echo signal can be expressed as:
对式(6)中做傅里叶变换后,相应的距离频率-慢时间域可表示为:For formula (6) After Fourier transform, the corresponding range frequency-slow time domain can be expressed as:
其中,fr是对应的距离频率,sinc函数为信号包络。wherefr is The corresponding distance frequency, the sinc function is the signal envelope.
从式(5)中可以看出,当变化量超过Δr=c/2fs时,距离徙动(Range Migration,RM)效应将会出现。由于目标运动的复杂性,信号在慢时间维呈现出高度非线性。式(7)的指数项指示了目标线性徙动的多普勒频率,即:It can be seen from equation (5) that when the variation exceeds Δr=c/2fs , the effect of distance migration (Range Migration, RM) will appear. Due to the complexity of target motion, the signal exhibits a high degree of nonlinearity in the slow time dimension. The exponential term of equation (7) indicates the Doppler frequency of the target linear migration, namely:
此时不仅要考虑信号包络的徙动现象,还要考虑多普勒频率的复杂变化,其中既有线性多普勒频率徙动又有二次多普勒频率徙动等问题。At this time, not only the migration phenomenon of the signal envelope, but also the complex change of the Doppler frequency should be considered, including both linear Doppler frequency migration and quadratic Doppler frequency migration.
假设某一空中复杂机动目标以三阶运动模型快速机动,雷达接收回波的脉冲压缩信号如式(5)所示,在此再次表达如下:Assuming that a complex maneuvering target in the air moves quickly with a third-order motion model, the pulse compression signal of the echo received by the radar is shown in Equation (5), which is expressed again as follows:
窄带雷达系统的带宽远小于载频,即满足B=fc。此时,可以假设在相参积累时间内由目标加速度和加加速度引起的距离徙动不超过一个距离采样单元,则对应于包络中加速度和加加速的徙动项可以忽略不计。因此,式(8)简化为:The bandwidth of the narrowband radar system is much smaller than the carrier frequency, that is, B=fc issatisfied . At this time, it can be assumed that the distance migration caused by the target acceleration and jerk within the coherent accumulation time does not exceed one distance sampling unit, and the migration terms corresponding to the acceleration and jerk in the envelope can be ignored. Therefore, equation (8) is simplified to:
式(9)的二维离散形式可表示为:The two-dimensional discrete form of equation (9) can be expressed as:
其中,表示距离分辨单元,fs=μB为信号采样率,μ为过采样率。因此,可得距离变量为r=nρ,目标距离为R0,k=nR,kρ,ρ=c/2fs表示距离采样单元,n和nR,k则分别为r和R0的离散化指数。m为慢时间的离散化指数,Tr为脉冲间隔时间。in, represents the distance resolution unit, fs = μB is the signal sampling rate, and μ is the oversampling rate. Therefore, the available distance variable is r=nρ, the target distance is R0,k =nR,k ρ,ρ=c/2fs represents the distance sampling unit, and n and nR,k are the difference between r and R0 respectively Discretization index. m is the discretization index of the slow time, and Tr is the pulse interval time.
为了消除由目标速度引起的RM效应,可设计MLRT算法来对坐标进行旋转变换。图2给出了MLRT算法的原理示意图,(a)目标RM效应,(b)MLRT结果(c)MLRT结果MLRT算法定义如下:In order to eliminate the RM effect caused by the target velocity, an MLRT algorithm can be designed to rotate the coordinates. Figure 2 shows the schematic diagram of the MLRT algorithm, (a) target RM effect, (b) MLRT result (c) MLRT results The MLRT algorithm is defined as follows:
其中,(m,n)和(m′,n′)分别表示旋转前后坐标,为旋转角度。具体地,旋转前后坐标满足关系式:Among them, (m,n) and (m',n') represent the coordinates before and after rotation, respectively, is the rotation angle. Specifically, the coordinates before and after the rotation satisfy the relation:
将式(12)代入式(10)中可得:Substitute equation (12) into equation (10) to get:
当时,式(13)变为:when , Equation (13) becomes:
由式(14)可知,由目标速度引起RM被矫正。由于目标能量集中于同一个距离单元中,所以本案实施例中,可沿着慢时间维进行能量积分进而估计旋转角度。因此,可以构建如下的代价函数实现角度估计,离散值可通过相加求和实现:It can be seen from equation (14) that the RM is corrected due to the target speed. Since the target energy is concentrated in the same distance unit, in the embodiment of this case, energy integration can be performed along the slow time dimension to estimate the rotation angle. Therefore, the following cost function can be constructed to achieve angle estimation, and discrete values can be achieved by adding and summing:
当达到最大值时,目标的RM效应被矫正。首先估计最大值对应的旋转角度,然后依次估计出目标真实速度和初始距离为:when When the maximum value is reached, the RM effect of the target is corrected. first estimate The rotation angle corresponding to the maximum value, and then sequentially estimate the true speed and initial distance of the target as:
进一步地,针对估计出的目标初始距离,沿慢时间维提取目标慢时间维信号,利用改进吕分布算法中参数对称自相关函数来提取信号中用于计算目标加速度和加加速度的过采样率和距离变量,其中,针对参数对称自相关函数提取过程,首先对信号进行尺度傅里叶变换的解耦合,然后并利用二维傅里叶变换来获取慢时间变量和变延时对应的频率,通过在频率构成的平面内二维傅里叶变换所聚集的峰值坐标来获取过采样率和距离变量。Further, for the estimated initial distance of the target, the target slow time dimension signal is extracted along the slow time dimension, and the parameter symmetric autocorrelation function in the improved Lv distribution algorithm is used to extract the oversampling rate and the jerk used to calculate the target acceleration and jerk in the signal. The distance variable, in which, for the extraction process of the parametric symmetric autocorrelation function, the signal is first decoupled from the scale Fourier transform, and then the two-dimensional Fourier transform is used to obtain the frequency corresponding to the slow time variable and the variable delay. The coordinates of the peaks gathered by the 2D Fourier transform in the plane of frequencies to obtain the oversampling rate and distance variables.
通过MLRT算法可估计出目标真实速度和初始距离,目标的高阶参数中加速度和加加速度可利用改进吕分布MLVD算法估计出。使用估计出的初始距离,可以在式(14)中提取出目标慢时间维信号为:The real speed and initial distance of the target can be estimated by the MLRT algorithm, and the acceleration and jerk of the high-order parameters of the target can be estimated by the improved Lv distribution MLVD algorithm. Using the estimated initial distance, the target slow time dimension signal can be extracted from equation (14) as:
其中,t′m=m′Tr为坐标旋转变换之后的慢时间变量。此时的信号为一维信号且只与慢时间变量有关。由式(17)可知,一维信号符合QFM信号的表达形式,因此可将式(17)改写为:Among them, t'm =m'Tr is the slow time variable after the coordinate rotation transformation. The signal at this time is a one-dimensional signal and is only related to slow time variables. It can be seen from equation (17) that the one-dimensional signal conforms to the expression form of QFM signal, so equation (17) can be rewritten as:
其中,in,
LVD算法可以估计LFM信号的载频和调频斜率,但是由于QFM信号含有三次项,导致LVD无法准确估计信号的三次项系数,即二次调频率。因此,针对QFM信号时频分析,本案实施例中利用MLVD算法对式(17)进行加速度和加加速度的估计。下面对其原理进行介绍:The LVD algorithm can estimate the carrier frequency and the frequency modulation slope of the LFM signal, but because the QFM signal contains a cubic term, the LVD cannot accurately estimate the cubic coefficient of the signal, that is, the quadratic frequency modulation. Therefore, for the time-frequency analysis of the QFM signal, in the embodiment of this case, the MLVD algorithm is used to estimate the acceleration and jerk in equation (17). The principle is described below:
MLVD算法的参数对称自相关函数(Parametric Symmetric Self-CorrelationFunction,PSSF) 定义为:The parametric symmetric autocorrelation function (PSSF) of the MLVD algorithm is defined as:
其中,τ为变延时,τ0与α为固定延时冗余。可设置τ0=0.178M,M为慢时间的长度,设置α=1。将式(18)代入式(19)中得到:Among them, τ is the variable delay, and τ0 and α are fixed delay redundancy. τ0 =0.178M can be set, M is the length of the slow time, and α=1. Substitute equation (18) into equation (19) to get:
由式(19)可知,PSSF降低了QFM信号的阶数,乘积后的结果可以提取目标的μ和γ。由于t′m和τ存在耦合项,需用定义尺度傅里叶变换SFT进行解耦合:It can be seen from equation (19) that PSSF reduces the order of the QFM signal, and the multiplied result can extract the μ and γ of the target. Since there is a coupling term between t'm and τ, the decoupling needs to be performed by the defined scale Fourier transform SFT:
其中,h为常数并影响γ的估计范围,tn为变换后的慢时间。将式(21)代入式(20)中可得:where h is a constant and affects the estimation range of γ, and tn is the transformed slow time. Substitute equation (21) into equation (20) to get:
由式(22)可知,t′m和τ的耦合项已经被消除。为估计两个参数μ和γ,可以对式(22)做二维傅里叶变换,即:It can be seen from equation (22) that the coupling term of t′m and τ has been eliminated. To estimate the two parameters μ and γ, a two-dimensional Fourier transform can be performed on Eq. (22), namely:
其中fn与fτ分别是tn与τ做FFT后对应的频率。Among them, fn and fτ are the frequencies corresponding to tn and τ after FFT.
由式(23)可知,在fn与fτ构成的平面内,L(fn,fτ)聚集成一个峰值。提取峰值对应的正纵坐标,可估计出相应μ和γ的数值,转换成目标的加速度和加加速度可表示为:It can be known from equation (23) that in the plane formed by fn and fτ , L(fn , fτ ) gathers into a peak. By extracting the positive ordinate corresponding to the peak value, the values of the corresponding μ and γ can be estimated, and converted into the acceleration and jerk of the target, which can be expressed as:
其中,fn,max和fτ,max是L(fn,fτ)峰值对应的坐标。Among them, fn,max and fτ,max are the coordinates corresponding to the peak value of L(fn ,fτ ).
在估计出目标的运动参数后,可以构建如下的相位函数用以校正LDFM和QDFM效应,即:After estimating the motion parameters of the target, the following phase functions can be constructed to correct the LDFM and QDFM effects, namely:
将式(25)和式(14)相乘,并对慢时间维t′m进行FFT,实现相参积累:Multiply equations (25) and (14), and perform FFT on the slow time dimension t′m to achieve coherent accumulation:
进一步地,针对多个机动目标相参检测的情形,依次遍历每个机动目标,并依次通过旋转坐标变换和改进吕分布算法估计,直至所有机动目标完成相参检测。Further, in the case of coherent detection of multiple maneuvering targets, each maneuvering target is traversed in turn, and is estimated by rotating coordinate transformation and improved Lv distribution algorithm in turn, until all maneuvering targets complete the coherent detection.
假设有K个目标,则多目标情况下式(11)可以重新写为:Assuming there are K targets, equation (11) can be rewritten as:
其中k=1,2,L K。将式(12)带入(27)中可得:where k=1,2,LK. Substituting equation (12) into (27), we can get:
类似地,第i个搜索角度满足时,式(28)变为:Similarly, the ith search angle Satisfy , Equation (28) becomes:
由式(29)可知,旋转角度后第i个目标的RM被矫正,而剩余K-1个目标依然存在RM效应。在R-D域表现出第i个目标脉冲压缩后的回波在同一距离单元内,而其余K-1个目标未矫正至同一距离单元内。It can be seen from equation (29) that the RM of the i-th target is corrected after the rotation angle, while the remaining K-1 targets still have the RM effect. In the R-D domain, the pulse-compressed echo of the ith target is in the same range unit, while the remaining K-1 targets are not corrected to the same range unit.
根据式(16),可以估计出第i个目标的真实速度和初始距离。提取对应初始距离的慢时间维信号:According to equation (16), the true speed and initial distance of the ith target can be estimated. Extract the slow-time-dimensional signal corresponding to the initial distance:
其中,为第i个目标初始距离估计值。然后,使用MLVD算法对一维慢时间信号进行参数估计得到加速度和加加速度。Among them, is the initial distance of the ith target estimated value. Then, the acceleration and jerk are obtained by parameter estimation of the one-dimensional slow-time signal using the MLVD algorithm.
其中,最后,构建加速度和加加速度的补偿项,完成相参积累。in, Finally, the compensation terms for acceleration and jerk are constructed to complete the coherent accumulation.
由式(29)可知,坐标轴旋转之后可提取在同一距离单元内的信号。提取的信号是一维信号,并且利用MLVD算法时,信号不受交叉项的影响,使得该算法的抗噪性能得到提升。It can be known from equation (29) that the signals in the same distance unit can be extracted after the coordinate axis is rotated. The extracted signal is a one-dimensional signal, and when the MLVD algorithm is used, the signal is not affected by the cross term, which improves the anti-noise performance of the algorithm.
基于以上内容,本案方案的实现算法可如图3所示,具体步骤可设计如下:Based on the above content, the implementation algorithm of the scheme in this case can be shown in Figure 3, and the specific steps can be designed as follows:
步骤1:对雷达回波进行脉冲压缩得到式(10);Step 1: Perform pulse compression on the radar echo to obtain equation (10);
步骤2:根据雷达的具体参数,以及预估目标距离-多普勒域内图像目标的倾斜角度,预先确定旋转角度搜索范围[θmin,θmax];Step 2: Predetermine the rotation angle search range [θmin , θmax ] according to the specific parameters of the radar and the estimated target distance-the inclination angle of the image target in the Doppler domain;
步骤3:利用MLRT算法对式(11)实现角度旋转,并对旋转后的信号进行能量积分。根据积分后的最大值,获得最佳的搜索角度带入式(13)消除距离徙动并估计出真实速度和初始距离Step 3: Use the MLRT algorithm to realize the angle rotation of the formula (11), and perform energy integration on the rotated signal. According to the maximum value after integration, get the best search angle Bring into equation (13) to eliminate distance migration and estimate Calculate the real speed and initial distance
步骤4:根据从式(14)沿慢时间维提取出校正后的一维信号;Step 4: According to Extract the corrected one-dimensional signal along the slow time dimension from equation (14);
步骤5:利用MLVD算法对一维信号式(17)进行参数估计,获得目标加速度和加加速度Step 5: Use the MLVD algorithm to estimate the parameters of the one-dimensional signal equation (17) to obtain the target acceleration and jerk
步骤6:构建加速度和加加速的补偿项与式(14)相乘,然后对慢时间维信号进行FFT实现相参积累。Step 6: Multiply the compensation terms of acceleration and jerk by equation (14), and then perform FFT on the slow time dimension signal to realize coherent accumulation.
步骤7:判断是否遍历所有目标。如果所有目标都已经完成积累则进行CFAR检测,否则返回步骤3对下一个目标重复步骤3至步骤7的操作。Step 7: Determine whether to traverse all targets. If all the targets have been accumulated, perform CFAR detection, otherwise go back to step 3 and repeat the operations from step 3 to step 7 for the next target.
进一步地,基于上述的方法,本发明实施例还提供一种基于改进坐标旋转和吕分布的机动目标相参检测方法,包含:坐标旋转估计模块、吕分布估计模块及相参积累模块,其中,Further, based on the above method, an embodiment of the present invention also provides a method for coherent detection of a maneuvering target based on improved coordinate rotation and distribution, including: a coordinate rotation estimation module, a distribution estimation module, and a coherence accumulation module, wherein,
坐标旋转估计模块,用于对雷达回波信号进行脉冲压缩和二维离散形式变换,并设置旋转搜索角度范围,通过旋转坐标变换使回波轨迹旋转到相同距离单元内来确定最佳旋转搜索角度,根据最佳旋转搜索角度估计目标速度和初始距离;The coordinate rotation estimation module is used to perform pulse compression and two-dimensional discrete form transformation on the radar echo signal, and set the rotation search angle range. Through the rotation coordinate transformation, the echo trajectory is rotated to the same distance unit to determine the optimal rotation search angle. , estimate the target speed and initial distance according to the optimal rotation search angle;
吕分布估计模块,用于根据初始距离提取相同距离单元内信号,并利用改进吕分布算法估计出目标加速度和加加速度参数;The Lv distribution estimation module is used to extract the signals in the same distance unit according to the initial distance, and use the improved Lv distribution algorithm to estimate the target acceleration and jerk parameters;
相参积累模块,用于利用相位函数对目标加速度和加加速度参数进行补偿,以校正加速度引起的线性多普勒频率偏移和加加速度引起的二次多普勒频率偏移,并通过傅里叶变换来实现相参积累。The coherent accumulation module is used to compensate the target acceleration and jerk parameters with the phase function to correct the linear Doppler frequency shift caused by acceleration and the quadratic Doppler frequency shift caused by jerk, and pass Fourier Leaf transformation to achieve coherent accumulation.
为验证本案方案有效性,下面结合试验数据做进一步解释说明:In order to verify the effectiveness of the scheme in this case, further explanations are given below in combination with the test data:
1)算法复杂度1) Algorithm complexity
选取GRFT,KT-GDP,KT-CPF,KT-PGA,PSICPF算法作为比较。假设Na、Ng、Nv分别表示加速度、加加速度、速度的搜索数量,NF、Np分别是角度搜索、折叠因子搜索数量和PGA迭代数,快时间单元数为Nr,脉冲数为M。Select GRFT, KT-GDP, KT-CPF, KT-PGA, PSICPF algorithms as comparisons. Assuming thatNa , Ng, andNv represent the number of searches foracceleration , jerk, and velocity, respectively,NF and Npare the angle search, the number of folding factor searches and the number of PGA iterations, respectively, the number of fast time units is Nr , and the number of pulses is M.
本案方案中的MLRT-MLVD算法的主要步骤和复杂度包括:MLRT操作和MLVD操作,计算复杂度分别为O(MNrNθ)和O(M2log2M)。因此,MLRT-MLVD算法的复杂度为The main steps and complexity of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in the scheme of this case include: MLRT operation and MLVD operation, and the computational complexity is O(MNr Nθ ) and O(M2 log2 M) respectively. Therefore, the complexity of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm is
GRFT算法通过多维参数搜索进行相位补偿实现相参积累,计算的复杂度约为 O(MNrNvNaNg)。The GRFT algorithm realizes coherent accumulation through phase compensation through multi-dimensional parameter search, and the computational complexity is about O(MNr Nv Na Ng ).
KT-GDP算法主要有KT变换(Keystone Transform,KT)矫正距离徙动,计算复杂度约为以及加速度和加加速度的参数搜索,计算复杂度约为 O(NaNgMNrlog2Nr)。因此,KT-GDP算法的总复杂度约为O[NrMNaNglog2Nr+NF(Mlog2M)]。The KT-GDP algorithm mainly includes KT transform (Keystone Transform, KT) to correct distance migration, and the computational complexity is about As well as the parametric search for acceleration and jerk, the computational complexity is about O(Na Ng MNr log2 Nr ). Therefore, the total complexity of the KT-GDP algorithm is about O[Nr MNa Ng log2 Nr +NF (Mlog2M )].
KT-CPF算法主要包括速度折叠因子搜索,需要执行NF次KT变换。因此,算法的总复杂度约为O(3NFNrMlog2M)。The KT-CPF algorithm mainly includes speed folding factor search, which needs to perform NFKT transformations. Therefore, the total complexity of the algorithm is about O(3NF Nr Mlog2 M).
KT-PGA算法主要包括粗积累和精积累。粗积累包括折叠因子的搜索,精积累包括PGA 迭代运算。因此,计算复杂度约为O(NFNpNrMlog2M)。KT-PGA algorithm mainly includes coarse accumulation and fine accumulation. Coarse accumulation includes the search for folding factors, and fine accumulation includes PGA iterative operations. Therefore, the computational complexity is about O(NF Np Nr Mlog2 M).
PSICPF算法主要包括双线性自相关运算,计算复杂度为O(M2),非均匀傅里叶变换(Scaled Nonuniform Fast Fourier Transform,SNUFFT)和IFT操作,计算复杂度分别为O(2M2log2M)和 O(M2log2M)。相对于慢时间的尺度傅里叶变换(Scaled Fourier Transform,SFT)和FT对信号进行积分,计算复杂度分别约为O(3M2log2M)和O(M2log2M)。KT和折叠因子搜索计算复杂度分别为O(4MNrlog2M)和O(NFNrMlog2NrM)。因此,算法总计算复杂度为 O(7NrM2log2M+NFMNrlog2MNr)。The PSICPF algorithm mainly includes bilinear autocorrelation operation, the computational complexity is O(M2 ), non-uniform Fourier transform (Scaled Nonuniform Fast Fourier Transform, SNUFFT) and IFT operation, the computational complexity is O(2M2 log respectively2 M) and O(M2 log2 M). Compared with the slow-time Scaled Fourier Transform (SFT) and FT to integrate the signal, the computational complexity is about O(3M2 log2 M) and O(M2 log2 M), respectively. The KT and fold factor search computational complexity is O(4MNr log2 M) and O(NF Nr Mlog2 NrM ), respectively. Therefore, the total computational complexity of the algorithm is O(7Nr M2 log2 M+NF MNr log2 MNr ).
表1不同算法的计算复杂度比较Table 1 Computational complexity comparison of different algorithms
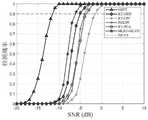
上述算法的计算复杂度在表1给出。假设Np=10,NF=20。图4 直观地展示了上述方法的计算复杂度。GRFT明显计算复杂度远高于其他算法,即花费的时间最长且不满足实际高效快速检测的需求。MLRT-MLVD相比于GRFT、KT-GDP和PSICPF 只搜索旋转角度,并且MLVD操作是在角度搜索之后进行,因此计算复杂度相对较低。此外,MLRT-MLVD算法在400个脉冲数之前,运算复杂度低于KT-PGA和KT-CPF算法,在400 个脉冲数之后运算复杂度在KT-PGA和KT-CPF算法之间,并且仅相差约一个数量级。因此, KT-CPF算法计算速度快于MLRT-MLVD,但是MLRT-MLVD算法在低SNR条件下检测性能由于KT-CPF。The computational complexity of the above algorithm is given in Table 1. Assumption Np =10,NF =20. Figure 4 visually shows the computational complexity of the above method. The computational complexity of GRFT is obviously much higher than other algorithms, that is, it takes the longest time and does not meet the needs of practical efficient and fast detection. Compared with GRFT, KT-GDP and PSICPF, MLRT-MLVD only searches for the rotation angle, and the MLVD operation is performed after the angle search, so the computational complexity is relatively low. In addition, the computational complexity of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm is lower than that of the KT-PGA and KT-CPF algorithms before 400 pulses, and the computational complexity is between the KT-PGA and KT-CPF algorithms after 400 pulses, and only The difference is about an order of magnitude. Therefore, the calculation speed of KT-CPF algorithm is faster than that of MLRT-MLVD, but the detection performance of MLRT-MLVD algorithm under low SNR conditions is due to KT-CPF.
2)、算法性能评估2), algorithm performance evaluation
通过单目标和多目标仿真实验来证明本案方案中MLRT-MLVD算法的有效性。仿真参数见表2。The effectiveness of the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in this scheme is proved by single-target and multi-target simulation experiments. The simulation parameters are shown in Table 2.
表2雷达仿真参数Table 2 Radar simulation parameters
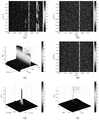
单目标的相参积累结果如图5所示,目标的运动参数为:R0=100km,v=250m/s,a=15m/s2, g=9m/s3,脉冲压缩后信噪比为5dB,(a)为目标脉冲压缩结果后运动轨迹,明显可以看出由于目标高速运动导致距离徙动出现;(b)为坐标轴旋转角度的搜索结果,在预先设置搜索范围内,得到最优旋转角度为并根据旋转角度计算出目标速度和初始距离分别为 v=250m/s,R0=100km:(c)为坐标旋转后矫正距离徙动后的结果,此时目标轨迹被矫正到同一距离单元内。然后,提取该距离单元内的慢时间维信号,利用MLVD算法估计加速度和加加速度;(d)为MLVD算法参数估计的结果,其峰值位置可估计出目标运动参数为a=15m/s2, g=9m/s3。最后,构建加速度和加加速度的补偿项后,LDFM和QDFM被消除即可实现相参积累,结果如(e)所示。The coherent accumulation result of a single target is shown in Figure 5. The motion parameters of the target are: R0 =100km, v=250m/s, a=15m/s2 , g=9m/s3 , the signal-to-noise ratio after pulse compression It is 5dB, (a) is the motion trajectory of the target pulse compression result, it can be clearly seen that the distance migration occurs due to the high-speed movement of the target; (b) is the search result of the rotation angle of the coordinate axis, within the preset search range, the most The optimal rotation angle is And according to the rotation angle, the target speed and initial distance are calculated as v=250m/s, R0 =100km: (c) is the result of the corrected distance migration after the coordinate rotation, at this time the target trajectory is corrected to the same distance unit . Then, the slow time dimension signal in the distance unit is extracted, and the MLVD algorithm is used to estimate the acceleration and jerk; (d) is the result of the parameter estimation of the MLVD algorithm, and its peak position can estimate the target motion parameter as a=15m/s2 , g=9m/s3 . Finally, after constructing the compensation terms for acceleration and jerk, the LDFM and QDFM are eliminated to achieve coherent accumulation, and the results are shown in (e).
为了对比低SNR条件下,MLRT-MLVD,KT-GDP,KT-CPF,GRFT,PSICPF和KT-PGA 相参积累的性能,图6给出了SNR=-5dB时不同算法的相参积累结果;具体地,图6中,(a) 和(b)分别为MLRT-MLVD和KT-GDP的相参积累结果。可以看出,两者具有较好的相参积累性能,然而MLRT-MLVD计算复杂度远低于KT-GDP的复杂度,能够更加快速的实时处理;(c)为KT-CPF的相参积累结果,可以发现该算法无法实现积累,由于CPF算法只利用了时间-调频率分布中的能量脊线构建最小二乘,未使用相参积累,因此积累性能效果较差;(d) 是GRFT的相参积累结果,虽然GRFT的抗噪性能相比于其他算法较好,但是四维搜索的高计算复杂度和盲速旁瓣的影响,给目标探测的实时性和准确性带来困难;(e)是PSICPF相参积累的结果,可以看出该算法由于对每一距离频率进行切片乘积估计参数,导致噪声的积累无法实现相参积累;(f)是KT-PGA的相参积累结果,可以看出目标能量聚焦的位置是与真实目标位置有一定的偏差,这是算法只利用信号的相位信息,并且在曲线拟合时参数拟合误差较大,导致未能完全补偿LDFM和QDFM效应。In order to compare the performance of MLRT-MLVD, KT-GDP, KT-CPF, GRFT, PSICPF and KT-PGA coherent accumulation under low SNR conditions, Figure 6 shows the coherent accumulation results of different algorithms when SNR=-5dB; Specifically, in Fig. 6, (a) and (b) are the coherent accumulation results of MLRT-MLVD and KT-GDP, respectively. It can be seen that the two have good coherent accumulation performance, but the computational complexity of MLRT-MLVD is much lower than that of KT-GDP, and can be processed in real time faster; (c) is the coherent accumulation of KT-CPF As a result, it can be found that the algorithm cannot achieve accumulation, because the CPF algorithm only uses the energy ridges in the time-frequency modulation distribution to construct the least squares, and does not use coherent accumulation, so the accumulation performance effect is poor; (d) is the GRFT For the coherent accumulation results, although the anti-noise performance of GRFT is better than other algorithms, the high computational complexity of the four-dimensional search and the influence of blind speed side lobes bring difficulties to the real-time and accuracy of target detection; (e ) is the result of coherent accumulation of PSICPF. It can be seen that the algorithm estimates parameters by slice product for each distance frequency, resulting in the accumulation of noise that cannot achieve coherent accumulation; (f) is the coherent accumulation result of KT-PGA, which can be It can be seen that the position where the target energy is focused has a certain deviation from the real target position. This is because the algorithm only uses the phase information of the signal, and the parameter fitting error is large during curve fitting, resulting in failure to fully compensate the LDFM and QDFM effects.
对微弱多目标的相参积累结果在如图7所示,表3给出两目标的运动参数。The coherent accumulation results for weak multi-targets are shown in Figure 7, and Table 3 gives the motion parameters of the two targets.
表3目标运动参数Table 3 Target motion parameters
图7中,(a)是两目标信号脉冲压缩结果,明显两目标都具有RM效应;(b)是搜索旋转角度的结果,两个目标的最优旋转角度分别为和并计算出两目标速度和初始距离分别为v1=150m/s,R1,0=100.001km和v2=-100m/s,R2,0=99.497km,估计的参数与设置参数相差较小;(c)和(d)分别是目标1和目标2消除RM效应后的结果。分别提取聚集在同一距离单元内的两个目标信号,利用MLVD算法估计各自的运动参数,结果如(e)和(f)所示,估计出的参数分别为a1=15m/s2,g1=9m/s3和a2=-20.25m/s2,g2=-15m/s3;(g)和(h)分别是两个目标相参积累后的结果,明显看出两个目标显示良好的相参积累效果,说明本案方案中的算法可以对多目标进行有效的相参积累和参数估计。In Figure 7, (a) is the pulse compression result of the two targets, obviously both targets have RM effect; (b) is the result of searching for the rotation angle, the optimal rotation angles of the two targets are and And the two target speeds and initial distances are calculated as v1 =150m/s, R1,0 =100.001km and v2 =-100m/s, R2,0 =99.497km, the estimated parameters are quite different from the set parameters. small; (c) and (d) are the results of
3)、抗噪性能评估3), anti-noise performance evaluation
如图8所示。As shown in Figure 8.
4)、参数估计性能评估4), parameter estimation performance evaluation
采用均方根误差RMSE作为评估标准,各算法参数估计曲线如图9所示,(a)速度参数 RMSE,(b)加速度参数RMSE,(c)加加速度参数RMSE。类似于目标检测曲线,参数估计曲线基本保持了相同的信噪比门限。从三个参数的误差估计曲线可以看出,GRFT算法参数估计性能是最好的。当信噪比高于-5dB时,本案方案中的MLRT-MLVD算法与KT-GDP算法拥有相近的估计性能。相比于KT-CPF、KT-PGA和PSICPF算法,参数估计性能具有明显优势。综合考虑检测性能、参数估计性能和计算复杂度,本案所提算法比其它算法实现了更好的折中。The root mean square error RMSE is used as the evaluation standard, and the estimated curve of each algorithm parameter is shown in Figure 9, (a) velocity parameter RMSE, (b) acceleration parameter RMSE, (c) jerk parameter RMSE. Similar to the target detection curve, the parameter estimation curve basically maintains the same signal-to-noise ratio threshold. It can be seen from the error estimation curves of the three parameters that the parameter estimation performance of the GRFT algorithm is the best. When the signal-to-noise ratio is higher than -5dB, the MLRT-MLVD algorithm in this case has similar estimation performance to the KT-GDP algorithm. Compared with KT-CPF, KT-PGA and PSICPF algorithms, the parameter estimation performance has obvious advantages. Considering the detection performance, parameter estimation performance and computational complexity, the algorithm proposed in this case achieves a better compromise than other algorithms.
5)、实测数据累计性能5), cumulative performance of measured data
采用真实数据检验本案方案中的算法。该真实数据以地物为噪声背景,采用Ka频段雷达对固定翼无人机目标进行探测,获取脉冲压缩回波数据。雷达参数如表4所示。Use real data to test the algorithm in this case. The real data uses ground objects as noise background, and uses Ka-band radar to detect fixed-wing UAV targets and obtain pulse compression echo data. The radar parameters are shown in Table 4.
表4Ka频段雷达基本参数Table 4 Basic parameters of Ka-band radar
选择公开数据集中data4数据进行处理,此数据含有64000个脉冲。由于数据按照50ms 的数据率给出标注结果,即每1600个脉冲输出1次结果。选择第1-1600个脉冲进行实测数据实验,雷达脉冲压缩结果如图10中(a)所示。由于此数据集的回波存在严重的地杂波,图 10中(b)给出两脉冲对消目标显示结果,此时杂波得到有效抑制。搜索旋转角度后,获得最佳角度如图10中(c)所示。根据式(16)计算目标速度和初始距离分别为然后,MLRT操作消除RM效应,如图10中的(d)所示。图10中的(e)是MLVD 算法估计目标运动参数,从聚焦的峰值位置可以估计目标的加速度和加加速分别为可知该无人机是匀速飞行状态。相位补偿后进行相参积累,目标位置聚集成显著的尖峰,如图10中的(f)所示。已知该数据的GPS定位数据为R0=1.554km,与本案方案中的算法估计的初始距离和速度差距较小。因此,可以证明本案方案中所提出算法能够有效实现目标相参积累且完成运动目标参数估计。The data4 data in the public data set is selected for processing, and this data contains 64000 pulses. Since the data gives the labeling result according to the data rate of 50ms, that is, the result is output once every 1600 pulses. Pulses 1-1600 are selected for the measured data experiment, and the result of radar pulse compression is shown in (a) in Figure 10. Since the echo of this data set has serious ground clutter, Figure 10 (b) shows the display result of the two-pulse cancellation target, and the clutter is effectively suppressed at this time. After searching for the rotation angle, get the best angle As shown in Fig. 10(c). According to formula (16), the target speed and initial distance are calculated as Then, the MLRT operation eliminates the RM effect, as shown in (d) of FIG. 10 . (e) in Figure 10 is the MLVD algorithm to estimate the target motion parameters. From the peak position of the focus, the target acceleration and jerk can be estimated as It can be seen that the drone is flying at a constant speed. After phase compensation and coherent accumulation, the target position gathers into prominent spikes, as shown in (f) in Figure 10. It is known that the GPS positioning data of this data is R0 =1.554km, The difference between the initial distance and speed estimated by the algorithm in this case is small. Therefore, it can be proved that the algorithm proposed in this solution can effectively achieve target coherent accumulation and complete the estimation of moving target parameters.
通过以上数据可以证明,相比于现有GRFT,KT-GDP,KT-CPF,KT-PGA,PSICPF算法,本案方案所提算法具有更低的计算复杂度和较高的检测性能和参数估计性能,在计算复杂度和抗噪声、参数估计性能之间取得的良好折中;利用Ka波段雷达探测的无人机实测数据进行验证,结果表明本案所提出算法具有良好的积累能力,能够满足实际应用场景需求。The above data can prove that compared with the existing GRFT, KT-GDP, KT-CPF, KT-PGA, PSICPF algorithms, the proposed algorithm in this case has lower computational complexity and higher detection performance and parameter estimation performance , a good compromise between computational complexity, anti-noise and parameter estimation performance; verified by the UAV measured data detected by Ka-band radar, the results show that the algorithm proposed in this case has good accumulation ability and can meet practical applications scene requirements.
除非另外具体说明,否则在这些实施例中阐述的部件和步骤的相对步骤、数字表达式和数值并不限制本发明的范围。The relative steps, numerical expressions and numerical values of the components and steps set forth in these embodiments do not limit the scope of the invention unless specifically stated otherwise.
最后应说明的是:以上所述实施例,仅为本发明的具体实施方式,用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制,本发明的保护范围并不局限于此,尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本发明揭露的技术范围内,其依然可以对前述实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改或可轻易想到变化,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改、变化或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明实施例技术方案的精神和范围,都应涵盖在本发明的保护范围之内。因此,本发明的保护范围应所述以权利要求的保护范围为准。Finally, it should be noted that the above-mentioned embodiments are only specific implementations of the present invention, and are used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, but not to limit them. The protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereto, although referring to the foregoing The embodiment has been described in detail the present invention, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand: any person skilled in the art who is familiar with the technical field within the technical scope disclosed by the present invention can still modify the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments. Or can easily think of changes, or equivalently replace some of the technical features; and these modifications, changes or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention, and should be covered in the present invention. within the scope of protection. Therefore, the protection scope of the present invention should be based on the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210072550.9ACN114966583B (en) | 2022-01-21 | 2022-01-21 | Coherent detection method and system for maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lu distribution |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210072550.9ACN114966583B (en) | 2022-01-21 | 2022-01-21 | Coherent detection method and system for maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lu distribution |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114966583Atrue CN114966583A (en) | 2022-08-30 |
| CN114966583B CN114966583B (en) | 2025-03-25 |
Family
ID=82974600
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210072550.9AActiveCN114966583B (en) | 2022-01-21 | 2022-01-21 | Coherent detection method and system for maneuvering targets based on improved coordinate rotation and Lu distribution |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114966583B (en) |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040148057A1 (en)* | 2000-05-08 | 2004-07-29 | Breed David S. | Vehicular exterior identification and monitoring system-agricultural product distribution |
| CN103323829A (en)* | 2013-06-04 | 2013-09-25 | 中国人民解放军海军航空工程学院 | Radar moving target long-time phase-coherent accumulation detecting method based on RFRAF |
| CN108089171A (en)* | 2018-02-07 | 2018-05-29 | 成都电科智达科技有限公司 | A kind of radar rapid detection method for unmanned plane target |
| CN108549067A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-09-18 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of phase-coherent accumulation detection method being applied to three rank maneuvering targets |
| CN110398730A (en)* | 2019-06-26 | 2019-11-01 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Coherent detection method of maneuvering target based on coordinate rotation and non-uniform Fourier transform |
| CN110646774A (en)* | 2019-09-30 | 2020-01-03 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Maneuvering target coherent detection method and device based on product variable-scale periodic Lu distribution |
| CN111045002A (en)* | 2019-12-13 | 2020-04-21 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Maneuvering target coherent accumulation method based on TRT and SNuFFT |
| CN113885006A (en)* | 2021-09-30 | 2022-01-04 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for detecting coherent accumulation of maneuvering turning target |
- 2022
- 2022-01-21CNCN202210072550.9Apatent/CN114966583B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040148057A1 (en)* | 2000-05-08 | 2004-07-29 | Breed David S. | Vehicular exterior identification and monitoring system-agricultural product distribution |
| CN103323829A (en)* | 2013-06-04 | 2013-09-25 | 中国人民解放军海军航空工程学院 | Radar moving target long-time phase-coherent accumulation detecting method based on RFRAF |
| CN108089171A (en)* | 2018-02-07 | 2018-05-29 | 成都电科智达科技有限公司 | A kind of radar rapid detection method for unmanned plane target |
| CN108549067A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2018-09-18 | 电子科技大学 | A kind of phase-coherent accumulation detection method being applied to three rank maneuvering targets |
| CN110398730A (en)* | 2019-06-26 | 2019-11-01 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Coherent detection method of maneuvering target based on coordinate rotation and non-uniform Fourier transform |
| CN110646774A (en)* | 2019-09-30 | 2020-01-03 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Maneuvering target coherent detection method and device based on product variable-scale periodic Lu distribution |
| CN111045002A (en)* | 2019-12-13 | 2020-04-21 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | Maneuvering target coherent accumulation method based on TRT and SNuFFT |
| CN113885006A (en)* | 2021-09-30 | 2022-01-04 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for detecting coherent accumulation of maneuvering turning target |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114966583B (en) | 2025-03-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111142105B (en) | ISAR imaging method for complex moving target | |
| CN101738606B (en) | Method for detecting coherent integration of radar target based on generalized Doppler filter bank | |
| CN109188385B (en) | High-speed weak target detection method in clutter background | |
| US7969345B2 (en) | Fast implementation of a maximum likelihood algorithm for the estimation of target motion parameters | |
| CN103399310B (en) | Method for detecting radar weak moving target based on PD (Phase Differentiation) RLVD (Radon-Lv Distribution) | |
| CN111736128A (en) | Coherent accumulation method based on SKT-SIAF-MSCFT | |
| CN106872954B (en) | A kind of hypersonic platform clutter recognition and motive target imaging method | |
| CN108089171B (en) | A kind of radar rapid detection method for unmanned plane target | |
| CN108761404A (en) | A kind of innovatory algorithm based on QP function parameter Estimation and compensation | |
| CN111551922A (en) | Three-dimensional space double/multi-base radar high-speed target detection method | |
| CN112083417B (en) | Distributed radar imaging topology design method based on wavenumber domain splicing | |
| CN109655802B (en) | Multi-target particle swarm long-time accumulation detection method based on CLEAN algorithm | |
| CN114545351B (en) | Coherent detection method and system for maneuvering targets based on range-frequency axis inversion transform and second-order WVD | |
| CN113391284A (en) | Temporary high-speed target detection method based on long-time accumulation | |
| CN109001700B (en) | A radar forward-looking imaging method for target contour reconstruction | |
| CN111007503A (en) | Moving target focusing and positioning method and system based on frequency spectrum accurate positioning | |
| CN108387884B (en) | Airborne radar clutter suppression method based on knowledge-assisted sparse progressive minimum variance | |
| CN110865344A (en) | Rapid side lobe suppression method under pulse Doppler radar system | |
| CN108549066B (en) | A high-speed target accumulation detection method for broadband radar based on scale RFT | |
| CN102608587B (en) | Air Maneuvering Target Detection Method Based on Nonlinear Least Squares | |
| CN108344982A (en) | Small drone target radar detection method based on long-time phase-coherent accumulation | |
| CN113311398B (en) | Tracking method for strong clutter complex background high maneuver weak and small target | |
| CN111045002A (en) | Maneuvering target coherent accumulation method based on TRT and SNuFFT | |
| CN118169686B (en) | SA-ISAR imaging and azimuth calibration method based on SCICPF method | |
| CN111965642A (en) | Front squint multi-channel SAR-GMTI clutter suppression method based on hypersonic platform |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | Country or region after:China Address after:450000 Science Avenue 62, Zhengzhou High-tech Zone, Henan Province Applicant after:Information Engineering University of the Chinese People's Liberation Army Cyberspace Force Address before:No. 62 Science Avenue, High tech Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province Applicant before:Information Engineering University of Strategic Support Force,PLA Country or region before:China | |
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |