CN114862901A - Road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing method and system for surface mine - Google Patents
Road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing method and system for surface mineDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114862901A CN114862901ACN202210441815.8ACN202210441815ACN114862901ACN 114862901 ACN114862901 ACN 114862901ACN 202210441815 ACN202210441815 ACN 202210441815ACN 114862901 ACN114862901 ACN 114862901A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- point cloud
- target
- fusion
- data
- module
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/20—Analysis of motion
- G06T7/215—Motion-based segmentation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/20—Analysis of motion
- G06T7/246—Analysis of motion using feature-based methods, e.g. the tracking of corners or segments
- G06T7/251—Analysis of motion using feature-based methods, e.g. the tracking of corners or segments involving models
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/20—Analysis of motion
- G06T7/277—Analysis of motion involving stochastic approaches, e.g. using Kalman filters
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/762—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using clustering, e.g. of similar faces in social networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/77—Processing image or video features in feature spaces; using data integration or data reduction, e.g. principal component analysis [PCA] or independent component analysis [ICA] or self-organising maps [SOM]; Blind source separation
- G06V10/80—Fusion, i.e. combining data from various sources at the sensor level, preprocessing level, feature extraction level or classification level
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/70—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning
- G06V10/82—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding using pattern recognition or machine learning using neural networks
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/10—Image acquisition modality
- G06T2207/10028—Range image; Depth image; 3D point clouds
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30241—Trajectory
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法和系统,尤其涉及一种露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法和系统。The invention relates to a road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception method and system, in particular to a road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception method and system in an open-pit mine.
背景技术Background technique
随着深度学习技术的发展以及边缘硬件平台算力的提升,自动驾驶正在成为未来车辆出行的核心技术。现有的自动驾驶算法大多关注单车智能,即在车上部署多种传感器以及AI算法,完成车的智能化。单车智能在简单的道路环境能够取得很好的效果,但是没法很好的应对复杂交叉路口环境。在交叉路口环境中,存在各种类型的车辆以及行人的复杂交互,并且由于车上传感器安装位置低,视野容易被大型车辆、桥梁以及房屋等障碍物遮挡。这些问题导致单车智能系统在复杂路口环境中存在系统性的缺陷,为解决这种缺陷,路侧协同感知系统应运而生。With the development of deep learning technology and the improvement of computing power of edge hardware platforms, autonomous driving is becoming the core technology of future vehicle travel. Most of the existing autonomous driving algorithms focus on bicycle intelligence, that is, deploying a variety of sensors and AI algorithms on the car to complete the intelligence of the car. Bicycle intelligence can achieve good results in simple road environments, but it cannot cope with complex intersection environments well. In the intersection environment, there are complex interactions of various types of vehicles and pedestrians, and due to the low installation position of the sensors on the vehicle, the field of view is easily blocked by obstacles such as large vehicles, bridges, and houses. These problems lead to the systematic defects of the bicycle intelligent system in the complex intersection environment. In order to solve this defect, the roadside collaborative perception system emerges as the times require.
路侧智能单元是部署在路口,监控整个区域内动态目标的一套系统,该系统能够为区域内的智能驾驶车辆提供该区域目标的全局位姿、速度以及预测轨迹等信息,为车辆的安全行驶提供额外保障。现有的三维感知框架多数是适配车端的,鲜有针对路侧环境的感知框架。将车端的感知算法迁移到路侧端是困难的,主要有三方面:1. 车端传感器是一直运动的,采集的数据背景也是不断变化的,而路侧端是固定的,基于车端数据开发的算法流程不适用于路侧端; 2. 车端的视角与路侧端视角有很大不同,路侧视角的场景信息更为全面丰富,这也意味着路侧感知更容易受环境干扰,譬如扬尘、雨雪等恶劣环境,这为路侧感知算法带来了新的挑战;3. 车端能用的计算资源相比于路侧端较为丰富,路侧端需要效率更好、功耗更低的算法以保证实时性。因此,需要专门为路侧场景开发一套环境感知算法。The roadside intelligent unit is a system that is deployed at intersections and monitors dynamic targets in the entire area. The system can provide intelligent driving vehicles in the area with information such as the global pose, speed and predicted trajectory of the target in the area, so as to ensure the safety of the vehicle. Driving provides additional protection. Most of the existing 3D perception frameworks are adapted to the vehicle end, and there are few perception frameworks for the roadside environment. It is difficult to migrate the perception algorithm on the vehicle side to the roadside side. There are three main aspects: 1. The vehicle-side sensors are always moving, and the collected data background is constantly changing, while the roadside side is fixed and developed based on vehicle-side data. 2. The perspective of the vehicle is very different from the perspective of the roadside, and the scene information of the roadside perspective is more comprehensive and rich, which also means that the roadside perception is more susceptible to environmental interference, such as Harsh environments such as dust, rain and snow have brought new challenges to the roadside perception algorithm; 3. Compared with the roadside side, the computing resources that can be used on the vehicle side are more abundant, and the roadside side needs to have better efficiency and higher power consumption. Low algorithm to ensure real-time performance. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a set of environment awareness algorithms specially for roadside scenarios.
专利CN112990129A提出了一种基于视觉和激光雷达联合的三维物体检测方法。该方法首先获取当前点云帧和视频帧,然后对视频帧进行视觉检测,得到视觉检测结果,之后再对视觉检测结果进行深度判断,得到视觉近视深度;对于点云帧数据,该方法首先将其转化为稀疏深度图,然后根据视觉检测结果提取稀疏深度图中的候选深度框,之后根据候选深度框与视觉近似深度构建当前点云帧的候选点簇,最后再根据点簇构造三维物体检测结果。该方法利用图像检测结果来提取目标点云簇,并利用图像深度估计模型估计检测目标的深度,来进一步分割点云。这种三维物体检测方法性能受限于图像检测,且无法很好的处理图像目标遮挡的情况,另外,由于图像的视野范围有限,算法无法利用超出图像视野范围的点云信息。Patent CN112990129A proposes a three-dimensional object detection method based on the combination of vision and lidar. The method first obtains the current point cloud frame and video frame, then performs visual inspection on the video frame to obtain the visual inspection result, and then performs depth judgment on the visual inspection result to obtain the visual depth of myopia; for the point cloud frame data, the method first It is converted into a sparse depth map, and then the candidate depth frame in the sparse depth map is extracted according to the visual detection result, and then the candidate point cluster of the current point cloud frame is constructed according to the candidate depth frame and the visual approximate depth, and finally the three-dimensional object detection is constructed according to the point cluster. result. The method uses the image detection results to extract the target point cloud cluster, and uses the image depth estimation model to estimate the depth of the detected target to further segment the point cloud. The performance of this 3D object detection method is limited by image detection, and cannot handle the occlusion of the image target well. In addition, due to the limited field of view of the image, the algorithm cannot use the point cloud information beyond the field of view of the image.
专利CN113095172A提出了一种基于深度学习的点云三维物体检测方法,该方法首先通过分层体素编码模块提取点云场景中点稀疏、点密集区域中非空体素的特征表示,然后通过注意力模块融合体素特征以获得有效的体素特征表示;另外,该方法还通过高度信息补充模块引入点云的鸟瞰图以补充体素特征图的高度信息,并通过通道注意力模块提取掩模处理后的特征图中有用的信息以提高网络的几何结构感知能力。该方法构建了一特征学习网络用于挖掘特征图中的高级语义信息,并在输出端增加了一个体素分割任务来判断非空体素是否属于目标物体。该方法提出的模型结构非常复杂,在工程部署上会有很多限制。另外,和所有基于深度学习的检测方法一样,该方法是数据驱动的,模型性能高度依赖于数据集,且网络泛化能力很差,换一个场景需要重新采集数据标注并训练,整个过程耗时耗材耗力,非常不利于落地。目前基于深度学习的方法还面临着可解释性的问题,对长尾情况的处理比较吃力。最后,基于网络的三维检测模型非常耗费计算资源,很难在边缘计算平台上达到实时检测的效果。Patent CN113095172A proposes a point cloud three-dimensional object detection method based on deep learning. The method first extracts the feature representation of non-empty voxels in the point cloud scene with sparse and dense points through the layered voxel coding module, and then through the attention The force module fuses voxel features to obtain an effective voxel feature representation; in addition, the method also introduces a bird’s-eye view of the point cloud to supplement the height information of the voxel feature map through a height information complement module, and extracts masks through a channel attention module Useful information in the processed feature maps to improve the network's geometry awareness. The method constructs a feature learning network to mine high-level semantic information in the feature map, and adds a voxel segmentation task at the output to judge whether the non-empty voxels belong to the target object. The model structure proposed by this method is very complex, and there are many restrictions on engineering deployment. In addition, like all detection methods based on deep learning, this method is data-driven, the model performance is highly dependent on the data set, and the network generalization ability is very poor. Changing a scene requires re-collecting data and labeling and training, the whole process is time-consuming The consumption of consumables is very unfavorable for landing. At present, deep learning-based methods still face the problem of interpretability, and it is difficult to deal with the long tail situation. Finally, the network-based 3D detection model consumes a lot of computing resources, and it is difficult to achieve real-time detection on the edge computing platform.
在轨迹预测领域,专利CN113763434A提出了一种基于卡尔曼滤波多运动模型切换的目标轨迹预测方法。该方法首先建立卡尔曼滤波多运动模型,然后采集目标一段时间内的运动信息(至少包括目标初始坐标、实时速度以及实时加速度),算法根据目标的运动信息获取目标的运动状态(至少包括减速直行、匀速直行、减速变道、匀速变道和加速变道等),然后根据运动状态的改变切换卡尔曼滤波运动模型,计算得到目标的预测轨迹。这种方法将目标的运动模型硬编码到不同的卡尔曼滤波器中,很难应对实际场景下行驶状态的复杂性。该方法也没有利用场景中道路先验信息,仅依赖卡尔曼滤波只能预测目标很短时间内的轨迹,而无法对目标长时间的运动趋势进行预测。In the field of trajectory prediction, patent CN113763434A proposes a target trajectory prediction method based on Kalman filter multi-motion model switching. The method first establishes a Kalman filter multi-motion model, and then collects the motion information of the target within a period of time (including at least the initial coordinates of the target, real-time speed and real-time acceleration). , constant speed straight, deceleration lane change, constant speed lane change and acceleration lane change, etc.), and then switch the Kalman filter motion model according to the change of the motion state, and calculate the predicted trajectory of the target. This method hard-codes the motion model of the target into different Kalman filters, which is difficult to deal with the complexity of the driving state in the actual scene. This method also does not use the prior information of the road in the scene, and only relies on the Kalman filter to predict the trajectory of the target in a short time, but cannot predict the long-term movement trend of the target.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提供一种露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法和系统,利用多源传感器融合技术实现了矿区精确可靠的三位目标检测以及跟踪,并能够结合目标跟踪结果和高精度地图信息预测目标未来的行驶轨迹信息,解决现有技术存在的缺陷。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing method and system for open-pit mines, which utilizes multi-source sensor fusion technology to achieve accurate and reliable three-dimensional target detection and tracking in the mining area, and can combine target tracking results with high The precision map information predicts the future driving trajectory information of the target, and solves the defects existing in the prior art.
本发明提供了下述方案:The present invention provides following scheme:
一种露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法,具体包括如下步骤:A road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing method for an open-pit mine, which specifically includes the following steps:
步骤一)数据采集:进行数据采集,从传感器设备读取数据,对数据进行格式转换;Step 1) Data collection: carry out data collection, read data from sensor equipment, and convert the data format;
步骤二)图像多任务感知:对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计,得到实例分割结果和深度图;Step 2) Image multi-task perception: perform instance segmentation and depth estimation on the collected road target images to obtain instance segmentation results and depth maps;
步骤三)点云目标检测:对点云数据进行多雷达融合,得到统一坐标的融合点云数据,然后通过背景滤波获得前景点云数据,通过聚类算法对前景点云数据进行聚类处理,对通过聚类处理得到的点云簇构建三维检测框,得到三维目标框;Step 3) Point cloud target detection: Multi-radar fusion is performed on the point cloud data to obtain the fusion point cloud data with unified coordinates, and then the foreground point cloud data is obtained through background filtering, and the foreground point cloud data is clustered through a clustering algorithm. Constructing a three-dimensional detection frame for the point cloud clusters obtained by clustering to obtain a three-dimensional target frame;
步骤四)异构信息融合:对图像实例分割、深度图、三维目标框进行异构信息融合,输出目标3D检测结果;Step 4) Heterogeneous information fusion: perform heterogeneous information fusion on image instance segmentation, depth map, and 3D target frame, and output target 3D detection results;
步骤五)多目标跟踪:根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,对目标观测值进行最优估计;Step 5) Multi-target tracking: establish a trajectory according to the first frame result after fusion of heterogeneous information, associate the fusion detection result with the trajectory, and perform an optimal estimation of the target observation value;
步骤六)轨迹预测:根据路侧区域的高精度地图信息,结合目标的追踪结果,输出未来的运动轨迹。Step 6) Trajectory prediction: According to the high-precision map information of the roadside area, combined with the tracking results of the target, output the future motion trajectory.
进一步的,在步骤一)中,对数据进行采集的同时进行时间同步,通过统一时钟源发送触发信号,触发不同的传感器采集数据,并给所有数据赋上触发时刻的时间戳,实现不同传感器数据的纳秒级时间同步。Further, in step 1), time synchronization is performed while data is collected, a trigger signal is sent through a unified clock source to trigger different sensors to collect data, and a timestamp of the trigger time is assigned to all data, so as to realize data from different sensors. nanosecond time synchronization.
进一步的,在步骤二)中,在路侧视角利用工业相机采集道路目标图像,对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计,利用多任务深度学习网络,在具体应用场景的数据集上训练并实现实例分割和深度估计。Further, in step 2), an industrial camera is used to collect a road target image from a roadside perspective, instance segmentation and depth estimation are performed on the collected road target image, and a multi-task deep learning network is used to perform a data set of specific application scenarios. Train and implement instance segmentation and depth estimation.
进一步的,在步骤三)中:Further, in step 3):
将不同激光雷达传感器输出的局部坐标系下的点云帧转到统一的坐标系下,得到一帧完整视野范围的融合点云帧;Transfer the point cloud frames in the local coordinate system output by different lidar sensors to a unified coordinate system to obtain a fused point cloud frame with a complete field of view;
接收融合点云帧数据并进行过滤操作,过滤操作包括下采样、非法点去除、离群点去除以及感兴趣区域过滤操作,输出处理后的点云数据;Receive the fused point cloud frame data and perform filtering operations. The filtering operations include downsampling, illegal point removal, outlier removal, and region-of-interest filtering operations, and output the processed point cloud data;
过滤点云帧中的背景点云,将检测范围划分为不同的体素,在线采集若干点云帧,统计每个体素的点云密度,制作背景表,根据当前点对应的体素在背景表中的点云密度值,设置阈值过滤背景点;Filter the background point cloud in the point cloud frame, divide the detection range into different voxels, collect several point cloud frames online, count the point cloud density of each voxel, and make a background table, according to the voxel corresponding to the current point in the background table. The point cloud density value in , set the threshold to filter the background points;
利用DBSCAN算法完成对前景点云的聚类,将同一目标的点云聚为一类;Use DBSCAN algorithm to complete the clustering of foreground point clouds, and group the point clouds of the same target into one category;
利用OBB方向包围框算法构建每一个点云簇的三维检测框。The 3D detection frame of each point cloud cluster is constructed using the OBB direction bounding box algorithm.
进一步的,在步骤四)中,将图像实例分割、深度估计、多雷达点云融合数据进行融合,输出目标3D检测结果,3D检测结果包括语义类别尺寸及3D位姿信息;Further, in step 4), the image instance segmentation, depth estimation, and multi-radar point cloud fusion data are fused, and the target 3D detection result is output, and the 3D detection result includes semantic category size and 3D pose information;
在步骤五)中,根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,当下一帧融合结果到来时,利用匈牙利二分图匹配算法将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,使用卡尔曼滤波技术,对目标观测值进行最优估计。In step 5), a trajectory is established according to the first frame result after the fusion of heterogeneous information. When the next frame fusion result arrives, the fusion detection result and the trajectory are associated with the Hungarian bipartite graph matching algorithm, and the Kalman filter technology is used to observe the target. value for the best estimate.
进一步的,在步骤六)中,根据目标的追踪结果以及高精度地图信息,输出未来的运动轨迹,地图信息包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度信息,运动轨迹包括位置信息、速度、加速度。Further, in step 6), according to the tracking result of the target and the high-precision map information, the future motion trajectory is output, the map information includes lane guide line, flatness and slope information, and the motion trajectory includes position information, speed, and acceleration.
一种露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知系统,具体包括:A road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception system for an open-pit mine, specifically comprising:
数据采集模块,进行数据采集,从传感器设备读取数据,对数据进行格式转换;The data acquisition module is used for data acquisition, reading data from the sensor device, and converting the data format;
图像多任务感知模块,对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计,得到实例分割结果和深度图;The image multi-task perception module performs instance segmentation and depth estimation on the collected road target images to obtain instance segmentation results and depth maps;
点云目标检测模块,对点云数据进行多雷达融合,得到统一坐标的融合点云数据,通过背景滤波获取前景点云数据,通过聚类算法对前景点云数据进行聚类处理,对通过聚类处理得到的点云簇构建三维检测框,得到三维目标框;The point cloud target detection module performs multi-radar fusion on point cloud data to obtain fused point cloud data with unified coordinates, obtains foreground point cloud data through background filtering, and performs clustering processing on foreground point cloud data through clustering algorithm. The point cloud cluster obtained by class processing constructs a 3D detection frame and obtains a 3D target frame;
异构信息融合模块,对图像实例分割、深度图、三维目标框进行异构信息融合,输出目标3D检测结果;Heterogeneous information fusion module, which performs heterogeneous information fusion on image instance segmentation, depth map, and 3D target frame, and outputs target 3D detection results;
多目标跟踪模块,用于根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,对目标观测值进行最优估计;The multi-target tracking module is used to establish a trajectory according to the first frame results after the fusion of heterogeneous information, associate the fusion detection results with the trajectory, and perform optimal estimation of target observations;
轨迹预测模块,用于根据目标追踪结果和高精度地图信息输出未来的运动轨迹,高精度地图信息包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度信息,运动轨迹包括位置信息、速度、加速度。The trajectory prediction module is used to output the future motion trajectory according to the target tracking result and high-precision map information. The high-precision map information includes lane guide line, flatness and slope information, and the motion trajectory includes position information, speed, and acceleration.
进一步的,在点云目标检测模块中,包括预处理模块、背景滤波模块、点云聚类模块、3D框重建模块,其中;Further, the point cloud target detection module includes a preprocessing module, a background filtering module, a point cloud clustering module, and a 3D frame reconstruction module, wherein;
预处理模块,用于接收来自原始点云帧数据或是多点云融合模块输出的融合点云帧数据,对融合点云帧数据进行过滤操作,过滤操作包括下采样、非法点去除、离群点去除以及感兴趣区域过滤操作,输出处理后的点云数据;The preprocessing module is used to receive the fused point cloud frame data from the original point cloud frame data or the output of the multi-point cloud fusion module, and perform filtering operations on the fused point cloud frame data. The filtering operations include downsampling, illegal point removal, and outliers. Point removal and region of interest filtering operations, and output processed point cloud data;
背景滤波模块,用于过滤点云帧中的背景点云,将检测范围形式化为三维体素表示,在线采集若干点云帧,统计每个体素的点云密度,制作背景表,根据当前点对应的体素在背景表中的点云密度值,根据阈值过滤背景点;The background filtering module is used to filter the background point cloud in the point cloud frame, formalize the detection range into a three-dimensional voxel representation, collect several point cloud frames online, count the point cloud density of each voxel, and make a background table. The point cloud density value of the corresponding voxel in the background table, and the background points are filtered according to the threshold;
点云聚类模块,用于利用DBSCAN算法完成对前景点云的聚类,将同一目标的点云聚为一类;The point cloud clustering module is used to use the DBSCAN algorithm to complete the clustering of the foreground point clouds, and group the point clouds of the same target into one category;
3D框重建模块,利用OBB方向包围框算法构建每一个点云簇的三维检测框,点云聚类模块得到的每一个点云簇都需要通过3D框重建模块构建对应的3D框;The 3D frame reconstruction module uses the OBB direction bounding box algorithm to construct the 3D detection frame of each point cloud cluster. Each point cloud cluster obtained by the point cloud clustering module needs to construct the corresponding 3D frame through the 3D frame reconstruction module;
在多目标跟踪模块中,异构信息融合模块的融合结果最终输入到多目标跟踪模块,多目标跟踪模块首先根据首帧融合结果建立轨迹,当下一帧融合结果到来时,利用匈牙利二分图匹配算法将融合检测结果和轨迹关联,然后使用卡尔曼滤波技术,对目标观测值进行最优估计。In the multi-target tracking module, the fusion result of the heterogeneous information fusion module is finally input to the multi-target tracking module. The multi-target tracking module first establishes a trajectory according to the fusion result of the first frame, and when the fusion result of the next frame arrives, the Hungarian bipartite graph matching algorithm is used. The fusion detection results are associated with the trajectory, and then the Kalman filtering technique is used to perform the optimal estimation of the target observations.
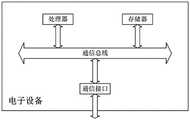
一种电子设备,包括:处理器、通信接口、存储器和通信总线,其中,处理器,通信接口,存储器通过通信总线完成相互间的通信;所述存储器中存储有计算机程序,当所述计算机程序被所述处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法的步骤。An electronic device, comprising: a processor, a communication interface, a memory, and a communication bus, wherein the processor, the communication interface, and the memory communicate with each other through the communication bus; a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the computer program is When executed by the processor, the processor is made to execute the steps of the road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception method of the open-pit mine.
一种计算机可读存储介质,其特征在于,其存储有可由电子设备执行的计算机程序,当所述计算机程序在所述电子设备上运行时,使得所述电子设备执行露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法的步骤。A computer-readable storage medium, characterized in that it stores a computer program that can be executed by an electronic device, and when the computer program is run on the electronic device, makes the electronic device execute the road-side multi-source of an open-pit mine. Steps of a sensor fusion object perception method.
本发明与现有技术相比具有以下的优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
本发明提供一种适用于露天矿山的路侧感知算法,该算法在露天矿山车路协同的具体应用场景中能够很好的契合路端感知的特点,实现场景中动态目标的精确感知,能够为车端感知提供补盲、超视距以及冗余验证的作用,为智能驾驶车辆在复杂路口的安全行驶提供保障。The invention provides a roadside perception algorithm suitable for open-pit mines. The algorithm can well fit the characteristics of roadside perception in the specific application scenario of vehicle-road coordination in open-pit mines, realize accurate perception of dynamic targets in the scene, and can provide In-vehicle perception provides blindness, over-the-horizon, and redundant verification, ensuring the safe driving of intelligent driving vehicles at complex intersections.
本发明针对路侧平台的点云目标检测技术,能够适应多数量、多类型激光雷达融合检测的情况。点云目标检测使用背景滤波提前过滤场景中的静态目标,显著提升了点云目标检测的速度与精度。图像检测结果与点云目标检测结果的异构信息进行融合,能够充分利用各个传感器的优势,实现路侧感知单元的超视距感知,以及在扬尘、雨雪等恶劣环境下的精确感知。The present invention is aimed at the point cloud target detection technology of the roadside platform, and can adapt to the situation of fusion detection of large numbers and types of laser radars. Point cloud target detection uses background filtering to filter static targets in the scene in advance, which significantly improves the speed and accuracy of point cloud target detection. The fusion of the image detection results and the heterogeneous information of the point cloud target detection results can make full use of the advantages of each sensor to realize the over-the-horizon perception of the roadside perception unit and accurate perception in harsh environments such as dust, rain and snow.
本发明还结合了高精度地图信息的目标轨迹预测算法,该算法在露天矿山车路协同的具体应用场景中,通过高精度地图中的车道引导线信息约束目标的运动方向,并利用平整度以及坡度信息约束目标的速度和加速度,从而实现目标未来运动轨迹的精准预测。The invention also combines the target trajectory prediction algorithm of high-precision map information. In the specific application scenario of vehicle-road coordination in open-pit mines, the algorithm constrains the moving direction of the target through the lane guide line information in the high-precision map, and uses the flatness and The gradient information constrains the speed and acceleration of the target, so as to achieve accurate prediction of the target's future trajectory.
本发明提出的多源传感器感知算法专门对车路协同感知环境做了适配,通过多相机、多激光雷达感知结果的融合实现场景范围感知的全覆盖,并提升了感知算法在恶劣天气下的鲁棒性。另外,本框架还提出了轨迹预测模块,通过结合高精度地图信息实现目标未来轨迹的精确预测,感知算法在具体应用场景中表现出功耗低、效果好、鲁棒性高的特点,很适合大规模商业落地与推广。The multi-source sensor perception algorithm proposed by the invention is specially adapted to the vehicle-road collaborative perception environment, realizes the full coverage of the scene range perception through the fusion of multi-camera and multi-lidar perception results, and improves the perception algorithm in bad weather. robustness. In addition, this framework also proposes a trajectory prediction module, which can accurately predict the target's future trajectory by combining high-precision map information. The perception algorithm has the characteristics of low power consumption, good effect and high robustness in specific application scenarios, which is very suitable for Large-scale commercial landing and promotion.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明具体实施方式或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对具体实施方式或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本发明的一些实施方式,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to illustrate the specific embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art more clearly, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings that need to be used in the description of the specific embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description The drawings are some embodiments of the present invention. For those of ordinary skill in the art, other drawings can also be obtained based on these drawings without creative efforts.
图1是露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法的流程图。Fig. 1 is a flow chart of the target perception method of roadside multi-source sensor fusion in open-pit mines.
图2是露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知系统的构架图。Figure 2 is the framework diagram of the road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception system of the open-pit mine.
图3是露天矿山路侧场景感知算法框图。Figure 3 is a block diagram of an open-pit mine roadside scene perception algorithm.
图4是点云目标检测模块的系统构架图。Figure 4 is a system architecture diagram of a point cloud target detection module.
图5是点云目标检测的流程图。Figure 5 is a flow chart of point cloud object detection.
图6是异构信息融合模块结构图。Figure 6 is a structural diagram of a heterogeneous information fusion module.
图7是Frenet坐标系示意图。Figure 7 is a schematic diagram of the Frenet coordinate system.
图8是电子设备的系统架构图。FIG. 8 is a system architecture diagram of an electronic device.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合附图对本发明的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The technical solutions of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Obviously, the described embodiments are a part of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
现有技术的三维环境感知算法多数是基于车端视角数据进行开发的,这些方法无法很好的迁移到路侧感知场景。一方面,车端与路侧端的传感器视角存在很大差异,这些差异进一步造成了数据的差异,这使得适应于车端的感知算法不能很好的在路侧场景工作;另一方面,车端传感器是运动的,采集的数据中背景信息一直在变化,这为感知算法带来了很大的挑战。而路侧立杆是固定的,场景中的背景信息可以基于高精度地图,采用背景滤波等方法过滤掉。这不仅较少了待处理的数据量,还提高了目标检测的精度。因此,路侧端与车端的感知算法流程也存在差异。本发明提出了一种针对路侧环境的感知算法,该算法使用了背景滤波以及多源传感器融合等策略提升路侧感知算法性能,能满足自动驾驶领域的实时性要求。Most of the existing 3D environment perception algorithms are developed based on vehicle-end perspective data, and these methods cannot be well transferred to roadside perception scenarios. On the one hand, there is a big difference in the viewing angles of the sensors at the vehicle end and the roadside end, and these differences further cause the difference in data, which makes the perception algorithm adapted to the vehicle end unable to work well in the roadside scene; on the other hand, the vehicle end sensor It is moving, and the background information in the collected data is constantly changing, which brings great challenges to the perception algorithm. The roadside poles are fixed, and the background information in the scene can be filtered out based on the high-precision map, using background filtering and other methods. This not only reduces the amount of data to be processed, but also improves the accuracy of object detection. Therefore, there are also differences in the perception algorithm process between the roadside end and the vehicle end. The invention proposes a perception algorithm for the roadside environment, which uses strategies such as background filtering and multi-source sensor fusion to improve the performance of the roadside perception algorithm, and can meet the real-time requirements in the field of automatic driving.
针对目标轨迹预测,现有方法有基于卡尔曼滤波的,也有基于深度学习技术的。对于前者,卡尔曼滤波技术高度依赖于目标的运动模型,对于目标运动较为复杂的情况无法给出准确的轨迹预测,另外该方法也很难预测目标长时间的运动轨迹。对于后者,深度学习方法泛化能力差,性能高度依赖于数据,标注成本高且计算量大,无法在嵌入式设备上达到自动驾驶的实时要求。本发明提出的目标轨迹预测方法结合了场景的高精度地图信息,包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度等信息,能够得到目标未来几秒的精确轨迹信息。这些预测信息能够显著增强自动驾驶车辆在复杂交叉路口的规划性能,提升车辆的行驶效率与安全性。For target trajectory prediction, there are existing methods based on Kalman filtering and deep learning technology. For the former, the Kalman filter technology is highly dependent on the motion model of the target, and cannot give accurate trajectory prediction for complex target motion. In addition, this method is also difficult to predict the target's long-term motion trajectory. For the latter, the generalization ability of deep learning methods is poor, the performance is highly dependent on data, the cost of labeling is high and the amount of computation is large, which cannot meet the real-time requirements of autonomous driving on embedded devices. The target trajectory prediction method proposed by the invention combines the high-precision map information of the scene, including information such as lane guide lines, flatness and slope, and can obtain accurate trajectory information of the target in the next few seconds. These predictive information can significantly enhance the planning performance of autonomous vehicles at complex intersections, and improve the driving efficiency and safety of vehicles.
通过背景技术中对于现有技术的描述可以看出,现有技术存在的缺陷包括:无法处理图像目标遮挡的情况,图像视野范围有限,无法利用超出图像视野范围的点云信息(CN112990129A,涉及视觉和激光雷达联合的三维物体检测方法);数据驱动型方法调试依赖于数据集,换场景就要重新训练,缺乏可解释性,非常耗费计算资源,难以在边缘计算平台上实时检测效果(CN113095172A,涉及深度学习点去三维物体检测);难以应对实际场景下行驶状态的复杂性,没有利用场景道路中的先验信息,仅依赖卡尔曼滤波只能预测目标很短时间内的轨迹,而无法对目标长时间的运动趋势进行预测(CN113763434A,涉及轨迹预测)。From the description of the prior art in the background art, it can be seen that the defects of the prior art include: it cannot handle the occlusion of the image target, the image field of view is limited, and the point cloud information beyond the image field of view cannot be used (CN112990129A, involving visual 3D object detection method combined with lidar); data-driven method debugging relies on data sets, and requires retraining when changing scenes, lacks interpretability, consumes computing resources, and is difficult to detect in real time on edge computing platforms (CN113095172A, Involving deep learning points to 3D object detection); it is difficult to deal with the complexity of the driving state in the actual scene, without using the prior information in the scene road, only relying on Kalman filtering can only predict the trajectory of the target in a short time, but cannot The long-term motion trend of the target is predicted (CN113763434A, involving trajectory prediction).
本发明提出的路侧感知算法针对露天矿山环境的具体应用场景,能够实现超视距感知以及恶劣天气下的高鲁棒性感知,并能够在边缘计算平台上实时高效的运行。现有的技术方案大多是车端视角的,并且大多功耗大,无法保证实时性。因此,本发明具有超越本领域技术人员预期的技术效果。The roadside perception algorithm proposed by the present invention is aimed at the specific application scenarios of the open-pit mine environment, and can realize over-the-horizon perception and high robustness perception in bad weather, and can run efficiently in real time on an edge computing platform. Most of the existing technical solutions are from the perspective of the vehicle end, and most of them consume a lot of power and cannot guarantee real-time performance. Therefore, the present invention has technical effects beyond expectations of those skilled in the art.
实施例1:如图1所示的用于露天矿山车路协同的露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法,具体包括:Embodiment 1: As shown in Figure 1, the road-end multi-source sensor fusion target perception method for open-pit mines in open-pit mines with vehicle-road coordination, specifically includes:
步骤S1)数据采集:进行数据采集,从传感器设备读取数据,对数据进行格式转换;在本实施例中,数据采集模块的执行主体包括路端/路侧设备:工业相机、多激光雷达,等等;Step S1) Data collection: carry out data collection, read data from sensor devices, and perform format conversion on the data; in this embodiment, the execution body of the data collection module includes road-end/road-side equipment: industrial cameras, multi-laser radars, and many more;
步骤S2)图像多任务感知:对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计,得到实例分割结果和深度图;Step S2) Image multi-task perception: perform instance segmentation and depth estimation on the collected road target images to obtain instance segmentation results and depth maps;
深度估计,就是利用一张或者唯一/多个视角下的RGB图像,估计图像中每个像素相对拍摄源的距离。现有技术中,对图像进行深度估计的方法通常为:利用单视角/多视角几何学原理启发构建深度估计的卷积神经网络模型;然后,采集大量图像并设法得到图像的深度图(例如利用激光雷达数据进行深度插值,或是直接利用深度相机采集数据)使用标注有每个像素点深度值的RGB图像对网络模型进行优化训练,进而可以采用优化训练后的网络模型对目标图像进行深度估计,获取目标图像中每个像素点的深度值。Depth estimation is to estimate the distance of each pixel in the image relative to the shooting source by using an RGB image from one or only/multiple viewing angles. In the prior art, the method for depth estimation of an image is usually: constructing a convolutional neural network model for depth estimation inspired by single-view/multi-view geometry; Depth interpolation of lidar data, or direct use of depth camera to collect data) Use RGB images marked with the depth value of each pixel to optimize the training of the network model, and then use the optimized trained network model to estimate the depth of the target image. , get the depth value of each pixel in the target image.
步骤S3)点云目标检测:对点云数据进行多雷达融合,得到统一坐标的融合点云数据,然后通过背景滤波获得前景点云数据,通过聚类算法对前景点云数据进行聚类处理,对通过聚类处理得到的点云簇构建三维检测框,得到三维目标框;Step S3) point cloud target detection: perform multi-radar fusion on point cloud data to obtain fused point cloud data with unified coordinates, then obtain foreground point cloud data through background filtering, and perform clustering processing on foreground point cloud data through a clustering algorithm, Constructing a three-dimensional detection frame for the point cloud clusters obtained by clustering to obtain a three-dimensional target frame;
步骤S4)异构信息融合:对图像实例分割、深度图、三维目标框进行异构信息融合,输出目标3D检测结果;在本实施例中,异构信息融合是将图像实例分割、深度估计、多雷达融合点云数据等不同数据来源、不同系统的异构数据进行融合;Step S4) Heterogeneous information fusion: perform heterogeneous information fusion on image instance segmentation, depth map, and three-dimensional target frame, and output the target 3D detection result; Fusion of heterogeneous data from different data sources and different systems such as multi-radar fusion point cloud data;
步骤S5)多目标跟踪:根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,对目标观测值进行最优估计,得到更加平滑准确的检测结果,同时也计算出目标的速度和加速度等信息。Step S5) Multi-target tracking: establish a trajectory according to the first frame result after fusion of heterogeneous information, associate the fusion detection result with the trajectory, and perform optimal estimation on the target observation value to obtain a smoother and more accurate detection result, and also calculate the target. information such as speed and acceleration.
步骤S6)轨迹预测:根据路侧区域的高精度地图信息,结合目标的追踪结果,输出未来的运动轨迹(可输出目标未来几秒的运动轨迹),地图信息包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度信息等,运动轨迹包括位置信息、速度、加速度。Step S6) Trajectory prediction: According to the high-precision map information of the roadside area, combined with the tracking results of the target, output the future motion trajectory (the motion trajectory of the target in the next few seconds can be output), and the map information includes the lane guide line, flatness and slope. information, etc. The motion trajectory includes position information, speed, and acceleration.
优选的,在对数据进行采集的同时进行时间同步,通过统一时钟源发送触发信号,触发不同的传感器采集数据,并给所有数据赋上触发时刻的时间戳,实现不同传感器数据的纳秒级时间同步。Preferably, the time synchronization is performed while the data is collected, a trigger signal is sent through a unified clock source to trigger different sensors to collect data, and a timestamp of the trigger time is assigned to all data, so as to realize the nanosecond time of different sensor data. Synchronize.
优选的,在路侧视角利用工业相机采集道路目标图像,对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计,利用多任务深度学习网络,在具体应用场景的数据集上训练并实现实例分割和深度估计。Preferably, an industrial camera is used to collect road target images from a roadside perspective, instance segmentation and depth estimation are performed on the collected road target images, and a multi-task deep learning network is used to train on a dataset of specific application scenarios and implement instance segmentation and depth estimation. Depth estimation.
优选的,将不同激光雷达传感器输出的局部坐标系下的点云帧转到统一的坐标系下,即,将不同视角下的点云数据拼接在一起,得到一帧完整视野范围的融合点云帧;Preferably, the point cloud frames under the local coordinate system output by different lidar sensors are transferred to a unified coordinate system, that is, the point cloud data under different viewing angles are spliced together to obtain a fused point cloud with a complete field of view. frame;
接收融合点云帧数据并进行过滤操作,过滤操作包括下采样(体素滤波)、非法点去除、离群点去除以及感兴趣区域过滤操作,输出处理后的点云数据;Receive the fused point cloud frame data and perform filtering operations. The filtering operations include downsampling (voxel filtering), illegal point removal, outlier removal, and region-of-interest filtering operations, and output the processed point cloud data;
过滤点云帧中的背景点云,将检测范围形式化为不同的体素进行表示,在线采集若干点云帧,统计每个体素的点云密度,制作背景表,根据当前点对应的体素在背景表中的点云密度值,根据阈值过滤背景点;Filter the background point cloud in the point cloud frame, formalize the detection range into different voxels to represent, collect several point cloud frames online, count the point cloud density of each voxel, make a background table, according to the voxel corresponding to the current point The point cloud density value in the background table, filter the background points according to the threshold;
利用DBSCAN(具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法)算法完成对前景点云的聚类,将同一目标的点云聚为一类;Using the DBSCAN (density-based clustering method with noise) algorithm to complete the clustering of the foreground point clouds, and cluster the point clouds of the same target into one category;
利用OBB方向包围框算法构建每一个点云簇的三维检测框。The 3D detection frame of each point cloud cluster is constructed using the OBB direction bounding box algorithm.
优选的,在步骤S4)中,将图像实例分割、深度估计、多雷达点云融合数据进行融合,输出目标3D检测结果,3D检测结果包括语义类别尺寸及3D位姿信息;Preferably, in step S4), image instance segmentation, depth estimation, and multi-radar point cloud fusion data are fused, and a 3D detection result of the target is output, and the 3D detection result includes semantic category size and 3D pose information;
在步骤S5)中,根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,当下一帧融合结果到来时,利用匈牙利二分图匹配算法将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,使用卡尔曼滤波技术,对目标观测值进行最优估计,得到更加平滑准确的检测结果,同时也计算出目标的速度和加速度等信息。In step S5), a trajectory is established according to the first frame result after the fusion of heterogeneous information. When the next frame fusion result arrives, the fusion detection result is associated with the trajectory using the Hungarian bipartite graph matching algorithm, and the Kalman filter technology is used to observe the target. The optimal estimation of the target value is performed to obtain a smoother and more accurate detection result, and information such as the speed and acceleration of the target is also calculated.
优选的,在步骤S6)中,根据目标的追踪结果以及高精度地图信息,输出未来的运动轨迹,地图信息包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度信息,运动轨迹包括位置信息、速度、加速度。Preferably, in step S6), according to the tracking result of the target and high-precision map information, output the future motion trajectory, the map information includes lane guide line, flatness and slope information, and the motion trajectory includes position information, speed, acceleration.
实施例2:如图2和图3所示,本实施例是与露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法相对应的系统,本系统包含六个模块,分别是数据采集模块、图像多任务感知模块、点云目标检测模块、异构信息融合模块、多目标跟踪模块以及轨迹预测模块,其中:数据采集模块负责采集实时的图像与点云数据,图像数据输入给图像多任务感知模块得到实例分割以及深度估计等结果,点云数据输入点云目标检测模块得到三维检测结果。图像多任务感知模块以及点云目标检测模块的结果会输入到异构信息融合模块,融合算法能够将点云的精确位置信息以及图像的丰富语义信息融合,得到更为精确的三维检测结果。之后,融合模块的结果会输入到多目标跟踪模块,得到目标的跟踪ID以及速度加速度等信息。最后,目标的跟踪信息会输入到轨迹预测模块,该模块能够结合高精度地图信息完成对目标未来运动轨迹的精确预测。Embodiment 2: As shown in Figures 2 and 3, this embodiment is a system corresponding to the target sensing method of road-end multi-source sensor fusion in open-pit mines. This system includes six modules, namely a data acquisition module, a multi-image Task perception module, point cloud target detection module, heterogeneous information fusion module, multi-target tracking module and trajectory prediction module, among which: the data acquisition module is responsible for collecting real-time image and point cloud data, and the image data is input to the image multi-task perception module to obtain Instance segmentation and depth estimation and other results, point cloud data is input to the point cloud target detection module to obtain 3D detection results. The results of the image multi-task perception module and the point cloud target detection module will be input to the heterogeneous information fusion module. The fusion algorithm can fuse the precise location information of the point cloud and the rich semantic information of the image to obtain more accurate 3D detection results. After that, the result of the fusion module will be input to the multi-target tracking module, and the tracking ID and speed acceleration of the target will be obtained. Finally, the tracking information of the target will be input to the trajectory prediction module, which can combine the high-precision map information to complete the accurate prediction of the target's future trajectory.
本系统能够通过软硬件结合的方式实现露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法,本系统的基本功能模块具体包括:This system can realize the target perception method of road-end multi-source sensor fusion in open-pit mines through the combination of software and hardware. The basic functional modules of this system include:
数据采集模块,进行数据采集,从传感器设备读取数据,对数据进行格式转换,并传输给点云目标检测模块;除了数据的编码功能外,数据采集模块还包括了数据间的时间同步、空间同步等功能。其中,数据的时间同步是利用硬件产生脉冲信号,所有传感器都被这个脉冲触发,每次触发都校正一次自己的时钟,这样就可以消除时钟源的累计误差,这对时序数据的在线处理非常重要,数据的时间同步保证了多源传感器数据融合的可能性。The data acquisition module performs data acquisition, reads the data from the sensor device, converts the data format, and transmits it to the point cloud target detection module; in addition to the data encoding function, the data acquisition module also includes time synchronization between data, space synchronization, etc. Among them, the time synchronization of the data is to use the hardware to generate a pulse signal. All sensors are triggered by this pulse. Each time the trigger is triggered, its own clock is corrected once, so that the accumulated error of the clock source can be eliminated, which is very important for the online processing of time series data. , the time synchronization of data ensures the possibility of multi-source sensor data fusion.
本模块通过统一时钟源发送触发信号触发不同的传感器采集数据,并给所有数据赋上触发时刻的时间戳,这样就实现了不同传感器数据的纳秒级时间同步。另外,数据的空间同步,即不同传感器的标定也是在数据采集模块进行。由于整套感知系统包含激光雷达与相机,因此传感器的标定包括激光雷达与激光雷达的标定以及相机与激光雷达的标定。This module sends trigger signals through a unified clock source to trigger different sensors to collect data, and assigns a time stamp of the trigger time to all data, thus realizing nanosecond-level time synchronization of different sensor data. In addition, the spatial synchronization of data, that is, the calibration of different sensors is also performed in the data acquisition module. Since the whole perception system includes lidar and camera, the calibration of the sensor includes the calibration of lidar and lidar as well as the calibration of camera and lidar.
图像多任务感知模块,用于对采集到的道路目标图像进行实例分割以及深度估计;图像多任务感知模块输入是路侧视角高速率工业相机采集的道路目标图像,输出为图像实例分割结果以及深度估计结果。该模块通过采集大量数据训练了一个轻量级多任务网络模型,该网络能够同时完成图像实例分割以及深度估计任务。不失一般性,可以利用已经开源的多任务深度网络,在具体应用场景数据集上训练实现实例分割以及深度估计。例如,在文章《Real-Time Joint Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation UsingAsymmetric Annotations》中,提出了一种轻量级多任务检测网络。本领域技术人员可以通过在线链接https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.04766v2.pdf访问并下载到该文章,该文章属于现有技术的一部分,该文章的相关信息:The image multi-task perception module is used to perform instance segmentation and depth estimation on the collected road target images; the input of the image multi-task perception module is the road target image collected by the roadside high-speed industrial camera, and the output is the image instance segmentation result and depth. estimated results. This module trains a lightweight multi-task network model by collecting a large amount of data, which can simultaneously perform image instance segmentation and depth estimation tasks. Without loss of generality, instance segmentation and depth estimation can be achieved by training on the dataset of specific application scenarios by using the open-source multi-task deep network. For example, in the article "Real-Time Joint Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Using Asymmetric Annotations", a lightweight multi-task detection network is proposed. Those skilled in the art can access and download the article through the online link https://arxiv.org/pdf/1809.04766v2.pdf, the article is part of the prior art, and the relevant information of the article:
作者:Vladimir Nekrasov1, Thanuja Dharmasiri2, Andrew Spek2, TomDrummond2, Chunhua Shen1 and Ian Reid1Authors: Vladimir Nekrasov1, Thanuja Dharmasiri2, Andrew Spek2, TomDrummond2, Chunhua Shen1 and Ian Reid1
1School of Computer Science, University of Adelaide, Australia2Monash University, Australia1School of Computer Science, University of Adelaide, Australia2Monash University, Australia
出处:2019-ICRASource: 2019-ICRA
引用:Nekrasov, V., Dharmasiri, T., Spek, A., Drummond, T., Shen, C.,& Reid, I. (2019, May). Real-time joint semantic segmentation and depthestimation using asymmetric annotations. In 2019 International Conference onRobotics and Automation (ICRA) (pp. 7101-7107). IEEE.Citation: Nekrasov, V., Dharmasiri, T., Spek, A., Drummond, T., Shen, C., & Reid, I. (2019, May). Real-time joint semantic segmentation and depthestimation using asymmetric annotations. In 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (pp. 7101-7107). IEEE.
改进自论文:Nekrasov 2018年的文章 Light-Weight RefineNet for Real-TimeSemantic SegmentationImproved from the paper: Nekrasov's 2018 paper Light-Weight RefineNet for Real-TimeSemantic Segmentation
本模块所使用的网络架构和上述轻量级多任务检测网络类似,都包含了一个编码器网络提取图像的高层语义特征,然后一个轻量级的解码器网络完成不同的预测任务。在网络处理阶段,同一时刻所有相机的图像会组成一个批次,同时输入到网络中进行处理,这样能够显著提高网络的处理速度以及吞吐量。为了进一步加速网络处理过程,本模块使用了NVIDIA 的TensorRT框架对模型进行加速,使得图像多任务感知模块在Xavier开发套件上能够满足自动驾驶实时要求。The network architecture used in this module is similar to the above-mentioned lightweight multi-task detection network. Both include an encoder network to extract high-level semantic features of images, and then a lightweight decoder network to complete different prediction tasks. In the network processing stage, the images of all cameras at the same time will form a batch and input into the network for processing at the same time, which can significantly improve the processing speed and throughput of the network. In order to further accelerate the network processing process, this module uses NVIDIA's TensorRT framework to accelerate the model, so that the image multi-task perception module can meet the real-time requirements of autonomous driving on the Xavier development kit.
如图4所示的点云目标检测模块,对点云数据进行多雷达融合,得到统一坐标的融合点云数据,通过背景滤波获取前景点云数据,通过聚类算法对前景点云数据进行聚类处理,对通过聚类处理得到的点云簇构建三维检测框,得到三维目标框。As shown in Figure 4, the point cloud target detection module performs multi-radar fusion on the point cloud data to obtain the fused point cloud data with unified coordinates. The foreground point cloud data is obtained through background filtering, and the foreground point cloud data is clustered through the clustering algorithm. Class processing, constructing a three-dimensional detection frame for the point cloud clusters obtained through clustering processing, and obtaining a three-dimensional target frame.
在多激光雷达协同感知的情况下,多传感器采集的点云数据首先会输入到多点云融合模块进行数据前融合,得到统一坐标系的融合点云数据,之后再输入到点云目标检测模块。In the case of multi-lidar collaborative sensing, the point cloud data collected by multi-sensors will first be input to the multi-point cloud fusion module for pre-data fusion to obtain the fused point cloud data of a unified coordinate system, and then input to the point cloud target detection module .
优选的,如图5所示,点云目标检测模块中包含了四个子模块,分别是预处理模块、背景滤波模块、点云聚类模块以及3D框重建模块。点云目标检测模块输出的三维目标检测信息最后会传入异构信息融合模块,和图像检测结果融合以得到信息更为丰富的检测结果。多点云融合模块用于将不同激光雷达传感器输出的局部坐标系下的点云帧转到统一的坐标系下,即将不同视角下的点云数据拼接在一起,得到一帧完整视野范围的融合点云帧;Preferably, as shown in FIG. 5 , the point cloud target detection module includes four sub-modules, which are a preprocessing module, a background filtering module, a point cloud clustering module and a 3D frame reconstruction module. The 3D target detection information output by the point cloud target detection module will finally be transmitted to the heterogeneous information fusion module, and fused with the image detection results to obtain more informative detection results. The multi-point cloud fusion module is used to transfer the point cloud frames in the local coordinate system output by different lidar sensors to a unified coordinate system, that is, splicing the point cloud data from different perspectives together to obtain a fusion of a complete field of view. point cloud frame;
预处理模块,用于接收来自原始点云帧数据或是多点云融合模块输出的融合点云帧数据,对融合点云帧数据进行过滤操作,过滤操作包括下采样、非法点去除、离群点去除以及感兴趣区域过滤操作,输出处理后的点云数据;The preprocessing module is used to receive the fused point cloud frame data from the original point cloud frame data or the output of the multi-point cloud fusion module, and perform filtering operations on the fused point cloud frame data. The filtering operations include downsampling, illegal point removal, and outliers. Point removal and region of interest filtering operations, and output processed point cloud data;
背景滤波模块,用于过滤点云帧中的背景点云,将检测范围形式化为三维体素表示,在线采集若干点云帧,统计每个体素的点云密度,制作背景表,根据当前点对应的体素在背景表中的点云密度值,根据阈值过滤背景点;The background filtering module is used to filter the background point cloud in the point cloud frame, formalize the detection range into a three-dimensional voxel representation, collect several point cloud frames online, count the point cloud density of each voxel, and make a background table. The point cloud density value of the corresponding voxel in the background table, and the background points are filtered according to the threshold;
点云聚类模块,用于利用DBSCAN(具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法)算法完成对前景点云的聚类,将同一目标的点云聚为一类;The point cloud clustering module is used to use the DBSCAN (density-based clustering method with noise) algorithm to complete the clustering of the foreground point clouds, and group the point clouds of the same target into one category;
预处理的点云经过背景滤波模块之后只剩下前景点云数据,点云聚类模块利用DBSCAN(具有噪声的基于密度的聚类方法)算法完成对前景点云的聚类,将同一目标的点云聚为一类。After the preprocessed point cloud passes through the background filtering module, only the foreground point cloud data remains. The point cloud clustering module uses the DBSCAN (density-based clustering method with noise) algorithm to complete the clustering of the foreground point cloud. Point clouds are grouped into one class.
具体的,DBSCAN聚类算法一般假定类别可以通过样本分布的紧密程度决定,通过将紧密相连的样本归为一类以达到聚类的目的。对于点云数据,可以根据点与点之间的欧式距离构建连接性,然后使用DBSCAN算法进行聚类。Specifically, the DBSCAN clustering algorithm generally assumes that the category can be determined by the tightness of the sample distribution, and the purpose of clustering is achieved by grouping closely connected samples into one category. For point cloud data, connectivity can be constructed based on the Euclidean distance between points and then clustered using the DBSCAN algorithm.
3D框重建模块,利用OBB方向包围框算法构建每一个点云簇的三维检测框。点云聚类模块得到的每一个点云簇都需要通过3D框重建模块构建对应的3D框。3D框重建模块利用OBB方向包围框算法构建点云簇的三维检测框。OBB算法的目的是在三维空间中构建能够包围点云簇的最小长方体,该算法主要利用主成分分析技术迭代计算点云三个长轴(XYZ)方向。得到三个长轴方向后,通过点云在三个方向上的投影就能够得到目标的位姿信息以及尺寸信息,从而完成目标检测功能。The 3D frame reconstruction module uses the OBB direction bounding box algorithm to construct the 3D detection frame of each point cloud cluster. Each point cloud cluster obtained by the point cloud clustering module needs to construct a corresponding 3D frame through the 3D frame reconstruction module. The 3D box reconstruction module uses the OBB direction bounding box algorithm to construct the 3D detection box of the point cloud cluster. The purpose of the OBB algorithm is to construct the smallest cuboid that can enclose the point cloud cluster in three-dimensional space. The algorithm mainly uses the principal component analysis technique to iteratively calculate the three long axis (XYZ) directions of the point cloud. After obtaining the three long-axis directions, the pose information and size information of the target can be obtained through the projection of the point cloud in the three directions, so as to complete the target detection function.
如图6所示,异构信息融合模块用于进行异构信息融合,优选的,将图像实例分割、深度估计(深度图)、融合点云数据(三维目标框)进行异构信息融合,并输出目标3D检测结果;优选的,3D检测结果包括语义类别尺寸及3D位姿信息。异构信息融合模块的输入为图像多任务感知模块以及点云目标检测模块的结果,输出为目标最终3D检测结果,包括语义类别尺寸以及3D位姿信息。融合模块根据距离的远近实现了两种不同的融合策略。在近程(激光雷达有效感知范围内),融合模块优先信任点云目标检测结果,但由于扬尘、雨雪等恶劣天气会给点云带来很多噪声,造成检测失误。相对而言,图像的感知算法受噪声影响较小,能够更好的处理扬尘雨雪等天气下的感知任务。因此,算法将三维检测目标的点云投影到图像空间,然后利用图像实例分割结果,过滤掉在投影在目标掩码之外的点,之后用剩下的点云重新计算3D包围框,从而在过滤掉误检结果的同时得到更为精确的目标三维检测结果。而在远程,目标的点云比较稀疏,点云目标检测算法往往无法很好的检测出目标,而图像的可视距离要比激光雷达大的多,二三百米远的目标也能够很好的检出。因此,融合模块首先利用图像实例分割结果以及深度估计信息,得到目标掩码区域的所有像素的深度信息,根据这些深度信息生成伪点云,然后计算出该目标的尺寸和三维位姿。由于深度估计存在误差,计算出来的目标信息一般不会很准确。为了尽可能准确地还原目标的尺寸和三维位姿,算法将原始点云数据投影到图像实例分割的掩码中,利用落在目标掩码内的点云的深度信息矫正图像深度估计的结果。融合模块充分考虑了各个传感器的优缺点,实现了路侧感知算法的超视距感知以及对扬尘、雨雪的适应,提升了感知算法的感知距离和对恶劣环境的鲁棒性。As shown in Figure 6, the heterogeneous information fusion module is used for heterogeneous information fusion. Preferably, image instance segmentation, depth estimation (depth map), fusion point cloud data (3D target frame) are used for heterogeneous information fusion, and Output the target 3D detection result; preferably, the 3D detection result includes semantic category size and 3D pose information. The input of the heterogeneous information fusion module is the result of the image multi-task perception module and the point cloud target detection module, and the output is the final 3D detection result of the target, including the semantic category size and 3D pose information. The fusion module implements two different fusion strategies according to the distance. At short range (within the effective perception range of lidar), the fusion module prioritizes the detection results of point cloud targets, but due to dust, rain and snow and other bad weather will bring a lot of noise to the point cloud, resulting in detection errors. Relatively speaking, the image perception algorithm is less affected by noise and can better handle perception tasks in weather such as dust, rain and snow. Therefore, the algorithm projects the point cloud of the 3D detection target into the image space, and then uses the image instance segmentation result to filter out the points projected outside the target mask, and then uses the remaining point cloud to recalculate the 3D bounding box, so that in the While filtering out the false detection results, a more accurate target 3D detection result is obtained. In the long-range, the point cloud of the target is relatively sparse, and the point cloud target detection algorithm often cannot detect the target well, and the visual distance of the image is much larger than that of the lidar, and the target two or three hundred meters away can also be well checkout. Therefore, the fusion module first uses the image instance segmentation results and depth estimation information to obtain the depth information of all pixels in the target mask area, generates a pseudo point cloud based on these depth information, and then calculates the size and 3D pose of the target. Due to errors in depth estimation, the calculated target information is generally not very accurate. In order to restore the size and 3D pose of the target as accurately as possible, the algorithm projects the original point cloud data into the mask of image instance segmentation, and uses the depth information of the point cloud falling within the target mask to correct the result of image depth estimation. The fusion module fully considers the advantages and disadvantages of each sensor, realizes the over-the-horizon perception of the roadside perception algorithm and the adaptation to dust, rain and snow, and improves the perception distance of the perception algorithm and the robustness to harsh environments.
多目标跟踪模块,用于根据异构信息融合后的首帧结果建立轨迹,将融合检测结果与轨迹关联,对目标观测值进行最优估计,得到更加平滑准确的检测结果,同时也计算出目标的速度和加速度等信息。异构信息融合模块的融合结果最终会输入到多目标跟踪模块。多目标跟踪模块首先根据首帧融合结果建立轨迹,当下一帧融合结果到来时,利用匈牙利二分图匹配算法将融合检测结果和轨迹关联,然后使用卡尔曼滤波技术,对目标观测值进行最优估计,得到更加平滑准确的检测结果,同时也计算出了目标的速度和加速度等信息。The multi-target tracking module is used to establish a trajectory according to the first frame results after the fusion of heterogeneous information, associate the fusion detection results with the trajectory, and perform optimal estimation of the target observation values to obtain smoother and more accurate detection results, and also calculate the target. information such as speed and acceleration. The fusion result of the heterogeneous information fusion module will finally be input to the multi-target tracking module. The multi-target tracking module first establishes a trajectory according to the fusion result of the first frame. When the fusion result of the next frame arrives, it uses the Hungarian bipartite graph matching algorithm to associate the fusion detection result with the trajectory, and then uses the Kalman filtering technology to perform the optimal estimation of the target observation value. , to obtain a smoother and more accurate detection result, and also calculate the speed and acceleration of the target.
卡尔曼滤波是一种最优估计算法,算法以K-1时刻的最优估计Xk-1为准,预测K时刻的状态变量X^k/k-1,同时又对该状态进行观测,得到观测变量Zk, 再在预测与观测之间进行分析,或者说是以观测量对预测量进行修正,从而得到K时刻的最优状态估计Xk。在多目标跟踪过程中,状态变量为目标的三维位置以及速度([x, y, z, vx, vy, vz]),可通过目标运动模型计算得到,观测变量为目标的三维位置([x, y, z]),通过目标检测算法得到。在实际情况中,还可以将目标的朝向以及尺寸信息加入状态变量和观测变量中,以得到目标朝向和尺寸信息的最优估计。经过多目标跟踪模块,每个融合目标都通过轨迹管理了起来,建立了帧间目标的时序相关性,方便轨迹预测模块对感知结果的使用。Kalman filter is an optimal estimation algorithm. The algorithm takes the optimal estimation Xk- 1 at time K-1 as the criterion, predicts the state variable X^k/k-1 at time K, and observes the state at the same time. The observation variable Zk is obtained, and then the analysis is performed between the prediction and the observation, or the prediction is corrected by the observation, so as to obtain the optimal state estimate Xk at time K. In the multi-target tracking process, the state variables are the three-dimensional position and velocity of the target ([x, y, z, vx , vy , vz ]), which can be calculated by the target motion model, and the observed variables are the three-dimensional position of the target ([x, y, z]), obtained by the target detection algorithm. In practical situations, the orientation and size information of the target can also be added to the state variables and observation variables to obtain the optimal estimation of the orientation and size information of the target. After the multi-target tracking module, each fusion target is managed through the trajectory, and the time-series correlation of the targets between frames is established, which is convenient for the trajectory prediction module to use the perception results.
如图7所示的轨迹预测模块,用于根据目标追踪结果和高精度地图信息输出未来的运动轨迹(可输出目标未来几秒的运动轨迹),高精度地图信息包括车道引导线、平整度以及坡度信息,运动轨迹包括位置信息、速度、加速度。The trajectory prediction module shown in Figure 7 is used to output the future motion trajectory according to the target tracking results and high-precision map information (the target's motion trajectory in the next few seconds can be output). The high-precision map information includes lane guide lines, smoothness and Slope information, motion trajectory includes position information, speed, acceleration.
轨迹预测模块输入为目标的跟踪结果,以及路侧区域的高精度地图信息,包括车道引导线(一般为车道中心线)、平整度以及坡度信息,输出为目标未来几秒的运动轨迹,包含位置信息以及速度、加速度信息。首先,预测模块利用多目标跟踪得到的目标位姿、速度以及加速度等信息初步构建目标的运动模型,然后利用车道引导线约束目标的运动方向。运动方向的约束是在Frenet坐标系下工作的。Frenet坐标系是以车道引导线为基准,延引导线方向为纵轴(s), 垂直于引导线方向为横轴(l),如图7所示。给定车道引导线,模块按照车辆位置,将其投影到引导线上,以投射点为基础,将地图坐标系下当前车辆的运动状态(x, y, θ, v, a)进行分解,获得延引导线方向的位置、速度、加速度,以及相对于引导线运动的位置、“速度”以及“加速度”,这里的“速度”和“加速度”不是一般意义的位移对时间的一阶/二阶导数,而是横向位移对纵向位移的一阶/二阶导数,它们描述了几何形状的变化趋势,计算公式如下:The input of the trajectory prediction module is the tracking result of the target, as well as the high-precision map information of the roadside area, including the lane guide line (usually the lane center line), flatness and slope information, and the output is the target's movement trajectory in the next few seconds, including the position information as well as speed and acceleration information. First, the prediction module uses the information of the target pose, speed and acceleration obtained by multi-target tracking to initially construct the target's motion model, and then uses the lane guide line to constrain the target's movement direction. Constraints on the direction of motion work in the Frenet coordinate system. The Frenet coordinate system is based on the lane guide line, and the direction along the guide line is the vertical axis (s), and the direction perpendicular to the guide line is the horizontal axis (l), as shown in Figure 7. Given the lane guide line, the module projects it onto the guide line according to the vehicle position, and based on the projection point, decomposes the current vehicle motion state (x, y, θ, v, a) in the map coordinate system to obtain The position, velocity, and acceleration along the direction of the guide line, and the position, "speed" and "acceleration" relative to the motion of the guide line. The "speed" and "acceleration" here are not the first/second order of displacement versus time in the general sense Derivatives, but the first/second derivative of the lateral displacement to the longitudinal displacement, they describe the changing trend of the geometry, and the calculation formula is as follows:
进行运动分解后,车辆在地图坐标系下的运动模型也能够相应转换到Frenet坐标系下。车辆未来运动方向的约束可以通过限制车辆在横轴l方向的运动分量实现,从而让车辆的预测轨迹方向尽可能沿着车道引导线,提升轨迹预测的准确性。After the motion decomposition, the motion model of the vehicle in the map coordinate system can also be transformed into the Frenet coordinate system accordingly. The constraint of the future motion direction of the vehicle can be realized by limiting the motion component of the vehicle in the direction of the horizontal axis l, so that the predicted trajectory direction of the vehicle can be along the lane guide line as much as possible, and the accuracy of the trajectory prediction can be improved.
此外,轨迹预测模块还会利用坡度信息对预测的速度做线性修正,然后再利用平整度信息约束目标的运动速度以及加速度,与运动方向的约束不同的是,这是在地图坐标系下进行的。In addition, the trajectory prediction module will use the slope information to linearly correct the predicted speed, and then use the flatness information to constrain the movement speed and acceleration of the target. Unlike the restriction of the movement direction, this is carried out in the map coordinate system. .
轨迹预测模块利用上述方案迭代计算目标未来的位姿以及速度、加速度信息,这些信息能够为车端提供场景的未来状态,从而提升车端路径规划和速度规划的准确性和效率。The trajectory prediction module uses the above scheme to iteratively calculate the future pose, speed, and acceleration information of the target, which can provide the vehicle with the future state of the scene, thereby improving the accuracy and efficiency of the vehicle's path planning and speed planning.
值得注意的是虽然在本系统的文字描述以及架构图中只披露了基本功能模块,但并不意味着本系统局限于基本功能模块,相反,本专利所要表达的意思是:在上述基本功能模块的基础之上本领域技术人员可以结合现有技术任意添加一个或多个功能模块,形成无穷多个实施例或技术方案,也就是说本系统是开放式而非封闭式的,不能因为本实施例仅仅披露了个别基本功能模块,就认为本专利权利要求的保护范围局限于所公开的基本功能模块。It is worth noting that although only the basic functional modules are disclosed in the text description and architecture diagram of the system, it does not mean that the system is limited to the basic functional modules. On the contrary, what this patent intends to express is: in the above-mentioned basic functional modules On the basis of the existing technology, those skilled in the art can arbitrarily add one or more functional modules to form an infinite number of embodiments or technical solutions, that is to say, the system is open rather than closed. If the example only discloses individual basic function modules, it is considered that the protection scope of the patent claims is limited to the disclosed basic function modules.
如图8所示,本发明在公开了露天矿山的路端多源传感器融合目标感知方法和系统的基础之上,还公开了与方法和系统对应的电子设备和存储介质:As shown in FIG. 8, the present invention also discloses electronic equipment and storage medium corresponding to the method and system on the basis of disclosing the method and system of road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing in open-pit mines:
一种电子设备,包括:处理器、通信接口、存储器和通信总线,其中,处理器,通信接口,存储器通过通信总线完成相互间的通信;所述存储器中存储有计算机程序,当所述计算机程序被所述处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行上述任一项所述方法的步骤。An electronic device, comprising: a processor, a communication interface, a memory, and a communication bus, wherein the processor, the communication interface, and the memory communicate with each other through the communication bus; a computer program is stored in the memory, and when the computer program is When executed by the processor, the processor is caused to execute the steps of any one of the methods described above.
一种计算机可读存储介质,其存储有可由电子设备执行的计算机程序,当所述计算机程序在所述电子设备上运行时,使得所述电子设备执行上述任一项所述方法的步骤。A computer-readable storage medium storing a computer program executable by an electronic device, when the computer program runs on the electronic device, causes the electronic device to perform the steps of any one of the above-mentioned methods.
电子设备包括硬件层,运行在硬件层之上的操作系统层,以及运行在操作系统上的应用层。该硬件层包括中央处理器(CPU,Central Processing Unit)、内存管理单元(MMU,Memory Management Unit)和内存等硬件。该操作系统可以是任意一种或多种通过进程(Process)实现电子设备控制的计算机操作系统,例如,Linux操作系统、Unix操作系统、Android操作系统、iOS操作系统或windows操作系统等。并且在本发明实施例中该电子设备可以是智能手机、平板电脑等手持设备,也可以是桌面计算机、便携式计算机等电子设备,本发明实施例中并未特别限定。本发明实施例中的电子设备控制的执行主体可以是电子设备,或者是电子设备中能够调用程序并执行程序的功能模块。The electronic device includes a hardware layer, an operating system layer running on the hardware layer, and an application layer running on the operating system. The hardware layer includes hardware such as a central processing unit (CPU, Central Processing Unit), a memory management unit (MMU, Memory Management Unit), and memory. The operating system may be any one or more computer operating systems that implement electronic device control through processes, such as a Linux operating system, a Unix operating system, an Android operating system, an iOS operating system, or a Windows operating system. Moreover, in the embodiment of the present invention, the electronic device may be a handheld device such as a smart phone and a tablet computer, or an electronic device such as a desktop computer and a portable computer, which is not particularly limited in the embodiment of the present invention. The execution subject controlled by the electronic device in the embodiment of the present invention may be an electronic device, or a functional module in the electronic device that can call a program and execute the program.
电子设备可以获取到存储介质对应的固件,存储介质对应的固件由供应商提供,不同存储介质对应的固件可以相同可以不同,在此不做限定。电子设备获取到存储介质对应的固件后,可以将该存储介质对应的固件写入存储介质中,具体地是往该存储介质中烧入该存储介质对应固件。将固件烧入存储介质的过程可以采用现有技术实现,在本发明实施例中不做赘述。The electronic device may obtain firmware corresponding to the storage medium, the firmware corresponding to the storage medium is provided by the supplier, and the firmware corresponding to different storage media may be the same or different, which is not limited herein. After acquiring the firmware corresponding to the storage medium, the electronic device can write the firmware corresponding to the storage medium into the storage medium, specifically, burn the firmware corresponding to the storage medium into the storage medium. The process of burning the firmware into the storage medium may be implemented by using the prior art, which will not be repeated in this embodiment of the present invention.
电子设备还可以获取到存储介质对应的重置命令,存储介质对应的重置命令由供应商提供,不同存储介质对应的重置命令可以相同可以不同,在此不做限定。此时电子设备的存储介质为写入了对应的固件的存储介质,电子设备可以在写入了对应的固件的存储介质中响应该存储介质对应的重置命令,从而电子设备根据存储介质对应的重置命令,对该写入对应的固件的存储介质进行重置。根据重置命令对存储介质进行重置的过程可以现有技术实现,在本发明实施例中不做赘述。The electronic device may also obtain a reset command corresponding to the storage medium. The reset command corresponding to the storage medium is provided by the supplier. The reset command corresponding to different storage media may be the same or different, which is not limited herein. At this time, the storage medium of the electronic device is the storage medium in which the corresponding firmware is written, and the electronic device can respond to the reset command corresponding to the storage medium in the storage medium in which the corresponding firmware is written, so that the electronic device can respond according to the corresponding reset command of the storage medium. The reset command resets the storage medium in which the corresponding firmware is written. The process of resetting the storage medium according to the reset command may be implemented in the prior art, which will not be repeated in this embodiment of the present invention.
通过以上的实施方式的描述可知,本领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到本申请可借助软件加必需的通用硬件平台的方式来实现。基于这样的理解,本申请的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品可以存储在存储介质中,如ROM/RAM、磁碟、光盘等,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,服务器,或者网络设备等)执行本申请各个实施方式或者实施方式的某些部分所述的方法。From the description of the above embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that the present application can be implemented by means of software plus a necessary general hardware platform. Based on this understanding, the technical solutions of the present application can be embodied in the form of software products in essence or the parts that make contributions to the prior art, and the computer software products can be stored in storage media, such as ROM/RAM, magnetic disks , CD, etc., including several instructions to make a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc.) to execute the methods described in various embodiments of the present application or some parts of the embodiments.
以上所描述的装置实施方式仅仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部模块来实现本实施方式方案的目的。本领域普通技术人员在不付出创造性劳动的情况下,即可以理解并实施。The device embodiments described above are only illustrative, wherein the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components shown as units may or may not be physical units, that is, they may be located in One place, or it can be distributed over multiple network elements. Some or all of the modules may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution in this implementation manner. Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand and implement it without creative effort.
本申请可用于众多通用或专用的计算系统环境或配置中。例如:个人计算机、服务器计算机、手持设备或便携式设备、平板型设备、多处理器系统、基于微处理器的系统、置顶盒、可编程的消费电子设备、网络PC、小型计算机、大型计算机、包括以上任何系统或设备的分布式计算环境等等。The present application may be used in numerous general purpose or special purpose computing system environments or configurations. For example: personal computers, server computers, handheld or portable devices, tablet devices, multiprocessor systems, microprocessor-based systems, set-top boxes, programmable consumer electronics, network PCs, minicomputers, mainframe computers, including A distributed computing environment for any of the above systems or devices, and the like.
本申请可以在由计算机执行的计算机可执行指令的一般上下文中描述,例如程序模块。一般地,程序模块包括执行特定任务或实现特定抽象数据类型的例程、程序、对象、组件、数据结构等等。也可以在分布式计算环境中实践本申请,在这些分布式计算环境中,由通过通信网络而被连接的远程处理设备来执行任务。在分布式计算环境中,程序模块可以位于包括存储设备在内的本地和远程计算机存储介质中。The application may be described in the general context of computer-executable instructions, such as program modules, being executed by a computer. Generally, program modules include routines, programs, objects, components, data structures, etc. that perform particular tasks or implement particular abstract data types. The application may also be practiced in distributed computing environments where tasks are performed by remote processing devices that are linked through a communications network. In a distributed computing environment, program modules may be located in both local and remote computer storage media including storage devices.
最后应说明的是:以上各实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述各实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分或者全部技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的范围。Finally, it should be noted that the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, but not to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: The technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments can still be modified, or some or all of the technical features thereof can be equivalently replaced; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention. scope.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210441815.8ACN114862901B (en) | 2022-04-26 | 2022-04-26 | A road-side multi-source sensor fusion target perception method and system for open-pit mines |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210441815.8ACN114862901B (en) | 2022-04-26 | 2022-04-26 | A road-side multi-source sensor fusion target perception method and system for open-pit mines |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114862901Atrue CN114862901A (en) | 2022-08-05 |
| CN114862901B CN114862901B (en) | 2025-08-26 |
Family
ID=82634250
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210441815.8AActiveCN114862901B (en) | 2022-04-26 | 2022-04-26 | A road-side multi-source sensor fusion target perception method and system for open-pit mines |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114862901B (en) |
Cited By (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115033586A (en)* | 2022-08-11 | 2022-09-09 | 上海伯镭智能科技有限公司 | Method for sensing mine road boundary and updating crowdsourcing map |
| CN115272493A (en)* | 2022-09-20 | 2022-11-01 | 之江实验室 | An abnormal target detection method and device based on continuous time series point cloud superposition |
| CN115273034A (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2022-11-01 | 江苏智行未来汽车研究院有限公司 | A traffic target detection and tracking method based on vehicle multi-sensor fusion |
| CN115527185A (en)* | 2022-09-28 | 2022-12-27 | 清智汽车科技(苏州)有限公司 | Method and device for testing automatic driving perception result |
| CN115755696A (en)* | 2022-11-17 | 2023-03-07 | 国能北电胜利能源有限公司 | Strip mine environment monitoring method and environment monitoring system |
| CN115909728A (en)* | 2022-11-02 | 2023-04-04 | 智道网联科技(北京)有限公司 | Roadside sensing method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium |
| CN115984827A (en)* | 2023-03-06 | 2023-04-18 | 安徽蔚来智驾科技有限公司 | Point cloud sensing method, computer device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN116030447A (en)* | 2023-01-09 | 2023-04-28 | 合众新能源汽车股份有限公司 | Perception method, system and vehicle supporting multi-camera dynamic input |
| CN116091533A (en)* | 2023-01-03 | 2023-05-09 | 中国人民解放军海军航空大学 | Laser radar target demonstration and extraction method in Qt development environment |
| CN116109675A (en)* | 2023-02-03 | 2023-05-12 | 北京天玛智控科技股份有限公司 | A method and device for capturing and sensing the reality of underground coal mine scenes |
| CN116166939A (en)* | 2023-02-09 | 2023-05-26 | 浙江九州云信息科技有限公司 | A data preprocessing method and system based on vehicle-road coordination |
| CN116226781A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-06-06 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method, device, storage medium and electronic equipment for fusing perception data |
| CN116453031A (en)* | 2023-05-16 | 2023-07-18 | 煤炭科学技术研究院有限公司 | A coal mine environment sensing method, device and storage medium |
| CN116883711A (en)* | 2023-04-03 | 2023-10-13 | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所 | Waste mine recycling intelligent classification method based on multi-source geographic data |
| CN116994436A (en)* | 2023-09-26 | 2023-11-03 | 青岛慧拓智能机器有限公司 | Intelligent mine road collision early warning method |
| CN117218517A (en)* | 2023-11-08 | 2023-12-12 | 诺比侃人工智能科技(成都)股份有限公司 | Outdoor moving object detection system in rainy and snowy weather |
| CN117251825A (en)* | 2023-11-20 | 2023-12-19 | 浙江大学 | Multi-sensor data fusion platform for new energy power station |
| CN117275232A (en)* | 2023-09-28 | 2023-12-22 | 广东省电信规划设计院有限公司 | Dynamic sensing method and device based on vehicle-road cooperation |
| CN117953459A (en)* | 2024-03-25 | 2024-04-30 | 安徽蔚来智驾科技有限公司 | Perception fusion result acquisition method, readable storage medium and intelligent device |
| WO2024146585A1 (en)* | 2023-01-06 | 2024-07-11 | 赵聪 | Method, apparatus and system for achieving rapid spatiotemporal calibration of multiple sensors in cooperative vehicle-infrastructure system |
| CN118776572A (en)* | 2023-04-10 | 2024-10-15 | 中车株洲电力机车研究所有限公司 | A global semantic map construction and updating method |
| CN118918330A (en)* | 2024-09-30 | 2024-11-08 | 成都浩孚科技有限公司 | Image background filtering method, system and storage medium |
| CN119197626A (en)* | 2023-12-25 | 2024-12-27 | 上海伟轩环保科技有限公司 | Environmental Monitoring System Based on Internet of Things |
| CN119254903A (en)* | 2024-11-29 | 2025-01-03 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | Method, device and electronic device for spatiotemporal alignment of point cloud and image pixels |
| CN119723481A (en)* | 2024-12-23 | 2025-03-28 | 同济大学 | A road domain full-factor credible perception method and system based on uncertainty quantification |
| CN119741436A (en)* | 2025-03-06 | 2025-04-01 | 山东交通学院 | Road three-dimensional model construction method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN120086618A (en)* | 2025-04-30 | 2025-06-03 | 智瞰深鉴(北京)科技有限公司 | A multi-source sensor autonomous intelligent perception method and system under complex dynamic environment |
| CN115273034B (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2025-10-10 | 江苏智行未来汽车研究院有限公司 | A traffic target detection and tracking method based on vehicle-mounted multi-sensor fusion |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111563442A (en)* | 2020-04-29 | 2020-08-21 | 上海交通大学 | Slam method and system for fusing point cloud and camera image data based on laser radar |
| CN112990049A (en)* | 2021-03-26 | 2021-06-18 | 常熟理工学院 | AEB emergency braking method and device for automatic driving of vehicle |
| CN113917475A (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2022-01-11 | 北京猎户星空科技有限公司 | Positioning method, apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN114119659A (en)* | 2021-11-12 | 2022-03-01 | 武汉理工大学重庆研究院 | Multi-sensor fusion target tracking method |
- 2022
- 2022-04-26CNCN202210441815.8Apatent/CN114862901B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111563442A (en)* | 2020-04-29 | 2020-08-21 | 上海交通大学 | Slam method and system for fusing point cloud and camera image data based on laser radar |
| CN113917475A (en)* | 2020-07-08 | 2022-01-11 | 北京猎户星空科技有限公司 | Positioning method, apparatus, electronic device, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN112990049A (en)* | 2021-03-26 | 2021-06-18 | 常熟理工学院 | AEB emergency braking method and device for automatic driving of vehicle |
| CN114119659A (en)* | 2021-11-12 | 2022-03-01 | 武汉理工大学重庆研究院 | Multi-sensor fusion target tracking method |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| VLADIMIR NEKRASOV ET AL.: "Real-Time Joint Semantic Segmentation and Depth Estimation Using Asymmetric Annotations", 《2019 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION (ICRA)》, 31 December 2019 (2019-12-31), pages 7101 - 7107* |
Cited By (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115273034B (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2025-10-10 | 江苏智行未来汽车研究院有限公司 | A traffic target detection and tracking method based on vehicle-mounted multi-sensor fusion |
| CN115273034A (en)* | 2022-08-08 | 2022-11-01 | 江苏智行未来汽车研究院有限公司 | A traffic target detection and tracking method based on vehicle multi-sensor fusion |
| CN115033586A (en)* | 2022-08-11 | 2022-09-09 | 上海伯镭智能科技有限公司 | Method for sensing mine road boundary and updating crowdsourcing map |
| CN115272493A (en)* | 2022-09-20 | 2022-11-01 | 之江实验室 | An abnormal target detection method and device based on continuous time series point cloud superposition |
| CN115272493B (en)* | 2022-09-20 | 2022-12-27 | 之江实验室 | Abnormal target detection method and device based on continuous time sequence point cloud superposition |
| CN115527185A (en)* | 2022-09-28 | 2022-12-27 | 清智汽车科技(苏州)有限公司 | Method and device for testing automatic driving perception result |
| CN115909728A (en)* | 2022-11-02 | 2023-04-04 | 智道网联科技(北京)有限公司 | Roadside sensing method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium |
| CN115755696A (en)* | 2022-11-17 | 2023-03-07 | 国能北电胜利能源有限公司 | Strip mine environment monitoring method and environment monitoring system |
| CN116226781A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-06-06 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method, device, storage medium and electronic equipment for fusing perception data |
| CN116091533A (en)* | 2023-01-03 | 2023-05-09 | 中国人民解放军海军航空大学 | Laser radar target demonstration and extraction method in Qt development environment |
| CN116091533B (en)* | 2023-01-03 | 2024-05-31 | 中国人民解放军海军航空大学 | Laser radar target demonstration and extraction method in Qt development environment |
| WO2024146585A1 (en)* | 2023-01-06 | 2024-07-11 | 赵聪 | Method, apparatus and system for achieving rapid spatiotemporal calibration of multiple sensors in cooperative vehicle-infrastructure system |
| CN116030447A (en)* | 2023-01-09 | 2023-04-28 | 合众新能源汽车股份有限公司 | Perception method, system and vehicle supporting multi-camera dynamic input |
| CN116109675A (en)* | 2023-02-03 | 2023-05-12 | 北京天玛智控科技股份有限公司 | A method and device for capturing and sensing the reality of underground coal mine scenes |
| CN116166939A (en)* | 2023-02-09 | 2023-05-26 | 浙江九州云信息科技有限公司 | A data preprocessing method and system based on vehicle-road coordination |
| CN115984827B (en)* | 2023-03-06 | 2024-02-02 | 安徽蔚来智驾科技有限公司 | Point cloud sensing method, computer equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN115984827A (en)* | 2023-03-06 | 2023-04-18 | 安徽蔚来智驾科技有限公司 | Point cloud sensing method, computer device and computer readable storage medium |
| CN116883711A (en)* | 2023-04-03 | 2023-10-13 | 中国科学院地理科学与资源研究所 | Waste mine recycling intelligent classification method based on multi-source geographic data |
| CN118776572A (en)* | 2023-04-10 | 2024-10-15 | 中车株洲电力机车研究所有限公司 | A global semantic map construction and updating method |
| CN116453031A (en)* | 2023-05-16 | 2023-07-18 | 煤炭科学技术研究院有限公司 | A coal mine environment sensing method, device and storage medium |
| CN116994436B (en)* | 2023-09-26 | 2024-02-20 | 青岛慧拓智能机器有限公司 | Intelligent mine road collision early warning method |
| CN116994436A (en)* | 2023-09-26 | 2023-11-03 | 青岛慧拓智能机器有限公司 | Intelligent mine road collision early warning method |
| CN117275232A (en)* | 2023-09-28 | 2023-12-22 | 广东省电信规划设计院有限公司 | Dynamic sensing method and device based on vehicle-road cooperation |
| CN117275232B (en)* | 2023-09-28 | 2024-05-31 | 广东省电信规划设计院有限公司 | Dynamic sensing method and device based on vehicle-road cooperation |
| CN117218517B (en)* | 2023-11-08 | 2024-01-26 | 诺比侃人工智能科技(成都)股份有限公司 | Outdoor moving object detection system in rainy and snowy weather |
| CN117218517A (en)* | 2023-11-08 | 2023-12-12 | 诺比侃人工智能科技(成都)股份有限公司 | Outdoor moving object detection system in rainy and snowy weather |
| CN117251825B (en)* | 2023-11-20 | 2024-02-09 | 浙江大学 | A multi-sensor data fusion platform for new energy power stations |
| CN117251825A (en)* | 2023-11-20 | 2023-12-19 | 浙江大学 | Multi-sensor data fusion platform for new energy power station |
| CN119197626A (en)* | 2023-12-25 | 2024-12-27 | 上海伟轩环保科技有限公司 | Environmental Monitoring System Based on Internet of Things |
| CN117953459A (en)* | 2024-03-25 | 2024-04-30 | 安徽蔚来智驾科技有限公司 | Perception fusion result acquisition method, readable storage medium and intelligent device |
| CN118918330B (en)* | 2024-09-30 | 2024-12-10 | 成都浩孚科技有限公司 | Image background filtering method, system and storage medium |
| CN118918330A (en)* | 2024-09-30 | 2024-11-08 | 成都浩孚科技有限公司 | Image background filtering method, system and storage medium |
| CN119254903A (en)* | 2024-11-29 | 2025-01-03 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | Method, device and electronic device for spatiotemporal alignment of point cloud and image pixels |
| CN119723481A (en)* | 2024-12-23 | 2025-03-28 | 同济大学 | A road domain full-factor credible perception method and system based on uncertainty quantification |
| CN119723481B (en)* | 2024-12-23 | 2025-09-19 | 同济大学 | A trusted perception method and system for all road elements based on uncertainty quantification |
| CN119741436A (en)* | 2025-03-06 | 2025-04-01 | 山东交通学院 | Road three-dimensional model construction method, device, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN120086618A (en)* | 2025-04-30 | 2025-06-03 | 智瞰深鉴(北京)科技有限公司 | A multi-source sensor autonomous intelligent perception method and system under complex dynamic environment |
| CN120086618B (en)* | 2025-04-30 | 2025-07-22 | 智瞰深鉴(北京)科技有限公司 | A multi-source sensor autonomous intelligent perception method and system under complex dynamic environment |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114862901B (en) | 2025-08-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114862901A (en) | Road-end multi-source sensor fusion target sensing method and system for surface mine | |
| CN108955702B (en) | Lane-level map creation system based on 3D laser and GPS inertial navigation system | |
| CN115879060B (en) | Multimodal-based automatic driving perception method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN106896353A (en) | A kind of unmanned vehicle crossing detection method based on three-dimensional laser radar | |
| Singh | Vision-radar fusion for robotics bev detections: A survey | |
| CN118608435B (en) | De-distortion method and device for point cloud, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN117611762B (en) | Multi-level map construction method, system and electronic equipment | |
| CN114550116A (en) | Object identification method and device | |
| CN117036607A (en) | Automatic driving scene data generation method and system based on implicit neural rendering | |
| Yan et al. | Int2: Interactive trajectory prediction at intersections | |
| WO2022237210A1 (en) | Obstacle information generation | |
| CN118015217A (en) | Robust online mapping method for robots based on loosely coupled 3D tracking | |
| Tian et al. | ICAT: an indoor connected and autonomous testbed for vehicle computing | |
| Shangguan et al. | Interactive perception-based multiple object tracking via CVIS and AV | |
| Lin et al. | Big Data-Driven Advancements and Future Directions in Vehicle Perception Technologies: From Autonomous Driving to Modular Buses | |
| CN116203576A (en) | 3D target detection method and system based on environment awareness | |
| Han et al. | Flexsense: Flexible infrastructure sensors for traffic perception | |
| Huo et al. | A Review of Key Technologies for Environment Sensing in Driverless Vehicles. | |
| Pantilie et al. | Real-time obstacle detection using dense stereo vision and dense optical flow | |
| Zhang et al. | Research on unmanned system environment perception system methodology | |
| CN118628860A (en) | Image processing method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN117671616A (en) | A target recognition method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| Shi et al. | Research Progress on Multi-Modal Fusion Object Detection Algorithms for Autonomous Driving: A Review. | |
| Tamayo et al. | Improving object distance estimation in automated driving systems using camera images, LiDAR point clouds and hierarchical clustering | |
| US11544899B2 (en) | System and method for generating terrain maps |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |